- 1Department of Pathology, Second Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University, Nanchang, China
- 2Department of Neurology, Affiliated Hospital of Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan, China
- 3Department of Pathology, Yangpu Hospital, School of Medicine, Tongji University, Shanghai, China
Spinal muscular atrophy is a hereditary disorder leading to severe neuromuscular impairment. With the introduction of disease-modifying therapies in recent years, the role of biomarkers has expanded from aiding diagnosis to monitoring treatment responses, prognostic assessment, and the development of individualized treatment strategies. This review systematically summarizes biomarkers in the field of spinal muscular atrophy, including physiological indicators, functional assessments, imaging features, and molecular markers, which are derived from the analysis of different tissues from human patients and animal models. This article provides a concise summary of the classic biomarkers widely used in current clinical practice and introduces the potential new biomarkers revealed by the latest research. It focuses on discussing the expression patterns, clinical correlations, and applicable conditions of various types of biomarkers, with the aim of providing more accurate basis for disease stratification, efficacy prediction, and treatment decision-making.
1 Introduction
Classic spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) is an autosomal recessive neuromuscular disease characterized by homozygous deletion of the survival of motor neuron 1 (SMN1) gene on chromosome 5q13.2 (1, 2). SMA affects populations worldwide, and its carrier frequency, incidence, and prevalence vary across regions, ethnicities, and genders. It has been reported that Caucasian and Asian populations carry a higher frequency of SMN1 mutations than populations of sub-Saharan African ancestry. However, carrier frequency cannot be directly translated to incidence and prevalence because the frequencies of very severe (intrauterine lethal) and very mild (asymptomatic in adults) phenotypes with biallelic SMN1 mutations are unknown (3). The analysis of pooled data based on TREAT-NMD Global SMA Registry and Cure SMA member database showed that the proportion of male SMA patients is higher than that of female patients, and the clinical symptoms of male patients are more significant, and the proportion of male family members is also higher. Meanwhile, head circumference data suggest that male patients may have more significant brain developmental abnormalities (4). Pure deletions of exons 7 and 8 or a single exon 7 of the SMN1 gene are present in approximately 96% of cases, but there is no direct correlation between the types of SMN1 genetic defects and the severity of the clinical phenotype; the remaining patients showed SMN1 point mutation and SMN1 deletion, or extremely rare biallelic point mutation (5, 6).
Both SMN1 and SMN2 are located in the 5q13 region of human chromosome 5. Both have 99% sequence homology; however, the c.840C > T variant in exon 7 of SMN2 results in aberrant splicing of SMN2 and less than 10% efficiency of functional full-length SMN protein production (7). Notably, the incidence of pure deletions of the SMN2 gene is approximately 3–5% in the general population, but does not increase the incidence of clinical phenotypes due to normal SMN1 expression (8). In patients with SMA types 2–4, gene conversion of SMN1 to SMN2 results in an increased number of SMN2 copies (9). Reverse gene conversion can integrate SMN2 sequences into the SMN1 locus, resulting in an increased number of SMN1 copies; however, this can result in an increased risk of delayed-onset motor neuron disease [e.g., amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)], suggesting that excessive SMN expression can be harmful to motor neurons (10).
Werdnig and Hoffmann first reported cases of SMA type 1, which they named Werdnig–Hoffmann disease. In 1956, Kugelberg and Welander reported Kugelberg–Welander disease, now known as SMA type 3 (11). Three common subtypes of classic SMA have been defined based on onset age and motor ability of untreated patients (7). SMA type 1 is the most common type, with an onset within the first 6 months of life, and death usually occurs within 2 years of age due to respiratory failure (mortality rate > 90%). Patients with SMA types 2 or 3 have relatively mild symptoms. The onset of SMA type 2 occurs at 6–18 months of age, and patients can sit unaided but are unable to walk. Patients with SMA type 3 can walk independently but gradually lose motor ability. Two other, rare subtypes of classic SMA have also been described. Type 0 has a prenatal disease onset; patients may present with reduced or absent fetal movements in utero, asphyxia, and severe weakness at birth, and they often survive only for days to weeks (12). Type 4 is characterized by adult onset; patients with this subtype have the mildest symptoms and a survival rate close to normal (13). Studies have shown that 80% of patients with SMA type 1 have one or two SMN2 copies, 78% of patients with SMA type 2 have three SMN2 copies, and 93% of patients with SMA type 3 have three or four SMN2 copies (7).
The diagnostic process for SMA can be divided into three key stages: preconception carrier screening, prenatal testing of the fetus, and postnatal testing of the neonate or infant. This tiered diagnostic system is important for early intervention and improving patient prognosis. Preconception carrier screening can help couples make informed reproductive decisions (14). Postnatal SMN proteins in the spinal cord are age-dependently depleted, and delayed treatment will accelerate the pathology (15). Early identification of patients with SMA in the presymptomatic stage and implementation of interventions considerably improve the prognosis of these patients (16), contribute to the improvement of their quality of life, and reduce the burden on society. Genetic testing is the gold standard for screening SMA carriers and diagnosing patients affected by SMA.
Multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification (MLPA) was once considered the method of choice for the molecular detection of SMA (2), but digital polymerase chain reaction (dPCR) has recently been shown to exhibit better accuracy in detecting copy number variants (17). In addition, the integration of long-read sequencing technology with conventional next-generation sequencing assays can improve the resolution of structural variants and avoid false-positive or false-negative gene detection (18).
With the application of disease-modifying therapies (e.g., nusinersen, onasemnogene abeparvovec, and risdiplam), the survival and motor function of most patients with SMA have improved. However, the therapeutic efficacy in some treated patients is low (19). New biomarkers, especially molecular ones, have been discovered in recent years through studies of amniotic fluid/chorionic villus samples, blood samples, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), and skeletal muscle tissues of patients with SMA. Understanding the characteristics of these markers not only improves the sensitivity of carrier screening and presymptomatic diagnosis but also dynamically monitors the progression of the disease, thus guiding clinical work.
2 Molecular biomarkers
2.1 SMN protein levels
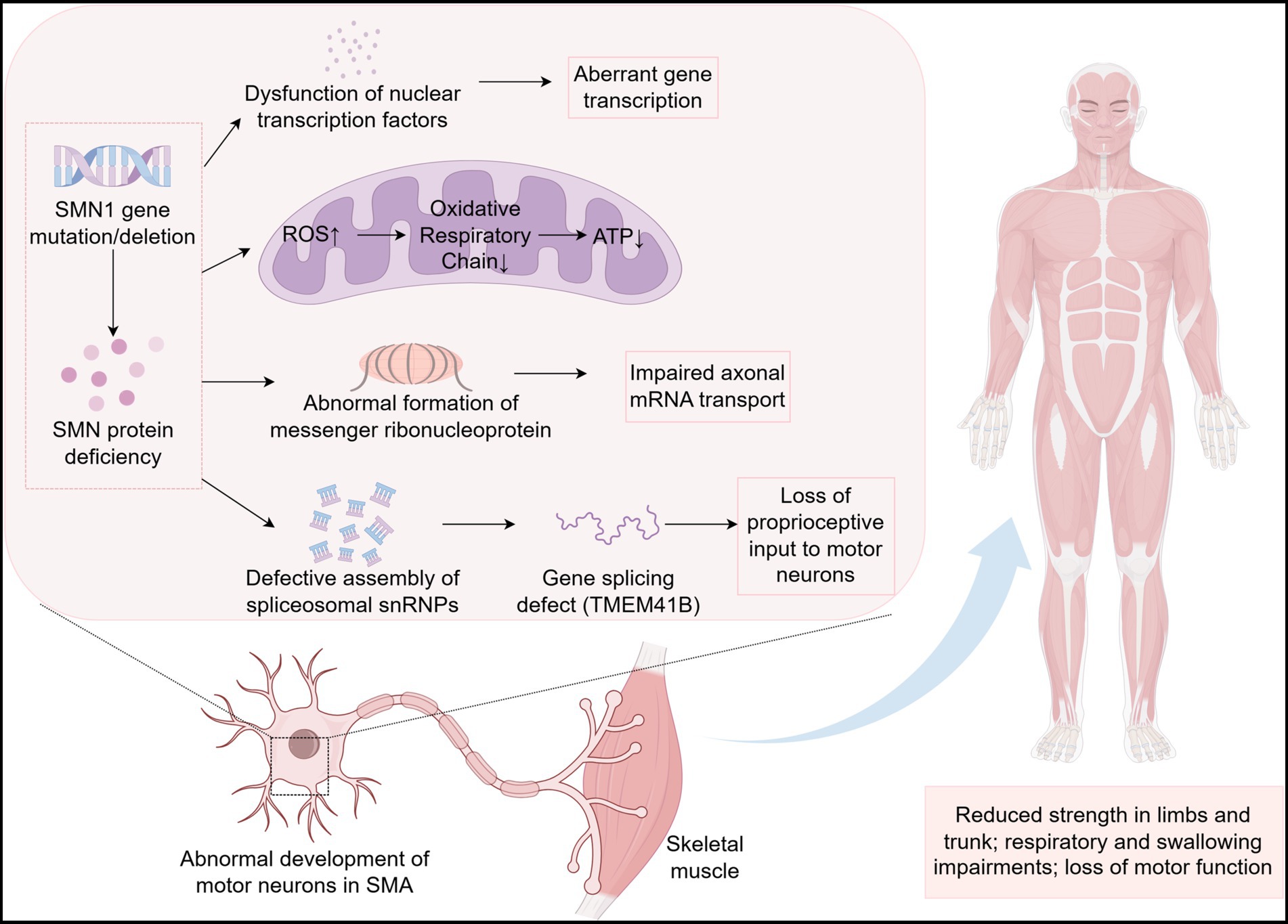
The expression level of SMN proteins is significantly correlated with the clinical type of SMA (types 1–4) and the copy number of the SMN2 gene (20); the higher the copy number of SMN2, the higher the expression of functional SMN proteins and the lower disease severity. SMN is widely expressed in various tissues and cell types, but the level of SMN expression is higher in the spinal cord (21). The spinal cord is the target organ for SMA therapy, but the difficulty in sampling spinal cord tissues limits its use in related studies. Typically, tissues available for biomarker studies are the blood and CSF. SMN is localized in the cytoplasm, nucleus (Cajal vesicles and gems), and nucleolus (22). SMN is involved in small nuclear ribonucleoprotein (snRNP) assembly and mRNA transport in the cytoplasm. SMN was enriched in bodies of Cajal (CBs) and gems, and CBs was the site of snRNP maturation and modification. SMN can be localized to the nucleolus in neurons and under stress conditions and may be related to ribosomal RNA processing or stress response. One imaging study quantified SMN protein expression levels in peripheral blood mononuclear cells using flow cytometry to obtain SMN spot values. In this study, SMN protein levels in maternal peripheral blood were positively correlated with those in neonatal umbilical cord blood (15). This suggests that it is possible to analyze maternal peripheral blood to predict the severity of postnatal SMA in the child and that induction of maternal SMN expression might be an effective therapeutic strategy for the fetus. The latest study to practice and report this treatment. Fetal type 1 SMA was confirmed by the investigators through family history and amniocentesis. Subsequently, Risdiplam was administered orally to the mother in the third trimester, and treatment was started on day 8 of life. So far, the child has not developed clinical symptoms of SMA (23). In another study, real-time counting of primary fibroblasts based on skin biopsy-derived primary fibroblasts efficiently quantified the amount of SMN protein-rich gems in the nucleus, and these values were highly positively correlated with the functional recovery of SMN proteins and the level of full-length SMN transcripts (24).
Both the amount of SMN protein and the number of gems, which are considered biomarkers of SMA, can be used to monitor disease progression and therapeutic efficacy. However, it remains unclear whether peripheral blood and central nervous system (CNS) SMN levels are directly correlated, with only a few reports confirming that increased peripheral blood SMN levels may reflect SMN levels in the CNS (25). The high cost of SMN protein assays may prevent their large-scale clinical dissemination. Manual microscopic counting of the number of gems in the nucleus is simple and easy to perform; however, subjective judgment errors may occur, and uniform cutoff values have not been established yet.
2.2 Biomarkers associated with synaptic dysfunction
The clinical manifestations of skeletal muscle weakness in patients with SMA are caused by the destruction of SMA motor units. Studies on human necropsy tissues and mouse models have shown that the initial stages of the disease are characterized by developmental disorders of the neuromuscular system including an abnormal acquisition of excitatory synaptic inputs to motor neurons, disturbed firing patterns in mature motor neurons, impaired radial growth of motor axons and Schwann cell sheaths, and reduced myelin formation. Impaired refinement of the synaptic structure, increased quantum content at the neuromuscular junction, and abnormal muscle fiber growth have also been reported (7). Recent studies have identified dysfunction and loss of proprioceptive synapses as key features of SMA pathology by analyzing patient specimens and mouse models of SMA (26). These findings strongly suggest that synaptic dysfunction plays a key role in the pathogenesis of SMA.
Hsc70-4 and HspA8 are members of the heat shock protein 70 family. These homologs of the same protein in different species play key roles in preventing protein aggregation and assist in the repair and degradation of misfolded proteins (27). In a mouse model, the G470R mutation in HspA8 significantly alleviated the severity of SMA by stabilizing the interaction between HspA8 and chaperone proteins, promoting the assembly of the SNARE complex at the neuromuscular junction, and directly enhancing synaptic function (28). In the Drosophila model, Hsc70-4 was identified as a chaperone protein that preferentially binds to SMN mutants, and the TDP-43 mutation triggers the downregulation of Hsc70-4/HspA8, which in turn disrupts synaptic function (29).
Plastin 3 (PLS3), identified as the first protective modifier in SMA, plays a key role in endocytosis, synaptic function, and cytoskeletal remodeling (30). PLS3 is an X-linked gene, and all asymptomatic SMN1-deficient individuals who exhibit PLS3 upregulation are female. These women have a 40-fold higher level of PLS3 expression compared to their diseased siblings, whereas men generally show reduced levels of PLS3 (31). Calcineurin-like EF-hand protein 1 (CHP1) is a directly interacting protein of PLS3 (32). In various SMA models, decreases in CHP1 expression promote calmodulin phosphatase activity and improve impaired synaptic endocytosis.
Thrombospondins 4 (TSP4), a member of the thrombospondins family, is mainly expressed in the heart and skeletal muscle in adult tissues and accumulates in the neuromuscular junction (NMJ), a specialized synaptic structure, and certain synapse-rich structures (33, 34). In SMA, in addition to the lack of SMN protein, retrograde signaling from the NMJ and skeletal muscle may also contribute to the damage of alpha motor neurons (α-mns) and significantly affect the overall clinical manifestations of the disease (35). Recent studies have found that the changes of TSP4 in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of SMA patients are age- and disease-specific: its level is significantly reduced only in children with SMA, but not in adults. Meanwhile, this reduction is specific to SMA, and similar changes have not been observed in the CSF of patients with other pediatric neurological diseases (e.g., multiple sclerosis, peripheral neuropathy, meningitis/encephalitis) (36). More importantly, TSP4 levels in CSF increased in pediatric SMA patients after the first dose of Nusinersen, suggesting that TSP4 has the potential to be a biomarker for monitoring treatment response in pediatric SMA patients. However, further studies are needed to clarify its specific mechanism of action and clinical application value.
Abnormalities in synaptic and molecular chaperone functions may precede the onset of clinical symptoms. Changes in the expression or activity of proteins associated with synaptic function may reflect disease severity and help in the early detection of disease and the assessment of therapeutic responses (37). Therefore, targeting synaptic dysfunction may be a future strategy for adjuvant therapy. However, synaptic dysfunction and protein disorders involve multiple molecules, and a single biomarker may not be sufficient to fully reflect the disease state. Analyses of synaptic vesicle cycling and molecular chaperone function require highly sensitive assays, which may be difficult to generalize for routine clinical applications. Currently, relevant studies are mainly conducted in animal and cell culture models, and further clinical studies are required to verify the reliability of these assays.
2.3 Non-coding RNAs
Non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) can be detected in various ways. ncRNAs, RNA molecules that do not encode proteins, are involved in cell proliferation, differentiation, metabolism, stress response, and other cellular processes through the regulation of gene expression. At present, the research focus is mainly on regulatory ncRNA. According to their length and structure, regulatory ncRNAs are divided into short ncRNA, long ncRNA (lncRNA), and circular RNA (circRNA).
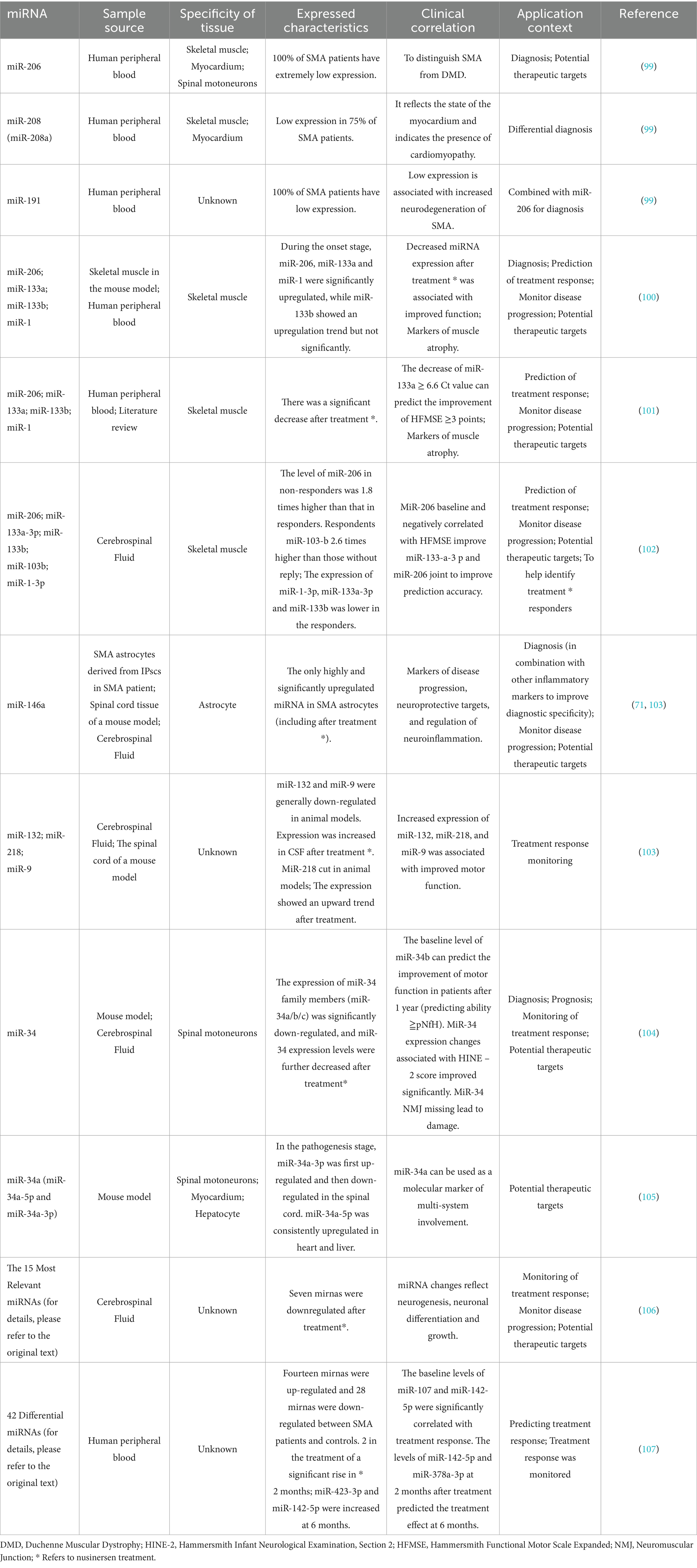
MiRNA belongs to short chain ncRNA, and its expression level is closely related to muscle atrophy caused by various causes (38, 39). In the field of SMA research, increasing evidence has revealed characteristic aberrant miRNA expression profiles (see Table 1 for a summary of the characteristics and applications of some representative mirnas). Among them, muscle-specific miRNA (myomiR) is relatively well studied: miR-133a and miR-133b mainly regulate and promote the proliferation of myoblasts, while miR-206 and miR-1 are mainly involved in the regulation of myoblast differentiation. In addition, miRNA expression changes in motor neurons and glial cells have received much attention. Combined detection of miRNA and neurofilament proteins, such as pNF-H, may provide a more comprehensive assessment of therapeutic effect. It should be noted that the expression of some mirnas is tissue specific, while neurofilament proteins also have some limitations as biomarkers. Therefore, the influence of these factors on the results must be fully considered when designing and applying the combined detection strategy of miRNA and neurofilament protein.
At present, studies on the role of lncrnas in the pathological process of SMA are relatively limited. Existing evidence shows that lncrNA-mediated regulatory network disorders may be involved in the pathogenesis of motor neuron disease (MND) (40). Therefore, we hope that in the future, more scholars will further explore the expression characteristics, functions and regulatory mechanisms of lncrnas in SMA.
Studies in the field of circRNAs have found that circ4-2b-3 is consistently highly expressed in serum exosomes of some super-responders among patients with SMA type 1. Its expression level is closely correlated with the degree of improvement in motor function (≥7-point elevation in the CHOP INTEND score) after nusinersen treatment (41). This suggests that circ4-2b-3 may be the first circRNA biomarker for assessing response to nusinersen treatment in patients with SMA type 1.
2.4 Neurodegeneration
2.4.1 Neurofilaments
Neurofilaments (NFs) are neuron-specific intermediate filaments and are classified into light chain (NF-L), medium chain (NF-M), heavy chain (NF-H), α-internexin, and peripherin (42). The expression levels of NF proteins in the CSF and peripheral blood are significantly correlated with the severity of axonal injury in inflammatory, degenerative, traumatic, and vascular neurological diseases (43). The diagnostic and prognostic roles of NF proteins in ALS are well-documented (44–46), and their value in SMA has been progressively confirmed (47).
Compared to healthy controls, plasma baseline pNfL levels were significantly higher in children with SMA type 2 or 3 (48). Adult CSF and serum NF-L levels were also significantly higher in patients with SMA, especially in those with SMA type 3 and “sitting patients” (49). Baseline CSF phosphorylated NF-H (pNF-H) levels were the highest in pediatric patients with SMA type 1; after nusinersen treatment, CSF pNF-H levels decreased significantly in all patients and remained elevated in all children. Moreover, CSF pNF-H levels decreased significantly and remained stable in all patients, and plasma pNF-H levels decreased significantly 2 months after treatment of patients with SMA type 1 or 2, but no significant differences were observed in patients with SMA type 3 (50). During long-term nusinersen treatment, NF-L concentrations were reduced (51). In addition, some studies have suggested that serum NF-L levels were significantly correlated with CSF NF-L levels, supporting the idea that these serum levels can be used as a surrogate marker for CSF levels in adult patients with SMA (49). Others found no association between sNF-L and cNF-L, but CSF and serum pNfH levels did correlate (52).
NF-L expression was significantly upregulated at the beginning of the treatment with nusinersen and then gradually returned to baseline levels (49). The use of onasemnogene abeparvovec for gene replacement therapy of serum NF-L levels showed paradoxical transient increases (53), possibly due to a transient immune response in the CNS or an inflammatory response resulting from the treatment. In addition, CSF NF-L and pNF-H levels may be useful biomarkers for the differential diagnosis of adult SMA and ALS (54).
Given the variety of causes of axonal injury, other motor neuron diseases should be strictly excluded before establishing neurofilament proteins (NFs) as specific biomarkers for spinal muscular atrophy (SMA). The application of NFs as a biomarker in SMA requires comprehensive consideration of factors such as patient age, clinical classification and disease stage. Previous studies have shown inconsistencies in the correlations between NF-L levels and motor function scores (48, 49, 55). NF-L levels are positively correlated with age (56), and serum NF-L levels are significantly positively correlated with disease duration (49). However, because of the intricate relationship between age and disease duration, more data are needed to explore whether disease duration affects NFs independently of age. Therefore, the use of serum NF levels as biomarkers of SMA still has some limitations.
2.4.2 Tau
Similar to NF proteins, tau protein expression varies among the different clinical subtypes of SMA. In a mixed cohort study of adult patients with SMA type 3, tau proteins failed to show applicability as potential biomarkers during the loading period of nusinersen treatment because of the slow disease progression and its mild degree of neurodegeneration (57). However, a study from 2024 noted that the measurement of total tau protein concentration in the CSF was a reliable biomarker for monitoring the response to nusinersen therapy in patients with SMA types 1–3 (58). A more recent study found that tau levels in the CSF of nusinersen-treated patients with SMA type 1 were unchanged (59).
These conflicting findings prompted us to ask what key factors led to these discrepancies. We speculate that the reasons may involve several aspects. First, sample size is often a limitation, which renders small-scale studies susceptible to chance bias. Second, the variability of laboratory testing methods (e.g., sample processing procedures, analytical techniques, and adjudication criteria) may significantly interfere with the comparability of the data. Third, the heterogeneity of study populations is also a cause for concern, as as-yet-undiscovered biological differences in patients of different races, age groups, or clinical subtypes may exist. This suggests the need for larger, standardized, multicenter studies, as well as systematic analyses of potential confounders.
2.4.3 Profilin
The profilin family of actin-binding proteins is essential in all organisms and plays a role in the regulation of the cytoskeletal structure, neuronal motility, and synaptic function (60). Among members of this family, profilin-1 is widely expressed throughout the body, whereas profilin-2 shows a CNS-specific expression pattern (61). Compared with profilin-1, SMN, through its proline-rich structural domain and profilin-2 binds more strongly (62, 63). However, a recent study (49) found that serum profilin-1 concentrations in patients with SMA decreased significantly during the first 2 months of nusinersen treatment; during the maintenance phase, profilin-1 decreased by 14.7% per month, eventually reaching levels similar to those of healthy controls after 26 months of treatment. The mechanism of action of the profilin family members in SMA has yet to be thoroughly investigated. The feasibility of using these markers for efficacy assessments must be verified in additional experiments.
2.5 Skeletal muscle
Creatine kinase (CK) and creatinine are involved in muscle energy metabolism, reflect muscle mass and muscle integrity, and are promising biomarkers for predicting and assessing responses to SMA treatment (64). Prior to nusinersen treatment, serum CK levels were strongly negatively correlated with disease severity scores, and the correlation of CK levels was greater than that of creatinine levels (65). During nusinersen treatment, adult patients with SMA had decreased CK levels and stable or slightly increased creatinine levels (65–67). CK is more suitable for assessing acute muscle injury or short-term response to treatment, whereas creatinine is more suitable for monitoring long-term trends in muscle atrophy. In addition, elevated urinary creatinine levels in patients with SMA type 1 correlate with improved motor function and may serve as a potential biomarker of treatment response (68). In addition, it has been found that myostatin expression is significantly decreased and follistatin expression is increased in muscle tissue in mouse and human SMA models. The low expression of myostatin in muscle tissue is related to the severity of the disease, may reflect denervated atrophy, or can be used as a marker of disease progression (69).
2.6 Inflammation and metabolism
Neuroinflammation is an emerging clinical feature in patients with SMA (70). The reason for these observed phenomena might be that elevated expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines in the spinal cord stimulates the proliferation of astrocytes and microglia of the pro-inflammatory M1 phenotype while activating the complement system (71). Some pro-inflammatory pathways (e.g., those involving CCL5 and TLR2) can exacerbate neuroinflammation by recruiting peripheral monocytes to the CNS (72).
Although the mainstream view in the past is that SMA pathological changes are closely related to neurological changes, evidence suggests that it may be a multisystem disease with pathological changes involving peripheral organs such as the heart, lungs, pancreas, and liver (73, 74). The liver is a key metabolic organ, and the loss of endogenous SMN protein in the liver can lead to hepatic injury and the replacement of hepatic tissue with fibrofatty tissue, causing systemic metabolic dysfunction (75). However, patients with SMA type 3 may have abnormal muscle-adipose tissue interactions (76), suggesting that muscle fat replacement may be related to insulin resistance and metabolic disorders in some patients with SMA.
Metabolic dysfunction in patients with SMA is characterized by significantly elevated levels of cholesteryl esters, decreased levels of free cholesterol, decreased phospholipid levels, increased lysophospholipid levels, abnormal high-density lipoprotein function, and increased levels of tryptophan and its metabolites (e.g., indoleacrylic acid) (77). Another study observed a significant negative correlation between glucose and lactate concentrations in the CSF and clinical improvement (Hammersmith Functional Motor Scale score) in adult patients with SMA type 2 or 3 (78). Moreover, serum copper concentrations in SMA are positively correlated with fat accumulation, and high copper may promote muscle degradation through oxidative stress or interfere with mitochondrial function, leading to muscle loss (79). These features may become biomarkers for disease diagnosis, staging, and therapeutic monitoring. Hepatic steatosis, dyslipidemia, abnormal iron metabolism, pancreatic endocrine imbalance, and other metabolic abnormalities improved after the correction of SMN protein levels in the liver (80).
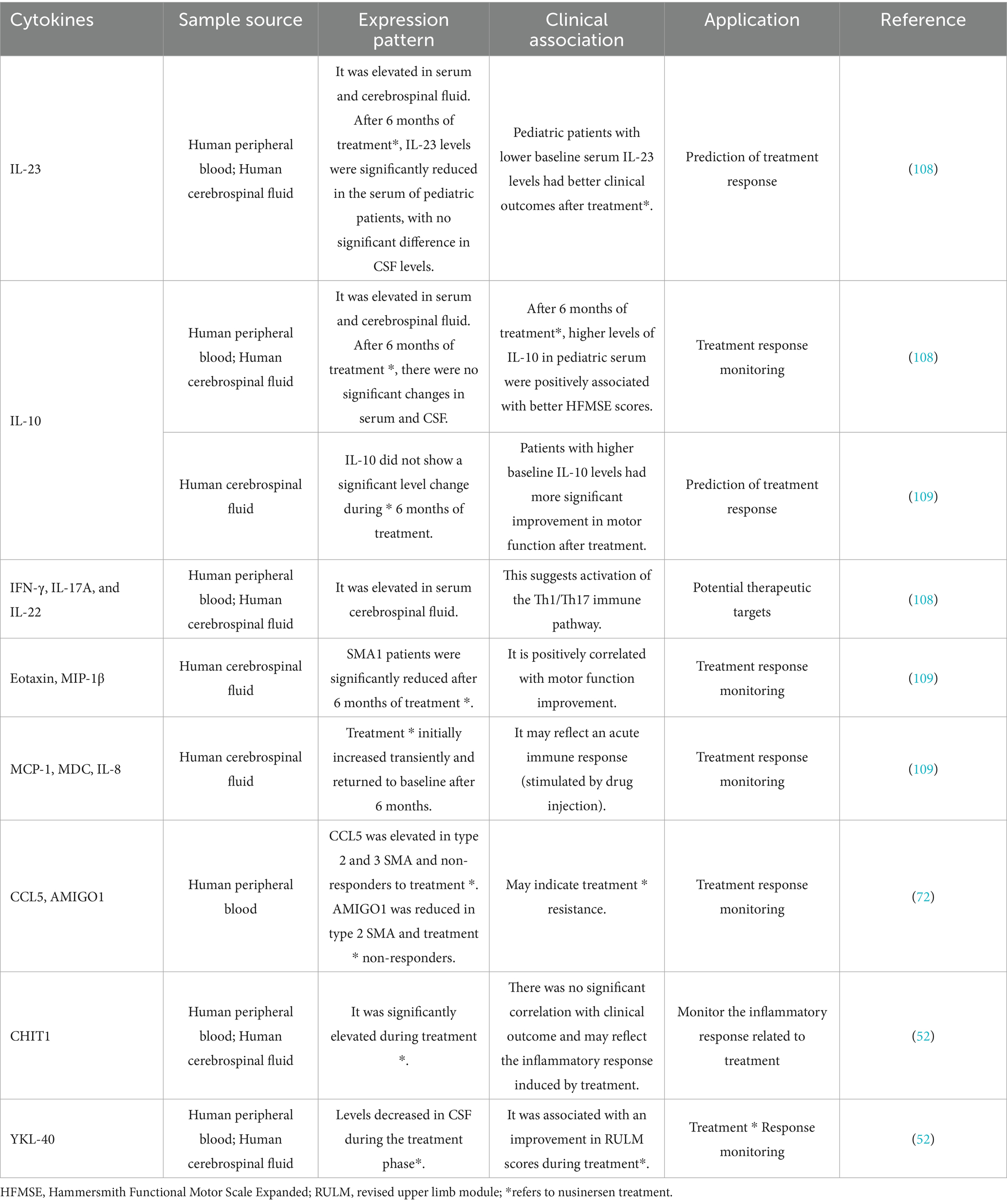
Inflammatory and metabolic processes cannot be separated from cytokines, and researchers have screened some cytokines that are mainly related to SMA inflammation and have specific pathological significance (see Table 2 for details). Compared with CSF testing, peripheral blood cytokine analysis has advantages in convenience and economy. However, whether peripheral blood indicators can replace the cytokine changes in CFS is still controversial. In addition, inflammatory activity in the body is universal and can be triggered by various triggers, even daily physiological fluctuations (e.g., changes in diet and exercise). Therefore, despite the relative convenience of cytokine detection, the interference of background inflammation has limited its application as a biomarker for SMA. As for metabolic-related cytokines, since metabolic disorders are mainly secondary pathological changes in SMA, the authors believe that such cytokines should be used as secondary biomarkers in combination with other biomarkers and included in the multidimensional evaluation system of SMA.
2.7 Other
Nusinersen can effectively increase the level of SMN protein in the central nervous system (CNS) and significantly improve the symptoms of patients. However, there are large numbers of non-responders, and treatment delay severely reduces efficacy – once motor neurons have entered an advanced stage of degeneration, their damage cannot be reversed by restoring SMN expression (81). Thus, it is critical to distinguish early between patients who have a response to Nusinersen and those who do not.
LARGE1 is a glycosyltransferase involved in neuromuscular function, and its increase may be associated with motor neuron protection or pathological processes. LARGE1 can be used as a potential biomarker for Nusinersen treatment response, especially in adult patients (82). LARGE1 protein was significantly increased in the CSF of adult SMA patients, especially in those who responded to nusinersen treatment. Serum LARGE1 levels were low at baseline in adult patients, increased significantly after treatment, and responders had significantly higher serum LARGE1 levels than non-responders. The level of LARGE1 in the CSF of pediatric SMA patients is already high at baseline and further increases in responders and decreases in non-responders after treatment, which can be used to monitor the response to treatment. However, there was no significant change in serum LARGE1 levels in pediatric patients.
However, we should not take treatment responders lightly. Clinical use of Nusinersen and Onasemnogene Abeparvovec (Zolgensma) has been associated with reported adverse events (83–85). The adverse reactions of Nusinersen involved 27 systemic organ categories, among which renal dysfunction, intrathecal injection complications and metabolic/psychiatric reactions were the potential risks that had not been fully appreciated. The adverse reactions of Onasemnogene Abeparvovec mainly included hepatotoxicity, hematological abnormalities, renal dysfunction, systemic reactions (fever, vomiting) and respiratory tract infection. For renal function, urine protein/creatinine ratio is more valuable than urine protein alone, and it is a more reliable index for evaluating renal function (68, 86).
These findings suggest that the implementation of individualized monitoring and treatment strategies is critical in the clinical management of SMA. Specifically, mechanisms for early identification of patients who have a poor response to treatment need to be established so that treatment can be adjusted in time to prevent disease progression to advanced stages and irreversible neuromuscular damage. At the same time, responders should be continuously monitored while receiving treatment, especially for potential adverse events that are not fully described in the drug labeling. This management strategy, based on stratification of treatment response, was designed to maximize clinical benefit and minimize associated risks.
3 Physiological biomarkers
In SMA, reduced levels of SMN protein trigger abnormal function and apoptosis of α-motor neurons in the spinal cord and in brainstem regions, which in turn progressively reduces the number of muscle fibers and decreases strength in trunk muscles including respiratory-related muscles, limb muscles, and swallowing-associated muscles (regulates by the medulla oblongata region).
3.1 Functionality
Maximal mouth opening (MMO) measurement is a part of the assessment of mandibular function and is a safe and easy-to-use method suitable for repeated testing. Due to medullary dysfunction, patients with SMA often have reduced MMO (87). In children aged 0–24 months, reduced MMO may be an early indicator of medullary functional involvement in SMA, particularly in children with two copies of the SMN2 gene (88). In adults, medullary functions, such as mandibular mobility and active MMO, decreased significantly over 4 years in patients with SMA type 2, but not in those with SMA type 3 (89).
Traditionally, SMA has not been thought to be directly related to primary heart disease. However, several studies have shown that arrhythmias and congenital cardiac structural abnormalities are not uncommon in SMA patients (90). Subclinical ventricular dysfunction is common in children with SMA (91). Notably, improvement in left ventricular (LV) function in children with SMA can be observed by echocardiographic monitoring after short-term Nusinersen treatment (92).
Perceived physical fatigability has been identified as the physiological factor most relevant to SMA pathophysiology. An assessment tailored to SMA patients, called SMA EFFORT, makes perceived physical fatigability ratings more objective, standardized, and better at assessing the impact of treatment on the physical health across the entire SMA spectrum (93).
3.2 Electrophysiology
The Hoffmann reflex (H-reflex), a spinal reflex evoked by electrophysiological methods, is primarily used to evaluate the excitability of spinal motor neurons and sensory nerve pathways. The H-reflex amplitude was reduced in mouse models of SMA and patients with SMA type 3 (26); after treatment, H-reflex function improved, along with significant improvements in motor function and fatigue in patients. H-reflex parameters can be used as quantitative biomarkers to track disease progression in real time and monitor treatment responses.
Important advances have recently been made in the electrophysiological assessment of the SMA by using two novel techniques, MScanFit motor unit number evaluation (MUNE) and disaggregated electromyography (dEMG), demonstrating their unique clinical applications (94). MScanFit focuses on the number of motor units and degree of reinnervation, whereas dEMG provides an in-depth analysis of the electrical discharge. dEMG complement each other and provide a multidimensional quantitative tool for the assessment of individualized therapeutic responses and the development of novel intervention strategies. However, longitudinal studies are needed to further validate its dynamic sensitivity in therapeutic monitoring.
4 Imaging biomarkers
Muscle fat replacement is common and often associated with various neuromuscular diseases (95). SMA can present with diffuse muscle fat replacement and has a complex pattern of muscle involvement: early onset of muscle fat replacement in the limbs, a strong correlation of fat content within the gastrocnemius muscle with disease severity and overall function, and relatively mild muscle fat replacement in medullary innervated muscles (e.g., masticatory and intrapterygoid). Significant fat accumulation has been observed in only a few patients (96). In seven nusinersen-treated children with SMA type 2 or 3, longitudinal MRI showed that an elevated intramuscular fat fraction of the thigh was significantly associated with decreased motor function (97). Meanwhile, patients with baseline IMFF < 20% had improvement in motor function (an increase in HFMSE score) after 4 years of treatment, whereas those with IMFF > 20% had a decline in function, suggesting that baseline IMFF can be used as a predictive marker of nusinersen response. Quantitative MRI study of eight children further found that although the thigh muscle fat fraction continued to increase after treatment, diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) showed that muscle microstructure may tend to be normalized, suggesting that IMFF can reflect the effect of drug intervention (98).
Muscle FF, as a biomarker, is of great value in SMA. FF can quantitatively provide objective muscle structure data through MRI, which can more accurately evaluate the patient’s condition and make up for the subjective limitations of traditional functional scores (such as HFMSE), especially for children and patients with severe movement disorders. FF can detect small changes in muscle at an early stage before complete factorization of muscle, which is more sensitive than clinical score. The baseline level and dynamic changes of muscle FF can be used as a long-term efficacy monitoring tool to help evaluate disease progression and treatment response.
5 Conclusion
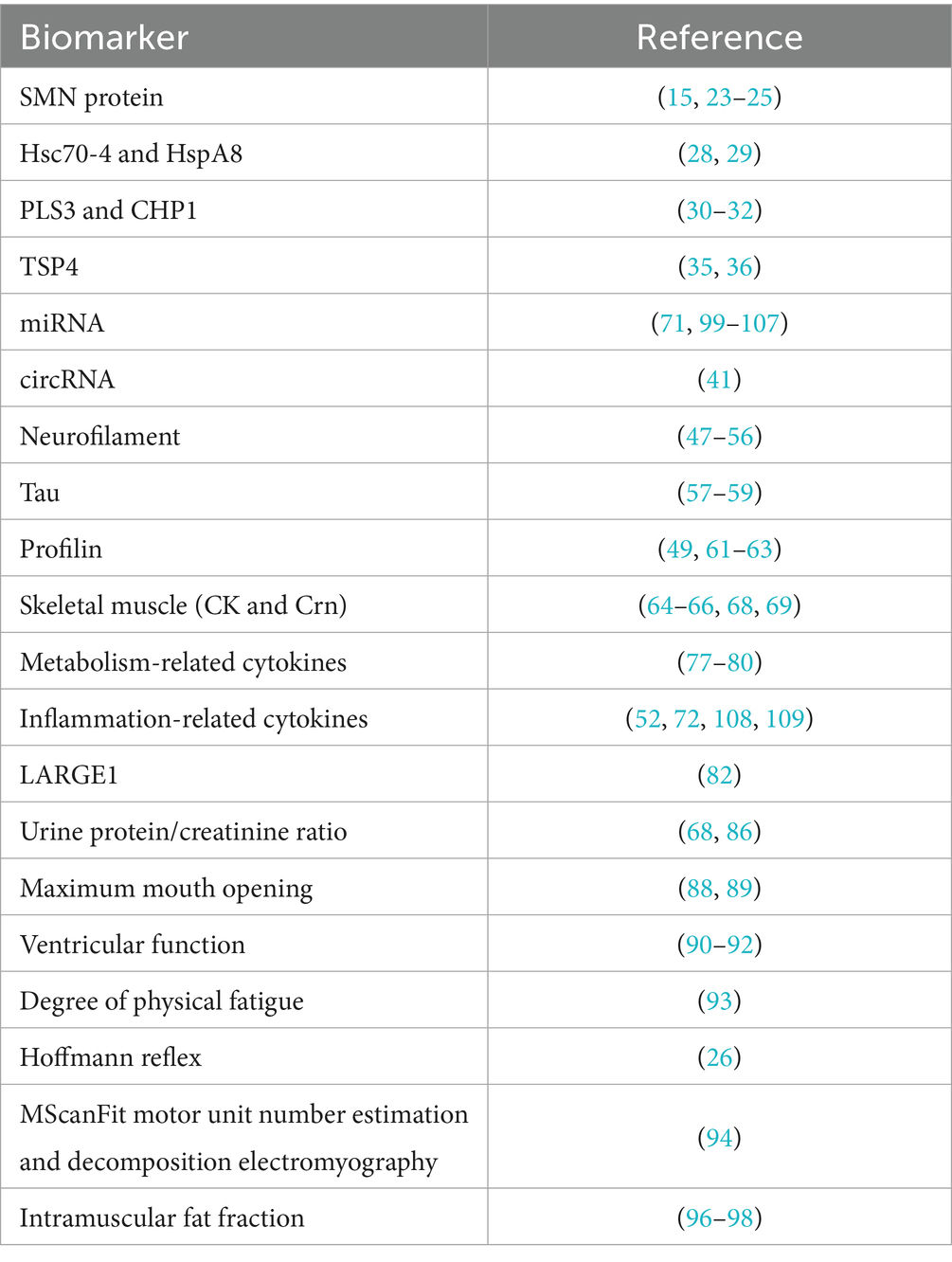
SMA is a rare disease, but the emergence of effective therapies has significantly prolonged the survival of patients. More specific biomarkers for diagnosis, treatment and prognosis are needed to help SMA patients achieve a better quality of life. This article systematically reviews the pathogenesis of SMA (Figure 1) and the biomarkers associated with SMA found in recent years (see Table 3 for details), focusing on molecular biomarkers. Among them, SMN protein level directly determines the survival ability of motor neurons and is still the core molecular marker of SMA. After the exclusion of other differential diagnoses and full consideration of confounding factors, NFs is still the most classical pathological index, which can reflect the state of nerve injury. Despite the increasing value of emerging molecular markers, their specificity and applicability still need to be further verified. In conclusion, the value of single indicator as a biomarker of SMA is limited, and the integration of multi-omics data analysis can obtain better evaluation effect.
However, existing studies are generally limited by insufficient sample sizes, which not only lead to conflicting results of the same biomarker, but also weaken its association with clinical outcomes. In addition, SMA patient populations have significant heterogeneity (e.g., subtype, age at onset, baseline motor function), which, if adjusted for in analyses, may mask the true association of markers with clinical outcomes. But statistical irrelevance does not mean that these markers are not biologically meaningless. Potential reasons for the missing association may include the following: the index is not related to the core pathological mechanism; Study design flaws. The signaling pathways interfere with each other. In addition, negative results may also suggest that the role of this indicator in SMA is independent of the motor function pathway, and the research perspective needs to be repositioned. In future studies, we look forward to more reliable data to clarify the application of biomarkers in SMA and ultimately benefit SMA patients.
Author contributions
LY: Writing – original draft, Conceptualization. JZha: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft. JZhe: Writing – original draft, Conceptualization. HH: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing, Funding acquisition, Supervision.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by Project of College-level Key Discipline of Yangpu Hospital Affiliated to Tongji University (No. 2023YJXK01), Fund of Yangpu Hospital Affiliated to Tongji University (No. Se1202318), Project of Yangpu District Health and Wellness Committee (No. YPM202414) and Project of Shanghai Municipal Health Commission (No. 202140232).
Acknowledgments
We thank Editage (http://www.editage.cn) for its linguistic assistance during the preparation of this manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Lefebvre, S, Bürglen, L, Reboullet, S, Clermont, O, Burlet, P, Viollet, L, et al. Identification and characterization of a spinal muscular atrophy-determining gene. Cell. (1995) 80:155–65. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90460-3
2. Mercuri, E, Finkel, RS, Muntoni, F, Wirth, B, Montes, J, Main, M, et al. Diagnosis and management of spinal muscular atrophy: part 1: recommendations for diagnosis, rehabilitation, orthopedic and nutritional care. Neuromuscul Disord. (2018) 28:103–15. doi: 10.1016/j.nmd.2017.11.005
3. Verhaart, IEC, Robertson, A, Wilson, IJ, Aartsma-Rus, A, Cameron, S, Jones, CC, et al. Prevalence, incidence and carrier frequency of 5q-linked spinal muscular atrophy – a literature review. Orphanet J Rare Dis. (2017) 12:124. doi: 10.1186/s13023-017-0671-8
4. Sun, J, Harrington, MA, and Porter, Bon behalf of the TREAT-NMD Global Registry Network for SMA. Sex difference in spinal muscular atrophy patients – are males more vulnerable? J. Neuromuscul. Dis. (2023) 10:847–67. doi: 10.3233/JND-230011
5. Kato, T, Yokomura, M, Osawa, Y, Matsuo, K, Kubo, Y, Homma, T, et al. Genomic analysis of the SMN1 gene region in patients with clinically diagnosed spinal muscular atrophy: a retrospective observational study. Orphanet J Rare Dis. (2025) 20:55. doi: 10.1186/s13023-025-03568-9
6. Wirth, B. Spinal muscular atrophy: in the challenge lies a solution. Trends Neurosci. (2021) 44:306–22. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2020.11.009
7. Mercuri, E, Sumner, CJ, Muntoni, F, Darras, BT, and Finkel, RS. Spinal muscular atrophy. Nat Rev Dis Primers. (2022) 8:52. doi: 10.1038/s41572-022-00380-8
8. Wirth, B. An update of the mutation spectrum of the survival motor neuron gene (SMN1) in autosomal recessive spinal muscular atrophy (SMA). Hum Mutat. (2000) 15:228–37. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1098-1004(200003)15:3<228::AID-HUMU3>3.0.CO;2-9
9. Hahnen, E, Schönling, J, Rudnik-Schöneborn, S, Zerres, K, and Wirth, B. Hybrid survival motor neuron genes in patients with autosomal recessive spinal muscular atrophy: new insights into molecular mechanisms responsible for the disease. Am J Hum Genet. (1996) 59:1057–65.
10. Corcia, P, Camu, W, Halimi, J-M, Vourc'h, P, Antar, C, Vedrine, S, et al. SMN1 gene, but not SMN2, is a risk factor for sporadic ALS. Neurology. (2006) 67:1147–50. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000233830.85206.1e
11. Kugelberg, E, and Welander, L. Heredofamilial juvenile muscular atrophy simulating muscular dystrophy. AMA Arch Neurol Psychiatry. (1956) 75:500–9. doi: 10.1001/archneurpsyc.1956.02330230050005
12. Dubowitz, V. Very severe spinal muscular atrophy (SMA type 0): an expanding clinical phenotype. Eur J Paediatr Neurol. (1999) 3:49–51.
13. Schorling, DC, Pechmann, A, and Kirschner, J. Advances in treatment of spinal muscular atrophy – new phenotypes, new challenges, new implications for care. J Neuromuscul Dis. (2020) 7:1–13. doi: 10.3233/JND-190424
14. Zhang, J, Wang, Y, Ma, D, Sun, Y, Li, Y, Yang, P, et al. Carrier screening and prenatal diagnosis for spinal muscular atrophy in 13,069 Chinese pregnant women. J Mol Diagn JMD. (2020) 22:817–22. doi: 10.1016/j.jmoldx.2020.03.001
15. Otsuki, N, Kato, T, Yokomura, M, Urano, M, Matsuo, M, Kobayashi, E, et al. Analysis of SMN protein in umbilical cord blood and postnatal peripheral blood of neonates with SMA: a rationale for prompt treatment initiation to prevent SMA development. Orphanet J Rare Dis. (2025) 20:91. doi: 10.1186/s13023-025-03597-4
16. Motyl, AAL, and Gillingwater, TH. Timing is everything: clinical evidence supports pre-symptomatic treatment for spinal muscular atrophy. Cell Rep Med. (2022) 3:100725. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2022.100725
17. Jiang, Y, Xia, Z, Zhou, Y, Lu, X, Du, X, and Guo, Q. Comparison of the accuracy of multiplex digital PCR versus multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification in quantification of the survival of motor neuron genes copy numbers. Clin Chim Acta. (2024) 553:117708. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2023.117708
18. Li, S, Hua, R, Han, X, Xu, Y, Li, M, Gao, L, et al. Targeted Long-read sequencing facilitates effective carrier screening for complex monogenic diseases including spinal muscular atrophy, α−/β-thalassemia, 21-hydroxylase deficiency, and fragile-X syndrome. J Transl Med. (2025) 23:307. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06345-1
19. Günther, R, Wurster, CD, Brakemeier, S, Osmanovic, A, Schreiber-Katz, O, Petri, S, et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of Nusinersen in adults with 5q spinal muscular atrophy: a prospective European multinational observational study. Lancet Reg Health Eur. (2024) 39:100862. doi: 10.1016/j.lanepe.2024.100862
20. Lefebvre, S, Burlet, P, Liu, Q, Bertrandy, S, Clermont, O, Munnich, A, et al. Correlation between severity and SMN protein level in spinal muscular atrophy. Nat Genet. (1997) 16:265–9. doi: 10.1038/ng0797-265
21. Coovert, DD, Le, TT, McAndrew, PE, Strasswimmer, J, Crawford, TO, Mendell, JR, et al. The survival motor neuron protein in spinal muscular atrophy. Hum Mol Genet. (1997) 6:1205–14. doi: 10.1093/hmg/6.8.1205
22. Han, K-J, Foster, D, Harhaj, EW, Dzieciatkowska, M, Hansen, K, and Liu, CW. Monoubiquitination of survival motor neuron regulates its cellular localization and Cajal body integrity. Hum Mol Genet. (2016) 25:1392–405. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddw021
23. Finkel, RS, Hughes, SH, Parker, J, Civitello, M, Lavado, A, Mefford, HC, et al. Risdiplam for prenatal therapy of spinal muscular atrophy. N Engl J Med. (2025) 392:1138–40. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2300802
24. Al-Hilal, H, Maretina, M, Egorova, A, Glotov, A, and Kiselev, A. Assessment of nuclear gem quantity for evaluating the efficacy of antisense oligonucleotides in spinal muscular atrophy cells. Methods Protoc. (2024) 7:9. doi: 10.3390/mps7010009
25. Markati, T, Fisher, G, Ramdas, S, and Servais, L. Risdiplam: an investigational survival motor neuron 2 (SMN2) splicing modifier for spinal muscular atrophy (SMA). Expert Opin Investig Drugs. (2022) 31:451–61. doi: 10.1080/13543784.2022.2056836
26. Simon, CM, Delestrée, N, Montes, J, Sowoidnich, L, Gerstner, F, Carranza, E, et al. Proprioceptive synaptic dysfunction is a key feature in mice and humans with spinal muscular atrophy. Brain J Neurol. (2025) awaf074. doi: 10.1093/brain/awaf074
27. Miles, J, Scherz-Shouval, R, and van Oosten-Hawle, P. Expanding the organismal Proteostasis network: linking systemic stress signaling with the innate immune response. Trends Biochem Sci. (2019) 44:927–42. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2019.06.009
28. Kim, J-K, Jha, NN, Awano, T, Caine, C, Gollapalli, K, Welby, E, et al. A spinal muscular atrophy modifier implicates the SMN protein in SNARE complex assembly at neuromuscular synapses. Neuron. (2023) 111:1423–1439.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2023.02.004
29. Matera, AG, Steiner, RE, Mills, CA, McMichael, BD, Herring, LE, and Garcia, EL. Proteomic analysis of the SMN complex reveals conserved and etiologic connections to the Proteostasis network. Front RNA Res. (2024) 2:1448194. doi: 10.3389/frnar.2024.1448194
30. Shi, T, Zhou, Z, Xiang, T, Suo, Y, Shi, X, Li, Y, et al. Cytoskeleton dysfunction of motor neuron in spinal muscular atrophy. J Neurol. (2024) 272:19. doi: 10.1007/s00415-024-12724-3
31. Strathmann, EA, Hölker, I, Tschernoster, N, Hosseinibarkooie, S, Come, J, Martinat, C, et al. Epigenetic regulation of Plastin 3 expression by the macrosatellite DXZ4 and the transcriptional regulator CHD4. Am J Hum Genet. (2023) 110:442–59. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2023.02.004
32. Janzen, E, Mendoza-Ferreira, N, Hosseinibarkooie, S, Schneider, S, Hupperich, K, Tschanz, T, et al. CHP1 reduction ameliorates spinal muscular atrophy pathology by restoring Calcineurin activity and endocytosis. Brain J Neurol. (2018) 141:2343–61. doi: 10.1093/brain/awy167
33. Lawler, J, Duquette, M, Whittaker, CA, Adams, JC, McHenry, K, DeSimone, DW, et al. Identification and characterization of Thrombospondin-4, a new member of the thrombospondin gene family. J Cell Biol. (1993) 120:1059–67. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.4.1059
34. Arber, S, and Caroni, P. Thrombospondin-4, an extracellular matrix protein expressed in the developing and adult nervous system promotes neurite outgrowth. J Cell Biol. (1995) 131:1083–94. doi: 10.1083/jcb.131.4.1083
35. Bottai, D, and Adami, R. Spinal muscular atrophy: new findings for an old pathology. Brain Pathol. (2013) 23:613–22. doi: 10.1111/bpa.12071
36. Dobelmann, V, Roos, A, Hentschel, A, Della Marina, A, Leo, M, Schmitt, LI, et al. Thrombospondin-4 as potential cerebrospinal fluid biomarker for therapy response in pediatric spinal muscular atrophy. J Neurol. (2024) 271:7000–11. doi: 10.1007/s00415-024-12670-0
37. Matera, AG. Chaperone dysfunction in motor neuron disease: new insights from studies of the SMN complex. Genetics. (2025) 229:iyae223. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyae223
38. Yedigaryan, L, and Sampaolesi, M. Therapeutic implications of miRNAs for muscle-wasting conditions. Cells. (2021) 10:3035. doi: 10.3390/cells10113035
39. Yedigaryan, L, Gatti, M, Marini, V, Maraldi, T, and Sampaolesi, M. Shared and divergent epigenetic mechanisms in Cachexia and sarcopenia. Cells. (2022) 11:2293. doi: 10.3390/cells11152293
40. Vangoor, VR, Gomes-Duarte, A, and Pasterkamp, RJ. Long non-coding RNAs in motor neuron development and disease. J Neurochem. (2021) 156:777–801. doi: 10.1111/jnc.15198
41. Guerra, M, Marini, A, Pagliarini, V, Pitolli, C, Coratti, G, Bonvissuto, D, et al. High expression of SMN Circ4-2b-3 in SMA I children treated with Nusinersen is associated with improved motor outcomes. Mol Neurobiol. (2025) 62:5640–9. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04605-7
42. Yuan, A, Rao, MV, Veeranna,, and Nixon, RA. Neurofilaments and Neurofilament proteins in health and disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. (2017) 9:a018309. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a018309
43. Gaetani, L, Blennow, K, Calabresi, P, Di Filippo, M, Parnetti, L, and Zetterberg, H. Neurofilament light chain as a biomarker in neurological disorders. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. (2019) 90:870–81. doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2018-320106
44. Shahim, P, Norato, G, Sinaii, N, Zetterberg, H, Blennow, K, Chan, L, et al. Neurofilaments in sporadic and familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. Genes. (2024) 15:496. doi: 10.3390/genes15040496
45. Benatar, M, Wuu, J, Andersen, PM, Lombardi, V, and Malaspina, A. Neurofilament light: a candidate biomarker of Presymptomatic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and Phenoconversion. Ann Neurol. (2018) 84:130–9. doi: 10.1002/ana.25276
46. Agah, E, Mojtabavi, H, Behkar, A, Heidari, A, Ajdari, A, Shaka, Z, et al. CSF and blood levels of Neurofilaments, T-tau, P-tau, and Abeta-42 in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. J Transl Med. (2024) 22:953. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05767-7
47. Bayoumy, S, Verberk, IMW, Vermunt, L, Willemse, E, den Dulk, B, van der Ploeg, AT, et al. Neurofilament light protein as a biomarker for spinal muscular atrophy: a review and reference ranges. Clin Chem Lab Med. (2024) 62:1252–65. doi: 10.1515/cclm-2023-1311
48. Jin, J, Feng, Y, Huang, S, Cui, Y, Jiang, L, Yan, Y, et al. Value of plasma Neurofilament light chain for monitoring efficacy in children with later-onset spinal muscular atrophy under Nusinersen treatment. Clin Chem Lab Med. (2024) 62:e132–5. doi: 10.1515/cclm-2023-1119
49. Musso, G, Bello, L, Capece, G, Bozzoni, V, Caumo, L, Sabbatini, D, et al. Neurofilament light chain and Profilin-1 dynamics in 30 spinal muscular atrophy type 3 patients treated with Nusinersen. Eur J Neurol. (2024) 31:e16393. doi: 10.1111/ene.16393
50. Brkušanin, M, Kosać, A, Branković-Srećković, V, Jovanović, K, Perić, S, Karanović, J, et al. Phosphorylated Neurofilament heavy chain in cerebrospinal fluid and plasma as a Nusinersen treatment response marker in childhood-onset SMA individuals from Serbia. Front Neurol. (2024) 15:1394001. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1394001
51. Cordts, I, Fuetterer, C, Wachinger, A, von Heynitz, R, Kessler, T, Freigang, M, et al. Long-term dynamics of CSF and serum Neurofilament light chain in adult patients with 5q spinal muscular atrophy treated with Nusinersen. Neurology. (2025) 104:e213371. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000213371
52. De Wel, B, De Schaepdryver, M, Poesen, K, and Claeys, KG. Biochemical and clinical biomarkers in adult SMA 3-4 patients treated with Nusinersen for 22 months. Ann Clin Transl Neurol. (2022) 9:1241–51. doi: 10.1002/acn3.51625
53. Flotats-Bastardas, M, Bitzan, L, Grell, C, Martakis, K, Winter, B, Zemlin, M, et al. Paradoxical increase of neurofilaments in SMA patients treated with Onasemnogene Abeparvovec-Xioi. Front Neurol. (2023) 14:1269406. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1269406
54. Li, J-Y, Dai, Y, Sun, X-H, Ren, HT, Shen, DC, Yang, XZ, et al. Comparison of Neurofilament light and heavy chain in spinal muscular atrophy and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a pilot study. Brain Behav. (2023) 13:e2997. doi: 10.1002/brb3.2997
55. Rich, KA, Fox, A, Yalvac, M, Heintzman, S, Tellez, M, Bartlett, A, et al. Neurofilament levels in CSF and serum in an adult SMA cohort treated with Nusinersen. J. Neuromuscul. Dis. (2022) 9:111–9. doi: 10.3233/JND-210735
56. Vågberg, M, Norgren, N, Dring, A, Lindqvist, T, Birgander, R, Zetterberg, H, et al. Levels and age dependency of Neurofilament light and glial fibrillary acidic protein in healthy individuals and their relation to the brain parenchymal fraction. PLoS One. (2015) 10:e0135886. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0135886
57. Totzeck, A, Stolte, B, Kizina, K, Bolz, S, Schlag, M, Thimm, A, et al. Neurofilament heavy chain and tau protein are not elevated in cerebrospinal fluid of adult patients with spinal muscular atrophy during loading with Nusinersen. Int J Mol Sci. (2019) 20:5397. doi: 10.3390/ijms20215397
58. Šimić, G, Vukić, V, Babić, M, Banović, M, Berečić, I, Španić, E, et al. Total tau in cerebrospinal fluid detects treatment responders among spinal muscular atrophy types 1-3 patients treated with Nusinersen. CNS Neurosci Ther. (2024) 30:e14051. doi: 10.1111/cns.14051
59. Sframeli, M, Polito, F, Vita, G, Macaione, V, Gitto, E, Aguennouz, M, et al. Cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers of efficacy in patients affected by spinal muscular atrophy type 1 treated with Nusinersen. Acta Neurol Belg. (2025) 125:819–827. doi: 10.1007/s13760-025-02784-1
60. Witke, W. The role of profilin complexes in cell motility and other cellular processes. Trends Cell Biol. (2004) 14:461–9. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2004.07.003
61. Jockusch, BM, Murk, K, and Rothkegel, M. The profile of profilins. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. (2007) 159:131–49. doi: 10.1007/112_2007_704
62. Hensel, N, and Claus, P. The actin cytoskeleton in SMA and ALS: how does it contribute to motoneuron degeneration? Neuroscientist. (2018) 24:54–72. doi: 10.1177/1073858417705059
63. Murk, K, Ornaghi, M, and Schiweck, J. Profilin isoforms in health and disease – all the same but different. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2021) 9:681122. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.681122
64. Lombardi, V, Querin, G, Ziff, OJ, Zampedri, L, Martinelli, I, Heller, C, et al. Muscle and not neuronal biomarkers correlate with severity in spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy. Neurology. (2019) 92:e1205–11. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000007097
65. Freigang, M, Wurster, CD, Hagenacker, T, Stolte, B, Weiler, M, Kamm, C, et al. Serum Creatine kinase and creatinine in adult spinal muscular atrophy under Nusinersen treatment. Ann Clin Transl Neurol. (2021) 8:1049–63. doi: 10.1002/acn3.51340
66. Zhao, X, Gong, Z, Luo, H, Li, Z, Gao, R, Yang, K, et al. A cross-sectional and longitudinal evaluation of serum creatinine as a biomarker in spinal muscular atrophy. Orphanet J Rare Dis. (2024) 19:489. doi: 10.1186/s13023-024-03515-0
67. Gavriilaki, M, Papaliagkas, V, Stamperna, A, Moschou, M, Notas, K, Papagiannopoulos, S, et al. Biomarkers of therapeutic efficacy in adolescents and adults with 5q spinal muscular atrophy: a systematic review. Acta Neurol Belg. (2023) 123:1735–45. doi: 10.1007/s13760-022-02028-6
68. Bahadır Şenol, H, Yıldız, G, Polat, Aİ, Aydın, A, Hız, AS, Soylu, A, et al. Safety and efficacy of Nusinersen focusing on renal and hematological parameters in spinal muscular atrophy. Brain Behav. (2025) 15:e70221. doi: 10.1002/brb3.70221
69. de Albuquerque, ALA, Chadanowicz, JK, Giudicelli, GC, Staub, ALP, Weber, AC, Silva, JMDS, et al. Serum Myostatin as a candidate disease severity and progression biomarker of spinal muscular atrophy. Brain Commun. (2024) 6:fcae062. doi: 10.1093/braincomms/fcae062
70. Wood, H. Neuroinflammation in spinal muscular atrophy. Nat Rev Neurol. (2023) 19:197. doi: 10.1038/s41582-023-00791-5
71. Belančić, A, Janković, T, Gkrinia, EMM, Kristić, I, Rajič Bumber, J, Rački, V, et al. Glial cells in spinal muscular atrophy: speculations on non-cell-autonomous mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Neurol Int. (2025) 17:41. doi: 10.3390/neurolint17030041
72. Leo, M, Schmitt, L-I, Mairinger, F, Roos, A, Hansmann, C, Hezel, S, et al. Analysis of free circulating messenger ribonucleic acids in serum samples from late-onset spinal muscular atrophy patients using nCounter NanoString technology. Cells. (2023) 12:2374. doi: 10.3390/cells12192374
73. Hamilton, G, and Gillingwater, TH. Spinal muscular atrophy: going beyond the motor neuron. Trends Mol Med. (2013) 19:40–50. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2012.11.002
74. Nash, LA, Burns, JK, Chardon, JW, Kothary, R, and Parks, RJ. Spinal muscular atrophy: more than a disease of motor neurons? Curr Mol Med. (2016) 16:779–92. doi: 10.2174/1566524016666161128113338
75. Vitte, JM, Davoult, B, Roblot, N, Mayer, M, Joshi, V, Courageot, S, et al. Deletion of murine Smn exon 7 directed to liver leads to severe defect of liver development associated with Iron overload. Am J Pathol. (2004) 165:1731–41. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63428-1
76. Miletić, M, Stević, Z, Perić, S, Tančić Gajić, M, Rakočević, J, Stojanović, M, et al. Adiponectin and leptin-considerations in adult patients with spinal muscular atrophy type 3. Diagnostics. (2025) 15:529. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15050529
77. Zandl-Lang, M, Züllig, T, Holzer, M, Eichmann, TO, Darnhofer, B, Schwerin-Nagel, A, et al. Multi-omics profiling in spinal muscular atrophy (SMA): investigating lipid and metabolic alterations through longitudinal CSF analysis of Nusinersen-treated patients. J Neurol. (2025) 272:183. doi: 10.1007/s00415-025-12909-4
78. Cebulla, G, Hai, L, Warnken, U, Güngör, C, Hoffmann, DC, Korporal-Kuhnke, M, et al. Long-term CSF responses in adult patients with spinal muscular atrophy type 2 or 3 on treatment with Nusinersen. J Neurol. (2025) 272:270. doi: 10.1007/s00415-025-12984-7
79. Long, Q, Feng, Y, Yu, Y, Chen, F, Ma, M, and Mao, S. Association between serum copper concentration and body composition in children with spinal muscular atrophy: a cross-sectional study. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. (2025) 34:84–90. doi: 10.6133/apjcn.202502_34(1).0008
80. Sutton, ER, Beauvais, A, Yaworski, R, et al. Liver SMN restoration rescues the Smn2B/− mouse model of spinal muscular atrophy. EBioMedicine. (2024) 110:105444
81. Hensel, N, Kubinski, S, and Claus, P. The need for SMN-independent treatments of spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) to complement SMN-enhancing drugs. Front Neurol. (2020) 11:45. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.00045
82. Roos, A, Schmitt, L-I, Hansmann, C, Hezel, S, Salmanian, S, Hentschel, A, et al. Alteration of LARGE1 abundance in patients and a mouse model of 5q-associated spinal muscular atrophy. Acta Neuropathol. (2024) 147:53. doi: 10.1007/s00401-024-02709-x
83. Wu, Y-F, Chen, J-A, and Jong, Y-J. Treating neuromuscular diseases: unveiling gene therapy breakthroughs and pioneering future applications. J Biomed Sci. (2025) 32:30. doi: 10.1186/s12929-025-01123-z
84. Jiang, Y, Shen, Y, Zhou, Q, and Zhu, H. Unveiling the adverse events of Nusinersen in spinal muscular atrophy management based on FAERS database. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:17138. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-67627-0
85. Zhang, W, Yin, Y, Yang, D, et al. Comprehensive analysis of adverse events associated with onasemnogene abeparvovec (Zolgensma) in spinal muscular atrophy patients: insights from FAERS database. Front Pharmacol. (2024) 15:1475884
86. Nagarajan, EK, Özütemiz, C, Rubin, N, and Nascene, DR. Stability of serial platelet and urine protein measurements in patients receiving Nusinersen for spinal muscular atrophy. Muscle Nerve. (2022) 66:76–9. doi: 10.1002/mus.27564
87. Wadman, RI, van Bruggen, HW, Witkamp, TD, Sparreboom-Kalaykova, SI, Stam, M, van den Berg, LH, et al. Bulbar muscle MRI changes in patients with SMA with reduced mouth opening and dysphagia. Neurology. (2014) 83:1060–6. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000000796
88. Zang, J, Weiss, D, Dumitrascu, C, Glinzer, J, Wegner, M, Strube, A, et al. Maximal mouth opening in infants and toddlers with spinal muscular atrophy: a prospective controlled study. Orphanet J Rare Dis. (2025) 20:24. doi: 10.1186/s13023-024-03524-z
89. van Bruggen, HW, Wijngaarde, CA, Asselman, F, Stam, M, Creugers, NHJ, Wadman, RI, et al. Natural history of mandibular function in spinal muscular atrophy types 2 and 3. J. Neuromuscul. Dis. (2024) 11:655–64. doi: 10.3233/JND-240007
90. Wijngaarde, CA, Blank, AC, Stam, M, Wadman, RI, van den Berg, LH, and van der Pol, WL. Cardiac pathology in spinal muscular atrophy: a systematic review. Orphanet J Rare Dis. (2017) 12:67. doi: 10.1186/s13023-017-0613-5
91. He, X, Li, X, Yan, M, Peng, H, Zhang, L, Liang, Y, et al. Cardiac function evaluation in children with spinal muscular atrophy: a case-control study. Pediatr Int. (2024) 66:e15769. doi: 10.1111/ped.15769
92. Fu, X, Feng, Y, Cui, Y, Fang, X, Yu, Y, Yu, J, et al. Echocardiographic evaluation of left ventricular function in children with spinal muscular atrophy before and after Nusinersen treatment. J Neurol Sci. (2025) 470:123415. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2025.123415
93. Rodriguez-Torres, R, Kanner, CH, Gay, EL, Uher, D, Corbeil, T, Coratti, G, et al. Development of the SMA EFFORT: a new approach to characterize perceived physical fatigability in spinal muscular atrophy. J. Neuromuscul. Dis. (2025) 12:22143602241313326. doi: 10.1177/22143602241313326
94. Kelly, KM, Mizell, J, Bigdeli, L, Paul, S, Tellez, MA, Bartlett, A, et al. Differential impact on motor unit characteristics across severities of adult spinal muscular atrophy. Ann Clin Transl Neurol. (2023) 10:2208–22. doi: 10.1002/acn3.51906
95. Verdú-Díaz, J, Alonso-Pérez, J, Nuñez-Peralta, C, Tasca, G, Vissing, J, Straub, V, et al. Accuracy of a machine learning muscle MRI-based tool for the diagnosis of muscular dystrophies. Neurology. (2020) 94:e1094–102. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000009068
96. Frølich, SV, Receveur, N, Poulsen, NS, Hansen, AE, and Vissing, J. Whole-body muscle MRI in patients with spinal muscular atrophy. J Neurol. (2025) 272:271. doi: 10.1007/s00415-025-13005-3
97. Iketani, K, Awano, H, Hashimura, H, Sonehara, S, Hanafusa, H, Nambu, Y, et al. Total intramuscular fat fraction of thigh muscles as a predictor of Nusinersen efficacy in pediatric SMA type II and III. Diagnostics. (2025) 15:753. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15060753
98. Otto, LAM, Froeling, M, van Eijk, RPA, Wadman, RI, Cuppen, I, van der Woude, DR, et al. Monitoring Nusinersen treatment effects in children with spinal muscular atrophy with quantitative muscle MRI. J Neuromuscul Dis. (2024) 11:91–101. doi: 10.3233/JND-221671
99. Mousa, NO, Abdellatif, A, Fahmy, N, El-Fawal, H, and Osman, A. Micrornas as a tool for differential diagnosis of neuromuscular disorders. NeuroMolecular Med. (2023) 25:603–15. doi: 10.1007/s12017-023-08763-0
100. Malacarne, C, Galbiati, M, Giagnorio, E, Cavalcante, P, Salerno, F, Andreetta, F, et al. Dysregulation of muscle-specific MicroRNAs as common pathogenic feature associated with muscle atrophy in ALS, SMA and SBMA: evidence from animal models and human patients. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22:5673. doi: 10.3390/ijms22115673
101. Bonanno, S, Marcuzzo, S, Malacarne, C, Giagnorio, E, Masson, R, Zanin, R, et al. Circulating MyomiRs as potential biomarkers to monitor response to Nusinersen in pediatric SMA patients. Biomedicines. (2020) 8:21. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines8020021
102. Magen, I, Aharoni, S, Yacovzada, NS, Tokatly Latzer, I, Alves, CRR, Sagi, L, et al. Muscle microRNAs in the cerebrospinal fluid predict clinical response to Nusinersen therapy in type II and type III spinal muscular atrophy patients. Eur J Neurol. (2022) 29:2420–30. doi: 10.1111/ene.15382
103. Welby, E, Rehborg, RJ, Harmelink, M, and Ebert, AD. Assessment of cerebral spinal fluid biomarkers and microRNA-mediated disease mechanisms in spinal muscular atrophy patient samples. Hum Mol Genet. (2022) 31:1830–43. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddab365
104. Chen, T-H, Chang, S-H, Wu, Y-F, Yen, YP, Hsu, FY, Chen, YC, et al. MiR34 contributes to spinal muscular atrophy and AAV9-mediated delivery of MiR34a ameliorates the motor deficits in SMA mice. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids. (2023) 32:144–60. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2023.03.005
105. Wu, L, Sun, J, Wang, L, Chen, Z, Guan, Z, du, L, et al. Whole-transcriptome sequencing in neural and non-neural tissues of a mouse model identifies miR-34a as a key regulator in SMA pathogenesis. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. (2025) 36:102490. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2025.102490
106. D’Silva, AM, Kariyawasam, D, Venkat, P, Mayoh, C, and Farrar, MA. Identification of novel CSF-derived miRNAs in treated Paediatric onset spinal muscular atrophy: an exploratory study. Pharmaceutics. (2023) 15:170. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15010170
107. Zaharieva, IT, Scoto, M, Aragon-Gawinska, K, Ridout, D, Doreste, B, Servais, L, et al. Response of plasma microRNAs to Nusinersen treatment in patients with SMA. Ann Clin Transl Neurol. (2022) 9:1011–26. doi: 10.1002/acn3.51579
108. Bonanno, S, Cavalcante, P, Salvi, E, Giagnorio, E, Malacarne, C, Cattaneo, M, et al. Identification of a cytokine profile in serum and cerebrospinal fluid of pediatric and adult spinal muscular atrophy patients and its modulation upon Nusinersen treatment. Front Cell Neurosci. (2022) 16:982760. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2022.982760
Keywords: SMA, SMN1, molecular biomarkers, physiological biomarkers, imaging biomarkers
Citation: Yan L, Zhang J, Zheng J and Hao H (2025) Biomarkers in spinal muscular atrophy. Front. Neurol. 16:1636992. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1636992
Edited by:
Erdem Tüzün, Istanbul University, TürkiyeReviewed by:
Stefania Marcuzzo, IRCCS Carlo Besta Neurological Institute Foundation, ItalyEmily Welby, Medical College of Wisconsin, United States
Copyright © 2025 Yan, Zhang, Zheng and Hao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hua Hao, aGFvaHVhNDEwQHRvbmdqaS5lZHUuY24=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Liping Yan
Liping Yan Jinping Zhang
Jinping Zhang Jian Zheng
Jian Zheng Hua Hao
Hua Hao