- 1Department of Neurosurgery, The First People’s Hospital of Chuzhou, Chuzhou, Anhui, China
- 2Department of Neurology, The First People’s Hospital of Chuzhou, Chuzhou, Anhui, China
Objective: The primary objective of this study was to systematically assess the prognostic utility of neutrophil-derived inflammatory indices—specifically the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and systemic inflammation response index (SIRI)—and subsequently develop a predictive model for thrombolysis outcomes through the integration of these hematological biomarkers with clinical parameters, including acute-phase neurological severity (as quantified by baseline National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale [NIHSS] scores) and therapeutic timeliness (door-to-needle time, DNT) in acute ischemic stroke patients receiving recombinant tissue plasminogen activator (rt-PA) therapy.
Methods: This retrospective cohort study analyzed consecutive patients with AIS who received intravenous thrombolysis with rt-PA at the First People’s Hospital of Chuzhou in Anhui Province, China, between January 2021 and July 2023. Peripheral blood samples were collected within 24 h of admission to evaluate the NLR and SIRI. Univariate and multivariate logistic regression models were employed to assess the associations of NLR, SIRI, NIHSS score at admission, and DNT with short-term prognosis after intravenous thrombolysis for acute cerebral infarction. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis was conducted to assess the predictive capacity of the NLR, SIRI, NIHSS scores, DNT for clinical outcomes in AIS patients.
Results: A total of 232 AIS patients treated with rt-PA IVT completed the 3-month follow-up. Multivariate logistic regression confirmed NIHSS score, DNT time, NLR, and SIRI as independently associated with worse prognosis (all p < 0.01). ROC analysis confirmed individual AUCs of 0.779 for NIHSS, 0.737 for NLR, 0.701 for SIRI, and 0.732 for DNT. The nomogram integrating NIHSS score, SIRI, NLR, and DNT was established, yielding an AUC of 0.885, and showing robust predictive accuracy with an internally validated AUC of 0.887 and externally validated AUC of 0.882.
Conclusion: This study affirms that specific inflammatory markers like NLR and SIRI, alongside initial stroke severity and treatment timeliness, emerge as significant prognosis predictors in thrombolysis-treated stroke patients. By amalgamating these biomarkers, the proposed nomogram empowers clinicians to foresee and manage patient outcomes more effectively.
Introduction
Acute Ischemic Stroke (AIS) represents a prominent contributor to long-term disability worldwide. Intravenous thrombolysis (IVT) employing alteplase stands as a well-established intervention significantly mitigating disability and mortality risks among AIS patients (1). Nevertheless, despite these advancements, some patients endure adverse functional outcomes stemming from intricate pathophysiological reactions triggered by reperfusion therapy (2, 3). Identifying prognosis-influencing factors, especially among those predisposed to poor outcomes post-treatment, remains paramount (4).
Stroke pathogenesis intricately intertwines with inflammatory cascades. Post-stroke immune responses and inflammation are recognized contributors to secondary brain damage post-reperfusion (4, 5). Recent investigations underscore the prognostic significance of neutrophils and associated inflammatory markers, such as the neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), and the platelet–neutrophil ratio (PNR), in acute coronary syndrome (ACS) prognosis (6–9). Furthermore, emerging markers like the systemic immune inflammation index (SII) and systemic inflammation response index (SIRI), derived from routine blood counts, correlate with ACS outcomes (10). Notably, the documented association between SIRI and early functional deterioration in AIS underscores the significance of exploring the combined impact of SIRI and SII on AIS prognosis (11).
Neutrophil-mediated thromboinflammatory responses are increasingly recognized as a major contributor to blood–brain barrier disruption in patients with AIS following rt-PA reperfusion, leading to hemorrhagic transformation and secondary neurological deterioration (12). This study aims to integrate neutrophil-related inflammatory biomarkers with clinical parameters, such as DNT and NIHSS scores, to enhance and specify the clinical value of neutrophils. Furthermore, we have developed a novel model that allows clinicians to rapidly evaluate the short-term prognosis of patients with cerebral infarction following intravenous thrombolysis, optimize subsequent treatment strategies, and thus enhance the prognosis and clinical outcomes for individuals with AIS.
Materials and methods
Study design and population
This retrospective study encompassed AIS patients receiving intravenous thrombolysis (IVT) at The First People’s Hospital of Chuzhou between January 2021 and July 2023. The inclusion criteria were: (1) confirmed diagnosis of cerebral infarction via MRI or CT; (2) presentation within 4.5 h from symptom onset and treatment with rt-PA IVT; (3) availability of complete clinical data; and (4) informed consent obtained from the patient or their family. The exclusion criteria were: (1) presence of rheumatic or immune diseases; (2) malignant tumors; (3) recent acute myocardial infarction; (4) incomplete data; (5) severe liver or kidney damage; and (6) chronic inflammatory diseases. This study was approved by the Ethic Committee of the First People’s Hospital of Chuzhou. This article is a retrospective study. The patient selection process is depicted in Figure 1.
Data collection and definition
Data were systematically collected from medical records, encompassing demographic information (age, gender), clinical history (atrial fibrillation, related diseases, smoking, alcohol consumption). And the patient has established cerebrovascular risk factors including hypertension (13) and diabetes mellitus (meeting international diagnostic criteria) (14). Hyperlipidemia diagnosis required meeting any one of these lipid threshold criteria: Total cholesterol (TC) ≥ 6.2 mmol/L; Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) ≥ 4.1 mmol/L; Triglycerides (TG) ≥ 2.3 mmol/L; High-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) < 1.0 mmol/L. The National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) scores at admission, door-to-needle time (DNT), and 3-month post-thrombolysis modified Rankin Scale (mRS) score were independently assessed by two board-certified neurologists. Discrepancies in ratings (defined as ≥1-point difference in NIHSS/mRS or ≥5-min variance in DNT) were resolved through blinded consensus review by a third senior neurologist. Laboratory parameters included complete blood count (CBC) measurements obtained within 24 h of hospital admission. Four inflammatory biomarkers were calculated as follows: Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (NLR): neutrophil count/lymphocyte count; Systemic Inflammation Response Index (SIRI): (Neutrophil count × monocyte count)/lymphocyte count; Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index (SII): (Neutrophil count × platelet count)/lymphocyte count; Platelet-to-Neutrophil Ratio (PNR): Platelet count/neutrophil count.
The etiology of AIS was classified according to the TOAST criteria, which includes large artery atherosclerosis (LAA), small artery occlusion (SAO), and cardio-embolism (CE). All enrolled patients underwent head CT, MRI (including diffusion-weighted imaging, DWI), and CTA examinations.
Outcomes were assessed using the 3-month modified Rankin Scale (mRS), with patients categorized into two groups: a good outcome group (mRS score ≤ 2) and a poor outcome group (mRS score ≥ 3).
Statistical analysis
Data analysis was performed using SPSS Statistics 26.0 and R software version 4.3.0. Continuous variables were expressed as either median (quartiles) or mean ± standard deviation, depending on their distribution, while categorical variables were presented as frequencies and percentages. Non-parametric tests were utilized for skewed data, and the chi-square or Fisher’s exact tests were applied to categorical variables as appropriate. Univariate logistic regression was conducted on all pertinent variables. Variables selected by the LASSO regression model were used in a multivariate logistic regression to develop a predictive model. The predictive accuracy of the inflammatory markers for adverse outcomes was assessed using Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curve analysis.
Results
Baseline demographic characteristics
A total of 300 patients diagnosed with AIS and treated with rt-PA IVT within 4.5 h of onset were initially enrolled. After excluding 68 patients due to incomplete data, 232 participants completed a 3-month follow-up and were included in the study. Based on the modified Rankin Scale (mRS) scoring criteria, patients were categorized into a good prognosis group (mRS 0–2 points, n = 163) and a poor prognosis group (mRS 3–6 points, n = 69). The median age of the patients was 70 years, with a gender distribution of 62.07% male (144 cases) and 37.93% female (88 cases). There was no significant difference in age between the groups (p > 0.05), but a significant gender difference was observed, with males more likely to have a good prognosis (p < 0.05). A history of alcohol consumption was more common in the good prognosis group (p < 0.05). The median values of NIHSS score, DNT time, NLR, SIRI, SII, and neutrophil count were all significantly higher in the poor prognosis group (p < 0.001), and PNR also showed a significant difference between the two groups (p < 0.05). The proportions of hypertension and diabetes showed no significant differences (p > 0.05). Stroke subtype appeared to influence the prognosis (p < 0.05) (Table 1).
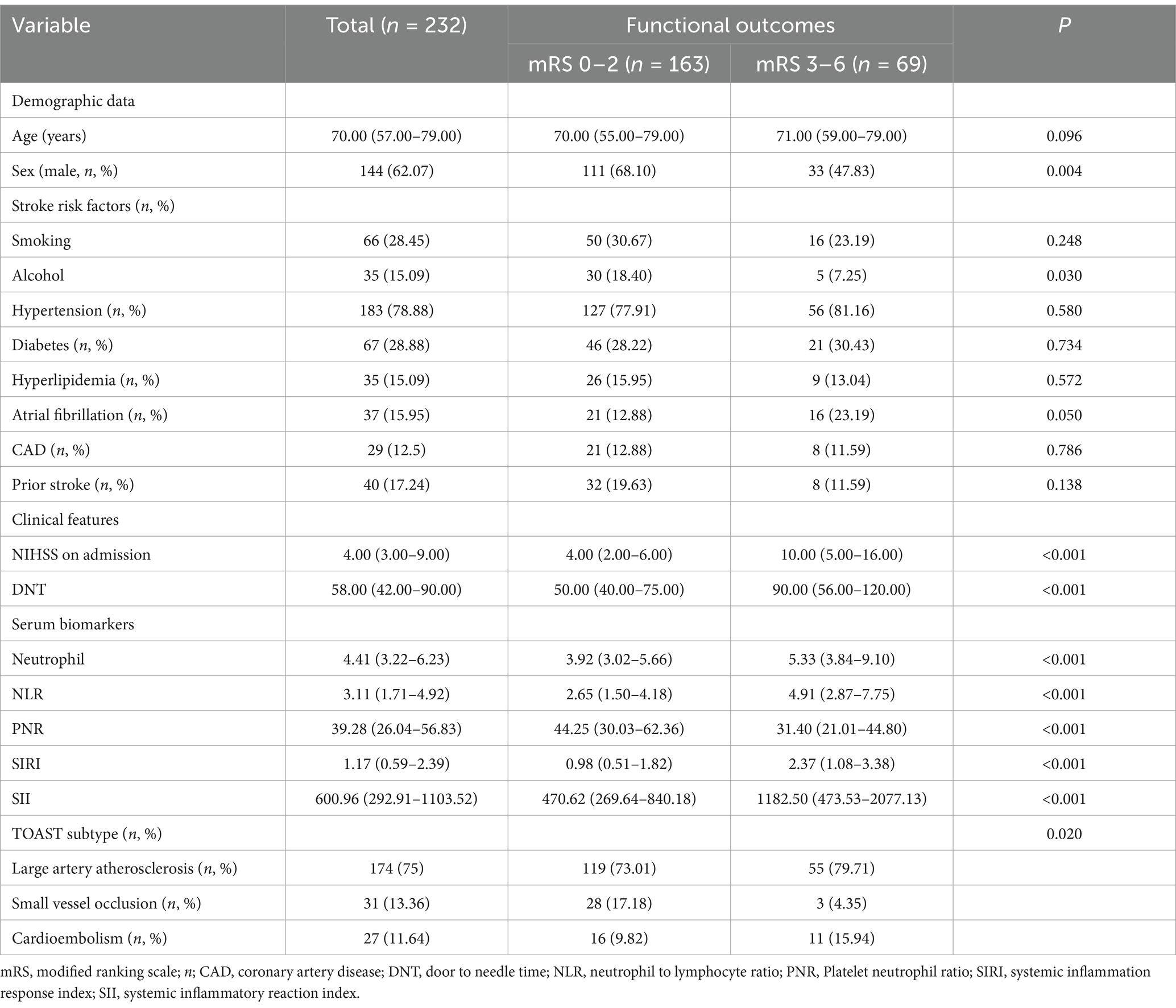
Table 1. General clinical characteristics of AIS patients receiving rt-PA treatment in the good and poor function outcomes groups.
Logistic regression analysis of AIS patients after 3 months of IVT treatment
Univariate binary logistic regression analysis (Supplementary Table S1) found that gender, alcohol consumption, NIHSS score at admission, DNT time, PNR, NLR, SII, and SIRI as significantly associated with adverse outcomes three months post-stroke (all p < 0.05). LASSO regression analysis was conducted to refine the selection of predictors, identifying four key variables: NIHSS score at admission, DNT, SIRI, and NLR (Figure 2). Multivariate logistic regression analysis revealed that NIHSS score at admission (OR = 1.21, 95% CI: 1.12–1.30, p < 0.001), DNT time (OR = 1.01, 95% CI: 1.01–1.02, p = 0.009), NLR (OR = 1.28, 95% CI: 1.13–1.46, p < 0.001), and SIRI (OR = 1.31, 95% CI: 1.07–1.59, p = 0.008) were associated with a worse prognosis (Supplementary Table S2).
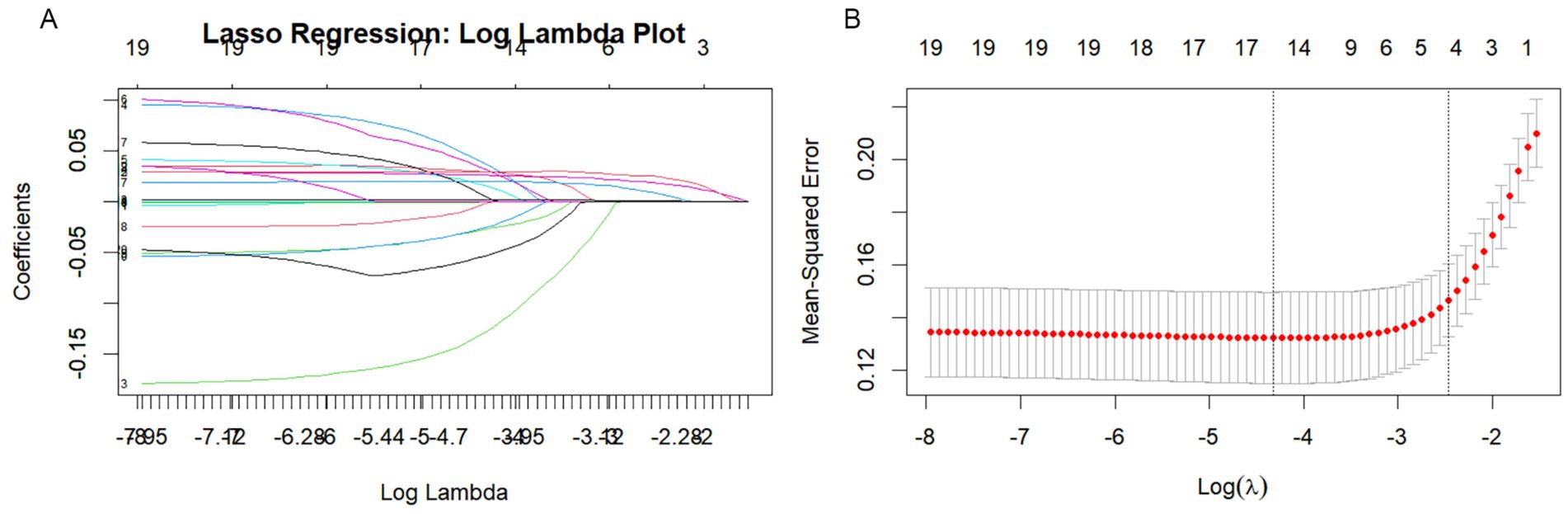
Figure 2. Lasso regression analysis based on Selection of predictors. (A) Lasso regression incorporated all the provided variables (NIHSS, SIRI, NLR, DNT) as features for the predictive model. (B) Cross-validation curve for LASSO regression analysis.
Establishment of nomogram model
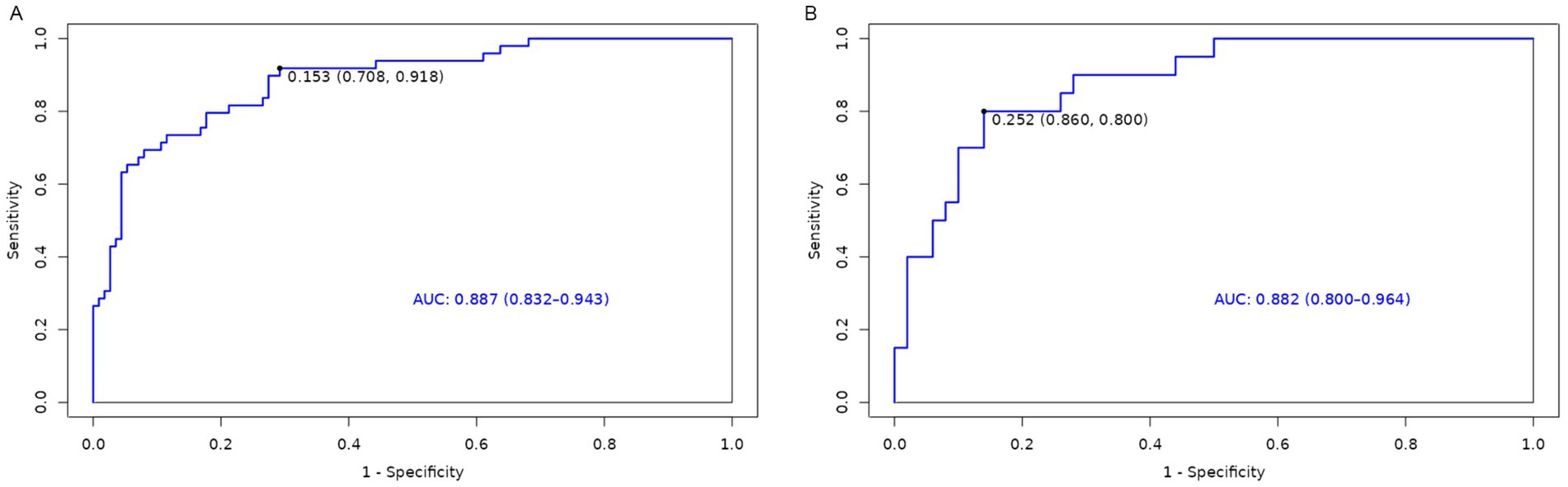
A nomogram model was developed using the key independent predictors identified (NIHSS score, SIRI, NLR and DNT) and represented in a nomogram to estimate the probability of an adverse outcome (Figure 3). ROC Curve Analysis assessed the predictive ability of NIHSS score at admission, DNT time, NLR, and SIRI for adverse outcomes. The AUC values were as follows: NIHSS score at admission 0.779, SIRI 0.701, NLR 0.737, and DNT 0.732. The combined index of NIHSS, DNT, NLR, and SIRI yielded an AUC of 0.885, indicating a strong predictive model (Figure 4). The model demonstrated robust predictive accuracy with an internally validated AUC value of 0.887 (95% CI: 0.832–0.934) and an externally validated AUC value of 0.882 (95% CI: 0.800–0.964), both exceeding the threshold AUC value of > 0.7 (Figure 5). Calibration curves for internal and external validation showed high concordance with the ideal curve, confirming the model’s reliability (Figure 6). The decision curve analysis indicated that when the probability threshold for unfavorable outcomes is between 0.04 and 0.86, patients with acute cerebral infarction may benefit from earlier interventions (Figure 7).
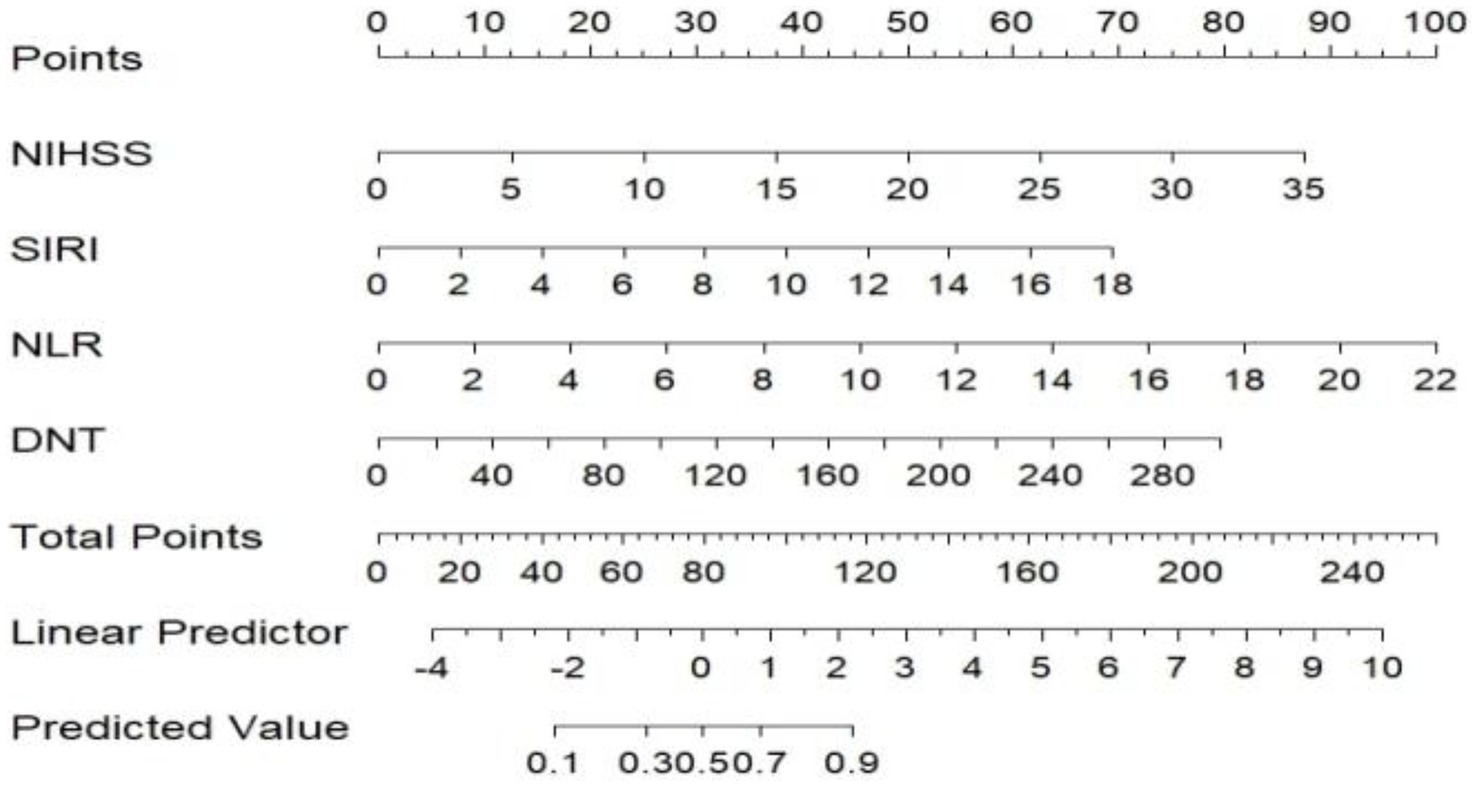
Figure 3. Predictive model for adverse outcomes after 3 months of rt-PA intravenous thrombolysis (Nomogram). NIHSS, National Institute of Health Stroke Scale; SIRI, systemic inflammation response index; NLR, neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio; DNT, door to needle time.
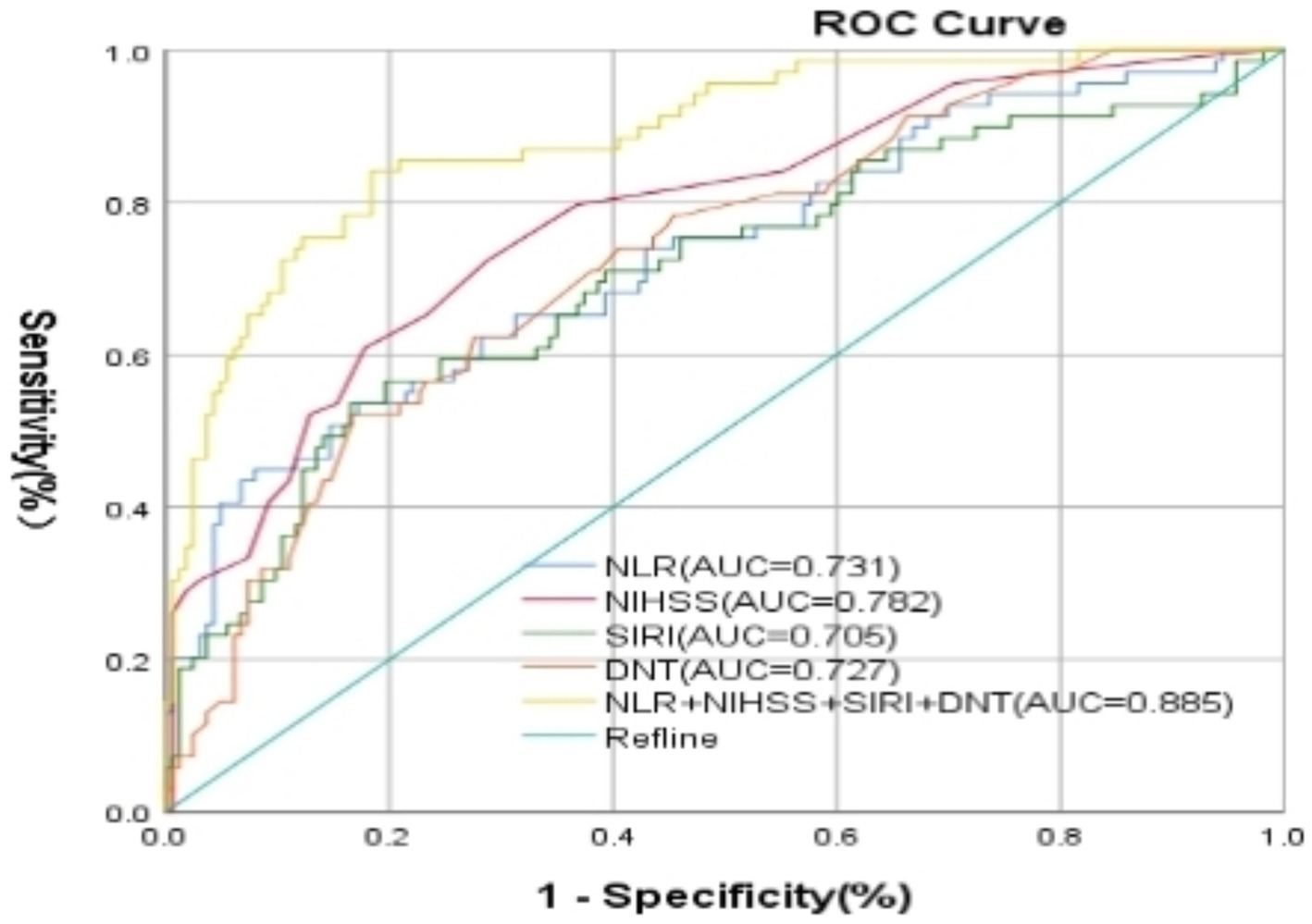
Figure 4. Characteristics of subject ROC curves for NIHSS score, DNT, NLR, and NLR + SIRI, and NIHSS + DNT + SIRI + NLR on prognosis of patients with AIS undergoing intravenous thrombolysis at admission. NIHSS, National Institute of Health Stroke Scale; SIRI, systemic inflammation response index; NLR, neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio; DNT, door to needle time.
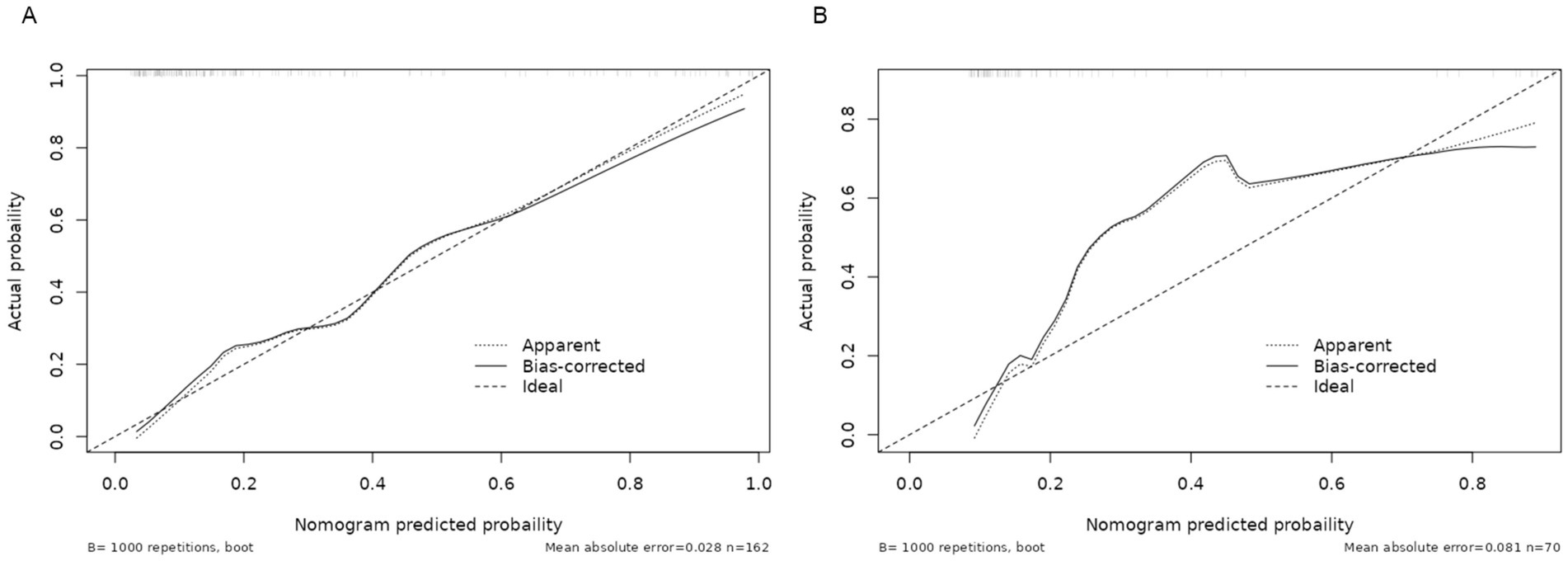
Figure 6. Calibration curve of the nomogram for the risk of adverse outcomes. (A) Training cohort. (B) Validation cohort.
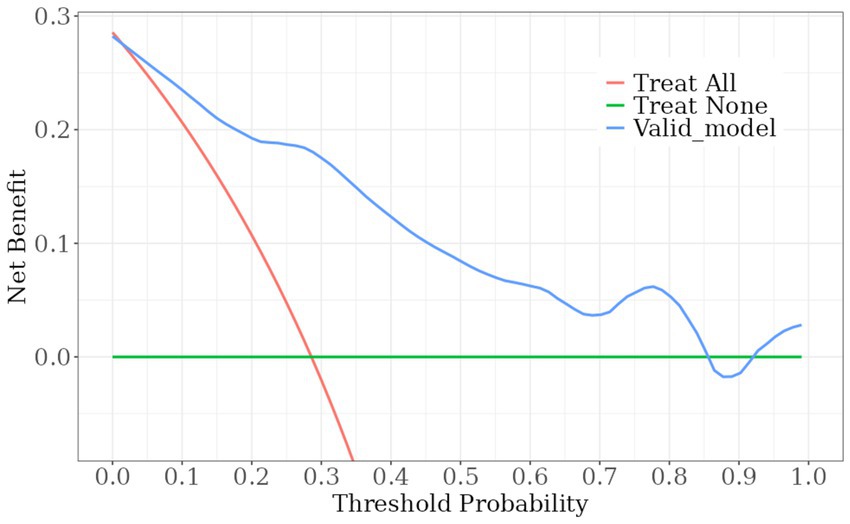
Figure 7. DCA curve. Decision curve assessment of the poor prognosis prediction model. The red line indicates the assumption that all patient outcomes were poor prognosis and interventions were implemented ahead of time; the green line indicates that no patient experienced a poor outcome and no interventions were implemented ahead of time; and the blue line indicates the constructed risk-nomogram for poor prognosis.
Discussion
This study significantly enhances our understanding of predictive factors for short-term adverse outcomes in AIS patients treated with IVT. By integrating multiple predictors-specifically, the NIHSS score at admission, DNT, NLR, and SIRI-our research demonstrates the superior predictive power of combining clinical features and inflammatory markers over traditional single-marker models. The developed predictive nomogram, achieving an AUC value of 0.885, effectively identifies patients at high risk of poor outcomes, enabling clinicians to tailor interventions more precisely and potentially improve patient management and outcomes. This approach not only underscores the importance of rapid treatment and comprehensive assessment in AIS but also sets the stage for future research to optimize and personalize stroke treatment strategies.
Current research on predicting short-term adverse outcomes after IVT has primarily focused on individual inflammatory markers, with limited analysis of NLR, PNR, SII, SIRI, DNT, and NIHSS score in combination. The objective of this study was to evaluate the predictive value of NLR, SIRI combined with NIHSS score, and DNT time on the prognostic outcome of IVT. Our findings indicate that elevated SIRI, NLR, NIHSS score, and DNT time were significantly associated with poor functional prognosis in patients. Even after adjusting for potential confounders, high SIRI remained significantly correlated with poor outcomes. Utilizing these metrics, we developed a novel Nomogram (15) to predict short-term prognosis for IVT patients at risk of adverse outcomes.
Multiple investigations have demonstrated that three months following IVT, the NLR can predict the functional result (7, 9). High NLR values could predict negative results (7). Circulating neutrophils promote disruption of the blood–brain barrier and increase brain tissue damage after ischemia (16). Histological studies have shown that neutrophils are associated with plaque formation in carotid atherosclerosis (16). T-lymphocytes act as preventive immunomodulators in the brain and can be significant in acute stroke, but they also increase the risk of ischemia–reperfusion injury (17). In addition to their complicated, interconnected roles in the removal of dead tissues, neutrophils, monocytes, microglia, T and B lymphocytes, and other immune cells can create persistent inflammation and inadvertently damage healthy brain cells, both of which impact the prognosis of stroke (18). The ratio of neutrophils to lymphocytes reflects the immune status, and even inflammatory cytokines secreted by neutrophils can trigger lymphocyte apoptosis (17). The present study corroborates the findings of previous research.
Some studies have found that systemic immune-inflammation index (SII), an indicator of systemic inflammation, is closely associated with the prognosis of malignant tumors (19, 20). Clinical studies have reported that SII can predict coronary artery disease (21, 22) and is correlated with short-term adverse prognosis of ischemic stroke (23), providing valuable clinical reference for assessing adverse prognosis. Another systemic inflammatory marker, SIRI, has been associated with prognosis after coronary vascular stenting (24) and recently linked to poor prognosis in ischemic stroke (25). In the present study, SIRI demonstrated better predictive ability than SII for poor prognosis after IVT. The likely reason for this is that SII includes platelets, unlike SIRI, which includes monocytes. Monocytes (and their derived macrophages) play an increasingly vital role in the development and propagation of atherosclerotic plaques (26). They not only participate in the initial formation of plaques but also influence plaque stability and susceptibility to rupture. A key feature of the inflammatory response following cerebral ischemia is the infiltration of monocytes (27). Platelets, conversely, are more active in the early stages of the disease, particularly in the initial formation of plaques and the stimulation of the inflammatory response (28). Monocytes primarily participate in tissue healing and the inflammatory response. Higher SIRI reflects intense pro-inflammatory reactivity generated by monocytes, neutrophils, and lymphocytes, correlated with elevated neutrophil/monocyte and/or lower lymphocyte numbers (29). Sensitivity and specificity analyses revealed that combining NLR, SIRI with DNT and NIHSS scores to create a new index improves sensitivity and specificity compared to NLR or SIRI alone. This biomarker can be easily calculated. Inflammation is a major contributing factor to thrombosis and ischemic brain tissue damage, and the combined application of inflammatory markers may more comprehensively assess patient prognosis. Thus, aiding physicians in early and relatively precise prognostic estimation for AIS patients.
While this study offers valuable insights into the predictive value of combined clinical and inflammatory markers in stroke prognosis, it has limitations. Being retrospective, it is susceptible to selection bias, and the findings rely on a relatively small sample size, potentially limiting generalizability. To address these limitations, we are currently expanding our data collection efforts prospectively. This includes increasing the sample size and extending beyond our hospital to improve the validity and clinical utility of our predictive model. Our future work aims to validate our findings in a larger, more diverse cohort, potentially strengthening the clinical applicability of our novel predictive nomogram.
In conclusion, the NIHSS score at admission, DNT time, and the neutrophil-based inflammatory indexes NLR and SIRI are effective predictors of poor prognosis following IVT in patients with AIS. Combining NLR and SIRI with the NIHSS score and DNT enhances the accuracy and reliability of predicting adverse outcomes. This integrated approach enables a more personalized and tailored treatment strategy compared to relying on a single index alone.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
This work has been carried out in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki (2000) of the World Medical Association. This study was approved by the Ethic Committee of the First People’s Hospital of Chuzhou. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The ethics committee/institutional review board waived the requirement of written informed consent for participation from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin because this article is a retrospective study.
Author contributions
SB: Data curation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YL: Data curation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. CZ: Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YR: Data curation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by Clinical Science Foundation Program of Anhui Medical University Chuzhou Science and Technology Program Project (Grant No. 2320xkj209).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fneur.2025.1500534/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Kwak, KA, Kwon, HB, Lee, JW, and Park, YS. Current perspectives regarding stem cell-based therapy for ischemic stroke. Curr Pharm Des. (2018) 24:3332–40. doi: 10.2174/1381612824666180604111806
2. Rodrigo, R, Fernández-Gajardo, R, Gutiérrez, R, Matamala, JM, Carrasco, R, Miranda-Merchak, A, et al. Oxidative stress and pathophysiology of ischemic stroke: novel therapeutic opportunities. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. (2013) 12:698–714. doi: 10.2174/1871527311312050015
3. Zhang, Q, Jia, M, Wang, Y, Wang, Q, and Wu, J. Cell death mechanisms in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Neurochem Res. (2022) 47:3525–42. doi: 10.1007/s11064-022-03697-8
4. Li, W, Hou, M, Ding, Z, Liu, X, Shao, Y, and Li, X. Prognostic value of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in stroke: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. Front Neurol. (2021) 12:686983. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2021.686983
5. Yang, K, Zeng, L, Ge, A, Wang, S, Zeng, J, Yuan, X, et al. A systematic review of the research progress of non-coding RNA in neuroinflammation and immune regulation in cerebral infarction/ischemia-reperfusion injury. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:930171. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.930171
6. Geng, L, Zuo, L, Li, H, Wang, Y, Zhang, Q, Ran, J, et al. Association of platelet-to-neutrophil ratios with 1-year outcome and mortality in patients with acute ischemic stroke. Neurosci Lett. (2023) 798:137016. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2022.137016
7. Nam, KW, Kim, TJ, Lee, JS, Park, SH, Jeong, HB, Yoon, BW, et al. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio predicts early worsening in stroke due to large vessel disease. PLoS One. (2019) 14:e0221597. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0221597
8. Pan, H, Fu, M, Ge, W, and Zhou, C. The effects of changes in platelet-to-neutrophil ratios 24 hours after intravenous thrombolysis on prognosis in acute ischemic stroke patients. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. (2020) 190:105739. doi: 10.1016/j.clineuro.2020.105739
9. Sarejloo, S, Shojaei, N, Lucke-Wold, B, Zelmanovich, R, and Khanzadeh, S. Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio and platelet to lymphocyte ratio as prognostic predictors for delirium in critically ill patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Anesthesiol. (2023) 23:58. doi: 10.1186/s12871-023-01997-2
10. Li, Q, Ma, X, Shao, Q, Yang, Z, Wang, Y, Gao, F, et al. Prognostic impact of multiple lymphocyte-based inflammatory indices in acute coronary syndrome patients. Front Cardiovasc Med. (2022) 9:811790. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.811790
11. Wang, J, Zhang, X, Tian, J, Li, H, Tang, H, and Yang, C. Predictive values of systemic inflammatory responses index in early neurological deterioration in patients with acute ischemic stroke. J Integr Neurosci. (2022) 21:94. doi: 10.31083/j.jin2103094
12. Huang, Y, Zhang, X, Zhang, C, Xu, W, Li, W, Feng, Z, et al. Edaravone Dexborneol downregulates neutrophil extracellular trap expression and ameliorates blood-brain barrier permeability in acute ischemic stroke. Mediat Inflamm. (2022) 2022:3855698–11. doi: 10.1155/2022/3855698
13. Unger, T, Borghi, C, Charchar, F, Khan, NA, Poulter, NR, Prabhakaran, D, et al. 2020 International Society of Hypertension Global Hypertension Practice Guidelines. Hypertension. (2020) 75:1334–57. doi: 10.1161/hypertensionaha.120.15026
14. ElSayed, NA, Aleppo, G, Aroda, VR, Bannuru, RR, Brown, FM, Bruemmer, D, et al. 17. Diabetes advocacy: standards of Care in Diabetes-2023. Diabetes Care. (2023) 46:S279–s280. doi: 10.2337/dc23-S017
15. Jalali, A, Alvarez-Iglesias, A, Roshan, D, and Newell, J. Visualising statistical models using dynamic nomograms. PLoS One. (2019) 14:e0225253. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0225253
16. Shi, K, Tian, DC, Li, ZG, Ducruet, AF, Lawton, MT, and Shi, FD. Global brain inflammation in stroke. Lancet Neurol. (2019) 18:1058–66. doi: 10.1016/s1474-4422(19)30078-x
17. Weng, Y, Hu, J, Ren, J, Huang, H, Yang, C, Shen, J, et al. Dynamic neutrophil-lymphocyte ratios predict short-term prognostic outcome of thrombolysis in patients with acute ischemic stroke. Neurotox Res. (2021) 39:1678–87. doi: 10.1007/s12640-021-00382-6
18. Endres, M, Moro, MA, Nolte, CH, Dames, C, Buckwalter, MS, and Meisel, A. Immune pathways in etiology, acute phase, and chronic sequelae of ischemic stroke. Circ Res. (2022) 130:1167–86. doi: 10.1161/circresaha.121.319994
19. Guo, W, Cai, S, Zhang, F, Shao, F, Zhang, G, Zhou, Y, et al. Systemic immune-inflammation index (SII) is useful to predict survival outcomes in patients with surgically resected non-small cell lung cancer. Thorac Cancer. (2019) 10:761–8. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.12995
20. Huang, H, Liu, Q, Zhu, L, Zhang, Y, Lu, X, Wu, Y, et al. Prognostic value of preoperative systemic immune-inflammation index in patients with cervical Cancer. Sci Rep. (2019) 9:3284. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-39150-0
21. Liu, Y, Ye, T, Chen, L, Jin, T, Sheng, Y, Wu, G, et al. Systemic immune-inflammation index predicts the severity of coronary stenosis in patients with coronary heart disease. Coron Artery Dis. (2021) 32:715–20. doi: 10.1097/mca.0000000000001037
22. Xu, M, Chen, R, Liu, L, Liu, X, Hou, J, Liao, J, et al. Systemic immune-inflammation index and incident cardiovascular diseases among middle-aged and elderly Chinese adults: the Dongfeng-Tongji cohort study. Atherosclerosis. (2021) 323:20–9. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2021.02.012
23. Zhou, YX, Li, WC, Xia, SH, Xiang, T, Tang, C, Luo, JL, et al. Predictive value of the systemic immune inflammation index for adverse outcomes in patients with acute ischemic stroke. Front Neurol. (2022) 13:836595. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.836595
24. Aydın, C, and Engin, M. The value of inflammation indexes in predicting patency of saphenous vein grafts in patients with coronary artery bypass graft surgery. Cureus. (2021) 13:e16646. doi: 10.7759/cureus.16646
25. Yan, D, Dai, C, Xu, R, Huang, Q, and Ren, W. Predictive ability of systemic inflammation response index for the risk of pneumonia in patients with acute ischemic stroke. Gerontology. (2023) 69:181–8. doi: 10.1159/000524759
26. Domschke, G, and Gleissner, CA. CXCL4-induced macrophages in human atherosclerosis. Cytokine. (2019) 122:154141. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2017.08.021
27. Zhang, W, Zhao, J, Wang, R, Jiang, M, Ye, Q, Smith, AD, et al. Macrophages reprogram after ischemic stroke and promote efferocytosis and inflammation resolution in the mouse brain. CNS Neurosci Ther. (2019) 25:1329–42. doi: 10.1111/cns.13256
28. Collins Yoder, AS, and Hines, CB. Thrombocytopenia: effect in ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke. Dimens Crit Care Nurs. (2021) 40:139–48. doi: 10.1097/dcc.0000000000000471
Keywords: acute ischemic stroke, thrombolysis, neutrophil inflammatory index, prognosis, nomogram model
Citation: Bai S, Liu Y, Zhang C and Ren Y (2025) A nomogram model for prognosis of acute ischemic stroke treated with recombinant tissue-type plasminogen activator. Front. Neurol. 16:1500534. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1500534
Edited by:
Per Svenningsson, Karolinska Institutet (KI), SwedenCopyright © 2025 Bai, Liu, Zhang and Ren. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Chenggang Zhang, NjUyOTY4MTFAcXEuY29t
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Song Bai1†
Song Bai1† Yan Liu
Yan Liu Chenggang Zhang
Chenggang Zhang