- Department of Endocrinology, The Quzhou Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University, Quzhou People’s Hospital, Quzhou, Zhejiang, China
Objective: To investigate the association between the Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index (SII) and the severity of acute ischemic stroke (AIS), as measured by the National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS), and to explore its potential as a predictive marker for clinical outcomes.
Methods: We used the data of 1723 AIS patients in the Stroke Center of Quzhou People’s Hospital from September 2016 to September 2022 for a cross-sectional study. SII was calculated as platelet count × neutrophil count divided by lymphocyte count. Stroke severity was classified as mild (NIHSS < 8) or severe (NIHSS ≥ 8). Multivariable logistic regression and subgroup analyses were performed to evaluate the relationship between SII levels and NIHSS scores, adjusting for confounders such as age, sex, and comorbidities. Nonlinear associations and threshold effects were further assessed using smooth curve fitting.
Results: Elevated SII levels were independently associated with higher stroke severity (OR: 1.04, 95% CI: 1.01–1.07). A nonlinear relationship was identified, with a critical range of SII/100 values (2.4–7.8) demonstrating the strongest correlation with NIHSS scores. Patients in the highest SII quartile (Q4) exhibited a 3.46-fold increase in odds of severe stroke compared to those in the lowest quartile (Q1) (p < 0.001). Subgroup analyses confirmed the robustness of these findings across diverse demographic and clinical profiles.
Conclusion: SII is a robust biomarker for predicting stroke severity in AIS patients. The observed nonlinear relationship highlights its potential utility in identifying critical inflammatory thresholds for risk stratification and personalized therapeutic interventions.
Introduction
Acute ischemic stroke (AIS) is a significant cause of morbidity and mortality on a global scale. Early identification of stroke severity is of critical importance for effective clinical management and prognosis (1). The conventional approach to the evaluation of stroke severity involves the utilisation of the National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS), a scale designed to assess neurological function based on a range of clinical signs. However, this scale does not capture the underlying pathophysiological processes, particularly the complex immune-inflammatory responses that contribute to stroke progression and outcomes (2).
Immune-inflammatory processes contribute not only to the initial pathogenesis of AIS, but also to secondary injury through mechanisms such as microglial activation, blood–brain barrier disruption, and neuroinflammation (3, 4). These inflammatory processes are not only central to stroke pathophysiology but also serve as important biomarkers for predicting stroke severity and recovery.
The SII calculated as platelet count × neutrophil count / lymphocyte count, has emerged as a promising prognostic biomarker in various diseases, including cardiovascular conditions and cancer (5–7). By reflecting both inflammatory and thrombotic components, SII may also hold potential value in AIS.
Notwithstanding its promising applications, the role of SII in AIS remains to be thoroughly explored. Previous studies have reported that elevated SII is associated with increased stroke severity and poorer outcomes in AIS patients (8).
However, these studies have primarily focused on linear associations. To date, the potential nonlinear relationship between SII and stroke severity, as well as the existence of critical threshold effects, remains underexplored (9). To address this, we applied a generalized additive model (GAM), a flexible analytical approach that allows for the data-driven identification of complex, non-monotonic associations without imposing a prespecified functional form. Understanding these dynamics could offer significant insights into stroke prognosis and inform clinical decision-making.
In order to address this paucity of research in the field, the present study aims to investigate the association between SII and stroke severity in AIS patients. It is hypothesised that elevated SII levels are significantly associated with greater stroke severity, and that SII may serve as an independent prognostic marker for AIS outcomes. The study will provide a more in-depth understanding of the potential utility of SII in clinical practice and its role in improving the prognostication of AIS patients.
Materials and methods
Study population
This study utilized data from a previously established cohort examining the prognosis of cerebral infarction. Data were collected from eligible patients admitted to our hospital between September 2016 and September 2022. The study protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of Quzhou People’s Hospital, and all participants provided written informed consent.
Inclusion criteria:
(1) Diagnosis of acute ischemic stroke (AIS) confirmed within 24 h of symptom onset.
(2) Age ≥ 18 years.
(3) Completion of head MRI within 48 h of admission.
Exclusion criteria:
(1) Patients with stroke in non-acute stages or those who have transitioned to recovery phases, or with a history of brain tumors, encephalitis, traumatic brain injury, or severe multi-organ dysfunction syndrome.
(2) Pregnant patients.
(3) Severe cardiovascular conditions (NYHA class III or IV or left ventricular ejection fraction < 40%), pulmonary conditions (oxygen saturation < 95%, with shortness of breath, cyanosis, or abnormal blood gas analysis), hepatic (serum ALT > 10 times the upper reference range), renal (serum creatinine > 443 μmol/L) and oncological diseases.
(4) Patients with autoimmune diseases.
(5) Presence of infection (oral temperature > 37.5°C and white blood cell count exceeding the upper reference range).
Data collection adhered to privacy protection principles, without involving personal information, and internal data collection has not been publicly released.
Data collection
Baseline demographic and clinical data were retrieved from medical records, including age, sex, smoking history, hypertension, type 2 diabetes, atrial fibrillation, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Clinical characteristics were assessed using the NIH Stroke Scale (NIHSS) for stroke severity, the A2DS2 score (Age, Atrial fibrillation, Dysphagia, Sex, and Stroke Severity) for pneumonia risk assessment, and the Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) for consciousness impairment.
NIHSS scores were initially assessed at the time of hospital admission by trained neurologists, and reassessed at 24 and 72 h to ensure consistency. For stroke severity, patients were classified into mild (NIHSS < 8) and severe (NIHSS ≥ 8) groups, with an NIHSS score of ≥ 8 indicating severe stroke, in accordance with previous studies that have adopted or validated this cutoff in similar AIS populations (10–12).
Laboratory testing
Blood samples were collected by trained nurses on the second morning after admission (between 6:00 and 7:30 a.m. following overnight fasting) using vacuum tubes, stored at 4°C, and processed within 2 h by certified laboratory technicians. This standardized timing was adopted to minimize acute-phase fluctuations and nutritional influences on inflammatory markers. Laboratory tests included: White blood cell count (WBC), Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), Platelet count (P), Aspartate transaminase (AST), Alanine transaminase (ALT), Glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c), Homocysteine (HCY), Serum creatinine (Scr), Albumin (ALB), Triglycerides (TG), Total cholesterol (TC), High-density lipoprotein (HDL-c), Low-density lipoprotein (LDL-c), C-reactive protein (CRP), and uric acid (UA), all measured from the same fasting blood samples using standardized enzymatic colorimetric methods. The neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio was calculated as the ratio of neutrophil count to lymphocyte count. The Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index (SII) was calculated as:
The estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) was calculated from serum creatinine using the CKD-EPI formula to assess renal function.
Statistical analysis
All statistical analyses were performed using R Studio (version 4.2.2) and Empower Stats (version 2.0). Descriptive statistics were used to summarize baseline characteristics. Continuous variables were tested for normality using the Shapiro–Wilk test. If normally distributed, they were expressed as mean ± standard deviation and compared using t-tests. For non-normally distributed data, the Mann–Whitney U test was used, and results were presented as median and interquartile range. Categorical variables were presented as counts and percentages, and analyzed using chi-square tests.
The Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index (SII) was categorized into four quartiles (Q1 to Q4), with Q1 representing the lowest values and Q4 the highest. Stroke severity (measured by NIHSS) was compared between SII quartiles using t-tests for continuous variables and chi-square tests for categorical variables.
To further explore the relationship between SII and stroke severity, multivariate logistic regression analysis was performed, adjusting for potential confounders such as age, sex, smoking status, diabetes, hypertension, COPD, atrial fibrillation, HbA1c, eGFR, HDL-c, LDL-c, WBC, CRP, UA, and TG. Three models were constructed:
Model 1: No covariate adjustments.
Model 2: Adjusted for age and sex.
Model 3: Adjusted for both core clinical and laboratory variables. Specifically, demographic and clinical variables (age, sex, smoking status, diabetes, hypertension, COPD, and atrial fibrillation) were selected a priori based on their established relevance to AIS prognosis. Laboratory variables (eGFR, HDL-c, LDL-c, WBC, CRP, UA, HbA1c and TG) were included based on their statistical significance in univariate analysis (p < 0.10) (see Supplementary Table 1).
Additionally, a smooth curve fitting method was applied to explore the potential non-linear relationship between SII and NIHSS scores. A threshold effect analysis model based on a piecewise linear regression approach was also employed, treating NIHSS as a continuous outcome, to identify potential inflection points in the association.
Subgroup analyses were performed based on age, sex, smoking, diabetes, hypertension, atrial fibrillation, and COPD. Interaction analyses were conducted within each subgroup to assess the effects of SII. All statistical tests were two-tailed, and a significance level of p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
We did not perform a priori sample size calculation, as this was a retrospective analysis. However, the relatively large sample size (N = 1,723) provided adequate power to detect clinically relevant associations.
Results
Baseline characteristics of participants
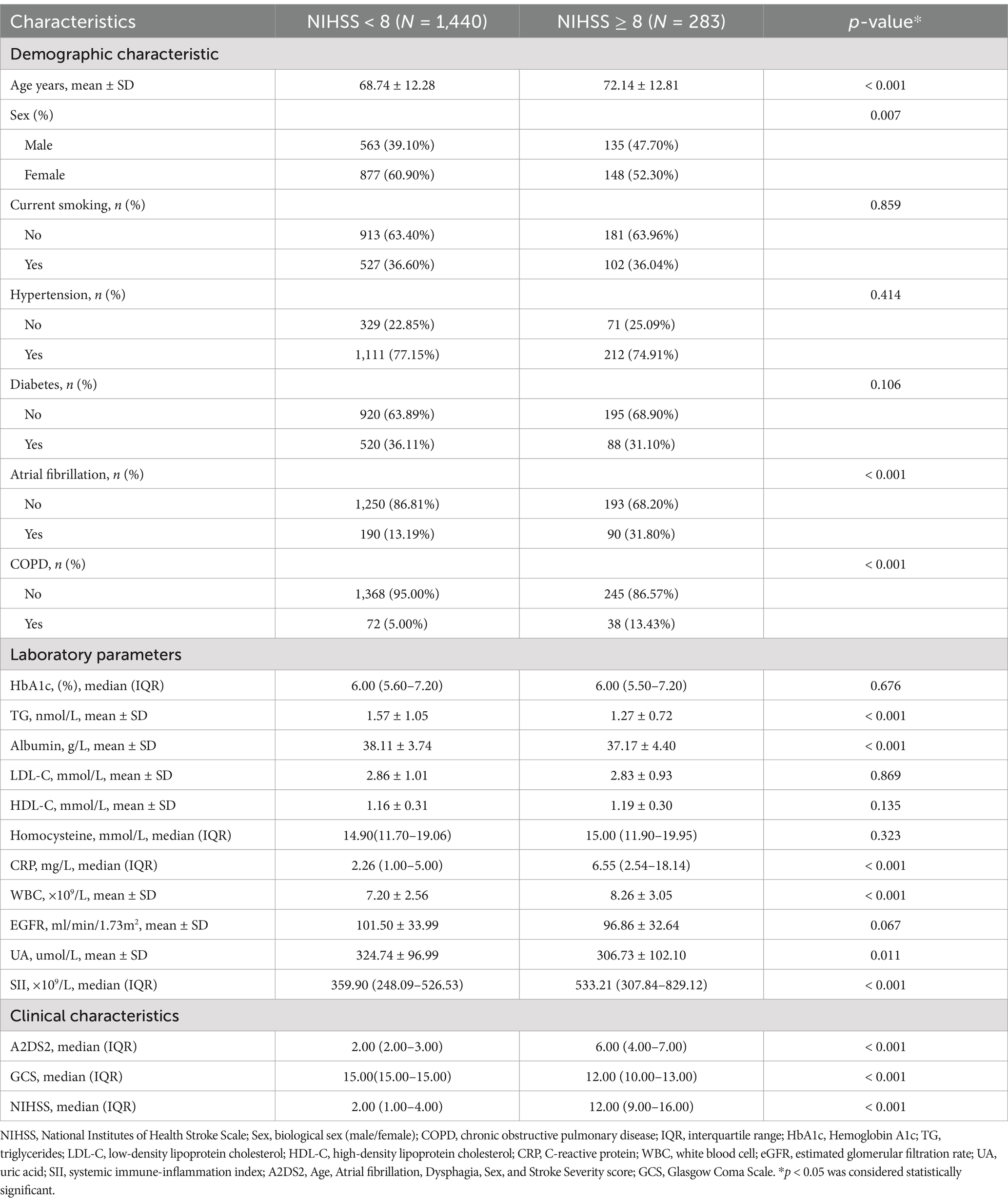
There were 1723participants enrolled, of whom 40.51% were male, with an average age of 69.29 ± 12.42 years. The mean SII median (IQR) concentrations were 378.13 (252.15–572.11). Among them, severe stroke patients accounted for16.42%.
The clinical characteristics of participants with stroke severity as a columnar stratified variable are shown in Table 1. Patients with NIHSS ≥ 8 were significantly older, had higher prevalence of atrial fibrillation (31.8% vs. 13.2%) and COPD (13.43% vs. 5.00%), and exhibited elevated inflammatory markers (SII: severe group 533.21 vs. mild group 359.90, p < 0.001; CRP: severe group 6.55 vs. mild group 2.26, p < 0.001). These patients also showed worse clinical scores (e.g., GCS: severe group 12 vs. mild group 15, p < 0.001). This highlights the association between systemic inflammation and stroke severity, alongside comorbidities like atrial fibrillation and COPD.
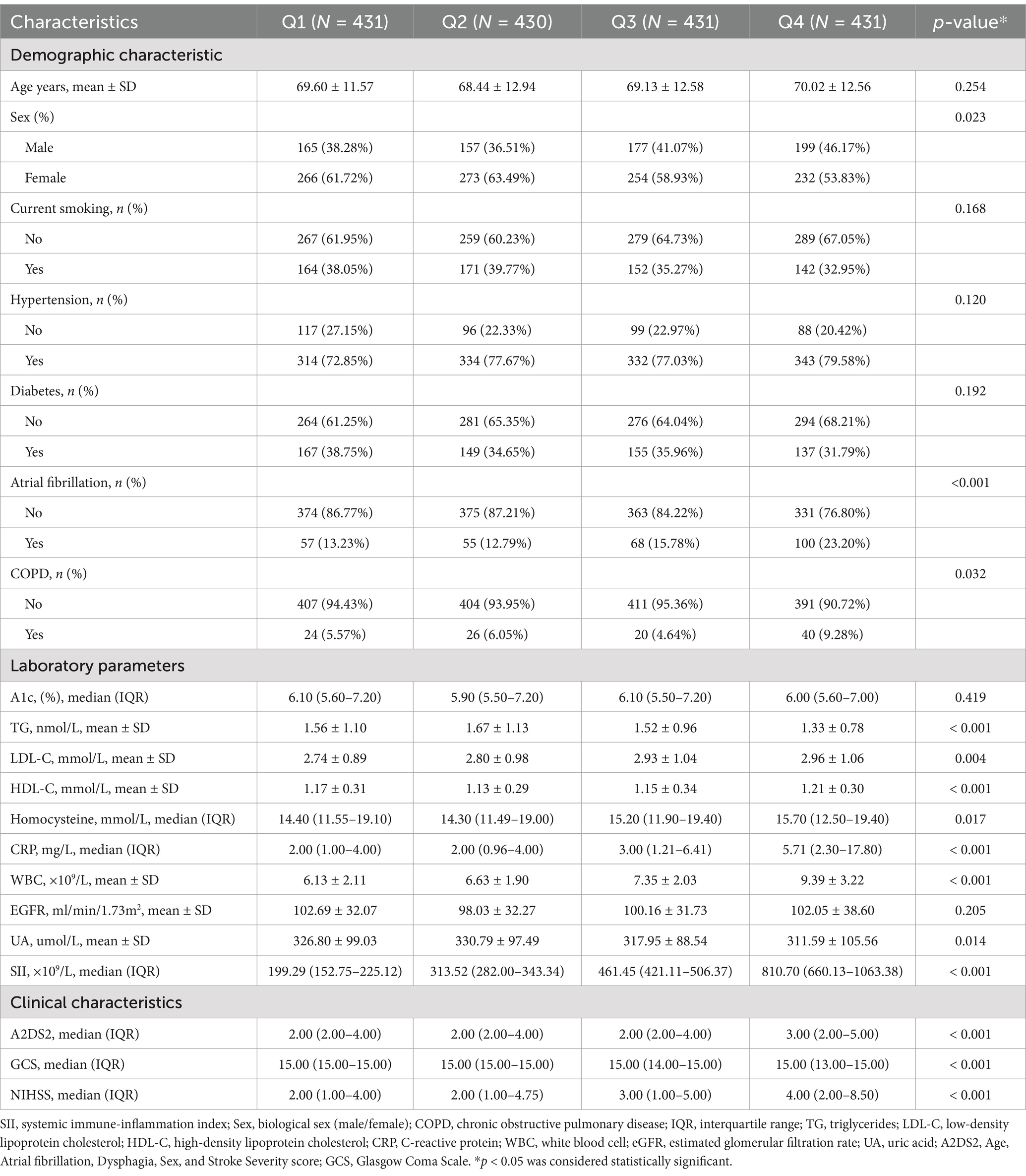
The clinical characteristics of the participants according to the quartiles of SII are shown in Table 2. In this study, significant differences in patient characteristics were observed across SII quartiles. Patients in the highest quartile (Q4) were more likely to have atrial fibrillation (23.20% vs. 13.23%, p < 0.001) and COPD (9.28% vs. 5.57%, p = 0.032) compared to the lowest quartile (Q1). Inflammatory markers, including CRP (5.71 mg/L vs. 2.00 mg/L, p < 0.001) and WBC (9.39 × 10⁹/L vs. 6.13 × 10⁹/L, p < 0.001), increased significantly with higher SII levels. Conversely, triglyceride levels decreased across quartiles (1.33 vs. 1.56 mmol/L, p < 0.001).
Stroke severity, as assessed by NIHSS scores, increased across SII quartiles, with the median NIHSS rising from 2 in Q1 to 4 in Q4 (p < 0.001). GCS and A2DS2 scores also differed significantly across quartiles, with lower GCS and higher A2DS2 scores observed in patients with higher SII levels (all p < 0.001).
Association between SII and NIHSS
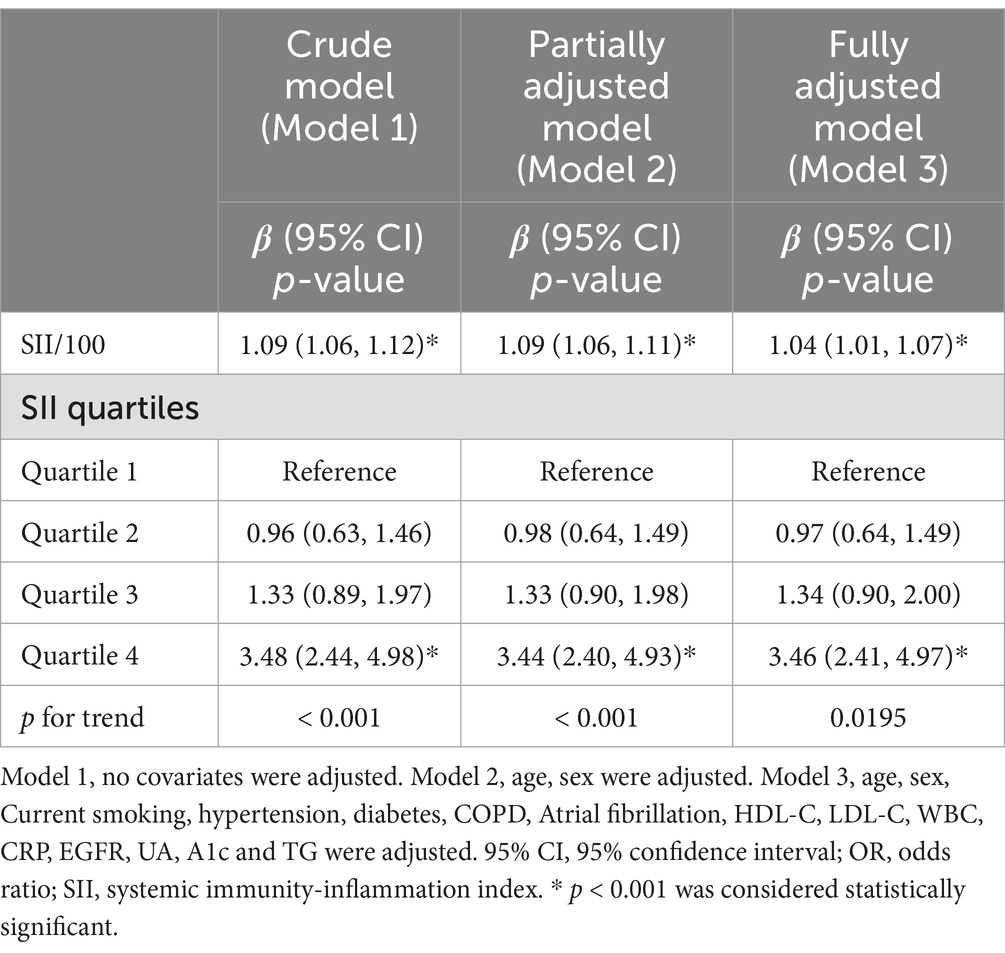
To improve interpretability and model scaling, the SII was divided by 100 before inclusion in regression analyses. Table 3 presents the results of the multivariable regression analysis between SII/100 and NIHSS. This association, modeled as a continuous variable (per 100-unit increase in SII), was significant in all three models: model 1 (OR = 1.09, 95% CI: 1.06–1.12), model 2 (OR = 1.09, 95% CI: 1.06–1.11), and model 3 (OR = 1.04, 95% CI: 1.01–1.07). Although statistically significant, the effect size was modest, suggesting limited predictive power of SII when treated as a continuous variable. In the fully adjusted model, SII in the highest quartile (Q4) was associated with 3.46-fold higher odds of severe stroke (NIHSS ≥ 8) compared to the lowest quartile (p < 0.001). These results confirm that elevated SII independently correlates with greater stroke severity, even after controlling for age, comorbidities, and other inflammatory markers.
Based on model 3, which adjusted for potential confounders including age, sex, smoking, diabetes, hypertension, COPD, atrial fibrillation, HbA1c, eGFR, HDL-c, LDL-c, WBC, CRP, UA, and TG, we performed smooth curve fitting and threshold effect analysis to examine the relationship between SII and NIHSS. The results are presented in Figure 1, Tables 4, 5.
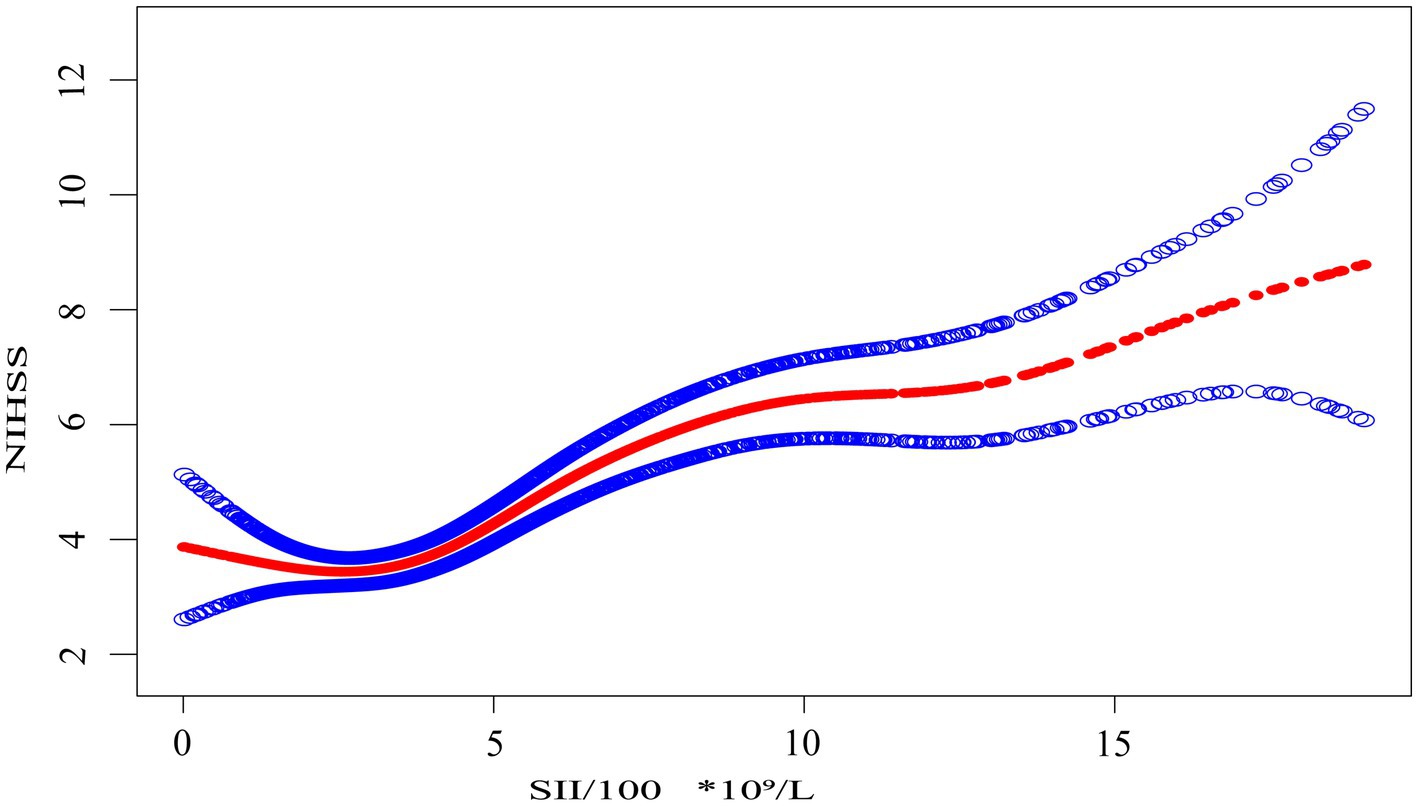
Figure 1. The association between the systemic immune-inflammation index scaled by 100 (SII/100, ×10⁹/L) and NIHSS score. The solid red line represents the smooth curve fit between the scaled SII and NIHSS. Shaded blue bands indicate the 95% confidence interval of the fit. SII was divided by 100 to facilitate interpretation of effect sizes in regression modeling.
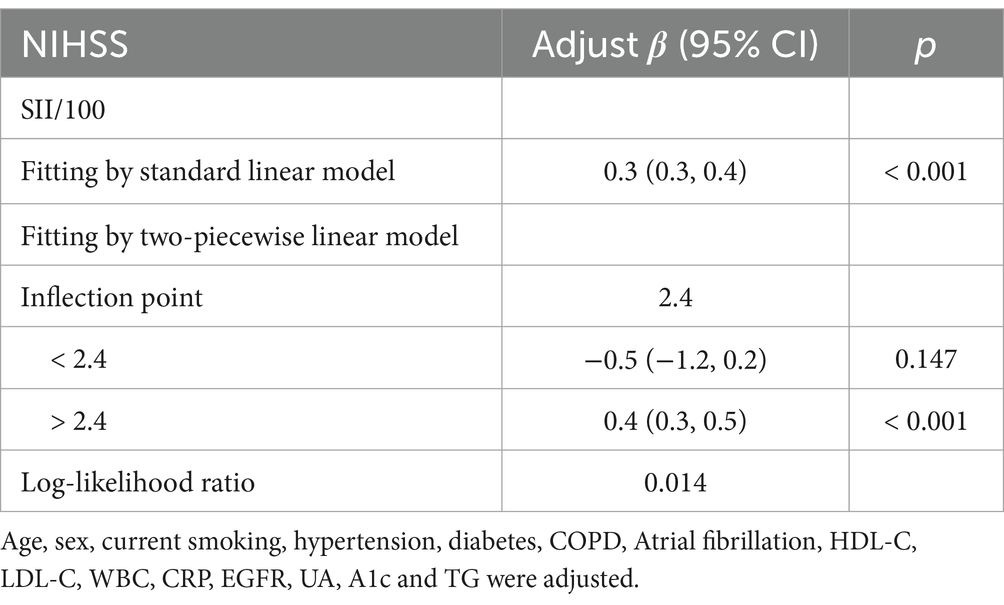
Table 4. Threshold effect analysis of SII on NIHSS at the inflection point of 2.4 using a two-piecewise linear regression model.
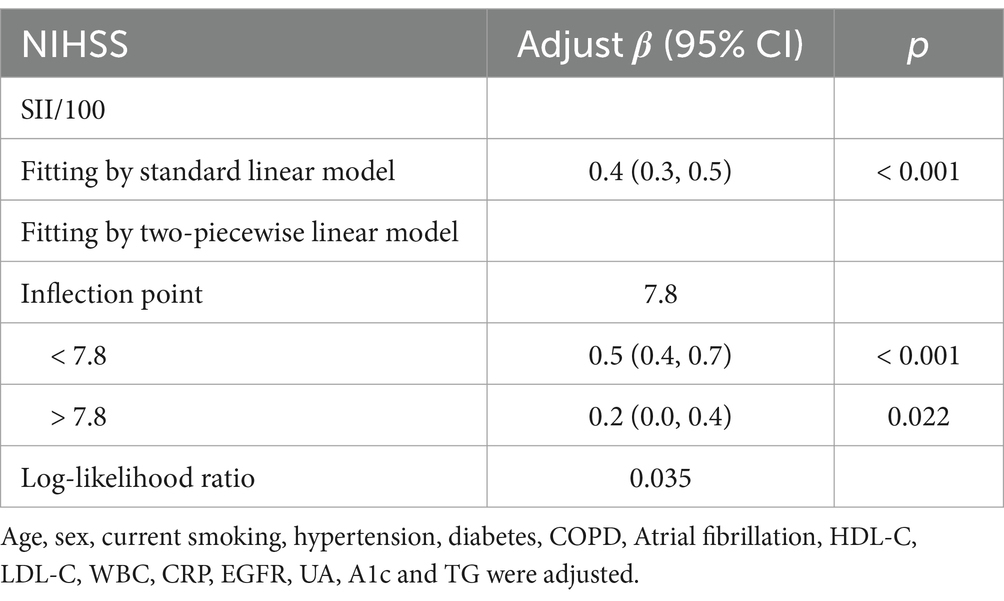
Table 5. Threshold effect analysis of SII on NIHSS at the inflection point of 7.8 using a two-piecewise linear regression model.
Smooth curve fitting, as shown in Figure 1, provides an intuitive visualization of the nonlinear relationship between SII/100 and NIHSS. The curve shows an initial flat segment, followed by an upward trend, and finally a plateauing tendency at higher SII/100 values. While the smooth curve fit suggests a nonlinear relationship, it does not allow for the precise identification of inflection points. To further quantify this relationship and identify key thresholds, we performed a threshold effect analysis using a two-piece linear regression model.
Threshold effect analysis identified two statistically significant inflection points at SII/100 values of 2.4 and 7.8. When modeled continuously, NIHSS increased by approximately 0.4–0.5 points per 100-unit increase in SII within the midrange (SII/100 = 2.4–7.8), but this association flattened beyond 7.8. Specifically, when SII/100 was below 2.4, the association was not statistically significant (adjusted β = −0.5, 95% CI: −1.2 to 0.2, p = 0.147). Between 2.4 and 7.8, a strong positive association was observed, with β increasing from 0.4 (95% CI: 0.3–0.5, p < 0.001) to 0.5 (95% CI: 0.4 to 0.7, p < 0.001). When SII/100 exceeded 7.8, the association was attenuated but remained statistically significant (adjusted β = 0.2, 95% CI: 0.0 to 0.4, p = 0.022). These values represent adjusted regression coefficients (β), indicating changes in NIHSS score per 100-unit increase in SII, not odds ratios.
A log-likelihood ratio test confirmed that the two-piecewise linear regression model provided a significantly better fit than a standard linear model (p < 0.05), supporting the presence of threshold effects without overcomplicating interpretation.
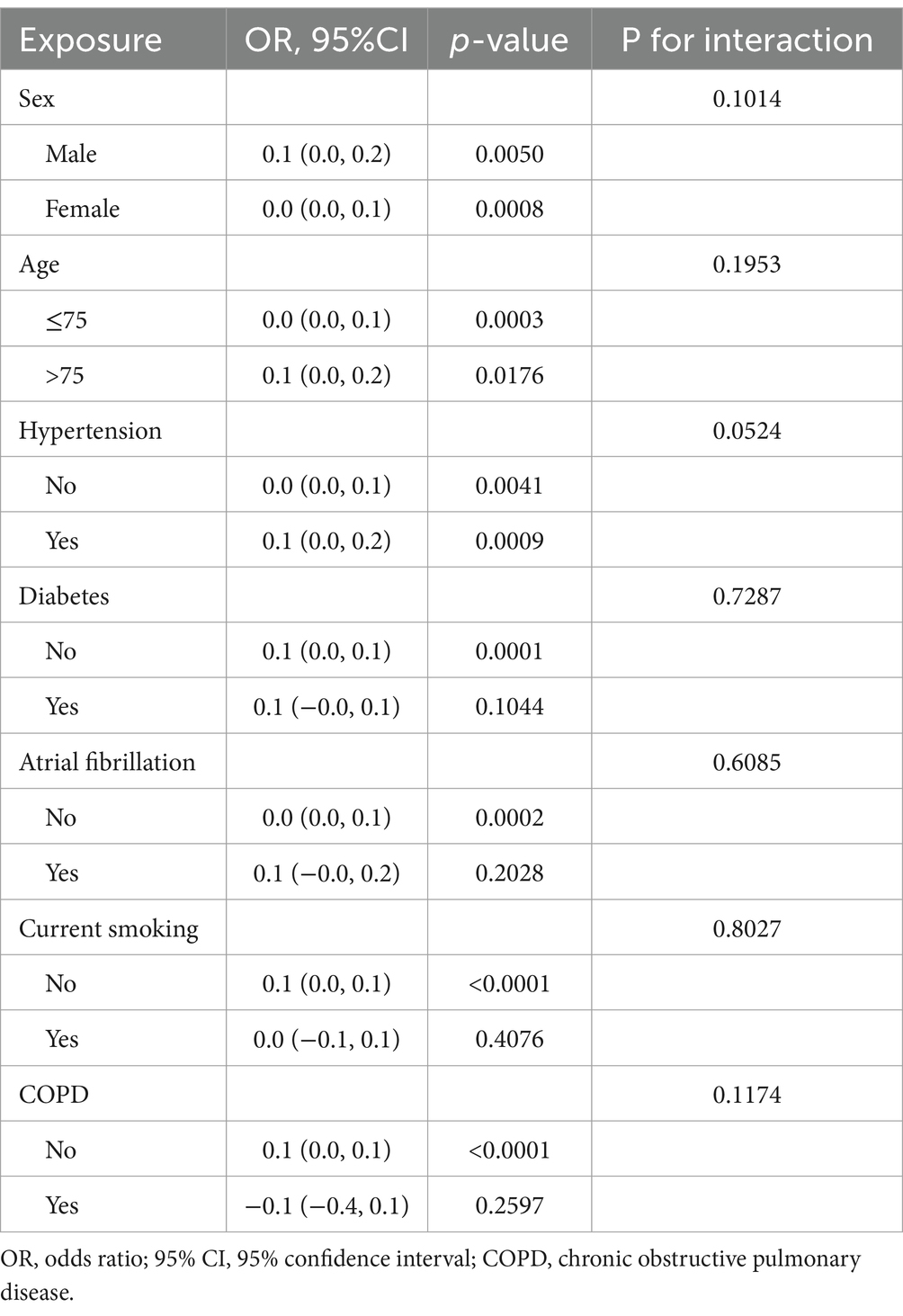
Further subgroup analysis showed that SII consistently predicted the severity of NIHSS, as shown in Table 6. No significant interactions were detected between SII and subgroups such as age, sex, hypertension, or atrial fibrillation (all P for interaction > 0.1). This supports the robustness of SII as a biomarker across diverse patient characteristics. However, the effect sizes in each subgroup were relatively small, with β values typically ranging from 0.0 to 0.1.
To enhance interpretability and address clinical relevance, we additionally performed subgroup analyses using logistic regression with NIHSS ≥ 8 as the outcome. These results, presented in Supplementary Table 1, demonstrate that SII remained a consistent predictor of severe stroke across all subgroups, with no significant effect modification detected.
Discussion
In this cross-sectional study, a significant association was identified between the Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index (SII) and stroke severity, as measured by the NIHSS score. Higher SII levels were consistently associated with more severe neurological deficits, even after adjusting for key demographic and clinical factors. Of particular note was the observation of a non-linear relationship, with critical thresholds identified at SII/100 values of 2.4 and 7.8, suggesting that the impact of SII on stroke severity varies across its range. Subgroup analyses further confirmed the robustness of this association across different patient characteristics, including age, sex, and comorbid conditions. These findings underscore the potential of SII as a reliable and easily accessible biomarker for assessing stroke severity upon admission.
In addition to elevated inflammatory markers, patients with severe stroke showed lower levels of triglycerides and serum albumin. This pattern may reflect metabolic stress or subclinical malnutrition, which are common in acute stroke. The reduction in albumin further supports a catabolic state, often associated with worse prognosis. These findings underscore the relevance of nutritional and metabolic markers in assessing stroke severity.
The role of inflammation in acute ischemic stroke (AIS) has become increasingly recognised, with mounting evidence associating elevated inflammatory biomarkers—such as C-reactive protein (CRP), interleukins (e.g., IL-6), and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α)-with more severe strokes and poorer functional recovery (13, 14). Furthermore, studies have identified the Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index (SII) as a potential marker for stroke severity and prognosis (7). For instance, Hou et al. (15) emphasised the predictive value of SII in distinguishing between severe and mild strokes. A previous study by Huang et al. (8) also demonstrated that elevated SII is associated with increased stroke severity and poor functional outcomes in AIS patients. However, unlike our work, their analysis did not explore nonlinear effects or threshold inflection points. The present study corroborates these findings by demonstrating a significant correlation between SII and NIHSS, thereby highlighting systemic inflammation’s central role in AIS pathophysiology. Elevated SII has been shown to reflect a heightened thrombosis state (increased platelet count), immune imbalance (elevated neutrophil count), and impaired adaptive immunity (reduced lymphocyte count) (7). Collectively, these factors contribute to increased ischemic brain injury through neuroinflammation, endothelial dysfunction, and blood–brain barrier disruption. Elevated SII reflects an imbalance in key immune-inflammatory components-neutrophils, platelets, and lymphocytes-that jointly mediate secondary brain injury in acute ischemic stroke. Neutrophils are among the earliest immune cells recruited to ischemic brain tissue, where they contribute to blood–brain barrier disruption, generate reactive oxygen species, and form neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs), all of which amplify neuroinflammation and exacerbate tissue damage (16). Platelets, in addition to their pro-thrombotic role, promote endothelial activation and leukocyte adhesion, facilitating microvascular occlusion and further ischemia in the penumbral region (17). Concurrently, lymphopenia, particularly reduced regulatory T cells, impairs immune homeostasis, diminishes anti-inflammatory regulation, and has been associated with worse functional outcomes in AIS (18). SII, as a composite index, captures this inflammatory triad-excessive neutrophilic and platelet activity combined with suppressed lymphocyte-mediated regulation-offering a more integrated representation of the systemic immune-inflammatory state than any single component alone. These mechanisms not only explain the observed association between SII and stroke severity, but also underscore the potential clinical value of targeting these pathways to mitigate secondary injury and improve neurological recovery. The exacerbation of tissue damage and acceleration of neuronal death is further compounded by the activation of immune cells, particularly the recruitment of neutrophils and macrophages to the ischemic site (19, 20). While inflammation undoubtedly contributes to the acute phase of stroke, emerging studies (21–23) suggest that early anti-inflammatory interventions may offer significant therapeutic benefits. Clinical trials employing anti-inflammatory agents, including corticosteroids, interleukin inhibitors, and other immunomodulatory drugs, have demonstrated encouraging results in mitigating post-stroke neuroinflammation and enhancing functional recovery. Nevertheless, challenges persist in identifying patients who would benefit most from such therapies and in balancing the risks of immune suppression with the benefits of controlling inflammation.
SII is a composite biomarker that integrates three critical components of the systemic inflammatory and thrombotic response: platelets, neutrophils, and lymphocytes (24). Unlike the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), which reflects only the balance between innate and adaptive immune cells, SII additionally incorporates platelet count, capturing the prothrombotic and microvascular contributions to stroke pathology (25). This may offer a more comprehensive representation of the inflammatory state in AIS. Furthermore, while cytokines such as interleukin-6 (IL-6) have been linked to stroke severity and outcomes (26), they are less accessible in routine clinical settings due to higher cost, longer turnaround time, and variability in measurement techniques. By contrast, SII is derived from standard complete blood counts, making it a cost-effective and easily obtainable marker with practical prognostic value.
The present study identifies a key ‘inflammatory tipping point’ between SII/100 values of 2.4 and 7.8, which may suggest that moderate levels of systemic inflammation are particularly associated with worse neurological deficits in AIS patients. When SII is low, it generally reflects a higher lymphocyte-to-neutrophil and platelet ratio, possibly indicating a less activated immune-inflammatory state. In such instances, the immune response may have limited capacity to influence stroke outcomes, and the presence of immune tolerance mechanisms could theoretically contribute to the modulation of ischemic injury (27), although this interpretation remains speculative and unsupported by direct evidence in our study. This may provide a rationale for the observation that patients with low SII tend to experience less severe strokes. Conversely, when SII is elevated, indicating heightened immune activation, the immune system might reach a saturation threshold beyond which additional activation may not further worsen ischemic damage. Moreover, elevated levels of systemic inflammation may potentially trigger immune dysregulation and activate compensatory anti-inflammatory pathways (28), which could help limit additional neurological deterioration, though this remains a hypothesis. Despite robust immune activation, excessive inflammation may not amplify ischemic damage, as the immune system’s self-regulatory mechanisms help constrain further injury (29). This proposed immunological feedback may partially explain the attenuated correlation observed between higher SII values and stroke severity, but further research is needed to confirm this mechanism (30).
To our knowledge, this study is one of the first to systematically examine the nonlinear association between SII and NIHSS in AIS patients, using smooth curve modeling and threshold effect analysis (31). The statistical adjustments and subgroup analyses employed in this study enhance the reliability and generalizability of the findings. However, as a single-center, cross-sectional study, it is not possible to infer causality, and the findings may not be fully generalizable to other populations. Regional differences in patient demographics, stroke subtypes, and institutional treatment protocols may influence baseline inflammatory levels and, consequently, the observed threshold effects of SII. Validation across diverse clinical settings is therefore necessary to confirm the broader applicability of these findings. While we adjusted for a wide range of potential confounders, the possibility of residual confounding from unmeasured variables cannot be excluded. Additionally, the cross-sectional design limits our ability to determine the temporal sequence between elevated SII and stroke severity. Additionally, since SII was measured on the second day of hospitalization rather than upon admission, it may partially reflect the early inflammatory response to stroke severity rather than purely predict it. Despite implementing extensive confounder adjustment, the potential for residual confounding from unmeasured variables remains unaccounted for. Future research should focus on the temporal dynamics of SII during the acute and recovery phases of AIS to determine its potential as a long-term prognostic marker. Hence, larger, multicentre, longitudinal studies are needed to further explore whether modulating SII levels could improve outcomes and reduce the burden of disability in AIS patients.
Conclusion
This study suggests that the SII is independently associated with stroke severity in patients with AIS, and that this association may be nonlinear, with critical threshold effects observed. SII may hold potential as a biomarker for stratifying stroke severity, but its clinical utility requires further validation. Future longitudinal and interventional studies are warranted to confirm these findings, elucidate causal pathways, and determine whether modulating systemic inflammation could improve clinical outcomes in AIS.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Quzhou People’s Hospital (Approval No. 2023-151) on November 3, 2023. Given the retrospective nature of the study, the requirement for written informed consent was waived by the ethics committee. All procedures were conducted in accordance with institutional and local ethical guidelines.
Author contributions
ZR: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Project administration, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YZ: Conceptualization, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. CZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Supervision, Visualization, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fneur.2025.1553730/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Phipps, MS, and Cronin, CA. Management of acute ischemic stroke. BMJ. (2020) 368:l6983. doi: 10.1136/bmj.l6983
2. Zhou, YX, Li, WC, Xia, SH, Xiang, T, Tang, C, Luo, JL, et al. Predictive value of the systemic immune inflammation index for adverse outcomes in patients with acute ischemic stroke. Front Neurol. (2022) 13:836595. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.836595
3. Ortega-Gutierrez, S, Farooqui, M, Zevallos, C, Quispe-Orozco, D, Dajles, A, Mendez Ruiz, A, et al. Abstract P512: immune correlates of functional outcome in acute ischemic stroke (Ais) patients. Stroke. (2021) 52:AP512. doi: 10.1161/str.52.suppl_1.P512
4. Xu, S, Lu, J, Shao, A, Zhang, JH, and Zhang, J. Glial cells: role of the immune response in ischemic stroke. Front Immunol. (2020) 11:294. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00294
5. Xia, Y, Xia, C, Wu, L, Li, Z, Li, H, and Zhang, J. Systemic immune inflammation index (SII), system inflammation response index (SIRI) and risk of all-cause mortality and cardiovascular mortality: a 20-year follow-up cohort study of 42,875 US adults. J Clin Med. (2023) 12:1128. doi: 10.3390/jcm12031128
6. Yang, R, Chang, Q, Meng, X, Gao, N, and Wang, W. Prognostic value of systemic immune-inflammation index in Cancer: a meta-analysis. J Cancer. (2018) 9:3295–302. doi: 10.7150/jca.25691
7. Huang, YW, Yin, XS, and Li, ZP. Association of the Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index (SII) and clinical outcomes in patients with stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:1090305. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1090305
8. Huang, L. Increased systemic immune-inflammation index predicts disease severity and functional outcome in acute ischemic stroke patients. Neurologist. (2023) 28:32–8. doi: 10.1097/NRL.0000000000000464
9. Kirzinger, B, Stroux, A, Rackoll, T, Endres, M, Floel, A, Ebinger, M, et al. Elevated serum inflammatory markers in subacute stroke are associated with clinical outcome but not modified by aerobic fitness training: results of the randomized controlled Phys-stroke trial. Front Neurol. (2021) 12:713018. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2021.713018
10. Yoshimura, S, Lindley, RI, Carcel, C, Sato, S, Delcourt, C, Wang, X, et al. NIHSS cut point for predicting outcome in supra- vs infratentorial acute ischemic stroke. Neurology. (2018) 91:e1695–701. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000006437
11. Schaefer, PW, Pulli, B, Copen, WA, Hirsch, JA, Leslie-Mazwi, T, Schwamm, LH, et al. Combining MRI with NIHSS thresholds to predict outcome in acute ischemic stroke: value for patient selection. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. (2015) 36:259–64. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A4103
12. Ding, GY, Xu, JH, He, JH, and Nie, ZY. Clinical scoring model based on age, NIHSS, and stroke-history predicts outcome 3 months after acute ischemic stroke. Front Neurol. (2022) 13:935150. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.935150
13. Luo, J, Cai, Y, Xiao, P, Cao, C, Huang, M, Zhang, X, et al. Inflammation-derived and clinical Indicator-based predictive model for ischemic stroke recovery. J Am Heart Assoc. (2024) 13:e035609. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.124.035609
14. Boltze, J, and Perez-Pinzon, MA. Focused update on stroke neuroimmunology: current progress in preclinical and clinical research and recent mechanistic insight. Stroke. (2022) 53:1432–7. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.122.039005
15. Hou, D, Wang, C, Luo, Y, Ye, X, Han, X, Feng, Y, et al. Systemic immune-inflammation index (SII) but not platelet-albumin-bilirubin (PALBI) grade is associated with severity of acute ischemic stroke (AIS). Int J Neurosci. (2021) 131:1203–8. doi: 10.1080/00207454.2020.1784166
16. Jickling, GC, Liu, D, Ander, BP, Stamova, B, Zhan, X, and Sharp, FR. Targeting neutrophils in ischemic stroke: translational insights from experimental studies. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. (2015) 35:888–901. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.2015.45
17. Semple, JW, Italiano, JE, and Freedman, J. Platelets and the immune continuum. Nat Rev Immunol. (2011) 11:264–74. doi: 10.1038/nri2956.
18. Liesz, A, Hu, X, Kleinschnitz, C, and Offner, H. Functional role of regulatory lymphocytes in stroke: facts and controversies. Stroke. (2015) 46:1422–30. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.114.008608
19. Candelario-Jalil, E, Dijkhuizen, RM, and Magnus, T. Neuroinflammation, stroke, blood-brain barrier dysfunction, and imaging modalities. Stroke. (2022) 53:1473–86. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.122.036946
20. Yang, C, Hawkins, KE, Dore, S, and Candelario-Jalil, E. Neuroinflammatory mechanisms of blood-brain barrier damage in ischemic stroke. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. (2019) 316:C135–53. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00136.2018
21. Kolosowska, N, Keuters, MH, Wojciechowski, S, Keksa-Goldsteine, V, Laine, M, Malm, T, et al. Peripheral Administration of IL-13 induces anti-inflammatory microglial/macrophage responses and provides neuroprotection in ischemic stroke. Neurotherapeutics. (2019) 16:1304–19. doi: 10.1007/s13311-019-00761-0
22. Feng, L, Dou, C, Xia, Y, Li, B, Zhao, M, Yu, P, et al. Neutrophil-like cell-membrane-coated Nanozyme therapy for ischemic brain damage and long-term neurological functional recovery. ACS Nano. (2021) 15:2263–80. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.0c07973
23. Zheng, Y, He, R, Wang, P, Shi, Y, Zhao, L, and Liang, J. Exosomes from LPS-stimulated macrophages induce neuroprotection and functional improvement after ischemic stroke by modulating microglial polarization. Biomater Sci. (2019) 7:2037–49. doi: 10.1039/c8bm01449c
24. Wu, S, Shi, X, Zhou, Q, Duan, X, Zhang, X, and Guo, H. The association between systemic immune-inflammation index and all-cause mortality in acute ischemic stroke patients: analysis from the mimic-iv database. Emerg Med Int. (2022) 2022:4156489. doi: 10.1155/2022/4156489
25. Fernandez-Garza, LE, Gonzalez-Aquines, A, Botello-Hernandez, E, Perez-Vazquez, G, Cristobal-Nino, M, and Gongora-Rivera, F. Segmented neutrophil-to-monocyte ratio and systemic immune-inflammation index associated with the severity and functional prognosis of acute ischemic stroke. Int J Neurosci. (2025) 135:228–36. doi: 10.1080/00207454.2023.2294705
26. Wang, Q, Li, WN, Otkur, W, Cui, Y, and Chen, HS. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio, systemic immune inflammation index and efficacy of remote ischemic conditioning in acute ischemic stroke: a post hoc exploratory analysis of the RICAMIS study. J Inflamm Res. (2024) 17:5543–53. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S460928
27. Xue, H, Zeng, Y, Zou, X, and Li, Y. Systemic immune inflammation index and risk of stroke: a cross-sectional study of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2005-2018. Front Neurol. (2024) 15:1431727. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1431727
28. Yang, C, Hu, BW, Tang, F, Zhang, Q, Quan, W, Wang, J, et al. Prognostic value of systemic immune-inflammation index (SII) in patients with glioblastoma: a comprehensive study based on Meta-analysis and retrospective single-center analysis. J Clin Med. (2022) 11:7514. doi: 10.3390/jcm11247514
29. Qin, X, Akter, F, Qin, L, Cheng, J, Guo, M, Yao, S, et al. Adaptive immunity regulation and cerebral ischemia. Front Immunol. (2020) 11:689. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00689
30. Jian, Z, Liu, R, Zhu, X, Smerin, D, Zhong, Y, Gu, L, et al. The involvement and therapy target of immune cells after ischemic stroke. Front Immunol. (2019) 10:2167. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02167
31. Ma, F, Li, L, Xu, L, Wu, J, Zhang, A, Liao, J, et al. The relationship between systemic inflammation index, systemic immune-inflammatory index, and inflammatory prognostic index and 90-day outcomes in acute ischemic stroke patients treated with intravenous thrombolysis. J Neuroinflammation. (2023) 20:220. doi: 10.1186/s12974-023-02890-y
Keywords: systemic immune-inflammation index (SII), acute ischemic stroke (AIS), NIHSS, inflammation, prognostic marker
Citation: Rao Z, Zhang Y and Zhu C (2025) Association of systemic immune-inflammation index with severity in acute ischemic stroke patients: a cross-sectional study. Front. Neurol. 16:1553730. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1553730
Edited by:
Mirjam R. Heldner, University Hospital Bern, SwitzerlandCopyright © 2025 Rao, Zhang and Zhu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yiming Zhang, emhhbmd5bTE2MTFAd211LmVkdS5jbg==
 Zichen Rao
Zichen Rao Yiming Zhang
Yiming Zhang Chunyan Zhu
Chunyan Zhu