- 1Department of Nursing, Shenzhen Hospital of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, Shenzhen, China
- 2School of Nursing, Fujian University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Fuzhou, China
- 3School of Nursing, Guangdong Pharmaceutical University, Guangzhou, China
- 4School of Nursing, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou, China
Background: Stroke is the third leading cause of death in the world, characterized by high morbidity, high mortality, high disability and high recurrence rates, which brings a heavy burden to families and society. The implementation of positioning management for stroke patients can effectively improve their clinical outcomes and quality of life; however, the current evidence related to stroke is fragmented, which is not conducive to its utilization by clinical healthcare professionals.
Objective: A systematic retrieval, critical appraisal, and synthesis of evidence on positioning management strategies for stroke patients were conducted to establish an evidence-based foundation for clinical decision-making in neurological rehabilitation.
Methods: Based on the “6S” evidence resource pyramid, a top-down search strategy was employed, searching relevant databases and guideline websites, including the Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network, National Institute of Health and Care Excellence, the American Heart Association, Cochrane Library, Embase, PubMed, Web of Science, CINAHL, CNKL, VIP, the Wanfang database, China Biology Medicine, UpToDate, Chinese Medical Association, the Yi Maitong Guidelines Network, Dingxiangyuan. Various types of literature such as clinical guidelines, expert consensus, systematic reviews, meta-analyses, and evidence summaries were also included. The search period covered February 2015 to February 2025. Two reviewers independently screened and critically assessed the literature, and then extracted and synthesized the evidence by grading it according to the Joanna Briggs Institute Centre for Evidence-Based Health Care Evidence Pre-grading System, Australia (2016 version).
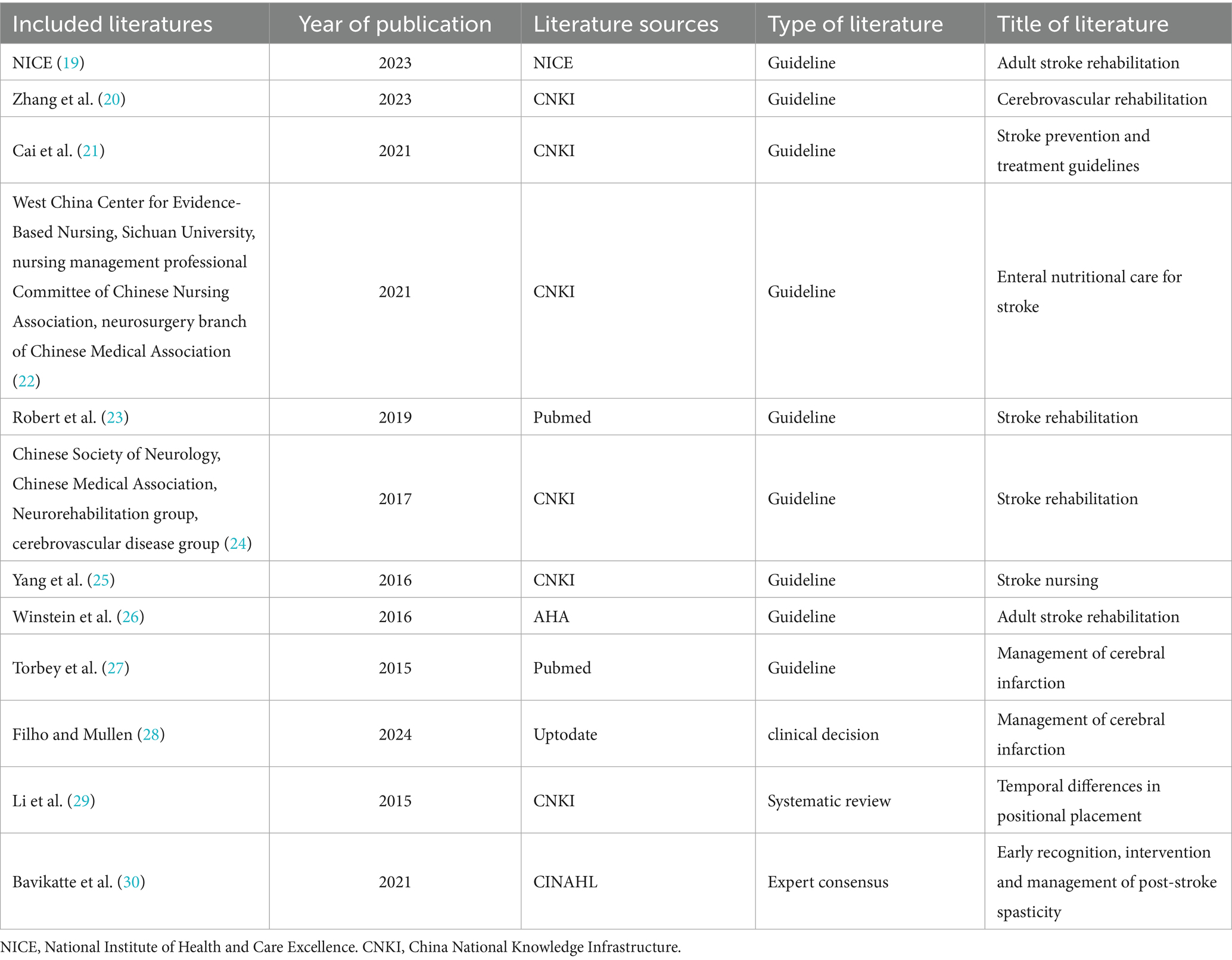
Results: A total of 9,605 publications were retrieved, resulting in the inclusion of 12 publications, including nine clinical guidelines, one clinical decision support tool, one systematic review, and one expert consensuses. The evidence was synthesized into seven thematic areas: team composition, comprehensive assessment, head-of-bed elevation angle, body positioning Strategies, early mobilization, assistive devices, and clinical considerations. Resulting in 37 evidence-based practice recommendations.
Conclusion: This study summarizes the best evidence for positional management of stroke patients, which provides an evidence-based basis for standardizing stroke positional management. However, the best evidence should be used in an individualized manner with comprehensive consideration of the actual clinical situation when the evidence is applied in order to improve the clinical outcomes and quality of life of stroke patients. In the future, it should also be combined with multi-sample and multi-center studies to validate its effect, as well as to further enrich the content of stroke position management.
1 Introduction
Stroke is the third leading cause of death globally, presenting a quadruple burden of high morbidity, disability, mortality and risk of recurrence. In 2021, there were 93.8 million stroke survivors and 11.9 million new stroke cases worldwide. There are 7.3 million global stroke deaths, accounting for 10.7% of all deaths (1). Motor impairment is one of the main disabilities associated with stroke (2). Movement disorders include weakness, spasticity, abnormal motor coordination and motor control disorders (3). During the recovery process, the gradual restoration of muscle strength is frequently accompanied by the development of spasticity (4). Post-stroke spasticity is the most common complication of stroke. The study showed that the total prevalence of spasticity after stroke was 25.3%, and 26.7% after the first stroke (5). Spasticity and its associated abnormal joint postures often interact with weakness and loss of dexterity, leading to dysfunctional motor control and functional limitations that can severely impact a patient’s ability to live and participate in society (6).
Patient positioning constitutes a fundamental nursing intervention (7). Notably, across diverse clinical scenarios, specific body positions can be utilized to confer therapeutic benefits for selected patients. In other words, under certain circumstances, goal-oriented therapeutic positions may take precedence over routine positioning, as they facilitate the improvement of patients’ physiological functions while promoting recovery (8).
In the application of positioning management for stroke patients, beyond its direct impact on spasticity, the clinical significance of postural changes further manifests in the regulation of vital signs during the acute phase (9). For stroke survivors, maintaining improper postures over an extended period can exacerbate spasticity in the affected limbs. This not only increases the risk of developing problems such as shoulder subluxation, shoulder pain, joint external rotation, foot inversion, or foot drop but also hinders the restoration of muscular strength, functional recovery, standing ability and walking performance. In addition, in the acute phase of stroke, postural changes play a crucial role in modulating vital physical signs. Specifically, they have a significant impact on oxygenation status, systemic blood pressure regulation, and cerebrovascular dynamics, including cerebral perfusion pressure, arterial flow velocity, and the maintenance of intracranial pressure balance (10, 11). Meanwhile, appropriate postural change is also intricately linked to the recovery of limb motor function and the prevention of secondary complications (12). In conclusion, positioning management is of great significance for stroke patients and serves as a key part of clinical nursing.
Given these circumstances, it becomes evident that implementing evidence-based postural management is of great significance in stroke rehabilitation. Positioning management involves the deliberate adjustment of body alignment, positioning, and support methods. Its core goals are to prevent complications, enhance functional capabilities, and improve patient comfort and quality of life. By understanding these aspects, we can better explore how to develop more effective positioning management strategies, which is precisely the focus of this study.
Currently, there are guidelines and systematic reviews available regarding postural management for critically ill patients (13), surgical patients (14), and patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) (15), which hold significant guiding value for the clinical management of patient positioning. However, there is still a lack of standardized and actionable protocols for positional management of stroke patients. The available evidence is scattered across multiple, often inconsistent guidelines and systematic reviews, which hinders effective translation into clinical practice. To address this gap, our study systematically synthesizes the best available evidence on postural management after stroke through thorough literature retrieval and rigorous critical appraisal. This consolidation aims to develop an evidence-based framework that can effectively guide clinical decision-making and ultimately improve rehabilitation outcomes for stroke patients.
2 Methodology
2.1 Establishment of evidence-based questions
This study utilized the PIPOST model, developed by the JBI Center for Evidence-Based Nursing at Fudan University in Shanghai, as the theoretical framework for the analysis. The PIPOST framework encompasses the following components: (i) P (Population): The target population consists of stroke patients, for whom evidence-based interventions are being applied. (ii) I (Intervention): This refers to studies focusing on postural management interventions aimed at improving patient outcomes. (iii) P (Professional): The professionals involved in the implementation of these interventions include nurses, physicians, rehabilitation specialists, and other healthcare providers. (iv) O (Outcome): The outcomes assessed in this study include changes in limb function, quality of life, and the incidence of complications related to postural management in stroke patients. (v) S (Setting): The settings for the implementation of interventions include inpatient wards, rehabilitation centers, and community-based environments. (vi) T (Type of Evidence): Eligible evidence types include clinical practice guidelines, expert consensus statements, practice recommendations, clinical decision-making protocols, evidence summaries, and systematic reviews.
2.2 Evidence retrieval
The following databases and websites were searched.
The following Chinese databases were used: China Knowledge Resource Integrated database (CNKI), Wanfang database, and VIP database.
The following English databases were used: PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, Cochrane Library, and CINAHL.
Guidelines networks: the Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network (SIGN), Ding Xiangyuan, YI Maitong, National Institute of Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE), UpToDate, American Heart Association/American Stroke Association (AHA/ASA), and Chinese Medical Association.
Search strategy. Since there are no specific guidelines or expert consensus on positioning management, and relevant content is scattered in the guidelines and expert consensus, to ensure the accuracy of the search, we used different search styles according to the type of literature. The search formula was as follows: (i) (stroke* OR apoplexy OR “cerebral infarction” OR “cerebral hemorrhage” OR “cerebrovascular accident*” OR “cerebrovascular stroke*” OR “brain vascular accident*” OR “neurological illness” OR “Cerebrovascular Accident” OR “cerebral infarctions”) AND (guideline∗ OR “practice guideline” OR routine∗ OR “recommended practice” OR consensus∗); (ii) (stroke* OR apoplexy OR “cerebral infarction” OR “cerebral hemorrhage” OR “cerebrovascular accident*” OR “cerebrovascular stroke*” OR “brain vascular accident*” OR rehabilitation OR “neurological illness” OR “Cerebrovascular Accident”) AND (“evidence summary” OR “systematic review” OR “meta-analysis”) AND (positioning OR spasticity OR “good limb position” OR rehabilitation). The search covered the period from the February 2015 to February 2025.
2.3 Inclusion and exclusion criteria
The inclusion criteria were as follows: (i) Studies focused on positioning management, spasticity management, and dyskinesia management in stroke patients, (ii) Studies including clinical guidelines, expert consensus statements, evidence summaries, and systematic reviews, (iii) Studies published in both Chinese and English languages.
Exclusion criteria were as follows: (i) Literature type was conference abstract, guideline interpretation, research plan/proposal or the old guide that has been replaced. (ii) Literatures with failed quality evaluation.
2.4 Literature screening
The literature was independently screened by two postgraduate students who had received specialized training in evidence-based nursing. The screening process followed a systematic approach, which included the following steps: (i) Deduplication: Duplicate entries were identified and removed using EndNote software, (ii) Initial Screening: The titles and abstracts of the articles were reviewed, and those not relevant to the research question were excluded, (iii) Rescreening: The remaining articles were subjected to a detailed review, and eligible studies were selected based on predefined inclusion criteria. Basic information was extracted from the selected studies, including the first author’s name, affiliation, publication year, source, evidence type, and article topic. To ensure accuracy, the screening results were cross-checked by both researchers. In cases of disagreement, a third expert in evidence-based nursing was consulted to resolve discrepancies.
2.5 Evaluation of the quality of the literature
The tool employed for the evaluation of the guidelines is the Assessment of Guidelines for Research and Evaluation II (AGREE II) (16), a widely recognized framework for assessing the methodological quality of clinical practice guidelines. The AGREE II tool evaluates guidelines across six key areas: scope and purpose, participants, rigor, clarity, applicability, and independence. Each of these areas is assessed using a scale from 1 to 7, where 1 represents strongly disagree and 7 represents strongly agree. The higher the degree to which the guidelines meet the specified criteria, the higher the corresponding score. The standardized percentage score for each item was calculated according to the following formula: (Actual Score−Lowest Possible Score) / (Highest Possible Score−Lowest Possible Score) × 100%. Items achieving a standardized percentage score of ≥60% were graded as A, those with a score between ≥30% and <60% were graded as B, and items with a score of <30% were graded as C. For the evaluation of systematic reviews, meta-analyses, and expert consensus, the Australian JBI Centre for Evidence-Based Health Care’s Quality Assessment Criteria (2016) (17) was applied. Evaluators provided judgments of “yes,” “no,” “unclear,” or “inapplicable” for each item based on a thorough review of the relevant literature. Following group discussions, consensus decisions were made regarding the inclusion, exclusion, or need for further clarification for any item rated as “no,” “unclear,” or “inapplicable.” At present, there is a lack of internationally recognized quality assessment tools specifically designed for the evaluation of clinical decision-making frameworks and evidence summaries. To address this methodological gap, the following approach was adopted: (i) Evidence derived from authoritative databases was classified a priori as high-quality, based on the credibility and reputation of the institution, (ii) For evidence obtained from alternative sources, a comprehensive full-text appraisal was conducted to ensure strict adherence to established evidence development protocols. The quality of the studies included in this analysis was independently assessed by two researchers, both of whom had undergone formal training in evidence-based methods. In instances of disagreement between the assessors, any discrepancies were resolved through collaborative discussion or by consulting a third specialist with expertise in evidence-based care.
2.6 Evidence extraction and summary
Studies that met the predefined inclusion and exclusion criteria were independently screened by two researchers with systematic evidence-based training and expertise in stroke care. This screening process involved reviewing titles, abstracts, and full texts of the studies. The researchers then extracted relevant data and basic information from the selected studies, cross-checking their results for consistency.
In cases of discrepancies, a consensus was reached through discussion with a third researcher to resolve any differences. When evidence from different sources was complementary or when conclusions were consistent, synthesis or generalization was employed. However, in instances where conflicting evidence emerged, the principles of evidence-based prioritization were applied, with preference given to high-quality evidence and the most recent authoritative publications.
Additionally, the synthesized evidence was graded using the Joanna Briggs Institute (JBI) methodology, as outlined by the JBI Center for Evidence-Based Medicine in Australia (18).
3 Results
3.1 Search results
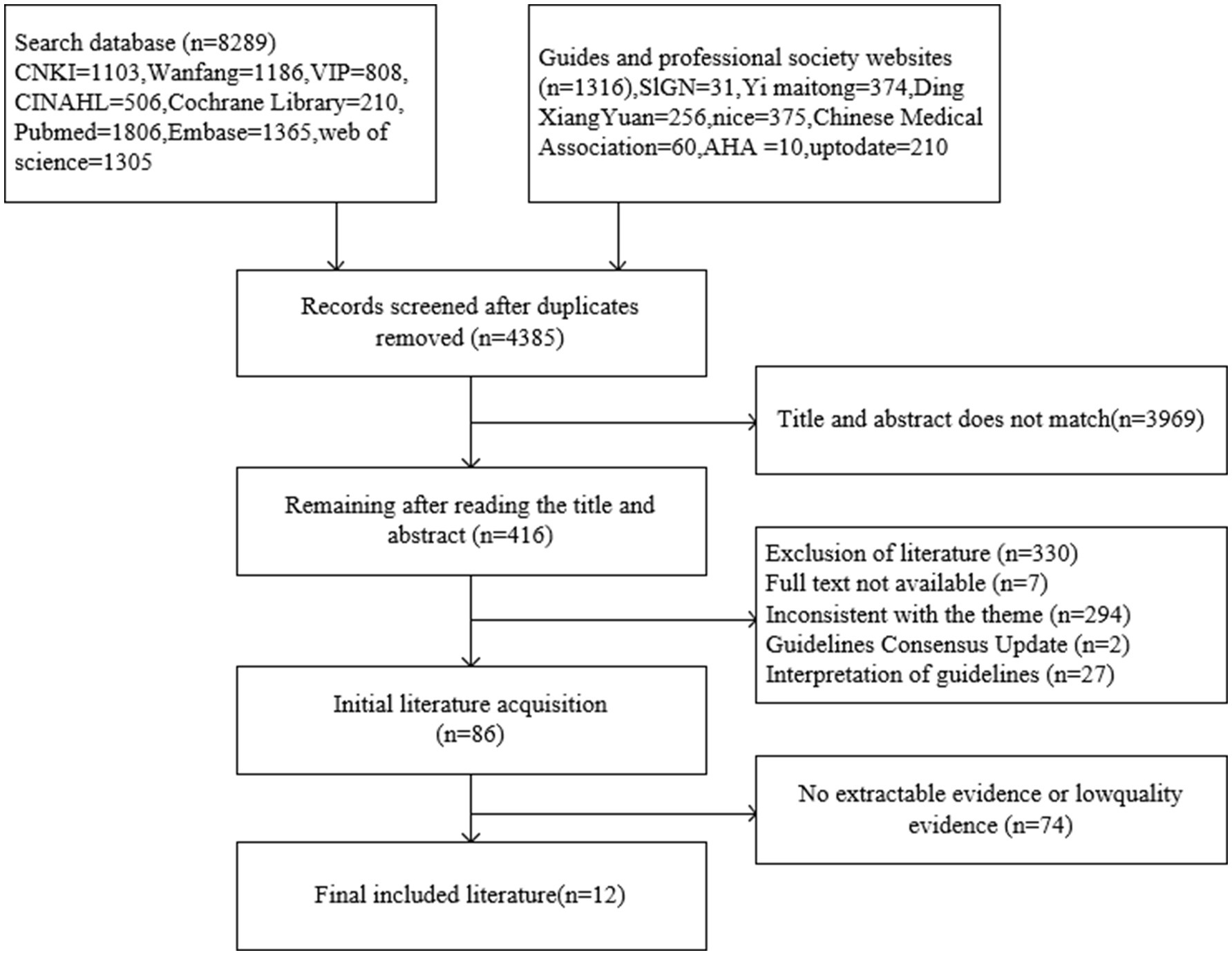
The initial database search identified a total of 9,605 articles. After removing duplicates, 4,385 articles remained for further review. Titles, abstracts, and full texts were systematically screened to exclude articles that did not meet the inclusion criteria. Following this process, a total of 12 articles were ultimately included in the study. These comprised nine clinical practice guidelines (19–27), one clinical decision-making article (28), one systematic review (29) and one expert consensus (30). The basic characteristics of the included articles are summarized in Table 1, and the detailed literature screening process is illustrated in Figure 1.
3.2 Results of the evaluation of the quality of the included studies
3.2.1 Quality evaluation results of the guidelines
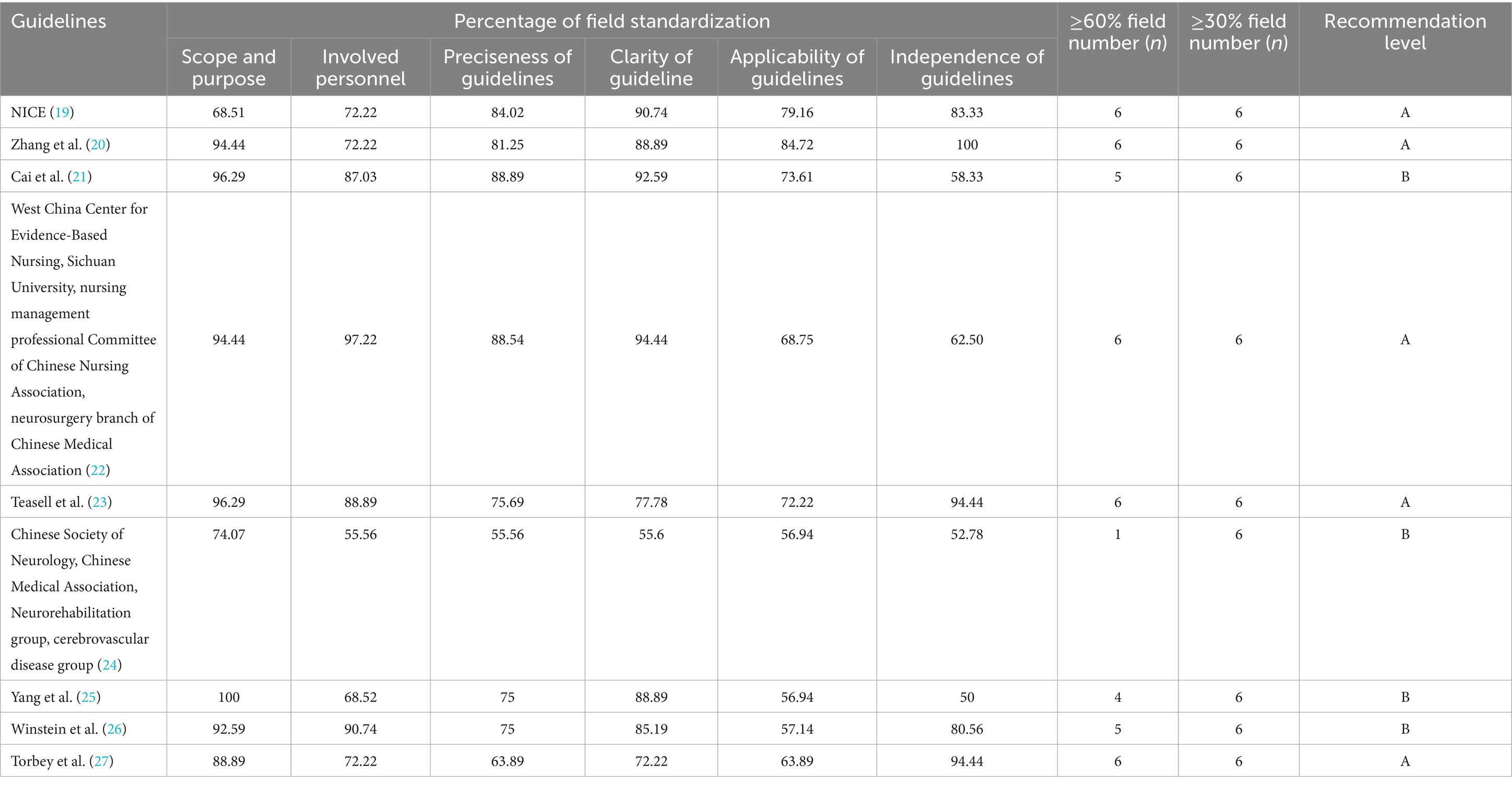
The guidelines were evaluated using AGREE II and the results are shown in Table 2, all with a recommendation level of A or B. The overall quality was high and inclusion was granted.
3.2.2 Systematic evaluation or meta-analysis quality evaluation results
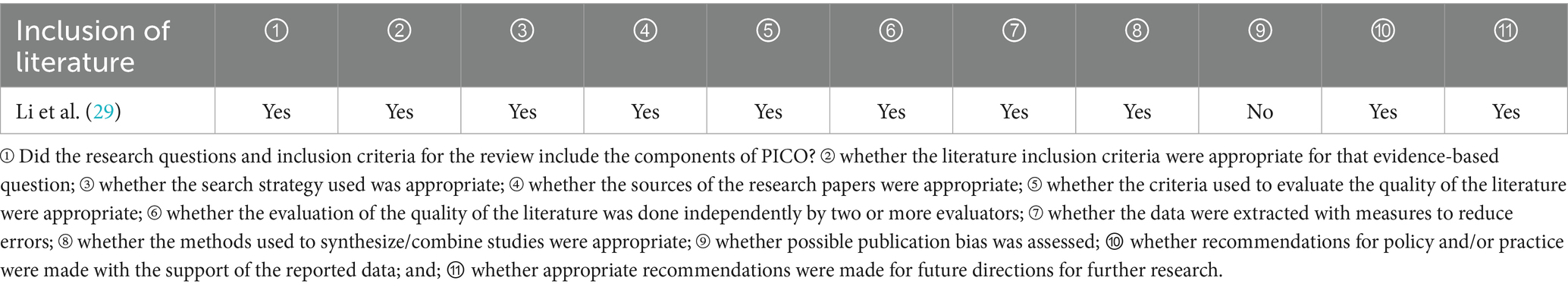
One systematic review (29) was included in the study. The evaluation results can be found in Table 3.
3.2.3 Quality evaluation results of the expert consensus
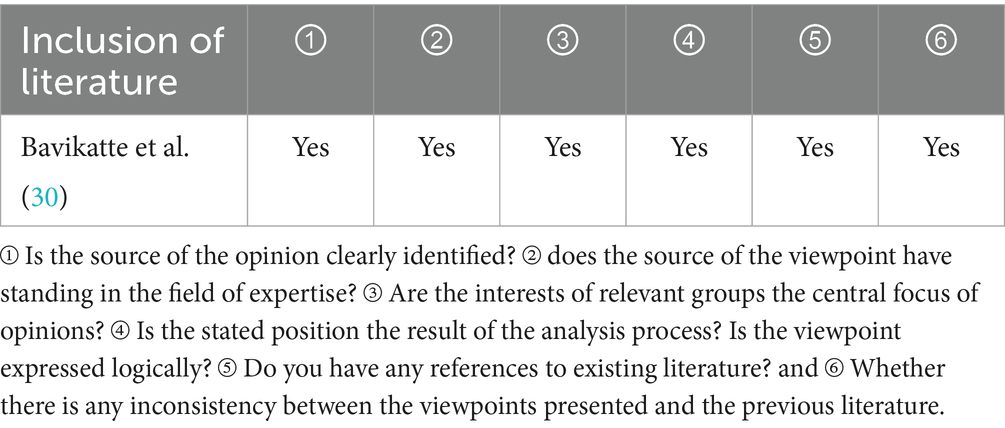
One expert consensuses (30) from CINAHL was included in the study. The details are shown in Table 4.
3.3 Summary and description of evidence
The evidence was extracted from the final literature. Through the induction and integration of the evidence, the evidence was finally summarized from six domains: team composition, comprehensive assessment, head-of-bed elevation angle, body positioning Strategies, early mobilization, assistive devices, and clinical considerations and 37 best evidences were formed, providing a comprehensive framework for neurorehabilitation practice, as shown in Table 5.
4 Discussion
4.1 Improve team building
Robust evidence demonstrates that organized, multidisciplinary stroke care not only reduces mortality rates and the likelihood of long-term disability but also enhances patient recovery and independence in activities of daily living (26). Clinical practice guidelines specify that core stroke rehabilitation teams should include physiotherapists, physicians with stroke rehabilitation expertise, occupational therapists, speech-language pathologists (SLPs), nurses, social workers, and dietitians, with patients and their caregivers systematically integrated as essential stakeholders in the therapeutic decision-making process (26). Familial support serves as a critical determinant in post-stroke recovery processes, with caregivers typically exhibiting stronger emotional bonds and functioning as primary care providers. Given the protracted trajectory of stroke rehabilitation, family members deliver multidimensional support—spanning emotional sustenance, instrumental assistance, and tangible care—throughout the disease continuum, directly influencing functional outcomes and psychosocial adaptation (31). Therefore, current evidence-based guidelines recommend early and active engagement of both patients and their caregivers in rehabilitation programs, emphasizing the strategic utilization of their self-efficacy to potentiate therapeutic outcomes and optimize health-related quality of life.
4.2 Raising awareness of positioning assessment
Positioning management, as a nursing intervention for stroke patients, boasts distinct advantages such as simple operation, low cost, diverse functions, strong clinical applicability, and high safety.
Existing evidence clearly indicates that posture exerts a significant impact on the hemodynamics of stroke patients (32, 33). From a theoretical perspective, different postures can produce differentiated clinical effects: when the supine position (0°) is adopted, the gravitational force helps increase cerebral blood flow in the ischemic penumbra, thereby improving the oxygenation status of brain tissue. This is of positive significance for alleviating neurological damage within the first few hours to days after a stroke. In contrast, the head-of-bed elevation position can effectively reduce intracranial pressure and lower the risk of aspiration pneumonia.
It is important to note that stroke patients are often accompanied by abnormal muscle strength and muscle tone. Therefore, posture management cannot follow a “one-size-fits-all” approach and must be tailored to the specific clinical conditions of individual patients. Hence, before implementing posture management, a comprehensive clinical assessment is required to consider multiple factors, including the type of cerebrovascular disease, physiological indicators such as cerebral blood flow and intracranial pressure, the patient’s own muscle strength and limb motor function level, as well as the presence of relevant comorbidities (28). Consequently, effective positioning management for stroke patients mandates a thorough assessment of the individual’s condition to determine the optimal and safest approach.
4.3 Head position
Head position significantly influences cerebral hemodynamics in stroke patients, with the supine position enhancing cerebral perfusion. A meta-analysis shows that in acute ischemic stroke patients, supine head positioning at 0° or 15° significantly increases blood flow velocity in the affected middle cerebral artery (MCA) compared with 30° head elevation and no significant changes in cerebral hemodynamics were observed in the contralateral hemisphere (34). However, whether this perfusion improvement translates to better clinical outcomes remains unclear. Randomized trials indicate that 30° head elevation does not significantly improve 3-month functional outcomes in moderate-to-severe stroke patients compared with the supine position (35). Despite these uncertainties about functional outcomes, current clinical evidence still recommends a supine position (0° head elevation) for cerebral infarction patients to maximize cerebral perfusion pressure (CPP). A multicenter randomized controlled trial found that initiating immediate supine positioning upon hospital admission and maintaining it for at least 24 h improves perfusion outcomes in acute ischemic stroke patients (36). Clinical guidelines also support maintaining a horizontal supine position during the acute phase to optimize CPP (22, 27). However, supine positioning should be temporary: most patients require repositioning after 24–48 h due to the increased risk of aspiration from prolonged flat lying (28).
Elevating the head position is a recommended practice in the management of patients with elevated intracranial pressure (ICP). In contrast to the general recommendation for supine positioning in acute ischemic stroke, elevating the head position is a recommended practice for patients with elevated intracranial pressure (ICP)—though the degree of elevation requires careful consideration, as angles exceeding 45° may reduce CPP. An observational study explored this balance: researchers systematically evaluated the hemodynamic effects of backrest elevation at 15° and 30°, followed by return to the baseline supine position (0°), with continuous monitoring of ICP, mean arterial pressure (MAP), CPP, and peak mean flow velocity in the MCA (37). Elevation to 30° significantly reduced ICP but was accompanied by concomitant decreases in MAP and CPP. Although the supine position achieved maximal CPP, it paradoxically correlated with the highest ICP levels. For patients with large-area cerebral infarction, the supine position may be considered when the risk of cerebral herniation is low and perfusion optimization is prioritized (38). However, prolonged supine positioning must be avoided to mitigate aspiration risk.
In summary, head-of-bed (HOB) positioning requires an individualized approach guided by comprehensive neurological and respiratory assessments, particularly with vigilant monitoring for aspiration risks in patients exhibiting impaired swallowing function or altered consciousness levels (26).
4.4 Implementation of positioning management
Positioning management for stroke patients should be individualized through comprehensive assessment to maximize its benefits. Multiple randomized controlled trials (39, 40) have demonstrated that stroke patients receiving enteral nutrition with the head of bed (HOB) elevated ≥30° exhibit significantly lower rates of aspiration, pulmonary infections, and gastric regurgitation compared to those positioned at angles <30°. Furthermore, a systematic review (41) has confirmed that maintaining HOB elevation between 30° and 45° during feeding further reduces the incidence of aspiration-related complications—including pulmonary infections, regurgitation, and abdominal distension—in post-stroke patients with dysphagia. Beyond preventing aspiration, positioning management also plays a critical role in addressing post-stroke spasticity—a common positive symptom following central nervous system injury that may present with dystonic features in stroke patients, characterized by abnormally increased muscle tone and motor impairments (42). Post-stroke spasticity not only compromises a patient’s functional independence but also imposes multiple clinical burdens (43). Of particular clinical relevance is the exacerbation of secondary complications—including shoulder-hand syndrome, pressure injuries, and disuse atrophy—when improper positioning strategies are employed. The anti-spasticity position is a temporary treatment position designed based on the theory of Bobath technology. The main principle is to fight against abnormal movement patterns, control muscle spasm and promote the emergence of separation movement through static reflex inhibition and continuous control (44). The anti-spasticity positioning protocol, a cornerstone intervention in neurorehabilitation, serves as an evidence-based strategy to prevent hemiplegic complications including but not limited to glenohumeral subluxation, shoulder pain, muscle contractures, equinovarus deformity, foot drop, and disuse syndrome. In addition to anti-spasticity positioning, systematic repositioning every 1–2 h achieves pressure redistribution, thereby mitigating tissue injury risks inherent in prolonged immobility. The position content mainly includes the healthy side lying position, the affected side lying position and the bed sitting position. Three therapeutic positions form the protocol’s core implementation framework. The hemiplegic-side lying position is prioritized for its dual capacity to enhance sensory integration in the affected limb while mechanically elongating spastic muscle groups, all without restricting functional use of the non-paretic extremity. In contrast, the healthy-side lying position requires vigilant monitoring to prevent neglect of the hemiplegic limb. Bed-sitting postures, when hemodynamically appropriate, offer advantages in trunk stabilization and nutritional support, provided intracranial hypotension has been conclusively ruled out (24). The post-stroke patient’s position should be placed without affecting the patient’s vital signs. Simultaneously, attention should be paid to protecting the affected limb, avoiding upper limb flexion and excessive extension of the lower limb (25). Regarding the duration of therapeutic positioning, formal guidelines on this parameter for post-stroke patients remain undefined. A meta-analysis (29) has shown no linear correlation between positioning duration and functional outcomes. Current evidence recommends a minimum intervention duration of 4 weeks, with specific timelines determined through individualized patient assessment.
4.5 Preventing complications
Proper positioning management can prevent many post-stroke complications. Pressure injury development is significantly correlated with patient positioning (45). In stroke patients, hemiplegia, sensory alterations, and consciousness level changes predispose individuals to risks of joint/muscle contractures and cutaneous breakdown (46). To address this, clinical guidelines emphasize minimizing friction, redistributing pressure via appropriate support surfaces, and controlling moisture.
Hemiplegic shoulder pain (HSP) is one of the common complications after stroke, with a prevalence of 22% to 47% (47), often causes moderate-to-severe pain that disrupts upper limb rehabilitation, delays functional recovery, and prolongs hospitalization. Shoulder-hand syndrome represents a specific subtype of shoulder pain, frequently complicating shoulder subluxation, where the primary management goal is to prevent progression. Numerous guidelines highlight positioning intervention as a key strategy in managing spasticity, shoulder pain, and shoulder-hand syndrome. Protective postures can mitigate the risk of shoulder pain and subluxation (20). For patients with existing post-stroke shoulder pain, positioning management should prioritize maintaining scapulohumeral symmetry, typically positioning the shoulder in 30° abduction, 15°external rotation, and 20° forward flexion. If shoulder pain or subluxation already occurs, positioning adjustments then focus on preventing further deterioration. Positioning devices such as arm rests and supportive slots can further aid this by providing stable support and maintaining proper joint alignment, thereby minimizing discomfort and subluxation (26). However, it is critical to avoid improper positioning practices. For example, pulley-like movements that lift the affected hand high above the head can cause excessive shoulder flexion and abduction, damaging local joint capsules and ligaments and exacerbating shoulder pain. Such inappropriate movements not only worsen existing shoulder injuries but also hinder patients’ active rehabilitation efforts (24).
4.6 Auxiliary appliances
An orthotic is an externally applied device designed to restore anatomical alignment, maintain functional positioning, and assist bodily function (48). The Chinese Stroke Nursing Guidelines explicitly recommend selecting hand, wrist, ankle, and foot orthoses as needed during post-stroke rehabilitation to prevent complications, with careful consideration of device appropriateness emphasized (25).
Spasticity is common in the upper extremities, most commonly in the elbow (79%), wrist (66%), and shoulder (58%) (6). Spasticity-related contractures not only cause pain but also impair self-care abilities, including dressing and personal hygiene. Static stretching is a widely used type of stretching that can be applied in a variety of ways, including the physical therapist’s hands, splints, orthotics, and cast models (49). For stroke patients specifically, orthotics aim to reduce spasticity, enhance function, prevent contractures, alleviate pain, and decrease swelling. Wrist and hand orthoses stabilize the limb in a functional position, serving as effective passive stretching tools to target wrist flexor spasticity. Meta-analyses indicate that orthotic interventions typically span 3–4 weeks, applied 6–7 days weekly for at least 20 min daily (49). However, while guidelines (23, 26) recommend hand splints to prevent wrist and finger contractures, their efficacy in reducing wrist spasticity remains controversial (50). In light of this uncertainty, current clinical guidelines advises cautious use: short-term splinting may prevent contractures, but long-term or routine use is generally discouraged (23). Thus, individualized splinting plans with regular efficacy monitoring are essential (23, 30).
Shoulder stabilization devices, including orthoses and slings recommended in guidelines, provide mechanical support to reduce early subluxation and late contracture. These devices maintain shoulder joint anatomy by stabilizing muscles and bones, thereby relieving pain and preventing/correcting subluxation. Proximal-distal orthopedic appliances for the affected arm have been shown to improve shoulder pain and reduce subluxation (51), while shoulder straps alleviate discomfort by immobilizing the limb (52). Lower limb orthoses are one of the earliest and most widely used orthoses in history. They support weight, prevent and correct lower limb deformities, effectively compensate for the function of paralyzed muscles, limit unwanted movement of lower limb joints, and help treat lower limb motor dysfunction by improving posture when standing and walking (53). Currently, hemiplegic patients commonly use various lower limb orthoses, which are categorized by the limb segment they target: knee orthoses, ankle orthoses, knee-ankle-foot orthoses, and hip-knee-ankle-foot orthoses. Of these, ankle-foot orthoses (AFOs) are the most frequently used. Beyond addressing motor function, such devices can also improve balance—for example, canes or AFOs. Ankle plantarflexion contracture after stroke, for instance, can compromise gait quality and safety; guidelines therefore recommend AFOs for patients with remediable gait disorders to compensate for foot drop, improve walking stability, and potentially prevent ankle contractures (26, 54).
Orthotic use must be guided by comprehensive patient assessment, incorporating factors such as spasticity severity, functional deficits, and comorbidities (e.g., intracranial pressure dynamics). While orthotics offer evidence-based benefits in preventing contractures and improving mobility, their application should always be individualized, with routine evaluation of efficacy and adjustment of intervention duration.
5 Limitations
This study aimed to summarize the best evidence for positioning management in patients with stroke. However, it has several limitations. First, the literature included in this study was restricted to Chinese and English, which may have led to the omission of evidence from other languages and thus compromised the comprehensiveness of the data. Second, the quality assessment of different types of literature using various tools may not be fully consistent, and the integration of conflicting or similar evidence may lack sufficient precision for practical application. Third, the evidence in this study was derived from different countries, where there are still certain differences in social status, clinical settings, and cultural backgrounds.
6 Conclusion
Positioning management of stroke usually involves several interdependent aspects. Scientific and standardized postural management is critical for preserving limb function and preventing complications in stroke patients. This study systematically screened and synthesized the best available evidence on postural management for stroke patients, categorizing it into seven domains: team composition, comprehensive assessment, head-of-bed elevation angle, body positioning strategies, early mobilization, assistive devices, and clinical considerations. A total of 37 pieces of best evidence were identified, providing an evidence-based framework for healthcare professionals to implement postural interventions. Therefore, it is recommended that future researchers conduct and implement relevant studies based on their countries’ actual conditions to further enrich the evidence and intervention strategies for posture management in stroke patients. On this basis, efforts should be made to promote the formulation of relevant guidelines, provide clear rules for positioning management, and ultimately ensure tangible benefits for patients.
Author contributions
YX: Project administration, Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing – original draft. MP: Investigation, Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Resources, Visualization, Data curation. WC: Formal analysis, Project administration, Writing – original draft, Data curation, Supervision, Methodology. HLe: Writing – original draft, Data curation, Resources, Methodology, Validation. HP: Writing – original draft. ZH: Writing – original draft. NL: Writing – original draft. YL: Writing – review & editing. LK: Writing – review & editing. HLi: Validation, Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization, Project administration, Supervision, Investigation.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work is supported by the Sanming Project of Medicine in Shenzhen (Grant Number: SZZYSM202311016).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. GBD 2021 Nervous System Disorders Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of disorders affecting the nervous system, 1990-2021: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2021. Lancet Neurol. (2024) 23:344–81. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(24)00038-3
2. Dimyan, MA, and Cohen, LG. Neuroplasticity in the context of motor rehabilitation after stroke. Nat Rev Neurol. (2011) 7:76–85. doi: 10.1038/nrneurol.2010.200
3. Li, S, Chen, YT, Francisco, GE, Zhou, P, and Rymer, WZ. A unifying pathophysiological account for post-stroke spasticity and disordered motor control. Front Neurol. (2019) 10:468. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2019.00468
4. Sommerfeld, DK, Eek, EU, Svensson, AK, Holmqvist, LW, and von Arbin, MH. Spasticity after stroke: its occurrence and association with motor impairments and activity limitations. Stroke. (2004) 35:134–9. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.0000105386.05173.5E
5. Zeng, H, Chen, J, Guo, Y, and Tan, S. Prevalence and risk factors for spasticity after stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Neurol. (2021) 11:616097. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.616097
6. Chih-Lin, K, and Gwo-Chi, H. Post-stroke spasticity: a review of epidemiology, pathophysiology, and treatments. Int J Gerontol. (2018) 12:280–4. doi: 10.1016/j.ijge.2018.05.005
7. Hawkins, S, Stone, K, and Plummer, L. An holistic approach to turning patients. Nurs Stand. (1999) 14:51–6. doi: 10.7748/ns1999.10.14.3.51.c2689
8. Griffiths, H, and Gallimore, D. Positioning critically ill patients in hospital. Nurs Stand. (2005) 19:56–66. doi: 10.7748/ns2005.06.19.42.56.c3902
9. Qin, W, Yang, M, Li, F, Chen, C, Zhen, L, and Tian, S. Influence of positional changes on spasticity of the upper extremity in poststroke hemiplegic patients. Neurosci Lett. (2019) 712:134479. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2019.134479
10. Chen, HS, Zhang, NN, Cui, Y, Li, XQ, Zhou, CS, Ma, YT, et al. A randomized trial of Trendelenburg position for acute moderate ischemic stroke. Nat Commun. (2023) 14:2592. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-38313-y
11. Lam, MY, Haunton, VJ, Robinson, TG, and Panerai, RB. Does gradual change in head positioning affect cerebrovascular physiology? Physiol Rep. (2018) 6:e13603. doi: 10.14814/phy2.13603
12. Pickenbrock, H, Ludwig, VU, Zapf, A, and Dressler, D. Conventional versus neutral positioning in central neurological disease: a multicenter randomized controlled trial. Dtsch Arztebl Int. (2015) 112:35–42. doi: 10.3238/arztebl.2015.0035
13. Schaller, SJ, Scheffenbichler, FT, Bein, T, Blobner, M, Grunow, JJ, Hamsen, U, et al. Guideline on positioning and early mobilisation in the critically ill by an expert panel. Intensive Care Med. (2024) 50:1211–27. doi: 10.1007/s00134-024-07532-2
14. Stanton, C. Guideline for positioning the patient. AORN J. (2022) 115:P5–7. doi: 10.1002/aorn.13680
15. Hadaya, J, and Benharash, P. Prone positioning for acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). JAMA. (2020) 324:1361. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.14901
16. Brouwers, MC, Kho, ME, Browman, GP, Burgers, JS, Cluzeau, F, Feder, G, et al. AGREE II: advancing guideline development, reporting and evaluation in health care. CMAJ. (2010) 182:E839–42. doi: 10.1503/cmaj.090449
17. The Joanna Briggs Institute. The Joanna Briggs institute critical appraisal tools for text and opinion papers. Chengdu: The Joanna Briggs Institute (2017).
18. Wang, CHQ, and Hu, Y. JBI evidence pregrading and evidence recommendation level system (2014 version). J Advanced Pract Nurs. (2015) 30:964–7. doi: 10.16821/j.cnki.hsjx.2015.11.002
19. National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE). Stroke rehabilitation in adults [EB/OL]. (2023). Available online at: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng236 (Accessed February 1, 2025).
20. Zhang, T, Zhao, J, Li, XP, Wang, BJ, Qu, Y, Li, BJ, et al. Chinese Stroke Association guidelines for clinical management of cerebrovascular diseases (second edition) (excerpt)—chapter eight cerebrovascular disease rehabilitation management [in Chinese]. Chin J Stroke. (2023) 18:1036–48. doi: CNKI:SUN:ZUZH.0.2023-09-010
21. National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China. Chinas troke prevention and treatment guidelines (2021). Beijing: National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China. (2021).
22. West China Center for Evidence-Based Nursing, Sichuan University, nursing management professional Committee of Chinese Nursing Association, neurosurgery branch of Chinese Medical Association. Nursing practice guideline for enteral nutrition in patients with stroke. Chin J Evid Based Med. (2021) 21:628–41. doi: CNKI:SUN:ZZXZ.0.2021-06-002
23. Teasell, R, Salbach, NM, Foley, N, Mountain, A, Cameron, JI, Jong, A, et al. Canadian stroke best practice recommendations: rehabilitation, recovery, and community participation following stroke. Part one: rehabilitation and recovery following stroke; 6th edition update 2019. Int J Stroke. (2020) 15:763–88. doi: 10.1177/1747493019897843
24. Chinese Society of Neurology, Chinese Medical Association, Neurorehabilitation group, cerebrovascular disease group. Guidelines for the early rehabilitation of stroke in China. Chin J Neurol. (2017) 50:405–12. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1006-7876.2017.06.002
25. Yang, X. China stroke nursing care guidelines. MedLink (2016). Available online at: http://guide.medlive.cn/guideline/14146 (Accessed February 3, 2025).
26. Winstein, CJ, Stein, J, Arena, R, Bates, B, Cherney, LR, Cramer, SC, et al. Guidelines for adult stroke rehabilitation and recovery: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. (2016) 47:e98–e169. doi: 10.1161/STR.0000000000000098
27. Torbey, MT, Bösel, J, Rhoney, DH, Rincon, F, Staykov, D, Amar, AP, et al. Evidence-based guidelines for the management of large hemispheric infarction: a statement for health care professionals from the Neurocritical Care Society and the German Society for Neuro-intensive Care and Emergency Medicine. Neurocrit Care. (2015) 22:146–64. doi: 10.1007/s12028-014-0085-6
28. Filho, JO, and Mullen, MT. Initial assessment and management of acute stroke. UpToDate (2018). Available online at: https://uptodatezju.p.985gx.top/contents/initial-assessment-and-management-of-acute-stroke?search=stroke&source=search_result&selectedTitle=1%7E150&display_rank=1 (Accessed February 3, 2025).
29. Li, XJ, Chen, JX, and Chen, TY. The effect of normal limb position on extremity dysfunction of stroke survivors with hemiplegia: effect of different lenpths of intervention and a meta-analysis. J Nurs Sci. (2015) 30:81–7. doi: 10.3870/j.issn.1001-4152.2015.21.081
30. Bavikatte, G, Subramanian, G, Ashford, S, Allison, R, and Hicklin, D. Early identification, intervention and Management of Post-stroke Spasticity: expert consensus recommendations. J Cent Nerv Syst Dis. (2021) 13:11795735211036576. doi: 10.1177/11795735211036576
31. Li, D, Guo, H, Sun, Y, Zhang, Z, and Liu, H. Knowledge, attitude, and practice of stroke patients' family members towards stroke rehabilitation: a cross-sectional study. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. (2025) 34:108177. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2024.108177
32. Carvalho, LB, Kramer, S, Borschmann, K, Chambers, B, Thijs, V, and Bernhardt, J. Cerebral haemodynamics with head position changes post-ischaemic stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. (2020) 40:271678X20922457. doi: 10.1177/0271678X20922457
33. Lam, MY, Haunton, VJ, Nath, M, Panerai, RB, and Robinson, TG. The effect of head positioning on cerebral hemodynamics: experiences in mild ischemic stroke. J Neurol Sci. (2020) 419:117201. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2020.117201
34. Olavarría, VV, Arima, H, Anderson, CS, Brunser, AM, Muñoz-Venturelli, P, Heritier, S, et al. Head position and cerebral blood flow velocity in acute ischemic stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Cerebrovasc Dis. (2014) 37:401–8. doi: 10.1159/000362533
35. Anderson, CS, Arima, H, Lavados, P, Billot, L, Hackett, ML, Olavarría, VV, et al. Investigators and coordinators. cluster-randomized, crossover trial of head positioning in acute stroke. N Engl J Med. (2017) 376:2437–47. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1615715
36. Muñoz-Venturelli, P, Arima, H, Lavados, P, Brunser, A, Peng, B, Cui, L, et al. Head Position in Stroke Trial (HeadPoST)–sitting-up vs lying-flat positioning of patients with acute stroke: study protocol for a cluster randomised controlled trial. Trials. (2015) 16:256. doi: 10.1186/s13063-015-0767-1
37. Schwarz, S, Georgiadis, D, Aschoff, A, and Schwab, S. Effects of body position on intracranial pressure and cerebral perfusion in patients with large hemispheric stroke. Stroke. (2002) 33:497–501. doi: 10.1161/hs0202.102376
38. Steiner, T, Ringleb, P, and Hacke, W. Treatment options for large hemispheric stroke. Neurology. (2001) 57:S61–8. doi: 10.1212/wnl.57.suppl_2.s61
39. van Nieuwenhoven, CA, Vandenbroucke-Grauls, C, van Tiel, FH, Joore, HC, van Schijndel, RJ, van der Tweel, I, et al. Feasibility and effects of the semirecumbent position to prevent ventilator-associated pneumonia: a randomized study. Crit Care Med. (2006) 34:396–402. doi: 10.1097/01.ccm.0000198529.76602.5e
40. Shi, HH, Xi, FJ, and Gong, SR. Influence of changing body position on incidence of gastric contents backstreaming in patients accepted nasal feeding. Chin Nurs Res. (2006) 29:2698–9. doi: CNKI:SUN:SXHZ.0.2006-29-049
41. Yang, CC, Ji, XF, Ma, HL, Li, YL, and Zheng, LW. Effects of feeding position on the incidence of complications for patients with dysphagia post-stroke: a meta-analysis. J Nurses Train. (2016) 31:2223–7. doi: 10.16821/j.cnki.hsjx.2016.24.006
42. Picelli, A, Tamburin, S, Gajofatto, F, Zanette, G, Praitano, M, Saltuari, L, et al. Association between severe upper limb spasticity and brain lesion location in stroke patients. Biomed Res Int. (2014) 2014:162754. doi: 10.1155/2014/162754
43. Chen, B, Yang, T, Liao, Z, Sun, F, Mei, Z, and Zhang, W. Pathophysiology and management strategies for post-stroke spasticity: an update review. Int J Mol Sci. (2025) 26:406. doi: 10.3390/ijms26010406
44. Li, Q, Jin, XQ, Ma, XM, and Tang, YX. Current status of good limb positioning during the stabilization period in stroke patients with hemiplegia and its influencing factors. Pract J Card Cereb Pneum Vasc Dis. (2024) 32:57–63. doi: 10.12114/j.issn.1008-5971.2024.00.091
45. Gillespie, BM, Walker, RM, Latimer, SL, Thalib, L, Whitty, JA, McInnes, E, et al. Repositioning for pressure injury prevention in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. (2020) 6:CD009958. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009958.pub3
46. Schott, M, Dalmolin, C, Golin, A, Alves, BP, Cassol, MC, Brondani, JE, et al. Nutritional factors and pressure injury risk in hospitalised patients post-stroke. J Wound Care. (2024) 33:S32–9. doi: 10.12968/jowc.2024.33.Sup2.S32
47. Anwer, S, and Alghadir, A. Incidence, prevalence, and risk factors of hemiplegic shoulder pain: a systematic review. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2020) 17:4962. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17144962
48. Choo, YJ, Boudier-Revéret, M, and Chang, MC. 3D printing technology applied to orthosis manufacturing: narrative review. Ann Palliat Med. (2020) 9:4262–70. doi: 10.21037/apm-20-1185
49. Salazar, AP, Pinto, C, Ruschel Mossi, JV, Figueiro, B, Lukrafka, JL, and Pagnussat, AS. Effectiveness of static stretching positioning on post-stroke upper-limb spasticity and mobility: systematic review with meta-analysis. Ann Phys Rehabil Med. (2019) 62:274–82. doi: 10.1016/j.rehab.2018.11.004
50. Lannin, NA, Cusick, A, McCluskey, A, and Herbert, RD. Effects of splinting on wrist contracture after stroke: a randomized controlled trial. Stroke. (2007) 38:111–6. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.0000251722.77088.12
51. Nadler, M, and Pauls, M. Shoulder orthoses for the prevention and reduction of hemiplegic shoulder pain and subluxation: systematic review. Clin Rehabil. (2017) 31:444–53. doi: 10.1177/0269215516648753
52. Ravichandran, H, Janakiraman, B, Sundaram, S, Fisseha, B, Gebreyesus, T, and Yitayeh Gelaw, A. Systematic review on effectiveness of shoulder taping in hemiplegia. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. (2019) 28:1463–73. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2019.03.021
53. Cui, Y, Cheng, S, Chen, X, Xu, G, Ma, N, Li, H, et al. Advances in the clinical application of orthotic devices for stroke and spinal cord injury since 2013. Front Neurol. (2023) 14:1108320. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1108320
Keywords: stroke, position, evidence-based nursing, summary of evidence, management
Citation: Xiong Y, Pan M, Chai W, Lei H, Peng H, Hu Z, Li N, Liang Y, Kuang L and Liu H (2025) Best evidence summary on positioning management in stroke patients. Front. Neurol. 16:1648841. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1648841
Edited by:
Giovanni Merlino, Udine University Hospital, ItalyReviewed by:
Luis Manuel Mota de Sousa, Universidade Atlântica, PortugalAhmed Magdy Alshimy, Mohammed Al-Mana Collage for Medical Sciences, Saudi Arabia
Copyright © 2025 Xiong, Pan, Chai, Lei, Peng, Hu, Li, Liang, Kuang and Liu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yongqi Liang, MTMzNDI4MTcyMjZAMTYzLmNvbQ==; Lingyu Kuang, NDEwMDMwNzUyQHFxLmNvbQ==; Hanjiao Liu, bGl1aGFuamlhbzAwMEAxNjMuY29t
 Yuanfang Xiong
Yuanfang Xiong Mingxia Pan
Mingxia Pan Wenting Chai2
Wenting Chai2 Huan Peng
Huan Peng Ziping Hu
Ziping Hu Hanjiao Liu
Hanjiao Liu