Abstract
Objective:
To explore the predictive role of the triglyceride-glucose index (TyG index) on the early neurological improvement in non-diabetic patients with acute ischemic stroke (AIS) undergoing alteplase intravenous thrombolysis (IV-rtPA).
Methods:
This study included 490 AIS patients without diabetes, whose time from onset to hospital time ≤3 h undergoing IV-rtPA in the Stroke Center of our hospital from September 2023 to September 2024 through the Stroke Emergency Map Management Platform in Dalian City. According to the National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) score at 24 h after IVT, the patients were divided into early neurological improvement (ENI) group (n = 332) and non-ENI group (n = 158). General information, risk factors, experimental data and the location of cerebral infarction were collected. Intergroup analyses were conducted using univariate or multivariate logistic regression.
Results:
(1) In the ENI group, blood glucose (FBG), triglycerides (TG), TyG index, and baseline NIHSS score were significantly lower than those in the non-ENI group (p < 0.05). (2) Binary logistic regression analysis indicated that a TyG index ≤7.15 and a low baseline NIHSS score could predict early neurological improvement undergoing intravenous thrombolysis (IVT) in AIS patients. The area under the curve (AUC) values for the TyG index, baseline NIHSS score, and the combined variable (Y) in predicting ENI were 0.640, 0.641, and 0.721, respectively, with the combined variable (Y) exhibiting the highest AUC value.
Conclusion:
The TyG index, baseline NIHSS score, and the combined variable (Y) are predictors of early neurological improvement, with the combined variable (Y) exhibiting a higher predictive efficiency.
1 Introduction
Currently, intravenous thrombolysis remains the primary treatment option for acute ischemic stroke (AIS) within the therapeutic time window (1), yet some patients still experience a poor long-term prognosis. It is therefore crucial to investigate the risk factors and measurable biomarkers that influence the early neurological outcomes of AIS patients post-intravenous thrombolysis.
Insulin resistance (IR), recognized as the primary pathophysiological mediator of metabolic syndrome, is deemed a significant contributor to the onset and progression of atherosclerosis and cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases (2). Research (3) has indicated that elevated IR levels are linked to adverse neurological outcomes in patients with AIS. Analysis of data from 273,368 cases in the UK Biobank has revealed that the triglyceride-glucose index (TyG index) surpasses individual blood glucose and triglyceride levels in forecasting stroke incidence, suggesting that the TyG index is an effective biomarker for IR in predicting stroke outcomes and a novel surrogate marker for IR (4). Recent studies have proposed that the TyG index is correlated with atherosclerosis (5, 6), serves as an independent predictor of cardiovascular events, and is associated with poor prognoses in patients with cardiovascular diseases (7, 8). Nevertheless, there is a relative scarcity of studies examining the correlation between the TyG index and the prognosis of AIS patients. This study aims to investigate the predictive value of the TyG index for the early neurological function of non-diabetic AIS patients undergoing alteplase intravenous thrombolysis (IV-rtPA), thereby aiding clinicians in rapidly assessing the prognosis of AIS patients post-intravenous thrombolysis with alteplase and in creating personalized treatment strategies.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Patient selection
This study conducted a retrospective analysis, included 490 non-diabetic patients with AIS who presented within 3 h of symptom onset and underwent IV-rtPA therapy in the Stroke Center of our hospital from September 2023 to September 2024 through the Stroke Emergency Map Management Platform in Dalian City. Inclusion criteria were as follows: meeting the Chinese Guidelines for Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute Ischemic Stroke 2023 and being first-time stroke cases, patients were eligible for IV-rtPA therapy, with successful completion of the procedure. Exclusion criteria included patients receiving bridging endovascular therapy; those diagnosed with non-stroke conditions; patients with severe cardiac, hepatic, renal, or other organ dysfunction; patients with recurrent AIS; diabetic patients; individuals who had previously taken statins; patients with incomplete clinical data; and those who failed neurological deficit assessment 24 h post-thrombolysis. According to the National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) score after IVT, patients showing a decrease of ≥4 points compared to baseline or achieving complete recovery (i.e., NIHSS score of 0) were classified as the early neurologic improvement (ENI) group (9, 10), other patients were classified as the non-ENI group. The ENI group (n = 332): 94 males and 64 females, with an average age of 68.48 ± 12.38 years; the non-ENI group (n = 158): 240 males and 92 females, with an average age of 68.19 ± 12.51 years (Figure 1).
Figure 1

Flow of included patients through the trial.
2.2 Data collection
Collect the general information of the patients (age, gender), Body Mass Index (BMI), cerebrovascular disease risk factors (hypertension, atrial fibrillation, smoking, drinking); systolic pressure (SBP), diastolic pressure (DBP) and NIHSS score before thrombolysis; time from onset to hospital arrival (min); and time from hospital arrival to IVT (min); The TOAST classification (11) for AIS was used for etiological classification of stroke [large-artery atherosclerosis (LAA), cardioembolism (CE), small-artery occlusion lacunar (SAO), stroke of other determined etiology (SOE), and stroke of undetermined etiology (SUE)]; the distribution of stroke (anterior circulation, posterior circulation, and both anterior and posterior circulation) and the occurrence of intracerebral hemorrhage transformation were assessed. The laboratory data included the white blood cell count and neutrophil count before thrombolysis; fasting blood glucose (FBG), total cholesterol (TC), triglycerides (TG), low-density lipoprotein (LDL), uric acid, and creatinine within 24 h after thrombolysis for analysis (instrument model: Siemens Healthineers ADVIA Chemistry XPT fully automated biochemical analysis system). TyG index = ln [TG (mg/dL) × FBG (mg/dL)/2] (12).
2.3 Statistical processing
SPSS 22.0 was used in statistical processing. Normally distributed measurement data were expressed as (−x ± s) and compared between groups via an independent sample t-test. Nonnormally distributed measurement data were described using M (interquartile range), and intergroup comparisons were performed using the Mann–Whitney U test. Enumeration data were presented as n (%) and compared through a chi-square test. Influencing factors were identified through binary or ordered multiclass logistic regression analysis. The predictive value of indicators was evaluated by plotting a receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve. p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3 Results
Based on the NIHSS score within 24 h, the 490 non-diabetic patients with AIS were divided into the ENI group (n = 332, 67.76%) and the non-ENI group (n = 158, 32.24%). The two groups exhibited no statistically significant differences in general patient data and vascular risk factors (p > 0.05), indicating comparability. In the ENI group, FBG, TG, TyG index and baseline NIHSS score were significantly lower than those in non-ENI group (p < 0.05), suggesting that the above factors are all influencing factors for early neurological improvement (Table 1).
Table 1
| Categories | ENI groups (n = 332) | Non-ENI groups (n = 158) | t/χ2 | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (year) | 68.19 ± 12.51 | 68.48 ± 12.38 | 0.173 | 0.863 |
| Gender (%) | 4.038 | 0.054 | ||
| Female | 92 (27.71) | 64 (40.51) | ||
| BMI (kg/m2) | 24.65 (23.23–25.9) | 24.46 (22.9–26.48) | 0.67 | 0.312 |
| Hypertension (%) | 220 (66.27) | 106 (67.09) | 0.016 | 0.898 |
| Atrial fibrillation (%) | 34 (10.24) | 6 (3.80) | 2.964 | 0.085 |
| Smoking (%) | 170 (51.20) | 70 (44.30) | 1.02 | 0.312 |
| Alcohol consumption (%) | 98 (29.52) | 40 (25.32) | 0.467 | 0.494 |
| Time from onset to hospital arrival (min) | 120.00 (60.0,180.0) | 120.00 (60.0,150.0) | −0.972 | 0.331 |
| Time from hospital arrival to IVT (min) | 29.00 (24.0,36.3) | 27.00 (21.0,36.0) | −1.907 | 0.057 |
| Baseline blood pressure (mmHg) | ||||
| Systolic blood pressure | 142.50 (126.0,159.0) | 147.00 (126.0,160.0) | −1.075 | 0.282 |
| Diastolic blood pressure | 86.00 (76.0,90.0) | 86.00 (82.0,90.0) | −1.614 | 0.107 |
| FBG (mmol/L) | 5.60 (0.22,0.43) | 6.07 (5.43,7.63) | −2.432 | 0.015 |
| TG (mmol/L) | 6.07 (5.43,7.63) | 6.07 (5.43,7.63) | −2.914 | 0.004 |
| TyGindex | 7.30 (6.86,7.66) | 7.51 (7.21,7.94) | −3.549 | 0.000 |
| TC (mmol/L) | 4.70 ± 1.18 | 4.67 ± 1.35 | −0.151 | 0.880 |
| LDL (mmol/L) | 3.00 ± 0.98 | 2.92 ± 1.00 | −0.588 | 0.557 |
| Uric acid (umol/L) | 333.09 ± 95.38 | 334.11 ± 88.74 | 0.080 | 0.936 |
| Creatinine (umol/L) | 66.00 (55.1,78.8) | 64.60 (56.1,79.3) | −0.148 | 0.883 |
| White blood cell count (109/L) | 6.965 (5.7,8.7) | 6.75 (5.9,8.8) | −0.324 | 0.746 |
| Neutrophil count (109/L) | 4.29 (3.2,5.5) | 4.42 (3.5,6.1) | −0.879 | 0.380 |
| Etiology of stroke (%) | ||||
| LAA | 158 (47.59) | 40 (50.63) | 0.198 | 0.656 |
| CE | 32 (9.64) | 6 (3.80) | 2.553 | 0.110 |
| SAO | 138 (41.57) | 70 (44.30) | 0.164 | 0.685 |
| SOE | 2 (0.60) | 2 (1.27) | 0.291 | 0.590 |
| SUE | 4 (1.20) | 2 (1.27) | 0.222 | 0.968 |
| Baseline NIHSS score (points) | 5.00 (4.0,6.0) | 7.00 (5.0,10.0) | −6.698 | 0.000 |
| Stroke distribution (%) | ||||
| Anterior circulation | 220 (66.27) | 112 (70.89) | 0.523 | 0.469 |
| Posterior circulation | 92 (27.71) | 42 (26.58) | 0.034 | 0.853 |
| Anterior and posterior circulation | 20 (6.02) | 2 (1.27) | 2.826 | 0.093 |
| Hemorrhagic transformation (%) | 4 (1.20) | 2 (1.27) | 0.002 | 0.968 |
Comparison of risk factors between ENI and non-ENI groups.
Binary Logistic regression analysis was conducted to identify the factors influencing early neurological improvement. Univariate and multivariate analyses were performed on the TyG index, TG, FBG and baseline NIHSS score. The results ultimately indicated that the TyG index and baseline NIHSS score were independent influencing factors for early neurological improvement in non-diabetic AIS patients. Specifically, the lower the TyG index and the lower the baseline NIHSS score, the better the early neurological improvement (Tables 2, 3).
Table 2
| Categories | B | S.E. | Wald | p | OR | 95% C.I. for OR | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TyG index | 0.615 | 0.227 | 7.361 | 0.007 | 1.850 | 1.186 | 2.884 |
| FBG | 0.004 | 0.003 | 1.745 | 0.187 | 1.004 | 0.998 | 1.010 |
| TG | 0.003 | 0.005 | 0.414 | 0.520 | 1.003 | 0.994 | 1.012 |
| Baseline NIHSS score | −0.307 | 0.055 | 31.372 | 0.000 | 0.736 | 0.661 | 0.819 |
Univariate regression analysis of early neurological improvement.
Table 3
| Categories | B | S.E. | Wald | p | OR | 95% C.I. for OR | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline NIHSS score | −0.318 | 0.056 | 31.714 | 0.000 | 0.728 | 0.652 | 0.813 |
| TyG index | 0.656 | 0.229 | 8.223 | 0.004 | 1.928 | 1.231 | 3.019 |
| Constant | −1.872 | 1.705 | 1.205 | 0.272 | 0.154 | ||
Multivariate regression analysis of early neurological function improvement.
After determining the optimal cutoff value of 7.15 for the TyG index from Table 4, we used 7.15 as the threshold to convert the TyG index into a binary variable. AIS patients were then divided into a high TyG index group (TyG index > 7.15, n = 195) and a low TyG index group (TyG index ≤ 7.15, n = 295). The proportions of ENI in the high and low TyG index groups were 43.3 and 77.5%, respectively, showing statistically significant differences (p ≤ 0.001). Combined with Figure 2, the AUC values of the TyG index and baseline NIHSS score are 0.640 (p < 0.001) and 0.641 (p < 0.001), respectively. The AUC value of the combined variable (Y) is the largest at 0.721 (p < 0.001), indicating a higher predictive efficacy than that of a single indicator.
Table 4
| Categories | AUC | p | 95% CI | Sensitivity | Specificity | Cutoff value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TyG index | 0.640 | <0.001 | (0.563,0.717) | 0.801 | 0.468 | 7.15 |
| Baseline NIHSS score | 0.641 | <0.001 | (0.651,0.774) | 0.814 | 0.489 | |
| Combined variable (Y) | 0.721 | <0.001 | (0.735,0.839) | 0.821 | 0.509 |
Predictive value of TyG index and baseline NIHSS score for ENI.
Figure 2
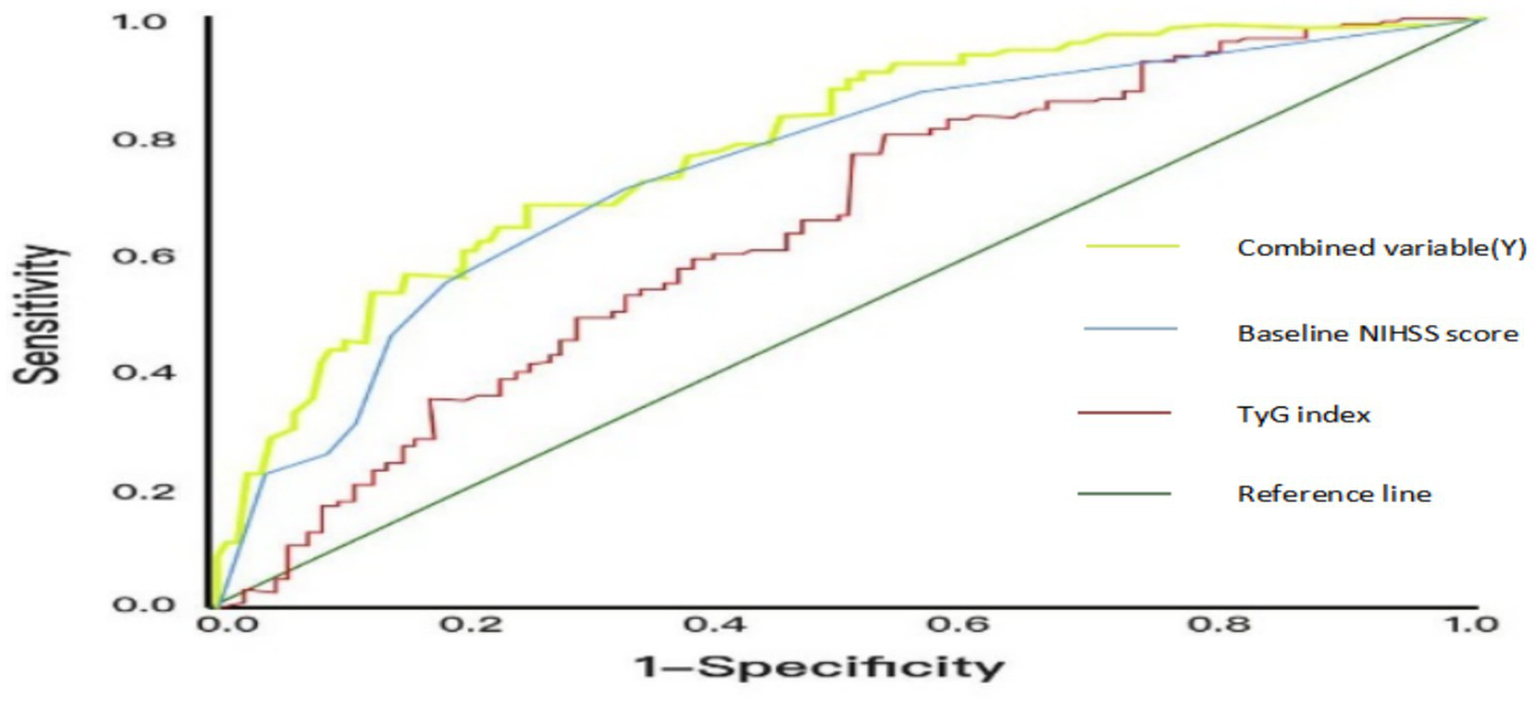
ROC curves of the predictive efficacy of TyG index, NIHSS score before thrombolysis and the combined variable (Y).
4 Discussion
Research on clinical prognostic predictors for AIS has consistently been a focal point in clinical studies, influenced by multiple factors. This paper compares various elements including patient gender, BMI index, vascular risk factors, baseline blood pressure, time from onset to intravenous thrombolysis, relevant laboratory indicators, etiological classification, cerebral infarction location, and cerebral hemorrhage transformation. Statistical differences were only observed in FBG, TG levels, TyG, and baseline NIHSS score.
In the pathological process of AIS, both metabolic disorder and inflammatory response in the body are closely related to the clinical prognosis of Homo sapiens (13). This study also focused on inflammatory markers, but primarily selected widely recognized cells that have damaging effects on ischemic brain tissue, namely leukocytes and neutrophils (14, 15). However, no statistically significant difference was observed between the ENI group and the non-ENI group in this research, which may be attributed to the limited scope of inflammatory markers examined. TyG is often closely associated with the body’s metabolic levels, particularly TG and blood glucose, and can indicate metabolic disorder. Furthermore, metabolic dysfunction can exacerbate the occurrence and progression of inflammatory response.
Currently, the pathogenesis of AIS resulting from IR is believed to involve primarily the following aspects: Firstly, reduced insulin activity diminishes glucose bioavailability, causing an imbalance in glucose and lipid metabolism. This imbalance leads to inflammation and oxidative stress. Excessive advanced glycation end products result in the proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells, collagen deposition, vascular fibrosis, increased wall stiffness, endothelial cell dysfunction, and foam cell formation. Consequently, atherosclerosis progresses (16). Secondly, IR triggers the phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrates, a process mediated by insulin-like growth factor-1 and insulin-like growth factor-2. This, in turn, initiates C-reactive protein-mediated platelet activation, leading to an increase in platelet number and volume (17). Thirdly, IR contributes to cerebrovascular reserve (CVR) via the Bayliss effect (a myogenic mechanism), as well as through chemical, neural, and metabolic mechanisms, leading to hemodynamic disturbances. The CVR in individuals with IR is lower than that observed in healthy individuals (18–20). Fourthly, IR can amplify risk factors via inflammation and oxidative stress (21, 22), such as hypertension and diabetes, accelerate the progression of atherosclerosis, reduce the level of cerebral blood flow metabolism, and lead to the occurrence and recurrence of stroke. The cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway (CAP) is a neuroimmune regulatory mechanism that plays a crucial role in immune balance and anti-inflammatory defense (23). Activating this pathway can alleviate obesity-induced inflammation and IR (24). The spleen and its sympathetic system constitute key components of the CAP pathway (23), with the spleen serving as a vital anti-inflammatory center in peripheral tissues. This suggests that spleen function may have played a significant role in early neurological improvement, though further exploration is required for confirmation.
In recent years, more and more studies have found that TyG index is closely related to ischemic stroke. However, a cohort study involving 5,014 healthy participants indicated that higher levels of the TyG index showed no significant correlation with cerebrovascular diseases (25). Nevertheless, some studies (26, 27) found that elevated TyG index was associated with stroke relapse in elderly AIS patients, and the TyG index might be a major risk factor for stroke among young adults in China. Cai et al. (28) found that TyG index can also be used as a potential risk stratification index for hospitalization and intensive care unit mortality in severe AIS patients. Lee et al. (29) found that a higher TyG index was significantly associated with a poor neurological prognosis in anterior circulation AIS patients receiving reperfusion therapy, and suggested that TyG index could help predict the short-term prognosis of AIS patients after reperfusion therapy. Zhang et al. (30) found that in patients receiving intravenous thrombolysis, a higher TyG index was associated with reduced early neurological improvement, suggesting that IR may play a role in the early neurological outcomes of AIS. Recently, a meta-analysis (31) indicates that elevated TyG index may increase cancer risk. Similarly, another meta-analysis (32) revealed significant IR resistance in cancer patients. Since IR may be a primary factor contributing to cancer-related metabolic dysfunction, this elevates risks of recurrence and mortality (32). Therefore, comprehensive tumor screening should be implemented for acute cerebral infarction patients to monitor Trophoblastic Tumor Syndrome (TTS). Additionally, attention should be paid to tumor development during long-term follow-up for secondary prevention of cerebral infarction patients.
Therefore, the choice of TyG index as a predictor of early neurological improvement in non-diabetic patients with AIS in this study is well justified. The results showed that the proportion of ENI was higher in the group with low TyG index than that in the group with high TyG index within 24 h of intravenous thrombolysis, proving that TyG index was an independent predictor of early neurological improvement in AIS patients after intravenous thrombolysis with alteplase. In addition, the NIHSS score before thrombolysis reflects the degree of neurological deficit and is also an important index for the clinical prognosis of patients, which is basically consistent with the results of previous studies (33). Therefore, the TyG index, when combined with the baseline NIHSS score, has a higher predictive value for early neurological improvement in non-diabetic patients with AIS than a single TyG index alone, which is basically consistent with previous studies. However, the combined AUC value of the two was only slightly higher than that of TyG index. The possible reasons are that the prognosis of acute cerebral infarction is affected by many factors, and the risk factors compared in this study are limited. In addition, the differences between pathogenesis, non-interventional risk factors and thrombolysis may also have an impact.
However, this study is retrospective and has certain limitations. Firstly, this experiment did not set up a healthy control group, and did not stratify and analyze the AIS patients subgroups with intravenous thrombolysis. Secondly, there are inevitable individual differences in the measurement of laboratory indicators, and only a single measurement of the TyG index after admission was evaluated, without a dynamic evaluation. The baseline NIHSS score, even if assessed by experienced neurologists, is subject to some subjective influences.
5 Conclusion
In conclusion, in patients with acute ischemic stroke treated with alteplase intravenously, the combination of TyG index and baseline NIHSS score had a higher predictive efficacy for early neurological improvement than the single TyG index. Large-scale, randomized controlled and multicenter prospective studies are needed for further demonstration in the future.
Statements
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Ethics Committee of Dalian University of Technology Affiliated Central Hospital (Dalian Municipal Central Hospital; Approval number: YN2024-072-01). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
FL: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. XS: Methodology, Writing – review & editing. XP: Supervision, Writing – review & editing. JL: Investigation, Writing – review & editing, Data curation. YG: Data curation, Writing – review & editing, Investigation. DS: Investigation, Writing – review & editing, Data curation. HZ: Writing – review & editing. DC: Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. The project was supported by the Clinical Research Project of Stroke prevention and treatment Technology (no. WKZX2023CZ0217).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1.
Powers WJ Rabinstein AA . 2018 guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American heart association/American stroke association. Stroke. (2019) 50:e344–418. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.119.026527
2.
Fahed G Aoun L Bou Zerdan M Allam S Bou Zerdan M Bouferraa Y et al . Metabolic syndrome: updates on pathophysiology and management in 2021. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:786. doi: 10.3390/ijms23020786
3.
Wu A Li YP Liu RC Qi D Yu G Yan X et al . Predictive value of insulin resistance as determined by homeostasis model assessment in acute ischemic stroke patients: a systematic review and metaanalysis. Horm Metab. (2021) 53:746–51. doi: 10.1055/a-1583-2912
4.
Si S Li J Li Y Li W Chen X Yuan T et al . Causal effect of the triglyceride-glucose index and the joint exposure of higher glucose and triglyceride with extensive cardio-cerebrovascular metabolic outcomes in the UK biobank: a Mendelian randomization study. Front Cardiovasc Med. (2021) 7:583473. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2020.583473
5.
Park GM Cho YR Won KB Yang YJ Park S Ann SH et al . Triglyceride glucose index is a useful marker for predicting subclinical coronary artery disease in the absence of traditional risk factors. Lipids Health Dis. (2020) 19:7. doi: 10.1186/s12944-020-1187-0
6.
Zhu Y Liu K Chen M Liu Y Gao A Hu C et al . Triglyceride-glucose index is associated with in-stent restenosis in patients with acute coronary syndrome after percutaneous coronary intervention with drug-eluting stents. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2021) 20:137. doi: 10.1186/s12933-021-01332-4
7.
Ding X Wang X Wu J Zhang M Cui M . Triglyceride-glucose index and the incidence of atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases: a meta-analysis of cohort studies. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2021) 20:76. doi: 10.1186/s12933-021-01268-9
8.
Wang A Wang G Liu Q Zuo Y Chen S Tao B et al . Triglyceride-glucose index and the risk of stroke and its subtypes in the general population: an 11-year follow-up. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2021) 20:46. doi: 10.1186/s12933-021-01238-1
9.
Lin CM Wu HC Wu YM Chen CH Chen WH Hsu LC et al . Computed tomography angiography in acute stroke patients receiving recombinant tissue plasminogen activator: outcome and safety evaluations in an asian population. Cerebrovasc Dis. (2020) 49:62–9. doi: 10.1159/000506679
10.
Tian C Ji Z Xiang W Zhang Y Zhang L Song J et al . Association of lower leukocyte count before thrombolysis with early neurological improvement in acute ischemic stroke patients. J Clin Neurosci. (2018) 56:44–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2018.06.044
11.
Adams HP Jr Bendixen BH Kappelle LJ Biller J Love BB Gordon DL et al . Classification of subtype of acute ischemic stroke. Definitions for use in a multicenter clinical trial. TOAST. trial of org 10172 in acute stroke treatment. Stroke. (1993) 24:35–41. doi: 10.1161/01.str.24.1.35
12.
Guerrero-Romero F Simental-Mendia LE Gonzalez-Ortiz M Martinez-Abundis E Ramos-Zavala MG Hernandez-Gonzalez SO et al . The product of triglycerides and glucose, a simple measure of insulin sensitivity. Comparison with the euglycemic-hyperinsulinemic clamp. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2010) 95:3347–51. doi: 10.1210/jc.2010-0288
13.
Zhang L Wang H Ma Q Liu Y Chen Y He Y et al . Value of the triglycerideglucose index and non-traditional blood lipid parameters in predicting metabolic syndrome in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Hormones. (2023) 22:263–71. doi: 10.1007/s42000-023-00435-9
14.
Macrez R Ali C Toutirais O Le Mauff B Defer G Dirnagl U et al . Stroke and the immune system: from pathophysiology to new therapeutic strategies. Lancet Neurol. (2011) 10:471–80. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(11)70066-7
15.
Yang K Zeng L Ge A Wang S Zeng J Yuan X et al . A systematic review of the research progress of non-coding RNA in neuroinflammation and immune regulation in cerebral infarction/ischemia-reperfusion injury. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:930171. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.930171
16.
Lu Y Chang C Chou R Li C Liu W Lin M et al . Gender difference in the association between TyG index and subclinical atherosclerosis: results from the I-lan longitudinal aging study. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2021) 20:206. doi: 10.1186/s12933-021-01399-z
17.
Xu X Huang R Lin Y Lin Y Yang C Chen Y et al . High triglyceride-glucose index in young adulthood is associated with incident cardiovascular disease and mortality in later life: insight from the CARDIA study. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2022) 21:155. doi: 10.1186/s12933-022-01590-w
18.
Deng X Liu Z Wang C Li Y Cai Z . Insulin resistance in ischemic stroke. Metab Brain Dis. (2017) 32:1323–34. doi: 10.1007/s11011-017-0050-0
19.
Baydar O Kilic A Okcuoglu J Apaydin Z Ozturk U Aslan B et al . The triglyceride-glucose index, a predictor of insulin resistance, is associated with subclinical atherosclerosis. Angiology. (2021) 72:994–1000. doi: 10.1177/00033197211007759
20.
Jung MH Yi SW An SJ Shin DH Han SW Kim HC et al . Associations between the triglyceride-glucose index and cardiovascular disease in over 150000 cancer survivors: a population-based cohort study. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2022) 21:52. doi: 10.1186/s12933-022-01482-z
21.
Xiao J Padrick MM Jiang T Liu Q Chen H Wang Y et al . Acute ischemic stroke versus transient ischemic attack: differential plaque morphological features in symptomatic intracranial atherosclerotic lesions. Atherosclerosis. (2021) 319:72–8. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2021.01.002
22.
Jing J Pan Y Zhao X Zheng H Jia Q Mi D et al . Insulin resistance and prognosis of nondiabetic patients with ischemic stroke: the ACROSS-China study (abnormal glucose regulation in patients with acute stroke across China). Stroke. (2017) 48:887–93. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.116.015613
23.
Wang W Xu H Lin H Chen L Zhao X Zhang Y . The role of the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway in septic cardiomyopathy. Int Immunopharmacol. (2021) 90:107160. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107160
24.
Costa SO Souza CM Lanza PG Almeida MV Lima RF Santos-Silva JC et al . Maternal high fat diet consumption reduces liver alpha 7 nicotinic cholinergic receptor expression and impairs insulin signalling in the offspring. Sci Rep. (2020) 10:48. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-56880-3
25.
Sánchez-Íñigo L Navarro-González D Fernández-Montero A Pastrana-Delgado J Martínez JA . The TyG index may predict the development of cardiovascular events. Eur J Clin Investig. (2016) 46:189–97. doi: 10.1111/eci.12583
26.
Wang F Wang JJ Han YF Hao P Zhang XM Guo ZN et al . Triglyceride-glucose index and stroke recurrence in elderly patients with ischemic stroke. Front Endocrinol. (2022) 13:1005614. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1005614
27.
Xu WQ Zhao HY Han X Guo ZN Yang Y Jin H . Relationship between early-onset stroke and triglyceride-glucose index among young Chinese adults. Lipids Health Dis. (2023) 22:3. doi: 10.1186/s12944-022-01763-2
28.
Cai W Xu J Wu X Chen Z Zeng Y Yuan Z et al . Association between triglyceride-glucose index and all-cause mortality in critically ill patients with ischemic stroke: analysis of the MIMIC-IV database. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2023) 22:138. doi: 10.1186/s12933-023-01870-z
29.
Lee M Kim C Kim Y Cho YJ Hong KS Lee JH et al . High triglyceride glucose index is associated with poor outcomes in ischemic stroke patients after reperfusion therapy. Cerebrovasc Dis. (2021) 50:691–9. doi: 10.1159/000519229
30.
Zhang B Lei H Ambler G Werring DJ Fang S Li H et al . Association between triglyceride-glucose index and early neurological outcomes after thrombolysis in patients with acute ischemic stroke. J Clin Med. (2023) 12:3471. doi: 10.3390/jcm12093471
31.
Wang H Yan F Cui Y Li J Zhang R Liu S et al . Association between triglyceride glucose index and risk of cancer: a meta-analysis. Front Endocrinol. (2023) 13:1098492. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1098492
32.
Marmol JM Carlsson M Raun SH Gerdes C Nielsen ML Madsen MA et al . Insulin resistance in patients with cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Oncol. (2023) 62:364–71. doi: 10.1080/0284186X.2023.2197124
33.
Ryu WS Hong KS Jeong SW Park HJ Bae HJ Choi JC et al . Association of ischemic stroke onset time with presenting severity, acute progression, and long-term outcome: a cohort study. PLoS Med. (2022) 19:e1003910. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1003910
Summary
Keywords
acute ischemic stroke, intravenous thrombolysis, early neurological improvement, triglyceride-glucose index, non-diabetic patients
Citation
Li F, Sui X, Pan X, Li J, Gao Y, Shi D, Zhao H and Chen D (2025) The predictive value of triglyceride-glucose index on early neurological functional improvement in non-diabetic patients with acute ischemic stroke undergoing intravenous thrombolysis. Front. Neurol. 16:1626196. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1626196
Received
03 June 2025
Accepted
02 September 2025
Published
22 September 2025
Volume
16 - 2025
Edited by
Shuling Liu, Tianjin Medical University, China
Reviewed by
Giovanni Tarantino, University of Naples Federico II, Italy
Deni Iriyadi, Universitas Islam Negeri Sultan Maulana Hasanuddin Banten, Indonesia
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Li, Sui, Pan, Li, Gao, Shi, Zhao and Chen.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hongling Zhao, zhaohongling2000@126.comDong Chen, neuro-chen@163.com
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.