- 1The Second Clinical Medical College of Zhejiang Chinese Medical University, Hangzhou, China
- 2Department of Neurology, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang Chinese Medical University, Hangzhou, China
- 3Department of Neurology, Zhejiang Provincial People's Hospital, Hangzhou, China
Neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD) is an autoimmune neuroinflammatory disease with high relapse risk and cumulative neurological disability. Identifying, providing early warning, and reproducible monitoring of disease progression and therapeutic efficacy in peripheral blood biomarkers is crucial for clinical management and personalized treatment. Numerous studies have investigated the relationship between peripheral blood immune-inflammatory markers including cytological ratios, cytokines, complement components and NMOSD disease activity, relapse risk, and long-term outcomes, aiming to evaluate their potential application in clinical prognostic assessment and treatment monitoring. Meta-analyses have shown that the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) is significantly elevated in patients with NMOSD compared with healthy controls (mean difference (MD) approximately 1.04, 95% CI 0.76–1.32; high heterogeneity). The NLR is associated with relapse risk and disability (EDSS ≥4) (OR for relapse, approximately 1.33–2.14; OR for EDSS ≥ 4, approximately 1.23–1.43), supporting the potential clinical application of peripheral blood Immune inflammatory markers in NMOSD. This review summarizes the current evidence for peripheral blood inflammatory markers in NMOSD, focusing on their clinical application.
1 Introduction
Neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD) is a rare but severe autoimmune inflammatory demyelinating disease of the central nervous system (CNS) (1, 2), characterized by high relapse rates, cumulative disability, and increased mortality (3, 4). It is primarily mediated by pathogenic immunoglobulin G antibodies targeting aquaporin-4 (AQP4), the most abundant water channel protein in astrocytic end-feet (5, 6). The disease predominantly affects the optic nerves and spinal cord (7–9), and less frequently the brainstem, leading to severe clinical manifestations such as recurrent optic neuritis (10), transverse myelitis (11), and brainstem encephalitis (12). Epidemiology of NMOSD is approximately 1 per 200,000 individuals (13). The mean age of NMOSD onset is between 30 and 40 years with a striking female predominance, and the female-to-male ratio is approximately 9–11:1 (14, 15).
The immunopathogenesis of NMOSD is complex and incompletely understood. Current evidence indicates that pathogenic AQP4-IgG antibodies initiate a cascade of complement-mediated astrocytic injury, inflammation, and demyelination, leading to irreversible neuronal and axonal damage. Pro-inflammatory cytokines and innate immune cells, including neutrophils, eosinophils, and natural killer (NK) cells, have been implicated as critical mediators in this process (16). The discovery of AQP4-IgG in 2005 represented a major breakthrough, allowing NMOSD to be distinguished from MS with high specificity and transforming diagnostic and therapeutic approaches (7, 17). The International Panel for NMO Diagnosis (IPND) revised the diagnostic criteria in 2015 to incorporate serological markers and clinical phenotypes, providing a standardized framework for global diagnosis (7).
While autoantibody-mediated astrocyte attack has been identified as a core mechanism, increasing evidence suggests that dysregulation of the peripheral immune system plays a crucial role in disease development, progression, and clinical outcome. Increasing evidence highlights the role of cytokines and peripheral immune cell activity in disease development and progression. Elevated levels of interleukin-6 (IL-6) (18), interleukin-17 (IL-17) (19, 20), and activated immune cell subsets have been identified as mediators of central nervous system inflammation in NMOSD (21). These findings have stimulated interest in peripheral blood inflammatory markers as convenient, non-invasive indicators of systemic immune responses. Comprehensive hematologic measures such as the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) (22), platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR) (23), and monocyte-to-lymphocyte ratio (MLR) may provide a comprehensive reflection of the immune-inflammatory balance (24). Unlike absolute cell counts, these ratios capture the dynamic interactions between immune cell subsets. These peripheral changes not only contribute to disease pathophysiology, diagnosis, and differential diagnosis, but also provide promising biomarkers for monitoring disease activity, predicting relapse risk, and assessing therapeutic efficacy (25). Given the challenges of repeated cerebrospinal fluid sampling and the need for noninvasive monitoring tools, identifying reliable peripheral biomarkers is particularly important for NMOSD.
This review synthesizes current evidence on peripheral blood inflammatory markers in NMOSD, focusing on their clinical applications. By integrating findings from cellular immunology, cytokine profiling, and complement biology, we aim to provide a structured overview of how these markers reflect and potentially influence disease activity and prognostic value in NMOSD.
2 Peripheral blood inflammatory indexes in NMOSD
2.1 Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR)
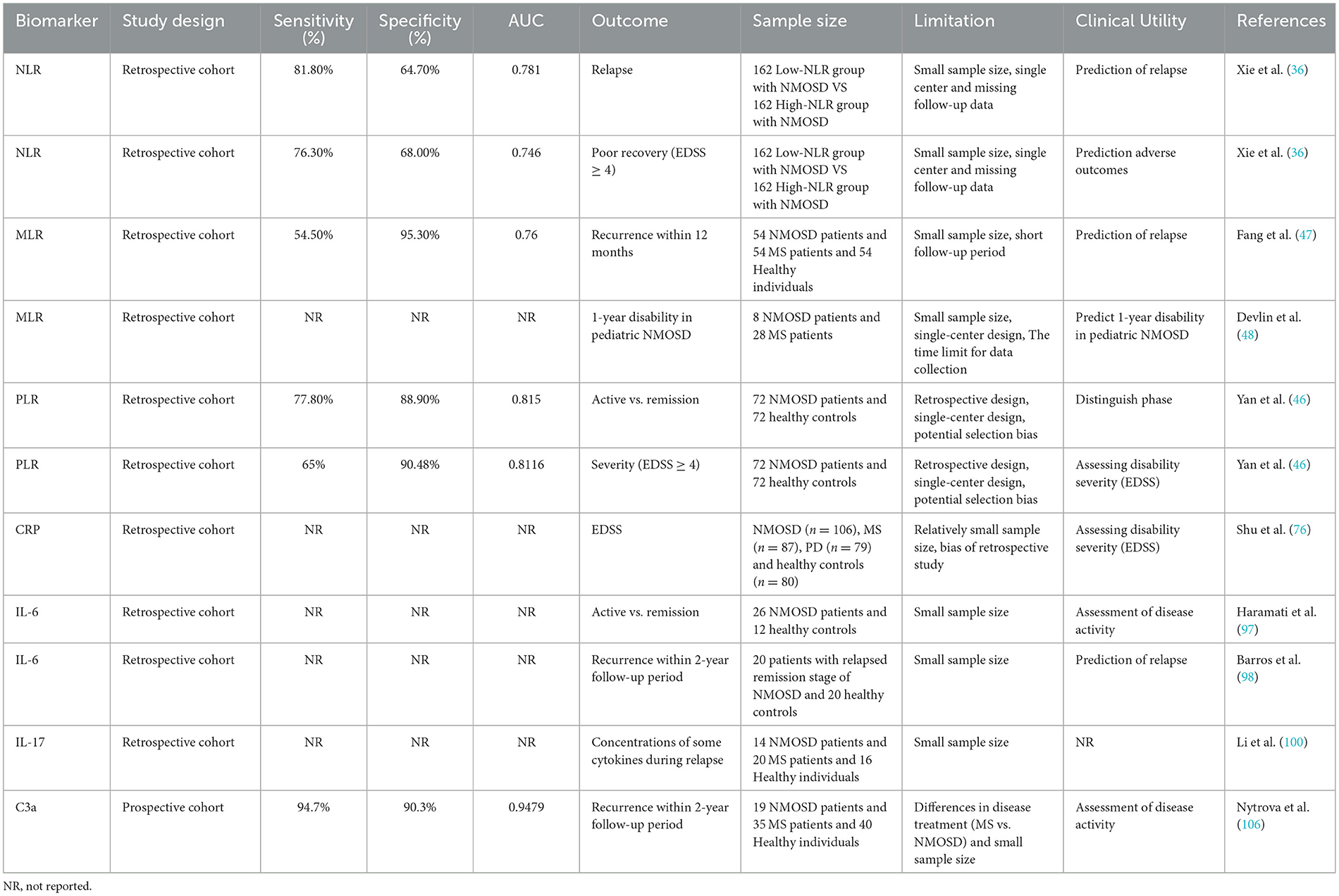
The neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) is defined as the absolute neutrophil count divided by the absolute lymphocyte count in peripheral blood (NLR = N/L) (23). NLR reflects systemic inflammation and provides a more sensitive indicator than total leukocyte or subtype counts. Elevated NLR has been associated with disease severity in malignancies (26, 27), endocrine disorders, and acute coronary syndromes (28, 29). NLR is also associated with autoimmune diseases, including multiple sclerosis (MS) (30), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) (31), Behçet's disease, primary Sjögren's syndrome (pSS) (32), and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) (33). NLR is also associated with disease severity in NMOSD (34). A retrospective study showed that NLR levels were significantly higher in NMOSD patients than in healthy controls (p < 0.001) (34). Another study compared data from 259 newly diagnosed NMOSD patients with 169 healthy controls undergoing physical examinations during the same period showing the same result (35). Furthermore, NLR levels were higher in patients with acute exacerbations than in those in remission (p < 0.001). NLR was positively correlated with increased disability from acute exacerbations [ΔEDSS (r = 0.301, p = 0.016)], suggesting that NLR may be a useful indicator for assessing NMOSD disease activity. Furthermore, NLR may reflect the severity of neurological dysfunction. In first-episode NMOSD patients, NLR may be an independent risk factor for the severity of neurological deficits. Among NMOSD patients, those with higher NLR had greater severity of neurological deficit at onset than those with lower NLR (P < 0.001); patients with severe neurological deficit had a higher NLR at onset than those with mild to moderate neurological deficit (P < 0.001). Both univariate logistic regression analysis (OR 1.180, 95% CI 1.046–1.331, P = 0.007) and multivariate logistic regression analysis (OR 1.146, 95% CI 1.003–1.308, P = 0.044) showed a positive correlation between NLR and the severity of neurological deficit at onset in NMOSD patients, with the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve was 0.687. Therefore, NLR is an independent risk factor for the severity of neurological deficits in patients with first-episode NMOSD (36). NLR has been identified as an independent prognostic marker in newly diagnosed NMOSD, significantly correlating with poor recovery. A retrospective study of 324 newly diagnosed NMOSD patients showed that high NLR was associated with significantly higher EDSS scores and recurrence rates. Multivariate analysis confirmed NLR as an independent predictor of recurrence (HR = 1.07, 95% CI: 1.03–1.10, P = 0.001) and poor recovery (HR = 1.08, 95% CI: 1.04–1.11, P = 0.001) (36). In the Xie et al. cohort, an NLR of 2.38 was used to predict relapse (sensitivity 81.8%, specificity 64.7%; AUC = 0.781); the optimal cutoff for predicting poor recovery was 2.63 (sensitivity 76.3%, specificity 68.0%; AUC = 0.746) (36). If the goal is to predict greater disability (e.g., increased EDSS score) or as a more conservative marker of “high risk,” some studies or meta-analyses have reported thresholds of 3.9–4.52 (sensitivity and specificity varies widely across studies). These findings suggest that the NLR correlates with NMOSD disease activity and is a valuable prognostic marker for NMOSD. However, its clinical utility is limited by its specificity, as the NLR may be confounded by systemic infection (37) or glucocorticoid therapy (38), both of which significantly increase neutrophil counts. Therefore, while the NLR may be most useful as an initial screening tool or for rapid risk stratification, confirmatory evaluation with other clinical and laboratory parameters is crucial before guiding treatment decisions.
2.2 Monocyte-to-lymphocyte ratio (MLR)
The monocyte-to-lymphocyte ratio (MLR) is calculated as the absolute monocyte count divided by the absolute lymphocyte count in peripheral blood (MLR = M/L) (39). MLR is recognized as an inflammatory marker and has been increasingly applied in cardiovascular diseases (40, 41), where it has demonstrated prognostic significance. Elevated neutrophil and monocyte counts, combined with reduced lymphocyte counts, are associated with the promotion of atherosclerosis (42, 43). Among these cells, monocytes play a central role by migrating into cardiac tissue, differentiating into macrophages, and secreting inflammatory cytokines, thereby contributing significantly to disease progression. Evaluation of monocyte activity, therefore, provides valuable prognostic information.
Beyond cardiovascular disorders, MLR has also been implicated in central nervous system demyelinating diseases and other autoimmune conditions (44, 45). As for NMOSD, a retrospective study comparing 72 NMOSD patients with 72 healthy controls found that serum MLR levels were significantly higher in patients (46). Regarding the prediction of NMOSD disease, recent prospective or retrospective cohorts with smaller sample sizes used receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis to identify an MLR of 0.34 as the optimal cutoff for predicting 12-month relapse (AUC ≈ 0.76; sensitivity ≈ 54.5%, specificity ≈ 95.3%) (47). This suggests that the MLR has high specificity but moderately low sensitivity for predicting relapse. Another retrospective study comparing the clinical data of 9 AQP4-positive NMOSD patients and 42 MS patients concluded that MLR can predict the 1-year disability level of children with NMOSD (48). The above research results require studies with larger sample sizes to be more convincing. Although the evidence for MLR is less robust than that for NLR or PLR (Table 1), it shows potential for predicting short-term relapse of NMOSD with a high positive predictive value and could serve as an aid in making decisions about accelerating or extending immunosuppressive therapy in established patients.
2.3 Platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR)
The platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR) is calculated as the absolute platelet count divided by the absolute lymphocyte count in peripheral blood (PLR = P/L) (49). PLR is recognized as a reliable marker of systemic inflammation (49). In oncology, PLR has been shown to have prognostic value, as tumor-associated inflammation (50) and inflammatory mediators, including cytokines and chemokines, influence disease outcomes (51, 52). By reflecting the systemic inflammatory burden, PLR provides an indirect measure of the extent of tumor-associated inflammation and may, in some contexts, outperform the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) in predicting disease severity (53, 54).
Beyond cancer, numerous studies have demonstrated the relevance of PLR across immune-mediated, metabolic, thrombotic, and neoplastic disorders (55). It has been identified as a predictor of severe disease progression, concurrent infections, aneurysmal coronary artery disease, and outcomes in inflammatory rheumatic diseases (56, 57). These findings highlight PLR as a broadly applicable inflammatory biomarker.
In NMOSD, PLR correlates positively with disease severity, as reflected by baseline EDSS scores (58). A retrospective analysis of 72 NMOSD patients and 72 healthy controls showed a significant correlation between NMOSD severity and PLR (P = 0.000) on univariate analysis, and multivariate analysis confirmed the significance of PLR (P = 0.000), indicating that serum PLR may independently contribute to the assessment of NMOSD severity (46). In addition, there was a positive correlation between PLR and baseline EDSS score, suggesting that serum PLR can serve as an independent indicator of NMOSD severity (46). These findings suggest that serum PLR can serve as a practical and cost-effective biomarker for assessing NMOSD severity and monitoring recurrence risk.
In some studies, with combining with the blood-brain barrier marker Qalb, a PLR ≥ 113 was significantly associated with moderate to severe NMOSD (EDSS ≥ 4) in the acute phase, serving as an independent risk factor in this cohort (59). PLR has also been discovered as superior specificity for the risk of disease severity compared to the NLR and is also helpful in distinguishing NMOSD from other demyelinating diseases. The PLR can be affected by thrombocytosis (60), infection (61), bleeding, or antiplatelet medications (62). Therefore, when using PLR in the clinical application of NMOSD, these interfering factors need to be considered. Future multicenter, prospective studies are needed to further enhance the role of PLR in assessing disease activity and predicting outcomes in NMOSD.
3 Other inflammatory factors and NMOSD
3.1 C-reactive protein (CRP)
C-reactive protein (CRP) is an acute-phase protein predominantly synthesized by the liver in response to cytokine signaling at sites of tissue injury or infection. It plays a central role in promoting acute inflammatory responses and has long been considered a component of the innate immune system, functioning as a pattern recognition receptor that binds phosphocholine ligands (63–65). Its rapid synthesis and short half-life make CRP a practical serological marker for the acute phase of inflammation, allowing both diagnostic assessment and monitoring of treatment response (66).
CRP levels were found to be associated with cancer risk, viral infections, and cardiovascular disease (67–69). It also serves as a biomarker for disease activity in various immune-mediated conditions, including Crohn's disease (70), Sjögren's syndrome (71), systemic lupus erythematosus (72), and rheumatoid arthritis (73). Besides, elevated CRP levels are established independent predictors of cardiovascular events (44, 74), including atherosclerosis, congestive heart failure, atrial fibrillation, myocarditis, and outcomes following heart transplantation.
Cross-sectional and retrospective cohort reports indicate that serum CRP levels are elevated in patients with active NMOSD (75), and in some cohorts, are positively correlated with acute disability scores such as EDSS (76). These studies suggest that CRP may reflect acute inflammatory burden or a concurrent systemic inflammatory state. On the other hand, several recent multi-marker and multi-omics comparative studies have demonstrated that elevated CRP levels are not consistently present in all cohorts, and its independent predictive power for relapse risk or long-term disability progression is often attenuated or lost in multivariate analyses (47, 77, 78). This discrepancy may be due to CRP's high sensitivity to various nonspecific stimuli such as infection, trauma, and concurrent autoimmune diseases (75), and its susceptibility to comorbidities (79) and treatments (e.g., corticosteroids) (80), leading to confounding bias in cohorts that haven't rigorously excluded concurrent infections or systemic diseases. Furthermore, many studies have employed cross-sectional designs or limited sample sizes, and lack consistency in sample collection or processing and testing methods, comparability and measurement accuracy across studies are limited. Limiting the value of CRP in independent prognostic models. Based on current evidence, CRP may not be supported as a standalone or primary diagnostic or prognostic biomarker for clinical decision-making in NMOSD. Its integration with other peripheral blood inflammatory markers may enhance the assessment of disease severity and prognosis, particularly in immune-mediated and acute inflammatory states. Further research and trials, such as prospective cohort studies, are needed to further clarify its potential value.
3.2 IL-6 (interleukin-6)
Interleukin (IL) family cytokines primarily regulate cell proliferation, differentiation, and activation within immune and inflammatory responses. Specifically, IL-1, IL-6, and IL-17 are key mediators in the pathogenesis of autoimmune neuroinflammatory disorders resulting from aberrant immune responses in the nervous system (81). IL-1 contributes to immune cell activation, promotes pro-inflammatory cytokine production, and disrupts the integrity of the blood-brain barrier (82). IL-17, a potent pro-inflammatory cytokine secreted by Th17 cells, critically recruits immune cells to sites of inflammation (83). IL-6 is produced by macrophages, dendritic cells, and B cells, and is essential for differentiating naïve T cells into Th17 cells (84). IL-6 contributes to neuroinflammation, enhances antibody production by activated B cells, and facilitates the differentiation of naïve T cells into Th17 cells (85).
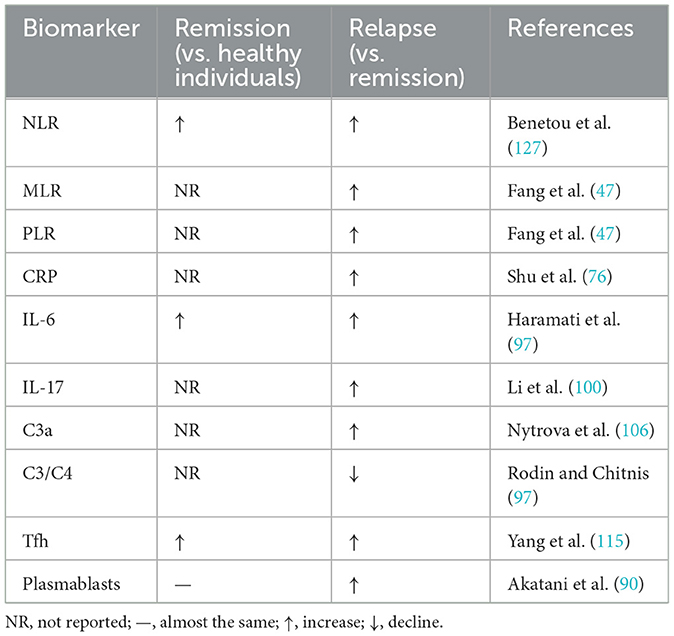
IL-6 is a key regulator of acute and chronic inflammation and hematopoiesis and is involved in inflammation, antigen-specific immune responses, host defense, hematopoiesis, and the synthesis of acute phase proteins (86). Within adaptive immunity, IL-6 promotes antibody production and supports effector T cell development (87). Aberrant IL-6 expression or signaling contributes to numerous diseases, including inflammatory and lymphoproliferative disorders such as giant cell arteritis, multiple myeloma, rheumatoid arthritis, and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) (88). After injury, neurons, astrocytes, microglia, and endothelial cells secrete IL-6, leading to elevated cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) IL-6 levels in neuroinflammatory diseases (88). In NMOSD patients, CSF IL-6 levels are typically elevated and correlate with disease severity (89). Studies have shown that the role of IL-6 in the pathogenesis of NMOSD is mediated by increased antibody production and antigen presentation, increased plasmablast and B cell levels, and decreased regulatory B cells (90). Increasing evidence indicates that NMOSD patients exhibit higher serum IL-6 levels compared with healthy individuals or patients with other diseases. Uzawa et al. reported elevated serum IL-6 in NMOSD patients compared with individuals with non-inflammatory neurological diseases (ONNDs) (91), a finding corroborated by Wang et al., who observed higher plasma IL-6 in NMO patients vs. healthy controls (92, 93). NMOSD patients exhibit markedly elevated CSF and serum IL-6 levels, and IL-6 inhibition has been shown to improve disease management (94, 95). For example, the IL-6 receptor antibody satralizumab has been approved for the treatment of NMOSD, but some neutrophils have decreased after treatment with this drug (96), suggesting that this drug has an effect on neutrophil activity. A cohort study comparing serum IL-6 levels in 26 NMOSD patients during relapse and remission showed that IL-6 levels were significantly elevated in NMOSD patients during relapse compared with remission (n = 19, 8.39 ± 10.84 pg/ml vs. n = 19, 2.02 ± 2.27 pg/ml, p = 0.001) and in HCC patients (n = 16, 1.23 ± 1.18 pg/ml, p < 0.01). This suggests that IL-6 levels are significantly elevated in NMOSD patients during relapse (97). Furthermore, elevated IL-6 levels correlate with relapse severity. Therefore, serum IL-6 levels can serve as a biomarker for NMOSD disease activity and IL-6 detection helps in disease stratification and personalized medication decision making. Regarding the role of IL-6 levels in the prognosis of NMOSD patients, studies have shown that IL-6 levels produced during remission can predict the severity of NMOSD relapse (98). However, this study involved a small sample size. Therefore, the role of IL-6 levels in NMOSD prognosis requires further clarification in multicenter, large-sample prospective studies. Future research will demonstrate significant potential for combined modeling of IL-6 with other peripheral blood inflammatory markers.
3.3 IL-17 (interleukin-17)
Cytokines are low molecular weight proteins that regulate immune and inflammatory responses. Cytokines play a crucial role in regulating neuroinflammatory responses by recruiting and activating different types of cells (99). IL-17 is a potent proinflammatory cytokine produced by Th17 cells that plays a crucial role in recruiting immune cells to inflammatory sites (83). It is well-known that IL-17 signaling is crucial for the development of autoimmune diseases and is involved in biological processes such as neutrophil infiltration into the CNS and promotion of neuroinflammation (100). Studies have shown that NMOSD patients exhibit activated IL-17 signaling (101). Compared with HCC, NMOSD patients have increased expression of the cytokine IL-7 in peripheral blood (102). A large number of studies have confirmed that certain cytokines or chemokines and related molecules such as IL-17 are associated with the clinical activity (102) and long-term prognosis of NMOSD. A meta-analysis included 17 studies reporting IL-17 levels in NMOSD patients and controls. The results showed that IL-17 levels in NMOSD patients were higher than those in the control group [0.87, (0.42, 1.33), P < 0.001], but there was significant heterogeneity, which was considered to be caused by the use of a random effects model. Accumulating evidence suggests that IL-17 is crucial for disease activity and adverse outcomes in AQP4-IgG-positive NMOSD (103), but evidence on their independent predictive value remains limited. Multiple cross-sectional and case-control studies have detected elevated IL-17A levels in serum and cerebrospinal fluid during relapse or active phases. Further meta-analyses and reviews have summarized these cross-sectional observations, suggesting that the proportion of Th17 cells and Th17 core cytokines are generally higher in NMOSD than in healthy controls, and are often associated with active disease (102). These evidences support the IL-17 or Th17 pathway as a candidate prognostic marker and “biomarker of treatment response,” but more adequate longitudinal cohort data are needed to demonstrate that baseline or early follow-up IL-17 levels can independently predict future outcomes such as relapse rate, disability progression, or death. In conclusion, IL-17 plays an important role in disease activity and worse clinical outcomes in NMOSD. However, its use as an independent prognostic marker requires further investigation.
3.4 Complement system
The complement system, a component of the innate immune system, facilitates pathogen clearance through antibody and phagocyte-mediated mechanisms. While complement activation is generally protective, excessive or dysregulated activation can cause tissue damage (104). Relevant studies have shown that there is a correlation between complement components and the ratio of neutrophils to lymphocytes. A retrospective study analyzing blood indicators, complement information and other related data of 75 healthy adolescents showed that there is a positive correlation between NLR and C3a and C4 levels (105). Plasma C3a levels correlate with NMOSD activity, as measured by the EDSS (106), highlighting the potential of C3a as a biomarker for disease activity (107). Recent evidence indicates that C3a mediates microglial activation and contributes to early CNS pathology in NMOSD (108). Accordingly, C3a levels may serve as an indicator of disease activity in NMOSD. Peripheral blood complement products play an important role in reflecting disease activity and predicting clinical outcomes (109). Multiple clinical cohorts and systematic reviews have demonstrated that activated complement fragments, such as Ba, C3a, C5a, and the terminal complex sC5b-9 are often significantly elevated during relapses or periods of increased disease activity (77). More significance is the association of complement markers with disease severity or short-term outcomes in several studies: serum or cerebrospinal fluid sC5b-9 levels are positively correlated with the EDSS score and higher sC5b-9 or Ba levels are associated with an increased risk of near-term relapse (110), a pattern replicated in multicenter and single-center samples. However, research on the relationship between complement levels and NMOSD disease activity and prognosis in clinical practice is lacking. Existing studies also have limitations, requiring further refinement, such as expanding sample sizes and conducting prospective studies. Additionally, studies have combined complement C3 and C3a with the neutrophil ratio for some inflammatory and disease activity assessments (111). Therefore, combining complement levels with conventional peripheral inflammatory markers for joint modeling may be a promising approach for future clinical application in NMOSD patients, thereby transforming complement markers into reliable prognostic biomarkers and influencing clinical decision-making.
3.5 Follicular helper T cells (Tfh)
Tfh cells are a novel type of CD4+ T cell that play a role in assisting B cell activation and maturation (112). In recent years, the role of Tfh cells in NMOSD has garnered increasing attention. Studies in an animal model have shown that Tfh is involved in the pathogenesis of neurological autoimmune diseases (113). Existing studies have shown that the proportion of peripheral blood Tfh cells is significantly elevated in patients with acute-phase NMOSD who are serum AQP4 antibody-positive (114). This increase correlates with acute disease activity, suggesting that the Tfh ratio is involved in the pathogenesis of NMOSD. Furthermore, a study comparing blood samples from 36 patients in the acute and recovery phases of NMOSD, 20 patients with other non-inflammatory neurological diseases (ONND), and 20 age- and sex-matched healthy volunteers showed that the proportion of peripheral blood Tfh cells in acute-phase NMOSD patients was positively correlated with EDSS scores (r = 0.596, P < 0.001), suggesting that Tfh cell levels may serve as a biomarker for disease severity (115). The current study still has a small sample size, and further multicenter, large-sample studies are needed in the future to further support the relationship between Tfh and NMOSD disease activity. However, their clinical application in predicting prognosis requires further investigation.
3.6 Plasmablasts
Plasmablasts are intermediate-stage cells that differentiate from B cells during the immune response (116). Plasmablasts are involved in disease pathogenicity and immune regulation. Analyzing plasmablast levels may enable the diagnosis and assessment of the disease status of autoantibody-related neuroimmune diseases, such as NMOSD (117). A study analyzing blood samples from patients with NMOSD and other neuroinflammatory diseases, as well as healthy individuals, demonstrated an increased frequency of plasmablasts in NMOSD patients compared with patients with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis and healthy individuals (118) (Table 2). Another study also suggests a direct correlation between plasmablast levels and AQP4-IgG production in NMOSD (119). These results may suggest a correlation between plasmablast levels and disease activity in NMOSD. But, the current study still involves a small sample size, and future large-sample, multi-center prospective studies are needed to further clarify the association between plasmablasts and NMOSD disease activity. However, research on the clinical application of plasmablasts in NMOSD prognosis is currently lacking and warrants further investigation. Furthermore, various B cell subsets involved in downregulating excessive immune and inflammatory responses have protective effects. These B cell subsets are often referred to as regulatory B cells (Bregs). Bregs play a crucial role in several immune diseases, and Breg subsets may play a complex role in the pathogenesis of NMOSDs (120). Current research has shown that Breg numbers or function are decreased in NMOSD patients, suggesting a possible correlation between Bregs and disease activity (90). However, research in this area remains limited, and further study is needed to clarify this issue. Current research on the role of Bregs in NMOSD prognosis is insufficient, and further research is needed to explore this relationship and inform clinical practice in NMOSD.
4 Conclusion
Peripheral blood inflammatory markers, including NLR, PLR, MLR, IL-6, IL-17, CRP, Plasmablasts, Tfh and the complement system, have become important tools for assessing disease activity and prognosis in NMOSD. In particular, NLR and PLR, according to existing research (34–36), have been shown to be significantly correlated with disease severity, relapse risk, and functional outcome, reflecting the systemic immune-inflammatory state and the underlying pathophysiology involving neutrophil-, platelet-, and monocyte-mediated processes, and therefore have relatively high clinical practical application value. However, more research is needed on MLR, IL-6, IL-17, CRP, Plasmablasts, Tfh and complement system to further clarify the reliability of their application value in clinical practice.
Timely assessment of disease activity and prediction of relapse are critical for NMOSD management. Although traditional methods such as imaging and serological tests can provide important information, for example, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is crucial in the early identification of NMOSD and guiding immediate acute treatment decisions (121). It is currently the standard for monitoring NMOSD lesions, especially in the diagnosis of NMOSD seronegative cases (122). It plays an increasingly important role, but they are often costly, invasive or time-consuming. In contrast, inflammatory markers detected by routine blood cell counts are simple, reproducible and cost-effective, and can dynamically monitor immune status and disease progression. Based on current research, routine clinical measurements such as NLR, PLR, MLR, CRP, complement C3/C4, and, if available, serum IL-6 are recommended upon diagnosis or initial visit (47). These measurements can serve as baseline references for follow-up. In the event of suspected or confirmed relapse, NLR, PLR, MLR, and CRP should be immediately repeated, and serum IL-6 and complement activation products should be measured, if possible, to assess inflammation and adjust clinical treatment (97). For patients at risk of relapse or who have recently discontinued medication, the use of NLR, PLR, and MLR as inexpensive and easily available routine follow-up markers for NMOSD disease assessment may be a good option. If used to predict short-term relapse, such as MLR, remeasurement can be performed 3–6 months after the initial hospitalization or baseline, and clinical judgment can be used to consider intensification or adjustment of maintenance therapy (47). Furthermore, when using anti-complement therapies such as IL-6R inhibitors or eculizumab, monitoring of relevant pathway markers such as IL-6, CRP, and complement products can help assess drug effects and complication risks (95), but understanding the effects of the medication itself on these markers is crucial. However, further in-depth research is needed on the specific application of these peripheral blood inflammatory indicators in clinical practice in the future. It is important to note that there is currently a lack of research directly comparing the effects of MRI and peripheral blood inflammatory markers on NMOSD disease outcomes (123). Future research should further improve direct comparisons of the two to further conclude that peripheral blood inflammatory markers may become a faster and cheaper method.
Each marker also has intrinsic strengths and weaknesses, and using a single parameter may provide an incomplete assessment. Existing studies on NLR, PLR, MLR, CRP, IL-6, IL-17, or complement C3 and C4 have mentioned that “multiple indicators have the potential to improve predictive or differential value in NMOSD” (47, 77, 123). However, there are few validated, clinically applicable combined prognostic scores or threshold systems (124). This is a clear gap in the current literature, suggesting that future research needs to improve multicenter, large sample size, and combined modeling with other indicators to build a comprehensive multi-indicator combined system (125, 126).
Future research should prioritize large-scale, prospective, multicenter studies to validate the prognostic value of peripheral blood inflammatory markers and establish standardized assessment protocols. Integrating these markers into comprehensive evaluation systems could improve the precision of disease monitoring, relapse prediction, and therapeutic decision-making. Overall, peripheral blood inflammatory markers offer a practical, accessible, and informative approach with substantial potential to guide prognosis and optimize clinical management in NMOSD, pending further validation.
Author contributions
BW: Investigation, Software, Writing – original draft, Supervision, Data curation, Project administration. BX: Resources, Validation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing, Supervision. FC: Software, Data curation, Writing – original draft, Investigation. XG: Project administration, Methodology, Investigation, Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Software, Writing – original draft. MM: Project administration, Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the “flagship” department construction project of the collaboration between Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Jarius S, Paul F, Weinshenker BG, Levy M, Kim HJ, Wildemann B. Neuromyelitis optica. Nat Rev Dis Primers. (2020) 6:85. doi: 10.1038/s41572-020-0214-9
2. Huda S, Whittam D, Bhojak M, Chamberlain J, Noonan C, Jacob A, et al. Neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders. Clin Med. (2019) 19:169–76. doi: 10.7861/clinmedicine.19-2-169
3. Papadopoulos MC, Bennett JL, Verkman AS. Treatment of neuromyelitis optica: state-of-the-art and emerging therapies. Nat Rev Neurol. (2014) 10:493–506. doi: 10.1038/nrneurol.2014.141
4. Wang Y, Xu Y. Advances in maintenance therapies for neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders: a new era of targeted drugs. Mult Scler Relat Disord. (2025) 96:106351. doi: 10.1016/j.msard.2025.106351
5. Lucchinetti CF, Guo Y, Popescu BFGh, Fujihara K, Itoyama Y, Misu T. The pathology of an autoimmune astrocytopathy: lessons learned from neuromyelitis optica. Brain Pathol. (2014) 24:83–97. doi: 10.1111/bpa.12099
6. Kawachi I, Lassmann H. Neurodegeneration in multiple sclerosis and neuromyelitis optica. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. (2017) 88:137–45. doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2016-313300
7. Wingerchuk DM, Banwell B, Bennett JL, Cabre P, Carroll W, Chitnis T, et al. International consensus diagnostic criteria for neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders. Neurology. (2015) 85:177–89. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000001729
8. Viswanathan S, Wah LM. A nationwide epidemiological study on the prevalence of multiple sclerosis and neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder with important multi-ethnic differences in Malaysia. Mult Scler. (2019) 25:1452–61. doi: 10.1177/1352458518792430
9. Jarius S, Wildemann B. The history of neuromyelitis optica. Part 2: ‘Spinal amaurosis', or how it all began. J Neuroinflammation. (2019) 16:280. doi: 10.1186/s12974-019-1594-1
10. Pittock SJ, Weinshenker BG, Lucchinetti CF, Wingerchuk DM, Corboy JR, Lennon VA. Neuromyelitis optica brain lesions localized at sites of high aquaporin 4 expression. Arch Neurol. (2006) 63:964. doi: 10.1001/archneur.63.7.964
11. Rivera VM, Hamuy F, Rivas V, Gracia F, Rojas JI, Bichuetti DB, et al. Status of the neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder in Latin America. Mult Scler Relat Disord. (2021) 53:103083. doi: 10.1016/j.msard.2021.103083
12. Waters P, Reindl M, Saiz A, Schanda K, Tuller F, Kral V, et al. Multicentre comparison of a diagnostic assay: aquaporin-4 antibodies in neuromyelitis optica. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. (2016) 87:1005–15. doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2015-312601
13. Pandit L, Asgari N, Apiwattanakul M, Palace J, Paul F, Leite M, et al. Demographic and clinical features of neuromyelitis optica: a review. Mult Scler. (2015) 21:845–53. doi: 10.1177/1352458515572406
14. Papp V, Illes Z, Magyari M, Koch-Henriksen N, Kant M, Pfleger CC, et al. Nationwide prevalence and incidence study of neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder in Denmark. Neurology. (2018) 91:6645. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000006645
15. Eskandarieh S, Nedjat S, Azimi AR, Moghadasi AN, Sahraian MA. Neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders in Iran. Mult Scler Relat Disord. (2017) 18:209–12. doi: 10.1016/j.msard.2017.10.007
16. Carnero Contentti E, Correale J. Neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders: from pathophysiology to therapeutic strategies. J Neuroinflammation. (2021) 18:208. doi: 10.1186/s12974-021-02249-1
17. Wingerchuk DM, Lennon VA, Pittock SJ, Lucchinetti CF, Weinshenker BG. Revised diagnostic criteria for neuromyelitis optica. Neurology. (2006) 66:1485–9. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000216139.44259.74
18. Uzawa A, Mori M, Sawai S, Masuda S, Muto M, Uchida T, et al. Cerebrospinal fluid interleukin-6 and glial fibrillary acidic protein levels are increased during initial neuromyelitis optica attacks. Clinica Chimica Acta. (2013) 421:181–3. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2013.03.020
19. Ishizu T, Osoegawa M, Mei F-J, Kikuchi H, Tanaka M, Takakura Y, et al. Intrathecal activation of the IL-17/IL-8 axis in opticospinal multiple sclerosis. Brain. (2005) 128:988–1002. doi: 10.1093/brain/awh453
20. Wojkowska DW, Szpakowski P, Ksiazek-Winiarek D, Leszczynski M, Glabinski A. Interactions between neutrophils, Th17 cells, and chemokines during the initiation of experimental model of multiple sclerosis. Mediators Inflamm. (2014) 2014:1–8. doi: 10.1155/2014/590409
21. Lin J, Li X, Xia J. Th17 cells in neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder: a review. Int J Neurosci. (2016) 126:1051–60. doi: 10.3109/00207454.2016.1163550
22. Zhou K, Cao J, Lin H, Liang L, Shen Z, Wang L, et al. Prognostic role of the platelet to lymphocyte ratio (PLR) in the clinical outcomes of patients with advanced lung cancer receiving immunotherapy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Oncol. (2022) 12:962173. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.962173
23. Zhang X, Duan J, Wen Z, Xiong H, Chen X, Liu Y, et al. Are the derived indexes of peripheral whole blood cell counts (NLR, PLR, LMR/MLR) clinically significant prognostic biomarkers in multiple myeloma? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Oncol. (2021) 11:766672. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.766672
24. Zhang C, Jiang X, Li Y, Pan X, Gao M, Chen Y, et al. Independent predictive value of blood inflammatory composite markers in ovarian cancer: recent clinical evidence and perspective focusing on NLR and PLR. J Ovarian Res. (2023) 16:36. doi: 10.1186/s13048-023-01116-2
25. Xie J, Guo Z, Zhu Y, Ma M, Jia G. Peripheral blood inflammatory indexes in breast cancer: a review. Medicine. (2023) 102:e36315. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000036315
26. Templeton AJ, McNamara MG, Šeruga B, Vera-Badillo FE, Aneja P, Ocaña A, et al. Prognostic role of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in solid tumors: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Natl Cancer Inst. (2014) 106:dju124. doi: 10.1093/jnci/dju124
27. Xia W-K, Liu Z-L, Shen D, Lin Q-F, Su J, Mao W-D. Prognostic performance of pre-treatment NLR and PLR in patients suffering from osteosarcoma. World J Surg Onc. (2016) 14:127. doi: 10.1186/s12957-016-0889-2
28. Guclu K, Celik M. Prognostic value of inflammation parameters in patients with non-ST elevation acute coronary syndromes. Angiology. (2020) 71:825–30. doi: 10.1177/0003319720936500
29. Hsu J-T, Wang C-C, Le P-H, Chen T-H, Kuo C-J, Lin C-J, et al. Lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratios predict gastric cancer surgical outcomes. J Surg Res. (2016) 202:284–90. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2016.01.005
30. Demirci S, Demirci S, Kutluhan S, Koyuncuoglu HR, Yurekli VA. The clinical significance of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in multiple sclerosis. Int J Neurosci. (2016) 126:700–6. doi: 10.3109/00207454.2015.1050492
31. Wu Y, Chen Y, Yang X, Chen L, Yang Y. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR) were associated with disease activity in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Int Immunopharmacol. (2016) 36:94–9. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2016.04.006
32. Hu Z-D, Sun Y, Guo J, Huang Y-L, Qin B-D, Gao Q, et al. Red blood cell distribution width and neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio are positively correlated with disease activity in primary Sjögren's syndrome. Clin Biochem. (2014) 47:287–90. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2014.08.022
33. Celikbilek M, Dogan S, Ozbakir O, Zararsiz G, Kücük H, Gürsoy S, et al. Neutrophil–lymphocyte ratio as a predictor of disease severity in ulcerative colitis. Clin Lab Anal. (2013) 27:72–6. doi: 10.1002/jcla.21564
34. Lin J, Xue B, Li J, Xu H, Huang X, Yao Z, et al. Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio may be a helpful marker to evaluate disease activity in NMOSD. Neurol Sci. (2017) 38:1859–63. doi: 10.1007/s10072-017-3068-5
35. Zhou Y, Xie H, Zhao Y, Zhang J, Li Y, Duan R, et al. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio on admission is an independent risk factor for the severity of neurological impairment at disease onset in patients with a first episode of neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder. NDT. (2021) 17:1493–503. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S311942
36. Xie H, Zhao Y, Pan C, Zhang J, Zhou Y, Li Y, et al. Association of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) with the prognosis of first attack neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD): a retrospective cohort study. BMC Neurol. (2021) 21:389. doi: 10.1186/s12883-021-02432-0
37. Chen J, Yasrebinia S, Ghaedi A, Khanzadeh M, Quintin S, Dagra A, et al. Meta-analysis of the role of neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio in neonatal sepsis. BMC Infect Dis. (2023) 23:837. doi: 10.1186/s12879-023-08800-0
38. Jia W-Y, Zhang J-J. Effects of glucocorticoids on leukocytes: genomic and non-genomic mechanisms. WJCC. (2022) 10:7187–94. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i21.7187
39. Liu H, Dong H, Guo M, Cheng H. Association between inflammation indicators (MLR, NLR, SII, SIRI, and AISI) and erectile dysfunction in US adults: NHANES 2001–2004. J Health Popul Nutr. (2024) 43:169. doi: 10.1186/s41043-024-00667-4
40. Heidarpour M, Bashiri S, Vakhshoori M, Heshmat-Ghahdarijani K, Khanizadeh F, Ferdowsian S, et al. The association between platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio with mortality among patients suffering from acute decompensated heart failure. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. (2021) 21:454. doi: 10.1186/s12872-021-02260-7
41. Urbanowicz T, Olasińska-Wiśniewska A, Michalak M, Rodzki M, Witkowska A, Straburzyńska-Migaj E, et al. The prognostic significance of neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR), monocyte to lymphocyte ratio (MLR) and platelet to lymphocyte ratio (PLR) on long-term survival in off-pump coronary artery bypass grafting (OPCAB) procedures. Biology. (2021) 11:34. doi: 10.3390/biology11010034
42. Pinheiro Machado G, Araujo GN, Carpes CK, Lech MC, Mariani S, Valle FH, et al. Elevated neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio can predict procedural adverse events in patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction undergoing primary percutaneous coronary intervention. Coron Artery Dis. (2019) 30:20–5. doi: 10.1097/MCA.0000000000000671
43. Her A-Y, Cho KI, Singh GB, An DS, Jeong Y-H, Koo B-K, et al. Plaque characteristics and inflammatory markers for the prediction of major cardiovascular events in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. (2017) 33:1445–54. doi: 10.1007/s10554-017-1135-x
44. Olsson A, Gustavsen S, Gisselø Lauridsen K, Chenoufi Hasselbalch I, Sellebjerg F, Bach Søndergaard H, et al. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and CRP as biomarkers in multiple sclerosis: a systematic review. Acta Neurol Scand. (2021) 143:577–86. doi: 10.1111/ane.13401
45. Huang W-C, Lin H-C, Yang Y-H, Hsu C-W, Chen N-C, Tsai W-C, et al. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and monocyte-to-lymphocyte ratio are associated with a 2-year relapse in patients with multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler Relat Disord. (2022) 58:103514. doi: 10.1016/j.msard.2022.103514
46. Yan H, Wang Y, Li Y, Shen X, Ma L, Wang M, et al. Combined platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio and blood-brain barrier biomarkers as indicators of disability in acute neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder. Neurol Sci. (2024) 45:709–18. doi: 10.1007/s10072-023-07058-3
47. Fang X, Sun S, Yang T, Liu X. Predictive role of blood-based indicators in neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders. Front Neurosci. (2023) 17:1097490. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1097490
48. Devlin L, Gombolay G. The neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and the monocyte-to-lymphocyte ratio predict expanded disability status scale score at one year in pediatric neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder but not in multiple sclerosis. Pediatr Neurol. (2023) 143:84–8. doi: 10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2023.03.009
49. Lu H-R, Zhu P-F, Deng Y-Y, Chen Z-L, Yang L. Predictive value of NLR and PLR for immune-related adverse events: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Transl Oncol. (2023) 26:1106–16. doi: 10.1007/s12094-023-03313-3
50. Kumarasamy C, Tiwary V, Sunil K, Suresh D, Shetty S, Muthukaliannan GK, et al. Prognostic utility of platelet–lymphocyte ratio, neutrophil–lymphocyte ratio and monocyte–lymphocyte ratio in head and neck cancers: a detailed PRISMA compliant systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancers. (2021) 13:4166. doi: 10.3390/cancers13164166
51. Singh N, Baby D, Rajguru J, Patil P, Thakkannavar S, Pujari V. Inflammation and cancer. Ann Afr Med. (2019) 18:121. doi: 10.4103/aam.aam_56_18
52. Yan M, Jurasz P. The role of platelets in the tumor microenvironment: From solid tumors to leukemia. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta. (2016) 1863:392–400. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2015.07.008
53. Kayhan F, Gündüz S, Ersoy SA, Kandeger A, Annagür BB. Relationships of neutrophil–lymphocyte and platelet–lymphocyte ratios with the severity of major depression. Psychiatry Res. (2017) 247:332–5. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2016.11.016
54. Turkmen K, Erdur FM, Ozcicek F, Ozcicek A, Akbas EM, Ozbicer A, et al. Platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio better predicts inflammation than neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in end-stage renal disease patients. Hemodial Int. (2013) 17:391–6. doi: 10.1111/hdi.12040
55. Kawamura Y, Takeshita S, Kanai T, Yoshida Y, Nonoyama S. The combined usefulness of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratios in predicting intravenous immunoglobulin resistance with Kawasaki disease. J Pediatr. (2016) 178:281–4.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2016.07.035
56. Savioli F, Morrow ES, Dolan RD, Romics L, Lannigan A, Edwards J, et al. Prognostic role of preoperative circulating systemic inflammatory response markers in primary breast cancer: meta-analysis. Br J Surg. (2022) 109:1206–15. doi: 10.1093/bjs/znac319
57. Zhang F, Gong W. Prognostic value of the platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio in patients with melanoma: a meta-analysis. Front Oncol. (2020) 10:1116. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.01116
58. Duan Z, Feng J. Comparison of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio between myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein antibody-associated disease and aquaporin-4 antibody-positive neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders in adults. J Clin Neurosci. (2022) 101:89–93. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2022.05.002
59. Carnero Contentti E, López PA, Criniti J, Pettinicchi JP, Cristiano E, Patrucco L, et al. Platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio differs between MS and NMOSD at disease onset and predict disability. Mult Scler Relat Disord. (2022) 58:103507. doi: 10.1016/j.msard.2022.103507
60. Gasparyan AY, Ayvazyan L, Mukanova U, Yessirkepov M, Kitas GD. The platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio as an inflammatory marker in rheumatic diseases. Ann Lab Med. (2019) 39:345–57. doi: 10.3343/alm.2019.39.4.345
61. Sarkar S, Kannan S, Khanna P, Singh AK. Role of platelet-to-lymphocyte count ratio (PLR), as a prognostic indicator in COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Med Virol. (2022) 94:211–21. doi: 10.1002/jmv.27297
62. Ishibashi Y, Tsujimoto H, Kouzu K, Itazaki Y, Tsuchiya S, Fujishima S, et al. Impact of antiplatelet and anticoagulant therapies on platelet-related prognostic markers in patients with esophageal cancer. In Vivo. (2020) 34:1941–9. doi: 10.21873/invivo.11991
63. Jimenez RV, Wright TT, Jones NR, Wu J, Gibson AW, Szalai AJ. C-reactive protein impairs dendritic cell development, maturation, and function: implications for peripheral tolerance. Front Immunol. (2018) 9:372. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00372
64. Cottin V, Valenzuela C. C-reactive protein as a candidate biomarker in fibrotic interstitial lung disease. Respirology. (2024) 29:195–8. doi: 10.1111/resp.14666
65. Olson ME, Hornick MG, Stefanski A, Albanna HR, Gjoni A, Hall GD, et al. Biofunctional review of C-reactive protein (CRP) as a mediator of inflammatory and immune responses: differentiating pentameric and modified CRP isoform effects. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1264383. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1264383
66. Lapić I, Padoan A, Bozzato D, Plebani M. Erythrocyte Sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein in acute inflammation. Am J Clin Pathol. (2020) 153:14–29. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/aqz142
67. Isaacs AW, Macaluso F, Smith C, Myburgh KH. C-reactive protein is elevated only in high creatine kinase responders to muscle damaging exercise. Front Physiol. (2019) 10:86. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2019.00086
68. Torzewski J, Brunner P, Ries W, Garlichs CD, Kayser S, Heigl F, et al. Targeting C-reactive protein by selective apheresis in humans: pros and cons. JCM. (2022) 11:1771. doi: 10.3390/jcm11071771
69. Hart PC, Rajab IM, Alebraheem M, Potempa LA. C-reactive protein and cancer—diagnostic and therapeutic insights. Front Immunol. (2020) 11:595835. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.595835
70. Zhou H-H, Tang Y-L, Xu T-H, Cheng B. C-reactive protein: structure, function, regulation, and role in clinical diseases. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1425168. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1425168
71. Plebani M. Why C-reactive protein is one of the most requested tests in clinical laboratories? Clin Chem Lab Med. (2023) 61:1540–5. doi: 10.1515/cclm-2023-0086
72. Vermeire S, Van Assche G. Rutgeerts P. C-reactive protein as a marker for inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. (2004) 10:661–5. doi: 10.1097/00054725-200409000-00026
73. Vogt B, Führnrohr B, Müller R, Sheriff A. CRP and the disposal of dying cells: consequences for systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis. Autoimmunity. (2007) 40:295–8. doi: 10.1080/08916930701358925
74. Osman R, L'Allier PL, Elgharib N, Tardif J-C. Critical appraisal of C-reactive protein throughout the spectrum of cardiovascular disease. Vasc Health Risk Manag. (2006) 2:221–37. doi: 10.2147/vhrm.2006.2.3.221
75. Zhang B, Zhong Y, Wang Y, Dai Y, Qiu W, Zhang L, et al. Neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders without and with autoimmune diseases. BMC Neurol. (2014) 14:162. doi: 10.1186/s12883-014-0162-7
76. Shu Y, Li R, Qiu W, Chang Y, Sun X, Fang L, et al. Association of serum gamma-glutamyltransferase and C-reactive proteins with neuromyelitis optica and multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler Relat Disord. (2017) 18:65–70. doi: 10.1016/j.msard.2017.09.021
77. Rodin RE, Chitnis T. Soluble biomarkers for neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders: a mini review. Front Neurol. (2024) 15:1415535. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1415535
78. Li X, Jiang W, Li G, Ding Y, Li H, Sun J, et al. Inflammatory and nutritional markers as indicators for diagnosing and assessing disease activity in MS and NMOSD. J Inflamm Res. (2024) 17:10065–78. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S489502
79. Mouliou DS. C-reactive protein: pathophysiology, diagnosis, false test results and a novel diagnostic algorithm for clinicians. Diseases. (2023) 11:132. doi: 10.3390/diseases11040132
80. Torres A, Ceccato A, Ferrer M, Gabarrus A, Sibila O, Cilloniz C, et al. Effect of corticosteroids on c-reactive protein in patients with severe community-acquired pneumonia and high inflammatory response: the effect of lymphopenia. J Clin Med. (2019) 8:1461. doi: 10.3390/jcm8091461
81. Khan S, Bilal H, Khan MN, Fang W, Chang W, Yin B, et al. Interleukin inhibitors and the associated risk of candidiasis. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1372693. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1372693
82. Mantovani A, Dinarello CA, Molgora M, Garlanda C. Interleukin-1 and related cytokines in the regulation of inflammation and immunity. Immunity. (2019) 50:778–95. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2019.03.012
83. Liu T, Li S, Ying S, Tang S, Ding Y, Li Y, et al. The IL-23/IL-17 pathway in inflammatory skin diseases: from bench to bedside. Front Immunol. (2020) 11:594735. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.594735
84. Kishimoto T. Interleukin-6: from basic science to medicine-−40 years in immunology. Annu Rev Immunol. (2005) 23:1–21. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.23.021704.115806
85. Bettelli E, Carrier Y, Gao W, Korn T, Strom TB, Oukka M, et al. Reciprocal developmental pathways for the generation of pathogenic effector TH17 and regulatory T cells. Nature. (2006) 441:235–8. doi: 10.1038/nature04753
86. Ataie-Kachoie P, Pourgholami MH, Morris DL. Inhibition of the IL-6 signaling pathway: a strategy to combat chronic inflammatory diseases and cancer. Cytok Growth Factor Rev. (2013) 24:163–73. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2012.09.001
87. Tanaka T, Kishimoto T. Targeting interleukin-6: all the way to treat autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. Int J Biol Sci. (2012) 8:1227–36. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.4666
88. Garbers C, Heink S, Korn T, Rose-John S. Interleukin-6: designing specific therapeutics for a complex cytokine. Nat Rev Drug Discov. (2018) 17:395–412. doi: 10.1038/nrd.2018.45
89. Fujihara K, Bennett JL, De Seze J, Haramura M, Kleiter I, Weinshenker BG, et al. Interleukin-6 in neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder pathophysiology. Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm. (2020) 7:e841. doi: 10.1212/NXI.0000000000000841
90. Akatani R, Chihara N, Hara A, Tsuji A, Koto S, Kobayashi K, et al. Interleukin-6 signaling blockade induces regulatory plasmablasts in neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder. Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm. (2024) 11:e200266. doi: 10.1212/NXI.0000000000200266
91. Li X, Zhao C. Interleukin-6 in neuroimmunological disorders: Pathophysiology and therapeutic advances with satralizumab. Autoimmun Rev. (2025) 24:103826. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2025.103826
92. Uzawa A, Mori M, Arai K, Sato Y, Hayakawa S, Masuda S, et al. Cytokine and chemokine profiles in neuromyelitis optica: significance of interleukin-6. Mult Scler. (2010) 16:1443–52. doi: 10.1177/135245851037
93. Wang H, Wang K, Wang C, Xu F, Qiu W, Hu X. Increased plasma interleukin-32 expression in patients with neuromyelitis optica. J Clin Immunol. (2013) 33:666–70. doi: 10.1007/s10875-012-9837-2
94. Aungsumart S, Youngkong S, Dejthevaporn C, Chaikledkaew U, Thadanipon K, Tansawet A, et al. Efficacy and safety of monoclonal antibody therapy in patients with neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Front Neurol. (2023) 14:1166490. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1166490
95. Yamamura T, Kleiter I, Fujihara K, Palace J, Greenberg B, Zakrzewska-Pniewska B, et al. Trial of satralizumab in neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder. N Engl J Med. (2019) 381:2114–24. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1901747
96. Matsuoka T, Araki M, Lin Y, Okamoto T, Gold R, Chihara N, et al. Long-term effects of IL-6 receptor blockade therapy on regulatory lymphocytes and neutrophils in neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder. Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm. (2024) 11:e200173. doi: 10.1212/NXI.0000000000200173
97. Haramati A, Rechtman A, Zveik O, Haham N, Brill L, Vaknin-Dembinsky A. IL-6 as a marker for NMOSD disease activity. J Neuroimmunol. (2022) 370:577925. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2022.577925
98. Barros PO, Cassano T, Hygino J, Ferreira TB, Centurião N, Kasahara TM, et al. Prediction of disease severity in neuromyelitis optica by the levels of interleukin (IL)-6 produced during remission phase. Clin Exp Immunol. (2016) 183:480–9. doi: 10.1111/cei.12733
99. Uzawa A, Mori M, Kuwabara S. Cytokines and chemokines in neuromyelitis optica: pathogenetic and therapeutic implications. Brain Pathol. (2014) 24:67–73. doi: 10.1111/bpa.12097
100. Li Y, Wang H, Long Y, Lu Z, Hu X. Increased memory Th17 cells in patients with neuromyelitis optica and multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimmunol. (2011) 234:155–60. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2011.03.009
101. Arellano G, Loda E, Chen Y, Neef T, Cogswell AC, Primer G, et al. Interferon-γ controls aquaporin 4-specific Th17 and B cells in neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder. Brain. (2024) 147:1344–61. doi: 10.1093/brain/awad373
102. Hou M-M, Li Y-F, He L-L, Li X-Q, Zhang Y, Zhang S-X, et al. Proportions of Th17 cells and Th17-related cytokines in neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders patients: a meta-analysis. Int Immunopharmacol. (2019) 75:105793. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.105793
103. Nishiyama S, Seok JM, Wright AE, Lotan I, Mikami T, Drosu NC, et al. Anti-aquaporin-4 immune complex stimulates complement-dependent Th17 cytokine release in neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:3146. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-53661-5
104. Assirelli E, Pulsatelli L, Dolzani P, Mariani E, Lisignoli G, Addimanda O, et al. Complement expression and activation in osteoarthritis joint compartments. Front Immunol. (2020) 11:535010. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.535010
105. Xu Z, Hou X-F, Feng C-M, Zheng L, Xu D-X, Zhao H, et al. The association between serum complement C3a and severity in patients with community-acquired pneumonia. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1034233. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1034233
106. Nytrova P, Potlukova E, Kemlink D, Woodhall M, Horakova D, Waters P, et al. complement activation in patients with neuromyelitis optica. J Neuroimmunol. (2014) 274:185–91. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2014.07.001
107. Asavapanumas N, Tradtrantip L, Verkman AS. Targeting the complement system in neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder. Expert Opin Biol Ther. (2021) 21:1073–86. doi: 10.1080/14712598.2021.1884223
108. Chen T, Lennon VA, Liu YU, Bosco DB, Li Y, Yi MH, et al. Astrocyte-microglia interaction drives evolving neuromyelitis optica lesion. J Clin Invest. (2020) 130:4025–38. doi: 10.1172/JCI134816
109. Coss SL, Zhou D, Chua GT, Aziz RA, Hoffman RP, Wu YL, et al. The complement system and human autoimmune diseases. J Autoimmun. (2023) 137:102979. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2022.102979
110. Miyamoto K, Minamino M, Kuwahara M, Tsujimoto H, Ohtani K, Wakamiya N, et al. Complement biomarkers reflect the pathological status of neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1090548. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1090548
111. Yu J, Zeng T, Wu Y, Tian Y, Tan L, Duan X, et al. Neutrophil-to-C3 ratio and neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio were associated with disease activity in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Lab Anal. (2019) 33:e22633. doi: 10.1002/jcla.22633
112. Shulman Z, Gitlin AD, Targ S, Jankovic M, Pasqual G, Nussenzweig MC, et al. Follicular helper cell dynamics in germinal centers. Science. (2013) 341:673–7. doi: 10.1126/science.1241680
113. Fan X, Lin C, Han J, Jiang X, Zhu J, Jin T. Follicular helper CD4+ T cells in human neuroautoimmune diseases and their animal models. Mediat Inflamm. (2015) 2015:638968. doi: 10.1155/2015/638968
114. Fan X, Jiang Y, Han J, Liu J, Wei Y, Jiang X, et al. Circulating memory T follicular helper cells in patients with neuromyelitis optica/neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders. Mediators Inflamm. (2016) 2016:3678152. doi: 10.1155/2016/3678152
115. Yang X, Peng J, Huang X, Liu P, Li J, Pan J, et al. Association of circulating follicular helper T cells and serum CXCL13 with neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:677190. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.677190
116. Fink K. Origin and function of circulating plasmablasts during acute viral infections. Front Immun. (2012) 3:78. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2012.00078
117. Chihara N, Matsumoto R, Yamamura T. Plasmablasts and neuroimmunological disorders. Immunol Med. (2019) 42:103–7. doi: 10.1080/25785826.2019.1659476
118. Hoshino Y, Noto D, Sano S, Tomizawa Y, Yokoyama K, Hattori N, et al. Dysregulated B cell differentiation towards antibody-secreting cells in neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder. J Neuroinflamm. (2022) 19:6. doi: 10.1186/s12974-021-02375-w
119. Kowarik MC, Astling D, Gasperi C, Wemlinger S, Schumann H, Dzieciatkowska M, et al. Aquaporin-4-specific B cells connect with multiple B-cell compartments in neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder. Ann Clin Transl Neurol. (2017) 4:369–80. doi: 10.1002/acn3.418
120. Han J, Sun L, Wang Z, Fan X, Wang L, Song Y, et al. Circulating regulatory B cell subsets in patients with neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders. Neurol Sci. (2017) 38:1205–12. doi: 10.1007/s10072-017-2932-7
121. Clarke L, Arnett S, Lilley K, Liao J, Bhuta S, Broadley SA. Magnetic resonance imaging in neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder. Clin Exp Immunol. (2021) 206:251–65. doi: 10.1111/cei.13630
122. Cai M-T, Zheng Y, Shen C-H, Yang F, Fang W, Zhang Y-X, et al. Evaluation of brain and spinal cord lesion distribution criteria at disease onset in distinguishing NMOSD from MS and MOG antibody-associated disorder. Mult Scler. (2021) 27:871–82. doi: 10.1177/1352458520939008
123. Cabanillas-Lazo M, Cruzalegui-Bazán C, Pascual-Guevara M, Quispe-Vicuña C, Terry-Escalante FA, Mori N, et al. Clinical and imagenologic significance of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder: a systematic review with meta-analysis. PLoS ONE. (2023) 18:e0281064. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0281064
124. Liu L, Guo K, Yang D. Advances in biomarkers for optic neuritis and neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders: a multi-omics perspective. Front Neurol. (2025) 16:1559172. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1559172
125. Lin L, Wu Y, Hang H, Lu J, Ding Y. Plasma complement 3 and complement 4 are promising biomarkers for distinguishing NMOSD from MOGAD and are associated with the blood-brain-barrier disruption in NMOSD. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:853891. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.853891
126. Li X, Zhang J, Zhang S, Shi S, Lu Y, Leng Y, et al. Biomarkers for neuromyelitis optica: a visual analysis of emerging research trends. Neural Regener Res. (2024) 19:2735–49. doi: 10.4103/NRR.NRR-D-24-00109
Keywords: optica spectrum disorder, peripheral blood immune inflammatory markers, lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio, neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio
Citation: Wu B, Cao F, Mao M, Gong X and Xu B (2025) Peripheral blood immune inflammatory markers in neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders. Front. Neurol. 16:1690767. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1690767
Received: 22 August 2025; Accepted: 09 October 2025;
Published: 06 November 2025.
Edited by:
Erdem Tüzün, Istanbul University, TürkiyeReviewed by:
Zuber Khan, Indo-Soviet Friendship College of Pharmacy, IndiaMilena Rodriguez Alvarez, Downstate Health Sciences University, United States
Copyright © 2025 Wu, Cao, Mao, Gong and Xu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Bin Xu, eHViaW4yMDA4LmxvdmVAMTYzLmNvbQ==
 Bin Wu
Bin Wu Fangzheng Cao
Fangzheng Cao Mengying Mao1
Mengying Mao1