Abstract
Objective:
To evaluate the value of ultrasound strain elastography in assessing carotid plaque stiffness for predicting short-term clinical changes after cerebral infarction.
Methods:
Patients with cerebral infarction and carotid atherosclerotic plaque identified through routine ultrasound examination at the Ultrasound Department of Beijing Chaoyang Hospital, Capital Medical University, were selected for this study. All patients underwent strain elastography. Based on changes in their clinical conditions within 30 days following cerebral infarction, they were divided into a deterioration group and a non-deterioration group. The differences between the two groups in terms of strain elastography results were compared for statistical significance. Logistic regression analysis was conducted to analyze factors affecting short-term clinical changes in patients with cerebral infarction. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was drawn.
Results:
A total of 110 patients were included in this study (83 males and 27 females, average age: 60.02 ± 10.67 years). The carotid plaque strain elastography value, arterial wall strain elastography value and plaque stiffness were1.17 ± 0.40, 0.53 ± 0.16 and 2.33 ± 0.97 in the deterioration group, 1.73 ± 0.58, 0.59 ± 0.18 and 3.04 ± 1.00 in the non-deterioration group. The differences between the two groups were statistically significant about carotid plaque strain elastography value and plaque stiffness. The AUC values for predicting non-deterioration after cerebral infarction were 0.790 for carotid plaque strain elastography value, 0.608 for arterial wall strain elastography value, and 0.740 for plaque stiffness.
Conclusion:
Carotid plaque ultrasound strain elastography can be utilized to assess short-term clinical changes after cerebral infarction. Patients who experience clinical deterioration have lower carotid plaque strain elastography values, indicating that this parameter is more effective in predicting the absence of deterioration after cerebral infarction.
1 Introduction
Cerebral infarction is a major cause of permanent disability, while vulnerable carotid plaques are a key factor in the occurrence and progression of acute cerebral infarction (1, 2). Studies have shown that vulnerable carotid plaques are an independent risk factor for the onset and recurrence of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. The thickness, size, surface morphology and internal neovascularization, and so on of carotid plaques are typically associated with the occurrence and recurrence of ischemic cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events (3, 4). While strain elastography is of certain value in assessing the occurrence of cerebral infarction, few studies have explored its role in predicting short-term clinical changes following cerebral infarction 5–9). In this study, by comparing carotid plaque strain elastography findings of patients with different short-term clinical changes after cerebral infarction, we aim to determine its effectiveness in evaluating short-term clinical changes in patients with cerebral infarction.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Research objects
Patients diagnosed with non-cardiogenic cerebral infarction who underwent carotid ultrasound examination at Beijing Chaoyang Hospital, Capital Medical University between February 2022 and December 2023 were selected for this study. All patients underwent both routine ultrasound and ultrasound strain elastography examinations within 3 days. All patients received standardized neurology treatment after cerebral infarction. Based on changes in their clinical conditions within 30 days after cerebral infarction, they were divided into a deterioration group and a non-deterioration group. The study had been approved by the Ethics Committee of Beijing Chaoyang Hospital, Capital Medical University and all participants had provided written informed consent prior to ultrasound examination.
Inclusion criteria: (1) age ≥ 18 years; (2) first-ever ischemic cerebral infarction affecting the anterior circulation within the past 30 days; (3) at least one non-hyperechoic carotid plaque on the side ipsilateral to the cerebral infarction; (4) no ≥50% stenosis in intracranial arteries, extracranial carotid arteries, or vertebral arteries on imaging.
Exclusion criteria: (1) prior history of neck radiotherapy; (2) diagnosed with cardiogenic cerebral infarction or cerebral infarction of undetermined etiology based on the TOAST classification; (3) unable to cooperate with the ultrasound examination due to consciousness disorders, soft tissue infections in the neck; (4) poor quality of ultrasound images caused by obesity and other reasons; (5) previous carotid endarterectomy or stent placement; (6) refusal to participate in this study; (7) loss to follow-up.
2.2 Instruments and technique
In this study, a LogiqE9 color Doppler ultrasound system manufactured by GE, equipped with strain elastography software and analysis software was employed. Probe selection: a 9 L linear array probe with a frequency of 5–10 MHz was selected. The gain was adjusted to ensure clear signals without noise. The dynamic range (DR) was set between 55 and 65% to clearly display the plaque and surrounding tissues. The focus point was placed in the region of interest (ROI) or slightly distally to it.
2.2.1 Routine ultrasound examination
The patients took a supine position with a thin pillow behind the neck, and the head was tilted backward and turned away from the examination side by about 45° to fully expose the neck. A routine grayscale ultrasound examination was performed to record the number of plaques, as well as the location, length and thickness of the largest non-hyperechoic plaque.
2.2.2 Real-time ultrasound strain elastography examination
Based on the routine ultrasound results, real-time ultrasound strain elastography was conducted. The probe was gently moved to center the target plaque on the screen, and the distance between the plaque and the surface of the probe ranges from 1.0 cm to 3.0 cm. After that, the elastography software was activated. Real-time grayscale ultrasound image and strain elastography image were displayed side by side. The sampling frame was adjusted, so that the entire plaque, as well as the anterior and posterior walls of the vessel, can be included within the sampling frame and remained stationary. Strain elastography was applied based on the pressure generated by vascular pulsation. The strain elastographic characteristics of plaques were observed, and both dynamic and static images were recorded for analysis. The examination was repeated three times in each patient. During the examination, pressure and compression rate were strictly maintained within the green range, with each recording lasting 3 s.
2.2.3 Strain elastography analysis
The carotid plaque region was defined as Region A and the mean strain value across the plaque was recorded as plaque elasticity (A) of this patient. The carotid arterial wall region was defined as Region B and its strain value was recorded as carotid arterial wall elasticity (B). The ratio of A/B was calculated as the plaque stiffness. Each subject’s target plaque was measured three times and the average value was used for analysis.
After undergoing ultrasound examination, the patients were followed up for 30 days and their clinical changes after cerebral infarction were assessed. They were then divided into a deterioration group and a non-deterioration group based on the presence or absence of clinical deterioration. Deterioration refers to the progression of disease within 30 days following the initial episode of cerebral infarction. This may manifest as a newly detected infarct or an increase in infarct size on CT or MRI, and an elevated NIHSS score compared to baseline.
2.3 Statistical analysis
Data analysis was performed using SPSS 22.0. Measurement data that followed a normal distribution, including age, plaque size, and strain value, were expressed as x ± s. Comparisons between two independent samples were conducted using the independent samples t-test. Enumeration data were compared using the x2 test. Logistic regression was applied to analyze the influence of carotid plaque elastography results on the disease changes after cerebral infarction. The ROC curve and the area under the curve (AUC) were applied to determine the predictive power of carotid plaque elasticity for clinical changes after cerebral infarction, with p < 0.05 indicating statistically significant.
3 Results
3.1 Baseline demographics
A total of 116 patients diagnosed with cerebral infarction between February 2022 and December 2023 were selected for this study, 3 of whom were screen failures, 3 of whom were lost to follow-up. Ultimately, 110 patients were included in the final analysis, consisting of 83 (75.5%) males and 27 (24.5%) females with an average age of 60.02 ± 10.67 years. Among them, 87 (79.1%) had hypertension, 54 (49.1%) had diabetes, 97 (88.2%) had dyslipidemia, and 64 (58.2%) had a history of smoking. Based on clinical changes after cerebral infarction, 48 patients were categorized into the deterioration group and 62 were categorized in the non-deterioration group. No significant differences were observed between the two groups in terms of baseline demographics (Table 1).
Table 1
| Baseline characteristics | Deterioration group | Non-deterioration group | Test value | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Cases | 48 | 62 | ||
| Gender (Male/Female) | 39 (81.3%)/9 (18.7%) | 44 (71.0%)/18 (29.0%) | 1.54 | 0.21 |
| Age (Years) | 58.60 ± 10.91 | 61.11 ± 10.43 | 1.23 | 0.22 |
| Smoking (Yes/No) | 29 (60.4%)/19 (39.6%) | 35 (56.5%)/27 (43.5%) | 0.18 | 0.68 |
| Diabetes (Yes/No) | 30 (62.5%)/18 (37.5%) | 33 (53.2%)/29 (46.8%) | 0.95 | 0.33 |
| Hypertension (Yes/No) | 38 (79.2%)/10 (20.8%) | 49 (79.0%)/13 (21.0%) | 0.00 | 0.98 |
| Dyslipidemia (Yes/No) | 42 (87.5%)/6 (12.5%) | 55 (88.7%)/7 (11.3%) | 0.04 | 0.85 |
Comparison of baseline demographics between the deterioration group and the non-deterioration group.
3.2 Basic characteristics of plaques
There were no significant differences between the deterioration group and the non-deterioration group in plaque length, thickness, echogenicity or surface morphology (p > 0.05; Table 2).
Table 2
| Characteristics | Deterioration group | Non-deterioration group | Test value | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of cases | 48 | 62 | ||
| Plaque length (mm) | 12.22 ± 5.32 | 14.64 ± 7.48 | 1.89 | 0.06 |
| Plaque thickness (mm) | 2.46 ± 0.82 | 2.64 ± 0.87 | 0.34 | 0.74 |
| Echogenicity (hypoechoic/isoechoic/mixed echoic) | 1 (2.1%)/19 (39.6%)/28 (58.3%) | 2 (3.2%)/20 (32.3%)/40 (64.5%) | 0.71 | 0.70 |
| Surface morphology (smooth/irregular) | 11 (22.9%)/37 (77.1%) | 13 (21.0%)/49 (79.0%) | 0.06 | 0.81 |
Basic characteristics of plaques in the deterioration group and the non-deterioration group after cerebral infarction.
3.3 Strain elastographic characteristics of plaques
Ultrasound strain elastography of carotid plaques revealed that plaques predominantly exhibited yellow-green or green color coding (Figure 1), while the arterial walls were predominantly coded as red. Comparison of plaque strain elastographic characteristics between the deterioration and non-deterioration groups after cerebral infarction demonstrated that statistically significant differences was found in carotid plaque strain elastography value and plaque stiffness (p < 0.05). However, no statistically significant difference was found in arterial wall elasticity value (p > 0.05). See Table 3 for details.
Figure 1

The carotid plaque strain elastography showed plaque strain elastography value and arterial wall strain elastography value.
Table 3
| Indicators | Deterioration group | Non-deterioration group | Test value | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of cases | 48 | 62 | ||
| Plaque strain elastography value | 1.16 ± 0.40 | 1.72 ± 0.58 | 5.74 | <0.001 |
| Arterial Wall strain elastography value | 0.53 ± 0.16 | 0.59 ± 0.18 | 1.95 | 0.053 |
| Plaque stiffness | 2.33 ± 0.97 | 3.04 ± 1.00 | 3.75 | <0.001 |
Comparison of the strain elastographic characteristics of plaques between the deterioration group and the non-deterioration group.
3.4 Binary logistic regression analysis
Clinical progression after cerebral infarction (coded as 0 = no deterioration, 1 = deterioration) served as the dependent variable. Separate models were constructed for each independent variable: carotid plaque elasticity, vessel wall elasticity, and plaque hardness. The model assumptions, including linearity in the logit, were met. Binary logistic regression identified carotid plaque elasticity and plaque hardness as significant independent predictors of clinical progression (p < 0.05).
3.5 ROC curve analysis
ROC curve analysis was leveraged to analyze the role of plaque elasticity value, arterial wall elasticity value and plaque stiffness in predicting clinical deterioration after cerebral infarction. The results indicated that the AUCs for plaque elasticity value, arterial wall elasticity value and plaque stiffness were 0.790 (95%CI 0.707–0.873), 0.608 (95%CI 0.501–0.715), and 0.740 (95%CI 0.644–0.835), respectively (Figure 2).
Figure 2
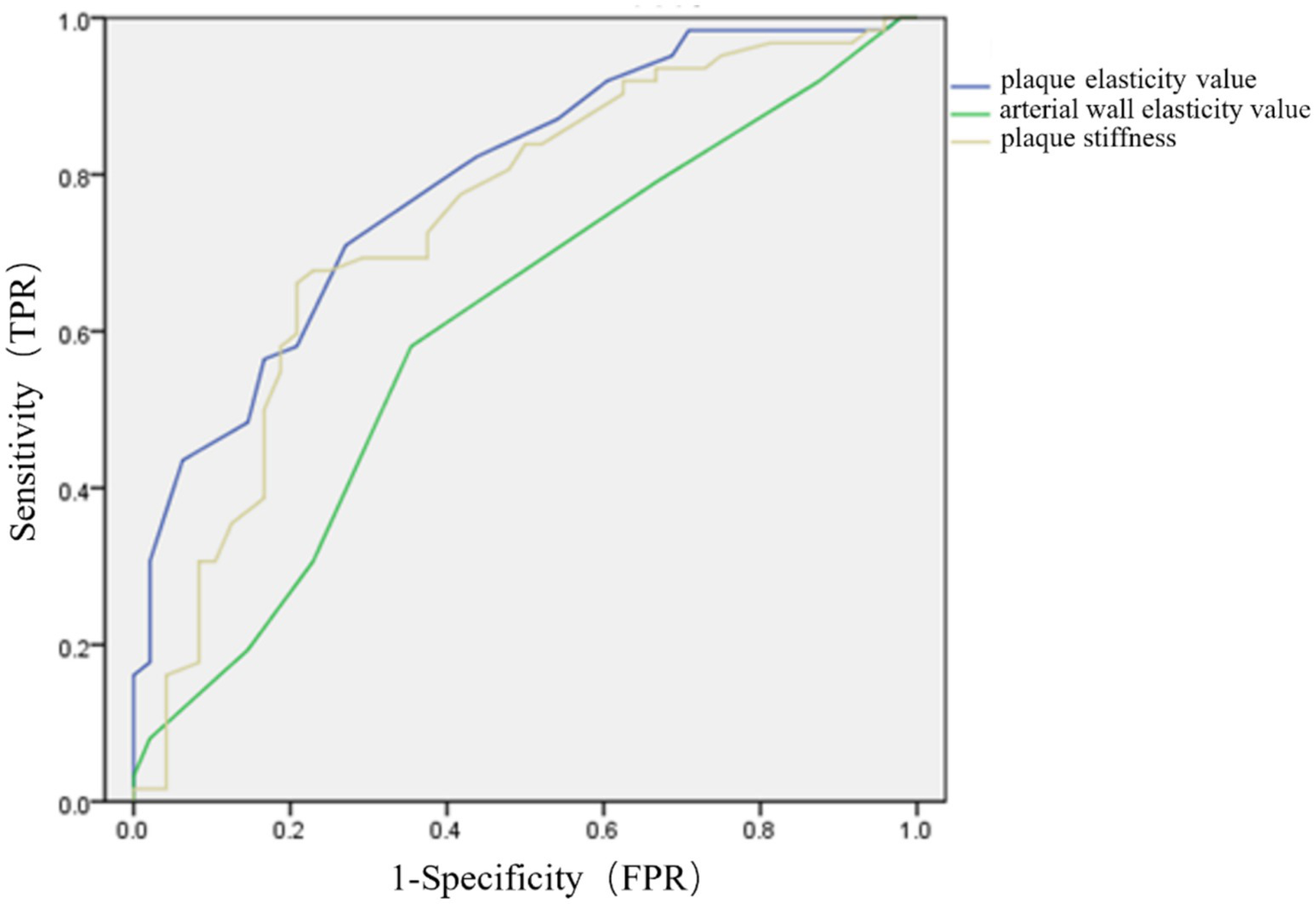
ROC curves for plaque elasticity value, arterial wall elasticity value and plaque stiffness in predicting clinical changes after cerebral infarction.
4 Discussion
Cerebral infarction is a leading cause of permanent disability, while vulnerable carotid plaques are recognized as a significant contributor to cerebral infarction (10, 11). Recent studies have identified common markers of plaque vulnerability—such as plaque thickness, size, and surface morphology—as being associated with the occurrence of ischemic cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events (12, 13). Routine ultrasound can determine the size, location, number, surface morphology of plaques and the degree of carotid stenosis, even the ulceration on the surface and bleeding within the plaques, but it has limited value in judging the nature of plaques (14, 15). Contrast-enhanced carotid plaque ultrasound provides information on intraplaque neovascularization, but is costly, time-consuming and carries the risk of allergies, limiting its clinical application (16). Ultrasound strain elastography, a recent ultrasound technique, has been widely used for organs such as the breast, thyroid and liver. Emerging evidence has suggested that the elastographic characteristics of plaques, including plaque stiffness, are associated with the occurrence of cerebral infarction, but few studies have investigated its potential in assessing clinical changes following cerebral infarction (17).
The basic principle of elastography is to apply an internal (including spontaneous) or external dynamic or static/quasi-static mechanical excitation to tissues. Under the physical laws of elasticity and biomechanics and so on. the tissues respond with certain changes in displacement, strain or velocity distribution, and so on. Common techniques include strain elastography and shear wave elastography, etc. (18) Studies have shown that soft plaques are lipid-rich, so they have low stiffness and high strain under compression, and mainly appear as yellow-green or green on elastographic imaging (19). In contrast, calcified plaques are lipid-poor and mainly composed of calcium, so they have high stiffness and low strain under compression and appear as blue. Mixed plaques are in between and present a mosaic pattern of blue and green.
In this study, patients with cerebral infarction who underwent carotid plaque strain elastography were classified into a deterioration group and a non-deterioration group based on clinical progression following infarction. Elastographic imaging showed that the deterioration group had lower plaque elasticity values and plaque stiffness than the non-deterioration group, with statistically significant differences. This indicates that patients with different changes in their condition after cerebral infarction have different carotid plaque elasticity values and plaque hardness. We can assess the risk of short-term deterioration of the patient’s condition through the results of carotid plaque elastography. This may be attributed to the fact that vulnerable plaques had a soft texture and were more prone to rupture, which can result in microthrombosis and persistent cerebral infarction. The microemboli detachment caused by vulnerable carotid plaques was also recognized as an independent risk factor for stroke progression, neurological impairment, and poor outcomes in patients with acute ischemic stroke (20, 21).
In this study, ROC curve analysis was leveraged to assess the predictive power of carotid plaque strain elastography value, arterial wall elasticity value, and plaque stiffness for clinical deterioration after cerebral infarction. The AUCs were 0.790, 0.608, and 0.740, respectively. These findings indicated that carotid plaque strain elastography held significant value in predicting clinical progression after cerebral infarction, especially in terms of plaque elasticity value. This provided important insights for clinical assessment of disease progression after cerebral infarction, followed by timely intervention when necessary.
However, due to inconsistent pressure applied, manual compression during elastography may introduce variability in the resulting strain and displacement measurements, thereby affecting the research results. In this study, the probe was gently placed over the carotid plaque and the pressure required for elastography was provided by the natural pulsations of carotid artery. This approach partly reduced operator-induced variability. All patients selected for this study showed no evidence of ≥50% stenosis in the intracranial or extracranial carotid artery, thereby reducing the impact of hemodynamics on the elastography results. This study analyzed the largest carotid plaque ipsilateral to the cerebral infarction. Although causation by this specific plaque cannot be confirmed, its characteristics reflect the patient’s overall atherosclerotic burden, providing useful information for clinical management. Given its single-center design, external validation via large-scale, multi-center studies is required. This analysis did not include a multivariable model to confirm if the relationship between plaque elastographic features and clinical deterioration is independent of covariates; addressing this limitation through a multimodal model will be our next research step.
5 Conclusion
In conclusion, carotid plaque ultrasound strain elastography provides a valuable adjunct for assessing plaque vulnerability. Patients experiencing clinical deterioration following cerebral infarction exhibit significantly lower plaque elasticity and lower plaque stiffness. Among these parameters, plaque elasticity value demonstrates enhanced predictive performance for post-cerebral infarction clinical deterioration. These findings may inform clinical intervention strategies for patients with cerebral infarction; however, multi-center studies with larger cohorts are required to validate the predictive utility of these parameters.
Statements
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Ethics Committee of Beijing Chaoyang Hospital, Capital Medical University. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
ML: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. SW: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. QS: Resources, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. HG: Conceptualization, Data curation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
We gratefully thank all participants for their collaboration in this study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1.
Sevco TJ Patel MK Deurdulian C . Carotid ultrasound. Radiol Clin North Am. (2025) 63:137–52. doi: 10.1016/j.rcl.2024.07.011
2.
Wang B Chen Y Qiao Q Dong L Xiao C Qi Z . Evaluation of carotid plaque vulnerability with different echoes by shear wave elastography and ceus. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. (2023) 32:106941. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2022.106941
3.
Zhang L Jia C Gu S Chen J Wu R . Intraplaque neovascularization combined with plaque elasticity for predicting ipsilateral stroke in patients with asymptomatic mild carotid stenosis. Quant Imaging Med Surg. (2024) 14:4815–24. doi: 10.21037/qims-24-202
4.
Kernan WN Ovbiagele B Black HR Bravata DM Chimowitz MI Ezekowitz MD et al . Guidelines for the prevention of stroke in patients with stroke and transient ischemic attack: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. (2014) 45:2160–236. doi: 10.1161/STR.0000000000000024
5.
Mozaffarzadeh M Saris A Menssen J de Korte CL . Simultaneous coherent and displacement compounding for 2-D noninvasive carotid strain imaging: a proof of principle study. IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Control. (2024) 71:897–909. doi: 10.1109/TUFFC.2024.3399836
6.
Wu Y Li X Wang Z Zhang S Feng Y Sun L . Real-time elastography and contrast-enhanced ultrasound for evaluating adventitia in the early diagnosis of vulnerable plaques: an exploratory study based on histopathology. Transl Stroke Res. (2024) 15:545–55. doi: 10.1007/s12975-023-01141-9
7.
Zavodni AE Wasserman BA McClelland RL Gomes AS Folsom AR Polak JF et al . Carotid artery plaque morphology and composition in relation to incident cardiovascular events: the multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis (mesa). Radiology. (2014) 271:381–9. doi: 10.1148/radiol.14131020
8.
Cheng L Zheng S Zhang J Wang F Liu X Zhang L et al . Multimodal ultrasound-based carotid plaque risk biomarkers predict poor functional outcome in patients with ischemic stroke or tia. BMC Neurol. (2023) 23:13. doi: 10.1186/s12883-023-03052-6
9.
Demeure F Bouzin C Roelants V Bol A Verhelst R Astarci P et al . Head-to-head comparison of inflammation and neovascularization in human carotid plaques: implications for the imaging of vulnerable plaques. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. (2017) 10:10. doi: 10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.116.005846
10.
Kamtchum-Tatuene J Noubiap JJ Wilman AH Saqqur M Shuaib A Jickling GC . Prevalence of high-risk plaques and risk of stroke in patients with asymptomatic carotid stenosis: a meta-analysis. JAMA Neurol. (2020) 77:1524–35. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2020.2658
11.
Li Y Zheng S Zhang J Wang F He W . Multimodal ultrasound parameters aided carotid plaque risk stratification in patients with asymptomatic carotid stenosis. Acta Radiol. (2022) 63:278–86. doi: 10.1177/0284185121989189
12.
Meng Q Xie X Li L Jiang C Zhao K Bai Z et al . Assessment of neovascularization of carotid artery atherosclerotic plaques using superb microvascular imaging: a comparison with contrast-enhanced ultrasound imaging and histology. Quant Imaging Med Surg. (2021) 11:1958–69. doi: 10.21037/qims-20-933
13.
Zhang XG Xue J Yang WH Xu XS Sun HX Hu L et al . Inflammatory markers as independent predictors for stroke outcomes. Brain Behav. (2021) 11:e1922. doi: 10.1002/brb3.1922
14.
Song Y Dang Y Wang J Cai H Feng J Zhang H et al . Carotid intraplaque neovascularization predicts ischemic stroke recurrence in patients with carotid atherosclerosis. Gerontology. (2021) 67:144–51. doi: 10.1159/000511360
15.
Kauw F de Jong PA Takx R de Jong H Kappelle LJ Velthuis BK et al . Effect of intravenous thrombolysis in stroke depends on pattern of intracranial internal carotid artery calcification. Atherosclerosis. (2021) 316:8–14. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2020.11.019
16.
Bulum A Ivanac G Manduric F Pfeifer L Bulum M Divjak E et al . Contribution of ultrafast ultrasound and shear wave elastography in the imaging of carotid artery disease. Diagnostics (Basel). (2022) 12:1168. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12051168
17.
Mitchell C Korcarz CE Gepner AD Kaufman JD Post W Tracy R et al . Ultrasound carotid plaque features, cardiovascular disease risk factors and events: the multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis. (2018) 276:195–202. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2018.06.005
18.
Li M Guo R . Study on the consistency of angiogenesis in carotid plaque evaluated by contrast-enhanced ultrasound and superb microvascular imaging and its correlation with stroke occurrence. J Ultrasound Med. (2024) 43:771–9. doi: 10.1002/jum.16409
19.
Ooi YC Gonzalez NR . Management of extracranial carotid artery disease. Cardiol Clin. (2015) 33:1–35. doi: 10.1016/j.ccl.2014.09.001
20.
Saba L Saam T Jager HR Yuan C Hatsukami TS Saloner D et al . Imaging biomarkers of vulnerable carotid plaques for stroke risk prediction and their potential clinical implications. Lancet Neurol. (2019) 18:559–72. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(19)30035-3
21.
Hagiwara Y Takao N Usuki N Yoshie T Takaishi S Shimizu T et al . Carotid ultrasound using superb microvascular imaging to identify patients developing in-stent restenosis after cas. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. (2022) 31:106627. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2022.106627
Summary
Keywords
carotid plaque, ultrasound strain elastography, cerebral infarction, clinicaldeterioration, short-term prognosis
Citation
Li M, Weng S, Song Q and Ge H (2025) Study on the prediction of short-term clinical changes after cerebral infarction using carotid plaque ultrasound strain elastography. Front. Neurol. 16:1652157. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1652157
Received
23 June 2025
Accepted
22 August 2025
Published
04 September 2025
Volume
16 - 2025
Edited by
Mónica Hernández, University of Zaragoza, Spain
Reviewed by
Zhiqun Bai, The First Affiliated Hospital of China Medical University, China
Lydia Foster, Medical University of South Carolina, United States
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Li, Weng, Song and Ge.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Huiyu Ge, ghyzmw@163.com
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.