Abstract
Target detection in side-scan sonar images under complex environments is challenging due to noisy backgrounds, occlusion, and blurred target boundaries, which reduce the accuracy and robustness of traditional methods. To address these issues, we propose RCDI-YOLO, an enhanced YOLOv8-based detection framework that integrates rotation-aware feature extraction, multi-scale feature integration, and implicit feature representations for noise suppression. In addition, a diversified complex environment side-scan sonar dataset (CESSSD) is constructed to mitigate data scarcity and imbalance. Experimental results demonstrate that RCDI-YOLO achieves a detection accuracy of 95.3% and a mean Average Precision of 95.7%, outperforming the original YOLOv8 by 2.5% and 2.0%, respectively. These findings confirm that RCDI-YOLO significantly improves detection performance in complex underwater environments, particularly in scenarios with occlusion, cluttered backgrounds, and noise interference, highlighting its potential for underwater detection and search-and-rescue applications.
1 Introduction
Side-scan sonar technology plays an important role in underwater detection and imaging and is widely used in target detection, marine resource exploration, environmental monitoring, engineering safety, and underwater archaeology. By emitting and receiving sound waves, a side-scan sonar generates high-resolution images to analyze the seabed environment. However, complex and dynamic underwater environments, such as target occlusion, different seabed textures, and noise interference, significantly increase detection difficulty. Traditional side-scan sonar target-detection methods rely mainly on techniques such as background suppression through filtering, local contrast analysis, edge detection, and manual feature extraction (Bae and Sohng, 2010; Li et al., 2016; Wu et al., 2017; Yang et al., 2022). Although effective under specific conditions, these methods have limitations in complex environments: poor robustness against noise, susceptibility to false detections caused by complex reflections and interference, reliance on prior knowledge and manual features, difficulty in adapting to variations in target size, shape, and orientation, and insufficient multi-scale target handling, leading to low detection accuracy. These problems render traditional methods unsuitable for modern high-precision underwater target detection.
In order to obtain high-resolution side-scan sonar images (Zhang and Yang, 2019) under complex underwater conditions, many researchers have explored advanced signal processing and imaging algorithms based on synthetic aperture sonar (SAS), particularly multi-receiver SAS systems. A series of works have proposed improved back-projection techniques (Wang et al., 2015; Zhang and Yang, 2022a), fast imaging algorithms (Zhang et al., 2018), and extended chirp scaling methods (Zhang et al., 2022c), enabling clearer reconstruction in noisy and nonuniform sampling environments (Zhang et al., 2024). These methods significantly improve the clarity and contrast of underwater acoustic images, forming the basis for modern sonar-based target detection tasks. Furthermore, Chebyshev-polynomial-based frequency-domain SAS (Zhang et al., 2022d), dual-interpolator back-projection (Zhang and Yang, 2022a), and experimental validations on novel sub-bottom profilers (Tan et al., 2019; Zhang et al., 2022b) have demonstrated enhanced robustness in real-world seabed imaging. Although such imaging algorithms improve the quality of acoustic imagery, challenges such as target occlusion, textured seabeds, and acoustic noise remain major obstacles for automatic detection.
Over the years, various underwater target-recognition algorithms based on sonar images have been proposed. Common feature extraction methods include traditional signal processing techniques such as the short-time Fourier transform (STFT) (Benesty and Cohen, 2018), Hilbert-Huang transform (Li et al., 2009), and wavelet transform (Tian et al., 2020), which effectively extract underwater acoustic signal features. Additionally, target-detection algorithms such as the Constant False Alarm Rate (CFAR) (Katyayani et al., 2023), Cell Average CFAR (CA-CFAR) (Aalo et al., 2015), and Accumulated Cell Average CFAR (ACA-CFAR) (Tanuja, 2016) are widely used in underwater target detection. These algorithms compare the threshold set with a grayscale sonar image to detect and identify targets. Myers and Fawcett (2010) used template matching to compare target features generated by acoustic models with actual sonar images and combined echo and projection shadows for classification, demonstrating that this method outperformed traditional normalized cross-correlation methods. Williams (2015) proposed an unsupervised algorithm for fast underwater target detection in synthetic aperture sonar (SAS) images, requiring no training data, adapting to environmental features, and verified its performance under various geographic conditions through large-scale experiments. Dura et al. (2005) proposed an adaptive algorithm for detecting and classifying side-scan sonar mine targets, training with a small number of labeled samples, adapting to environmental changes, and optimizing detection performance. Acosta and Villar (2015) modeled seabed reverberation as a Gaussian distribution and used CFAR detection to identify sunken ships. However, as the resolution of acoustic images increases, the Gaussian distribution gradually becomes ineffective in describing the statistical characteristics of the seabed, prompting researchers to introduce non-Gaussian distribution models such as Weibull, Gamma, K-distribution, and α-stable distributions to improve underwater target detection (Klausner and Azimi-Sadjadi, 2015). Abu and Diamant (2019) combined the β-distribution to describe seabed textures and target highlights while using the Gaussian distribution to model target shadows, employing likelihood ratio tests for target judgment. Overall, traditional side-scan sonar target-detection methods have limitations in terms of noise interference, target occlusion, and multi-scale detection. To address these challenges, researchers have proposed advanced feature extraction, unsupervised learning, data-adaptive algorithms, and non-Gaussian distribution models, which significantly improve underwater target detection accuracy and robustness, thus advancing modern underwater detection technology.
Deep learning technologies have advanced significantly in computer vision in recent years, especially convolutional neural network (CNN)-based target-detection algorithms, which are now being progressively used in underwater image processing. CNNs enhance robustness and accuracy through automatic feature extraction, allowing adaptation to multi-scale, multi-angle targets and lighting changes. Traditional methods perform poorly due to the complexity of the underwater environment, which includes target occlusion, changes in seabed texture, and sonar noise. R-CNN (Girshick et al., 2014), Fast R-CNN (Girshick, 2015), Faster R-CNN (Ren et al., 2017), and Mask R-CNN (He et al., 2015) are two-stage detection algorithms that work well in complex situations but are unsuitable for real-time applications due to their high computational load and slow processing speed. On the other hand, one-stage detection algorithms that balance speed and accuracy, including SSD (Liu et al., 2016), RetinaNet (Lin et al., 2017b), and YOLO (Redmon et al., 2016), are more suited for real-time underwater surveillance applications. Additionally, deep learning has been used to improve subsequent processing by applying enhancement techniques like image denoising and dehazing, which make images sharper. The multi-scale target-detection performance is further improved with multi-scale fusion structures, like the feature pyramid network (FPN) (Lin et al., 2017a). All things considered, deep learning has a lot of promise for processing underwater images, increasing the speed and accuracy of detection, and offering fresh solutions to problems posed by the underwater environment. In order to address the practical needs of highway autonomous driving, Wang et al. (2024) introduced the YOLOv8-QSD network, which provides efficient and precise small-target identification in driving scenarios with an accuracy of 64.5% and a computational burden of just 7.1 GFLOPs. Liangjun et al. (2024) introduced the MSFA-YOLO method, which demonstrated notable performance improvements over YOLOv8n and greatly increased the SAR image ship detection accuracy, particularly for low-quality photos and ships of various sizes. By adding receptive field attention convolution, SPPF-LSKA modules, and dynamic detection heads, Zhao et al. (2024) developed the YOLO-RLDW algorithm, which increases the accuracy of small object identification, background interference suppression, and multi-scale object localization. The algorithm performs better than alternative approaches on a variety of datasets, according to the testing results. Furthermore, Aboah et al. (2023) created a real-time multiclass helmet violation detection system based on YOLOv8 that showed great robustness and usefulness in real-world applications while achieving effective detection with few-shot data.
Although deep learning algorithms have shown great potential for underwater target detection, in side-scan sonar images, targets often suffer from low contrast, complex backgrounds, and occlusions, which cause classical deep learning algorithms such as YOLO to perform poorly in underwater detection. To address these issues, this paper proposes a target-detection method for complex environment side-scan sonar images based on an improved YOLOv8 called RCDI-YOLO. The core idea of this paper is to improve the structure of the YOLOv8 model to enhance its adaptability to multi-scale targets and complex backgrounds and to tackle the detection challenges posed by target occlusion and high-noise environments in complex seabed conditions. Several core improvements have been proposed to adapt the model to the complex conditions of sonar images.
-
To address the issues of multi-scale targets, complex backgrounds, and occlusion in the marine environment, this paper uses the SimpleCopy-Paste data augmentation method to construct a complex environment side-scan sonar dataset (CESSSD). This dataset addresses the problems of uneven target distribution and insufficient samples, enhances the data richness, and improves the robustness and recognition ability of the model in complex scenarios.
-
To tackle the issues of low-contrast target separation and noise interference in the side-scan sonar images, the C2f module of YOLOv8 is replaced with the LANConvNeXtv2 module (R in RCDI), which enhances multi-scale feature extraction and implements the rotating convolution concept in practice, thereby providing stronger perception capabilities for small- and low-contrast targets.
-
To overcome the limitations of fixed sampling methods in traditional YOLO algorithms when handling multi-scale targets, this paper introduces a dynamic sampling mechanism, Dysample (D in RCDI), which realizes dilated integration by refining multi-scale sampling to improve feature extraction and robustness to object size variations, thus enhancing detection performance in complex backgrounds.
-
To address target occlusion and noise interference, this paper introduces the ImplicitHead module (I in RCDI) in the probe section. This lightweight head module increases detection robustness and accuracy while lowering false positives and missed detections, complementing the RC and D modules without adding excessive computational cost.
In order to increase the detection effectiveness and resilience of the model, this work suggests a number of enhancements for sonar-image target detection in complicated situations. The model’s ability to adapt to complicated and multi-scale settings is enhanced by building a diverse CESSSD dataset and applying the SimpleCopy-Paste data augmentation method. The Dysample method improves feature extraction and target-focusing capabilities, while the LANConvNeXtv2 module improves target feature extraction. The ImplicitHead module decreases missed detections and false positives while increasing detection accuracy. These enhancements demonstrate RCDI-YOLO’s promise in underwater detection and search-and-rescue missions by enabling it to perform very well in target occlusion, complicated backgrounds, and noise interference.
2 Dataset and preprocessing
To effectively address the various challenges encountered in side-scan sonar image target detection, this paper specifically focuses on target detection in complex environments. Through SimpleCopy-Paste, the original aircraft and shipwreck side-scan sonar datasets are augmented to generate a complex seabed side-scan sonar target dataset, and several data augmentation techniques are employed. These augmentation techniques aim to enhance the diversity of training samples, enabling the model to demonstrate stronger robustness and generalization when facing real-world issues such as noise interference, low contrast, and target occlusion. The data augmentation methods primarily include Cutout, Mosaic, and noise addition. These techniques help build a more diversified side-scan sonar image dataset that simulates complex underwater environments. The following section provides a detailed introduction to the principles, applications, and improvements to model performance achieved by these methods.
The original aircraft and shipwreck side-scan sonar target images, along with side-scan sonar data from different seabed textures, are sourced from the SeabedObjects-KLSG dataset (Liu et al., 2022), which was constructed with support from sonar equipment suppliers such as Lcocean, Hydro-tech Marine, Klein Marine, Tritech, and EdgeTech. This dataset contains 578 seabed sonar images, 385 shipwreck images, and 62 aircraft sonar images, as shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1
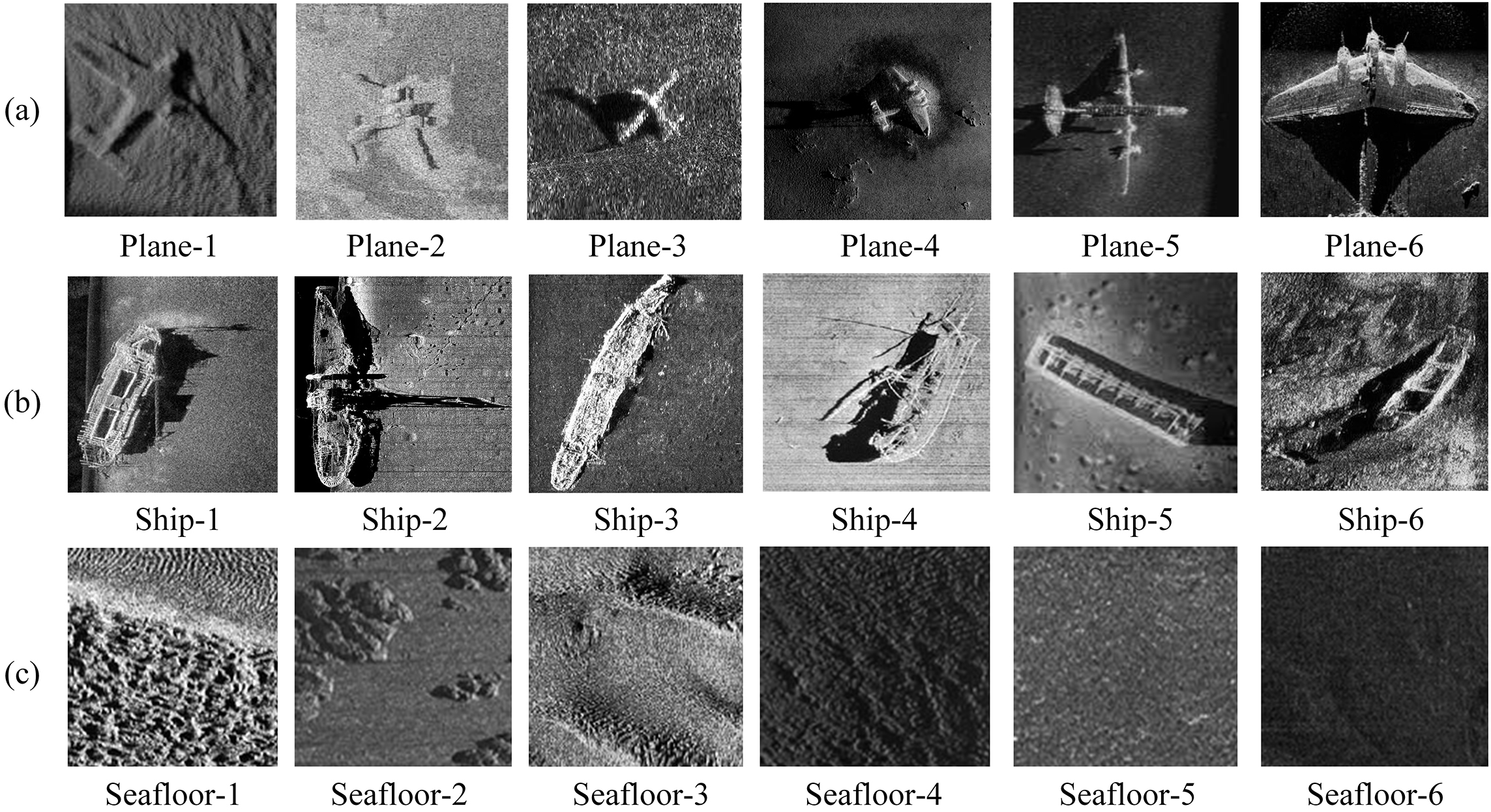
Aircraft, shipwreck, and seabed side-scan sonar data examples: (a) aircraft side-scan sonar data (b) shipwreck side-scan sonar data (c) seabed side-scan sonar data.
SimpleCopy-Paste (Ghiasi et al., 2021) is a straightforward and effective data augmentation method that primarily generates new data samples by extracting target objects from source images and pasting them into other target images. As shown in Figure 2, this data augmentation method is particularly useful for simulating different complex backgrounds in side-scan sonar images, helping the model adapt to variations in target objects across different background environments. This increases the diversity of the dataset and enhances the robustness of the model when facing background changes, noise interference, and target occlusion. The core operation can be described by the following mathematical formula:
Figure 2
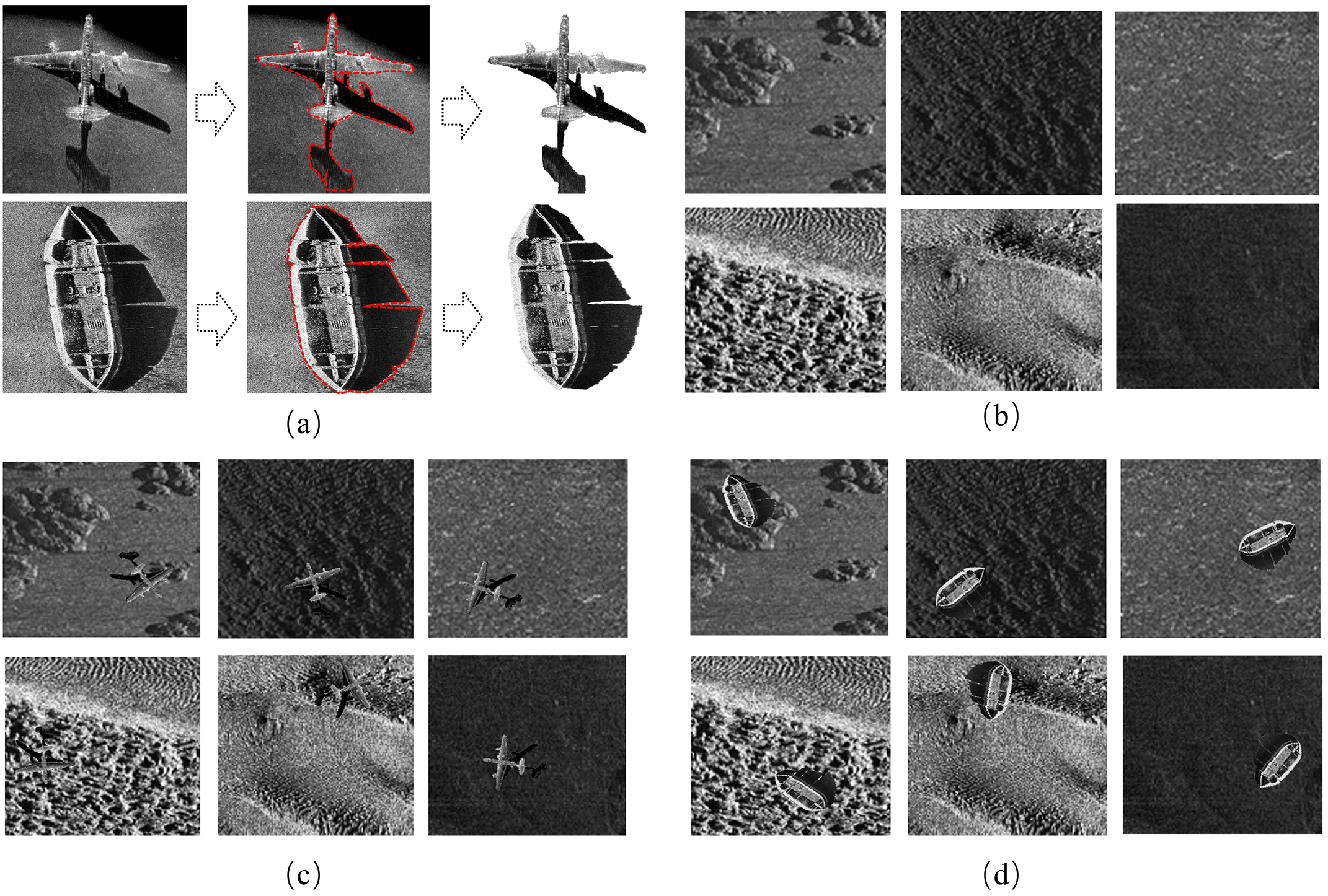
Schematic diagram of simple copy-paste data augmentation process: (a) seafloor target extraction process (b) original sonar images of six types of seafloor substrates (c) example of aircraft data after the simple copy-paste operation (d) example of shipwreck data after the simple copy-paste operation.
The target object is extracted from the source image using a mask, as shown in the formula below:
In the formula (Equation 1), Isource represents the source image, which contains the target object to be extracted; Mmask denotes the binary mask of the target in the source image; and Iobject denotes the extracted object image obtained by applying Mmask to Isource. For pixel coordinates (x, y), if the pixel belongs to the target, then Mmask (x, y) = 1; otherwise, Mmask (x, y) = 0. Accordingly, Iobject (x, y) retains only the pixels belonging to the target, with other pixels set to 0.
The target is then pasted into the target image Itarget. To ensure that the background of the target image remains unchanged in the regions where the target is not pasted, and to replace the specified region with the target, the following formula is used for the composition:
In the formula (Equation 2), Inew denotes the composed image obtained after placing the target into Itarget, Itarget (x, y) · (1 - Mmask (x, y)) retains the background region of the target image where target is absent; and Iobject (x, y) places the target in the corresponding region.
This method ensures seamless integration of the target object and background, generating a new image that retains the background information while introducing the target object.
The final augmented image Ifinal is generated using the following formula (Equation 3):
The final augmented image, Ifinal, is generated using the following formula.Through the SimpleCopy-Paste augmentation technique, the diversity of the dataset was significantly improved, especially when simulating complex seabed environments. This enhanced the robustness of the model in scenarios involving noise interference, background changes, and partial occlusion of target objects. This method expands the number of data samples and effectively improves the generalization ability of the model when handling changing backgrounds and complex target detection scenarios. Ultimately, the targets from 385 shipwreck and 62 aircraft sonar source images were extracted and pasted onto 578 seabed sonar target images, resulting in a total of 5,700 images of aircraft and shipwreck data, as shown in Figure 2.
To enhance the target detection capability of the model in complex seabed environments, various data augmentation techniques were applied to an expanded set of 5,700 side-scan sonar images, including Cutout (DeVries and Taylor, 2017), Mosaic (Bochkovskiy et al., 2020), and noise addition techniques. Cutout randomly generates square occlusion regions in images, simulating the partial occlusion of targets by sediment, seabed structures, or marine clutter. This technique enhances the ability of the model to infer target shapes under conditions of missing information, thereby improving generalization performance and robustness. Mosaic augmentation constructs entirely new images by cutting and stitching four or nine source images together, each containing multiple targets and complex backgrounds. Specifically, 2,400 medium-scale target images were generated using four-image mosaics, and 1,900 small-scale target images were created using nine-image mosaics. This simulates complex underwater scenes characterized by multiple objects and diverse backgrounds, thereby increasing data diversity and enhancing the capability of the model in multi-object detection and handling multi-scale targets. By simulating seafloor noise interference, noise addition techniques include adding Gaussian noise and salt-and-pepper noise improve the model’s tolerance to noise and lessen its effect on detection, which lowers the possibility of false positives and false negatives. Figure 3 displays the data samples following preprocessing. An augmented dataset of 10,000 photos was produced by combining the SimpleCopy-Paste, Cutout, Mosaic, and noise addition techniques. This greatly increased the data’s authenticity and diversity and improved the model’s capacity to locate targets in challenging seafloor situations.
Figure 3
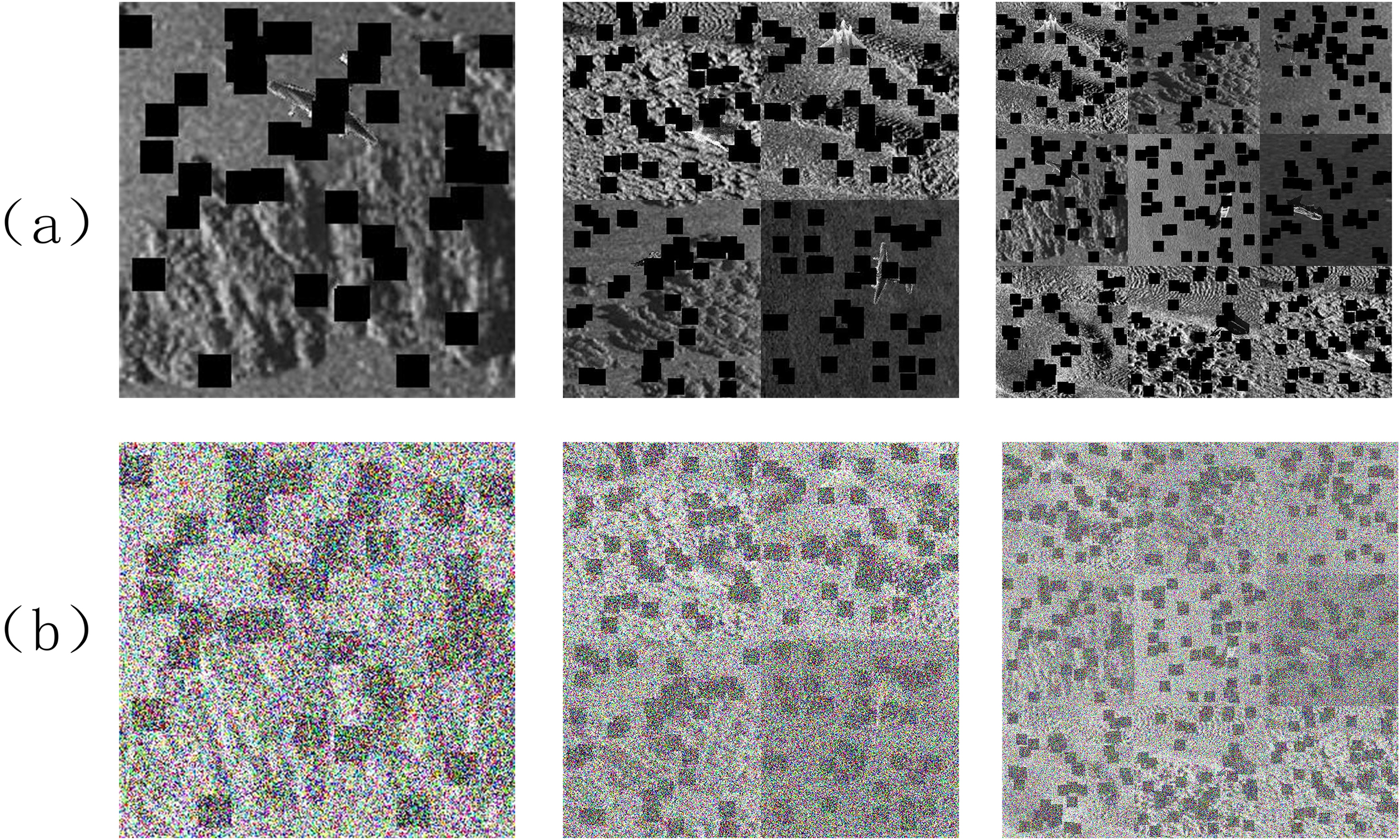
Examples of data after preprocessing: (a) examples of data processed with cutout and mosaic (b) examples of data processed with noise addition.
This work created a diverse complex environment side-scan sonar dataset (CESSSD) using the four data augmentation approaches previously discussed. In addition to increasing the dataset’s size, these data augmentation techniques greatly enhanced the model’s resilience and capacity for generalization in complicated situations. The 10,000 photos were divided into 8:2 training and validation sets. Table 1 contains the dataset’s comprehensive information.
Table 1
| Category | Large-scale (images) | Medium-scale (images) | Small-scale (images) | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training Set | 4500 | 2000 | 1500 | 8000 |
| Validation Set | 1200 | 400 | 400 | 2000 |
| Total | 5700 | 2400 | 1900 | 10000 |
Detailed information of CESSSD.
3 Model and method
3.1 YOLOv8 model
The base model for object detection in side-scan sonar pictures of complex environments chosen for this investigation is YOLOv8. YOLOv8 is a variant of the You Only Look Once (YOLO) series that retains the series’ high speed and accuracy while making notable improvements to its architecture, detection power, and efficiency. Because of its superior detection accuracy, real-time performance, and processing power, YOLOv8 is particularly well-suited for target detection in side-scan sonar images of complex environments.
YOLOv8 has powerful multi-scale detection capabilities, utilizing FPNs to extract multilevel resolution information and path aggregation networks (PANs) to fuse features, significantly improving the detection performance for targets of different scales in complex backgrounds. It excels in handling common issues in side-scan sonar images, such as noise, target shape diversity, and background interference, and accurately detects prominent and subtle targets. Simultaneously, the architecture of YOLOv8 is lightweight and efficient, with an adaptive anchor box design and optimized inference processes, improving computational efficiency and adapting to various hardware conditions to meet real-time processing requirements. This allows YOLOv8 to process large numbers of sonar images quickly for underwater exploration, search and rescue, and other tasks, enabling timely target detection and supporting decision-making. YOLOv8 uses an improved version of CSPNet as its backbone network, which reduces the redundant gradient flow by segmenting the feature map calculations. This design reduces the computational load and maintains an efficient feature extraction capability. This is especially critical when handling low-resolution side-scan sonar images where the target and background differences are small, optimizing computational efficiency while enhancing the ability of the model to separate important features from complex backgrounds.
3.2 LANConvNeXtv2 module structure
In underwater environments, targets in sonar images typically have extremely low contrast, which presents significant challenges for target detection. Unlike traditional optical images, sonar images are often acquired under complex underwater conditions due to the special nature of their generation, resulting in a very low contrast between the target objects and background in the images. This low-contrast phenomenon significantly increases the difficulty of distinguishing targets from the background, making it difficult for traditional computer vision techniques to effectively recognize target objects. In addition to the low-contrast issues, numerous complex noise sources and interference factors exist in underwater environments. These noises include seabed reflections, marine clutter, and sensor noise from the sonar devices. This noise often creates false targets or strong interference signals in an image, which can affect the ability of the model to detect real targets. Although YOLOv8 is a powerful target-detection model that performs excellently in general target-detection tasks, it still faces challenges in terms of feature extraction when dealing with low-contrast and complex, noisy sonar images. The standard convolutional module of YOLOv8 struggles to extract sufficient and effective target features, particularly when the target boundaries are blurred or the background noise is overly complex. As a result, the model often fails to focus on the true target regions, leading to suboptimal detection performance in complex underwater environments. To address these specific issues, RCDI-YOLO introduces the LANConvNeXtv2 (lightweight attention network with ConvNeXt v2) module. This module is specifically designed to improve feature extraction capabilities and is particularly optimized for low-contrast and noise-complex scenarios. The LANConvNeXtv2 module integrates the advantages of lightweight attention mechanisms and the ConvNeXt v2 network to enhance the feature extraction performance of the model, particularly in complex underwater environments.
RCDI-YOLO replaces the original C2f module in the backbone and neck networks of YOLOv8 with a LANConvNeXtv2 module. This module integrates a lightweight attention mechanism (Zhang et al., 2023) and the ConvNeXt v2 architecture (Woo et al., 2023) and has the following characteristics:
-
LANConvNeXtv2 expands the receptive field and reduces computational complexity using depthwise separable convolution and dilated convolution, improving the recognition accuracy of blurred and occluded targets in underwater environments.
-
It introduces a lightweight attention mechanism that focuses on important regions, suppresses noise interference, and enhances detection accuracy without increasing the computational burden, thereby improving adaptability in noisy environments.
-
A multi-scale convolution strategy improves the ability of the model to detect targets at different scales, reducing false negatives and false positives, and ensuring high-accuracy recognition in complex backgrounds.
As shown in Figure 4, LANConvNeXtv2 is an improved module based on the lightweight attention mechanism and ConvNeXt architecture, offering very high feature extraction efficiency. The use of more refined convolution operations and attention mechanisms can accurately enhance the features of low-contrast targets in noisy environments. The design of LANConvNeXtv2 focuses on multi-scale feature extraction, which enables the capture of key target features at different scales and resolutions, thereby improving model performance in complex backgrounds.
Figure 4
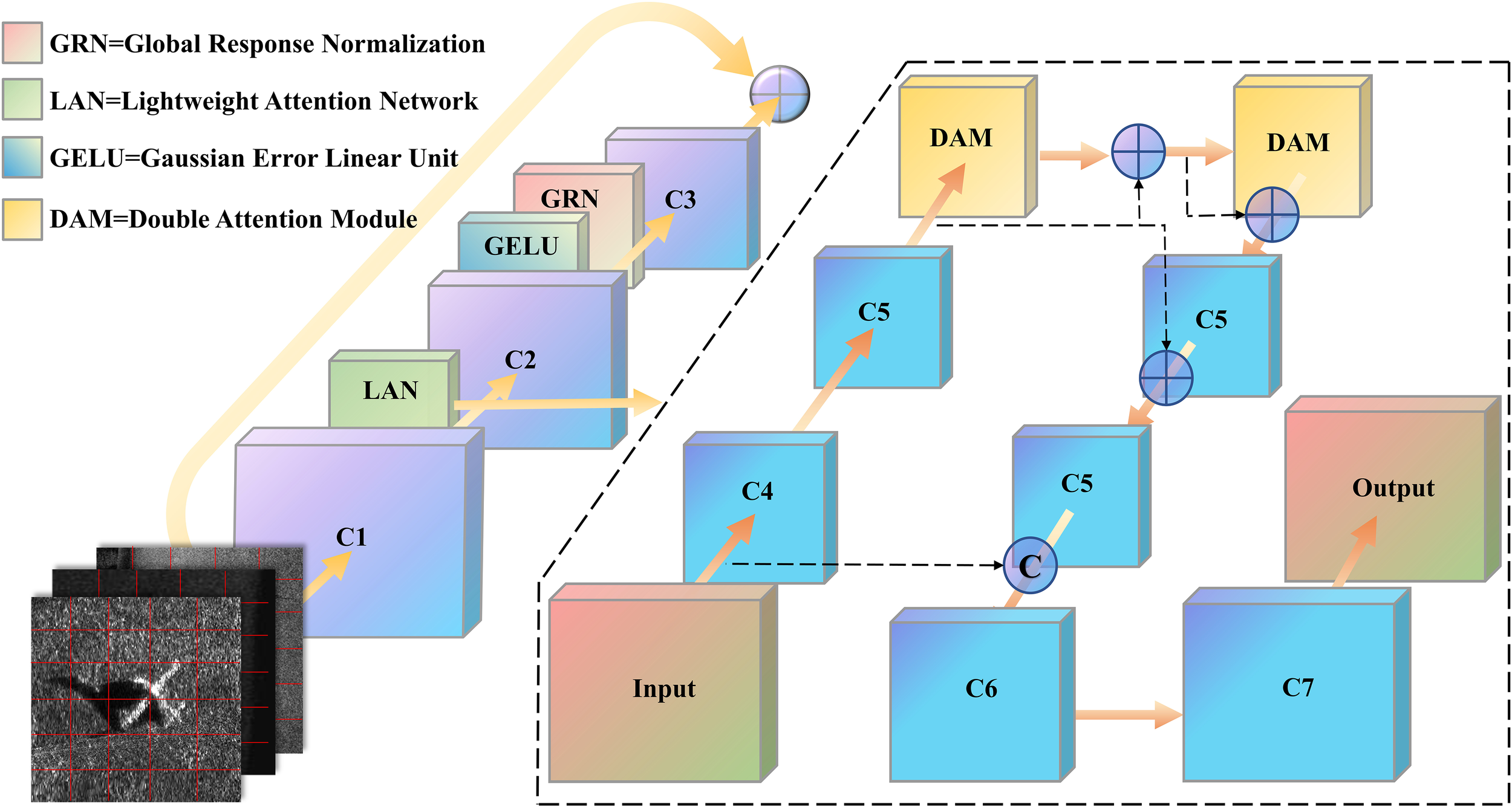
LANConvNeXtv2 architecture diagram.
The core principle of LANConvNeXtv2 is a combination of convolution operations and attention mechanisms. The convolution layers extract multilevel features, and the attention mechanism dynamically adjusts the feature weights at different levels to enhance the critical features. The formula is as follows:
Convolution Operation: The two-dimensional convolution operation extracts local features as represented by the following formula (Equation 4):
Where W is the convolution kernel, X is the input feature map, ∗ represents the convolution operation, and b is the bias term.
To capture the target features at different scales, LANConvNeXtv2 introduces multi-scale convolution operations. At different scales s ∈ S, convolution is performed using kernels of different sizes (Equation 5):
where S is the set of scales, Ws is the convolution kernel weight at scale s, X is the input feature map, bs is the bias term corresponding to scale s, and Fs is the output feature map at scale s.
The feature maps Fs at different scales are fused to form a comprehensive feature F. Fusion methods include addition and concatenation fusion (Equations 6, 7):
Then, a 1×1 convolution is applied to reduce the dimensionality of the channels (Equation 8):
where Wreduce is the dimensionality reduction convolution kernel, and breduce is the corresponding bias term.
Attention Mechanism: The mechanism is used to dynamically adjust the importance of different parts of a feature map. The weights are calculated using the sigmoid function as follows (Equation 9):
Where Wa is the attention weight, x is the input feature map, and σ is the sigmoid activation function. The attention mechanism enables the model to focus on key target features while reducing attention to noisy areas, thereby improving detection accuracy.
The LANConvNeXtv2 module significantly enhances the target-detection capabilities of the RCDI-YOLO model in low-contrast, complex, noisy backgrounds. This module improves the feature extraction efficiency and accuracy of the model and strengthens its robustness in complex underwater environments, enabling RCDI-YOLO to better handle the detection challenges in side-scan sonar images. These improvements provide strong technical support for practical tasks, such as underwater detection, marine exploration, and search and rescue, making the target-detection system more reliable and efficient in complex environments.
3.3 Dysample module structure
In multi-scale target detection, a significant size variation exists among targets, and the model needs to be flexible in handling different scales. However, the traditional YOLOv8 model uses fixed upsampling operations, which, although somewhat effective, have limitations when faced with significant changes in scale. Especially in side-scan sonar images, small targets have very small sizes, whereas large targets occupy larger regions, and marine noise, reflections, and clutter interference in complex backgrounds further exacerbate the detection difficulty. Fixed upsampling struggles to adapt to dynamically changing target scales, leading to false positives and missed detections.
The RCDI-YOLO model replaces the conventional upsampling process with the Dysample mechanism (Liu et al., 2023) based on YOLOv8 in order to overcome these problems. In order to meet the feature extraction needs of targets of varying sizes, the adaptive sampling technique known as “dysample” dynamically modifies the sampling rate according to the true scale and features of targets. Compared to fixed upsampling, Dysample allows flexible adjustments to the sampling density, ensuring the accurate capture of small targets and effective resolution of large targets. This mechanism enhances detection accuracy and stability, particularly in cases of target partial occlusion or complex background noise. Additionally, Dysample increases the sampling density in complex background areas and reduces the sampling rate in simpler areas, thereby optimizing computational efficiency. Overall, Dysample improves the adaptability of RCDI-YOLO in handling multi-scale targets and complex backgrounds, thereby enhancing the detection performance of the model in side-scan sonar images.
The core of Dysample is adaptive sampling rate adjustment, which dynamically modifies the sampling rate based on the scale information of the target object to enhance the feature extraction capability of targets of different sizes. Figure 5a shows the dynamic sampling mechanism of the RCDI-YOLO model. It utilizes a sampling point generator to dynamically generate a sampling point set, Sampling_Set, based on the input feature and then performs dynamic upsampling through the Grid Sample operation. This ensures that the output feature χ’ better adapts to the actual scale and characteristics of the target. Figure 5a demonstrates the upsampling process based on dynamic sampling, which is mathematically described as follows (Equation 10):
Figure 5
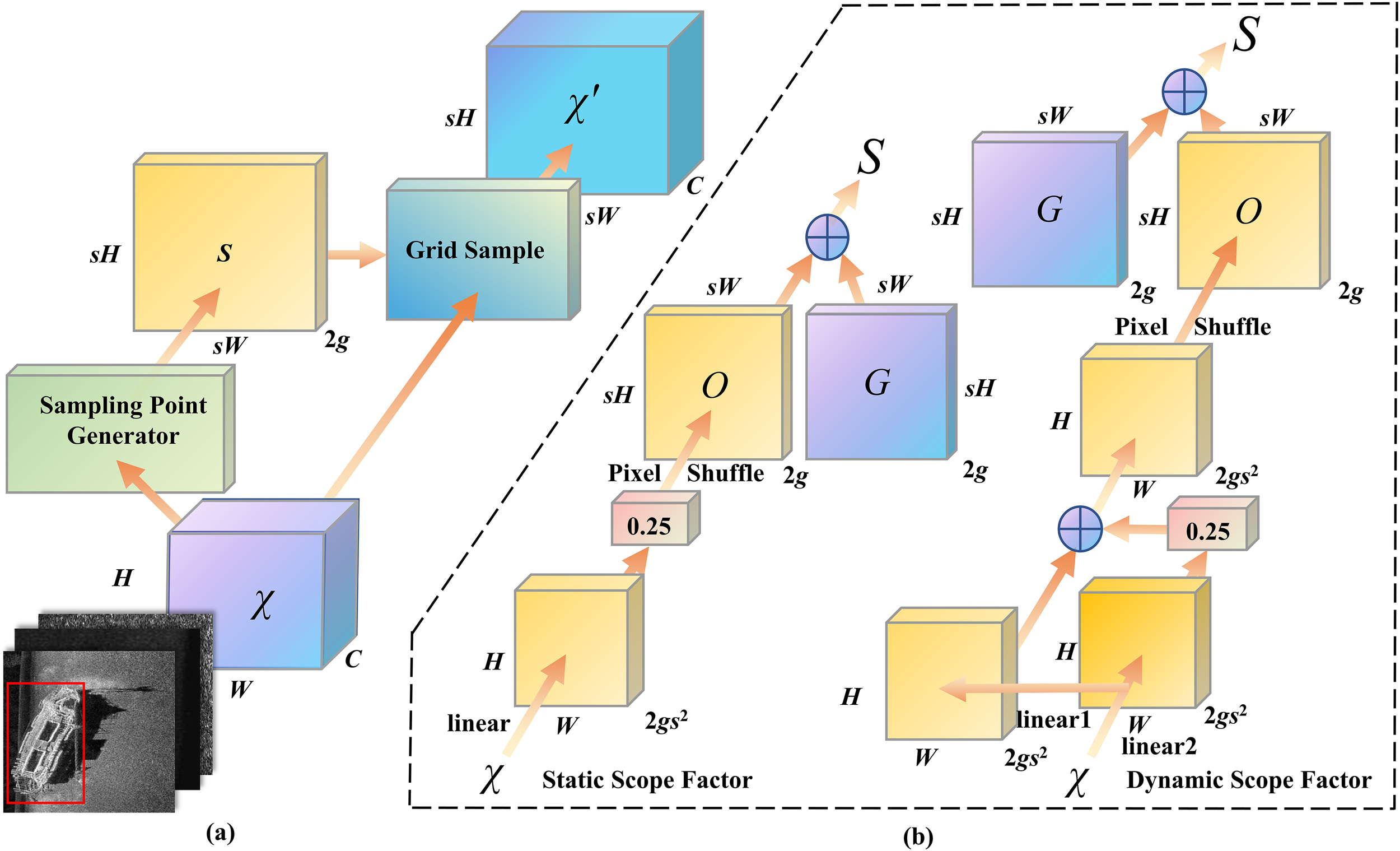
Sampling-based dynamic upsampling and module design in dysample: (a) dynamic sampling mechanism (b) workflow of sampling point generator.
Where is the input feature map with dimensions H×W×C; S is the set of sampling points generated by the sampling point generator, with dimensions sH×sW×2g; χ′ is the output feature map after dynamic sampling, with dimensions sH×sW×C; s is the upsampling factor; and g is the dimension of each sampling point.
Dynamic sampling adjusts the values of S by dynamically modifying the sampling positions based on the input features, thereby achieving an adaptive upsampling operation.
The sampling point generator is responsible for generating S, which is achieved by combining the range factor and offset. The formula used is as follows (Equation 11):
Where G is the scope factor that provides the initial sampling distribution with dimensions sH×sW×2g, O is the offset that introduces dynamic adjustments to refine the scope factor.
Figure 5b details the workflow of the sampling point generator, including the Static Scope Factor and the Dynamic Scope Factor. Both are generated by combining the scope factor G and the offset O. The Static Scope Factor follows a fixed offset generation strategy, whereas the Dynamic Scope Factor incorporates two linear transformations, further enhancing the flexibility and adaptability of sampling.
The offset O for the Static Scope Factor is generated using the following formula (Equation 12):
In the formula, the input feature χ first undergoes a linear transformation, producing an output with dimensions H×W×2gs2. After being scaled by a factor of 0.25, it is rearranged using the Pixel Shuffle operation to obtain final dimensions of sH×sW×2g.
The offset O for the Dynamic Scope Factor is computed as follows (Equation 13):
In the formula, the feature map χ is transformed into two sets of tensors through two linear transformations. These two sets of tensors are element-wise added, multiplied by a factor of 0.25, and then converted to the target size sH×sW×2g through Pixel_Shuffle.
In summary, the RCDI-YOLO model significantly improves multi-scale target detection capability by introducing the Dysample (dynamic sampling) mechanism. Compared to traditional fixed upsampling operations, Dysample can dynamically adjust the sampling rate according to the actual scale and characteristics of the target, enabling precise feature extraction for targets of different sizes.
The versatility and adaptability of Dysample enable RCDI-YOLO to capture target features more correctly, lowering false negatives and false positives, especially when working with complex, noisy backgrounds and targets with large size fluctuations in side-scan sonar images. Dysample considerably improves the detection effectiveness and robustness of the model in complex environments by concentrating on target regions and optimizing computational resources. This strengthens the technological support for a variety of real-world applications, including undersea exploration.
3.4 ImplicitHead module structure
In side-scan sonar images, underwater noise interference often generates false targets, thereby increasing the difficulty of target detection. In particular, when targets are occluded or submerged in noise, the traditional YOLOv8 model struggles to distinguish between noise and real targets, resulting in false positives and missed detections. To address this issue, RCDI-YOLO introduced the ImplicitHead module (Yu et al., 2024) in addition to YOLOv8, which utilizes implicit feature representation to reduce reliance on explicit features and enhance robustness in complex, noisy backgrounds. Unlike traditional detection heads, the ImplicitHead extracts key information more efficiently, reduces noise interference, and improves target-detection accuracy.
The advantage of ImplicitHead is its ability to achieve strong feature extraction capabilities with minimal parameters, particularly in sonar images, by handling seabed reflections and marine clutter. It effectively differentiates real targets from noise interference, automatically filters out false targets in the background, and significantly reduces the number of false positives. Additionally, when targets are partially occluded or have blurry boundaries, ImplicitHead, with its powerful implicit learning ability, can better comprehend the overall characteristics of a target. Even if some information is missing, it maintains high detection accuracy and significantly reduces the computational complexity of the model, allowing RCDI-YOLO to improve detection accuracy while maintaining high real-time performance and computational efficiency in practical applications.
As shown in Figure 6, the ImplicitHead module consists of a sequential feature processing path, a distribution fitting loss (DFL) optimization module, and ImplicitA/ImplicitM implicit learning modules. The combination of these three components forms an efficient and flexible target-detection head, effectively enhancing feature representation capability and significantly improving detection performance.
Figure 6
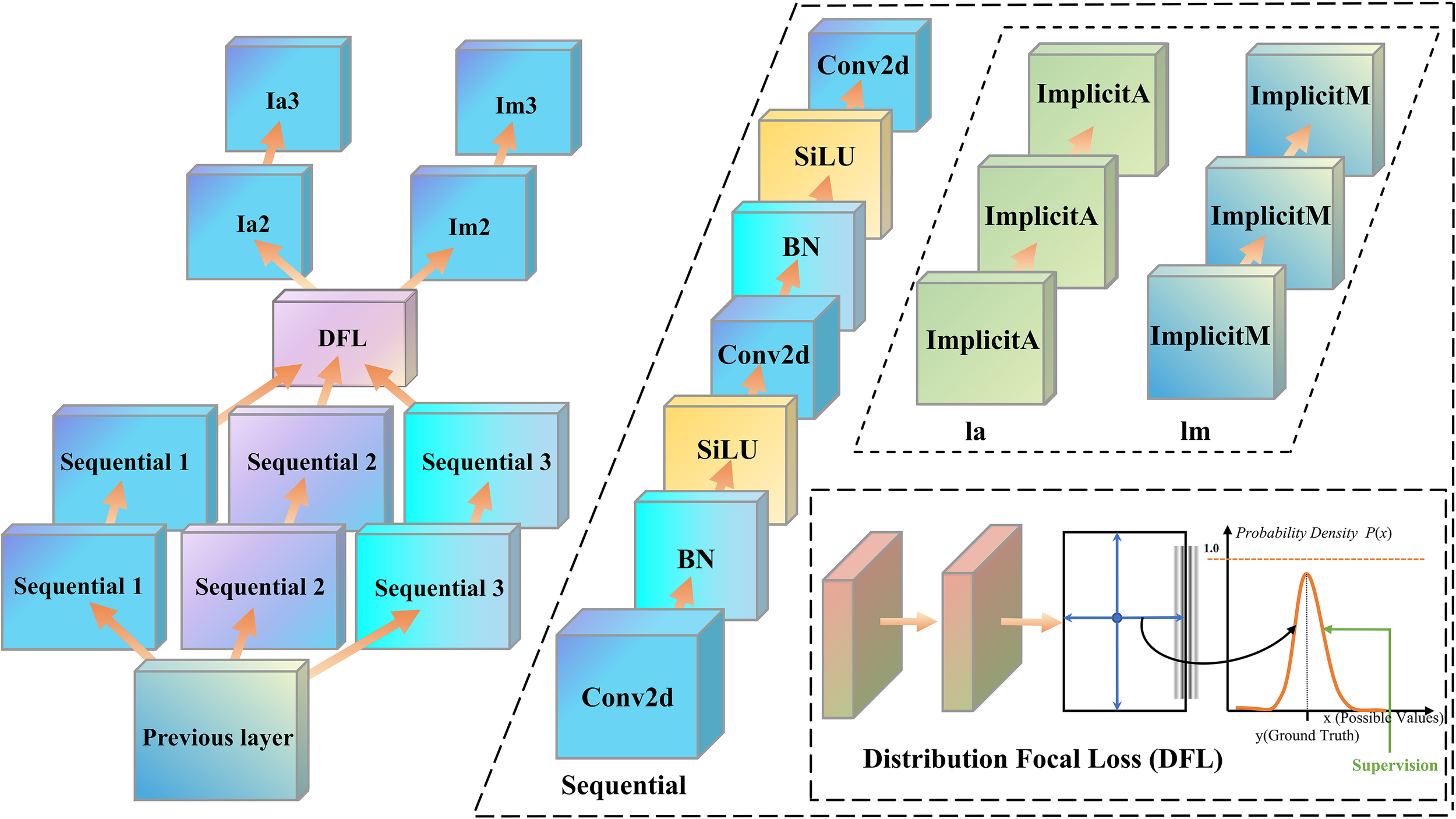
ImplicitHead architecture diagram.
The input features originate from the previous layer of the network backbone and are denoted as . To extract high-level and multi-scale features, ImplicitHead includes multiple parallel sequential modules, each consisting of convolution operations (Conv2d), an activation function (SiLU), and batch normalization (BatchNorm). The computation was performed using the following formula (Equation 14):
The multipath processing design of the sequential module enabled efficient feature extraction from the input features, enhanced the semantic representation capability of the features, and provided richer information for subsequent modules.
The DFL module improves the accuracy of the target position estimation and bounding box regression quality by fitting the difference between the predicted and real distributions. This module optimizes the bounding box regression loss during target detection, which is formulated as follows (Equation 15):
Where Pipred represents the predicted distribution, Pigt represents the ground truth distribution, and SmoothL1(·) is the regression loss function used for the bounding boxes.
The Implicit module was designed to dynamically adjust the characteristics of the feature maps, making the feature representation of the model more robust for different targets. Two types of implicit learning modules exist: ImplicitA and ImplicitM. These implicit learning modules introduce learnable parameters to adaptively adjust the feature distribution. The formulae are as follows (Equation 16):
where ImplicitA adapts to local features, whereas ImplicitM optimizes the global feature distribution.
In summary, the ImplicitHead module enhances the robustness and noise resistance of the model, thereby improving the performance of RCDI-YOLO in handling complex sonar images. It effectively mitigates underwater noise interference, significantly reduces false positives and false negatives, and optimizes computational efficiency. This makes it well-suited for real-time applications such as underwater detection, marine exploration, and search-and-rescue missions. These improvements provide reliable and efficient technical solutions for underwater target detection.
3.5 Improved YOLOv8 model
By combining the LANConvNeXtv2, Dysample, and ImplicitHead modules, RCDI-YOLO considerably improves YOLOv8 and significantly increases the target-detection capacity in side-scan sonar images in complicated situations (Figure 7). The model can reliably detect targets even in high-noise situations with blurred boundaries thanks to LANConvNeXtv2, which is specifically made to improve feature extraction for low-contrast targets. It works especially well on small targets or items that are partially obscured. To get beyond the stiffness of conventional upsampling when working with multi-scale objects, Dysample offers a dynamic sampling technique. It ensures accurate feature extraction for objects of various scales by adaptively modifying the sample rate according to the target’s size and attributes. ImplicitHead reduces false positives and negatives under high noise interference by using implicit learning. This improves the model’s resilience in high-noise settings by efficiently filtering background erroneous targets. Furthermore, the ImplicitHead’s lightweight design speeds up inference and lowers computational complexity, which makes RCDI-YOLO better suited for real-time applications. All things considered, these enhancements boost the model’s generalization ability in challenging situations and raise detection stability and accuracy. RCDI-YOLO performs exceptionally well in scenarios with high levels of noise interference, obscured targets, or complicated backdrops, which makes it a perfect choice for underwater detection, maritime exploration, and search and rescue operations.
Figure 7
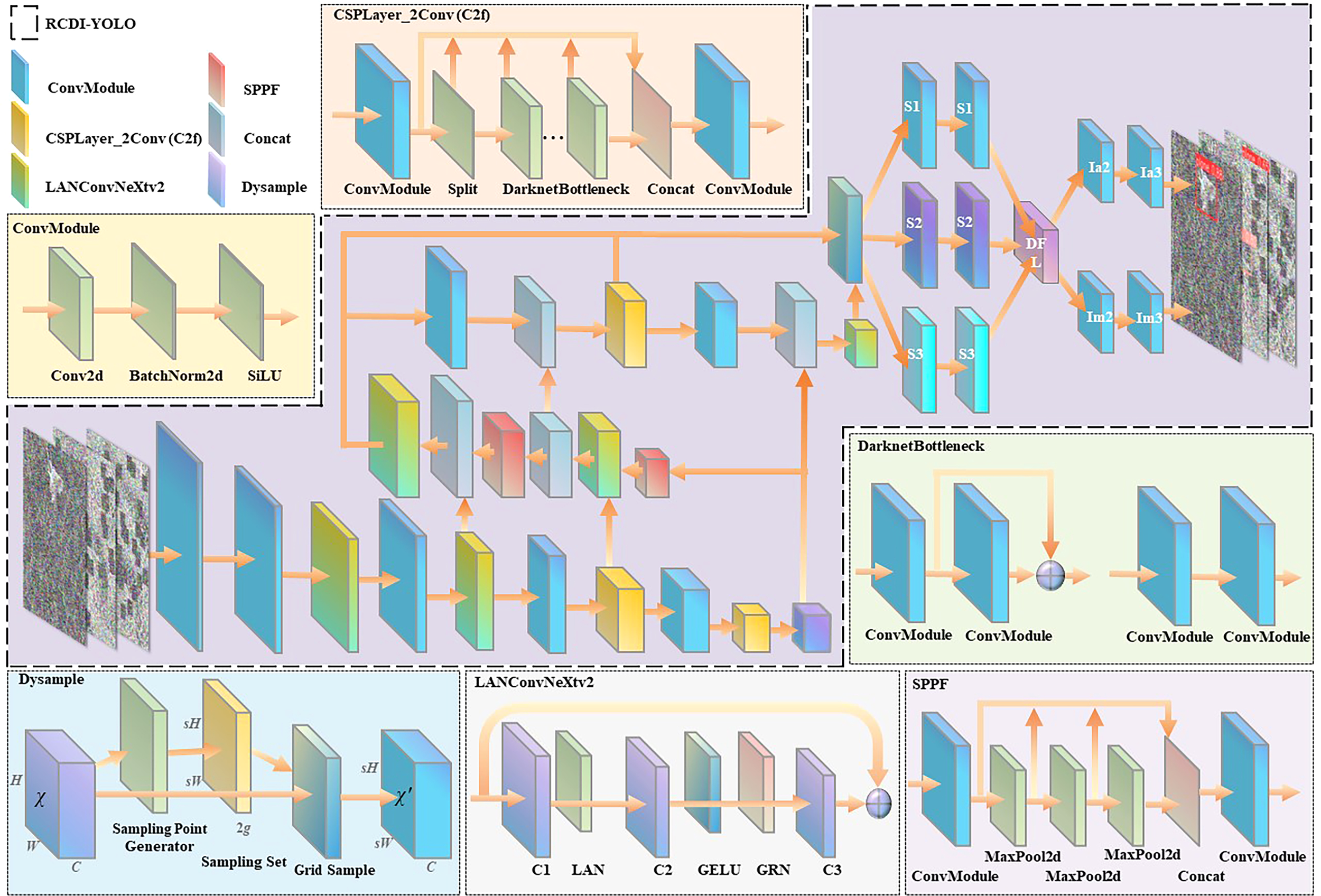
Architecture diagram of improved RCDI-YOLO.
4 Experimental results and analysis
4.1 Experimental setup and implementation details
Experiments were conducted on a Windows 10 system equipped with an Intel i7-13700K CPU and an NVIDIA RTX 3090 GPU, using the PyTorch framework for model training and validation. The dataset comprises 10,000 images, split 80% for training and 20% for validation. Input images were resized to 640×640. Models were trained using the SGD optimizer with an initial learning rate of 0.01 and a fixed learning rate schedule, a batch size of 32, and a warmup period of 3 epochs. Training lasted up to 100 epochs with early stopping patience set to 50 epochs, and random seed 0 was fixed to ensure reproducibility. Loss weights were set to 7.5 for box regression, 0.5 for classification, and 1.5 for DFL loss. Data augmentation included Mosaic (enabled with probability 1.0, disabled in the last 10 epochs), random horizontal flips (p=0.5), and HSV adjustments (H: ± 0.015, S: ± 0.7, V: ± 0.4). During inference, NMS IoU threshold was set to 0.7 and anchors were auto-computed. A full summary of the experimental setup is provided in Table 2.
Table 2
| Category | Item | Specification | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardware | CPU | Intel Core i7-13700K @ 3.40 GHz | |
| GPU | NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090 32GB | ||
| Operating System | Windows 10 | ||
| Training Settings | Image Resolution | 640 × 640 | |
| Optimizer | SGD | ||
| Initial Learning Rate | 0.01 | ||
| Learning Rate Schedule | 0.01 | ||
| Batch Size | 32 | ||
| Warmup Epochs | 3 | ||
| Training Epochs | 100 | ||
| Early Stopping | Patience = 50 epochs | ||
| Random Seed | 0 (Fixed) | ||
| Epochs | 100 | ||
| Loss Weights | Box Loss | 7.5 | |
| Cls Loss | 0.5 | ||
| DFL Loss | 1.5 | ||
| Data Augmentation | Mosaic | Enabled (p=1.0, disabled last 10 epochs) | |
| Random Flip (Horizontal) | p=0.5 | ||
| HSV Augmentation | H: ± 0.015, S: ± 0.7, V: ± 0.4 | ||
| Inference | NMS IoU Threshold | 0.7 | |
| Anchor Settings | Auto-computed | ||
| Dataset | Total Images | 10,000 | |
| Train/Validation Split | 80%/20% | ||
Experimental setup summary.
4.2 Model evaluation metrics
The model’s performance was assessed in this study using a Confusion Matrix, Precision (P, Equation 17), Recall (R, Equation 18), Average Precision (AP, Equation 19), and Mean Average Precision (mAP, Equation 20).
4.3 Comparison tests on the enhanced method’s effectiveness
Each detection accuracy increase’s performance was thoroughly examined through comparative trials to see how much it contributed to the total performance improvement. The goal was to offer data support for model structure optimization and to elucidate the precise effect of each structural modification on the final model performance.
4.3.1 Comparison experiments on backbone and neck network improvements
Four C2f modules are present in the neck and backbone networks of the YOLOv8 model. The LANConvNeXtv2 module, which combines a lightweight attention mechanism with an enhanced ConvNeXt v2 architecture, was used to replace all eight C2f modules in order to identify the best locations to enhance the backbone and neck network structures. Tests of the updated model’s accuracy showed that the best overall performance was obtained by swapping out the first and second C2f modules in the backbone network and the first, second, and fourth C2f modules in the neck network. Additionally, this work used the GhostNet and EfficientNet modules to do comparison studies.
According to Table 3, the LANConvNeXtv2 module obtained the highest Precision of 94.4% in the backbone and neck network improvement comparison experiments. This was 1.6%, 1.8%, and 1.1% higher than the original YOLOv8, EfficientNet-based, and GhostNet-based models, respectively. The LANConvNeXtv2-based network outperformed all other models in side-scan sonar target detection in challenging situations, as evidenced by its maximum recall (88.8%), mAP0.5 (95.1%), and mAP0.5-0.95 (60.1%).
Table 3
| Algorithm | Backbone+neck | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | mAP0.5 (%) | mAP0.5-0.95 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv8 | – | 92.8 | 85.9 | 93.7 | 56.6 |
| EfficientNet (Tan and Le, 2019) | 92.6 | 86.6 | 93.4 | 54.8 | |
| GhostNet (Han et al., 2020) | 93.3 | 86.0 | 93.9 | 55.9 | |
| LANConvNeXtv2 | 94.4 | 88.8 | 95.1 | 60.1 |
Comparison results of backbone and neck network improvements.
4.3.2 Comparison experiments on detection head
Compared to the original YOLOv8 detection head, this study adopted ImplicitHead, a module based on implicit feature representation. By implicitly processing input features, ImplicitHead captures key information in images more efficiently while reducing the dependence on explicit feature learning, thereby enhancing the robustness of the model in high-noise backgrounds. Additionally, we conducted comparative experiments with the LADH and DynamicHead detection heads.
Target-detection accuracy for side-scan sonar images in complicated situations is much enhanced by the ImplicitHead detection head, as shown by the comparison findings of the detection heads in Table 4. With a precision of 95.0%, it outperformed the original YOLOv8, LADH, and DynamicHead by 2.2%, 1.2%, and 1.7%, respectively. This remarkable advantage indicates that ImplicitHead excels in precise target localization, particularly in challenging environments. In addition to its superior Precision, ImplicitHead also demonstrates stability and reliability in Recall (86.2%) and mAP0.5 (93.0%), confirming its ability to maintain high accuracy while effectively capturing more targets. Moreover, ImplicitHead achieves 56.4% in the more challenging mAP0.5-0.95 metric, which matches LADH and significantly surpasses DynamicHead (54.9%). These results further validate the generalization capability of ImplicitHead in multi-scale and complex scenarios.
Table 4
| Algorithm | Head | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | mAP0.5 (%) | mAP0.5-0.95 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv8 | – | 92.8 | 85.9 | 93.7 | 56.6 |
| LADH (Liu et al., 2020) | 93.8 | 86.2 | 93.3 | 56.4 | |
| DynamicHead (Dai et al., 2021) | 93.3 | 85.9 | 93.2 | 54.9 | |
| ImplicitHead | 95.0 | 86.2 | 93.0 | 56.4 |
Comparison results of detection heads.
4.3.3 Ablation experiments
To investigate the contribution of each improvement module to YOLOv8, we conducted ablation experiments under the same training protocol, with results summarized in Tables 5 and 6. Introducing LANConvNeXtv2 (RC) as the improved backbone significantly enhanced feature extraction under low-contrast and noisy conditions, increasing Precision by 1.6%, Recall by 2.9%, mAP0.5 by 1.4%, and mAP0.5-0.95 by 3.5%, demonstrating its effectiveness in capturing richer and more discriminative feature representations. The Dysample (D) multi-scale upsampling mechanism provided modest but consistent gains—Precision +1.0%, Recall +0.6%, mAP0.5 +0.3%, and mAP0.5-0.95 +0.7%—primarily by increasing sampling density to better capture feature details and distinguish true targets from background noise. ImplicitHead (I), a lightweight implicit detection head, improved Precision by 2.2% and Recall by 0.3%, highlighting its ability to process features implicitly, efficiently capture key image information, and suppress noise, although its effect on mAP metrics is more pronounced when combined with other modules.
Table 5
| Algorithm | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | mAP0.5 (%) | mAP0.5-0.95 (%) | Params (M) | GFLOPs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv8 (baseline) | 92.8 | 85.9 | 93.7 | 56.6 | 3.01 | 8.1 |
| + RC | 94.4 | 88.8 | 95.1 | 60.1 | 3.23 | 9.3 |
| + D | 93.8 | 86.5 | 94.0 | 57.3 | 3.02 | 8.1 |
| + I | 95.0 | 86.2 | 93.0 | 56.4 | 2.57 | 5.7 |
| + RC+ D | 94.5 | 88.3 | 95.0 | 60.1 | 3.23 | 9.3 |
| +RC+ I | 93.9 | 88.4 | 95.2 | 59.4 | 3.23 | 9.3 |
| + I+ D | 94.4 | 86.5 | 93.7 | 57.0 | 2.72 | 7.8 |
| RCDI-YOLO | 95.3 | 88.8 | 95.7 | 60.8 | 3.23 | 9.3 |
Ablation experiment results.
Table 6
| Algorithm | mAP0.5_ medium (%) | mAP0.5-0.95_ medium (%) | mAP0.5_ large (%) | mAP0.5-0.95 _ large (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv8 (baseline) | 79.0 | 44.6 | 36.3 | 22.7 |
| + RC | 80.3 | 48.0 | 39.6 | 25.1 |
| + D | 79.3 | 45.8 | 37.5 | 23.4 |
| + I | 78.9 | 45.6 | 29.3 | 18.2 |
| + RC+ D | 80.2 | 48.4 | 35.0 | 22.4 |
| +RC+ I | 80.4 | 48.3 | 32.0 | 19.6 |
| + I+ D | 78.9 | 46.2 | 35.0 | 19.4 |
| RCDI-YOLO | 80.4 | 49.1 | 36.9 | 23.6 |
Performance comparison of different improvements on various object sizes.
Pairwise module combinations further confirmed their complementarity: LANConvNeXtv2 + Dysample increased mAP0.5 and mAP0.5-0.95 to 95.0% and 60.1%, LANConvNeXtv2 + ImplicitHead reached 95.2% and 59.4%, and Dysample + ImplicitHead maintained baseline mAP0.5 while slightly improving mAP0.5-0.95 to 57.0%. Integrating all three modules into RCDI-YOLO achieved the best overall performance, with Precision 95.3%, Recall 88.8%, mAP0.5 95.7%, and mAP0.5-0.95 60.8%, representing gains of +2.5, +2.9, +2.0, and +4.2 percentage points over the original YOLOv8 at essentially the same lightweight scale.
Performance across different object sizes was further analyzed according to the official COCO dataset standards, where small objects are defined as area ≤ 32² pixels (1024), medium objects as 32² < area ≤ 96² pixels (9216), and large objects as area > 96² pixels (9216). LANConvNeXtv2 (RC) consistently improves medium- and large-object detection, with mAP0.5 and mAP0.5-0.95 increasing by up to 3.3% and 3.4%, demonstrating its strong capability in extracting multi-scale features. Dysample (D) contributes moderate improvements, particularly in mAP0.5-0.95, by refining multi-scale sampling to better distinguish objects from noise. ImplicitHead (I) slightly reduces performance on large objects when applied alone, suggesting its lightweight implicit processing prioritizes noise suppression over detailed large-object features. The combination of all three modules in RCDI-YOLO yields the highest performance across both medium and large objects, with mAP0.5 reaching 80.4% and 36.9%, and mAP0.5-0.95 reaching 49.1% and 23.6%, highlighting the complementary effects of LANConvNeXtv2 (RC), Dysample (D), and ImplicitHead (I) in enhancing robustness and detection accuracy across diverse object scales.
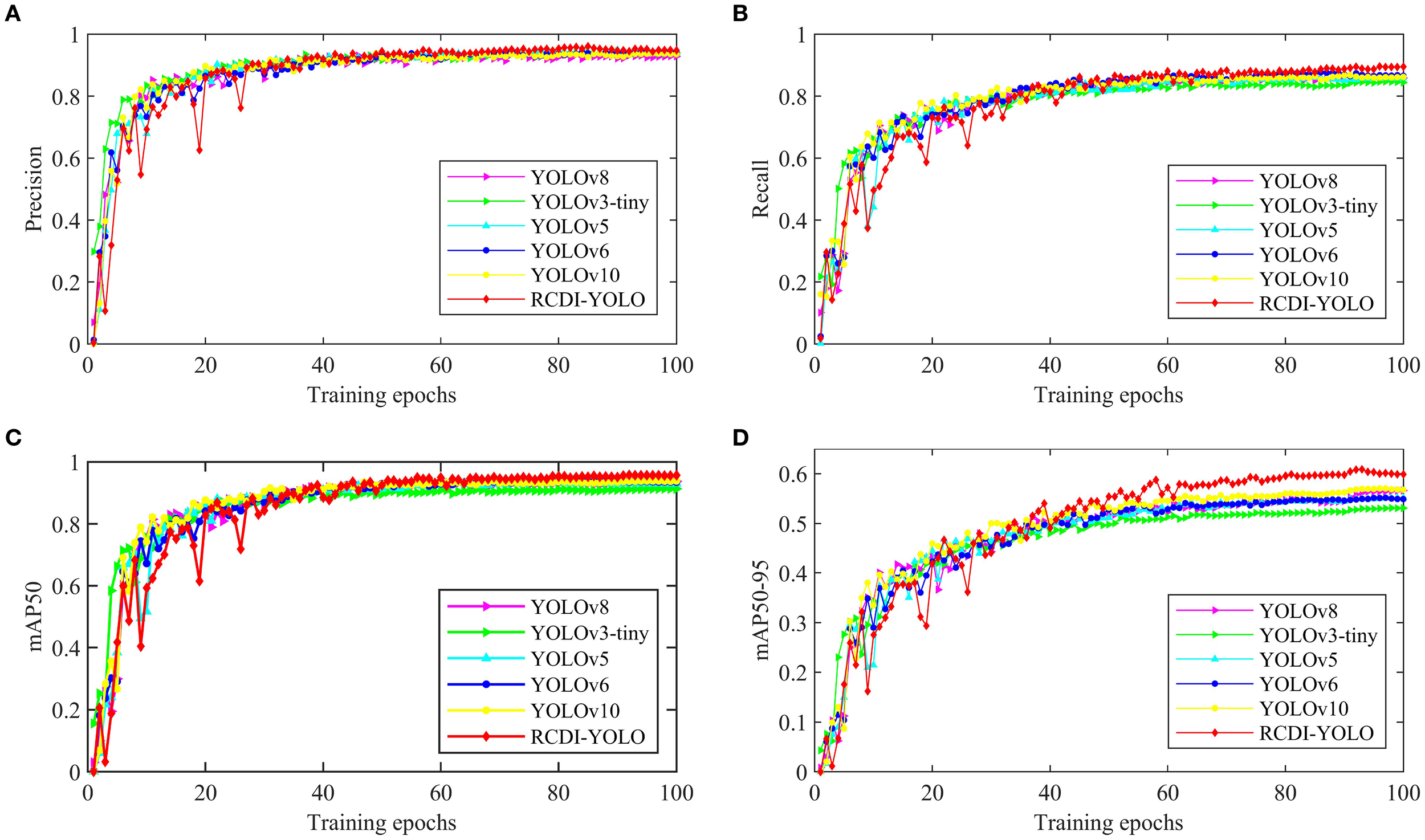
Figure 8 illustrates the learning dynamics. Across all experiments, accuracy stabilized after approximately 60 epochs. The LANConvNeXtV2 curve consistently remained above the baseline early on, demonstrating its contribution to enhanced feature extraction. The ImplicitHead accelerated convergence around the 40th epoch when used in fusion, reducing training time to reach optimal results. RCDI-YOLO exhibited greater fluctuations during the first 30 epochs, but after the 65th epoch, both mAP0.5 and mAP0.5-0.95 consistently surpassed other variants, reflecting strong adaptability to multi-scale targets and complex, high-noise backgrounds. Overall, the ablation study confirms that LANConvNeXtv2 strengthens feature extraction, Dysample improves multi-scale sampling, and ImplicitHead contributes synergistically, enabling RCDI-YOLO to deliver superior detection performance for challenging side-scan sonar imagery.
Figure 8
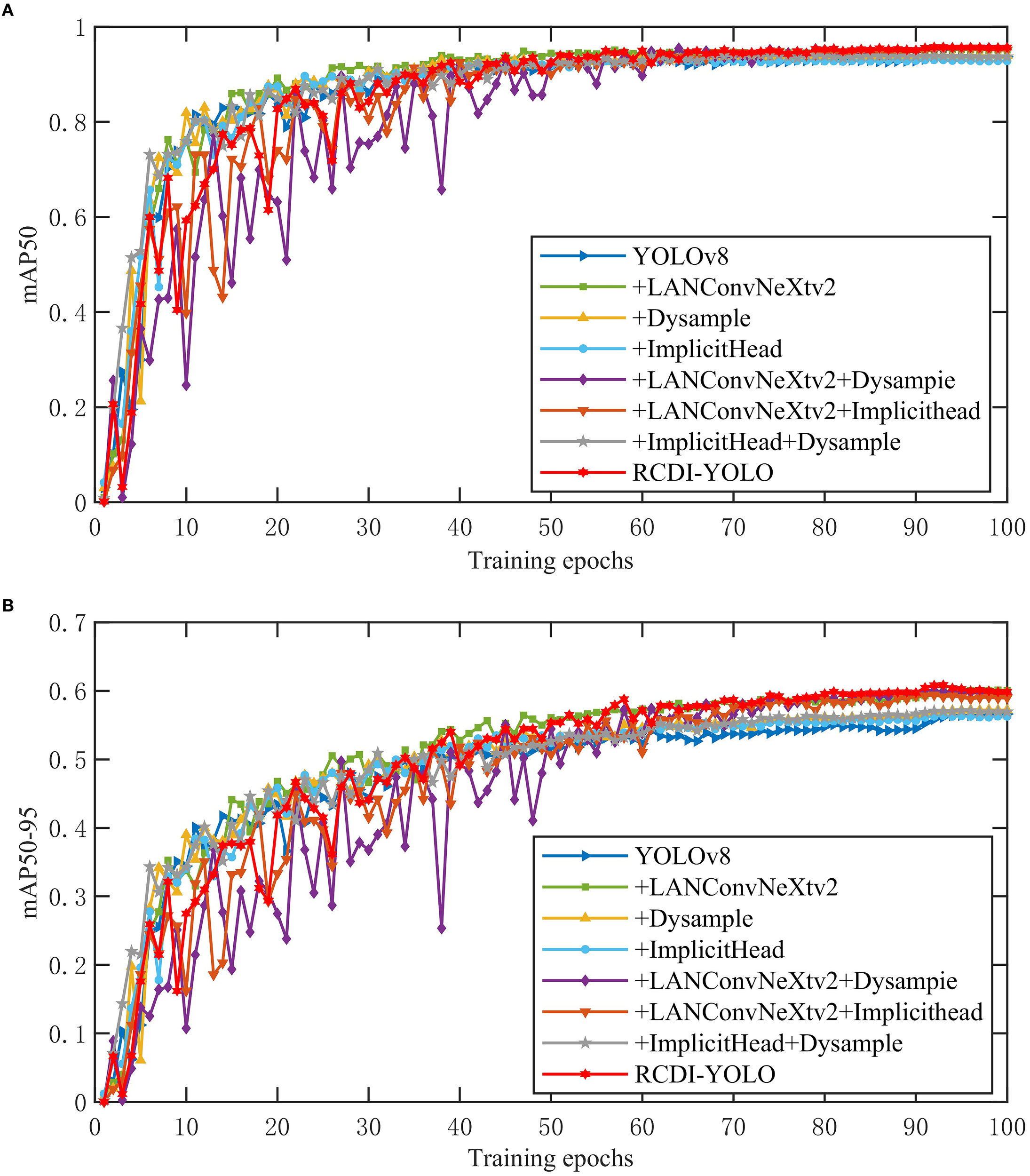
The mAP of ablation experiment: (a) mAP0.5 of fusion experiment (b) mAP0.5-0.95 of fusion experiment.
4.3.4 Comparison experiments of different models
RCDI-YOLO is a specialized target-detection method for complex side-scan sonar images, built upon an improved YOLOv8 backbone. As shown in Table 7, it demonstrates superior overall performance compared with both lightweight and heavier detection models. Specifically, RCDI-YOLO achieves a Precision of 95.3% and Recall of 88.8%, surpassing YOLOv8-n (92.8%/85.9%) and YOLOv6 (94.2%/86.7%), and matching or exceeding larger YOLO variants such as YOLOv8-s (95.6%/86.4%) and YOLOv8-l (95.6%/86.4%).
Table 7
| Structure | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | mAP0.5 (%) | mAP0.5-0.95 (%) | Params (M) | GFLOPs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv8-n (baseline) | 92.8 | 85.9 | 93.7 | 56.6 | 3.01 | 8.1 |
| YOLOv8-s | 95.6 | 86.4 | 95.0 | 60.0 | 11.13 | 28.4 |
| YOLOv8-m | 94.5 | 87.5 | 94.8 | 61.4 | 25.84 | 78.7 |
| YOLOv8-l | 95.6 | 86.4 | 95.0 | 61.0 | 43.61 | 164.8 |
| YOLOv3-tiny (Redmon et al., 2018) | 93.7 | 84.6 | 91.4 | 53.1 | 12.13 | 18.9 |
| YOLOv6 | 94.2 | 86.7 | 93.5 | 55.2 | 4.23 | 11.8 |
| YOLOv9 | 96.6 | 88.0 | 94.6 | 64.6 | 25.53 | 103.6 |
| YOLOv10 (Wang et al., 2024) | 93.8 | 86.0 | 93.8 | 57.0 | 2.58 | 7.8 |
| RetinaNet-50 | 88.4 | 90.2 | 87.0 | 50.8 | 36.35 | 81.93 |
| RCDI-YOLO | 95.3 | 88.8 | 95.7 | 60.8 | 3.23 | 9.3 |
Comparison of experimental results with other detection models.
In terms of detection accuracy, RCDI-YOLO reaches 95.7% for mAP0.5 and 60.8% for the more stringent mAP0.5-0.95 metric, significantly outperforming YOLOv8-n (93.7%/56.6%) and YOLOv6 (93.5%/55.2%). Compared with YOLOv9, which achieves 94.6%/64.6% in mAP0.5/mAP0.5-0.95, RCDI-YOLO maintains slightly lower mAP0.5-0.95 but with far fewer parameters (3.23M vs. 25.53M) and lower GFLOPs (9.3 vs. 103.6), illustrating a superior accuracy-to-efficiency trade-off. Lightweight models such as YOLOv3-tiny and YOLOv10, although smaller in scale, achieve only 53.1% and 57.0% mAP0.5-0.95, highlighting RCDI-YOLO’s stronger generalization and adaptability in complex, high-noise sonar environments. Non-YOLO detectors such as RetinaNet-50, despite having large capacity (36.35M parameters, 81.93 GFLOPs), achieve much lower mAP0.5-0.95 of 50.8%, further confirming the advantage of the proposed architecture in challenging detection scenarios.
As shown in Figure 9, RCDI-YOLO significantly outperforms the other comparison models in terms of Precision and Recall. In terms of Precision, RCDI-YOLO achieves 95.3%, which is notably higher than other models, such as YOLOv8 (92.8%) and YOLOv6 (94.2%). Regarding Recall, RCDI-YOLO also excelled, reaching 88.8%, slightly surpassing YOLOv10 (86.0%) and YOLOv6 (86.7%). By contrast, YOLOv3-tiny performed relatively poorly, with a Recall rate of only 84.6%. These results indicate that RCDI-YOLO achieves faster training convergence and exhibits higher positive sample recognition rates, with lower false and missed detection rates. This makes it more accurate and stable for complex sonar-image detection tasks in challenging environments.
Figure 9
Accuracy–efficiency trade-offs (batch=1, 640×640, end-to-end including pre/post; same device for all models). (a) mAP₀.₅ vs FPS. (b) mAP₀.₅–₀.₉₅ vs FPS. RCDI is highlighted; the thin line denotes the Pareto frontier.
In terms of mAP0.5 and mAP0.5-0.95, RCDI-YOLO also outperforms other models: For mAP0.5, RCDI-YOLO achieves 95.7%, demonstrating exceptional detection accuracy compared to YOLOv8 (93.7%) and YOLOv10 (93.8%). In the more challenging mAP0.5-0.95 metric, RCDI-YOLO reaches 60.8%, significantly surpassing YOLOv6 (55.2%) and YOLOv3-tiny (53.1%). This high performance indicates that RCDI-YOLO possesses stronger detection and generalization capabilities across different IoU thresholds, making it particularly suitable for sonar-image target-detection tasks in complex environments.
Under a unified setup—batch 1, 640×640, same device, end to end with pre/post—Figure 10 summarizes the accuracy–efficiency trade-offs and consistently places RCDI-YOLO on or near the Pareto frontier. In the mAP0.5–FPS plane, RCDI-YOLO reaches mAP0.5=0.9569 at ≈163 FPS with ≈6.13 ms latency, delivering real-time throughput without sacrificing accuracy; in the mAP0.5-0.95–FPS view it records mAP0.5-0.95=0.6084 at the same operating point, while competitors that score higher are notably heavier. Parameter-wise, RCDI-YOLO uses 3.23M parameters and 9.3 GFLOPs yet attains 0.9569/0.6084 on mAP0.5/mAP0.5-0.95, outperforming or matching much larger models in mAP per parameter: relative to YOLO-m/l with 25.84M/43.61M parameters and mAP0.5-0.95 of 0.6136/0.6101, RCDI-YOLO delivers nearly comparable accuracy with ≈8–13× fewer parameters; compared with lightweight baselines n and s, it secures a clear accuracy margin while remaining real-time—n offers mAP0.5=0.9367 at 358 FPS and s yields mAP0.5-0.95=0.5993 at 327 FPS. Memory-wise, RCDI-YOLO sustains top-tier mAP0.5 and competitive mAP0.5-0.95 at ≈145 MB peak, whereas methods with slightly higher mAP0.5-0.95—such as YOLOv9 at 0.6479—require substantially more capacity around 218 MB and run slower near 119 FPS, reinforcing RCDI-YOLO’s superior balance of accuracy, latency, and cost. These outcomes align with our architectural choices—LANConvNeXtv2 for robust feature enhancement under low contrast and clutter, Dysample for multi-scale adaptivity, and ImplicitHead for noise-resistant representation—and, together with earlier ablations, explain why RCDI-YOLO combines high mAP0.5/mAP0.5-0.95, low latency, small footprint, and modest memory, making it well suited for real-time, resource-constrained deployment.
Figure 10
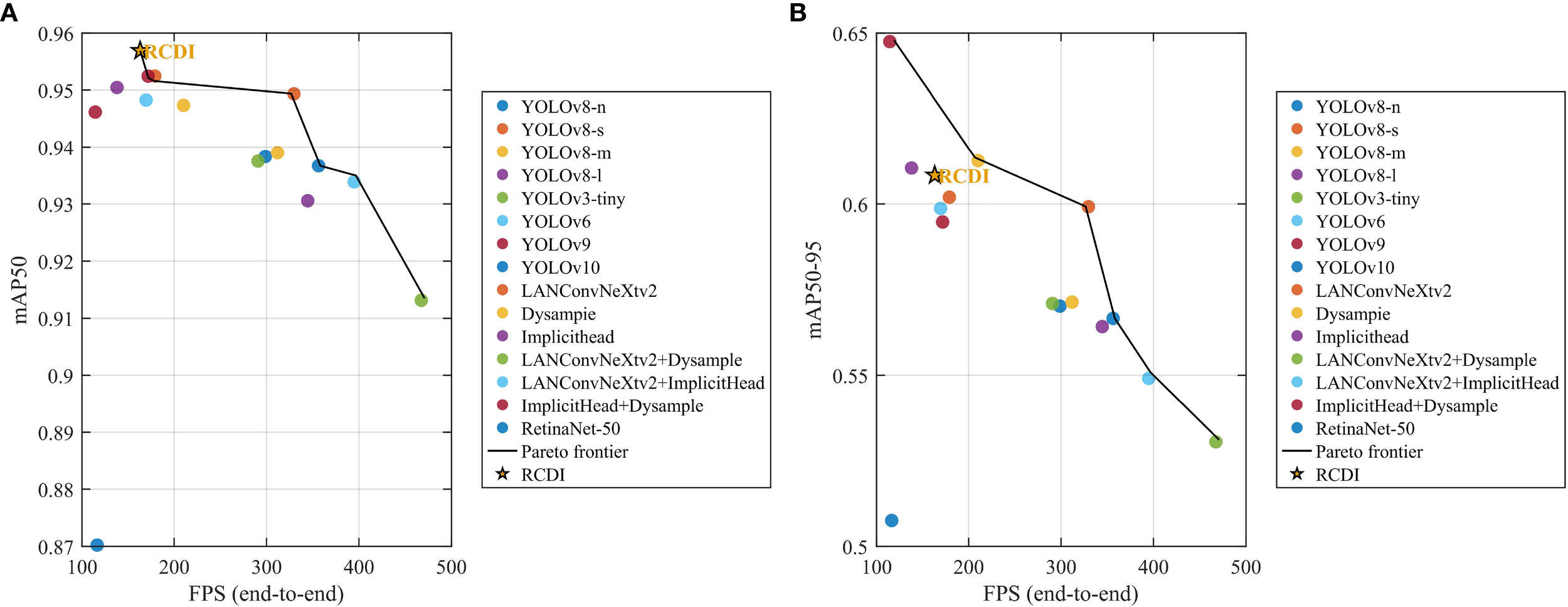
Accuracy–efficiency trade-offs (batch=1, 640×640, end-to-end including pre/post; same device for all models). (a) mAP0.5 vs FPS. (b) mAP0.5-0.95 vs FPS. RCDI is highlighted; the thin line denotes the Pareto frontier.
5 Conclusion
The proposed RCDI-YOLO model demonstrated outstanding performance for side-scan sonar target detection in complex marine environments. By incorporating the LANConvNeXtv2 module, Dysample dynamic sampling mechanism, and ImplicitHead module, the model achieved significant advancements in low-contrast target detection, multi-scale target processing, and noise resistance. The key improvements lie in enhancing feature extraction capabilities, improving adaptability to multi-scale targets, and significantly reducing the impact of noise backgrounds on detection accuracy. Experimental results show that compared to the original YOLOv8 model, RCDI-YOLO achieves a 2.0% increase in mAP0.5, reaching 95.7%, whereas the more challenging mAP0.5-0.95 improves by 4.2%, reaching 60.8%. These improvements highlight the significant advantages of the model in handling complex backgrounds, target occlusion, and noise interference. Additionally, the diversified CESSSD dataset, constructed using data augmentation techniques such as SimpleCopy-Paste, Cutout, Mosaic, and noise addition, further enhanced the generalization ability and robustness of the model.
However, the applicability of RCDI-YOLO is primarily validated on side-scan sonar images. Its performance on other sonar types, such as synthetic aperture sonar (SAS), or in drastically different marine environments, remains to be investigated. Despite the excellent accuracy and robustness, a trade-off remains in terms of training time and computational resource demands. In real-world applications, such as marine resource exploration, rescue missions, and underwater target detection, real-time performance and detection accuracy are crucial. Therefore, future research could focus on further optimizing computational efficiency while exploring more lightweight modules to achieve a better balance between performance and computational cost.
In summary, RCDI-YOLO provides strong technical support for target-detection tasks in complex underwater environments, with demonstrated effectiveness in side-scan sonar images, while its applicability to other sonar scenarios requires further validation.
Statements
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
JZ: Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. BG: Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 12374427).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1
Aalo V. A. Peppas K. P. Efthymoglou G. (2015). Performance of CA-CFAR detectors in nonhomogeneous positive alpha-stable clutter. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst.51, 2027–2038. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2015.140043
2
Aboah A. Wang B. Bagci U. Adu-Gyamfi Y. (2023). “ Real-time multiclass helmet violation detection using few-shot data sampling technique and YOLOv8,” in Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW). (New York, NY, USA: IEEE), 5350–5358.
3
Abu A. Diamant R. (2019). A statistically based method for the detection of underwater objects in sonar imagery. IEEE Sens. J.19, 6858–6871. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2019.2912325
4
Acosta G. G. Villar S. A. (2015). Accumulated CA-CFAR process in 2-D for online object detection from sidescan sonar data. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng.40, 558–569. doi: 10.1109/JOE.2014.2356951
5
Bae T.-W. Sohng K.-I. (2010). Small target detection using bilateral filter based on edge component. J. Infrared Milli. Terahz Waves31, 735–743. doi: 10.1007/s10762-010-9633-0
6
Benesty J. Cohen I. (2018). Single channel speech enhancement in the STFT domain (Cham, Switzerland: Springer).
7
Bochkovskiy A. Wang C.-Y. Liao H.-Y. M. (2020). YOLOv4: Optimal speed and accuracy of object detection. arXiv preprint arXiv:2004.10934. Available online at: https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.10934 (Accessed October 20, 2025).
8
Dai X. Chen Y. Xiao B. Chen D. Liu M. Yuan L. et al . (2021). “ Dynamic head: Unifying object detection heads with attentions,” Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). (New York, NY, USA: IEEE), 7373–7382.
9
DeVries T. Taylor G. W. (2017). Improved regularization of convolutional neural networks with cutout. arXiv preprint arXiv:1708.04552. Available online at: https://arxiv.org/abs/1708.04552 (Accessed October 20, 2025).
10
Dura E. Zhang Y. Liao X. Dobeck G. J. Carin L. (2005). Active learning for detection of mine-like objects in side-scan sonar imagery. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng.30, 360–371. doi: 10.1109/JOE.2005.850931
11
Ghiasi G. Cui Y. Srinivas A. Qian R. Lin T.-Y. Cubuk E. et al . (2021). “ Simple copy-paste is a strong data augmentation method for instance segmentation,” in Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) ( IEEE, New York), 2917–2927. doi: 10.1109/CVPR46437.2021.00294
12
Girshick R. (2015). “ Fast R-CNN,” in Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) ( IEEE, New York), 1440–1448. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2015.169
13
Girshick R. Donahue J. Darrell T. Malik J. (2014). “ Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation,” in Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) ( IEEE, New York), 580–587. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2014.81
14
Han K. Zhang J. Wang Y. Chen Z. Wang C. Xu C. et al . (2020). “ GhostNet: More features from cheap operations,” in Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). (New York, NY, USA: IEEE), 1580–1589.
15
He K. Zhang X. Ren S. Sun J. (2015). Spatial pyramid pooling in deep convolutional networks for visual recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell.37, 1904–1916. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2015.2389824
16
Katyayani K. Bhardwaj K. Poongodi T. (2023). “ Deep learning approach for multi-object detection using YOLO algorithm,” in Proceedings of the 2023 6th International Conference on Contemporary Computing and Informatics ( IEEE, New York), 689–693. doi: 10.1109/IC3I59117.2023.10398124
17
Klausner N. Azimi-Sadjadi M. R. (2015). Non-gaussian target detection in sonar imagery using the multivariate Laplace distribution. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng.40, 452–464. doi: 10.1109/JOE.2014.2328211
18
Li X. K. Xie L. Qin Y. (2009). Underwater target feature extraction using Hilbert-Huang transform. J. Harbin Eng. Univ.30, 542–546. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4866.2014.07.063
19
Li Z. Zheng J. Zhu Z. Yao W. Wu S. (2016). Edge guidance filtering for structure extraction. Visual Comput.35, 57–66. doi: 10.1007/s00371-015-1124-4
20
Liangjun Z. Feng N. Yubin X. Gang L. Zhongliang H. Yuanyang Z. (2024). MSFA-YOLO: A multi-scale SAR ship detection algorithm based on fused attention. IEEE Access.12, 24554–24568. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3365777
21
Lin T.-Y. Dollar P. Girshick R. He K. Hariharan B. Belongie S. (2017a). “ Feature pyramid networks for object detection,” in Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) ( IEEE, New York), 936–944. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.106
22
Lin T.-Y. Goyal P. Girshick R. He K. Dollar P. (2017b). Focal loss for dense object detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell.42, 318–327. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2018.2858826
23
Liu W. Anguelov D. Erhan D. Szegedy C. Reed S. Fu C.-Y. et al . (2016). “ SSD: Single shot multibox detector,” in Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), vol. 9905 . Eds. LeibeB.MatasJ.SebeN.WellingM. ( Springer International Publishing, Cham), 21–37. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-46448-0_2
24
Liu H. Yang Y. Ge S. Luo P. (2020). Learning attentive deep hashing for large-scale image retrieval. IEEE Trans. Image Process.29, 1894–1907.
25
Liu X. Jie R. Bera S. Rao Y. Zhou C. Liu B. (2022). “ High-performance Raman distributed high-temperature sensing system based on single crystal YAG fiber.” In: 2022 Asia Communications and Photonics Conference (ACP). (Shenzhen, China: IEEE). doi: 10.1109/ACP55869.2022.10089015
26
Liu W. Lu Fu H. H. Cao Z . (2023). “ Learning to upsample by learning to sample,” in Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Paris, France, 6004–6014. doi: 10.1109/ICCV51070.2023.00554
27
Myers V. Fawcett J. (2010). A template matching procedure for automatic target recognition in synthetic aperture sonar imagery. IEEE Signal Process. Lett.17, 683–686. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2010.2051574
28
Redmon J. Divvala S. Girshick R. Farhadi A. (2016). “ You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection,” in Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) ( IEEE, New York), 779–788. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.91
29
Redmon J. Divvala S. Girshick R. B. Farhadi A. (2018). YOLOv3: An incremental improvement. arXiv preprint arXiv:1804.02767. Available online at: https://arxiv.org/abs/1804.02767 (Accessed October 20, 2025).
30
Ren S. He K. Girshick R. Sun J. (2017). Faster R-CNN: towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell.39, 1137–1149. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2577031
31
Tan M. Le Q. V. (2019). “ EfficientNet: Rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks,” in Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML). (Long Beach, CA, USA: PMLR), 6105–6114.
32
Tan C. Zhang X. Yang P. (2019). A novel sub-bottom profiler and signal processor. Sensors19, 5052. doi: 10.3390/s19235052
33
Tanuja D. A. (2016). Two-dimensional object detection using accumulated cell average constant false alarm rate. Int. J. Cybern.5, 235–245.
34
Tian Y. Lan L. Guo H. (2020). A review on the wavelet methods for sonar image segmentation. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst.17, 4. doi: 10.1177/1729881420936091
35
Wang A. Chen H. Liu L. Chen K. Lin Z. Han J. et al . (2024). YOLOv10: real-time end-to-end object detection. arXiv preprint arXiv:2405.14458. Available online at: https://arxiv.org/abs/2405.14458 (Accessed October 20, 2025).
36
Wang X. Zhang X. Zhu S. (2015). “ Upsampling based back projection imaging algorithm for multi-receiver synthetic aperture sonar,” in 2015 Int. Industrial Informatics and Computer Engineering Conf. (IIICEC), (Xi’an, China: Atlantis Press), 1610–1615.
37
Williams D. P. (2015). Fast target detection in synthetic aperture sonar imagery: A new algorithm and large-scale performance analysis. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng.40, 71–92. doi: 10.1109/JOE.2013.2294532
38
Woo S. Debnath S. Hu R. Chen X. Liu Z. Kweon I. S. et al . (2023). ConvNeXt V2: Co-designing and scaling ConvNets with masked autoencoders. Proc. IEEE/CVF Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit. (CVPR). (New York, NY, USA: IEEE), 16133–16142.
39
Wu B. Zhu W. Shi F. Zhu S. Chen X. (2017). Automatic detection of microaneurysms in retinal fundus images. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph55, 106–112. doi: 10.1016/j.compmedimag.2016.08.001
40
Yang D. Bai Z. Zhang J. (2022). Infrared weak and small target detection based on top-hat filtering and multi-feature fuzzy decision-making. Electronics11, 3549. doi: 10.3390/electronics11213549
41
Yu Z. Bai Z. Meka A. Tan F. Xu Q. Pandey R. et al . (2024). One2Avatar: Generative Implicit Head Avatar for Few-shot User Adaptation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.11909.
42
Zhang X. Dai X. Yang B. (2018). Fast imaging algorithm for the multiple receiver synthetic aperture sonars. IET Radar Sonar Navigation12, 1276–1284. doi: 10.1049/iet−rsn.2018.5040
43
Zhang Z. Li L. Wang W. (2023). LAN: Lightweight attention-based network for RAW-to-RGB smartphone image processing. IEEE Trans. Image Process.30, 1234–1245.
44
Zhang X. Yang P. (2019). Imaging algorithm for multireceiver synthetic aperture sonar. J. Electrical Eng. Technol.14, 471–478. doi: 10.1007/s42835-018-00046-0
45
Zhang X. Yang P. (2022a). Back projection algorithm for multireceiver synthetic aperture sonar based on two interpolators. J. Mar. Sci. Eng.10, 718. doi: 10.3390/jmse10060718
46
Zhang X. Yang P. Cao D. (2024). Synthetic aperture image enhancement with near−coinciding nonuniform sampling case. Comput. Electrical Eng.120, 109818. doi: 10.1016/j.compeleceng.2024.109818
47
Zhang X. Yang P. Huang P. Sun H. Ying W. (2022c). Wide−bandwidth signal−based multireceiver SAS imagery using extended chirp scaling algorithm. IET Radar Sonar Navigation16, 531–541. doi: 10.1049/rsn2.12200
48
Zhang X. Yang P. Sun M. (2022b). Experiment results of a novel sub−bottom profiler using synthetic aperture technique. Curr. Sci.122, 461–464. doi: 10.18520/cs/v122/i4/461-464
49
Zhang X. Yang P. Sun H. (2022d). Frequency−domain multireceiver synthetic aperture sonar imagery with Chebyshev polynomials. Electron. Lett.58, 995–998. doi: 10.1049/ell2.12691
50
Zhao L. Liang G. Hu Y. Xi Y. Ning F. He Z. (2024). YOLO-RLDW: An algorithm for object detection in aerial images under complex backgrounds. IEEE Access.12, 128677–128693. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3414620
Summary
Keywords
side-scan sonar images, complex underwater environments, data augmentation, target detection, YOLOv8
Citation
Zhang J and Gao B (2025) RCDI-YOLO: a target-detection method for complex environment side-scan sonar images based on improved YOLOv8. Front. Mar. Sci. 12:1679077. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2025.1679077
Received
04 August 2025
Accepted
10 October 2025
Published
29 October 2025
Volume
12 - 2025
Edited by
Chengbo Wang, University of Science and Technology of China, China
Reviewed by
Tingkai Chen, Dalian Maritime University, China; Yanan Zhu, Hefei University of Technology, China
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Zhang and Gao.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jiaoyang Zhang, zhangjiaoyang@stu.ouc.edu.cn
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.