- 1Department of Neurosurgery, QuZhou KeCheng People’s Hospital, Quzhou, China
- 2Department of Neurology, QuZhou KeCheng People’s Hospital, Quzhou, China
- 3Brain Center, Zhejiang Hospital, Hangzhou, China
Purpose: The ratio of serum uric acid (UA) to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-c), known as UHR, has been identified as a novel marker for oxidative stress and metabolic disorders. This study focused on exploring the association between UHR and stroke risk among older adults in the United States.
Methods: This cross-sectional study utilized data from individuals aged 60 years and older, collected through the 1999–2018 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES). Stroke assessment was based on participants’ self-reported history. The association between UHR and stroke risk was analyzed using logistic regression, restricted cubic splines (RCS), subgroup analysis, and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves.
Results: This study included a total of 16,562 older adults, and the proportion of stroke cases increased with higher UHR levels. After adjusting for confounders, multivariable logistic regression analysis revealed that individuals in the highest UHR quartile had an odds ratio of 1.48 (1.23–1.80) for stroke risk compared to those in the lowest quartile. Subgroup analyses further demonstrated a stronger association in non-diabetic populations. RCS analysis suggested a linear relationship. Based on ROC results, UHR outperformed UA and HDL-c.
Conclusion: Higher UHR levels are strongly associated with an increased risk of stroke in older adults. Additional large-scale prospective studies are required.
1 Introduction
With the global aging population on the rise, health issues among the elderly have become a critical focus in public health research (1). Stroke, as one of the leading causes of disability and mortality in older adults, continues to exhibit high incidence, death, and disability rates, imposing a substantial burden on healthcare systems worldwide (2, 3). Consequently, an in-depth investigation into the risk factors and underlying mechanisms of stroke is essential for developing effective prevention and treatment strategies.
The serum uric acid-to-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio (UHR), an emerging composite indicator, might offer a more comprehensive reflection of the body’s metabolic state and oxidative stress levels (4, 5). Uric acid (UA), the final product of purine metabolism, is associated with various conditions, including hypertension, diabetes, and chronic kidney disease (6). Previous studies suggest that UA may directly contribute to atherosclerosis and thrombosis by promoting oxidative stress, inflammatory responses, and endothelial dysfunction, thereby elevating the risk of stroke (6–8). Conversely, high-density lipoprotein (HDL-c), often referred to as “good cholesterol,” is well-known for its cardiovascular protective effects, which are attributed to its roles in reverse cholesterol transport, as well as its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties (9, 10). The inverse relationship between these two parameters creates a synergistic effect where high UA combined with low HDL-c may amplify stroke risk beyond what either parameter would predict individually. Previous research has also highlighted that UHR, compared to individual markers, exhibits stronger associations with cardiometabolic diseases such as diabetes, hypertension, cardiovascular diseases, metabolic syndrome, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) (11–14).
Older adults frequently present a complex interplay of metabolic disorders, making them a distinct population for investigating multifactorial contributors to cerebrovascular risk. Notably, they are more susceptible to the concurrent presence of hyperuricemia and low HDL-c, both of which have independently been linked to elevated stroke risk. Despite the increasing incidence of stroke in this age group, most current risk-stratification tools are derived from general or mixed-age populations and may not adequately reflect the unique metabolic profiles of older adults. To date, no studies have specifically examined the association between the UHR and stroke in this demographic. Thus, this study seeks to address this gap by investigating the relationship between UHR and stroke among older adults in the United States, utilizing data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES). We hypothesize that elevated UHR levels are associated with increased stroke prevalence in older adults and may demonstrate stronger associations compared to UA or HDL-c alone.
2 Method
2.1 Data source
NHANES, organized by the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), used a multi-stage, stratified, and randomized sampling design to create a representative sample of the U. S. population.1 The study was approved by the NCHS Ethics Review Board,2 and written informed consent was obtained from all participants. This study analyzed data from 10 NHANES cycles (1999–2000 to 2017–2018). Of the original 101,316 participants, individuals younger than 60 years or missing UHR data or stroke questionnaire information were excluded, leaving a final analytical sample of 16,562 participants (Figure 1).
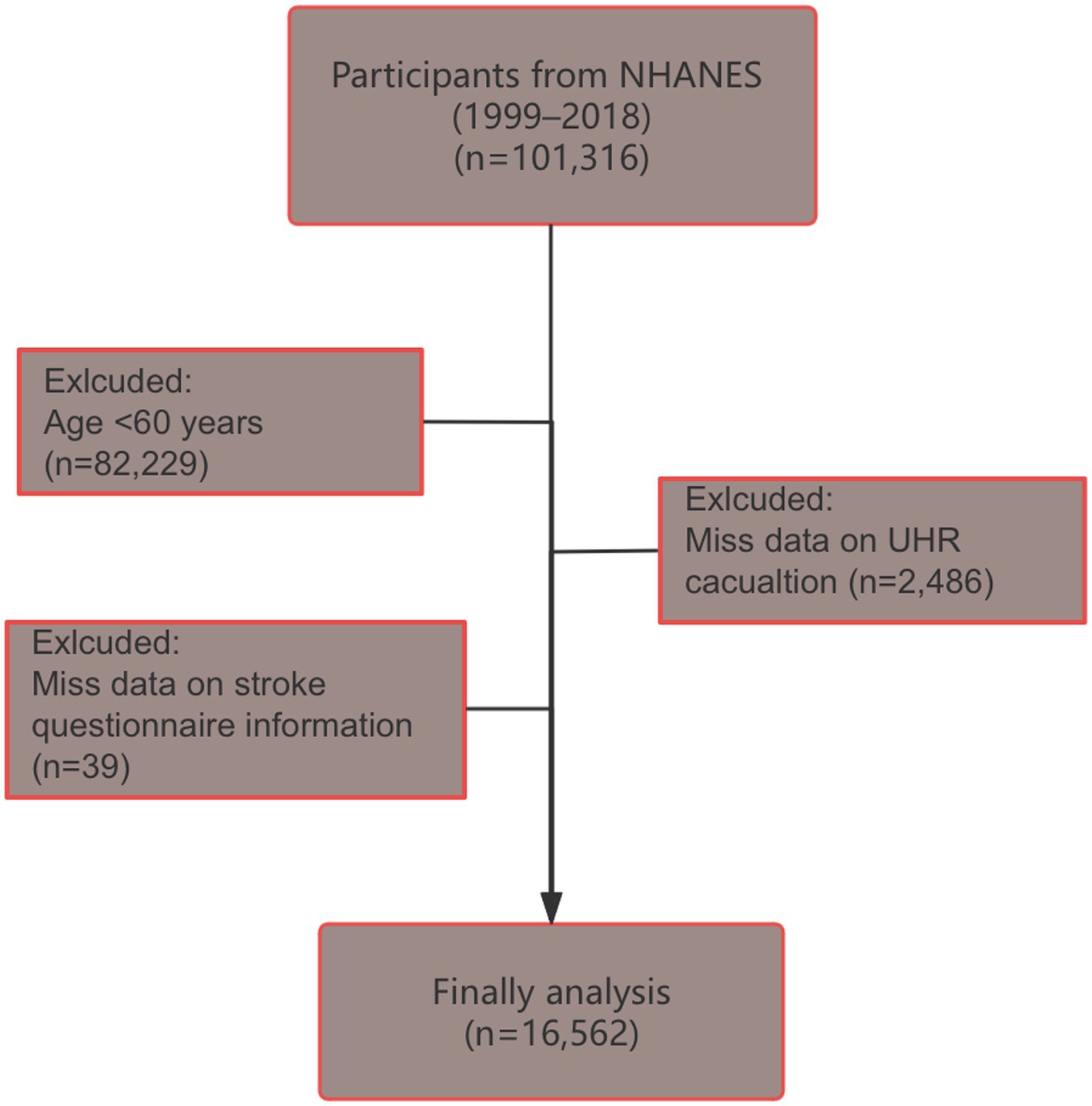
Figure 1. Flow chart of participant screening (selection process from NHANES 1999–2018 database to final study population of 16,562 older adults aged ≥60 years after excluding participants with missing UHR or stroke data).
2.2 Definition of UHR and stroke
UHR, serving as the exposure in this study, was calculated by comparing UA (μmol/L) with HDL-c (mg/dL) (4, 15). UA levels were determined through enzymatic analysis using a DxC800 automated analyzer via the timed endpoint methodology. The process involved uricase-mediated oxidation of UA, generating allantoin and hydrogen peroxide as products. Subsequently, hydrogen peroxide underwent a peroxidase-catalyzed reaction with 4-aminoantipyrine (4-AAP) and 3,5-dichloro-2-hydroxybenzenesulfonate (DCHBS), yielding a chromogenic compound measured spectrophotometrically at 520 nm wavelength. For HDL-c quantification, magnesium sulfate/dextran solution was introduced to create water-soluble complexes with non-HDL-c fractions, preventing their interference in subsequent analytical steps. Polyethylene glycol esterase was then employed to hydrolyze HDL-c esters into free HDL-c. The resulting hydrogen peroxide reacted with 4-aminoantipyrine and HSDA, producing a purple-blue chromophore that was quantified photometrically at 600 nm. Participants were categorized into quartiles (Q1, Q2, Q3, and Q4) based on their UHR levels, with Q1 serving as the reference group. In our study, the definition of stroke was based on self-reported physician diagnosis from the NHANES database, and specific subtypes of stroke (ischemic vs. hemorrhagic) were not distinguished due to the database limitations (16–18).
2.3 Covariates
Our study controlled for various potential confounders, including demographic characteristics (age, sex, and ethnicity), socio-economic factors (education level and family income-to-poverty ratio (PIR)), health behaviors (smoking status), medical conditions (diabetes and hypertension), and medication use (antihypertensive, lipid-lowering, and urate-lowering drugs). Physiological and biochemical indicators such as body mass index (BMI), hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), triglycerides (TG), total cholesterol (TC), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-c), and serum creatinine (Scr) were also included. Ethnicity was classified into Mexican American, non-Hispanic White, non-Hispanic Black, other Hispanic, and other. Educational attainment was divided into three categories: less than high school, high school graduate, and college or higher. Smoking status was categorized as smokers (including both current and former smokers) versus non-smokers. Hypertension was defined as systolic blood pressure (SBP) ≥ 140 mmHg, diastolic blood pressure (DBP) ≥ 90 mmHg, self-reported diagnosis, or the use of antihypertensive medications. Diabetes was identified based on self-reported diabetes, use of insulin or hypoglycemic agents, HbA1c ≥ 6.5%, or fasting plasma glucose (FPG) ≥ 126 mg/dL. Medication use included antihypertensive, lipid-lowering, and urate-lowering drugs. History of medications was assessed by asking: “During the past 30 days, have you used or taken any prescription medications?”
2.4 Statistical analysis
Our analysis adhered to the NHANES guidelines, incorporating sample weights, clustering, and stratification to address the complex sampling design.3 Sample weighting was performed as recommended by NHANES, utilizing the formula Weights = 2/10 * WTMEC4YR + 1/10 * WTMEC2YR. We employed random forest-based iterative imputation to handle incomplete covariate data. Continuous variables were presented as means with standard deviations (SD), while categorical variables were described as counts with weighted percentages. Missing data were assumed to occur randomly, and the random forest algorithm was utilized for iterative imputation of missing covariates. Group comparisons were performed using the Kruskal-Wallis test and the Rao-Scott chi-square test. Logistic regression models were employed to examine the association between UHR (continuous/quartile) and stroke risk across three models (Model 1–3). Model 1 included no covariate adjustments, Model 2 adjusted for age, sex, and ethnicity, and Model 3 further adjusted for additional factors such as education level, PIR, smoking status, hypertension, diabetes, medication use (antihypertensive, lipid-lowering, and urate-lowering drugs), BMI, HbA1c, ALT, AST, TG, LDL-c, and Scr. Restricted cubic spline (RCS) analysis was applied to explore potential nonlinear relationships. Spearman correlation analysis was conducted to evaluate the correlation between UHR and other parameters. Stratified analyses were conducted to assess effect modifiers, including age, sex, ethnicity, NHANES cycles, BMI, hypertension, and diabetes. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis were used to evaluate the predictive performance of UHR for stroke. All statistical analyses were performed using R software (version 4.2.0), with statistical significance defined as p < 0.05.
3 Results
3.1 Baseline characteristics of study population
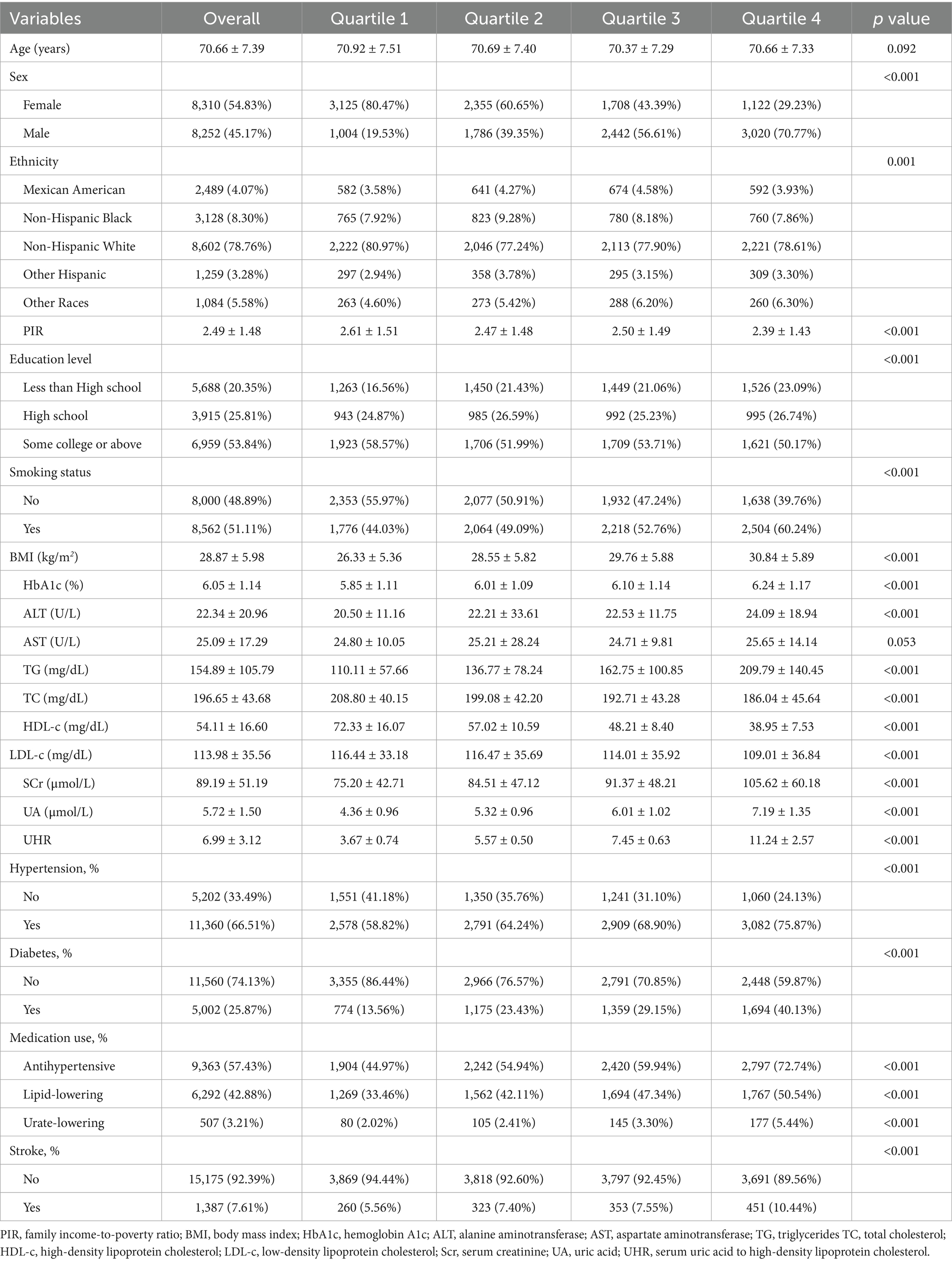
A total of 16,562 older adults participated in the study, with an average age of 70.66 years. Among them, 2,489 (weighted 4.07%) were Mexican American, 3,128 (weighted 8.30%) were non-Hispanic Black, 8,602 (weighted 78.76%) were non-Hispanic White, 1,259 (weighted 3.28%) were other Hispanic, and 1,084 (weighted 5.58%) were classified as other racial groups. Table 1 summarizes the baseline characteristics by UHR quartiles. Participants in the higher quartiles were predominantly male, had lower levels of PIR and education, smoked more frequently, and exhibited higher BMI, increased medication usage (including antihypertensive, lipid-lowering, and urate-lowering drugs), as well as higher proportions of hypertension and diabetes, compared to those in the lowest quartile (p < 0.001). Significant differences were observed in biochemical parameters such as HbA1c, ALT, TG, TC, HDL-c, LDL-c, SCr, and UA across quartiles (p < 0.001). Furthermore, the proportion of stroke cases increased with higher UHR levels (p < 0.001).
3.2 Association between UHR and stroke
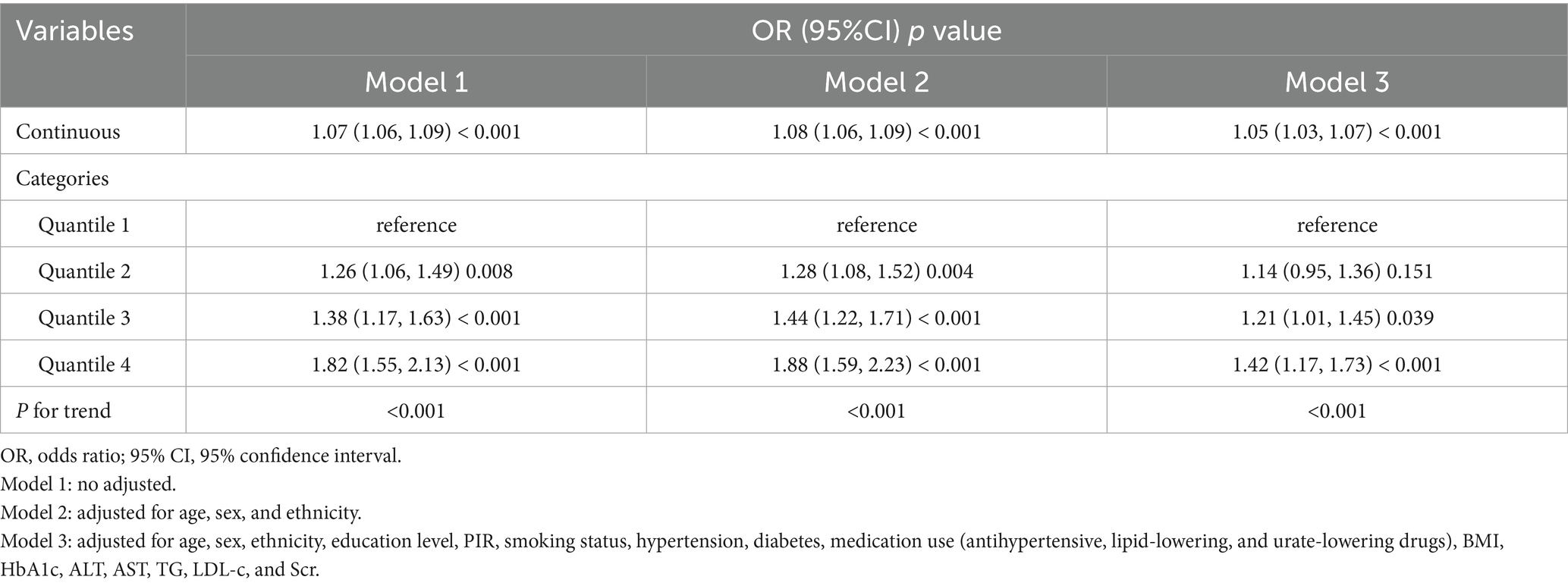
To explore the independent relationship between UHR and stroke risk, we constructed three logistic regression models (Table 2). In the unadjusted analysis, the odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for stroke across quartiles were 1.00 (reference), 1.26 (1.06–1.49), 1.38 (1.17–1.63), and 1.82 (1.55–2.13). After adjusting for age, sex, and ethnicity in Model 2, a significant trend of increasing stroke risk with higher UHR levels was observed (P for trend<0.001). In Model 3, which included additional adjustments for education level, PIR, smoking status, hypertension, diabetes, medication use, BMI, HbA1c, ALT, AST, TG, LDL-c, and Scr, the ORs and 95% CIs for stroke risk were 1.00 (reference), 1.14 (0.95–1.36), 1.21 (1.01–1.45), and 1.42 (1.17–1.73) across quartiles, with a trend test p < 0.001. When UHR was analyzed as a continuous variable, each 1-unit increase in UHR was associated with 5% higher odds of stroke after full adjustment (Model 3: OR = 1.05, 95% CI: 1.03–1.07, p < 0.001). RCS analysis further supported a linear positive relationship between UHR and stroke risk, with no evidence of a nonlinear pattern ( P for nonlinear = 0.598) (Figure 2).
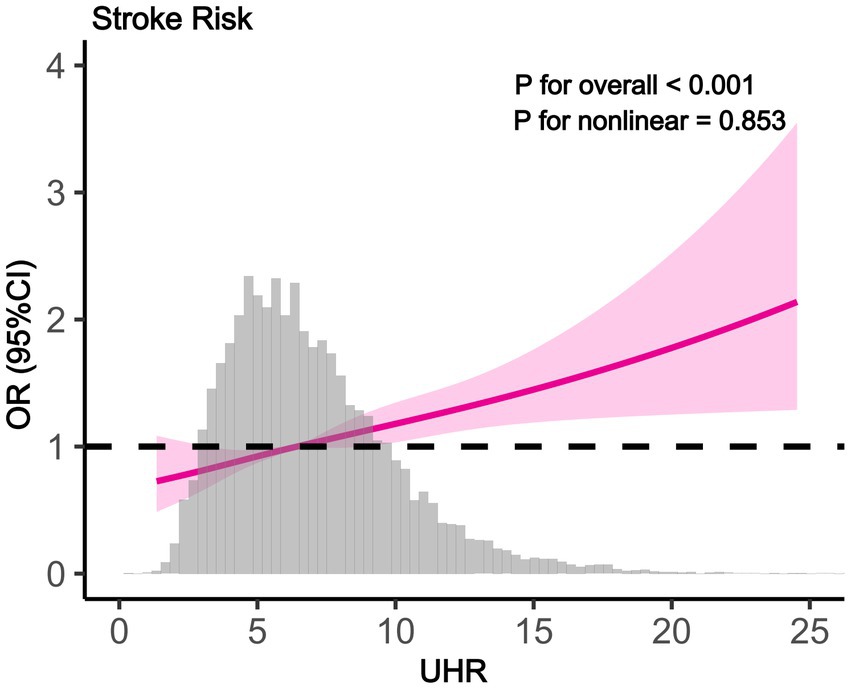
Figure 2. The results of RCS analysis (RCS showing linear positive association between UHR and stroke odds ratio (95% CI). Gray histogram shows UHR distribution. P for overall <0.001, P for nonlinear = 0.853).
3.3 Correlation of UHR with clinical parameters
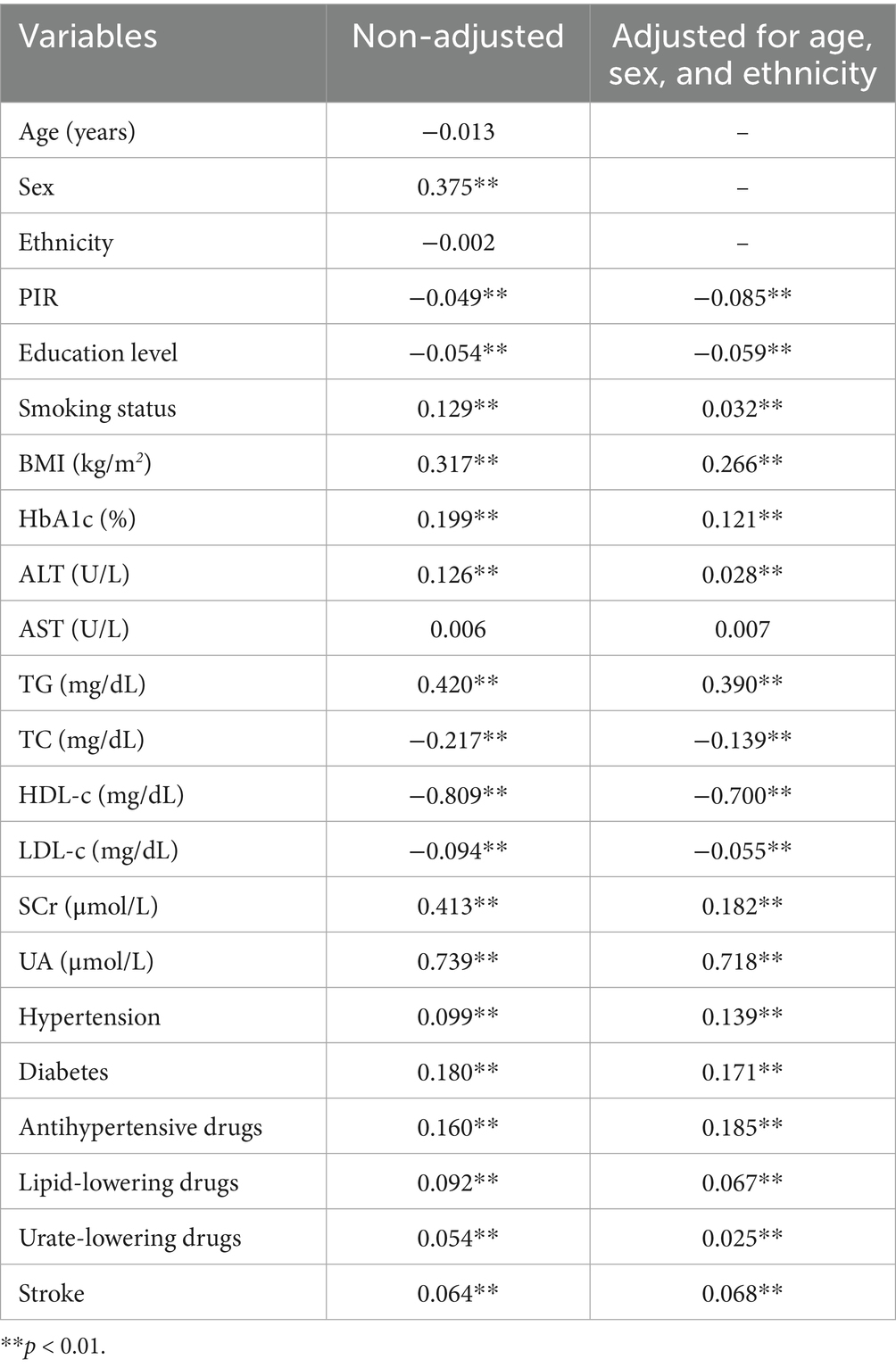
Spearman correlation analysis revealed that UHR exhibited consistent positive correlations with smoking status, BMI, HbA1c, ALT, TG, SCr, UA, hypertension, diabetes, medication use, and stroke, and negative correlations with PIR, education level, TC, HDL-c, and LDL-c (p < 0.01) (Table 3). These associations remained significant both before and after adjustments for age, sex, and ethnicity (p < 0.01).
3.4 Subgroup analysis and ROC analysis
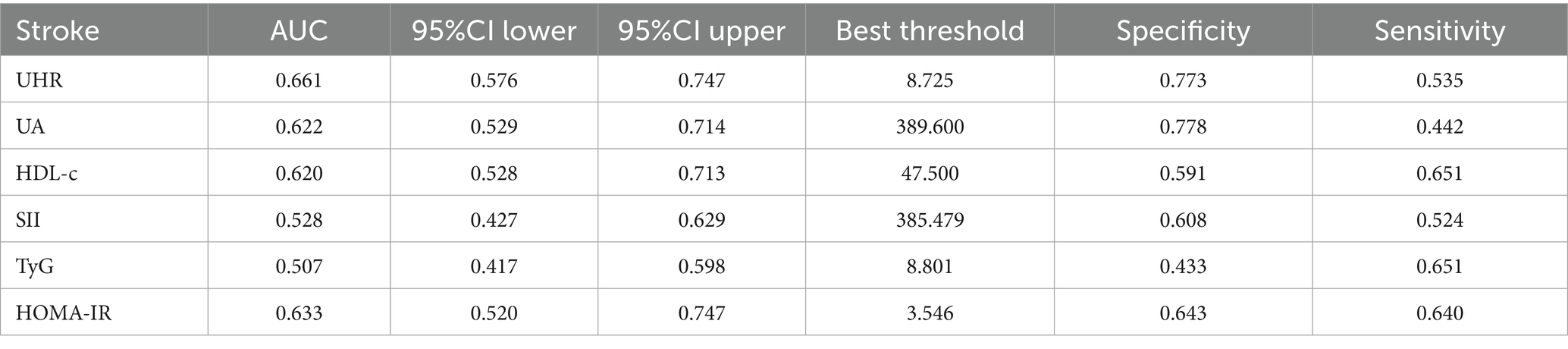
Subgroup analysis was carried out to investigate the link between UHR and stroke risk, stratified by variables such as age, sex, ethnicity, NHANES cycles, BMI, hypertension, and diabetes (Figure 3). The analysis showed that diabetes status significantly impacted these associations (P for interaction <0.05). Interaction analysis highlighted that the association between UHR and stroke was stronger in non-diabetic individuals (OR = 1.06; 95%CI = 1.04–1.09) than in diabetic individuals (OR = 1.03; 95%CI = 1.00–1.05). We compared the discriminative value of UHR with different markers of inflammation [systemic immune-inflammation index (SII)] (19), metabolic disorders [triglyceride-glucose index (TyG)] (17), and insulin resistance [homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR)] (20) for stroke. According to ROC analysis, UHR demonstrated superior predictive performance compared to other indices, with AUC values of 66.1% for UHR, 62.2% for UA, 62.0% for HDL-c, 52.8% for SII, 50.7% for TyG, and 63.3% for HOMA-IR (Delong test: p < 0.001) (Figure 4; Table 4).
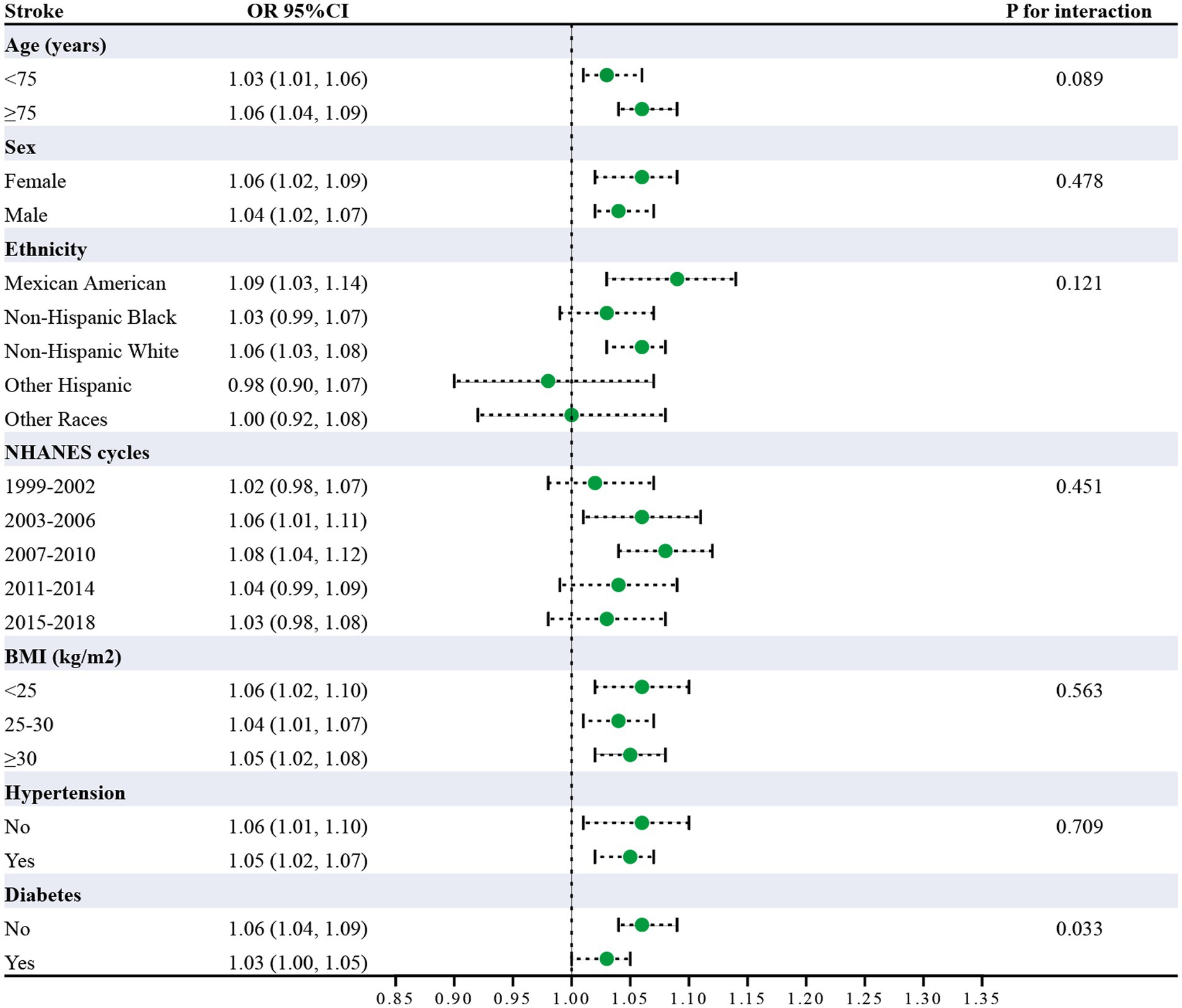
Figure 3. Subgroup analysis of UHR and stroke risk (Odds ratios (95% CI) for stroke per unit UHR increase across demographic and clinical characteristics. Diabetes showed significant interaction (p = 0.033). All analyses adjusted for confounders).
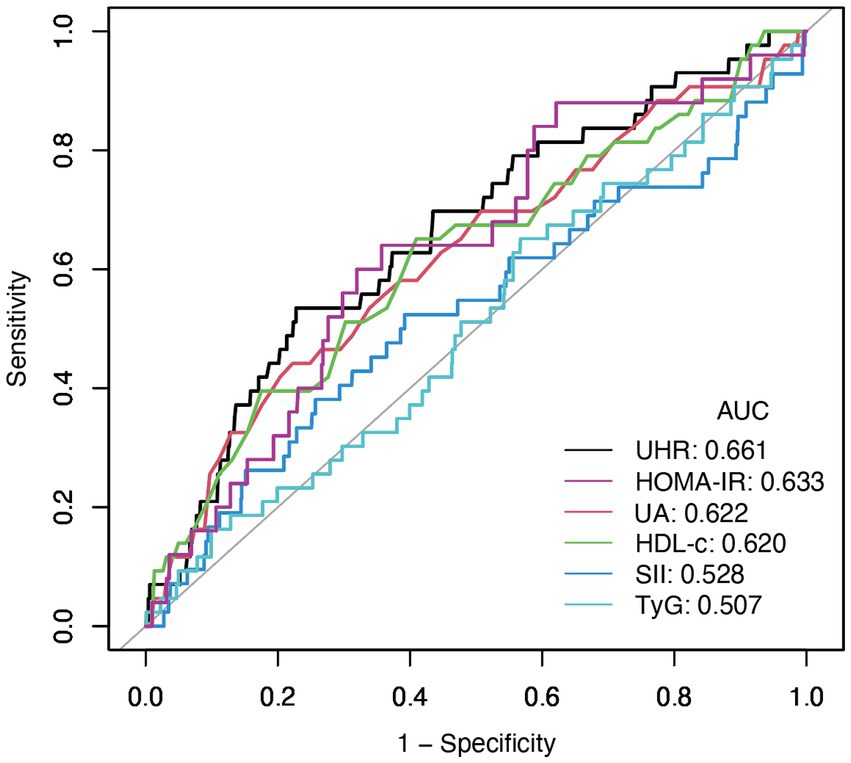
Figure 4. The results of ROC analysis (UHR showed highest AUC (0.661) compared to UA (0.622), HDL-c (0.620), HOMA-IR (0.633), SII (0.528), and TyG (0.507) for stroke risk discrimination).
4 Discussion
This study, utilizing cross-sectional data from an elderly population, is the first to investigate the association between the UHR and stroke risk in older adults. The findings reveal that an elevated UHR is significantly associated with an increased risk of stroke in this population. Subgroup analyses further indicate that this relationship is more pronounced in non-diabetic individuals. ROC analysis demonstrates that the diagnostic value of UHR surpasses that of UA or HDL-c alone.
Previous studies have predominantly focused on single indicators, often neglecting the interaction between UA and HDL-c and the potential clinical significance of their ratio. For example, hyperuricemia has been consistently linked to an elevated risk of stroke, particularly in elderly populations (21, 22). Similarly, low HDL-c levels have been identified as an independent risk factor for stroke (23). However, evidence suggests an antagonistic relationship between UA and HDL-c in the context of metabolism and cardiovascular diseases. First, as the product of purine metabolism, elevated UA levels can induce oxidative stress and endothelial dysfunction, thereby promoting atherosclerosis. Research has shown that high UA levels are associated with reduced vascular endothelial nitric oxide (NO) production, which may lead to vasoconstriction, increased blood pressure, and thrombosis, ultimately heightening stroke risk (8, 24, 25). Second, HDL-c exerts protective effects through its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and reverse cholesterol transport functions. By removing cholesterol from vascular walls and inhibiting the oxidation of LDL-c, HDL-c helps preserve endothelial function (26). A reduction in HDL-c levels diminishes this protective effect (26). When UA levels are elevated and HDL-c levels are decreased, their combined effects may exacerbate vascular damage and further increase stroke risk. Additionally, an elevated UHR might also reflect the presence of metabolic syndrome, which is characterized by insulin resistance, hypertension, obesity, and dyslipidemia-all of which are closely associated with stroke risk (27). On the other hand, the stronger association in non-diabetic populations may be attributed to several potential mechanisms that require further investigation. First, diabetic patients already have elevated baseline stroke risk due to existing vascular complications, which may obscure the independent predictive value of UHR. Second, diabetic patients may have developed severe metabolic dysfunction that could mask the additional risk contribution of UHR. However, the exact mechanisms underlying this difference remain unclear and warrant validation. Compared to analyzing UA or HDL-c individually, UHR may offer greater clinical utility. On one hand, UHR reflects the combined effects of oxidative stress and metabolic dysfunction. On the other hand, its calculation is straightforward and easily applicable in clinical practice. Therefore, this study provides novel evidence supporting UHR as a predictive marker for stroke risk (28).
This study identified a significant association between the UHR and stroke risk in older adults; however, several limitations should be acknowledged. First, as a cross-sectional study, it cannot establish causality or determine the temporal sequence between UHR elevation and stroke occurrence. The elevated UHR observed in stroke patients could potentially be a consequence of the stroke itself rather than a causal factor. The study by Ding et al. (29), demonstrating UHR’s association with post-stroke mortality, provides complementary evidence. These findings may suggest UHR reflects underlying metabolic dysfunction relevant to post-stroke outcomes (29). Additionally, previous studies have shown UHR associations with cardiovascular risk factors linked to stroke. While mediation analysis could explore these pathways, our cross-sectional design and lack of temporal data precluded such analysis. Second, the data were obtained from a specific population, which may introduce selection bias, limiting the generalizability of the results to other populations. Third, the study did not fully account for other potential confounding factors, such as dietary habits and the use of lipid-lowering medications, which could have influenced the observed outcomes. Finally, it should be noted that although our study and some previous reports suggest a correlation between UHR and various cardiometabolic diseases, there is still a lack of large-scale prospective clinical studies to confirm the diagnostic or predictive value of UHR. Currently, UHR is not recommended by clinical guidelines as a routine marker, and its clinical utility requires further validation through multi-center and large cohort studies.
5 Conclusion
Our study found that higher UHR levels are significantly associated with increased stroke risk in older adults, particularly in non-diabetic individuals. UHR showed better predictive value for stroke risk compared to UA or HDL-c alone. This research underscores the importance of composite biomarkers in assessing stroke risk.
Data availability statement
Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. This data can be found at: https://wwwn.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Ethics Review Board of the National Center for Health Statistics. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation was not required from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin in accordance with the national legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
QJ: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. GZha: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. YL: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. CJ: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. KW: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. GZhe: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. WL: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. JM: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. MW: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. ZT: Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study is funded by the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (LY21H090008), the Key Project Jointly Built by Zhejiang Province and the Ministry (WKJ-ZJ-2340) and the General Project Funds from the Health Department of Zhejiang Province (2025KY001).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Footnotes
1. ^https://wwwn.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/
2. ^https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/about/erb.html
3. ^https://wwwn.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/analyticguidelines.aspx
References
1. Dalecka, A, Bartoskova Polcrova, A, Pikhart, H, Bobak, M, and Ksinan, AJ. Living in poverty and accelerated biological aging: evidence from population-representative sample of U.S. adults. BMC Public Health. (2024) 24:458. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-17960-w
2. Boehme, AK, Esenwa, C, and Elkind, MS. Stroke risk factors, genetics, and prevention. Circ Res. (2017) 120:472–95. doi: 10.1161/circresaha.116.308398
3. GBD 2019 Stroke Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of stroke and its risk factors, 1990-2019: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2019. Lancet Neurol. (2021) 20:795–820. doi: 10.1016/s1474-4422(21)00252-0
4. Li, Z, Liu, Q, and Yao, Z. The serum uric acid-to-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio is a predictor for all-cause and cardiovascular disease mortality: a cross-sectional study. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2024) 15:1417485. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1417485
5. Sun, H, Su, H, Zheng, R, Liu, C, Wang, Y, and Fang, C. Serum uric acid to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio is associated with visceral fat in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. (2023) 16:959–67. doi: 10.2147/dmso.S403895
6. Copur, S, Demiray, A, and Kanbay, M. Uric acid in metabolic syndrome: does uric acid have a definitive role? Eur J Intern Med. (2022) 103:4–12. doi: 10.1016/j.ejim.2022.04.022
7. Zhong, J, Cai, H, Zhang, Z, Wang, J, Xiao, L, Zhang, P, et al. Serum uric acid and prognosis of ischemic stroke: cohort study, meta-analysis and Mendelian randomization study. Eur Stroke J. (2024) 9:235–43. doi: 10.1177/23969873231209620
8. Du, L, Zong, Y, Li, H, Wang, Q, Xie, L, Yang, B, et al. Hyperuricemia and its related diseases: mechanisms and advances in therapy. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2024) 9:212. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-01916-y
9. Podrez, EA. Anti-oxidant properties of high-density lipoprotein and atherosclerosis. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. (2010) 37:719–25. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.2010.05380.x
10. Jia, C, Anderson, JLC, Gruppen, EG, Lei, Y, Bakker, SJL, Dullaart, RPF, et al. High-density lipoprotein anti-inflammatory capacity and incident cardiovascular events. Circulation. (2021) 143:1935–45. doi: 10.1161/circulationaha.120.050808
11. Zhao, H, Qiu, X, Li, HZ, Cui, JJ, and Sun, YY. Association between serum uric acid to HDL-cholesterol ratio and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease risk among Chinese adults. Biomed Environ Sci. (2023) 36:1–9. doi: 10.3967/bes2022.111
12. Yu, X, Sun, F, Ming, J, Liang, S, Zhang, W, Wang, L, et al. Serum uric acid to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio is a promising marker for identifying metabolic syndrome in nondiabetic Chinese men. Postgrad Med. (2023) 135:741–9. doi: 10.1080/00325481.2023.2263372
13. Ahari, RK, Sahranavard, T, Mansoori, A, Fallahi, Z, Babaeepoor, N, Ferns, G, et al. Association of atherosclerosis indices, serum uric acid to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio and triglycerides-glucose index with hypertension: a gender-disaggregated analysis. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). (2024) 26:645–55. doi: 10.1111/jch.14829
14. Zhou, X, and Xu, J. Association between serum uric acid-to-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio and insulin resistance in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes Investig. (2024) 15:113–20. doi: 10.1111/jdi.14086
15. Huang, X, Hu, L, Tao, S, Xue, T, Hou, C, and Li, J. Relationship between uric acid to high-density cholesterol ratio (UHR) and circulating α-klotho: evidence from NHANES 2007-2016. Lipids Health Dis. (2024) 23:244. doi: 10.1186/s12944-024-02234-6
16. Micha, R, Peñalvo, JL, Cudhea, F, Imamura, F, Rehm, CD, and Mozaffarian, D. Association between dietary factors and mortality from heart disease, stroke, and type 2 diabetes in the United States. JAMA. (2017) 317:912–24. doi: 10.1001/jama.2017.0947
17. Jiang, Y, Shen, J, Chen, P, Cai, J, Zhao, Y, Liang, J, et al. Association of triglyceride glucose index with stroke: from two large cohort studies and Mendelian randomization analysis. Int J Surg. (2024) 110:5409–16. doi: 10.1097/js9.0000000000001795
18. Zheng, X, Li, X, Zhen, J, Xue, D, Hu, J, Cao, Q, et al. Periodontitis is associated with stroke. J Transl Med. (2023) 21:697. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04545-1
19. Cheng, W, Bu, X, Xu, C, Wen, G, Kong, F, Pan, H, et al. Higher systemic immune-inflammation index and systemic inflammation response index levels are associated with stroke prevalence in the asthmatic population: a cross-sectional analysis of the NHANES 1999-2018. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1191130. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1191130
20. Qiu, HC, Liu, HZ, Li, X, Zeng, X, and Zhao, JZ. Insulin resistance as estimated by homeostasis model assessment predicts incident post-stroke depression in Chinese subjects from ischemic stroke. J Affect Disord. (2018) 231:1–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2018.01.023
21. Li, M, Hou, W, Zhang, X, Hu, L, and Tang, Z. Hyperuricemia and risk of stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective studies. Atherosclerosis. (2014) 232:265–70. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2013.11.051
22. Tu, W, Wu, J, Jian, G, Lori, J, Tang, Y, Cheng, H, et al. Asymptomatic hyperuricemia and incident stroke in elderly Chinese patients without comorbidities. Eur J Clin Nutr. (2019) 73:1392–402. doi: 10.1038/s41430-019-0405-1
23. Hu, Y, Song, M, Wu, D, Zhang, Y, Li, G, and Luo, H. The association between HDL-C and stroke in the middle-aged and elderly: a cross-sectional study. Brain Behav. (2023) 13:e2901. doi: 10.1002/brb3.2901
24. Masi, S, Georgiopoulos, G, Alexopoulos, G, Pateras, K, Rosada, J, Seravalle, G, et al. The complex relationship between serum uric acid, endothelial function and small vessel remodeling in humans. J Clin Med. (2020) 9:2027. doi: 10.3390/jcm9072027
25. Maxwell, AJ, and Bruinsma, KA. Uric acid is closely linked to vascular nitric oxide activity. Evidence for mechanism of association with cardiovascular disease. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2001) 38:1850–8. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(01)01643-6
26. Campbell, S, and Genest, J. HDL-C: clinical equipoise and vascular endothelial function. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. (2013) 11:343–53. doi: 10.1586/erc.13.17
27. Zhou, X, and Xu, J. Association between serum uric acid-to-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio and insulin resistance in an American population: a population-based analysis. J Diabetes Investig. (2024) 15:762–71. doi: 10.1111/jdi.14170
28. Kim, KY, Shin, KY, and Chang, KA. Potential biomarkers for post-stroke cognitive impairment: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:602. doi: 10.3390/ijms23020602
29. Ding, L, Guo, H, Zhang, C, Liang, X, and Liu, Y. Association between serum uric acid to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio and all-cause and cardiovascular disease mortality after stroke: a cross-sectional study from 2005 to 2018. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. (2025) 35:103909. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2025.103909
Keywords: serum uric acid, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, ratio, stroke, NHANES
Citation: Jiang Q, Zhan G, Liu Y, Jiang C, Wang K, Zheng G, Liu W, Ma J, Wang M and Tang Z (2025) Serum uric acid to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio is associated with stroke in the elderly: a population-based study. Front. Neurol. 16:1594080. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1594080
Edited by:
Ying Liu, Huzhou Central Hospital, ChinaCopyright © 2025 Jiang, Zhan, Liu, Jiang, Wang, Zheng, Liu, Ma, Wang and Tang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zhuxiao Tang, dGFuZ3p4QHpqdS5lZHUuY24=
 Qingsong Jiang1
Qingsong Jiang1 Kang Wang
Kang Wang Jiangchun Ma
Jiangchun Ma Ming Wang
Ming Wang Zhuxiao Tang
Zhuxiao Tang