Abstract
Sea surface temperature (SST) serves as a critical indicator for assessing marine ecosystem health. Given the increasing human exploitation of marine resources, accurate SST prediction has garnered significant attention. While existing neural network based approaches effectively capture spatio temporal dependencies within SST data, they often suffer from high computational complexity. To address this, we propose TFLinear, a lightweight SST prediction model that incorporates a novel Residual Temporal Frequency (RTF) module which combines residual linking, depthwise separable convolution, and fast Fourier transform (FFT) into the DLinear framework. The method operates in three key stages: spatial feature extraction via depthwise separable convolution, time frequency decoupling of SST sequences using FFT to isolate trend, seasonal, and transient components, and multi step prediction through dedicated linear channels followed by component wise fusion. We evaluated TFLinear using OSTIA SST data from the East China Sea for 1 to 10 days forecasts, comparing it against state of the art benchmarks. Results show that TFLinear achieves superior performance in MAE, RMSE, and R², with improvements of 7.9% to 23%, while maintaining significantly lower computational cost — demonstrating strong potential for efficient and accurate SST forecasting in practical scenarios.
1 Introduction
Sea surface temperature (SST) (Andrews et al., 2022), a core parameter governing energy exchange and material transport at the ocean atmosphere interface, profoundly regulates the evolution of the multi scale coupled ocean atmosphere system. SST fluctuations not only directly influence atmospheric circulation patterns and drive extreme oceanic events, but also serve as a critical indicator for assessing marine ecosystem health and sustainability. Consequently, accurate SST prediction holds significant scientific and practical value, enhancing short term weather forecasting, optimizing early warning systems for marine disasters, ensuring maritime navigation safety and fisheries efficiency, and supporting blue carbon resource management decisions (Gao et al., 2024). Deepening our understanding of SST multi scale variability and overcoming prediction accuracy bottlenecks are thus paramount challenges in ocean atmosphere science and crucial for national environmental security and sustainable development.
However, the strong seasonality and multi scale temporal and spatial variability inherent in SST data, especially in the near shore area regulated by complex shoreline topography and local air sea interactions, have posed serious challenges to its accurate prediction. The core scientific difficulty lies in efficiently capturing the complex spatial and temporal dependencies in the SST field that evolve significantly with geographic regions and time dimensions. Traditional numerical ocean models based on physical mechanism constraints provide the theoretical cornerstone for SST prediction by solving the Navier Stokes (Temam, 2024) system of equations to simulate ocean dynamics processes. Although the development of high performance computing and data assimilation techniques has driven the increase in model complexity, numerical methods (Wang et al., 2024) are still difficult to completely circumvent the characterization errors of parameterized schemes for SST nonlinearities and seasonal abruptness features. Meanwhile, the high computational cost of model training, the limitation of cognition of small and medium scale processes, and the sensitivity to the initial field error together constrain their prediction efficiency and operational generalization capability.
With advances in satellite remote sensing and buoy array observation technologies, ocean data have witnessed an exponential increase in volume and multi source heterogeneity, and data driven machine learning methods have demonstrated breakthrough potential in SST prediction. Such methods construct predictive mapping relations by mining implicit laws in historical SST data, avoiding the explicit solution of complex physical equations. Early research mainly utilized machine learning models such as Support Vector Machines (SVM) (Nawi et al., 2021) and Gaussian Process Regression (GPR) (Zhang et al., 2021). In recent years, however, deep learning methods (Xu et al., 2023) have emerged as a key approach for tackling high dimensional modeling challenges in this field, owing to their powerful nonlinear fitting capabilities. In a systematic assessment of multiple sea areas in the Indian Ocean, Vytla et al (Vytla et al., 2025). compared various models and found that the deep learning model performed the best. Their research further validated the advantages of deep learning in capturing the spatiotemporal dependencies of SST, and provided data support for the early warning of extreme weather events such as tropical cyclones.
Aiming at the complex dependencies and instability of SST data in spatio temporal dimension (Elafi et al., 2024), and considering the current computational challenges in neural network model training, we propose a lightweight SST prediction model named TFLinear by combining the advantages of depthwise separable convolution in acquiring spatial features and the use of FFT (Yu et al., 2023) to decompose temporal dimension characteristics into the time frequency domain, so as to better capture the cyclicity and trendiness of the data. The model incorporates a linear combination of the RTF module—which consists of residual connection (Dai et al., 2024), depthwise separable convolution, and FFT—with traditional linear models, ensuring lightweight architecture while maintaining efficient spatio temporal feature extraction. The main contributions of this paper are summarized in the following three points:
-
We propose TFLinear, a lightweight linear predictive network for sea surface temperature (SST) forecasting. The model exhibits strong learning ability and effectively handles SST prediction tasks involving complex spatio temporal correlation features.
-
Through comparative analysis of model parameter complexity and computational load, we demonstrate that TFLinear significantly enhances efficiency while maintaining competitive prediction accuracy.
-
To evaluate TFLinear under realistic conditions, we conduct short term forecasting experiments using a dataset from the East China Sea. Performance is assessed over a 1 to 10 days prediction horizon by comparing evaluation metrics against current mainstream models. Results indicate that the proposed method outperforms most existing approaches, and ablation studies further validate the contribution of each component within the framework.
2 Related works
The evolution of sea surface temperature (SST) forecasting has progressed through distinct methodological paradigms, each addressing specific shortcomings of its predecessors while introducing new trade-offs between accuracy, computational cost, and model capability.
Initial data-driven approaches focused on modeling temporal dynamics at individual grid points. Techniques such as Multilayer Perceptrons (MLPs) (Yan, 2024), Long Short-Term Memory networks (LSTMs) (Wei and Guan, 2022), and Gated Recurrent Units (GRUs) (Han et al., 2023) demonstrated superior accuracy over traditional statistical models in localized settings. For instance, Jia et al (Jia et al., 2022). successfully applied LSTM to model SST evolution in the East China Sea. While effective at capturing local temporal dependencies, this paradigm fundamentally neglects spatial correlations inherent in oceanographic fields. Consequently, scaling these models to large, high-resolution areas leads to a prohibitive increase in parameters and poor computational efficiency.
To jointly model spatial and temporal dependencies, hybrid models integrating Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) became mainstream. ConvLSTM (Li et al., 2022) pioneered this direction by embedding convolutional operations within LSTM cells. Subsequent variants like PredRNN (Qiao et al., 2023) enhanced gradient flow via spatiotemporal memory, and ConvGRU (Xu et al., 2022) improved efficiency with simplified gating. Recently, Conforti et al (Conforti et al., 2024). transformed SST series into 2D time-frequency representations using wavelet transforms before convolutional processing, outperforming LSTM baselines. Although these models improved regional scale forecasting, their capacity to capture long-range spatial dependencies—critical for ocean circulation patterns—remains limited by the local receptive field of convolution kernels.
The advent of the Transformer architecture, with its global self-attention mechanism, offered a paradigm shift for handling long-term dependencies. Models like Informer (Zhou et al., 2021) and Autoformer (Wu et al., 2021) adapted this mechanism for time-series forecasting. This success translated to temperature prediction; for example, Di Ciaccio et al (Di Ciaccio et al., 2025). showed that an autoregressive Transformer outperformed CNN-RNN hybrids for urban temperature forecasting. In SST-specific research, deformable attention mechanisms (Wang et al., 2023) were introduced to adaptively focus on heterogeneous feature regions in complex coastal zones, and Sun et al (Sun and Wang, 2025). proposed CResU-Net, combining coordinate attention with depthwise separable convolution for high-resolution SST prediction. Despite their powerful representational capacity, the quadratic computational complexity and high memory footprint of standard Transformers render them impractical for large-scale, high-resolution, or real-time SST prediction scenarios.
In response to the computational bottlenecks of complex models, recent work has re-examined the efficiency-accuracy trade-off. Notably, Zeng et al (Zeng et al., 2023). demonstrated that lightweight linear models like DLinear can surpass sophisticated Transformer variants on many time-series benchmarks by decomposing series into trend and seasonal components for linear projection. While standard DLinear operates on single-point series and lacks explicit spatial modeling, its design philosophy underscores the potential of efficient architectures. The value of lightweight design is further evidenced in broader remote sensing tasks, such as the CGTC-RYOLO model (Gao et al., 2025) for efficient ship detection. Therefore, there is a significant gap in this field: the existing high-precision models have high computational costs, such as hybrid convolutional neural networks - recurrent neural networks, Transformers, etc., while efficient models such as linear baseline models often fail to adequately simulate the complex spatio-temporal dependencies that are crucial for SST. Our proposed TFLinear model seeks to bridge this gap. It draws inspiration from the efficiency of linear projection frameworks like DLinear but fundamentally extends them by integrating a dedicated module for joint spatial feature extraction and multi-scale temporal frequency decoupling. This approach aims to achieve high predictive accuracy for SST while maintaining a lightweight, deployable architecture, directly addressing the limitations highlighted in this review.
3 Model approach and design
3.1 Problem formulation
Sea surface temperature prediction is based on historical temperature data obtained from sensors used to predict future temperatures. In this paper, for an SST dataset B, given the historical data , where T is the size of the observation window, and Xi denotes the value of the SST data at the i time. For the spatial dimension, each observation contains two coordinates, w and h. In a realistic sense w represents the latitude of the observation and h represents the longitude of the observation. The goal of this paper is to train a model based on temperature data from past moments to predict SST data from subsequent moments. The Iterative Multi Step Prediction Method (IMS) is a single step prediction and iterated to obtain the results of multi step prediction, and due to the small prediction intervals of the SST data, the results of the IMS method are more desirable than the Direct Multi Step Prediction Method (DMS), IMS is as shown in Equation 1:
where is the observed value from the i past moment to moment t, is the predicted value from moment t for the next l moments, and θ represents the model trainable parameters.
3.2 Model structure
This study proposes TFLinear, a lightweight SST prediction architecture. Its core innovation integrates a Residual Temporal Frequency Module (RTF) with the DLinear framework to enable efficient modeling of complex spatio temporal dependencies. As illustrated in Figure 1, input SST data first enters the RTF module. This module employs: (1) a depthwise separable convolutional layer for spatial feature extraction, and (2) a Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) layer for temporal frequency decoupling, enhanced by residual connections. The decoupled components low frequency trend (A), mid frequency seasonal (S), and high frequency transient (D)—are routed to dedicated prediction channels. Each channel processes its component through independent linear layers for multi step forecasting. Finally, outputs from all three channels are fused via summation to generate the final SST prediction sequence. The mathematical formalization and design principles of each component are elaborated in subsequent sections.
Figure 1
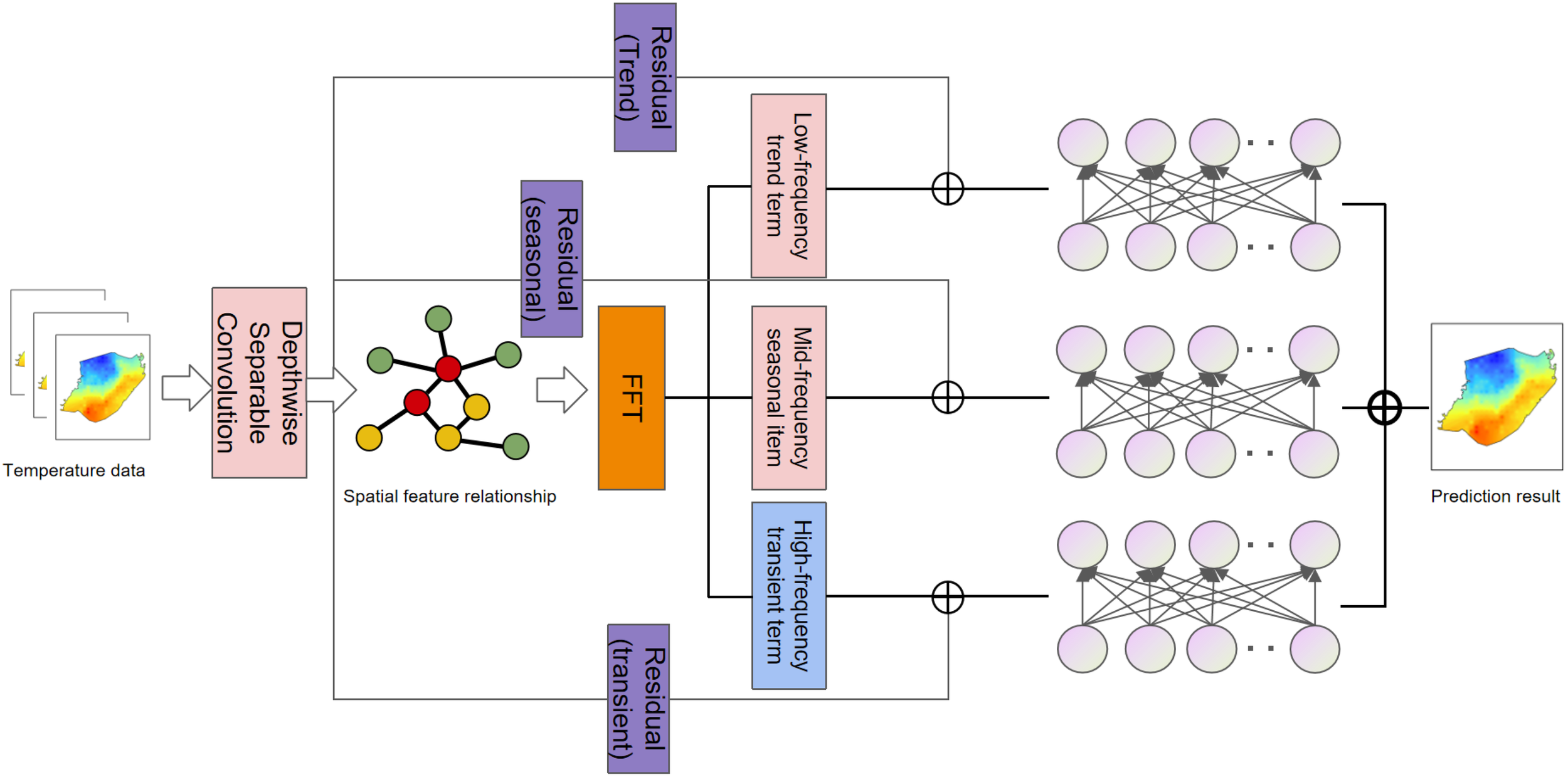
The model structure diagram of TFLinear.
3.2.1 Time frequency decoupling module with spatial feature extraction capability
Historical SST data first enter the depthwise separable convolution layer, the operation can be decomposed into two steps of depth convolution and point by point convolution (Li et al., 2020), as in Equations 2 and 3:
Where the k ∗ k convolution kernel extracts local features in the spatial dimension, while the 1 ∗ 1 convolution achieves cross channel information fusion. This design significantly reduces the computational and parametric quantities of traditional convolution and significantly reduces the model complexity while maintaining the spatial feature extraction capability. The implementation of the depth separable convolution is shown in Figure 2. The output spatial feature maps are FFT transformed along the time axis, and the time series of each spatial position (w, h) is decomposed into low frequency trend terms αw,h, mid frequency seasonal terms Sw,h and high frequency transient terms Dw,h, which are used to represent the periodicity and trend of SST data. The specific expression is as shown in Equation 4.
Figure 2
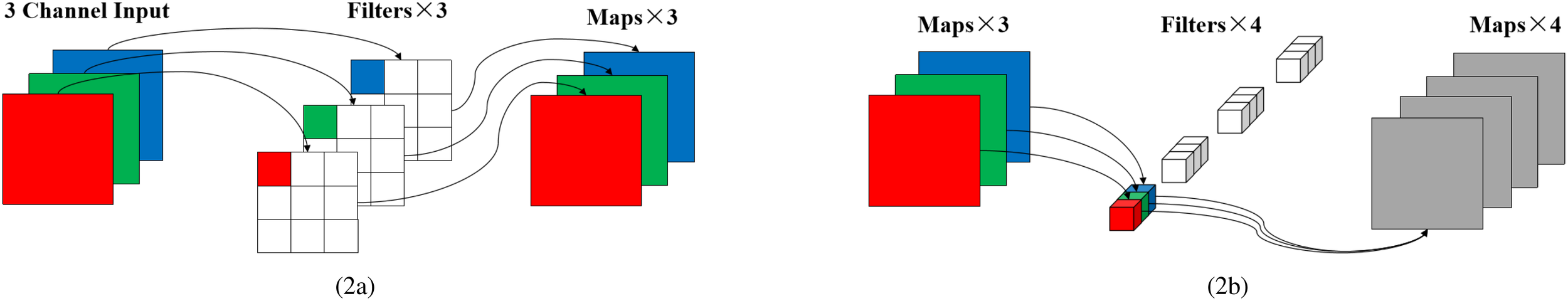
The depth separable convolution steps can be divided into channel by channel convolution and point by point convolution. (a) Depthwise Convolution, One convolution kernel is responsible for one channel, and one channel is convolved by only one convolution kernel. (b) Pointwise Convolution, which is performed using a 1x1 sized convolution kernel, which can be used to change the number of channels and perform linear combinations between channels.
The FFT operation is used to decompose the time series into different frequency components, and then the filtering operation is used to extract the slowly varying trend component, the seasonally varying seasonal component and the short term fluctuating transient component. The specific process can be formalized as Equation 5:
It is classified through frequency domain filtering low frequency trend terms αw,h, mid frequency seasonal terms Sw,h and high frequency transient terms Dw,h. Their expressions are as follows (Equations 6–8):
where and . The mechanism of time frequency decoupling enables the model to better adapt to the long period phenomena such as El Niño and short term abrupt changes caused by storm surges in the sea area. The SST data exhibits strong non stationarity. To mitigate gradient vanishing in deep networks and enhance feature propagation, we introduce component specific residual connections within the RTF module. Specifically, after decomposing the spatial features into trend, seasonal, and transient components via FFT, we apply independent residual pathways to each component. The enhanced output for each component is obtained by summing the decomposed feature with a dimension matched transformation of the original input through dedicated 1×1 convolutions. Their expressions are as follows (Equations 9–11):
This design adapts the ResNet principle to multi scale oceanic dynamics, enabling direct gradient propagation to shallow layers while preserving component specific characteristics.
3.2.2 DLinear three channel prediction
The trend term αw,h, the seasonal term Sw,hand high frequency transient terms Dw,h are input into independent linear layers for multi step prediction. Their expressions are as follows (Equations 12–15):
Where the weight matrix maps historical features to future T step predictions, which are ultimately generated by component superposition. The design inherits the advantages of the DLinear framework for efficiently modeling global time dependence using linear layers, with the core innovation being the use of FFT for time frequency decoupling as input, replacing the simple moving average decomposition in the original DLinear. This enables the model to explicitly and adaptively capture the multi scale dynamic properties embedded in the SST data, significantly enhancing the ability to learn complex spatio temporal patterns (e.g., different time scale responses of oceanic phenomena).
4 Experiments
4.1 Datasets
The data used in this study are sourced from the Operational Sea Surface Temperature and Sea Ice Analysis (OSTIA) system (Donlon et al., 2012). OSTIA optimally integrates satellite observations from multiple sensors (including infrared and microwave) and in situ measurements through advanced data assimilation techniques, providing a gap free, high resolution global SST analysis. This multi satellite collaborative observation strategy, highlights the importance of onboard information fusion and synergistic data utilization from constellation satellites to enhance the spatial coverage, temporal resolution, and overall accuracy of ocean remote sensing products like SST, despite challenges in data consistency and computational efficiency (Gao et al., 2023). In order to verify the performance of the TFLinear model in real scenarios, we extracted the sea surface temperature of the East China Sea for our experiments. The dataset spatially covers the latitude from 25° to 33°N and the longitude from 122° to 130°E. We set the spatial resolution of the data at 0.05° in each of the latitude and longitude.
Our experiment aimed to predict sea surface temperature (SST) values for the subsequent 10 days using corresponding historical SST data from the preceding 10 days. In order to avoid the possibility that the acquisition performance of the ocean sensors in the past may affect the present data, the data taken in this paper ranges from 1 January 2020 to 1 May 2025 for a total of 1,581 days of SST observations, and a sliding window is used to generate 1,562 data samples, each of which contains 25,600 different observation points. We partitioned the dataset into training, validation, and test sets following a 7:1:2 ratio. Since the dataset is collected and stored in a complex environment, many outliers inevitably appear in the process. We began the data preprocessing phase by thoroughly examining the dataset for missing values and outliers. Given that SSTs are continuous data, they are scaled to the [0,1] interval using the Min-Max normalization (Patel et al., 2022) technique, thus avoiding the disproportionate impact of outliers on model training.
4.2 SST time scale feature resolution based on FFT decomposition
Figure 3 demonstrates the FFT decomposition results of the SST sequence at a fixed point in the central East China Sea, revealing the central role of the RTF module in the decoupling of multi scale temporal features. Figure 3a shows significant periodic fluctuations superimposed with nonlinear trends, and its complex morphology confirms the typical characteristics of the near shore sea area affected by multi scale air sea interactions. Figure 3b extracts the slowly evolving trend terms, and the smooth curves reflect the persistent influence of the annual cycle changes on the sea area. Figure 3c precisely isolates the pattern of change with a quarterly cycle, and its more stable amplitude and phase correspond to the seasonal thermocline change of the ocean. Figure 3d captures the high frequency perturbation signals, focusing on characterizing the sudden temperature changes triggered by extreme events such as typhoon crossings and storm surges. This time frequency decomposition mechanism provides the physical basis for TFLinear’s two channel prediction architecture: the linear layer of the trend channel focuses on modeling the slow change process at the climate scale, while the period channel synergistically portrays the weather seasonal scale dynamic response by fusing the seasonal and transient terms. It is demonstrated that this design enables the model to maintain a significant predictive advantage over both low frequency oscillations with long term impacts (see and high frequency pulses with short term outbreaks) over a 10 days prediction period.
Figure 3
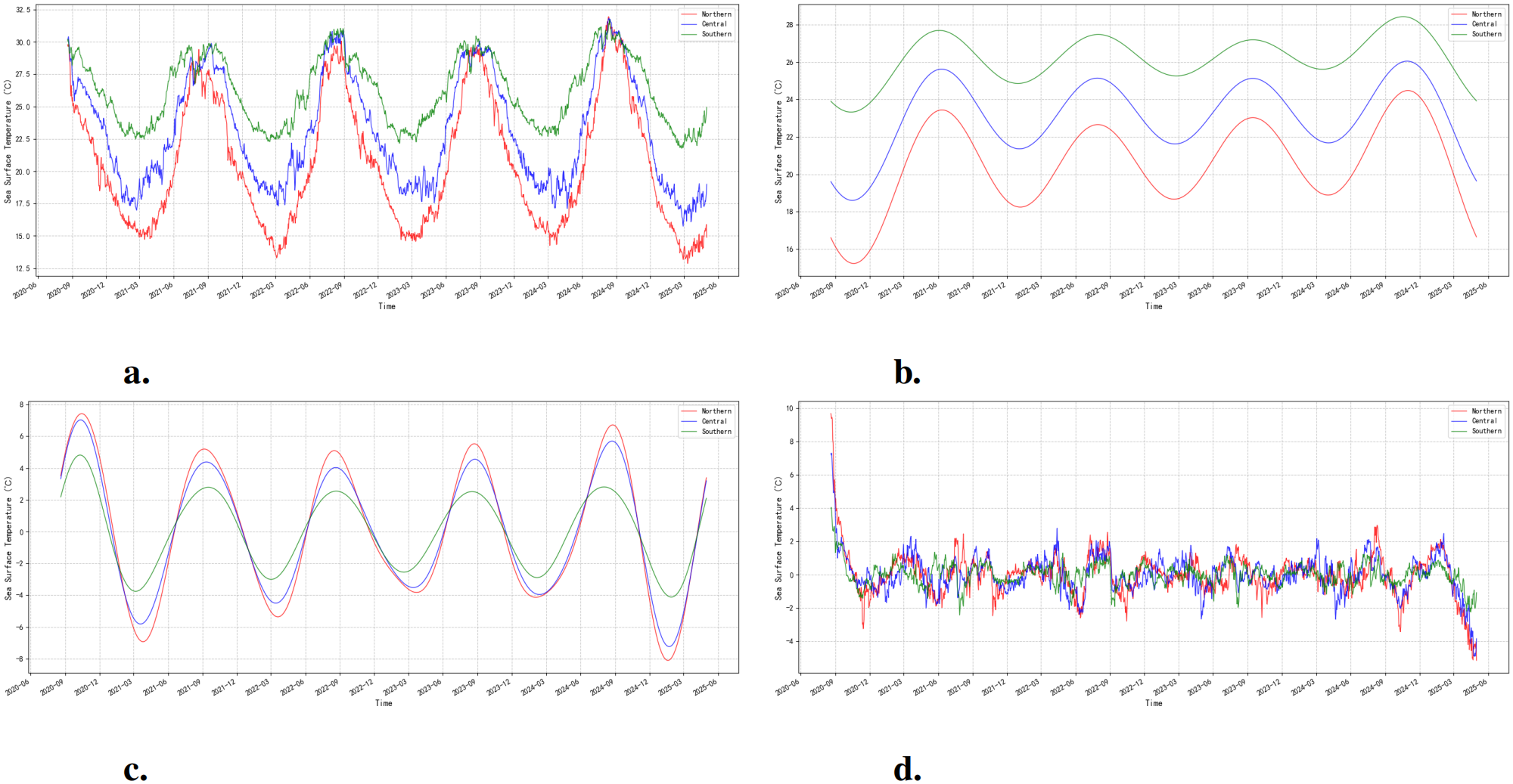
(a) Raw sea surface temperature data for different locations in the East China Sea. (b) Trend changes in sea surface temperature in different regions of the East China Sea. (c) Seasonal changes in sea surface temperature in different areas of the East China Sea. (d) Transient changes in sea surface temperature in different areas of the East China Sea.
4.3 Experimental hyperparameter selection and evaluation indexes
We evaluate the performance comparison between the proposed TFLinear model and several state of the art models, such as ConvLSTM, PredRNN, TSGN (Sun et al., 2021), SwinLSTM (Tang et al., 2023), and DatLSTM (Shi et al., 2024), through prediction experiments with SST data from 1 to 10 days in the East China Sea waters. It is worth noting that all of the above models have loop structures, gating structures and attention mechanisms that are computationally and parametrically large.
In this study, the model training parameters are configured as follows: the L2 loss function is used, along with the Adam optimizer. The total number of training epochs is set to 50, with a batch size of 32. The initial learning rate is 0.001, and it is dynamically adjusted using a cosine annealing strategy, decaying by 50% every 5 cycles to facilitate better convergence of the optimizer. In addition, to avoid overfitting, Early Stopping (ESP) strategy is used. Specifically, the monitoring metric is the loss value on the validation set, and the training will be stopped early if the validation loss does not improve significantly within 3 to 5 consecutive rounds. For the model evaluation metrics, we use mean absolute error (MAE), root mean square error (RMSE) and coefficient of determination (R²). MAE and RMSE can illustrate the magnitude and distribution of the error between the predicted value and the true value and R² is used to evaluate the model’s ability to identify the anomalous changes in SST data. Combining the above three assessment indicators can comprehensively assess the model’s prediction performance for SST data, and their formulas are as shown in Equations 16–18:
4.4 Experimental results
We make the same SST data prediction experiments for different models under the same conditions mentioned above. Table 1 represents the results of different models under various evaluation metrics. The results show that the lightweight model TFLinear proposed in this paper outperforms other baseline models in several evaluation metrics. Specifically, we find that the TSGN model yields higher MAE and RMSE values, indicating suboptimal performance for this task. Furthermore, all models exhibit deteriorating prediction accuracy as the forecasting horizon extends, while TFLinear has a decrease in performance under this effect, but the degree of decrease and the prediction metrics of the maximum prediction range are both better than the other models. In addition, the R² values in the table also show that TFLinear outperforms the other benchmark models in predicting the SST data. The TSGN model shows lower values at the beginning, which indicates a weaker prediction performance. The ConvLSTM model, although it has a high R² value at the beginning, as the prediction time increases, the R² value decreases more significantly, indicating that the model is only suitable for dealing with short term dependent relationships in SST data.
Table 1
| Model | Indicator | Day 1 | Day 2 | Day 3 | Day 4 | Day 5 | Day 6 | Day 7 | Day 8 | Day 9 | Day 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ConvLSTM | MAE | 0.737 | 0.96 | 1.228 | 1.255 | 1.223 | 1.368 | 1.559 | 1.378 | 1.443 | 1.047 |
| RMSE | 0.924 | 1.227 | 1.618 | 1.648 | 1.603 | 1.816 | 2.067 | 1.826 | 1.947 | 1.974 | |
| R² | 0.972 | 0.951 | 0.915 | 0.912 | 0.917 | 0.894 | 0.862 | 0.892 | 0.878 | 0.875 | |
| PredRNN | MAE | 0.6 | 0.639 | 0.698 | 0.792 | 0.884 | 0.877 | 0.972 | 0.994 | 1.046 | 1.027 |
| RMSE | 0.751 | 0.889 | 0.966 | 1.024 | 1.124 | 1.126 | 1.242 | 1.272 | 1.339 | 1.33 | |
| R² | 0.982 | 0.974 | 0.971 | 0.966 | 0.959 | 0.959 | 0.95 | 0.948 | 0.942 | 0.943 | |
| TSGN | MAE | 0.868 | 0.88 | 0.897 | 0.917 | 0.94 | 0.966 | 0.995 | 1.026 | 1.059 | 1.093 |
| RMSE | 1.143 | 1.157 | 1.177 | 1.201 | 1.229 | 1.259 | 1.293 | 1.329 | 1.368 | 1.408 | |
| R² | 0.958 | 0.957 | 0.955 | 0.953 | 0.951 | 0.949 | 0.946 | 0.943 | 0.939 | 0.936 | |
| SwimLSTM | MAE | 0.355 | 0.495 | 0.468 | 0.515 | 0.574 | 0.656 | 0.729 | 0.768 | 0.812 | 0.93 |
| RMSE | 0.462 | 0.637 | 0.611 | 0.66 | 0.732 | 0.788 | 0.917 | 0.945 | 1.076 | 1.114 | |
| R² | 0.993 | 0.987 | 0.988 | 0.986 | 0.983 | 0.98 | 0.973 | 0.971 | 0.963 | 0.96 | |
| DatLSTM | MAE | 0.311 | 0.377 | 0.456 | 0.5 | 0.573 | 0.655 | 0.76 | 0.768 | 0.818 | 0.93 |
| RMSE | 0.411 | 0.487 | 0.608 | 0.658 | 0.741 | 0.83 | 0.945 | 0.96 | 1.019 | 1.139 | |
| R² | 0.995 | 0.992 | 0.988 | 0.986 | 0.982 | 0.978 | 0.973 | 0.967 | 0.962 | 0.958 | |
| Ours | MAE | 0.258 | 0.375 | 0.454 | 0.538 | 0.594 | 0.652 | 0.705 | 0.752 | 0.797 | 0.839 |
| RMSE | 0.355 | 0.448 | 0.606 | 0.676 | 0.736 | 0.826 | 0.934 | 0.988 | 1.035 | 1.092 | |
| R² | 0.996 | 0.992 | 0.988 | 0.983 | 0.98 | 0.976 | 0.972 | 0.969 | 0.966 | 0.962 |
MAE, RMSE and R² for different models for the prediction range of 1 to 10 days.
The best results are shown in bold.
Figure 4 visualizes the predicted SST spatial distributions across the East China Sea from 21 to 30 April 2025, with observations corresponding to the preceding 10 days period. Ground truth OSTIA data reveals distinct thermal heterogeneity: the northwestern sector exhibits cooler temperatures, contrasting with warmer conditions in the southeastern and central regions. This spatial pattern is primarily driven by differential solar radiation exposure, accelerated warming in lower latitude zones, and localized coastal topographic effects. Quantitative analysis demonstrates TFLinear’s superior performance: its prediction deviations from real data remain consistently low across all subregions and forecast horizons (1 to 10 days). In contrast, the TSGN model exhibits systematic cold bias throughout the domain. While ConvLSTM and PredRNN show competitive accuracy in 1 to 3 day predictions, their performance degrades markedly at longer lead times (>5 days), with increasing underestimation of SST values.
Figure 4
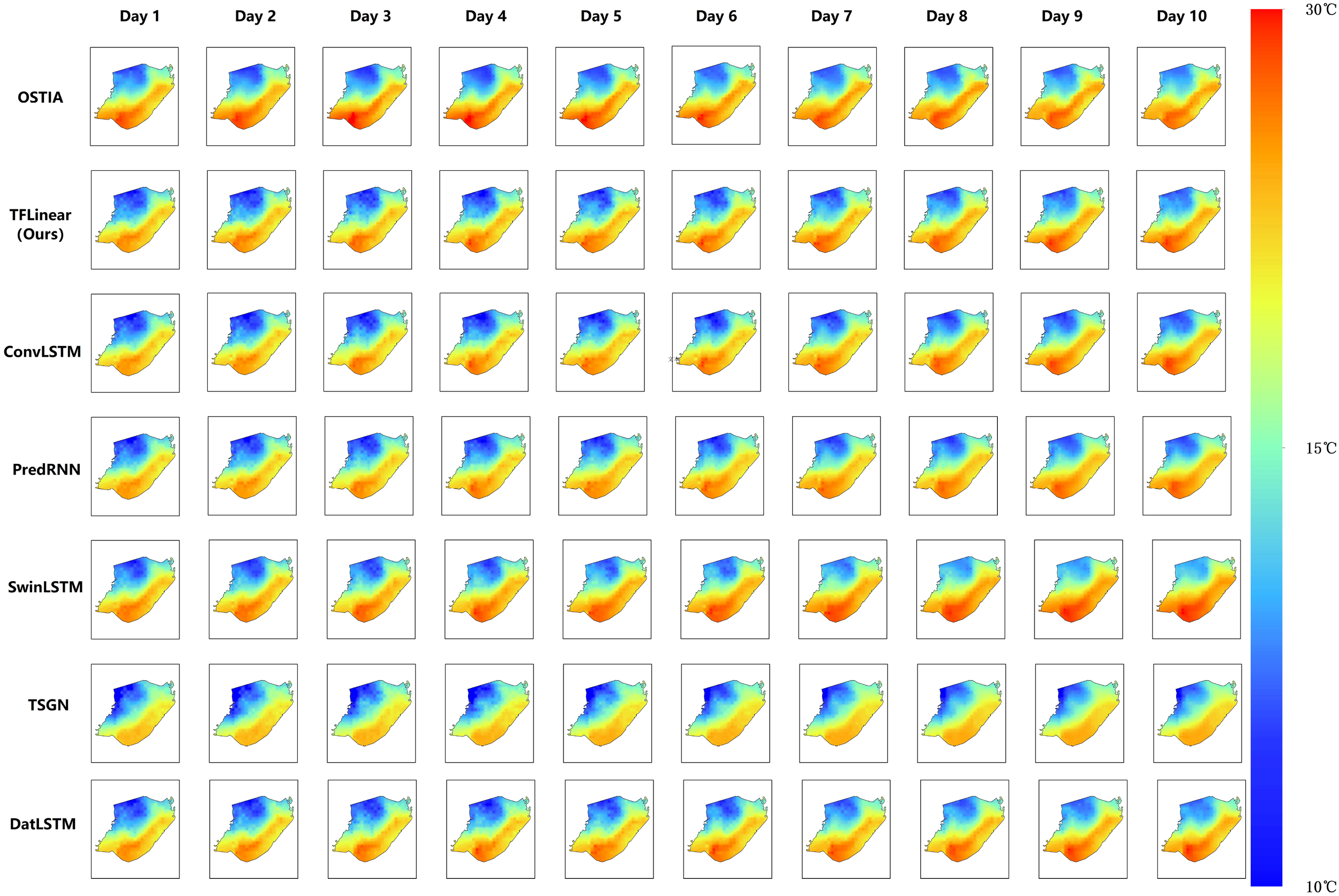
A snapshot of the sea surface temperature forecast from April 21st to April 30th, 2025 based on the current mainstream models. The prediction period ranges from 1 day to 10 days. The color bars indicate the temperature values.
Figure 5 illustrates the loss convergence behavior of different models across training epochs. All models exhibit rapid loss reduction in initial epochs, with convergence rates decelerating after epoch 10. Notably, TFLinear achieves a lower initial loss value and demonstrates smoother, more stable convergence compared to benchmark models, which display pronounced volatility in their loss curves. This stability is attributed to TFLinear’s unique time frequency decoupling mechanism, which jointly captures spatio temporal dependencies through integrated spatial feature extraction and adaptive frequency domain decomposition. The synergistic modeling of multi scale dynamics enhances feature representation robustness, thereby improving optimization efficiency and final prediction performance.
Figure 5
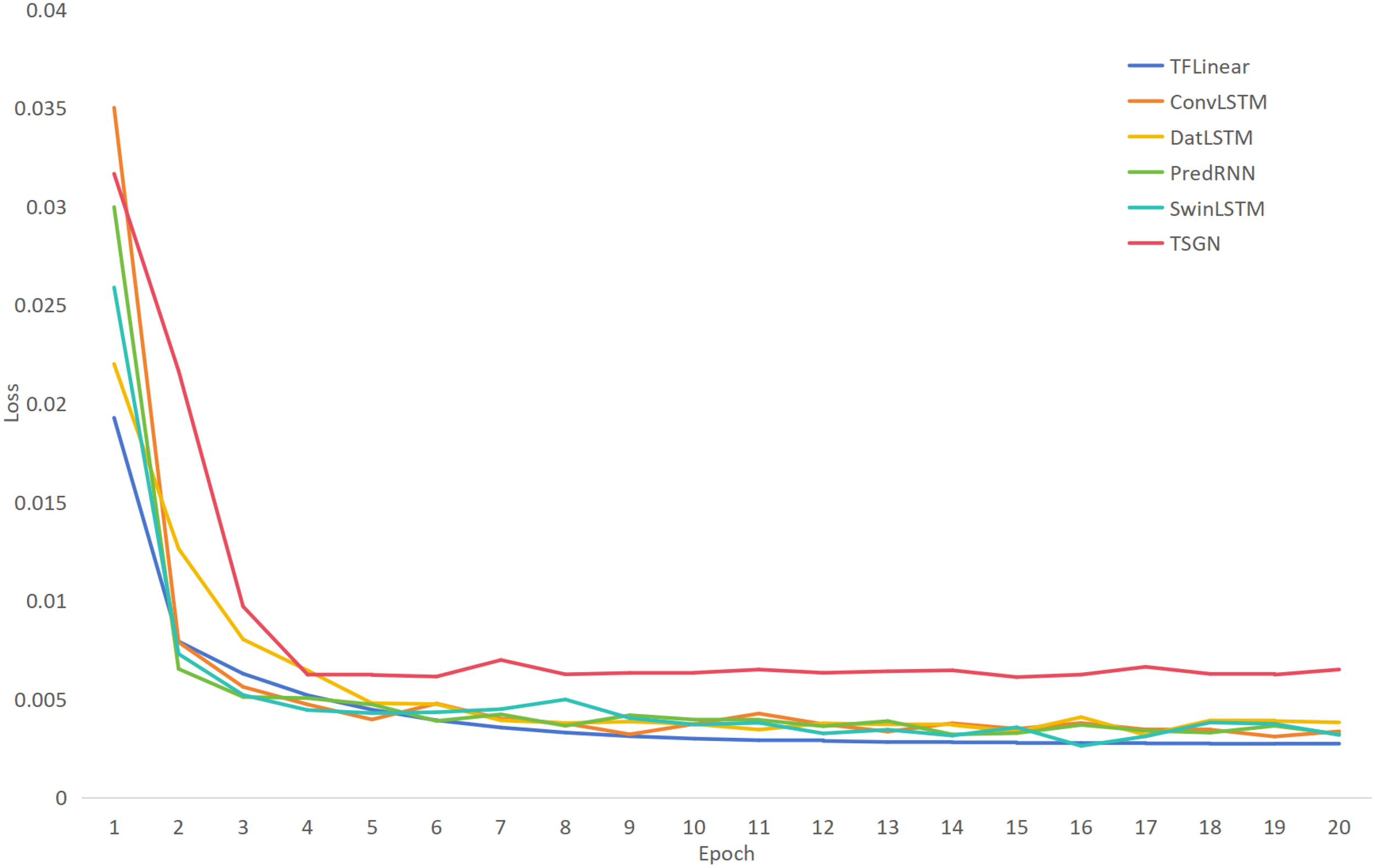
The loss value varies with the number of training rounds.
4.5 Ablation experiments
The TFLinear model proposed in this paper is a combination of a Residual Temporal Frequency Module (RTF) and the DLinear linear prediction framework, in order to validate the help of each part of the components on the performance enhancement, we additionally compare the three versions, and we still use the Adam optimizer, train the 50 epochs, and the learning rate varies with the training process, comparing the training efficiency and evaluation metrics of different versions: (1) Normal Convolution + FFT + DLinear (2) Depth Separable Convolution + Sliding division of period and trend terms + DLinear (3) Depth Separable Convolution + FFT + Self Attention. The results are shown in the Table 2. The results of several other combinations showed significant performance degradation, even worse than some baseline models. Compared to deep separable convolutions, simple convolutions have poorer spatial information extraction capabilities. Simple sliding partitioning of trend and periodic terms performs poorly in complex marine environments with seasonal term variations. The self attention mechanism may lead to the loss of temporal information. Therefore, we found that each component of TFLinear contributes to the final model performance: deep separable convolutions are used to extract spatial feature relationships from local to global scales, FFT is used to extract trend components, seasonal components and perturbation components to help the model capture feature information from multiple dimensions, and the linear combination avoids the loss of temporal information and the large computational load caused by the self attention mechanism.
Table 2
| Model composition | Indicator | Day 1 | Day 5 | Day 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Convolution | MAE | 0.437 | 0.696 | 1.028 |
| + FFT | RMSE | 0.473 | 0.846 | 1.225 |
| + Self Attention | R² | 0.737 | 0.96 | 0.941 |
| Depth Separable Convolution | MAE | 0.866 | 1.021 | 1.253 |
| + Sliding division | RMSE | 0.931 | 1.25 | 1.461 |
| + DLinear | R² | 0.965 | 0.944 | 0.933 |
| Depth Separable Convolution | MAE | 0.577 | 0.756 | 1.015 |
| + FFT | RMSE | 0.525 | 1.004 | 1.138 |
| + DLinear | R² | 0.976 | 0.952 | 0.934 |
| Ours | MAE | 0.258 | 0.594 | 0.839 |
| RMSE | 0.355 | 0.736 | 1.092 | |
| R² | 0.996 | 0.98 | 0.962 |
Performance ablation experiments of different modules of TFLinear.
4.6 Extent of effect of different hyperparameters on the model
4.6.1 Effect of different input lengths on model performance
Longer historical observation periods indicate that the model can utilize more historical information in time series forecasting, and thus models with strong ability to capture long term temporal correlations should perform better when the input period is increased. To validate our model, we conducted experiments with different input lengths at the same prediction length. As shown in Figure 6a, for evaluating the impact of the metrics, we found that TFLinear presents a stable increase in performance when the input period increases. Cyclic structure based models such as ConvLSTM and PredRNN also show some performance increase, while some Transformer based models suffer from performance degradation with increasing input length due to repetitive short term patterns. Longer input length means that more amount of data has to be input for each batch, which has an impact on the memory footprint. As the results in Figure 6b show, TFLinear’s memory footprint grows in a smoother growth trend with longer inputs, which has the advantage of being lighter compared to the sharp jumps in memory footprint of the models with cyclic structure and Transformer architecture.
Figure 6
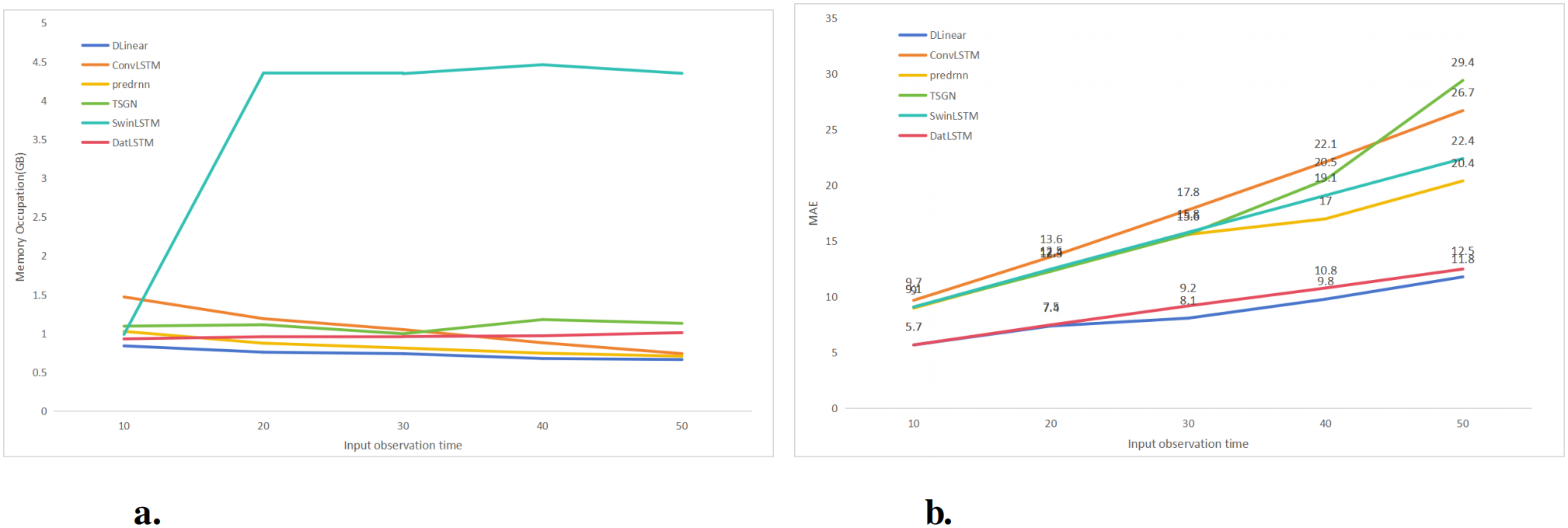
The influence of different input lengths on MAE and training memory usage. (a) The variation law of MAE with the input length. (b) The variation pattern of memory usage with input length.
4.6.2 Comparison of training complexity of different models
Current models require a large number of parameters and computational resources due to their gated structures and self attention mechanisms. In contrast, TFLinear benefits from its efficient depth separable convolutions and simple linear prediction structure, with no adjustable parameters in FFT operations, resulting in only a moderate increase in computational complexity. As shown in Table 3, we find that TFLinear has significantly fewer parameters and computational requirements than current mainstream models, while maintaining and even outperforming their predictive performance despite reduced model complexity. In real world applications involving complex maritime environments, TFLinear is better suited for lightweight deployment.
Table 3
| Module | Params | FLOPs |
|---|---|---|
| ConvLSTM | 1982849 | 4.25G |
| PredRNN | 6785345 | 4.45G |
| TSGN | 521921 | 7.58G |
| SwimLSTM | 1502065 | 23.5G |
| DatLSTM | 2612933 | 61.9G |
| ours | 866 | 0.58G |
Comparison of model training parameters and computing power.
5 Conclusion and future work
In this study, we proposed TFLinear, a lightweight and efficient architecture for sea surface temperature prediction. The core of our approach lies in the integration of a novel Residual Temporal Frequency (RTF) module with the DLinear framework, designed to model complex spatio temporal dependencies. Our methodological process began by framing the SST prediction as a spatio temporal sequence forecasting problem, utilizing historical SST grids to forecast future temperatures over a 1 to 10 day horizon. The TFLinear model first processes the input data through a depthwise separable convolution layer to efficiently extract spatial features. Subsequently, the temporal sequences are decomposed into interpretable trend, seasonal, and transient components via Fast Fourier Transform (FFT). Each of these decoupled components is then routed to dedicated linear layers for multi step prediction, with the final output generated through a synergistic fusion of all channels. Extensive experiments on OSTIA SST data from the East China Sea demonstrated that TFLinear achieves superior accuracy in key metrics such as MAE, RMSE, and R², while maintaining significantly lower computational complexity compared to state of the art benchmarks.
The remotely sensed SST data used in this paper provide strong support for our model evaluation. The long period spanning SST data makes the model training more effective. For the real world scenario of sea surface temperature prediction, single point time series data cannot cover the whole sea area to satisfy the requirements of model training. Ocean sensors provide critical remotely sensed SST data, which allows our model to learn the key information desired by spatial and temporal features. The excellent performance of the TFLinear model in the East China Sea provides the possibility of applying it to forecast accurately on a worldwide ocean scale.
The RTF module proved effective in capturing the complex nonlinear spatial dynamics and multi scale temporal patterns inherent in the East China Sea SST data. It reliably handles the impacts of significant seasonal fluctuations and dynamic oceanic processes such as upwelling and currents on prediction performance. Meanwhile, the inherent linear processing framework of DLinear ensured robust modeling of long term trends and global patterns. The use of long term, spatially continuous remote sensing data was crucial for training and validating the model, enabling it to learn essential spatio temporal features beyond the limitations of single point time series. The excellent performance of TFLinear in this regional context underscores its potential for accurate SST forecasting on a broader, even global, ocean scale.
Although TFLinear demonstrates good performance in the prediction of SST in the East China Sea, there are still the following directions that deserve to be further explored to improve the model’s generalizability, accuracy and application value. Firstly, as the prediction time increases, the predictive performance of the model will decline. In practical applications, such as in fishery ecology (Guan et al., 2025), there are more data sources to consider, and the prediction cycle of sea surface temperature may be longer. Re-inputting the predicted output back into the model for the next round of prediction may result in a cumulative jump in error rather than a simple summation. Subsequent modifications are needed to enable it to cope with longer time span prediction tasks. Secondly, the SST data prediction only considers univariate factors, and the discrimination of specific extreme conditions has yet to be investigated. In the future, satellite remote sensing wind field data and current data should be introduced into the modeling framework, and multimodal inputs should be constructed to improve the prediction accuracy in a more comprehensive way, especially during extreme events.
Statements
Data availability statement
OSTIA SST is accessible through the Copernicus Marine Environment Monitoring Service (CMEMS) website: http://marine.copernicus.eu/.
Author contributions
BX: Writing – review & editing, Resources, Funding acquisition, Writing – original draft, Visualization, Software, Methodology, Supervision, Validation, Conceptualization, Investigation, Data curation. KT: Writing – original draft, Investigation, Formal analysis, Conceptualization. CL: Writing – review & editing, Formal analysis, Project administration, Validation, Methodology, Supervision. XC: Project administration, Funding acquisition, Resources, Visualization.
Funding
The author(s) declared that financial support was received for this work and/or its publication. This work was supported by Xiamen Ocean and Fishery Development Special Fund Project (Grant No. 21CZB013HJ15), and Xiamen Key Laboratory of Marine Intelligent Terminal R&D and Application (Grant No. B2024008).
Conflict of interest
The authors declared that this work was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declared that generative AI was not used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1
Andrews T. Bodas-Salcedo A. Gregory J. M. Dong Y. Armour K. C. Paynter D. et al . (2022). On the effect of historical sst patterns on radiative feedback. J. Geophysical Research: Atmospheres127, e2022JD036675.
2
Conforti P. M. Russo P. Di Ciaccio F. (2024). “ Advancing sea surface temperature forecasting with deep learning techniques on copernicus data: An application in the gulf of trieste,” in 2024 IEEE International Workshop on Metrology for the Sea; Learning to Measure Sea Health Parameters (MetroSea). 83–88 (SRINAGAR, India: IEEE). doi: 10.1109/MetroSea62823.2024.10765620
3
Dai H. He Z. Wei G. Lei F. Zhang X. Zhang W. et al . (2024). Long-term prediction of sea surface temperature by temporal embedding transformer with attention distilling and partial stacked connection. IEEE J. Selected Topics Appl. Earth Observations Remote Sens.17, 4280–4293. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2024.3357191
4
Di Ciaccio F. Russo P. Parisi E. I. Angelini R. Tucci G. (2025). Towards sustainable heritage conservation: Transformer-based temperature forecasting in the city of florence. Int. Arch. Photogrammetry Remote Sens. Spatial Inf. Sci.48, 399–405.
5
Donlon C. J. Martin M. Stark J. Roberts-Jones J. Fiedler E. Wimmer W. (2012). The operational sea surface temperature and sea ice analysis (ostia) system. Remote Sens. Environ.116, 140–158. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2010.10.017
6
Elafi I. Zrira N. Kamal-Idrissi A. Khan H. A. Ettouhami A. (2024). Sta-sst: Spatio-temporal time series prediction of moroccan sea surface temperature. J. Sea Res.200, 102515. doi: 10.1016/j.seares.2024.102515
7
Gao G. Wang Y. Chen Y. Yang G. Yao L. Zhang X. et al . (2025). An oriented ship detection method of remote sensing image with contextual global attention mechanism and lightweight task-specific context decoupling. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens.63, 1–18. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2024.3520658
8
Gao G. Yao B. Li Z. Duan D. Zhang X. (2024). Forecasting of sea surface temperature in eastern tropical pacific by a hybrid multiscale spatial–temporal model combining error correction map. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens.62, 1–22. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2024.3353288
9
Gao G. Yao L. Li W. Zhang L. Zhang M. (2023). Onboard information fusion for multisatellite collaborative observation: Summary, challenges, and perspectives. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Magazine11, 40–59. doi: 10.1109/MGRS.2023.3274301
10
Guan Y. Zhang X. Gao G. Cao C. Li Z. Fu S. et al . (2025). A new indicator for assessing fishing ecological pressure using multi-source data: A case study of the south China sea. Ecol. Indic.170, 113096. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2025.113096
11
Han Y. Sun K. Yan J. Dong C. (2023). The cnn-gru model with frequency analysis module for sea surface temperature prediction. Soft Computing27, 8711–8720. doi: 10.1007/s00500-023-08172-2
12
Jia X. Ji Q. Han L. Liu Y. Han G. Lin X. (2022). Prediction of sea surface temperature in the east China sea based on lstm neural network. Remote Sens.14, 3300. doi: 10.3390/rs14143300
13
Li C. Feng Y. Sun T. Zhang X. (2022). Long term Indian ocean dipole (iod) index prediction used deep learning by convlstm. Remote Sens.14, 523. doi: 10.3390/rs14030523
14
Li X. Li J. Zhao C. Qu Y. He D. (2020). Gear pitting fault diagnosis with mixed operating conditions based on adaptive 1d separable convolution with residual connection. Mechanical Syst. Signal Process.142, 106740. doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2020.106740
15
Nawi W. Lola M. S. Zakariya R. Zainuddin N. H. Abd Hamid A. A. K. Aruchunan E. et al . (2021). Improved of forecasting sea surface temperature based on hybrid arima and support vector machines models. Malaysian J. Fundam. Appl. Sci.17, 609–620. doi: 10.11113/mjfas.v17n5.2356
16
Patel C. Pandey A. Wadhvani R. Patil D. (2022). “ Forecasting nonstationary wind data using adaptive min-max normalization,” in 2022 1st International Conference on Sustainable Technology for Power and Energy Systems (STPES). 1–6 (SRINAGAR, India: IEEE). doi: 10.1109/STPES54845.2022.10006473
17
Qiao B. Wu Z. Ma L. Zhou Y. Sun Y. (2023). Effective ensemble learning approach for sst field prediction using attention-based predrnn. Front. Comput. Sci.17, 171601. doi: 10.1007/s11704-021-1080-7
18
Shi B. Ge C. Lin H. Xu Y. Tan Q. Peng Y. et al . (2024). Sea surface temperature prediction using convlstm-based model with deformable attention. Remote Sens.16, 4126. doi: 10.3390/rs16224126
19
Sun Z. Wang Y. (2025). A coordination attention residual u-net model for enhanced short and mid-term sea surface temperature prediction. Environ. Model. Software183, 106251. doi: 10.1016/j.envsoft.2024.106251
20
Sun Y. Yao X. Bi X. Huang X. Zhao X. Qiao B. (2021). Time-series graph network for sea surface temperature prediction. Big Data Res.25, 100237. doi: 10.1016/j.bdr.2021.100237
21
Tang S. Li C. Zhang P. Tang R. (2023). “ Swinlstm: Improving spatiotemporal prediction accuracy using swin transformer and lstm,” in Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision. IEEE, Paris France13470–13479.
22
Temam R. (2024). Navier–Stokes equations: theory and numerical analysis Vol. 343 ( American Mathematical Society, London, United Kingdom).
23
Vytla V. Baduru B. Kolukula S. S. Ragav N. N. Kumar J. P. (2025). Forecasting of sea surface temperature using machine learning and its applications. J. Earth System Sci.134, 25. doi: 10.1007/s12040-024-02483-0
24
Wang C. Sun M. Yang Y. Wang H. Liu X. Xiong D. et al . (2024). Improved sst turbulence model for supersonic flows with apg/separation. Comput. Fluids274, 106237. doi: 10.1016/j.compfluid.2024.106237
25
Wang H. Xiang X. Tian Y. Yang W. Liao Q. (2023). Stdan: deformable attention network for space-time video super-resolution. IEEE Trans. Neural Networks Learn. Syst.35, 10606–10616. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2023.3243029
26
Wei L. Guan L. (2022). Seven-day sea surface temperature prediction using a 3dconv-lstm model. Front. Mar. Sci.9, 905848. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2022.905848
27
Wu H. Xu J. Wang J. Long M. (2021). Autoformer: Decomposition transformers with auto-correlation for long-term series forecasting. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst.34, 22419–22430.
28
Xu S. Dai D. Cui X. Yin X. Jiang S. Pan H. et al . (2023). A deep learning approach to predict sea surface temperature based on multiple modes. Ocean Model.181, 102158. doi: 10.1016/j.ocemod.2022.102158
29
Xu G. Xian D. Fournier-Viger P. Li X. Ye Y. Hu X. (2022). Am-convgru: a spatio-temporal model for typhoon path prediction. Neural Computing Appl.34, 5905–5921. doi: 10.1007/s00521-021-06724-x
30
Yan X. (2024). “ Using multi-layer perceptron to predict sea surface temperature,” in Journal of Physics: Conference Series, vol. 2798. ( IOP Publishing), 012052. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/2798/1/012052
31
Yu T. Wang E. Jin S. Wang Y. Huang J. Liu X. et al . (2023). Responses of gnss ztd variations to enso events and prediction model based on fft-lstme. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens.61, 1–17. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3251375
32
Zeng A. Chen M. Zhang L. Xu Q. (2023). ). Are transformers effective for time series forecasting? Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell.37, 11121–11128.
33
Zhang Y. Feng M. Zhang W. Wang H. Wang P. (2021). A gaussian process regression-based sea surface temperature interpolation algorithm. J. Oceanology Limnology39, 1211–1221. doi: 10.1007/s00343-020-0062-1
34
Zhou H. Zhang S. Peng J. Zhang S. Li J. Xiong H. et al . (2021). “ Informer: Beyond efficient transformer for long sequence time-series forecasting,” in Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, In Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, AAAI Vol. 35. 11106–11115.
Summary
Keywords
depthwise separable convolution, Fast Fourier Transform, linear prediction, residual linking, sea surface temperature
Citation
Xiang B, Tang K, Li C and Cao X (2026) High precision lightweight prediction of short term sea surface temperature in the East China Sea: TFLinear model. Front. Mar. Sci. 12:1674064. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2025.1674064
Received
27 July 2025
Revised
04 December 2025
Accepted
08 December 2025
Published
13 January 2026
Volume
12 - 2025
Edited by
Tien Anh Tran, Seoul National University, Republic of Korea
Reviewed by
Fabiana Di Ciaccio, Università di Firenze, Italy
Qiao Wu, Hubei University of Technology, China
Updates
Copyright
© 2026 Xiang, Tang, Li and Cao.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Chaopeng Li, licp@jmu.edu.cn; Xiaochun Cao, caoxiaochun@mail.sysu.edu.cn
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.