Abstract
Background:
Parkinson’s disease with mild cognitive impairment (PD-MCI) is one of the primary non-motor symptoms of Parkinson’s disease (PD). PD-MCI represents an early stage of cognitive impairment in PD and serves as a potential precursor to PDD. To date, research on the treatment of mild cognitive impairment in PD remains limited. Acupuncture, a classical therapeutic modality in Traditional Chinese Medicine, exhibits superior therapeutic outcomes to pharmacotherapy for mild cognitive impairment while avoiding drug-associated adverse effects.
Objective:
This randomized, single-blind clinical trial aims to evaluate the efficacy and safety of acupuncture for PD-MCI. To improve the credibility of acupuncture research evidence through employing a sham acupuncture device as a control.
Methods and analysis:
This is a prospective, sham-controlled, subject-blinded and assessor-blinded trial, which conducted at a single center in China. A total of 72 eligible PD-MCI volunteers will be randomized using a simple randomization method in a 1:1 ratio into the acupuncture group and the placebo acupuncture group to receive either acupuncture or placebo acupuncture for 20 sessions over a succession of 5 weeks. The primary outcome measure will be the Montreal Cognitive Assessment Scale (MoCA) score. The secondary outcome measures will be the scores of Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE), Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale Motor Examination (UPDRSIII) and the level of neurofilament light polypeptide (NfL) and glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF). The evaluation will be assessed before and after treatment.
Discussion:
This study represents the first randomized, single-blind clinical trial investigating acupuncture treatment for cognitive dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease. An auxiliary device designed by our team, featuring a flat-head needle and adjustable sleeve, will be used for placebo acupuncture procedure to achieve a single-blind effect. Serum NfL and GDNF levels will be incorporated to elucidate the mechanisms underlying acupuncture’s effects and explore specific biomarkers of PD. The aim of this study is to provide reliable clinical evidence for the treatment of PD-MCI and improve patients’ survival and quality of life.
Clinical trial registration:
https://www.chictr.org.cn/, identifier ChiCTR2400082082.
1 Introduction
Parkinson’s disease (PD) represents a progressive neurodegenerative disorder primarily affecting individuals aged 50 years and older. While its clinical manifestations are mainly characterized by bradykinesia, resting tremor, and rigidity, the disease’s substantial burden also often stems from its non-motor symptoms such as mental disorders, cognitive impairment, sleep disorders, and sensory disorders. Among these, Parkinson’s disease with mild cognitive impairment (PD-MCI) has emerged as a particularly significant concern, affecting 30–40% of PD patients and progressing to Parkinson’s disease dementia (PDD) at an annual rate of 6–15% (1). PD-MCI as both a clinical precursor and modifiable risk factor for PDD (2), highlighting the critical importance of early detection and intervention.
At present, the pathogenesis of PD-MCI remains incompletely understood. Relevant studies suggest the involvement of neurotransmitter system impairments, such as dopaminergic and cholinergic systems (3, 4). In clinical practice, while cholinesterase inhibitors and dopamine receptor agonists constitute the mainstay of PD-MCI pharmacotherapy, their clinical benefits remain suboptimal and are frequently accompanied by adverse effects. Therefore, more treatment options for PD-MCI need to be explored.
Acupuncture, as a well-established therapeutic approach in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), demonstrates clinical advantages including procedural simplicity and favorable safety characteristics. It has gained widespread clinical adoption as a non-pharmacological therapy. In recent years, many researches show that acupuncture can modulate the brain activities through Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and EEG (5–7). It was proved that acupuncture promotes cognitive function and affords neuroprotective effects against inflammation in animal experiment (8). Accumulated clinical evidence indicates that acupuncture can improve cognitive function by regulating neurotransmitters, enhancing neurotrophic factor signaling, and reducing cell apoptosis (9). More importantly, it was demonstrated that acupuncture treatment could ameliorate the non-motor symptoms, quality of life and activities of daily living in PD patients (10).
This randomized controlled trial is designed based on previous acupuncture research. It aims to evaluate the cognitive function improvement in PD-MCI patients receiving either verum or placebo acupuncture. In this study, we focus on the clinical efficacy of acupuncture for PD-MCI in order to provide an evidence-based assessment of acupuncture’s therapeutic value. We hope that we can expand the clinical treatment option for PD-MCI through the study, help to delay the disease progression, and enhance the quality of life of PD patients.
2 Materials and methods
This study will be a prospective, single-blind, randomized controlled clinical trial targeting Chinese PD-MCI patients. The trial will be conducted at the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine.
The ethics committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine has approved the research protocol, which will follow the Declaration of Helsinki. The protocol has also been registered in the Chinese Clinical Trial Registry (ChiCTR2300074675).
A total of 72 eligible PD-MCI volunteers will be included in this study, and the flowchart is shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1

Flowchart of the trial.
2.1 Diagnostic criteria
Diagnostic criteria for PD refer to the Movement Disorder Society Clinical Diagnostic Criteria for PD (2015) (11). The diagnostic criteria for mild cognitive impairment in PD refer to the Diagnostic Criteria for Mild Cognitive Impairment in Parkinson’s Disease formulated by the International Association of Dyskinesia in 2012 (12).
2.1.1 Inclusion criteria
-
Meet the diagnostic criteria for idiopathic PD and PD-MCI.
-
Meet the diagnostic criteria of TCM tremor syndrome and stupidness.
-
Patients aged 50–70 years.
-
MoCA scale score range of 18 to 25.
-
MMSE scale score range of 21 to 26.
-
Hoehn-Yahr staging scale staged 1–3.
-
Do not participate in other drugs, acupuncture and other treatments or clinical trials within 1 month.
-
Voluntarily join the study and sign the informed consent.
2.1.2 Exclusion criteria
The exclusion criteria are as follows:
-
Do not meet the diagnostic criteria and inclusion criteria.
-
Users of pharmaceutical products improving cognitive function, such as Donepezil, galantamine, memantine hydrochloride, etc.
-
Diagnosed with severe mental complications such as major depression and schizophrenia.
-
Cognitive dysfunction caused by other diseases.
-
Had participated in other drug or acupuncture studies within 30 days of treatment initiation.
-
Diagnosed with other severe illnesses such as stroke, hematopoietic system diseases, malignant tumors, etc.
-
Allergic or intolerant to acupuncture.
2.2 Sample size
Aligned with the study’s objective, Montreal Cognitive Assessment Scale (MoCA) was chosen as the primary outcome. According to the results of previous experiments and literature review (13, 14), the mean and standard deviation of MoCA scale in PD-MCI patients received acupuncture combined with anti-PD drug treatment were 25.32 and 4.34, while there were 21.48 and 4.44, respectively, in PD-MCI patients who received sham acupuncture combined with anti-PD drug treatment. PASS V.15.0 (NCSS, Kaysville, UT, United States) was used to calculate the sample size. We set 90% for power level and 5% for two-sided significance level. It was estimated that there were about 29 patients in each group, and considering the dropout rate of 20%, the total sample size needed for study is 72, with 36 patients in each group.
2.3 Randomization
Subjects with PD-MCI who met the inclusion and exclusion criteria will be randomized using a simple randomization method in a 1:1 ratio into the acupuncture group and the placebo acupuncture group. Random sequence will be generated by a third party who do not participate in the study using SPSS Statistics 26.0 (IBM SPSS Statistics Inc., Chicago, United States).
2.4 Blinding
To ensure the objectivity and accuracy of the results, this study adopts the single blind method to blind the subjects and the efficacy evaluator. Due to the limitations of needle operation, it is impossible to blind the operating physician, so the efficacy evaluator is a third party independent of the treatment operation and grouping to avoid subjective bias of the researcher. During the treatment, both groups of participants will be required to wear an eye mask to ensure the implementation of the blind method. At the end of the study, the blind will be uncovered and the participants will be informed of their group and acupuncture method.
2.5 Interventions
All the acupuncturists have obtained the doctor qualification certificate and have certain clinical experience. At the same time, before the start of the study, all treating physicians should undergo systematic training to ensure the consistency of operation. During the treatment process, each patient will be treated by the same acupuncturist throughout the entire procedure.
An auxiliary device designed by our team will be used during the acupuncture procedure in order to achieve a single-blind effect, which has passed the national utility model patent (patent number: ZL202121352221.7), and the article introducing the device has been published in the journal of Chinese Acupuncture & Moxibustion (15). This new auxiliary acupuncture device includes an acupuncture device and a placebo acupuncture device with exactly the same appearance, which consists of a base sticking to the skin and a sleeve. The base of the acupuncture device is hollow, while the placebo acupuncture device is sealed by a bonding layer (Figure 2). A flat head needle (Tianxie, Suzhou Medical Appliance Factory, Suzhou, China; 0.30 mm × 10 mm) (Figure 3) will be used for the procedure. The acupuncturist can adjust the sleeve according to the insertion angle of needles (Figure 4).
Figure 2
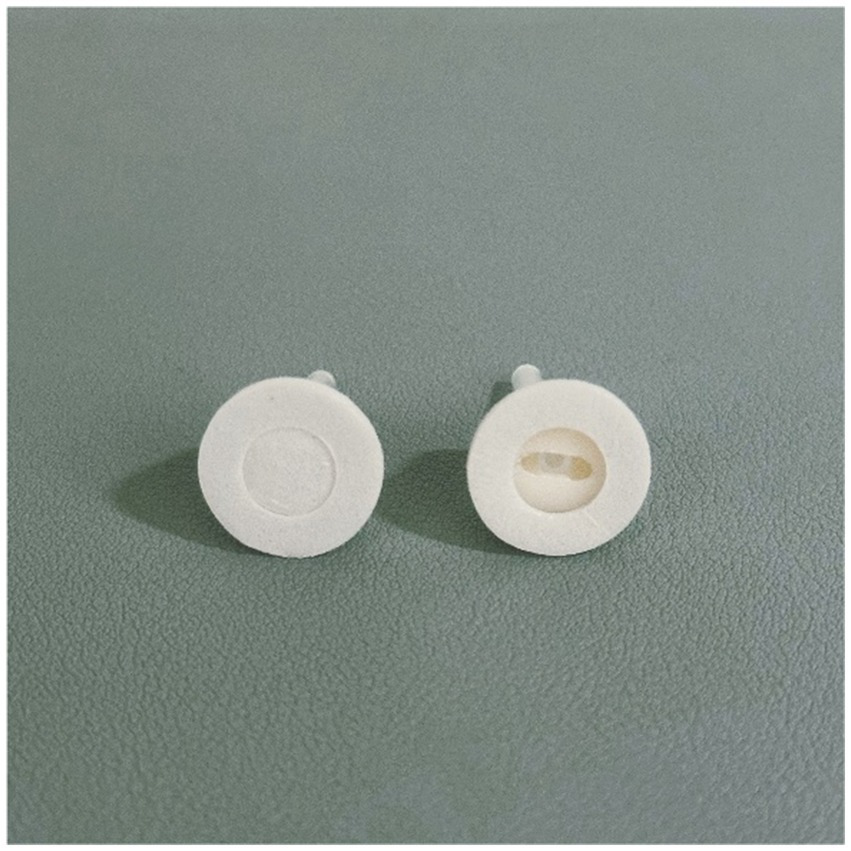

The placebo acupuncture device and the acupuncture device.
Figure 3
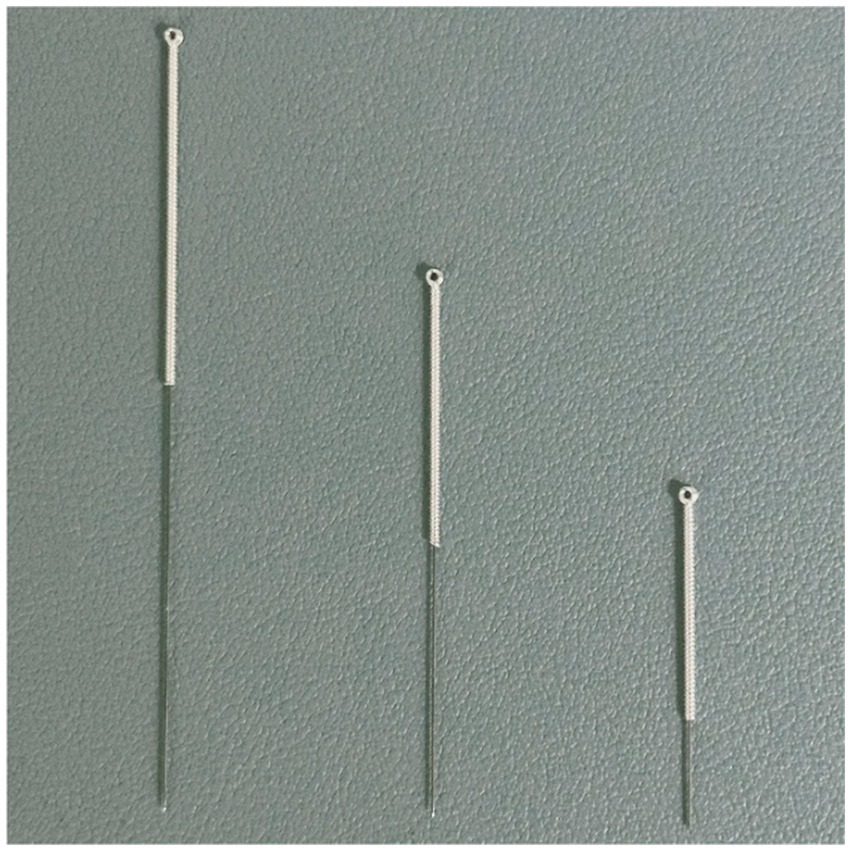

The flat head needle (40 mm, 25 mm real needle and 10 mm sham needle).
Figure 4
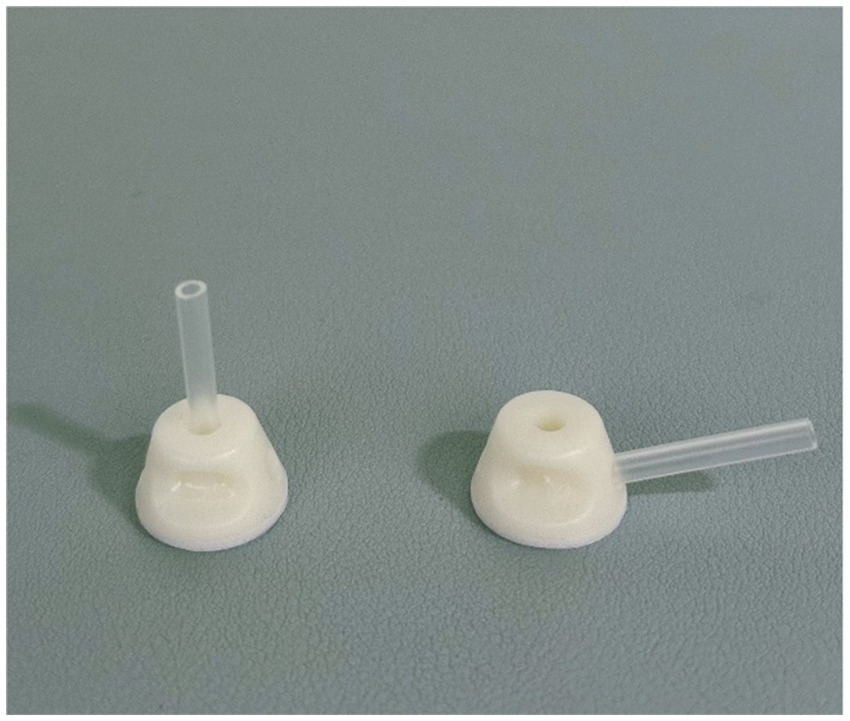
The angle of the sleeve (needle at 90-degree and 15-degree).
2.5.1 Acupuncture group
Patients in the acupuncture group will receive 20 sessions of acupuncture (four times a week for 5 weeks), during which the original effective dose of anti-Parkinson’s disease drugs will be maintained. If there is a need to increase or decrease the dose under special circumstances, the change will be recorded in the case report form. Acupuncture points of the acupuncture group include Si Shen Zhen (Four acupoints, consisting of GV21, GV19, and next to GV20 1.5 cun bilateral), Shen Ting (GV24), Yin Tang (GV29), Su Liao (DU25), Shen Men (HT7) (bilateral), San Yin Jiao (SP6) (bilateral), Hegu (LI4) (bilateral), and Taichong (LR3) (bilateral). The positioning of Si Shen Zhen is in accordance with the “Application of Jin San Zhen acupoint Group” (16), and other acupoints are in accordance with the National Standard of the People’s Republic of China’s (GB/T 12346–2006) standard (17). Acupuncture will be processed with disposable, sterile steel needles (Tianxie, Suzhou Medical Appliance Factory, Suzhou, China; 0.25 × 25 mm, 0.25 × 40 mm). Patients will wear the blindfold throughout the treatment. After routine skin disinfection, the acupuncturist will affix the acupuncture device (Guangzhou Suixin Medical Equipment Co., LTD.) to the acupoint skin. 0.25 × 25 mm acupuncture needles will be used for Si Shen Zhen, Shen Ting (GV24) and Yin Tang (GV29) with a 15-degree angle. 0.25 × 40 mm acupuncture needles will be used for Su Liao (DU25), Shen Men (HT7) (bilateral), San Yin Jiao (SP6) (bilateral), Hegu (LI4) (bilateral), and Taichong (LR3) (bilateral) with a 90-degree angle. The acupuncture needle is inserted through the sleeve and the perforated base into the skin. The location of each acupoint is shown in Table 1 and Figure 5. The needle will be retained for 30 min.
Table 1
| Acupoint | Location |
|---|---|
| Si Shen Zhen | Four acupoints, consisting of GV21, GV19, and next to GV20 1.5 cun bilateral |
| Shen Ting | On the head, 0.5 cun directly above the midpoint of the anterior hairline. |
| Yin Tang | On the head, in the depression between the medial ends of the two eyebrows. |
| Su Liao | On the face, at the tip of the nose, in the exact center. |
| Shen Men | In the anterior wrist region, at the ulnar end of the distal wrist crease, on the radial side of the tendon of the ulnar flexor muscle of the wrist. |
| San Yin Jiao | On the medial side of the leg, 3 cun above the tip of the medial malleolus, posterior to the medial border of the tibia. |
| Hegu | On the dorsum of the hand, between the 1st and 2nd metacarpal bones, at the midpoint of the radial side of the 2nd metacarpal bone. |
| Taichong | On the dorsum of the foot, in the depression between the 1st and 2nd metatarsal bones, at the junction of the two bones. |
The location of each acupoint.
Figure 5
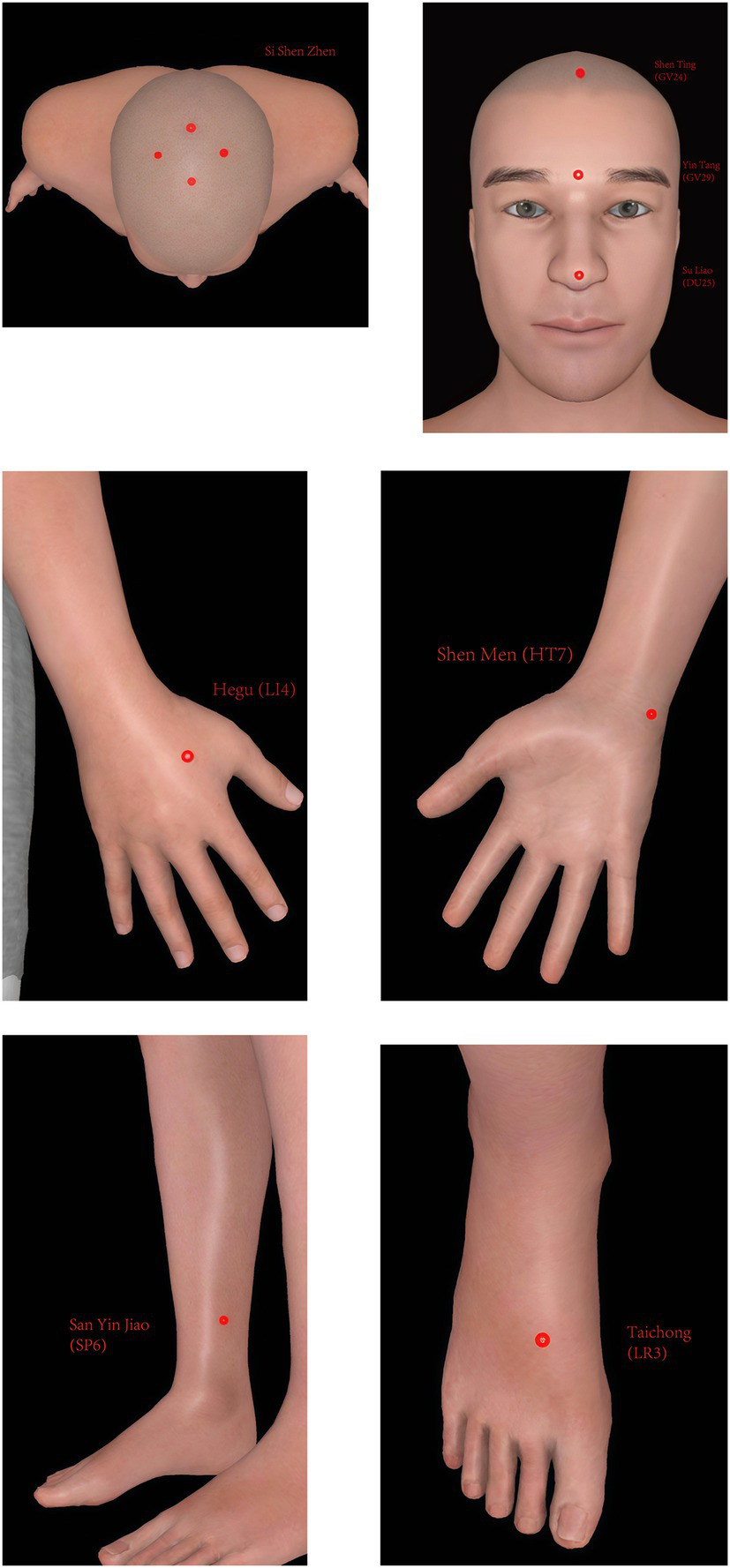
The location of each acupoint.
2.5.2 The placebo acupuncture group
Patients in the acupuncture group will receive 20 sessions of placebo acupuncture using sham acupuncture needles (four times a week for 5 weeks), during which the original effective dose of anti-Parkinson’s disease drugs will be maintained. If there is a need to increase or decrease the dose under special circumstances, the change will be recorded in the case report form. The acupuncture points of the placebo acupuncture group will be the same as those of the acupuncture group. Patients will wear the blindfold throughout the treatment. After routine skin disinfection, the acupuncturist will affix the placebo acupuncture device (Guangzhou Suixin Medical Equipment Co., LTD.) to the acupoint skin. The acupuncturist adjusts the sleeve according to the insertion angle of needles. The flat head needle (Tianxie, Suzhou Medical Appliance Factory, Suzhou, China; 0.30 mm × 10 mm) will be used for the procedure, and will be inserted through the cannulas to make patients feel slightly needled. The needle will be maintained for 30 min.
2.6 Outcome measure
General information of the participants, including name, age, sex, disease duration, education, Levodopa-equivalent dose, will be collected before the study begin. Primary outcome measure will be the Montreal Cognitive Assessment Scale (MoCA). The secondary outcome will be the Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE), Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale Motor Examination (UPDRSIII), serum neurofilament light polypeptide (NfL) and serum glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF). Serological indicators will be measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The schedule of the outcome measurements is shown in Table 2.
Table 2
| Study period | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time point (Week) | −1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 25 |
| Enrollment | ||||||||
| Eligibility screen | × | |||||||
| Informed consent | × | |||||||
| Randomization | × | |||||||
| Allocation | × | |||||||
| Intervention | ||||||||
| Acupuncture |

|
|||||||
| Placebo Acupuncture |

|
|||||||
| Assessments | ||||||||
| MoCA | × | × | × | |||||
| MMSE | × | × | × | |||||
| UPDRSIII | × | × | × | |||||
| NfL | × | × | ||||||
| GDNF | × | × | ||||||
| Safety | ||||||||
| Vital signs | × | × | × | × | ||||
| Adverse events | × | × | × | × | × | × | ||
Schedule of enrollment, intervention, assessment and safety.
2.6.1 Primary outcome
2.6.1.1 The Montreal cognitive assessment scale (MoCA)
The MoCA has a certain sensitivity to screening PD-MCI, and the content of the scale is divided into 8 cognitive domains, including visuospatial and executive, naming, memory, attention, language, abstract ability, delayed recall, and orientation. The total score is 30 points. A score above 26 is normal, and a score between 18 and 25 refers to mild cognitive impairment. If when using this table, Add 1 point as correction when patients have less than 12 years of education.
2.6.2 Secondary outcomes
2.6.2.1 Mini-mental state examination (MMSE)
MMSE includes five cognitive areas of orientation, memory, attention and calculation, recall ability, and language ability. The total score is 30, and the score between 21 and 26 is considered mild cognitive impairment.
2.6.2.2 Unified Parkinson’s disease rating scale motor examination (UPDRSIII)
The UPDRS is a commonly used scale for the overall evaluation of PD patients and consists of four parts. UPDRSIII mainly evaluates the motor function of the patients. There are 14 items in total, the highest score of each item is 4 points, and the total score is 56 points. The higher the score, the more serious the motor symptoms of PD patients.
The above scales will be assessed before and after treatment.
2.6.2.3 Blood serum index
Cognitive impairment in PD is associated with dysfunction of a variety of neurotransmitter systems, including acetylcholinergic, dopaminergic, norepinephrine and 5-hydroxytryptaminergic. When the axons of nerve cells are damaged, they release serum neurofilament light polypeptide (NfL) into the cerebrospinal fluid and eventually into the blood (18). Serum glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) promotes the survival of dopaminergic (DA) neurons in the substantia nigra. GDNF may act in combination with neurotransmitters (HVA, 5-HT, GABA and Ach) to affect attention, memory and executive function in PD-MCI patients (19). Therefore, NfL and GDNF levels can reflect the activity of brain neurons, and NfL and GDNF can be used as biomarkers related to cognitive function.
Serum concentrations of NfL and GDNF will be measured before and at the end of treatment using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), which follows the kit instructions strictly. Both ELISA kits will be provided by Jiangsu Enzyme Free Industrial Co., LTD.
2.7 Safety evaluation
During the implementation of the study, adverse events of acupuncture, such as infection, bleeding, fainting, broken needles and subcutaneous hematoma will be handled promptly and recorded in the Adverse Event record Form. In case of serious adverse events, acupuncture treatment will be stopped and timely treatment measures will be carried out immediately. We will report to the Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine at the same time. All adverse events will be classified and reported following CONSORT harm guideline (20).
2.8 Follow-up
Patients will be followed up 6 months after the end of treatment. The outcomes scales will be assessed to evaluate the long-term efficacy of acupuncture.
2.9 Data management and quality control
To ensure trial consistency and accuracy, all team members will receive standardized training prior to study initiation. All members will receive training on the localization of acupoints, the application of sham needles, the evaluation of assessment scales, patient communication, as well as the methods and time points for follow-up. The researcher responsible for the assessment needs to be proficient in the questions and operations in the case report form (CRF), conduct an objective assessment of the subjects, and both the assessor and the subjects need to sign the CRF to ensure the reliability and integrity of the data. Researchers will strictly keep the case observation forms and set access permissions for electronic data, allowing only authorized personnel to enter, modify and view the data to ensure data security and protect the privacy of the subjects. Data quality will be monitored regularly to check whether the data are missing, wrong or invalid, and to ensure the completeness and rationality of the data.
2.10 Statistical analysis
In this study, IBM SPSS Statistics 26.0 statistical software will be used to analyze the collected clinical data. Shapiro–Wilk will be used to test the normality before statistical analysis. Counting data is expressed as a percentage using a chi-square test. The measurement data meeting the normal distribution will be represented by mean ± standard deviation, while those not meeting the normal distribution will be represented by quartile. The independent sample t test will be used to compare the two groups with normal distribution and homogeneous variance, and the Mann–Whitney U test will be used to compare the two groups with non-normal distribution. The comparison difference before and after treatment will be treated by paired sample t test with normal distribution, and Wilcoxon rank sum test with abnormal distribution. The two groups of repeated measurement data do not meet the normal distribution of the generalized estimation equation, the simple effect in the group will be analyzed by Friedman test. Two-sided test will be applied uniformly in this study, and p ≤ 0.05 will be the standard of statistical significance.
To evaluate the clinical relevance of the findings, we will perform a responder analysis based on the minimal clinically important difference (MCID) for the MoCA. Based on previous literature in cognitive impairment (21), a change of ≥1.22 points on the MoCA scale will be considered clinically meaningful. Participants who show an improvement of ≥1.22 points from baseline to post-treatment will be classified as ‘responders’. The difference in the proportion of responders between the study groups will be compared using a Chi-square test, with a p-value < 0.05 considered statistically significant.
3 Discussion
Parkinson’s disease with mild cognitive impairment (PD-MCI) is a primary non-motor symptom of PD. Recent studies have demonstrated widespread cognitive decline among PD patients, often accompanied by more severe depression compared to those without cognitive impairment (22). Additional research indicates that PD-MCI patients have a 39–59% probability of progressing to Parkinson’s disease dementia (PDD) within 5 years (23). This suggests that PD-MCI represents an early stage of cognitive impairment in PD and a probable transitional stage preceding PDD. Therefore, preventing factors that contribute to the conversion from PD-MCI to PDD is of significant importance in delaying the onset of PDD. Additionally, cognitive dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease is associated with the progression of motor dysfunction (24). Improving cognitive function can contribute to the amelioration of motor symptoms in patients (25), highlighting the importance of early intervention for cognitive impairment.
This study represents the first clinical trial investigating the efficacy of acupuncture therapy for cognitive dysfunction in PD. Currently, research on the treatment of mild cognitive impairment in PD remains limited. The pathogenesis of PD-MCI has not yet been fully elucidated, and western medicine lacks targeted therapeutic approaches. Clinical trials of pharmacological interventions have failed to demonstrate consistent or sustained efficacy. The drugs treating cognitive dysfunction mostly accompanied by adverse effects such as nausea, vomiting, decreased appetite, and other gastrointestinal disturbances (26, 27). Given these limitations, there is an urgent need to explore additional safe and effective therapeutic strategies for PD-MCI.
As a classical therapeutic modality in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), acupuncture has demonstrated clinically meaningful efficacy in the management of post-stroke cognitive impairment (28). Notably, acupuncture exhibits superior therapeutic outcomes to pharmacotherapy for certain psychiatric disorders while avoiding drug-associated adverse effects (29, 30). Acupuncture is a well-established clinical intervention in China. Acupuncture has regionally specific, quantifiable effects on relevant brain structures (31). Acupuncture was found to activate a wide range of brain function areas and promote the neural plasticity of motor and cognitive brain regions neural plasticity (32). Studies has proved that acupuncture can improve cognitive function, restore impaired neurological function, and lower related serum factor levels (8, 33). Recent advanced works evaluate therapeutic effect of acupuncture on human brain through different brain imaging methods, including MRI, fMRI and EEG. Acupuncture may affect brain function by enhancing or inhibiting the connectivity between brain regions, leading to indirect effects on the limb system (5). Scalp EEG and Transformer elucidated the dynamic regulatory effects of acupuncture throughout the treatment process (34). Yu et al. (35) used the EEG decoder to demonstrate that needle insertion can evoke immediate tactile sensations, stimulate peripheral nerves directly and ultimately affect brain regions via central nervous system pathways. Acupuncture increases long-range connections between left and right hemispheres (36). Nierhaus et al. (37) proved that stimulation at acupuncture points is more effective than stimulation at non-acupuncture point locations measured with EEG and fMRI.
In the previous clinical research on acupuncture treatment for PD, we found that acupuncture not only improved Parkinson’s anxiety, but also enhanced the Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale (UPDRS) scores of patients (38). UPDRS is a commonly used scale for evaluating PD patients’ quality of life, which can objectively evaluate the mental, emotional, daily living ability, motor symptoms and other aspects of PD patients. These findings suggest acupuncture has an overall improvement on the emotional and cognitive functions of Parkinson’s patients. Yan’s study (39) proved that acupuncture can significantly improve the sleep quality of PD patients. Li′s research (40) found that acupuncture treatment for constipation in PD is effective and safe. Xia et al. (41) using electroacupuncture to treat PD combined with depression can improve depressive symptoms, increase the level of BDNF in serum, and the therapeutic effect is superior to that of drug treatment alone. All research above further supports acupuncture’s multimodal benefits for PD non-motor symptoms. Regarding cognitive dysfunction specifically, both clinical studies (42, 43) and preclinical models (44, 45) across various etiologies have consistently shown acupuncture’s therapeutic potential. Therefore, based on the clinical efficacy of acupuncture in treating non-motor symptoms of PD and cognitive dysfunction in previous studies, this study will adopt acupuncture to investigate cognitive dysfunction in PD.
When it comes to acupoint selection, the acupoints located on the head like “Baihui” acupoint and “Shen Ting” acupoint are the most frequently used acupoints for enhancing cognitive performance (46, 47). We use “Si Shen Zhen,” which are next to “Baihui” 1.5 cun bilateral, and add the acupuncture point “Yin Tang” and “Su Liao” to expand the brain stimulus area. The researches showed that acupoints located at the extremities (“Shen Men,” “Hegu,” “San Yin Jiao,” “Taichong”) can stimulate cognitive, emotional brain regions, central nervous system and enhance cerebral blood circulation (48), effectively manage various health conditions (49). Therefore, this study incorporates acupoints from both the head and limbs to achieve holistic improvement.
Recent years have witnessed a growing number of clinical studies investigating acupuncture therapy. However, high-quality clinical research demands more rigorous control designs to examine potential placebo effects in acupuncture interventions. To enhance blinding effectiveness, this study employed a novel sham acupuncture device specifically designed and developed by our research team (15). The device has the advantages of adjustable angle and high stability, which can be applied to both real and sham acupuncture procedures. The special flat-head needle is used on the needle tool, and the appearance of the needle handle is consistent with that of the ordinary acupuncture needle. The device has been extensively utilized in our team’s clinical trials (50–57), with validation studies confirming its excellent blinding efficacy and yielding significant research outcomes.
To comprehensively evaluate acupuncture’s impact on the nervous system, we incorporated serum measurements of NfL and GDNF levels as secondary efficacy indicators. Both NfL and GDNF are closely related to neural cell function. Neural cell degeneration and damage can alter their blood levels. Higher NfL levels indicate more severe axonal degeneration, while more severe cognitive dysfunction correlates with lower GDNF levels. Previous studies have shown that plasma NfL levels are associated with cognitive function in PD patients (58) and can predict clinical conversion of cognitive function (59). It can also reflect changes of cognitive function level (60–62). Therefore, we adopted these indicators to assess acupuncture’s therapeutic effects. Since PD-MCI is difficult to diagnose due to its insidious onset and lack of specific biomarkers, this study also holds clinical value for exploring PD-MCI pathogenesis and improving diagnosis.
This study represents the first randomized, single-blind clinical trial investigating acupuncture treatment for cognitive dysfunction in PD. We employ a sham acupuncture device independently developed by our team as a control, thereby enhancing the credibility of evidence in acupuncture studies. Although some studies in acupuncture research have explored its therapeutic effects on cognitive impairment, no specific acupuncture intervention has yet targeted cognitive dysfunction in PD. Motor and non-motor symptoms in PD often interact and influence each other. Our study simultaneously assessed interventions for motor dysfunction, which may offer new insights into holistic management of PD. Additionally, the study explores the therapeutic mechanisms of acupuncture through clinical biofluid samples.
However, several limitations should be acknowledged. First, all enrolled cases are recruited from a single hospital, which may limit the generalizability of the findings across different regions. Second, minor stimulation may still occur in the sham group. Third, while patient blinding is successfully implemented, practitioners could not be blinded due to the nature of the acupuncture devices used in the study.
This study will provide reliable clinical evidence for the treatment of PD-MCI, thereby improving patients’ survival and quality of life while delaying or preventing its progression to PDD.
Statements
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Research Branch of Medical Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
SW: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. IL: Writing – review & editing. JF: Writing – review & editing. XL: Writing – review & editing. EL: Writing – review & editing. SL: Writing – review & editing. XX: Writing – review & editing. KL: Writing – review & editing. L-XZ: Methodology, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was funded by General Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China general program (82474622), Scientific research projects of university of Guangdong Provincial Education Office (2022KCXTD006) and National Special Project of Traditional Chinese Medicine Heritage and Innovation Center (2022ZD04).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1.
Wang L Feng S Nie K . Chinese guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of Parkinson's disease with mild cognitive impairment (2020). Chin J Nerv Ment Dis. (2021) 47:1–12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0152.2021.01.001
2.
Hoogland J Boel JA de Bie RMA Geskus RB Schmand BA Dalrymple-Alford JC et al . Mild cognitive impairment as a risk factor for Parkinson's disease dementia. Mov Disord. (2017) 32:1056–65. doi: 10.1002/mds.27002
3.
Christopher L Marras C Duff-Canning S Koshimori Y Chen R Boileau I et al . Combined insular and striatal dopamine dysfunction are associated with executive deficits in Parkinson's disease with mild cognitive impairment. Brain. (2014) 137:565–75. doi: 10.1093/brain/awt337
4.
Weil RS Costantini AA Schrag AE . Mild cognitive impairment in Parkinson's disease – what is it?Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. (2018) 18:17. doi: 10.1007/s11910-018-0825-7
5.
Wong KKL Xu J Chen C Ghista D Zhao H . Functional magnetic resonance imaging providing the brain effect mechanism of acupuncture and moxibustion treatment for depression. Front Neurol. (2023) 14:1151421. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1151421
6.
Yu H Li F Liu J Liu D Guo H Wang J et al . Evaluation of acupuncture efficacy in modulating brain activity with periodic-aperiodic EEG measurements. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng. (2024) 32:2450–9. doi: 10.1109/TNSRE.2024.3421648
7.
Yu H Li X Lei X Wang J . Modulation effect of acupuncture on functional brain networks and classification of its manipulation with EEG signals. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng. (2019) 27:1973–84. doi: 10.1109/TNSRE.2019.2939655
8.
Cao Y Wang L Lin LT Wang XR Ma SM Yang NN et al . Acupuncture attenuates cognitive deficits through α7nAChR mediated anti-inflammatory pathway in chronic cerebral hypoperfusion rats. Life Sci. (2021) 266:118732. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118732
9.
Hanyu P Wang A . The effectiveness and safety of acupuncture for the treatment of cognitive impairment from Parkinson disease: a meta-analysis and systematic review. Medicine (Baltimore). (2025) 104:e42148. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000042148
10.
Li Q Wu C Wang X Li Z Hao X Zhao L et al . Effect of acupuncture for non-motor symptoms in patients with Parkinson's disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Aging Neurosci. (2022) 14:995850. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.995850
11.
Postuma RB Berg D Stern M Poewe W Olanow CW Oertel W et al . MDS clinical diagnostic criteria for Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord. (2015) 30:1591–601. doi: 10.1002/mds.26424
12.
Litvan I Goldman JG Tröster AI Schmand BA Weintraub D Petersen RC et al . Diagnostic criteria for mild cognitive impairment in Parkinson's disease: Movement Disorder Society task force guidelines. Mov Disord. (2012) 27:349–56. doi: 10.1002/mds.24893
13.
Huang L Yin X Li W Qin W Xu S Zhang Q . Effects of acupuncture on vascular cognitive impairment with no dementia: a randomized controlled trial. J Alzheimer's Dis. (2021) 81:1391–401. doi: 10.3233/JAD-201541
14.
Liu H Li PF Sun PY Zhang Y Wang LM Chen X et al . Effects of Tongdu Tiaoshen acupuncture on vascular endothelial function and inflammatory factors in patients with mild cognitive impairment after ischemic stroke. Int J Trad Chin Med. (2024) 46:175–80. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115398-20230129-00218
15.
Wang YT Liu X Xu ZQ Li JM Zhao N Wu K et al . An auxiliary device for double-blind placebo acupuncture research. Chin Acupunct Moxibust. (2022) 42:351–4. doi: 10.13703/j.0255-2930.20210227-k0001
16.
Zhuang LX . Atlas of Jin's three-needle Acupoint groups. Beijing: China Medical Science Press (2021).
17.
Standardization Administration of China . Nomenclature and location of acupuncture points: GB/T 12346–2006. Beijing: China Standards Press (2006).
18.
Thebault S Booth RA Freedman MS . Blood neurofilament light chain: the neurologist's troponin?Biomedicine. (2020) 8:523. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines8110523
19.
Liu Y Tong S Ding L Liu N Gao D Chen S et al . Serum levels of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor and multiple neurotransmitters: in relation to cognitive performance in Parkinson's disease with mild cognitive impairment. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. (2020) 35:153–62. doi: 10.1002/gps.5221
20.
Hopewell S Chan AW Collins GS Hróbjartsson A Moher D Schulz KF et al . CONSORT 2025 statement: updated guideline for reporting randomised trials. BMJ. (2025) 389:e081123. doi: 10.1136/bmj-2024-081123
21.
Wu CY Hung SJ Lin KC Chen KH Chen P Tsay PK . Responsiveness, minimal clinically important difference, and validity of the MoCA in stroke rehabilitation. Occup Ther Int. (2019) 2019:1–7. doi: 10.1155/2019/2517658
22.
Baiano C Barone P Trojano L Santangelo G . Prevalence and clinical aspects of mild cognitive impairment in Parkinson's disease: a meta-analysis. Mov Disord. (2020) 35:45–54. doi: 10.1002/mds.27902
23.
Pedersen KF Larsen JP Tysnes OB Alves G Lange J Maple-Grødem J et al . Natural course of mild cognitive impairment in Parkinson disease: a 5-year population-based study. Neurology. (2017) 88:767–74. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000003634
24.
Wang YX Zhao J Li DK Peng F Wang Y Yang K et al . Associations between cognitive impairment and motor dysfunction in Parkinson's disease. Brain Behav. (2017) 7:e00719. doi: 10.1002/brb3.719
25.
Kiper P Richard M Stefanutti F Pierson-Poinsignon R Cacciante L Perin C et al . Combined motor and cognitive rehabilitation: the impact on motor performance in patients with mild cognitive impairment. Systematic review and meta-analysis. J Pers Med. (2022) 12:276. doi: 10.3390/jpm12020276
26.
Li QS . (2016) the correlation of traditional Chinese medicine syndromes with cognitive features in PD and the clinical study of Kangzheng Zhijing capsule treating PD-MCI with blood stasis and wind agitation [master's thesis]. Hefei: Anhui University of Chinese Medicine (2016).
27.
Huang G . Efficacy of memantine hydrochloride in the treatment of Parkinson's disease dementia and its effects on cognitive function and activities of daily living. Clin Med J. (2017) 37:107–8. doi: 10.19528/j.issn.1003-3548.2017.12.052
28.
Zhang Q . (2021) clinical observation of mind-regulating acupuncture for post-stroke cognitive impairment [master's thesis]. Guangzhou: Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine (2021).
29.
Zeng XL . (2015) clinical research on Jin's spirit-regulation method for tumor-related depression [master's thesis]. Guangzhou: Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine (2015).
30.
Wu JL Pan WD Yu HL Chen XM Li Y Zhao K et al . Analysis of the therapeutic effect of "Jin's three-needle" mind-regulating acupuncture on sleep disorders in elderly patients with post-stroke depression. Clin J Chin Med. (2021) 13:95–7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7860.2021.21.034
31.
Kaptchuk TJ . Acupuncture: theory, efficacy, and practice. Ann Intern Med. (2002) 136:374–83. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-136-5-200203050-00010
32.
Zhang J Lu C Wu X Nie D Yu H . Neuroplasticity of acupuncture for stroke: an evidence-based review of MRI. Neural Plast. (2021) 2021:2662585. doi: 10.1155/2021/2662585
33.
Wang G Tong T Wang Y Li K Zhang L Wu X et al . Effect and mechanism of Tongdu Tiaoshen electroacupuncture pretreatment-mediated miR-124-3p/GSK-3β/Cyp-D signaling pathway on mitochondrial permeability transition pore in cerebral cortex of rats with cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Chin Gen Pract. (2023) 26:3050–60. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn114798-20230210-00128
34.
Rao W Xu M Wang H Hua W Guo J Zhang Y et al . Acupuncture state detection at Zusanli (ST-36) based on scalp EEG and transformer. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. (2025) 29:4023–34. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2025.3540924
35.
Yu H Zeng F Liu D Wang J Liu J . Neural manifold decoder for acupuncture stimulations with representation learning: an acupuncture-brain Interface. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. (2025) 29:4147–60. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2025.3530922
36.
Yu H Wu X Cai L Deng B Wang J . Modulation of spectral power and functional connectivity in human brain by acupuncture stimulation. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng. (2018) 26:977–86. doi: 10.1109/TNSRE.2018.2828143
37.
Nierhaus T Pach D Huang W Long X Napadow V Roll S et al . Differential cerebral response to somatosensory stimulation of an acupuncture point vs. two non-acupuncture points measured with EEG and fMRI. Front Hum Neurosci. (2015) 9:74. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2015.00074
38.
Fan JQ Lu WJ Tan WQ Liu X Wang YT Wang NB et al . Effectiveness of acupuncture for anxiety among patients with Parkinson disease: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Netw Open. (2022) 5:e2232133. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.32133
39.
Yan M Fan J Liu X Li Y Chen R Wang Y et al . Acupuncture and sleep quality among patients with Parkinson disease: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Netw Open. (2024) 7:e2417862. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.17862
40.
Li YJ Leong II Fan JQ Yan MY Liu X Lu WJ et al . Efficacy of acupuncture for the treatment of Parkinson's disease-related constipation (PDC): a randomized controlled trial. Front Neurosci. (2023) 17:1126080. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1126080
41.
Xia Y Wang HD Ding Y Kang B Liu WG . Parkinson's disease combined with depression treated with electroacupuncture and medication and its effect on serum BDNF. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. (2012) 32:1071–4. doi: 10.13703/j.0255-2930.2012.12.007
42.
Yin Z Li Y Zhang X Wang J Chen H Liu M et al . Effects and neuroimaging findings of acupuncture for amnestic mild cognitive impairment: a randomized controlled trial. J Evid Based Med. (2025) 18:e70047. doi: 10.1111/jebm.70047
43.
Chi JY Zhu RX Chen C Li W Zhang Y Wang L et al . Therapeutic effect of Tiaoshen Yizhi acupuncture on cognitive impairment during recovery period of ischemic stroke and its impact on serum level of P-tau protein. J Clin Acupunct Moxibust. (2025) 41:30–5. doi: 10.19917/j.cnki.1005-0779.025110
44.
Li G Liu J Zhang K . Electroacupuncture improves sleep deprivation-induced cognitive impairment by suppressing hippocampal inflammatory response in mice. Stress. (2025) 28:2502742. doi: 10.1080/10253890.2025.2502742
45.
Liu QL Jiang L Jin J Chen X Wang Y Zhang H et al . Study on neuroprotective effect of acupuncture modulating Shh/Ptch1 signaling pathway on cognitive impairment in rat models of Parkinson's disease. J Clin Acupunct Moxibust. (2024) 40:78–84. doi: 10.19917/j.cnki.1005-0779.024159
46.
Han JZ Yang Y Wang YF Feng JH Song CN Wu WJ et al . Effectiveness and safety of governor vessel acupuncture therapy for post-stroke cognitive impairment: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Ageing Res Rev. (2024) 99:102355. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2024.102355
47.
Birch S Robinson N . Acupuncture as a post-stroke treatment option: a narrative review of clinical guideline recommendations. Phytomedicine. (2022) 104:154297. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154297
48.
Lu G Chen F Guo C Wu J . Acupuncture for senile insomnia: a systematic review of acupuncture point. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. (2024) 127:105586. doi: 10.1016/j.archger.2024.105586
49.
Zhang XR Zhou L Zhai JY Lu JH Zhang TW Liu JJ et al . Siguan points-based acupuncture treatment for migraine: a systematic review with meta-analysis of clinical efficacy and neurovascular regulatory effects. Complement Ther Clin Pract. (2025) 1:2019. doi: 10.1016/j.ctcp.2025.102019
50.
Zhou SY . (2024) clinical observation of Jin's three-needle mind-regulating acupuncture for post-stroke anxiety disorder [master's thesis]. Guangzhou: Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine (2024).
51.
Tan WQ . (2023) clinical efficacy of depression three-needle acupuncture for depression in Parkinson's disease [master's thesis]. Guangzhou: Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine (2023).
52.
Li YJ . (2023) efficacy of Jin's three-needle therapy for constipation in Parkinson's disease [master's thesis]. Guangzhou: Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine (2023).
53.
Chen YY . (2023) clinical observation of fatigue three-needle acupuncture for fatigue in Parkinson's disease [master's thesis]. Guangzhou: Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine (2023).
54.
Yan MY . (2023) clinical observation of mind-regulating and qiao-unblocking acupuncture for sleep disorders in Parkinson's disease [master's thesis]. Guangzhou: Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine (2023).
55.
Li MC . (2023) clinical observation of Jin's three-needle Shen-regulating therapy for post-stroke anxiety [master's thesis]. Guangzhou: Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine (2023).
56.
Liu X . (2022) clinical effects of mind-regulating acupuncture for generalized anxiety disorder in perimenopausal women [master's thesis]. Guangzhou: Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine (2022).
57.
Lu WJ . (2022) clinical observation of mind-regulating acupuncture for anxiety in Parkinson's disease [master's thesis]. Guangzhou: Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine (2022).
58.
Lin YS Lee WJ Wang SJ Fuh JL Yang CC Chen YF et al . Levels of plasma neurofilament light chain and cognitive function in patients with Alzheimer or Parkinson disease. Sci Rep. (2018) 8:17368. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-35766-w
59.
Aamodt WW Waligorska T Shen J Tropea TF Siderowf A Weintraub D et al . Neurofilament light chain as a biomarker for cognitive decline in Parkinson disease. Mov Disord. (2021) 36:2945–50. doi: 10.1002/mds.28779
60.
Zheng W Zhang X Chen J Li Y Wang L Zhou M et al . The effect of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation of the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex on the amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients with cognitive impairment: a double-blinded, randomized, and sham control trial. CNS Neurosci Ther. (2025) 31:e70316. doi: 10.1111/cns.70316
61.
Bhai S Levine T Moore D Katz J Jackson C Rivner M et al . A 40-week phase 2B randomized, multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled study evaluating the safety and efficacy of memantine in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Muscle Nerve. (2025) 71:63–72. doi: 10.1002/mus.28287
62.
Pan TY . (2023) clinical study of correlation between plasma S100β, NFL and α-syn and postoperative cognitive dysfunction in elderly patients undergoing gastrointestinal tumor surgery [master's thesis]. Nanchang: Nanchang University (2023).
Summary
Keywords
Parkinson’s disease, mild cognitive impairment, acupuncture, protocols, randomized controlled trial
Citation
Wu S, Leong II, Fan J, Liu X, Liu E, Lei S, Xu X, Liao K and Zhuang L-X (2025) Efficacy of acupuncture for Parkinson’s disease with mild cognitive impairment: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Front. Neurol. 16:1674098. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1674098
Received
29 July 2025
Accepted
29 September 2025
Published
24 October 2025
Volume
16 - 2025
Edited by
Roger David Adams, University of Canberra, Australia
Reviewed by
Haitao Yu, Tianjin University, China
Xiao Li, Henan University of Chinese Medicine, China
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Wu, Leong, Fan, Liu, Liu, Lei, Xu, Liao and Zhuang.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Li-Xing Zhuang, zhuanglixing@163.com
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.