Abstract
Introduction:
Ship wakes exhibit more distinctive characteristics than vessels themselves, making wake detection more feasible than direct ship detection. However, challenges persist due to sea surface interference, meteorological conditions, and coastal structures, while practical applications demand lightweight models with fast detection speeds.
Methods:
We propose OptWake-YOLO, a lightweight ship wake detection model with three key innovations: A RepConv-based RCEA module in the Backbone combining efficient layer aggregation with reparameterization to enhance feature extraction. An Adaptive Dynamic Feature Fusion Network (ADFFN) in the Neck integrating channel attention with Dynamic Upsampling (Dysample). A Shared Lightweight Object Detection Head (SLODH) using parameter sharing and Group Normalization.
Results:
Experiments on the SWIM dataset show OptWake-YOLO improves mAP50 by 1.5% (to 93.2%) and mAP50-95 by 2.9% (to 66.5%) compared to YOLOv11n, while reducing parameters by 40.7% (to 1.6M) and computation by 25.8% (to 4.9 GFLOPs), maintaining 303 FPS speed.
Discussion:
The model demonstrates superior performance in complex maritime conditions through: RCEA's multi-branch feature extraction. ADFFN's adaptive multi-scale fusion. SLODH's efficient detection architecture. Ablation studies confirm each component's contribution to balancing accuracy and efficiency for real-time wake detection.
1 Introduction
Maritime safety monitoring plays a crucial strategic role in national defense security and marine resource protection. Although modern Automatic Identification Systems (AIS) have been widely applied to vessel tracking, their mandatory use is limited to large vessels exceeding 300 tons. This limitation creates a significant vulnerability as smaller vessels can intentionally disable their AIS transmitters to evade monitoring, providing opportunities for illicit activities such as illegal fishing, smuggling operations, and environmental pollution. These security gaps have prompted researchers to develop more reliable remote sensing detection technologies to complement the limitations of AIS systems.
With the rapid advancement of remote sensing technology, ship detection based on satellite imagery has made remarkable progress (IMO, 2024). However, when detection targets are small vessels, direct identification of ship hulls often faces tremendous challenges due to sensor resolution constraints. In contrast, wakes generated by moving vessels can extend for dozens of kilometers (Pichel et al., 2004), presenting more prominent features in remote sensing images and providing critical information such as heading and speed. Consequently, wake detection offers greater feasibility and practical value compared to direct vessel detection (Mook and Jin, 2019).
Currently, wake image acquisition primarily relies on two technologies: Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) and optical remote sensing. Although SAR technology emerged earlier and holds a dominant position (Vesecky and Stewart, 1982), optical remote sensing is gradually becoming a research hotspot (Xue et al., 2021) due to its higher spatial resolution and non-coherent imaging characteristics, which enable clearer capture of wake texture details. Nevertheless, optical remote sensing wake detection confronts multiple challenges, including sea surface background interference, meteorological condition variations, and coastal structure influences, while practical applications also impose higher requirements for model lightweighting design and real-time performance.
Traditional approaches to ship wake detection have relied on transformations such as Radon and Hough, which are applied to images to enhance linear features. However, due to atmospheric and sea surface disturbances and clutter, wakes in complex sea conditions don’t show as clearly in satellite imagery. Therefore, these methods are typically only suitable for wakes centered around vessels and under low sea state conditions, making them impractical for large-scale applications (Mazzeo et al., 2024). As the development of deep learning techniques continues to flourish, Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) have made breakthrough progress in image feature extraction and object detection, leading to increasing attention on applying deep learning-based detection models to solve ship wake detection problems. Among numerous object detection algorithms, the YOLO series has garnered significant attention for its balanced performance in accuracy and real-time capability. The recently released YOLOv11 model supports multi-scale feature fusion, achieving high-precision detection at relatively low computational cost, while its modular design facilitates customized optimization for specific application scenarios.
To address the aforementioned challenges, a lightweight ship wake detection model, OptWake-YOLO, is put forward in this paper based on YOLOv11n. The main contributions are as follows:
-
Design of an efficient RCEA module in the Backbone, the employment of a multi-branch structure in conjunction with reparameterization technology has been demonstrated to improve the capability of feature extraction whilst concomitantly reducing the parameter count;
-
Implementation of a newly designed feature fusion network ADFFN in the model’s Neck, combining channel attention mechanisms with Dynamic Upsampling technology to accomplish the efficient fusion of multi-scale features;
-
Redesign of a more lightweight detection head SLODH using Group Normalization operations and shared convolutions, significantly reducing model complexity through parameter sharing and group normalization techniques;
-
A substantial series of experiments on the public SWIM dataset has been conducted, the results of which demonstrate that, in comparison with other state-of-the-art algorithms, the proposed method maintains excellent detection accuracy while attaining superior lightweight functionality in ship wake detection missions. Among many models, the WakeNet model (Xue et al., 2022) pioneered by Xue et al. has made a significant breakthrough in CNN-based ship wake detection. Specifically, WakeNet improves detection accuracy by extracting wake features more efficiently mainly through the use of the FcaNet backbone network and the newly designed multiscale attention module (MSAM). The OptWake-YOLO model proposed in this paper uses the reparameterization technique and parameter sharing mechanism to achieve light weight while maintaining high detection accuracy, striking a balance between the accuracy and real-time requirements necessary for maritime monitoring applications.
The rest of the paper is arranged as follows: Section 2 gives a full overview of the related work; Section 3 provides detailed elaboration on the architecture of the proposed OptWake-YOLO model; Section 4 presents the experimental setup and results analysis; and finally; Section 5 is the conclusion of the paper, with a discussion of the future directions for research.
2 Related work
Ship wakes detectable in remote sensing images can be classified into four primary categories (Pichel et al., 2004): Kelvin wakes, turbulent wakes, internal wave wakes, and narrow V-shaped wakes. Among these, internal wave wakes and narrow V-shaped wakes are only observable within a limited range of specific environmental circumstances and imaging methods (Zilman et al., 2015). In general research, the more commonly observed Kelvin wakes and turbulent wakes are typically used as detection targets, with structures as shown in Figure 1. Kelvin wakes and turbulent wakes exhibit characteristic features in both SAR and optical images. In the context of SAR images, Kelvin arms appear as bright outer lines while turbulent wakes manifest as dark central lines. However, owing to the coherent imaging nature and commonly lower spatial resolution of SAR, these two types of wakes display relatively limited textural details in SAR imagery. In contrast, optical remote sensing imaging offers higher resolution and non-coherent characteristics, allowing wake features to exhibit more distinct textural details in most optical images as long as the wake energy exceeds that of sea clutter (Liu and Deng, 2018). From this perspective, the phenomenon of wakes in optical remote sensing images presents more extractable and interpretable features compared to those in SAR images. Nevertheless, since the development of wake detection techniques in optical remote sensing is relatively recent, the majority of extant wake detection algorithms have been designed principally for SAR imagery.
Figure 1
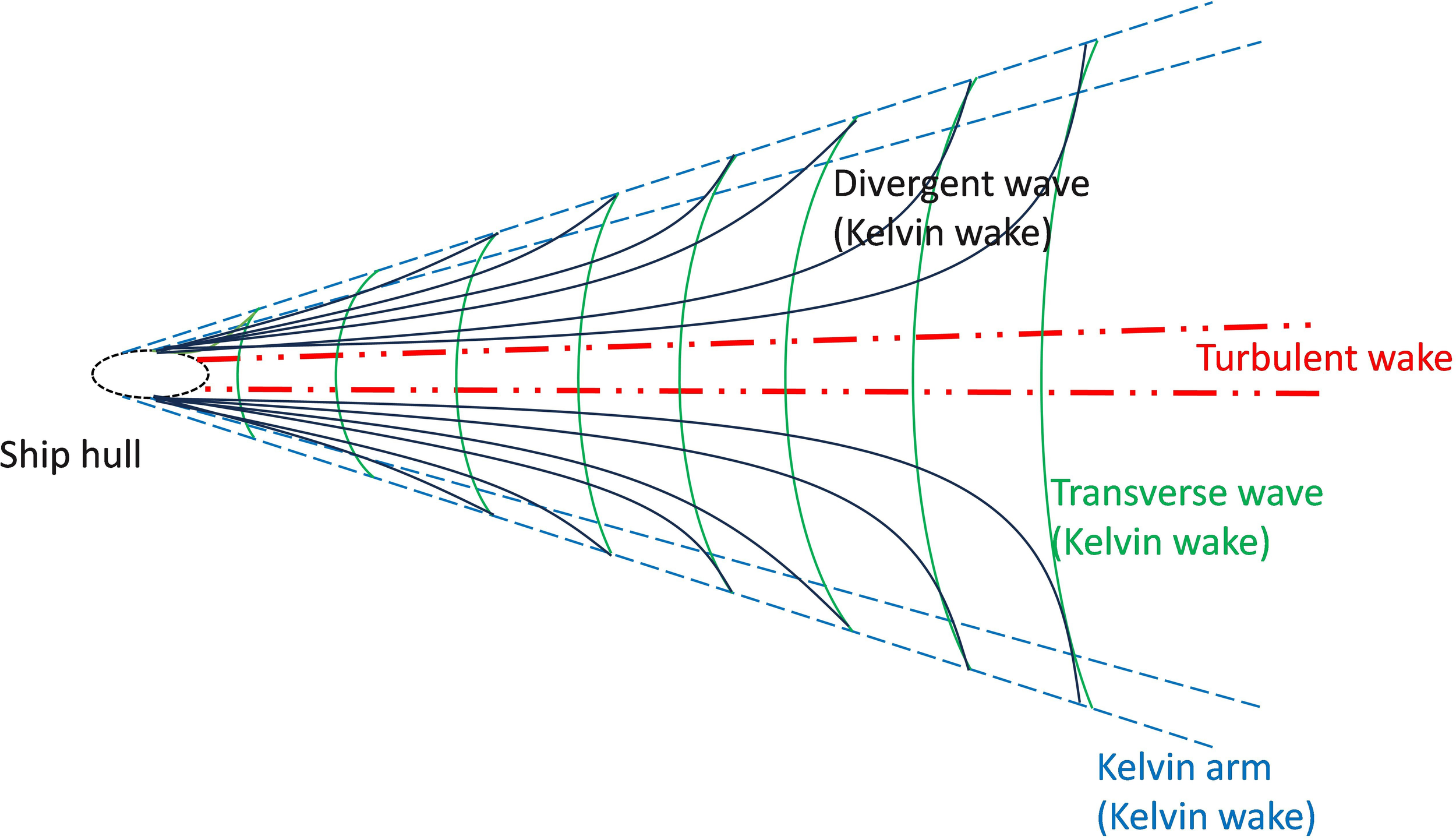
Schematic diagram of the elementary structure of a ship’s wake.
2.1 Traditional wake detection methods
Traditional ship wake detection methods primarily leverage the linear characteristics of wakes, simplifying the detection problem to the recognition of linear features in remote sensing images (Liu et al., 2021). Common linear detection methods include Radon transformation (Radon, 1986) and Hough transformation (Hough, 1962). Taking RT as an example, ship wakes in SAR remote sensing images appear either brighter or darker than the surrounding sea surface. After Radon transformation, these linear features are highlighted in the Radon domain, manifesting as X-shaped features as shown in Figure 2. Specific wake components are then extracted through threshold setting (Graziano, 2020).
Figure 2
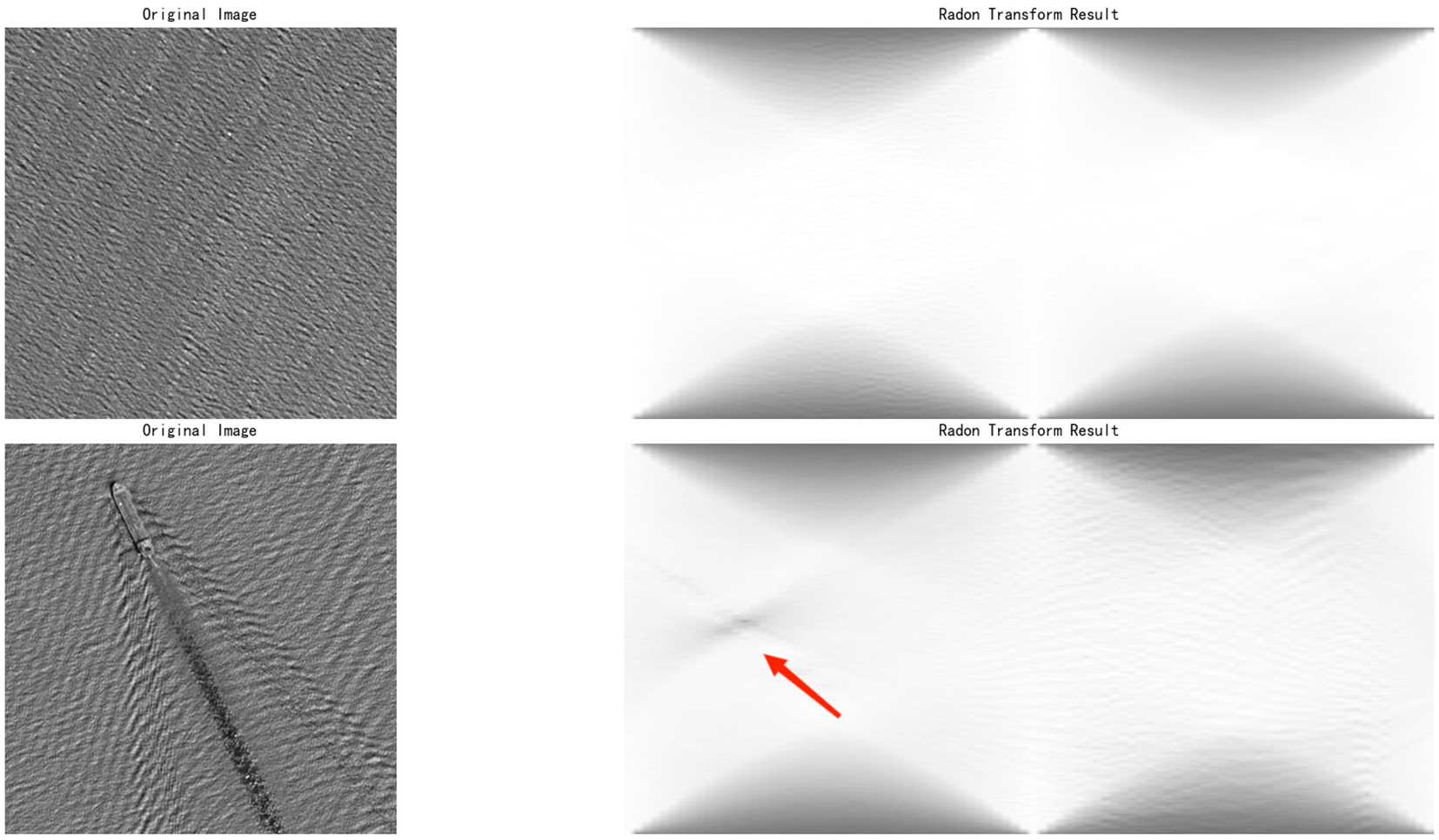
Processing effects of Radon transformation on normal sea surfaces and sea surfaces with ship wakes.
Despite the linear characteristics of ship wakes, the presence of atmospheric and sea surface phenomena, such as clutter, in satellite imagery hinders the visibility of wakes as uniform lines of brightness. Consequently, the aforementioned methods may result in lower detection accuracy. Although some research has attempted to improve detection performance through image enhancement techniques (Karakus et al., 2020), these methods still struggle to resolve false detection issues caused by other linear sea surface phenomena (such as waves), limiting their practical application to small-scale images centered around vessels and low sea state environments. With the development of high-quality spaceborne remote sensing datasets, the research focus has gradually shifted toward solutions based on deep neural networks.
2.2 Deep learning methods for ship wake detection
Object detection is the process of detecting one or more instances of specific object categories in images or videos. This task is implemented based on various object detection models, more specifically, object detectors based on deep learning (Zilman et al., 2015). Deep learning object detection models typically comprise three components: Backbone, Neck, and Detection head (Kateb et al, 2021). Depending on whether candidate regions need to be generated, object detection models can be one-stage or two-stage (Li et al., 2022). Two-stage models, e.g. the R-CNN suite (Girshick et al., 2014; Girshick, 2015; Ren et al., 2017) first generate candidate regions before conducting classification and regression, achieving higher accuracy but slower inference speed. One-stage models like Single Shot multibox Detector (SSD) (Liu et al., 2016) and the You Only Look Once (YOLO) series (Ge et al., 2021; Bochkovskiy et al., 2004; Redmon et al., 2016; Redmon and Farhadi, 2017; Redmon and Farhadi, 2018) directly perform classification and regression on images, sacrificing some accuracy for better detection.
In SAR image ship wake detection, Del Prete et al (Del Prete et al., 2021). were the first to put forward a deep learning method specifically for ship wake detection, validating the performance of Cascade Mask R-CNN (Cai and Vasconcelos, 2018) on their self-built SSWD dataset. Ding et al (Ding et al., 2023). designed a lightweight YOLO variant incorporating attention mechanisms for military-embedded devices. Wang et al (Wang et al., 2022). combined electromagnetic scattering models with YOLOv5 to achieve non-linear wake detection. Xu and Wang (2024) introduced the OpenSARWake dataset and developed a dedicated SWNet detector, utilizing a ConvNeXt-T (Liu et al., 2022) backbone and a specially designed HR-FPN* neck structure.
In the case of optical image wake detection, Xue et al (Xue et al., 2022). first developed an end-to-end CNN-based detector called WakeNet, with innovations including an additional wake feature regression head, a ResNet backbone integrated with Fca modules, and a redesigned FPN with multi-scale attention modules. They also constructed the SWIM dataset containing 11,600 images. Esposito et al (Esposito et al., 2022). applied Mask R-CNN (He et al., 2020) to multi-band wake detection. Liu and Zhao et al (Liu and Zhao, 2024). employed GoogLeNet (Szegedy et al., 2015) with inception modules to transform wake detection into a classification problem, addressing detection challenges in large, high-resolution images.
Current studies on ship wake detection based on optical remote sensing images have focused on improving feature extraction capabilities but have not prioritized model lightweighting. Moreover, these improvements may lead to extended detection times, failing to meet real-time requirements. Addressing this issue, this paper proposes the lightweight OptWake-YOLO model, which significantly reduces computational complexity while ensuring detection accuracy, achieving efficient and accurate wake detection.
2.3 YOLOv11n detection model
YOLOv11 is a new generation of universal object detection model proposed by Ultralytics. This model supports multi-scale feature fusion, achieving high-precision detection tasks at relatively low computational cost, while its high rate of detection also makes it appropriate for real-time detection scenarios. YOLOv11 continues the efficient detection framework optimization design of the YOLO series. The Backbone employs C3k2 as its core module, adopting hierarchical progressive convolution and cross-stage modules to gradually extract multi-scale features. The Neck employs a bi-directional feature fusion strategy to maximally preserve detailed information. The Detection head outputs prediction results from three scales, adapting to detection requirements for targets of different sizes. Its modular structural design not only provides flexible scaling capabilities but also supports rapid adaptation to different hardware platforms. Therefore, YOLOv11 serves as a baseline model for further development to meet practical requirements across numerous different fields in both industry and academia.
3 Proposed network
To meet the practical requirements of ship wake detection in optical remote sensing imagery, we propose the OptWake-YOLO model. This model systematically optimizes the YOLOv11n architecture, focusing innovation on three key aspects: feature extraction capability, multi-scale feature fusion efficiency, and model lightweighting. As shown in Figure 3, the OptWake-YOLO employs the newly designed RCEA module in the backbone, which combines reparameterization technology with multi-branch aggregation mechanisms to enhance feature representation capabilities; the neck structure utilizes the newly designed ADFFN network, which integrates channel attention mechanisms and Dynamic Upsampling (Dysample) operations to achieve adaptive channel adjustment and efficient fusion across different scales; and we redesign the light-weight detection head SLODH, significantly reducing model parameter count and computational complexity through parameter sharing and group normalization techniques. These innovative designs collectively constitute an end-to-end lightweight detection framework. The following subsections will elaborate on the design principles, mathematical expressions, and functional mechanisms of each improved module.
Figure 3
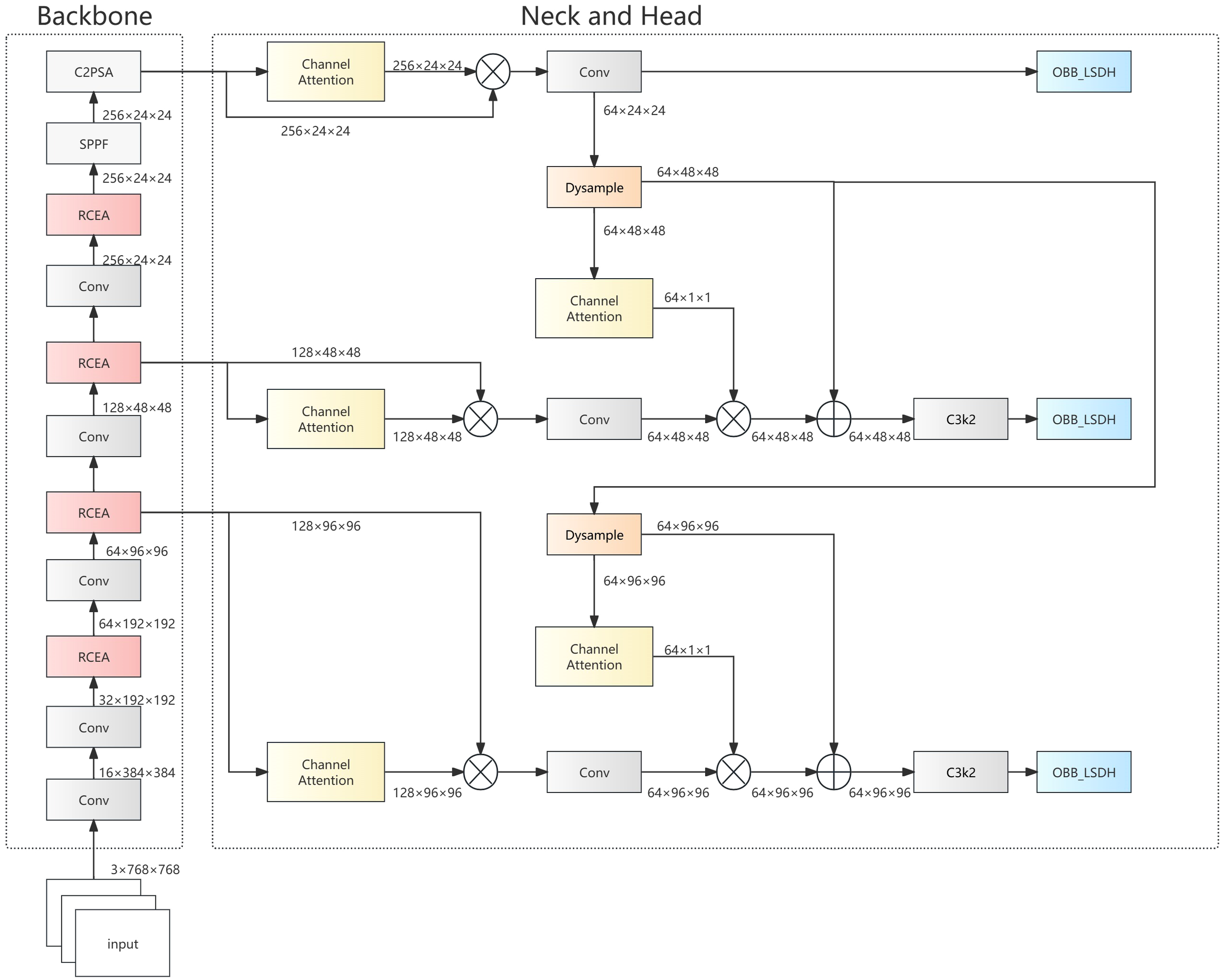
OptWake-YOLO architecture diagram.
3.1 RCEA
In ship wake detection tasks, the traditional YOLOv11n architecture employs the C3k2 module as its primary feature extraction unit. However, the C3k2 module exhibits significant limitations when processing slender, low-contrast targets like ship wakes. First, the C3k2 module’s feature extraction capability is relatively limited, insufficient for capturing the subtle texture features characteristic of ship wakes; second, simply reducing channel numbers during model lightweighting leads to a dramatic decline in feature representation capability. This paper puts forward the Rep Cheap Operation Efficient Aggregation (RCEA) feature extraction module to overcome these problems, which effectively integrates the advantages of the RepConv (Ding et al., 2021) reparameterization module, Cheap operation concept, and multi-branch efficient aggregation connections. This module not only decreases the number of parameters and computational complexity but also improves the ability to extract features. The RCEA module employs channel separation and reorganization strategies, complemented by residual learning and feature reuse mechanisms, not only improving the accuracy of detecting ship wakes but also reducing model parameters and computational overhead. The module structure is illustrated in Figure 4a.
Figure 4
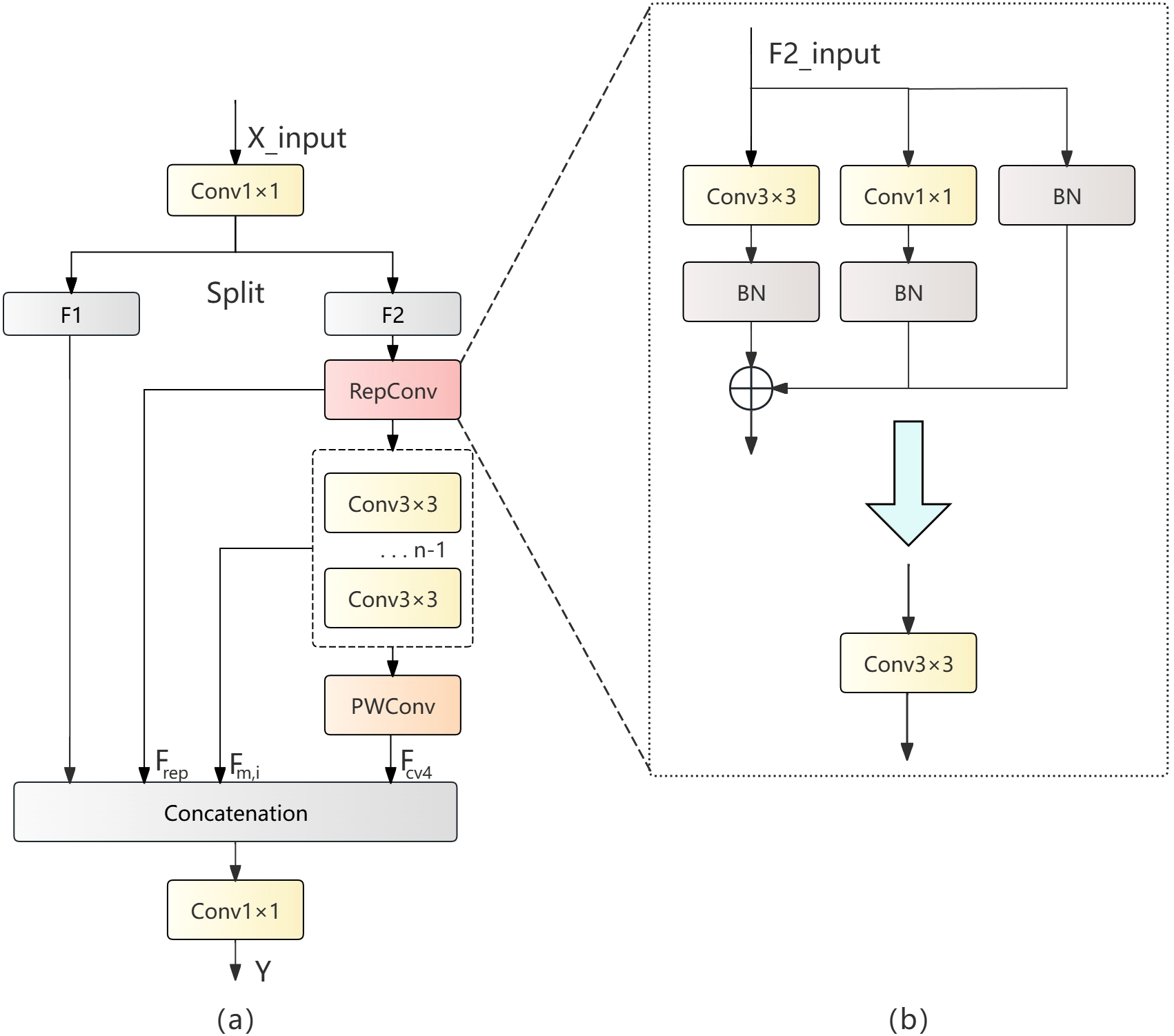
(a) RCEA structure diagram, (b) RepConv structure diagram.
The design of the RCEA module is based on fine control and optimized allocation of feature flow. It processes the input feature map by first performing channel transformation through a 1×1 convolution, then separating it into F1 and F2, where the second path feature F2 is processed through RepConv operations. RepConv combines identity mapping and 3×3 convolution, using reparameterization operations to convert the multi-branch convolution structure during the training phase into a single 3×3 convolution operation, improving computational efficiency.
The reparameterization operation of RepConv is executed in two steps. During the training phase, parameters are first individually fused for each branch, and then during the inference phase, the branch fusion results are transformed into an equivalent 3×3 convolution operation. Figure 4b visualizes the above workflow. During training, the input images pass through three branches: 3×3 convolution followed by batch normalization, 1×1 convolution followed by batch normalization, and batch normalization alone. The computation process for convolution and batch normalization is as followed as Equation 1:
Where represents the scaling factor, the bias term, the mean value, the variance, the constant, and denotes convolution operation with an n×n kernel, is the input feature map, and , are the fused convolution weights and bias after reparameterization. The fusion result of the three branches is as followed as Equation 2:
Through these calculations, the three branches are fused into a new single convolution operation. This new single convolution can equivalently represent the output of the multi-branch structure during training, thereby directly utilizing this equivalent convolution layer for calculation during inference, reducing computational load and improving inference speed while ensuring feature extraction accuracy.
To further refine the features generated by RepConv, (n-1) cascaded 3×3 convolutions are employed to extract additional features as Equation 3:
Where .
Finally, the channels of the final features are reorganised using pointwise convolution (PWConv) to form . This step embodies the idea of ‘Cheap Operations’ in RCEA. The core idea of cheap operations is to generate additional feature maps with as little computation as possible. Low computation and parameter count are the key features. PWConv is a 1×1 convolutional operation with the same input and output channels. Compared to a normal convolutional operation (K×K), PWConv is only 1/K. Reducing the computational complexity while ensuring that maintains the same feature dimensions as the other branching features () for subsequent concatenation operations. The goal of providing feature enhancement with minimal computational overhead and maintaining overall efficiency is achieved. Finally, all features are fused and output dimensions are adjusted by channel concatenation and 1×1 convolution as shown as Equation 4:
The key innovation of the feature extraction module proposed in this paper lies in its use of reparameterization technology and the cheap operation concept. Reparameterization technology allows the use of multi-branch structures during training while transforming them into a single efficient structure during inference through equivalent transformation. Combined with the multi-branch efficient aggregation connection mechanism, RCEA can efficiently extract and transmit useful feature information at each scale level. This module successfully addresses the limitations of traditional C3k2 modules in lightweight ship wake detection, achieving an optimized balance between feature extraction capability and computational efficiency.
3.2 ADFFN
Currently, feature fusion networks in most object detection algorithms typically adopt simple feature pyramid structures (FPN) or their variants, such as PANet (Liu et al., 2018) and BiFPN (Tan et al., 2020). Although these methods improve detection performance to some extent, they still have obvious limitations when processing targets like ship wakes that exhibit high complexity, scale variation, and low-contrast features. The main problems with traditional feature fusion networks include insufficient information flow transmission, limited feature representation capability, and inadequate feature extraction capability after lightweighting. To solve these problems, this paper puts forward the Adaptive Dynamic Feature Fusion Network (ADFFN), which employs channel attention mechanisms and dynamic learnable upsampling strategies to adaptively adjust feature representations according to input content. This significantly enhances feature expression capability and scale transformation accuracy while maintaining low computational cost and achieving effective fusion of features at different levels, effectively solving the problem of insufficient feature fusion in previous lightweight networks.
The ADFFN network is an improved Hierarchical Scale-based Feature Pyramid Network (Chen et al., 2024) (HS-FPN), with Dynamic Upampling (Liu et al., 2023) (Dysample) as its core, combined with channel attention mechanisms to achieve efficient feature fusion. Compared to traditional FPN structures, the ADFFN network adopts a more flexible feature fusion strategy. Traditional FPNs typically employ simple feature concatenation followed by convolution processing, while the ADFFN network uses channel attention mechanisms to modulate the feature weighting at different levels and dynamic learnable upsampling to precisely control the scale transformation process of features. This design allows the network to make more effective use of complementary information between multi-scale features, improving the model’s ability to detect complex targets such as ship wakes. The workflow is shown in Figure 5.
Figure 5
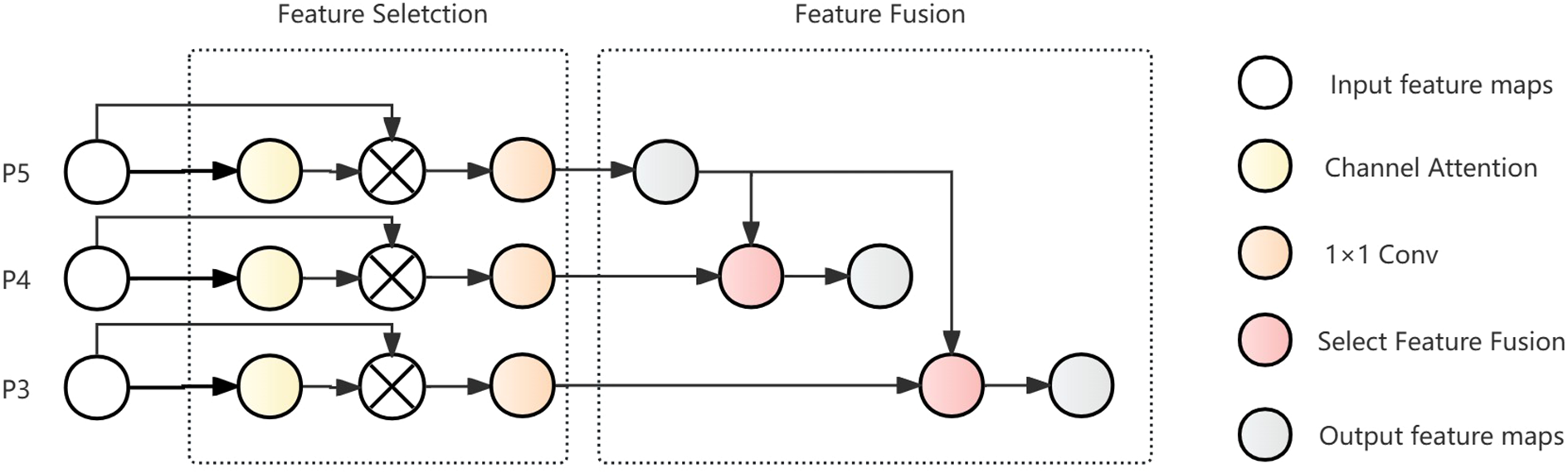
ADFFN structure diagram.
The ADFFN network consists mainly of two parts: feature selection and feature fusion. In the feature selection part, features output by the Backbone serve as input, are enhanced through channel attention mechanisms, multiplied with the original input features, and then undergo channel transformation using 1×1 convolution to facilitate subsequent feature fusion. During the process of feature fusion, high-level and low-level features are synergistically integrated by the selective feature fusion (SFF) mechanism modified by Dysample. The features produced by this fusion contain rich semantic content, aiding in the detection of subtle features in ship wake images.
Feature Selection: In the feature selection module, the Channel Attention(CA) mechanism is a core component that can adaptively adjust the importance of feature channels, and eliminate irrelevant channel noise while enhancing the discriminative power of channel features. The workflow is illustrated in Figure 6.
Figure 6
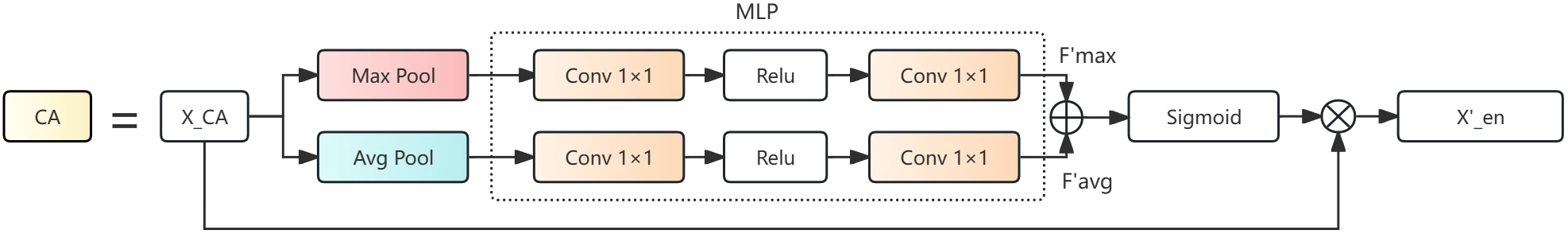
Channel Attention (CA) structure diagram.
Given the input feature map , where C, H, and W represent the number of channels, height, and width respectively, the CA module first calculates each channel’s average and maximum values through global average and maximum pooling, as shown in the Equations 5, 6:
Where represents the value of feature map at position (i,j) in channel C. Subsequently, these two features are processed through a multi-layer perceptron (MLP) consisting of two 1×1 convolutions and a ReLU activation function. The features processed by MLP are and , respectively. The two processed features are then added together and passed through a Sigmoid function to generate channel attention weights. Finally, the channel attention weights are multiplied with the original feature map to obtain an enhanced feature representation as shown as Equation 7:
Where represents the Sigmoid activation function and represents element-wise multiplication by channel. is the enhanced feature.
The CA module extracts the most representative information from each channel through a combination of pooling operations while minimizing information loss. The MLP structure achieves lightweight design while maximizing the preservation of spatial information through cross-channel feature integration, non-linear enhancement, and parameter-sharing mechanisms. Through these operations, the feature selection component of ADFFN can adaptively learn the importance of each channel, effectively enhancing discriminative channel features without introducing excessive computational overhead, and achieving screening of feature maps at different scales.
Feature Fusion: To more effectively fuse features from different levels, the ADFFN network adopts a feature fusion strategy called Selective Feature Fusion (SFF). Unlike traditional simple feature concatenation or additive fusion, SFF combines multiplicative and additive operations, high-level features are used as weights to filter low-level features to extract important semantic information that is embedded in them, better capturing complementary information between different feature levels. Simultaneously, it employs the dynamic learnable upsampling Dysample module to complete upsampling operations. This module can adaptively learn sampling positions and weights according to the content of input features. The SFF workflow is illustrated in Figure 7.
Figure 7
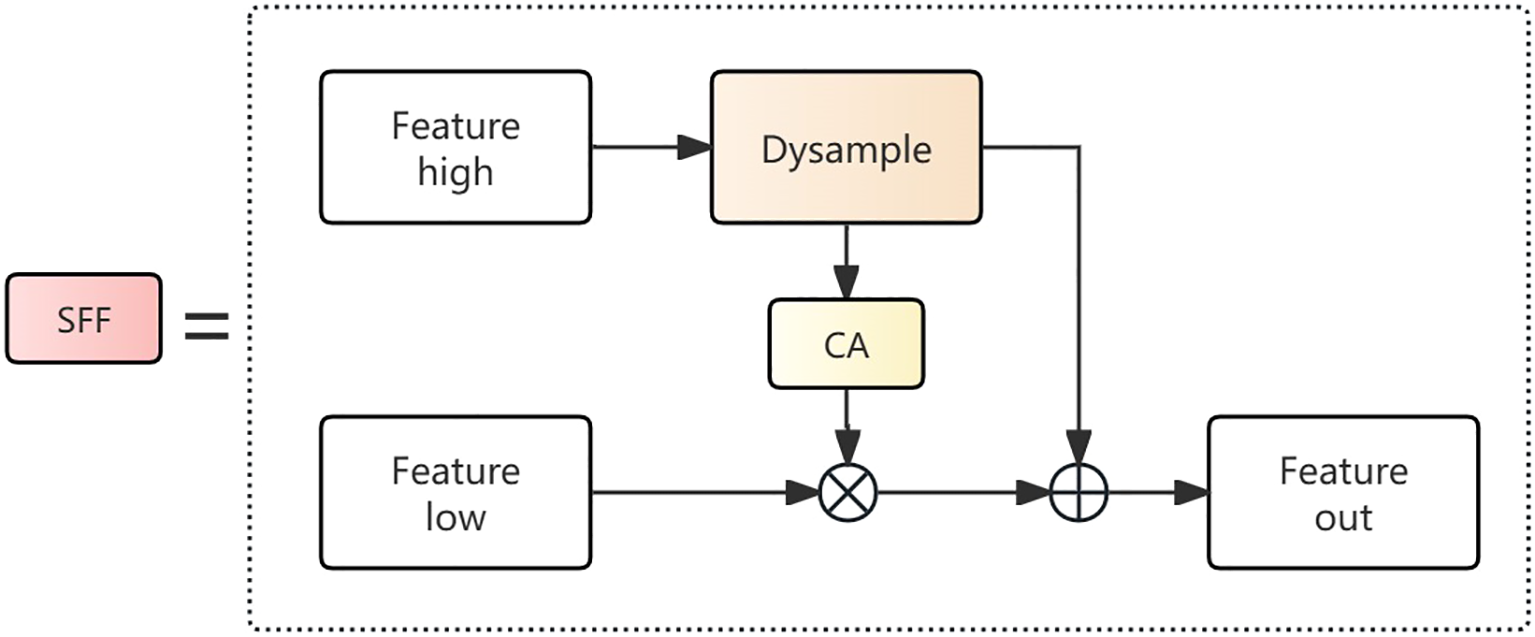
Selective Feature Fusion (SFF) structure diagram.
For a given high-level feature , the upsampling operation is first completed through the Dysample module, and then the CA module converts the high-level feature into corresponding attention weights, filtering dimensionally consistent low-level features using multiplication operations. Finally, the filtered low-level feature is additively fused with the high-level feature to form the final fused feature. The advantage of SFF in feature fusion lies in that multiplication operations can emphasize areas that are commonly important in features from both levels, while addition operations can maximally preserve the information of the original features, preventing the loss of useful information.
Traditional upsampling methods such as nearest neighbor or bilinear interpolation typically adopt fixed interpolation weights, making it difficult to adaptively adjust according to the content of input features, which may result in missing critical details when detecting ship wakes with complex structures. To solve this problem, SFF employs the Dynamic Upsampling (DySample) module, which can adaptively learn sampling positions and weights according to input features. The DySample workflow is illustrated in Figure 8.
Figure 8
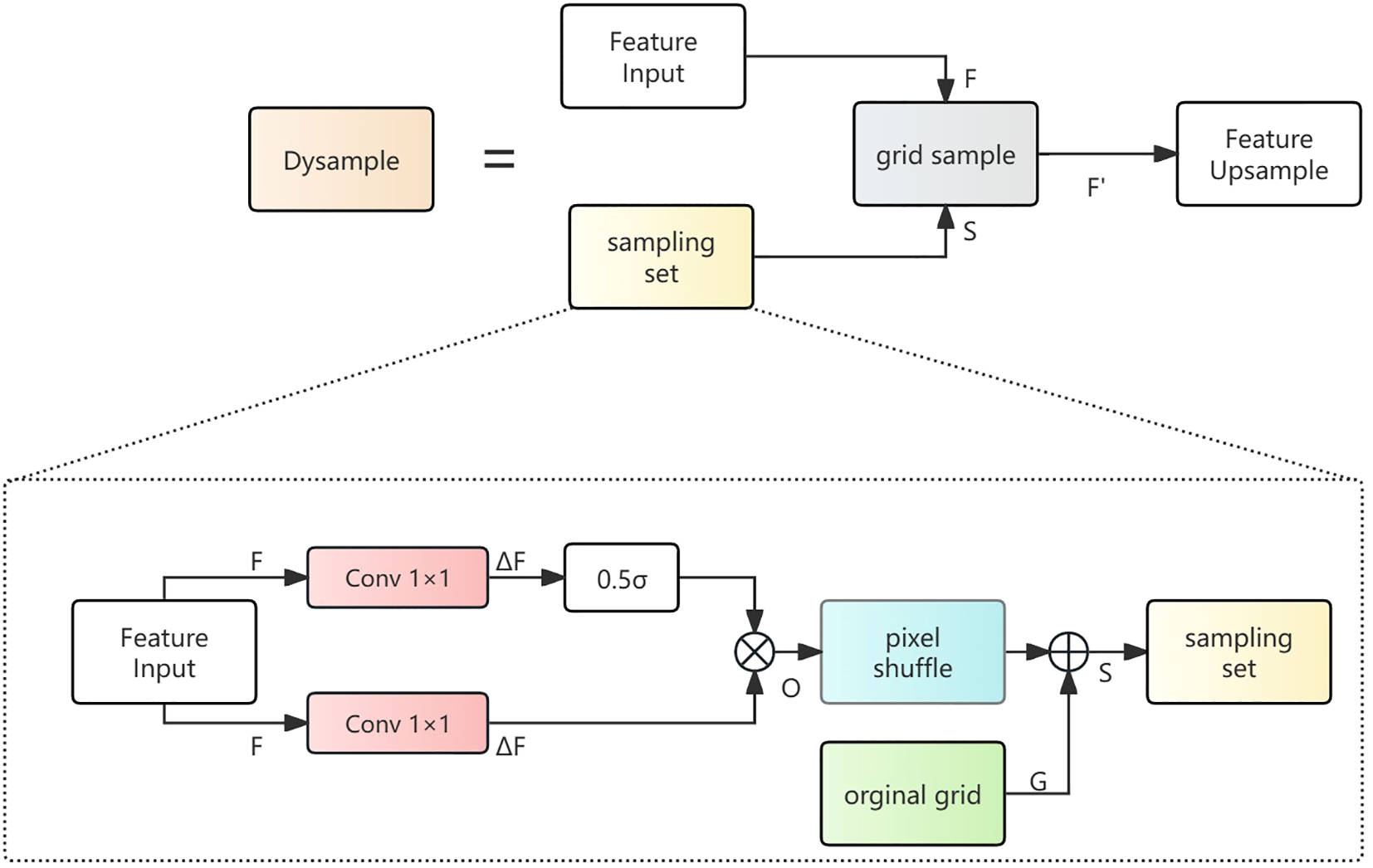
DySample (Dynamic Upsampling) structure diagram.
Dysample achieves dynamic adaptive feature resampling by learning the offset field in feature space. According to geometric information modeling, we revisit the essence of upsampling as point sampling. The formation process of the sampling set is shown in Figure 8. The input feature generates sampling offsets through a 1×1 convolution layer. To increase the flexibility of the offsets, we further generate per-point dynamic range factors through linear projection of the input features. The dynamic range factors are formed by combining a sigmoid activation function with a static factor of 0.5. The generation process of offset is shown as Equations 8, 9:
The above equations represent the sigmoid activation function, and 0.5 is used to limit the offset magnitude, preventing sampling points from deviating too far and causing information distortion. In addition to dynamically generated offsets, the sampling set also requires an original grid G as basic positioning to make sure that the upsampling process is fundamentally stable. The original grid G is a two-dimensional initial position field, serving as the starting reference coordinates for sampling. The offset O is processed through pixel shuffle to increase spatial resolution, then added to the original grid G to obtain the sampling set S. Finally, Dysample applies the grid sample module to complete the upsampling operation, obtaining the sampled feature as Equation 10:
The ADFFN feature fusion network significantly enhances the performance of the YOLOv11n lightweight network in ship wake detection tasks through the use of channel attention mechanisms, dynamic learnable sampling, and efficient feature fusion strategies. Compared to traditional feature fusion networks, the ADFFN network significantly enhances discriminative channel features through channel attention mechanisms, improving the ability of the model to detect complicated targets (e.g. ship wakes). Furthermore, dynamic learnable sampling Dysample can adaptively adjust sampling positions and weights according to input features, preserving key details of ship wakes.
3.3 SLODH
Traditional object detection heads exhibit obvious limitations when addressing ship wake detection in specialized scenarios. First, standard Oriented Bounding Box (OBB) detection heads typically contain numerous convolution layers and parameters, resulting in a heavy computational burden and slow inference speed, making it hard to satisfy the demands of real-time detection. Second, as a special target with high directionality and slender structure, ship wakes are difficult for traditional detection heads to effectively capture in terms of angular features, thereby affecting detection accuracy. Based on these issues, this paper designs a lightweight detection head named Shared Lightweight Orientation-aware Detection Head (SLODH), which significantly reduces model parameter count while improving perception capability for directional features of ship wakes through parameter sharing mechanisms and lightweight convolution design, achieving more efficient detection capability. Its workflow is illustrated in Figure 9.
Figure 9

SLODH structure diagram.
The core concept of the SLODH detection head is to significantly reduce computational complexity while maintaining detection accuracy through the use of parameter-sharing mechanisms and lightweight structures. Compared to traditional OBB detection heads, the main innovations of SLODH proposed in this paper are: first, designing independent feature transformation convolution modules for each feature layer (P3, P4, P5) at the multi-scale feature input end, mapping input features to feature spaces of the same dimension, establishing the foundation for subsequent shared convolution; then adopting a convolution block (Share_Conv) shared among multiple feature layers, where all feature layers are mapped to the same dimension through their respective feature transformations and then commonly utilize this module for further processing. This operation significantly reduces the model’s parameter count. This shared convolution consists of a Depth Wise convolution (DWConv) and a standard convolution in series as shown as Equation 11:
This operation both reduces computational complexity and ensures feature extraction capability. The normalization operation in the shared convolution employs group normalization (Wu and He, 2020) (GN). GN accelerates convergence, stabilizes gradient propagation, and provides regularization to prevent overfitting during the training process. When the input dimension is represented as , where N is the batch size, C is the number of channels, and H×W represents height and width, GN requires dividing the input channel number C into G groups before calculation, computing statistics for all samples and spatial positions within each group g. The calculation process is as followed as Equations 12, 13:
The above equations represent the mean value and the variance. The normalized output is shown as Equation 14:
From the above calculation process, it is evident that GN performs grouping within feature channels and then conducts normalization calculations within each group. This unique calculation method reduces the model’s dependence on batch size while improving training stability and generalization ability.
For the selection of the number of groups G, this paper integrates the number of input channels C and the seminal group normalization study of Wu and He (2020).
According to the overall structure of the model, the number of feature channels input to SLODH after ADFFN feature fusion operation is 64. In the seminal Group Normalization (GN) study (Wu and He, 2020), Wu and He conducted a comprehensive analysis of ImageNet classification, COCO object detection and semantic segmentation, and finally proved that a group containing 8-32 channels can provide the best performance for vision tasks. When G=8, the number of channels per group for SLODH, C/G=64/8 = 8, is just within the above optimal performance range. This case achieves both the highest computational efficiency and the best feature diversity, without the increased thread overhead caused by too large a group size or the statistical instability caused by too small a group size. In addition, G=8 also meets the hardware suitability: 8 is an integer factor of GPU warp (32 threads), which can minimize thread waste.
Thus G=8 satisfies the theoretically optimal configuration established in the pioneering research on Group Normalization, and achieves an optimal balance between the statistical stability of multiscale features and the computational efficiency of hardware.
In summary, the SLODH lightweight detection head proposed in this paper effectively addresses the problems of high computational complexity and parameter redundancy in traditional OBB detection heads for ship wake detection through the use of feature transformation layers, shared convolution structures, and lightweight group normalization.
4 Experiment
To validate the effectiveness of the newly designed OptWake-YOLO model, we conducted extensive experiments on the public SWIM dataset. Through comparisons between OptWake-YOLO and other network models, we have demonstrated the effectiveness of our proposed model.
4.1 Experimental environment and dataset
Ship Wake Imagery Mass (SWIM) dataset is a large-scale maritime object detection dataset. The creators of this dataset collected images from Google Earth of coastal areas around the world taken between 2009 and 2021. The detection targets include various ship wakes ranging from yachts to large cargo ships, with backgrounds including open seas, harbors, straits, and canals to ensure background variety. The spatial resolution of the images varies from 2.5 to 0.5 meters, with a uniform pixel count of 768 x 768. The dataset comprises a total of 11,600 images providing up to 15,356 precisely annotated wake instances. The dataset was divided into a 6:2:2 ratio, with the training set containing 6,960 images, while the validation and test sets containing 2,320 images each. Figure 10 illustrates the essential condition of the dataset. Figure 10a demonstrates that the dataset contains only one type of target ship wake; Figure 10b represents the size and quantity information of target boxes, reflecting the size distribution of target instances in each image; Figure 10c shows the position of target box centers relative to the entire image, indicating that target instances are relatively central in the images; Figure 10d represents the aspect ratio of target boxes relative to the image, showing that the box sizes are moderate, with few extreme cases of oversized or undersized boxes.
Figure 10
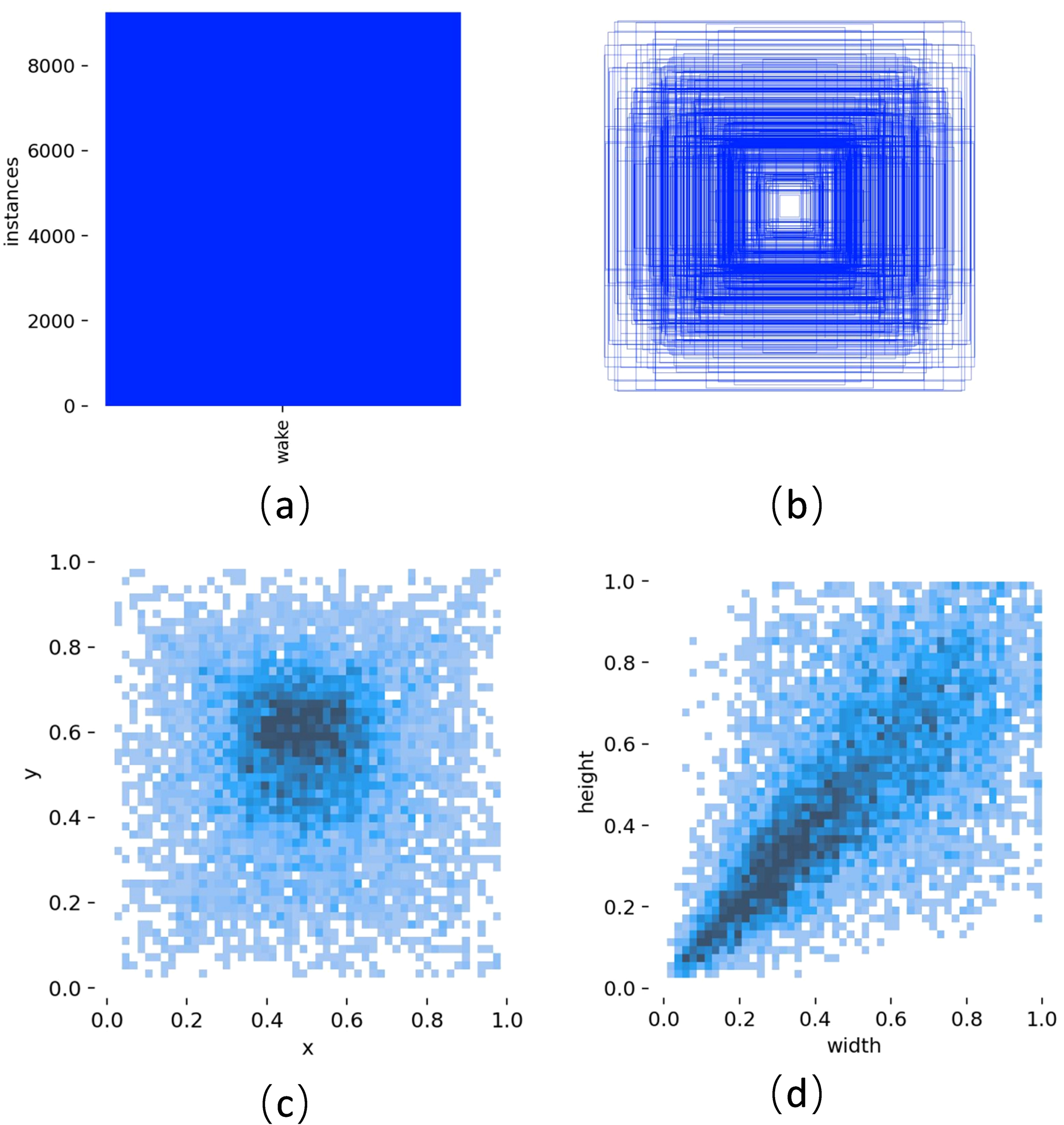
SWIM dataset distribution diagram. (a) Number of wake instances; (b) Box size and quantity; (c) Center point position relative to the entire image; (d) Target width-height ratio rela-tive to the entire image.
All experiments were conducted on the Ubuntu 22.04 operating system with the deep learning framework PyTorch 2.1.0, Python 3.10 as the programming language, CUDA version 12.2, Intel Xeon Gold 6342 CPU, and NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090 GPU. Hyperparameter settings were as follows: initial learning rate of 0.01, weight decay co-efficient of 0.0005, SGD optimizer, input image size of 768×768 pixels, 100 epochs, batch size of 16, with remaining parameters set to YOLOv11n default values. The configuration is shown in Table 1. While our evaluation focuses on the SWIM dataset due to its comprehensive coverage and public availability, we acknowledge this represents a limitation in terms of generalizability assessment across diverse optical remote sensing scenarios.
Table 1
| Parameter | Configuration |
|---|---|
| Computer operating system | Ubuntu22.04 |
| CPU | Intel Xeon Gold 6342 |
| GPU | NVIDIA RTX 3090 |
| CUDA | V12.2 |
| Python | V3.10 |
| Pytorch | V2.1.0 |
| Initial Learning Rate | 0.01 |
| Weight Decay | 0.0005 |
| Momentum | 0.937 |
| Optimizer | SGD |
| Batch Size | 16 |
| Input Resolution | 768×768 |
| Training Epochs | 100 |
| Warmup Epochs | 3 |
| Data Augmentation | Mosaic, MixUp, HSV |
| Label Smoothing | 0.0 |
| IoU Loss Weight | 7.5 |
| Classification Loss Weight | 0.5 |
| Object Loss Weight | 1.0 |
Experimental environment configuration and hyperparameters.
4.2 Evaluation metrics
To accurately evaluate the performance improvements of the new model, metrics such as mean Average Precision (mAP), Recall (R), Precision (P), Frames Per Second (FPS), parameter count (Params), and computational complexity (GFLOPs) were used to quantitatively validate the effectiveness of the proposed network. The metrics are defined as Equations 15–18:
In the above equations, TP, FP, and FN represent correctly detected targets, incorrectly detected targets, and targets that failed to be detected, respectively. A ship wake is considered correctly detected if the Intersection over Union (IoU) is greater than 0.5. P(R) represents the precision-recall curve.
4.3 Ablation experiments
To evaluate the impact of each improved module on the model’s detection performance, we conducted a series of ablation experiments on the SWIM dataset. The experiments used YOLOv11 as the baseline network, separately adding the RCEA, ADFFN, and SLODH modules and their different combinations to verify the effectiveness of their improvements. The results are shown in Table 2, where the activation of a specific module or modules is indicated √. To better visualize the effects of model improvements, heatmaps are used to intuitively represent the performance before and after improvements, as shown in Figure 11.
Table 2
| RCEA | ADFFN | SLODH | mAP50(%) | mAP50-95 (%) | Param (M) | GFLOPs | FPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 91.7 | 63.6 | 2.7 | 6.6 | 302.57 | |||
| ✓ | 92.6 | 64.5 | 2.5 | 6.8 | 305.92 | ||
| ✓ | 92.3 | 64.6 | 1.9 | 5.5 | 303.74 | ||
| ✓ | 92.1 | 64.4 | 2.4 | 5.7 | 315.26 | ||
| ✓ | ✓ | 92.7 | 63.4 | 1.8 | 5.7 | 276.68 | |
| ✓ | ✓ | 92.1 | 62.8 | 2.3 | 5.9 | 312.27 | |
| ✓ | ✓ | 92.0 | 62.8 | 1.8 | 4.6 | 231.21 | |
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 93.2 | 66.5 | 1.6 | 4.9 | 303.43 |
Ablation experiment results.
Figure 11
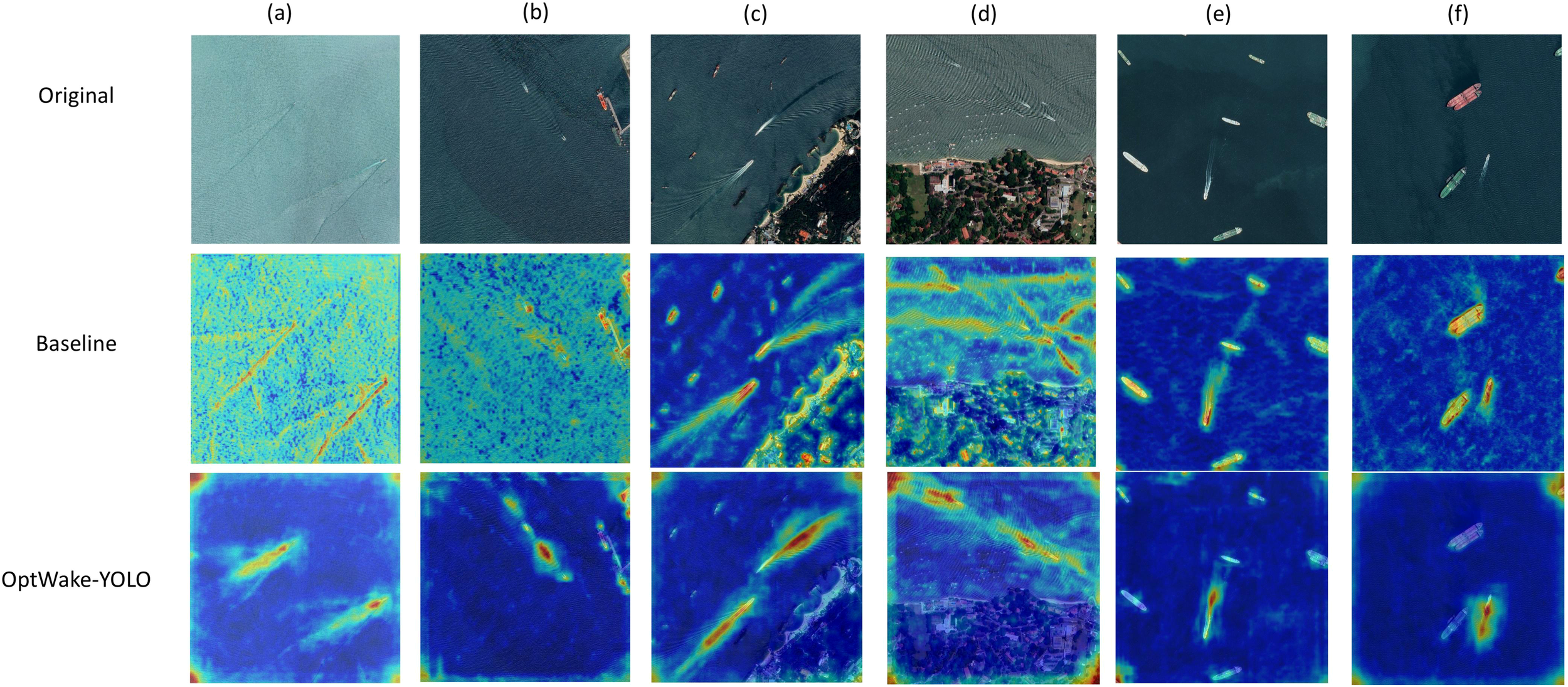
Heat maps of baseline and improved model. (a, b) Comparison of the heatmaps of the baseline model and that of the OptWake-YOLO model when noise is present on the sea surface. (c, d) Comparison of the heat maps of the baseline model and the Optwak-Yolo model when there is interference from coastal buildings around the wake. (e, f) Comparison of the heat maps of the baseline model and the Optwak-Yolo model when there are multiple stationary vessels around the wake.
As shown in Table 2, the baseline YOLOv11n achieves 91.7% mAP50 and 63.6% mAP50-95 with 2.7M parameters and 6.6 GFLOPs. Then we assessed the improvement of each module added individually to the baseline model. From the results, each module improves the detection performance, among which the RCEA accuracy is the most obvious, precisely because of its re-parameterization and multi-branch aggregation which effectively enhances the feature extraction capability. And ADFFN’s selective feature fusion mechanism strategy eliminates redundant computation and significantly improves efficiency.
In the case of a two-module combination, the combination of RCEA+ADFFN exhibits an interesting performance pattern: mAP50 rises to 92.7% (+1.0%), but mAP50-95 falls to 63.4% (-0.2%). This phenomenon occurs due to feature over-enhancement, with the reparameterization of RCEA amplifying certain channels, while the attentional mechanism of ADFFN creates a positive feedback loop that overemphasizes strong features while suppressing weaker, but important details. This leads to an increase in overall detection capability (higher mAP50 values), but a decrease in localization accuracy (lower mAP50-95 values) at tighter IoU thresholds. For the other two combination cases, RCEA+SLODH and ADFFN+SLODH, the performance improvement is not significant. Compared with the baseline model, the mAP50 of ADFFN+SLODH only improves by 0.4% despite the reduction of the computational cost, indicating that the advantage of lightweight detection will be limited without the enhanced feature extraction of RCEA; RCEA+SLODH exhibits a similar scenario, suggesting that without proper multi-scale feature fusion, even if the enhanced backbone features are coupled with the highly efficient detection head cannot achieve optimal performance.
By adding SLODH to both, the feature imbalance problem of RCEA+ADFFN is solved, and the Group Normalization operation and parameter sharing mechanism in SLODH achieves feature balancing for optimal performance of the complete system, with 93.2% mAP50 (+1.5%) and 66.5% mAP50-95 (+2.9%) detection accuracies while maintaining excellent efficiencies of 1.6M parameters (-40.7%) and 4.9 GFLOPs (-25.8%). This excellent performance demonstrates the synergistic effect of the three modules: RCEA for enhanced feature extraction through reparameterization, ADFFN for effective multi-scale feature fusion through the attention mechanism, and SLODH for efficient detection through shared convolution and group normalization.
The heatmap comparison provided in Figure 11 clearly demonstrates the significant advantages of the improved model in ship wake detection tasks. The heatmaps intuitively present the distribution of model attention, with red areas indicating high-attention regions and blue areas indicating low-attention regions. In the comparison between Figures 11a, b, the baseline model’s attention is dispersed when processing sea surface backgrounds, with substantial noise interference, making it difficult for the model to precisely locate wakes. In contrast, our proposed OptWake-YOLO model significantly enhances attention by focusing on the wake itself while effectively suppressing sea surface noise interference. This is primarily attributed to the multi-branch structure and reparameterization technology used in the model. The separated feature flow design and efficient feature aggregation mechanism enable the model to effectively extract rich texture and geometric features under complex sea conditions, improving wake recognition accuracy while maintaining computational efficiency.
In Figures 11c, f, baseline models exhibited high false positive rates due to the linear structures of coastlines, port facilities, and stationary vessels that closely resemble ship wake characteristics. In contrast, OptWake-YOLO significantly reduced attention to non-target linear features. This performance enhancement primarily stems from ADFFN module’s dual innovations: the channel attention mechanism adaptively weights features across different levels, effectively amplifying wake-related channel features while suppressing interference channels, thereby achieving precise feature screening; meanwhile, the Selective Feature Fusion (SFF) mechanism emphasizes common salient regions across multi-level features through multiplicative operations, combined with additive operations that maximally preserve original feature information, enabling the model to accurately capture the distinctive morphology and texture patterns of wakes. This allows precise discrimination between wakes and non-target linear features, with the module’s robust feature fusion capabilities in complex backgrounds establishing a critical foundation for OptWake-YOLO’s high-precision detection performance.
A comprehensive analysis of the table and heatmaps comparison results clearly demonstrates that OptWake-YOLO exhibits excellent detection performance in various complex environments. The RCEA module enhances feature extraction capability, the ADFFN optimizes feature fusion effects, and the SLODH detection head significantly reduces computational complexity while ensuring detection accuracy. The synergistic effect of these three modules enables our model to accurately detect ship wakes when faced with complex situations such as sea surface background noise, coastal structure interference, and stationary vessels, while maintaining low computational cost and high detection efficiency, providing reliable technical support for practical applications.
To more comprehensively evaluate the performance of different components in the ship wake detection task, we further designed a series of comparative experiments targeting various modules, exploring the impact of different types of Backbone, Neck, and upsampling operations on model performance. These experiments aimed to verify the superiority of the improved modules among similar methods while providing a scientific basis for model structure selection. Using the controlled variable method, we evaluated performance by replacing only a single module while keeping other components unchanged, ensuring the reliability and comparability of experimental results. The results are shown in Tables 3-5, corresponding to comparative experiments of Backbone, Neck, and upsampling operations, respectively. These experiments not only verified the effectiveness of our proposed modules but also revealed their unique advantages in feature extraction, feature fusion, and fine feature reconstruction, providing deep insights into understanding the working mechanisms of wake detection models.
-
Backbone: To assess the effect of different backbones on ship wake detection capability, in this ablation experiment, we compared experimental results of ship wake detection by replacing different backbones, keeping other structures and parameters unchanged. The results are shown in Table 3. Compared to other commonly used backbone networks such as Fasternet (Chen et al., 2023), EfficientViT (Liu et al., 2023), Convnextv2 (Woo et al., 2023), and Mo-bilenetV4 (Qin et al., 2024), our backbone network improved with the RCEA module achieved the highest detection accuracy at 92.6% with the most lightweight model size.
-
Neck: To evaluate the impact of different Neck improvements on ship wake detection capability, we compared experimental results of different improved neck structures, with results shown in Table 4. Our model improved with the ADFFN module and achieved optimal performance. Among the comparative neck structures, models improved with BiFPN, GFPN (Xu et al., 2022), and MAFPN (Yang et al., 2024) also showed increased detection accuracy compared to the baseline model, but their degree of model lightweighting was not as significant as ADFFN.
-
Upsample: Upsampling operations play an important role in object detection models, enabling resolution recovery, detail reconstruction, and other operations that can facilitate precise detection and localization of targets by detection models. To further investigate the impact of upsampling operations on detection models, we experimented and compared results with ConvTranspose, CARAFE (Wang et al., 2019), and WaveletUnpool (Xu et al., 2023) against the Dysample upsampling operation used in this paper on the SWIM dataset, as shown in Table 5. Different upsampling operations all helped improve detection accuracy, while the Dysample upsampling operation used in this paper achieved the best detection performance.
Table 3
| Backbone | mAP50 (%) | mAP50-95 (%) | Param (M) | GFLOPs | FPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fasternet | 92.6 | 63.6 | 4.0 | 9.4 | 259.87 |
| EfficientViT | 91.3 | 62.5 | 3.8 | 8.2 | 147.43 |
| Convnextv2 | 89.7 | 58.9 | 5.5 | 12.8 | 144.34 |
| MobilenetV4 | 89.6 | 60.5 | 5.5 | 21.3 | 256.71 |
| RCEA | 92.6 | 64.5 | 2.5 | 6.8 | 305.92 |
Comparison of detection performance with different backbones.
Table 4
| Neck | mAP50(%) | mAP50-95 (%) | Param(M) | GFLOPs | FPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BiFPN | 91.9 | 62.1 | 2.0 | 6.5 | 291.81 |
| Slimneck | 90.9 | 62.1 | 2.6 | 6.2 | 301.10 |
| GFPN | 92.4 | 64.0 | 3.7 | 8.4 | 300.53 |
| GoldYOLO | 89.2 | 58.3 | 5.9 | 9.4 | 205.31 |
| MAFPN | 92.2 | 62.7 | 2.7 | 7.3 | 197.28 |
| ADFFN | 92.3 | 64.6 | 1.9 | 5.5 | 293.56 |
Comparison of detection performance with different necks.
Table 5
| Upsample | mAP50 (%) | mAP50-95 (%) | Param (M) | GFLOPs | FPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ConvTranspose | 92.4 | 63.6 | 2.0 | 6.0 | 286.77 |
| CARAFE | 92.3 | 63.4 | 2.1 | 5.7 | 218.57 |
| Waveletunpool | 92.3 | 64.3 | 2.2 | 5.5 | 311.86 |
| Dysample | 92.3 | 64.6 | 1.9 | 5.5 | 293.56 |
Comparison of detection performance with different upsampling operations.
In addition to the model components, we also explored the effect of the number of samples of the model during training on the effectiveness of model detection. The model detection performance for the following batch sizes N ∈ {4, 8, 16, 32, 64} was evaluated under the same training conditions (same hardware, same hyper-parameters except for the batch size, and consistent data augmentation), and the results of the tests are shown in Table 6.
Table 6
| Batchsize | mAP50(%) | mAP50-95(%) | Param(M) | GFLOPs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 93.0 | 66.1 | 1.6 | 4.9 |
| 8 | 92.8 | 65.9 | 1.6 | 4.9 |
| 16 | 93.2 | 66.5 | 1.6 | 4.9 |
| 32 | 92.5 | 66.0 | 1.6 | 4.9 |
| 64 | 92.0 | 65.5 | 1.6 | 4.9 |
Comparison of detection performance with different batchsize.
From the experimental results, the model with Batchsize=16 performs optimally in several key metrics. First, its mAP50 reaches 93.2%, which is higher than other configurations, indicating that it has higher accuracy in the target detection task. Second, the mAP50-95 (66.5%) is also higher than other configurations, indicating that it is more robust to different IoU thresholds.
In summary, the model configuration of Batchsize=16 strikes an optimal balance between training stability and model performance, and is a reasonable choice for balancing performance, speed and stability.
4.4 Comparison with state-of-the-art methods
To comprehensively evaluate the performance advantages of our proposed method, this study selected multiple cutting-edge object detection algorithms widely recognized in both academic and industrial communities, including the classic YOLOv3-tiny, the industrial-grade PP-YOLOE-R, mainstream YOLOv5n to YOLOv12n series, S2Anet (Han et al., 2022) specialized for oriented objects, the innovative Mamba-T (Wang et al., 2024) architecture based on state space models and Hyper-YOLO (Feng et al., 2025), a target detection model based on hypergraph computation. Rigorous comparative experiments have been accomplished on the public SWIM dataset. To ensure a comprehensive and objective performance assessment, the evaluation employed the aforementioned multi-dimensional metric system, with detailed comparison results shown in Table 7.
Table 7
| Model | mAP50(%) | mAP50-95 (%) | Param(M) | GFLOPs | FPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv3-tiny | 90.0 | 56.2 | 10.0 | 15.2 | 286.16 |
| PP-YOLOE-R | 78.4 | 54.2 | 8.2 | 12.3 | 46.69 |
| YOLOv5n | 92.0 | 63.2 | 2.6 | 7.3 | 294.43 |
| S2ANet | 69.7 | 47.1 | 37.4 | 130.9 | 35.12 |
| YOLOv6 | 88.5 | 55.9 | 4.3 | 11.8 | 309.11 |
| YOLOv8n | 92.1 | 64.4 | 2.8 | 7.1 | 313.79 |
| YOLOv9t | 90.3 | 59.4 | 2.0 | 7.8 | 277.96 |
| YOLOv10n | 91.8 | 63.7 | 3.1 | 8.7 | 267.21 |
| Mamba-T | 93.0 | 66.5 | 5.7 | 12.6 | 75.61 |
| YOLOv11n | 91.7 | 63.6 | 2.7 | 6.6 | 302.57 |
| YOLOv12n | 88.5 | 55.2 | 2.6 | 6.1 | 277.78 |
| Hyper-YOLOt | 92.4 | 64.6 | 2.8 | 7.9 | 243.90 |
| Ours | 93.2 | 66.5 | 1.6 | 4.9 | 303.43 |
Detection results of the improved model versus other state-of-the-art detection models.
Analysis of the experimental results demonstrates that the OptWake-YOLO model proposed in this paper achieves an optimal balance between detection accuracy and computational efficiency on the SWIM dataset. Specifically, compared to all benchmark models, our method achieves optimal performance on key evaluation metrics with mAP50 and mAP50-95 reaching 93.2% and 66.5%, respectively, while establishing the best result for model lightweighting with only 1.6M parameters and 4.9 GFLOPs computational overhead. Notably, although YOLOv6 and YOLOv8n slightly lead in detection speed (309.11 and 313.79 FPS, respectively), their detection accuracy is significantly lower than our method (mAP50 decreased by 4.7% and 1.1%, respectively), with computational loads 140.8% and 44.9% higher. Meanwhile, although Mamba-T approaches our method in mAP50 (93.0% vs. 93.2%) with both achieving 66.5% in mAP50-95, its model parameter count (5.7M) and computational complexity (12.6 GFLOPs) are significantly higher than our method, resulting in a detection speed of only 75.6 FPS, far below the threshold for real-time applications.
To intuitively demonstrate the superiority of our method in practical applications, Figure 12 presents the detection results of various algorithms addressing typical complex environments. As shown in Figures 12a, b, under severe sea conditions where wakes are partially submerged by waves causing indistinct features, YOLOv3-tiny, YOLOv5n, YOLOv8n, and YOLOv11n all exhibit varying degrees of missed detections, while OptWake-YOLO successfully overcomes sea condition interference with its powerful feature extraction capability, precisely detecting wakes obscured by waves. Figure 12c illustrates the detection challenges in coastal port or vessel berthing areas, where linear features presented by embankments and coastlines easily interfere with detection systems. In this situation, YOLOv5n and YOLOv11n in-correctly identify embankments with similar linear shapes as ship wakes, while our method successfully avoids such misidentifications by effectively extracting wake-specific texture features. Figure 12d further validates OptWake-YOLO’s robustness in environments obscured by clouds and fog, where comparative algorithms all exhibit missed detections, while our method maintains high accuracy, successfully detecting all wake targets.
Figure 12
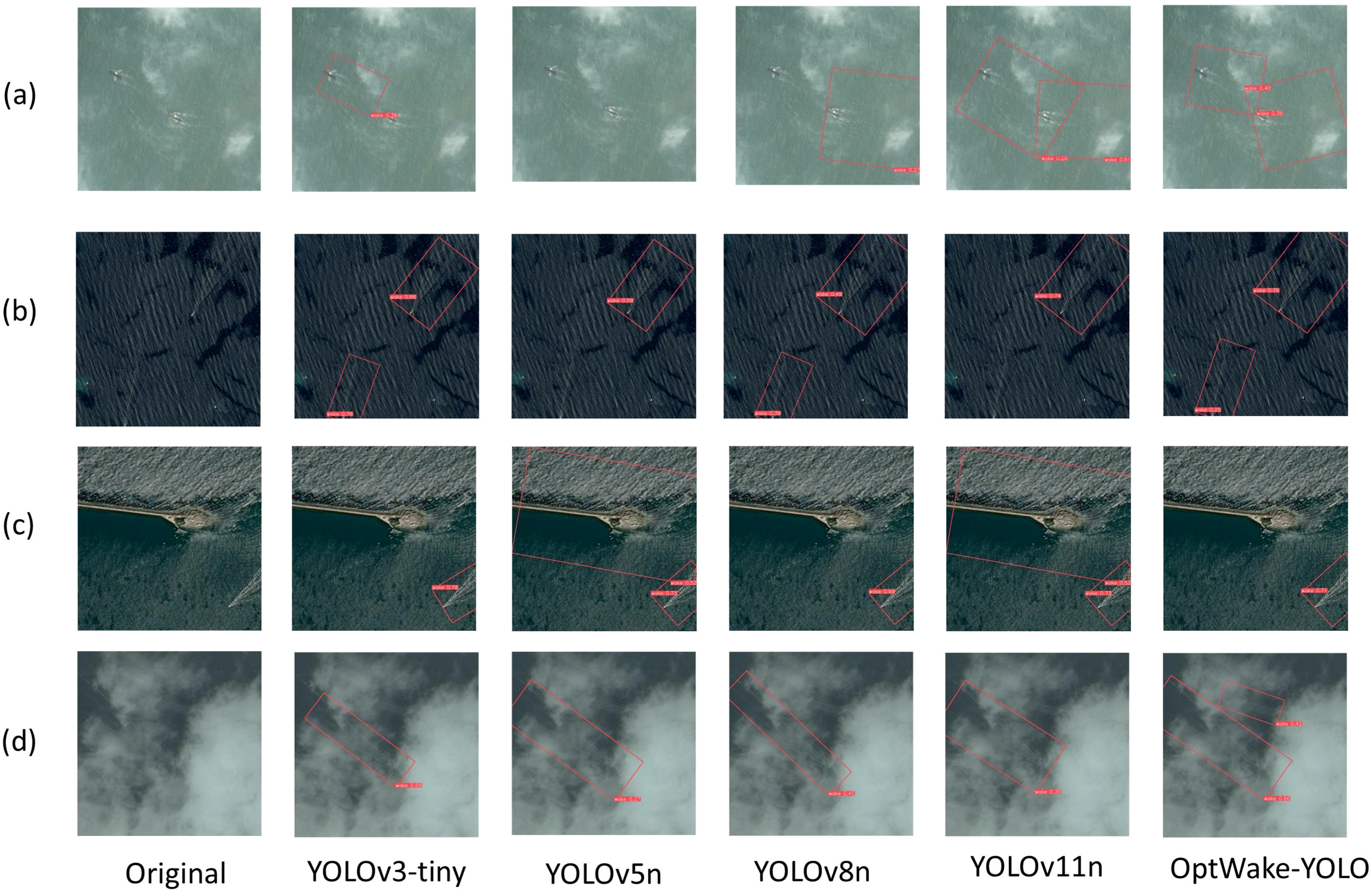

Detection results of different algorithms in typical complex scenarios. (a, b) Comparison of wake detection effects of different detection models under adverse sea conditions. (c) Comparison of wake detection effects of different detection models around coastal ports or ship mooring areas. (d) Comparison of wake detection effects of different detection models under cloud and fog occlusion conditions.
Comprehensive analysis indicates that compared to existing state-of-the-art algorithms, the OptWake-YOLO proposed in this paper demonstrates significant advantages in feature extraction capability, recognition of wake-specific high-level semantic features (such as the V-shaped distribution of Kelvin wakes, and the dark-line patterns of turbulent wakes), and adaptability to complex environments. These advantages stem from three core innovations of the model: enhanced feature extraction capability from the RCEA module, efficient feature fusion implemented by the ADFFN module, and the lightweight computational architecture provided by the SLODH detection head. The synergistic effect of these three components enables OptWake-YOLO to maintain excellent detection performance when facing complex scenarios such as sea surface background noise, coastal structure interference, and meteorological condition variations, while meeting the strict requirements of practical applications for computational resources and real-time performance, providing ideal technical support for maritime safety monitoring systems.
While our experiments were conducted on RTX 3090 for standardized comparison, the lightweight nature of OptWake-YOLO (1.6M parameters, 4.9 GFLOPs) makes it well-suited for edge deployment. Based on the computational complexity of the model and parametric analysis of commonly used edge devices, OptWake-YOLO’s inference speed is estimated to be 40-67 FPS when deployed on the entry-level edge device, NVIDIA Jetson Nano (Zhang et al., 2022); and when deployed on the more capable Jetson Xavier NX (Wang et al., 2022) The inference speed can exceed 100FPS. The lightweight nature of the model is perfectly suited to ships and coastal monitoring stations with limited computational resources.
5 Conclusions
This paper addresses the challenge of real-time ship wake detection by proposing an improved wake detection model OptWake-YOLO based on YOLOv11n. The model perfectly balances detection accuracy and efficiency through three key innovations: first, implementing the RCEA module in the Backbone, which integrates reparameterization technology with multi-branch structures to significantly enhance feature extraction capabilities; second, designing a novel ADFFN feature fusion network in the Neck, combining channel attention mechanisms with dynamic upsampling techniques to achieve efficient multi-scale feature fusion; and finally, developing the new SLODH lightweight detection head, which substantially reduces model complexity through parameter sharing and group normalization techniques.
Extensive experiments on the public SWIM dataset demonstrate that, compared to the YOLOv11n, the OptWake-YOLO improves mAP50 and mAP50-95 evaluation metrics by 1.5% and 2.9% respectively, while significantly reducing parameter count and computational load by 40.7% and 25.8%, maintaining a high detection speed of 303.43 FPS. Heatmap analysis and visualization comparisons in complex environments further verify the robustness and accuracy of the model in different sea states, meteorological circumstances, and coastal interferences. Compared to current mainstream object detection algorithms (e.g. YOLOv5, YOLOv8, YOLOv10, and Mamba), OptWake-YOLO achieves optimal lightweight performance while maintaining the highest detection accuracy, fully satisfying the requirements for high-precision, low-latency wake detection in practical application scenarios including edge device deployment for real-time maritime surveillance systems.
The lightweight design of the OptWake-YOLO offers a high degree of engineering and practical value, making it particularly suitable for practical maritime surveillance deployment scenarios: (1) Autonomous Maritime Vehicles: The model’s low computational requirements (4.9 GFLOPs) and small memory footprint (6.4MB) enable integration into unmanned surface vehicles and autonomous underwater vehicles for real-time wake detection and vessel tracking. (2) Coastal Monitoring Systems: Edge device compatibility allows deployment in remote coastal monitoring stations with limited power and computational resources, enabling 24/7 surveillance coverage. (3) Satellite Integration: The model’s efficiency makes it suitable for on-board satellite processing, reducing data transmission requirements and enabling near real-time maritime surveillance from space. (4) Multi-sensor Fusion: The lightweight architecture facilitates integration with other sensing modalities (radar, AIS, infrared) in comprehensive maritime domain awareness systems.
Despite the significant achievements of this work, there remain scope for future research: (1) Dataset limitations: Our experiments were conducted solely on the SWIM dataset, which may introduce geographical and environmental biases. The dataset primarily contains images from coastal areas with specific resolution ranges (0.5-2.5m), which may not fully represent diverse maritime conditions globally. Future work will therefore need to be supported by multiple datasets with different geographical distributions, seasonal conditions and sensor characteristics. (2) Extreme weather performance: While our model demonstrates robust performance under various sea conditions present in SWIM, its effectiveness in extreme weather scenarios (heavy storms, dense fog) or different water types (polar regions, inland waters) requires further validation. (3) Wake classification: Current model focuses on detection; extension to wake classification (vessel type, size estimation) would enhance practical utility. (4) The possibility of further optimizing the model size and deployment cost: e.g. using model compression techniques such as pruning and knowledge distillation.
In conclusion, the method proposed in this paper provides an efficient and reliable technical solution for real-time ship wake detection in optical remote sensing images, offering significant theoretical and practical value for maritime surveillance and security protection.
Statements
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
RQ: Validation, Data curation, Visualization, Methodology, Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. NB: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing, Funding acquisition, Resources. CY: Writing – review & editing, Software, Data curation, Visualization.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmars.2025.1624323/full#supplementary-material
References
1
Bochkovskiy A. Wang C.-Y. Liao. H.-Y. M. (2004). “Yolov4: Optimal speed and accuracy of object detection,” in arXiv preprint (2020) (Ithaca, New York, USA: arXiv), 10934.
2
Cai Z. Vasconcelos N. (2018). “Cascade R-CNN: delving into high quality object detection,” in 2018 IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (Los Angeles, California, USA: IEEE). doi: 10.1109/cvpr.2018.00644
3
Chen J. Kao S. He H. Zhuo W. Wen S. Lee C. H. et al . (2023). “Run, don’t walk: chasing higher FLOPS for faster neural networks,” in 2023 IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (Los Angeles, California, USA: IEEE), 12021–12031.
4
Chen Y. Zhang C. Chen B. Huang Y. Sun Y. Wang C. et al . (2024). Accurate leukocyte detection based on deformable-DETR and multi-level feature fusion for aiding diagnosis of blood diseases. Comput. Biol. Med.170, 107917. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2024.107917
5
Del Prete R. Graziano M. D. Renga A. (2021). First results on wake detection in SAR images by deep learning. Remote Sens.4573, 1–8. doi: 10.3390/rs13224573
6
Ding K. Yang J. Lin H. Wang Z. Wang D. Wang X. et al . (2023). Towards real-time detection of ships and wakes with lightweight deep learning model in Gaofen-3 SAR images. Remote Sens. Environ.284, 113345. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2022.113345
7
Ding X. Zhang X. Ma N. Han J. Ding G. Sun J. (2021). “RepVGG: making VGG-style convNets great again,” in 2021 IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (Los Angeles, California, USA: IEEE). doi: 10.1109/cvpr46437.2021.01352
8
Esposito C. Del Prete R. Graziano M. D. Renga A. (2022). “First results of ship wake detection by deep learning techniques in multispectral spaceborne images,” in IGARSS 2022 - 2022 IEEE international geoscience and remote sensing symposium (Los Angeles, California, USA: IEEE). doi: 10.1109/igarss46834.2022.9883511
9
Feng Y. Huang J. Du S. Ying S. Yong J. H. Li Y. et al . (2025). “Hyper-YOLO: when visual object detection meets hypergraph computation,” in IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence, vol. 47. (Los Angeles, California, USA: IEEE), 2388–2401.
10
Ge Z. Liu S. Wang F. Li Z. Sun J. (2021). “Yolox: Exceeding yolo series in 2021,” in arXiv preprint (Ithaca, New York, USA: arXiv), 2107.08430.
11
Girshick R. (2015). “Fast R-CNN,” in 2015 IEEE international conference on computer vision (ICCV) (Los Angeles, California, USA: IEEE). doi: 10.1109/iccv.2015.169
12
Girshick R. Donahue J. Darrell T. Malik J. (2014). “Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation,” in 2014 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (Los Angeles, California, USA: IEEE). doi: 10.1109/cvpr.2014.81
13
Graziano M. D. (2020). Preliminary results of ship detection technique by wake pattern recognition in SAR images. Remote Sens.2869, 5–9. doi: 10.3390/rs12182869
14
Han J. Ding J. Li J. Xia G. S. (2022). “Align deep features for oriented object detection,” in IEEE transactions on geoscience and remote sensing (Los Angeles, California, USA: IEEE), 1–11.
15
He K. Gkioxari G. Dollar P. Girshick R. (2020). IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence (Los Angeles, California, USA: IEEE). 386–397.
16
Hough P. V. C. (1962). A method and means for recognition complex patterns (Alexandria, Virginia, USA: United States Patent and Trademark Office, USPTO). US3069654A.
17
IMO (2024). AIS transponders—Regulations for carriage of AIS (London, UK: IMO).
18
Karakus O. Rizaev I. Achim A. (2020). Ship wake detection in SAR images via sparse regularization. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens., 1665–1677. doi: 10.1109/tgrs.2019.2947360
19
Kateb F. A. Monowar M. M. Hamid M. Ohi A. Q. FruitDet M. M.F. (2021). Attentive feature aggregation for real-time fruit detection in orchards. Agronomy. 2440, 3–10. doi: 10.3390/agronomy11122440
20
Li Z. Wang Yongcheng Zhang Ning Zhang Yuxi Zhao Zhikang Xu Dongdong et al . (2022). Deep learning-based object detection techniques for remote sensing images: A survey. Remote Sens.14, 10. doi: 10.3390/rs14102385
21
Liu W. Anguelov D. Erhan D. Szegedy C. Reed S. Fu C. Y. et al . (2016). “SSD: single shot multiBox detector,” in Computer vision – ECCV 2016,Lecture notes in computer science (Berlin, Germany: Springer), 21–37. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-46448-0_2
22
Liu Y. Deng R. (2018). “Ship wakes in optical images,” in Journal of atmospheric and oceanic technology (Boston, Massachusetts, USA: American Meteorological Society, AMS), 1633–1648. doi: 10.1175/jtech-d-18-0021.1
23
Liu Y. Zhao J. (2024). Kelvin wake detection from large-scale optical imagery using simulated data trained deep neural network. Ocean Engineering297, 117075.
24
Liu W. Lu H. Fu H. Cao Z. (2023). “Learning to upsample by learning to sample,” in Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision (Los Angeles, California, USA: IEEE), 6027–6037.
25
Liu Z. Mao H. Wu C.-Y. Feichtenhofer C. Darrell T. Xie S. (2022). “A convNet for the 2020s,” in 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (Los Angeles, California, USA: IEEE). doi: 10.1109/cvpr52688.2022.01167
26
Liu X. Peng H. Zheng N. Yang Y. Hu H. Yuan Y. (2023). “EfficientViT: memory efficient vision transformer with cascaded group attention,” in 2023 IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR) (Los Angeles, California, USA: IEEE), 14420–14430.
27
Liu S. Qi L. Qin H. Shi J. Jia J. (2018). “Path aggregation network for instance segmentation,” in IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. doi: 10.1109/cvpr.2018.00913
28
Liu Y. Zhao J. Qin Y. (2021). A novel technique for ship wake detection from optical images. Remote Sens. Environ.258, 112375. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2021.112375
29
Mazzeo A. Renga A. Graziano M. (2024). A systematic review of ship wake detection methods in satellite imagery. Remote Sens.16, 3775. doi: 10.3390/rs16203775
30
Mook K. K. Jin K. D. (2019). Ship velocity estimation from ship wakes detected using convolutional neural networks. IEEE J. Selected Topics Appl. Earth Observations Remote Sens., 4379–4388. doi: 10.1109/jstars.2019.2949006
31
Pichel W. G. Clemente-Colón P. Wackerman C. C. Friedman K. S. (2004). “Ship and wake detection,” in Synthetic aperture radar marine user’s manual, vol. 277. (Silver Spring, Maryland, USA: National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA)), 303.
32
Qin D. Leichner C. Delakis M. Fornoni M. Luo S. Yang F. et al . (2024). “MobileNetV4: universal models for the mobile ecosystem,” in European conference on computer vision (Berlin, Germany: Springer), 78–96.
33
Radon J. (1986). On the determination of functions from their integral values along certain manifolds. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging5, 170–176. doi: 10.1109/tmi.1986.4307775
34
Redmon J. Divvala S. Girshick R. Farhadi A. (2016). You Only Look Once: Unified, Real-Time Object Detection. In: 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). doi: 10.1109/cvpr.2016.91
35
Redmon J. Farhadi A. (2017). “YOLO9000: better, faster, stronger,” in 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (Los Angeles, California, USA: IEEE). doi: 10.1109/cvpr.2017.690
36
Redmon J. Farhadi A. (2018). “YOLOv3: an incremental improvement,” in arXiv: computer vision and pattern recognition (Ithaca, New York, USA: arXiv).
37
Ren S. He K. Girshick R. Sun J. (2017). Faster R-CNN: towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence39, 1137–1149. doi: 10.1109/tpami.2016.2577031
38
Szegedy C. Liu W. Jia Y. Sermanet P. Reed S. Anguelov D. et al . (2015). “Going deeper with convolutions,” in 2015 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (Los Angeles, California, USA: IEEE). doi: 10.1109/cvpr.2015.7298594
39
Tan M. Pang R. Le Q. V. (2020). “EfficientDet: scalable and efficient object detection,” in 2020 IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (Los Angeles, California, USA: IEEE). doi: 10.1109/cvpr42600.2020.01079
40
Vesecky J. F. Stewart R. H. (1982). The observation of ocean surface phenomena using imagery from the SEASAT synthetic aperture radar: An assessment. J. Geophysical Research: Oceans, 3397–3430. doi: 10.1029/jc087ic05p03397
41
Wang J. Chen K. Xu R. et al . (2019). “CARAFE: content-aware reAssembly of FEatures,” in 2019 EEE/CVF international conference on computer vision (ICCV). doi: 10.1109/iccv.2019.00310
42
Wang H. Nie D. Zuo Y. Tang L. Zhang M. (2022). Nonlinear ship wake detection in SAR images based on electromagnetic scattering model and YOLOv5. Remote Sens.14, 22. doi: 10.3390/rs14225788
43
Wang Z. Li C. Xu H. Zhu X. Li H. (2024). Mamba YOLO: SSMs-based YOLO for object detection arXiv preprint (Ithaca, New York, USA: arXiv), 2406.05835.
44
Wang G. Zhao Y. Li B. Chen X. Liu Z. Kweon I. et al . (2022). Improved YOLO v4-tiny for real-time flame detection. Comput. Eng. Sci.44, 2196–2205.
45
Woo S. Debnath S. Hu R. Chen X. Liu Z. Kweon I. et al . (2023). “ConvNeXt V2: co-designing and scaling convNets with masked autoencoders,” in 2023 IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR (Los Angeles, California, USA: IEEE). doi: 10.1109/cvpr52729.2023.01548
46
Wu Y. He K. (2020). Group normalization. Int. J. Comput. Vision 2020, 742–755. doi: 10.1007/s11263-019-01198-w
47
Xu G. Liao W. Zhang X. Li C. He X. Wu X. (2023). Haar wavelet downsampling: A simple but effective downsampling module for semantic segmentation. Pattern recognition143, 109819. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2023.109819
48
Xu X. Jiang Y. Chen W. Huang Y. Zhang Y. Sun X. (2022). “DAMO-YOLO: A report on real-time object detection design,” in Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (Los Angeles, California, USA: IEEE), 11734–11743.
49
Xu C. Wang X. (2024). OpenSARWake: A large-scale SAR dataset for ship wake recognition with a feature refinement oriented detector. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett.21, 1–5. doi: 10.1109/lgrs.2024.3392681
50
Xue F. Jin W. Qiu S. Yang J. (2022). Rethinking automatic ship wake detection: state-of-the-art CNN-based wake detection via optical images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens.60, 1–22. doi: 10.1109/tgrs.2021.3128989
51
Xue F. Jin W. Qiu S. Yang J. (2021). Airborne optical polarization imaging for observation of submarine Kelvin wakes on the sea surface: Imaging chain and simulation. ISPRS J. Photogrammetry Remote Sens., 136–154. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2021.06.001
52
Yang Z. Guan Q. Zhao K. Yang J. Xu X. Long H. et al . (2024). “Multi-branch auxiliary fusion YOLO with re-parameterization heterogeneous convolutional for accurate object detection,” in Chinese conference on pattern recognition and computer vision (Berlin, Germany: Springer), 492–505.
53
Zhang Y. Yu J. Chen Y. Yu J. Chen Y. Yang W. Zhang W. He Y. (2022). Real-time strawberry detection using deep neural networks on embedded system (rtsd-net): An edge AI application. Comput. Electron. Agric.192, 106586. doi: 10.1016/j.compag.2021.106586
54
Zilman G. Zapolski A. Marom M. (2015). On detectability of a ship’s kelvin wake in simulated SAR images of rough sea surface. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens., 609–619. doi: 10.1109/tgrs.2014.2326519
Summary
Keywords
ship wake detection, YOLOv11n, RepConv, lightweight detector, DySample
Citation
Qiu R, Bi N and Yin C (2025) OptWake-YOLO: a lightweight and efficient ship wake detection model based on optical remote sensing images. Front. Mar. Sci. 12:1624323. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2025.1624323
Received
08 May 2025
Accepted
15 July 2025
Published
01 August 2025
Volume
12 - 2025
Edited by
Ting Zou, Memorial University of Newfoundland, Canada
Reviewed by
Keyu Chen, Xiamen University, China
Chengbo Wang, University of Science and Technology of China, China
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Qiu, Bi and Yin.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Nan Bi, 2202300392@neepu.edu.cn
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.