Abstract
Introduction:
Blood-based biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease (AD), such as phosphorylated tau (p-tau181, p-tau217) and amyloid beta (Aβ), have the potential to serve as screening tools for probable AD in the elderly population.
Methods:
AD screening [Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) and Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA)] was conducted among very elderly individuals residing in a nursing community and a geriatric hospital. Based on cognitive evaluation, participants were categorized into two groups: cognitively normal (n = 62) and probable AD (n = 78). Plasma concentrations of Aβ42, Aβ40, p-tau181, p-tau217, and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) were measured using the single molecule array (Simoa) platform. Group comparisons of plasma biomarker levels were performed, and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analyses were conducted for each biomarker relative to AD diagnosis.
Results:
Significant differences were observed in plasma p-tau181, p-tau217, and GFAP levels between the cognitively normal and probable AD groups (p < 0.01). In contrast, Aβ42, Aβ40, and the Aβ42/Aβ40 ratio showed no significant differences (p > 0.01). The area under the ROC curve (AUC) was 0.886 for p-tau181, 0.655 for p-tau217, and 0.869 for GFAP.
Discussion:
Plasma biomarkers p-tau181, p-tau217, and GFAP demonstrate clinical utility in distinguishing AD from normal cognition, suggesting that blood-based testing may serve as a feasible screening tool for early identification of AD in very elderly populations.
Introduction
With the rising incidence of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) in China, early screening and diagnosis have become increasingly important. Currently, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) biomarkers and amyloid positron emission tomography (PET) imaging are not widely applied in clinical practice due to their invasiveness, limited accessibility, and high costs. By contrast, blood-based biomarkers offer a more practical approach for screening and diagnosing AD, particularly in the context of disease-modifying therapies (DMTs) such as anti-amyloid immunotherapies, which primarily target individuals with mild cognitive impairment (MCI) or early-stage AD. Compared with CSF or PET examinations, plasma biomarkers are less invasive, more cost-effective, and easier to implement at the community level. As DMTs continue to develop, blood testing could serve as an efficient preliminary tool to identify patients with underlying AD pathology and to determine who should subsequently undergo confirmatory CSF or PET testing before initiating therapy.
Recent studies have demonstrated the diagnostic potential of several plasma analytes. For example, plasma Aβ42/Aβ40 correlates well with CSF biomarkers and amyloid PET, while plasma glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) has been associated with increased dementia risk and accelerated cognitive decline. Furthermore, phosphorylated tau species, particularly p-tau181 and p-tau217, have been proposed as promising prescreening biomarkers, as they are elevated in Aβ-positive compared with Aβ-negative individuals (1). Both p-tau181 and p-tau217 exhibit strong diagnostic performance in distinguishing AD from cognitively normal individuals and from other forms of dementia. In older cohorts, these markers may help identify individuals with underlying amyloid and tau pathology (2). Pathologically, phosphorylated tau and Aβ are key components of neurofibrillary tangles and amyloid plaques, respectively. Plasma p-tau181 levels are reported to be 1.5–3.5 times higher in AD compared with cognitively normal controls, and 1.8–3.7 times higher in AD compared with clinically and pathologically confirmed frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD) (3–5). CSF p-tau217, in particular, has demonstrated superior accuracy in differentiating AD dementia from other neurodegenerative diseases. When measured using the same immunoassay, CSF p-tau217 showed stronger correlations with amyloid- and tau-PET signals than p-tau181 (6). Similarly, large cohort studies have shown that plasma p-tau217 performs comparably to CSF p-tau217 and tau-PET, and outperforms plasma p-tau181 in clinical AD diagnosis (7).
However, very elderly individuals are often less willing to undergo invasive CSF testing or expensive PET imaging, due to factors such as frailty, comorbidities, and limited accessibility. To address this, we employed the commercially available Quanterix HD-X single molecule array (Simoa) platform, which measures plasma Aβ42, Aβ40, GFAP, p-tau181, and p-tau217. In a sample of very elderly individuals residing in nursing communities and geriatric hospitals, we combined plasma biomarker measurements with cognitive assessments to evaluate whether blood-based biomarkers retain diagnostic value for AD in this age group. The aim of this study was to investigate whether plasma biomarkers, including p-tau181, p-tau217, Aβ42, Aβ40, and GFAP, can serve as diagnostic tools for distinguishing AD from normal cognition in very elderly individuals.
Methods
Participants
Data were collected between January and May 2025 from a geriatric hospital and a nursing community. The cohort included cognitively normal controls (n = 62; mean age = 86.0 ± 5.72 years) and patients with clinically diagnosed AD (n = 78; mean age = 85.0 ± 5.35 years). AD diagnosis was made based on recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease (8). All the patients had completed neuroimaging of structural MRI detection, and a small number of patients underwent cerebrospinal fluid biomarker testing or amyloid-β PET detection.
All AD participants presented with mild, moderate, or severe cognitive impairment, with Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) scores ranging from 0 to 23. None of the participants had a history of severe disease other than AD. The cognitively normal control group (n = 62) was defined by MMSE scores ≥ 27. There were no significant differences in age or sex distribution between the two groups.
Inclusion criteria required completion of both plasma biomarker measurements (Aβ42, Aβ40, Aβ42/Aβ40, p-tau217, p-tau181, and GFAP) and cognitive assessments (MMSE and MoCA). All participants provided written informed consent at the time of recruitment. The study protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of Beijing Geriatric Hospital.
Procedures
Blood samples were collected in the clinic after an overnight fast, centrifuged, aliquoted, and stored at −80 °C until analysis. Plasma biomarker measurements were performed at the Beijing Kingmed Clinical Laboratory using the single molecule array (Simoa) platform (Quanterix Corporation). The principles and technology of Simoa have been previously described (9). Additional details of the Neurology 4-Plex E assay for Aβ and tau quantification are available on the manufacturer’s website.1 Plasma Aβ40, Aβ42, and GFAP levels were measured using the Simoa Neurology 4-Plex E Advantage Kit (N4PE, item #103670). Plasma p-tau181 concentrations were measured on the HD-X Analyzer (Quanterix Corporation) with the Simoa p-tau181 Advantage Kit, version 2, following the manufacturer’s instructions. Plasma p-tau217 concentrations were measured on the HD-X Analyzer (Quanterix Corporation) using the Simoa pTau-217 Advantage Kit (Quanterix Corporation) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. All assays were performed by a board-certified laboratory technician using a single batch of reagents to minimize variability.
Statistical analysis
Data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD) or as absolute numbers. Group comparisons of clinical and demographic characteristics, cognitive assessments, and plasma biomarkers (AD vs. NC) were conducted using SPSS software. Between-group differences in plasma biomarkers were evaluated to control for potential confounding effects, using an ANCOVA, with age, sex, and MoCA entered as covariates. Spearman correlation analyses were performed to examine the associations between plasma p-tau181, p-tau217, and GFAP levels and MoCA scores among AD participants. The diagnostic performance of plasma biomarkers in discriminating AD from NC was assessed using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis, with sensitivity and specificity calculated from the area under the curve (AUC). A two-tailed p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Result
A total of 140 participants were analyzed. No significant correlations between age or sex and plasma biomarker levels were detected in either group. Clinical and demographic characteristics, along with plasma biomarker data, are summarized in Table 1.
Table 1
| NC (n = 62) | AD (n = 78) | t-value | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 86 ± 5.72 | 85 ± 5.35 | 0.341 | |
| Sex, male | 35 | 43 | ||
| MoCA | 26 ± 1.76 | 6 ± 3.58 | −8.209 | 0.000** |
| P-tau181 | 2.92 ± 1.74 | 5.62 ± 2.13 | −8.171 | 0.000** |
| P-tau217 | 5.63 ± 8.25 | 15.72 ± 23.70 | −3.356 | 0.001** |
| GFAP | 24.30 ± 16.13 | 67.92 ± 61.76 | −5.588 | 0.000** |
| Aβ42 | 51.59 ± 44.65 | 83.37 ± 110.92 | −1.911 | 0.061 |
| Aβ40 | 300.37 ± 214.72 | 339.55 ± 207.14 | −0.890 | 0.378 |
| Aβ42/Aβ40 | 0.36 ± 0.78 | 0.79 ± 2.94 | −1.058 | 0.294 |
Participants’ characteristics and plasma biomarkers assessed by Simoa platforms.
** p < 0.01 and *p < 0.05.
Plasma levels of p-tau181, p-tau217, and GFAP were significantly higher in AD patients compared with NC (p < 0.01). In contrast, no significant differences were observed in plasma Aβ42, Aβ40, or the Aβ42/Aβ40 ratio between groups (Figure 1).
Figure 1
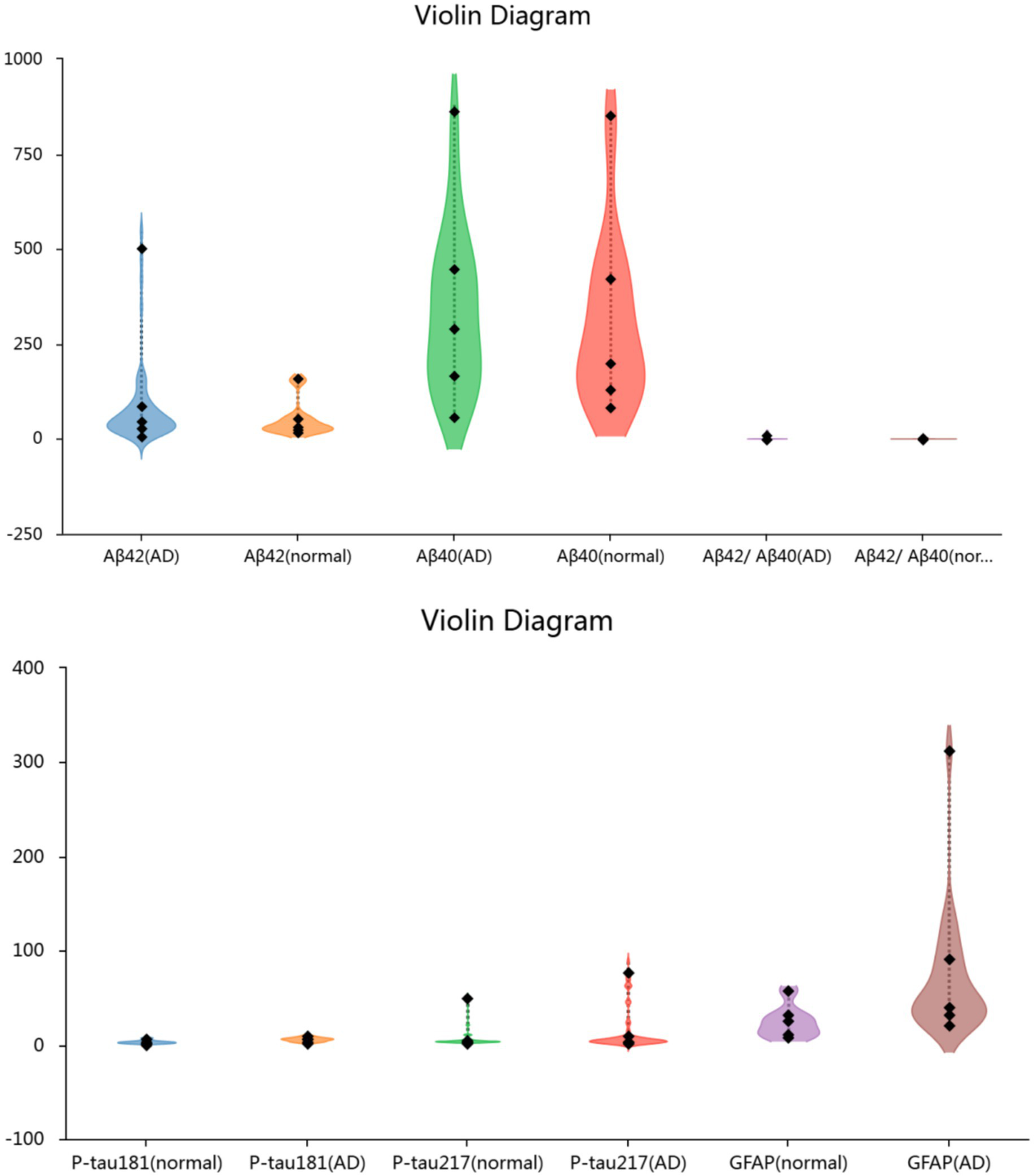
Plasma biomarkers levels in the two groups of participants.
Correlation analyses demonstrated negative associations between MoCA scores and plasma biomarker levels of p-tau181 (p < 0.001), p-tau217 (p = 0.024), and GFAP (p = 0.002) among AD patients (Table 2).
Table 2
| MoCA | ||
|---|---|---|
| P-tau181 | Pearson’s R | −0.482 |
| p-value | 0.000** | |
| P-tau217 | Pearson’s R | −0.226 |
| p-value | 0.024* | |
| GFAP | Pearson’s R | −0.303 |
| p-value | 0.002** |
The Pearson’s relationship between plasma biomarkers and MoCA scores.
** p < 0.01 and *p < 0.05.
The ROC analysis revealed that the strongest diagnostic performance was achieved by p-tau181 (AUC = 0.886, 95% CI: 0.821–0.951) and GFAP (AUC = 0.869, 95% CI: 0.803–0.935). In contrast, p-tau217 (AUC = 0.655, 95% CI: 0.555–0.756) and Aβ42 (AUC = 0.605, 95% CI: 0.499–0.710) demonstrated lower diagnostic accuracy. The remaining biomarkers showed AUCs ranging from 0.548 for the Aβ42/Aβ40 ratio (95% CI: 0.438–0.658) to 0.578 for Aβ40 (95% CI, 0.470–0.685) (Figure 2 and Table 3).
Figure 2
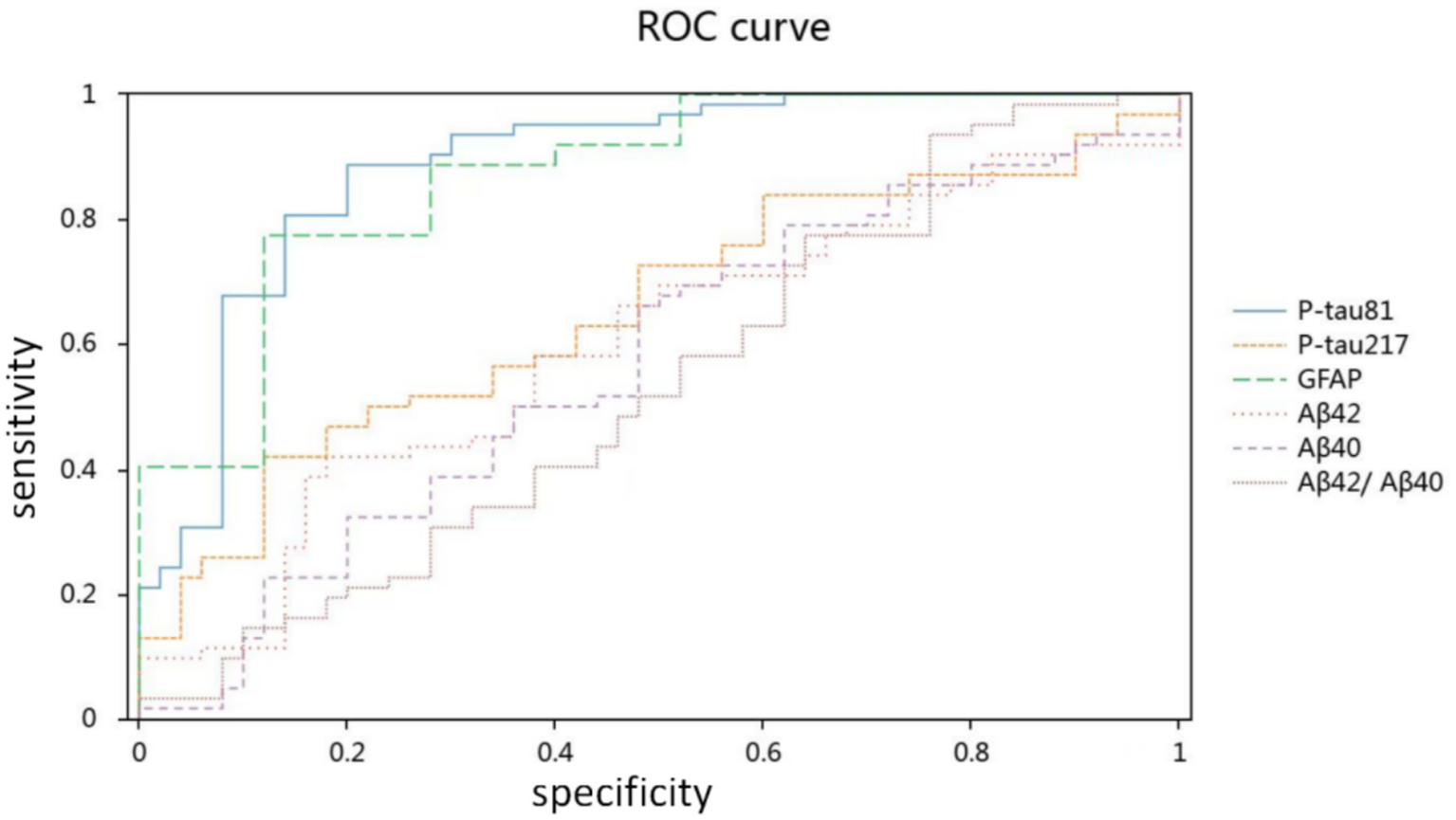
Diagnostic accuracy of plasma biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease.
Table 3
| AUC | p | 95% CI | |
|---|---|---|---|
| P-tau181 | 0.886 | 0.000** | 0.821–0.951 |
| P-tau217 | 0.655 | 0.005** | 0.555–0.756 |
| GFAP | 0.869 | 0.000** | 0.803–0.935 |
| Aβ42 | 0.605 | 0.058 | 0.499–0.710 |
| Aβ40 | 0.578 | 0.158 | 0.470–0.685 |
| Aβ42/Aβ40 | 0.548 | 0.385 | 0.438–0.658 |
AUC for plasma biomarkers in ROC.
** p < 0.01 and *p < 0.05.
Discussion
In 2024 the Alzheimer’s Association Workgroup revised the diagnostic and staging criteria for AD. The updated framework highlights core 1 biomarkers, including CSF or plasma Aβ42, p-tau217, p-tau181, p-tau231, and amyloid PET, all of which map onto either the amyloid beta pathway or the AD tauopathy pathway (10). Core 2 biomarkers include tau proteinopathy markers such as microtubule-binding region tau (MTBR-tau243) and p-tau205, which correlate more strongly with tau PET than with amyloid PET (11, 12). The revised framework also emphasizes other biomarkers that reflect non-specific processes in AD pathophysiology. These include CSF or plasma neurofilament light chain (NfL) and GFAP, which indicate axonal injury, neuronal dysfunction, synaptic degeneration, and neuroinflammation. In addition, the new criteria introduced biomarker categories for vascular brain injury (V) and alpha-synucleinopathy (S). These categories are relevant to AD diagnosis and staging because AD frequently co-occurs with other pathologies and comorbid processes play an important role in disease progression (10). We refer to this framework in order to situate our findings within the most recent international consensus on biomarker-based diagnosis, rather than to propose a novel classification. The biomarker-positive cognitively normal individuals should be considered as being at risk for AD, but cannot be diagnosed with AD according to recommendations of the International Working Group (13). These new guides highlight the diagnostic value of plasma biomarkers, demonstrating their growing recognition in clinical practice, which also underscores the value of our research.
Our results confirmed that tau-related plasma biomarkers were altered in very elderly AD patients, in line with previous studies (14–16). Among the tau isoforms, p-tau181 and p-tau217 have consistently been highlighted as strong diagnostic markers in both CSF and plasma (7, 17). Brickman et al. (16) measured plasma biomarkers in 113 autopsied participants, 29% of whom had high AD neuropathological changes, and in 300 clinically evaluated individuals, 42% of whom were diagnosed with AD. Their results indicated that plasma p-tau181, p-tau217, and NfL concentrations were elevated in both pathologically and clinically diagnosed AD. In addition, a decreased Aβ42/Aβ40 ratio together with increased p-tau217 and p-tau181 was associated with subsequent AD diagnosis (16). In our cohort of very elderly participants, plasma p-tau181 and GFAP demonstrated stronger diagnostic performance than p-tau217. This finding contrasts with previous reports where p-tau217 outperformed other plasma markers, particularly in younger or mixed-age cohorts. Several factors may explain this discrepancy. First, the relatively small sample size in our study may have limited statistical power. Second, very elderly individuals often present with multiple comorbid pathologies, such as vascular brain injury and neuroinflammation, which may alter biomarker dynamics and attenuate the discriminative value of p-tau217. Janelidze et al. (4) have established the high diagnostic accuracy of p-tau217 but also noted variations in performance across cohorts, which could be influenced by age and comorbid factors. A higher prevalence of co-pathologies (vascular lesions or TDP-43 pathology) and altered blood–brain barrier dynamics might differentially affect the sequestration, clearance, or expression of these p-tau isoforms in biofluids, thereby modulating their diagnostic performance. Third, technical factors including assay sensitivity and batch effects may also have contributed. These considerations suggest that our findings should be interpreted with caution, and further validation in larger longitudinal cohorts is warranted.
Previous studies in younger or mixed-age cohorts consistently reported that plasma p-tau217 outperformed p-tau181 and amyloid-related markers in detecting early AD pathology (6, 7, 16, 18). In contrast, our results suggest that in a very elderly cohort, p-tau181 and GFAP may provide stronger diagnostic accuracy. Importantly, several independent studies have also supported the robustness of p-tau181 and GFAP as biomarkers in clinical and elderly populations. Baiardi et al. (19) demonstrated that both plasma p-tau181 and GFAP show strong diagnostic value in dementia screening cohorts. Ingannato et al. (20) further reported that GFAP and p-tau181 levels increase across SCD, MCI, and AD, highlighting their utility in prodromal and symptomatic stages. GFAP, in particular, has been validated as an astrocytic marker closely associated with amyloid pathology (21), and has shown stability in longitudinal tracking of AD-related decline (22). Moreover, a recent community-based study in older adults found that elevated baseline p-tau181 and GFAP—but not p-tau217—were more strongly associated with future dementia onset in individuals aged 78 years and above (23).
Although plasma p-tau217 has been widely validated and recently approved by the FDA for clinical use, our findings suggest that its discriminative accuracy may be attenuated in very elderly populations compared with p-tau181 and GFAP. On May 16, 2025, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the first in vitro diagnostic device, the Lumipulse G pTau217/β-Amyloid 1–42 Plasma Ratio, for clinical use to aid in the diagnosis of AD (24). The FDA evaluation was based on data from a multicenter clinical study involving 499 plasma samples collected from cognitively impaired adults. Plasma test results using the Lumipulse G pTau217/β-amyloid 1-42 plasma ratio were compared with amyloid PET scans and CSF biomarkers. In this study, 91.7% of individuals with positive plasma results had evidence of amyloid plaques confirmed by PET or CSF, whereas 97.3% of those with negative plasma results were amyloid-negative by PET or CSF. Plasma phosphorylated tau 217 (p-tau217) has been shown to be one of the most accurate diagnostic markers for AD. Both Lumipulse and single molecule array (Simoa) technologies are widely used to measure plasma p-tau217 and p-tau181 levels. In a head-to-head comparison between Lumipulse and ALZpath Simoa assays, plasma p-tau217 demonstrated excellent diagnostic accuracy for detecting AD. The two platforms showed comparable performance in distinguishing AD from other neurodegenerative diseases (18).
Simoa technology was applied to measure plasma biomarkers in our study. In recent years, low-sensitivity plasma assays have been replaced by ultra-sensitive platforms such as Mesoscale Discovery (MSD), Simoa, and immunoprecipitation-mass spectrometry (IP-MS), all of which offer improved accuracy in detecting plasma biomarkers of AD (6, 25–27). Further validation is still required to determine which of these methods can be most effectively promoted for clinical use. Electrochemiluminescence (ECL) immunoassay and Simoa currently represent the most promising approaches, and the development of accurate and efficient reagent kits will also be critical for precise biomarker detection. Beyond Aβ42 or Aβ40, the diagnostic accuracy of plasma p-tau217 for detecting Aβ pathology has been demonstrated in several studies (28–31). However, our findings indicated that plasma p-tau181 and GFAP were more accurate than p-tau217 in distinguishing cognitive impairment in the very elderly population. This discrepancy may reflect the relatively small sample size in our study, or it may indicate that AD patients in advanced age groups present different biomarker profiles compared with younger populations. Taken together, our results suggest that plasma p-tau217, p-tau181, and GFAP have diagnostic value in distinguishing AD from normal cognition in the very elderly population. The cross-sectional design does not allow conclusions regarding predictive value, and further longitudinal studies are needed.
The difference in plasma Aβ levels between the patient group and the control group did not reach statistical significance. A part of AD patients included in this study had confirmed β-amyloid pathology via CSF or PET imaging. This lack of significant difference may be attributed to the limited sensitivity of the Aβ assay kit used, which could have impeded the accurate detection of trace amounts of Aβin plasma. However, the possibility cannot be ruled out that some patients clinically diagnosed with AD may actually have other underlying neuropathologies, such as primary age-related tauopathy (PART) which is an Aβ-independent accumulation of neurofibrillary degeneration in medial temporal lobe structures. The cognitive status in PART subjects has been shown to be related to the overall hippocampal p-tau burden, as well as the presence of additional comorbid neuropathologic findings (32).
Limitations of this study should be acknowledged. First, the sample size was relatively small, which may have limited statistical power to detect more subtle biomarker effects. Second, plasma biomarkers were not validated against CSF or PET measures in this very elderly cohort. Most participants were unwilling or unable to undergo lumbar puncture or amyloid/tau PET imaging due to frailty, comorbidities, and limited accessibility, so diagnosis was based on clinical criteria according to the NIA–AA 2011 guidelines rather than biomarker confirmation. This limits the strength of claims regarding diagnostic reliability. Third, normative reference values and cut-off points for plasma biomarkers were not established, which constrains clinical applicability. Taken together, these limitations underscore the need for replication in larger, longitudinal, and multimodal studies with CSF or PET validation and standardized thresholds to confirm the diagnostic accuracy of plasma biomarkers in very elderly populations.
Statements
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Beijing Geriatric Hospital (BGH) Ethics Committee. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation in this study was provided by the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin.
Author contributions
SZ: Funding acquisition, Writing – original draft, Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing. HW: Data curation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Investigation, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. LM: Supervision, Project administration, Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization, Writing – original draft. LZ: Data curation, Methodology, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. LL: Methodology, Supervision, Data curation, Writing – review & editing, Investigation. XH: Methodology, Investigation, Writing – review & editing, Data curation, Project administration. TZ: Writing – review & editing, Data curation, Project administration, Methodology, Resources. RL: Data curation, Writing– review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 62177004).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Footnotes
References
1.
Mielke MM Frank RD Dage JL Jeromin A Ashton NJ Blennow K et al . Comparison of plasma phosphorylated tau species with amyloid and tau positron emission tomography, neurodegeneration, vascular pathology, and cognitive outcomes. JAMA Neurol. (2021) 78:1108–17. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2021.2293
2.
Thijssen EH La Joie R Strom A Fonseca C Iaccarino L Wolf A et al . Association of plasma P-tau217 and P-tau181 with clinical phenotype, neuropathology, and imaging markers in Alzheimer’s disease and frontotemporal lobar degeneration: a retrospective diagnostic performance study. Lancet Neurol. (2021) 20:739–52. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(21)00214-3
3.
Thijssen EH La Joie R Wolf A Strom A Wang P Iaccarino L et al . Diagnostic value of plasma phosphorylated tau181 in Alzheimer’s disease and frontotemporal lobar degeneration. Nat Med. (2020) 26:387–97. doi: 10.1038/s41591-020-0762-2
4.
Janelidze S Mattsson N Palmqvist S Smith R Beach TG Serrano GE et al . Plasma P-tau181 in Alzheimer’s disease: relationship to other biomarkers, differential diagnosis, neuropathology and longitudinal progression to Alzheimer’s dementia. Nat Med. (2020) 26:379–86. doi: 10.1038/s41591-020-0755-1
5.
Karikari TK Pascoal TA Ashton NJ Janelidze S Benedet AL Rodriguez JL et al . Blood phosphorylated tau 181 as a biomarker for Alzheimer’s disease: a diagnostic performance and prediction modelling study using data from four prospective cohorts. Lancet Neurol. (2020) 19:422–33. doi: 10.1016/s1474-4422(20)30071-5
6.
Janelidze S Stomrud E Smith R Palmqvist S Mattsson N Airey DC et al . Cerebrospinal fluid p-tau217 performs better than p-tau181 as a biomarker of Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Commun. (2020) 11:1683. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-15436-0
7.
Palmqvist S Janelidze S Quiroz YT Zetterberg H Lopera F Stomrud E et al . Discriminative accuracy of plasma Phospho-tau217 for Alzheimer disease vs other neurodegenerative disorders. JAMA. (2020) 324:772–81. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.12134
8.
McKhann GM Knopman DS Chertkow H Hyman BT Jack CR Jr Kawas CH et al . The diagnosis of dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease: recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. (2011) 7:263–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2011.03.005
9.
Lue LF Guerra A Walker DG . Amyloid beta and tau as Alzheimer’s disease blood biomarkers: promise from new technologies. Neurol Ther. (2017) 6:25–36. doi: 10.1007/s40120-017-0074-8
10.
Jack CR Jr Andrews JS Beach TG Buracchio T Dunn B Graf A et al . Carrillo MC Revised criteria for diagnosis and staging of Alzheimer’s disease: Alzheimer’s association workgroup. Alzheimers Dement. (2024) 20:5143–69. doi: 10.1002/alz.13859
11.
Horie K Barthélemy NR Spina S VandeVrede L He Y Paterson RW et al . CSF tau microtubule-binding region identifies pathological changes in primary tauopathies. Nat Med. (2022) 28:2547–54. doi: 10.1038/s41591-022-02075-9
12.
Salvadó G Horie K Barthélemy NR Vogel JW Binette AP Chen CD et al . Novel CSF tau biomarkers can be used for disease staging of sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 19:e075367. doi: 10.1002/alz.075367
13.
Dubois B Villain N Schneider L Fox N Campbell N Galasko D et al . Alzheimer disease as a clinical-biological construct-an international working group recommendation. JAMA Neurol. (2024) 81:1304–11. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2024.3770
14.
Rissman RA Langford O Raman R Donohue MC Abdel‐Latif S Meyer MR et al . Plasma Aβ42/Aβ40 and phospho-tau217 concentration ratios increase the accuracy of amyloid PET classification in preclinical Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. (2024) 20:1214–24. doi: 10.1002/alz.13542
15.
Wennström M Janelidze S Nilsson KPR Serrano GE Beach TG Dage JL et al . Cellular localization of p-tau217 in brain and its association with p-tau217 plasma levels. Acta Neuropathol Commun. (2022) 10:3. doi: 10.1186/s40478-021-01307-2
16.
Brickman AM Manly JJ Honig LS Sanchez D Reyes-Dumeyer D Lantigua RA et al . Plasma p-tau181, p-tau217, and other blood-based Alzheimer’s disease biomarkers in a multi-ethnic, community study. Alzheimers Dement. (2021) 17:1353–64. doi: 10.1002/alz.12301
17.
Suarez-Calvet M Karikari TK Ashton NJ Lantero Rodriguez J Mila-Aloma M Gispert JD et al . Novel tau biomarkers phosphorylated at T181, T217 or T231 rise in the initial stages of the preclinical Alzheimer’s continuum when only subtle changes in aβ pathology are detected. EMBO Mol Med. 12:e12921. doi: 10.15252/emmm.202012921
18.
Pilotto A Quaresima V Trasciatti C Tolassi C Bertoli D Mordenti C et al . Plasma p-tau217 in Alzheimer’s disease: lumipulse and ALZpath SIMOA head-to-head comparison. Brain. (2025) 148:408–15. doi: 10.1093/brain/awae368
19.
Baiardi S Quadalti C Mammana A Dellavalle S Zenesini C Sambati L et al . Diagnostic value of plasma p-tau181, NfL, and GFAP in a clinical setting cohort of prevalent neurodegenerative dementias. Alzheimer Res Ther. (2022) 14:153. doi: 10.1186/s13195-022-01093-6
20.
Ingannato A Bagnoli S Mazzeo S Giacomucci G Bessi V Ferrari C et al . Plasma GFAP, NfL and pTau 181 detect preclinical stages of dementia. Front Endocrinol. (2024) 15:1375302. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1375302
21.
Pereira JB Janelidze S Smith R Mattsson-Carlgren N Palmqvist S Teunissen CE et al . Plasma GFAP is an early marker of amyloid-β but not tau pathology in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain. (2021) 144:3505–16. doi: 10.1093/brain/awab223
22.
Ally M Sugarman MA Zetterberg H Blennow K Ashton NJ Karikari TK et al . Cross-sectional and longitudinal evaluation of plasma glial fibrillary acidic protein to detect and predict clinical syndromes of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. (2023) 15:e12492. doi: 10.1002/dad2.12492
23.
Valletta M Vetrano DL Rizzuto D Winblad B Canevelli M Andersson S et al . Blood biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease in the community: variation by chronic diseases and inflammatory status. Alzheimers Dement. (2024) 20:4115–25. doi: 10.1002/alz.13860
24.
Food and Drug Administration . FDA clears first blood test used in diagnosing Alzheimer’s disease. Silver Spring, MD: Food and Drug Administration (2025).
25.
Ashton NJ Brum WS Di Molfetta G Benedet AL Arslan B Jonaitis E et al . Diagnostic accuracy of a plasma phosphorylated tau 217 immunoassay for Alzheimer disease pathology. JAMA Neurol. (2024) 81:255–63. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2023.5319
26.
Gonzalez-Ortiz F Ferreira PCL González-Escalante A Montoliu-Gaya L Ortiz-Romero P Kac PR et al . A novel ultrasensitive assay for plasma p-tau217: performance in individuals with subjective cognitive decline and early Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. (2024) 20:1239–49. doi: 10.1002/alz.13525
27.
Mielke MM Aakre JA Algeciras-Schimnich A Proctor NK Machulda MM Eichenlaub U et al . Comparison of CSF phosphorylated tau 181 and 217 for cognitive decline. Alzheimers Dement. (2022) 18:602–11. doi: 10.1002/alz.12415
28.
Mendes AJ Ribaldi F Lathuiliere A Ashton NJ Janelidze S Zetterberg H et al . Head-to-head study of diagnostic accuracy of plasma and cerebrospinal fluid p-tau217 versus p-tau181 and p-tau231 in a memory clinic cohort. J Neurol. (2024) 271:2053–66. doi: 10.1007/s00415-023-12148-5
29.
Ashton NJ Puig-Pijoan A Milà-Alomà M Fernández-Lebrero A García-Escobar G González-Ortiz F et al . Plasma and CSF biomarkers in a memory clinic: head-to-head comparison of phosphorylated tau immunoassays. Alzheimers Dement. (2023) 19:1913–24. doi: 10.1002/alz.12841
30.
Kivisäkk P Fatima HA Cahoon DS Otieno B Chacko L Minooei F et al . Clinical evaluation of a novel plasma pTau217 electrochemiluminescence immunoassay in Alzheimer’s disease. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:629. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-51334-x
31.
Mundada NS Rojas JC Vandevrede L Thijssen EH Iaccarino L Okoye OC et al . Head-to-head comparison between plasma p-tau217 and flortaucipir-PET in amyloid-positive patients with cognitive impairment. Alzheimers Res Ther. (2023) 15:157. doi: 10.1186/s13195-023-01302-w
32.
Walker JM Orr ME Orr TC Thorn EL Christie TD Yokoda RT et al . Spatial proteomics of hippocampal subfield-specific pathology in Alzheimer’s disease and primary age-related tauopathy. Alzheimers Dement. (2023) 20:783–97. doi: 10.1002/alz.13484
Summary
Keywords
blood-based biomarkers, single molecule array (Simoa), p-tau181, p-tau217, GFAP
Citation
Zhang S, Wu H, Ma L, Li R, Zhang L, Liu L, He X and Zhao T (2025) The exploration of using plasma biomarkers of p-tau217 and p-tau181 for screening Alzheimer’s disease in very elderly people. Front. Neurol. 16:1668512. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1668512
Received
18 July 2025
Accepted
22 September 2025
Published
16 October 2025
Volume
16 - 2025
Edited by
Martin Paucar, Karolinska Institutet (KI), Sweden
Reviewed by
Antonio Tartaglione, Independent Researcher, La Spezia, Italy
Pankaj Kumar, BC Neuroimmunology Laboratory Inc., BC, Canada
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Zhang, Wu, Ma, Li, Zhang, Liu, He and Zhao.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Shouzi Zhang, lanczsz@126.com
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.