- 1Department of Interventional Neuroradiology, Beijing Tiantan Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China
- 2China National Clinical Research Center for Neurological Diseases, Beijing, China
- 3Center of Stroke, Beijing Institute for Brain Disorders, Beijing, China
- 4Department of Neurology, Beijing Tiantan Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China
Introduction: In this study, we investigated the differences in clinical outcomes following endovascular thrombectomy among ischemic stroke subtypes caused by large artery atherosclerosis (LAA) versus cardioembolism (CE) and the time-dependent nature of these clinical outcomes based on the stroke subtypes. Methods: Study participants were selected from the Endovascular Treatment Key Technique and Emergency Workflow Improvement of Acute Ischemic Stroke Registry to conduct a post-hoc analysis of a prospective, observational study. We included 1,046 patients, who had either LAA or CE stroke subtypes based on the Trial of Org 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment criteria, drawn from the thrombectomy cohort. The association between clinical outcomes and time from stroke onset-to-recanalization time (ORT) was analyzed using a logistic regression model.
Results: Overall, 545 (52.6%) and 491 (47.4%) patients were included in the LAA and CE groups, respectively. No significant difference was found in the 90-day clinical functional outcome between the LAA and CE patients when ORT was achieved within 240 min. Beyond 240 min, the rate of achieving a modified Rankin Scale score of 0–2 in patients with LAA was higher than that of patients with CE [48.17% versus 38.66%; odds ratio (OR) = 0.678, 95% confidence interval (CI) = 0.521–0.884, p = 0.0040], and after adjustment, the OR was 0.732 (95% CI: 0.537–0.998, p = 0.0486).
Conclusion: In cases where the ORT exceeded 240 min, the clinical outcomes of patients with LAA were better than those of patients with CE, demonstrating a stronger time-dependency for achieving a favorable prognosis in patients with cardioembolic stroke.
1 Introduction
Mechanical thrombectomy (MT) has become the gold standard treatment for patients with acute large-vessel occlusion stroke, as demonstrated by multiple clinical studies (1–7). Guidelines recommend that patients with circulation occlusion undergo endovascular treatment (EVT) within 24 h of symptom onset, provided rigorous imaging screening is performed (8–10). Numerous studies have identified that surgical complications and clinical outcomes vary among patients with different stroke subtypes, suggesting that thrombectomy strategies should be tailored to the specific stroke subtype to optimize patient outcomes. Among patients with acute large vessel occlusion, cardioembolism (CE) is associated with an increased risk of hemorrhagic transformation within 24 h following EVT compared to large artery atherosclerosis (LAA) (11). For patients with vertebrobasilar occlusion stroke undergoing EVT, those with embolic stroke of undetermined origin have poorer outcomes and higher mortality rates compared to those with LAA or cardioembolic stroke (12). Additionally, in the cardioembolic group, the proportion of patients achieving a modified Rankin Scale (mRS) score of 0–2, indicative of good functional recovery, decreased as the onset-to-puncture time increased, a trend not observed in the LAA group (13).
Additionally, most current research focuses on the time window for patient selection but neglects the timing of surgical recanalization, including onset-to-door time, door-to-puncture time, puncture-to-recanalization time, and onset-to-recanalization time (ORT). Research on these times would be more beneficial for establishing better quality control metrics for thrombectomy. In this study, we aimed to explore the relationship between thrombectomy effectiveness and the ORT in patients with LAA and CE stroke.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Study population
Data used in this study were obtained from the Endovascular Treatment Key Technique and Emergency Workflow Improvement of Acute Ischemic Stroke (ANGEL-ACT), a prospective nationwide registry comprising 2004 consecutive adult patients diagnosed with acute ischemic stroke (AIS) who underwent EVT across 111 hospitals in China between November 2017 and March 2019. Detailed methods of the registry, including inclusion and exclusion criteria as well as data collection standards, have been previously documented (14). The study protocol was approved by the ethics committee of each center, and all participants (or legal representatives) provided written informed consent. The study was conducted in accordance with the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its subsequent amendments.
This study included patients aged ≥18 years diagnosed with AIS who underwent initiation of EVT. Of the 2004 patients registered in the ANGEL-ACT database, 211 were excluded for the following reasons: 83 had isolated extracranial large-vessel occlusion, 98 had no evidence of large-vessel occlusion on digital subtraction angiography, and 30 had missing baseline data. Among the remaining 1793 patients, we further excluded those who did not undergo thrombectomy (n = 186), those with tandem lesions (n = 318), those with Trial of Org 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment (TOAST) criteria for stroke of other determined etiology (n = 40), those with stroke of undetermined etiology (n = 203), and those whose 90-day mRS scores were missing (n = 10). Ultimately, 1,036 patients met the inclusion criteria for this analysis, comprising 545 with LAA and 491 with CE (Figure 1).
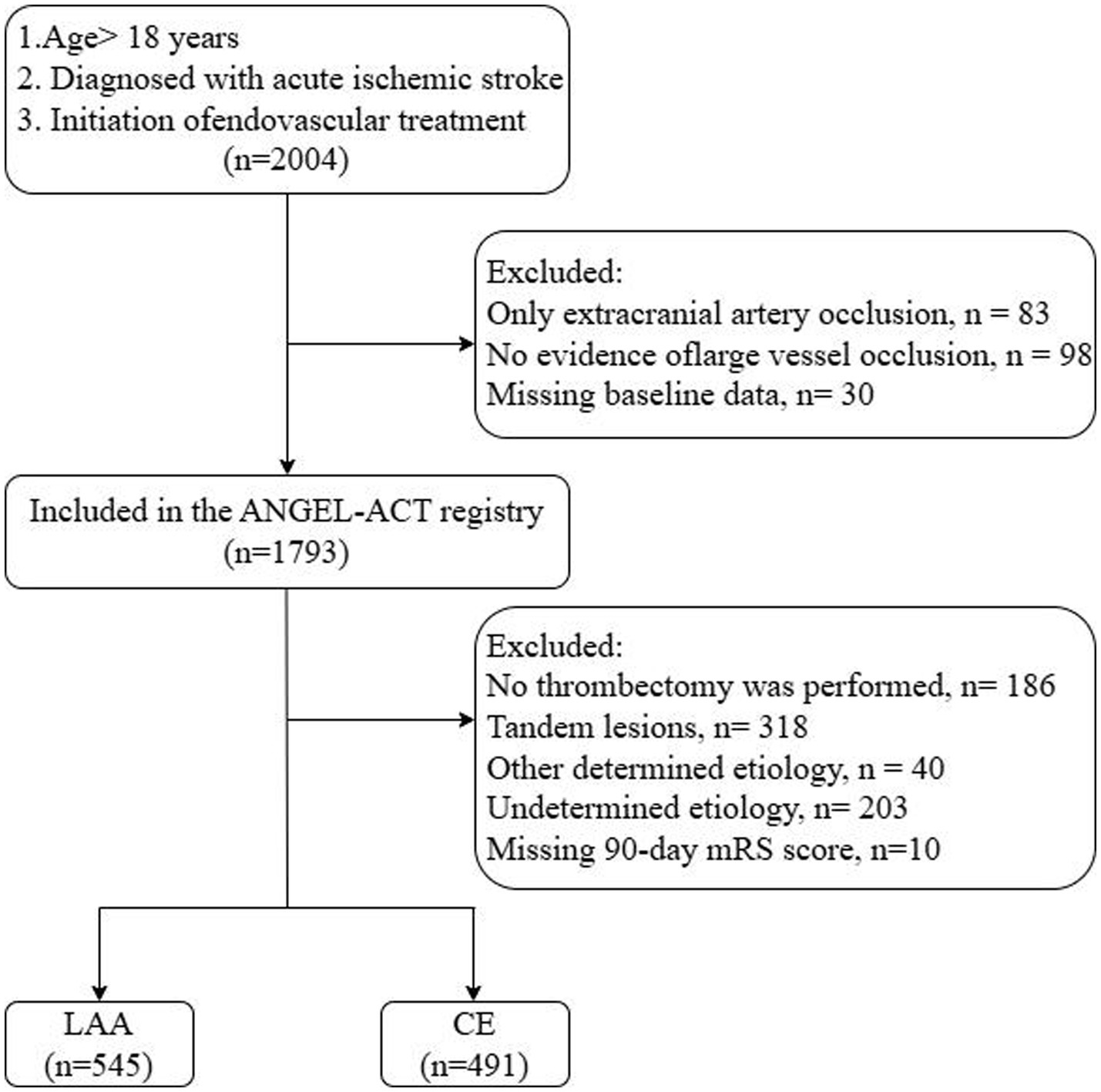
Figure 1. Patient selection flowchart. ANGEL-ACT, endovascular treatment key technique and emergency work flow improvement of acute ischemic stroke; LAA, large artery atherosclerosis; CE, cardioembolism.
2.2 Data collection
Information regarding baseline demographic characteristics (age and sex), medical history (presence of hypertension, hyperlipidemia, or diabetes mellitus; prior stroke; mRS score ≥ 1 before stroke; use of GP IIb/IIIa receptor inhibitors; pretreatment with anti-platelets, intravenous thrombolysis, and anticoagulants), clinical features [systolic blood pressure (SBP), Alberta Stroke Program Early Computed Tomography Score (ASPECTS), National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) score, onset-to-door time, door-to-puncture time, puncture-to-recanalization time, and ORT], location of the intracranial occlusion [anterior circulation included internal carotid artery, anterior cerebral artery (A1/A2), and middle cerebral artery (M1/M2); posterior circulation included vertebral, basilar, and posterior cerebral arteries (P1)], anesthesia type, and successful recanalization after the final attempt was documented.
2.3 EVT and stroke subtype
Prior to MT, intravenous thrombolysis was administered to eligible patients without contraindications. The choice between local and general anesthesia depended on the patient’s cooperation and condition. Following digital subtraction angiography, the neurointerventionist determined the optimal strategy and materials for the EVT. The surgical approach was determined based on the surgical situation and the personal experience of the neurointerventionist. To address in situ stenosis, several strategies were employed, including balloon expansion angioplasty alone (using Kalamazoo, MI, USA, Gateway, Stryker; or Neuro-RX SINOMED, Tianjin, China), balloon-mounted stents alone (such as Apollo, MicroPort, Shanghai, China), or a combination of balloon-mounted and self-expanding stents (Enterprise, Codman & Shurtleff Inc., Miami, FL, USA; Wingspan or EZ, Stryker, Kalamazoo, MI, USA; or Solitaire AB, Medtronic, Minneapolis, Minnesota, USA), following balloon expansion.
Stroke subtype classification was performed by two separate neurologists or onsite investigators using the 1993 version of the TOAST criteria (15). Prior to patient enrollment, all evaluators underwent training by committee-assigned stroke specialists and were provided with a manual containing detailed descriptions of the TOAST subtyping system and operational guidelines for determining the etiological subtype. Diagnosis of CE stroke typically requires identification of at least one cardiac source of embolism (via electrocardiogram or echocardiogram), characterized by clinical symptoms and brain imaging findings demonstrating occlusion of a major cerebral or branch cortical artery. Using a standardized diagnostic process, trained evaluators reviewed the patients’ clinical history, imaging findings, and laboratory features and categorized them into LAA or CE stroke subtypes according to the TOAST system.
2.4 Outcome measurement
Experienced investigators meticulously recorded all data. We considered a favorable functional recovery outcome at 90 days post-procedure (defined as a 90-day mRS score of 0–2) as the efficacy endpoint. We also recorded the onset-to-door time, door-to-puncture time, puncture-to-recanalization time, and ORT.
2.5 Statistical analysis
Data are presented as the median (interquartile range) or frequency (percentage). A comparison of baseline characteristics between patients with LAA and those with CE was performed using the Kruskal–Wallis test or chi-square test, as appropriate. A multivariate logistic regression model was used to examine the association between the stroke subtypes (LAA vs. CE) and ORT. Variables including age; sex; presence of hypertension, diabetes mellitus, or hyperlipidemia; SBP; baseline NIHSS score; ASPECTS; and pretreatment with antiplatelet agents (aspirin and clopidogrel) were adjusted for in the analysis. The adjusted odds ratio (OR) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) was calculated to measure the strength of the association.
The cumulative percentage of good prognoses was used to determine the point at which the prognosis in the LAA group surpassed that in the CE group (Figure 2).
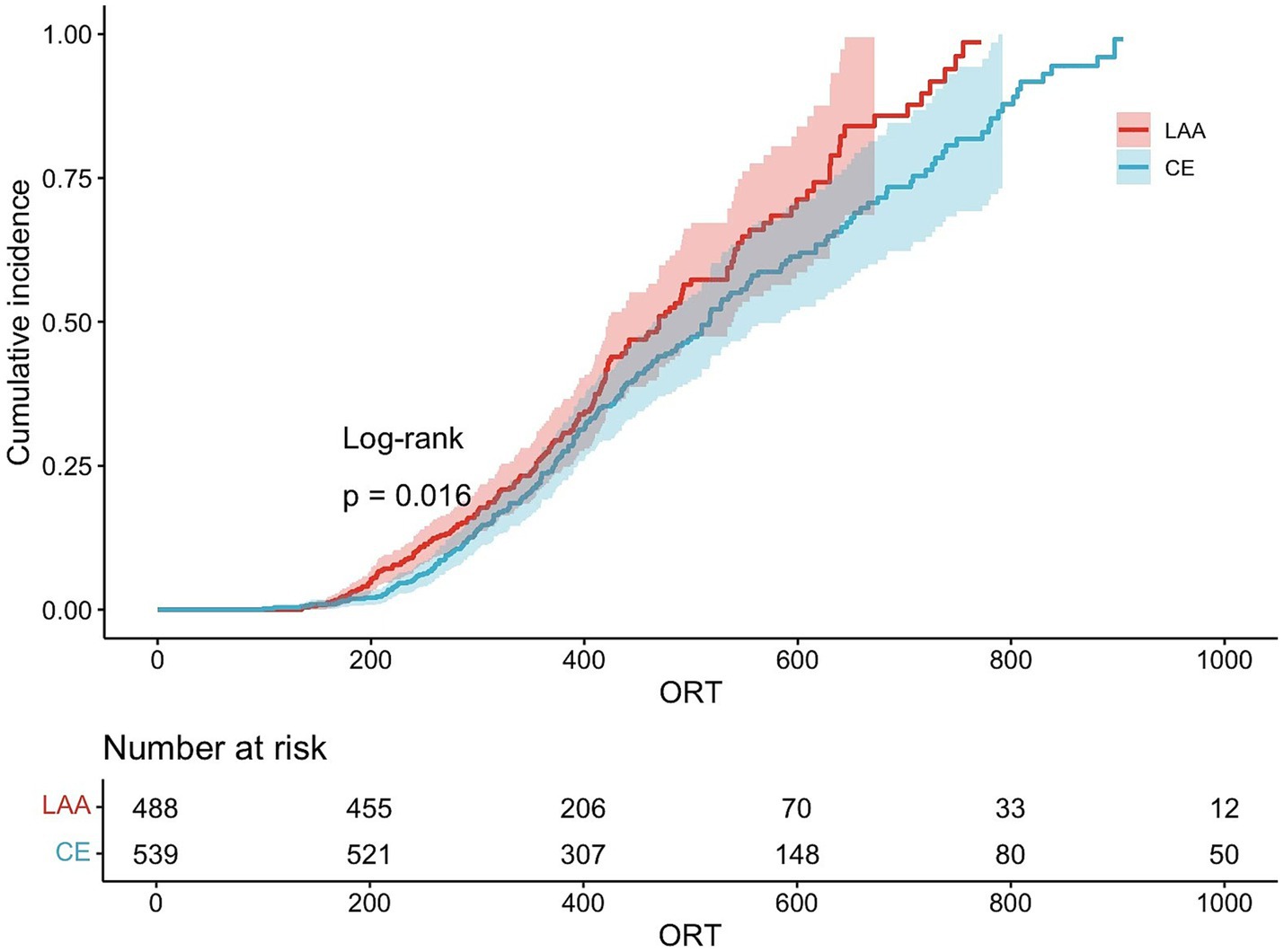
Figure 2. Cumulative percentage of good prognoses. LAA, large artery atherosclerosis; CE, cardioembolism.
According to the statistical data, we analyzed the proportion of mRS scores of 0–2 across various time segments and identified 240 min as the optimal cutoff. The correlation between good functional outcomes and ORT in the two groups was analyzed separately for cases occurring before and after 240 min.
Mediation models were used to examine whether the relationship between stroke subtype and ORT was mediated by the following factors: NIHSS score, site of occlusion, prior use of anticoagulants, type of thrombectomy (stent retriever alone or stent retriever plus aspiration), number of thrombectomy passes, and emergency angioplasty/stenting. The detailed methods of mediation analysis can be found in Supplementary Material. All statistical analyses were conducted using SAS software (version 9.4; SAS Institute, Inc., Cary, NC, USA). A two-sided p-value <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3 Results
3.1 Baseline characteristics of patients with LAA versus CE
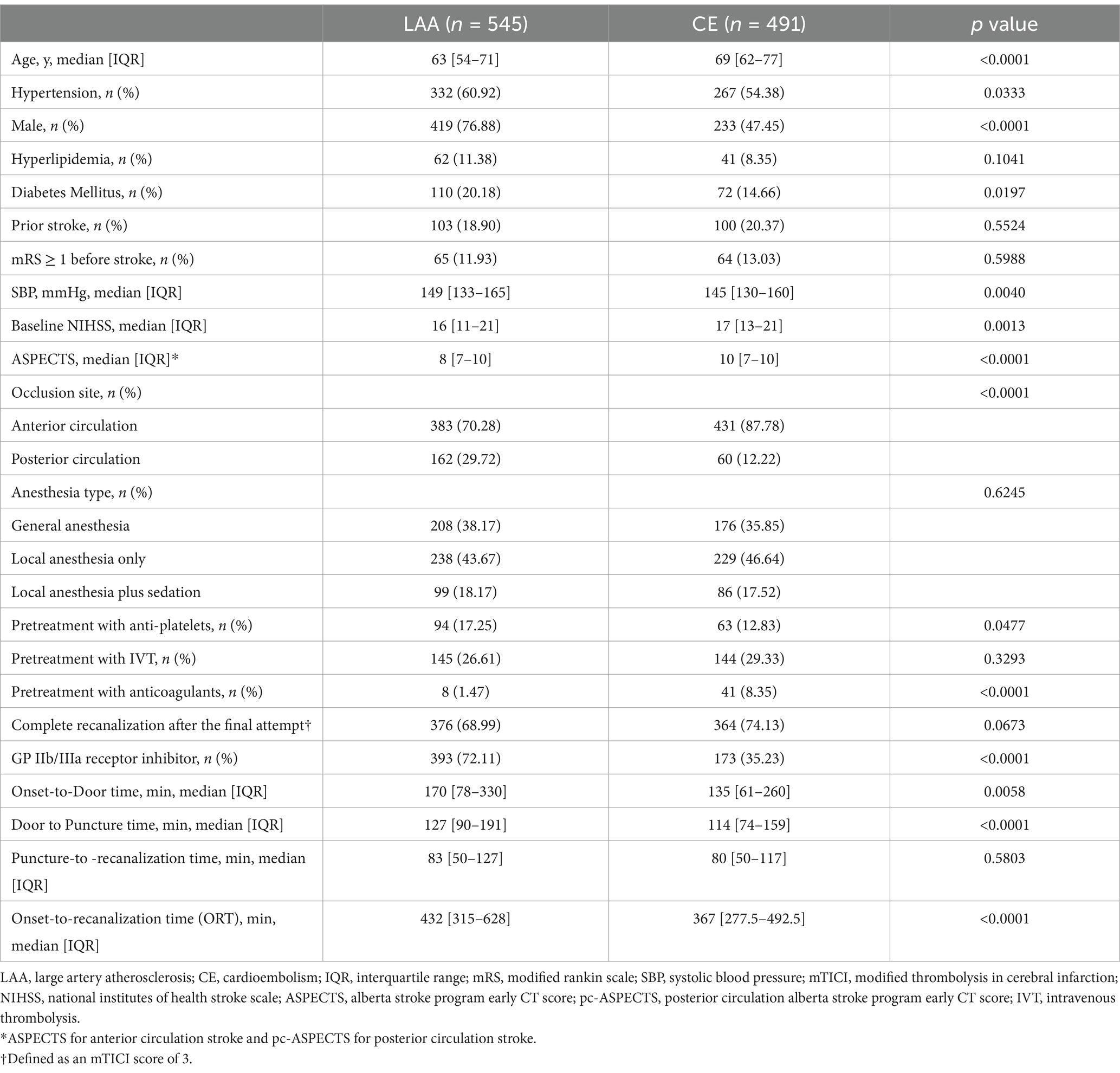
Of the 1,036 patients included in this study, 545 with LAA and 491 with CE were compared for baseline characteristics. As shown in Table 1, several baseline variables differed significantly between the two groups. Compared with the LAA group, the CE group exhibited the following characteristics: (1) a higher mean age (69 vs. 63 years); (2) a higher median NIHSS score (17 vs. 16); (3) a higher median ASPECTS (10 vs. 8); (4) a significantly larger proportion of women (52.55% vs. 23.12%); (5) a greater percentage of anterior circulation strokes (87.78% vs. 70.28%); and (6) a greater percentage of pretreatment with anticoagulants (8.35% vs. 1.47%). Meanwhile, the CE group had a smaller proportion of patients with hypertension (54.38% vs. 60.92%), diabetes mellitus (14.66% vs. 20.18%), and those who received antiplatelet agents before the procedure (12.83% vs. 17.25%). The CE group used GP IIb/IIIa receptor inhibitors less frequently during the procedure (35.23% vs. 72.11%). However, the CE group experienced shorter onset-to-door times (135 vs. 170 min), shorter door-to-puncture times (114 vs. 127 min), and shorter ORTs (367 vs. 432 min) than the LAA group. No significant difference was found between the two groups regarding the presence of hyperlipidemia, prior stroke, mRS scores ≥ 1 before stroke, initiation of intravenous thrombolysis pretreatment, type of anesthesia, puncture-to-recanalization time, or complete recanalization after the final attempt (Table 1).
3.2 Distribution of mRS scores across ORT categories and stroke subtypes
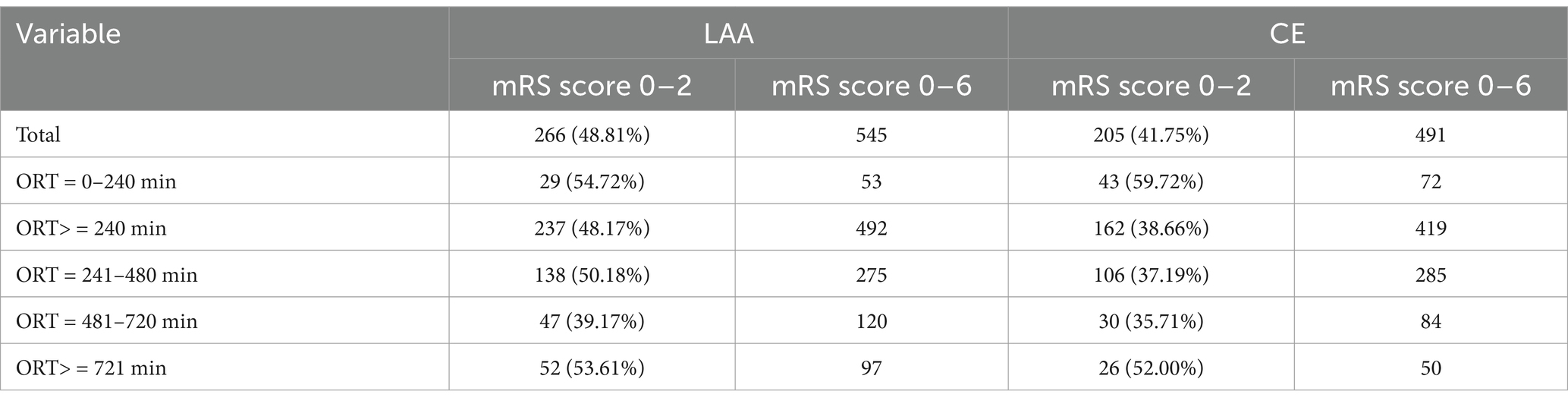
Among all enrolled participants, patients with LAA stroke had a higher percentage of favorable functional outcomes (mRS score of 0–2) than those with CE stroke. In the subgroup with an ORT < 240 min, 54.72% of patients with LAA stroke and 59.72% of patients with CE stroke achieved mRS scores of 0–2. In the subgroup with an ORT ≥ 240 min, 48.17% of patients with LAA stroke and 38.66% of patients with CE stroke achieved mRS scores of 0–2 (Table 2).
3.3 Logistic regression analysis of ORTs and mRS scores of 0–2 in patients with LAA and CE
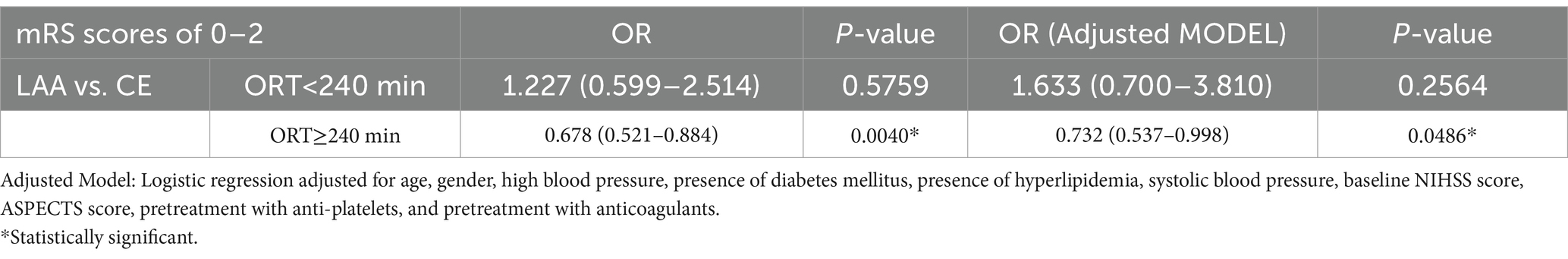
Table 3 presents the results of the single and multifactor analyses examining the association between the ORTs and favorable functional outcomes (as indicated by mRS scores of 0–2). For cases with an ORT < 240 min, there was no statistically significant difference in the rate of favorable functional outcomes between the LAA and CE groups (OR: 1.227; 95% CI: 0.599–2.514; p = 0.5759). Similar results were observed in the adjusted models, with p > 0.05. After adjusting for age, sex, high blood pressure, presence of diabetes mellitus, presence of hyperlipidemia, SBP, baseline NIHSS score, ASPECTS score, pretreatment with anti-platelets, and pretreatment with anticoagulants in the adjusted model, the OR was 1.633 (95% CI: 0.700–3.810, p = 0.2564).
For cases with an ORT ≥ 240 min, there was a statistically significant difference in favorable functional outcomes between the LAA and CE groups. The unadjusted OR was 0.678 (95% CI: 0.521–0.884; p = 0.0040), indicating that CE stroke is a risk factor compared to LAA stroke. Similar results are obtained for the adjusted model. After adjustment, the OR was 0.732 (95% CI: 0.537–0.998, p = 0.0486).
4 Discussion
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to investigate the association between the ORT and favorable clinical functional recovery (defined as mRS scores of 0–2) in patients with CE and LAA stroke subtypes. The study indicated no significant difference in clinical outcomes between patients with LAA and CE stroke within 240 min of stroke onset. However, beyond 240 min, the clinical outcomes of patients with LAA stroke were better than those of patients with CE stroke, demonstrating a stronger time dependency for favorable prognosis in patients with CE stroke. A possible reason for this is that patients with LAA stroke tend to have better collateral recruitment due to the chronic process of ischemic preconditioning (16). Researchers have found that patients with stroke due to cervical carotid atherosclerosis had better cerebral collateral circulation and slightly better median mRS scores at 90 days compared to those with CE stroke (17).
The findings suggest that CE stroke patients have a stronger time-dependent aspect. While early recanalization remains critical for both subtypes, CE strokes exhibit a stronger decline in favorable outcomes with delayed reperfusion, likely due to shortage of collateral circulation. Therefore, we recommend shortening the time from symptom onset to recanalization in patients with CE. Understanding the implications of these findings can significantly impact various aspects of stroke management.
Firstly, CE stroke was associated with a higher risk of any hemorrhagic transformation compared to LAA stroke (11). One possible explanation is that the difference in thrombus composition between stroke subtypes may account for the higher number of thrombectomy passes associated with CE stroke. These findings underscore the importance of accurately identifying the stroke subtype.
Secondly, given the time-sensitive nature of CE stroke outcomes, the choice of devices that can facilitate quicker and more efficient reperfusion is crucial to optimize the chances of favorable outcomes within the critical time window. Moreover, We found that the CE group experienced shorter onset-to-door times, shorter door-to-puncture times, and shorter ORTs than the LAA group. We hypothesize that CE patients presented with more severe symptoms (e.g., higher NIHSS due to abrupt vessel occlusion), prompting faster triage (18).
Finally, establishing stringent quality control standards for CE patients is essential for ensuring optimal clinical outcomes. Stringent medical quality control is crucial for a country like China with an uneven healthcare distribution.
This study has some limitations. Firstly, this was not a randomized study, and thus can only partly illustrate the issue. This study is a real-world investigation with a large sample size. However, due to the relatively early timeframe, the efficiency of thrombectomy was not very high, possibly because of insufficient thrombectomy experience and equipment. During the study period, researchers found that a subset of the population underwent direct aspiration as the primary thrombectomy approach, which was linked to lower rates of successful recanalization with the initial device, indicating the need for employing additional rescue treatments, and a higher risk of intracranial hemorrhage compared to using a stent retriever as the primary thrombectomy approach (19). Secondly, there is a high portion of patients with intracranial athero-occlusive disease in China, which decreases the external validity or generalizability of the findings.
In conclusion, this study suggests that patients with LAA stroke had better clinical outcomes compared to those with CE stroke when the ORT ≥ 240 min, demonstrating a stronger time-dependency for favorable prognoses in CE stroke. Further research is necessary to elucidate the factors mediating the relationship between stroke subtypes and the ORT and to inform the development of clinical management strategies.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author/s.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the IRB of Beijing Tiantan Hospital, Capital Medical University. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
YY: Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. HC: Software, Writing – original draft. AW: Methodology, Software, Writing – review & editing. XZ: Methodology, Software, Writing – review & editing. ML: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. LS: Data curation, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. BJ: Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing. NM: Supervision, Writing – review & editing. DM: Resources, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. XS: Resources, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. FG: Resources, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. YD: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. ZM: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Software, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 82171562); Continuing Education Center of the National Health (grant number GWJJ2023100103).
Acknowledgments
We thank all participating hospitals, relevant clinicians, statisticians, and imaging and laboratory technicians.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fneur.2025.1574948/full#supplementary-material
Abbreviations
AIS, Acute ischemic stroke; ASPECTS, Alberta Stroke Program Early Computed Tomography Score; CE, Cardioembolism; CI, Confidence interval; EVT, Endovascular treatment; ANGEL-ACT, Endovascular Treatment Key Technique and Emergency Workflow Improvement of Acute Ischemic Stroke; LAA, Large artery atherosclerosis; MT, Mechanical thrombectomy; mRS, Modified Rankin Scale; NHISS, National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale; OR, Odds ratio; ORT, Onset-to-recanalization time; SBP, Systolic blood pressure; TOAST, Trial of Org 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment.
References
1. Berkhemer, OA, Fransen, PSS, Beumer, D, van den Berg, LA, Lingsma, HF, Yoo, AJ, et al. A randomized trial of intraarterial treatment for acute ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med. (2015) 372:11–20. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1411587
2. Campbell, BCV, Mitchell, PJ, Kleinig, TJ, Dewey, HM, Churilov, L, Yassi, N, et al. Endovascular therapy for ischemic stroke with perfusion-imaging selection. N Engl J Med. (2015) 372:1009–18. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1414792
3. Jovin, TG, Chamorro, A, Cobo, E, de Miquel, MA, Molina, CA, Rovira, A, et al. Thrombectomy within 8 hours after symptom onset in ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med. (2015) 372:2296–306. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1503780
4. Saver, JL, Goyal, M, Bonafe, A, Diener, HC, Levy, EI, Pereira, VM, et al. Stent-retriever thrombectomy after intravenous t-PA vs. t-PA alone in stroke. N Engl J Med. (2015) 372:2285–95. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1415061
5. Nogueira, RG, Jadhav, AP, Haussen, DC, Bonafe, A, Budzik, RF, Bhuva, P, et al. Thrombectomy 6 to 24 hours after stroke with a mismatch between deficit and infarct. N Engl J Med. (2018) 378:11–21. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1706442
6. Albers, GW, Marks, MP, Kemp, S, Christensen, S, Tsai, JP, Ortega-Gutierrez, S, et al. Thrombectomy for stroke at 6 to 16 hours with selection by perfusion imaging. N Engl J Med. (2018) 378:708–18. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1713973
7. Limaye, K, Van de Walle, JA, Shaban, A, Desai, S, Al Kasab, S, Almallouhi, E, et al. Endovascular management of acute large vessel occlusion stroke in pregnancy is safe and feasible. J Neurointerv Surg. (2020) 12:552–6. doi: 10.1136/neurintsurg-2019-015578
8. Neurology Branch of the Chinese Medical Association; Cerebrovascular Disease Study Group, Neurology Branch of the Chinese Medical Association; Neurovascular Intervention Cooperative Group, Neurology Branch of the Chinese Medical Association. Chinese guidelines for the endovascular treatment of acute ischemic stroke. Chin. J Neurol. (2022) 55:565–580. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn113694-20220225-00137
9. Tanaka, S, Tomio, R, Akao, N, Shimizu, T, Ishikawa, T, Fujimoto, T, et al. Aphagia strongly suspected to be caused by an allergic reaction to a gelatin-based hemostatic agent after anterior cervical decompression and fusion for central cervical cord injury. NMC Case Rep. (2022) 9:ER1–ER81. doi: 10.2176/jns-nmc.er.2022-0017
10. Powers, WJ, Rabinstein, AA, Ackerson, T, Adeoye, OM, Bambakidis, NC, Becker, K, et al. Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: 2019 update to the 2018 guidelines for the early management of acute ischemic stroke: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. (2019) 50:e344–418. doi: 10.1161/STR.0000000000000211
11. Tong, X, Burgin, WS, Ren, Z, Jia, B, Zhang, X, Huo, X, et al. Association of stroke subtype with hemorrhagic transformation mediated by thrombectomy pass: data from the Angel-ACT registry. Stroke. (2022) 53:1984–92. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.121.037411
12. Abdelrady, M, Derraz, I, Dargazanli, C, Cagnazzo, F, Ognard, J, Riquelme, C, et al. Outcomes following mechanical thrombectomy in different etiological subtypes of acute basilar artery occlusion: stroke etiology and outcome after EVT in BAO. Clin Neuroradiol. (2023) 33:361–74. doi: 10.1007/s00062-022-01217-3
13. Shirakawa, M, Matsukawa, H, Sakai, N, Yamagami, H, Tanaka, K, Imamura, H, et al. Endovascular therapy for acute ischemic stroke in patients with large-vessel occlusion due to atherosclerotic stenosis. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. (2021) 30:105960. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2021.105960
14. Tong, X, Wang, Y, Fiehler, J, Bauer, CT, Jia, B, Zhang, X, et al. Thrombectomy versus combined thrombolysis and thrombectomy in patients with acute stroke: a matched-control study. Stroke. (2021) 52:1589–600. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.120.031599
15. Adams, HP Jr, Bendixen, BH, Kappelle, LJ, Biller, J, Love, BB, Gordon, DL, et al. Classification of subtype of acute ischemic stroke. Definitions for use in a multicenter clinical trial. TOAST. Trial of org 10172 in acute stroke treatment. Stroke. (1993) 24:35–41. doi: 10.1161/01.str.24.1.35
16. Haussen, DC, Bouslama, M, Dehkharghani, S, Grossberg, JA, Bianchi, N, Bowen, M, et al. Automated CT perfusion prediction of large vessel acute stroke from intracranial atherosclerotic disease. Interv Neurol. (2018) 7:334–40. doi: 10.1159/000487335
17. Guglielmi, V, LeCouffe, NE, Zinkstok, SM, Compagne, KCJ, Eker, R, Treurniet, KM, et al. Collateral circulation and outcome in atherosclerotic versus Cardioembolic cerebral large vessel occlusion. Stroke. (2019) 50:3360–8. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.119.026299
18. Yue, C, Liu, X, Guo, C, Wang, L, Zhao, W, Sun, W, et al. Efficacy and safety of tirofiban in acute ischemic stroke patients with ideal reperfusion: a cohort study of LAA and CE subgroups. Eur J Neurol. (2025) 32:e70034. doi: 10.1111/ene.70034
Keywords: thrombectomy, time dependency, large artery atherosclerosis, cardioembolism, stroke subtypes
Citation: Yin Y, Chen H, Wang A, Zhang X, Li M, Song L, Jia B, Ma N, Mo D, Sun X, Gao F, Deng Y and Miao Z (2025) Time dependency of thrombectomy for large artery atherosclerosis versus cardioembolic stroke subtypes: evidence from the ANGEL-ACT registry. Front. Neurol. 16:1574948. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1574948
Edited by:
Arthur Sá Ferreira, University Center Augusto Motta, BrazilReviewed by:
Jan Hendrik Schaefer, Goethe University, GermanyOzge Altintas Kadirhan, Kırklareli University, Türkiye
Copyright © 2025 Yin, Chen, Wang, Zhang, Li, Song, Jia, Ma, Mo, Sun, Gao, Deng and Miao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yiming Deng, cGFya2VyZGVuZ0AxNjMuY29t; Zhongrong Miao, emhvbmdyb25nbUAxMjYuY29t
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Yue Yin
Yue Yin Hanlin Chen
Hanlin Chen Anxin Wang
Anxin Wang Xiaoli Zhang
Xiaoli Zhang Miao Li
Miao Li Ligang Song1,2,3
Ligang Song1,2,3 Baixue Jia
Baixue Jia Ning Ma
Ning Ma Dapeng Mo
Dapeng Mo Xuan Sun
Xuan Sun Feng Gao
Feng Gao Yiming Deng
Yiming Deng Zhongrong Miao
Zhongrong Miao