Abstract
Spinal cord injury (SCI) presents a significant clinical challenge due to its complex pathology and limited capacity for self-repair, often resulting in substantial physical dysfunction. Conventional treatments emphasize symptom management, yet usually fail to achieve nerve regeneration and full functional recovery. Recently, Exosomes(Exos) have gained attention as key modulators in biological processes such as immune regulation, intercellular communication, and tissue repair, showing promise in nerve injury and regeneration. This review synthesizes recent research on Exosome-based SCI therapies, including their biological origins, mechanisms, potential applications, and current limitations. Although Exos' research in SCI is nascent, early studies indicate promising safety and efficacy. Future studies are encouraged to delve deeper into Exos preparation, optimization, and delivery to maximize therapeutic effectiveness, potentially advancing SCI treatment options.
1 Introduction
SCI is a spinal cord dysfunction resulting from external trauma or disease, which frequently leads to sensory and motor dysfunction below the injury level (1–3). It also significantly impacts the normal functioning of the autonomic nervous system, causing patients to face numerous challenges such as paralysis, sensory loss, and disruptions in basic life activities like breathing and heartbeat (4). Consequently, this greatly diminishes the quality of life for patients while imposing a substantial burden on their families and society (5, 6). The incidence rate of traumatic spinal cord injury (TSCI) is estimated at 26.48 per 1 million people, whereas non-traumatic spinal cord injury (NTSCI) occurs at a rate of 17.93 per 1 million people. Notably, Central and Eastern Europe as well as Central Asia exhibit significantly higher rates of SCI compared to other regions worldwide; moreover, male patients constitute a much larger proportion than female patients (7, 8). When SCI occurs, it damages the blood-spinal cord barrier (BSCB), leading to complex pathophysiological changes including local metabolic disorders, calcium overload, inflammation, oxidative stress, iron death, apoptosis, glial scarring, neuroplasticity changes, and autonomic nervous dysfunction (1, 9). These interconnected chain reactions exacerbate patient conditions and rehabilitation difficulties. Currently, within the medical field, active efforts are being made to explore effective treatments for spinal cord injuries. However, despite existing treatment methods such as surgical decompression, drug therapy, and postoperative rehabilitation training being able to alleviate symptoms to some extent, they often yield unsatisfactory results in terms of neurological function recovery (6, 10). Therefore, finding new, more effective treatment approaches has become an urgent issue that needs addressing within the medical field.
With the continuous advancement of scientific research, Exos have emerged as a promising therapeutic strategy for SCI treatment (11–13). Exos are small vesicles secreted by cells that contain a diverse array of bioactive substances such as lipids, proteins, nucleic acids, and cytokines (14). They play crucial roles in intercellular communication and regulation while influencing the microenvironment of the injured spinal cord (15, 16). Numerous studies have demonstrated that Exos derived from various cell types, including mesenchymal stem cells, neural stem cells, and macrophages, can effectively facilitate nerve repair following SCI (17, 18). These Exos exert their effects through multiple mechanisms, including the inhibition of ferroptosis and apoptosis, as well as the promotion of axon regeneration. Moreover, they also exhibit anti-inflammatory properties while regulating glial scar formation and providing nutritional support to damaged nerve cells (16, 19), thereby instilling renewed hope for SCI treatment. Notably, microRNAs (miRNAs) contained within Exos have exhibited significant potential in the therapeutic management of SCI (20). Furthermore, due to its non-toxic nature upon infusion along with easy accessibility and absence of ethical concerns (18), Exos has emerged as an alternative to cell-based therapies offering improved safety profiles and enhanced therapeutic efficacy across various regenerative applications (21, 22). Concurrently, hypoxic preconditioning has been shown to enhance the secretion of Exos, thereby further augmenting their therapeutic efficacy (23, 24). Exos derived from hypoxic preconditioning exhibit particularly enhanced therapeutic potential. Lastly, as natural nanocarriers, Exos possess intrinsic advantages, including stable physical and chemical properties, low immunogenicity, and superior penetration capabilities across the blood-brain barrier (BBB) and BSCB. These characteristics render them an ideal candidate for nanotherapeutic applications (25, 26). The utilization of Exos as carriers in the construction of nanomedical drug delivery systems (NDDS), combined with biological scaffolds in a synergistic therapy approach (27–29), has not only improved the therapeutic effectiveness of Exos in SCI treatment but also overcome the limitations associated with single therapy.
Although the research on Exos treatment for SCI is still in a continuous development phase, the existing research findings have established a solid foundation for future clinical application (30, 31). Further investigation into the mechanisms underlying Exos treatment for SCI, alongside the optimization of Exos preparation and delivery methods (32, 33), as well as the assessment of its long-term efficacy and safety (21, 34), are critical steps necessary to facilitate the translation of this therapy into clinical practice. At present, the therapeutic strategy based on Exos has shifted from single-molecule regulation to multimodal collaborative intervention, such as local sustained release in combination with light-curing hydrogels, or the construction of engineered Exos with enhanced functions through gene editing technology (35, 36). It is essential to conduct additional high-quality studies to advance the clinical application of Exos treatment for SCI, thereby offering new hope and effective therapeutic strategies for patients with SCI.
2 Exosomes
Exos are nanoscale membrane vesicles secreted by cells (37), typically measuring between 30 and 150 nm in diameter (33). The formation of Exos begins in the endosomal system within the cell, where the cytoplasmic membrane invagination forms the early endosomes, and the early endosomes further mature to form the late endosomes, also known as multivesicular bodies (MVBs). MVBs fuse with the plasma membrane of the cell and release the small vesicles contained within them into the extracellular environment, which are called Exos (38–40). Exos encompass a diverse array of biomolecules, including proteins (such as cytoskeletal proteins, membrane transport and fusion proteins, and members of the tetraspanin family like CD9, CD37, CD53, CD63, CD81, and CD82), lipids (including cholesterol, sphingomyelin, and phosphatidylserine), and nucleic acids (such as DNA, mRNA, miRNA, lncRNA, and circRNA) (15, 41, 42). Additionally, they contain proteins such as ALIX, TSG101, and heat shock proteins (HSP70, HSP90), which serve as markers and are involved in Exosome biogenesis (39, 43, 44) (Figure 1). The composition of Exos reflects the physiological and pathological states of their originating cells and can be transferred to recipient cells to facilitate various biological functions. Based on the extent of artificial modification, Exos can be broadly categorized into natural Exos and engineered Exos (28). A diverse array of human cells, such as stem cells, Schwann cells (SC), endothelial cells (EC), macrophages, microglial cells (MG), and even tumor cells (18), are capable of producing Exos. Exos from these various cell types may offer unique therapeutic benefits in treating SCI. In recent years, induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC) -derived Exos have become a research hotspot due to their unlimited proliferation, multi-directional differentiation, and personalized treatment potential. It has been confirmed that iPSC-Exos can effectively promote the polarization of M1 macrophages to anti-inflammatory M2 macrophages by targeting hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) by delivery of miR-199b-5p, and enhance nerve regeneration through the PI3K signaling pathway (45). Another group further developed a gene-edited engineered exosome that could be targeted to the site of SCI by intranasal delivery of BDNF-overexpressing mesenchymal stem cell exosomes (BDNF-sEV) to significantly promote neurological recovery in rat and monkey models. In addition, hypoxic preconditioning was confirmed to significantly enhance the therapeutic effect of MSC-derived Exos, and the mechanism was related to enhancing the activities of antioxidant enzymes and promoting the secretion of angiogenic factors (46). Liang et al. (47) found that hypoxic preconditioning of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes (BMSC-HSEV) inhibited the IRAK1/TRAF6/NF-κB pathway by carrying miR-146a-5p, which could effectively regulate macrophage polarization and alleviate SCI.
Figure 1
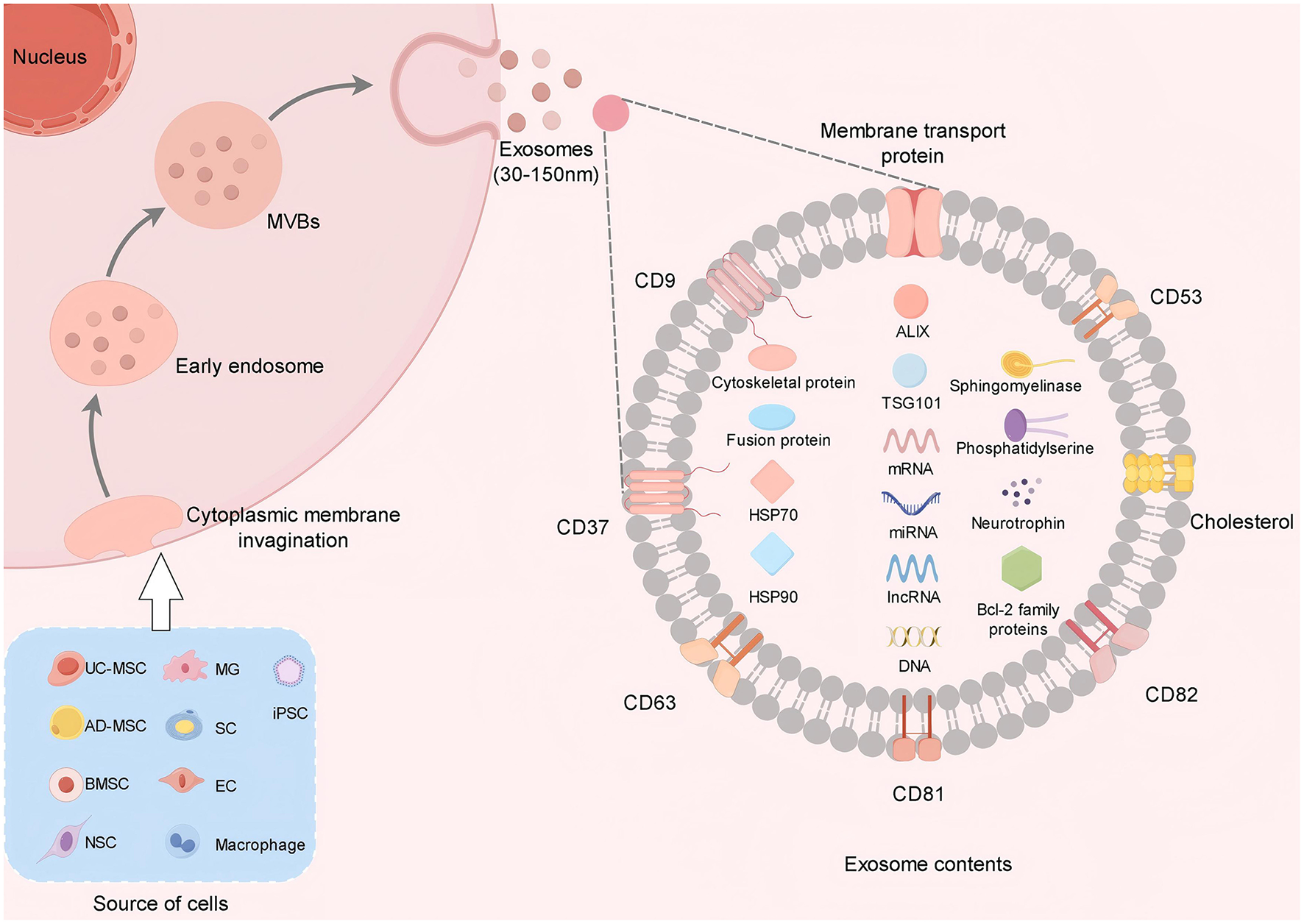
Exos are derived from a variety of cells. Exos are released after the fusion of MVBs with the cell membrane. Its contents include protein, RNA and lipids. Proteins are involved in signal transduction, RNA regulates gene expression, and lipids provide structural support.
In summary, the diversity of Exos sources plays a critical role in determining their biological functions and potential clinical applications, underscoring their importance as a key medium for intercellular communication. Each Exos source offers unique advantages and limitations within specific research and application contexts. Therefore, selecting the appropriate Exos source is essential for optimizing their utilization in medical and biological fields (Table 1).
Table 1
| Different cell sources | Main functions/research directions | Source and acquisition difficulty | In vitro preparation and amplification capabilities | Pathologic and immunogenicity | Primary competitive advantages | Main limitations | Clinical translational potential |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell (UC-MS) (111, 155–157) | Tissue repair Immune regulation, and inflammation suppression | Umbilical cord Huatong's gel, easy to obtain (postpartum waste, non-invasive) | It is easy to separate, has strong amplification ability and can be cultivated on a large scale | Low immunogenicity (Low expression of HLA-DR) | Rich in sources and with little ethical controversy; Strong paracrine function; High security | The functional activity is slightly lower than that of other MSCS. The proliferation ability decreases after long-term passage | Relatively high (multiple clinical trial stages) |
| adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell (AD-MS) (157–160) | Soft tissue repair, metabolic regulation, and immune regulation | Adipose tissue is relatively easy to obtain (liposuction, minimally invasive) | The volume of adipose tissue is large and the efficiency of separation and amplification is high | Low immunogenicity | High yield (a large number of cells can be obtained from each gram of fat); Rich in paracrine factors | The function is affected by the donor's age and obesity status. It is prone to aging outside the body | Relatively high (in some clinical applications) |
| bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell (BMSC) (72, 157, 161, 162) | Bone/cartilage repair, hematopoietic support, and nerve regeneration | Bone marrow, moderate acquisition (puncture sampling, invasive) | The separation difficulty is moderate, and the amplification capacity is moderate | Low immunogenicity | The most in-depth research and clear functions; It has strong osteogenic/chondrogenic differentiation ability | The materials are creative. Low content in bone marrow | Relatively high (with relatively mature clinical application) |
| neural stem cell (NSC) (163–165) | Neural regeneration, synaptic repair, and neural circuit reconstruction | Embryonic brain tissue/adult brain regions are difficult to obtain (with significant ethical controversy) | The separation and purification are complex, and amplification is limited (prone to differentiation) | Moderate immunogenicity (Allogeneic transplantation may cause rejection) | It has strong targeting ability and can directly differentiate into neurons/glial cells | The risk of tumor formation is relatively high; Adult-derived cells have weak proliferation ability | Moderate (mostly in basic research) |
| microglial cell (MG) (166–168) | Neuroimmune regulation, Aβ clearance, and injury repair | Brain tissue is difficult to obtain (primary isolation is difficult) | In vitro culture is easy to activate (phenotypic unstable) | Moderate immunogenicity (Enhanced immune activity under pathological conditions) | Precise regulation of neuroinflammation; Participate in the pathological process of neurodegenerative diseases | Dual functionality (it can both protect and cause damage); Difficult to maintain externally | Moderate (mechanism research stage) |
| schwann cell (SC) (169–172) | Peripheral nerve regeneration, axon guidance, and myelin formation | Peripheral nerves (such as the sciatic nerve) are more difficult to obtain (surgical sampling is required) | The separation and purification steps are complex and the amplification capacity is limited | Low immunogenicity | The “gold standard” cells for peripheral nerve repair; It has a strong ability to promote axonal regeneration | Limited source; Its effect on the repair of the central nervous system is unknown | Relatively high (Clinical application of peripheral nerve repair) |
| endothelial cell (EC) (71, 101, 173) | Angiogenesis, improvement of local blood supply, and repair of the BBB | Vascular tissue/pluripotent stem cell induction, moderate acquisition | Specific selection of culture medium is required, and the purification is difficult | Moderate immunogenicity (expressing vascular endothelial antigen) | Promote revascularization of ischemic tissue; Maintain vascular homeostasis | The effect is limited when applied alone. It is prone to form abnormal vascular networks | Moderate (often used in combination with other cells |
| Macrophagocyte (94, 174, 175) | Immune regulation, inflammation clearance, and tissue remodeling | Peripheral blood mononuclear cell induction, moderate acquisition | Monocytes are easy to isolate and have poor controllability in inducing differentiation | Moderate immunogenicity (affected by polarization state) | Strong ability to remove necrotic tissue; The M1/M2 phenotypic transition can be regulated | Strong functional plasticity (easily disturbed by the micro-environment); Risk of inflammation | Moderate (Immune-related disease research) |
| induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) (176–178) | Personalized treatment, multi-directional differentiation (such as nerve cells, myocardial cells) | Adult cells (such as skin fibroblasts) are relatively easy to obtain | Reprogramming technology is complex and the differentiation steps are cumbersome | Low immunogenicity (Self-origin can avoid rejection) | It can differentiate into any cell type; Suitable for personalized medicine | Tumorigenic risk (genomic instability); The preparation cycle is long (4 to 6 weeks) | High (Great potential, many challenges) |
Comparison of advantages and disadvantages of Exos from different cell sources.
3 Mechanism of exosomes in the treatment of SCI
The potential of Exos in the treatment of SCI is evident, and the subsequent mechanisms of action are as follows (Table 2):
Table 2
| Mechanism of action | Core function | Key molecules/components | Involving signal pathways |
|---|---|---|---|
| Promote neuroprotection | 1. Inhibition of neuronal apoptosis: blocking the mitochondrial apoptotic cascade by activating survival signaling pathways and transmitting anti-apoptotic proteins; 2. Enhanced neuronal survival: enhanced neuronal tolerance to injury through activation of intracellular protective pathways by neurotrophic factors; 3. Inhibition of ferroptosis: reduce iron accumulation in neurons, enhance antioxidant capacity, and block lipid peroxidation; 4. Promote functional recovery: targeted delivery of high concentration of nutritional factors to improve the efficiency of nerve repair at the injured site. | 1. Neurotrophic factors: BDNF, NGF, GDNF 2. Anti-apoptotic proteins: Bcl-2, Bcl-xL Heat shock proteins: HSP70, HSP90 3. miRNAs: miR-21a-3p, miR-27a-3p; 4. Iron death regulatory molecules: PINK1, Parkin (related to mitochondrial phagocytosis), Nrf2 (antioxidant transcription factor), GCH1 (4-hydroxypterin synthase), BH4 (4-hydroxypterin); 5. Others: MaR1 (anti-inflammatory and regenerative) Nrg1 (myelin protection), Natural products (resveratrol, 7,8 - dihydroxyflavone, propofol, chuanxiong chenpiine, etc.). |
Survival and anti-apoptosis pathways: MAPK (ERK/JNK/p38); PI3K/Akt/mTOR TLR4/MyD88/NF-κβ 2. Ferroptosis regulatory pathway: PINK1/Parkin/mitochondrial phagocytosis Nrf2/ARE/GCH1/BH4 3. Neurotrophic factor pathway: BDNF/TrkB/MAPK/PI3K/Akt |
| 2. Promote axon regeneration and synaptic remodeling | 1. Axonal growth and extension: enhanced axonal extension by promoting microtubule/neurofilament assembly through axon growth factors; 2. Myelin regeneration and protection: regulating oligodendrocyte differentiation, promoting myelin formation, and protecting axon structure; 3. Synapse formation and circuit reconstruction: promote the expression of synapse-associated proteins, regulate neural connections, and restore signal transduction; 4. Relieve the inhibition of regeneration: regulate glial scar-related molecules to reduce axonal growth retardation. | 1. Axonal growth factors: Neurofilament proteins (such as NF-L, NF-M), Microtubule-associated proteins (such as MAP2, Tau); 2. miRNA: miR-26a, miR-199-5p, miR-431-3p; 3. Ubiquitin ligases and associated molecules: Neural precursor cell expressed developmentally downregulated protein 4 (NEDD4), NEDD4-1, NEDD4-2, Ndfip1, Ndfip2 (NEDD4-binding proteins), Roundabout (Robo) receptor (axonal guidance receptor); 4. Others: Exercise training synergy factor (enhanced through the JNK1/c-Jun pathway). |
1. Axonal regeneration pathway: miR-199-5p / Inhibiting PTEN/PI3K/Akt/mTOR; NF-κβ / Promoting M2 polarization of microglia / Enhancing the recruitment of NSC; 2. Synaptic remodeling pathway: JNK1/c-Jun / Regulating the expression of synaptic-related genes (such as synaptophysin, PSD95) 3. Axonal guidance pathway: NEDD4/Robo receptor ubiquitination / Proteasome degradation / Removing axonal growth inhibition |
| 3. Inflammation suppression and immune regulation | 1. Inhibit the release of pro-inflammatory factors: Reduce inflammatory factors such as TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6, and alleviate nerve cell damage; 2. Regulate macrophage polarization: Promote M2-type (anti-inflammatory and repair-type) polarization and inhibit M1-type (pro-inflammatory and damaging) activation; 3. Enhance anti-inflammatory cell function: Through Treg cell-derived Exos to inhibit excessive immune response; 4. Synergize with drug effects: combine with ibrutinib to block excessive neural-immune activation. | 1. miRNA: miR-23a-3p, miR-222-3p, miR-216a-5p, miR-2861, miR-709; 2. Immune regulatory molecules: SOCS3, JAK2, STAT3, IRAK1; 3. Immune cell-related: M2 type macrophage markers (CD206, IL-10), Treg cells; 4. Others: Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK), ibrutinib (BTK inhibitor). |
1. Macrophage polarization pathway: SOCS3 / Inhibiting JAK2/STAT3; ROS/MAPK/NF-κβ P65; 2. Neuroinflammation regulation pathway: miR-2861 / Inhibiting IRAK1/TLR4/NF-κβ; BTK / Inhibiting microglia/astrocyte activation (Ibrutinib combined mechanism) |
| 4. Promote angiogenesis and maintain BSCB integrity | 1. Angiogenesis: Promotes the proliferation, migration, and lumen formation of vascular endothelial cells at the injured site, improving blood supply; 2. BSCB repair: Enhances the stability of tight junctions, reduces vascular permeability, and prevents inflammatory cells / harmful substances from invading; 3. Microcirculation improvement: Mediated by NO, it causes vasodilation and enhances the oxygen and nutrient supply in the injured area. | 1. Angiogenic factors: VEGF, FGF, PDGF; 2. miRNA: miR-210, miR-501-5p; 3. Proteins: OTULIN (deubiquitinating enzyme, activates Wnt pathway), tight junction proteins (Claudin-5, Occludin, ZO-1), Janus kinase 1 (JAK1), signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3), myosin light chain kinase (MLCK); 4. Others: Hypoxia-inducible factor - 1α (HIF-1α, related to hypoxia preconditioning). |
Angiogenesis pathway: PI3K/Akt/eNOS; OTULIN / Activates Wnt/β-catenin/VEGF; HIF-1α / VEGF; 2. BSCB repair pathway: miR-210 / JAK1 / STAT3 / Expression of tight junction proteins; miR-501-5p / Inhibits MLCK / Reduces degradation of tight junction proteins |
| 5. Regulation of the extracellular matrix | 1. ECM remodeling: Regulates the synthesis and degradation of components such as collagen and fibronectin, maintaining the stability of the matrix structure; 2. Gliosis inhibition: Reduces the deposition of chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans (CSPG), inhibits the activation of type A astrocytes; 3. Microenvironment improvement: Regulates matrix metabolism through the balance of MMPs/TIMP, creating a favorable environment for neural regeneration; 4. Barrier protection: Regulates proteins related to the blood-brain-spinal cord barrier, reducing ECM damage. | 1. Matrix regulatory molecules: Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs, such as MMP-2, MMP-9), tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases (TIMP, such as TIMP-1, TIMP-2), ADAMTS (polypeptide proteases that degrade CSPG); 2. miRNA: miR-467b-3p (carried by UTX–/–EC-Exos); 3. Scar-related molecules: Chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan (CSPG), A1 type astrocyte marker (complement C3), Rab27a (small G protein that mediates CSPG release); 4. Others: Transforming growth factor β (TGF-β, promotes vascular stability), arginine-glycine-aspartic acid (RGD, targeting-modifying peptide), phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN, inhibited by miR-467b-3p) |
1. ECM remodeling pathway: MMPs/TIMP balance / Regulating collagen / Fibronectin degradation and synthesis; miR-467b-3p / Inhibiting PTEN/PI3K/Akt/mTOR (Promoting M2 macrophages / Reducing ECM destruction) 2. Scar inhibition pathway: Inhibiting A1- type astrocyte activation / Reducing CSPG synthesis; ADAMTS / Degradation of CSPG / Inhibiting RhoA/ROCK (Relieving axonal inhibition) |
Summary of the mechanisms of exosomes therapy for spinal cord injury.
3.1 Promote neural protection
Exos encompass a diverse array of neurotrophic factors, including brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), nerve growth factor (NGF), and glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) (48, 49) (Figure 2). These neurotrophic elements are capable of activating intracellular survival signaling pathways, such as the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (Akt) pathways. Such activation inhibits the initiation of apoptotic processes and enhances the survival capacity of neuronal cells (50). In addition, Exos contain anti-apoptotic proteins, including members of the B-cell lymphoma-2 (Bcl-2) family and heat shock proteins (HSPs) (Figure 2). These proteins modulate mitochondrial function, stabilize mitochondrial membrane potential, and inhibit the release of cytochrome C, thereby obstructing the apoptotic cascade and reducing neuronal apoptosis (51–53).
Figure 2
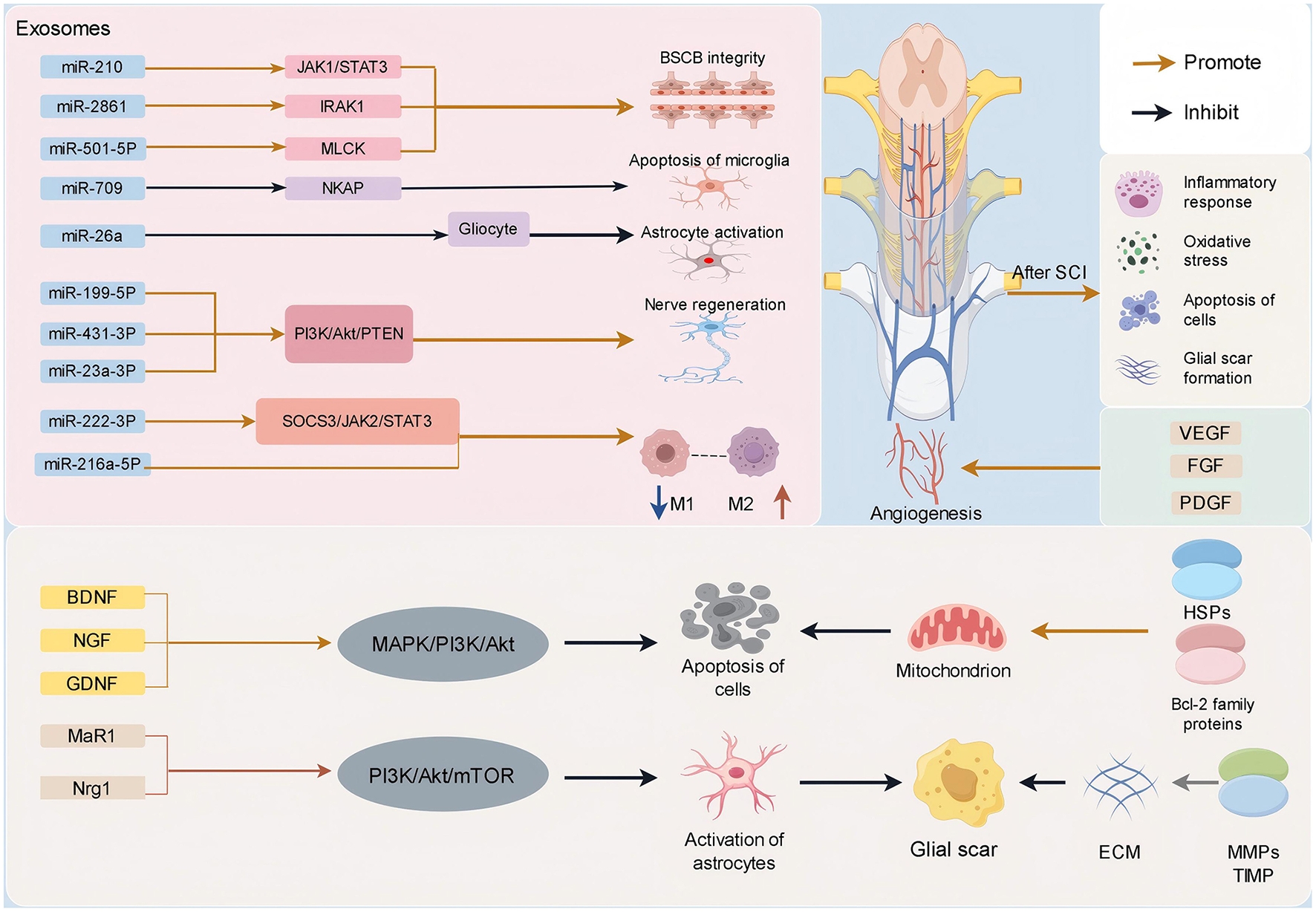
SCI can trigger a series of complex cascade reactions, including inflammatory response, oxidative stress, apoptosis, glial scar formation, etc. Exos can treat SCI through a variety of mechanisms. It can carry biological active molecules such as miRNA, neurotrophins, cytokines, Bcl-2 family proteins, HSPs anti-apoptotic proteins, and so on. It plays an important role in inhibiting inflammatory response, inhibiting glial scar formation, promoting nerve cell survival and axon regeneration, inhibiting cell apoptosis, promoting angiogenesis, and maintaining the integrity of BSCB.
Fu et al. (54) demonstrated that Exos derived from human adipose tissue mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) inhibit neuronal apoptosis and promote neurogenesis via the miR-21a-3p/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Zhu et al. developed a nanofiber scaffold composed of a hyaluronic acid hydrogel patch designed to deliver Exos and methylprednisolone to the injured spinal cord in a non-invasive manner. This approach effectively inhibited inflammation and neuronal apoptosis while enhancing neuronal survival through the modulation of TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB, MAPK, and Akt/mTOR pathways (55). Furthermore, Maresin 1 (MaR1), recognized as an anti-inflammatory and pro-resolving mediator, exhibits potential for tissue regeneration. Wei et al. (56) found that MaR1 suppresses astrocyte activation via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway, reduces the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines in the spinal dorsal horn of mice, and facilitates the regeneration of injured nerves. Neuregulin-1 (Nrg1) is crucial for the differentiation of oligodendrocytes. Ding et al. demonstrated in a study involving SCI in rats that intravaginal administration of Nrg1 can induce the transformation of reactive astrocytes into oligodendrocyte lineage cells, a process mediated by the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. This pathway inhibits astrocyte proliferation, promotes myelin regeneration, and protects axons (57). Furthermore, natural compounds such as resveratrol, 7,8-dihydroxyflavones, propofol, and cephalin have been shown to exert neuroprotective effects through modulation of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway (58). The potential for combining Exos with these substances to treat SCI and achieve a synergistic therapeutic effect presents a promising strategy for the regulation of nerve damage, warranting further investigation.
In recent years, a breakthrough has been made in the mechanism research of Exos in the field of neuroprotection. Pay, etc. confirmed that the high expression of BDNF nasal delivery non-greeks secrete body (MSCs–sEV) can be targeted enrichment in SCI, its concentration of neurotrophic factor is a natural body secretion of eight times, in the rhesus monkey model, to realize motor function recovery rate was 67% (46). Sun et al. also found that nasal delivery of a specific subset of MSC-derived small extracellular vesicles, CD146+CD271+ ucmsc-sev, could target and enrich at the site of SCI and inhibit DLL4 through the transfer of miR-27a-3p to regulate inflammation, inhibit apoptosis, and promote nerve regeneration. It can effectively reduce traumatic SCI and improve neurological function recovery (59). In addition, Exos have shown remarkable potential for inhibiting iron death and thus promoting neuroprotection (60, 61). Exos can play a role by transferring specific proteins, miRNAs, and other molecules, regulating iron metabolism, enhancing antioxidant capacity, and regulating related signaling pathways. These mechanisms, on the one hand, reduce the accumulation of iron ions in neurons, on the other hand, alleviate oxidative stress and lipid peroxidation, and ultimately inhibit ferroptosis (62, 63). Zhang et al. (64) were the first to show that in vitro Exos therapy activates mitochondrial phagocytosis via the PINK1/Parkin pathway, thereby reducing ferroptosis in neuronal cells, which plays a crucial role in neuroprotection following trauma. Similarly, Chen et al. (65) demonstrated that mesenchymal stem cell-derived Exosomes (MSC-Exos) alleviate ferroptosis in microglia through the Nrf2/GCH1/BH4 signaling pathway, indicating their promising potential in protecting and restoring neural function after SCI.
Consequently, Exos exhibit anti-apoptotic and neuroprotective properties through the transmission of anti-apoptotic signaling molecules, modulation of intracellular signaling pathways, and inhibition of ferroptosis. These mechanisms suggest a wide range of potential applications for Exos in the treatment of neurological disorders.
3.2 Promote axon regeneration and synaptic plasticity
Exos play a crucial role in axon regeneration and synaptic remodeling (66). They are enriched with various axon growth factors, including neurofilament and microtubule-associated proteins (MAPs) (Figure 2), which are instrumental in facilitating axonal growth and extension (67, 68). Concurrently, the transfer of RNA is critical in tissue formation. Exos are rich in diverse miRNAs that can modulate gene expression to enhance axon regeneration and myelination (69) (Figure 2). In a study by Gao et al. (70) the delivery of miR-26a to damaged neurons via an in vivo regenerative system led to decreased astrocyte activation at the injury site and promoted neuronal axon growth. Furthermore, research by Huang et al. demonstrated that Exos derived from endothelial cell (EC) culture medium can activate the PI3K/Akt/PTEN signaling pathway by upregulating miR-199-5p, thereby facilitating nerve regeneration. Their findings also indicated that EC-derived Exos exhibit strong neuronal affinity both in vitro and in vivo (71). In a study utilizing the SCI model, Sun et al. successfully isolated Exos characterized by CD271+CD56+ markers from a specific CD271+CD56+ bone marrow stromal cell (BMSC) subgroup through on-site implantation. Their findings indicated that miR-431-3p plays a crucial role in the mechanism by which CD271+CD56+ BMSC-derived Exos facilitate functional recovery and axonal regeneration post-SCI (72). Similarly, Fan et al. identified that BMSC-derived Exos modulate M2 polarization of microglia via the NF-κB signaling pathway, resulting in a marked decrease in CD68-positive microglia, enhanced recruitment of local neural stem cells (NSCs), and increased axonal growth through the PTEN/PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. This process significantly contributes to early functional recovery in mouse models of SCI (73). Additionally, other research has demonstrated that exercise training may work synergistically with BMSC-derived Exos to regulate neuronal apoptosis via the JNK1/c-Jun signaling pathway, thereby reconstructing neural circuits, promoting synaptic formation and axonal regeneration, and ultimately enhancing neural function recovery (74).
In recent years, breakthroughs have been made in the molecular mechanism of Exos in synaptic remodeling, which has become the core strategy for SCI repair by regulating the dynamic balance of synaptic structure and function at multiple levels. Postsynaptic density (PSD) is a key structure in synaptic plasticity, and its dynamic assembly depends on protein phase separation. The study by Zhang's team found that the scaffold protein SAPAP carried by mesenchymal stem cell Exos regulates the fusion and separation of PSD core and PSD pallium through phosphorylation: when the phosphorylation level of SAPAP increased, PSD core fused with PSD pallium to form a homogeneous concentrated phase, which enhanced the aggregation of NMDA receptors on the postsynaptic membrane. Under low phosphorylation, the PSD structure dissociates to maintain synaptic stability. In the SCI rat model, exosome intervention increased the PSD volume by 2.1 times and the synaptic transmission efficiency by 40% (75). Another study confirmed that the postsynaptic density protein 95 (PSD-95) carried by Exos of neural stem cells could participate in the assembly of PSD and promote the recovery of synaptic connection strength in the injured area (76). In addition, RVG-BDNF-Exos (BDNF-targeted delivery Exos modified by rabies virus glycoprotein) developed by Cheng's team penetrated the BBB after tail vein injection, specifically bound to nicotinic acetylcholine receptors on the surface of neurons, and delivered the BDNF gene to postsynaptic neurons. The Exos significantly up-regulated the expression of PSD95 and Syn-1 in the hippocampus and the injured area of the spinal cord, restored the synaptic density to 68% of the normal level, and reversed the synaptic loss by activating the TrkB/ERK pathway. A similar strategy improved axonal regeneration to 58% in a macaque model of SCI, demonstrating the clinical potential of targeted delivery for the first time in a non-human primate (77). According to Piette et al. (78) neural energy metabolism is closely related to synaptic plasticity. Kochan et al. found in animal experiments that there will be a transient surge in mitochondrial fusion dynamics when newborn neurons enter the critical period. This process can stabilize the elongated mitochondrial morphology in dendrites and provide energy support for synaptic plasticity, which is crucial for the plasticity of new synapses and the improvement of existing brain circuits (79).
In addition, neural precursor cells expressing developmentally down-regulated protein 4 (NEDD4) combined with Exos may play an important role in the treatment of SCI. After wrapping NEDD4 in Exos, NEDD4 can be transported to related cells at the site of injury, such as neurons and glial cells. Thus, it can play a more effective role in relieving the inhibition of nerve regeneration and regulating the microenvironment of nerve regeneration (80, 81). NEDD4, as an E3 ubiquitin ligase, is involved in the regulation of axon guidance during neural development. NEDD4-1 and NEDD4-2 were found to be required for axon guidance at the spinal commissural, and they regulate Roundabout (Robo) receptor endocytosis, ubiquitination, and degradation by interacting with Ndfip1 and Ndfip2 proteins to form a complex. Robo receptor is an axon guidance receptor that plays an important role in axon growth cone guidance (82, 83). Ding et al. (84) discovered that Nedd4 is required for developmental myelination by stabilizing the E3 ligase VHL through K63-linked ubiquitination, revealing a new role for Nedd4 in glial biology. Fimiani et al. (85) demonstrated in animal experiments that Nedd4 is required for the correct accumulation of differentiated oligodendrocytes and can promote myelination in the central and peripheral nervous systems of mice. Sullivan and Bashaw et al. (86) demonstrated that commissuless (Comm) promotes the growth of the axon midline by promoting Robo1 ubiquitination of Nedd4 and eventually leading to its degradation. Shi et al. (87) also found in animal experiments that NEDD4 may control the molecular mechanism of the endocytosis pathway and play an important role in the initiation stage of demyelination and axon regeneration. After SCI, NEDD4 may regulate related receptors through a similar mechanism, affect the regeneration and growth direction of axons, and promote the correct extension of axons at the injury site. In addition, it has been found that MiR-155-5p overexpression inhibits nuclear PTEN expression by targeting Nedd4 family interacting protein 1 (Ndfip1), which in turn aggravates astrocyte activation and glial scarring in SCI models (88). NEDD4 may regulate the expression and function of related proteins in glial cells, inhibit the over-expressed proteins that hinder nerve regeneration in the glial scar, and promote the secretion of some factors that are beneficial to nerve regeneration, thereby improving the microenvironment of nerve regeneration.
Exos have exhibited tremendous potential and diverse mechanisms in promoting nerve regeneration; however, there remain numerous unexplored areas that require further investigation to fully harness their role in nerve regeneration and disease treatment while advancing their development and application in clinical settings.
3.3 Inflammation suppression and immune regulation
The occurrence of inflammation is a prominent pathological process following SCI, and effective management of both local and systemic inflammation plays a pivotal role in enhancing patient prognosis (89, 90). SCI triggers a robust inflammatory response, leading to the release of numerous inflammatory mediators such as tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-1 (IL-1), and interleukin-6 (IL-6) (91, 92), thereby exacerbating neuronal damage (Figure 2).
In the event of SCI, macrophages accumulate at the injury site and play a pivotal role in the subsequent immune response (93). Macrophage-derived Exos significantly influence the immune microenvironment in SCI, with the miR-23a-3p/PTEN/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway potentially playing a critical role (94). Exos can modulate macrophage polarization by promoting the M2 subtype while inhibiting the activation of the M1 subtype. M2 macrophages exhibit anti-inflammatory properties and facilitate tissue repair, whereas M1 macrophages release pro-inflammatory cytokines that intensify inflammation (95–97). Ren et al. demonstrated that spinal cord-derived Exos can mitigate inflammation following SCI by suppressing M1 polarization and promoting M2 polarization. The SOCS3/STAT3 signaling pathway is essential in enhancing the inflammatory microenvironment and inhibiting neuronal apoptosis (98). Additionally, reactive oxygen species (ROS) can induce M1 macrophage polarization via the MAPK/NF-κB P65 signaling pathway. Liu et al. (99) reported that Exos derived from dental pulp stem cells ameliorate SCI by reducing M1 macrophage polarization through the ROS/MAPK/NF-κB P65 signaling pathway. Peng et al. (100) also observed that histone demethylase UTX deletion (UTX–/–EC) in endothelial cells promotes neural recovery mainly through Exos from UTX–/–EC polarizing macrophages toward an M2 subtype after SCI.
Moreover, bioactive molecules such as miRNAs and proteins within Exos may contribute to the modulation of inflammatory responses. Yuan et al. (101) reported that endothelial cell-derived Exosomes (EC-Exos) enhanced the prognosis of SCI via the SOCS3/JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway, while the upregulation of miR-222-3p in EC-Exos led to a reduction in pro-inflammatory macrophages and an increase in anti-inflammatory macrophages. Liu et al. further demonstrated the potential involvement of miR-216a-5p in the polarization of microglial cells. Additionally, it has been observed that MSC-Exos produced under hypoxic conditions exert a more pronounced effect on neurological function recovery compared to normoxic MSC-Exos (24). Regulatory T (Treg) cells, recognized as potent anti-inflammatory agents, play a crucial role in mitigating neuroinflammation following SCI. Kong et al. (102) demonstrated that Exos derived from Treg cells can encapsulate and deliver miR-2861 to modulate IRAK1 expression, thereby influencing BSCB integrity and reducing neuroinflammation in murine models of SCI. Furthermore, Xiong et al. (103) confirmed through animal studies that Treg cells target NKAP with miR-709, leading to decreased microglial apoptosis and enhanced motor function recovery post-SCI. These findings suggest that by strategically designing and applying specific combinations of these miRNAs, synergistic effects could potentially enhance the effectiveness of SCI repair.
In addition, the activation of Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK) is associated with microglia/astrocytes and B-cell neuroimmune response mechanisms. Ibrutinib is a BTK inhibitor in innate immune cells. Torabi et al. (104) found that ibrutinib can reduce neutrophil infiltration, protect nerve tissue, and enhance the recovery of motor ability in SCI model mice. Yu et al. (105) also found in animal experiments that ibrutinib blocked excessive neuroimmune responses and promoted neuroprotection in SCI rat models through BTK-mediated activation of microglia/astrocytes and B cell/antibody responses. Therefore, Exos combined with ibrutinib may provide a new strategy for the treatment of SCI.
3.4 Promote angiogenesis and maintain BSCB integrity
Effective angiogenesis is essential for the reparative processes following SCI. Exos contain a variety of angiogenesis-related factors, including vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), fibroblast growth factor (FGF), and platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) (106, 107). These factors facilitate the proliferation and migration of vascular endothelial cells and support the formation of vascular lumens at the site of injury, thereby ensuring an adequate supply of nutrients and oxygen necessary for the survival and regeneration of nerve cells (19, 108). Li et al. demonstrated that cerebrospinal fluid-derived Exosomes (CSF-Exos) can activate the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway, promoting vascular regeneration and enhancing motor function recovery post-SCI. This discovery indicates a potential novel therapeutic strategy for acute SCI (109). Additionally, Luo et al. (36) reported that Exos derived from M2 macrophages (M2-Exos) augment angiogenic activity in vitro by activating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway through the transfer of OTULIN protein, thereby promoting vascular regeneration and functional recovery in murine models of SCI. Li et al. (23) on the other hand, effectively repaired neural tissue in mice by stimulating angiogenesis using Exos derived from human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) through hypoxia pretreatment.
Furthermore, Exos exhibit the potential to facilitate the repair of the BSCB and preserve its integrity. In a study conducted by Gao et al. (110) the administration of Exos into mice with SCI demonstrated that miR-210 activates the JAK1/STAT3 signaling pathway, thereby modulating endothelial barrier function, enhancing BSCB integrity, and promoting the recovery of motor function. In another animal experiment conducted by Xie et al. (111) CD146+CD271+ MSC-Exos were found to upregulate tight junction protein expression and promote BSCB repair through the miR-501-5p/MLCK signaling pathway.
Although there is some understanding of how Exos promote angiogenesis and BSCB repair, further investigation is necessary to elucidate their mechanisms for better therapeutic efficacy.
3.5 Regulate the extracellular matrix (ECM)
The ECM is integral to the reparative processes following SCI (112). The lack of nerve regeneration is largely due to the absence of intrinsic nerve growth programs and the development of glial scars (113, 114). Exos, as essential mediators of intercellular communication, possess significant potential in facilitating ECM remodeling post-SCI (115, 116).
Exos play a crucial role in maintaining spinal stability by modulating the synthesis and degradation of collagen, regulating fibronectin levels, and influencing other components of the ECM. This modulation leads to alterations in both the structure and function of the ECM, while simultaneously inhibiting the release of inflammatory mediators and reducing the formation of glial scars. As a result, a conducive microenvironment for nerve regeneration is established (117, 118). Additionally, Exos can transport matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) or their inhibitors, such as tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases (TIMPs) (119), thereby managing ECM degradation and reconstruction by regulating the balance of these molecules (120). During tissue repair and regeneration, Exos enhance pathological microenvironments by preventing or mitigating scar tissue formation, thereby promoting repair (116). Liu et al. (121) demonstrated through animal studies that bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived Exosomes (BMSC-Exos) effectively suppress inflammation following traumatic SCI, inhibit the activation of A1 neurotoxic reactive astrocytes, reduce glial scar formation, and facilitate nerve regeneration. In another animal experiment, Cheng et al. also found that human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (HucMSC-EX) exosomes-embedded gelatin foam delivered miRNAs or proteins to inhibit the expression of chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan (CSPG) synthesis-related genes, while upregulating the activity of metalloproteinases such as ADAMTS to promote their degradation. On the other hand, it directly blocked the activation of CSPG receptors PTPσ and NgR, inhibited the downstream RhoA/ROCK pathway, and released the inhibition of axon growth. Gelatin sponge scaffolds can enhance the regulatory effect by sustained-release Exos and guide their directional distribution, and ultimately improve the microenvironment of nerve regeneration (122). Singh et al. found that Rab27a could mediate the release of CSPG-containing EVs from astrocytes, increase CSPG expression through the Rho/ROCK pathway, affect pAkt and β-tubulin III levels, and promote axonal degeneration and glial scar formation. This suggests that Rab27a-related mechanisms in Exos affect the content and distribution of CSPG in the ECM, which in consequence affects the repair process after SCI. Inhibition of Rab27a-mediated EVs release may reduce CSPG deposition, inhibit glial scar formation, and create a better ECM environment for nerve regeneration (123). Another team found that Exos secreted by UTX-depleted vascular endothelial cells carried miR-467b-3p, which transferred to macrophages, inhibited PTEN expression, activated PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway, and promoted macrophage polarization to anti-inflammatory M2 type, reducing inflammatory response. It can reduce the destruction of ECM by inflammation, and at the same time may promote the repair and remodeling of ECM, providing a more favorable microenvironment for nerve regeneration (100). In addition, some Exos can regulate the expression and function of BBB-related proteins in the blood. For example, arginine-glycine-aspartic acid (RGD) -modified Exos derived from CD163 + macrophages can deliver transforming growth factor β (TGF-β) to the neovascularization in the center of SCI, promote angiogenesis and stability of the blood-brain spinal barrier, and reduce the invasion of inflammatory cells and harmful substances. Maintaining the stability of ECM is beneficial to nerve regeneration (124).
Overall, Exos influence cellular behavior and tissue repair processes by modulating the composition, structure, and functionality of the ECM. These regulatory mechanisms are essential for the maintenance of normal tissue and recovery following injury.
4 Combination treatment strategy
The investigation into the integration of Exos with various materials for the treatment of SCI has attracted growing scholarly interest, owing to its potential to improve therapeutic outcomes and facilitate SCI repair. In this context, we outline several pivotal research directions and categories of materials (Table 3, Figure 3).
Table 3
| Types of nanodrug delivery systems | Type of loaded drugs | Therapeutic goal | Advantage | Disadvantage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exosome-liposome complex system (132, 179–181) |
Small molecule anti-inflammatory drugs, nucleic acid drugs, neurotrophic peptides | Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, stroke | High drug loading, strong BBB penetration, and good compatibility | It is difficult to prepare, unstable and has a high mass production cost |
| Exosome-polymer nanoparticle composite system (132, 182–184) |
Chemotherapy drugs, neurotrophic factors, targeted siRNA | Glioma, multiple sclerosis, SCI | Sustained-release, enhanced targeting, and good homology | It may cause inflammation, be easily cleared, and have a decreased targeting ability |
| Exosome-inorganic nanoparticle composite system (132, 185, 186) |
Photothermal reagents, chemotherapy drugs, contrast agents | Glioma, brain metastases | It can be guided by imaging, has low toxicity and strong synergistic killing power | It is difficult to degrade, prone to accumulation, has a low encapsulation rate and is likely to clog blood vessels |
| Exosome-micellar composite system (132, 187, 188) |
Hydrophobic chemotherapy drugs, fat-soluble antioxidants | Glioma, multiple sclerosis | Hydrophobic drugs have a high encapsulation rate and small particle size, making them easy to penetrate | Micelles are prone to disintegration, their structures are easily damaged, and there is a risk of transfer |
| Exosome-hydrogel composite system (132, 189, 190) |
Neurotrophic factor, miRNA | Stroke, SCI | Sustainable release, supported by physical means, with low local toxicity | Micelles are prone to disintegration, their structures are easily damaged, and there is a risk of transfer |
| Exosome-metal-organic framework (MOF) composite system (132, 191, 192) |
Chemotherapy drugs, immune siRNA, PET contrast agents | Glioma | High targeting, can respond to drug release, and also has imaging functions | The safety of the degradation products remains to be verified, their preparation is difficult, and the binding rate is low |
| Exosome-virus-like particle (VLPs) complex system (132, 193, 194) |
Gene drugs, siRNA | Depression, neurodegenerative diseases | Strong uptake, high targeting, and capable of mucosal deliveryimaging functions | It may trigger an immune response, but the efficiency varies and the safety remains to be investigated |
Summary of nanodrug delivery systems.
Figure 3

Exos combined with different materials can significantly improve the therapeutic effect on SCI. Combined with biological scaffolds, it can provide a stable release carrier for Exos and promote nerve tissue regeneration. Combined with nanomaterials, it can enhance targeted delivery and increase the concentration of Exos at the injury site. This combination method gives full play to the therapeutic potential of Exos to achieve precision medicine and personalized care.
4.1 Combining Exos with biomaterials
Firstly, hydrogel, as a scaffold material, exhibits excellent biocompatibility and possesses loose and porous structural characteristics. It can serve as a carrier for Exos, thereby prolonging their residence time in specific areas and facilitating controlled release (106). Numerous studies have demonstrated that the combination of Exos with hydrogels promotes the survival and regeneration of nerve cells while reducing inflammatory responses (72, 73). Han et al. (125) utilized Exos combined with hydrogel to treat SCI, ensuring more reliable, convenient, and effective delivery of Exos to targeted regions. Guan et al. (126) combined M2-Exos with hydrogel, while Li et al. (127) combined MSC-Exos with hydrogel; both treatment approaches resulted in accelerated neuron and axon regeneration as well as significantly enhanced functional recovery in SCI rats. Secondly, bioscaffolds composed of natural polysaccharides, protein polymers, self-assembled peptides, and biocompatible polymers such as polylactic acid (PLA) and polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) have been extensively utilized in the repair of spinal cord injuries (128). Liu et al. (129) incorporated collagen scaffolds with Exos' surface to facilitate the retention of miR21-loaded Exos at the lesion site and ensure a sustained release of miR21 into cells. Zhang et al. (130) fused umbilical cord MSC-Exos with multifunctional collagen scaffolds to offer a versatile therapeutic approach for various diseases including SCI. The combination of Exos with these scaffold materials can augment the biological activity of the scaffold and promote nerve regeneration.
4.2 Combining Exos with nanomaterials
Exos is a natural nanocarrier secreted by a variety of cells. It has the characteristics of high stability, targeting, low immunogenicity, and good biocompatibility, and is suitable for various drug delivery and therapeutic applications (26, 28, 35, 131). Through genetic engineering and chemical modification techniques, drugs can be encapsulated inside or attached to the surface of Exos to construct targeted drug delivery systems (NDDS) that can specifically deliver drugs to certain types of cells or tissues (27, 132). The most common bioactive molecules loaded in Exos include miRNA, mRNA, proteins, and small molecules (39, 133). Moreover, engineered Exos can also be combined with metal nanoparticles, graphene, and other nanomaterials to enhance their targeting ability and bioavailability (134, 135). In the treatment of nervous system diseases specifically, Exos have emerged as promising carriers for delivering drugs due to their inherent capability to cross the BBB and BSCB (111, 136). Guo et al. (137) delivered Exos loaded with phosphatase and tenin homologous siRNA to SCI rats and found that Exos could cross the BBB and migrate to the injured spinal cord area, improving motor function, sensory function, and faster recovery of urinary reflex. Cui et al. (138) on the other hand, utilized immune Exos loaded nano micelles capable of crossing the BBB for treating glioblastoma, which not only exhibited improved efficacy but also prevented postoperative recurrence. In another study conducted by Gao et al. (139) M2-Exos loaded with berberine were employed for treating mice with SCI, resulting in significant improvement in motor function. As carriers for NDDS, Exos exhibit great potential and application prospects. With further research advancements, Exos-based therapies will find wider utility in precision medicine, personalized therapy, and other related fields.
5 Current status of clinical research
Clinical studies investigating the therapeutic potential of Exos in SCI are currently underway, and although still in its early stages, significant progress has been made. Several small-scale clinical trials have been conducted to assess the safety and initial efficacy of Exos (140). Most studies have demonstrated that short-term treatment with Exos is well-tolerated (21, 141), with no reports of serious adverse reactions (142, 143). These trials typically involve the utilization of MSC-derived Exos to evaluate their application in patients with SCI (144, 145).
Akhlaghpasand et al. conducted the initial phase I clinical trial of Exos in treating SCI, wherein intradermal injection of allogenic Exos derived from human umbilical cord MSC was administered to patients with acute SCI. The findings demonstrated favorable tolerability and the absence of significant adverse reactions associated with Exos (Iranian Registry of Clinical Trials, IRCT20200502047277N1) (146). This pioneering study not only establishes the safety profile of stem cell Exosome therapy for SCI in human subjects but also highlights its potential clinical benefits, instilling renewed hope among SCI patients and providing a crucial scientific foundation for the medical community.
Overall, Exos exhibits promising safety and efficacy in SCI treatment; however, further evidence is required to ascertain its clinical translational potential (147).
6 The challenges and prospects of Exos therapy for SCI
6.1 The challenges faced
In the progress of researching Exos-based SCI therapies, despite significant achievements, the field still faces numerous challenges and unanswered questions. Firstly, a major issue lies in the source and quality control of Exos (32, 131). Exos derived from different cell origins may exhibit substantial variations in composition, function, and therapeutic effects (148). Currently, various Exos separation technologies have been developed based on size, density, compatibility, and surface protein characteristics (149), but large-scale mass production (13) and ensuring the purity, stability, and biological activity of Exos remain crucial issues that need to be addressed. Additionally, during storage and transportation processes, Exos are prone to aggregation and degradation, which can impact their therapeutic efficacy (150, 151). Secondly, the therapeutic mechanism of Exos is not fully understood. While it is known that Exos can exert therapeutic effects by delivering bioactive molecules, little is known about their specific signaling pathways or cell-cell interactions among other mechanisms (16, 115). This lack of understanding makes it challenging to optimize and personalize Exos therapy. Furthermore, targeted delivery of Exos also poses a challenge. Despite improvements in targeting ability through combining with biological scaffolds, the presence of BSCB at the SCI site, along with the complex microenvironment, still presents significant obstacles for efficient targeted delivery (152). Lastly, long-term efficacy and safety concerns regarding Exos therapy cannot be ignored. Although short-term animal experiments have shown certain effectiveness of Exos treatment (122, 153), further investigation is required to assess long-term effects and potential complications such as tumor formation and neurodegeneration (34, 154). Designing well-designed clinical trials to evaluate the safety and effectiveness of Exos therapy is an important step toward the clinical translation of the therapy.
Future research should focus more on these issues, pushing the field forward through technological innovation and rigorous scientific validation, ultimately providing more effective treatment options for SCI patients.
6.2 Prospects
With the ongoing advancement of Exos research, significant breakthroughs are expected in the treatment of SCI. The future research directions mainly focus on optimizing the methods for the separation and purification of Exos to enhance both yield and quality. Furthermore, investigating the underlying mechanisms of Exos will provide a solid theoretical foundation for their clinical application. Additionally, developing targeted therapeutic strategies for Exos and improving their efficacy aims to boost treatment outcomes. Lastly, carrying out large-scale clinical trials is essential to validate the safety and effectiveness of Exos in treating SCI.
7 Conclusion
As a severe medical condition, SCI not only imposes significant physical and psychological burdens on patients, but also places immense pressure on the social healthcare system. In recent years, there has been considerable attention given to Exos-based SCI therapies due to their distinctive biological characteristics and therapeutic potential. Through an in-depth analysis of relevant literature, it can be observed that utilizing Exos as carriers for specific miRNAs exhibits unprecedented therapeutic promise. Firstly, the advantage of Exos as bioactive carriers lies in their efficient ability to transport various biomolecules such as proteins, mRNA, and miRNA between cells. Particularly when these Exos are enriched with specific classes of miRNAs, they demonstrate remarkable effects in regulating nerve regeneration, inhibiting inflammatory responses, and promoting angiogenesis. Furthermore, research has revealed hypoxia preconditioning as a potential method to enhance the efficacy of Exos therapy. This finding provides a crucial experimental basis for improving the efficiency of Exos treatment for SCI. However, despite the significant potential shown by Exos-based therapies, their clinical application still faces numerous challenges. In conclusion, although Exos-based SCI treatment is still at an early stage of research development, it has demonstrated substantial therapeutic potential and promising prospects for further advancement. Future research should focus on overcoming existing technical barriers and expediting the transition from this emerging treatment to clinical application. Additionally, continuous exploration and optimization of Exos conte ts, nparticularly in the search for more efficient combinations with miRNA and nanomaterials, will further propel advancements in this field toward providing substantial assistance to patients with SCI.
Statements
Author contributions
ZC: Writing – original draft. YL: Writing – original draft. JP: Writing – original draft. YZ: Writing – original draft. QL: Writing – original draft. WH: Writing – original draft. TL: Writing – original draft. XL: Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant NO. 82460248); the Fund of Yunnan Spinal Cord Disease Clinical Medical Center (ZX2022000101-2024JSKFKT-01); Yunnan Fundamental Research Projects (Grant No. 202401CF070007); Joint Projects of Yunnan Provincial Science and Technology Department and Kunming University of Science and Technology (Grant No. KUST-KH2023005Z); Joint Projects of Yunnan Provincial Science and Technology Department and Kunming Medical University for Applied Basic Research (Grant No. 202501AY070001-117); Joint Projects of Yunnan Provincial Science and Technology Department and Kunming Medical University for Applied Basic Research (Grant No. 202501AY070001-113); Yunnan Provincial Clinical Medical Center for Blood Diseases and Thrombosis Prevention and Treatment (Grant No. 2024YNLCYXZX0167); Yunnan Provincial Clinical Medical Center for Blood Diseases and Thrombosis Prevention and Treatment (Grant No. 2024YNLCYXZX0265).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1.
Cowan H Lakra C Desai M . Autonomic dysreflexia in spinal cord injury. BMJ. (2020) 371:m3596. 10.1136/bmj.m3596
2.
Zha X . Exosome-based therapy for spinal cord injury: a narrative review. Adv Technol Neurosci. (2025) 2:128–34. 10.4103/ATN.ATN-D-25-00001
3.
Zha X . Identification of novel biomarkers and immune characteristics of spinal cord injury based on comprehensive bioinformatic analysis: a retrospective observational study. NeuroMarkers. (2025) 2:100077. 10.1016/j.neumar.2025.100077
4.
Shang P Wen L Zheng R Cheng R Gao Y Wen M et al . The applications of spinal cord stimulation in diseases with motor disorders, pain, and cognitive disturbance. Adv Technol Neurosci. (2024) 1:2–17. 10.4103/ATN.ATN-D-24-00001
5.
Crispo JAG Kuramoto LK Cragg JJ . Global burden of spinal cord injury: future directions. Lancet Neurol. (2023) 22:976–8. 10.1016/S1474-4422(23)00366-6
6.
McDonald JW Sadowsky C . Spinal-cord injury. Lancet. (2002) 359:417–25. 10.1016/S0140-6736(02)07603-1
7.
Lu Y Shang Z Zhang W Pang M Hu X Dai Y et al . Global incidence and characteristics of spinal cord injury since 2000-2021: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Med. (2024) 22:285. 10.1186/s12916-024-03514-9
8.
GBD 2016 Traumatic Brain Injury and Spinal Cord Injury Collaborators . Global, regional, and national burden of traumatic brain injury and spinal cord injury, 1990-2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. (2019) 18:56–87. 10.1016/S1474-4422(18)30415-0
9.
Anjum A Yazid MD Fauzi Daud M Idris J Ng AMH Selvi Naicker A et al . Spinal cord injury: pathophysiology, multimolecular interactions, and underlying recovery mechanisms. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21:7533. 10.3390/ijms21207533
10.
Karsy M Hawryluk G . Modern medical management of spinal cord injury. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. (2019) 19:65. 10.1007/s11910-019-0984-1
11.
EL Andaloussi S Mäger I Breakefield XO Wood MJ . Extracellular vesicles: biology and emerging therapeutic opportunities. Nat Rev Drug Discov. (2013) 12:347–57. 10.1038/nrd3978
12.
Thery C Witwer KW Aikawa E Jose Alcaraz M Anderson JD Andriantsitohaina R et al . Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): a position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J Extracell Vesicles. (2018) 7:1535750. 10.1080/20013078.2018.1535750
13.
Debbi L Guo S Safina D Levenberg S . Boosting extracellular vesicle secretion. Biotechnol Adv. (2022) 59:107983. 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2022.107983
14.
Li H Wang Z . Blood biomarkers for clinical applications in Alzheimer's disease: a narrative review. NeuroMarkers. (2025) 2:100078. 10.1016/j.neumar.2025.100078
15.
Kalluri R LeBleu VS . The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science. (2020) 367:eaau6977. 10.1126/science.aau6977
16.
Yu T Yang LL Zhou Y Wu MF Jiao JH . Exosome-mediated repair of spinal cord injury: a promising therapeutic strategy. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2024) 15:6. 10.1186/s13287-023-03614-y
17.
Miron RJ Estrin NE Sculean A Zhang Y . Understanding exosomes: part 2-emerging leaders in regenerative medicine. Periodontol 2000. (2024) 94:257–414. 10.1111/prd.12561
18.
Tan F Li X Wang Z Li J Shahzad K Zheng J . Clinical applications of stem cell-derived exosomes. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2024) 9:17. 10.1038/s41392-023-01704-0
19.
Nie X Yuan T Yu T Yun Z Yu T Liu Q . Non-stem cell-derived exosomes: a novel therapeutics for neurotrauma. J Nanobiotechnology. (2024) 22:108. 10.1186/s12951-024-02380-0
20.
Pan D Liu W Zhu S Fan B Yu N Ning G et al . Potential of different cells-derived exosomal microRNA cargos for treating spinal cord injury. J Orthop Translat. (2021) 31:33–40. 10.1016/j.jot.2021.09.008
21.
Giovannelli L Bari E Jommi C Tartara F Armocida D Garbossa D et al . Mesenchymal stem cell secretome and extracellular vesicles for neurodegenerative diseases: risk-benefit profile and next steps for the market access. Bioact Mater. (2023) 29:16–35. 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2023.06.013
22.
Lener T Gimona M Aigner L Börger V Buzas E Camussi G et al . Applying extracellular vesicles based therapeutics in clinical trials - an ISEV position paper. J Extracell Vesicles. (2015) 4:30087. 10.3402/jev.v4.30087
23.
Li L Mu J Zhang Y Zhang C Ma T Chen L et al . Stimulation by exosomes from hypoxia preconditioned human umbilical vein endothelial cells facilitates mesenchymal stem cells angiogenic function for spinal cord repair. ACS Nano. (2022) 16:10811–23. 10.1021/acsnano.2c02898
24.
Liu W Rong Y Wang J Zhou Z Ge X Ji C et al . Exosome-shuttled miR-216a-5p from hypoxic preconditioned mesenchymal stem cells repair traumatic spinal cord injury by shifting microglial M1/M2 polarization. J Neuroinflammation. (2020) 17:47. 10.1186/s12974-020-1726-7
25.
Yang B Chen Y Shi J . Exosome biochemistry and advanced nanotechnology for next-generation theranostic platforms. Adv Mater. (2019) 31:e1802896. 10.1002/adma.201802896
26.
Tenchov R Sasso JM Wang X Liaw WS Chen CA Zhou QA . Exosomes horizontal line nature's lipid nanoparticles, a rising star in drug delivery and diagnostics. ACS Nano. (2022) 16:17802–46. 10.1021/acsnano.2c08774
27.
Dad HA Gu TW Zhu AQ Huang LQ Peng LH . Plant exosome-like nanovesicles: emerging therapeutics and drug delivery nanoplatforms. Mol Ther. (2021) 29:13–31. 10.1016/j.ymthe.2020.11.030
28.
Mondal J Pillarisetti S Junnuthula V Saha M Hwang SR Park IK et al . Hybrid exosomes, exosome-like nanovesicles and engineered exosomes for therapeutic applications. J Control Release. (2023) 353:1127–49. 10.1016/j.jconrel.2022.12.027
29.
Cully M . Exosome-based candidates move into the clinic. Nat Rev Drug Discov. (2021) 20:6–7. 10.1038/d41573-020-00220-y
30.
Dutta D Khan N Wu J Jay SM . Extracellular vesicles as an emerging frontier in spinal cord injury pathobiology and therapy. Trends Neurosci. (2021) 44:492–506. 10.1016/j.tins.2021.01.003
31.
Singh N Guha L Kumar H . From hope to healing: exploring the therapeutic potential of exosomes in spinal cord injury. Extracellular Vesicle. (2024) 3:100044. 10.1016/j.vesic.2024.100044
32.
Ma CY Zhai Y Li CT Liu J Xu X Chen H et al . Translating mesenchymal stem cell and their exosome research into GMP compliant advanced therapy products: promises, problems and prospects. Med Res Rev. (2024) 44:919–38. 10.1002/med.22002
33.
Jia Y Yu L Ma T Xu W Qian H Sun Y et al . Small extracellular vesicles isolation and separation: current techniques, pending questions and clinical applications. Theranostics. (2022) 12:6548–75. 10.7150/thno.74305
34.
Liu WZ Ma ZJ Li JR Kang XW . Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes: therapeutic opportunities and challenges for spinal cord injury. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2021) 12:102. 10.1186/s13287-021-02153-8
35.
Kim HI Park J Zhu Y Wang X Han Y Zhang D . Recent advances in extracellular vesicles for therapeutic cargo delivery. Exp Mol Med. (2024) 56:836–49. 10.1038/s12276-024-01201-6
36.
Luo Z Peng W Xu Y Xie Y Liu Y Lu H et al . Exosomal OTULIN from M2 macrophages promotes the recovery of spinal cord injuries via stimulating Wnt/beta-catenin pathway-mediated vascular regeneration. Acta Biomater. (2021) 136:519–32. 10.1016/j.actbio.2021.09.026
37.
Yao X Zhou Y Liu Y Jie J Xue W Yang P . Engineered exosome-based treatment for peripheral nerve regeneration: a narrative review of clinical prospects. Adv Technol Neurosci. (2025) 2:135–43. 10.4103/ATN.ATN-D-25-00009
38.
Pegtel DM Gould SJ . Exosomes. Annu Rev Biochem. (2019) 88:487–514. 10.1146/annurev-biochem-013118-111902
39.
Arya SB Collie SP Parent CA . The ins-and-outs of exosome biogenesis, secretion, and internalization. Trends Cell Biol. (2024) 34:90–108. 10.1016/j.tcb.2023.06.006
40.
van Niel G D'Angelo G Raposo G . Shedding light on the cell biology of extracellular vesicles. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. (2018) 19:213–28. 10.1038/nrm.2017.125
41.
Kimiz-Gebologlu I Oncel SS . Exosomes: large-scale production, isolation, drug loading efficiency, and biodistribution and uptake. J Control Release. (2022) 347:533–43. 10.1016/j.jconrel.2022.05.027
42.
Jeppesen DK Fenix AM Franklin JL Higginbotham JN Zhang Q et al . Reassessment of exosome composition. Cell. (2019) 177:428–45.e18. 10.1016/j.cell.2019.02.029
43.
Gurung S Perocheau D Touramanidou L Baruteau J . The exosome journey: from biogenesis to uptake and intracellular signalling. Cell Commun Signal. (2021) 19:47. 10.1186/s12964-021-00730-1
44.
Baietti MF Zhang Z Mortier E Melchior A Degeest G Geeraerts A et al . Syndecan-syntenin-ALIX regulates the biogenesis of exosomes. Nat Cell Biol. (2012) 14:677–85. 10.1038/ncb2502
45.
Li J Jing Y Bai F Wu Y Wang L Yan Y et al . Induced pluripotent stem cells as natural biofactories for exosomes carrying miR-199b-5p in the treatment of spinal cord injury. Front Pharmacol. (2022) 13:1078761. 10.3389/fphar.2022.1078761
46.
Huang Z Li J Wo J Li CL Wu ZC Deng XH et al . Intranasal Delivery of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF)-loaded small extracellular vesicles for treating acute spinal cord injury in rats and monkeys. J Extracell Vesicles. (2025) 14:e70066. 10.1002/jev2.70066
47.
Liang Z Yang Z Xie H Rao J Xu X Lin Y et al . Small extracellular vesicles from hypoxia-preconditioned bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells attenuate spinal cord injury via miR-146a-5p-mediated regulation of macrophage polarization. Neural Regen Res. (2024) 19:2259–69. 10.4103/1673-5374.391194
48.
Liu B Kong Y Shi W Kuss M Liao K Hu G et al . Exosomes derived from differentiated human ADMSC with the Schwann cell phenotype modulate peripheral nerve-related cellular functions. Bioact Mater. (2022) 14:61–75. 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2021.11.022
49.
Zhang Y Yi D Hong Q Liu C Chi K Liu J et al . Platelet-rich plasma-derived exosomes enhance mesenchymal stem cell paracrine function and nerve regeneration potential. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2024) 699:149496. 10.1016/j.bbrc.2024.149496
50.
Liu B Zhang Y Yang Z Liu M Zhang C Zhao Y et al . Omega-3 DPA Protected Neurons from Neuroinflammation by balancing Microglia M1/M2 polarizations through inhibiting NF-kappaB/MAPK p38 signaling and activating Neuron-BDNF-PI3K/AKT pathways. Mar Drugs. (2021) 19:587. 10.3390/md19110587
51.
Yuan J Yankner BA . Apoptosis in the nervous system. Nature. (2000) 407:802–9. 10.1038/35037739
52.
Opferman JT Kothari A . Anti-apoptotic BCL-2 family members in development. Cell Death Differ. (2018) 25:37–45. 10.1038/cdd.2017.170
53.
Regimbeau M Abrey J Vautrot V Causse S Gobbo J Garrido C . Heat shock proteins and exosomes in cancer theranostics. Semin Cancer Biol. (2022) 86:46–57. 10.1016/j.semcancer.2021.07.014
54.
Fu Y Zhang YL Liu RQ Xu MM Xie JL Zhang XL et al . Exosome lncRNA IFNG-AS1 derived from mesenchymal stem cells of human adipose ameliorates neurogenesis and ASD-like behavior in BTBR mice. J Nanobiotechnology. (2024) 22:66. 10.1186/s12951-024-02338-2
55.
Zhu B Gu G Ren J Song X Li J Wang C et al . Schwann cell-derived exosomes and methylprednisolone composite patch for spinal cord injury repair. ACS Nano. (2023) 17:22928–43. 10.1021/acsnano.3c08046
56.
Wei J Su W Zhao Y Wei Z Hua Y Xue P et al . Maresin 1 promotes nerve regeneration and alleviates neuropathic pain after nerve injury. J Neuroinflammation. (2022) 19:32. 10.1186/s12974-022-02405-1
57.
Ding Z Dai C Zhong L Liu R Gao W Zhang H et al . Neuregulin-1 converts reactive astrocytes toward oligodendrocyte lineage cells via upregulating the PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway to repair spinal cord injury. Biomed Pharmacother. (2021) 134:111168. 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.111168
58.
Fakhri S Iranpanah A Gravandi MM Moradi SZ Ranjbari M Majnooni MB et al . Natural products attenuate PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway: a promising strategy in regulating neurodegeneration. Phytomedicine. (2021) 91:153664. 10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153664
59.
Sun Y Zhao J Liu Q Xu Y Qin Y He R et al . Intranasal delivery of small extracellular vesicles from specific subpopulation of mesenchymal stem cells mitigates traumatic spinal cord injury. J Control Release. (2024) 369:335–50. 10.1016/j.jconrel.2024.03.037
60.
Wu J Li Z Wu Y Cui N . The crosstalk between exosomes and ferroptosis: a review. Cell Death Discov. (2024) 10:170. 10.1038/s41420-024-01938-z
61.
Zhou Z You B Ji C Zhang L Wu F Qian H . Implications of crosstalk between exosome-mediated ferroptosis and diseases for pathogenesis and treatment. Cells. (2023) 12:311. 10.3390/cells12020311
62.
Stockwell BR . Ferroptosis turns 10: emerging mechanisms, physiological functions, and therapeutic applications. Cell. (2022) 185:2401–21. 10.1016/j.cell.2022.06.003
63.
Song QF Cui Q Wang YS Zhang LX . Mesenchymal stem cells, extracellular vesicles, and transcranial magnetic stimulation for ferroptosis after spinal cord injury. Neural Regen Res. (2023) 18:1861–8. 10.4103/1673-5374.367838
64.
Zhang L Lin Y Bai W Sun L Tian M . Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosome suppresses programmed cell death in traumatic brain injury via PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy. CNS Neurosci Ther. (2023) 29:2236–58. 10.1111/cns.14159
65.
Chen Y Li B Quan J Li Z Li Y Tang Y . Inhibition of ferroptosis by mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes in acute spinal cord injury: role of Nrf2/GCH1/BH4. Axis Neurospine. (2024) 21:642–55. 10.14245/ns.2448038.019
66.
Jin S Chen X Tian Y Jarvis R Promes V Yang Y . Astroglial exosome HepaCAM signaling and ApoE antagonization coordinates early postnatal cortical pyramidal neuronal axon growth and dendritic spine formation. Nat Commun. (2023) 14:5150. 10.1038/s41467-023-40926-2
67.
Sioka C Fotopoulos A Giannopoulos S . Reader response: first-ever ischemic stroke and increased risk of incident heart disease in older adults. Neurology. (2021) 96:723–4. 10.1212/WNL.0000000000011782
68.
Court FA Alvarez J . Schwann cell and axon: an interlaced unit-from action potential to phenotype expression. Adv Exp Med Biol. (2016) 949:183–201. 10.1007/978-3-319-40764-7_9
69.
Patel P Buchanan CN Zdradzinski MD Sahoo PK Kar AN Lee SJ et al . Intra-axonal translation of Khsrp mRNA slows axon regeneration by destabilizing localized mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. (2022) 50:5772–92. 10.1093/nar/gkac337
70.
Gao X Li S Yang Y Yang S Yu B Zhu Z et al . A novel magnetic responsive miR-26a@SPIONs-OECs for spinal cord injury: triggering neural regeneration program and orienting axon guidance in inhibitory astrocytic environment. Adv Sci. (2023) 10:e2304487. 10.1002/advs.202304487
71.
Huang J Zhang G Li S Li J Wang W Xue J et al . Endothelial cell-derived exosomes boost and maintain repair-related phenotypes of Schwann cells via miR199-5p to promote nerve regeneration. J Nanobiotechnology. (2023) 21:10. 10.1186/s12951-023-01767-9
72.
Sun Y Liu Q Qin Y Xu Y Zhao J Xie Y et al . Exosomes derived from CD271(+)CD56(+) bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell subpopoulation identified by single-cell RNA sequencing promote axon regeneration after spinal cord injury. Theranostics. (2024) 14:510–27. 10.7150/thno.89008
73.
Fan L Liu C Chen X Zheng L Zou Y Wen H et al . Exosomes-loaded electroconductive hydrogel synergistically promotes tissue repair after spinal cord injury via immunoregulation and enhancement of myelinated axon growth. Adv Sci. (2022) 9:e2105586. 10.1002/advs.202105586
74.
Jiang XH Li HF Chen ML Zhang YX Chen HB Chen RH et al . Treadmill exercise exerts a synergistic effect with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes on neuronal apoptosis and synaptic-axonal remodeling. Neural Regen Res. (2023) 18:1293–9. 10.4103/1673-5374.357900
75.
Feng Z Chen X Zeng M Zhang M . Phase separation as a mechanism for assembling dynamic postsynaptic density signalling complexes. Curr Opin Neurobiol. (2019) 57:1–8. 10.1016/j.conb.2018.12.001
76.
Eitan E Thornton-Wells T Elgart K Erden E Gershun E Levine A et al . Synaptic proteins in neuron-derived extracellular vesicles as biomarkers for Alzheimer's disease: novel methodology and clinical proof of concept. Extracell Vesicles Circ Nucl Acids. (2023) 4:133–50. 10.20517/evcna.2023.13
77.
Liu S Chen L Guo M Li Y Liu Q Cheng Y . Targeted delivery of engineered RVG-BDNF-exosomes: a novel neurobiological approach for ameliorating depression and regulating neurogenesis. Research. (2024) 7:0402. 10.34133/research.0402
78.
Piette C Gervasi N Venance L . Synaptic plasticity through a naturalistic lens. Front Synaptic Neurosci. (2023) 15:1250753. 10.3389/fnsyn.2023.1250753
79.
Kochan SMV Malo MC Jevtic M Jahn-Kelleter HM Wani GA Ndoci K et al . Enhanced mitochondrial fusion during a critical period of synaptic plasticity in adult-born neurons. Neuron. (2024) 112:1997–2014.e6. 10.1016/j.neuron.2024.03.013
80.
Anand S Foot N Ang CS Gembus KM Keerthikumar S Adda CG et al . Arrestin-domain containing protein 1 (Arrdc1) regulates the protein cargo and release of extracellular vesicles. Proteomics. (2018) 18:e1800266. 10.1002/pmic.201800266
81.
Putz U Howitt J Lackovic J Foot N Kumar S Silke J et al . Nedd4 family-interacting protein 1 (Ndfip1) is required for the exosomal secretion of Nedd4 family proteins. J Biol Chem. (2008) 283:32621–7. 10.1074/jbc.M804120200
82.
Donovan P Poronnik P . Nedd4 and Nedd4-2: ubiquitin ligases at work in the neuron. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. (2013) 45:706–10. 10.1016/j.biocel.2012.12.006
83.
Hsia HE Kumar R Luca R Takeda M Courchet J Nakashima J et al . Ubiquitin E3 ligase Nedd4-1 acts as a downstream target of PI3K/PTEN-mTORC1 signaling to promote neurite growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. (2014) 111:13205–10. 10.1073/pnas.1400737111
84.
Ding X Jo J Wang CY Cristobal CD Zuo Z Ye Q et al . The Daam2-VHL-Nedd4 axis governs developmental and regenerative oligodendrocyte differentiation. Genes Dev. (2020) 34:1177–89. 10.1101/gad.338046.120
85.
Fimiani C Pereira JA Gerber J Berg I DeGeer J Bachofner S et al . The E3 ubiquitin ligase Nedd4 fosters developmental myelination in the mouse central and peripheral nervous system. Glia. (2025) 73:422–44. 10.1002/glia.24642
86.
Sullivan KG Bashaw GJ . Commissureless acts as a substrate adapter in a conserved Nedd4 E3 ubiquitin ligase pathway to promote axon growth across the midline. bioRxiv. 31:2023.10.13.562283 (2024). 10.7554/eLife.92757.2
87.
Shi G Hao D Zhang L Qin J Tian G Ma B et al . Endocytosis-associated patterns in nerve regeneration after peripheral nerve injury. J Orthop Translat. (2021) 31:10–9. 10.1016/j.jot.2021.09.004
88.
He L Chang Q Zhang Y Guan X Ma Z Chen X et al . MiR-155-5p Aggravated astrocyte activation and glial scarring in a spinal cord injury model by inhibiting Ndfip1 expression and PTEN nuclear translocation. Neurochem Res. (2023) 48:1912–24. 10.1007/s11064-023-03862-7
89.
Hellenbrand DJ Quinn CM Piper ZJ Morehouse CN Fixel JA Hanna AS . Inflammation after spinal cord injury: a review of the critical timeline of signaling cues and cellular infiltration. J Neuroinflammation. (2021) 18:284. 10.1186/s12974-021-02337-2
90.
Salvador AFM Dykstra T Rustenhoven J Gao W Blackburn SM Bhasiin K et al . Age-dependent immune and lymphatic responses after spinal cord injury. Neuron. (2023) 111:2155–69.e9. 10.1016/j.neuron.2023.04.011
91.
Zhang Q Yu B Zhang Y Tian Y Yang S Chen Y et al . Combination of single-cell and bulk RNA seq reveals the immune infiltration landscape and targeted therapeutic drugs in spinal cord injury. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1068359. 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1068359
92.
Freyermuth-Trujillo X Segura-Uribe JJ Salgado-Ceballos H Orozco-Barrios CE Coyoy-Salgado A . Inflammation: a target for treatment in spinal cord injury. Cells. (2022) 11:2692. 10.3390/cells11172692
93.
Milich LM Ryan CB Lee JK . The origin, fate, and contribution of macrophages to spinal cord injury pathology. Acta Neuropathol. (2019) 137:785–97. 10.1007/s00401-019-01992-3
94.
Peng P Yu H Xing C Tao B Li C Huang J et al . Exosomes-mediated phenotypic switch of macrophages in the immune microenvironment after spinal cord injury. Biomed Pharmacother. (2021) 144:112311. 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.112311
95.
Locati M Curtale G Mantovani A . Diversity, mechanisms, and significance of macrophage plasticity. Annu Rev Pathol. (2020) 15:123–47. 10.1146/annurev-pathmechdis-012418-012718
96.
Wu H Zheng J Xu S Fang Y Wu Y Zeng J et al . Mer regulates microglial/macrophage M1/M2 polarization and alleviates neuroinflammation following traumatic brain injury. J Neuroinflammation. (2021) 18:2. 10.1186/s12974-020-02041-7
97.
Tang Y Le W . Differential roles of M1 and M2 microglia in neurodegenerative diseases. Mol Neurobiol. (2016) 53:1181–94. 10.1007/s12035-014-9070-5
98.
Ren J Zhu B Gu G Zhang W Li J Wang H et al . Schwann cell-derived exosomes containing MFG-E8 modify macrophage/microglial polarization for attenuating inflammation via the SOCS3/STAT3 pathway after spinal cord injury. Cell Death Dis. (2023) 14:70. 10.1038/s41419-023-05607-4
99.
Liu C Hu F Jiao G Guo Y Zhou P Zhang Y et al . Dental pulp stem cell-derived exosomes suppress M1 macrophage polarization through the ROS-MAPK-NFkappaB P65 signaling pathway after spinal cord injury. J Nanobiotechnology. (2022) 20:65. 10.1186/s12951-022-01273-4
100.
Peng W Xie Y Luo Z Liu Y Xu J Li C et al . UTX deletion promotes M2 macrophage polarization by epigenetically regulating endothelial cell-macrophage crosstalk after spinal cord injury. J Nanobiotechnology. (2023) 21:225. 10.1186/s12951-023-01986-0
101.
Yuan F Peng W Yang Y Xu J Liu Y Xie Y et al . Endothelial progenitor cell-derived exosomes promote anti-inflammatory macrophages via SOCS3/JAK2/STAT3 axis and improve the outcome of spinal cord injury. J Neuroinflammation. (2023) 20:156. 10.1186/s12974-023-02833-7
102.
Kong G Xiong W Li C Xiao C Wang S Li W et al . Treg cells-derived exosomes promote blood-spinal cord barrier repair and motor function recovery after spinal cord injury by delivering miR-2861. J Nanobiotechnol. (2023) 21:364. 10.1186/s12951-023-02188-4
103.
Xiong W Li C Kong G Zeng Q Wang S Yin G et al . Treg cell-derived exosomes miR-709 attenuates microglia pyroptosis and promotes motor function recovery after spinal cord injury. J Nanobiotechnology. (2022) 20:529. 10.1186/s12951-022-01724-y
104.
Torabi S Anjamrooz SH Zeraatpisheh Z Aligholi H Azari H . Ibrutinib reduces neutrophil infiltration, preserves neural tissue and enhances locomotor recovery in mouse contusion model of spinal cord injury. Anat Cell Biol. (2021) 54:350–60. 10.5115/acb.20.299
105.
Yu CG Bondada V Iqbal H Moore KL Gensel JC Bondada S et al . Inhibition of bruton tyrosine kinase reduces neuroimmune cascade and promotes recovery after spinal cord injury. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 23:355. 10.3390/ijms23010355
106.
Ju Y Hu Y Yang P Xie X Fang B . Extracellular vesicle-loaded hydrogels for tissue repair and regeneration. Mater Today Bio. (2023) 18:100522. 10.1016/j.mtbio.2022.100522
107.
Saumell-Esnaola M Delgado D García Del Caño G Beitia M Sallés J González-Burguera I et al . Isolation of platelet-derived exosomes from human platelet-rich plasma: biochemical and morphological characterization. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:2861. 10.3390/ijms23052861
108.
Cao Y Xu Y Chen C Xie H Lu H Hu J . Local delivery of USC-derived exosomes harboring ANGPTL3 enhances spinal cord functional recovery after injury by promoting angiogenesis. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2021) 12:20. 10.1186/s13287-020-02078-8
109.
Li C Qin T Jin Y Hu J Yuan F Cao Y et al . Cerebrospinal fluid-derived extracellular vesicles after spinal cord injury promote vascular regeneration via PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. J Orthop Translat. (2023) 39:124–34. 10.1016/j.jot.2023.02.001
110.
Gao P Yi J Chen W Gu J Miao S Wang X et al . Pericyte-derived exosomal miR-210 improves mitochondrial function and inhibits lipid peroxidation in vascular endothelial cells after traumatic spinal cord injury by activating JAK1/STAT3 signaling pathway. J Nanobiotechnology. (2023) 21:452. 10.1186/s12951-023-02110-y
111.
Xie Y Sun Y Liu Y Zhao J Liu Q Xu J et al . Targeted delivery of RGD-CD146(+)CD271(+) human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes promotes blood-spinal cord barrier repair after spinal cord injury. ACS Nano. (2023) 17:18008–24. 10.1021/acsnano.3c04423
112.
Wang S Zhu C Zhang B Hu J Xu J Xue C et al . BMSC-derived extracellular matrix better optimizes the microenvironment to support nerve regeneration. Biomaterials. (2022) 280:121251. 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2021.121251
113.
Goncalves MB Malmqvist T Clarke E Hubens CJ Grist J Hobbs C et al . Neuronal RARbeta signaling modulates PTEN activity directly in neurons and via exosome transfer in astrocytes to prevent glial scar formation and induce spinal cord regeneration. J Neurosci. (2015) 35:15731–45. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1339-15.2015
114.
Zhang C Kang J Zhang X Zhang Y Huang N Ning B . Spatiotemporal dynamics of the cellular components involved in glial scar formation following spinal cord injury. Biomed Pharmacother. (2022) 153:113500. 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113500
115.
Fan B Wei Z Feng S . Progression in translational research on spinal cord injury based on microenvironment imbalance. Bone Res. (2022) 10:35. 10.1038/s41413-022-00199-9
116.
Mi S Chang Z Wang X Gao J Liu Y Liu W et al . Bioactive spinal cord scaffold releasing neurotrophic exosomes to promote in situ centralis neuroplasticity. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. (2023) 15:16355–68. 10.1021/acsami.2c19607
117.
Xu Y Zhu ZH Xu X Sun HT Zheng HM Zhang JL et al . Neuron-derived exosomes promote the recovery of spinal cord injury by modulating nerve cells in the cellular microenvironment of the lesion area. Mol Neurobiol. (2023) 60:4502–16. 10.1007/s12035-023-03341-8
118.
Li Z Wang Q Hu H Zheng W Gao C . Research advances of biomaterials-based microenvironment-regulation therapies for repair and regeneration of spinal cord injury. Biomed Mater. (2021) 16. 10.1088/1748-605X/ac1d3c
119.
Shimoda M Khokha R . Metalloproteinases in extracellular vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. (2017) 1864:1989–2000. 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2017.05.027
120.
Shen K Sun G Chan L He L Li X Yang S et al . Anti-Inflammatory nanotherapeutics by targeting matrix metalloproteinases for immunotherapy of spinal cord injury. Small. (2021) 17:e2102102. 10.1002/smll.202102102
121.
Liu W Wang Y Gong F Rong Y Luo Y Tang P et al . Exosomes derived from bone mesenchymal stem cells repair traumatic spinal cord injury by suppressing the activation of A1 neurotoxic reactive astrocytes. J Neurotrauma. (2019) 36:469–84. 10.1089/neu.2018.5835
122.
Poongodi R Yang TH Huang YH Yang KD Chen HZ Chu TY et al . Stem cell exosome-loaded Gelfoam improves locomotor dysfunction and neuropathic pain in a rat model of spinal cord injury. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2024) 15:143. 10.1186/s13287-024-03758-5
123.
Singh N Pathak Z Kumar H . Rab27a-mediated extracellular vesicle release drives astrocytic CSPG secretion and glial scarring in spinal cord injury. Biomater Adv. (2025) 176:214357. 10.1016/j.bioadv.2025.214357
124.
Peng W Xie Y Liu Y Xu J Yuan F Li C et al . Targeted delivery of CD163(+) macrophage-derived small extracellular vesicles via RGD peptides promote vascular regeneration and stabilization after spinal cord injury. J Control Release. (2023) 361:750–65. 10.1016/j.jconrel.2023.08.025
125.
Han M Yang H Lu X Li Y Liu Z Li F et al . Three-dimensional-cultured MSC-derived exosome-hydrogel hybrid microneedle array patch for spinal cord repair. Nano Lett. (2022) 22:6391–401. 10.1021/acs.nanolett.2c02259
126.
Guan P Fan L Zhu Z Yang Q Kang X Li J et al . M2 microglia-derived exosome-loaded electroconductive hydrogel for enhancing neurological recovery after spinal cord injury. J Nanobiotechnology. (2024) 22:8. 10.1186/s12951-023-02255-w
127.
Li L Zhang Y Mu J Chen J Zhang C Cao H et al . Transplantation of human mesenchymal stem-cell-derived exosomes immobilized in an adhesive hydrogel for effective treatment of spinal cord injury. Nano Lett. (2020) 20:4298–305. 10.1021/acs.nanolett.0c00929
128.
Poongodi R Chen YL Yang TH Huang YH Yang KD Lin HC et al . Bio-scaffolds as cell or exosome carriers for nerve injury repair. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22. 10.3390/ijms222413347
129.
Liu X Zhang L Xu Z Xiong X Yu Y Wu H et al . A functionalized collagen-I scaffold delivers microRNA 21-loaded exosomes for spinal cord injury repair. Acta Biomater. (2022) 154:385–400. 10.1016/j.actbio.2022.10.027
130.
Zhang L Fan C Hao W Zhuang Y Liu X Zhao Y et al . NSCs migration promoted and drug delivered exosomes-collagen scaffold via a bio-specific peptide for one-step spinal cord injury repair. Adv Healthc Mater. (2021) 10:e2001896. 10.1002/adhm.202001896
131.
Li YJ Wu JY Liu J Xu W Qiu X Huang S et al . Artificial exosomes for translational nanomedicine. J Nanobiotechnology. (2021) 19:242. 10.1186/s12951-021-00986-2
132.
Liang Y Duan L Lu J Xia J . Engineering exosomes for targeted drug delivery. Theranostics. (2021) 11:3183–95. 10.7150/thno.52570
133.
Cecchin R Troyer Z Witwer K Morris KV . Extracellular vesicles: the next generation in gene therapy delivery. Mol Ther. (2023) 31:1225–30. 10.1016/j.ymthe.2023.01.021
134.
Tian J Han Z Song D Peng Y Xiong M Chen Z et al . Engineered exosome for drug delivery: recent development and clinical applications. Int J Nanomed. (2023) 18:7923–40. 10.2147/IJN.S444582
135.
He C Zheng S Luo Y Wang B . Exosome theranostics: biology and translational medicine. Theranostics. (2018) 8:237–55. 10.7150/thno.21945
136.
Rehman FU Liu Y Zheng M Shi B . Exosomes based strategies for brain drug delivery. Biomaterials. (2023) 293:121949. 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2022.121949
137.
Guo S Perets N Betzer O Ben-Shaul S Sheinin A Michaelevski I et al . Intranasal delivery of mesenchymal stem cell derived exosomes loaded with phosphatase and tensin homolog siRNA repairs complete spinal cord injury. ACS Nano. (2019) 13:10015–28. 10.1021/acsnano.9b01892
138.
Cui J Wang X Li J Zhu A Du Y Zeng W et al . Immune exosomes loading self-assembled nanomicelles traverse the blood-brain barrier for chemo-immunotherapy against glioblastoma. ACS Nano. (2023). 10.1021/acsnano.2c10219
139.
Gao ZS Zhang CJ Xia N Tian H Li DY Lin JQ et al . Berberine-loaded M2 macrophage-derived exosomes for spinal cord injury therapy. Acta Biomater. (2021) 126:211–23. 10.1016/j.actbio.2021.03.018
140.
Fais S O'Driscoll L Borras FE Buzas E Camussi G Cappello F et al . Evidence-based clinical use of nanoscale extracellular vesicles in nanomedicine. ACS Nano. (2016) 10:3886–99. 10.1021/acsnano.5b08015
141.
Crivelli B Chlapanidas T Perteghella S Lucarelli E Pascucci L Brini AT et al . Mesenchymal stem/stromal cell extracellular vesicles: from active principle to next generation drug delivery system. J Control Release. (2017) 262:104–17. 10.1016/j.jconrel.2017.07.023
142.
Al-Masawa ME Alshawsh MA Ng CY Ng AMH Foo JB Vijakumaran U et al . Efficacy and safety of small extracellular vesicle interventions in wound healing and skin regeneration: a systematic review and meta-analysis of animal studies. Theranostics. (2022) 12:6455–508. 10.7150/thno.73436
143.
Shi MM Yang QY Monsel A Yan JY Dai CX Zhao JY et al . Preclinical efficacy and clinical safety of clinical-grade nebulized allogenic adipose mesenchymal stromal cells-derived extracellular vesicles. J Extracell Vesicles. (2021) 10:e12134. 10.1002/jev2.12134
144.
Rohde E Pachler K Gimona M . Manufacturing and characterization of extracellular vesicles from umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stromal cells for clinical testing. Cytotherapy. (2019) 21:581–92. 10.1016/j.jcyt.2018.12.006
145.
Lotfy A AboQuella NM Wang H . Mesenchymal stromal/stem cell (MSC)-derived exosomes in clinical trials. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2023) 14:66. 10.1186/s13287-023-03287-7
146.
Akhlaghpasand M Tavanaei R Hosseinpoor M Yazdani KO Soleimani A Zoshk MY et al . Safety and potential effects of intrathecal injection of allogeneic human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes in complete subacute spinal cord injury: a first-in-human, single-arm, open-label, phase I clinical trial. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2024) 15:264. 10.1186/s13287-024-03868-0
147.
Kang X-W Lu YB Yang YN Kang XW Wang YG Ma B et al . Progress in clinical trials of cell transplantation for the treatment of spinal cord injury: how many questions remain unanswered?Neural Regen Res. (2021) 16:405–13. 10.4103/1673-5374.293130
148.
Meng W He C Hao Y Wang L Li L Zhu G . Prospects and challenges of extracellular vesicle-based drug delivery system: considering cell source. Drug Deliv. (2020) 27:585–98. 10.1080/10717544.2020.1748758
149.
Li P Kaslan M Lee SH Yao J Gao Z . Progress in exosome isolation techniques. Theranostics. (2017) 7:789–804. 10.7150/thno.18133
150.
Gorgens A Corso G Hagey DW Jawad Wiklander R Gustafsson MO Felldin U et al . Identification of storage conditions stabilizing extracellular vesicles preparations. J Extracell Vesicles. (2022) 11:e12238. 10.1002/jev2.12238
151.
Maroto R Zhao Y Jamaluddin M Popov VL Wang H Kalubowilage M et al . Effects of storage temperature on airway exosome integrity for diagnostic and functional analyses. J Extracell Vesicles. (2017) 6:1359478. 10.1080/20013078.2017.1359478
152.
Wang T Huang G Yi Z Dai S Zhuang W Guo S . Advances in extracellular vesicle-based combination therapies for spinal cord injury. Neural Regen Res. (2024) 19:369–74. 10.4103/1673-5374.377413
153.
Chen J Wu J Mu J Li L Hu J Lin H et al . An antioxidative sophora exosome-encapsulated hydrogel promotes spinal cord repair by regulating oxidative stress microenvironment. Nanomedicine. (2023) 47:102625. 10.1016/j.nano.2022.102625
154.
Rezaie J Feghhi M Etemadi T . A review on exosomes application in clinical trials: perspective, questions, and challenges. Cell Commun Signal. (2022) 20:145. 10.1186/s12964-022-00959-4
155.
Yaghoubi Y Movassaghpour A Zamani M Talebi M Mehdizadeh A Yousefi M . Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells derived-exosomes in diseases treatment. Life Sci. (2019) 233:116733. 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.116733
156.
Krishnan I Chan AML Law JX Ng MH Jayapalan JJ Lokanathan Y . Proteomic analysis of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles: a systematic review. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25:5340. 10.3390/ijms25105340
157.
Wang ZG He ZY Liang S Yang Q Cheng P Chen AM . Comprehensive proteomic analysis of exosomes derived from human bone marrow, adipose tissue, and umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2020) 11:511. 10.1186/s13287-020-02032-8
158.
Hong P Yang H Wu Y Li K Tang Z . The functions and clinical application potential of exosomes derived from adipose mesenchymal stem cells: a comprehensive review. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2019) 10:242. 10.1186/s13287-019-1358-y
159.
Liang Y Wu JH Zhu JH Yang H . Exosomes secreted by hypoxia-pre-conditioned adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells reduce neuronal apoptosis in rats with spinal cord injury. J Neurotrauma. (2022) 39:701–14. 10.1089/neu.2021.0290
160.
Yu HR Huang HC Chen IL Li SC . Exosomes secreted by wharton's jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells promote the ability of cell proliferation and migration for keratinocyte. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25:4758. 10.3390/ijms25094758
161.
Wen L Wang YD Shen DF Zheng PD Tu MD You WD et al . Exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells inhibit neuroinflammation after traumatic brain injury. Neural Regen Res. (2022) 17:2717–24. 10.4103/1673-5374.339489
162.
Liu S Fan M Xu JX Yang LJ Qi CC Xia QR et al . Exosomes derived from bone-marrow mesenchymal stem cells alleviate cognitive decline in AD-like mice by improving BDNF-related neuropathology. J Neuroinflammation. (2022) 19:35. 10.1186/s12974-022-02393-2
163.
Sharma P Mesci P Carromeu C McClatchy DR Schiapparelli L Yates JR et al . Exosomes regulate neurogenesis and circuit assembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci. (2019) 116:16086–94. 10.1073/pnas.1902513116
164.
Zhong L Wang J Wang P Liu X Liu P Cheng X et al . Neural stem cell-derived exosomes and regeneration: cell-free therapeutic strategies for traumatic brain injury. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2023) 14:198. 10.1186/s13287-023-03409-1
165.
Li J Luo W Xiao C Zhao J Xiang C Liu W et al . Recent advances in endogenous neural stem/progenitor cell manipulation for spinal cord injury repair. Theranostics. (2023) 13:3966–87. 10.7150/thno.84133
166.
Pait MC Kaye SD Su Y Kumar A Singh S Gironda SC et al . Novel method for collecting hippocampal interstitial fluid extracellular vesicles (EV(ISF) ) reveals sex-dependent changes in microglial EV proteome in response to Abeta pathology. J Extracell Vesicles. (2024) 13:e12398. 10.1002/jev2.12398
167.
Huang S Ge X Yu J Han Z Yin Z Li Y et al . Increased miR-124-3p in microglial exosomes following traumatic brain injury inhibits neuronal inflammation and contributes to neurite outgrowth via their transfer into neurons. FASEB J. (2018) 32:512–28. 10.1096/fj.201700673r
168.
Cai Y Liu J Wang B Sun M Yang H . Microglia in the neuroinflammatory pathogenesis of Alzheimer's Disease and related therapeutic targets. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:856376. 10.3389/fimmu.2022.856376
169.
Ghosh M Pearse DD . Schwann cell-derived exosomal vesicles: a promising therapy for the injured spinal cord. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:17317. 10.3390/ijms242417317
170.
Brecknell JE Fawcett JW . Axonal regeneration. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. (1996) 71:227–55. 10.1111/j.1469-185X.1996.tb00748.x
171.
Kromer LF Cornbrooks CJ . Transplants of Schwann cell cultures promote axonal regeneration in the adult mammalian brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. (1985) 82:6330–4. 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6330
172.
Akhlaghpasand M Tavanaei R Hosseinpoor M Heidari R Mohammadi I Chamanara M et al . Effects of combined intrathecal mesenchymal stem cells and schwann cells transplantation on neuropathic pain in complete spinal cord injury: a phase II randomized active-controlled trial. Cell Transplant. (2025) 34:9636897241298128. 10.1177/09636897241298128
173.
Qiu J Hirschi KK . Endothelial cell development and its application to regenerative medicine. Circ Res. (2019) 125:489–501. 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.119.311405
174.
Ge X Tang P Rong Y Jiang D Lu X Ji C et al . Corrigendum to “Exosomal miR-155 from M1-polarized macrophages promotes EndoMT and impairs mitochondrial function via activating NF-kappaB signaling pathway in vascular endothelial cells after traumatic spinal cord injury” [Redox Biol. 41 (2021) 101932/PMID:33714739]. Redox Biol. (2021) 47:102121. 10.1016/j.redox.2021.102121
175.
Zeng J Gu C Sun Y Chen X . Engineering of M2 macrophages-derived exosomes via click chemistry for spinal cord injury repair. Adv Healthc Mater. (2023) 12:e2203391. 10.1002/adhm.202203391
176.
Yamanaka S . Induced pluripotent stem cells: past, present, and future. Cell Stem Cell. (2012) 10:678–84. 10.1016/j.stem.2012.05.005
177.
Ohnuki M Takahashi K . Present and future challenges of induced pluripotent stem cells. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. (2015) 370:20140367. 10.1098/rstb.2014.0367
178.
Kim JW Kim J Mo H Han H Rim YA Ju JH . Stepwise combined cell transplantation using mesenchymal stem cells and induced pluripotent stem cell-derived motor neuron progenitor cells in spinal cord injury. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2024) 15:114. 10.1186/s13287-024-03714-3
179.
Chew BC Liew FF Tan HW Chung I . Chemical advances in therapeutic application of exosomes and liposomes. Curr Med Chem. (2022) 29:4445–73. 10.2174/0929867329666220221094044
180.
Passeri E Elkhoury K Morsink M Broersen K Linder M Tamayol A et al . Alzheimer's disease: treatment strategies and their limitations. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:3954. 10.3390/ijms232213954
181.
Evers MJW van de Wakker SI de Groot EM de Jong OG Gitz-François JJJ Seinen CS et al . Functional siRNA delivery by extracellular vesicle-liposome hybrid nanoparticles. Adv Healthc Mater. (2022) 11:e2101202. 10.1002/adhm.202101202
182.
Liu JJJ Liu D To SKY Wong AST . Exosomes in cancer nanomedicine: biotechnological advancements and innovations. Mol Cancer. (2025) 24:166. 10.1186/s12943-025-02372-0
183.
Grzegorzewski J Michalak M Wołoszczuk M Bulicz M Majchrzak-Celińska A . Nanotherapy of glioblastoma-where hope grows. Int J Mol Sci. (2025) 26:1814. 10.3390/ijms26051814
184.
Shao J Zaro J Shen Y . Advances in exosome-based drug delivery and tumor targeting: from tissue distribution to intracellular fate. Int J Nanomedicine. (2020) 15:9355–71. 10.2147/IJN.S281890
185.
Duan L Ouyang K Xu X Xu L Wen C Zhou X et al . Nanoparticle delivery of CRISPR/Cas9 for genome editing. Front Genet. (2021) 12:673286. 10.3389/fgene.2021.673286
186.
Jang Y Park J Kim P Park EJ Sun H Baek Y et al . Development of exosome membrane materials-fused microbubbles for enhanced stability and efficient drug delivery of ultrasound contrast agent. Acta Pharm Sin B. (2023) 13:4983–98. 10.1016/j.apsb.2023.08.022
187.
Ansari MA Thiruvengadam M Venkidasamy B Alomary MN Salawi A Chung IM et al . Exosome-based nanomedicine for cancer treatment by targeting inflammatory pathways: current status and future perspectives. Semin Cancer Biol. (2022) 86:678–96. 10.1016/j.semcancer.2022.04.005
188.
Khan AR Yang X Fu M Zhai G . Recent progress of drug nanoformulations targeting to brain. J Control Release. (2018) 291:37–64. 10.1016/j.jconrel.2018.10.004
189.
Fan MH Pi JK Zou CY Jiang YL Li QJ Zhang XZ et al . Hydrogel-exosome system in tissue engineering: A promising therapeutic strategy. Bioact Mater. (2024) 38:1–30. 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2024.04.007
190.
Wang G Li Q Liu S Li M Liu B Zhao T et al . An injectable decellularized extracellular matrix hydrogel with cortical neuron-derived exosomes enhances tissue repair following traumatic spinal cord injury. Mater Today Bio. (2024) 28:101250. 10.1016/j.mtbio.2024.101250
191.
Qin X Wei B Xiang Y Lu H Liu F Li X et al . Exosome-tuned MOF signal amplifier boosting tumor exosome phenotyping with high-affinity nanostars. Biosens Bioelectron. (2024) 245:115828. 10.1016/j.bios.2023.115828
192.
Mansouri S . Emerging biosensing platforms based on metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) for detection of exosomes as diagnostic cancer biomarkers: case study for the role of the MOFs. J Mater Chem B. (2025) 13:1586–98. 10.1039/D4TB02465F
193.
Cocozza F Martin-Jaular L Lippens L Di Cicco A Arribas YA Ansart N et al . Extracellular vesicles and co-isolated endogenous retroviruses from murine cancer cells differentially affect dendritic cells. Embo J. (2023) 42:e113590. 10.15252/embj.2023113590
194.
Izquierdo-Useros N Naranjo-Gómez M Archer J Hatch SC Erkizia I Blanco J et al . Capture and transfer of HIV-1 particles by mature dendritic cells converges with the exosome-dissemination pathway. Blood. (2009) 113:2732–41. 10.1182/blood-2008-05-158642
Summary
Keywords
spinal cord injury, exosomes, nerve repair, immunoregulation, miRNA, NDDS
Citation
Cha Z, Li Y, Pu J, Zhang Y, Lu Q, Huang W, Li T and Lu X (2025) Exosome-mediated repair of spinal cord injury: cellular sources, mechanisms of action, and combined therapeutic strategies. Front. Neurol. 16:1645457. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1645457
Received
26 June 2025
Accepted
28 August 2025
Published
13 October 2025
Volume
16 - 2025
Edited by
Esther Giraldo, Universitat Politècnica de València, Spain
Reviewed by
B. Martínez-Rojas, Laboratorio Associado ICVS 3B's, Portugal
Nidhi Singh, National Institute of Pharmaceutical Education and Research, Ahmedabad, India
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Cha, Li, Pu, Zhang, Lu, Huang, Li and Lu.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Tao Li taoli_kh@163.comXiaoyang Lu xiaoyang-lu@foxmail.com
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.