- 1Department of Neurology, The Second People’s Hospital of Hunan Province (Brain Hospital of Hunan Province), Changsha, Hunan, China
- 2Department of Neurology, The Affiliated Changsha Central Hospital, Hengyang Medical School, University of South China, Changsha, Hunan, China
- 3Department of Pharmacy, School of Pharmacy, Phase I Clinical Trial Centre, The Affiliated Changsha Central Hospital, Hengyang Medical School, University of South China, Changsha, China
Background: The non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio (NHHR) is a recently emerging composite biomarker of atherogenic lipid metabolism. However, the relationship between NHHR and early-onset post-stroke depression (PSD) remains underexplored.
Methods: Early-onset PSD was diagnosed 2 weeks after an acute ischemic stroke (AIS). Depression severity was assessed using the Hamilton Depression Scale-17 items (HAMD-17). Patients with scores ≥7 were classified into the early-onset PSD group. Spearman rank correlation analysis was used to examine the relationship between NHHR and HAMD scores. Logistic regression analysis was conducted to evaluate the association between NHHR and early-onset PSD. Sensitivity analyses were performed to assess the robustness of the results. The predictive performance of NHHR for early-onset PSD was evaluated using receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC) analysis.
Results: Among 846 prospectively enrolled patients, 283 (33.45%) were diagnosed with early-onset PSD. NHHR was positively correlated with HAMD-17 scores (r = 0.498, p < 0.001). Binary logistic regression indicated that NHHR (odds ratio [OR], 1.796; 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.452–1.996, p < 0.001) was an independent risk factor for early-onset PSD. The area under the curve (AUC) for NHHR in predicting early-onset PSD was 0.798.
Conclusion: The findings suggest that NHHR may serve as an independent risk factor for early-onset PSD, providing valuable insights for preventive strategies and prognostic management in these patients.
Introduction
Stroke continues to be the second greatest cause of mortality globally and the main cause of long-term impairment in people (1). Many stroke survivors continue to experience long-term disability although the fatality rate from ischemic stroke has been considerably decreased by the use of intravenous thrombolysis and endovascular therapy (2). With around 35% of stroke patients developing depression at some point in their lifetime, depression is the most common neuropsychiatric side effect connected with stroke (3, 4). Post-stroke depression (PSD) has been shown to have a negative impact on survivors’ quality of life and long-term rehabilitation. Patients with PSD also have higher death rates and are more likely to experience cognitive and functional deficits (5–7). Early-onset PSD denotes patients displaying depressive symptoms within 2 weeks following the onset of an acute stroke (8–10). Early-onset PSD exhibits a greater prevalence of depressive symptoms and is significantly associated with a heightened risk of adverse outcomes in comparison to late-onset PSD (11). Consequently, identifying new biomarkers for assessing the risk of early-onset PSD is essential for improving prevention and treatment strategies.
Lipid-related ratios are not only markers of vascular risk (12–14) but also predictors of adverse cognitive and functional recovery. A recent study showed that the potential for the early predictive value of medical conditions with chronic lipid dyshomeostasis for the risk of depression and cognitive decline (15). A growing body of research links disruptions in lipid metabolism to the development of PSD. According to a prospective study, there is a correlation between elevated PSD risk and lower levels of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) and higher ratios of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) to HDL-C levels (16). Another study identified apolipoprotein A1, HDL-C, intestinal fatty acid binding protein, and lipoprotein (a) as potential biomarkers for PSD (6). Additionally, the ratio of monocytes to HDL-C is known to be a new composite inflammatory measure; higher levels are linked to an increased risk of developing PSD (17). The non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio (NHHR) serves as a novel composite indicator for assessing atherogenic lipids (18). The NHHR offers a more effective evaluation of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease risk compared to other lipid parameters (19). According to earlier studies, among American adults, NHHR is a separate risk factor for depression and suicidal thoughts (20–22). Infertility and depression among American women were partially mediated by NHHR, which was also strongly correlated with the severity of depression (23). Body mass index (BMI) and depression risk are correlated, and the relationship between BMI and depression is significantly mediated by NHHR (24). Moreover, a recent cross-sectional investigation revealed a substantial correlation between NHHR and an elevated risk of PSD in adult Americans (25). Further large-scale prospective studies are needed to confirm the causal relationship between NHHR and PSD. Moreover, the association between the NHHR and early-onset PSD remains inadequately studied and lacks substantial evidence.
Early-onset PSD is marked by a higher prevalence of depressive symptoms and is significantly linked to an increased likelihood of adverse outcomes (26). The relationship between NHHR and early-onset PSD is not yet well-defined due to a lack of conclusive evidence. This prospective study investigates the association between NHHR and early-onset PSD.
Materials and methods
Study design and participants
This study was approved by Changsha Central Hospital’s Ethics Committee. From August 2023 to April 2025, Changsha Central Hospital prospectively included patients with acute ischemic stroke (AIS). The following patients met the inclusion criteria: (1) those who were between the ages of 18 and 85; (2) those who met the diagnostic criteria for ischemic stroke as stated in the Chinese guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of acute ischemic stroke 2018 (27); and (3) those who were admitted to the hospital within 72 h of the stroke onset. Exclusion criteria: (1) patients with dysarthria or aphasia and a consciousness disorder that made it difficult for them to complete tests and questionnaires; (2) patients with dementia or significant cognitive impairment before the stroke; (3) patients with severe heart, liver, or renal insufficiency; (4) patients with a mental illness, such as depression, or who were using psychotropic drugs before the stroke; (5) patients with a history of other diseases in the central nervous system, like Parkinson’s disease or epilepsy; (6) patients with malignant tumors; and (7) patients with lost follow-up and incomplete clinical data. Between August 2023 and April 2025, we enrolled 846 AIS patients (Figure 1).
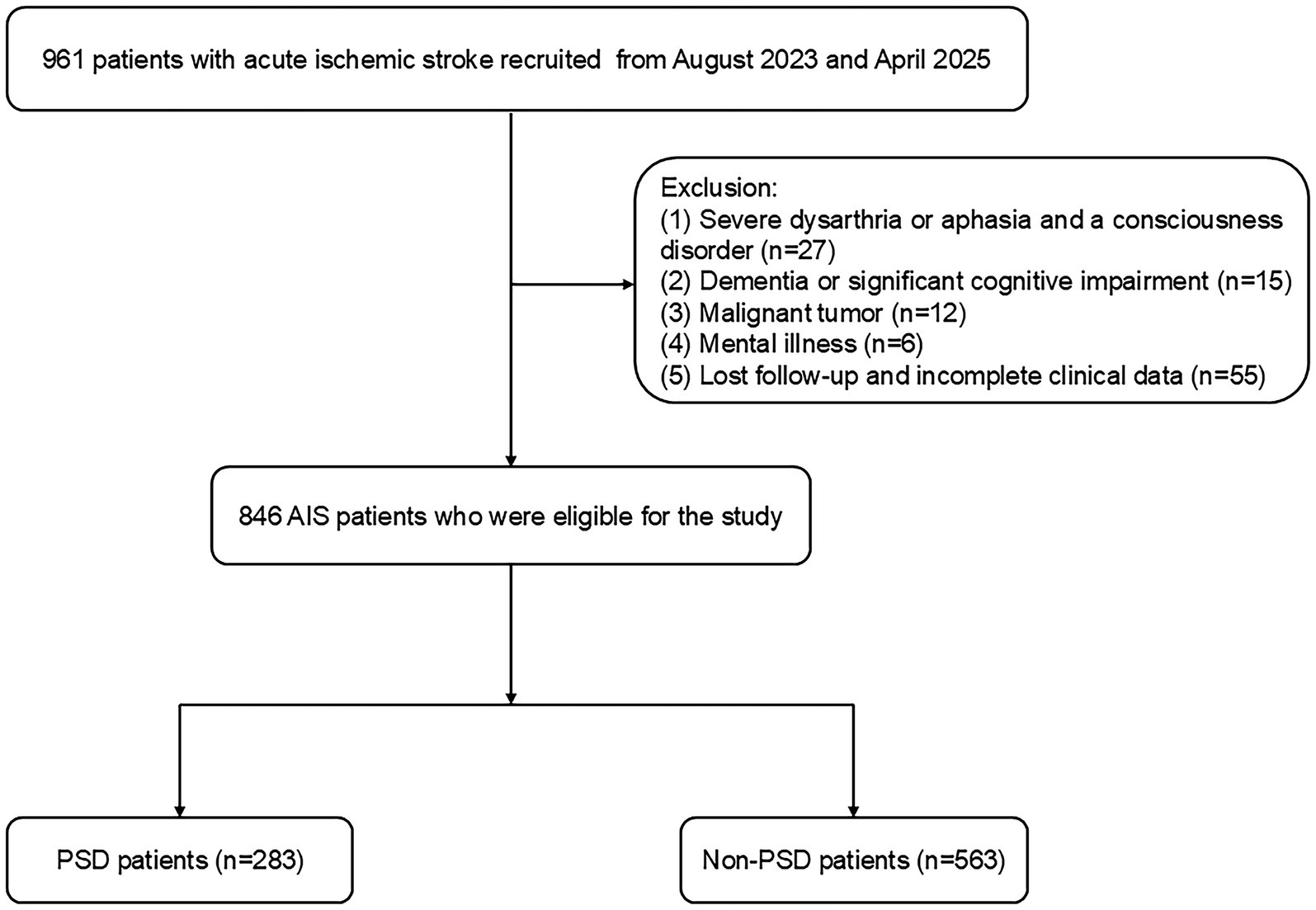
Figure 1. Flowchart of the study participant selection process. PSD, post-stroke depression; AIS, acute ischemic stroke.
Data collection
Upon admission, all participants underwent standardized assessment of demographic characteristics (age, sex), body mass index (BMI), and vascular risk factors—including hypertension, coronary artery disease, atrial fibrillation, diabetes mellitus, as well as current smoking and drinking status—along with routine laboratory testing. Current smoking was defined as consumption of at least 10 cigarettes per day for the preceding 5 years. Current drinking was defined as consistent alcohol consumption over 5 years with an intake of at least 20 grams of ethanol per day. Stroke severity was evaluated by experienced neurologists using the National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS), with scores recorded within 24 h of admission. Functional status was assessed at discharge using the Barthel Index (BI), and again at one-month follow-up using the modified Rankin Scale (mRS). Imaging and diagnostic studies—including computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, echocardiography, electrocardiography, carotid ultrasonography, and transcranial Doppler—were performed to determine lesion location and classify stroke subtype.
Blood samples were collected from all patients within 72 h after stroke onset. Following an overnight fast of at least 8 h, venous blood was drawn between 6:00 and 7:00 a.m. the next morning. Complete blood count, including white blood cell (WBC) count, was performed using an automated hematology analyzer (BZ6800, China). Standard biochemical parameters-including creatinine (Cr), uric acid (UA), triglycerides (TG), total cholesterol (TC), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C)-were measured using an automated biochemical analyzer (HITACHI 7600, Japan). Each blood sample was analyzed in triplicate.
Definition of early-onset PSD and NHHR measurement
Two weeks after AIS, patients were assessed for early-onset PSD by certified neurologists and psychiatrists according to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th Edition (DSM-5). The severity of depressive symptoms was evaluated using the Hamilton Depression Scale 17 items (HAMD-17). Participants with HAMD-17 scores < 7 were classified into the non-PSD group, while those with scores ≥ 7 were assigned to the early-onset PSD group. Mild depression is defined by a score of 7–17, moderate depression by 18–23, and severe depression by greater than 24 (28). The non-HDL-C level was calculated by subtracting the HDL-C level from the TC level. The NHHR was then computed using the formula: NHHR = non-HDL-C/HDL-C (20).
Statistical analysis
The normality of all variables was assessed using the Kolmogorov–Smirnov test. Continuous variables with normal distribution were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD), while non-normally distributed variables were presented as median (interquartile range). Categorical variables were expressed as percentages. Group comparisons were made using the chi-square test or Fisher’s exact test for categorical data, and the Student’s t-test or Mann–Whitney U test for continuous variables, as appropriate. The distribution of variables across different severity levels of early-onset PSD was visualized using box plots. Spearman rank correlation analysis was conducted to evaluate the relationships between variables and HAMD-17 scores across all patients. To assess for multicollinearity, we calculated the Variance Inflation Factor (VIF) for all independent variables. VIF values were all less than 5 (or 10), indicating no severe multicollinearity. If the VIF is indeed high, we will build two models for comparison: one containing NHHR but not its components (TC, HDL-C), and another containing TC and HDL-C but not NHHR. Binary logistic regression was performed to identify risk factors associated with early-onset PSD. Furthermore, sensitivity analyses were performed to test the robustness of our findings. The discriminative ability of NHHR in predicting early-onset PSD was evaluated using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis. A two-tailed p-value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Statistical analyses were performed using SPSS software (version 25.0; IBM Corp.).
Results
Comparison of clinical and demographic characteristics between non-PSD and early-onset PSD patients
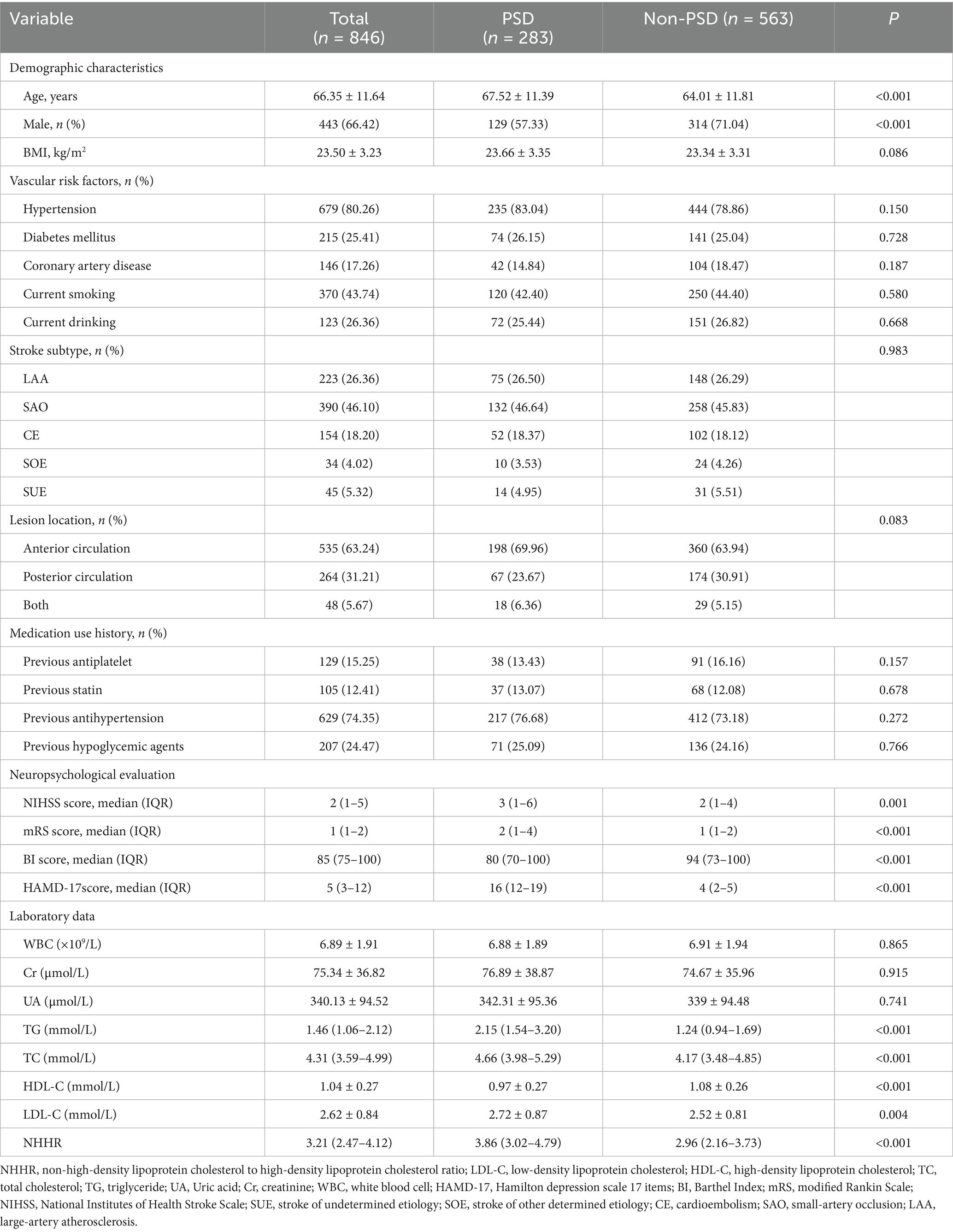
Table 1 presents a comprehensive overview of the clinical and demographic characteristics. This study observed 283 patients (33.45%) in the early-onset PSD group and 563 patients (66.55%) in the non-PSD group. The early-onset PSD group showed significantly lower in the percent of male patients (p < 0.001), BI scores (p < 0.001), and HDL-C (p < 0.001) than the non-PSD group, but significantly higher ages (p < 0.001), NIHSS scores (p = 0.001), mRS scores (p < 0.001), HAMD-17 scores (p < 0.001), TG (p < 0.001), TC (p < 0.001), LDL-C (p = 0.004), and NHHR (p < 0.001) than the non-PSD group. Additionally, Figure 2 illustrates the comparison of NHHR, age, TG, TC, HDL-C, and LDL-C among early-onset PSD categorized by varying severity levels.
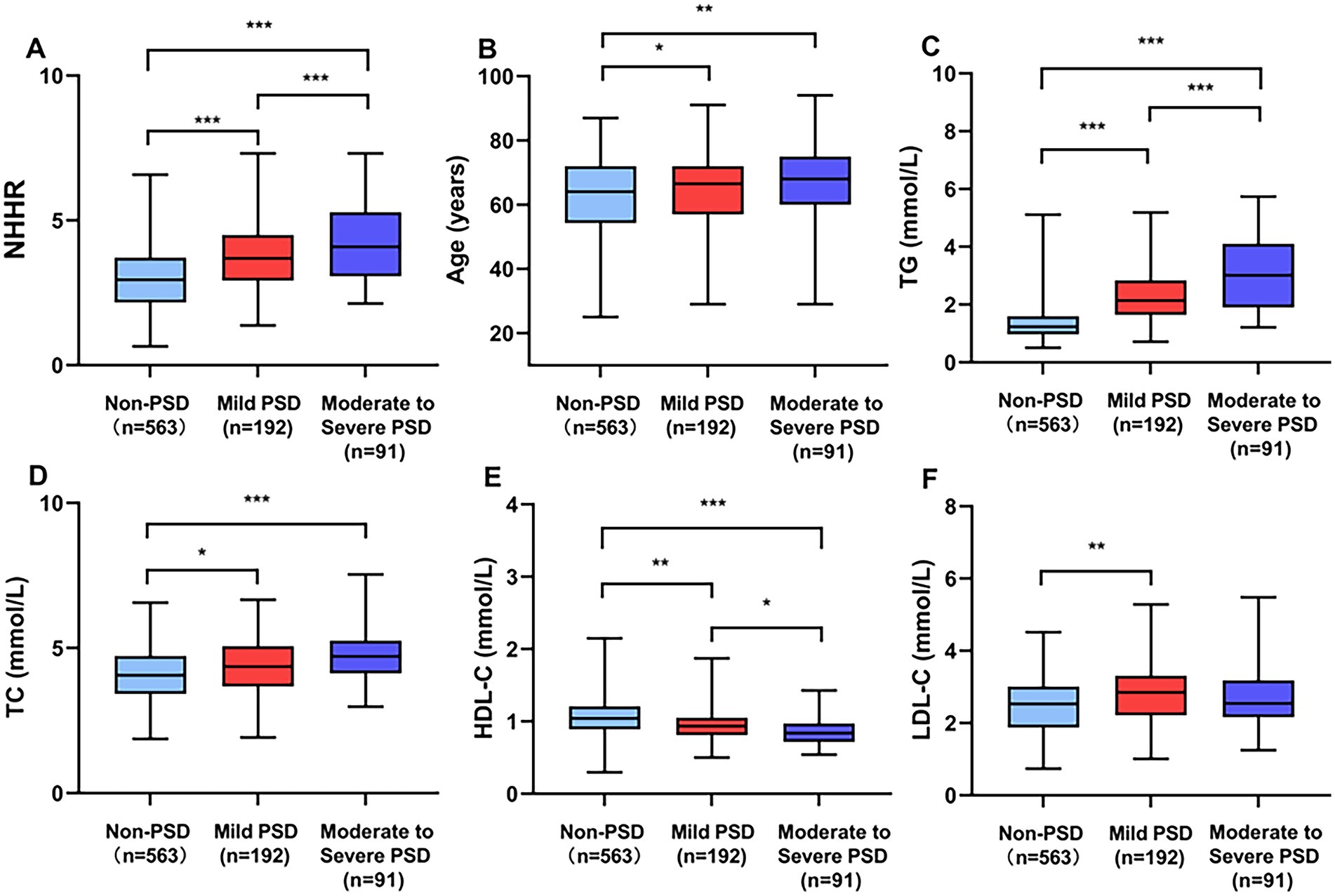
Figure 2. Comparing clinical biomarkers stratified by early-onset PSD severity. Box plots show the distribution of (A) NHHR, (B) age, (C) TG, (D) TC, (E) HDL-C, and (F) LDL-C. ***p < 0.001, **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05.
Associations between clinical variables and HAMD-17 scores
A positive correlation was observed between HAMD-17 scores and NHHR (r = 0.498, p < 0.001), age (r = 0.112, p = 0.001), TG (r = 0.440, p < 0.001), TC (r = 0.199, p < 0.001), and LDL-C (r = 0.116, p < 0.001). Conversely, HAMD-17 scores showed a significant negative correlation with HDL-C (r = −0.225, p < 0.001) (Figure 3).
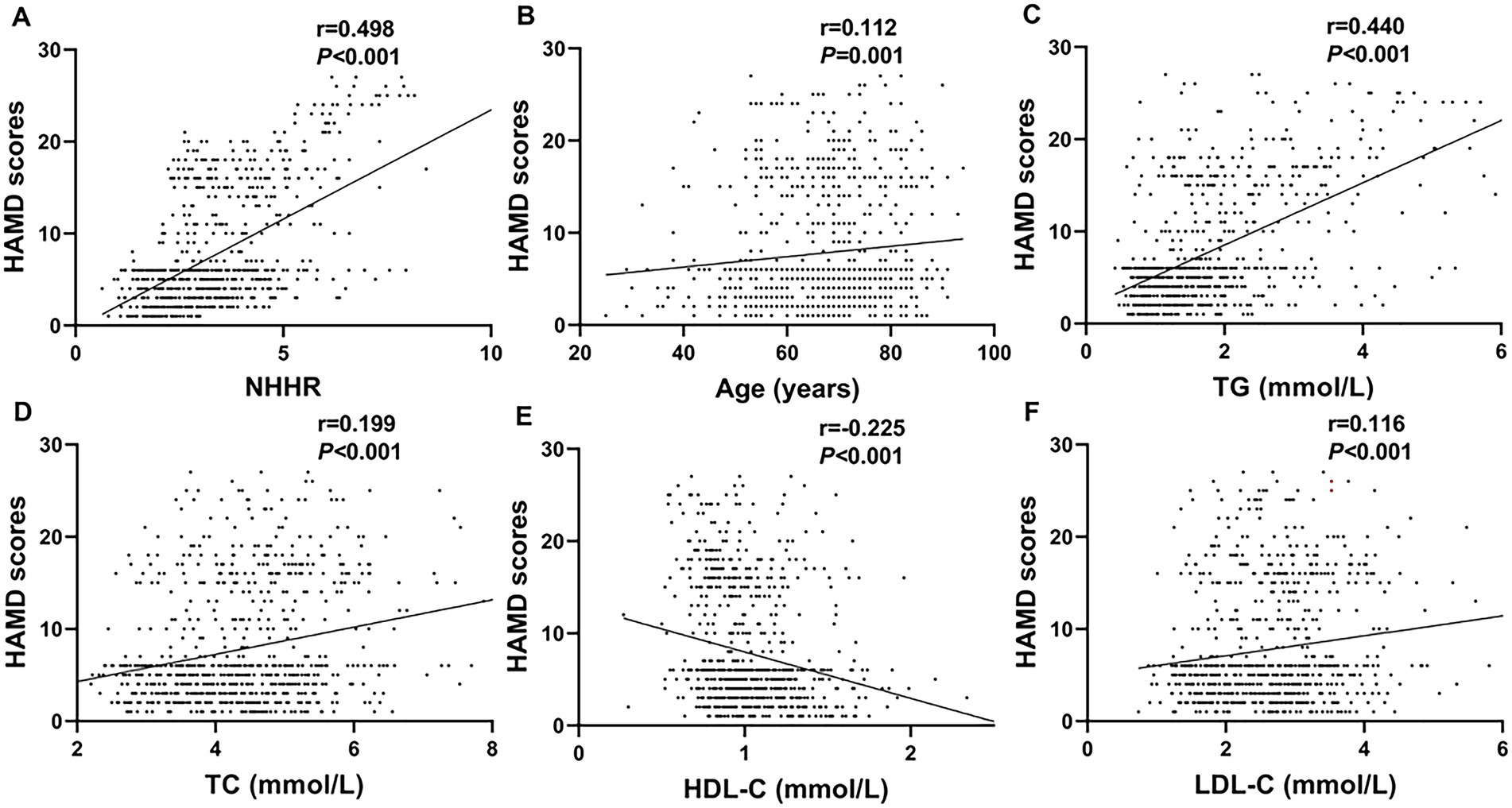
Figure 3. Scatter plots demonstrating correlations between clinical parameters and HAMD scores. Parameters positively correlated include NHHR (A; r = 0.498, p < 0.001), age (B; r = 0.112, p = 0.001), TG (C; r = 0.440, p < 0.001), TC (D; r = 0.199, p < 0.001), and LDL-C (F; r = 0.116, p < 0.001). The HDL-C (E; r = −0.225, p < 0.001) was negatively correlated.
Multivariate logistic regression analysis of determinants associated with early-onset PSD
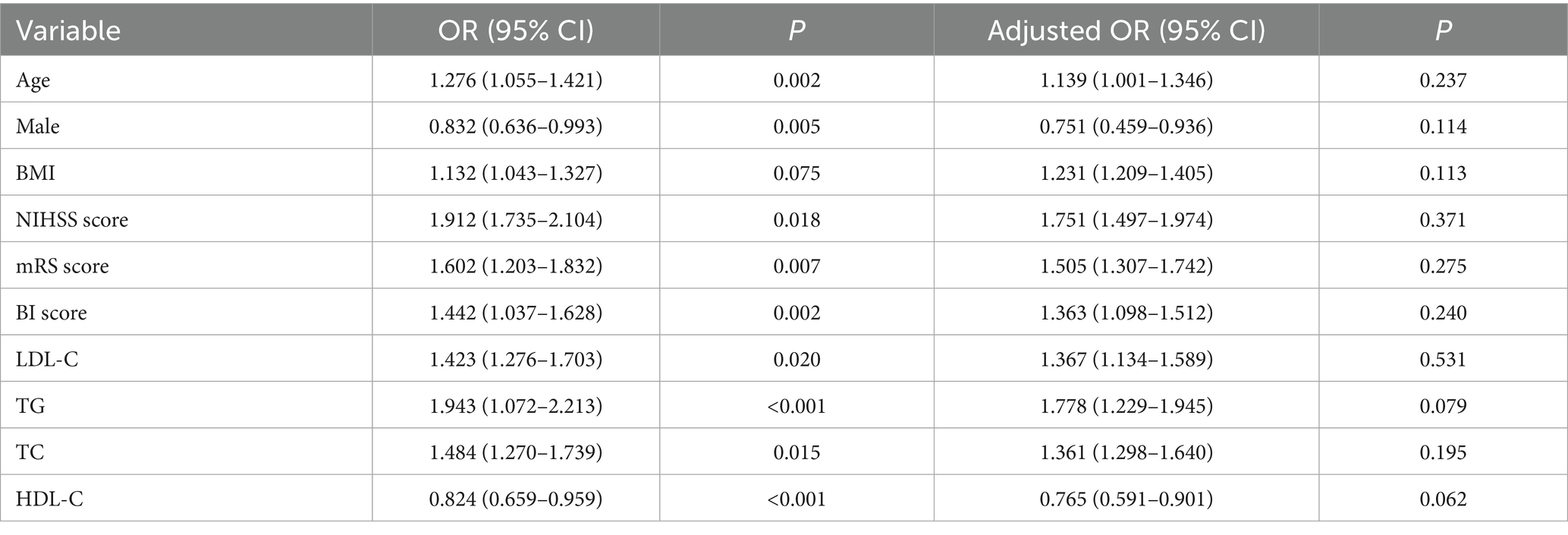
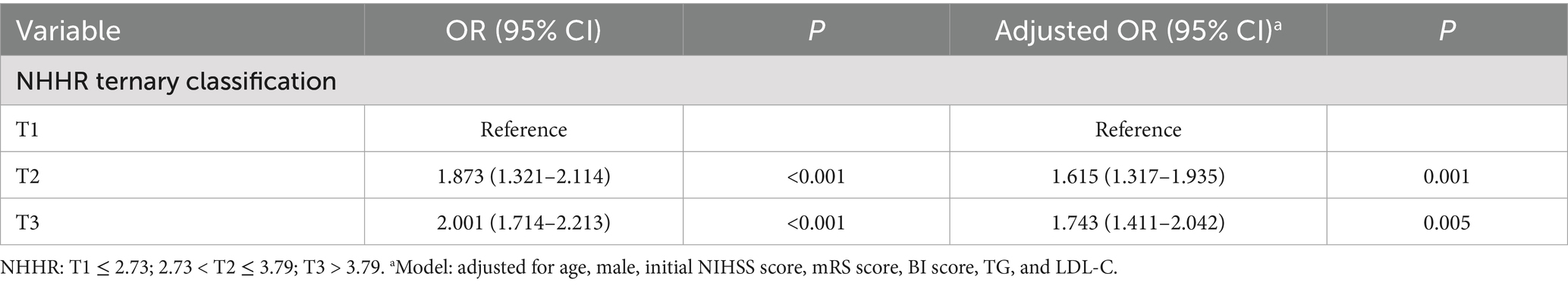
A binary logistic regression model was employed to identify independent risk factors for early-onset PSD, using all variables that demonstrated statistical significance in Table 1. In addition, BMI was considered as a co-variate and has previously been associated with depression and should be included in multivariate analysis. To assess for multicollinearity, we calculated the VIF for all independent variables. However, there were collinearity between TC (VIF = 32), HDL-C (VIF = 25) and NHHR. We build two logistic regression analysis models for comparison: Table 2 containing NHHR but not its components (TC, HDL-C), and Table 3 containing TC and HDL-C but not NHHR. Multivariable logistic regression analysis revealed that a higher NHHR (OR, 1.796; 95% CI 1.452–1.996, p < 0.001) was significantly associated with an increased risk of early-onset PSD (Table 2). In this study, TC and HDL-C were the constituent variables of NHHR, but were not independent risk factors or protective factors for early-onset PSD (Table 3). In addition, after stratifying NHHR into tertiles and adjusting for confounders, patients exhibiting elevated NHHR levels (3rd quartile vs. 1st quartile; OR, 1.743; 95% CI, 1.411–2.042, p = 0.005) demonstrated a heightened risk of early-onset PSD (Table 4).
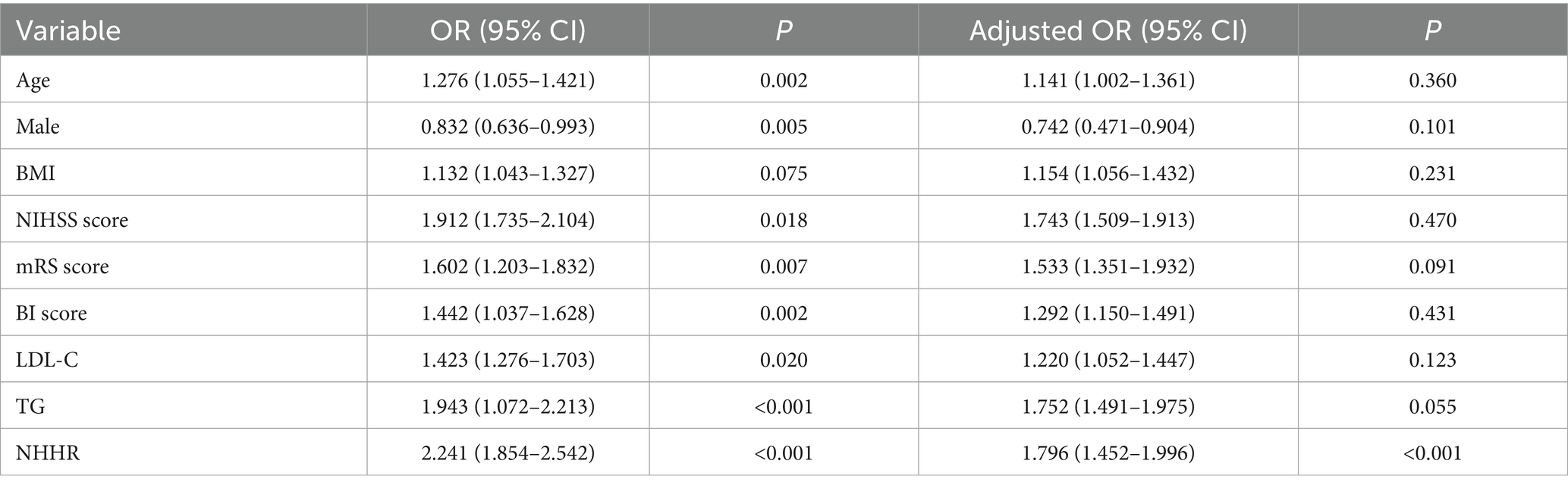
Table 2. Logistic regression analysis for early-onset PSD, containing NHHR but not its components (TC, HDL-C).
Subgroup analyses and interaction test
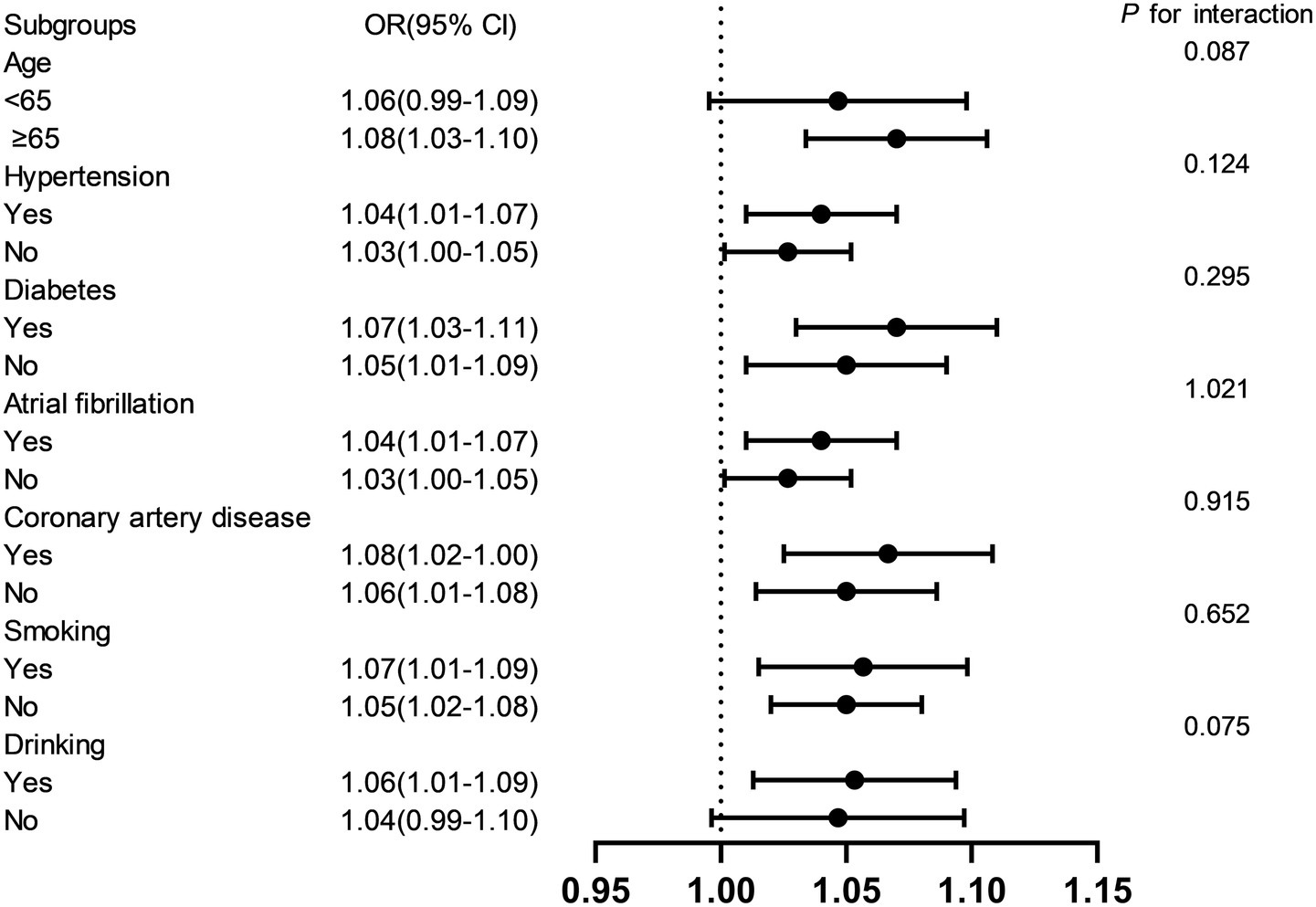
Stratified analyses were performed to evaluate the consistency of the association between NHHR and early-onset PSD across key demographic and clinical subgroups (Figure 4). Results demonstrated that the positive association remained robust across subgroups stratified by age (<65, ≥65 years), diabetes mellitus, hypertension, coronary artery disease, atrial fibrillation, alcohol consumption, and smoking status. Interaction tests revealed no statistically significant effect modification by any of these covariates (p > 0.05), indicating that the relationship between NHHR and early-onset PSD was not significantly influenced by these factors.
The discriminative ability of NHHR for early-onset PSD was evaluated using ROC curve analysis
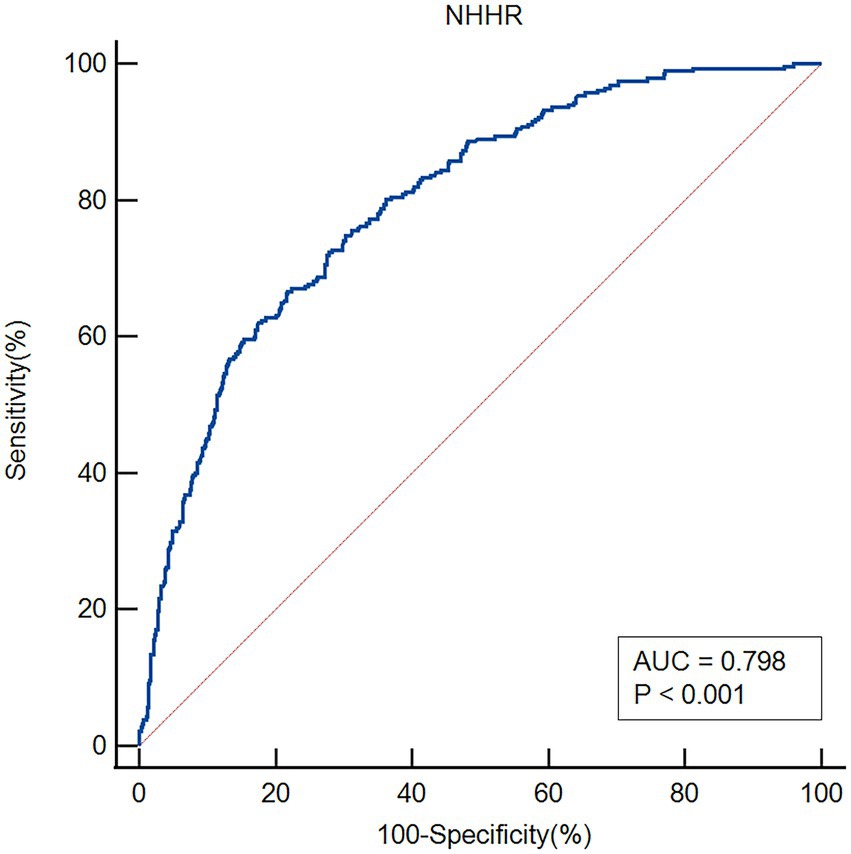
The ROC analysis was used to evaluate the ability of NHHR to discriminate patients with early-onset PSD (Figure 5). The area under the curve (AUC) for NHHR was 0.798 (95% CI: 0.769–0.824; p < 0.001). At the optimal cut-off value of 3.56, sensitivity was 66.67% and specificity was 78.15%.
Discussion
Researchers have extensively studied the associations between serum lipids and stroke, along with post-stroke depression complications. PSD is the most common psychiatric comorbidity after stroke; given the significant impact of PSD on individuals and society, identifying and managing modifiable risk factors is crucial (29). This study examines the correlation between NHHR and early-onset PSD. This study produced several new findings. Patients in the early-onset PSD group initially demonstrated significantly higher NHHR, NIHSS, and mRS scores, along with lower BI scores, compared to those in the non-PSD group. HAMD-17 scores were positively correlated with NHHR levels. Logistic regression identified NHHR as an independent risk factor for early-onset PSD. Furthermore, subgroup analyses revealed no significant interactions (all p > 0.05), supporting the consistency of the association between NHHR and early-onset PSD across different patient subgroups and underscoring the robustness and broad applicability of our findings. Finally, ROC analysis indicated that NHHR has clinically meaningful discriminatory power for early-onset PSD. The results demonstrate a correlation between elevated NHHR and early-onset PSD.
There is evidence linking the risk of PSD to the dysregulation of lipid profiles. Higher LDL-C/HDL-C ratios and lower HDL-C levels are associated with a higher risk of PSD (16). Elevated MHR was strongly linked to an increased risk of PSD, according to another cross-sectional investigation (17), which indirectly confirmed that lower levels of HDL-C were associated with increased risk of PSD. However, a retrospective study with 8,207 participants indicated a significant association between higher levels of HDL-C and an increased risk of depressive symptoms (30). Finding new biomarkers to evaluate the risk of early-onset PSD is crucial to improving preventative and treatment approaches because lipids have not been thoroughly taken into account in previous research. The NHHR is a developing comprehensive metric of atherosclerotic lipids (31). This ratio provides a more comprehensive assessment of atherosclerotic potential than traditional lipid parameters (32). Prior research has demonstrated that when assessing the risk of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (33) and chronic kidney disease (34), the NHHR performs better in terms of predictive and diagnostic capabilities than conventional blood lipid levels. Numerous recent studies have highlighted NHHR’s predictive worth and its strong prognostic value in people with cardiovascular disease (1, 35–37). A prior study indicated that NHHR is associated with an increased prevalence of stroke and may become a new predictor of stroke (38). Moreover, there have been several previous studies that have shown the relationship between NHHR and depression. Elevated NHHR levels were significantly correlated with an increased likelihood of suicidal ideation (22). In American adults, NHHR was substantially linked to an increased risk of depression (20). Recently, a cross-sectional study indicated that NHHR was significantly correlated with an increased risk of PSD among U. S. adults (25). Further large-scale prospective studies are needed to confirm the causal relationship between NHHR and PSD. To date, few studies have specifically analyzed the role of NHHR in predicting the risk of early-onset PSD. In our study, 283 patients (33.45%) experienced early-onset PSD, and the proportion was consistent with the results of previous studies (10, 39). The NHHR had a positive relationship with the severity of early-onset PSD. There were collinearity between TC, HDL-C and NHHR. We build two logistic regression analysis models for comparison: one containing NHHR but not its components (TC, HDL-C), and another containing TC and HDL-C but not NHHR. In this study, TC and HDL-C were the constituent variables of NHHR, but were not independent risk factors or protective factors for early-onset PSD. After adjusting for potential confounders, binary logistic regression confirmed that NHHR served as an independent predictor of early-onset PSD. When analyzed as a tertile-based categorical variable, elevated NHHR levels remained significantly associated with increased risk of early-onset PSD. Moreover, NHHR demonstrated good discriminative ability for early-onset PSD, with an AUC of 0.798. This study provides new insights into the role of NHHR in PSD risk and supports its potential as a novel indicator for early-onset PSD risk assessment.
The underlying mechanism by which NHHR increases the risk of early-onset PSD remains incompletely understood. However, several potential pathophysiological pathways may help explain this association. Firstly, inflammatory reactions may be triggered or made worse by lipid abnormalities, specifically low levels of HDL-C and high levels of LDL-C. Numerous pro-inflammatory cytokines can be released by inflammatory reactions following an acute stroke, according to studies, which may raise the likelihood of depressive symptoms (40). Furthermore, oxidative stress is thought to be a major contributor to PSD pathogenesis. Lipid and protein peroxidation brought on by oxidative stress can impact neurotransmitter synthesis and metabolism, resulting in pathogenic alterations in the nervous system (41, 42). Low HDL-C levels may impair antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, leaving the brain more vulnerable to these damaging processes (43, 44). Therefore, through pathways including oxidative stress and inflammation, alterations in the lipid profile may raise the risk of PSD. In addition, studies on lipid-related regulation of neurovascular integrity, microglial activation, and neuroendocrine dysregulation have been reported. The vessel-adjacent microglia were specifically activated by the leakage of plasma low-density lipoprotein (LDL), which led to blood–brain barrier (BBB) breakdown and ischemic demyelination (45). A recent study showed that palmitoylation of microglial protein kinase Cδ (PKCδ) in the hypothalamus plays a role in modulating peripheral lipid metabolism through hypothalamus-liver communication (46). Of particular interest, recent work has shown that specific lipid–glucose interactions, modulated by genetic background, can shape vascular injury distribution and systemic metabolic profiles (47). These data support the concept that composite lipid markers like NHHR may act as integrators of metabolic and vascular risk pathways. Our research in order to strengthen and optimize the understanding of NHHR and early-onset PSD between risk provides a new perspective and strong evidence. In addition to conventional lipid-lowering therapies, novel agents such as PCSK9 inhibitors and inclisiran have been shown to exert anti-inflammatory and endothelial-protective effects (48), which could potentially mitigate PSD risk in dyslipidemic stroke survivors. Similarly, lifestyle interventions and dietary patterns that improve NHHR can also reduce the risk of early-onset PSD.
Furthermore, patients in the early-onset PSD group exhibited higher NIHSS and mRS scores, along with lower BI scores, indicating more severe stroke-related impairment and functional disability. Unfavorable physical conditions may worsen psychological problems, including depression (49). According to this study, early-onset PSD was more common in female stroke patients than in male ones. Some potential solutions include social factors, such as exposure to gender-specific stressors; psychological factors, such as gender-specific symptom profiles; and physiological factors, such as genetic variances and sex hormones (50). Multiple studies have identified a strong association between atherogenic factors and depression. A previous study has shown that the level of TG was one of the most important features in predicting depression (51). However, another study reported conflicting results, TG was negatively correlated with depressive symptom severity (52). At present, the relationship between TC and depression is not clear. Low levels of TC were not associated with an increased risk of depression (53), while other studies reported an inverse relationship between depression and levels of TC (52, 54–56). In addition, a recent study showed that high HDL-C levels were negatively associated with depression (57). In our study, TG, TC or HDL-C were not independent risk factors or protective factors for early-onset PSD. We propose that discrepancies across studies may be attributed to differences in the ethnic composition of study populations, limited sample sizes, variations in medication use, and heterogeneity in disease severity.
The following are the limitations of this study: (1) Several risk factors that could influence depressive episodes, such as mounting life stress, educational background, and social support, were not included in our study; (2) patients who experienced severe aphasia, coma, or dementia while in the hospital were excluded; (3) this study was a single-center study and only included Chinese patients, suggesting the presence of potential inherent biases. Consequently, future research should multicenter validation across different geographic and ethnic groups would reinforce external validity; (4) TC and HDL-C are the component variables of NHHR and may themselves be independent risk factors or protective factors; so, the study findings still need to be further confirmed by multi-center and large-sample clinical studies; (5) future research needs to integrating circulating biomarkers such as high-sensitivity C-reactive protein, IL-6, or neurotrophic factors (e.g., brain-derived neurotrophic factor) could refine risk stratification and help elucidate causal pathways; and (6) conclusions from short-term observational studies may not be comprehensive enough.
Conclusion
According to our research, NHHR can be utilized as a predictive indicator and may be an independent risk factor for early-onset PSD. There are important therapeutic ramifications for early-onset PSD screening, treatment plan formulation, etiology research, and prognosis evaluation if an association between NHHR and early-onset PSD is discovered. Incorporating NHHR into assessment and treatment strategies is expected to improve overall clinical outcomes for patients. However, to precisely understand the role of NHHR in the pathophysiology of early-onset PSD, more research is necessary.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
This study was approved by Changsha Central Hospital’s Ethics Committee. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
MD: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. KS: Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. LG: Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Writing – review & editing, Project administration, Validation. ZW: Data curation, Formal analysis, Project administration, Writing – review & editing, Resources, Supervision. WZ: Data curation, Writing – review & editing, Investigation. WX: Data curation, Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization, Validation, Visualization. TF: Data curation, Validation, Project administration, Writing – review & editing. FL: Data curation, Validation, Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Software, Supervision, Visualization, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was funded by the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province (Grant no. 2023JJ40072) and the Science and Technology Planning Project of Hunan Health Committee (Grant no. D202303076376).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Zhang, S, and Zhu, Z. The association between non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio (NHHR) and the risk of ischemic heart disease in type 2 diabetes mellitus participants: a large-scale cohort study from the UK biobank. Diabetol Metab Syndr. (2025) 17:99. doi: 10.1186/s13098-025-01646-3
2. Tsao, CW, Aday, AW, Almarzooq, ZI, Alonso, A, Beaton, AZ, Bittencourt, MS, et al. Heart disease and stroke Statistics-2022 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. (2022) 145:e153–639. doi: 10.1161/cir.0000000000001052
3. Towfighi, A, Ovbiagele, B, El Husseini, N, Hackett, ML, Jorge, RE, Kissela, BM, et al. Poststroke depression: a scientific statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. (2017) 48:e30–43. doi: 10.1161/str.0000000000000113
4. Castilla-Guerra, L, Fernandez Moreno, MDC, Esparrago-Llorca, G, and Colmenero-Camacho, MA. Pharmacological management of post-stroke depression. Expert Rev Neurother. (2020) 20:157–66. doi: 10.1080/14737175.2020.1707666
5. Blöchl, M, Meissner, S, and Nestler, S. Does depression after stroke negatively influence physical disability? A systematic review and meta-analysis of longitudinal studies. J Affect Disord. (2019) 247:45–56. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2018.12.082
6. Zhong, J, Chen, J, Cao, M, Fang, L, Wang, Z, Liao, J, et al. Elevated plasma intestinal fatty acid binding protein and aberrant lipid metabolism predict post-stroke depression. Heliyon. (2022) 8:e11848. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e11848
7. Cai, W, Mueller, C, Li, YJ, Shen, WD, and Stewart, R. Post stroke depression and risk of stroke recurrence and mortality: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ageing Res Rev. (2019) 50:102–9. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2019.01.013
8. Huang, J, Zhou, FC, Guan, B, Zhang, N, Wang, A, Yu, P, et al. Predictors of remission of early-onset poststroke depression and the interaction between depression and cognition during follow-up. Front Psych. (2018) 9:738. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2018.00738
9. Lin, W, Xiong, L, Yang, Z, Deng, X, Zhu, J, Chen, C, et al. Severe periodontitis is associated with early-onset poststroke depression status. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. (2019) 28:104413. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2019.104413
10. Deng, M, Zhou, N, Song, K, Wang, Z, Zhao, W, Guo, J, et al. Higher homocysteine and fibrinogen are associated with early-onset post-stroke depression in patients with acute ischemic stroke. Front Psych. (2024) 15:1371578. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1371578
11. Zeng, YY, Wu, MX, Geng, DD, Cheng, L, Zhou, SN, Fan, KL, et al. Early-onset depression in stroke patients: effects on unfavorable outcome 5 years post-stroke. Front Psych. (2021) 12:556981. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2021.556981
12. Deng, M, Song, K, Xu, W, He, G, Hu, J, Xiao, H, et al. Association of higher triglyceride-glucose index and triglyceride-to-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio with early neurological deterioration after thrombolysis in acute ischemic stroke patients. Front Neurol. (2024) 15:1421655. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1421655
13. Zhu, Y, Chen, M, Liu, K, Gao, A, Kong, X, Liu, Y, et al. Atherogenic index of plasma and the risk of in-stent restenosis in patients with acute coronary syndrome beyond the traditional risk factors. J Atheroscler Thromb. (2022) 29:1226–35. doi: 10.5551/jat.63136
14. Min, Q, Wu, Z, Yao, J, Wang, S, Duan, L, Liu, S, et al. Association between atherogenic index of plasma control level and incident cardiovascular disease in middle-aged and elderly Chinese individuals with abnormal glucose metabolism. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2024) 23:54. doi: 10.1186/s12933-024-02144-y
15. Mehdi, SMA, Costa, AP, Svob, C, Pan, L, Dartora, WJ, Talati, A, et al. Depression and cognition are associated with lipid dysregulation in both a multigenerational study of depression and the National Health and nutrition examination survey. Transl Psychiatry. (2024) 14:142. doi: 10.1038/s41398-024-02847-6
16. Shen, H, Tu, X, Luan, X, Zeng, Y, He, J, and Tang, W. Serum lipid profiles and post-stroke depression in acute ischemic stroke patients. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. (2019) 15:1573–83. doi: 10.2147/ndt.S204791
17. Li, Y, Zhang, M, Xue, M, Liu, D, and Sun, J. Elevated monocyte-to-HDL cholesterol ratio predicts post-stroke depression. Front Psych. (2022) 13:902022. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2022.902022
18. Sheng, G, Liu, D, Kuang, M, Zhong, Y, Zhang, S, and Zou, Y. Utility of non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio in evaluating incident diabetes risk. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. (2022) 15:1677–86. doi: 10.2147/dmso.S355980
19. Zhu, L, Lu, Z, Zhu, L, Ouyang, X, Yang, Y, He, W, et al. Lipoprotein ratios are better than conventional lipid parameters in predicting coronary heart disease in Chinese Han people. Kardiol Pol. (2015) 73:931–8. doi: 10.5603/KP.a2015.0086
20. Qi, X, Wang, S, Huang, Q, Chen, X, Qiu, L, Ouyang, K, et al. The association between non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio (NHHR) and risk of depression among US adults: a cross-sectional NHANES study. J Affect Disord. (2024) 344:451–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2023.10.064
21. Yan, C, Wang, H, Liu, C, Fu, J, and Zhou, Y. Association between non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio (NHHR) with depressive symptoms: recent findings from NHANES 2005-2018. Front Psych. (2024) 15:1467142. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1467142
22. Qing, G, Deng, W, Zhou, Y, Zheng, L, Wang, Y, and Wei, B. The association between non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio (NHHR) and suicidal ideation in adults: a population-based study in the United States. Lipids Health Dis. (2024) 23:17. doi: 10.1186/s12944-024-02012-4
23. Yang, Q, Tao, J, Xin, X, Zhang, J, and Fan, Z. Association between depression and infertility risk among American women aged 18-45 years: the mediating effect of the NHHR. Lipids Health Dis. (2024) 23:178. doi: 10.1186/s12944-024-02164-3
24. Zhang, L, Lai, Y, Yan, L, Fang, J, and Wang, K. The joint and interactive effects of the non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio (NHHR) and body mass index on the risk of depression, as well as the mediating role of NHHR: results from NHANES 2005-2023. Lipids Health Dis. (2025) 24:77. doi: 10.1186/s12944-025-02493-x
25. Xiong, B, Li, Z, Zhang, S, Wang, Z, Xie, Y, Zhang, M, et al. Association between non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio (NHHR) and the risk of post-stroke depression: a cross-sectional study. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. (2024) 33:107991. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2024.107991
26. Zeng, YY, Wu, MX, Zhou, SN, Geng, DD, Cheng, L, Fan, KL, et al. Corrigendum: early-onset depression in stroke patients: effects on Unfavorable outcome 5 years post-stroke. Front Psych. (2021) 12:732437. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2021.732437
27. Neurology C and society C Chinese guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of acute ischemic stroke 2018. Chin J Neurol. (2018) 51:666–82. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1006-7876.2018.09.004
28. Zhang, Y, He, JR, Liang, HB, Lu, WJ, Yang, GY, Liu, JR, et al. Diabetes mellitus is associated with late-onset post-stroke depression. J Affect Disord. (2017) 221:222–6. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2017.06.045
29. Jørgensen, TS, Wium-Andersen, IK, Wium-Andersen, MK, Jørgensen, MB, Prescott, E, Maartensson, S, et al. Incidence of depression after stroke, and associated risk factors and mortality outcomes, in a large cohort of Danish patients. JAMA Psychiatr. (2016) 73:1032–40. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2016.1932
30. Shin, HY, Kang, G, Kang, HJ, Kim, SW, Shin, IS, Yoon, JS, et al. Relationships between high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and depressive symptoms: findings of the Korean National Health and nutrition examination survey (KNHANES). Psychiatry Res. (2016) 241:172–4. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2016.05.003
31. Lin, W, Luo, S, Li, W, Liu, J, Zhou, T, Yang, F, et al. Association between the non-HDL-cholesterol to HDL- cholesterol ratio and abdominal aortic aneurysm from a Chinese screening program. Lipids Health Dis. (2023) 22:187. doi: 10.1186/s12944-023-01939-4
32. Zhao, W, Gong, W, Wu, N, Li, Y, Ye, K, Lu, B, et al. Association of lipid profiles and the ratios with arterial stiffness in middle-aged and elderly Chinese. Lipids Health Dis. (2014) 13:37. doi: 10.1186/1476-511x-13-37
33. Wang, K, Shan, S, Zheng, H, Zhao, X, Chen, C, and Liu, C. Non-HDL-cholesterol to HDL-cholesterol ratio is a better predictor of new-onset non-alcoholic fatty liver disease than non-HDL-cholesterol: a cohort study. Lipids Health Dis. (2018) 17:196. doi: 10.1186/s12944-018-0848-8
34. Chiu, H, Wu, PY, Huang, JC, Tu, HP, Lin, MY, Chen, SC, et al. There is a U shaped association between non high density lipoprotein cholesterol with overall and cardiovascular mortality in chronic kidney disease stage 3-5. Sci Rep. (2020) 10:12749. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-69794-2
35. Cui, Y, and Choi, M. Association between the non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio (NHHR) and angina pectoris in US adults: a cross-sectional retrospective study based on NHANES 2009-2018. Lipids Health Dis. (2024) 23:347. doi: 10.1186/s12944-024-02343-2
36. Wang, B, Li, L, Tang, Y, Lin, T, Wu, J, Wang, G, et al. Changes in non-high-density lipoprotein to high-density lipoprotein ratio (NHHR) and cardiovascular disease: insights from CHARLS. Lipids Health Dis. (2025) 24:112. doi: 10.1186/s12944-025-02536-3
37. Yu, B, Li, M, Yu, Z, Zheng, T, Feng, X, Gao, A, et al. The non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio (NHHR) as a predictor of all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in US adults with diabetes or prediabetes: NHANES 1999-2018. BMC Med. (2024) 22:317. doi: 10.1186/s12916-024-03536-3
38. Ma, HX, Chen, HQ, and Wang, PC. Association between non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio (NHHR) and stroke among adults in the USA: a cross-sectional NHANES study. Biomed Environ Sci. (2025) 38:37–46. doi: 10.3967/bes2025.001
39. Zhou, H, Wang, C, Wang, W, Li, H, Hu, Q, Huang, N, et al. Lesion location and serum levels of homocysteine are associated with early-onset post-stroke depression in acute ischemic stroke. Brain Behav. (2023) 13:e3210. doi: 10.1002/brb3.3210
40. Jayaraj, RL, Azimullah, S, Beiram, R, Jalal, FY, and Rosenberg, GA. Neuroinflammation: friend and foe for ischemic stroke. J Neuroinflammation. (2019) 16:142. doi: 10.1186/s12974-019-1516-2
41. Zhang, H, and Dhalla, NS. The role of pro-inflammatory cytokines in the pathogenesis of cardiovascular disease. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25:1082. doi: 10.3390/ijms25021082
42. Alsbrook, DL, Di Napoli, M, Bhatia, K, Biller, J, Andalib, S, Hinduja, A, et al. Neuroinflammation in acute ischemic and Hemorrhagic stroke. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. (2023) 23:407–31. doi: 10.1007/s11910-023-01282-2
43. Immanuel, J, and Yun, S. Vascular inflammatory diseases and endothelial phenotypes. Cells. (2023) 12:1640. doi: 10.3390/cells12121640
44. Morris, G, Puri, BK, Bortolasci, CC, Carvalho, A, Berk, M, Walder, K, et al. The role of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, apolipoprotein a and paraoxonase-1 in the pathophysiology of neuroprogressive disorders. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. (2021) 125:244–63. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2021.02.037
45. Zhou, LQ, Chu, YH, Dong, MH, Yang, S, Chen, M, Tang, Y, et al. Ldl-stimulated microglial activation exacerbates ischemic white matter damage. Brain Behav Immun. (2024) 119:416–30. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2024.04.014
46. Wang, YH, Chen, X, Bai, YZ, Gao, P, Yang, Z, Guo, Q, et al. Palmitoylation of PKCδ by ZDHHC5 in hypothalamic microglia presents as a therapeutic target for fatty liver disease. Theranostics. (2024) 14:988–1009. doi: 10.7150/thno.89602
47. Di Giacomo Barbagallo, F, Bosco, G, Di Marco, M, Scilletta, S, Miano, N, Musmeci, M, et al. Evaluation of glycemic status and subclinical atherosclerosis in familial hypercholesterolemia subjects with or without LDL receptor mutation. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2025) 24:126. doi: 10.1186/s12933-025-02683-y
48. Di Giacomo-Barbagallo, F, Andreychuk, N, Scicali, R, Gonzalez-Lleó, A, Piro, S, Masana, L, et al. Inclisiran, reasons for a novel agent in a crowded therapeutic field. Curr Atheroscler Rep. (2025) 27:25. doi: 10.1007/s11883-024-01271-x
49. Thabrew, H, Stasiak, K, Hetrick, SE, Donkin, L, Huss, JH, Highlander, A, et al. Psychological therapies for anxiety and depression in children and adolescents with long-term physical conditions. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. (2018) 12:CD012488. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012488.pub2
50. Volz, M, Ladwig, S, and Werheid, K. Gender differences in post-stroke depression: a longitudinal analysis of prevalence, persistence and predictive value of known risk factors. Neuropsychol Rehabil. (2021) 31:1–17. doi: 10.1080/09602011.2019.1648301
51. Lin, Z, Lawrence, WR, Huang, Y, Lin, Q, and Gao, Y. Classifying depression using blood biomarkers: a large population study. J Psychiatr Res. (2021) 140:364–72. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2021.05.070
52. Jia, QF, Yang, HX, Zhuang, NN, Yin, XY, Zhu, ZH, Yuan, Y, et al. The role of lipoprotein profile in depression and cognitive performance: a network analysis. Sci Rep. (2020) 10:20704. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-77782-9
53. Cepeda, MS, Kern, DM, Blacketer, C, and Drevets, WC. Low levels of cholesterol and the cholesterol type are not associated with depression: results of a cross-sectional NHANES study. J Clin Lipidol. (2020) 14:515–21. doi: 10.1016/j.jacl.2020.06.001
54. Shin, JY, Suls, J, and Martin, R. Are cholesterol and depression inversely related? A meta-analysis of the association between two cardiac risk factors. Ann Behav Med. (2008) 36:33–43. doi: 10.1007/s12160-008-9045-8
55. Morgan, RE, Palinkas, LA, Barrett-Connor, EL, and Wingard, DL. Plasma cholesterol and depressive symptoms in older men. Lancet. (1993) 341:75–9. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)92556-9
56. Sampson, M, Ling, C, Sun, Q, Harb, R, Ashmaig, M, Warnick, R, et al. A new equation for calculation of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in patients with Normolipidemia and/or hypertriglyceridemia. JAMA Cardiol. (2020) 5:540–8. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2020.0013
Keywords: post-stroke depression, acute ischemic stroke, non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio, abnormal lipid metabolism, depression
Citation: Deng M, Song K, Gao L, Wang Z, Zhao W, Xu W, Feng T and Li F (2025) Association between non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio and the risk of early-onset post-stroke depression: a prospective study. Front. Neurol. 16:1645765. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1645765
Edited by:
Yachen Shi, Wuxi People's Hospital, ChinaReviewed by:
Laura Beth McIntire, Weill Cornell Medical Center, NewYork-Presbyterian, United StatesFrancesco Di Giacomo Barbagallo, University of Catania, Italy
Ran Wang, The First hospital of Hebei Medical University, China
Copyright © 2025 Deng, Song, Gao, Wang, Zhao, Xu, Feng and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Fangyi Li, NDc1MDQwOTQyQHFxLmNvbQ==
 Mingzhu Deng
Mingzhu Deng Kangping Song
Kangping Song Lichen Gao
Lichen Gao Zhen Wang
Zhen Wang Wei Zhao2
Wei Zhao2 Wei Xu
Wei Xu Fangyi Li
Fangyi Li