Abstract
Background:
Recent trials of large core thrombectomy have shown that our traditional understanding of infarct characteristics and reperfusion benefit may be incomplete for patients with acute ischemic stroke (AIS). The Alberta Stroke Program Early CT Score (ASPECTS) has wide inter-rater variability, and modern studies have also shown that reperfusion therapies can benefit some patients regardless of the ASPECTS. Reproducible imaging metrics that account for the degree of hypo-attenuation on non-contrast computed tomography (NCCT) may be better suited to guide treatments. Here, we evaluate Net Water Uptake (NWU), a novel NCCT metric that can be calculated in a rapid and automated fashion, to determine its predictive performance for identifying clinical outcomes in patients with AIS compared to ASPECTS.
Methods:
From our prospectively collected registry encompassing 11 certified stroke centers, we identified patients with AIS. CT images were pre-processed and segmented, then NWU was calculated by automated comparison of density on ipsilateral and contralateral brain regions. Primary outcome was the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC) for competing multivariable regression models with Average NWU versus ASPECTS to predict 90-day outcome measured by modified Rankin Scale (mRS). Regression models were adjusted for age, National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS), tPA administration, and endovascular therapy. Secondary analyses included subgroup comparisons of patients with large infarct core and late time window.
Results:
Among 402 subjects with anterior circulation AIS, median age was 69 [IQR 57–80], 49.3% were female, median NIHSS was 11 [IQR 5–19], median ASPECTS was 9 [IQR 7–10], and median 90-day mRS was 3 [IQR 1–5]. The ASPECTS-based model performance was not significantly different from the NWU-based model to classify 90-day mRS outcome, with AUROC 0.732 and 0.749, respectively, (p = 0.513 with Delong test). Among the subgroups, performance was again similar, including patients with large infarct core (AUROC 0.795 vs. 0.863, p = 0.312) and late time window (AUROC 0.638 vs. 0.677, p = 0.267).
Conclusion:
NWU is a quantitative metric that can be rapidly and automatically obtained from non-contrast CT with comparable performance to ASPECTS when predicting 90-day functional outcome across a wide range of AIS presentations.
Introduction
Stroke is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality in the United States, and despite the development of thrombolysis and endovascular therapy (EVT) for patients with acute ischemic stroke (AIS), up to half of patients still experience poor clinical outcomes (1–6). Recent randomized trials have shown us that our traditional paradigm to predict who will return to functional independence after AIS is incomplete, and our understanding will now need to go beyond “time is brain” and existing estimates of infarct size on pre-treatment imaging (5–12).
Most stroke centers utilize non-contrast computed tomography (NCCT) to triage patients with ischemic stroke, and a common marker to estimate early infarct severity is the Alberta Stroke Program Early CT Score (ASPECTS) (13, 14). Modern trials have shown us that reperfusion therapies can benefit some patients regardless of how low the ASPECTS is, and there are also a large proportion of patients who do poorly despite having a good ASPECTS (8–10, 15–17). Furthermore, ASPECTS has wide inter-rater variability, and unfortunately in many settings there is limited access to neuroradiology expertise (18, 19). CT perfusion (CTP) imaging has also been used for treatment selection; however, CTP is resource intensive, only effective in a narrow set of circumstances, and can otherwise be plagued with overestimation of the infarct core and inability to identify many infarcts (20–22).
Therefore, we aimed in this study to evaluate net water uptake (NWU) as a new NCCT biomarker that could be automated and highly reliable to predict post-stroke outcomes. NWU is a measurement of brain injury and edema based on the degree of hypoattenuation in the stroke area compared to contralateral normal tissue (23). The equation to calculate net water uptake is Net Water Uptake (%) = 1 - (Density_ipsilateral / Density_contralateral) × 100. NWU is a tissue-level measurement and more granular than traditional imaging scores which are evaluated at the subject level. Early studies have shown NWU reliably predicts malignant cerebral edema and poor outcomes after AIS (24–28). Here, we used a prospectively collected registry cohort to evaluate our recently developed automated algorithm that calculates NWU in the primary regions of the anterior circulation territory on NCCT after image registration and segmentation (see Figure 1). We hypothesized that automated NWU will have non-inferior performance compared to neuroradiologist-assessed ASPECTS when predicting post-stroke functional outcomes.
Figure 1

The algorithm for automated net water uptake calculation includes pre-processing, segmentation, and density calculations. On the right, the example results demonstrate how NWU quantifies the degree of injury in each stroke region. DICOM, Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine; NIfTI, Neuroimaging Informatics Technology Initiative; MNI, Montreal Neurological Institute; ASPECTS, Alberta Stroke Program Early CT Score; NWU, net water uptake; and HU, Hounsfield Units.
Methods
Study cohort
From our prospective registry including 11 certified stroke centers in Houston, TX, USA, we identified consecutive patients who were treated for acute ischemic stroke between 2018 and 2022. All included subjects underwent acute screening in the emergency department with non-contrast CT. The final stroke diagnosis was confirmed clinically and radiographically by a board-certified vascular neurologist, and subjects were excluded if the stroke occurred in the posterior circulation, if the imaging was not interpretable, or if follow-up outcomes were not recorded. The STROBE guidelines were used for the formulation of this study design and manuscript. This study was performed under the guidelines from the Helsinki Declaration and IRB HSC-MS-19-0630 approved by the University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston (UTHealth Houston) IRB and Memorial Hermann Hospital. Data and code will be made available upon reasonable request.
Clinical measurements
Demographic data and baseline clinical characteristics were recorded, including the use of thrombolysis and endovascular therapy. Imaging characteristics were determined using the radiology reports of the NCCT and CT angiography. Specifically, ASPECTS was determined by expert neuroradiologists and interventional neurologists each with several years of clinical experience. For subjects who underwent EVT, the reperfusion grades were recorded prospectively at the time of the procedure using the thrombolysis in cerebral infarction (TICI) score. The discharge and 90-day clinical outcomes were adjudicated by independent investigators who were not involved in the treatments and were trained in evaluating the modified Rankin Scale and secondary outcomes.
Imaging analysis
All subjects underwent non-contrast CT at the time of presentation to the emergency department. The acquisition scanners vary between the certified stroke centers and include machines manufactured by GE (LightSpeed, Optima, Discovery, or Revolution), Philips (Ingenuity), Siemens (SOMATOM, Emotion, or Sensation), and Toshiba (Aquilion). All images had a slice thickness of 5 mm, and standardized field of view was applied prior to analysis. All imaging data were de-identified to ensure blinded evaluation. The imaging analysis algorithm developed for this study utilized recommendations from previously validated pre-processing pipelines for CT brain imaging and the steps followed a simple pathway including DICOM to NIfTI format conversion, field of view selection, voxel smoothing, skull stripping (brain extraction), and registration to a standard brain atlas (29–35). The MNI-152 atlas was utilized for this registration (36). The brain images were then segmented into the 10 stroke regions of the anterior circulation using custom image masking (caudate, lentiform nucleus, internal capsule, insula, M1, M2, M3, M4, M5, and M6). Segmentations were visually inspected for accuracy. Voxels were excluded from the density calculation if they were outside the range of 20–50 Hounsfield units, which allowed automatic exclusion of encephalomalacia, calcifications, and acute hemorrhage. Finally, the voxel densities in each region were averaged and the NWU was calculated. In doing so, the output for each NCCT is a list of 10 NWU values corresponding to the 10 standard stroke regions. To derive a single final measurement per subject, two methods of averaging were evaluated: in the primary analysis, a conventional average of all 10 NWU values, and in secondary analysis, a weighted average where the weight is the volume of each region. The conventional average NWU across all 10 regions can reflect both the size of the infarct and the degree of hypoattenuation.
Study outcomes
The primary outcome was the performance of average NWU and clinical variables to predict 90-day functional outcome measured by the modified Rankin Scale (mRS). Good functional outcome was defined as mRS 0–2, and poor outcome mRS 3–6. The NWU model’s performance was directly compared against a parallel model based on ASPECTS. This 90-day outcome was assessed in secondary subgroups as well, including subjects in the very early time window (0–3 h from last known well), late time window (6–24 h), small presenting infarct core (ASPECTS 6–10), and large infarct core (ASPECTS 0–5). The additional outcomes included the presence of precise neurologic deficits at time of hospital discharge: language impairment, visual impairment, the need for walking assistance, decreased level of consciousness (LOC), arm and leg motor weakness, and severe dysphagia requiring gastrostomy placement. Language impairment was defined as any deficit with fluency or comprehension, and visual impairment was defined as persistent quadrantanopia or hemianopia. Walking assistance was defined as requiring a device for mobility such as a rolling walker or wheelchair. LOC deficit was defined as obtundation or comatose state, and motor weakness was defined as 0 to 3 on the Medical Research Council scale for muscle strength.
Statistical analysis
Descriptive statistics were used to evaluate the patient demographics and stroke presentation data to understand the baseline characteristics of the entire cohort. The Fisher test for categorical variables and the Wilcoxon Rank Sum test for continuous variables were used to evaluate the differences between patients with favorable and unfavorable primary outcomes. Additionally, imaging characteristics and treatment data were compared for variables such as occlusion location, ASPECTS, tPA administration, and whether or not EVT was performed.
To evaluate the primary outcome, two multivariable logistic regression models were created, adjusting for confounding clinical variables. The first model used the automated average NWU calculation, and the second model used neuroradiologist-assessed ASPECTS. The included confounders were chosen a priori because of their known association with post-stroke clinical outcomes, including age, National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS), received tPA, and received EVT. The predictive performance was quantified by the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC), and the two models were compared with the Delong test. The cohort was randomly divided 80:20 into training and testing sets to perform this AUROC analysis, and the data partitions maintained the representation of the two outcome classes. To evaluate the secondary outcomes, multivariable logistic regression models were developed and compared in a similar fashion. In addition, to further study the nuanced new biomarker, univariable logistic regression was conducted to determine the association between NWU from specific brain regions and the individual neurologic outcomes. Lastly, we evaluated subsets of the study cohort to explore where NWU and ASPECTS may perform better or worse, including the very early and late time windows as well as small and large infarct cores. For all statistical tests, a p-value < 0.05 was considered significant. Analyses were performed with the open-source statistical software R (37).
Results
Among 402 patients with AIS, median age was 69 [IQR 57–80], 49.3% were female, median NIHSS was 11 [IQR 5–19], and median pre-morbid mRS was 0 [IQR 0–1] (see Table 1). In addition, 67.2% had a large vessel occlusion, median ASPECTS was 9 [IQR 7–10], 44.3% received tPA, 39.1% received endovascular therapy, and median 90-day mRS was 3 [IQR 1–5]. All 402 subjects had successful automated NCCT image processing, and the median time to perform NWU calculations was 87 s [IQR 77–95].
Table 1
| Variable | Total cohort (n = 402) | 90-day mRS 0–2 (n = 180) | 90-day mRS 3–6 (n = 222) | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years), median [IQR] | 69 [57, 80] | 67 [54, 77] | 71 [59, 82] | 0.009 |
| Female Sex, n (%) | 198 (49.3%) | 89 (49.4%) | 109 (49.1%) | 0.51 |
| Race: | ||||
| White, n (%) | 245 (60.9%) | 121 (67.2%) | 124 (55.9%) | -- |
| Black or African American, n (%) | 102 (25.4%) | 34 (18.9%) | 68 (30.6%) | 0.007 |
| Asian, n (%) | 17 (4.2%) | 8 (4.4%) | 9 (4.1%) | 1 |
| Other, n (%) | 38 (9.5%) | 17 (9.4%) | 21 (9.5%) | 0.61 |
| Ethnicity: Hispanic, n (%) | 86 (21.4%) | 42 (23.3%) | 44 (19.8%) | 0.39 |
| Diabetes history, n (%) | 108 (26.9%) | 46 (25.6%) | 62 (27.9%) | 0.50 |
| Hypertension history, n (%) | 276 (68.7%) | 125 (69.4%) | 151 (68.0%) | 0.91 |
| Hyperlipidemia history, n (%) | 152 (37.8%) | 74 (41.1%) | 78 (35.1%) | 0.35 |
| Atrial fibrillation history, n (%) | 65 (16.2%) | 27 (15.0%) | 38 (17.1%) | 0.50 |
| Tobacco use, n (%) | 78 (19.4%) | 46 (25.6%) | 32 (14.4%) | 0.011 |
| LKW to Arrival (minutes), median [IQR] | 280 [103, 670] | 202 [98, 510] | 407 [106, 738] | 0.047 |
| NIHSS on Arrival, median [IQR] | 11 [5, 19] | 6 [3, 12] | 16 [7, 21] | <0.001 |
| Baseline mRS, median [IQR] | 0 [0, 1] | 0 [0, 1] | 0 [0, 2] | <0.001 |
| Occlusion location: | ||||
| Intracranial ICA, n (%) | 59 (14.7%) | 20 (11.1%) | 39 (17.6%) | -- |
| MCA M1, n (%) | 132 (32.8%) | 44 (24.4%) | 88 (39.6%) | 1 |
| MCA distal, n (%) | 61 (15.2%) | 29 (16.1%) | 32 (14.4%) | 0.12 |
| ACA, n (%) | 4 (1.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 4 (1.8%) | 1 |
| No LVO, n (%) | 132 (32.8%) | 84 (46.7%) | 48 (21.6%) | <0.001 |
| ASPECTS, median [IQR] | 9 [7, 10] | 10 [8, 10] | 8 [5, 10] | <0.001 |
| CTP infarct core estimation (mL), mean +/− SD | 27.1 +/− 45.4 | 4.8 +/− 15.4 | 18.3 +/− 41.8 | 0.007 |
| Received IV tPA, n (%) | 178 (44.3%) | 90 (50.0%) | 88 (39.6%) | 0.043 |
| Received Endovascular Therapy, n (%) | 157 (39.1%) | 57 (31.7%) | 100 (45.0%) | 0.007 |
| Endovascular outcome TICI 2b-3, n (% of those who received EVT) | 139 (88.5%) | 55 (96.5%) | 84 (84.0%) | 0.052 |
| Length of Stay (days), median [IQR] | 4 [2, 7] | 3 [2, 5] | 5 [3, 9] | <0.001 |
| 90-day mRS, median [IQR] | 3 [1, 5] | 1 [0, 1] | 4 [4, 6] | <0.001 |
Baseline and imaging characteristics of patient cohort.
IQR, interquartile range; LKW, last known well; NIHSS, National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale; mRS, modified Rankin Scale; ICA, internal carotid artery; MCA, middle cerebral artery; ACA, anterior cerebral artery; LVO, large vessel occlusion; ASPECTS, Alberta Stroke Program Early CT Score; CTP, CT Perfusion, mL, milliliters; tPA, tissue plasminogen activator; TICI = thrombolysis in cerebral infarction; EVT, endovascular therapy. Continuous variables were compared using Wilcoxon rank sum test, and categorical variables were compared using Fisher’s exact test. All analyses were performed in the R statistical software.
In multivariable logistic regression, lower ASPECTS and higher average NWU was associated with greater likelihood of poor functional outcome measured by 90-day mRS (OR 0.84 [CI 0.74, 0.95] and OR 1.14 [CI 1.02, 1.26], respectively). See Table 2 for full results. In ROC analysis, the ASPECTS-based model performed the same as the NWU-based model when classifying 90-day mRS outcome, with AUROC 0.732 and 0.749, respectively, (p = 0.513 with Delong test, see Figure 2).
Table 2
| Variable | Odds ratio | 95% Confidence interval | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| ASPECTS-based Model | |||
| Age (years) | 1.02 | [1.00, 1.03] | 0.017 |
| NIHSS on arrival | 1.10 | [1.06, 1.14] | <0.001 |
| Received IV tPA | 0.48 | [0.31, 0.76] | 0.002 |
| Received Endovascular Therapy | 0.71 | [0.42, 1.21] | 0.21 |
| ASPECTS | 0.84 | [0.74, 0.95] | 0.008 |
| NWU-based Model | |||
| Age (years) | 1.02 | [1.00, 1.03] | 0.046 |
| NIHSS on arrival | 1.11 | [1.07, 1.15] | <0.001 |
| Received IV tPA | 0.50 | [0.31, 0.78] | 0.003 |
| Received Endovascular Therapy | 0.79 | [0.46, 1.33] | 0.37 |
| Average NWU | 1.14 | [1.02, 1.26] | 0.019 |
Multivariable regression analysis to predict poor 90-day clinical outcome (mRS 3–6) with ASPECTS-based model and NWU-based model.
ASPECTS, Alberta Stroke Program Early CT Score, NIHSS, National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale, tPA, tissue plasminogen activator, NWU, net water uptake. All analyses were performed in the R statistical software.
Figure 2
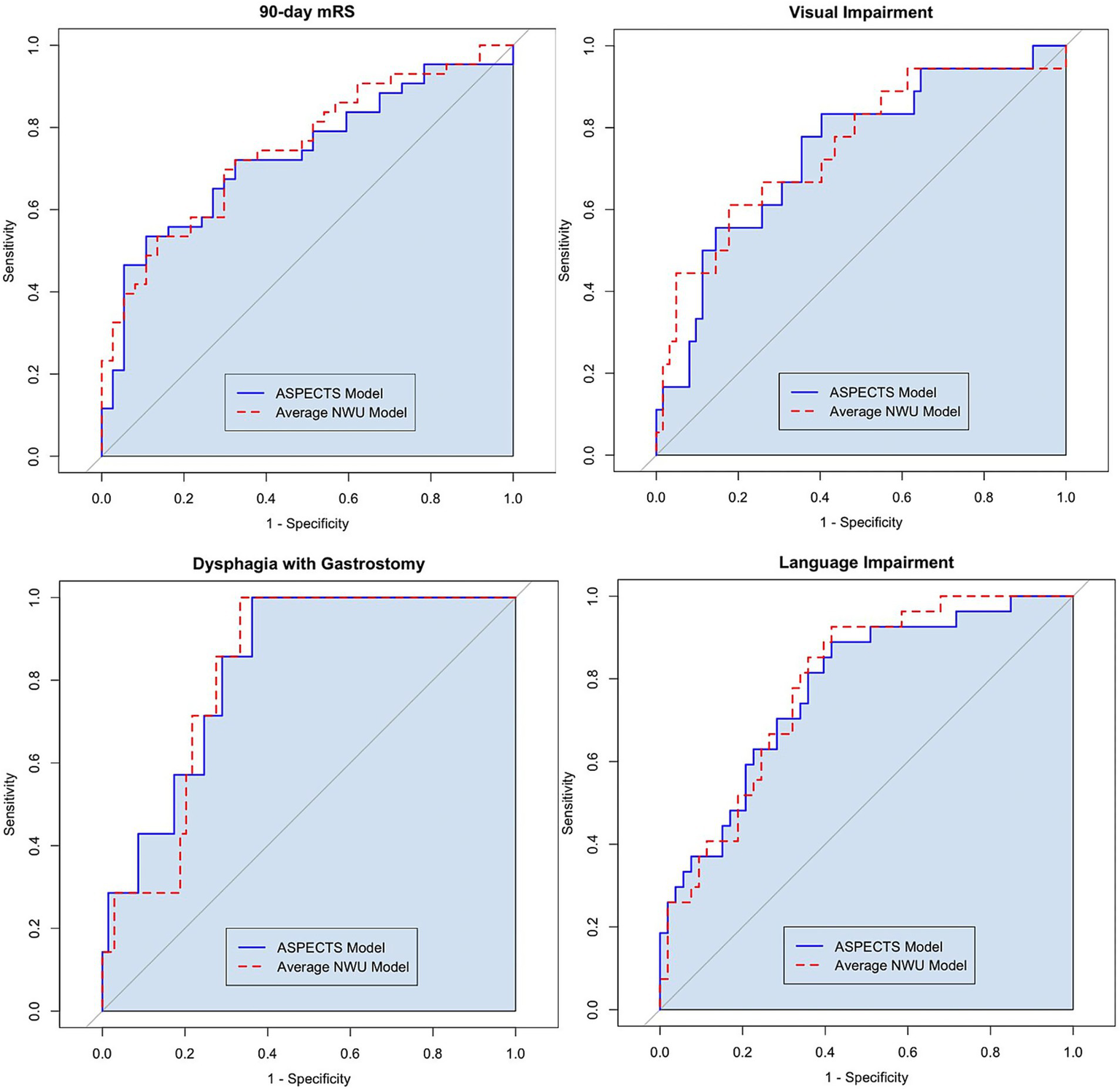
To evaluate the predictive performance of the ASPECTS and NWU models, the AUROC values were compared with the Delong test. When predicting 90-day mRS 3–6, AUROC 0.732 for the ASPECTS-based model vs. AUROC 0.749 for the NWU-based model (p = 0.513). When predicting visual Impairment, AUROC 0.743 for the ASPECTS-based model vs. AUROC 0.752 for the NWU-based model (p = 0.773). When predicting dysphagia with gastrostomy, AUROC 0.832 for the ASPECTS-based model vs. AUROC 0.822 for the NWU-based model (p = 0.724). When predicting language Impairment, AUROC 0.776 for the ASPECTS-based model vs. AUROC 0.787 for the NWU-based model (p = 0.639).
In the secondary analysis, the ASPECTS and NWU models showed varying levels of performance to predict 90-day mRS outcome among different clinically relevant subgroups (see Table 3). The NWU-based model had excellent performance when classifying 90-day mRS outcome for patients with large infarct core at presentation defined as ASPECTS 0–5 (AUROC 0.863). In addition, the models seemed to perform better for the subgroup presenting in the very early time window (less than 3 h from last known well) compared to the late time window. Overall, the differences in performance between subgroups that were seen by the ASPECTS-based model were mirrored by the NWU-based model.
Table 3
| Patient subset | ASPECTS model performance (AUROC) | NWU model performance (AUROC) | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Large vessel occlusion, n = 270 | 0.775 | 0.770 | 0.76 |
| Very early time window (presenting less than 3 h from last known well), n = 86 | 0.734 | 0.743 | 0.34 |
| Late time window (presenting 6 to 24 h from last known well), n = 100 | 0.638 | 0.677 | 0.27 |
| Small estimated infarct core at presentation (ASPECTS 6–10), n = 336 | 0.713 | 0.715 | 0.76 |
| Large estimated infarct core at presentation (ASPECTS 0–5), n = 66 | 0.795 | 0.863 | 0.31 |
Exploring the performance of NWU and ASPECTS in clinically relevant subgroups to predict poor 90-day functional outcome.
Both models included the confounder variables age, NIHSS, received tPA, and received EVT. Multivariable logistic regression models were developed to predict poor 90-day mRS 3–6, and AUROC values were statistically compared using the Delong test. All analyses were performed in the R statistical software. ASPECTS, Alberta Stroke Program Early CT Score; NWU, net water uptake; AUROC, area under the receiver operating characteristic curve; NIHSS, National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale; tPA, tissue plasminogen activator; EVT, endovascular therapy; mRS, modified Rankin Scale.
Among the secondary outcomes, average NWU showed a significant association in multivariable logistic regression with several individual neurologic deficits including language impairment, visual impairment, severe dysphagia, arm and leg motor weakness, and LOC deficit at hospital discharge (see Supplemental Table 1). The NWU and ASPECTS-based models performed similarly, and this performance was consistently excellent or very good based on AUROC (see Figure 2 and Supplementary Figure 1). For example, when predicting language impairment at discharge, the NWU-based model showed an AUROC of 0.787 versus the ASPECTS-based model AUROC of 0.776 (p = 0.639 with Delong test).
When examining the association between individual brain regions and specific neurologic deficits, logistic regression showed that most of the brain regions showed consistently significant predictive power for the precise deficits except for the caudate and M4 region (see Figure 3 and Supplemental Figure 2). Particular deficits were not isolated to certain brain regions, but rather NWU in almost any region showed significant association to each precise outcome. Lastly, four case examples are shown in Figure 4 to demonstrate some common clinical scenarios and the resulting ASPECTS and NWU findings.
Figure 3
![Forest plot showing the odds ratios for various brain regions' impact on 90-day mRS outcomes. Each row represents a region with a point estimate and confidence interval. Regions include Caudate, Lentiform, Internal Capsule, and others, with odds ratios ranging from 1.05 to 1.33. Average NWU has the highest odds ratio of 1.33 [1.19-1.48].](https://www.frontiersin.org/files/Articles/1629434/xml-images/fneur-16-1629434-g003.webp)
The secondary analysis evaluated the association of NWU from individual regions and 90-day Functional Outcome. The 10 stroke regions are represented as well as Average NWU and Weighted Average NWU. On the right, the results of univariable logistic regression are displayed for the prediction of 90-day mRS outcome (represented with Odds Ratio and 95% confidence intervals).
Figure 4
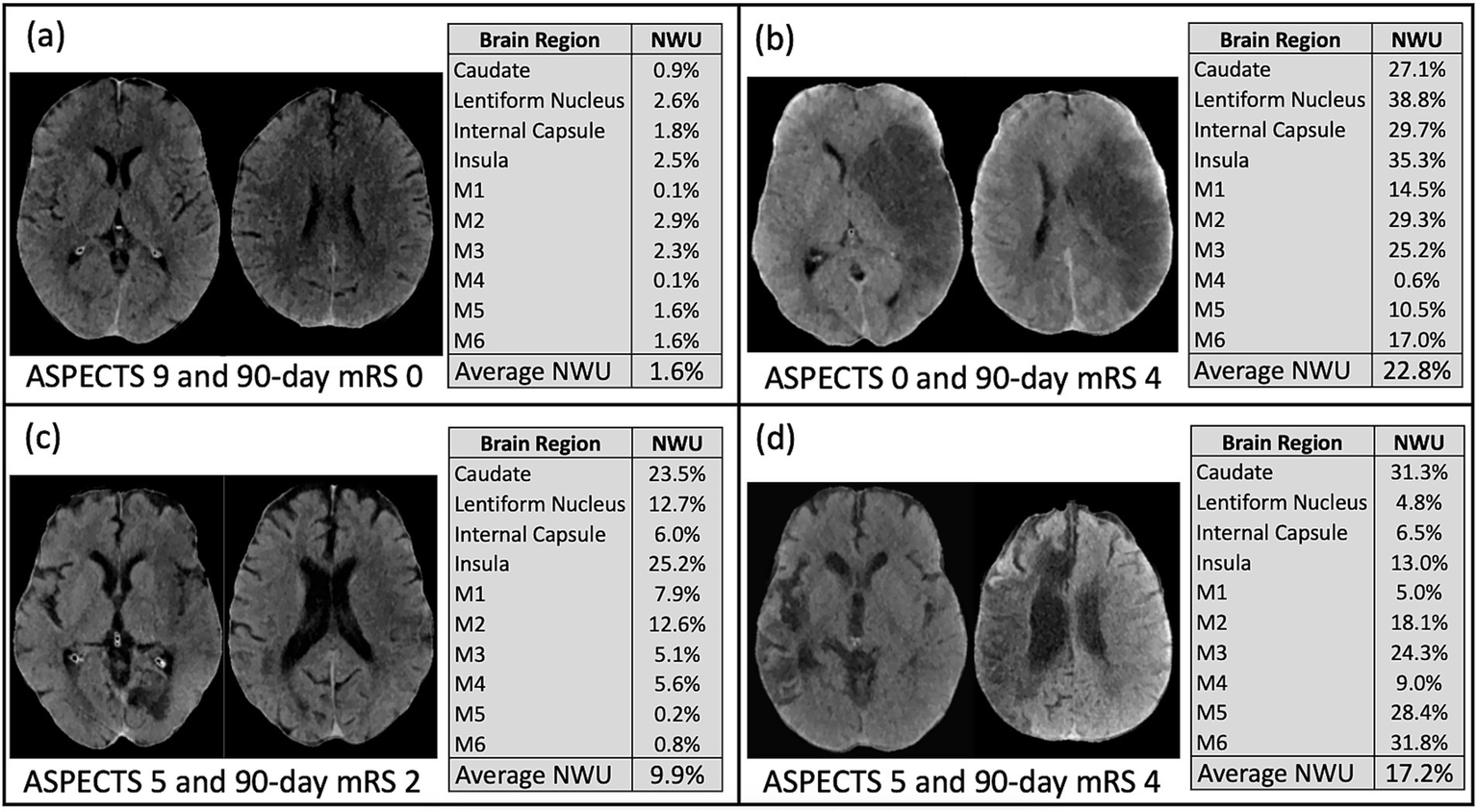
These four examples from the study cohort demonstrate common clinical scenarios. (a) Subject with ASPECTS 9, average NWU 1.6%, and 90-day mRS 0; (b) Subject with ASPECTS 0, average NWU 22.8%, and 90-day mRS 4; (c) Subject with ASPECTS 5, average NWU 9.9%, and 90-day mRS 2; (d) Subject with ASPECTS 5, average NWU 17.2%, and 90-day mRS 4.
Discussion
In this cohort study of over 400 patients with anterior circulation acute ischemic stroke, we demonstrate the utility of a novel imaging biomarker, net water uptake, that quantifies hypoattenuation in brain regions on NCCT in a fully automated manner. We found that the performance of this marker, which can be calculated within 2 min, is equivalent to expert neuroradiologist-defined ASPECT scoring, across the entire cohort as well as select crucial subgroups.
One of the first clinical studies of NWU investigated its use as a “tissue-clock” to predict ischemic stroke time window based on non-contrast CT (23). Studies have also demonstrated that NWU is useful for predicting midline shift and the presence of malignant cerebral edema to potentially inform the need for decompressive hemicraniectomy (24, 27, 28). Some of these early studies have relied on advanced imaging for segmentation of infarct core prior to calculating NWU in the predicted core or region-of-interest, so we sought to develop an agnostic approach that calculated NWU in 10 standard regions using NCCT alone (23, 24, 27, 28, 38). In addition, some studies have relied on commercial software from biotechnology companies which limits widespread use compared to this open-access approach (26–28). Lastly, instead of predicting imaging outcomes, our study focused on the prediction of long-term clinical outcomes that can help guide treatment decision-making and patient expectations. This study demonstrated that automated NWU is highly reliable as an independent predictor of these clinical outcomes and performs equally to the ASPECT score which requires a subjective visual assessment by a trained neuroradiologist or neurologist. NWU provides a granular measurement of tissue injury and edema which adds new quantitative information beyond the 0 to 10 scale of the ASPECTS. We suspect this imaging marker is quantifying localized edema from irreversible ischemia and early immunological response (38–41). Not only could NWU be studied in future trials to improve treatment selection for thrombolysis and EVT, but it could also prove to be useful to stratify patients for new investigative treatments such as neuroprotectants and immunomodulatory agents.
In the secondary analysis, we observed that NWU and ASPECTS generally have a stronger association with 90-day outcome for patients in the very early time window and also those who are presenting with a large infarct core. This study was not powered to identify differences in biomarker performance among these subpopulations, so future studies will be focused on evaluating the utility of NWU to triage these difficult cases. For example, recent randomized controlled trials showed a benefit of endovascular therapy for patients with ASPECTS in the range of 0 to 5, suggesting the scale can no longer be relied upon for EVT decision-making (8–10). Automated NWU could not only fill this gap, but it could be accomplished with freely available software and only non-contrast CT.
Clinical scales like the mRS and the NIHSS are not always reflective of how patients rate their own disability after stroke, are biased toward motor disability, and are not fully reliable to gage long-term disability (42–47). We anticipate that a more personalized approach is required in the future of stroke care, and in this study NWU has also shown strong association with individual neurologic outcomes that impact a patient’s quality of life and daily activities. The NWU from individual regions of the brain were shown to have a strong association with precise neurologic deficits such as language impairment, visual impairment, and severe dysphagia. Furthermore, these secondary outcomes were assessed at time of hospital discharge instead of long-term follow up, because 90-day outcomes are influenced by many factors that are not directly stroke related including insurance status, resource availability, and systemic disparities. For example, recent studies have demonstrated that lower rates of acute and post-acute treatments were observed in Black patients with stroke compared to their White counterparts (48–51). Our study demonstrated a similar finding in that there was a significant difference in rate of good 90-day mRS among Non-Hispanic Black patients compared to White patients (Table 1), but there was no significant difference in disability between races at the time of hospital discharge (26% vs. 20% respectively, p = 0.117). Although this study was not focused on this research question, the finding suggests that there may be disparities in post-hospital stroke care that affect long-term recovery and should be further investigated in future studies.
This study has limitations. Because of the observational and retrospective nature of this cohort study, the lack of randomization can introduce confounding factors that are not fully accounted for in the baseline comparison in Table 1. The primary analysis did not include all possible co-variables, so there is potential for residual confounding. On the other hand, the population is representative of commonly seen cohorts with AIS in both real-world practice and prospective randomized trials (1, 4, 7). Also, the study cohort only sampled from a single geographic region, a large metropolitan area in the southern United States (Houston, TX), so the findings will need to be replicated in a geographically diverse future study. Additionally, the study population contained both patients with and without LVO, yet the novel imaging marker was still strongly associated with the outcomes in subgroups. As an automated and easy-to-use NCCT triage tool, NWU could be widely applicable among patients with AIS, however future trials can investigate its potential benefit for treatment decision-making among sub-populations and for specific reperfusion or neuroprotectant therapies. When compared to ASPECTS, automated NWU is invulnerable to subjectivity and inter-rater variability, provides a new degree of nuance to NCCT evaluation, and could be used even in settings where vascular neurology and neuroradiology expertise are not available.
In summary, we found that a fully automated NWU assessment provided quantitative evaluation of ischemia equivalent to expert neuroradiologist-assessed ASPECT scoring when predicting clinical outcomes. Because of its ease of acquisition and quantified outputs that are not subject to inter-rater disagreements, NWU may serve as a useful tool for clinical practice and upcoming clinical trials.
Statements
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston Institutional Review Board (Approval number: HSC-MS-19-0630). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The ethics committee/institutional review board waived the requirement of written informed consent for participation from the participants or the participants' legal guardians/next of kin because data collection and analysis were performed in a de-identified and aggregate design. Individual data cannot be identified in this observational cohort study.
Author contributions
MM: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. HK: Conceptualization, Data curation, Methodology, Supervision, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. AI: Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. SS: Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. AY: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Supervision, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. LG: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. SS: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. JJ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. JJ has received partial funding support through the Texas Neurological Society and NIH R25 NS113757. SS and LG have received partial funding through NIH grant R01NS121154 and R01NS138765. LG is also supported in part by NIH grant U01AG070112.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the Memorial Hermann Health System for enabling the data collection effort.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fneur.2025.1629434/full#supplementary-material
Abbreviations
AIS, Acute ischemic stroke; ASPECTS, Alberta Stroke Program Early CT Score; AUROC, Area under the receiver operating characteristic curve; CTA, Computed tomography angiography; EVT, Endovascular therapy; LOC, Level of consciousness; LVO, Large vessel occlusion; mRS, Modified Rankin Scale; NIHSS, National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale; SD, Standard deviation; STROBE, Strengthening the reporting of observational studies in epidemiology; TICI, Thrombolysis in cerebral infarction; tPA, Tissue plasminogen activator.
References
1.
Benjamin EJ Virani SS Callaway CW Chamberlain AM Chang AR Cheng S et al . Heart disease and stroke statistics-2018 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. (2018) 137:e67–e492. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000558
2.
GBD 2015 Mortality and Causes of Death Collaborators . Global, regional, and national life expectancy, all-cause mortality, and cause-specific mortality for 249 causes of death, 1980-2015: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2015. Lancet. (2016) 388:1459–544. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31012-1
3.
National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke rt-PA Stroke Study Group . Tissue plasminogen activator for acute ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med. (1995) 333:1581–7. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199512143332401
4.
Goyal M Menon BK van Zwam WH Dippel DW Mitchell PJ Demchuk AM et al . Endovascular thrombectomy after large-vessel ischaemic stroke: a meta-analysis of individual patient data from five randomised trials. Lancet. (2016) 387:1723–31. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)00163-X
5.
Nogueira RG Jadhav AP Haussen DC Bonafe A Budzik RF Bhuva P et al . Thrombectomy 6 to 24 hours after stroke with a mismatch between deficit and infarct. N Engl J Med. (2018) 378:11–21. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1706442
6.
Albers GW Marks MP Kemp S Christensen S Tsai JP Ortega-Gutierrez S et al . Thrombectomy for stroke at 6 to 16 hours with selection by perfusion imaging. N Engl J Med. (2018) 378:708–18. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1713973
7.
Jovin TG Nogueira RG Lansberg MG Demchuk AM Martins SO Mocco J et al . Thrombectomy for anterior circulation stroke beyond 6 h from time last known well (AURORA): a systematic review and individual patient data meta-analysis. Lancet. (2022) 399:249–58. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01341-6
8.
Huo X Ma G Tong X Zhang X Pan Y Nguyen TN et al . Trial of endovascular therapy for acute ischemic stroke with large infarct. N Engl J Med. (2023) 388:1272–83. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2213379
9.
Bendszus M Fiehler J Subtil F Bonekamp S Aamodt AH Fuentes B et al . Endovascular thrombectomy for acute ischaemic stroke with established large infarct: multicentre, open-label, randomised trial. Lancet. (2023) 402:1753–63. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(23)02032-9
10.
Costalat V Jovin TG Albucher JF Cognard C Henon H Nouri N et al . Trial of thrombectomy for stroke with a large infarct of unrestricted size. N Engl J Med. (2024) 390:1677–89. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2314063
11.
Roaldsen MB Eltoft A Wilsgaard T Christensen H Engelter ST Indredavik B et al . Safety and efficacy of tenecteplase in patients with wake-up stroke assessed by non-contrast CT (TWIST): a multicentre, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Neurol. (2023) 22:117–26. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(22)00484-7
12.
Ringleb P Bendszus M Bluhmki E Donnan G Eschenfelder C Fatar M et al . Extending the time window for intravenous thrombolysis in acute ischemic stroke using magnetic resonance imaging-based patient selection. Int J Stroke. (2019) 14:483–90. doi: 10.1177/1747493019840938
13.
Barber PA Demchuk AM Zhang J Buchan AM . Validity and reliability of a quantitative computed tomography score in predicting outcome of hyperacute stroke before thrombolytic therapy. ASPECTS study group. Alberta stroke Programme early CT score. Lancet. (2000) 355:1670–4. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(00)02237-6
14.
Pop NO Tit DM Diaconu CC Munteanu MA Babes EE Stoicescu M et al . The Alberta stroke program early CT score (ASPECTS): a predictor of mortality in acute ischemic stroke. Exp Ther Med. (2021) 22:1371. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.10805
15.
Schroder J Thomalla G . A critical review of Alberta stroke program early CT score for evaluation of acute stroke imaging. Front Neurol. (2017) 7:7. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2016.00245
16.
Ali Raza S Xiang B Jovin TG Liebeskind DS Shields R Nogueira RG et al . Pittsburgh response to endovascular therapy score as a pre-treatment prognostic tool: external validation in Trevo 2. Int J Stroke. (2017) 12:494–501. doi: 10.1177/1747493016677984
17.
Zaidat OO Fifi JT Nanda A Atchie B Woodward K Doerfler A et al . Endovascular treatment of acute ischemic stroke with the penumbra system in routine practice. Stroke. (2022) 53:769–78. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.121.034268
18.
van Horn N Kniep H Broocks G Meyer L Flottmann F Bechstein M et al . ASPECTS Interobserver agreement of 100 investigators from the TENSION study. Clin Neuroradiol. (2021) 31:1093–100. doi: 10.1007/s00062-020-00988-x
19.
Farzin B Fahed R Guilbert F Poppe AY Daneault N Durocher AP et al . Early CT changes in patients admitted for thrombectomy: Intrarater and interrater agreement. Neurology. (2016) 87:249–56. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000002860
20.
Ballout AA Oh SY Huang B Patsalides A Libman RB . Ghost infarct core: a systematic review of the frequency, magnitude, and variables of CT perfusion overestimation. J Neuroimaging. (2023) 33:716–24. doi: 10.1111/jon.13127
21.
García-Tornel Á Campos D Rubiera M Boned S Olivé-Gadea M Requena M et al . Ischemic Core overestimation on computed tomography perfusion. Stroke. (2021) 52:1751–60. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.120.031800
22.
Cao W Yassi N Sharma G Yan B Desmond PM Davis SM et al . Diagnosing acute lacunar infarction using CT perfusion. J Clin Neurosci. (2016) 29:70–2. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2016.01.001
23.
Minnerup J Broocks G Kalkoffen J Langner S Knauth M Psychogios MN et al . Computed tomography-based quantification of lesion water uptake identifies patients within 4.5 hours of stroke onset: a multicenter observational study. Ann Neurol. (2016) 80:924–34. doi: 10.1002/ana.24818
24.
Chen C Yang J Han Q Wu Y Li J Xu T et al . Net water uptake within the ischemic penumbra predicts the presence of the midline shift in patients with acute ischemic stroke. Front Neurol. (2023) 14:1246775. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1246775
25.
Hacke W Schwab S Horn M Spranger M De Georgia M von Kummer R . 'Malignant' middle cerebral artery territory infarction: clinical course and prognostic signs. Arch Neurol. (1996) 53:309–15. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1996.00550040037012
26.
Lu SS Wu RR Cao YZ Xu XQ Jia ZY Shi HB et al . Automated estimation of quantitative lesion water uptake as a prognostic biomarker for patients with ischemic stroke and large-vessel occlusion. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. (2023) 44:33–9. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A7741
27.
Broocks G Flottmann F Scheibel A Aigner A Faizy TD Hanning U et al . Quantitative lesion water uptake in acute stroke computed tomography is a predictor of malignant infarction. Stroke. (2018) 49:1906–12. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.118.020507
28.
Shi J Wu H Dong Z Liang X Liu Q Zhu W et al . Automated quantitative lesion water uptake in acute stroke is a predictor of malignant cerebral edema. Eur Radiol. (2022) 32:2771–80. doi: 10.1007/s00330-021-08443-2
29.
Muschelli J . Recommendations for processing head CT data. Front Neuroinform. (2019) 13:61. doi: 10.3389/fninf.2019.00061
30.
Muschelli J Ullman NL Mould WA Vespa P Hanley DF Crainiceanu CM . Validated automatic brain extraction of head CT images. NeuroImage. (2015) 114:379–85. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.03.074
31.
Li X Morgan PS Ashburner J Smith J Rorden C . The first step for neuroimaging data analysis: DICOM to NIfTI conversion. J Neurosci Methods. (2016) 264:47–56. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2016.03.001
32.
Cauley KA Och J Yorks PJ Fielden SW . Automated segmentation of head computed tomography images using FSL. J Comput Assist Tomogr. (2018) 42:104–10. doi: 10.1097/RCT.0000000000000660
33.
Jenkinson M Beckmann CF Behrens TE Behrens TEJ Woolrich MW Smith SM . FSL. Neuroimage. (2012) 62:782–90. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.09.015
34.
Smith SM . Fast robust automated brain extraction. Hum Brain Mapp. (2002) 17:143–55. doi: 10.1002/hbm.10062
35.
Jenkinson M Bannister P Brady M Smith S . Improved optimization for the robust and accurate linear registration and motion correction of brain images. Neuroimage. (2002) 17:825–41. doi: 10.1016/s1053-8119(02)91132-8
36.
Mazziotta JC Toga AW Evans A Fox P Lancaster J . A probabilistic atlas of the human brain: theory and rationale for its development. The international consortium for brain mapping (ICBM). NeuroImage. (1995) 2:89–101. doi: 10.1006/nimg.1995.1012
37.
R Core Team . R: A language and environment for statistical computing. Vienna, Austria: R Foundation for Statistical Computing (2021).
38.
Broocks G Flottmann F Ernst M Faizy TD Minnerup J Siemonsen S et al . Computed tomography-based imaging of voxel-wise lesion water uptake in ischemic brain: relationship between density and direct Volumetry. Investig Radiol. (2018) 53:207–13. doi: 10.1097/RLI.0000000000000430
39.
Dzialowski I Klotz E Goericke S Doerfler A Forsting M von Kummer R . Ischemic brain tissue water content: CT monitoring during middle cerebral artery occlusion and reperfusion in rats. Radiology. (2007) 243:720–6. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2432060137
40.
Simard JM Kent TA Chen M Tarasov KV Gerzanich V . Brain oedema in focal ischaemia: molecular pathophysiology and theoretical implications. Lancet Neurol. (2007) 6:258–68. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(07)70055-8
41.
Stokum JA Gerzanich V Simard JM . Molecular pathophysiology of cerebral edema. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. (2016) 36:513–38. doi: 10.1177/0271678X15617172
42.
Pożarowszczyk N Kurkowska-Jastrzębska I Sarzyńska-Długosz I Nowak M Karliński M . Reliability of the modified Rankin scale in clinical practice of stroke units and rehabilitation wards. Front Neurol. (2023) 14:1064642. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1064642
43.
Cummock JS Wong KK Volpi JJ Wong ST . Reliability of the National Institutes of Health (NIH) stroke scale between emergency room and neurology physicians for initial stroke severity scoring. Cureus. (2023) 15:e37595. doi: 10.7759/cureus.37595
44.
Rajashekar D Hill MD Demchuk AM Goyal M Fiehler J Forkert ND . Prediction of clinical outcomes in acute Ischaemic stroke patients: a comparative study. Front Neurol. (2021) 12:663899. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2021.663899
45.
Fargen KM Kittel C Curry BP Hile CW Wolfe SQ Brown P et al . Mechanical thrombectomy decision making and prognostication: stroke treatment assessments prior to thrombectomy in neurointervention (SATIN) study. J Neurointerv Surg. (2023) 15:e381–7. doi: 10.1136/jnis-2022-019741
46.
Ospel JM Brown S Kappelhof M van Zwam W Jovin T Roy D et al . Comparing the prognostic impact of age and baseline National Institutes of Health stroke scale in acute stroke due to large vessel occlusion. Stroke. (2021) 52:2839–45. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.120.032364
47.
González RG Lev MH Goldmacher GV Smith WS Payabvash S Harris GJ et al . Improved outcome prediction using CT angiography in addition to standard ischemic stroke assessment: results from the STOPStroke study. PLoS One. (2012) 7:e30352. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030352
48.
Kim Y Sharrief A Kwak MJ Khose S Abdelkhaleq R Salazar-Marioni S et al . Underutilization of endovascular therapy in black patients with ischemic stroke: an analysis of state and Nationwide cohorts. Stroke. (2022) 53:855–63. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.121.035714
49.
Buie JNJ Zhao Y Burns S Magwood G Adams R Sims-Robinson C et al . Racial disparities in stroke recovery persistence in the post-acute stroke recovery phase: evidence from the health and retirement study. Ethn Dis. (2020) 30:339–48. doi: 10.18865/ed.30.2.339
50.
Man S Bruckman D Uchino K Schold JD Dalton J . Racial, ethnic, and regional disparities of post-acute service utilization after stroke in the United States. Neurol Clin Pract. (2024) 14:e200329. doi: 10.1212/CPJ.0000000000200329
51.
Ikeme S Kottenmeier E Uzochukwu G Brinjikji W . Evidence-based disparities in stroke care metrics and outcomes in the United States: a systematic review. Stroke. (2022) 53:670–9. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.121.036263
Summary
Keywords
net water uptake, ischemic stroke, computed tomography, aspects, neuroimaging
Citation
Mallavarapu M, Kim HW, Iyyangar A, Salazar-Marioni S, Yoo AJ, Giancardo L, Sheth SA and Jeevarajan JA (2025) A novel automated CT biomarker to predict outcomes in acute ischemic stroke: net water uptake. Front. Neurol. 16:1629434. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1629434
Received
15 May 2025
Accepted
08 August 2025
Published
22 August 2025
Volume
16 - 2025
Edited by
Gabriel Broocks, Medical School Hamburg, Germany
Reviewed by
Andre Kemmling, University of Marburg, Germany
Qing Han, Ningbo First Hospital, China
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Mallavarapu, Kim, Iyyangar, Salazar-Marioni, Yoo, Giancardo, Sheth and Jeevarajan.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jerome A. Jeevarajan, Jerome.A.Jeevarajan@uth.tmc.edu
†ORCID: Hyun Woo Kim, orcid.org/0000-0001-8953-388X
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.