- 1Department of Neurology, Uijeongbu Eulji Medical Center, Eulji University School of Medicine, Uijeongbu, Republic of Korea
- 2Department of Radiology, Asan Medical Center, College of Medicine, University of Ulsan, Seoul, Republic of Korea
- 3Department of Neurology, Asan Medical Center, College of Medicine, University of Ulsan, Seoul, Republic of Korea
- 4Department of Neurology, Gil Medical Center, Gachon University, Incheon, Republic of Korea
Background: Mechanisms underlying delayed neurological improvement (DNI) after endovascular thrombectomy (EVT) in patients with anterior (ACS) and posterior circulation stroke (PCS) may differ. This study aims to compare the factors associated with DNI in patients with ACS and PCS.
Materials and methods: Data of patients who underwent EVT with National Institute of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) score more than 6 and achieved successful reperfusion were retrospectively analyzed. DNI was defined as achieving favorable functional outcomes at 90 days, even without early neurological improvement. The factors associated with DNI in patients with ACS and PCS were investigated.
Results: A total of 241 patients were included. The proportions of DNI (30.8% vs. 20.0%; p = 0.184) were not significantly different between patients with ACS and PCS. In patients with ACS, absence of atrial fibrillation (aOR = 0.500; 95% CI, 0.264–0.945; p = 0.033), statin use (aOR = 2.842; 95% CI, 1.174–6.882; p = 0.021), lower NIHSS score after 24 h (aOR = 0.816; 95% CI 0.757–0.880; p < 0.001), and shorter onset-to-door time (aOR = 0.999; 95% CI, 0.998–1.000; p = 0.025) were significantly associated with DNI. In patients with PCS, male sex (aOR = 31.809; 95% CI, 1.816–557.074; p = 0.018) and lower initial NIHSS scores (aOR = 0.626; 95% CI, 0.410–0.957; p = 0.031) were significantly associated with DNI.
Conclusion: The proportions of DNI were similar in patients with ACS and PCS. However, the factors associated with DNI were different between the two groups.
Introduction
Endovascular thrombectomy (EVT) has become an established treatment for acute ischemic stroke with emergent large vessel occlusion (1). When complete arterial recanalization is achieved, it is often accompanied with early neurological improvement (ENI), a robust predictor of favorable long-term clinical outcomes (2). Nevertheless, cases have been noted where patients do not exhibit a clinical response within the initial hours following successful recanalization (3).
Lack of an early clinical response after recanalization does not always indicate a poor long-term outcome. Instead, it can be attributed to delayed neurological improvement (DNI). This phenomenon is associated with the “stunned brain” phenomenon, which involves various factors such as the resolution of brain edema, delayed improvement in microcirculation within ischemic tissues, and neuronal reorganization (4). The DNI occurring after EVT were associated with long-term outcomes, although most previous studies were focused on the patients with anterior circulation stroke (ACS) (2, 5). Moreover, it remains unclear whether the factors related to the outcome for DNI differ in patients receiving EVT with posterior circulation stroke (PCS).
This study aimed to compare clinical and radiographic findings and clinical outcomes after complete endovascular reperfusion. We also aimed to identify the factors associated with DNI in patients with ACS and in those with PCS.
Materials and methods
Patients and clinical data
We reviewed patients with acute ischemic stroke who were admitted to single-center, Seoul, Korea between January 2017 and June 2022. Patients were included in this study if they were ≥18 years-old; presented a National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) score of >6 at baseline; underwent EVT with an arterial occlusion in one of the following locations: internal carotid artery (cervical or intracranial), middle cerebral artery (M1 or proximal M2 segment), basilar artery, and vertebral artery, and achieved modified thrombolysis in cerebral infarction 2b/3 reperfusion (6). All EVT procedures were conducted in accordance with national clinical practice guidelines and local protocols (7). The local ethics committee approved this study (IRB number: 2022-0236), and informed consent was waived owing to the retrospective nature of the study.
Demographics and risk factors were documented from medical records. We studied NIHSS scores at admission, 24 h after EVT, and at discharge (8). The presumed cause of stroke was categorized according to the Trial of Org 10172 in the Acute Stroke Treatment (TOAST) classification (9). Processing times (from stroke onset to hospital arrival, from door to groin puncture, stroke onset to groin puncture, and puncture to reperfusion times) were also assessed.
Imaging variables
Multi-modal magnetic resonance imaging (MRI; Philips Healthcare, Eindhoven, The Netherlands) was performed, which included DWI, perfusion-weighted (PWI), FLAIR, gradient-echo imaging, and time-of-flight MRA (intracranial) and contrast-enhanced (extracranial) MRA (10). We used the Olea Sphere® imaging system (Olea Medical SAS, La Ciotat, France) for automatic post processing of PWI and DWI studies (11). To measure the DWI lesion volume, we set a value threshold of the apparent diffusion coefficient value. The volume of hypoperfused brain tissue was calculated using the T max (defined as a >6-s delay) (12).
Revascularization procedure and outcome
To perform digital subtraction angiography, we used a 6F ENVOY guiding catheter (Cordis, Miami Lakes, FL, United States) or an 8F Merci balloon guide catheter (Concentric Medical, Mountain View, CA, United States). In certain cases, other rescue strategies (angioplasty, stent insertion, and glycoprotein IIb/IIIa receptor inhibitor treatment) were used when the mechanical thrombectomy failed or if residual stenosis prevented adequate reperfusion. Reperfusion status was assessed in final cerebral angiography and graded according to the modified Thrombolysis in Cerebral Infarction (mTICI) scale (13). Successful reperfusion was defined as a scale score of 2b or 3 (13). An MRI follow-up was conducted to validate the presence of any intracranial hemorrhage subsequent to EVT, and the classification of hemorrhage was determined according to the definition outlined in the European Cooperative Acute Stroke Study (14).
ENI was defined a reduction of at least 8 NIHSS points or NIHSS equals to 0–1 at 24 h after EVT (15–17). DNI was defined if, despite absence of ENI during the first 24 h, patients achieved favorable functional outcomes (mRS 0–2) at 90 days (5). Functional outcome was measured by a stroke neurologist, either during patients’ physical visits to our stroke prevention clinic or by telephone with a structured interview.
Statistical analysis
The characteristics of patients with and without DNI were compared. The chi-square test (Fisher’s exact test) and the Student’s t-test was used adequately. In this study, we performed univariable and multivariable analyses to evaluate the factors associated with DNI in each group. The selection of adjusted variables for multivariable analysis was based on the results of univariable analysis and demographic factors, where only variables with a p-value <0.1, age, and sex were included in the final model. We assessed collinearity and excluded variables with a tolerance <1, variance inflation factor (VIF) ≥10, or a correlation coefficient ≥0.9. We used the IBM SPSS Statistics software, version 21.0 (IBM, Armonk, NY), and significance was set at p < 0.05 (18).
Results
A total of 382 patients underwent EVT during the study period, with 56 (14.7%) exhibiting an NIHSS score of < 6 points, 39 (10.2%) displaying a mTICI scale below 2b and 46 (12.0%) experienced ENI. Ultimately, the study included 241 (63.1%) patients (Figure 1).
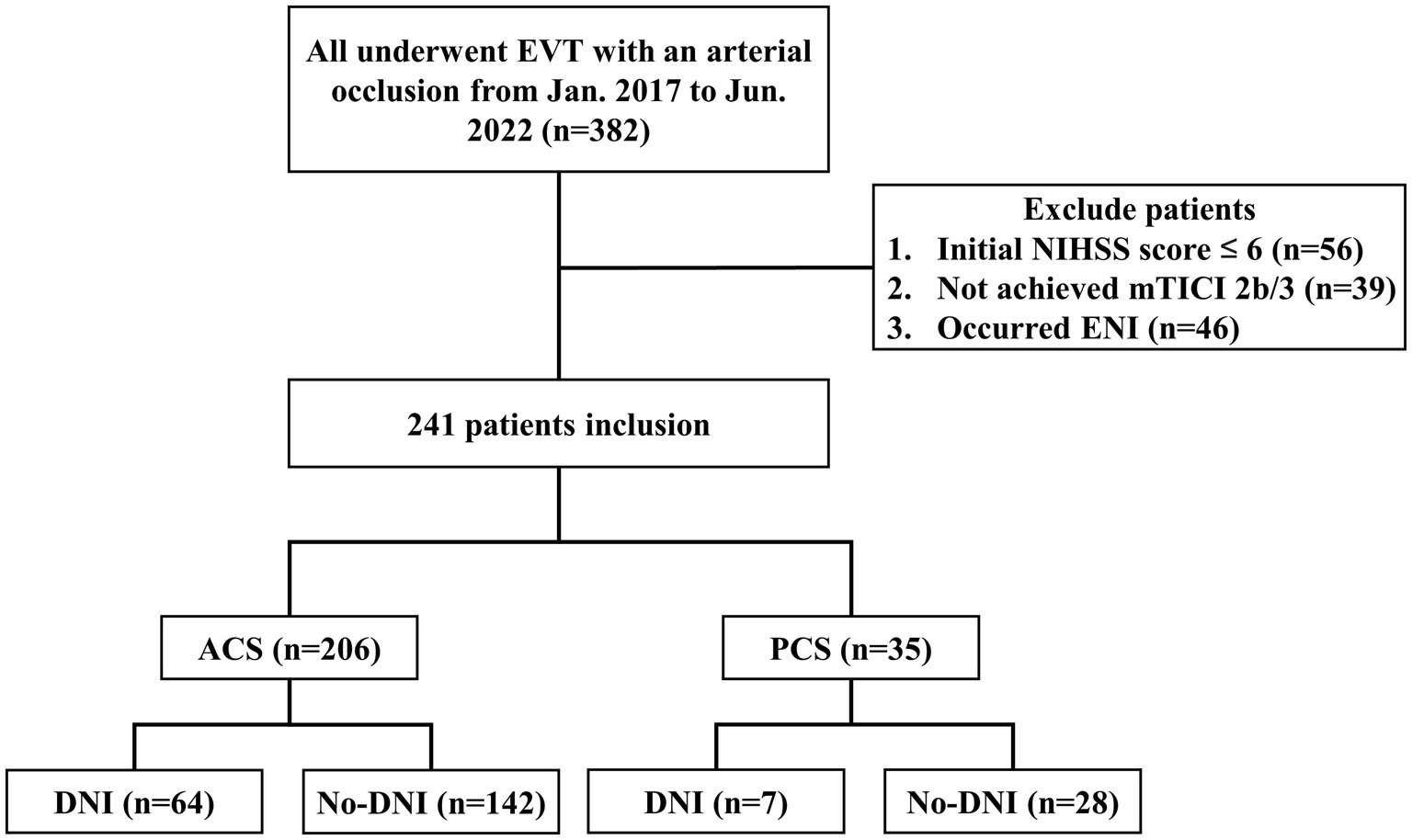
Figure 1. Study flowchart. DNI, delayed neurological improvement; ENI, early neurological improvement; EVT, endovascular thrombectomy, mTICI, modified treatment in cerebral infarction; NIHSS, National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale.
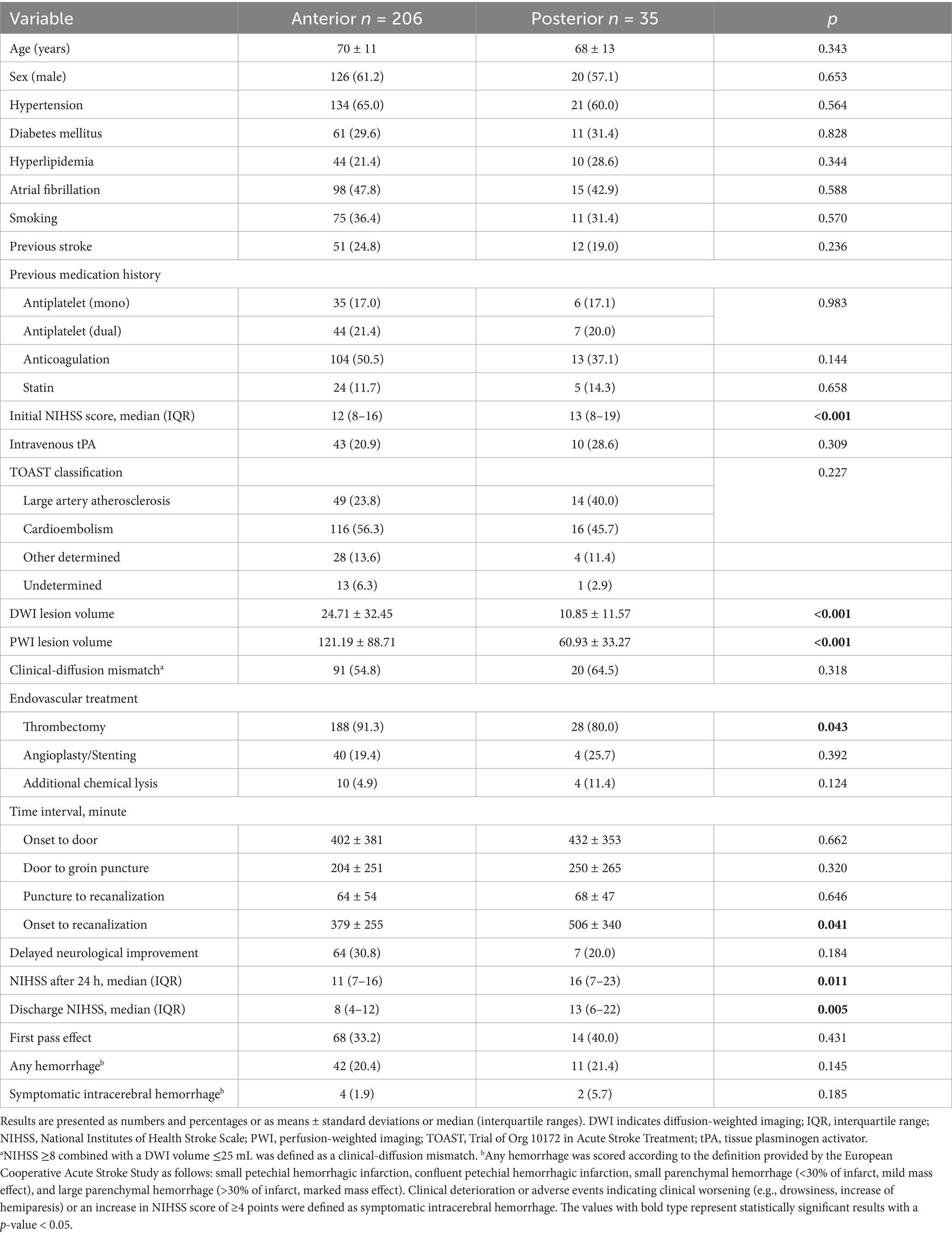
The mean age of the patients was 70 ± 4 years, and 146 (60.6%) were male. The median NIHSS score at admission was 12.0 points (interquartile range, 8.0–16.0). Among them, 206 (85.5%) patients had ACS, and 35 (14.5%) patients had PCS. DNI was observed in 71 (29.5%) patients; 64 (30.8%) in ACS and 7 (20.0%) in PCS patients.
Among the seven PCS patients with DNI, the lesions were located in various areas, including the cerebellum (n = 6), dorsolateral pons (n = 2), temporo-occipital lobe (n = 2), and medial thalamus (n = 2).
Comparison between patients with and without DNI
No significant differences in demographics and vascular risk factors were observed between the patients with and without DNI. Compared to patients without, those with DNI had more common prior statin medications (8.2 vs. 21.1%; p = 0.005), lower proportion of large artery atherosclerosis (30.6 vs. 15.5%) and higher rate of other determined etiology (10.0 vs. 21.1%; p = 0.027), shorter door to groin puncture time (230 ± 278 vs. 164 ± 171 min; p = 0.026), and onset to recanalization time (422 ± 286 vs. 341 ± 228 min; p = 0.036). There was no significant difference in initial NIHSS score before EVT. However, the NIHSS score after 24 h [13 (9–18) vs. 7 (3–11); p < 0.001] and at discharge [10 (5–14) vs. 4 (1–10); p < 0.001] were significantly lower in those with DNI than in those without DNI (Table 1).
Comparison of patient characteristics in ACS vs. PCS
In comparison to patients with PCS, those with ACS showed lower initial NIHSS scores [12 (8–16) vs. 13 (8–19); p < 0.001], higher DWI (24.71 ± 32.45 vs. 10.85 ± 11.57 cc; p < 0.001) and PWI lesion volume (121.19 ± 88.71 vs. 60.93 ± 33.27 cc; p < 0.001), higher thrombectomy rate (91.3 vs. 80.0%; p = 0.043), shorter onset to recanalization time (379 ± 255 vs. 506 ± 340 min; p = 0.041), lower NIHSS scores 24 h after EVT [11 (7–16) vs. 16 (7–23); p = 0.011] and at discharge [8 (4–12) vs. 13 (6–22); p = 0.005; Table 2].
Factors associated with DNI
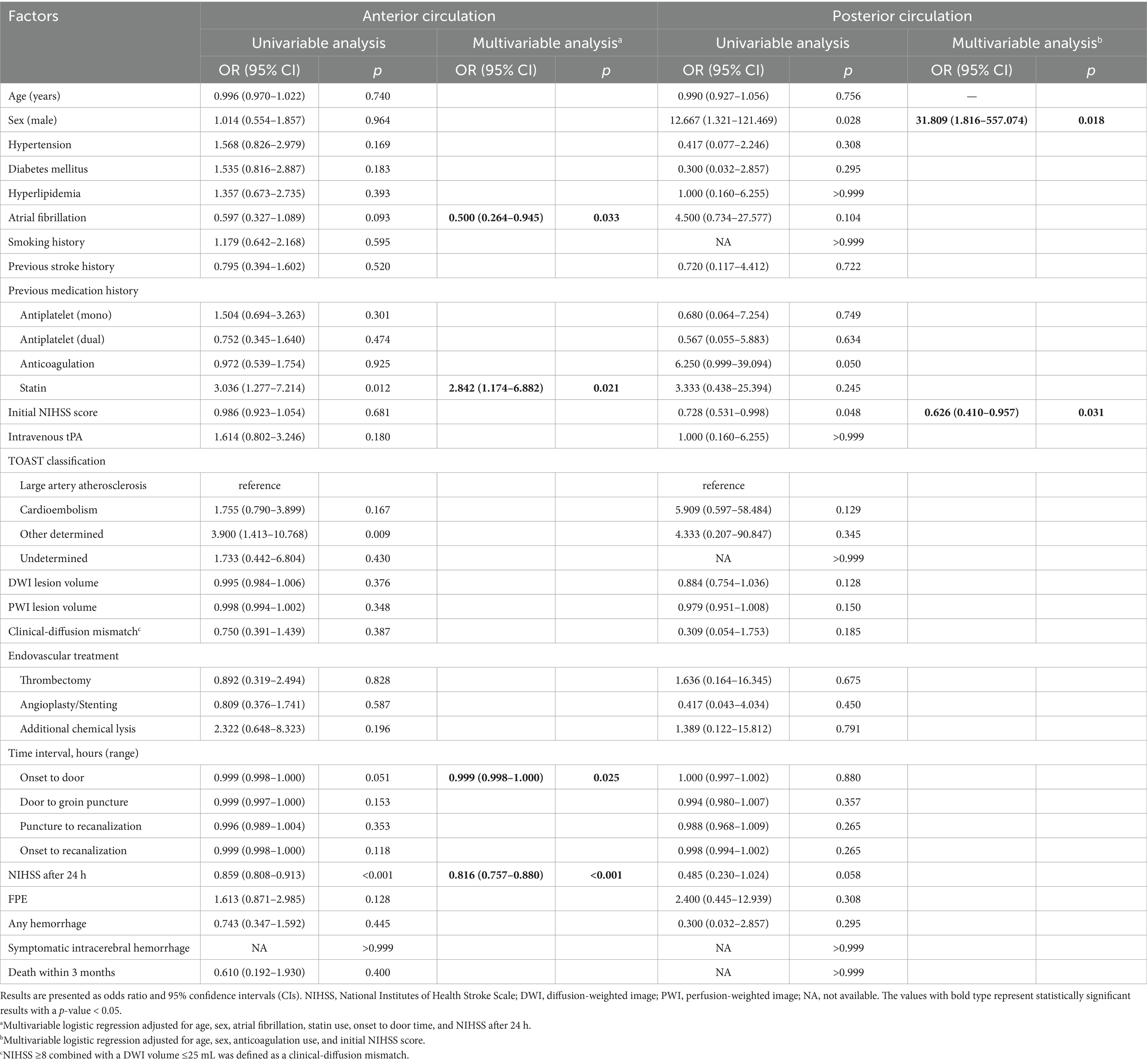
In patients with ACS, the prior use of statins, other determined etiology, and lower NIHSS score after 24 h were associated with DNI. In the multivariable logistic regression analysis, prior use of statins [adjusted odds ratio (aOR) = 2.842; 95% confidential interval (CI), 1.174–6.882; p = 0.021], lower NIHSS after 24 h (aOR = 0.816; 95% CI 0.757–0.880; p < 0.001), and a shorter onset-to-door time (aOR = 0.999; 95% CI, 0.998–1.000; p = 0.025) were significantly associated with DNI (Table 3).
Otherwise, in patients with PCS, being male and having a lower initial NIHSS score were associated with DNI. The multivariable logistic regression analyses revealed that being male (aOR = 31.809; 95% CI, 1.816–557.074; p = 0.018) and having a lower initial NIHSS score (aOR = 0.626; 95% CI, 0.410–0.957; p = 0.031) were significantly associated with DNI (Table 3).
Discussion
In this study, 29.5% patients receiving EVT with achieving successful recanalization showed DNI. The incidence of DNI between ACS and PCS was similar, but the factors associated with DNI were different between ACS and PCS. For patients with ACS, the use of prior statins, shorter onset-to door time and lower NIHSS after 24 h were associated with DNI. On the other hand, being male and lower initial NIHSS score were associated with DNI in patients with PCS.
Even though the extent does not meet the definition of ENI, the improvement in NIHSS scores 24 h after EVT was associated with DNI, but only in ACS group. Early improvement of reperfusion in the ischemic penumbra, which can lead to the rapid resolution of cortical symptoms predominantly seen in ACS may explain the association between 24 h neurological improvement and DNI (19).
In contrast, in PCS, a lower initial NIHSS score was significantly associated with DNI. The location of the stroke, influencing the initial severity, may be a more critical factor in determining recovery in PCS patients. While the general course of clinical recovery is relatively rapid during the first few weeks and then decelerates 1–3 months later, severe paralysis has been identified as valid associated factors of poor functional outcomes (20). In our current study, seven PCS patients with DNI exhibited various lesion locations, including the cerebellum (n = 6), dorsolateral pons (n = 2), temporo-occipital lobe (n = 2), and medial thalamus (n = 2), with the corticospinal tracts preserved in these patients. This finding suggests that the preservation of motor pathways may play a role in facilitating early neurological recovery in PCS patients.
We also found that rapid reperfusion was the important factor for DNI in ACS. A previous study has indicated that patients with PCS had a significantly longer onset-to-door time than those with ACS, and despite prolonged symptom onset to recanalization initiation intervals in PCS cases, functional outcomes at 3 months were comparable between ACS and PCS groups (21, 22). A better collateral flow in PCS may result in a slower evolution of irreversible ischemia, contributing to better tolerance to the time window (23).
Several studies have suggested a potential beneficial effect of premorbid statin use on functional outcomes following acute stroke (24). These benefits may arise from the pleiotropic effects of statins, including their anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and neuroprotective properties, which could mitigate the extent of neuronal damage and improve post-stroke recovery (25). We found that prior statin use was more associated with DNI in patients with ACS, but less in those with PCS. One plausible explanation for this contrast lies in the disparity of the extent of lesion volume between ACS and PCS. Although not statistically significant, we observed that patients with ACS exhibited larger ischemic core and penumbra compared to those with PCS, potentially resulting in more extensive neuronal damage. Hence, the pleiotropic effects of statins might exert a more pronounced impact in the context of ACS, characterized by greater neuronal injury and inflammation.
An intriguing observation was that male sex was significantly associated with long-term recovery compared to female sex if there was no improvement within the first 24 h following complete arterial recanalization. This aligns with prior research indicating worse outcomes for women after stroke in general, as well as after endovascular therapy (2, 26). Also, this disparity may be influenced by both biological and social factors. Biologically, sex hormones such as estrogen have been suggested to modulate neuroprotection and inflammatory responses after stroke, potentially influencing recovery trajectories. On the social side, differences in participation in post-stroke rehabilitation, caregiver support, and access to healthcare resources may further impact these outcomes (27). However, this variable was not specifically analyzed due to the retrospective nature of our study. Moreover, given the small number of patients with DNI, we cannot exclude the possibility that this association might be the result of an artifact or an unexamined selection bias. Consequently, these finding warrants confirmation in future studies on endovascular therapy.
This study has several limitations. First, the limited sample size and observational design at a single center may introduce selection bias and reduce statistical power, particularly in the PCS group (n = 35), limiting the generalizability of the findings. Second, multiple comparisons were not adjusted for, increasing the risk of type I errors, and some significant results may not survive correction. Third, the small number of DNI events (n = 7) in the PCS group raises concerns about the robustness of multivariable modeling, as indicated by wide confidence intervals and potential quasi-complete separation. Fourth, PCS patients frequently present with symptoms such as dizziness, diplopia, visual field defects, and gait ataxia, which are often underrepresented or underappreciated in NIHSS score assessment. This highlights the challenges associated with using NIHSS score to assess stroke severity and recovery in cases of PCS. Fifth, we identified factors associated with DNI; however, these findings need to be validated through randomized controlled trials to establish clear clinical practice. Finally, the definition of ENI and DNI varied among studies; but we chose to definitions based on prior research supporting its relevance (2, 28).
Conclusion
We found that the proportions of DNI were similar in patients with ACS and PCS, but the factors associated with DNI may differ. For ACS patients, prior statin use, rapid reperfusion, and early response to neurological improvement may be crucial. In contrast, for PCS patients, initial stroke severity and male sex were significant factors.
Data availability statement
The data analyzed in this study is subject to the following licenses/restrictions: the dataset used in this study is derived from patient medical records and is subject to restrictions due to patient confidentiality, institutional policies, and ethical guidelines. Access to the data requires approval from the Institutional Review Board (IRB) of Asan Medical Center. Requests to access these datasets should be directed to BKi, bWVkaWNqODBAaGFubWFpbC5uZXQ=.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Institutional Review Board of Asan Medical Center (Approval Number: 2022-0236). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The Ethics Committee of Asan Medical Center waived the requirement of written informed consent for participation from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin owing to the study’s retrospective design.
Author contributions
SP: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. BKw: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. JC: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. YS: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. DL: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. SH: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. BKi: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Goyal, M, Menon, BK, van Zwam, WH, Dippel, DW, Mitchell, PJ, Demchuk, AM, et al. Endovascular thrombectomy after large-vessel ischaemic stroke: a meta-analysis of individual patient data from five randomised trials. Lancet. (2016) 387:1723–31. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(16)00163-x
2. Talavera, B, Gómez-Vicente, B, Martínez-Galdámez, M, López-Cancio, E, García-Cabo, C, Castellanos, M, et al. Delayed neurological improvement after full endovascular reperfusion in acute anterior circulation ischemic stroke. Stroke. (2021) 52:2210–7. doi: 10.1161/strokeaha.120.032066
3. Heit, JJ, Mlynash, M, Kemp, SM, Lansberg, MG, Christensen, S, Marks, MP, et al. Rapid neurologic improvement predicts favorable outcome 90 days after thrombectomy in the DEFUSE 3 study. Stroke. (2019) 50:1172–7. doi: 10.1161/strokeaha.119.024928
4. Alexandrov, AV, Hall, CE, Labiche, LA, Wojner, AW, and Grotta, JC. Ischemic stunning of the brain: early recanalization without immediate clinical improvement in acute ischemic stroke. Stroke. (2004) 35:449–52. doi: 10.1161/01.Str.0000113737.58014.B4
5. Desai, SM, Tonetti, DA, Morrison, AA, Molyneaux, BJ, Starr, M, Rocha, M, et al. Delayed functional independence after thrombectomy: temporal characteristics and predictors. J Neurointerv Surg. (2020) 12:837–41. doi: 10.1136/neurintsurg-2020-016111
6. Dargazanli, C, Fahed, R, Blanc, R, Gory, B, Labreuche, J, Duhamel, A, et al. Modified thrombolysis in cerebral infarction 2C/thrombolysis in cerebral infarction 3 reperfusion should be the aim of mechanical thrombectomy: insights from the ASTER trial (contact aspiration versus stent retriever for successful revascularization). Stroke. (2018) 49:1189–96. doi: 10.1161/strokeaha.118.020700
7. Hong, KS, Ko, SB, Yu, KH, Jung, C, Park, SQ, Kim, BM, et al. Update of the Korean clinical practice guidelines for endovascular recanalization therapy in patients with acute ischemic stroke. J Stroke. (2016) 18:102–13. doi: 10.5853/jos.2015.01655
8. Lyden, P. Using the National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale: a cautionary tale. Stroke. (2017) 48:513–9. doi: 10.1161/strokeaha.116.015434
9. Chung, JW, Park, SH, Kim, N, Kim, WJ, Park, JH, Ko, Y, et al. Trial of ORG 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment (TOAST) classification and vascular territory of ischemic stroke lesions diagnosed by diffusion-weighted imaging. J Am Heart Assoc. (2014) 3:3. doi: 10.1161/jaha.114.001119
10. Eaton-Rosen, Z, Melbourne, A, Orasanu, E, Cardoso, MJ, Modat, M, Bainbridge, A, et al. Longitudinal measurement of the developing grey matter in preterm subjects using multi-modal MRI. NeuroImage. (2015) 111:580–9. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.02.010
11. Deutschmann, H, Hinteregger, N, Wießpeiner, U, Kneihsl, M, Fandler-Höfler, S, Michenthaler, M, et al. Automated MRI perfusion-diffusion mismatch estimation may be significantly different in individual patients when using different software packages. Eur Radiol. (2021) 31:658–65. doi: 10.1007/s00330-020-07150-8
12. Kerleroux, B, Janot, K, Dargazanli, C, Daly-Eraya, D, Ben-Hassen, W, Zhu, F, et al. Perfusion imaging to select patients with large ischemic core for mechanical thrombectomy. J Stroke. (2020) 22:225–33. doi: 10.5853/jos.2019.02908
13. LeCouffe, NE, Kappelhof, M, Treurniet, KM, Lingsma, HF, Zhang, G, van den Wijngaard, IR, et al. 2B, 2C, or 3: what should be the angiographic target for endovascular treatment in ischemic stroke? Stroke. (2020) 51:1790–6. doi: 10.1161/strokeaha.119.028891
14. Neuberger, U, Möhlenbruch, MA, Herweh, C, Ulfert, C, Bendszus, M, and Pfaff, J. Classification of bleeding events: comparison of ECASS III (European Cooperative Acute Stroke Study) and the new Heidelberg bleeding classification. Stroke. (2017) 48:1983–5. doi: 10.1161/strokeaha.117.016735
15. Cai, H, Han, Y, Sun, W, Zha, M, Shi, X, Huang, K, et al. Delayed neurological improvement is predictive to long-term clinical outcome on endovascular thrombectomy patients. Interv Neuroradiol. (2022) 28:404–10. doi: 10.1177/15910199211038207
16. Eryildiz, ES, and Özdemir, A. Factors associated with early recovery after intravenous thrombolytic therapy in acute ischemic stroke. Noro Psikiyatr Ars. (2018) 55:80–3. doi: 10.29399/npa.22664
17. Kobeissi, H, Ghozy, S, Bilgin, C, Kadirvel, R, and Kallmes, DF. Early neurological improvement as a predictor of outcomes after endovascular thrombectomy for stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Neurointerv Surg. (2023) 15:547–51. doi: 10.1136/neurintsurg-2022-019008
18. Park, S, Kim, HJ, Kim, S, Rhee, SY, Woo, HG, Lim, H, et al. National trends in physical activity among adults in South Korea before and during the COVID-19 pandemic, 2009–2021. JAMA Netw Open. (2023) 6:e2316930. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.16930
19. Wilson, SM, Eriksson, DK, Brandt, TH, Schneck, SM, Lucanie, JM, Burchfield, AS, et al. Patterns of recovery from aphasia in the first 2 weeks after stroke. J Speech Lang Hear Res. (2019) 62:723–32. doi: 10.1044/2018_JSLHR-L-18-0254
20. Lee, KB, and Lim, SH. Prognosis and recovery of motor function with lesion–symptom mapping in patients with stroke. Brain Neurorehabil. (2017) 10:e5. doi: 10.12786/bn.2017.10.e5
21. Reid, JM, Dai, D, Cheripelli, B, Christian, C, Reidy, Y, Gubitz, GJ, et al. Differences in wake-up and unknown onset stroke examined in a stroke registry. Int J Stroke. (2015) 10:331–5. doi: 10.1111/ijs.12388
22. Ha, SH, Ryu, JC, Bae, JH, Koo, S, Kwon, B, Lee, DH, et al. Early response to endovascular thrombectomy after stroke: early, late, and very late time windows. Cerebrovasc Dis. (2023) 52:28–35. doi: 10.1159/000525083
23. Ostrem, JL, Saver, JL, Alger, JR, Starkman, S, Leary, MC, Duckwiler, G, et al. Acute basilar artery occlusion: diffusion-perfusion MRI characterization of tissue salvage in patients receiving intra-arterial stroke therapies. Stroke. (2004) 35:e30–4. doi: 10.1161/01.Str.0000113783.45745.Be
24. Hong, KS, and Lee, JS. Statins in acute ischemic stroke: a systematic review. J Stroke. (2015) 17:282–301. doi: 10.5853/jos.2015.17.3.282
25. Xu, Y, Guo, S, Jiang, H, Han, H, Sun, J, and Wu, X. Collateral status and clinical outcomes after mechanical thrombectomy in patients with anterior circulation occlusion. J Healthc Eng. (2022) 2022:7796700–7. doi: 10.1155/2022/7796700
26. Kobeissi, H, Ghozy, S, Seymour, TJ, Bilgin, C, Liu, M, Kadirvel, R, et al. Patient characteristics associated with delayed neurological improvement following acute ischemic stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Interv Neuroradiol. (2023) 3:15910199221149787. doi: 10.1177/15910199221149787 [Epub ahead of print].
27. Ospel, JM, Schaafsma, JD, Leslie-Mazwi, TM, Amin-Hanjani, S, Asdaghi, N, Gordon-Perue, GL, et al. Toward a better understanding of sex- and gender-related differences in endovascular stroke treatment: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. (2022) 53:e396–406. doi: 10.1161/str.0000000000000411
Keywords: endovascular thrombectomy, early neurological improvement, delayed neurological improvement, anterior circulation stroke, posterior circulation stroke
Citation: Park S, Kwon B, Chang JY, Song Y, Lee DH, Ha SH and Kim BJ (2025) Factors associated with delayed neurologic improvement after complete endovascular reperfusion in anterior and posterior ischemic stroke. Front. Neurol. 16:1543743. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1543743
Edited by:
Promod Pillai, Loma Linda University Health Care, United StatesReviewed by:
Sharon Yeatts, Medical University of South Carolina, United StatesJessica Jesser, Heidelberg University Hospital, Germany
Bowen Sun, First Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, China
Copyright © 2025 Park, Kwon, Chang, Song, Lee, Ha and Kim. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Sang Hee Ha, c2hoYS4wNzExQGdtYWlsLmNvbQ==; Bum Joon Kim, bWVkaWNqODBAaGFubWFpbC5uZXQ=
 Sangil Park
Sangil Park Boseong Kwon
Boseong Kwon Jun Young Chang
Jun Young Chang Yunsun Song2
Yunsun Song2 Deok Hee Lee
Deok Hee Lee Sang Hee Ha
Sang Hee Ha Bum Joon Kim
Bum Joon Kim