Abstract
Epilepsy is one of the most common nervous system diseases, which is characterized by recurrent seizures caused by abnormal neuronal discharges in the brain. Drug-resistant epilepsy (DRE) brings great challenges to clinical treatment. Benzodiazepines (BZDs), as the first-line treatment for acute seizures and Status Epilepticus (SE), are widely used because of their potent inhibitory neuromodulation by regulating γ-aminobutyric acid-A(GABAA) receptors. However, long-term use of BZDs may induce drug resistance, leading to a significant decrease in efficacy and increasing the difficulty of treatment. This study begins with the definition of BZDs-resistant epilepsy. It explores the underlying resistance mechanisms, including the down-regulation, decreased activity, and structural changes of GABAA receptors, synapse and neural network remodeling, genetic variation in drug metabolism, and the effects of drug efflux mechanisms. In addition, combined with clinical practice and research progress, this study evaluates the effectiveness and potential of drug combination therapies, personalized treatments, and new treatment methods, highlighting the advantages of simultaneous multi-drug therapy in controlling drug-resistant epilepsy. Further research on the mechanisms of BZDs resistance and optimization of treatment strategies can not only improve the therapeutic effect of drug-resistant epilepsy but also provide a scientific basis for the development of antiepileptic drugs in the future.
1 Introduction
Epilepsy is one of the most common neurological disorders and is characterized by recurrent seizures caused by abnormal neuronal discharges in the brain (1). Drug-resistant epilepsy (DRE) refers to the seizure frequency that lasts for 3 months or longer and is not effectively controlled under appropriate drug treatment, or the number of seizures increases significantly in a short period under appropriate treatment (2). It is estimated that more than 70 million people worldwide are affected by epilepsy, and nearly a third of them have DRE (3, 4). As the population ages and lifestyle changes, the prevalence of DRE is likely to rise further (5). The financial burden and care needs of such patients are much higher than those of patients with drug-sensitive epilepsy, imposing heavy pressure on global medical systems and social resources (6).
Benzodiazepines (BZDs) are a class of drugs that exert sedative, anxiolytic, and antiepileptic effects by acting on γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptors in the central nervous system (7). These drugs are widely used as a first-line treatment for acute seizures, especially in status epilepticus (SE) (8, 9). Benzodiazepine-resistant epilepsy refers to the condition in which patients develop resistance to BZDs after long-term use, leading to ineffective treatment or a significant decline in therapeutic efficacy.
This suggests that resistance to BZDs, as a first-line drug for treating acute seizures, is a challenge for patients with epilepsy, and it is essential to seek the most effective treatment methods and strategies (8). Recent studies have focused on the elucidation of the mechanisms of drug-resistant epilepsy in phenytoin and carbamazepine (9, 10). This article reviews the definition, mechanisms of resistance, and treatment methods of benzodiazepine-resistant epilepsy. An in-depth study of the mechanism is helpful to the development of clinical treatment, and looks forward to new treatment methods and potential drug development of benzodiazepine-resistant epilepsy, hoping to provide scientific guidance for the research of benzodiazepine-resistant epilepsy.
2 Mechanisms of action and resistance of benzodiazepines
2.1 Action mechanism of benzodiazepines
BZDs are positive allosteric modulators of GABAA receptors and regulate the allosteric function of the receptor by binding to the BZDs site of the receptor, the interface site between the α2/α3 and γ2 subunits of the GABA receptor (11). The conformation of the receptor changes, which increases the affinity of the binding site of GABA (between α and β subunits) to endogenous GABA and enhances the amplification effect of the GABA signal (12). Even if the regulation of BZDs on the receptor is positively correlated with the concentration of endogenous GABA (11), it can also cause a strong inhibitory response to low concentrations of GABA. Moreover, BZDs increase the probability of chloride (Cl−) channel opening, prolong the open duration of Cl− channels, and enhance Cl− influx, resulting in neuronal hyperpolarization and further inhibition of neuronal firing. Activation of GABA receptors causes Cl− influx through Cl− channels, leading to hyperpolarization of the neuronal membrane potential, thereby reducing neuronal excitability (13).
2.2 Resistance mechanisms of benzodiazepines
2.2.1 Drug target-related mechanisms
2.2.1.1 Decreased GABAA receptor number
Long-term use of BZDs enhances receptor endocytosis, leading to a decrease in the total amount of GABAA receptors, especially in the key brain areas involved in drug action (e.g., hippocampus and cortex) (14). For example, chronic exposure of neurons to diazepam activates the downstream Ca2+ signaling cascade of GABAA receptors, leading to a gradual decrease in cell surface GABA receptors through dynamin-dependent endocytosis. The endocytosis process is regulated by protein kinases and phosphatases that determine the phosphorylation status at specific sites of the β and γ subunits of the receptor. When specific residues are dephosphorylated by protein phosphatase 1, 2A, or calcineurin—that is, when the GABAAAR γ2 subunit is dephosphorylated at Ser327 in cortical neurons—receptor internalization is promoted, removing it from the postsynaptic membrane. This ultimately triggers disaggregation of inhibitory synapses, resulting in a decrease in the total amount of GABA receptors (15, 16).
2.2.1.2 Decreased GABAA receptor activity
Astrocytes take up glutamate and convert it to glutamine by the enzyme glutamine synthetase (GS), which is catalyzed by glutamate decarboxylase to form GABA in GABAergic neurons (17). Decreased GS activity leads to decreased GABA production. GABA concentration is insufficient in the synaptic cleft, and the modulation of receptors by BZDs is positively correlated with the concentration of endogenous GABAA (11), impairing the activity of GABA receptors.
2.2.1.3 Altered GABAA receptor structure
Changes in GABAA receptor subunit composition and gene mutations can lead to drug-resistant epilepsy.
The mechanisms underlying changes in receptor subunit composition mainly include the decrease of γ2 subunit expression and the substitution of α subunit. The γ2 subunit is the binding site of BZDs, and its reduction directly affects the binding and action of BZDs. In SE, GABAA receptors containing synaptic γ2 subunits selectively transport and relocalize to the cell interior, leading to loss of synaptic inhibition and development of BZDs resistance in early SE (18). In drug-resistant refractory epilepsy, the expression of the α1 subunit is decreased, while the α4 or α5 subunits, which are less sensitive to BZDs, are relatively increased (19). The α1 subunit may inhibit dynamin-mediated endocytosis (20), which is enhanced by decreased α1 subunit expression, thereby reducing the number of cell surface GABAA receptors.
GABA-A receptor variants can be classified into loss-of-function (LOF) and gain-of-function (GOF) types, which affect receptor structure and function through distinct mechanisms. LOF variants (e.g., GABRA1, GABRB2, GABRB3, GABRG2) lead to reduced surface expression, assembly defects, or decreased GABA-induced currents, resulting in weakened inhibitory neurotransmission and abnormal synchronous discharges in the cortico-thalamic network. These patients typically respond well to GABA-enhancing agents such as BZDs (21–24). In contrast, GOF variants (e.g., GABRB3, GABRD) increase receptor sensitivity to GABA or induce constitutive activation, often with mild expression defects. These variants primarily cause excessive inhibition in specific neural circuits like the thalamic reticular nucleus, leading to network desynchronization and abnormal rhythms, including spike-and-wave discharges (SWDs). For such patients, GABA-enhancing drugs may exacerbate symptoms or trigger paradoxical reactions. Thus, both LOF and GOF variants can contribute to DRE (25, 26).
2.2.2 Synaptic and neural network remodeling
Cytokines released after brain injury can induce astrocyte dysfunction, leading to impaired ion and neurotransmitter homeostasis, which increases susceptibility to seizures (27, 28). Synaptic and neural network remodeling mainly includes three aspects: the involvement of neuroinflammation, the functional decline of inhibitory synapses, and the enhancement of excitatory synapses.
2.2.2.1 Involvement of neuroinflammation
Seizures can cause neuroinflammatory responses, and neuroinflammation plays an important role in epilepsy (29). “Neurogenic neuroinflammation” refers to the synthesis and release of pro-inflammatory molecules triggered by enhanced neuronal activity in astrocytes and other brain cells (27, 30, 31). Astrocytes and microglia contribute to neuronal hyperexcitability and seizures (27, 32).
Microglia release specific signaling molecules, such as TNFα, IL-1α, and complement component subunit 1q (C1q). These signaling molecules induce the generation of the A1 reactive astrocytes. The proinflammatory phenotype (A1) exhibits IP3 R2-mediated Ca2+ hyperactivity, which leads to excessive production of proinflammatory cytokines and reactive oxygen species, thereby exacerbating neural damage (27, 33–35). In SE and chronic epilepsy stages, IL-1β produced by microglia can increase extracellular glutamate concentration by inhibiting astrocytic glutamate transporters. It can also suppress GABA-mediated Cl− influx into neurons, resulting in increased neuronal excitability (29). The release of the inflammatory cytokine TNF-α causes endocytosis of GABAA receptors, causing a reduction in surface GABAA receptors and a decrease in inhibitory synaptic strength. TNF-α effectively induces neuronal cell death through apoptosis or necroptosis signaling pathways (33), regulating neuronal circuit homeostasis, which may exacerbate excitotoxic damage caused by neuronal injury and further disrupt synaptic network balance (36).
Astrocytes play an important role in the regulation of synaptic function and plasticity. Astrocytes release gliotransmitters, such as ATP and D-serine, which directly modulate synaptic strength and plasticity (33). In addition, under the control of TGFβR and IL-1β signaling, inflammatory astrocytes express high levels of matrix metallopeptidase family proteins, which can promote extracellular matrix remodeling and further promote pathological synaptic plasticity (27).
2.2.2.2 Functional decline of inhibitory synapses
Glial cells that synthesize GABA, such as astrocytes, release GABA through non-vesicular mechanisms (e.g., channel-mediated release), serving as a source of extracellular GABA in the brain (37, 38). The reduction of intercellular GABA may be due to decreased GABA synthesis. GS participates in the process of GABA synthesis (17, 39). Beta-amyloid, oxidative stress, nitrosative stress, tissue inflammation, and several environmental factors can easily lead to the downregulation or inhibition of GS in astrocytes (17). The decrease in GS activity promotes an increase in extracellular glutamate regulated by astrocytes and reduces GABA production in neurons due to decreased glutamine supply (27).
2.2.2.3 Enhancement of excitatory synapses
In the constant electrical activity of neurons and interneurons in SE, two major neurotransmitters, glutamate and GABA, are released in excess in the mammalian brain. Sustained hyperactivity and overstimulation trigger changes in synaptic receptor function, in which the AMPA and NMDA types of glutamate receptors on major cells are functionally enhanced, leading to further augmentation of excitatory synaptic activity; at the same time, the function of GABAA receptors is inhibited, which weakens the inhibitory effect of BZDs on neuronal hyperexcitability (40). The dominant role of these two receptor functions in the development of epilepsy has not been clearly defined and still requires further investigation (27). Excessive glutamate not only increases the likelihood of seizures but also causes neuronal loss through its excitotoxic properties, further aggravating the pathological remodeling of neural networks (17).
2.2.3 Metabolism-related pathway gene variants
Genetic variations in the CYP450 enzyme system may influence the rate of BZDs metabolism, thereby altering the effective concentration of the drug in the body. The CYP3A subfamily is primarily responsible for the metabolism of anti-seizure medications (ASMs) (41), with the CYP3A4 gene being involved in the 1′-hydroxylation of BZDs. Mutations in this gene may increase the efficiency of this process, resulting in a shortened drug half-life or reduced drug efficacy, potentially affecting the metabolism of ASMs and resulting in lower drug concentrations in the body, which can impact the therapeutic effects of the drug (42, 43).
2.2.4 Drug efflux-related mechanisms
The transporter hypothesis suggests that overexpression of P-glycoprotein (P-gp) in the blood–brain barrier (BBB) is a key mechanism of resistance in ASMs (44). As an efflux transporter that influences the distribution of drugs in the central nervous system, P-gp actively exports BZDs and other drugs from brain tissue (45). P-gp is encoded by the ABCB1 gene, and the CC genotype of the ABCB1 C3435T polymorphism is associated with elevated P-gp protein levels and increased activity (46). Up-regulation of P-gp expression can significantly reduce the concentration of the drug in the central nervous system, thereby diminishing its efficacy. In patients with drug-resistant epilepsy, glutamate and inflammatory mediators released by perivascular astrocytes may further exacerbate this drug-resistance phenomenon by inducing the up-regulation of P-gp (27). In addition to P-gp, other efflux transporters, such as multidrug resistance-associated proteins (MRPs), may efflux some metabolites of BZDs, such as glucuronic acid (47) (see Figure 1).
Figure 1
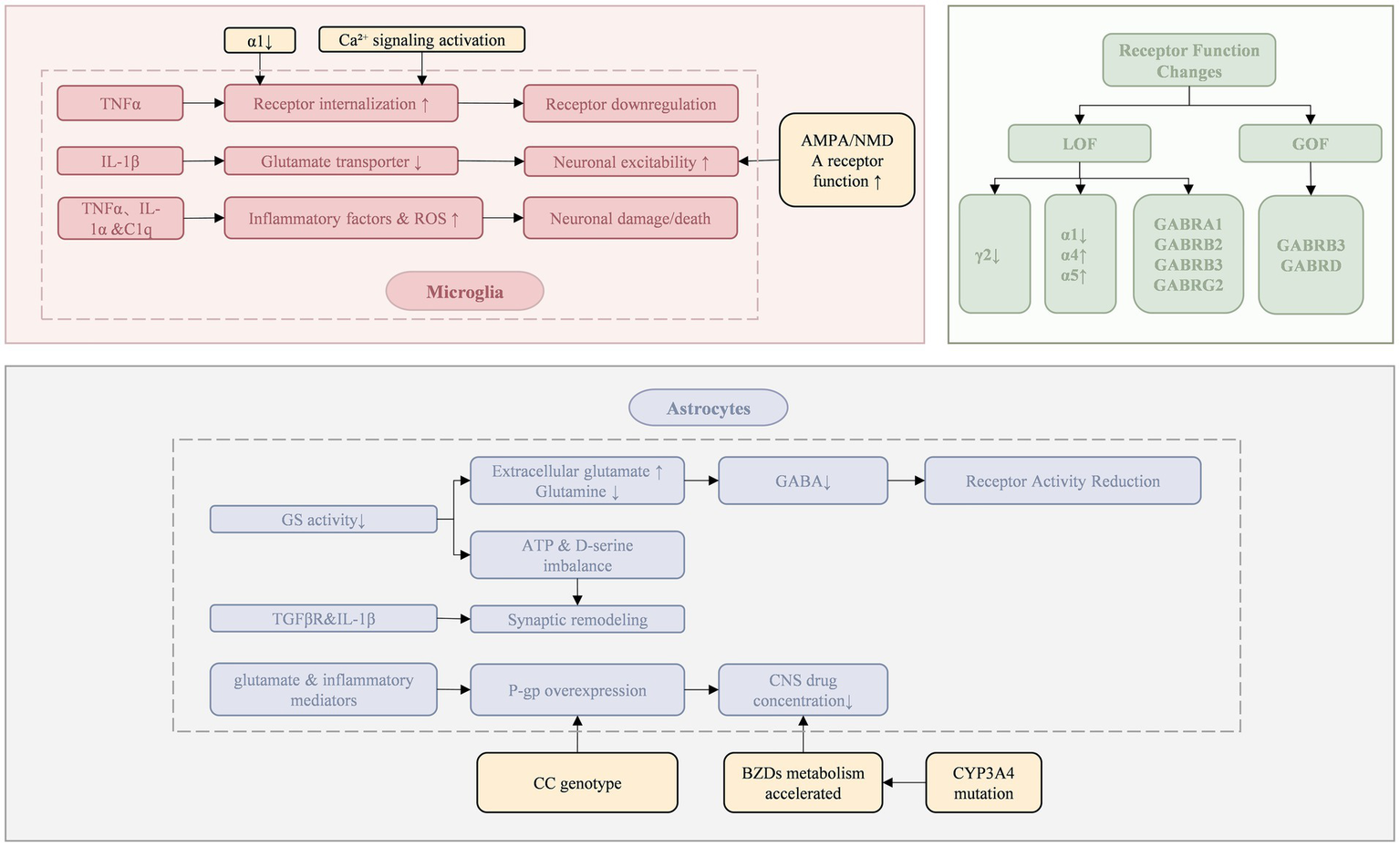
Resistance mechanisms of benzodiazepines.
3 Treatment methods
BZDs, such as diazepam and lorazepam, are widely used in the treatment of epilepsy (48). Because of its rapid onset of action and significant effect, BZDs have become the first-line treatment for acute seizures and SE. However, the problem of drug resistance is common in clinical practice, which not only limits the effectiveness of drugs but also increases the complexity of patients’ conditions and the difficulty of treatment. To solve the treatment problem of BZDs-resistant epilepsy, a variety of innovative approaches have been developed in recent years.
3.1 Pharmacological treatment
3.1.1 Medication use optimization
The optimal use of drugs includes two aspects: drug combination and individualized treatment.
Early identification of refractory epilepsy syndrome and drug-resistant epilepsy is crucial for formulating treatment strategies. For patients with a potential risk of drug resistance and easy-to-develop drug-resistant epilepsy, the combination therapy of ASMs can be attempted early. The following key considerations should be taken into account when implementing combination therapy: (1) the selected ASMs should have distinct mechanisms of action; (2) pharmacodynamic studies should demonstrate a synergistic enhancement of efficacy between the drugs; (3) pharmacokinetic evaluations should indicate no significant drug interactions or, at the very least, no adverse synergistic effects; (4) adverse reactions should not be synergistic or cumulative (49, 50). If combination therapy does not yield clinical benefits, it is advisable to transition to monotherapy or adjust the combination regimen to achieve an optimal balance between therapeutic efficacy and tolerability of adverse effects.
Different drugs have different mechanisms of action in the treatment of epilepsy (51). BZDs inhibit seizures by regulating neuronal inhibition, while drugs such as levetiracetam, lamotrigine, and sodium valproate inhibit seizures by regulating neuronal excitability, and drugs such as phenytoin, sodium valproate, and levetiracetam inhibit seizures by regulating voltage-gated ion channels (52). The combination of drugs is usually two drugs with different mechanisms, such as the combination of GABAA receptor agonists and NMDA receptor antagonists. In the synaptic GABAA receptor loss and NMDAR increase caused by status epilepsies (SE) (53), BZDs restore the inhibitory effect by stimulating the remaining GABA receptors, as long as a sufficient number of receptors remain present on the postsynaptic membrane. However, this only partially solves the problem, as the increase in functional NMDA receptors and the resulting excitotoxicity have not been addressed. Thus, treatment of receptor transport abnormalities induced by SE requires at least two drugs: a GABAA receptor agonist, such as BZDs, and an NMDA receptor antagonist (54). Their combination may not only terminate RSE but also reduce or eliminate some of its long-term consequences: neuronal damage, spatial memory deficits, and seizures. At the same time, their therapeutic index is improved by synergistic interaction (53).
The advantage of combination therapy is that it can enhance the efficacy of drugs, reduce adverse reactions, and reduce the occurrence of drug resistance. However, attention must be given to the different mechanisms of action of the drugs to avoid interactions that could increase drug side effects. BZDs such as lorazepam or diazepam are usually used first for rapid onset of treatment. When patients become resistant to BZDs, BZDs can be combined with drugs such as phenytoin sodium, valproate sodium, and levetiracetam, which is an effective strategy for the treatment of BZDs-resistant epilepsy (55).
The standard approach for treating SE is sequential multidrug therapy, where a second drug is administered after the failure of the first drug, and a third drug is given after the failure of the second (53). Typically, BZDs are followed by another anticonvulsant, then another novel anticonvulsant, followed by general anesthesia, and, after a few failed episodes of anesthesia, ketamine or another less commonly used drug (54, 56). The advantage of this approach is that it maximizes the delivery and minimizes drug toxicity for responders. However, the downside is that sequential polytherapy requires time, as each treatment must wait until the failure of the previous one before starting the next. Delay delivery of the second drug by at least 30 min, and delay delivery of the third drug by at least 1 h (53). During this time, untreated receptor alterations induced by the initial drug may worsen, potentially complicating the efficacy of subsequent targeted therapies (e.g., ketamine). If the first-line treatment is BZDs, the increased internalization of GABA receptors may lead to an upregulation of untreated NMDARs, resulting in heightened neuronal excitability. We should consider concurrent multidrug therapy to reverse the effects of receptor trafficking early before it becomes irreversible (54). One study demonstrated that simultaneous multidrug therapy was far more effective than sequential monotherapy or higher-dose midazolam in reducing electroencephalography power (EEG power) and stopping SE (53).
Individualized treatment is an important way to treat drug-resistant epilepsy, which needs to be carried out under the guidance of specialists. In individualized treatment, detailed etiological diagnosis and analysis of drug metabolism characteristics are needed first, and then individualized treatment plans are designed according to the specific conditions of patients, and the most suitable drugs are selected for treatment to achieve the best therapeutic outcome. In cases where BZDs fail to control seizures at their maximum recommended dosage, or when patients exhibit intolerable adverse effects, alternative therapeutic options may include the administration of intravenous anesthetic agents such as thiopental sodium or propofol. Additionally, other mechanisms of ASM should also be considered (57). Furthermore, in individualized treatment, the dose and administration regimen of drugs need to be adjusted according to the specific condition of the patient. For example, for patients with rapid drug metabolism, it is necessary to increase the drug dose or shorten the dosing interval to ensure therapeutic efficacy. Genetic testing can help predict the rate of BZDs metabolism and guide the selection of personalized drug doses. In patients with a low-active CYP3A4 allele, the dose of BZDs may need to be adjusted to avoid toxicity or inefficiency issues (58); Tariquidar is a P-glycoprotein inhibitor that can be used in patients with genotypes associated with P-gp overexpression (59).
3.1.2 Novel drug treatments
3.1.2.1 New drugs
New drugs, such as other Positive allosteric modulators of GABAA receptors, include neuroactive steroids and other drugs. Neuroactive steroids are at various stages of clinical development, such as Ganaxolone, Zuranolone, LYT-300, Sage-324, PRAX 114, and ETX-155. Other medications include nonsteroid compounds (e.g., GRX-917, a TSPO-binding site ligand), α2/3-preferring BAER-101, α2/3/5-preferring SAN711, and KRM-II-81, raising new therapeutic prospects for this highly leveraged drug target in neurology and psychiatry (60, 61).
Ganaxolone is a neurosteroid analogue that exerts antiepileptic effects by enhancing the inhibitory function of GABAA receptors. Unlike BZDs that bind to the γ subunit of GABAA receptors, ganaxolone acts at the neurosteroid binding site, mainly at the β-α subunit interface of GABAA receptors, thereby avoiding the common dependence and resistance issues of BZDs. Ganaxolone has been proven to be effective in various refractory epilepsy syndromes, especially those related to CDKL5 deficiency syndrome (62). Its intravenous formulation is also under development and is expected to become a potential treatment option for SE. However, except for BZDs, most drugs that enhance GABA function usually exacerbate the occurrence of absence epilepsy in the brain. Ganaxolone, as a GABA enhancer, also exhibits similar characteristics. It enhances the tonic inhibition mediated by GABAA receptors, particularly in regions such as the thalamus and visual cortex. These regions are the key structures highly related to the thalamocortical circuit of absence epilepsy. Therefore, although ganaxolone shows broad therapeutic potential in many epilepsy types (63), it should be used with caution in patients with absence epilepsy, as its mechanism of action may instead induce or exacerbate seizures (64, 65).
Cenobamate (CNB) is a novel antiepileptic drug characterized by a dual mechanism of action: inhibition of persistent sodium currents and positive modulation of GABAA receptor function. In recent years, its potential efficacy in drug-resistant genetic generalized epilepsy (GGE) has attracted increasing attention. Preclinical animal studies have demonstrated that CNB exhibits significant anticonvulsant effects across multiple models of generalized seizures, including the GAERS rat model, the 6 Hz psychomotor seizure model, and seizure models induced by maximal electroshock (MES) and pentylenetetrazol (PTZ). CNB was shown to reduce SWDs and the duration of absence seizures, suggesting broad-spectrum efficacy against various types of generalized seizures (66, 67).
3.1.2.2 New drug delivery forms
Novel drug delivery modalities include changing from tablets to nasal sprays, oral mucosal delivery, and intravenous formulations. Inhaled BZDs are a group of central nervous system drugs delivered by aerosol or vapor. They are mainly used for the rapid treatment of anxiety attacks, panic attacks, and SE (68). Compared with traditional oral or intravenous forms, inhaled BZDs have the advantages of faster onset of action and patient compliance. For example, midazolam aerosol has been approved in some countries for the emergency management of both out-of-hospital and in-hospital seizures (69). As a derivative of Levetiracetam, Brivaracetam (BRV), which enhances inhibitory neurotransmission by positively regulating GABAA receptors, has a higher affinity and faster onset and can be used in the form of intravenous injection. It provides a new option, especially when rapid control of seizures is needed (70).
3.1.2.3 Improved drugs
Modified drugs, such as Fosphenytoin sodium, are suitable for SE. It is a water-soluble prodrug of phenytoin that is rapidly converted to Phenytoin in the body (71). Fosphenytoin sodium is widely used in the treatment of acute seizures, especially in SE, because of its excellent water solubility, safety, few side effects, and the ability to quickly reach therapeutic concentrations by intravenous or intramuscular injection (72).
3.2 Adjuvant therapy
Several other treatments can aid in the treatment of epilepsy. Neuromodulation techniques such as vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) send electrical signals to the vagus nerve through implantable devices to modulate neuronal activity in the brain, thereby reducing seizures (73). Additionally, non-invasive VNS is an emerging method (74). Acupuncture is a traditional Chinese medicine therapy that regulates the body’s functions by stimulating specific acupoints to alleviate epilepsy symptoms and reduce the side effects of drugs (75). For example, auricular acupoint therapy with transcutaneous auricular VNS is used to treat epilepsy (76).
Simultaneously, some traditional Chinese medicine can be used as an auxiliary treatment for epilepsy, such as Curcumae Longae Rhizoma, Scorpio, Acori Tatarinowii Rhizoma, Uncariae Ramulus Cum Uncis, and Ganoderma, etc., with sedative and anticonvulsant effects (77). The ketogenic diet (KD) has shown remarkable anti-epileptic and disease-modifying characteristics by restricting glucose utilization, promoting ketogenesis, and regulating astrocyte metabolism. Its mechanisms include inhibition of glycolysis, such as the use of 2-deoxy-D-glucose, regulation of glutamate signaling, and reduction of abnormal expression of astrocyte-related genes. Furthermore, the ketogenic diet also blocks the epileptogenic process in epigenetic pathways by increasing the level of adenosine and down-regulating the expression of adenosine kinase (ADK), it also reduces the progression of epilepsy and related risks, such as sudden unexpected death in epilepsy (SUDEP) and drug resistance (27, 78).
In rare cases, surgical treatment can be considered (79). If the acute phase of epilepsy is triggered by an obvious brain trauma or structural lesion, such as a brain tumor or vascular malformation, surgery can be used to deal with the underlying cause, thereby helping to control the seizures (80, 81). If a patient presents with refractory SE, does not respond to multiple medications, and is life-threatening, surgery may be considered as a last resort, and such surgery usually involves callosotomy or local excision of the lesion (82). However, these methods are not a substitute for conventional epilepsy treatment.
3.3 Frontier treatment
Stem cell therapy, gene therapy, anti-inflammatory therapy, and small molecule drug research provide new insights for the cutting-edge treatment of epilepsy.
3.3.1 Stem cell therapy
Stem cell-based therapies offer a new avenue for long-term control of DRE through regenerative properties. Its mechanisms include specific cell substitution, rescue and repair of degeneration cells, reorganization of synapses, modulation of the secretion of neurotransmitters, and beneficial neurotrophic factors. Stem cell transplantation can not only alleviate seizures, but also inhibit the progression of epilepsy, prevent the development of chronic epilepsy, and improve cognitive function, showing many therapeutic potentials. It has been used to treat epilepsy in preclinical animal studies and clinical trials (83).
3.3.2 Gene therapy
Optogenetics and chemogenetics have shown great potential in the research and treatment of DRE. Gene therapy selectively manipulates excitatory or inhibitory neurons to regulate abnormal neural activity at the molecular level. Optogenetics uses light to control the excitability of specific neuronal populations and can be used in a closed-loop paradigm to activate light sources only when a seizure is detected. Chemical genetics relies on the modification of endogenous receptors or modified chimeric receptors in response to exogenous ligands (79). These two techniques have successfully suppressed seizures in various epilepsy models in mice, rats, and monkeys, showing significant promise in the study of neuropathological states and the treatment of epilepsy (84). Additionally, significant breakthroughs have been made in the study of neuropeptide Y (NPY) in gene therapy. By overexpressing NPY in the brain using viral vectors, seizures can be significantly suppressed through the activation of Y2 and Y5 receptors. Once the obstacles of gene therapy are overcome, the endogenous neuroregulatory system can be used to treat epilepsy (85).
3.3.3 Anti-inflammatory therapy
Anti-inflammatory therapy reduces seizure frequency, provides neuroprotection, and improves cognitive function by targeting inflammatory molecules induced by reactive astrocytes. Some anti-inflammatory drugs, such as Anakinra, have shown efficacy in refractory status epilepticus and pediatric epileptic encephalopathy, particularly in patients for whom traditional drug treatments are ineffective (27). The various inflammatory pathways in neuroinflammation include neurodegeneration, neurogenesis, glial proliferation, axonal injury and sprouting, dendritic plasticity, blood–brain barrier (BBB) damage, neuroinflammatory processes, extracellular matrix reorganization, and neuronal molecular structure reorganization. Only a few molecular mechanisms have been targeted to prevent or modify the epilepsy development or phenotype, and no such therapy has as yet been developed, which can provide new ideas for antiepileptic drugs (86).
3.3.4 Small molecule drugs
Small molecule drugs are still the core field of epilepsy treatment. As a Negative Allosteric Modulator (NAM), methyl-6,7-dimethoxy-4-ethyl-β-carboline-3-carboxylate (DMCM) can reduce GABAA receptor activity at low concentrations. However, at high concentrations, especially when coexisting with flumazenil, DMCM can turn into a positive modulator and enhance GABA-induced current. This dual-action mechanism offers new strategies for exploring drug combination approaches, potentially optimizing the therapeutic effects of epilepsy treatment in specific situations (87).
Although technical and clinical translation challenges remain, these therapies are expected to become important treatments for DRE in the future.
4 Summary
Benzodiazepines are one of the main drugs for the treatment of epilepsy, but the problem of drug resistance seriously restricts their clinical application (8). The development of benzodiazepine resistance is the result of the joint efforts of many factors, and its mechanism covers many aspects, such as the drug target-related mechanisms, synaptic and neural network remodeling, metabolism-related pathway gene variants, and the mechanism related to drug efflux. Current treatment options for DRE include optimization of drug use, new drug therapy, and adjuvant therapy. Although some progress has been made in the mechanism analysis and treatment strategies in recent years, there are still many unresolved issues to be explored. Future studies should focus on combining multidisciplinary techniques to reveal the underlying mechanisms of BZDs resistance and develop more precise and personalized treatment methods to improve the clinical outcomes of DRE patients. Furthermore, with the rapid development of neuropharmacology and molecular biology, new drugs, stem cell therapy, and gene therapy intervention strategies may provide breakthroughs to solve the problem of BZDs resistance, thus promoting the treatment of neurological diseases into a new era (79, 83).
Statements
Author contributions
YH: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YZ: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YL: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1.
Wang Y Chen Z . The role of central cholinergic system in epilepsy. Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. (2017) 46:15–21. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-9292.2017.02.03
2.
Mesraoua B Brigo F Lattanzi S Abou-Khalil B al Hail H Asadi-Pooya AA . Drug-resistant epilepsy: definition, pathophysiology, and management. J Neurol Sci. (2023) 452:120766. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2023.120766
3.
Thijs RD Surges R O'Brien TJ Sander JW . Epilepsy in adults. Lancet. (2019) 393:689–701. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32596-0Epilepsy
4.
Klein P Kaminski RM Koepp M Löscher W . New epilepsy therapies in development. Nat Rev Drug Discov. (2024) 23:682–708. doi: 10.1038/s41573-024-00981-w
5.
Lezaic N Roussy J Masson H Jetté N Keezer MR . Epilepsy in the elderly: unique challenges in an increasingly prevalent population. Epilepsy Behav. (2020) 102:106724. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2019.106724
6.
Löscher W Potschka H Sisodiya SM Vezzani A . Drug resistance in epilepsy: clinical impact, potential mechanisms, and new innovative treatment options. Pharmacol Rev. (2020) 72:606–38. doi: 10.1124/pr.120.019539
7.
Olkkola KT Ahonen J . Midazolam and other benzodiazepines In: SchüttlerJSchwildenH, editors. Modern anesthetics: handbook of experimental pharmacology. New York: Springer (2008). 335–60.
8.
Humphries LK Eiland LS . Treatment of acute seizures: is intranasal midazolam a viable option?J Pediatr Pharmacol Ther. (2013) 18:79–87. doi: 10.5863/1551-6776-18.2.79
9.
Lai ML Tien YE Huang YS Huang JD . Studies on pharmacokinetic mechanism of phenytoin resistance in refractory epilepsy. J Pharm Sci. (2013) 102:3189–95. doi: 10.1002/jps.23593
10.
Zhao GX Zhang Z Cai WK Shen ML Wang P He GH . Associations between CYP3A4, CYP3A5 and SCN1A polymorphisms and carbamazepine metabolism in epilepsy: a meta-analysis. Epilepsy Res. (2021) 173:106615. doi: 10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2021.106615
11.
Goldschen-Ohm MP . Benzodiazepine modulation of GABAA receptors: a mechanistic perspective. Biomol Ther. (2022) 12:1784. doi: 10.3390/biom12121784
12.
Zhu S Noviello CM Teng J Walsh RM Jr Kim JJ Hibbs RE . Structure of a human synaptic GABAA receptor. Nature. (2018) 559:67–72. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0255-3
13.
Oreland L . The benzodiazepines: a pharmacological overview. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. (1988) 32:13–6. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-6576.1988.tb02826.x
14.
Kubová H Bendová Z Moravcová S Pačesová D Rocha L Mareš P . Neonatal clonazepam administration induced long-lasting changes in GABAA and GABAB receptors. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21:3184. doi: 10.3390/ijms21093184
15.
Nicholson MW Sweeney A Pekle E Alam S Ali AB Duchen M et al . Diazepam-induced loss of inhibitory synapses mediated by PLCδ/ca 2+/calcineurin signalling downstream of GABAA receptors. Mol Psychiatry. (2018) 23:1851–67. doi: 10.1038/s41380-018-0100-y
16.
Vithlani M Terunuma M Moss SJ . The dynamic modulation of GABAA receptor trafficking and its role in regulating the plasticity of inhibitory synapses. Physiol Rev. (2011) 91:1009–22. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00015.2010
17.
Eid T Lee TSW Patrylo P Zaveri HP . Astrocytes and glutamine synthetase in epileptogenesis. J Neurosci Res. (2019) 97:1345–62. doi: 10.1002/jnr.24267
18.
Naylor DE . In the fast lane: receptor trafficking during status epilepticus. Epilepsia Open. (2023) 8:S35–65. doi: 10.1002/epi4.12718
19.
Foitzick MF Medina NB García LCI Iglesias García LC Gravielle MC . Benzodiazepine exposure induces transcriptional down-regulation of GABAA receptor α1 subunit gene via L-type voltage-gated calcium channel activation in rat cerebrocortical neurons. Neurosci Lett. (2020) 721:134801. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2020.134801
20.
Han DY Guan BJ Wang YJ Hatzoglou M Mu T-W . L-type calcium channel blockers enhance trafficking and function of epilepsy-associated α1 (D219N) subunits of GABAA receptors. ACS Chem Biol. (2015) 10:2135–48. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.5b00479
21.
Feng Y Wei ZH Liu C Li GY Qiao XZ Gan YJ et al . Genetic variations in GABA metabolism and epilepsy. Seizure. (2022) 101:22–9. doi: 10.1016/j.seizure.2022.07.007
22.
Maillard P Baer S Schaefer É Desnous B Villeneuve N Lépine A et al . Molecular and clinical descriptions of patients with GABAA receptor gene variants (GABRA1, GABRB2, GABRB3, GABRG2): a cohort study, review of literature, and genotype–phenotype correlation. Epilepsia. (2022) 63:2519–33. doi: 10.1111/epi.17336
23.
Chuang SH Reddy DS . Genetic and molecular regulation of extrasynaptic GABA-A receptors in the brain: therapeutic insights for epilepsy. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. (2018) 364:180–97. doi: 10.1124/jpet.117.244673
24.
Ding L Feng HJ Macdonald RL Botzolakis EJ Hu N Gallagher MJ . GABAA receptor α1 subunit mutation A322D associated with autosomal dominant juvenile myoclonic epilepsy reduces the expression and alters the composition of wild type GABAA receptors. J Biol Chem. (2010) 285:26390–405. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.142299
25.
Tanaka M DeLorey TM Delgado-Escueta A Richard WO . GABRB3, epilepsy, and neurodevelopment. Epilepsia. (2012) 51:77. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1167.2010.02863.x
26.
Absalom NL Lin SXN Liao VWY Chua HC Møller RS Chebib M et al . GABAA receptors in epilepsy: elucidating phenotypic divergence through functional analysis of genetic variants. J Neurochem. (2024) 168:3831–52. doi: 10.1111/jnc.15932
27.
Vezzani A Ravizza T Bedner P Aronica E Steinhäuser C Boison D . Astrocytes in the initiation and progression of epilepsy. Nat Rev Neurol. (2022) 18:707–22. doi: 10.1038/s41582-022-00727-5
28.
Javalgekar M Jupp B Vivash L O’Brien TJ Wright DK Jones NC et al . Inflammasomes at the crossroads of traumatic brain injury and post-traumatic epilepsy. J Neuroinflammation. (2024) 21:172. doi: 10.1186/s12974-024-03167-8
29.
Zhang S Chen F Zhai F Liang S . Role of HMGB1/TLR4 and IL-1β/IL-1R1 signaling pathways in epilepsy. Front Neurol. (2022) 13:904225. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.904225
30.
Xanthos DN Sandkühler J . Neurogenic neuroinflammation: inflammatory CNS reactions in response to neuronal activity. Nat Rev Neurosci. (2014) 15:43–53. doi: 10.1038/nrn3617
31.
Carta AR Mulas G Bortolanza M Duarte T Pillai E Fisone G et al . L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia and neuroinflammation: do microglia and astrocytes play a role?Eur J Neurosci. (2017) 45:73–91. doi: 10.1111/ejn.13482
32.
Hiragi T Ikegaya Y Koyama R . Microglia after seizures and in epilepsy. Cells. (2018) 7:26. doi: 10.3390/cells7040026
33.
Zhao Y Huang Y Cao Y Yang J . Astrocyte-mediated neuroinflammation in neurological conditions. Biomol Ther. (2024) 14:1204. doi: 10.3390/biom14101204
34.
Liddelow SA Guttenplan KA Clarke LE Bennett FC Bohlen CJ Schirmer L et al . Neurotoxic reactive astrocytes are induced by activated microglia. Nature. (2017) 541:481–7. doi: 10.1038/nature21029
35.
Liu L Liu J Bao J Bai QQ Wang GQ . Interaction of microglia and astrocytes in the neurovascular unit. Front Immunol. (2020) 11:1024. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01024
36.
Stellwagen D Beattie EC Seo JY Malenka RC . Differential regulation of AMPA receptor and GABA receptor trafficking by tumor necrosis factor-α. J Neurosci. (2005) 25:3219–28. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4486-04.2005
37.
Koh W Kwak H Cheong E Lee CJ . GABA tone regulation and its cognitive functions in the brain. Nat Rev Neurosci. (2023) 24:523–39. doi: 10.1038/s41583-023-00724-7
38.
Kilb W Kirischuk S . GABA release from astrocytes in health and disease. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:15859. doi: 10.3390/ijms232415859
39.
Sears SMS Hewett SJ . Influence of glutamate and GABA transport on brain excitatory/inhibitory balance. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). (2021) 246:1069–83. doi: 10.1177/1535370221989263
40.
Aroniadou-Anderjaska V Figueiredo TH Furtado MDA De Araujo Furtado M Pidoplichko VI Lumley LA et al . Alterations in GABAA receptor-mediated inhibition triggered by status epilepticus and their role in epileptogenesis and increased anxiety. Neurobiol Dis. (2024) 200:106633. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2024.106633
41.
Klotz U . The role of pharmacogenetics in the metabolism of antiepileptic drugs: pharmacokinetic and therapeutic implications. Clin Pharmacokinet. (2007) 46:271–9. doi: 10.2165/00003088-200746040-00001
42.
Li J Chen Y Tang Y Li W Tu Y . Homotropic cooperativity of midazolam metabolism by cytochrome P450 3A4: insight from computational studies. J Chem Inf Model. (2021) 61:2418–26. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.1c00266
43.
Balestrini S Sisodiya SM . Pharmacogenomics in epilepsy. Neurosci Lett. (2018) 667:27–39. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2017.01.014
44.
Tang F Hartz AMS Bauer B . Drug-resistant epilepsy: multiple hypotheses, few answers. Front Neurol. (2017) 8:301. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2017.00301
45.
Wang GX Wang DW Liu Y Ma YH . Intractable epilepsy and the P-glycoprotein hypothesis. Int J Neurosci. (2016) 126:385–92. doi: 10.3109/00207454.2015.1038710
46.
Siddiqui A Kerb R Weale ME Brinkmann U Smith A Goldstein DB et al . Association of multidrug resistance in epilepsy with a polymorphism in the drug-transporter gene ABCB1. N Engl J Med. (2003) 348:1442–8. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa021986
47.
Borst P Evers R Kool M Wijnholds J . A family of drug transporters: the multidrug resistance-associated proteins. J Natl Cancer Inst. (2000) 92:1295–302. doi: 10.1093/jnci/92.16.1295
48.
Almohaish S Tesoro EP Brophy GM . Status epilepticus: an update on pharmacological management. Semin Neurol. (2024) 44:324–32. doi: 10.1055/s-0044-1785503
49.
Abou-Khalil B . Selecting rational drug combinations in epilepsy. CNS Drugs. (2017) 31:835–44. doi: 10.1007/s40263-017-0471-7
50.
French JA Faught E . Rational polytherapy. Epilepsia. (2009) 50:63–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1167.2009.02238.x
51.
Johannessen Landmark C Eyal S Burns ML Franco V Johannessen SI . Pharmacological aspects of antiseizure medications: from basic mechanisms to clinical considerations of drug interactions and use of therapeutic drug monitoring. Epileptic Disord. (2023) 25:454–71. doi: 10.1002/epd2.20069
52.
Sills GJ Rogawski MA . Mechanisms of action of currently used antiseizure drugs. Neuropharmacology. (2020) 168:107966. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2020.107966
53.
Niquet J Lumley L Baldwin R Rossetti F Schultz M de Araujo Furtado M et al . Early polytherapy for benzodiazepine-refractory status epilepticus. Epilepsy Behav. (2019) 101:106367. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2019.06.011
54.
Niquet J Baldwin R Suchomelova L Lumley L Naylor D Eavey R et al . Benzodiazepine-refractory status epilepticus: pathophysiology and principles of treatment. Ann N Y Acad Sci. (2016) 1378:166–73. doi: 10.1111/nyas.13147
55.
Glauser T Shinnar S Gloss D Alldredge B Arya R Bainbridge J et al . Evidence-based guideline: treatment of convulsive status epilepticus in children and adults: report of the guideline Committee of the American Epilepsy Society. Epilepsy Curr. (2016) 16:48–61. doi: 10.5698/1535-7597-16.1.48
56.
Rossetti AO Claassen J Gaspard N . Status epilepticus in the ICU. Intensive Care Med. (2024) 50:1–16. doi: 10.1007/s00134-023-07263-w
57.
Rai S Drislane FW . Treatment of refractory and super-refractory status epilepticus. Neurotherapeutics. (2018) 15:697–712. doi: 10.1007/s13311-018-0640-5
58.
Tani N Ikeda T Ishikawa T . Relationship between clock gene expression and CYP2C19 and CYP3A4 with benzodiazepines. Hum Exp Toxicol. (2023) 42:09603271231171643. doi: 10.1177/09603271231171643
59.
Ilyas-Feldmann M Langer O Bauer M Asselin MC Hendrikse NH Sisodiya SM et al . Tolerability of tariquidar–a third generation P-gp inhibitor as add-on medication to antiseizure medications in drug-resistant epilepsy. Seizure. (2024) 119:44–51. doi: 10.1016/j.seizure.2024.05.007
60.
Witkin JM Lippa A Smith JL Jin X Ping X Biggerstaff A et al . The imidazodiazepine, KRM-II-81: an example of a newly emerging generation of GABAkines for neurological and psychiatric disorders. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. (2022) 213:173321. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2021.173321
61.
MacLean A Chappell AS Kranzler J Evrard A Monchal H Roucard C . BAER-101, a selective potentiator of α2-and α3-containing GABAA receptors, fully suppresses spontaneous cortical spike-wave discharges in genetic absence epilepsy rats from Strasbourg (GAERS). Drug Dev Res. (2024) 85:e22160. doi: 10.1002/ddr.22160
62.
Richardson RJ Petrou S Bryson A . Established and emerging GABAA receptor pharmacotherapy for epilepsy. Front Pharmacol. (2024) 15:1341472. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1341472
63.
Lamb YN . Ganaxolone: first approval. Drugs. (2022) 82:933–40. doi: 10.1007/s40265-022-01724-0
64.
Snead OC III . Ganaxolone, a selective, high-affinity steroid modulator of the γ-aminobutyric acid-a receptor, exacerbates seizures in animal models of absence. Ann Neurol. (1998) 44:688–91. doi: 10.1002/ana.410440417
65.
Reddy DS . Neurosteroids as novel anticonvulsants for refractory status epilepticus and medical countermeasures for nerve agents: a 15-year journey to bring ganaxolone from bench to clinic. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. (2024) 388:273–300. doi: 10.1124/jpet.123.001816
66.
Perucca E Bialer M White HS . New GABA-targeting therapies for the treatment of seizures and epilepsy: I. Role of GABA as a modulator of seizure activity and recently approved medications acting on the GABA system. CNS Drugs. (2023) 37:755–79. doi: 10.1007/s40263-023-01027-2
67.
Schmitz B Lattanzi S Vonck K Kälviäinen R Nashef L Ben-Menachem E . Cenobamate in refractory epilepsy: overview of treatment options and practical considerations. Epilepsia Open. (2023) 8:1241–55. doi: 10.1002/epi4.12830
68.
Kienitz R Kay L Beuchat I Gelhard S von Brauchitsch S Mann C et al . Benzodiazepines in the management of seizures and status epilepticus: a review of routes of delivery, pharmacokinetics, efficacy, and tolerability. CNS Drugs. (2022) 36:951–75. doi: 10.1007/s40263-022-00940-2
69.
Mohammed MZ Elagouza I El Gaafary M El-Garhy R El-Rashidy O . Intranasal versus buccal versus intramuscular midazolam for the home and emergency treatment of acute seizures in pediatric patients: a randomized controlled trial. Pediatr Neurol. (2024) 158:135–43. doi: 10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2024.06.014
70.
Brigo F Lattanzi S Nardone R Trinka E . Intravenous brivaracetam in the treatment of status epilepticus: a systematic review. CNS Drugs. (2019) 33:771–81. doi: 10.1007/s40263-019-00652-0
71.
Browne TR . Fosphenytoin (cerebyx). Clin Neuropharmacol. (1997) 20:1–12. doi: 10.1097/00002826-199702000-00001
72.
Clay JL Fountain NB . A critical review of fosphenytoin sodium injection for the treatment of status epilepticus in adults and children. Expert Rev Neurother. (2022) 22:1–13. doi: 10.1080/14737175.2021.2001328
73.
Pérez-Carbonell L Faulkner H Higgins S Koutroumanidis M Leschziner G . Vagus nerve stimulation for drug-resistant epilepsy. Pract Neurol. (2020) 20:189–98. doi: 10.1136/practneurol-2019-002210
74.
Hilz MJ . Transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation-a brief introduction and overview. Auton Neurosci. (2022) 243:103038. doi: 10.1016/j.autneu.2022.103038
75.
Cheuk DKL Wong V . Acupuncture for epilepsy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. (2014) 2014:CD005062. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005062.pub4
76.
Zhang Q Luo X Wang X Wang XH Li JY Qiu H et al . Transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation for epilepsy. Seizure. (2024) 119:84–91. doi: 10.1016/j.seizure.2024.05.005
77.
Wu J Cao M Peng Y Dong B Jiang Y Hu C et al . Research progress on the treatment of epilepsy with traditional Chinese medicine. Phytomedicine. (2023) 120:155022. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155022
78.
Kossoff EH Zupec-Kania BA Auvin S Ballaban-Gil KR Christina Bergqvist AG Blackford R et al . Optimal clinical management of children receiving dietary therapies for epilepsy: updated recommendations of the international ketogenic diet study group. Epilepsia open. (2018) 3:175–92. doi: 10.1002/epi4.12225
79.
Walker MC Kullmann DM . Optogenetic and chemogenetic therapies for epilepsy. Neuropharmacology. (2020) 168:107751. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2019.107751
80.
Marashly A Karia S Zonjy B . Epilepsy surgery: special circumstances. Semin Pediatr Neurol. (2021) 39:100921. doi: 10.1016/j.spen.2021.100921
81.
Lee SK . Who are the better candidates for epilepsy surgery?J Epilepsy Res. (2023) 13:37–41. doi: 10.14581/jer.23006
82.
Rugg-Gunn F Miserocchi A McEvoy A . Epilepsy surgery. Pract Neurol. (2020) 20:4–14. doi: 10.1136/practneurol-2019-002192
83.
Chang BL Chang KH . Stem cell therapy in treating epilepsy. Front Neurosci. (2022) 16:934507. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.934507
84.
Krut VG Kalinichenko AL Maltsev DI Jappy D Shevchenko EK Podgorny OV et al . Optogenetic and chemogenetic approaches for modeling neurological disorders in vivo. Prog Neurobiol. (2024) 235:102600. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2024.102600
85.
Cattaneo S Verlengia G Marino P Simonato M Bettegazzi B . NPY and gene therapy for epilepsy: how, when,… and Y. Front Mol Neurosci. (2021) 13:608001. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2020.608001
86.
Łukasiuk K Lasoń W . Emerging molecular targets for anti-epileptogenic and epilepsy modifying drugs. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:2928. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032928
87.
Zhu S Sridhar A Teng J Howard RJ Lindahl E Hibbs RE . Structural and dynamic mechanisms of GABAA receptor modulators with opposing activities. Nat Commun. (2022) 13:4582. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-32212-4
Summary
Keywords
benzodiazepines, drug resistance, treatment strategies, epilepsy, seizure
Citation
Huang Y, Zhang Y and Liang Y (2025) Benzodiazepine-resistant epilepsy: unraveling molecular mechanisms and developing multimodal therapeutic strategies. Front. Neurol. 16:1615079. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1615079
Received
20 April 2025
Accepted
23 May 2025
Published
06 June 2025
Volume
16 - 2025
Edited by
Vassiliy Tsytsarev, University of Maryland, United States
Reviewed by
Prosper N’Gouemo, Howard University, United States
Ming Soh, University of Melbourne, Australia
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Huang, Zhang and Liang.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yi Liang, liangyi3377@163.com
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
‡ORCID: Yanqiu Huang, orcid.org/0009-0001-7372-761X
Yangfan Zhang, orcid.org/0009-0003-7703-9851
Yi Liang, orcid.org/0000-0002-0201-9114
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.