- 1Institute of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, N.C.S.R. Demokritos, Agia Paraskevi, Greece
- 2Department of Physics, School of Science, University of Athens, Athens, Greece
- 3Nanometrisis p.c., Agia Paraskevi, Greece
Nanometrology is vital for the advancement of nanotechnology but faces significant computational demands due to the complexity of measurements at the nanoscale. This review identifies two primary challenges: first, achieving super-resolution in microscopy imaging, where capturing detailed nanoscale information over large areas is handled with various strategies; second, characterizing the stochastic nature of nanostructure morphologies, which requires advanced methods to accurately analyze random and disordered features. We examine the limitations of existing image enhancement techniques and explore computational strategies for analyzing both discrete and continuous nanostructured surfaces. Addressing these challenges emphasizes the critical need for developing new computational methods to enhance precision and reliability in nanoscale measurements, thereby fostering continued innovation in nanotechnology.
1 Introduction
According to the International Bureau for Measurements and Standards “Metrology is the science of measurement, embracing both experimental and theoretical determinations at any level of uncertainty in any field of science and technology” (BIPM, 2012). During the last decades, both experimental and theoretical metrology have been endowed by the development of properly designed computational methods which is partially due to the complicated nature of several modern measurement techniques and of obtained measurement data. As an example, we may consider the measurement of the thickness of a thin film which is a critical metrological step in several applications of thin film technology. In order to extract the value of thickness from the measurement process, advanced computational methods for the physics-based modelling of the measurement process are required exploiting the theory of electromagnetism to solve the so-called inverse problem in metrology, i.e., to predict a physical quantity (film thickness) from the measured spectrum (Park et al., 2024). Additionally, computational methods have been extensively utilized in the statistical analysis of the measurement results to quantify their uncertainty. These methods encompass Monte Carlo simulations of the propagation of measurand distributions as well as recent Bayesian-based considerations (Committee for Guides in Metrology, 2008; Meija et al., 2023).
Therefore, the main focus of the conventional computational approaches in metrology is twofold: a) First to provide the means for a deeper understanding of the measurement process with the additional benefit of using the obtained knowledge to facilitate the translation of measured data to measurand values and b) Secondly, to offer the tools for the statistical analysis of measurement results aiming at the reliable estimation of the holy grail of metrology, i.e., the measurement uncertainty.
The rapid advancements in nanotechnology have raised unpresented metrology challenges which demand computational solutions besides the realm of the conventional ones outlined above. The aim of this review is to focus on some of these challenges and describe mathematical and computational methods enabling their treatment. The proposed methods can be based on either totally new insights or strong updates of well-known mathematical tools. In order to explore the new challenges and the efforts to cope with these, we divide our paper into three sections addressing the questions of why, how and where. First, in the next section, we explore the question of why we need innovative mathematical and computational methods in nanometrology. Then we pose the question of how this need can be further elaborated considering a) the challenge of super-resolution in microscopy imaging and b) the characterization of the stochasticity in nanostructure morphology and surfaces. Finally, a short reference is made on where these new approaches can be applied and deliver new insights and results.
2 Why do we need novel computational methods in nanometrology?
The vast majority of applications in nanotechnology are based on nanostructuring surfaces of selected materials or the reinforcing material matrices with nanofillers such as nanowires, nanoparticles, nanotubes, nanosheets, etc. The core idea is that the added nanostructuring to the materials surface or bulk can modify significantly the physicochemical properties (optical, mechanical, thermal, wetting, bioadhesive, tribological) of materials enhancing accordingly their functionality (Logothetidis, 2012). The quantitative characterization and control of these nano-enabled properties and functionalities of materials requires a well-founded metrology of nanostructure size and morphology since the latter define in a critical manner the obtained material properties (Gao, 2021). To achieve this aim, two challenges should first be faced.
The first emanates from the tiny size of nanostructures in relation to the macroscopic scale of the material structures used in the final application. In most cases, the obtained device or system contains billions or even trillions of nanostructures which may have the form of peaks or grooves (surface features) in the case of surface roughness or manifest as nanoparticles or nanofibers when we functionalize a material with enforcing fillers in its bulk. The obtained functionality usually depends on the specific shapes and sizes of the embedded nanostructures as well as on their uniform distribution on material surface or bulk. Therefore, to control both contributions to nano-enabled functionality, the imaging and measurement of nanostructured surfaces or materials needs to extend from nanoscale details to the whole picture on a macroscopic scale of hundreds of micrometers or even millimeters to capture both small and high scale variabilities. In order to achieve this aim in the case of surface nanostructures with a scanning microscope, the sampling interval of measurement or pixel size of the microscopy image should be on the nanometer scale while the measurement range (inspection area or field of view) should reach at least some hundreds of micrometers. This requirement elevates the measurement points (or pixels) of the image to the level of trillions making the measurement process very slow and vulnerable to errors. The problem to compromise measurement resolution with field of view in scanning microscope measurements comprises the metrology challenge of super-resolution. The computational methods developed to cope with this challenge and enhance computationally the resolution of obtained microscopy images will be the first focus point of our paper, analysed in Section 3. A short overview of the previous works encountered in literature will be followed by a more detailed description of a recent proposed method based on the Fourier spectra stitching process.
The second challenge has to do with the geometrical morphology and spatial distribution of nanostructures created on material surfaces or reinforced into bulk. In most fabrication processes (especially those of bottom-up approach), nanostructures appear to be characterized by a kind of randomness in shape and spatial distribution although they are apparently different from the patterns of uncorrelated noise. Usually, the geometrical morphology of nanostructured materials seems to be an intricate combination of local correlations of nanostructure points with random and disordered characteristics which can span a large gamut of appearances and morphologies. In the case of surfaces, this combination is related to what is usually called nano-roughness, while in discrete nanostructures the randomness is demonstrated by the variability of their shapes, sizes and spatial positions. The so-called challenge of stochasticity on the nanoscale has recently attracted a lot of interest in semiconductor research and industry since the aggressive scaling down of nanostructure dimensions in modern circuits brought about the issue of stochastic deviations of their shapes and positions from the designed ones. They have been called for the increased effects of Edge Placement Error and Line Edge Roughness on the performance of semiconductor devices and the concomitant enhancement of yield losses (Bristol and Krysak, 2017; Constantoudis et al., 2018; Constantoudis et al., 2019a). Also, in semiconductor manufacturing, the presence of stochastic deviations from flatness is critical in Chemical Mechanical Polishing (CMP) used for achieving wafer-level planarization and thickness uniformity. Recent research (Deng et al., 2021) highlights the importance of roughness measurement and prediction by using a modified Preston equation and employing a back-propagation neural network. This approach enables real-time optimization of key CMP process parameters, thereby effectively bridging theoretical process models and practical semiconductor manufacturing. However, the presence of stochastic features in nanomorphologies is not limited to semiconductor structures and patterns. It penetrates the whole spectrum of nanofabrication processes, and it can be considered the hallmark of the geometry of derived nanostructures and patterns. Nanostochasticity ranges from the appearance of edge roughness on nanostructures with well-defined geometries (lines, holes, nanopillars, …), goes through the randomization of shapes and positions of nanostructures and reaches the stochastic fluctuations of rough surfaces. In all these cases, the development of proper mathematical concepts and computational methods for their implementation is a prerequisite for a well-founded metrology of nanostochasticity. Although, this challenge has been partially elaborated in previous works, a concise and integrated framework is still missing (Leach, 2024). The aim of Section 4 is to fill this gap and present a mathematical toolset and computational methods for the quantitative characterization of nanostructured surfaces incorporating both conventional approaches and recent alternative proposals based on modern advances in complex systems and stochastic geometry.
Besides the above-mentioned challenges, recent studies have shown that the role of computational preprocessing of microscopy images is also significant in nanometrology results. For instance, flattening AFM images via polynomial detrending effectively removes background curvature, yet if applied too aggressively, it can eliminate real nanoscale features, leading to an underestimation of roughness (Nečas et al., 2020). Also, the measurement of edge roughness in nanolithography may be strongly biased by SEM image noise leading to overestimation of high-frequency contributions and variance metrics (Villarrubia and Bunday, 2005). Several methods for noise filtering have been tested and a concise comparison of their efficiency has been reported in (Constantoudis and Pargon, 2013). Integrating preprocessing with advanced analytical methods—such as power spectral density (PSD) spectrum (Jacobs et al., 2017; Constantoudis et al., 2018; Lorusso et al., 2018) — seem to yield a more robust framework for noise reduced characterization of both edge and surface roughness. Similarly, SEM imaging benefits from contrast enhancement and noise filtering (Lorusso et al., 2018), but improper calibration of these steps risks obscuring high-frequency details essential for accurate edge detection. By calibrating preprocessing parameters within noise-correction algorithms, researchers can ensure the control of roughness measurement dependencies across varying imaging conditions. This integrated approach is key to establishing standardized protocols in computational nanometrology, ultimately enabling more reliable comparisons and correlations between surface topography and material functionality. Despite the crucial significance of computational tools for image preprocessing before analysis, the focus of this review will be on the first two challenges of enhancing resolution and stochasticity characterization leaving the review of computational prepossessing effects on nanometrology results for a future work.
3 The challenge of enhancing resolution
Scanning Microscopies (SM), such as Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) and Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM), have driven significant advances in nanoscience and nanotechnology. SM and nanofabrication are collaborative: SM enables precise imaging and inspection of nanostructures fuelling further advances in nanofabrication, while new nanofabrication techniques challenge SM techniques pushing them to overcome their current operation limits. However, despite their crucial importance, SM suffer from the limitation of the finite number of measurement points due to the very nature of the scanning process, which undermines the acquisition of large-scale nanostructured surface measurements with high resolution. This limitation is related to the more general issue of enhancing resolution in images using computational post-processing methods which is commonly referred to as the super-resolution challenge.
In recent years, a lot of works have explored computational methods to cope with the super-resolution issue, particularly in camera- and microscopy-based imaging (Yue et al., 2016; Sreehari et al., 2017). Patil M. and Khare S. provide an overview of various techniques for enhancing image resolution in image processing applications ranging from medical imaging and astronomy to satellite and object recognition (Patil Mayuri and Surbhi, 2012). The focus is on methods that improve image quality by increasing resolution, particularly through image interpolation and complex wavelet transforms. Traditional interpolation techniques, such as bilinear and bicubic methods, often introduce artefacts like blurring and blocking of edges. To address these limitations, advanced methods are reviewed, including dual-tree complex wavelet transform (DTCWT) and discrete wavelet transform (DWT), which offer enhanced resolution, reduced artefacts, and improved image clarity. Comparative results of these techniques highlight their effectiveness in producing high-quality images for diverse applications (Bhatt et al., 2012). In a more general context, Kaur and Singh (2013) reviews the image enhancement computational techniques, focusing on methods that improve image quality for applications such as medical imaging, satellite analysis, and object recognition. It explores both spatial and frequency domain approaches, including contrast stretching, histogram equalization, wavelet transforms, and advanced methods like stochastic resonance. By examining the strengths and limitations of each technique, this paper aims to offer insights into effective image enhancement methods, assisting researchers in selecting or designing techniques that best suit their specific application needs.
Machine learning methods and particularly convolutional neural networks (CNNs) have been widely used recently to generate high-resolution images from low-resolution inputs by learning complex mappings within large datasets. Models such as Super-Resolution Convolutional Neural Network (SRCNN) (Dong et al., 2014) and GAN-based architectures effectively enhance resolution by identifying and reconstructing intricate details between low- and high-resolution data. The drawback of these approaches is that they often require substantial training time, large training data sets and computational resources.
The Combined Attention Network for Single Image Super-Resolution (CANS) (Muhammad et al., 2024) introduces an advanced architecture designed to address key limitations in traditional CNN-based single image super-resolution (SISR). CANS utilizes a multi-pathway design that integrates shallow, deep, and dense block-based networks, enabling the extraction of local, global, and dense features necessary for high-resolution image reconstruction. By achieving exceptional image quality with reduced computational demands, CANS outperforms existing SISR methods.
Additionally, a frequency domain-based SISR approach (Seo et al., 2024) leverages CNNs and GANs alongside a novel mutual loss function and a two-dimensional structure consistency (TSC) mask. This approach adapts to high- and low-frequency image regions, enhancing resolution adaptively by balancing perceptual and contextual losses to produce visually realistic high-resolution images. These innovations position this model effectively within the machine learning-based super-resolution field. Machine learning techniques (de Haan et al., 2019; Ooi and Ibrahim, 2021) have enabled resolution enhancement by factors of 3–4 in most cases. However, as noted in (Qian et al., 2020), direct application of these methods to SM images is restricted due to the different physics underlying SM image formation and analysis. Additionally, traditional super-resolution methods usually ignore frequency mapping, a process that arranges spatial scales in a sequence, allowing for more flexible adjustments.
A more traditional approach is frequency domain methods, such as Fourier and wavelet transforms, which enhance resolution by manipulating the image’s frequency components. For example, Fourier-based methods can increase sharpness by amplifying high-frequency details, which correspond to edges and fine textures. Wavelet-based methods allow multiresolution analysis, enhancing specific scales within an image. These techniques are powerful for detailed enhancements but often require expertise to apply effectively.
The Fourier transform is a widely utilized tool across several scientific (Kujdowicz et al., 2023; Lizhong et al., 2023; Pierret and Galerne, 2023) and technological domains (Ciulla et al., 2023), particularly in image processing, where it is commonly applied for filtering, reconstruction (John et al., 2020), and compression (Pandey et al., 2015).
A study by Bagawade Ramdas et al. (2012). examines the application of wavelet transform-based techniques for enhancing image resolution, an essential attribute in fields such as satellite imaging, medical diagnostics, and digital photography. By comparing methods like the Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT), Stationary Wavelet Transform (SWT), and Dual-Tree Complex Wavelet Transform (DT-CWT), the paper assesses their ability to preserve high-frequency details while minimizing artifacts.
The above computational approaches aim at increasing the resolution of an image with a specific content which is kept fixed during the super-resolution process. However, in the SM images of nanorough surfaces, the motivation behind the super-resolution challenge is somewhat different. In most cases, the obtained SM image is a small segment from a large area of the nanorough surface which exhibits strong stochastic features. Therefore, the super-resolution challenge is transformed to the generation of stochastic replicas of the initial Low-Resolution image, which have increased resolution. The generated High-Resolution image should have similar statistical properties with the LR image (stochastic replicas) but it is not required that it has a pixel-by-pixel similarity.
In order to meet the new aspects of the super-resolution challenge in SM images of nanostructured surfaces, a method called generative Fourier Spectra Stitching (gFSS) has been proposed and tested in both simulated and real surfaces (Stai et al., 2025). The gFSS method is based on the Fourier Transform (FT) of HR and LR images exploiting the structural simplicity of the image in the frequency domain. It is well-known that FT decomposes an image into sinusoidal frequency components, enabling frequency-domain representation where each point signifies a unique frequency in the spatial domain. Working in Fourier space simplifies many image-processing tasks, making noise reduction, edge enhancement, and pattern recognition more computationally efficient by converting complex convolutional operations into simple multiplications. This approach also allows selective frequency-based filtering: low frequencies capture large structures, while high frequencies represent details such as edges.
The first key idea of gFSS is to stitch together Fourier spectra from images taken at different magnifications, delivering an enhanced spectrum that combines the high-frequency details of high-magnification images with the large field of view from low magnification ones. The inverse Fourier transform of this stitched spectrum provides an image with both high resolution and large measurement range. However, to address the stochastic aspects of SM images, the gFSS method introduces a second concept: phase randomization. The Fourier transform produces both amplitude and phase spectra, which can be manipulated separately. In rough surface textures, the phase spectrum is typically random and uncorrelated, meaning that altering phase values does not impact the primary surface features, which are governed by the amplitude spectrum. By randomly adjusting the phase spectrum, we can generate a large gamut of morphologies of the same surface texture, effectively simulating multiple SM measurements across several surface regions. This generative aspect of phase randomization is central to the proposed gFSS method, designed to address both spatial and scale limitations of SM images of rough surfaces.
Although there is not a systematic study comparing gFSS with Machine Learning super resolution techniques on the same dataset of microscopy images, Table 1 summarizes the basic characteristics of both approaches identifying benefits and shortcomings.
For the validation and application of the gFSS method, a combination of synthesized and experimental images provides a comprehensive approach. Synthesized surfaces were computationally generated with predetermined roughness features, while experimental surfaces were obtained via AFM or SEM. The synthesized data are used to validate the gFSS method, while experimental data demonstrate its effectiveness in real-world applications. By integrating both data types, the evaluation of the gFSS method becomes more thorough considering its reliability and applicability.
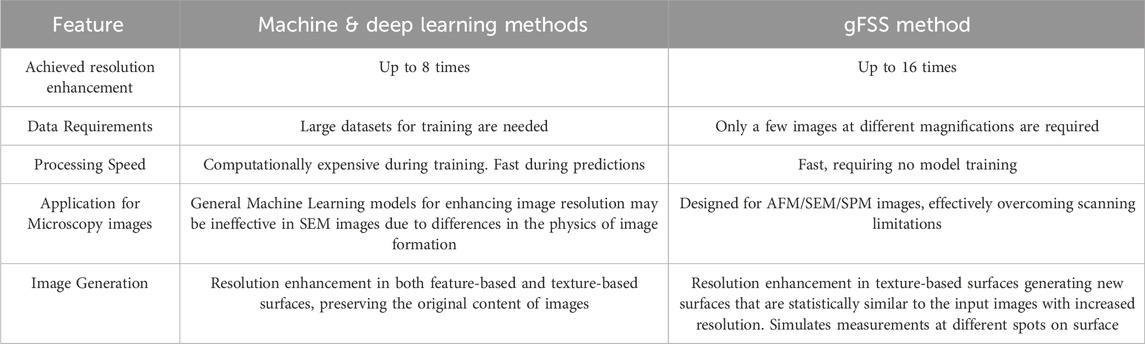
The gFSS method is implemented through a multi-step workflow. Initially, few images of a surface are captured at multiple magnifications and resolutions using SEM or AFM, allowing different levels of details and measurement ranges: low magnification images capture a larger area with lower resolution while high magnification captures fine details at a smaller scale (high resolution images). Assuming isotropic surface textures, the next step is the calculation of the 1D radial average of the 2D Fourier spectra of both low- and high-resolution images. The obtained 1D Fourier spectra are then stitched together to construct an extended Fourier spectrum that spans a broad range of frequencies. This expanded spectrum is converted back into two dimensions and by means of an inverse Fourier transform with randomized phase values, we result in a synthesized wide-scale image that combines the high-resolution details from the HR image and the large measurement range from the LR image. A histogram equalization may also be applied to the output image to match surface amplitudes to those of the LR image. Additionally, each application of the phase randomization step generates different morphologies, effectively simulating SM measurements on different spots of a rough surface areas. In Figure 1 there is a workflow of the gFSS method tested on synthesized surfaces. Simulated measurements at various magnifications with similar pixel density (200 × 200 pixels), are extracted from the high-resolution reference surface (3,200 × 3,200 pixels with pixel size = 1 nm) playing the role of the ground truth in our calculations. In this example, the input to the gFSS method are three images with different magnifications (low, middle and high) shown in Figure 1a which are processed by stitching their Fourier spectra (see Figures 1b,c) in order to extract a high-resolution image with large measurement area shown in Figure 1d.
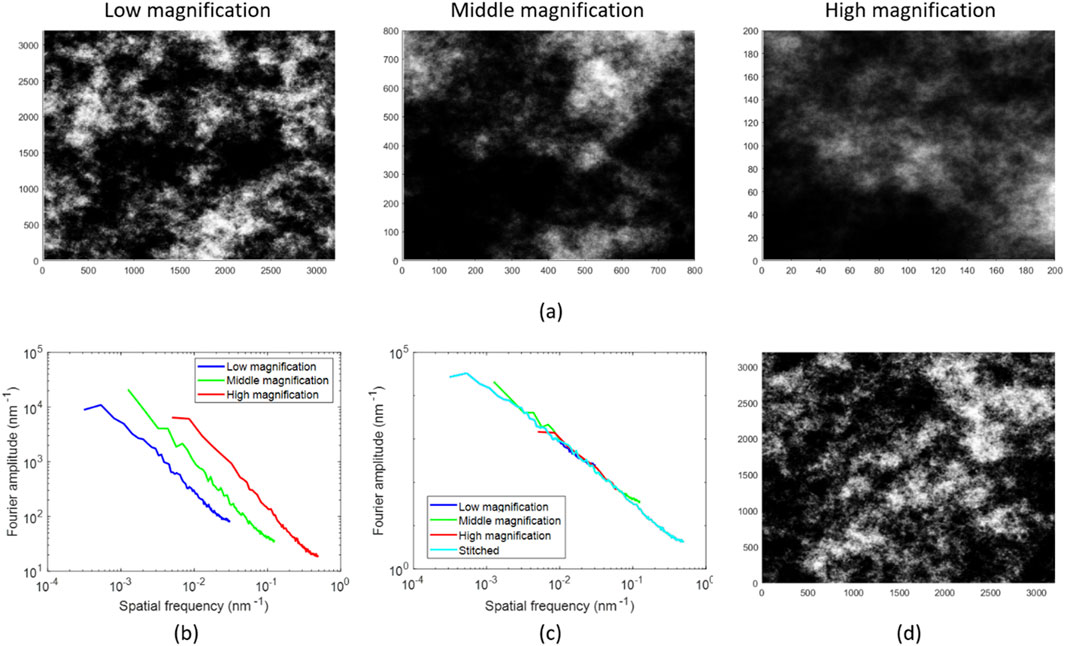
Figure 1. (a) Low, middle, and high magnification images of a synthetic rough surface used as input to the gFFS algorithm. (b) Circularly averaged Fourier spectra obtained from the 2D Fourier Transform (FT) of each image. (c) Stitched FT combining frequency data across all magnification levels. (d) Reconstructed gFFS image by applying randomization of phases followed by an inverse FT, achieving the measurement range of the low magnification image (3.2 × 3.2 μm2) and the pixel-size of the high magnification image (1 nm).
Figure 2 demonstrates the success of the gFSS method. In Figure 2a we display a low-magnification image of the synthetic rough surface with a measurement range of 3.2 × 3.2 μm2 and pixel size equal to 16nm, while Figure 2b shows the image of the surface after the application of the gFSS method, retaining the measurement range of the low magnification image (3.2 × 3.2 μm2) but reducing significantly the pixel size to 1 nm, i.e., achieving the astonishing enhancement of resolution by 16 times. Insets in both images show 4× magnified regions, highlighting the method’s ability to improve significantly the resolution of an image. The capability of the gFSS method to achieve the generation of multiple stochastic replicas of the initial LR surface with enhanced resolution is critical, as essential surface parameters such as roughness metrics and grain size statistics rely on both the resolution and measurement range of AFM/SEM images (Stai et al., 2025).
Figure 2. (a) Low magnification image of a synthetic rough surface with a measurement range of 3.2 × 3.2 μm2 and a pixel size of 16 nm. (b) Image generated after applying the gFFS method, maintaining the measurement range of 3.2 × 3.2 μm2 but with reduced pixel size to 1 nm increasing the resolution by 16 times. Insets show 4× magnified regions for detailed comparison.
More specifically, the gFSS method has been applied in AFM images of CoFeTa thin film surfaces to improve both resolution (i.e., reduce pixel size) and measurement range (Stai et al., 2025). The measured sample surface is rough with well-defined grains and therefore, the critical feature to be measured with accuracy is the grain size. By combining images of different magnifications, gFSS managed to reconstruct an image of the surface with the large field of view of the low-magnification image and the details of the high-magnification one. This increased the resolution five times, making it easier to see tiny surface details. The Fourier spectrum of the reconstructed image closely follows the spectrum of the high-magnification image at high frequencies while maintaining the low-magnification spectrum’s coverage at low frequencies. This confirms that gFSS successfully enhances resolution. The method also fixed errors in grain size measurements that appear when image pixels are too large. Grain size in AFM images was measured at different resolutions, showing that larger pixel sizes overestimate grain size. In low-magnification image (9.8 nm pixel size), the mean grain size was 53.7 nm, while in high-magnification image (1.96 nm pixel size), it was 43 nm. The gFSS method improved accuracy in the reconstructed image of the surface resulting in a 42.5 nm grain size, close to the high-resolution measurement. When the gFSS image was computationally downsampled to match the low-magnification image, the grain size increased to 53.3nm, demonstrating that lower resolution deteriorates accuracy in grain metrology, which can be remedied by the application of the gFSS method.
4 The challenge of characterizing stochastic nanostructured surfaces
4.1 Discrete surfaces
The term “discrete surfaces” refers to individual, distinguishable features or entities on a material’s surface, such as particles, grains, pores, or other morphological structures that are separate from one another. These discrete features are distinct in that they do not form a continuous or interconnected surface, allowing for identification and measurement of individual properties. In practice, this means that each feature can generally be isolated and analyzed independently to assess parameters such as size and shape (Section 4.1.1), spatial relationships (Section 4.1.2) or an investigation of both (uniformity analysis-Section 4.1.3).
Analyzing discrete features in microscopy images presents multiple challenges due to the complexities of both the imaging process and the inherent properties of the materials being studied. One significant challenge is the resolution limit of microscopy techniques, which may be insufficient to clearly capture features at the nanoscale or features closely packed together, leading to blurred or overlapping boundaries that complicate segmentation (Hofer, 2003; Shindo and Kenji, 2012). Additionally, contrast between features and their surroundings can be low, particularly in heterogeneous samples, making it difficult to distinguish individual entities or accurately define feature edges (Aspelmeier et al., 2015). Imaging artefacts, such as noise, beam-induced damage, or charging effects in electron microscopy, can distort the appearance of features, causing inaccurate measurements or false positives during analysis (Wuhrer and Moran, 2016). The complex topographies of certain materials further add difficulty, as surface irregularities or overlapping structures may obscure discrete features, challenging the segmentation process and potentially resulting in misidentification (Duval et al., 2015). Thresholding, a common technique to separate features from the background based on grayscale levels, can be particularly difficult to optimize in cases of low contrast or non-uniform illumination, as global thresholding may fail to capture subtle features or introduce noise (Lee et al., 2020). Adaptive thresholding or advanced machine learning algorithms may improve segmentation accuracy, yet these methods are computationally demanding and introduce their own challenges in terms of parameter selection and processing time (Xing et al., 2018; Cunha et al., 2024). Consequently, accurate analysis of discrete features often requires careful preprocessing, meticulous adjustment of imaging parameters, and the use of robust, sometimes hybrid computational methods to achieve reliable results.
4.1.1 Size distribution and shape analysis
Shape and size distribution analysis of discrete features in microscopy images is key for characterizing particles, pores, or other morphological entities within a material. The analysis typically begins with image preprocessing steps such as noise filtering and contrast adjustment to enhance feature visibility (Cardell et al., 2002). Segmentation methods, including thresholding, edge detection, or watershed algorithms, are then employed to isolate individual features from the background (Gamarra et al., 2019). Once features are segmented, their geometric properties, such as area, perimeter, and equivalent diameter, can be calculated and used to generate the appropriate size and shape data (Vivier et al., 1989).
The size distribution analysis of these features provides statistical descriptors such as mean size, median, mode, and standard deviation, which are essential for understanding the heterogeneity of the sample (Crouzier et al., 2019). The distribution data can be visualized through histograms or cumulative distribution curves, offering insights into the range and frequency of feature sizes. Studies on the size distribution of discrete features in microscopy images have gained significant attention with the advent of computational methods that enhance the accuracy and efficiency of feature extraction (Hojat et al., 2022). Computational approaches, including image processing algorithms, machine learning models, and advanced statistical tools, have proven essential in analyzing discrete features (Safari et al., 2021). These methods facilitate accurate segmentation, classification, and quantification of features, which is crucial for applications ranging from materials science to biomedical research. For instance, algorithms such as watershed segmentation, Gaussian mixture models, and k-means clustering have demonstrated effectiveness in distinguishing individual features within dense, overlapping regions, enabling a comprehensive assessment of size distribution in complex images. Recent advancements also incorporate deep learning frameworks like convolutional neural networks (CNNs) to automatically identify and measure features with minimal human intervention. These computational methods leverage large datasets and high-performance computing to yield precise measurements and reduce the variability commonly encountered in manual analysis. Studies have demonstrated that automated approaches not only increase the reproducibility of size distribution analyses but also allow researchers to explore larger datasets than would be feasible manually (Kim et al., 2020; Gumbiowski et al., 2023; Vagenknecht et al., 2023; Papia et al., 2024b).
In Figure 3a, discrete particles are represented by computationally generated, non-overlapping circles with random radii. These circles serve as a mock model to examine size variability among particles, providing a simple scenario of size distribution analysis. The radius of each circle is recorded, and a histogram is generated to visualize the frequency distribution of circle sizes.
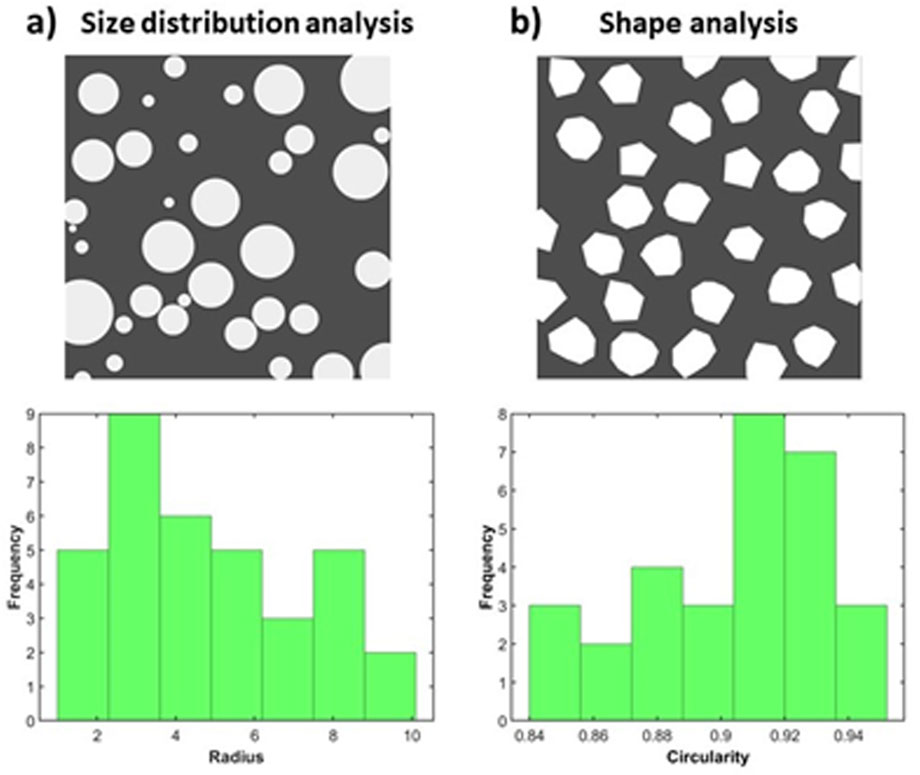
Figure 3. Example cases of size distribution (a) and shape (b) analysis, tested on simple simulated cases. (a) Top: Computationally generated non-overlapping circles of random radii representing discrete particles. Bottom: Histogram for the size distribution of the circles, based on radius value. (b) Top: Computationally generated non-overlapping polygons with random number of edges. Bottom: Histogram of the circularity values of the depicted polygons, as an example of shape analysis.
Accordingly, shape analysis of discrete features in SEM images is a crucial aspect of characterizing material microstructures, offering valuable information on the geometry and morphology of individual entities. Through this approach, geometric descriptors like circularity, elongation, and aspect ratio can be calculated to quantify the shape properties of these features. These shape parameters are essential for understanding how the morphology of discrete features impacts material performance, influencing properties like mechanical strength, surface area, and flow characteristics (Kim et al., 2013; Tanis et al., 2021). Traditional methods for shape analysis of discrete features in microscopy images have been fundamental in the early development of quantitative microscopy, providing tools to characterize shape with precision and reproducibility (Zou and Malzbender, 2015). Classical image processing techniques such as edge detection, contour tracing, and morphological operations have long been employed to define and measure shape features. For example, the Canny edge detector and Sobel operator are widely used to highlight boundaries, while methods such as the Hough transform and active contours refine these boundaries for more accurate shape definition (Cardell et al., 2002; Mourdikoudis et al., 2018). Fourier descriptors and moment invariants, which transform spatial information into compact, rotationally invariant representations, are also widely used to capture shape features quantitatively. These methods provide robust metrics for comparing shapes and enable researchers to distinguish subtle differences in shape that are essential for applications in materials science or cell morphology (Bowman et al., 2001; Su and Yan, 2020). More recently, advancements in machine learning, particularly in deep learning, have begun to transform shape analysis by enabling automated, high-throughput quantification with minimal manual intervention. Convolutional neural networks (CNNs), for example, excel in recognizing and classifying shapes based on intricate spatial patterns in microscopy images. Hybrid approaches that combine classical image processing with machine learning have also emerged, leveraging the strengths of traditional methods for initial shape delineation and machine learning for refinement and classification (Bals and Epple, 2023; Glaubitz et al., 2024). This integration of traditional and new methods allows to efficiently analyze larger, more complex datasets, achieving levels of sensitivity and reproducibility previously unattainable in shape analysis.
In Figure 3b, a simple case of shape analysis in a test image is provided. Particles are modelled as non-overlapping polygons with a random number of edges, introducing diversity in shape complexity. Circularity, defined as:
is calculated for each polygon. This metric quantifies how close each polygon is to a circular shape, with values near one indicating more circular shapes and lower values indicating less circular, irregular forms. A histogram of circularity values illustrates the range of shapes within the dataset and aids in characterizing particle morphology based on shape deviation from circularity. Figure 4 delves deeper, showcasing the application of size distribution analysis in three real-world examples of materials with discrete features, imaged with SEM [image source (Aversa et al., 2018)].
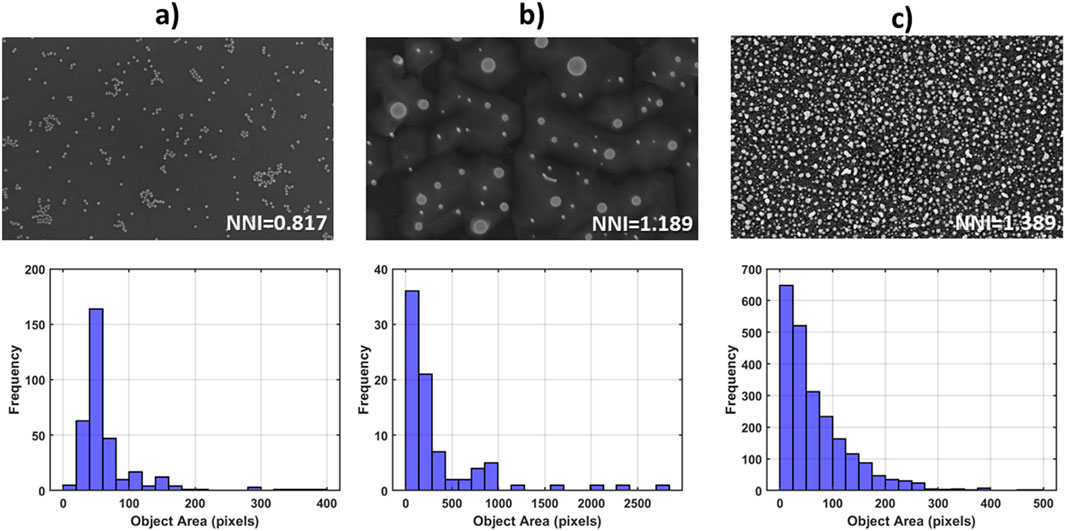
Figure 4. Top row: Three cases of discrete feature SEM images [image source in (Aversa et al., 2018)], and their respective Nearest Neighbour Index values. Bottom row: Histograms showcasing the size distributions (pixels) of particles depicted in (a–c) top row.
4.1.2 Spatial analysis
Analyzing the spatial distribution of features helps to reveal whether they are arranged in a random, clustered, or uniform manner. Such patterns play a critical role in understanding material behavior, as the spatial layout directly affects properties like diffusion, permeability, and structural resilience. For instance, clusters of features could signal regions weakness or increased reactivity, potentially impacting material stability, while a more periodic distribution could suggest greater homogeneity in material performance (Hull et al., 2018).
Techniques are drawn mainly from the field of stochastic geometry such as nearest-neighbor distance analysis, Voronoi tessellation, and spatial autocorrelation functions which are used to quantify the feature arrangement (Barthelemy, 2010; Chiu et al., 2013). Stochastic geometry by definition focuses on the analysis of random spatial configurations. Central to this approach is the investigation of random point patterns i.e., point pattern analysis (Janine Illian, 2008), a powerful mathematical toolbox for quantitatively characterizing the spatial distribution of discrete features on surfaces captured by microscopes. The reasoning is to pinpoint the locations of features like particles, pores, or grains by mainly calculating their centroid and treating an object as a mere point in space. Then, statistical methods are applied to examine the points’ arrangement across the surface. Frequently this is in reference to the degree of clustering or repulsion between points and the spatial scale at which they act.
This type of analysis provides deeper insights into the underlying material structure, beyond simple size and shape, offering critical information on how features interact and affect material properties like mechanical strength, porosity, and diffusion pathways (Eichhorn and Sampson, 2005; Sampson, 2012). Thus, analysis of a point pattern can reveal the geometrical characteristics of the structure the pattern represents as well as the underlying processes that led to the pattern. Point pattern statistics can be used to classify point patterns and identify structural changes in them as a function of time or physical parameters (Janine Illian, 2008; Mavrogonatos et al., 2022). They can also be used to model these structures and determine suitable model parameters. This approach may generally do both: characterize a whole pattern using a limited number of comprehensible integers (e.g., indices, such as the Nearest Neighbor Index NNI) or curves (e.g., Ripley’s K-function), and characterize the individual points using real or made-up markers (marked point pattern analysis) (Janine Illian, 2008). Marked point pattern analysis extends the point pattern attributes by incorporating additional information into the point data, such as size, color, or other relevant properties, allowing for a more nuanced understanding of spatial distributions. The advantage provided by using markers is to investigate how specific characteristics of individual features influence the overall pattern, providing insights into phenomena such as interaction dynamics, or the influence of external factors on feature arrangement.
Spatial distribution analysis of discrete features in microscopy images has become increasingly significant with computational advancements that enable precise quantification of spatial patterns. Point pattern analysis methods, including nearest neighbor analysis, Ripley’s K-function, and pair correlation functions, have been applied to understand the spatial organization of microscopic features such as cells, nanoparticles, and tissue structures. Figure 4 presents the computation of a well-established metric in spatial distribution analysis, the Nearest Neighbour Index (NNI) for 3 cases of real-world SEM images. NNI<1 indicates clustering, NNI∼1 indicates randomness in object distribution, while NNI>1 indicates tendency towards periodicity. The results of the analysis showcase how this metric from stochastic geometry responds to each peculiar particle formation pattern.
Studies leveraging such methods find applications in a range of scientific fields, such as biology, where point pattern analysis can reveal critical insights into cell organization, and in materials science, where it is essential for understanding the arrangement of particles and defects (Hu et al., 2014; Yang et al., 2017). To address the challenges of how image processing steps (noise filtering, binarization thresholds, and edge correction methods) impact the measurement of spatial randomness in micro- and nanostructure distributions, point pattern analysis has also been utilized to optimize and ensure accurate estimations for evaluating nanostructure randomness (Mavrogonatos et al., 2022).
Recent developments in computational approaches, including machine and deep learning, have further expanded the potential for spatial distribution analysis by automating pattern recognition and spatial mapping. For example, convolutional neural networks (CNNs) have been adapted to learn spatial relationships directly from images, allowing for high-throughput, automated analysis of spatial patterns in large microscopy datasets. Hybrid methods combining classical point pattern analysis with machine learning have also emerged, enhancing the detection and classification of spatial arrangements through more nuanced computational modeling (Zelenty et al., 2017; Ilett et al., 2020; Sipkens and Rogak, 2021). Such integration allows for the analysis of complex, heterogeneous samples with high precision and minimal manual input, improving reproducibility and scalability.
In Figure 5a, illustrated with simple simulated cases, an example of different particle arrangements in a discrete surface. Computationally generated non-overlapping circles with random radii are shown in: a random distribution (left) and a periodic distribution (right).
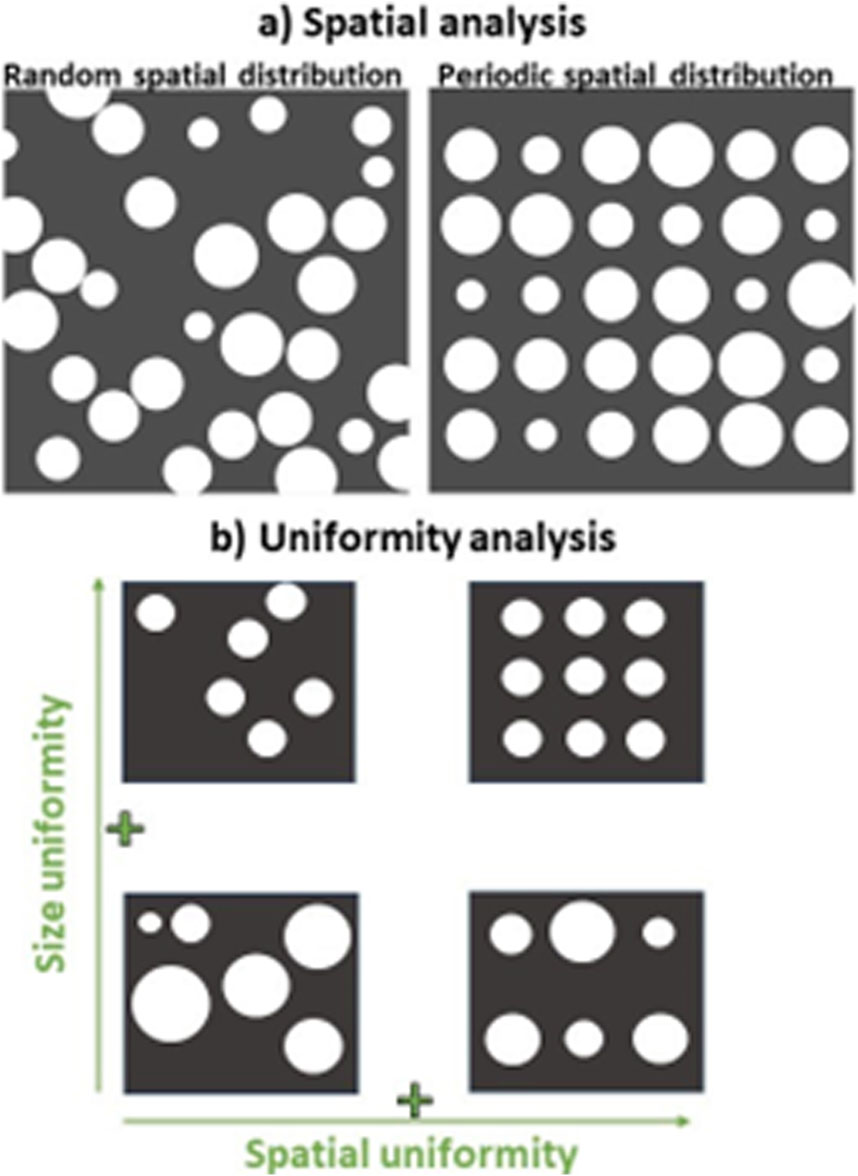
Figure 5. Example cases for spatial distribution (a) and uniformity analysis (b), illustrated with simple simulated cases. (a) Computationally generated non-overlapping circles of random radii which are spatially distributed randomly (left) and in a periodic manner (right). (b) Uniformity plane with schematic representations of four basic particle arrangements, with size uniformity on the y-axis and spatial uniformity on the x-axis. Clockwise starting from top left. Low size and spatial uniformity: Particles vary in size and are unevenly distributed across the material. High size uniformity, low spatial uniformity: Particles are consistent in size but are unevenly distributed across the material. High size and spatial uniformity: Particles are uniform in size and are evenly distributed across the material. Low size uniformity, high spatial uniformity: Particles vary in size but are evenly distributed across the material.
4.1.3 Uniformity analysis
Special interest should be placed on the quantification of uniformity in materials, as it plays a critical role in determining their overall performance and reliability across various applications. Uniformity affects mechanical properties, such as strength and durability, ensuring that materials behave predictably under different conditions (Hussain et al., 2010; Miskelly, 2018). In fields ranging from membrane science (Papia et al., 2024a) to biomedical engineering (Choi et al., 2010), consistent microstructural features—such as pore sizes and distributions—are essential for optimal function and longevity. Even minor variations in these properties can lead to significant differences in material behavior, potentially resulting in failure or inefficiency. Therefore, a detailed understanding of material uniformity can guide material selection, processing techniques, and design considerations (Kam et al., 2013).
More specifically, size-spatial uniformity plays a pivotal role in optimizing the performance of advanced materials across diverse applications. In supercapacitors, for instance, the development of carbon-based materials for electric double-layer capacitors (EDLCs) hinges on the delicate balance between achieving extremely high surface areas and maintaining good electrical conductivity (Lu et al., 2013). Similarly, in biomedical applications (Hollister, 2005) the three-dimensional arrangement of pores within scaffolds or implants directly influences mechanical strength, tissue integration, and effective permeability. Topology optimization techniques have been employed to design microstructures that meet stringent requirements, balancing porosity with elastic and permeability properties to ensure both biological compatibility and structural integrity.
In other areas, such as porous media fluid transport (Dullien, 1992), acoustics (Allard and Atalla, 2009), and cellular solids (Gibson, 2003), size-spatial uniformity analysis is equally crucial. For porous rocks, understanding the spatial distribution of permeabilities and porosities is essential for predicting fluid flow, which has implications in both natural and engineered systems. In acoustics, the distribution and size of macro-pores affect the absorption characteristics, which are critical for noise control and sound management. Meanwhile, in cellular solids like foams and honeycombs, the uniformity of cell sizes and their spatial arrangement dictate macroscopic properties such as density and stiffness. Moreover, in network materials (Picu, 2022), the drag forces resulting from internal flows are intimately linked to the free volume distribution within the network. Collectively, these examples underscore that precise control over size-spatial uniformity is fundamental to engineering materials that meet specific functional requirements, from energy storage to structural performance.
A size-spatial uniformity plane (Papia et al., 2024a) provides a framework for quantifying material uniformity by integrating both size and spatial metrics into a comprehensive assessment. In discrete feature analysis of microscopy images, this approach allows for the simultaneous evaluation of particle size constancy and distribution regularity. Together, these approaches enable a holistic assessment, merging size and spatial metrics into a unified approach to characterize material uniformity at the microstructural level. In Figure 5b, illustrated with simple simulated cases, such a size-spatial uniformity plane is plotted. The four configurations include: Bottom left: Low size and spatial uniformity, where particles vary in size and are unevenly distributed. Top left: High size uniformity, low spatial uniformity, where particles are consistent in size but unevenly spaced. Top right: High size and spatial uniformity, where particles are uniform in both size and distribution. Bottom right: Low size uniformity, high spatial uniformity, where particles vary in size but are evenly distributed across the material.
4.2 Continuous surfaces
Characterizing continuous rough surfaces (Vander Voort, 1999; Zhao et al., 2001; Almqvist, 2006; Hameed et al., 2019; Dusséaux and Vannier, 2022; Okuyama and Ohmori, 2023; Podulka et al., 2023; Kondi et al., 2024; Navajas et al., 2024) necessitates a comprehensive suite of mathematical and computational methods capable of capturing the intricate and multiscale features inherent in these materials. Traditional techniques like Fourier and correlation analysis provide foundational insights into the spatial frequency components and the degree of correlation between surface features. Fourier analysis decomposes surface height data into frequency spectra, revealing dominant periodic structures or random roughness. The autocorrelation function measures the similarity between surface heights at different spatial separations, offering information about surface coherence and roughness characteristics. Derived from the autocorrelation function, the correlation length quantifies the distance over which surface features remain correlated, bridging microscopic surface details with macroscopic material properties.
However, these conventional methods may not fully capture the complexity of surfaces exhibiting hierarchical and scale-dependent roughness. To address this limitation, fractal and multifractal methods have been introduced (Barabási and Stanley, 1995), providing advanced tools for understanding surfaces with self-affinity or irregularity across multiple scales. Fractal analysis quantifies surface roughness through the fractal dimension, indicating how surface details scale across different magnification levels. Multifractal analysis extends this concept by offering a spectrum of fractal dimensions, capturing the variability in scaling behaviour across different regions or features of the surface.
Methods inspired by complexity science (Mitchell, 2009; Nicolis and Nicolis, 2012) further expand this framework, introducing advanced measures that capture chaotic, nonlinear, and multiscale behaviour inherent in nanostructured surfaces. Methods such as the chaos-based, and Multiscale Entropy based (MSE) complexities provide us with different insights than those from traditional tools.
In this section, we will explore these techniques and their significance in the quantitative characterization of continuous surfaces. We will begin with foundational methods—Fourier analysis, the autocorrelation function, and correlation length—before progressing to fractal and multifractal methods. Finally, we will delve into complexity measures that offer a more general and comprehensive understanding of surface morphology, illustrating how these approaches collectively contribute to advancing nanometrology.
4.2.1 Fourier analysis, autocorrelation function and correlation length
Fourier analysis is a fundamental tool for characterizing rough surfaces (Zhao et al., 2001), enabling the transformation of surface height data from real space to frequency space (see also Section 3). Based on the principle that any surface profile can be decomposed into a sum of sinusoidal waves with varying frequencies, amplitudes, and phases, the FT converts spatial variations in surface height into a frequency spectrum. This spectrum reveals the contribution of different spatial frequencies to the overall surface structure. For nanostructured rough surfaces, Fourier analysis quantifies the spatial frequency components that constitute the surface morphology. The power spectral density (PSD) obtained from the FT indicates the amplitude associated with each frequency component, facilitating the identification of dominant features such as periodic structures or random roughness. This is particularly useful for surfaces exhibiting self-affine or fractal properties, where the power spectrum may follow a power-law distribution indicative of scale invariance. Importantly, Fourier analysis is closely related to the autocorrelation function, as the PSD is essentially the Fourier transform of the autocorrelation function of the surface heights. This relationship highlights how Fourier analysis and the autocorrelation function together describe spatial frequencies and the degree of correlation between surface features, bridging the frequency and spatial domains in surface characterization.
The autocorrelation function (ACF) is a statistical tool used to quantify the degree of similarity between surface height values as a function of spatial separation. Essentially, it measures how the surface height at one point is correlated with the height at another point a certain distance away. For random surfaces, the ACF typically decays to zero as the separation distance increases, indicating that surface features become uncorrelated over larger distances. In the context of nanostructured surfaces, the ACF provides valuable information about the periodicity, coherence, and roughness characteristics of the surface features. A rapidly decaying ACF suggests that the surface roughness is dominated by short-range features, whereas a slowly decaying ACF implies the presence of long-range order or correlation among features. Additionally, the shape of the ACF can be related with self-affine or fractal properties of the surface, indicating statistical similarity across different scales. Mathematically, for a homogeneous and isotropic surface, the ACF depends only on the magnitude of the separation vector and not on its direction. By analyzing the ACF, parameters such as the correlation length can be derived, offering further insights into the spatial scale over which surface features are correlated. This links directly to the concept of correlation length, which quantifies the distance over which surface heights remain significantly correlated.
The correlation length (ξ) is a key parameter derived from the autocorrelation function, representing the characteristic distance over which surface features remain correlated. It is commonly defined as the separation distance at which the ACF reduces to one/e (approximately 37%) of its maximum value. Essentially, the correlation length quantifies how far one must move across the surface before the height values become effectively uncorrelated. In nanostructured rough surfaces, the correlation length provides critical information about the spatial scale of surface features. A short correlation length indicates that the surface morphology is dominated by fine, closely packed features, whereas a longer correlation length suggests the presence of larger, more widely spaced structures. This parameter is particularly useful when comparing different surfaces or monitoring changes in surface morphology during processes such as growth, erosion, or deposition. Moreover, for self-affine surfaces, the correlation length is related to the roughness exponent, which describes how surface roughness scales with the size of the observation window. This connection further bridges the autocorrelation function with fractal analysis, which is concerned with scaling properties of surfaces.
4.2.2 Fractal and multifractal methods
While Fourier analysis and the autocorrelation function are powerful, they may not fully characterize surfaces exhibiting complexity across multiple scales. To address this, fractal and multifractal methods (Sarkar et al., 1994; Barabási and Stanley, 1995; Jin et al., 1995; Chen et al., 2003; Li et al., 2006; Florindo et al., 2013; Risović and Pavlović, 2013; Liu et al., 2014; So et al., 2017; Panigrahy et al., 2019; 2020; Zhou et al., 2022) provide advanced tools for understanding the hierarchical and scale-dependent roughness of nanostructured surfaces. These methods are particularly suited for surfaces that display self-affinity across a range of scales, where a single scaling exponent, such as the fractal dimension, quantifies surface roughness, and multifractal analysis captures the variability in scaling behavior across different regions of the surface.
Fractal geometry allows surfaces to be characterized by their roughness across multiple scales through the concept of the fractal dimension (FD) assuming some kind of statistical scale invariance. Unlike traditional geometric shapes, fractal objects exhibit self-similarity, meaning their appearance remains consistent regardless of the scale of observation. For nanostructured surfaces, this property implies that roughness features persist across different magnification levels, making FD an ideal measure of surface morphology in these cases. Methods such as the box-counting technique, power spectral density analysis, and Higuchi’s method (Zhou et al., 2022) are commonly used to calculate the FD, with higher values indicating rougher, more complex surfaces. Typically, the FD ranges between two and three for surfaces, with a higher FD indicating a rougher, more complex surface.
Extending beyond a single scaling exponent we reach the realm of multifractal analysis which extends the concept of a single fractal dimension to a spectrum of dimensions, providing a more detailed description of surfaces with heterogeneous scale behaviours. In many cases, a single fractal dimension does not fully capture the complexity of nanostructured surfaces, especially when the surface exhibits regions with varying roughness characteristics. Multifractal analysis provides a spectrum of dimensions, each corresponding to different regions of surfaces with different characteristics (height, slope, local roughness, …). A key component of multifractal analysis is the singularity exponent which represents how the surface roughness changes locally at different scales. The distribution of singularity exponents across the surface is called the multifractal spectrum. A wider spectrum suggests that the surface has more diverse roughness properties, with regions that may be smoother or rougher than others.
Similarly, the challenges associated with Line Edge Roughness (LER) in advanced lithography have been addressed using these sophisticated computational metrology techniques (Constantoudis and Gogolides, 2008; Constantoudis et al., 2018a; Constantoudis et al., 2018; Constantoudis et al., 2019b; Giannatou et al., 2019; Kizu et al., 2023). In lithographic processes, where pattern precision and edge definition are critical, fractal and multifractal analyses have been employed to characterize the scaling behavior of LER (Constantoudis et al., 2018). By calculating the fractal dimension or deriving a detailed multifractal spectrum, researchers can complement the more widely used power spectral density (PSD) approaches, leading to a more comprehensive characterization of edge irregularities.
These advanced analytical techniques have practical implications. For instance, studies investigating the impact of LER on device uniformity—such as in ReRAM crossbar architectures (Constantoudis et al., 2019b)—and analyses linking fractal dimensions to transistor performance (Constantoudis and Gogolides, 2008) highlight the importance of accurate LER metrology. Furthermore, recent frameworks (Kizu et al., 2023) that establish SI-traceable LER reference standards using both atomic force microscopy (AFM) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) have significantly enhanced measurement reliability. Improved characterization not only enables the optimization of lithographic processes by minimizing edge roughness, thereby enhancing device performance and increasing manufacturing yields, but also exemplifies how advanced computational techniques in metrological characterization can transform lithographic patterning for superior outcomes.
It should also be noted that attempts to utilize machine learning techniques have also been implemented to address the challenges posed by noise in SEM images, particularly when measuring LER in sub-10 nm semiconductor features. Recent work (Giannatou et al., 2019) has demonstrated the effectiveness of deep Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) in this domain. The CNN-based SEM image denoising model (SEMD) is trained on synthesized SEM images to effectively identify and remove noise while preserving the underlying pattern. This approach ensures the retention of critical edge details necessary for accurate LER measurements, outperforming traditional denoising techniques. Moreover, SEMD can be integrated with standard state-of-the-art methods such as the PSD-based approach to achieve a balance between noise reduction and the preservation of fine structural details, thereby improving measurement accuracy in low signal-to-noise environments.
4.2.3 Complexity measures in rough surface characterization
Traditional metrics like root-mean-square roughness or correlation lengths may not fully capture the intricacies of surfaces exhibiting multiscale or chaotic behavior. Advanced methods derived from complexity science are applied to gain deeper insights into surface morphology. Two such complexity measures in rough surface characterization are the chaos-based and the entropy-based complexity metrics. These methods are particularly useful for quantifying complex surface morphologies, enabling a more thorough analysis than traditional tools.
The chaos-based metric is a method stemming from chaos theory (Arnold, 1968; Franks, 1977; Skokos and Bountis, 2012), providing a way to characterize the chaotic nature of surfaces using the Arnold Cat Map (ACM) as its basis. ACM (Dyson and Falk, 1992; Bao and Yang, 2012) is a two-dimensional nonlinear transformation that operates by stretching and folding a surface image, scrambling the spatial organization of pixels with each iteration. Initially, the image undergoes slight distortions, but as the number of iterations increases, the image becomes increasingly random-like and unrecognizable.
In the context of rough surface characterization (Kondi et al., 2023), the ACM enhances high-frequency components—features corresponding to fine details of the surface morphology. By observing the number of iterations needed for a surface image to become fully chaotic, we can measure the degree of order and chaos present in the surface. This method provides both a visually intuitive and quantitative way to analyze the progression from ordered to chaotic surface behavior, complementing the information obtained from Fourier and fractal analyses by focusing on the chaotic dynamics of surface features.
The entropy-based method (Arapis et al., 2022; Papia et al., 2023; Veinidis et al., 2025) extends traditional entropy measures (López-Ruiz et al., 1995; Andraud et al., 1997; Van Siclen, 1997; Feldman and Crutchfield, 1998; Alamino, 2015; Bagrov et al., 2020; Lakhal et al., 2020; Srenevas and Poutous, 2023; 2024; Wang et al., 2023) by accounting for surface complexity across different spatial scales. In surface characterization, it analyses how the predictability or randomness of surface features changes from finer to coarser observation levels. This is particularly useful for nanostructured surfaces where roughness or irregularities manifest differently depending on the scale of observation.
The method calculates the entropy at multiple resolutions of a surface profile or image, with higher entropy values indicating more irregular or complex surface features. It differentiates between structured surface roughness and pure noise, providing a powerful tool for analyzing surfaces. Surfaces with high complexity, such as those with heterogeneous textures and rich multiscale morphology, exhibit higher entropy values, whereas smoother or more uniform noisy surfaces display lower complexity values (see Figure 6).
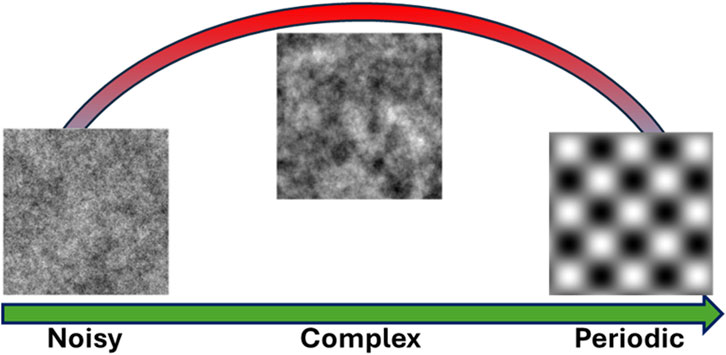
Figure 6. Schematic of the relationship of a complexity measure with the transition from full randomness to periodicity. From left to right we present examples of different surfaces ranging from randomness to order (symmetry or homogeneity) and their relation to an ideal complexity measure.
5 Conclusion
Nanometrology—the science of measurement at the nanoscale—is crucial for advancing nanotechnology applications, enabling precise fabrication and characterization of nanomaterials, nanostructures, and devices. This review explored computational methods in nanometrology, highlighting two primary challenges regarding the need to capture the stochastic and multiscale features inherent in nanostructured materials.
We first discuss why sometimes existing computational methods fall short in nanometrology, highlighting two primary challenges. The first is the issue of super-resolution in microscopy imaging, where the need to capture both nanoscale details and macroscopic-scale features leads to impractical data sizes and resolution limitations when using conventional scanning microscopes. We review existing image enhancement techniques and discuss the limitations they face in nanometrology applications, emphasizing the need for methods that can enhance image resolution effectively while maintaining a large measurement range.
The second challenge involves the characterization of stochasticity in nanostructure morphology and surfaces. We delve into the computational methods required for analyzing both discrete and continuous nanostructured surfaces. For discrete surfaces, we examine size distribution and shape analysis, spatial distribution using stochastic geometry and point pattern analysis, and uniformity analysis that integrates size and spatial metrics. For continuous surfaces, we review traditional methods such as Fourier analysis, autocorrelation functions, and correlation length, and explore advanced techniques including fractal and multifractal analysis, as well as complexity measures derived from chaos theory and entropy-based metrics.
The development and adoption of these advanced methods are crucial for enhancing measurement accuracy and reliability at the nanoscale. Future research should focus on refining these computational techniques, developing standardized protocols, and creating accessible software tools to facilitate their widespread use. By embracing these innovative computational strategies, the field of nanometrology can overcome current limitations, ultimately driving progress and enabling the precise control of nano-enabled functionalities in materials and devices.
Our review underscores the critical need for developing and adopting novel computational approaches in nanometrology. This integration of advanced mathematical concepts and computational techniques is essential for controlling nano-enabled functionalities of materials and devices, thereby facilitating continued innovation and application in the field of nanotechnology.
Author contributions
AK: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. E-MP: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. ES: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. VC: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work has received financial support by the T12EPA5-00067 Project ‘‘CarbyneSense’’ (MIS 5161208), under the call ERA.NET 2021A.
Conflict of interest
VC was employed by the company Nanometrisis p.c.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Alamino, R. C. (2015). Measuring complexity through average symmetry. J. Phys. A Math. Theor. 48, 275101. doi:10.1088/1751-8113/48/27/275101
Allard, J. F., and Atalla, N. (2009). Propagation of sound in porous media: modelling sound absorbing materials. Second Edition. doi:10.1002/9780470747339
Almqvist, A. (2006). On the effects of surface roughness in lubrication. Available online at: http://urn.kb.se/resolve?urn=urn:nbn:se:ltu:diva-18259.
Andraud, C., Beghdadi, A., Haslund, E., Hilfer, R., Lafait, J., and Virgin, B. (1997). Local entropy characterization of correlated random microstructures. Phys. A Stat. Mech. its Appl. 235, 307–318. doi:10.1016/S0378-4371(96)00354-8
Arapis, A., Constantoudis, V., Kontziampasis, D., Milionis, A., Lam, C. W. E., Tripathy, A., et al. (2022). Measuring the complexity of micro and nanostructured surfaces. Mater Today Proc. 54, 63–72. doi:10.1016/j.matpr.2021.10.120
Arnold, V. I. A. A. (1968). Ergodic problems of classical mechanics. New York, Benjamin: W.A. Benjamin. Inc.
Aspelmeier, T., Egner, A., and Munk, A. (2015). Modern statistical challenges in high-resolution fluorescence microscopy. Annu. Rev. Stat. Appl. 2, 163–202. doi:10.1146/annurev-statistics-010814-020343
Aversa, R., Modarres, M. H., Cozzini, S., Ciancio, R., and Chiusole, A. (2018). The first annotated set of scanning electron microscopy images for nanoscience. Sci. Data 5, 180172. doi:10.1038/sdata.2018.172
Bagawade Ramdas, P., Bhagawat Keshav, S., and Patil Pradeep, M. (2012). Wavelet transform techniques for image resolution enhancement: a study. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Adv. Eng. 2, 167–172.
Bagrov, A. A., Iakovlev, I. A., Iliasov, A. A., Katsnelson, M. I., and Mazurenko, V. V. (2020). Multiscale structural complexity of natural patterns. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 117, 30241–30251. doi:10.1073/pnas.2004976117
Bals, J., and Epple, M. (2023). Deep learning for automated size and shape analysis of nanoparticles in scanning electron microscopy. RSC Adv. 13, 2795–2802. doi:10.1039/D2RA07812K
Bao, J., and Yang, Q. (2012). Period of the discrete Arnold cat map and general cat map. Nonlinear Dyn. 70, 1365–1375. doi:10.1007/s11071-012-0539-3
Barabási, A. L., and Stanley, H. E. (1995). Fractal concepts in surface growth. Cambridge University Press. Available online at: https://books.google.gr/books?id=W4SqcNr8PLYC.
Barthelemy, M. (2010). Spatial networks. Phys. Reports-review Sect. Phys. Lett. - PHYS REP-REV SECT PHYS LETT 499, 1–101. doi:10.1016/j.physrep.2010.11.002
Bhatt, P., Shah, A., Patel, S., and Patel, S. (2012). Image enhancement using various interpolation methods. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Inf. Technol. & Secur. 2.
Bipm (2012). International vocabulary of metrology-Basic and general concepts and associated terms (VIM) 3rd edition 2008 version with minor corrections Vocabulaire international de métrologie-Concepts fondamentaux et généraux et termes associés (VIM) 3 e édition.
Bowman, E., Soga, K., and Drummond, W. (2001). Particle shape characterisation using Fourier descriptor analysis. Geotechnique 51, 545–554. doi:10.1680/geot.51.6.545.40465
Bristol, R. L., and Krysak, M. E. (2017). Lithographic stochastics: beyond 3σ. J. Nanolithogr. MEMS, MOEMS 16, 023505. doi:10.1117/1.JMM.16.2.023505
Cardell, C., Yebra, A., and Van Grieken, R. E. (2002). Applying digital image processing to SEM-EDX and BSE images to determine and quantify porosity and salts with depth in porous media. Microchim. Acta 140, 9–14. doi:10.1007/s006040200063
Chen, W.-S., Yuan, S.-Y., and Hsieh, C.-M. (2003). Two algorithms to estimate fractal dimension of gray-level images. Opt. Eng. - Opt. Eng. 42, 2452–2464. doi:10.1117/1.1585061
Chiu, S. N., Stoyan, D., Kendall, W. S., and Mecke, J. (2013). Stochastic geometry and its applications. Wiley. Available online at: https://books.google.gr/books?id=GCRI8Q-RUEkC.
Choi, S.-W., Zhang, Y. S., and Xia, Y. (2010). Three-dimensional scaffolds for tissue engineering: the importance of uniformity in pore size and structure. Langmuir 26, 19001–19006. doi:10.1021/la104206h
Ciulla, C., Xhaferri, I., Deek, F. P., Muzhaqi, E., Veljanovski, D., Shikoska, U. R., et al. (2023). Sampling technique for Fourier convolution theorem based k-space filtering. Appl. Res. 2, e202200109. doi:10.1002/appl.202200109
Committee for Guides in Metrology, J. (2008). First edition 2008 Evaluation of measurement data-Supplement 1 to the “Guide to the expression of uncertainty in measurement”-Propagation of distributions using a Monte Carlo method Évaluation des données de mesure-Supplément 1 du “Guide pour l’expression de l’incertitude de mesure”-Propagation de distributions par une méthode de Monte Carlo.
Constantoudis, V., and Gogolides, E. (2008). Fractal dimension of line width roughness and its effects on transistor performance. Proc. SPIE 6922, 692223. doi:10.1117/12.791850
Constantoudis, V., Papavieros, G., and Gogolides, E. (2019a). Edge placement error and line edge roughness. Proc. SPIE, 111. doi:10.1117/12.2523419
Constantoudis, V., Papavieros, G., Karakolis, P., Khiat, A., Prodromakis, T., and Dimitrakis, P. (2019b). Impact of line edge roughness on ReRAM uniformity and scaling. Materials 12, 3972. doi:10.3390/ma12233972
Constantoudis, V., Papavieros, G., Lorusso, G., Rutigliani, V., Roey, F. V., and Gogolides, E. (2018). Line edge roughness metrology: recent challenges and advances toward more complete and accurate measurements. J. Nanolithogr. MEMS, MOEMS 17, 041014. doi:10.1117/1.JMM.17.4.041014
Constantoudis, V., Papavieros, G., Lorusso, G., Rutigliani, V., Roey, F. van, and Gogolides, E. (2018a). Multifractal analysis of line-edge roughness. Proc. SPIE, 113. doi:10.1117/12.2306508
Constantoudis, V., and Pargon, E. (2013). Evaluation of methods for noise-free measurement of LER/LWR using synthesized CD-SEM images. Proc. SPIE 8681, 86812L. doi:10.1117/12.2018245
Crouzier, L., Delvallée, A., Ducourtieux, S., Devoille, L., Tromas, C., and Feltin, N. (2019). A new method for measuring nanoparticle diameter from a set of SEM images using a remarkable point. Ultramicroscopy 207, 112847. doi:10.1016/j.ultramic.2019.112847
Cunha, I., Latron, E., Bauer, S., Sage, D., and Griffie, J. (2024). Machine learning in microscopy - insights, opportunities and challenges. J. Cell Sci. 137, jcs262095. doi:10.1242/jcs.262095
de Haan, K., Ballard, Z. S., Rivenson, Y., Wu, Y., and Ozcan, A. (2019). Resolution enhancement in scanning electron microscopy using deep learning. Sci. Rep. 9, 12050. doi:10.1038/s41598-019-48444-2
Deng, J., Zhang, Q., Lu, J., Yan, Q., Pan, J., and Chen, R. (2021). Prediction of the surface roughness and material removal rate in chemical mechanical polishing of single-crystal SiC via a back-propagation neural network. Precis. Eng. 72, 102–110. doi:10.1016/j.precisioneng.2021.04.012
Dong, C., Loy, C. C., He, K., and Tang, X. (2014). “Learning a deep convolutional network for image super-resolution,” in Computer vision – eccv 2014. Editors D. Fleet, T. Pajdla, B. Schiele, and T. Tuytelaars (Cham: Springer International Publishing), 184–199.
Dullien, F. A. L. (1992). Porous media: fluid transport and pore structure. Academic Press. Available online at: https://books.google.gr/books?id=S50RAQAAIAAJ.
Dusséaux, R., and Vannier, E. (2022). Soil surface roughness modelling with the bidirectional autocorrelation function. Biosyst. Eng. 220, 87–102. doi:10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2022.05.012
Duval, L., Moreaud, M., Couprie, C., Jeulin, D., Talbot, H., and Angulo, J. (2015). “Image processing for materials characterization: issues, challenges and opportunities,” in 2014 IEEE international conference on image processing, ICIP 2014, 4862–4866. doi:10.1109/ICIP.2014.7025985
Dyson, F. J., and Falk, H. (1992). Period of a discrete cat mapping. Am. Math. Mon. 99, 603–614. doi:10.1080/00029890.1992.11995900
Eichhorn, S., and Sampson, W. (2005). Statistical geometry of pores and statistics of porous nanofibrous assemblies. J. R. Soc. Interface/R. Soc. 2, 309–318. doi:10.1098/rsif.2005.0039
Feldman, D. P., and Crutchfield, J. P. (1998). Measures of statistical complexity: why? Phys. Lett. A 238, 244–252. doi:10.1016/S0375-9601(97)00855-4
Florindo, J. B., Sikora, M. S., Pereira, E. C., and Bruno, O. M. (2013). Characterization of nanostructured material images using fractal descriptors. Phys. A Stat. Mech. its Appl. 392, 1694–1701. doi:10.1016/j.physa.2012.11.020
Franks, J. M. (1977). Invariant sets of hyperbolic toral automorphisms. Am. J. Math. 99, 1089. doi:10.2307/2374001
Gamarra, M., Zurek, E., Escalante, H. J., Hurtado, L., and San-Juan-Vergara, H. (2019). Split and Merge Watershed: a two-step method for cell segmentation in fluorescence microscopy images. Biomed. Signal Process Control 53, 101575. doi:10.1016/j.bspc.2019.101575
Giannatou, E., Papavieros, G., Constantoudis, V., Papageorgiou, H., and Gogolides, E. (2019). Deep learning denoising of SEM images towards noise-reduced LER measurements. Microelectron. Eng. 216, 111051. doi:10.1016/j.mee.2019.111051
Glaubitz, C., Bazzoni, A., Ackermann-Hirschi, L., Baraldi, L., Haeffner, M., Fortunatus, R., et al. (2024). Leveraging machine learning for size and shape analysis of nanoparticles: a shortcut to electron microscopy. J. Phys. Chem. C 128, 421–427. doi:10.1021/acs.jpcc.3c05938
Gumbiowski, N., Loza, K., Heggen, M., and Epple, M. (2023). Automated analysis of transmission electron micrographs of metallic nanoparticles by machine learning. Nanoscale Adv. 5, 2318–2326. doi:10.1039/D2NA00781A
Hameed, N. A., Ali, I. M., and Hassun, H. K. (2019). Calculating surface roughness for a large scale SEM images by mean of image processing. Energy Procedia 157, 84–89. doi:10.1016/j.egypro.2018.11.167
Hofer, W. (2003). Challenges and errors: interpreting high resolution images in scanning tunneling microscopy. Prog. Surf. Sci. 71, 147–183. doi:10.1016/S0079-6816(03)00005-4
Hojat, N., Gentile, P., Ferreira, A., and Šiller, L. (2022). Automatic pore size measurements from scanning electron microscopy images of porous scaffolds. J. Porous Mater. 30, 93–101. doi:10.1007/s10934-022-01309-y
Hollister, S. J. (2005). Porous scaffold design for tissue engineering. Nat. Mater 4, 518–524. doi:10.1038/nmat1421
Hu, C., Sedghi, S., Madani, S. H., Silvestre-Albero, A. M., Sakamoto, H., Kwong, P., et al. (2014). Control of the pore size distribution and its spatial homogeneity in particulate activated carbon. Carbon N. Y. 78, 113–120. doi:10.1016/j.carbon.2014.06.054
Hull, R., Keblinski, P., Lewis, D., Maniatty, A., Meunier, V., Oberai, A. A., et al. (2018). Stochasticity in materials structure, properties, and processing—a review. Appl. Phys. Rev. 5, 011302. doi:10.1063/1.4998144
Hussain, D., Loyal, F., Greiner, A., and Wendorff, J. (2010). Structure property correlations for electrospun nanofiber nonwovens. Polym. Guildf. 51, 3989–3997. doi:10.1016/j.polymer.2010.06.036
Ilett, M., Wills, J., Rees, P., Sharma, S., Micklethwaite, S., Brown, A., et al. (2020). Application of automated electron microscopy imaging and machine learning to characterise and quantify nanoparticle dispersion in aqueous media. J. Microsc. 279, 177–184. doi:10.1111/jmi.12853
Jacobs, T., Junge, T., and Pastewka, L. (2017). Quantitative characterization of surface topography using spectral analysis. Surf. Topogr. 5 5, 013001. doi:10.1088/2051-672X/aa51f8
Janine Illian, H. S. D. S. A. P. (2008). Statistical analysis and modelling of spatial point patterns. 1st Edn. Newark: Wiley. doi:10.1002/9780470725160
Jin, X. C., and Ong, S. H.Jayasooriah (1995). A practical method for estimating fractal dimension. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 16, 457–464. doi:10.1016/0167-8655(94)00119-N
John, A. M., Khanna, K., Prasad, R. R., and Pillai, L. G. (2020). “A review on application of fourier transform in image restoration,” in 2020 fourth international conference on I-smac (IoT in social, mobile, analytics and cloud)(I-smac) (IEEE), 389–397.
Kam, K. M., Zeng, L., Zhou, Q., Tran, R., and Yang, J. (2013). On assessing spatial uniformity of particle distributions in quality control of manufacturing processes. J. Manuf. Syst. 32, 154–166. doi:10.1016/j.jmsy.2012.07.018
Kaur, N., and Singh, K. (2013). Image enhancement techniques: a selected review. Int. J. Eng. Res. Technol. (IJERT) 2.
Kim, H., Han, J., and Han, T. (2020). Machine vision-driven automatic recognition of particle size and morphology in SEM images. Nanoscale 12, 19461–19469. doi:10.1039/D0NR04140H
Kim, H. Y., Maruta, R. H., Huanca, D. R., and Salcedo, W. J. (2013). Correlation-based multi-shape granulometry with application in porous silicon nanomaterial characterization. J. Porous Mater. 20, 375–385. doi:10.1007/s10934-012-9607-9
Kizu, R., Misumi, I., Hirai, A., Gonda, S., and Takahashi, S. (2023). Developmental framework of line edge roughness reference standards for next-generation functional micro-/nanostructures. Precis. Eng. 83, 152–158. doi:10.1016/j.precisioneng.2023.06.003
Kondi, A., Constantoudis, V., Sarkiris, P., Ellinas, K., and Gogolides, E. (2023). Using chaotic dynamics to characterize the complexity of rough surfaces. Phys. Rev. E 107, 014206. doi:10.1103/PhysRevE.107.014206
Kondi, A., Papia, E.-M., and Constantoudis, V. (2024). “Machine learning applications in nanotechnology manufacturing: from etching accuracy to deposition prediction,” in Proceedings of the 13th hellenic conference on artificial intelligence (New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery). doi:10.1145/3688671.3688740
Kujdowicz, M., Perez-Guaita, D., Chlosta, P., Okon, K., and Malek, K. (2023). Fourier transform IR imaging of primary tumors predicts lymph node metastasis of bladder carcinoma. Biochimica Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Molecular Basis Dis. 1869, 166840. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2023.166840
Lakhal, S., Darmon, A., Bouchaud, J.-P., and Benzaquen, M. (2020). Beauty and structural complexity. Phys. Rev. Res. 2, 022058. doi:10.1103/PhysRevResearch.2.022058
R. Leach (2024). Characterization of areal surface texture. Second edition (Springer International Publishing). doi:10.1007/978-3-031-59310-9
Lee, B., Yoon, S., Lee, J. W., Kim, Y., Chang, J., Yun, J., et al. (2020). Statistical characterization of the morphologies of nanoparticles through machine learning based electron microscopy image analysis. ACS Nano 14, 17125–17133. doi:10.1021/acsnano.0c06809
Li, J., Sun, C., and Du, Q. (2006). A new box-counting method for estimation of image fractal dimension, 3029, 3032. doi:10.1109/ICIP.2006.313005
Liu, Y., Chen, L., Wang, H., Jiang, L., Zhang, Y., Zhao, J., et al. (2014). An improved differential box-counting method to estimate fractal dimensions of gray-level images. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent 25, 1102–1111. doi:10.1016/j.jvcir.2014.03.008
Lizhong, J., Shaohui, L., Wangbao, Z., Jian, Y., Kang, P., and Zhenbin, R. (2023). Evolutionary power spectral density study of the earthquake-induced dynamic irregularity based on short-time Fourier transform. Eng. Struct. 296, 116901. doi:10.1016/j.engstruct.2023.116901
Logothetidis, S. (2012). Nanostructured materials and their applications. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-22227-6
López-Ruiz, R., Mancini, H. L., and Calbet, X. (1995). A statistical measure of complexity. Phys. Lett. A 209, 321–326. doi:10.1016/0375-9601(95)00867-5
Lorusso, G. F., Rutigliani, V., Van Roey, F., and Mack, C. A. (2018). Unbiased roughness measurements: subtracting out SEM effects. Microelectron. Eng. 190, 33–37. doi:10.1016/j.mee.2018.01.010
Lu, M., Beguin, F., and Frackowiak, E. (2013). Supercapacitors: materials, systems, and applications. Wiley. Available online at: https://books.google.gr/books?id=uIt1kMzOduIC.
Mavrogonatos, A., Papia, E.-M., Dimitrakellis, P., and Constantoudis, V. (2022). Measuring the randomness of micro and nanostructure spatial distributions: effects of Scanning Electron Microscope image processing and analysis. J. Microsc. 289, 48–57. doi:10.1111/jmi.13149
Meija, J., Bodnar, O., and Possolo, A. (2023). Ode to Bayesian methods in metrology. Metrologia 60, 052001. doi:10.1088/1681-7575/acf66b
Miskelly, G. M. (2018). “Methods to evaluate spatial uniformity in porous silicon,” in Handbook of porous silicon. Editor L. Canham (Cham: Springer International Publishing), 755–772. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-71381-6_123
Mourdikoudis, S., Pallares, R., and Thanh, N. (2018). Characterization techniques for nanoparticles: comparison and complementarity upon studying nanoparticle properties. Nanoscale 10, 12871–12934. doi:10.1039/C8NR02278J
Muhammad, W., Aramvith, S., and Onoye, T. (2024). CANS: combined attention network for single image super-resolution. IEEE Access 1, 167498–167517. doi:10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3487918
Navajas, D., Pérez-Escudero, J. M., and Liberal, I. (2024). “Exploring surface roughness in epsilon-near-zero materials,” in 2024 eighteenth international congress on artificial materials for novel wave phenomena (metamaterials), 1–3. doi:10.1109/Metamaterials62190.2024.10703296
Nečas, D., Valtr, M., and Klapetek, P. (2020). How levelling and scan line corrections ruin roughness measurement and how to prevent it. Sci. Rep. 10, 15294. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-72171-8
Nicolis, G., and Nicolis, C. (2012). Foundations of complex systems: emergence, information and prediction. 2nd edition. doi:10.1142/8260
Okuyama, Y., and Ohmori, T. (2023). Automated measurement method based on deep learning for cross-sectional SEM images of semiconductor devices. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 62, SA1016. doi:10.35848/1347-4065/ac923d
Ooi, Y. K., and Ibrahim, H. (2021). Deep learning algorithms for single image super-resolution: a systematic review. Electron. (Basel) 10, 867. doi:10.3390/electronics10070867
Pandey, S. S., Singh, M. P., and Pandey, V. (2015). Image transformation and compression using Fourier transformation. Int. J. Curr. Eng. Technol. 5, 1178–1182.
Panigrahy, C., Seal, A., and Mahato, N. K. (2019). Quantitative texture measurement of gray-scale images: fractal dimension using an improved differential box counting method. Measurement 147, 106859. doi:10.1016/j.measurement.2019.106859
Panigrahy, C., Seal, A., and Mahato, N. K. (2020). Image texture surface analysis using an improved differential box counting based fractal dimension. Powder Technol. 364, 276–299. doi:10.1016/j.powtec.2020.01.053
Papia, E.-M., Constantoudis, V., Ioannou, D., Zeniou, A., Hou, Y., Shah, P., et al. (2024a). Quantifying pore spatial uniformity: application on membranes before and after plasma etching. Micro Nano Eng. 24, 100278. doi:10.1016/j.mne.2024.100278
Papia, E.-M., Kondi, A., and Constantoudis, V. (2023). Entropy and complexity analysis of AI-generated and human-made paintings. Chaos Solit. Fractals 170, 113385. doi:10.1016/j.chaos.2023.113385
Papia, E.-M., Kondi, A., and Constantoudis, V. (2024b). “Inverse design of hexagonal moiré materials: machine learning for tunable pore properties,” in Proceedings of the 13th hellenic conference on artificial intelligence (New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery). doi:10.1145/3688671.3688744
Park, J., Cho, Y. J., Chegal, W., Lee, J., Jang, Y.-S., and Jin, J. (2024). A review of thin-film thickness measurements using optical methods. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 25, 1725–1737. doi:10.1007/s12541-024-00955-3
Patil Mayuri, D., and Surbhi, K. (2012). Overview of techniques used for image resolution enhancement. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Eng. (IJCSE) 4, 1345–1347.
Picu, C. R. (2022). Network materials: structure and properties. Cambridge University Press. Available online at: https://books.google.gr/books?id=xkiJEAAAQBAJ.
Pierret, É., and Galerne, B. (2023). “Stochastic super-resolution for Gaussian textures,” in ICASSP 2023-2023 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP) (IEEE), 1–5.
Podulka, P., Macek, W., Zima, B., Lesiuk, G., Branco, R., and Królczyk, G. (2023). Roughness evaluation of turned composite surfaces by analysis of the shape of autocorrelation function. Measurement 222, 113640. doi:10.1016/j.measurement.2023.113640
Qian, Y., Xu, J., Drummy, L. F., and Ding, Y. (2020). Effective super-resolution methods for paired electron microscopic images. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 29, 7317–7330. doi:10.1109/tip.2020.3000964
Risović, D., and Pavlović, Ž. (2013). Performance assessment of methods for estimation of fractal dimension from scanning electron microscope images. Scanning 35, 402–411. doi:10.1002/sca.21081
Safari, H., Balcom, B., and Afrough, A. (2021). Characterization of pore and grain size distributions in porous geological samples – an image processing workflow. Comput. Geosci. 156, 104895. doi:10.1016/j.cageo.2021.104895
Sampson, W. W. (2012). Spatial variability of void structure in thin stochastic fibrous materials. Model Simul. Mat. Sci. Eng. 20, 015008. doi:10.1088/0965-0393/20/1/015008
Sarkar, N., Chaudhuri, B., and Choudhuri, B. B. (1994). An efficient differential box counting approach to compute fractal dimension of image. IEEE Trans. 24, 115–120. doi:10.1109/21.259692
Seo, Y. L., Kang, S.-J., and Moon, Y.-K. (2024). Frequency domain-based super resolution using two-dimensional structure consistency for ultra-high-resolution display. J. Imaging 10, 266. doi:10.3390/jimaging10110266
Shindo, D., and Kenji, H. (2012). High-resolution electron microscopy for materials science. Japan: Springer. Available online at: https://books.google.gr/books?id=tCHpCAAAQBAJ.
Sipkens, T. A., and Rogak, S. N. (2021). Technical note: using k-means to identify soot aggregates in transmission electron microscopy images. J. Aerosol Sci. 152, 105699. doi:10.1016/j.jaerosci.2020.105699
So, G.-B., So, H.-R., and Jin, G.-G. (2017). Enhancement of the Box-Counting Algorithm for fractal dimension estimation. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 98, 53–58. doi:10.1016/j.patrec.2017.08.022
Sreehari, S., Venkatakrishnan, S. V., Bouman, K. L., Simmons, J. P., Drummy, L. F., and Bouman, C. A. (2017). “Multi-resolution data fusion for super-resolution electron microscopy,” in Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition workshops, 88–96.
Srenevas, S., and Poutous, M. K. (2023). Shannon’s entropy and structural complexity of random antireflective nanostructures on fused silica surfaces. Proc. SPIE, 8. doi:10.1117/12.2676013
Srenevas, S., and Poutous, M. K. (2024). Complexity imbalance of nanostructured antireflective surfaces., in Cleo 2024, (Charlotte, North Carolina: Optica Publishing Group), JTu2A.156. doi:10.1364/CLEO_AT.2024.JTu2A.156
Stai, E., Constantoudis, V., Kaidatzis, A., Singh, V., Tiwari, M. K., and Gogolides, E. (2025). Generative resolution-enhanced microscopy based on computational stitching of Fourier spectra.
Su, D., and Yan, R. W. M. (2020). Prediction of 3D size and shape descriptors of irregular granular particles from projected 2D images. Acta Geotech. 15, 1533–1555. doi:10.1007/s11440-019-00845-3
Tanis, B., Dávila, R., Calvo, J., Hernández, A., and Chew, J. W. (2021). Porosimetric membrane characterization techniques: a review. J. Memb. Sci. 619, 118750. doi:10.1016/j.memsci.2020.118750
Vagenknecht, M., Soukup, J., Chen, A., and Irizarry, R. (2023). A deep learning solution for particle size analysis in low resolution inline microscopy images based on generative adversarial network. Powder Technol. 426, 118641. doi:10.1016/j.powtec.2023.118641
Vander Voort, G. F. (1999). Metallography, principles and practice. Ohio: ASM International. Available online at: https://books.google.gr/books?id=GRQC8zYqtBIC.
Van Siclen, C. D. W. (1997). Information entropy of complex structures. Phys. Rev. E 56, 5211–5215. doi:10.1103/PhysRevE.56.5211
Veinidis, C. N., Akriotou, M., Kondi, A., Papia, E.-M., Constantoudis, V., and Syvridis, D. (2025). Complexity analysis of challenges and speckle patterns in an optical physical unclonable function. Chaos Solit. Fractals 191, 115938. doi:10.1016/j.chaos.2024.115938
Villarrubia, J. S., and Bunday, B. D. (2005). Unbiased estimation of linewidth roughness. Proc. SPIE 5752, 480–488. doi:10.1117/12.599981
Vivier, H., Pons, M.-N., and Portala, J.-F. (1989). Study of microporous membrane structure by image analysis. J. Memb. Sci. 46, 81–91. doi:10.1016/S0376-7388(00)81172-2
Wang, P., Gu, C., Yang, H., Wang, H., and Moore, J. M. (2023). Characterizing systems by multi-scale structural complexity. Phys. A Stat. Mech. its Appl. 609, 128358. doi:10.1016/j.physa.2022.128358
Wuhrer, R., and Moran, K. (2016). Low voltage imaging and X-ray microanalysis in the SEM: challenges and opportunities. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater Sci. Eng. 109, 012019. doi:10.1088/1757-899X/109/1/012019
Xing, F., Xie, Y., Su, H., Liu, F., and Yang, L. (2018). Deep learning in microscopy image analysis: a survey. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn Syst. 29, 4550–4568. doi:10.1109/tnnls.2017.2766168
Yang, Q. I. U., Liu, W., Wang, B., Zhang, W., Zeng, X., Zhang, C., et al. (2017). Regulating the spatial distribution of metal nanoparticles within metal-organic frameworks to enhance catalytic efficiency. Nat. Commun. 8, 14429. doi:10.1038/ncomms14429
Yue, L., Shen, H., Li, J., Yuan, Q., Zhang, H., and Zhang, L. (2016). Image super-resolution: the techniques, applications, and future. Signal Process. 128, 389–408. doi:10.1016/j.sigpro.2016.05.002
Zelenty, J., Dahl, A., Hyde, J., Smith, G., and Moody, M. (2017). Detecting clusters in atom probe data with Gaussian mixture models. Microsc. Microanal. 23, 269–278. doi:10.1017/S1431927617000320
Zhao, Y., Wang, G.-C., and Lu, T.-M. (2001). Characterization of amorphous and crystalline rough surface: principles and applications. Charact. Amorph. Cryst. Rough Surf. Princ. Appl. 37, 15.
Zhou, W., Cao, Y., Zhao, H., Li, Z., Feng, P., and Feng, F. (2022). Fractal analysis on surface topography of thin films: a review. Fractal Fract. 6, 135. doi:10.3390/fractalfract6030135
Keywords: resolution, Fourier analysis, stochasticity, roughness, point patterns, fractal, multifractal, spatial complexity
Citation: Kondi A, Papia E-M, Stai E and Constantoudis V (2025) Computational methods in nanometrology: the challenges of resolution and stochasticity. Front. Nanotechnol. 7:1559523. doi: 10.3389/fnano.2025.1559523
Received: 13 January 2025; Accepted: 09 May 2025;
Published: 30 May 2025.
Edited by:
Umapathi Krishnamoorthy, M. Kumarasamy College of Engineering, IndiaReviewed by:
Zimu Zhou, Western Digital, United StatesZihao Wang, Argonne National Laboratory (DOE), United States
Copyright © 2025 Kondi, Papia, Stai and Constantoudis. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Vassilios Constantoudis, di5jb25zdGFudG91ZGlzQGlubi5kZW1va3JpdG9zLmdy
 Alex Kondi1,2
Alex Kondi1,2 Efi-Maria Papia
Efi-Maria Papia Vassilios Constantoudis
Vassilios Constantoudis