Abstract
Objective:
This study aimed to explore the prevalence and risk factors for painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy through meta-analysis, and to provide countermeasures for early intervention and active prevention of diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain.
Methods:
We conducted a systematic search of PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, and Cochrane Library for articles published from the establishment of the database to November 2024. A total of 14 studies (nine cross-sectional studies and five cohort studies) qualified for meta-analysis. We used a random-effects meta-analysis and assessed heterogeneity and publication bias.
Results:
A total of 14 studies (nine cross-sectional, five cohort) were included. The prevalence of PDPN was estimated at 33.9% (95% CI [19.4%−48.5%]). Significant risk factors included female gender (OR = 1.29, P = 0.004), glycosylated hemoglobin levels (WMD = 0.14, P < 0.001), nephropathy (OR = 1.41, P < 0.001), retinopathy (OR = 1.32, P = 0.040), cardiovascular disease (OR = 1.46, P < 0.001), arterial hypertension (OR = 1.25, P = 0.047), triglycerides levels (WMD = −0.10, P < 0.001), low density lipoprotein levels (WMD = −0.20, 1. 0.001), smoking (OR = 0.90, P = 0.001), drinking alcohol (OR = 0.87, P = 0.001), glomerular filtration rate levels (WMD = −7.11, P < 0.001), obesity (OR = 2.00, P = 0.001). The multivariate analysis results showed that female gender (OR = 1.42, P = 0.032), age of onset (OR = 1.19, P < 0.001), duration of diabetes (OR = 1.29, P < 0.001), and retinopathy (OR = 1.90, P = 0.032) were indicated as risk factors for painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy.
Conclusion:
This meta-analysis suggests that female gender, glycosylated hemoglobin levels, nephropathy, retinopathy, cardiovascular disease, arterial hypertension, smoking, drinking alcohol, glomerular filtration rate levels, obesity, age of onset and duration of diabetes are indicated as risk factors for painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy in diabetic patients.
Systematic review registration:
https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/, identifier CRD42025629060.
1 Background
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is one of the chronic diseases that afflicts all age groups around the world, the associated neuropathy is its most costly and disabling complication (1, 2), affects up to 50% or more of patients (3, 4). And the prevalence of PDPN is increasing year by year and getting younger and younger (1, 5). PDPN, also known as diabetic neuropathic pain. For diabetic patients, PDPN occurs in about 50% of diabetic patients (6, 7). Despite its common nature, PDPN is underdiagnosed and undertreated and is often the main reason for medical visits. The prevalence PDPN determined in a community-based study is about 26% (8). However, the incidence of PDPN is far higher than this. PDPN is usually characterized by distal lower limb pain (9, 10). It was characterized by burning pain, tearing pain and stinging pain (10). In addition to presenting as unbearable pain, it may be accompanied by problems such as poor sleep quality (11)and mood disorders (12, 13). At present, the treatment of PDPN is challenging (14–16). Although Alabdali et al. (17) showed that anticonvulsant, antidepressant, and opioid drugs reduced pain in patients with PDPN to some extent, a series of adverse effects brought by pain symptoms significantly reduced the quality of life of patients. At present, there are more and more studies on diabetic peripheral neuropathy, and more and more evidence shows that it is related to advanced glycation terminal pathway (2), however, the pathophysiological, biochemical, molecular and pharmacological mechanisms of PDPN are not fully understood. Therefore, it is of great positive significance to explore the related influencing factors of PDPN. This study explores the prevalence and risk factors for PDPN through Meta-analysis and systematic review and resolves the controversy about the risk factors of PDPN, in order to improve the quality of life and prognosis of patients. It is an important update for clinicians to provide treatment and prevention of PDPN.
2 Materials and methods
This systematic review is conducted according to the preferred reporting items of the Protocol for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses (PRISMA-P) guidelines. The review will be conducted according to PRISMA criteria (18). The registration number is CRD42025629060.
2.1 Search strategy
PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, and Cochrane Library were searched by computer for articles on influencing factors of diabetic patients with peripheral neuropathic pain. The search time limit was from the establishment of the database to November 2024. A combination of subject headings and free words was used to search, and references of included studies were also searched to supplement the acquisition of relevant information (see Supplementary Tables 1–4 for specific retrieval strategies).
2.2 Literature inclusion and exclusion criteria
Inclusion criteria: (1) patients with confirmed diagnosis of diabetes type 1 or type 2 (19); (2) the influencing factors of diabetic peripheral neuropathy pain in diabetic patients in the study; (3) study types were case-control study, cohort study or cross-sectional study; (4) outcome indicators were whether diabetes patients were complicated with PDPN and related measurement data.
Exclusion criteria: (1) non-English literature; (2) review literature, conference papers, case reports, etc. (3) repeated publications; (4) articles without full text or with low quality evaluation.
2.3 Literature data extraction
Two researchers independently screened the literature and extracted the data according to the inclusion and exclusion criteria of the literature. If there were differences of opinion, the third researcher participated in the consultation and discussion to decide whether to be included. Original study authors were contacted by mail if they did not report important information needed for the study. The data extracted included the first author, publication year, study type, country, sample size, number of PDPN cases, PDPN diagnostic criteria, regression model and influencing factors.
2.4 Literature quality evaluation
Two researchers independently evaluated the quality of the included studies using the Newcastle-Ottawa scale (NOS) (20). The NOS scale assesses the quality of literature from three aspects: population selection, comparability between groups and exposure assessment. The total score of NOS is 9 points, and it is generally considered that the score of NOS 0–3 is low quality, 4–6 is moderate quality, and 7–9 is high quality. If two researchers disagreed during the evaluation process, the decision would be discussed, or a third party would decide.
2.5 Statistical methods
Stata15.0 software was used to perform a meta-analysis of the extracted data. The continuous variables were expressed as weighted mean difference (WMD) and 95% confidence interval (CI), and the dichotomous variables were expressed as odds ratio (OR). The positive and negative signs of WMD indicate the direction, and the value indicates the actual clinical effect. An OR > 1 indicates an increased risk. P value and I2 were used to judge the heterogeneity among the studies. If P ≥ 0.10 and I2 < 50%, there was no significant heterogeneity among the studies, and the fixed effect model was used for analysis. If P < 0.10 and I2 ≥ 50%, it indicated that there was significant heterogeneity among the studies. Subgroup analysis was performed on the year of publication, country and region, study type, literature quality score, and pain questionnaire adopted by PDPN diagnosis to explore the suspected sources of heterogeneity (see Supplementary Figures 1–7, Supplementary Table 1). A random effect model was used for data analysis. For I2 > 50%, the sensitivity analysis was performed by the test method of elimination one by one (see Supplementary Figures 8–12), and Egger's test was used to analyze the publication bias (see Supplementary Tables 5, 6). The significance level was set at 0.05.
3 Results
3.1 Results of literature search
By searching PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, and Web of Science databases, 520 documents were initially obtained, 453 documents were retained after removing duplicate documents, 348 articles were preliminarily screened by reading the titles and abstracts, and 14 documents were included after reading the full text (see Figure 1).
Figure 1

Flow chart of the literature search.
3.2 Basic features of the included literature
A total of 14 studies (21–34) were included, of which 5 were cohort studies (23, 24, 26, 28, 32) and 9 were cross-sectional studies (21, 22, 25, 27, 29–31, 33, 34). There were 16,829 patients with PDPN and 17,281 patients with painless diabetic peripheral neuropathy. The age of the study ranged from 0 to 96 years (see Supplementary Tables 7, 8). The included 14 articles were evaluated by NOS quality evaluation, and two of them scored 6 points, indicating that the study quality was moderate. The remaining scores were 7–8, and the overall quality of the studies included was high (see Supplementary Table 9 for specific quality evaluations).
3.3 Prevalence of painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy
The heterogeneity test (I2 = 99.8%, P < 0.001) was conducted based on the random-effects model. It was found that the prevalence of PDPN was estimated at 33.9% (95% CI [19.4%-48.5%]). The analysis results indicated that sensitivity was low, and the analysis results were stable. The Egger test was performed on the index to evaluate publication bias (P = 0.642), and the prevalence may not have been subject to publication bias (see Figures 2–4).
Figure 2

Forest plot of the meta-analysis of the prevalence of PDPN.
Figure 3

Sensitivity analysis of the prevalence of PDPN.
Figure 4

Egger test of the prevalence of PDPN.
3.4 Results of single factors meta-analysis
3.4.1 Female gender
Fourteen studies (21–34) mentioned female as a risk factor for PDPN, and the heterogeneity test (I2 = 72.3%, P < 0.001) was performed based on the random-effects model. It was found that female was considered a statistically significant risk factor for PDPN (OR = 1.29, 95% CI [1.09,1.54], P = 0.004) (see Figure 5, Supplementary Table 5).
Figure 5

Forest plot of the meta-analysis of female gender.
3.4.2 Glycosylated hemoglobin levels
Eleven studies (22–24, 26–32, 34) mentioned glycosylated hemoglobin levels as a risk factor, and the heterogeneity test (I2 = 26.1%, P = 0.196) was performed based on the fixed-effects model. It was found that glycosylated hemoglobin levels was considered a statistically significant risk factor for PDPN (OR = 0.14, 95% CI [0.09, 0.19], P < 0.001) (see Figure 6, Supplementary Table 5).
Figure 6

Forest plot of the meta-analysis of glycosylated hemoglobin levels.
3.4.3 Concomitant nephropathy
Nephropathy (22, 26, 27, 29–31, 33) was mentioned as a risk factor for PDPN, and the heterogeneity test (I2 = 31.0%, P = 0.191) was performed based on the fixed-effects model. It was found that nephropathy was considered a statistically significant risk factor for PDPN (OR = 1.41, 95% CI [1.34, 1.49], P < 0.001) (see Figure 7, Supplementary Table 5).
Figure 7

Forest plot of the meta-analysis of concomitant nephropathy.
3.4.4 Associated retinopathy
Seven studies (22, 23, 26, 27, 29, 31, 33) mentioned retinopathy as a risk factor for PDPN, and the heterogeneity test (I2 = 65.5%, P = 0.008) was performed based on the random-effects model. It was found that retinopathy was considered a statistically significant risk factor for PDPN (OR = 1.32, 95% CI [1.01, 1.71], P = 0.040) (see Figure 8, Supplementary Table 5).
Figure 8

Forest plot of the meta-analysis of associated retinopathy.
3.4.5 Concomitant cardiovascular disease
Cardiovascular disease (22, 23, 26–29, 31, 33) was mentioned as a risk factor in eight studies, and the heterogeneity test (I2 = 57.8%, P = 0.020) was performed based on the random-effects model. It was found that cardiovascular disease was considered a statistically significant risk factor for PDPN (OR = 1.46, 95% CI [1.19, 1.80], P < 0.001) (see Figure 9, Supplementary Table 5).
Figure 9

Forest plot of the meta-analysis of concomitant cardiovascular disease.
3.4.6 Arterial hypertension
Twelve studies (22–24, 26–34) mentioned arterial hypertension as a risk factor, and the heterogeneity test (I2 = 73.1%, P = 0.000) was performed based on the random-effects model. It was found that arterial hypertension was considered a statistically significant risk factor for PDPN (OR = 1.25, 95% CI [1.00, 1.55], P = 0.047) (see Figure 10, Supplementary Table 5).
Figure 10
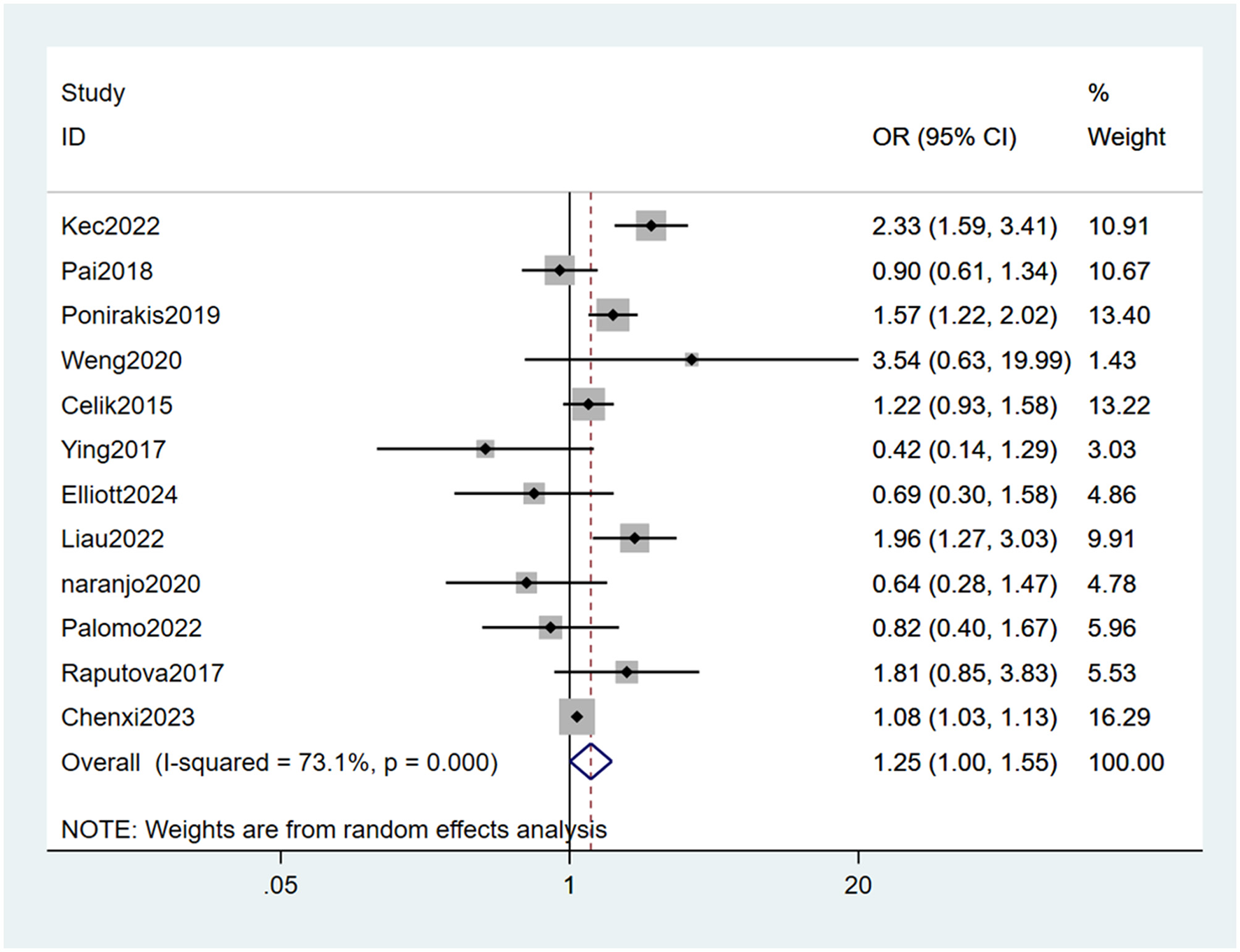
Forest plot of the meta-analysis of arterial hypertension.
3.4.7 Triglycerides levels
Five studies (23, 27, 28, 32, 33) mentioned triglycerides levels as a risk factor, and the test (I2 = 50.0%, P = 0.091) indicates moderate heterogeneity. It was found that triglycerides levels were considered a statistically significant risk factor for PDPN (WMD = −0.10, 95% CI [−0.13, −0.08], P < 0.001) (see Figure 11, Supplementary Table 5).
Figure 11

Forest plot of the meta-analysis of triglycerides levels.
3.4.8 Low density lipoprotein levels
Four studies (23, 27, 32, 33) mentioned low density lipoprotein levels as a risk factor, and the heterogeneity test (I2 = 27.6%, P = 0.251) was performed based on the fixed-effects model. It was found that low density lipoprotein levels were considered a statistically significant risk factor for PDPN (WMD = −0.20, 95% CI [−0.22, −0.17], P < 0.001) (See Figure 12, Supplementary Table 5).
Figure 12

Forest plot of the meta-analysis of low density lipoprotein levels.
3.4.9 Smoking
Smoking (21, 23–25, 27, 28, 30, 32) was mentioned as a risk factor in eight studies, and the heterogeneity test (I2 = 0.0%, P = 0.564) was performed based on the fixed-effects model. It was found that smoking was considered a statistically significant risk factor for PDPN (OR = 0.90, 95% CI [0.84, 0.95], P = 0.001) (see Figure 13, Supplementary Table 5).
Figure 13

Forest plot of the meta-analysis of smoking.
3.4.10 Drinking alcohol
Drinking alcohol (24, 27, 30) was mentioned as a risk factor in three studies, and the heterogeneity test (I2 = 27.6%, P = 0.251) was performed based on the fixed-effects model. It was found that drinking alcohol was considered a statistically significant risk factor for PDPN (OR = 0.87, 95% CI [0.80,0.95], P = 0.001) (see Figure 14, Supplementary Table 5).
Figure 14

Forest plot of the meta-analysis of drinking alcohol.
3.4.11 Glomerular filtration rate levels
Five studies (27, 28, 30, 33, 34) mentioned glomerular filtration rate levels as a risk factor, and the heterogeneity test (I2 = 23.2%, P = 0.267) was performed based on the fixed-effects model. It was found that glomerular filtration rate levels was considered a statistically significant risk factor for PDPN (WMD = −7.11, 95% CI [−8.03,-6.20], P < 0.001) (see Figure 15, Supplementary Table 5).
Figure 15

Forest plot of the meta-analysis of glomerular filtration rate levels.
3.4.12 Obesity
Five studies (27, 29–32) mentioned obesity as a risk factor, and the heterogeneity test (I2 = 60.4%, P = 0.056) was performed based on the random-effects model. It was found that obesity was considered a statistically significant risk factor for PDPN (OR = 2.00, 95% CI [1.33, 3.02], P = 0.001) (see Figure 16, Supplementary Table 5).
Figure 16

Forest plot of the meta-analysis of obesity.
3.4.13 Other meta-analysis results
Differences in the correlations between BMI, dyslipidemia levels, cholesterol levels, high density lipoprotein levels, retirement, work regularly, oral hypoglycemic agents, lipid-lowering agents, insulin therapy, sports and exercise, diabetic foot ulcers and serum creatinine levels were not statistically significant (see Supplementary Table 5).
3.5 Results of multiple factors meta-analysis
The results of the multifactorial analysis mentioned in the research study were analyzed and combined. It was found that female gender (OR = 1.42, 95% CI [1.03, 1.97], P = 0.032), age of onset (OR = 1.19, 95% CI [1.11,1.27], P < 0.001), duration of diabetes (OR = 1.29, 95% CI [1.15, 1.45], P < 0.001) and retinopathy (OR = 1.90, 95% CI [1.06, 3.40], P = 0.032) were considered a statistically significant risk factor for PDPN (see Supplementary Table 6).
4 Publication bias
The egger test was used to evaluate the publication bias of each risk factor, and the P values of most indicators were >0.05, suggesting that almost all risk factors did not have publication bias (see Supplementary Tables 5, 6).
5 Discussion
Although many previous reports have used review and meta-analysis to report the prevalence of diabetic peripheral neuropathy, this study is the first to use meta-analysis to investigate the risk factors for PDPN, a subtype of diabetic peripheral neuropathy and one of the common chronic complications of diabetes. The prevalence of PDPN can be reduced by the risk factors described above, such as a lower probability of developing PDPN in persons without diabetic retinopathy than in those with retinopathy. PDPN is characterized by persistent pain in the lower extremity from bottom to top, distal to proximal, presenting with a range of neuropathic symptoms that include burning, deep pain, needling, and electric shock-like pain (11, 35). In addition to the underlying factors such as cultural, environmental and psychosocial factors, the pathogenesis of pain also includes peripheral structure, molecular biomarkers and the central nervous system (36), heredity (37) and gender (38). However, more attention is needed to clarify the pathogenesis of PDPN.
This study found that female is a risk factor for PDPN through univariate and multivariate analysis, indicating that female diabetic patients are more likely to have peripheral nerve pain than male diabetic patients, which is consistent with the results of previous studies (39, 40). The reason for this may be related to the emotional instability of female patients or may be affected by estrogen and thus have a low tolerance to pain. Huang et al. (41) also reported that about two thirds of female diabetic patients are susceptible to peripheral neuropathy. Recent studies have also highlighted female sex as a potential risk factor for PDPN (32, 38, 42), our study just adds to the evidence.
The present study also found that advanced age is a risk factor for PDPN, which is consistent with the results of Sang et al. (30) in a multi-center, large-sample cross-sectional study in Korea. The longer the duration of diabetes, the more likely it is to develop PDPN, this finding has been confirmed by other studies (32, 43, 44). The possible reason may be that the continuous high concentration of blood glucose leads to nerve damage (45), it is consistent with our study that PDPN is more likely to occur with higher Hba1c concentration. Therefore, it is necessary to strengthen the focus of attention and education for diabetic patients to prevent the occurrence of PDPN. It is a risk factor for PDPN in patients with arterial hypertension, which is consistent with the results of previous studies (40, 46, 47), the likely reason is that the cumulative effect of hypertension damages the myelin sheath of the nerve (48), PDPN is then induced. In addition, diabetic complications such as nephropathy, retinopathy, cardiovascular disease, hyperlipidemia levels, obesity and other comorbidities are not independent of each other, but mutually affect the occurrence of PDPN (39, 40, 49). Studies have shown that (50), diabetic nephropathy and retinopathy are independent risk factors for PDPN, which was again confirmed in our study. Studies have shown that (51, 52), smoking and alcohol consumption were associated with the occurrence of PDPN, again consistent with the conclusions obtained in our study. This study also found that oral hypoglycemic drugs, lipid-lowering drugs and insulin therapy were protective factors, suggesting that the occurrence of PDPN may not be related to clinical medication. Regular exercise was reported as a protective factor (53, 54), this is consistent with the conclusion of this study, which may be related to the fact that exercise can promote blood glucose metabolism and slow down nerve conduction. Although many risk factors for PDPN have been identified, there are still unknown risk factors for PDPN. Therefore, during clinical treatment, the patient's condition should be comprehensively considered, all risk factors leading to PDPN should be screened and prevented in advance as far as possible, and the early prevention and treatment of PDPN should be actively carried out to reduce the risk of PDPN and improve the prognosis of patients.
This study still has the following limitations: firstly, the number of articles included is small, and the types of articles are cross-sectional studies and cohort studies, which may have selection bias. Prospective studies may be needed in the future to avoid publication bias. Secondly, although no source of heterogeneity was identified by subgroup analysis, perhaps we can identify potential sources of heterogeneity in future studies. Thirdly, although the egger test did not show significant bias, publication bias does exist, studies with negative results may not have been published, leading us to overestimate the risk. Prospective studies and uniform diagnostic methods for PDPN may be needed in the future to avoid publication bias. Finally, because the original studies did not control confounders consistently (for example, no universal adjustment for socioeconomic status), the results of this meta-analysis may be affected by residual confounding.
6 Conclusion
Based on the available evidence, female gender, glycosylated hemoglobin levels, nephropathy, retinopathy, cardiovascular disease, arterial hypertension, triglycerides levels, low density lipoprotein levels, smoking, drinking alcohol, glomerular filtration rate levels, obesity, age of onset and duration of diabetes are identified as risk factors for PDPN, and clinical practitioners can combine these indicators for early detection, diagnosis, and intervention in such kind of cases, thereby improving the quality of life of affected individuals.
Statements
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found in the article/Supplementary material.
Author contributions
PZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. JZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. JL: Investigation, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft. LQ: Investigation, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft. WH: Investigation, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft. XZ: Investigation, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft. JW: Investigation, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft. ZS: Investigation, Methodology, Software, Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the platelet-rich Plasma Therapy Clinical Application Foundation (the fund number: Scientific Research projects of Provincial Key Laboratory in 2021–40) and Feasibility study of transforming growth factor-β3 inducing bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to differentiate into chondrocytes (the fund number: YZ-1844).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fneur.2025.1564867/full#supplementary-material
References
1.
Peltier A Goutman SA Callaghan BC . Painful diabetic neuropathy. BMJ. (2014) 348:g1799. 10.1136/bmj.g1799
2.
Zhu J Hu Z Luo Y Liu Y Luo W Du X et al . Diabetic peripheral neuropathy: pathogenetic mechanisms and treatment. Front Endocrinol. (2023) 14:1265372. 10.3389/fendo.2023.1265372
3.
Callaghan BC Cheng HT Stables CL Smith AL Feldman EL . Diabetic neuropathy: clinical manifestations and current treatments. Lancet Neurol. (2012) 11:521–34. 10.1016/S1474-4422(12)70065-0
4.
Girach A Julian TH Varrassi G Paladini A Vadalouka A Zis P . Quality of life in painful peripheral neuropathies: a systematic review. Pain Res Manag. (2019) 2019:2091960. 10.1155/2019/2091960
5.
Tesfaye S Boulton AJ Dyck PJ Freeman R Horowitz M Kempler P et al . Diabetic neuropathies: update on definitions, diagnostic criteria, estimation of severity, and treatments. Diabetes Care. (2010) 33:2285–93. 10.2337/dc10-1303
6.
Schreiber AK Nones CF Reis RC Chichorro JG Cunha JM . Diabetic neuropathic pain: Physiopathology and treatment. World J Diabetes. (2015) 6:432–44. 10.4239/wjd.v6.i3.432
7.
Tesfaye S Selvarajah D Gandhi R Greig M Shillo P Fang F et al . Diabetic peripheral neuropathy may not be as its name suggests: evidence from magnetic resonance imaging. Pain. (2016) 157:S72–s80. 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000000465
8.
Daousi C Macfarlane IA Woodward A Nurmikko TJ Bundred PE Benbow SJ . Chronic painful peripheral neuropathy in an urban community: a controlled comparison of people with and without diabetes. Diabet Med. (2004) 21:976–82. 10.1111/j.1464-5491.2004.01271.x
9.
D'souza RS Barman R Joseph A Abd-Elsayed A . Evidence-based treatment of painful diabetic neuropathy: a systematic review. Curr Pain Headache Rep. (2022) 26:583–94. 10.1007/s11916-022-01061-7
10.
D'souza RS Langford B Dombovy-Johnson M Abd-Elsayed A . Neuromodulation interventions for the treatment of painful diabetic neuropathy: a systematic review. Curr Pain Headache Rep. (2022) 26:365–77. 10.1007/s11916-022-01035-9
11.
Galer BS Gianas A Jensen MP . Painful diabetic polyneuropathy: epidemiology, pain description, and quality of life. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. (2000) 47:123–8. 10.1016/S0168-8227(99)00112-6
12.
Gore M Brandenburg NA Hoffman DL Tai KS Stacey B . Burden of illness in painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy: the patients' perspectives. J Pain. (2006) 7:892–900. 10.1016/j.jpain.2006.04.013
13.
Selvarajah D Cash T Sankar A Thomas L Davies J Cachia E et al . The contributors of emotional distress in painful diabetic neuropathy. Diab Vasc Dis Res. (2014) 11:218–225. 10.1177/1479164114522135
14.
Staudt MD Prabhala T Sheldon BL Quaranta N Zakher M Bhullar R et al . Current strategies for the management of painful diabetic neuropathy. J Diabetes Sci Technol. (2022) 16:341–52. 10.1177/1932296820951829
15.
Arora V Campbell JN Chung MK . Fight fire with fire: neurobiology of capsaicin-induced analgesia for chronic pain. Pharmacol Ther. (2021) 220:107743. 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2020.107743
16.
James CF Tripathi S Karampatou K Gladston DV Pappachan JM . Pharmacotherapy of painful diabetic neuropathy: a clinical update. Sisli Etfal Hastan Tip Bul. (2022) 56:1–20. 10.14744/SEMB.2021.54670
17.
Alabdali M Qrimli M Barnett C Abraham A Breiner A Katzberg HD et al . Choosing drugs for the treatment of diabetic neuropathy. Expert Opin Pharmacother. (2015)16:1805–14. 10.1517/14656566.2015.1067680
18.
Liberati A Altman DG Tetzlaff J Mulrow C Gøtzsche PC Ioannidis JP et al . The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: explanation and elaboration. PLoS Med. (2009) 6:e1000100. 10.1371/journal.pmed.1000100
19.
Kerner W Brückel J . Definition, classification and diagnosis of diabetes mellitus. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabet. (2014) 122:384–6. 10.1055/s-0034-1366278
20.
Stang A . Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur J Epidemiol. (2010) 25:603–5. 10.1007/s10654-010-9491-z
21.
Alamri A Sr Alharbi K Hassan K Alhakami S Alosaimi M Rofidi K et al . Frequency of Neuropathic sensory symptoms among patients with uncontrolled diabetes mellitus in security forces hospital, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. Cureus. (2021) 13:e17528. 10.7759/cureus.17528
22.
Celik S Yenidunya G Temel E Purisa S Uzum AK Gul N et al . Utility of DN4 questionnaire in assessment of neuropathic pain and its clinical correlations in Turkish patients with diabetes mellitus. Prim Care Diabetes. (2016) 10:259–64. 10.1016/j.pcd.2015.11.005
23.
Elliott J Sloan G Stevens L Selvarajah D Cruccu G Gandhi RA et al . Female sex is a risk factor for painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy: the EURODIAB prospective diabetes complications study. Diabetologia. (2024) 67:190–8. 10.1007/s00125-023-06025-z
24.
Goh LY Shahrom EE Ganesan CC Vethakkan SR Goh KJ . The prevalence and associated factors of neuropathic pain symptoms in a cohort of multi-ethnic Malaysian patients with diabetes mellitus. Neurology Asia. (2017) 22:325–31.
25.
Jacovides A Bogoshi M Distiller LA Mahgoub EY Omar MK Tarek IA et al . An epidemiological study to assess the prevalence of diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain among adults with diabetes attending private and institutional outpatient clinics in South Africa. J Int Med Res. (2014) 42:1018–28. 10.1177/0300060514525759
26.
Kec D Rajdova A Raputova J Adamova B Srotova I Nekvapilova EK et al . Risk factors for depression and anxiety in painful and painless diabetic polyneuropathy: A multicentre observational cross-sectional study. Eur J Pain. (2022) 26:370–89. 10.1002/ejp.1865
27.
Li C Wang W Ji Q Ran X Kuang H Yu X et al . Prevalence of painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy in type 2 diabetes mellitus and diabetic peripheral neuropathy: a nationwide cross-sectional study in mainland China. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. (2023) 198:110602. 10.1016/j.diabres.2023.110602
28.
Liau YJ Lin SF Lee IT . Scores of peripheral neuropathic pain predicting long-term mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes: a retrospective cohort study. Front Endocrinol. (2022)13:969149. 10.3389/fendo.2022.969149
29.
Naranjo C Ortega-Jiménez P Del Reguero L Moratalla G Failde I . Relationship between diabetic neuropathic pain and comorbidity. Their impact on pain intensity, diabetes complications and quality of life in patients with type-2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. (2020) 165:108236. 10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108236
30.
Pai YW Lin CH Lee IT Chang MH . Prevalence and biochemical risk factors of diabetic peripheral neuropathy with or without neuropathic pain in Taiwanese adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Metab Syndr. (2018) 12:111–6. 10.1016/j.dsx.2017.09.013
31.
Palomo-Osuna J Dueñas M Naranjo C De Sola H Salazar A Failde I . Factors related to cognitive function in type-2 diabetes and neuropathic pain patients, the role of mood and sleep disorders in this relationship. Sci Rep. (2022) 12:15442. 10.1038/s41598-022-18949-4
32.
Ponirakis G Elhadd T Chinnaiyan S Dabbous Z Siddiqui M Al-Muhannadi H et al . Prevalence and risk factors for painful diabetic neuropathy in secondary healthcare in Qatar. J Diabetes Investig. (2019) 10:1558–64. 10.1111/jdi.13037
33.
Raputova J Srotova I Vlckova E Sommer C Üçeyler N Birklein F et al . Sensory phenotype and risk factors for painful diabetic neuropathy: a cross-sectional observational study. Pain. (2017) 158:2340–53. 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000001034
34.
Weng YC Tsai SS Lyu RK Chu CC Ro LS Liao MF et al . Diabetic distal symmetrical polyneuropathy: correlation of clinical, laboratory, and electrophysiologic studies in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes Res. (2020) 2020:6356459. 10.1155/2020/6356459
35.
Abbott CA Malik RA Van Ross ER Kulkarni J Boulton AJ . Prevalence and characteristics of painful diabetic neuropathy in a large community-based diabetic population in the U.K. Diabet Care. (2011) 34:2220–4. 10.2337/dc11-1108
36.
Sloan G Shillo P Selvarajah D Wu J Wilkinson ID Tracey I et al . A new look at painful diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. (2018) 144:177–91. 10.1016/j.diabres.2018.08.020
37.
Blesneac I Themistocleous AC Fratter C Conrad LJ Ramirez JD Cox JJ et al . Rare NaV1.7 variants associated with painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Pain. (2018) 159:469–80. 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000001116
38.
Truini A Spallone V Morganti R Tamburin S Zanette G Schenone A et al . A cross-sectional study investigating frequency and features of definitely diagnosed diabetic painful polyneuropathy. Pain. (2018) 159:2658–66. 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000001378
39.
Jane SW Lin MS Chiu WN Beaton RD Chen MY . Prevalence, discomfort and self-relief behaviours of painful diabetic neuropathy in Taiwan: a cross-sectional study. BMJ Open. (2016) 6:e011897. 10.1136/bmjopen-2016-011897
40.
Kim SS Won JC Kwon HS Kim CH Lee JH Park TS et al . Prevalence and clinical implications of painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy in type 2 diabetes: results from a nationwide hospital-based study of diabetic neuropathy in Korea. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. (2014) 103:522–9. 10.1016/j.diabres.2013.12.003
41.
Huang CC Chen TW Weng MC Lee CL Tseng HC Huang MH . Effect of glycemic control on electrophysiologic changes of diabetic neuropathy in type 2 diabetic patients. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. (2005) 21:15–21. 10.1016/S1607-551X(09)70271-2
42.
Ponirakis G Elhadd T Al Ozairi E Brema I Chinnaiyan S Taghadom E et al . Prevalence and risk factors for diabetic peripheral neuropathy, neuropathic pain and foot ulceration in the Arabian Gulf region. J Diabetes Investig. (2022) 13:1551–9. 10.1111/jdi.13815
43.
Halawa MR Karawagh A Zeidan A Mahmoud AE Sakr M Hegazy A . Prevalence of painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy among patients suffering from diabetes mellitus in Saudi Arabia. Curr Med Res Opin. (2010) 26:337–43. 10.1185/03007990903471940
44.
Garoushi S Johnson MI Tashani OA . A cross-sectional study to estimate the point prevalence of painful diabetic neuropathy in Eastern Libya. BMC Public Health. (2019) 19:78. 10.1186/s12889-018-6374-9
45.
Edwards JL Vincent AM Cheng HT Feldman EL . Diabetic neuropathy: mechanisms to management. Pharmacol Ther. (2008) 120:1–34. 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2008.05.005
46.
Abdissa D . Prevalence and associated factors of painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy among diabetic patients on follow up at Jimma University Medical Center. J Diabetes Metab Disord. (2020) 19:1407–13. 10.1007/s40200-020-00661-7
47.
Barbosa M Saavedra A Oliveira S Reis L Rodrigues F Severo M et al . Prevalence and determinants of painful and painless neuropathy in type 1 diabetes mellitus. Front Endocrinol. (2019) 10:402. 10.3389/fendo.2019.00402
48.
De Visser A Hemming A Yang C Zaver S Dhaliwal R Jawed Z et al . The adjuvant effect of hypertension upon diabetic peripheral neuropathy in experimental type 2 diabetes. Neurobiol Dis. (2014) 62:18–30. 10.1016/j.nbd.2013.07.019
49.
Van Acker K Bouhassira D De Bacquer D Weiss S Matthys K Raemen H et al . Prevalence and impact on quality of life of peripheral neuropathy with or without neuropathic pain in type 1 and type 2 diabetic patients attending hospital outpatients clinics. Diabetes Metab. (2009) 35:206–13. 10.1016/j.diabet.2008.11.004
50.
Jambart S Ammache Z Haddad F Younes A Hassoun A Abdalla K et al . Prevalence of painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy among patients with diabetes mellitus in the Middle East region. J Int Med Res. (2011) 39:366–77. 10.1177/147323001103900204
51.
Aslam A Singh J Rajbhandari S . Prevalence of painful diabetic neuropathy using the self-completed leeds assessment of neuropathic symptoms and signs questionnaire in a population with diabetes. Can J Diabetes. (2015) 39:285–95. 10.1016/j.jcjd.2014.12.007
52.
Bouhassira D Letanoux M Hartemann A . Chronic pain with neuropathic characteristics in diabetic patients: a French cross-sectional study. PLoS ONE. (2013) 8:e74195. 10.1371/journal.pone.0074195
53.
Ziegler D Rathmann W Meisinger C Dickhaus T Mielck A . Prevalence and risk factors of neuropathic pain in survivors of myocardial infarction with pre-diabetes and diabetes. The KORA myocardial infarction registry. Eur J Pain. (2009) 13:582–7. 10.1016/j.ejpain.2008.07.007
54.
Smith AG Russell J Feldman EL Goldstein J Peltier A Smith S et al . Lifestyle intervention for pre-diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes Care. (2006) 29:1294–9. 10.2337/dc06-0224
Summary
Keywords
diabetes mellitus (DM), painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy (PDPN), risk factor, systematic review, meta-analysis
Citation
Zhou P, Zhou Js, Li Jj, Qin L, Hu Wf, Zhang Xy, Wang Jx and Shi Z (2025) Prevalence and risk factors for painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Neurol. 16:1564867. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1564867
Received
22 January 2025
Accepted
16 April 2025
Published
13 May 2025
Volume
16 - 2025
Edited by
Peng Mao, China-Japan Friendship Hospital, China
Reviewed by
Idris Long, University of Science Malaysia (USM), Malaysia
Roberta Bonomo, Kore University of Enna, Italy
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Zhou, Zhou, Li, Qin, Hu, Zhang, Wang and Shi.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zhen Shi 89435674@qq.com
†These authors share first authorship
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.