Abstract
Objective:
To explore the therapeutic effect of mindfulness-based stress reduction in patients with post-stroke mild depression.
Methods:
A total of 80 patients with mild depression after stroke received by our hospital from January 2023 to December 2023 were selected as the study subjects. Randomly divide the patients into two groups: 40 in the control group and 40 in the combination group. The control group received conventional intervention therapy, while the combination group was treated with a mindfulness-based stress reduction plan combined with conventional intervention therapy. Patients in both groups were treated for 8 weeks. The general information of patients in the two groups was statistically analyzed. Self-rating Depression Scale (SDS), Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HAMD-17), Mini Mental State Examination (MMSE), Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) scores and inflammatory factors (including TNF-α, hs-CRP, IL-6) expression levels were used to evaluate the efficacy of patients before and after treatment, and the total effective rate was counted for the two groups.
Results:
After treatment, compared with that before treatment, the HAMD-17 and SDS scores and inflammatory factor levels of patients in the control group and combination group were significantly decreased (all p < 0.05), while the MMSE and MoCA scores of patients in the control group and combination group were significantly increased (all p < 0.05). However, after treatment, the HAMD-17 and SDS scores and inflammatory factor levels of patients in the combination group were significantly lower than those in the control group (all p < 0.05). The scores of MMSE and MoCA were significantly higher than those in the control group (p < 0.05).
Conclusion:
In the treatment of stroke patients with mild depression, mindfulness-based stress reduction combined with conventional intervention therapy can improve the overall response rate compared with conventional intervention therapy alone and has a significant advantage in reducing depression.
1 Introduction
Stroke is a common cerebrovascular disease in middle-aged and elderly people, including cerebral hemorrhage and cerebral infarction (1, 2). The disease usually occurs suddenly with high mortality and disability rates, which seriously threatens the life safety and quality of life of patients. With the development of medical level, the mortality rate of stroke has been further controlled, but various complications caused by stroke still seriously affect the quality of life of patients. Depression is one of its common complications (3). Patients usually present with depression and unhappiness, chest tightness and discomfort, loss of interest or pleasure, and inattention (4, 5). Clinically, antidepressants are mostly used for treatment of patients with mild depression after stroke. However, the duration of drug treatment is long, and it is easy to relapse after treatment (6–8), so clinicians are looking for new non-drug methods to treat patients with mild depression. According to literature reports, mindfulness-based stress reduction can reduce the level of anxiety and depression in patients (9, 10), which has been widely used in patients with post-tumor depression and a low recurrence rate after improvement. This makes non-pharmacotherapy for depression a hot research field, but it is still relatively rare in the treatment of post-stroke depression. In this study, stroke patients with mild depression were treated by mindfulness-based stress reduction plan combined with conventional intervention therapy to provide a clinical basis for the promotion of non-pharmacotherapy in stroke patients with mild depression.
2 Data and methods
2.1 General data
This study was approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of the hospital. A total of 80 patients with mild depression after stroke admitted to our hospital from January 2023 to December 2023 were selected as the subjects. Inclusion criteria: (1) the degree of depression meets the diagnostic criteria for mild depression in ICD (international classification of diseases); (2) the diagnostic criteria for stroke established by the National Academic Conference on Cerebrovascular Diseases are met; 3 No antidepressant treatment was received before enrollment; 4 Hamilton Depression Rating Scale score is greater than or equal to 7 points and less than 17 points. Exclusion criteria: (1) previous history of depression; (2) accompanied by other serious diseases, such as cardiopulmonary dysfunction or tumor history; (3) accompanied by other mental disorder history; 4 Failure to complete the full course of treatment. They were divided into the control group and the combination group according to different intervention regimens, with 40 patients in each group. There was no significant difference in gender, age, education level, disease type and course of disease between the two groups (p > 0.05), but they were comparable (see Table 1). All patients gave informed consent for the study and signed an informed consent form.
Table 1
| Group | n | Gender (male/female, n) | Age (years) | Education level (below middle school/above senior high school, n) | Disease type (cerebral hemorrhage/infarction, n) | Course of disease (d) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control group | 40 | 25/15 | 53.26 ± 11.60 | 27/13 | 13/27 | 15.42 ± 6.25 |
| Combination group | 40 | 24/16 | 54.20 ± 10.52 | 24/16 | 15/25 | 15.36 ± 6.13 |
| χ 2/t-value | 0.0527 | 0.380 | 0.487 | 0.2120 | 0.043 | |
| p-value | 0.819 | 0.705 | 0.485 | 0.639 | 0.966 |
Comparison of general data between the two groups.
2.2 Methods
Control group: Implement routine interventions by conducting a comprehensive assessment of the patient’s condition upon admission and understanding their level of disease awareness. Provide health education to both the patient and their family, explaining the causes, clinical manifestations, and other relevant knowledge. Focus on areas where the patient and family have limited understanding. Nursing staff should offer targeted psychological counseling to help patients develop a positive and optimistic mindset, encouraging active cooperation with treatment. Assess the patient’s previous dietary habits in detail, formulate an appropriate dietary plan based on their condition, and guide them in maintaining a balanced diet. Create a quiet and hygienic ward environment, and instruct patients to develop healthy sleep habits. Advise them to avoid consuming beverages such as coffee or strong tea before bedtime. Play soothing music before sleep to promote relaxation and improve sleep quality.
Combination group: Mindfulness-based stress reduction was added on the basis of the control group. Mindfulness-based stress reduction plan: (1) breathing meditation: in a quiet environment, the medical staff instructs the patient to take a supine position, place both hands on the patient’s abdomen, guide the patient to breathe calmly, feel the expansion of the abdomen during inhalation and the contraction of the abdomen during expiration, and pay attention to the patient’s breathing and emotional changes. The training time is once a day, 30 min/time. (2) Body scanning: The medical staff instruct the patient to take a supine position, and focus attention on the soles of feet, instep, calves, thighs, hips, back, shoulders, arms, head, face, etc. from bottom to top, while paying attention to the ups and downs of the abdomen, once/day, 15 min/ time. (3) Meditation: first feel the abdominal breathing for a period of time, then pay attention to the feeling of surrounding sounds, and pay attention to the pitch and timbre of sounds, once/day, 30 min/time.
2.3 Observation indicators
(1) HAMD-17, SDS, MMSE and MoCA scores and SDS score of patients before and after treatment (11): There are 20 items in total. The scale adopts a four-grade scoring method (1–4 points). The sum of the scores of each item is the total rough score, which is multiplied by 1.25 and taken as the standard score. The standard score of 53–62 is mild depression, 63–72 is moderate depression, and >72 is severe depression; HAMD-17 score (12): A total of 17 items were included, including the total score and 5 factor scores of physical anxiety, suicide, sleep disorder, despair and retardation. Each item was graded according to 0–4 levels. The higher the score, the more severe the depression degree. The higher the total score, the more severe the depression. <7 points indicate no depression, >17 points and ≤24 points indicate mild to moderate depression, and >24 points indicate severe depression; MMSE score (13): It includes 5 items, namely orientation, memory, attention, calculation, recall and language. After integration, the scores of each item are divided into normal (≥27 points), mild cognitive impairment (24–26 points) and moderate to severe cognitive impairment (≤23 points) according to the cognitive status of the subjects; MoCA score (14): It includes 8 items, namely, visual space and executive function, naming, memory, attention, language, abstraction, delayed recall and orientation. The total score is the sum of the scores of each cognitive domain, ranging from 0 to 33 points. If the education years are ≤12 years, 1 point will be added. The higher the score, the better the cognitive function. A score ≥26 indicates no cognitive impairment. (2) Gender, age, education level, disease type and course of disease of patients; (3) Clinical effect after treatment: Markedly effective if the HAMD-17 score of patients is below the depression level, effective response was defined as a ≥ 40% reduction in HAMD-17 score, and ineffective if the above criteria are not met after treatment. Total effective rate = (significantly effective + effective)/total number of cases × 100%; (4) Inflammatory factors: 3 mL of fasting venous blood was collected from patients in the morning, centrifuged for 10 min at a speed of 2,500 r/min, and serum was collected. Tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), hypersensitive C-reactive protein (HSRP) hs-CRP and interleukin-6 (IL-6).
2.4 Statistical processing
SPSS21.0 statistical software was used to analyze and process the data. Measurement data were expressed as “ ± s”, and t-test was used for comparison between groups; enumeration data were expressed as cases or %, and χ2 test was used for comparison between two groups. p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3 Results
3.1 Comparison of clinical effects between the two groups
The total effective rate of the combination group was significantly higher than that of the control group (χ2 = 6.13, p < 0.05) (see Table 2).
Table 2
| Group | n | Significantly effective | Effective | Ineffective | Overall response rate (n, %) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control group | 40 | 12 | 20 | 8 | 32 (80.00) |
| Combination group | 40 | 17 | 22 | 1 | 39 (97.5) |
| χ 2 | – | – | – | – | 6.13 |
| p-value | – | – | – | – | 0.01 |
Comparison of clinical effects between the two groups.
3.2 Comparison of general data between the two groups
The general data of the participants who completed the whole process in the two groups were counted, including gender, age, education level, disease type and duration of disease course. The results showed that there was no statistically significant difference in general data between the two groups (all p > 0.05) (see Table 1).
3.3 Comparison of depression scores before and after treatment between the two groups
Before treatment, there was no significant difference in depression scores (including HAMD-17 and SDS scores) between the control group and the combination group (all p > 0.05); After treatment, the scores of HAMD and SDS in control group and combination group were significantly lower than those before treatment (all p < 0.05); After treatment, the HAMD-17 and SDS scores of patients in the combination group were significantly lower than those in the control group (all p < 0.05) (see Table 3).
Table 3
| Group | n | SDS score | HAMD score | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before treatment | Post-treatment | Before treatment | Post-treatment | ||
| Control group | 40 | 59.42 ± 2.93 | 45.62 ± 2.43* | 14.65 ± 2.17 | 8.65 ± 3.12* |
| Combination group | 40 | 61.25 ± 3.04 | 34.15 ± 2.12*△ | 14.12 ± 2.35 | 5.14 ± 2.10*△ |
Comparison of SDS and HAMD-17 scores before and after treatment.
*Refers to p < 0.05 compared to Before treatment; △Refers to p < 0.05 compared to Control group.
3.4 Comparison of MoCA and MMSE scores between the two groups
Before treatment, there was no statistically significant difference in MoCA and MMSE scores between the control group and the combination group (all p > 0.05); after treatment, compared with that before treatment, the MoCA and MMSE scores of patients in the control group and the combination group were significantly increased (all p < 0.05); after treatment, the MoCA and MMSE scores of patients in the combination group were significantly higher than those in the control group (all p < 0.05) (see Figures 1, 2).
Figure 1

Comparison of MoCA scores between the two groups before and after treatment Compared with the control group, the MoCA scores in the combined group was significantly higher after treatment (p < 0.05).
Figure 2
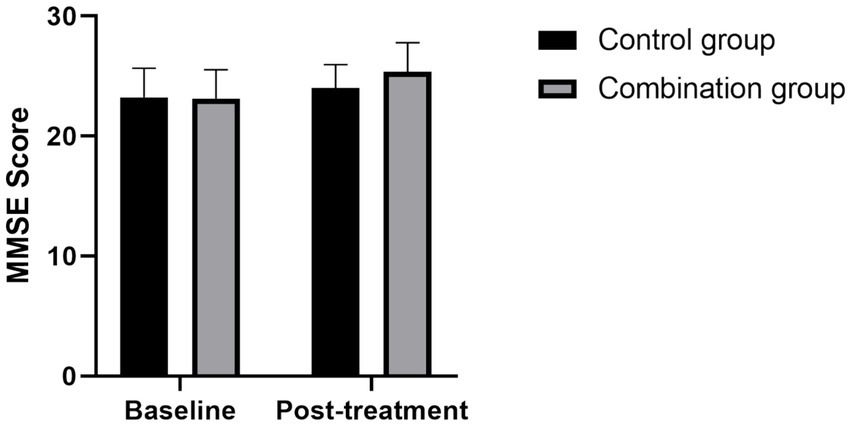
Comparison of MMSE scores between the two groups before and after treatment Compared with the control group, the MMSE scores in the combined group was significantly higher after treatment (p < 0.05).
3.5 Comparison of inflammatory factors between the two groups
Before treatment, there was no significant difference in the levels of inflammatory factors (including TNF-α, hs-CRP and IL-6) between the control group and the combination group (all p > 0.05); After treatment, the inflammatory factors of control group and combination group decreased significantly compared with those before treatment (all p < 0.05); After treatment, the inflammatory factors of patients in the combination group were significantly lower than those in the control group (all p < 0.05) (see Table 4).
Table 4
| Group | n | TNF-α (ng/L) | hs-CRP (mg/L) | IL-6 (ng/L) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before treatment | Post-treatment | Before treatment | Post-treatment | Before treatment | Post-treatment | ||
| Control group | 40 | 29.43 ± 4.51 | 23.10 ± 4.07 | 6.58 ± 1.07 | 5.43 ± 0.91 | 26.29 ± 4.13 | 20.46 ± 2.89 |
| Combination group | 40 | 28.69 ± 5.25 | 17.85 ± 3.42 | 6.70 ± 1.12 | 4.35 ± 0.72 | 25.49 ± 3.22 | 16.54 ± 3.24 |
| t-value | 0.676 | 6.246 | 0.490 | 5.886 | 0.966 | 5.710 | |
| p-value | 0.501 | <0.001 | 0.626 | <0.001 | 0.337 | <0.001 | |
Comparison of inflammatory factor levels.
4 Discussion
Stroke is a common cerebrovascular disease in the elderly, which usually has rapid onset and high mortality. Patients with stroke are often accompanied by a significant decrease in motor ability, which not only significantly reduces the quality of life of patients but may also have a serious impact on their mental health. Post-stroke depression (PSD) is a common complication (15, 16). It is an affective disorder that usually manifests as depressed mood, cognitive decline and decreased interest. In severe cases, it may even lead to suicidal behavior (17). There is a large difference in the incidence of PSD in relevant reports, which may be related to different selection and assessment methods by researchers. At present, the standard treatment for depression includes drug therapy and psychotherapy, but there is still uncertainty about the efficacy of these treatments in stroke patients (18–20). Although drug therapy is effective quickly, it also faces the problem of high recurrence rate (21). Studies have shown that psychological intervention can effectively reduce the recurrence rate of depression (22, 23). Therefore, there is an urgent clinical need for a safe and effective non-pharmacological treatment to deal with PSD. Conventional psychological interventions have previously achieved good therapeutic effects, but their efficacy remains limited and ineffective for some patients. This study aimed to explore the possibility of treating PSD with a combined intervention of mindfulness-based stress reduction and conventional intervention therapy. Mindfulness-based stress reduction is a technique to reduce stress by improving the individual’s awareness of the current moment. This combination method may provide a new scientific basis and practical guidance for non-pharmacological treatment of post-stroke depression. Through this study, we hope to provide more options for clinical practice that will help improve the quality of life and overall well-being of patients with PSD.
Mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR) was pioneered by Dr. Jon Kabat-Zinn at the University of Massachusetts Medical Center in 1979 (24). This therapy is designed to help patients with various medical conditions relieve symptoms such as pain, anxiety and depression through the use of mindfulness techniques. The concept of mindfulness, derived from the Buddhist and Yogic traditions, emphasizes a conscious and non-judgmental focus on immediate experiences, including aspects of one’s feelings, thoughts, and moods. Mindfulness-based stress reduction is a systematic psychological intervention method, which usually includes exercises such as sitting meditation, body scanning and thinking (25–27). The standard treatment cycle is 8 weeks. Initially, Mindfulness-based stress reduction was used in clinical practice as an adjuvant therapy. With the gradual emergence of its efficacy, its application has gradually expanded to chronic physical diseases, mental illness rehabilitation and other fields (28). In recent years, mindfulness-based stress reduction has gained wide attention and acceptance in the treatment of post-tumor mood disorders (29, 30), showing good clinical results. However, for patients with mild depression after stroke, there are still relatively few studies on the application and effect of mindfulness-based stress reduction, which is also a direction that this study focuses on exploring. This study conducted an intervention experiment on stroke patients with mild depression. Patients were divided into two groups according to different intervention methods: The control group received conventional intervention therapy, while the combination group was treated with a mindfulness-based stress reduction plan combined with conventional intervention therapy. The study results showed that the overall clinical response rate of patients in the combination group was significantly higher than that in the control group (χ2 = 6.13, p < 0.05). In addition, compared with the control group, the combination group showed significantly lower scores in Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HAMD-17), Self-rating Depression Scale (SDS) and levels of inflammatory factors (including TNF-α, hs-CRP, IL-6) (all p < 0.05), while also showed significant advantages in Mini Mental State Examination (MMSE) and Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) scores (all p < 0.05).
In conclusion, both conventional intervention therapy and mindfulness-based stress reduction are safe and effective in the treatment of mild depression after stroke. However, mindfulness-based stress reduction combined with conventional intervention therapy can significantly improve the total clinical response rate of patients and significantly reduce their depressive symptoms, which provides an important reference for promoting non-pharmacotherapy in the treatment of mild depression after stroke.
Statements
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of J Jinhua Hospital of TCM (2024032610). Written informed consent to participate in this study was provided by the patients.
Author contributions
XP: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. DQ: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. XH: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. JX: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1.
Ashrafi-Asgarabad A Safiri S . Malondialdehyde: a novel predictive biomarker for post-stroke depression-methodological issues. J Affect Disord. (2018) 227:847–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2017.11.086
2.
Bolgeo T De Maria M Vellone E Ambrosca R Simeone S Alvaro R et al . The Association of Spirituality with anxiety and depression in stroke survivor-caregiver dyads: an actor-partner interdependence model. J Cardiovasc Nurs. (2022) 37:E97–E106. doi: 10.1097/JCN.0000000000000798
3.
Elias S Benevides ML Pereira Martins AL Martins GL Sperb Wanderley Marcos AB Nunes JC . In-hospital symptoms of depression and anxiety are strong risk factors for post-stroke depression 90 days after ischemic stroke. Neurohospitalist. (2023) 13:121–9. doi: 10.1177/19418744221132675
4.
Liang Y Shi X Chen L Li Y Zhong J . Homocysteine level at the acute stage of ischemic stroke as a biomarker of poststroke depression: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Psych. (2022) 13:1016700. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2022.1016700
5.
Osipova OA Klushnikov NI Gosteva EV Belousova ON Zhernakova NI Khachaturov AN . The role of inflammation in the development of post-stroke depression in elderly patients. Adv Gerontol. (2021) 34:841–7. PMID:
6.
Viguera AC Fan Y Thompson NR Lapin B Chaitoff A Griffith SD et al . Prevalence and predictors of depression among patients with epilepsy, stroke, and multiple sclerosis using the Cleveland Clinic knowledge program within the neurological institute. Psychosomatics. (2018) 59:369–78. doi: 10.1016/j.psym.2017.12.003
7.
Vujkovic Z Radivojevic Vuckovic D Stojiljkovic MP Spasojevic G Skrbic R . The impact of thrombolytic therapy on anxiety, depression and quality of life of patients with acute ischemic stroke. Psychiatr Danub. (2022) 34:86–92.
8.
Kristensen MS Jorgensen PB Bogh SB Kierkegaard S Mechlenburg I Dalgas U . Acute and chronic effects of early progressive resistance training on knee pain and knee joint effusion after unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. Acta Orthop Belg. (2018) 84:262–8.
9.
Medeiros GC Roy D Kontos N Beach SR . Post-stroke depression: a 2020 updated review. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. (2020) 66:70–80. doi: 10.1016/j.genhosppsych.2020.06.011
10.
Guo J Wang J Sun W Liu X . The advances of post-stroke depression: 2021 update. J Neurol. (2022) 269:1236–49. doi: 10.1007/s00415-021-10597-4
11.
Al Najjar T Allam NK El Sawy EN . Anionic/nonionic surfactants for controlled synthesis of highly concentrated sub-50 nm polystyrene spheres. Nanoscale Adv. (2021) 3:5626–35. doi: 10.1039/D1NA00438G
12.
Wu P Zhang A Sun N Lei L Liu P Wang Y et al . Cortical thickness predicts response following 2 weeks of SSRI regimen in first-episode, drug-naive major depressive disorder: an MRI study. Front Psych. (2021) 12:751756. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2021.751756
13.
Gallegos M Morgan ML Cervigni M Martino P Murray J Calandra M et al . 45 years of the mini-mental state examination (MMSE): a perspective from ibero-america. Dement Neuropsychol. (2022) 16:384–7. doi: 10.1590/1980-5764-DN-2021-0097
14.
Volter C Fricke H Gotze L Labrenz F Tokic M Wirth R et al . Evaluation of the non-auditory neurocognitive test MoCA-HI for hearing-impaired. Front Neurol. (2022) 13:1022292. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.1022292
15.
Amrutesh Reddy A Gopi Chander N Ramesh Reddy J Muthukumar B . Assessment of differences in stress markers of edentulous patients rehabilitated with complete dentures. Med J Armed Forces India. (2024) 80:428–32. doi: 10.1016/j.mjafi.2022.08.014
16.
Brown-Whitehorn T Spergel JM . Food allergy and eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders. J Food Allergy. (2020) 2:39–43. doi: 10.2500/jfa.2020.2.200010
17.
Casale TB Settipane RA . A roadmap for optimal care of the patient with food allergy. J Food Allergy. (2020) 2:1–2. doi: 10.2500/jfa.2020.2.200029
18.
Chen M Zhang W Lee L Saxena J Sindher S Chinthrajah RS et al . Biologic therapy for food allergy. J Food Allergy. (2020) 2:86–90. doi: 10.2500/jfa.2020.2.200004
19.
Dharmadjati BB Sargowo D Aulanni'am Pikir BS Oktaviono YH Sativa O et al . Reversine enhances the conversion of dedifferentiated fat cells into mature cardiomyocytes. F1000Res. (2022) 11:851. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.122788.3
20.
Lapidot R Faits T Ismail A Allam M Khumalo Z MacLeod W et al . Nasopharyngeal Dysbiosis precedes the development of lower respiratory tract infections in young infants, a longitudinal infant cohort study. Gates Open Res. (2022) 6:48. doi: 10.12688/gatesopenres.13561.1
21.
Odisho N Carr TF Cassell H . Food allergy: labelling and exposure risks. J Food Allergy. (2020) 2:115–8. doi: 10.2500/jfa.2020.2.200027
22.
Shiraishi R Shiraishi N Fujimoto Y Ogawa T . Malnutrition suppresses improvements in depression symptoms in older adult patients with stroke undergoing convalescent rehabilitation. Clin Nutr ESPEN. (2024) 63:508–14. doi: 10.1016/j.clnesp.2024.07.013
23.
Suetake H Tanjo T Ishii M Kinoshita B Fujino T Hachiya T et al . Sapporo: a workflow execution service that encourages the reuse of workflows in various languages in bioinformatics. F1000Res. (2022) 11:889. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.122924.1
24.
Arlt Mutch VK Evans S Wyka K . The role of acceptance in mood improvement during mindfulness-based stress reduction. J Clin Psychol. (2021) 77:7–19. doi: 10.1002/jclp.23017
25.
Chen TL Chang SC Hsieh HF Huang CY Chuang JH Wang HH . Effects of mindfulness-based stress reduction on sleep quality and mental health for insomnia patients: a meta-analysis. J Psychosom Res. (2020) 135:110144. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychores.2020.110144
26.
Gerber B Scriba J Geissler A Reckling H Fischer M Karl D et al . Pilot study on subjectively and objectively measurable stress reduction in the daily routine of a university anesthesia department by an intervention program according to mindfulness-based stress reduction. Anaesthesist. (2020) 69:623–31. doi: 10.1007/s00101-020-00802-w
27.
Laubacher C Kral TRA Imhoff-Smith T Klaus DR Goldman RI Sachs J et al . Resting state functional connectivity changes following mindfulness-based stress reduction predict improvements in disease control for patients with asthma. Brain Behav Immun. (2024) 115:480–93. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2023.10.026
28.
Napadow V . The mindful migraine: does mindfulness-based stress reduction relieve episodic migraine?Pain. (2020) 161:1685–7. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000001859
29.
Prohaska S Matthias K . Effectiveness of mindfulness-based stress reduction as a nondrug preventive intervention in patients with migraine: a systematic review with meta-analyses. Complement Med Res. (2023) 30:525–34. doi: 10.1159/000534653
30.
Tran T Donnelly C Nalder EJ Trothen T Finlayson M . Occupational therapist-led mindfulness-based stress reduction for older adults living with subjective cognitive decline or mild cognitive impairment in primary care: a feasibility randomised control trial protocol. BMJ Open. (2020) 10:e035299. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2019-035299
Summary
Keywords
mindfulness-based stress reduction, progressive resistance training, stroke, mild depression, depression
Citation
Pang X, Qiu D, He X and Xu J (2025) Application of mindfulness-based stress reduction plan in post-stroke patients with mild depression. Front. Neurol. 16:1629576. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1629576
Received
16 May 2025
Accepted
16 September 2025
Published
30 September 2025
Volume
16 - 2025
Edited by
Daniele Corbo, University of Brescia, Italy
Reviewed by
Zhen-Dong Wang, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, China
Thangaraj Devadoss, Karpagam Academy of Higher Education, India
Eppy Setiyowati, Nahdlatul Ulama University of Surabaya, Indonesia
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Pang, Qiu, He and Xu.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Dong Qiu, 15058597295@163.com
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.