Abstract
Introduction:
The triglyceride-glucose (TyG) index, a robust surrogate marker of metabolic dysregulation reflecting both insulin resistance and lipid-glucose homeostasis, has emerged as a significant predictor of cerebrovascular outcomes. Given the critical role of metabolic-nutritional status in post-stroke recovery, we supposed that the TyG index may predict the prognosis of ischemic stroke patients who underwent thrombectomy in the posterior circulation.
Methods:
We studied 60 patients with cerebral infarction who underwent emergency posterior circulation interventional thrombectomy at a comprehensive stroke center from January 2018 to July 2024. The TyG index was used as the cut-off value of 8.53, and the formula was calculated as TyG index = ln [fasting glucose(mg/dL) × fasting triglycerides(mg/dL) /2]. Univariate analysis and multivariate logistic regression were used to adjust for age, the National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) score at onset, APOA-1, and diabetes. A modified Rankin scale score of 0–2 at 90 days defined a good functional outcome, and the incidence of death within 90 days was investigated.
Results:
The number of patients with good functional outcome in the high TyG index group was significantly less than that in the low TyG index group (adjusted OR 6.85, 95%CI 1.83, 32.13, p = 0.008). TyG index was significantly associated with 90-day mortality (adjusted OR: 5.113, 95%CI 1.274 to 20.519, p = 0.021).
Discussion:
This study found that TyG index was linearly correlated with the 90-day neurological recovery in patients with acute posterior circulation cerebral infarction after interventional thrombectomy. The higher the TyG index, the worse the neurological recovery and the higher the risk of death.
Introduction
Posterior circulation stroke, characterized by cerebral infarction in the vertebrobasilar system, and is collectively referred to as vertebrobasilar artery occlusion (VBAO), with basilar artery occlusion (BAO) being a common form of this condition (1), presents distinct metabolic challenges due to the high energy demands of brainstem and cerebellar structures. Although posterior circulation strokes account for a relatively small proportion of all cerebral infarctions, they often lead to severe neurological deficits due to the involvement of critical structures such as the brainstem, cerebellum, and occipital lobes. In severe cases, these strokes can be life-threatening (2). Research has shown that among patients with acute BAO who underwent interventional thrombectomy, half still did not achieve a favorable outcome within 90 days, and approximately 40% progressed to a fatal outcome. Notably, patients with poor collateral circulation faced worse clinical prognoses (3, 4). Despite advances in imaging techniques, including computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), the diagnosis of posterior circulation cerebral infarction has significantly improved; however, these methods do not predict functional recovery. Therefore, there is an urgent need for sensitive and reliable prognostic indicators to guide clinical treatment (5).
Crucially, emerging evidence suggests that metabolic-nutritional status may determine post-stroke recovery through mitochondrial bioenergetics, oxidative stress regulation, and neurovascular unit maintenance (6). However, current prognostic models predominantly focus on anatomical parameters, neglecting the critical dimension of systemic metabolism. The triglyceride-glucose (TyG) index, calculated as ln[fasting triglycerides (mg/dL) × fasting glucose (mg/dL) /2], serves as a composite biomarker of metabolic flexibility by integrating lipid handling efficiency and glucose homeostasis (5). Beyond quantifying insulin resistance (7), an elevated TyG index reflects fundamental metabolic derangements, including: (1) impaired adipose tissue lipolysis regulation, (2) ectopic lipid deposition, and (3) neuroendocrine dysregulation of nutrient partitioning (8). These disturbances may exacerbate the cerebral energy crisis during stroke recovery by limiting substrate availability for neuronal repolarization and axonal regeneration (9). As research progresses, the TyG index has been shown to be associated with various metabolic abnormalities and cardiovascular diseases (CVD). Studies by Wang et al. (10) and Zhu et al. (11)have demonstrated that the TyG index can significantly predict the likelihood of severe cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events in patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS) when incorporated into a mature and reliable risk assessment model. In recent years, increasing attention has been given to the relationship between the TyG index and cerebrovascular diseases, particularly its prognostic value in cerebral infarction (12). For example, Hou et al. (13) found that all-cause mortality and risk of stroke recurrence were significantly increased in patients with ischemic stroke with higher TyG index through the analysis of data from CNSR II. In addition, Nam et al. (14) noted that patients with higher TyG indices were more likely to experience early neurological deterioration following acute ischemic stroke. A large-scale meta-analysis revealed that, among patients with anterior circulation cerebral infarction, those with a high TyG index had significantly worse outcomes, including higher mortality rates and an increased likelihood of recurrent cerebral infarction (15). For patients with cerebral infarction resulting from large-vessel occlusion in the posterior circulation, emergency interventional thrombectomy remains the most effective treatment due to the complexity of vascular anatomy and the relatively low incidence rate (16). However, the predictive value of the TyG index for functional recovery following thrombectomy remains unclear.
Based on the above-mentioned research, we assume that the TyG index may predict the prognosis of AIS patients who underwent thrombectomy in the posterior circulation by quantifying their blood glucose and lipid levels. To test this hypothesis, we conducted a cohort study of 60 VBAO patients undergoing thrombectomy (2018–2024), stratified by a TyG index threshold of 8.53. Using multivariable models adjusted for APOA-1 (a key regulator of reverse cholesterol transport) and diabetes status, we specifically examined the relationship between the TyG levels and 90-day functional outcomes, and mortality risk.
Methods and materials
Study population
This is a retrospective observational cohort study from a single center, and the prediction value of the TyG index for the prognosis of the vertebrobasilar artery system is assessed. Sixty acute ischemic stroke (AIS) patients who underwent emergency vertebrobasilar system thrombectomy from January 2018 to July 2024 were enrolled. Exclusion criteria were as follows: (1) previous modified Rankin scale score ≥2; (2) a lack of follow-up information on outcomes; (3) progressive cerebral infarction; (4) failure of vascular recanalization (17). A total of sixty-seven patients underwent posterior circulation thrombectomy in our center during the study period. Five patients were excluded because of progressive cerebral infarction, and two patients were excluded because of missing follow-up data. The research samples were selected based on strict diagnostic criteria. For instance, only patients with definite posterior - circulation cerebral infarction, a clear onset time, and successful recanalization after thrombectomy were included. This approach, to a certain extent, ensured the pertinence and homogeneity of the samples. Although the sample size was relatively smaller compared to some large - scale studies, in the context of researching the rare disease of large-vessel occlusion in the posterior circulation and predicting subsequent functional recovery, the samples are fairly representative.
All participants received acute stroke management based on international and domestic guidelines. In each case, the angioneurologist was responsible for determining whether thrombolytic therapy should be carried out. In the process of internal treatment, the interventional physician chose the intervention strategy for each patient.
Data collection and clinical variables
Baseline demographic, clinical, imaging, and laboratory data were collected for all enrolled patients. Baseline data included: (1) demographic data, such as age and gender; (2) Past medical histories, including previous stroke, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, current smoker status, atrial fibrillation, and use of anticoagulants; (3) Stroke characteristics included the NIHSS score, stroke modified Rankin scale (mRS) score, posterior circulation Alberta Stroke Program Early CT score (PC-ASPECTS), Basilar Artery Treatment and Management (BATMAN) score, stroke classification and occlusion location; (4) Reperfusion therapy, including thrombolytic therapy or not, time from onset to thrombolysis, time from onset to puncture, time from puncture to recanalization, number of thrombectomy attempts and thrombectomy methods; (5) Laboratory data, including fasting lipoprotein (a), fasting apolipoprotein A-1 (APOA-1), fasting apolipoprotein B(APOB), APOA-1/APOB, fasting low-density lipoprotein, fasting blood glucose, and fasting triglyceride. We collected a relatively large number of different lipid indices in the baseline table. The reason is that some lipid indices are independent risk factors for cerebral infarction (18), and this not only allows us to observe their differences in the groups but also can be used for subsequent multivariate regression analysis.
The TyG index was calculated in the following way. During the first 24 h after the onset of illness, each patient fasted for more than 8 h overnight, and blood glucose and lipid levels were measured in the early morning hours. The TyG index was calculated: TyG index = ln[fasting glucose(mg/dL) × fasting triglycerides(mg/dL) /2] (19). Characteristics of patients with ‘Low TyG’ and ‘High TyG’ indices were then compared using≥8.53 as a cut-off value.
Clinical outcomes
We evaluated the primary clinical outcomes of favorable functional outcome status defined by the modified Rankin Scale (mRS) score of 0–2 (20, 21). Secondary outcomes included mRS scores 0–1, 0–3 and 0–4 at 90 days. Safety outcomes included death, symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage (sICH), procedural complications, and severe adverse events within 90 days.
Statistical analysis
The analysis included measures such as mean (standard deviation) for normally distributed variables and median (interquartile range, IQR) for non-normally distributed variables for continuous variables, and frequencies and percentages for categorical variables. Normality tests and Quantile-Quantile (QQ) plots were used to assess the distribution of the data, and appropriate descriptive statistics methods were applied to both normally and non-normally distributed variables. Group comparisons for continuous variables with normal distribution were performed using Welch’s t-test or ANOVA, and non-normally distributed variables were compared using the Wilcoxon rank-sum test or Kruskal-Wallis test. For comparison between groups of categorical data, we used the Fisher exact test for expected frequencies <5; otherwise, we used the Chi-squared test. We employed rigorous statistical methods to analyze the limited data, aiming to unearth the latent relationships and differences within the data, thus enhancing the credibility of the results.
In our study, all statistical analyses were performed using the R software (version 4.2.2). Variables were screened by Elastic net regression. Univariate Logistic regression analysis was performed to assess the association between each individual factor and functional outcome. Multivariate Logistic regression analysis was performed to determine the independent factors significantly associated with mRS scores, while adjusting for potential confounders. All variables from the univariate analysis were included in the multivariate Logistic regression model, regardless of their significance in the univariate analysis. This comprehensive approach ensured that all potential influencing factors were considered and adjusted for, providing a more accurate estimation of the independent clinical factors that significantly impacted mRS scores.
Result
Study participants and baseline characteristics
A total of 60 patients satisfying the eligibility criteria were included in the final analysis. The baseline characteristics of the study population were summarized (Table 1). The baseline characteristics of patients, categorized by clinical outcomes, reveal several key findings. The median age was slightly higher among those with poor clinical outcomes (73 years) compared to those with good outcomes (70 years), though this difference was not statistically significant (p = 0.099). Gender distribution was similar between groups with a predominance of males in both (73.9% in good outcomes, 70.3% in poor outcomes). Notably, a significant difference was observed in Apolipoprotein A-1 levels, with better outcomes associated with higher levels (1.26 ± 0.17 vs. 1.14 ± 0.17, p = 0.015). Fasting glucose levels presented a significant disparity, showing lower levels in good outcomes (5.5) compared to the poor (7.6, p < 0.001). Additionally, the TyG index was more favorable in patients with good outcomes, with a significant portion having an index below 8.53 (69.6% vs. 37.8%, p = 0.017). The baseline NIHSS score showed a modest significance, with median values clustering around 36 for both groups, but with variation in distribution (p = 0.045). Other variables, such as history of hypertension, diabetes, smoking, drinking, ischemic stroke, and thrombolysis interventions, presented no significant differences between the groups, suggesting similar exposure profiles. No significant differences were observed in triglycerides, low-density lipoprotein, and lipoprotein a levels.
Table 1
| Characteristic | mRS scores | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0–2, N = 231 | 3–6, N = 371 | ||
| Age | 70 (64, 75) | 73 (68, 79) | 0.0992 |
| Sex | 0.7613 | ||
| Female | 6 (26.1%) | 11 (29.7%) | |
| Male | 17 (73.9%) | 26 (70.3%) | |
| Smoking | 0.5973 | ||
| No | 14 (60.9%) | 25 (67.6%) | |
| Yes | 9 (39.1%) | 12 (32.4%) | |
| Drinking | 0.6033 | ||
| No | 16 (69.6%) | 28 (75.7%) | |
| Yes | 7 (30.4%) | 9 (24.3%) | |
| History of hypertension | >0.9994 | ||
| No | 4 (17.4%) | 6 (16.2%) | |
| Yes | 19 (82.6%) | 31 (83.8%) | |
| History of atrial fibrillation | 0.7494 | ||
| No | 19 (82.6%) | 28 (75.7%) | |
| Yes | 4 (17.4%) | 9 (24.3%) | |
| History of anticoagulants | >0.9994 | ||
| No | 21 (91.3%) | 34 (91.9%) | |
| Yes | 2 (8.7%) | 3 (8.1%) | |
| History of diabetes mellitus | 0.0903 | ||
| No | 18 (78.3%) | 21 (56.8%) | |
| Yes | 5 (21.7%) | 16 (43.2%) | |
| History of ischemic stroke | >0.9994 | ||
| No | 20 (87.0%) | 33 (89.2%) | |
| Yes | 3 (13.0%) | 4 (10.8%) | |
| Lipoprotein a | 16 (12, 29) | 12 (7, 28) | 0.2102 |
| Apolipoprotein A-1 | 1.26 ± 0.17 | 1.14 ± 0.17 | 0.0155 |
| Apolipoprotein B | 0.85 (0.67, 0.95) | 0.74 (0.58, 0.91) | 0.2212 |
| Low density lipoprotein | 76 (56, 105) | 74 (59, 107) | 0.9646 |
| Triglycerides | 1.05 (0.78, 1.52) | 1.15 (0.68, 1.57) | >0.9992 |
| Fasting glucose | 5.5 (4.8, 6.0) | 7.6 (6.0, 8.9) | <0.0012 |
| APOA-1/APOB | 1.44 (1.20, 1.83) | 1.45 (1.26, 1.88) | 0.8852 |
| Cause of stroke | 0.8494 | ||
| Atherosclerosis | 12 (52.2%) | 18 (48.6%) | |
| Cardiac embolism | 7 (30.4%) | 13 (35.1%) | |
| Other causes | 3 (13.0%) | 3 (8.1%) | |
| Unknown | 1 (4.3%) | 3 (8.1%) | |
| Time from symptom onset to groin puncture | 290 (198, 419) | 280 (206, 415) | 0.8672 |
| Time from symptom onset to recanalization | 355 (260, 483) | 352 (266, 498) | 0.7732 |
| Puncture to recanalization time | 60 (46, 78) | 66 (38, 89) | 0.8082 |
| Door to recanalization time | 177 (150, 214) | 178 (152, 270) | 0.7272 |
| First thrombectomy attempt | 0.5934 | ||
| Aspiration | 4 (17.4%) | 9 (24.3%) | |
| Stenting | 12 (52.2%) | 21 (56.8%) | |
| Stenting+stenting | 7 (30.4%) | 7 (18.9%) | |
| Location of intracranial artery occlusion | 0.8764 | ||
| Distal | 1 (4.3%) | 2 (5.4%) | |
| Middle | 4 (17.4%) | 5 (13.5%) | |
| Tip of the basilar artery occlusion | 18 (78.3%) | 30 (81.1%) | |
| Number of thrombectomy maneuvers per-intervention | 0.5803 | ||
| 1 | 12 (52.2%) | 22 (59.5%) | |
| 2 | 11 (47.8%) | 15 (40.5%) | |
| Triglyceride-glucose index | 0.0173 | ||
| <8.53 | 16 (69.6%) | 14 (37.8%) | |
| ≥8.53 | 7 (30.4%) | 23 (62.2%) | |
| Intravenous thrombolysis | 0.5003 | ||
| No | 11 (47.8%) | 21 (56.8%) | |
| Yes | 12 (52.2%) | 16 (43.2%) | |
| Tirofiban | 0.6823 | ||
| No | 15 (65.2%) | 26 (70.3%) | |
| Yes | 8 (34.8%) | 11 (29.7%) | |
| BATMAN score | 0.5243 | ||
| 0–8 | 15 (65.2%) | 27 (73.0%) | |
| 9–10 | 8 (34.8%) | 10 (27.0%) | |
| PC-ASPECTS | 0.3913 | ||
| 0–8 | 4 (17.4%) | 10 (27.0%) | |
| 9–10 | 19 (82.6%) | 27 (73.0%) | |
| Baseline NIHSS score | 36.0 (25.5, 36.0) | 36.0 (36.0, 36.0) | 0.0452 |
Patient demographics and baseline characteristics.
1Median (interquartile range, IQR); n (%); Mean ± SD.
2Wilcoxon rank sum test.
3Pearson's Chi-squared test.
4Fisher's exact test.
5Welch two sample t-test.
6Wilcoxon rank sum exact test.
Regarding reperfusion therapy, all patients underwent endovascular thrombectomy, with more than half of the patients receiving stent thrombectomy (n = 33, 55%), while the remaining patients underwent aspiration techniques (n = 13, 21.7%) and a combination of aspiration and stent thrombectomy (n = 14, 23.3%). Approximately half of the patients received intravenous thrombolysis (IVT) (n = 28, 46.7%, p = 0.5), and a minority received tirofiban antiplatelet therapy (n = 19, 31.7%, p = 0.682). These treatments did not significantly affect the prognosis of the patients after three months. The average time from symptom onset to puncture was 287.5 min (IQR: 205.75–413, p = 0.752), the average time from symptom onset to recanalization was 353.5 min (IQR: 262–490, p = 0.672), the average time from puncture to recanalization was 65.5 min (IQR: 40–79, p = 0.454), and the average time from hospital arrival to recanalization was 177.5 min (IQR: 149.75–220, p = 0.471).
Functional outcomes by the TyG index
For 90 - day clinical outcomes, compared with patients with high TyG index, patients with low TyG index had mRS scores of 0–1 (33.3% vs. 10%, p = 0.028), 0–3 (70% vs. 26.7%, p = 0.017). p < 0.001 and 0–4 (73.3% vs. 46.7%, p = 0.038). After adjusting for age, NIHSS score at onset, APOA-1 and diabetes, TyG index remained an independent predictor of good outcome by multivariate logistic regression (Table 2).
Table 2
| Characteristic | OR1 | 95% CI1 | p value | adjusted OR1 | 95% CI1 | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical outcomes | ||||||
| mRS scores at 90 days according, range — no. (%) | ||||||
| 0 or 1 | 4.5 | 1.09, 18.50 | 0.037 | 7.459 | 1.43, 38.87 | 0.017 |
| 0 to 3 | 6.42 | 2.08, 19.76 | 0.001 | 16.572 | 3.34, 82.14 | 0.001 |
| 0 to 4 | 3.14 | 1.07, 9.27 | 0.038 | 5.319 | 1.37, 20.70 | 0.016 |
| Imaging outcomes | ||||||
| sICH at 24–72 h no. (%) | 1.18 | 0.38, 3.63 | 0.775 | 0.958 | 0.24, 3.76 | 0.951 |
| Safety outcomes | ||||||
| Death within 90 days — no. (%) | 3.06 | 0.97, 9.66 | 0.057 | 5.113 | 1.27, 20.52 | 0.021 |
| sICH at 24–72 h — no. (%) | 1.39 | 0.28, 6.70 | 0.688 | 1.334 | 0.27, 6.70 | 0.727 |
| Severe adverse events | 1.46 | 0.44, 4.86 | 0.543 | 1.22 | 0.32, 4.60 | 0.769 |
Comparison of clinical outcomes and safety between low ‘low TyG’ and ‘high TyG’ patients.
1OR, odds ratio; CI, confidence interval.
At the same time, patients with high TyG had a higher risk of death within 90 days. Using multivariate logistic regression, after adjusting for age, NIHSS score at onset, APOA-1, and diabetes, TyG was also found to be an independent predictor of mortality risk (adjusted OR 5.113, 95% CI 1.274 to 20.519, p = 0.021). Compared with the high Tyg group, patients in the low Tyg group had a lower risk of ICH within 90 days, a lower incidence of symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage (sICH) at 24–72 h, and a lower number of adverse events. However, these differences were not statistically significant (Table 2).
We also explored the overall distribution of mRS scores at 90 days in the high and low TyG index groups (Figure 1).
Figure 1

Comparison of mRS distribution between “low TyG” and “high TyG” patients.
Logistic regression analyses
The 27 variables were screened by Elastic net regression (Figure 2A). When λ = 0.134, the following variables were selected for multivariate analysis: TyG index (Coefficient = 0.58221679), Age (Coefficient = 0.01415229), Apolipoprotein A-1 (Coefficient = −1.46789936), Baseline NIHSS score (Coefficient = 0.01621730) (Figure 2B). The details of the selected features were presented (Figure 3).
Figure 2
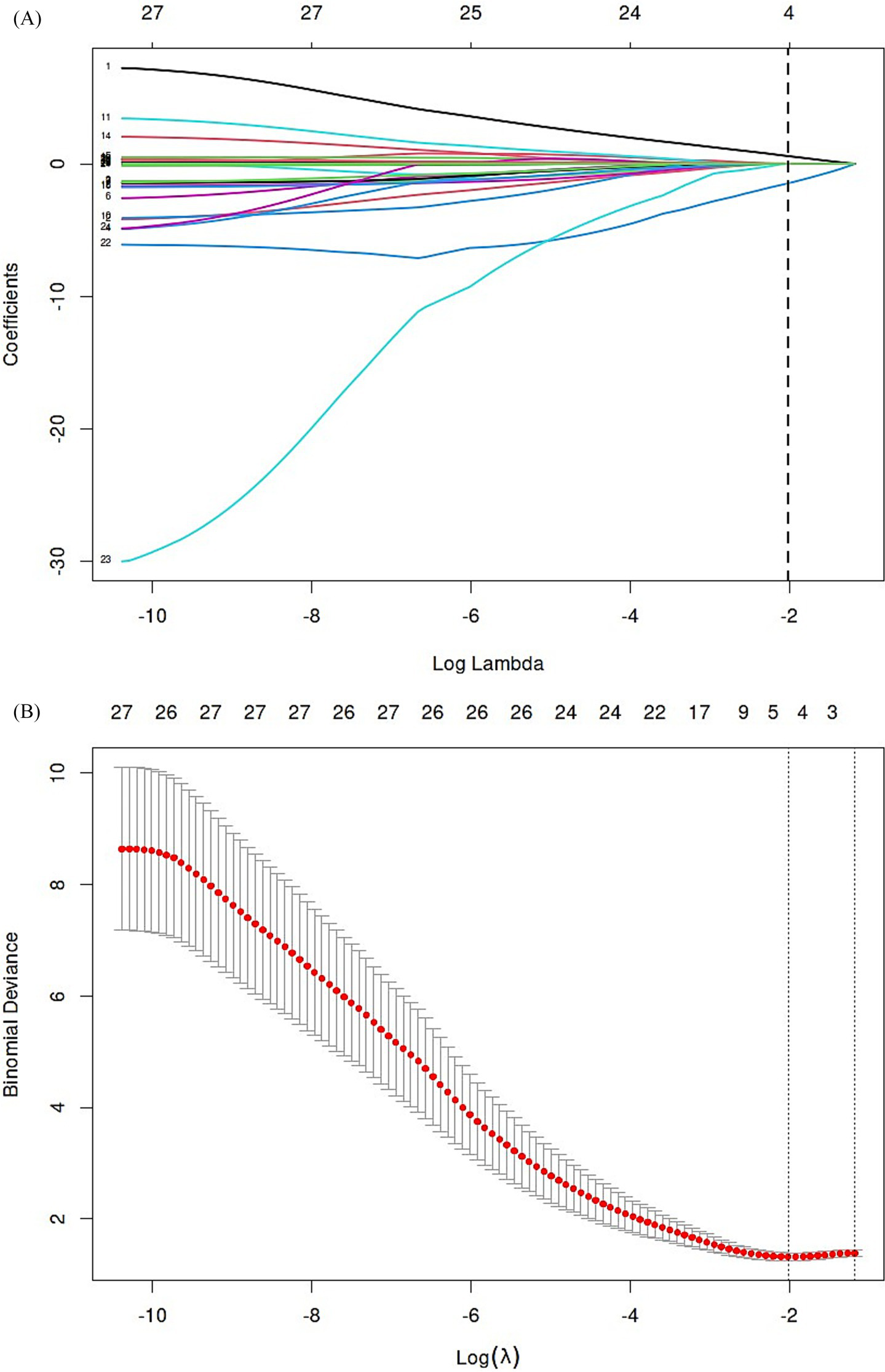
Elastic net regression and tenfold cross-validation were used to select the radiomics features. (A) Elastic net coefficient profiles of the radiomic features. (B) Optimal feature selection of mRS.
Figure 3
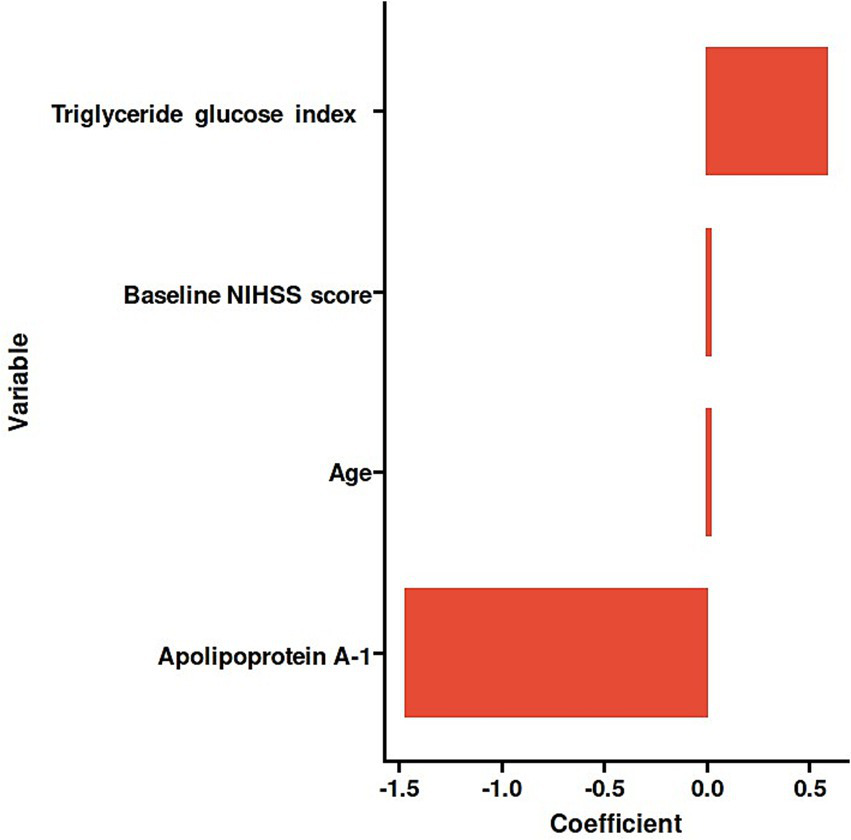
Histogram of the coefficients of the selected features.
In the analysis of factors associated with the outcome measured by mRS scores, several key findings emerged (Table 3). Each one-year increase in age was associated with an 8% increase in the odds of the outcome (adjusted OR, 1.08; 95% CI, 1.01–1.16; p = 0.027), indicating a significant association. The level of APOA-1 demonstrated a protective effect, where each unit increase was associated with a 98% reduction in odds (adjusted OR, 0.02; 95% CI, 0.00–0.59; p = 0.034). In contrast, while the baseline NIHSS score appeared to suggest a 5% increase in odds per unit increase, this association was not statistically significant (adjusted OR, 1.05; 95% CI, 0.96–1.15; p = 0.291). Regarding the TyG index, individuals with a value of ≥8.53 had significantly higher odds of the outcome compared to the reference group, with an adjusted odds ratio of 6.85 (95% CI, 1.83–32.13; p = 0.008), highlighting a strong and statistically significant relationship (Figure 4).
Table 3
| Characteristic | Univariable | Multivariable | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR1 | 95% CI1 | p-value | OR1 | 95% CI1 | P value | |
| Age | 1.04 | 0.99, 1.09 | 0.115 | 1.08 | 1.01, 1.16 | 0.027 |
| Apolipoprotein A-1 | 0.02 | 0.00, 0.42 | 0.019 | 0.02 | 0.00, 0.59 | 0.034 |
| Baseline NIHSS score | 1.08 | 1.00, 1.17 | 0.051 | 1.05 | 0.96, 1.15 | 0.291 |
| TyG index | ||||||
| <8.53 | — | — | — | — | ||
| ≥8.53 | 3.76 | 1.28, 11.97 | 0.019 | 6.85 | 1.83, 32.13 | 0.008 |
Univariate and multivariate analysis of influencing factors (Logistic regression).
1OR, odds ratio; CI, confidence interval.
Null deviance = 79.9; Null df = 59.0; Log-likelihood = −30.2; AIC = 70.3; BIC = 80.8; Deviance = 60.3; Residual df = 55; No. Obs. = 60.
Figure 4
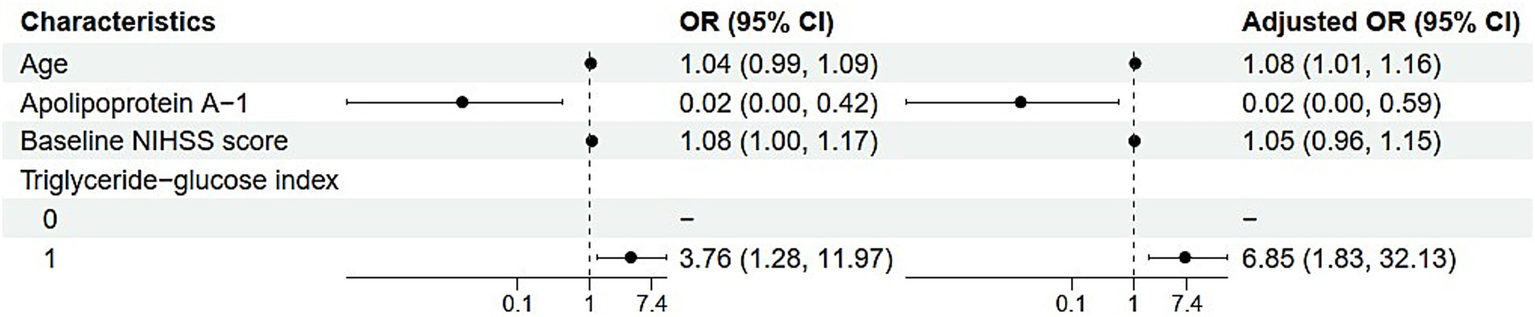
Forest plot of univariate and multivariate analysis of influencing factors.
Discussion
This real-world study investigated the predictive value of the TyG index for postoperative functional recovery in patients with posterior circulation ischemic stroke undergoing thrombectomy. The results indicate that a low TyG index is significantly associated with better functional recovery and reduced mortality in these patients, supporting our hypothesis. Compared to the high TyG index group, the low TyG index group demonstrates an 8- to 16-fold reduction in the risk of poor functional outcomes. Furthermore, no significant correlation was observed between the TyG index sICH outcomes within 36 h. These findings provide preliminary evidence supporting the predictive value of the TyG index for postoperative neurological recovery in patients with VBAO. Despite the limited sample size, this study offers valuable insights and serves as a foundation for future research in this area.
The TyG index, a composite indicator combining fasting blood glucose and triglycerides, serves as a marker of insulin resistance and is classified as an insulin-related metric (22). In recent years, increasing attention has been given to the relationship between insulin-related indicators, including the TyG index, and ischemic stroke, as glucose and lipid metabolism abnormalities exacerbate cardiovascular and cerebrovascular atherosclerosis. Insulin measurement is not routine in clinical practice, and various methods exist for its assessment, such as the hyperinsulinemic euglycemic clamp (HEC), the minimal model of the intravenous glucose tolerance test (IVGTT), the homeostasis model assessment (HOMA), and the quantitative insulin sensitivity check index (QUICKI). These methods are all based on the interaction between the glucose-insulin system (23, 24). Among them, HEC is considered the “gold standard” for measuring insulin resistance because it requires minimal additional parameters to determine blood glucose levels (25). However, accurate HEC results depend on highly skilled operators and specialized testing facilities (26, 27). In contrast, the TyG index is a practical alternative that can be routinely measured in clinical practice, demonstrating excellent consistency across different platforms (28).
The association between a low TyG index and a reduced risk of poor functional outcomes may be attributed to several factors. The TyG index, calculated using fasting blood glucose and triglycerides, incorporates two components independently linked to stroke risk (9). In insulin resistance states, microglial cell function is disrupted, causing polarization toward the pro-inflammatory M1 phenotype and the release of inflammatory factors such as TNF-α (Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha) and IL-1β (Interleukin-1 beta), which result in cellular damage. Concurrently, an increase in neutrophil levels damages the blood–brain barrier, contributing to worse stroke outcomes (29, 30). Moreover, insulin resistance accelerates atherosclerosis through various mechanisms, including promoting vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration, enhancing lipid deposition, narrowing or occluding blood vessels, and impairing cerebral blood flow, all of which negatively affect patient prognosis (31, 32). Research also indicates that platelets exhibit hyperactivity under IR conditions, potentially forming pathological clots that reduce the efficacy of reperfusion therapy (33, 34). Additionally, elevated triglyceride levels are recognized as a stroke risk factor, as triglyceride-rich lipoproteins (TRLs) exacerbate atherosclerosis through their toxic and pro-inflammatory effects (22). The lipolytic products of TRLs can induce endothelial cell apoptosis and accelerate atherosclerosis progression by increasing oxidative stress via activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway, ultimately heightening stroke risk and hindering recovery outcomes (35).
Our findings revealed an association between the TyG index and the prognosis of posterior circulation AIS patients following thrombectomy. A prospective multicenter study involving 914 patients demonstrated a strong correlation between the TyG index and the functional outcomes of AIS patients treated with IVT. Patients with a higher TyG index exhibited worse functional outcomes, while no significant differences were observed in the incidence of sICH (36). Similarly, Minwoo Lee’s team confirmed these findings through a retrospective study, showing that a high TyG index was independently associated with poor functional outcomes three months after ischemic reperfusion therapy in AIS patients and was linked to an increased frequency of early neurological deterioration (37). Another study further established that the TyG index serves as an independent factor influencing early neurological recovery after thrombolytic therapy in AIS patients (38). Consistent results were reported in a Chinese study: utilizing data from CNSR II, a prospective cohort of 16,310 ischemic stroke patients, multivariable Cox regression and logistic regression analyses indicated that the TyG index was associated with a higher risk of neurological deterioration and increased all-cause mortality in stroke patients (39). Additionally, studies in Chinese AIS patients identified a higher TyG index as an independent predictor of mortality within three and twelve months (40), as well as an elevated risk of stroke recurrence. Patients in the highest TyG index group exhibited the greatest mortality risk (41). Furthermore, among patients with cerebral infarction in intensive care units, the TyG index demonstrated a linear relationship with mortality (42).
Our results also showed no significant association between the TyG index and sICH outcomes or the incidence of adverse events. This finding aligns with previous studies that assessed insulin resistance using the homeostasis model in patients receiving early IVT treatment for stroke (43). Similarly, prior research on triglycerides suggested no strong correlation between triglycerides and ICH in stroke patients who did not undergo thrombolysis (44). Based on these findings, we conclude that the TyG index is not a reliable predictor of hemorrhagic transformation in patients with cerebral infarction.
In this study, we observed statistically significant differences in age and APOA-1 levels among neurological outcome groups. Advanced age and lower APOA-1 levels were associated with poorer neurological recovery. Age is widely recognized as a critical factor in ischemic stroke, with elderly patients exhibiting higher mortality rates and worse functional recovery compared to younger patients (45, 46). Laboratory experiments using middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) models in young and aged mice have explored the effects of age on stroke severity and underlying mechanisms. These studies revealed that aged mice experienced greater neutrophil-mediated blockages in the ischemic brain microcirculation, exacerbating perfusion deficits. Additionally, aged mice showed higher levels of atypical neutrophils in their blood, characterized by increased oxidative stress, phagocytosis, and prothrombotic properties (47). Furthermore, research has demonstrated that APOA-1, the primary component of high-density lipoprotein (HDL), facilitates cellular cholesterol efflux and reverse cholesterol transport, forming nascent HDL (48, 49). Higher HDL levels are associated with a reduced risk of stroke (50).
While most studies have investigated the relationship between the TyG index and the incidence of ischemic stroke, few have focused on its role in neurological recovery among stroke patients. Additionally, the cutoff values for the TyG index vary across studies (51–54). Based on findings from a Chinese study, we selected a cutoff value of 8.53, as the study identified this value as predictive of stroke prognosis in non-diabetic patients. Although the study did not distinguish between anterior and posterior circulation strokes, it is one of the few prospective studies to examine the correlation between the TyG index and stroke prognosis. After reviewing the literature, we adopted the 8.53 cutoff value. Future studies should aim to refine the TyG grouping criteria by conducting large-scale, multicenter investigations to identify the optimal specificity and sensitivity of this prognostic indicator.
Most current studies have not differentiated between subtypes of AIS, with some focusing only on the prognostic value of factors such as the TyG index in anterior circulation infarction patients. Posterior circulation infarction, however, carries a higher risk of disability and mortality compared to anterior circulation infarction and places a significant burden on families and society. Therefore, investigating prognostic indicators in posterior circulation thrombectomy patients is critically important (2, 5). Our study focuses specifically on patients who underwent thrombectomy, as successful thrombectomy rapidly restores cerebral blood flow, significantly improves neurological function in some patients, and enhances favorable outcomes. This information is also valuable for providing patients and their families with a clearer understanding of potential recovery trajectories after diagnosis. Consequently, this study exclusively included posterior circulation infarction patients who received interventional treatment, aiming to provide new evidence for prognostic indicators in Chinese patients with posterior circulation AIS treated with thrombectomy.
Posterior circulation infarction, as a critical subtype of ischemic stroke, presents complex prognostic outcomes but remains under-researched. Using real-world data, our study innovatively demonstrated the predictive value of the TyG index for neurological recovery three months after thrombectomy in posterior circulation infarction patients, addressing a significant research gap in this field. These findings establish a foundation for future multicenter validation studies and provide evidence for incorporating metabolic factors into stroke prediction models. Based on data from Chinese patients, our research offers specific evidence to optimize clinical practice and prediction models for Asian populations. However, further studies are required to generalize these findings to broader Asian and other racial populations. The TyG index, derived from simple laboratory measurements of lipid and glucose levels, is both practical and consistent. For patients with high TyG index values, closer monitoring and more aggressive therapeutic interventions may be warranted. However, whether maintaining the TyG index below 8.5 improves neurological outcomes and accelerates recovery remains uncertain and necessitates further investigation. For example, large-scale, multicenter, prospective randomized controlled clinical trials with stringent patient selection criteria are needed to minimize confounding factors and comprehensively analyze the predictive value of the TyG index.
Our study also has potential limitations, including selection bias and information bias. Additionally, despite clear inclusion and exclusion criteria, accurate measurement of key variables, and the use of appropriate statistical methods, the relatively small sample size may not fully represent the target population. Future studies with larger sample sizes and multicenter designs are required to validate the predictive value of the TyG index and its combined effects with other indicators. Furthermore, the TyG index is calculated from a single baseline blood test, which may largely reflect stress-induced hyperglycemia. Fasting blood glucose and triglyceride levels may also be influenced by pre-hospital interventions, potentially affecting the calculated TyG index to varying degrees. Finally, while this study adjusted for many potential confounding factors, the limited sample size may have resulted in unmeasured or inadequately adjusted confounders, which could influence the predictive value of the TyG index. Future studies with larger samples and more advanced regression algorithms are needed to further optimize these findings. Considering the significant role of the TyG index in predicting the 90 - day neurological recovery and mortality of these patients, future research could expand the sample size to multi - center studies, which would enhance the generalizability of our findings. Additionally, further exploration could focus on the underlying molecular mechanisms by which the TyG index influences post-stroke recovery, such as delving into its impact on the neurovascular unit and inflammatory responses. Long-term follow-up studies could also be conducted to determine the persistent effects of the TyG index on patients’ quality of life and recurrent stroke risk. These potential research directions aim to deepen our understanding of metabolic markers in stroke prognosis and guide more personalized post - stroke management.
In conclusion, this study supports that a higher TyG index is significantly associated with poor neurological outcome and death at 90 days in patients with acute posterior circulation ischemic stroke undergoing interventional therapy. For patients with acute posterior circulation cerebral infarction with high disability and high mortality, the data required by TyG index are simple and easy to obtain, which has potential value in helping clinicians to predict the recovery of neurological function of patients in the early stage. In the future, it is necessary to further expand the number of patients enrolled and more prospective experimental design, so as to make the TyG index more universal.
Statements
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Ethics Committee of Huzhou Central Hospital. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The ethics committee/institutional review board waived the requirement of written informed consent for participation from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin because this was a retrospective clinical study.
Author contributions
JW: Writing – original draft, Investigation, Software, Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Conceptualization. HM: Supervision, Resources, Writing – review & editing. XJ: Writing – review & editing, Validation, Resources. RP: Writing – review & editing, Investigation, Software, Methodology. BZ: Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Funding acquisition, Resources, Project administration, Visualization, Validation. YL: Validation, Project administration, Visualization, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Resources, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was supported by Zhejiang Provincial Medical and Healthcare Science and Technology Plan under Grant No. 2024KY1641 from Bing Zhang.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Correction note
A correction has been made to this article. Details can be found at: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1704033.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fneur.2025.1597323/full#supplementary-material
- ACS
Acute coronary syndrome
- AIS
Acute ischemic stroke
- APOA-1
Apolipoprotein A-1
- APOB
Fasting apolipoprotein B
- BAO
Basilar artery occlusion
- BATMAN
The Basilar Artery Treatment and Management
- CNSR II
The analysis of data from China National Stroke Registry II
- CT
Computed tomography
- CVD
Cardiovascular diseases
- HDL
High-density lipoprotein
- HEC
Hyperinsulinemic euglycemic clamp
- HOMA
The homeostasis model assessment
- IL-1β
Interleukin-1 beta
- IQR
Interquartile range
- IVGTT
the minimal model of the intravenous glucose tolerance test
- IVT
Intravenous thrombolysis
- MAPK
Mitogen-activated protein kinase
- MCAO
Middle cerebral artery occlusion
- MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging
- mRS
modified Rankin Scale
- NIHSS
National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale
- PC-ASPECTS
Posterior circulation Alberta Stroke Program Early CT score
- QQ plots
Quantile-Quantile Plots
- QUICKI
The quantitative insulin sensitivity check index
- sICH
Symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage
- TNF-α
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha
- TRLs
Triglyceride-rich lipoproteins
- TyG
Triglyceride-glucose
- VBAO
Vertebasilar artery occlusion
Glossary
References
1.
Kwak HS Park JS . Mechanical Thrombectomy in basilar artery occlusion: clinical outcomes related to posterior circulation collateral score. Stroke. (2020) 51:2045–50. doi: 10.1161/strokeaha.120.029861
2.
Hilkens NA Casolla B Leung TW de Leeuw F-E . Stroke. Lancet. (2024) 403:2820–36. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(24)00642-1
3.
Jovin TG Li C Wu L Wu C Chen J Jiang C et al . Trial of Thrombectomy 6 to 24 hours after stroke due to basilar-artery occlusion. N Engl J Med. (2022) 387:1373–84. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2207576
4.
Luo C Tao C Li R Nguyen TN Jing X Yuan S et al . Thrombectomy improves functional independence in severe basilar artery occlusion with favorable collateral circulation. Eur J Neurol. (2024) 31:e16380. doi: 10.1111/ene.16380
5.
Mattle HP Arnold M Lindsberg PJ Schonewille WJ Schroth G . Basilar artery occlusion. Lancet Neurol. (2011) 10:1002–14. doi: 10.1016/s1474-4422(11)70229-0
6.
Shin TH Lee DY Basith S Manavalan B Paik MJ Rybinnik I et al . Metabolome changes in cerebral ischemia. Cells. (2020) 9:7. doi: 10.3390/cells9071630
7.
Guerrero-Romero F Simental-Mendía LE Gonzalez-Ortiz M Martínez-Abundis E Ramos-Zavala MG Hernandez-Gonzalez SO et al . The product of triglycerides and glucose, a simple measure of insulin sensitivity. Comparison with the Euglycemic-Hyperinsulinemic clamp. J Clin Endocrinol Metabol. (2010) 95:3347–51. doi: 10.1210/jc.2010-0288
8.
El-Sehrawy AAMA Khachatryan LG Kubaev A Rekha MM Rab SO Kaur M et al . Triglyceride–glucose index: a potent predictor of metabolic risk factors and eating behavior patterns among obese individuals. BMC Endocr Disord. (2025) 25:71. doi: 10.1186/s12902-025-01887-3
9.
Wang A Wang G Liu Q Zuo Y Chen S Tao B et al . Triglyceride-glucose index and the risk of stroke and its subtypes in the general population: an 11-year follow-up. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2021) 20:46. doi: 10.1186/s12933-021-01238-1
10.
Wang L Cong H-l Zhang J-x Hu Y-c Wei A Zhang Y-y et al . Triglyceride-glucose index predicts adverse cardiovascular events in patients with diabetes and acute coronary syndrome. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2020) 19:80. doi: 10.1186/s12933-020-01054-z
11.
Zhu Y Liu K Chen M Liu Y Gao A Hu C et al . Triglyceride-glucose index is associated with in-stent restenosis in patients with acute coronary syndrome after percutaneous coronary intervention with drug-eluting stents. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2021) 20:137. doi: 10.1186/s12933-021-01332-4
12.
Barzegar N Tohidi M Hasheminia M Azizi F Hadaegh F . The impact of triglyceride-glucose index on incident cardiovascular events during 16 years of follow-up: Tehran lipid and glucose study. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2020) 19:155. doi: 10.1186/s12933-020-01121-5
13.
Hou Z Pan Y Yang Y Yang X Xiang X Wang Y et al . An analysis of the potential relationship of triglyceride glucose and body mass index with stroke prognosis. Front Neurol. (2021) 12:12. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2021.630140
14.
Nam K-W Kang MK Jeong H-Y Kim TJ Lee E-J Bae J et al . Triglyceride-glucose index is associated with early neurological deterioration in single subcortical infarction: early prognosis in single subcortical infarctions. Int J Stroke. (2021) 16:944–52. doi: 10.1177/1747493020984069
15.
Yang Y Huang X Wang Y Leng L Xu J Feng L et al . The impact of triglyceride-glucose index on ischemic stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2023) 22:2. doi: 10.1186/s12933-022-01732-0
16.
Tao C Nogueira RG Zhu Y Sun J Han H Yuan G et al . Trial of endovascular treatment of acute basilar-artery occlusion. N Engl J Med. (2022) 387:1361–72. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2206317
17.
Guo C Song J Li L Yang J Huang J Xie D et al . Association of Procedure Time with Clinical and Procedural Outcome in patients with basilar occlusion undergoing Embolectomy. Neurology. (2023) 101:e253–66. doi: 10.1212/wnl.0000000000207395
18.
Guo B-Q Li H-B Xu P-W Zhao B . Lipid-lowering therapies and long-term stroke prevention in east Asians: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Int J Stroke. (2024) 20:29–41. doi: 10.1177/17474930241264686
19.
Park K Ahn CW Lee SB Kang S Nam JS Lee BK et al . Elevated TyG index predicts progression of coronary artery calcification. Diabetes Care. (2019) 42:1569–73. doi: 10.2337/dc18-1920.
20.
Seners P Dargazanli C Piotin M Sablot D Bracard S Niclot P et al . Intended bridging therapy or intravenous thrombolysis alone in minor stroke with basilar artery occlusion. Stroke. (2021) 52:699–702. doi: 10.1161/strokeaha.120.030992
21.
Abdelrady M Ognard J Cagnazzo F Derraz I Lefevre PH Riquelme C et al . Frontline thrombectomy strategy and outcome in acute basilar artery occlusion. J Neurointerv Surg. (2023) 15:27–33. doi: 10.1136/neurintsurg-2021-018180
22.
Liang H-j Zhang Q-y Hu Y-t Liu G-q Qi R . Hypertriglyceridemia: a neglected risk factor for ischemic stroke?J StrokeIF-6.967,. (2022) 24:21–40. doi: 10.5853/jos.2021.02831
23.
Lee SH Han K Yang HK Kim HS Cho JH Kwon HS et al . A novel criterion for identifying metabolically obese but normal weight individuals using the product of triglycerides and glucose. Nutrition Diabetes. (2015) 5:e149. doi: 10.1038/nutd201446
24.
Pacini G Mari A . Methods for clinical assessment of insulin sensitivity and β-cell function. Best Practice Research Clin Endocrinol Metabol. (2003) 17:575–598. doi: 10.1016/S1521-690X(03)00086-6
25.
Radziuk J . Insulin sensitivity and its measurement: structural commonalities among the methods. J Clin Endocrinol Metabol. (2000) 85:4426–33. doi: 10.1210/jcem.85.12.7025
26.
Tam CS Xie W Johnson WD Cefalu WT Redman LM Ravussin E . Defining insulin resistance from Hyperinsulinemic-Euglycemic clamps. Diabetes Care. (2012) 35:1605–10. doi: 10.2337/dc11-2339
27.
Rudvik A Månsson M . Evaluation of surrogate measures of insulin sensitivity - correlation with gold standard is not enough. BMC Med Res Methodol. (2018) 18:521. doi: 10.1186/s12874-018-0521-y
28.
Li X Hao J Han Q Wang D Lu Y Tu J et al . Triglyceride-glucose index prediction of stroke incidence risk in low-income Chinese population: a 10-year prospective cohort study. Front Endocrinol. (2024) 15:15. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1444030
29.
Huang Z Ding X Yue Q Wang X Chen Z Cai Z et al . Triglyceride-glucose index trajectory and stroke incidence in patients with hypertension: a prospective cohort study. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2022) 21:141. doi: 10.1186/s12933-022-01577-7
30.
Sojitra MH Garg VS Shah K Joshi S Vadnagara H Gandhi SK et al . Exploring the role of insulin resistance in Fueling stroke vulnerability and worsening post-stroke prognosis: a narrative review of current literature. Cureus. (2023) 15:e48034. doi: 10.7759/cureus.48034
31.
Deng X-L Liu Z Wang C Li Y Cai Z . Insulin resistance in ischemic stroke. Metabolic Brain Disease. (2017) 32:1323–34. doi: 10.1007/s11011-017-0050-0
32.
Ding P-F Zhang H-S Wang J Gao Y-Y Mao J-N Hang C-H et al . Insulin resistance in ischemic stroke: mechanisms and therapeutic approaches. Front Endocrinol. (2022) 13:13. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1092431
33.
van Rooy M-J Duim W Ehlers R Buys AV Pretorius E . Platelet hyperactivity and fibrin clot structure in transient ischemic attack individuals in the presence of metabolic syndrome: a microscopy and thromboelastography® study. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2015) 14:86. doi: 10.1186/s12933-015-0249-5
34.
Liang W Ouyang H . The association between triglyceride-glucose index combined with obesity indicators and stroke risk: a longitudinal study based on CHARLS data. BMC Endocr Disord. (2024) 24:234. doi: 10.1186/s12902-024-01729-8
35.
Wang L Gill R Pedersen TL Higgins LJ Newman JW Rutledge JC . Triglyceride-rich lipoprotein lipolysis releases neutral and oxidized FFAs that induce endothelial cell inflammation. J Lipid Research. (2009) 50:204–13. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M700505-JLR200
36.
Lin S-F Hu H-H Chao H-L Ho B-L Chen C-H Chan L et al . Triglyceride-glucose index and intravenous thrombolysis outcomes for acute ischemic stroke: a Multicenter prospective–cohort study. Front Neurol. (2022) 13:13. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.737441
37.
Lee M Kim C-H Kim Y Jang MU Mo HJ Lee S-H et al . High triglyceride glucose index is associated with poor outcomes in ischemic stroke patients after reperfusion therapy. Cerebrovascular Diseases. (2021) 50:691–9. doi: 10.1159/000516950
38.
Deng M Song K Xu W He G Hu J Xiao H et al . Association of higher triglyceride–glucose index and triglyceride-to-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio with early neurological deterioration after thrombolysis in acute ischemic stroke patients. Front Neurol. (2024) 15:15. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1421655
39.
Zhou Y Pan Y Yan H Wang Y Li Z Zhao X et al . Triglyceride glucose index and prognosis of patients with ischemic stroke. Front Neurol. (2020) 11:11. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.00456
40.
Liu R Li L Wang L Zhang S . Triglyceride-glucose index predicts death in patients with stroke younger than 65. Front Neurol. (2023) 14:14. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1198487
41.
Yang X Wang G Jing J Wang A Zhang X Jia Q et al . Association of triglyceride-glucose index and stroke recurrence among nondiabetic patients with acute ischemic stroke. BMC Neurol. (2022) 22:79. doi: 10.1186/s12883-022-02588-3
42.
Zhang B Liu L Ruan H Zhu Q Yu D Yang Y et al . Triglyceride-glucose index linked to hospital mortality in critically ill stroke: an observational multicentre study on eICU database. Front Med. (2020) 7:7. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2020.591036
43.
Calleja AI García-Bermejo P Cortijo E Bustamante R Rojo Martínez E González Sarmiento E et al . Insulin resistance is associated with a poor response to intravenous thrombolysis in acute ischemic stroke. Diabetes Care. (2011) 34:2413–7. doi: 10.2337/dc11-1242
44.
Wieberdink RG Poels MMF Vernooij MW Koudstaal PJ Hofman A van der Lugt A et al . Serum lipid levels and the risk of intracerebral Hemorrhage: the Rotterdam study. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2011) 31:2982–9. doi: 10.1161/atvbaha.111.234948
45.
Roy-O’Reilly M McCullough LD . Age and sex are critical factors in ischemic stroke pathology. Endocrinology. (2018) 159:3120–31. doi: 10.1210/en.2018-00465
46.
Savino JA Halperin JL . Age, ethnicity, and stroke risk in patients with atrial fibrillation. J American College Cardiol. (2015) 66:1348–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2015.08.003
47.
Gullotta GS De Feo D Friebel E Semerano A Scotti GM Bergamaschi A et al . Age-induced alterations of granulopoiesis generate atypical neutrophils that aggravate stroke pathology. Nature Immunol. (2023) 24:925–40. doi: 10.1038/s41590-023-01505-1
48.
Guerrero-Romero F Lim J Kim J Koo SH Kwon GC . Comparison of triglyceride glucose index, and related parameters to predict insulin resistance in Korean adults: an analysis of the 2007-2010 Korean National Health and nutrition examination survey. PLoS One. (2019) 14:e0212963. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0212963
49.
Rader DJ . Apolipoprotein A-I infusion therapies for coronary Disease_ two outs in the ninth inning and swinging for the fences. JAMA Cardiol. (2018) 3:799–801. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2018.2168
50.
Reina SA Llabre MM Allison MA Wilkins JT Mendez AJ Arnan MK et al . HDL cholesterol and stroke risk: the multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis. (2015) 243:314–9. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2015.09.031
51.
Chiu H Tsai H-J Huang J-C Wu P-Y Hsu W-H Lee M-Y et al . Associations between triglyceride-glucose index and micro- and macro-Angiopathies in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nutrients. (2020) 12:12(2). doi: 10.3390/nu12020328
52.
Zhang N Chi X Zhou Z Song Y Li S Xu J et al . Triglyceride-glucose index is associated with a higher risk of stroke in a hypertensive population. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2023) 22:346. doi: 10.1186/s12933-023-02082-1
53.
Miao M Bi Y Hao L Bao A Sun Y Du H et al . Triglyceride-glucose index and short-term functional outcome and in-hospital mortality in patients with ischemic stroke. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. (2023) 33:399–407. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2022.11.004
54.
Toh EMS Lim AYL Ming C Yeo LLL Sia C-H Tan BWQ et al . Association of triglyceride-glucose index with clinical outcomes in patients with acute ischemic stroke receiving intravenous thrombolysis. Sci Rep. (2022) 12:1596. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-05467-6
Summary
Keywords
triglyceride-glucose index, vertebrobasilar system thrombectomy, modified Rankin score, ischemic stroke, metabolic-nutritional status
Citation
Wang J, Ma H, Jiang X, Pan R, Zhang B and Liu Y (2025) The predictive value of TyG index in patients with vertebrobasilar system thrombectomy. Front. Neurol. 16:1597323. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1597323
Received
14 April 2025
Accepted
04 August 2025
Published
15 August 2025
Volume
16 - 2025
Edited by
Fulvio Tartara, University Hospital of Parma, Italy
Reviewed by
Zhang Daopei, First Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, China
Daji Guo, Sun Yat-sen University, China
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Wang, Ma, Jiang, Pan, Zhang and Liu.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Bing Zhang, sjnkhz@163.com; Ying Liu, liuy2365@mail.sysu.edu.cn
†ORCID: Ying Liu, orcid.org/0009-0000-7018-0711
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.