- School of Acupuncture-Moxibustion, Tuina and Rehabilitation, Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha, Hunan, China
Sciatic nerve injury is one of the most frequent peripheral nerve injuries in the world. The loss of motor and sensory function, along with chronic pain caused by sciatic nerve injury, significantly impacts patients’ quality of life. However, there are numerous restrictions on in vitro studies on the regeneration and healing of sciatic nerve damage. In contrast, in vivo studies can more accurately mimic clinical pathology through a variety of experimental animal models and a variety of modeling methods. However, the selection of different models has its focus, so this paper reviews the selection of experimental animals, modeling methods, and common treatment protocols. The advantages and disadvantages of each species are discussed, and the modeling methods of five common sciatic nerve injury models, along with their characteristics and applications, are highlighted. Additionally, we briefly summarize the common treatments for sciatica and nerve injury. This review is of great significance for further exploring model selection, the mechanisms underlying sciatic nerve injury, and therapies for nerve regeneration and repair.
1 Introduction
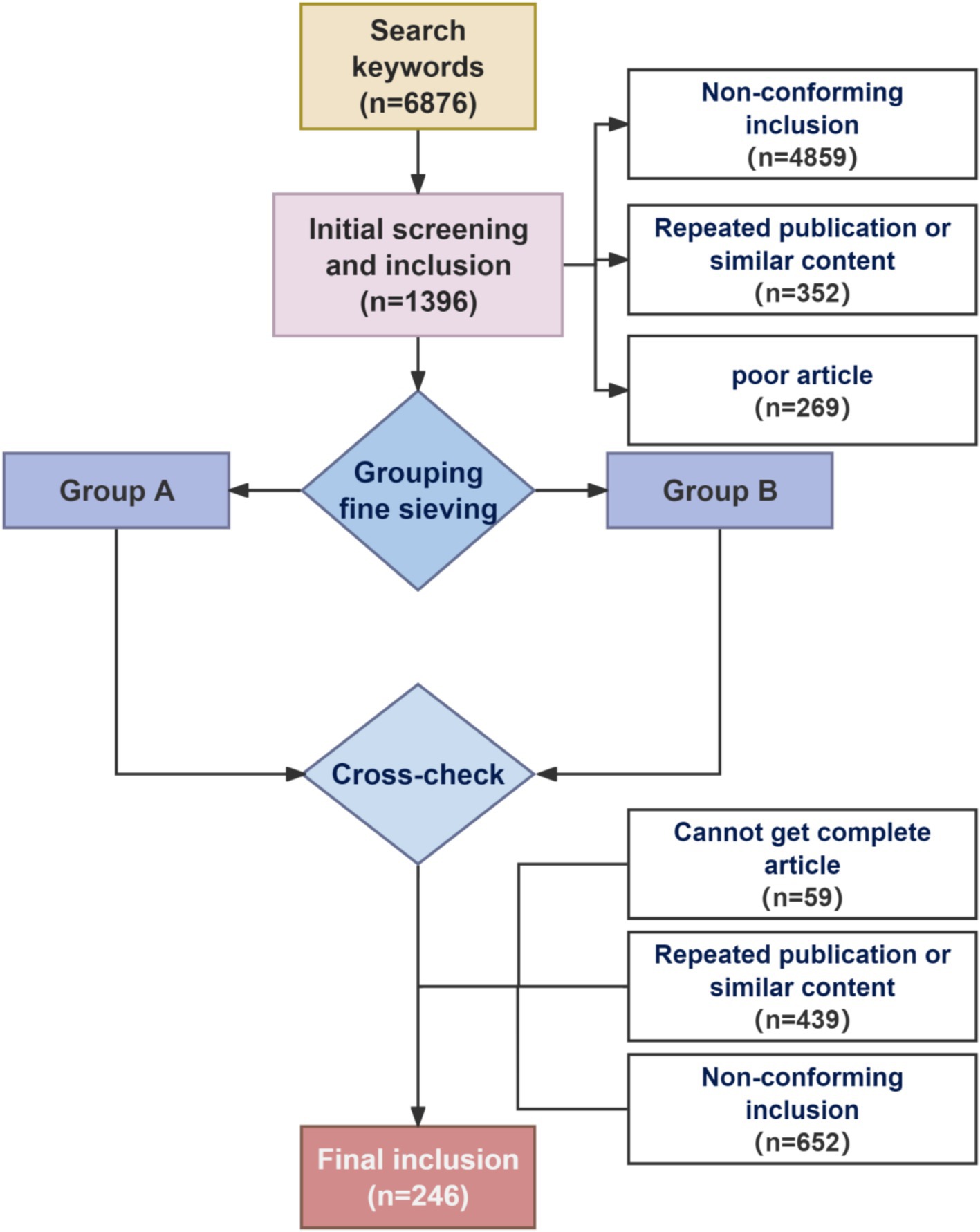
Sciatic nerve injury is one of the most common peripheral nerve injuries and can cause chronic pain as well as a partial loss of motor and sensory function (1). In severe cases, nutritional deficiencies may arise, leading to joint problems, autonomic nervous system malfunction, and paralysis of the regulated muscles, substantially affecting the quality of life of patients and placing an additional burden on their family and community (2–5). Peripheral nerve injury induces plasticity within the spinal cord and cerebral cortex, including sensitization of spinal cord dorsal horn neurons and apoptosis of inhibitory interneurons; these alterations subsequently impact pain signaling and modulation, ultimately resulting in the manifestation of pain (6). Although the nerve has a certain endogenous regeneration ability, the degree of sensory and motor function recovery, the regeneration effect of injured nerve tissue, and the analgesic treatment effect are still not satisfactory after sciatic nerve injury. This clinical problem needs to be solved urgently. Therefore, related basic research has become a research hotspot worldwide (7–9). Currently, a wide variety of mammalian models with varying sizes and anatomical structures, including mice, rats, hamsters, guinea pigs, rabbits, pigs, sheep, cats, dogs, and non-human primates (6), are used in research to assess nerve regeneration and repair function, investigate the mechanism of nerve damage, and examine the effects of various analgesic treatments. The most common peripheral nerve injury models include ligating, crushing, and transecting, with the chronic constriction injury (CCI) model and the partial sciatic nerve ligation (pSNL) model being frequently utilized in investigations of pain mechanisms. The spared nerve injury (SNI) model, the sciatic nerve crush injury (SNI) model, and the sciatic nerve transection (SNT) model are often employed in studies of nerve regeneration and repair. The treatment of peripheral nerve injury mainly involves drugs and surgical repair, including neurotrophic agents, antioxidants, anti-inflammatory drugs, tissue engineering, and stem cell therapy. However, only a few reviews have been conducted on these surgical models and treatments. Therefore, in order to understand the general situation of the above-mentioned research on sciatic nerve injury, this paper focuses on comparing the benefits and drawbacks of each operation-induced sciatic nerve injury model and discusses current typical treatment approaches (Figure 1).
2 Search strategy
The following keywords were used for searches of publications published from 2014 to 2024 in Chinese and English databases, including China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), PubMed, and Web of Science (SCIE): “sciatic nerve injury,” “animal models,” “Chronic constriction injury,” “Partial sciatic nerve ligation,” “Spared nerve injury,” “Sciatic nerve crush injury,” “Sciatic nerve transection,” “treatment of sciatic nerve,” “Neurotrophic agents,” “Antioxidant,” “Anti-inflammatory,” “Tissue engineering” and “stem cell therapy.” In addition to focusing on the relevant articles between 2014 and 2024, we also traced many of the original literature on sciatic nerve injury modeling methods to ensure a comprehensive understanding of sciatic nerve injury modeling (Figure 2).
3 Animal species
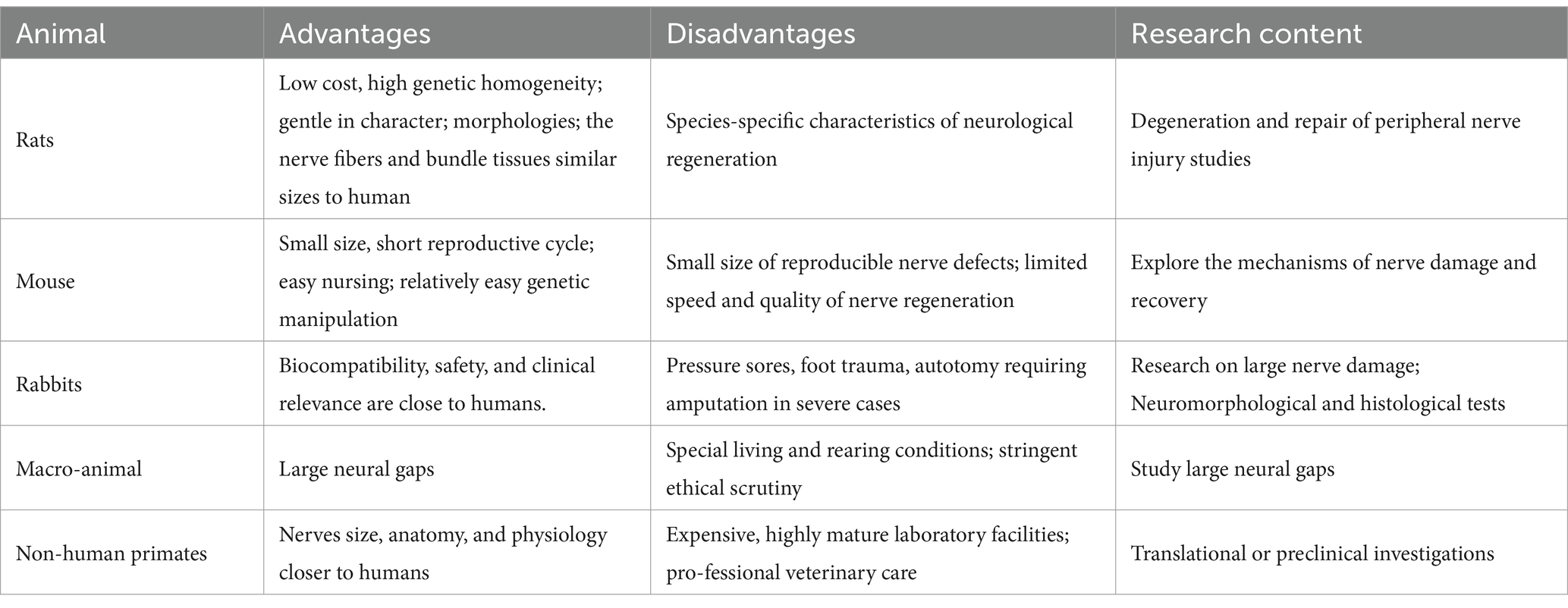
Animal selection for the sciatic nerve injury model is based on a number of design factors and criteria, such as experimental cost, feasibility of operation, ethical considerations, and experimental locations (10). Currently, rats are the most commonly used species, with more than 7,600 entries available in PubMed as of August 2024. With 2,500 entries, mice rank as the second most popular animal species. Rabbits are the third most regularly utilized species, with only approximately 320 entries. In addition, other larger mammals (11) have also been used in experiments, such as pigs (12–14), guinea pigs (15–17), dogs (18–20), and cats (18, 21, 22). However, their utilization rate is low owing to their different evolutionary nerve injury protection and regeneration characteristics. Non-human primates are often used in preclinical testing of nerve scaffolds because of their close similarity to humans (23–25), but strict ethical reviews limit their use. Non-mammalian species, such as avian (26, 27) and frogs (28–30) are widely used in experimental models to study the mechanisms for axon regeneration and nerve repair. While model organisms such as zebrafish and C. elegans are widely employed in the investigation of nerve regeneration mechanisms, the absence of a sciatic nerve in these species often leads to their use as simplified models for peripheral nerve regeneration studies (31, 32), or for elucidating the core pathways and cellular biology of in vivo axonal regeneration (33, 34).
In terms of animal selection, rats also have many advantages, such as low cost, high genetic homogeneity, and tolerance to surgery (due to their recovery ability), and functional results are easily obtained and identifiable (10). Most importantly, the nerve fibers of rats and humans have similar sizes, bundled tissues, and morphologies (35). Rats can easily repair a reasonable space size using microsurgery and allow for large-sample comparisons. It is often used in experimental studies related to degeneration and repair of peripheral nerve injuries (6, 36). While this model offers utility, it presents notable constraints within the context of nerve grafting investigations. Specifically, the rat sciatic nerve exhibits a capacity for complete regeneration following injury, a stark contrast to the clinically irreversible damage frequently observed in human patients. Furthermore, the critical nerve gap in this model is approximately 1.5 cm, significantly less than the clinical demands, which often necessitate repairs spanning approximately 4 cm in humans. The majority of experimental data is derived from short-gap repairs, typically not exceeding 10 mm. However, clinical repairs necessitate significantly longer gaps, ranging from 5 cm to over 30 cm. This discrepancy in scale renders direct mechanistic analogies problematic, thereby limiting the translational potential of these models (36). For example, in contrast to human nerve injury, the defects produced after nerve rupture injury in rats are fully restored. In addition, the volume, length, and diameter of the sciatic nerve in rats limit the size of devices that can be tested compared to rabbits and other large animals, in turn, reduces the model translational potential (36, 37). While the use of mice in assessing nerve gap repair has limitations in replicating nerve defect size and evaluating the speed and quality of regeneration, they offer advantages in the application of gene manipulation techniques. For instance, the use of transgenic mice enables overexpression or ablation of a particular gene which allows enables researchers to explore the molecular mechanisms of nerve injury and recovery in complex in vivo models (38). Coupled with the characteristics of small size, short breeding cycles, and ease of care, mice provide an efficient platform for studying the molecular mechanisms of peripheral nerve repair.
Rabbits are less costly and easier to perform than larger animals. Its in vivo functions, biocompatibility, safety, and clinical relevance are similar to those of humans. The rabbit model can provide both a first-stage test model of artificial neural guidance and an adequate preclinical model (37). Thus, they are often used for neuromorphologic and histological tests. Nevertheless, rabbit studies may also produce a number of adverse side effects (6), such as pressure sores, foot trauma, autotomy, and other unexpected adverse effects. These serious injuries may cause unnecessary pain and suffering to the animals, thus requiring euthanasia and early termination of the experiment for ethical reasons. These complications are incompatible with animal ethics and lower the quality of the nerve repair mechanisms. Large animals, such as cats, dogs, and sheep, are often used to study large neural gaps (39–41). However, unique living and raising circumstances, as well as more intense ethical examination, have significantly decreased their utilization. Porcine and nonhuman primates have nerves closer to those of humans in terms of size, anatomy, and physiology. They are considered the gold standard and are thus used in translational or preclinical investigations (23, 42). However, these models are costly, necessitating state-of-the-art laboratory facilities and expert veterinary care (Table 1).
4 Model methods
4.1 Chronic constriction injury (CCI)
The present study adopted internationally recognized methods for the preparation of CCI rat models (43). After the rats were anesthetized, a 1.5 cm incision was made 0.5 cm below the pelvis, and the gluteus maximus and biceps femoris were bluntly dissected to expose the common sciatic nerve. Four loose ligations, each 1 mm apart, were ligated using 4.0 chromium catgut, 2 mm away from the front of the trigeminal branch. The tightness of all ligations was the same, and shaking was observed around the nerves or legs of the rats during ligation. After ligation, the nerve was restored to the original suture and skin layer (Figure 3a).
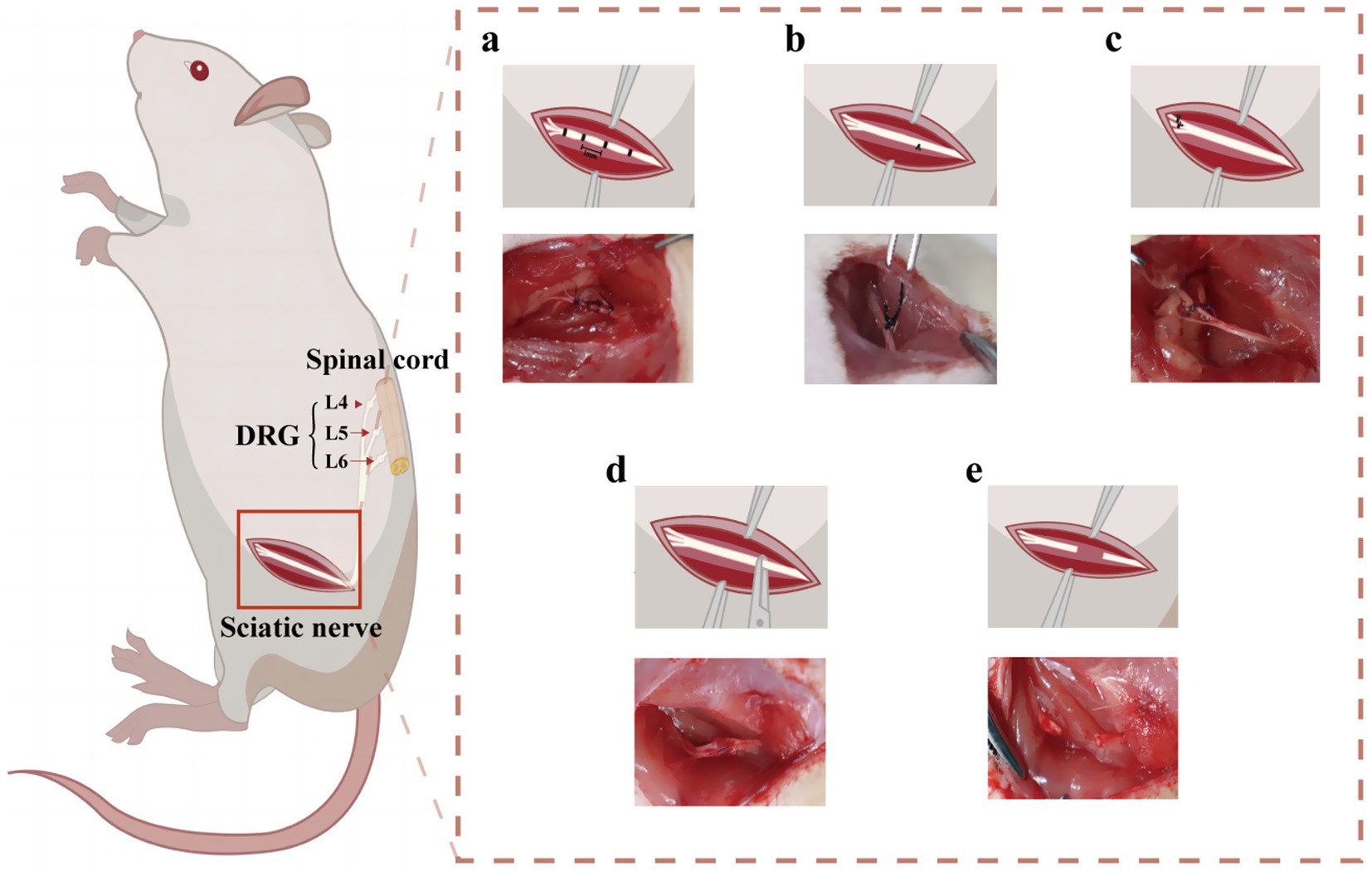
Figure 3. Schematic diagram of SNI model modeling. (a) The method used to create CCI in rats. (b) The method used to create pSNL in rats. (c) The method used to create Spared Nerve Injury in rats. (d) The method used to create Sciatic Nerve Crush Injury in rats. (e) The method used to create SNT in rats.
The CCI model has become a significant tool in neuropathic pain research due to its ease of operation and high experimental reproducibility. The model was initially established using rats as the experimental subject, and was initially established in rats and later expanded to mice (43, 44). Sprague–Dawley (SD) rats and C57BL/6 mice are commonly employed strains in the CCI model. From a pathophysiological perspective, the CCI model exhibits dual mimetic characteristics. On the one hand, it primarily mimics the signs of persistent nerve compression in clinical settings, including trauma or tumor growth (45). On the other hand, it simulates nerve fiber damage mainly located on the surface of peripheral nerves. Following nerve injury, abnormal discharges from damaged nerves trigger changes in the plasticity of the central nervous system, which is thought to be a key mechanism in the generation of pain hypersensitivity, i.e., central sensitization (46). Histopathological analyses have demonstrated that the chronic constriction injury (CCI) model is typified by nerve fiber demyelination, axonal degeneration, and a decrease in Aβ fibers (45, 47), while the majority of C-fibers remain relatively intact, and this specific injury pattern is closely associated with mechanical and thermal nociceptive sensitization in neuropathic pain (46).
As the initial animal model incorporating quantitative assessments of mechanical allodynia (von Frey filament testing) and thermal hyperalgesia (Hargreaves test), the CCI model is extensively utilized in investigations of the peripheral and central nervous systems due to its potential for high similarity to neuropathic pain experienced in clinical settings (48). Compared to partial sciatic nerve ligation (pSNL), the CCI model demonstrates more pronounced effects in inducing mechanical allodynia, thermal hyperalgesia, and cold allodynia (4, 49, 50), and reliably elicits spontaneous pain-like behaviors (51, 52), along with fewer ectopic pain-like behaviors (53), typically within 10–14 days post-surgery. Thus, this approach is commonly used in behavioral studies. However, in this model, in addition to causing neuropathic pain, the chromium line also leads to inflammation (54–56), and the different tensions of the ligation can significantly affect the number and type of damaged fibers (57) (Table 2).
4.2 Partial sciatic nerve ligation (pSNL)
After anesthesia, the upper segment of the sciatic nerve was treated with 8–0 silk suture, and 1/3–1/2 its diameter was ligated. The strength of ligation was measured using the diameter of the nerve with little contraction. Following ligation, the nerve was restored to the original suture and skin layer (58) (Figure 3b).
The pSNL is a model of pathogenic-type diversity syndrome induced by partial nerve injury and is maintained by sympathetic nerve activity. The model was initially developed in rats and later generalized to C57BL/6J mice (59) and is still mainly used in SD rats or C57BL/6J mice, and the intensity of mechanical nociceptive sensitization varies between strains, with C57BL/6J mice showing strong and persistent mechanical nociceptive sensitization, and C3H/HeSlc mice being less sensitive than other mice Strain (60). It embodies many characteristics of human pain, including the rapid onset of tactile painless hyperalgesia, mirror images, and dependence on sympathetic output (61). The partial injury caused by this model produces selective amplification of the response. Hyperalgesia, mainly heat pain and mechanical ectopic pain, develops within a few hours after surgery and lasts for several months (45). Spontaneous pain and signs such as considerable exercise hypersensitivity and hyperalgesia can be induced on the contralateral side (58, 62). However, other fibers in the unligated part of the nerve in this model were degraded due to the destruction of the nerve bundle membrane and the local vascular system. Injured and uninjured primary afferent nerves are mixed; hence, researching the alterations in the dorsal root ganglion is challenging (45) (Table 2).
4.3 Spared nerve injury (SNI)
After anesthesia, on the lateral aspect of the left thigh, the proximal and distal portions of the biceps femoris were cut, exposing the sciatic nerve and its three distal branches (from left to right: common peroneal nerve, tibial nerve, and sural nerve). The distal 2–3 mm common peroneal nerve and tibial nerve were tightly ligated, and then sectioned with micro-scissors approximately 5 mm away from the ligation. During surgery, extra attention must be used throughout the surgery to prevent contacting or straining the sural nerve that is still intact (63) (Figure 3c).
The SNI model was originally established for SD rats and can be applied to both rats and mice, with C57BL/6 mice also being a commonly used strain in newer studies (64). The model has high reproducibility and success rates (65). Changes in nearby intact sensory neurons and wounded main sensory neurons may be directly studied, allowing for an analysis of their respective roles in the pathophysiology of pain. Owing to the presence of the sural nerve, it is capable of rapid allergy in skin areas near denervation, with considerable and long-term changes in mechanical sensitivity and heat reactivity (65). These alterations bear many similarities to clinical neuropathic pain characteristics, including mechanical pain, which is longer than CCI (66), and demonstrated a sustained rise in the ipsilateral response to suprathreshold thermal and cold stimulation (65). The SNI model had a clear anatomical distribution: at the distal end of the injury, the injured and non-injured nerves were not intermingled (67). The mixture was limited to the boundary region between the damaged tibial nerve and the intact sural nerve model. Therefore, injured and uninjured sites are easily identified and modified, allowing biochemical and cellular studies of both damaged and undamaged nerves and skin areas at the peripheral (neural tissue, dorsal root ganglia) or central (spinal dorsal horn) levels, further retrograde tracing, specific nerve therapy, and behavioral evaluation (68) (Table 2).
4.4 Sciatic nerve crush injury (SNI)
A single oblique incision was made at the lower edge of the hip joint of the hind limb, and the lateral muscle was separated by ophthalmic shear force until the sciatic nerve was exposed. A mark was made on the sciatic nerve membrane using an 8–0 suture needle at a fixed position near the piriform fossa in the middle of the rat femur. Professional pinch forceps were used to pinch the distal nerve near the marker with a 3-mm length for 30 s (10 s each) before muscle and skin suture (69). The same individual performed all surgical preparations to minimize differences among the animals (Figure 3d).
In the rat model of sciatic nerve crush injury, microscopic surgery is not required, which greatly reduces the experimenter’s technical requirements. In this model, functional changes are mainly caused, leading to permanent anatomical damage (70, 71). It is similar to ligation, but without destroying the nerve connective tissue, especially the epineurium (72), it breaks only the continuity of axons and, therefore, does not induce losses in the continuity of the nerve trunk (73, 74). Thus, the proximal and distal nerve segments of the lesion site remain connected, enabling the severed axons to recover and return to the original nerve target via the best regeneration pathway—the distal Wallerian degeneration regeneration environment (61). These characteristics make the sciatic nerve crush injury model more appropriate for studying the biology of peripheral nerve regeneration and developing therapeutic strategies to enhance nerve regeneration (75). The model can be evaluated by behavioral tests for recovery of sensory and motor functions. Mechanical abnormalities of pain were quantitatively analyzed using the von Frey test to determine the Paw withdrawal threshold (PWT) or in combination with the pinprick assay (76). Recovery of thermal hyperalgesia could be detected by the Hargreaves test for Paw withdrawal latency (PWL) (The gut metabolite indole-3 propionate promotes nerve regeneration and repair). Recovery of motor function can be systematically evaluated using a grip strength test, Sciatic Function Index (SFI), and toe extension (8). For histopathological verification, SCG10 immunofluorescence staining assessed axonal regeneration (77), while PGP9.5 staining specifically traced the degree of reinnervation of cutaneous sensory nerve endings (78). The high reproducibility of the model makes it easier to identify changes in whole tissue at the cellular and molecular levels. Hence, it is particularly suitable for research on the changes over the time course of regeneration. Additionally, alterations in the results of nerve regeneration after sciatic nerve crush injury can serve as preclinical indicators of the efficacy of therapeutic agents or tissue-engineering strategies for nerve regeneration (Table 2).
4.5 Sciatic nerve transection (SNT)
After anesthesia, the proximal and distal portions of the biceps muscle were severed on the lateral surface of the thigh. After sciatic nerve exposure, the nerve was transected approximately 5 mm to prevent nerve reconnection due to regeneration (79). The muscle and skin layers were closed after surgery. In order to prevent axon regeneration, which is more prominent in animals than in humans and happens spontaneously following full transection, even in the absence of nerve repair, extra care should be taken to flip the proximal nerve stump and suture it to nearby tissue. However, clinically, if there is no material loss, the broken end anastomosis can restore nerve continuity, that is, the direct suture of the two-nerve stump. If the broken end is defective, nerve transplantation can be performed, allowing the axon to regenerate the original motor and sensory targets along the distal end (80) (Figure 3e).
The sciatic nerve transection model is an extremely ancient animal neuropathic pain model with the most serious nerve damage (81). It is a suitable model for phantom limb pain, mimicking the human experience of pain anesthesia after amputation, where pain is felt without any sensory input. This model also causes damage to the adjacent cryptic nerve (82), resulting in the complete denervation of the distal hind limb, mechanical hyperalgesia, abnormal tactile pain, increased spinal cord pain, motor incoordination, and axonal degeneration. In addition to causing motor function impairment, it can also cause autonomic dysfunction (83). After transfection, the proximal nerve loses its corresponding distal nerve and innervation target, easily grows in all directions, and is entangled with the surrounding hyperplastic fibers, in the local formation of scar-like structures, namely neuroma. Neuroma can further cause pain or sensory abnormality through tearing and stretching of surrounding tissues (84). In this model, self-resection of animals occurs (self-attack and cutting of denervated limbs in injured animals), which is considered to be accompanied by neuropathic pain and is ethically questioned because of the possibility of excessive self-resection (Table 2).
5 Treatment options for sciatic nerve injury
5.1 Neurotrophic agents
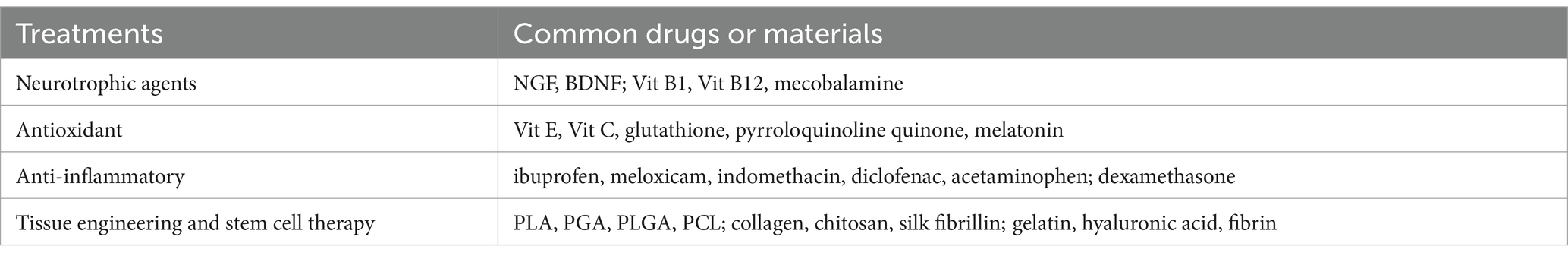
Neurotrophic agent can aid the regeneration and repair of injured nerve by reducing cell death, participating in nerve metabolism and improving blood circulation. It mainly includes neurotrophic factors (e.g., NGF, BDNF), B vitamins and their derivatives (e.g., B1, B12, mecobalamine) (Figure 4a and Table 3).
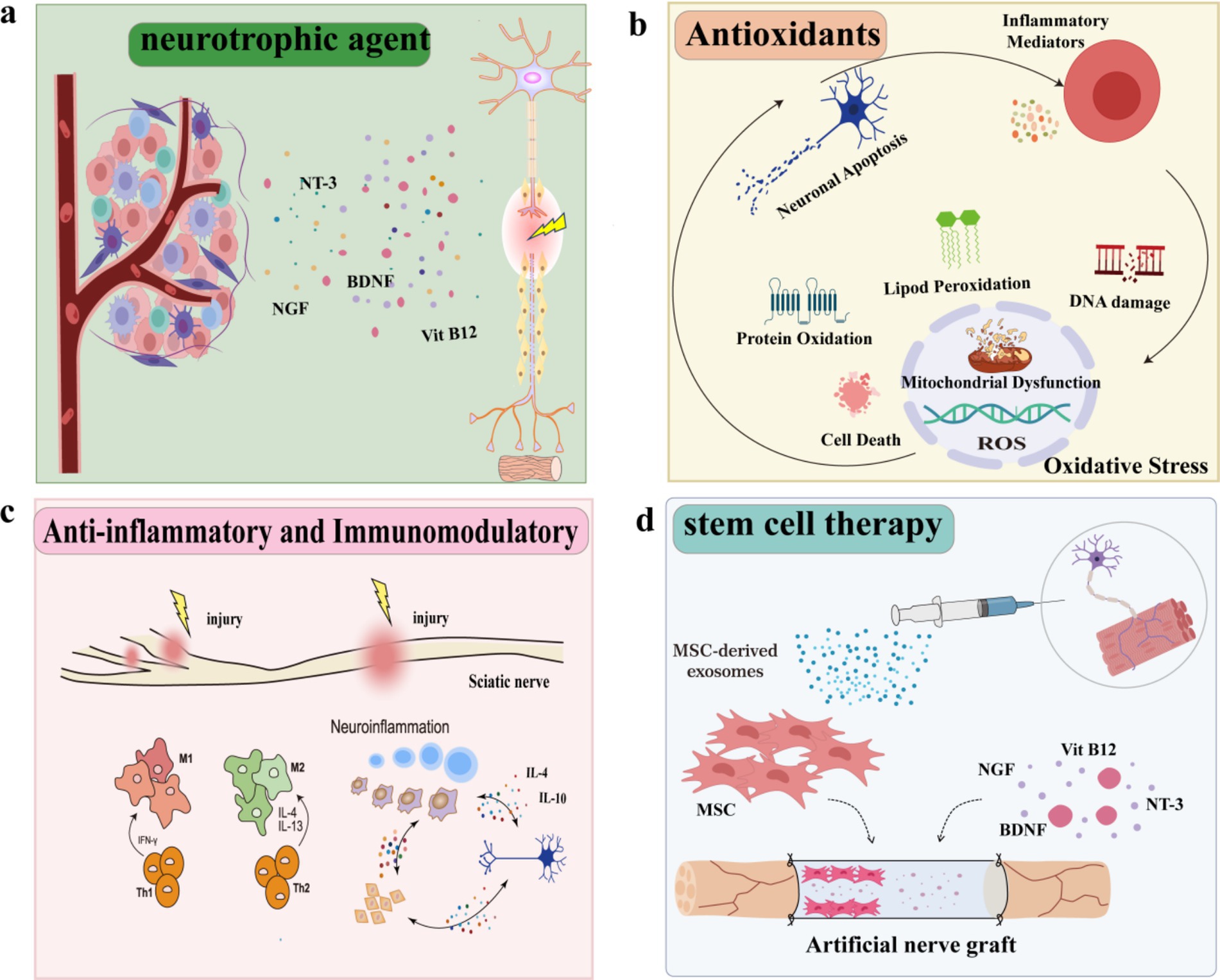
Figure 4. Treatments of sciatic nerve injury. (a) Neurotrophic agent. (b) Antioxidants. (c) Anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory. (d) Tissue engineering and stem cell therapy.
Accurately, in peripheral nerve injury, the increase or enhancement of neurotrophin activity can protect the damaged neurons and promote neuronal axon regeneration and nerve repair, which provides a potential pathway for molecular therapy to enhance nerve regeneration (85). Numerous lines of evidence suggest that NGF is essential for the healing of nerve damage (86, 87), promoting the proliferation and differentiation of neurons, enhancing the ability of axon regeneration, regulating the recovery of damaged nerve structure and function, and has the potential to promote the regeneration of peripheral nerves (88). Nevertheless, as the unnecessary side effects of intravenous NGF on the peripheral nerve are limited by its low stability, short half-life, and high cost (89, 90), it is not encouraged to try exogenous NGF in humans (91). In this light, using safe strategies to induce increased NGF production may be an optimal choice. Let-7 is one of the most conserved members of the MicroRNA (miRNAs) family, involved in regulating the fate of neurons and influencing their degeneration and regeneration (92). Evidence shows that regulating the let-7/NGF axis can reduce oxidative stress, thereby promoting myelination, nerve regeneration, and the restoration of nerve function after peripheral nerve injury (93, 94). In addition, collagen-bound NGF can be localized at the site of nerve injury in the rat model of sciatic nerve crush injury, facilitating nerve repair and enhancing functional recovery (69). Additionally, Sang et al. found that curcumin can stimulate the release of NGF, thereby playing a protective role in damaged neurons and further activating TrkA and PI3K/Akt cell survival signals (95). Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) is a neuropeptide and involved in many aspects of synaptic formation and plasticity (96–99). Certainly, previous research has shown that viral vector-mediated BDNF gene therapy has confirmed the protective effect of BDNF in neuronal survival after injury (100). Likewise, according to Catia Lopes et al., injecting non-viral TMCSH-HC nanoparticles intramuscularly with therapeutic transgenes encoding neurotrophic factors may be able to prevent long-term neurodegenerative changes and thus accelerate nerve regeneration (101).
The vitamin B (Vit B) complex, in particular vitamin B12, has neuroprotective properties as well as anti-apoptotic and anti-necrosis effects on neurons (102). Vit B complex or Vit B12 may reduce the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and increase the expression of anti-inflammatory cytokines in the process of peripheral nerve injury or inflammation, which is propitious to the regression of nerve inflammation (103). Moreover, it can also promote the regeneration of myelinated nerve fibers and the proliferation of Schwann cells by boosting the quantity of Schwann cells, myelinated nerve fibers, and the diameter of axons (104, 105). Noticeably, Several studies have reported that Vit B12 can improve nerve conduction, promote the regeneration of injured nerves, and inhibit the spontaneous ectopic discharge of injured primary sensory neurons (106). It can promote regeneration and functional recovery of injured sciatic nerves by upregulating BDNF expression (89). It has also been proposed that tissue levels of Vit B complex and Vit B12 change as compression-induced peripheral nerve injury progresses and may help to speed up neuron regeneration (107).
Moreover, in addition to promoting neuroregeneration and repair, multiple studies have indicated that Vit B12 can also be employed in pain management, alleviating neuropathic pain through various mechanisms, including the promotion of myelination, enhancement of nerve regeneration, and reduction of ectopic discharges (108–110). In summary, B vitamins exhibit therapeutic potential in the context of neuroinflammation and neural regeneration, concurrently ameliorating pain symptomatology in affected patients.
5.2 Antioxidant
Antioxidants exhibit a dual role in the neuroprotective effects: they can promote neuroregeneration and indirectly achieve analgesic effects by modulating pain signaling pathways. In PNI, inflammation leads to a buildup of oxidizing agents and free radicals (111). Notably, Oxidative stress plays an important role after nerve injury, ROS can induce neuronal apoptosis via the mitochondrial pathway (112) and regulate the expression of some apoptotic genes involved in pain generation (113) and central sensitization of neuropathic pain (114, 115). Multiple lines of evidence suggest that pro-oxidant enzymes or ROS scavengers can reduce injury hypersensitivity in rodent models of neuropathic pain (116–118). Hence, the use of antioxidants after peripheral nerve injury can reduce free radical production and protect nerve cells from oxidative damage (119). Commonly used antioxidants include Vitamin E, Vitamin C, glutathione, pyrroloquinoline quinone, and melatonin (Figure 4b and Table 3).
Vitamin C (Vit C) and Vitamin E (Vit C) are potent antioxidants (120–122). Vitamin E deficiency affects the central and peripheral nervous system and may lead to peripheral neuropathy (123). Morani et al. showed that vitamin E inhibits neuropathic pain after sciatic nerve constriction in rats (124). According to certain studies, the underlying process via which vitamin E restores sciatic nerve function following crush injuries may include the regulation of oxidative stress pathways (125, 126). Research indicates that administering exogenous Vit C and Vit C in combination has a synergistic analgesic effect. It also prevents neuropathic pain behavior following peripheral nerve damage and the early behavioral reaction to formalin injections (117). Further, the combination of pregabalin and vitamins significantly reversed sciatic nerve Wallerian degeneration and inflammatory response (127). Similarly, in another study, researchers proved that a combination of Vit C and gabapentin bacillus for nerve injury increases anti-inflammatory and anti-injury effects (128, 129).
Interestingly, certain antioxidants facilitate structural repair and functional recovery by enhancing the expression of regeneration-associated proteins. Pyrroloquinoline quinone (PQQ), an anti-lipid peroxidation antioxidant, enhances NGF synthesis in Schwann cells, improving the remarkable ability of peripheral nerve regeneration after injury (130). Interestingly, a study in SNT rats revealed that Vit E combined with PQQ treatment accelerates and improves peripheral nerve regeneration (131). In addition, melatonin has a stronger antioxidant capacity (132), and a study has demonstrated that melatonin nerve-directed conduits improve the immunological milieu by minimizing oxidative stress, inflammation, and mitochondrial dysfunction, providing energy to the nerves, and reducing neuronal apoptosis, which promotes neural debris removal and neural proliferation (111). There is accumulating evidence that antioxidants such as curcumin, isoquercitrin, and ginger oil, and mitochondrially targeted antioxidant such as MitoTEMPO have crucial roles in axonal regeneration after peripheral nerve injury and in reducing pain hypersensitivity (133–136). Furthermore, the mitochondrially-targeted small molecule M1 offers similar ability to promote axon regeneration following sciatic nerve injury, similar to MitoTempo (137).
5.3 Anti-inflammatory drugs
Inflammation is an inevitable process in the process of sciatic nerve injury and repair. Inhibition of inflammation can reduce the degree of nerve injury and neuropathic pain and promote nerve repair and regeneration (138, 139), thereby improving pain. Therefore, neuroinflammation and neuropathic pain can be partially reversed by inhibiting essential pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines. Anti-inflammatory drugs such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (e.g., ibuprofen, meloxicam, indomethacin, diclofenac, acetaminophen) and glucocorticoids (e.g., dexamethasone) can regulate inflammation-related signaling pathways, such as inhibiting the activation of NF-κB and regulating the expression of cytokines (e.g., TNF-α, IL-1β), reduce nerve inflammation and local tissue damage, promote nerve regeneration, and widely used in the treatment of nerve injury (140) (Figure 4c and Table 3).
The crucial of NF-κB in the repair of peripheral nerve injury has been recognized for several years, which may control the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines and express the main proteins in cytokine-induced inflammatory and immune responses (141). The activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway has been shown to have a vital effect on the survival and plasticity of neurons (142, 143). In addition, in a CCI rat study, it was revealed that local inhibition of NF-κB activity in dorsal spinal cord glial cells was sufficient to reduce thermal hyperalgesia and mechanical ectopic pain in CCI rats and may be related to the prevention of IL-6 and iNOS expression (144). Apparently, diclofenac sodium is a common non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medication which has analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and antipyretic properties (145, 146). The process could include preventing NF-κB from being activated, which would impact the synthesis of pro-inflammatory cytokines like IL-6 (147). In addition, it has been suggested that diclofenac sodium (DS) improves the mechanical extraction threshold and cold ectopic pain induced by SNI (148). Indeed, acetaminophen is a multimodal analgesic. A study identified that acetaminophen can effectively reduce TNF-αand IL-βin rats induced by CCI and exert anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects (149). This study further verified that the combination of L-carnosine and acetaminophen increased antioxidant capabilities and eliminated ROS by reducing GSH and stimulating the synthesis of antioxidant enzymes (SOD). An interesting animal study used celecoxib loaded with near-infrared labeled nano-emulsion (NE) to act on CCI-induced rats. It was found that CXB-NE, in turn, affected the regulation and expression of genes in sciatic nerve induced by CCI through targeted inhibiting macrophage COX2 and lowering macrophage PGE2, which was characterized by decreased expression of several neuroinflammatory genes (150, 151). Similarly, dexamethasone is an effective anti-inflammatory glucocorticoid. Dexamethasone’s immunosuppressive action and neurotrophic potential can improve the functional and morphological indexes of the injured peripheral nerve by reducing the infiltration of inflammatory cells (102), contributing to the production of inflammatory mediators, lessening the severity of Waller’s degeneration, and delaying the clearance of myelin fragments after PNI (152, 153), improving the functional and morphological indexes of the injured peripheral nerve. Actually, it can up-regulate BDNF and increase the immunoreactivity, fibrosis, and oxidative stress of NGF in nerve tissue (154, 155).
The above studies revealed the potential of traditional drugs to alleviate neuroinflammation by targeting the regulation of NF-κB and other pathways. In addition, some natural products have gradually become the new focus of nerve repair research due to their multi-target synergistic mechanism of action. Berberine (BBR) is a natural isoquinoline alkaloid which has the effects of anti-inflammation, antioxidation, and anti-apoptosis (156). BBR has been shown to support axon regeneration, neurite outgrowth, and remyelination following damage in the PNS (157). Additionally, BBR significantly reduced the pro-inflammatory M1 polarization of macrophages by inactivating NLRP3 inflammatory bodies, confirming its anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective benefits in PNI (158). Of note is that Tian et al. summarized the neuroprotective properties of BBR. They found that BBR mediates neuroprotection by inhibiting MAPKs, AMPK, NF-κB, TLR4, and NLRP3 pathways and directly regulating the secretion of inflammatory factors (159).
5.4 Tissue engineering and stem cell therapy
In addition to drug therapy, tissue engineering and stem cell therapy are also hot topics of current research. Through the implantation of specific cells, biological scaffolds or stem cells cultured in vitro, nerve regeneration and repair can be promoted and better therapeutic effects can be provided (Figure 4d and Table 3).
This treatment scheme is mostly used in the sciatic nerve transection model, usually using graft or biomaterial engineering structure, namely synthetic nerve guide conduit (NGCs) (160, 161). Grafts can be divided into Autografts and Allografts (162). The autograft is derived from a healthy part of the patient’s body and is most commonly used in blood vessels, muscles, and tendons, thus reducing the chance of immune rejection (163). However, tissue damage at the donor site causes morbidity at the donor site, which limits its applicability. In allografts, the tissue is taken from a different member of the same species donor. Although this technique is characterized by increased tissue availability, it carries a small risk of disease transmission and immune response. Owing to the limitations of these two methods and advances in tissue engineering in the field of nerve transplantation, nerve catheters made of different materials have also been increasingly employed. These catheters are biocompatible synthetic polymers and natural polymers. The most commonly used materials for manufacturing synthetic polymers include polylactic acid (PLA), polyglycolic acid (PGA), polylactic acid, polyglycolic acid copolymer (PLGA), and polyhexide lactone (PCL) (164–167). Natural polymers include collagen, chitosan, and silk fibrillin (163, 168, 169). Other materials used to observe the effects of different tissue engineering materials on regenerative repair after nerve injury include gelatin (170, 171), hyaluronic acid (172), and fibrin (173).
In addition, the implantation of biosynthetic nerve conduits containing neuroprotective cytokines is also an effective treatment for the repair and regeneration of sciatic nerve injuries. A recent study (174) selected Vit B12 and NGF as anti-inflammatory and regenerative drugs. It developed a response cascade drug delivery stent (RCDDS) which can regulate the kinetics of drug release by opening the polymer chain in layers triggered by ultrasound. The results showed that the controllable release of Vit B12 reduced the degree of inflammation at the site of PNI by diminishing the local ROS levels and causing macrophages to transform into anti-inflammatory M2 cells. Clearly, Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are adult-derived stem cells which can secrete various nerve growth factors and stimulate peripheral nerve regeneration (175, 176). It should also be noted that combined therapy (stent + stem cell + drug) is considered to be the best strategy for repairing nerve defects (154). Studies have shown that the combination of MSCs and melatonin can effectively promote the repair and regeneration of sciatic nerve and improve the function of damaged meridian tissue by reducing lipid peroxidation and increasing the level of BDNF (177). In addition, Wei Zhang et al. (178) created a novel method of treating sciatic nerve damage by sandwiching MSCs laden with EPO with chitosan nerve conduit (EPO/Chi), which may greatly speed up nerve healing and enhance morphological recovery. Interestingly, in another study (179), a biodegradable conductive hydrogel was created by combining polydopamine-modified silicon phosphorus (SiP@PDA) nanosheets with a combination of methacryloyl gelatin and acellular extracellular matrix (GelMA/ECM). MSCs cultured in 3D in GelMA/ECM-SiP@PDA conductive hydrogel showed a significant up-regulated in the expression of genes related to the differentiation of SC-like cells, promoting myelin formation and axonal regeneration.
6 Conclusion and future perspectives
In this paper, the model and treatment of sciatic nerve injury were reviewed, the results show that rats, mice, and rabbits are the most commonly used animals for the development of such models, although animals of different species and sizes can be used for sciatic nerve injury modeling. The primary considerations for this choice are the economic cost, nursing difficulty, experimental operability, and ethical welfare issues (10). The shape and size of nerve fibers and the distribution of nerve stem in rats are similar to those in humans (35), and they have many advantages, such as resistance to infection, vitality, and low cost. Therefore, rats are often selected for physiological function testing. Mice are easy to reproduce and convenient for genetic manipulation and are often used in the study of drugs to repair sciatic nerve injury. Compared to the sciatic nerve of rats and mice, the sciatic nerve of rabbits is slightly closer to the human sciatic nerve morphology, and it is easy to observe and study the nerve microstructure. Therefore, it is often used in the morphological and histological detection of the sciatic nerve (37). We also discovered that sciatic nerve research in bigger mammals and non-mammalian models has been declining, and the relevant literature is rather old. As a result, the study of the vast nerve space requires more investigation.
Currently, basic research on sciatic nerve injury is mainly aimed at finding effective analgesic treatments and exploring the mechanisms of nerve repair and regeneration. In terms of model replication, the main differences focus on the location and nature of the injury. The sites of the injury include distal or proximal nerve roots and spinal cord roots, and the nature of injury is characterized by tight or loose nerve ligation, compression, transection, and neuroinflammation (74, 81). Ligation is used as a modeling method to study the changes in the proximal and distal nerves, other centers, including neuronal cell bodies, and distal anatomical structures, including muscles. It can induce functional changes resulting in spontaneous pain-like behaviors, mechanical hyperalgesia, thermal hyperalgesia, and cold hyperalgesia (180, 181). Therefore, it is commonly used to explore rational chronic pain in sciatic neuropathy, its analgesic mechanism, and inflammatory factors. However, the most common problem with the ligation model is that the surgical technique, proficiency of the experimenter, and ligation strength are difficult to control consistently. These factors are key to the success of model replication and have a particular impact on the effect of the model. In the crush injury model, nerve edema is caused by nerve injury. The continuity of the nerve trunk is preserved by interrupting the continuity of most axons without damaging nerve connective tissue (9, 73, 74), including the epineural membrane. It induces the regeneration of injured axons along the best regeneration pathway (61, 80). This model is more suitable for studying the architecture and activity of nerves in order to investigate the recovery of motor and sensory functions after nerve injury. In contrast, the nerve transection model is help in studying the distal nerve trunk and skeletal muscle denervation to investigate effective preventive strategies. This model involves irreversible disconnection of neurons from their respective distal nerve destinations (79, 81), resulting in significant loosening of the sensory or motor function and muscle atrophy.
In the choice of treatment, the current drug therapy is mainly neurotrophic agents, antioxidants and anti-inflammatory drugs, and surgery is combined with tissue engineering and stem cell transplantation. Although a large number of studies have proved the effectiveness of drug therapy, the half-life and side effects of drugs limit the development prospect of drug therapy. Therefore, the combined treatment of tissue engineering scaffolds, stem cells and drugs is considered to be the best strategy for repairing nerve defects (154). However, only 5 physical damage models of the sciatic nerve were reviewed in this study, and freezing injury and pharmacological (chemical) injury were excluded, which may not be sufficient to offer a thorough overview of current research on sciatic nerve injury models. Furthermore, in the treatment of sciatic and peripheral nerves, only medication therapy, tissue engineering, and stem cell therapy are briefly covered, while developing technologies such as electrical stimulation, magnetic therapy, laser therapy, and rehabilitation therapy are not included. These will be the subject of further investigation.
Overall, an appropriate animal model of sciatic nerve injury can provide valuable information for the pathogenesis and clinical treatment of sciatic nerve injury and is also an indispensable part of understanding the pathophysiological mechanism of sciatic nerve injury and developing new drugs. The advantages and disadvantages of various models and animals in the preparation of the sciatic nerve model are well understood. The model should be designed based on the specific research purpose of the experiment, with selection of the most appropriate animals. Such a model would provide a reliable basis for subsequent studies on the repair and regeneration mechanisms after sciatic nerve injury. Our study provides an overview of species selection commonly used in sciatic nerve injury models but does not address potential differences within species, particularly at the strain level. This limitation is noteworthy given that differences in genetic background between animal strains may affect nerve regeneration outcomes. With continuous advances in science and technology, more effective sciatic nerve injury models must be developed. New methods for sciatic nerve injury modeling should be introduced, which will provide a valuable clinical and scientific basis for revealing the pathogenesis of sciatic nerve injury and contribute to the development of new drugs and other treatments.
Author contributions
PZ: Writing – original draft. RZ: Writing – original draft, Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing. LX: Visualization, Writing – review & editing. LN: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. PL: Visualization, Writing – review & editing. QL: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. ML: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation Youth Fund Project of China (82405595), State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine 2022 Youth Qihuang Scholars Training Program (National Letter of Traditional Chinese Medicine Education [2022] 256), Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation Youth Fund Project (2023JJ40480), the Science and Technology Innovation Program of Hunan Province (No. 2024JK2132, 2024RC1061), Outstanding Youth Project of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine (2022XJB003), Graduate Student Research Innovation Project of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine (2023CX166, 2024CX160), and Special Project of “Laboratory Animal Science Popularization” of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine (2023DWKP06).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Correction note
This article has been corrected with minor changes. These changes do not impact the scientific content of the article.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Yang, J, Zhang, S, Li, X, Chen, Z, Xu, J, Chen, J, et al. Convergent and divergent transcriptional reprogramming of motor and sensory neurons underlying response to peripheral nerve injury. J Adv Res. (2024). doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2024.07.008, [Online ahead of print]
2. Awad-Igbaria, Y, Ferreira, N, Keadan, A, Sakas, R, Edelman, D, Shamir, A, et al. HBO treatment enhances motor function and modulates pain development after sciatic nerve injury via protection the mitochondrial function. J Transl Med. (2023) 21:545. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04414-x
3. Bekelis, K, Missios, S, and Spinner, RJ. Falls and peripheral nerve injuries: an age-dependent relationship. J Neurosurg. (2015) 123:1223–9. doi: 10.3171/2014.11.JNS142111
4. Foudah, AI, Alqarni, MH, Devi, S, Singh, A, Alam, A, Alam, P, et al. Analgesic action of catechin on chronic constriction injury-induced neuropathic pain in Sprague-Dawley rats. Front Pharmacol. (2022) 13:895079. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.895079
5. Simpson, AH, Halliday, J, Hamilton, DF, Smith, M, and Mills, K. Limb lengthening and peripheral nerve function-factors associated with deterioration of conduction. Acta Orthop. (2013) 84:579–84. doi: 10.3109/17453674.2013.859418
6. Orozco, E, Masuda, K, and Shah, SB. A guide to reducing adverse outcomes in rabbit models of sciatic nerve injury. Lab Anim Res. (2021) 37:13. doi: 10.1186/s42826-021-00085-1
7. Asthana, P, Zhang, G, Sheikh, KA, and Him Eddie Ma, C. Heat shock protein is a key therapeutic target for nerve repair in autoimmune peripheral neuropathy and severe peripheral nerve injury. Brain Behav Immun. (2021) 91:48–64. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2020.08.020
8. Au, N, Wu, T, Chen, X, Gao, F, Li, Y, Tam, WY, et al. Genome-wide study reveals novel roles for formin-2 in axon regeneration as a microtubule dynamics regulator and therapeutic target for nerve repair. Neuron. (2023) 111:3970–3987.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2023.11.011
9. Wang, BB, Guo, C, Sun, SQ, Zhang, XN, Li, Z, Li, WJ, et al. Comparison of the nerve regeneration capacity and characteristics between sciatic nerve crush and transection injury models in rats. Biomed Environ Sci. (2023) 36:160–73. doi: 10.3967/bes2023.001
10. DeLeonibus, A, Rezaei, M, Fahradyan, V, Silver, J, Rampazzo, A, and Bassiri, GB. A meta-analysis of functional outcomes in rat sciatic nerve injury models. Microsurgery. (2021) 41:286–95. doi: 10.1002/micr.30713
11. Server, A, Reina, MA, Boezaart, AP, Prats-Galino, A, Esteves Coelho, M, and Sala-Blanch, X. Microanatomical nerve architecture of 6 mammalian species: is trans-species translational anatomic extrapolation valid. Reg Anesth Pain Med. (2018) 43:496–501. doi: 10.1097/AAP.0000000000000772
12. Lee, MG, Choi, SU, Lim, JK, Lee, MJ, Hong, JS, Baek, MO, et al. Ultrasound-guided sciatic nerve block at the midthigh level in a porcine model: a descriptive study. Vet Med Sci. (2020) 6:543–9. doi: 10.1002/vms3.265
13. Strauss, I, Niederhoffer, T, Giannotti, A, Panarese, AM, Bernini, F, Gabisonia, K, et al. Q-PINE: a quick to implant peripheral intraneural electrode. J Neural Eng. (2020) 17:066008. doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/abc52a
14. Tamaki, T, Natsume, T, Katoh, A, Nakajima, N, Saito, K, Fukuzawa, T, et al. Differentiation capacity of porcine skeletal muscle-derived stem cells as intermediate species between mice and humans. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:9862. doi: 10.3390/ijms24129862
15. Lim, TK, Macleod, BA, Ries, CR, and Schwarz, SK. The quaternary lidocaine derivative, QX-314, produces long-lasting local anesthesia in animal models in vivo. Anesthesiology. (2007) 107:305–11. doi: 10.1097/01.anes.0000270758.77314.b4
16. McCarthy, CJ, Ikeda, Y, Skennerton, D, et al. Characterisation of nerve-mediated ATP release from bladder detrusor muscle and its pathological implications. Br J Pharmacol. (2019) 176:4720–30. doi: 10.1111/bph.14840
17. Rafee, MA, Amarpal,, Kinjavdekar, P, Aithal, HP, Wani, SA, and Bhat, IA. Guinea pigs as an animal model for sciatic nerve injury. Neural Regen Res. (2017) 12:452–7. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.202929
18. Dell'Apa, D, Auletta, L, Okonji, S, Cauduro, A, Dondi, M, Opreni, M, et al. Traumatic and iatrogenic sciatic nerve injury in 38 dogs and 10 cats: clinical and electrodiagnostic findings. J Vet Intern Med. (2024) 38:1626–38. doi: 10.1111/jvim.17076
19. Khaled, MM, Ibrahium, AM, Abdelgalil, AI, el-Saied, MA, Yassin, AM, Abouquerin, N, et al. Efficacy of using adipose-derived stem cells and PRP on regeneration of 40 -mm long sciatic nerve defect bridged by polyglycolic-polypropylene mesh in canine model. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2024) 15:212. doi: 10.1186/s13287-024-03796-z
20. Properzi, R, Collivignarelli, F, Paolini, A, Bianchi, A, Vignoli, M, Falerno, I, et al. Evaluation of the iatrogenic sciatic nerve injury following double pelvic osteotomy performed with piezoelectric cutting tool in dogs. Vet Sci. (2022) 9:259. doi: 10.3390/vetsci9060259
21. Dalrymple, AN, Ting, JE, Bose, R, Trevathan, JK, Nieuwoudt, S, Lempka, SF, et al. Stimulation of the dorsal root ganglion using an Injectrode(®). J Neural Eng. (2021) 18:056068. doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/ac2ffb
22. Herzig, R, Wang-Leandro, A, Steffen, F, Matiasek, K, and Beckmann, KM. Imaging and histopathologic features of reversible nerve root and peripheral nerve edema secondary to disc herniation in a cat. J Vet Intern Med. (2021) 35:1566–72. doi: 10.1111/jvim.16112
23. Fadia, NB, Bliley, JM, DiBernardo, GA, Crammond, DJ, Schilling, BK, Sivak, WN, et al. Long-gap peripheral nerve repair through sustained release of a neurotrophic factor in nonhuman primates. Sci Transl Med. (2020) 12:eaav7753. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aav7753
24. Kudo, M, Wupuer, S, Fujiwara, M, Saito, Y, Kubota, S, Inoue, KI, et al. Specific gene expression in unmyelinated dorsal root ganglion neurons in nonhuman primates by intra-nerve injection of AAV 6 vector. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. (2021) 23:11–22. doi: 10.1016/j.omtm.2021.07.009
25. Seong, D, Choi, Y, Choi, IC, Lee, J, Choi, JH, Park, JH, et al. Sticky and strain-gradient artificial epineurium for Sutureless nerve repair in rodents and nonhuman primates. Adv Mater. (2024) 36:e2307810. doi: 10.1002/adma.202307810
26. Hiroi, S, Tsukamoto, Y, Sasaki, F, Miki, N, and Taira, E. Involvement of gicerin, a cell adhesion molecule, in development and regeneration of chick sciatic nerve. FEBS Lett. (2003) 554:311–4. doi: 10.1016/S0014-5793(03)01176-1
27. Nyati, KK, Prasad, KN, Agrawal, V, and Husain, N. Matrix metalloproteinases-2 and -9 in Campylobacter jejuni-induced paralytic neuropathy resembling Guillain-Barré syndrome in chickens. Microb Pathog. (2017) 111:395–401. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2017.09.018
28. Kumamoto, E. Inhibition of fast nerve conduction produced by analgesics and analgesic adjuvants-possible involvement in pain alleviation. Pharmaceuticals. (2020) 13:62. doi: 10.3390/ph13040062
29. Medler, S. Effects of local anesthetics on compound action potentials generated from the frog sciatic nerve. Adv Physiol Educ. (2022) 46:658–66. doi: 10.1152/advan.00095.2022
30. Suzuki, R, Fujita, T, Mizuta, K, and Kumamoto, E. Inhibition by non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs of compound action potentials in frog sciatic nerve fibers. Biomed Pharmacother. (2018) 103:326–35. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.04.041
31. Arena, KA, Zhu, Y, and Kucenas, S. Transforming growth factor-beta signaling modulates perineurial glial bridging following peripheral spinal motor nerve injury in zebrafish. Glia. (2022) 70:1826–49. doi: 10.1002/glia.24220
32. Walker, LJ, Guevara, C, Kawakami, K, and Granato, M. Target-selective vertebrate motor axon regeneration depends on interaction with glial cells at a peripheral nerve plexus. PLoS Biol. (2023) 21:e3002223. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3002223
33. Chisholm, AD. Cytoskeletal dynamics in Caenorhabditis elegans axon regeneration. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. (2013) 29:271–97. doi: 10.1146/annurev-cellbio-101512-122311
34. Noblett, N, Wu, Z, Ding, ZH, Park, S, Roenspies, T, Flibotte, S, et al. DIP-2 suppresses ectopic neurite sprouting and axonal regeneration in mature neurons. J Cell Biol. (2019) 218:125–33. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201804207
35. Nichols, CM, Myckatyn, TM, Rickman, SR, Fox, IK, Hadlock, T, and Mackinnon, SE. Choosing the correct functional assay: a comprehensive assessment of functional tests in the rat. Behav Brain Res. (2005) 163:143–58. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2005.05.003
36. Kaplan, HM, Mishra, P, and Kohn, J. The overwhelming use of rat models in nerve regeneration research may compromise designs of nerve guidance conduits for humans. J Mater Sci Mater Med. (2015) 26:226. doi: 10.1007/s10856-015-5558-4
37. Merolli, A, Li, M, Voronin, G, and Bright, L. A sciatic nerve gap-injury model in the rabbit. J Mater Sci Mater Med. (2022) 33:14. doi: 10.1007/s10856-022-06642-x
38. Jager, SB, Ronchi, G, Vaegter, CB, and Geuna, S. The mouse median nerve experimental model in regenerative research. Biomed Res Int. (2014) 2014:701682:1–6. doi: 10.1155/2014/701682
39. Contreras, E, Traserra, S, Bolívar, S, Forés, J, Jose-Cunilleras, E, García, F, et al. Repair of Long nerve defects with a new Decellularized nerve graft in rats and in sheep. Cells. (2022) 11:4074. doi: 10.3390/cells11244074
40. Vela, FJ, Martínez-Chacón, G, Ballestín, A, Campos, JL, Sánchez-Margallo, FM, and Abellán, E. Animal models used to study direct peripheral nerve repair: a systematic review. Neural Regen Res. (2020) 15:491–502. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.266068
41. Yao, Y, Cui, Y, Zhao, Y, Xiao, Z, Li, X, Han, S, et al. Efect of longitudinally oriented collagen conduit combined with nerve growth factor on nerve regeneration after dog sciatic nerve injury. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. (2018) 106:2131–9. doi: 10.1002/jbm.b.34020
42. Su, CF, Chang, LH, Kao, CY, Lee, DC, Cho, KH, Kuo, LW, et al. Application of amniotic fluid stem cells in repairing sciatic nerve injury in minipigs. Brain Res. (2018) 1678:397–406. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2017.11.010
43. Bennett, GJ, and Xie, YK. A peripheral mononeuropathy in rat that produces disorders of pain sensation like those seen in man. Pain. (1988) 33:87–107. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(88)90209-6
44. Wen, J, Jones, M, Tanaka, M, Selvaraj, P, Symes, AJ, Cox, B, et al. WWL70 protects against chronic constriction injury-induced neuropathic pain in mice by cannabinoid receptor-independent mechanisms. J Neuroinflammation. (2018) 15:9. doi: 10.1186/s12974-017-1045-9
45. Challa, SR. Surgical animal models of neuropathic pain: pros and cons. Int J Neurosci. (2015) 125:170–4. doi: 10.3109/00207454.2014.922559
46. Latremoliere, A, and Woolf, CJ. Central sensitization: a generator of pain hypersensitivity by central neural plasticity. J Pain. (2009) 10:895–926. doi: 10.1016/j.jpain.2009.06.012
47. Chao, D, Zhang, Z, Mecca, CM, Hogan, QH, and Pan, B. Analgesic dorsal root ganglionic field stimulation blocks conduction of afferent impulse trains selectively in nociceptive sensory afferents. Pain. (2020) 161:2872–86. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000001982
48. Chen, QY, Tan, CY, Wang, Y, Ma, KT, Li, L, and Si, JQ. Mechanism of persistent hyperalgesia in neuropathic pain caused by chronic constriction injury. Neural Regen Res. (2019) 14:1091–8. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.250631
49. Huang, L, and Wang, L. Upregulation of miR-183 represses neuropathic pain through inhibiton of MAP3K4 in CCI rat models. J Cell Physiol. (2020) 235:3815–22. doi: 10.1002/jcp.29276
50. Liu, C, Shan, F, Gao, F, Ji, Q, Chen, Y, Wang, C, et al. DAP12 deletion causes age-related motor function impairment but promotes functional recovery after sciatic nerve crush injury. Exp Neurol. (2023) 360:114296. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2022.114296
51. Ohmichi, Y, Ohmichi, M, and Naito, M. The superoxide scavenger tempol attenuates DNA oxidative injury and spontaneous pain-like behavior in chronic post-cast pain model rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2020) 533:745–50. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.09.044
52. Suárez-Pereira, I, López-Martín, C, Camarena-Delgado, C, Llorca-Torralba, M, González-Saiz, F, Ruiz, R, et al. Nerve injury triggers time-dependent activation of the locus Coeruleus, influencing spontaneous pain-like behavior in rats. Anesthesiology. (2024) 141:131–50. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000005006
53. Niikura, K, Takahashi, Y, Iino, M, Funatsu, Y, and Matsuda, R. An automated method by which effects of compounds on locomotor activity and spontaneous neuropathic pain-specific movements can be simultaneously evaluated in rats with chronic-constriction nerve injury. Eur J Pharm Sci. (2017) 96:551–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2016.10.037
54. He, N, Qu, YJ, Li, DY, and Yue, SW. RIP3 inhibition ameliorates chronic constriction injury-induced neuropathic pain by suppressing JNK signaling. Aging. (2021) 13:24417–31. doi: 10.18632/aging.203691
55. Hua, T, Kong, E, Zhang, H, Lu, J, Huang, K, Ding, R, et al. PRMT6 deficiency or inhibition alleviates neuropathic pain by decreasing glycolysis and inflammation in microglia. Brain Behav Immun. (2024) 118:101–14. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2024.02.027
56. Zhang, D, Jing, B, Chen, ZN, Li, X, Shi, HM, Zheng, YC, et al. Ferulic acid alleviates sciatica by inhibiting neuroinflammation and promoting nerve repair via the TLR4/NF-κB pathway. CNS Neurosci Ther. (2023) 29:1000–11. doi: 10.1111/cns.14060
57. Wang, C, Chen, P, Lin, D, Chen, Y, Lv, B, Zheng, K, et al. Effects of varying degrees of ligation in a neuropathic pain model induced by chronic constriction injury. Life Sci. (2021) 276:119441. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119441
58. Seltzer, Z, Dubner, R, and Shir, Y. A novel behavioral model of neuropathic pain disorders produced in rats by partial sciatic nerve injury. Pain. (1990) 43:205–18. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(90)91074-S
59. Korah, HE, Cheng, K, Washington, SM, Flowers, ME, Stratton, HJ, Patwardhan, A, et al. Partial sciatic nerve ligation: a mouse model of chronic neuropathic pain to study the Antinociceptive effect of novel therapies. J Vis Exp. (2022) 188:64555. doi: 10.3791/64555
60. Isami, K, Imai, S, Sukeishi, A, Nagayasu, K, Shirakawa, H, Nakagawa, T, et al. The impact of mouse strain-specific spatial and temporal immune responses on the progression of neuropathic pain. Brain Behav Immun. (2018) 74:121–32. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2018.08.013
61. Liu, T, Wang, Y, Lu, L, and Liu, Y. SPIONs mediated magnetic actuation promotes nerve regeneration by inducing and maintaining repair-supportive phenotypes in Schwann cells. J Nanobiotechnol. (2022) 20:159. doi: 10.1186/s12951-022-01337-5
62. Guo, F, Lin, SD, Du, Y, Hu, TT, Wang, Y, Chen, Z, et al. Secondary somatosensory cortex glutamatergic innervation of the thalamus facilitates pain. Pain. (2024) 165:1142–53. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000003117
63. Decosterd, I, and Woolf, CJ. Spared nerve injury: an animal model of persistent peripheral neuropathic pain. Pain. (2000) 87:149–58. doi: 10.1016/S0304-3959(00)00276-1
64. Mitsi, V, Terzi, D, Purushothaman, I, Manouras, L, Gaspari, S, Neve, RL, et al. RGS9-2--controlled adaptations in the striatum determine the onset of action and efficacy of antidepressants in neuropathic pain states. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2015) 112:E5088–97. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1504283112
65. Guida, F, Gregorio, DD, Palazzo, E, Ricciardi, F, Boccella, S, Belardo, C, et al. Behavioral, biochemical and electrophysiological changes in spared nerve injury model of neuropathic pain. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21:3396. doi: 10.3390/ijms21093396
66. D'Aniello, A, Luongo, L, Romano, R, Iannotta, M, Marabese, I, Boccella, S, et al. D-aspartic acid ameliorates painful and neuropsychiatric changes and reduces β-amyloid Aβ(1-42) peptide in a long lasting model of neuropathic pain. Neurosci Lett. (2017) 651:151–8. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2017.04.041
67. Tran, EL, and Crawford, LK. Revisiting PNS plasticity: how uninjured sensory afferents promote neuropathic pain. Front Cell Neurosci. (2020) 14:612982. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2020.612982
68. Pertin, M, Gosselin, RD, and Decosterd, I. The spared nerve injury model of neuropathic pain. Methods Mol Biol. (2012) 851:205–12. doi: 10.1007/978-1-61779-561-9_15
69. Sun, W, Sun, C, Lin, H, Zhao, H, Wang, J, Ma, H, et al. The effect of collagen-binding NGF-beta on the promotion of sciatic nerve regeneration in a rat sciatic nerve crush injury model. Biomaterials. (2009) 30:4649–56. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2009.05.037
70. Liu, F, Zhang, L, Su, S, Fang, Y, Yin, XS, Cui, H, et al. Neuronal C-reactive protein/FcγRI positive feedback proinflammatory signaling contributes to nerve injury induced neuropathic pain. Adv Sci. (2023) 10:e2205397. doi: 10.1002/advs.202205397
71. Pannunzio, B, Amo-Aparicio, J, Julián, C, López-Vales, R, Peluffo, H, and Lago, N. CD200R1 contributes to successful functional reinnervation after a sciatic nerve injury. Cells. (2022) 11:1786. doi: 10.3390/cells11111786
72. Wang, X, Yang, C, Wang, X, Miao, J, Chen, W, Zhou, Y, et al. Driving axon regeneration by orchestrating neuronal and non-neuronal innate immune responses via the IFNγ-cGAS-STING axis. Neuron. (2023) 111:236–255.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2022.10.028
73. Caillaud, M, Richard, L, Vallat, JM, Desmoulière, A, and Billet, F. Peripheral nerve regeneration and intraneural revascularization. Neural Regen Res. (2019) 14:24–33. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.243699
74. Siwei, Q, Ma, N, Wang, W, Chen, S, Wu, Q, Li, Y, et al. Construction and effect evaluation of different sciatic nerve injury models in rats. Transl Neurosci. (2022) 13:38–51. doi: 10.1515/tnsci-2022-0214
75. Mirzakhani, N, Farshid, AA, Tamaddonfard, E, Imani, M, Erfanparast, A, and Noroozinia, F. Carnosine improves functional recovery and structural regeneration after sciatic nerve crush injury in rats. Life Sci. (2018) 215:22–30. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2018.10.043
76. Serger, E, Luengo-Gutierrez, L, Chadwick, JS, Kong, G, Zhou, L, Crawford, G, et al. The gut metabolite indole-3 propionate promotes nerve regeneration and repair. Nature. (2022) 607:585–92. doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-04884-x
77. Yang, C, Wang, X, Wang, J, Wang, X, Chen, W, Lu, N, et al. Rewiring neuronal Glycerolipid metabolism determines the extent of axon regeneration. Neuron. (2020) 105:276–292.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2019.10.009
78. De Virgiliis, F, Mueller, F, Palmisano, I, Chadwick, JS, Luengo-Gutierrez, L, Giarrizzo, A, et al. The circadian clock time tunes axonal regeneration. Cell Metab. (2023) 35:2153–2164.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2023.10.012
79. Wall, PD, Devor, M, Inbal, R, Scadding, JW, Schonfeld, D, Seltzer, Z, et al. Autotomy following peripheral nerve lesions: experimental anaesthesia dolorosa. Pain. (1979) 7:103–13. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(79)90002-2
80. Geuna, S, Raimondo, S, Ronchi, G, di Scipio, F, Tos, P, Czaja, K, et al. Chapter 3: histology of the peripheral nerve and changes occurring during nerve regeneration. Int Rev Neurobiol. (2009) 87:27–46. doi: 10.1016/S0074-7742(09)87003-7
81. Kumar, A, Kaur, H, and Singh, A. Neuropathic pain models caused by damage to central or peripheral nervous system. Pharmacol Rep. (2018) 70:206–16. doi: 10.1016/j.pharep.2017.09.009
82. Woolf, CJ, and Ma, Q. Nociceptors—noxious stimulus detectors. Neuron. (2007) 55:353–64. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2007.07.016
83. Gu, J, Hu, W, Deng, A, Zhao, Q, Lu, S, and Gu, X. Surgical repair of a 30 mm long human median nerve defect in the distal forearm by implantation of a chitosan-PGA nerve guidance conduit. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. (2012) 6:163–8. doi: 10.1002/term.407
84. Wu, J, Zhang, Y, Zhang, X, Lin, Z, and Li, G. Regenerative peripheral nerve interfaces effectively prevent neuroma formation after sciatic nerve transection in rats. Front Mol Neurosci. (2022) 15:938930. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2022.938930
85. Gudasheva, TA, Povarnina, PY, Tarasiuk, AV, and Seredenin, SB. Low-molecular mimetics of nerve growth factor and brain-derived neurotrophic factor: design and pharmacological properties. Med Res Rev. (2021) 41:2746–74. doi: 10.1002/med.21721
86. Li, R, Wu, J, Lin, Z, Nangle, MR, Li, Y, Cai, P, et al. Single injection of a novel nerve growth factor coacervate improves structural and functional regeneration after sciatic nerve injury in adult rats. Exp Neurol. (2017) 288:1–10. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2016.10.015
87. Zhang, W, Zhang, L, Liu, J, Zhang, L, Zhang, J, and Tang, P. Repairing sciatic nerve injury with an EPO-loaded nerve conduit and sandwiched-in strategy of transplanting mesenchymal stem cells. Biomaterials. (2017) 142:90–100. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2017.06.024
88. Gavioli, E, Mantelli, F, Cesta, MC, Sacchetti, M, and Allegretti, M. The history of nerve growth factor: from molecule to drug. Biomol Ther. (2024) 14:635. doi: 10.3390/biom14060635
89. Gan, L, Qian, M, Shi, K, Chen, G, Gu, Y, du, W, et al. Restorative effect and mechanism of mecobalamin on sciatic nerve crush injury in mice. Neural Regen Res. (2014) 9:1979–84. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.145379
90. Gu, X, Ding, F, and Williams, DF. Neural tissue engineering options for peripheral nerve regeneration. Biomaterials. (2014) 35:6143–56. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2014.04.064
91. Apfel, SC. Nerve growth factor for the treatment of diabetic neuropathy: what went wrong, what went right, and what does the future hold. Int Rev Neurobiol. (2002) 50:393–413. doi: 10.1016/S0074-7742(02)50083-0
92. Chen, O, Jiang, C, Berta, T, Powell Gray, B, Furutani, K, Sullenger, BA, et al. MicroRNA let-7b enhances spinal cord nociceptive synaptic transmission and induces acute and persistent pain through neuronal and microglial signaling. Pain. (2024) 165:1824–39. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000003206
93. Chen, L, Song, X, Yao, Z, Zhou, C, Yang, J, Yang, Q, et al. Gelatin nanofiber-reinforced decellularized amniotic membrane promotes axon regeneration and functional recovery in the surgical treatment of peripheral nerve injury. Biomaterials. (2023) 300:122207. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2023.122207
94. Zhang, J, Zhang, Y, Chen, L, Rao, Z, and Sun, Y. Ulinastatin promotes regeneration of peripheral nerves after sciatic nerve injury by targeting let-7 microRNAs and enhancing NGF expression. Drug Des Devel Ther. (2020) 14:2695–705. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S255158
95. Sang, Q, Sun, D, Chen, Z, and Zhao, W. NGF and PI3K/Akt signaling participate in the ventral motor neuronal protection of curcumin in sciatic nerve injury rat models. Biomed Pharmacother. (2018) 103:1146–53. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.04.116
96. Bazzari, AH, and Bazzari, FH. BDNF therapeutic mechanisms in neuropsychiatric disorders. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:8417. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158417
97. Brigadski, T, and Leßmann, V. The physiology of regulated BDNF release. Cell Tissue Res. (2020) 382:15–45. doi: 10.1007/s00441-020-03253-2
98. Merighi, A. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor, nociception, and pain. Biomol Ther. (2024) 14:539. doi: 10.3390/biom14050539
99. Wang, CS, Kavalali, ET, and Monteggia, LM. BDNF signaling in context: from synaptic regulation to psychiatric disorders. Cell. (2022) 185:62–76. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.12.003
100. Alrashdan, MS, Sung, MA, Kwon, YK, Chung, HJ, Kim, SJ, and Lee, JH. Effects of combining electrical stimulation with BDNF gene transfer on the regeneration of crushed rat sciatic nerve. Acta Neurochir. (2011) 153:2021–9. doi: 10.1007/s00701-011-1054-x
101. Lopes, C, Gonçalves, NP, Gomes, CP, Saraiva, MJ, and Pêgo, AP. BDNF gene delivery mediated by neuron-targeted nanoparticles is neuroprotective in peripheral nerve injury. Biomaterials. (2017) 121:83–96. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2016.12.025
102. Sun, H, Yang, T, Li, Q, Zhu, Z, Wang, L, Bai, G, et al. Dexamethasone and vitamin B(12) synergistically promote peripheral nerve regeneration in rats by upregulating the expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Arch Med Sci. (2012) 8:924–30. doi: 10.5114/aoms.2012.31623
103. Ehmedah, A, Nedeljkovic, P, Dacic, S, Repac, J, Draskovic Pavlovic, B, Vucevic, D, et al. Vitamin B complex treatment attenuates local inflammation after peripheral nerve injury. Molecules. (2019) 24:4615. doi: 10.3390/molecules24244615
104. Ehmedah, A, Nedeljkovic, P, Dacic, S, Repac, J, Draskovic-Pavlovic, B, Vučević, D, et al. Effect of vitamin B complex treatment on macrophages to Schwann cells association during Neuroinflammation after peripheral nerve injury. Molecules. (2020) 25:5426. doi: 10.3390/molecules25225426
105. Suzuki, K, Tanaka, H, Ebara, M, Uto, K, Matsuoka, H, Nishimoto, S, et al. Electrospun nanofiber sheets incorporating methylcobalamin promote nerve regeneration and functional recovery in a rat sciatic nerve crush injury model. Acta Biomater. (2017) 53:250–9. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2017.02.004
106. Zhang, M, Han, W, Hu, S, and Xu, H. Methylcobalamin: a potential vitamin of pain killer. Neural Plast. (2013) 2013:424651:1–6. doi: 10.1155/2013/424651
107. Altun, I, and Kurutaş, EB. Vitamin B complex and vitamin B12 levels after peripheral nerve injury. Neural Regen Res. (2016) 11:842–5. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.177150
108. Buesing, S. Vitamin B12 as a treatment for pain. Pain Physician. (2019) 22:E45–52. doi: 10.36076/ppj/2019.22.e45
109. Düzenli, N, Ülker, S, Şengül, G, Kayhan, B, and Önal, A. Effects of cyanocobalamin and its combination with morphine on neuropathic rats and the relationship between these effects and thrombospondin-4 expression. Korean J Pain. (2022) 35:66–77. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2022.35.1.66
110. Julian, T, Syeed, R, Glascow, N, Angelopoulou, E, and Zis, P. B12 as a treatment for peripheral neuropathic pain: a systematic review. Nutrients. (2020) 12:2221. doi: 10.3390/nu12082221
111. Qian, Y, Han, Q, Zhao, X, Song, J, Cheng, Y, Fang, Z, et al. 3D melatonin nerve scaffold reduces oxidative stress and inflammation and increases autophagy in peripheral nerve regeneration. J Pineal Res. (2018) 65:e12516. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12516
112. Zajączkowska, R, Kocot-Kępska, M, Leppert, W, Wrzosek, A, Mika, J, and Wordliczek, J. Mechanisms of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. Int J Mol Sci. (2019) 20:1451. doi: 10.3390/ijms20061451
113. Siniscalco, D, Fuccio, C, Giordano, C, Ferraraccio, F, Palazzo, E, Luongo, L, et al. Role of reactive oxygen species and spinal cord apoptotic genes in the development of neuropathic pain. Pharmacol Res. (2007) 55:158–66. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2006.11.009
114. Guedes, RP, Araújo, AS, Janner, D, Belló-Klein, A, Ribeiro, MF, and Partata, WA. Increase in reactive oxygen species and activation of Akt signaling pathway in neuropathic pain. Cell Mol Neurobiol. (2008) 28:1049–56. doi: 10.1007/s10571-008-9279-9
115. Park, ES, Gao, X, Chung, JM, and Chung, K. Levels of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species increase in rat neuropathic spinal dorsal horn neurons. Neurosci Lett. (2006) 391:108–11. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2005.08.055
116. Kim, D, You, B, Jo, EK, Han, SK, Simon, MI, and Lee, SJ. NADPH oxidase 2-derived reactive oxygen species in spinal cord microglia contribute to peripheral nerve injury-induced neuropathic pain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. (2010) 107:14851–6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1009926107
117. Lu, R, Kallenborn-Gerhardt, W, Geisslinger, G, and Schmidtko, A. Additive antinociceptive effects of a combination of vitamin C and vitamin E after peripheral nerve injury. PLoS One. (2011) 6:e29240. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0029240
118. Yowtak, J, Lee, KY, Kim, HY, Wang, J, Kim, HK, Chung, K, et al. Reactive oxygen species contribute to neuropathic pain by reducing spinal GABA release. Pain. (2011) 152:844–52. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2010.12.034
119. Mallet, ML, Hadjivassiliou, M, Sarrigiannis, PG, and Zis, P. The role of oxidative stress in peripheral neuropathy. J Mol Neurosci. (2020) 70:1009–17. doi: 10.1007/s12031-020-01495-x
120. Aljuhr, SA, Abdelaziz, G, Essa, BM, Zaghary, WA, and Sakr, TM. Hepatoprotective, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory potentials of Vit-E/C@SeNPs in rats: synthesis, characterization, biochemical, radio-biodistribution, molecular and histopathological studies. Bioorg Chem. (2021) 117:105412. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105412
121. Caritá, AC, Fonseca-Santos, B, Shultz, JD, Michniak-Kohn, B, Chorilli, M, and Leonardi, GR. Vitamin C: one compound, several uses. Advances for delivery, efficiency and stability. Nanomedicine. (2020) 24:102117. doi: 10.1016/j.nano.2019.102117
122. Mussa, A, Mohd Idris, RA, Ahmed, N, Ahmad, S, Murtadha, AH, Tengku Din, TADAA, et al. High-dose vitamin C for cancer therapy. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). (2022) 15:711. doi: 10.3390/ph15060711
123. Samuels, N, and Ben-Arye, E. Integrative approaches to chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. Curr Oncol Rep. (2020) 22:23. doi: 10.1007/s11912-020-0891-2
124. Morani, AS, and Bodhankar, SL. Early co-administration of vitamin E acetate and methylcobalamin improves thermal hyperalgesia and motor nerve conduction velocity following sciatic nerve crush injury in rats. Pharmacol Rep. (2010) 62:405–9. doi: 10.1016/S1734-1140(10)70281-4
125. Jiang, Q, Yin, X, Lill, MA, Danielson, ML, Freiser, H, and Huang, J. Long-chain carboxychromanols, metabolites of vitamin E, are potent inhibitors of cyclooxygenases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2008) 105:20464–9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0810962106
126. Tamaddonfard, E, Farshid, AA, Maroufi, S, Kazemi-Shojaei, S, Erfanparast, A, Asri-Rezaei, S, et al. Effects of safranal, a constituent of saffron, and vitamin E on nerve functions and histopathology following crush injury of sciatic nerve in rats. Phytomedicine. (2014) 21:717–23. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2013.10.031
127. Meymandi, MS, Sepehri, G, Abdolsamadi, M, Shaabani, M, Heravi, G, Yazdanpanah, O, et al. The effects of co-administration of pregabalin and vitamin E on neuropathic pain induced by partial sciatic nerve ligation in male rats. Inflammopharmacology. (2017) 25:237–46. doi: 10.1007/s10787-017-0325-4
128. Li, R, Shen, L, Yu, X, Ma, C, and Huang, Y. Vitamin C enhances the analgesic effect of gabapentin on rats with neuropathic pain. Life Sci. (2016) 157:25–31. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2016.05.035
129. Riffel, A, de Souza, JA, Santos M do, C, Horst, A, Scheid, T, Kolberg, C, et al. Systemic administration of vitamins C and E attenuates nociception induced by chronic constriction injury of the sciatic nerve in rats. Brain Res Bull. (2016) 121:169–77. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2016.02.004
130. Liu, S, Li, H, Ou Yang, J, Peng, H, Wu, K, Liu, Y, et al. Enhanced rat sciatic nerve regeneration through silicon tubes filled with pyrroloquinoline quinone. Microsurgery. (2005) 25:329–37. doi: 10.1002/micr.20126
131. Azizi, A, Azizi, S, Heshmatian, B, and Amini, K. Improvement of functional recovery of transected peripheral nerve by means of chitosan grafts filled with vitamin E, pyrroloquinoline quinone and their combination. Int J Surg. (2014) 12:76–82. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2013.10.002
132. Tesoriere, L, D'Arpa, D, Conti, S, Giaccone, V, Pintaudi, AM, and Livrea, MA. Melatonin protects human red blood cells from oxidative hemolysis: new insights into the radical-scavenging activity. J Pineal Res. (1999) 27:95–105. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-079X.1999.tb00602.x
133. Celen, MC, Akkoca, A, Tuncer, S, Dalkilic, N, and Ilhan, B. Protective vs. therapeutic effects of mitochondria-targeted antioxidant MitoTEMPO on rat sciatic nerve crush injury: a comprehensive electrophysiological analysis. Biomedicines. (2023) 11:3306. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11123306
134. Delibaş, B, Kaplan, AA, Marangoz, AH, Eltahir, MI, Altun, G, and Kaplan, S. The effect of dietary sesame oil and ginger oil as antioxidants in the adult rat dorsal root ganglia after peripheral nerve crush injury. Int J Neurosci. (2024) 134:714–24. doi: 10.1080/00207454.2022.2145475
135. Limcharoen, T, Dasuni Wasana, PW, Hasriadi,, Muangnoi, C, Vajragupta, O, Rojsitthisak, P, et al. Curcumin diglutaric acid, a prodrug of curcumin reduces pain hypersensitivity in chronic constriction injury of sciatic nerve induced-neuropathy in mice. Pharmaceuticals. (2020) 13:212. doi: 10.3390/ph13090212
136. Su, X, Jing, X, Jiang, W, Li, M, Liu, K, Teng, M, et al. Curcumin-containing polyphosphazene nanodrug for anti-inflammation and nerve regeneration to improve functional recovery after spinal cord injury. Int J Pharm. (2023) 642:123197. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2023.123197
137. Au, N, Chand, R, Kumar, G, Asthana, P, Tam, WY, Tang, KM, et al. A small molecule M1 promotes optic nerve regeneration to restore target-specific neural activity and visual function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2022) 119:e2121273119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2121273119
138. Cui, M, Liang, J, Xu, D, Zhao, L, Zhang, X, Zhang, L, et al. NLRP3 inflammasome is involved in nerve recovery after sciatic nerve injury. Int Immunopharmacol. (2020) 84:106492. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106492
139. Molnár, K, Nógrádi, B, Kristóf, R, Mészáros, Á, Pajer, K, Siklós, L, et al. Motoneuronal inflammasome activation triggers excessive neuroinflammation and impedes regeneration after sciatic nerve injury. J Neuroinflammation. (2022) 19:68. doi: 10.1186/s12974-022-02427-9
140. Ma, Y, Liu, W, Liang, L, Ye, J, Huang, C, Zhuang, T, et al. Synergistic antinociceptive effects of indomethacin-pregabalin and meloxicam-pregabalin in paclitaxel-induced neuropathic pain. Biomedicines. (2022) 10:1413. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10061413
141. Guo, Q, Jin, Y, Chen, X, Ye, X, Shen, X, Lin, M, et al. NF-κB in biology and targeted therapy: new insights and translational implications. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2024) 9:53. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-01757-9
142. Bhakar, AL, Tannis, LL, Zeindler, C, Russo, MP, Jobin, C, Park, DS, et al. Constitutive nuclear factor-kappa B activity is required for central neuron survival. J Neurosci. (2002) 22:8466–75. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-19-08466.2002
143. Purcell, NH, Tang, G, Yu, C, Mercurio, F, DiDonato, JA, and Lin, A. Activation of NF-kappa B is required for hypertrophic growth of primary rat neonatal ventricular cardiomyocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2001) 98:6668–73. doi: 10.1073/pnas.111155798
144. Meunier, A, Latrémolière, A, Dominguez, E, Mauborgne, A, Philippe, S, Hamon, M, et al. Lentiviral-mediated targeted NF-kappaB blockade in dorsal spinal cord glia attenuates sciatic nerve injury-induced neuropathic pain in the rat. Mol Ther. (2007) 15:687–97. doi: 10.1038/sj.mt.6300107
145. Boarescu, I, Pop, RM, Boarescu, PM, Bocșan, I, Gheban, D, Râjnoveanu, RM, et al. Anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects of curcumin nanoparticles associated with diclofenac sodium in experimental acute inflammation. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:11737. doi: 10.3390/ijms231911737
146. Zauska, L, Bova, S, Benova, E, Bednarcik, J, Balaz, M, Zelenak, V, et al. Thermosensitive drug delivery system SBA-15-PEI for controlled release of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug diclofenac sodium salt: a comparative study. Materials. (2021) 14:1880. doi: 10.3390/ma14081880
147. Barcelos, RP, Bresciani, G, Cuevas, MJ, Martínez-Flórez, S, Soares, F, and González-Gallego, J. Diclofenac pretreatment modulates exercise-induced inflammation in skeletal muscle of rats through the TLR4/NF-κB pathway. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. (2017) 42:757–64. doi: 10.1139/apnm-2016-0593
148. Zhang, Y, Yang, D, Shuai, B, Ding, H, Yang, J, Wang, J, et al. Diclofenac sodium nanomedicine results in pain-relief and differential expression of the RNA transcriptome in the spinal cord of SNI rats. Int J Pharm. (2024) 659:124276. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2024.124276
149. Owoyele, BV, Bakare, AO, Olaseinde, OF, Ochu, MJ, Yusuff, AM, Ekebafe, F, et al. Synergistic interaction between acetaminophen and L-carnosine improved neuropathic pain via NF-κB pathway and antioxidant properties in chronic constriction injury model. Korean J Pain. (2022) 35:271–9. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2022.35.3.271
150. Stevens, AM, Liu, L, Bertovich, D, Janjic, JM, and Pollock, JA. Differential expression of Neuroinflammatory mRNAs in the rat sciatic nerve following chronic constriction injury and pain-relieving Nanoemulsion NSAID delivery to infiltrating macrophages. Int J Mol Sci. (2019) 20:5269. doi: 10.3390/ijms20215269
151. Stevens, AM, Saleem, M, Deal, B, Janjic, J, and Pollock, JA. Targeted cyclooxygenase-2 inhibiting nanomedicine results in pain-relief and differential expression of the RNA transcriptome in the dorsal root ganglia of injured male rats. Mol Pain. (2020) 16:1744806920943309. doi: 10.1177/1744806920943309
152. de Souza, LG, Marcolino, AM, Kuriki, HU, Gonçalves, E, Fonseca, M, and Barbosa, RI. Comparative effect of photobiomodulation associated with dexamethasone after sciatic nerve injury model. Lasers Med Sci. (2018) 33:1341–9. doi: 10.1007/s10103-018-2494-9
153. Çömez, MS, Borazan, Y, Özgür, T, İşler, CT, Cellat, M, Güvenç, M, et al. Effects of dexamethasone on bupivacaine-induced peripheral nerve injection injury in the rat sciatic model. J Investig Surg. (2021) 34:1339–47. doi: 10.1080/08941939.2020.1805053
154. Bolandghamat, S, and Behnam-Rassouli, M. Recent findings on the effects of pharmacological agents on the nerve regeneration after peripheral nerve injury. Curr Neuropharmacol. (2020) 18:1154–63. doi: 10.2174/1570159X18666200507084024
155. Uzun, T, Toptas, O, Saylan, A, Carver, H, and Turkoglu, SA. Evaluation and comparison of the effects of artesunate, dexamethasone, and tacrolimus on sciatic nerve regeneration. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. (2019) 77:1092.e1–1092.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2018.12.019
156. Lin, X, and Zhang, N. Berberine: pathways to protect neurons. Phytother Res. (2018) 32:1501–10. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6107
157. Chen, S, He, B, Zhou, G, Xu, Y, Wu, L, Xie, Y, et al. Berberine enhances L1 expression and axonal remyelination in rats after brachial plexus root avulsion. Brain Behav. (2020) 10:e01792. doi: 10.1002/brb3.1792
158. Sun, J, Zeng, Q, Wu, Z, Huang, L, Sun, T, Ling, C, et al. Berberine inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation and proinflammatory macrophage M1 polarization to accelerate peripheral nerve regeneration. Neurotherapeutics. (2024) 21:e00347. doi: 10.1016/j.neurot.2024.e00347
159. Tian, E, Sharma, G, and Dai, C. Neuroprotective properties of Berberine: molecular mechanisms and clinical implications. Antioxidants. (2023) 12:1883. doi: 10.3390/antiox12101883
160. Ferrigno, B, Bordett, R, Duraisamy, N, Moskow, J, Arul, MR, Rudraiah, S, et al. Bioactive polymeric materials and electrical stimulation strategies for musculoskeletal tissue repair and regeneration. Bioact Mater. (2020) 5:468–85. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2020.03.010
161. Moskow, J, Ferrigno, B, Mistry, N, Jaiswal, D, Bulsara, K, Rudraiah, S, et al. Review: bioengineering approach for the repair and regeneration of peripheral nerve. Bioact Mater. (2019) 4:107–13. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2018.09.001
162. Belanger, K, Dinis, TM, Taourirt, S, Vidal, G, Kaplan, DL, and Egles, C. Recent strategies in tissue engineering for guided peripheral nerve regeneration. Macromol Biosci. (2016) 16:472–81. doi: 10.1002/mabi.201500367
163. Manoukian, OS, Baker, JT, Rudraiah, S, Arul, MR, Vella, AT, Domb, AJ, et al. Functional polymeric nerve guidance conduits and drug delivery strategies for peripheral nerve repair and regeneration. J Control Release. (2020) 317:78–95. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2019.11.021
164. Hsu, SH, Chan, SH, Chiang, CM, Chen, CC, and Jiang, CF. Peripheral nerve regeneration using a microporous polylactic acid asymmetric conduit in a rabbit long-gap sciatic nerve transection model. Biomaterials. (2011) 32:3764–75. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2011.01.065
165. Jiao, H, Yao, J, Yang, Y, Chen, X, Lin, W, Li, Y, et al. Chitosan/polyglycolic acid nerve grafts for axon regeneration from prolonged axotomized neurons to chronically denervated segments. Biomaterials. (2009) 30:5004–18. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2009.05.059
166. Pinto, M, Silva, V, Barreiro, S, Silva, R, Remião, F, Borges, F, et al. Brain drug delivery and neurodegenerative diseases: polymeric PLGA-based nanoparticles as a forefront platform. Ageing Res Rev. (2022) 79:101658. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2022.101658
167. Yao, Z, Yuan, W, Xu, J, Tong, W, Mi, J, Ho, PC, et al. Magnesium-encapsulated injectable hydrogel and 3D-engineered Polycaprolactone conduit facilitate peripheral nerve regeneration. Adv Sci. (2022) 9:e2202102. doi: 10.1002/advs.202202102
168. Guan, W, Gao, H, Sun, S, Zheng, T, Wu, L, Wang, X, et al. Multi-scale, multi-level anisotropic silk fibroin/metformin scaffolds for repair of peripheral nerve injury. Int J Biol Macromol. (2023) 246:125518. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.125518
169. Ma, F, Xu, F, Li, R, Zheng, Y, Wang, F, wei, N, et al. Sustained delivery of glial cell-derived neurotrophic factors in collagen conduits for facial nerve regeneration. Acta Biomater. (2018) 69:146–55. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2018.01.001
170. Bernard, M, McOnie, R, Tomlinson, JE, Blum, E, Prest, TA, Sledziona, M, et al. Peripheral nerve matrix hydrogel promotes recovery after nerve transection and repair. Plast Reconstr Surg. (2023) 152:458–67. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000010261
171. Chen, QQ, Liu, QY, Wang, P, Qian, TM, Wang, XH, Yi, S, et al. Potential application of let-7a antagomir in injured peripheral nerve regeneration. Neural Regen Res. (2023) 18:1584–90. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.357914
172. Yang, J, Hsu, CC, Cao, TT, Ye, H, Chen, J, and Li, YQ. A hyaluronic acid granular hydrogel nerve guidance conduit promotes regeneration and functional recovery of injured sciatic nerves in rats. Neural Regen Res. (2023) 18:657–63. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.350212
173. Du, J, Liu, JH, Yao, SL, Mao, HQ, Peng, J, Sun, XJ, et al. Prompt peripheral nerve regeneration induced by a hierarchically aligned fibrin nanofiber hydrogel. Acta Biomater. (2017) 55:296–309. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2017.04.010
174. Shan, Y, Xu, L, Cui, X, Wang, E, Jiang, F, Li, J, et al. A responsive cascade drug delivery scaffold adapted to the therapeutic time window for peripheral nerve injury repair. Mater Horiz. (2024) 11:1032–45. doi: 10.1039/D3MH01511D
175. Alrashdan, MS, Park, JC, Sung, MA, Yoo, SB, Jahng, JW, Lee, TH, et al. Thirty minutes of low intensity electrical stimulation promotes nerve regeneration after sciatic nerve crush injury in a rat model. Acta Neurol Belg. (2010) 110:168–79.
176. Babu, S, Krishnan, M, Panneerselvam, A, and Chinnaiyan, M. A comprehensive review on therapeutic application of mesenchymal stem cells in neuroregeneration. Life Sci. (2023) 327:121785. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2023.121785
177. Khodir, SA, Imbaby, S, Abdel Allem Amer, MS, Atwa, MM, Ashour, FA, and Elbaz, AA. Effect of mesenchymal stem cells and melatonin on experimentally induced peripheral nerve injury in rats. Biomed Pharmacother. (2024) 177:117015. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.117015
178. Zhang, W, Zhou, G, Gao, Y, Zhou, Y, Liu, J, Zhang, L, et al. A sequential delivery system employing the synergism of EPO and NGF promotes sciatic nerve repair. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. (2017) 159:327–36. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2017.07.088
179. Xu, C, Wu, P, Yang, K, Mu, C, Li, B, Li, X, et al. Multifunctional biodegradable conductive hydrogel regulating microenvironment for stem cell therapy enhances the nerve tissue repair. Small. (2024) 20:e2309793. doi: 10.1002/smll.202309793
180. Li, Y, Chen, C, Li, S, and Jiang, C. Ginsenoside Rf relieves mechanical hypersensitivity, depression-like behavior, and inflammatory reactions in chronic constriction injury rats. Phytother Res. (2019) 33:1095–103. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6303
Keywords: sciatic nerve injury, animal models, chronic constriction injury, partial sciatic nerve ligation, sciatic nerve crush injury, sciatic nerve transection, treatments of sciatic nerve sciatic nerve injury
Citation: Zhou P, Zhang R, Xian L, Ning L, Lu P, Liu Q and Liu M (2025) Selection of sciatic nerve injury models: implications for pathogenesis and treatment. Front. Neurol. 16:1521941. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1521941
Edited by:
Mehmet Emin Onger, Ondokuz Mayıs University, TürkiyeReviewed by:
Ngan Pan Bennett Au, University of Surrey, United KingdomTiancheng Xu, Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, China
Copyright © 2025 Zhou, Zhang, Xian, Ning, Lu, Liu and Liu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Mi Liu, bmV3bWVhbkBobnVjbS5lZHUuY24=; Qianyan Liu, bHF5ZmFtaWx5QGhudWNtLmVkdS5jbg==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Pinxi Zhou
Pinxi Zhou Ruhan Zhang
Ruhan Zhang Liangmei Xian
Liangmei Xian Mi Liu
Mi Liu