- Business and Economic Education, Mannheim Business School, University of Mannheim, Mannheim, Germany
Rapid technological advances are constantly changing our workplaces and the organization of work. Formerly established workflows and role descriptions give way to short-term, skills-based project structures. The resulting skill shift heightens the importance of sustained informal workplace learning—ranging from unconscious, small-scale, everyday adaptation processes to intentional self-regulated learning activities. This concept paper explores informal workplace learning through the lens of problem solving, categorizing informal learning activities into reasoning, experimenting, researching, and observing, linked to personal, representative, social, and retrievable resources. It further examines how AI technologies can support these informal workplace learning activities. It is argued that AI's capacity for contextualized assistance within collaboration platforms, simulation environments and electronic performance support systems (EPSS) can support problem-solving and learning—if users maintain “process ownership” rather than delegating tasks entirely to AI. The concept of nudging (subtle prompts to foster reflection and learning) is proposed to ensure active engagement and prevent an “AI ghost-learner effect” (i.e., performing successfully through AI assistance without perceiving oneself as competent and as developing). Future research should focus on the empirical evaluation of these interventions and consider employees' utilization of AI to exploit the full potential for fostering informal workplace learning.
1 Introduction
Characteristics and requirements of work have always been shaped by applied technologies (Allvin and Movitz, 2017). In recent years, rapid technological advancements have dramatically reshaped modern workplaces. Automation and digitalization have streamlined routine tasks and changed work practices, while—above all—recent developments in artificial intelligence (AI) have continued these transformations and fostered the emergence of novel job roles and industries (Frey and Osborne, 2017; Harteis et al., 2022). These developments have changed the nature of many workplaces and the respective competencies required of employees (Billett, 2021; Korunka and Vartiainen, 2017; Kubicek et al., 2015). These changes in requirements are often labeled “skill shift” (Bughin et al., 2018; Lund et al., 2021). Following the European Commission's DigiComp framework, these competences include information and data literacy, communication and collaboration, digital content creation, safety, and problem solving (Vuorikari et al., 2022). Problem solving as a component of digital competence refers to identifying and resolving problems in digital environments, using digital tools to innovate processes and products, and keeping up to date with the digital technologies (Vuorikari et al., 2022) and points to fundamental changes in the organization of work. According to the management consultancy sector, recent developments affect not only the types of skills required but also how skill requirements and individual capabilities shape the way work is orchestrated in what is referred to as “skills-based organizations” (Cantrell et al., 2022). Instead of long-term definitions of jobs, roles, and processes, work is evermore organized around ever-changing work tasks and agile project teams (Junker et al., 2023; Meier and Seufert, 2022). In skills-based organizations, as is enthusiastically described by accounting and consulting firms, “… people can be freed from being defined by their jobs and instead be seen as whole individuals with skills and capabilities that can be fluidly deployed to work matching their interests.” (Cantrell et al., 2022, p. 2). In their meta-analysis, Kim et al. (2018) confirmed that these kinds of empowering leadership indeed provide motivating work conditions, autonomy, and participation in decision-making and foster continuous learning within resourceful work environments. On the flipside, the vanishing of secure organizational roles not only allows for but also necessitates lifelong learning and a proactive engagement with new technologies to remain productive and competitive (Bughin et al., 2018; Kubicek et al., 2015; Parker and Grote, 2022). As a result, workplace learning has become even more critical (Billett, 2021; Harteis et al., 2022; Watkins and Marsick, 2023) and the concept of “new learning” as a response to the similarly enigmatic “new work” (Bergmann, 2019) describes an ideal of highly motivated and self-regulated learning in the workplace (Decius et al., 2022).
Workplace learning is understood here to include all learning processes—formal or informal, intentional or unintentional, conscious or unconscious—that result in changes to one's professional competences, with competence defined broadly as the combination of domain-specific knowledge, skills, attitudes, and other characteristics that enable work performance (Kanfer and Ackerman, 2005; Noe, 2017; OECD, 2005). The formality of workplace learning refers to the organizational context in which learning takes place. Formal learning is typically characterized by scheduled start and end points; it is usually based on predefined learning goals and designed or guided from an educational perspective (Doornbos et al., 2004; Tannenbaum et al., 2010). By contrast, the concept of informal learning, which goes back to Dewey's (1938, p. 48) “collateral learning,” basically refers to the absence of the above-mentioned structuredness of formal learning (Cerasoli et al., 2018). Work environments can, of course, be highly structured regarding the organization of work, but this structuredness then refers to the work processes, not to the potential learning within these work processes (Eraut, 2004; Harteis, 2002). Following Eraut (2004), informal and formal learning are defined here not as dichotomous categories but located rather on a continuum. Non-formal learning is often located between the ends of this continuum, “as it may be planned, but it is not provided by an educational institution” (Jacobs and Park, 2009, p. 142). Billett (2002), Jarvis (1987), and Malcolm et al. (2003) criticized the use of formality to distinguish learning processes because formality refers to the environment and not to types of learning. Nevertheless, the distinction between informal, non-formal, and formal learning points to substantial differences between these environments. Cerasoli et al. (2018) distinguished between formal and informal learning behaviors, thereby emphasizing that the difference lies not in the learning but in the activities that lead to it, while Jarvis (1987) considered situations the distinguishing feature. Informal learning activities are usually triggered by a work-related problem situation, which is defined by a lack of knowledge on how to achieve a current work goal (Dörner, 1997; Duncker, 1945). Any problem-solving activity that aims to close a current (or an anticipated) knowledge gap concerning work goal achievement is hereinafter referred to as an informal workplace learning activity, regardless of whether actual learning takes place or is sustainable. Oftentimes this learning is not even perceived as such because, for many people, learning is associated with formal learning environments only. The primary goal of these problem-solving activities is preventing anticipated or solving existing problems (Jacobs and Park, 2009), harking back to Dewey. Considering knowledge gaps as triggers for activities, problem-solving research provides a very fruitful basis for analyzing informal learning in the workplace. Therefore, this article builds on a theoretical framework based on action regulation and problem-solving research to categorize informal workplace learning activities. This framework is then used to discuss the impact of recent applications of AI on the various workplace learning activities.
Apparently, new technologies such as AI not only require new competences but may also provide powerful resources of informal workplace learning (Bell, 2017; Kim et al., 2018; Karhapää et al., 2023; Littlejohn and Margaryan, 2014; Littlejohn and Pammer-Schindler, 2022; Za et al., 2014). While Holmes and Littlejohn (2024) rightly point out that “… currently there are few innovative or targeted examples of the application of AI to support workplace learning” (p. 200) many recent technologies aim at performance improvements by supporting problem solving in the workplace. For instance, collaboration platforms make it easier to ask colleagues for advice and to solve problems in distributed teams, AI-based chatbots make it easier to search through and process information, and performance monitoring can foster the awareness of and the reflection on aspects of one's work performance that would otherwise remain unrecognized. Following the above line of argument, this problem-solving support represents an informal workplace learning support and therefore is a vital area of human resources development. Technology-based nudges (i.e. subtle interventions that guide individuals' behaviors) can further trigger opportunities to learn and awareness of learning. However, AI also runs the risk of reduced skill requirements and skill acquisition in the workplace. This is the case, if it is used merely to provide orders to humans and restrict job autonomy, instead of providing humans with information resources for problem solving within high-performance work practices (Holm and Lorenz, 2022). Moreover, if AI “… takes over complex tasks and leaves workers with unstimulating ones, [the result will be] fewer learning opportunities and less autonomy.” (Lane and Williams, 2023, p. 19). From a perspective of problem solving, in this case, there are no more knowledge gaps in goal achievement to learn from, since the respective tasks are completely assigned to an AI. These ambivalent roles of recent technologies have been under-conceptualized and under-analyzed from the perspective of informal workplace learning.
To fill this gap, this conceptual paper builds on the concept of problem solving to combine approaches to informal workplace learning activities and AI support in the workplace. Problem solving mediates between work requirements and informal learning, and AI tools are considered problem-solving resources. The two streams of research have distinct backgrounds, but elements of each can be complementary to developing a more holistic understanding of digital workplace learning support. Hence, this paper aims to categorize informal workplace learning activities, discuss the benefits and pitfalls of selected AI technologies, provide recommendations for fostering informal workplace learning, and identify research gaps in the field. Section 2 provides theoretical foundations of informal workplace learning activities and a framework for informal workplace learning activities from the perspective of problem solving. Section 3 delves into each of the areas of this framework to illustrate the effects of AI technologies on informal workplace learning. The contribution concludes with a discussion of the central findings, possible lines of development, and research requirements.
2 Informal workplace learning from a problem-solving perspective
2.1 A taxonomy of informal workplace learning processes
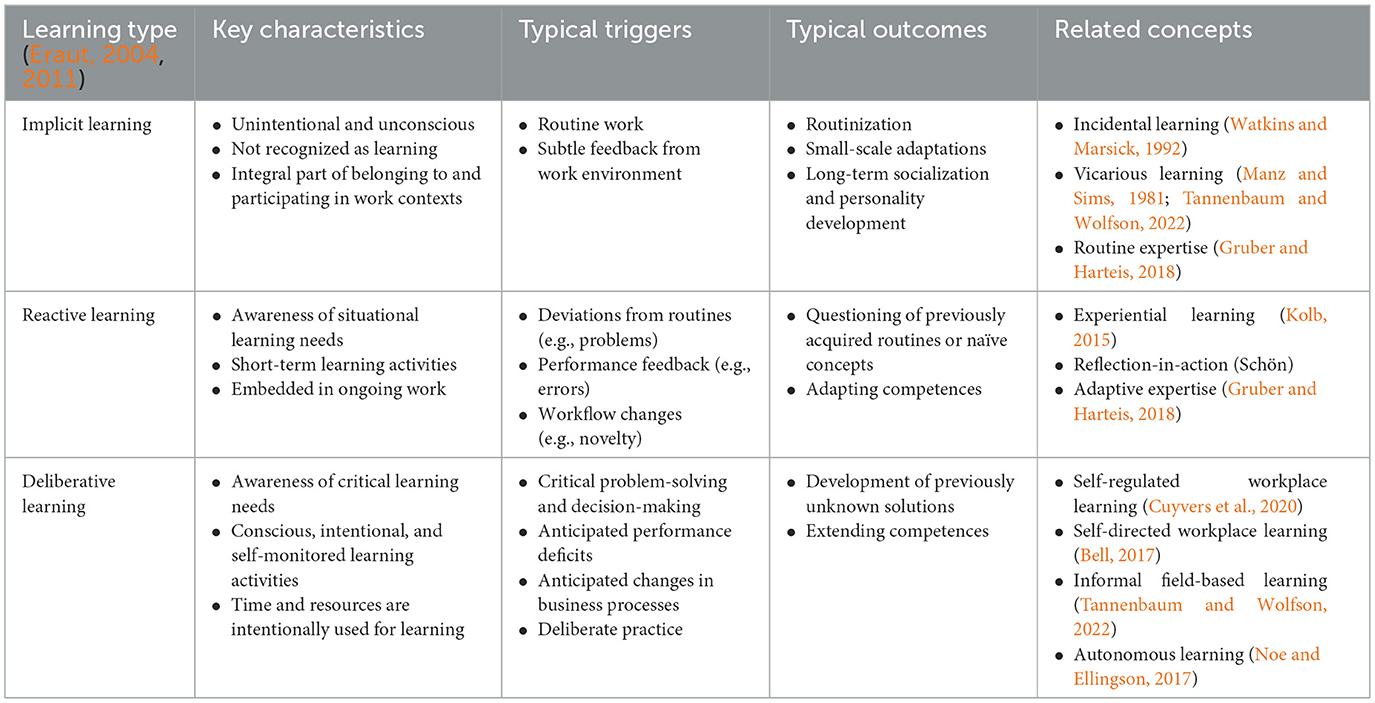
Building on Eraut (2004, 2011), in this paper, informal workplace learning is understood as an umbrella term to include a range of learning processes from unconscious everyday adaptation processes to self-regulated learning activities in the workplace. Informal workplace learning activities are often classified by intentionality, that is by the degree to which learning “… occurs purely by accident (unintentionally or incidentally) or through conscious deliberation (intentionally).” (Cerasoli et al., 2018, p. 205). This distinction builds on Watkins and Marsick's (1992, 2023) definition of incidental learning as the unintentional and unconscious by-product of some other activity. In the workplace, this other activity is usually a work activity that is, of course, also intentional, however, the intention refers to the completion of work tasks, not to learning while completing it. Marsick and Watkins (1990) used the term informal learning as the intentional and conscious counterpart to incidental learning (Watkins and Marsick, 2023). However, this definition of informal learning conflicts with the mainstream literature, because learning processes that are unintended and unrecognized by the learner are usually core characteristics of the definition of informal learning (Johnson and Majewska, 2022). In line with a systematic overview provided by Wolfson et al. (2018), informal learning comprises both, incidental and intentional learning. It also includes self-regulated learning which can take place in both, formal as well as informal settings. In his seminal publications on informal learning in the workplace, Eraut (2004, 2011) distinguished between implicit, reactive, and deliberative learning, which he understands as being located on a continuum.
Implicit learning refers to routine activities in which learning goals, learning processes, and learning outcomes are secondary and where the actor is unconscious of learning. It includes all the small-scale, day-to-day adjustments in an individual's knowledge, skills, attitudes, or other characteristics based on subtle feedback from the task environment. These processes are usually not perceived as learning by employees and workers (Eraut, 2004; Simons, 2005; Tynjälä, 2008). Referring to a “non-educational perspective,” Doornbos et al. (2004, p. 256) considered implicit learning to be “… part of belonging to and participating in a real-life context.” These everyday adaptation processes that happen in the background result in broad socialization outcomes (e.g., the gradual adoption of corporate culture; also promoted by “vicarious learning”; Manz and Sims, 1981; Tannenbaum and Wolfson, 2022) and long-term personality developments (e.g., developing confidence in client interactions or greater conscientiousness in bookkeeping) (Hodkinson and Hodkinson, 2004). Implicit learning also enables ongoing routinization of already well-known work procedures (e.g., efficiency gains in wall leveling or greater spontaneity in customer discussions). As (Hatano and Inagaki 1984, p. 31), put it, sometimes, “people merely learn to perform a skill faster and more accurately, without constructing/enriching their conceptual knowledge.” In many domains, these individual routines mirror organizational routines. Organizational routines are day-to-day, repetitive patterns of interdependent organizational actions based on a shared understanding of how tasks are to be completed. Organizational core routines “… are specific to the firm, most vital to value creation, and represent the key components of the business model.” (Parmigiani and Howard-Grenville, 2011, p. 419). Therefore, individual routine skills that improve actions within these organizational routines are an essential element of one's professional competence (Gruber and Harteis, 2018; Kim, 2021). These skills are also referred to as “routine expertise” (Gruber and Harteis, 2018; Hatano and Inagaki, 1984). Routine expertise results from proceduralization (Gruber and Harteis, 2018), and expertise, in general, is characterized, among other things, by having “available lots of routines and automatised procedures.” (p. 5). Furthermore, routine expertise can also be developed through closely monitored practice, as opposed to “mindless, routine performance” (Gruber and Harteis, 2018, p. 96) but this planned learning and rehearsing refers to deliberative learning (see below).
Reactive learning is intentional and activated when problems arise, that is when routines are not available, or the available routines are not effective in achieving a current work goal. According to Eraut (2004, 2011), reactive learning includes the awareness of short-term situational learning needs, learning activities, and learning outcomes in terms of competence gains. Reactive learning can be illustrated very well using Kolb's (2015) concept of experiential learning as continuous, cyclical processes of adaptation to the world based on concrete experience, reflective observation, abstract conceptualization, and active experimentation. This concept of experiential learning is very prominent in theories of workplace learning (e.g., Tannenbaum et al., 2010; Decius et al., 2019). Triggers for reactive learning are, for instance, unknown variations in otherwise familiar work tasks or changes in well-established workflows (e.g., updated software tools with a slightly changed interface or new product versions in the sales portfolio with unfamiliar features). These changes might lead to errors and often go along with emotional states such as confusion or surprise (Rausch et al., 2017). These incidents trigger reflections that lead to the questioning of previously acquired routines (Nieuwenhuis and Van Woerkom, 2007) once these routines have become ineffectual (e.g., cumbersome, error-prone, unethical, or simply wrong). The increasing flexibility to deal with changing situations and contexts is referred to as “adaptive expertise” (Gruber and Harteis, 2018). “Plausibly, in the acquisition of expertise, the development of routine expertise occurs before professional adaptive expertise is being developed.” (Gruber and Harteis, 2018, p. 44). Deliberative learning, as defined by Eraut (2004, 2011), refers to conscious, intentional, self-monitored problem-solving and decision-making activities in which learning goals emerge that are critical for achieving current or future work goals. Eraut (2004) admitted that reactive and deliberative learning are similar but explained that he used “… the term ‘reactive learning' because, although it is intentional, it occurs in the middle of the action, when there is little time to think” (p. 250) and no time set aside for intentional learning. Hilkenmeier et al. (2021), describe these learning activities as being “… driven by employees' needs to tackle unfolding and pressing tasks or problems at work.” (p. 413). Hence, the shorter the time set aside for learning, the more the episode falls into problem solving and decision making in the workplace. The longer the (anticipated) time lag between learning (i.e., pursuing learning goals) and performance (i.e., pursuing work goals), the more deliberative learning resembles participation in designated learning opportunities as defined by Hilkenmeier et al. (2021) and corresponds to autonomous learning (Kyndt and Beausaert, 2017; Noe and Ellingson, 2017) to self-directed workplace learning (Bell, 2017; Lemmetty and Collin, 2020), to informal field-based learning (Decius et al., 2024; Tannenbaum and Wolfson, 2022; Wolfson et al., 2019), and, in particular, to self-regulated workplace learning (Cuyvers et al., 2020; Decius et al., 2024; Endedijk and Cuyvers, 2022; Holmes and Littlejohn, 2024; Kittel et al., 2021; Margaryan et al., 2013). Based on a literature review and meta-analysis of self-regulated learning, Sitzmann and Ely (2011) conclude that self-regulation might be even more important in the context of informal learning than in formal learning settings, since “… employees must independently identify knowledge gaps, determine where they can access relevant and accurate information, monitor the accuracy of information obtained, and control their emotions if relevant information is difficult to obtain,” (Sitzmann and Ely, 2011, p. 437) or in Eraut's words: “planning learning opportunities.” (Eraut, 2004, p. 250). Hence, deliberative learning includes the utilization of formal learning resources, such as textbooks or learning videos, and formal structures, such as mentoring relationships—outside formalized learning environments, however. Furthermore, deliberative learning also includes “rehearsing for future events” (Eraut, 2004, p. 250). This resembles “deliberate practice” which refers to the focused and supervised practice of designed (part-task) exercises conducted apart from (but in service of) actual performance (Ericsson et al., 1993). Deliberate practice is considered a key factor in developing outstanding expertise, at least in well-structured (sub-)domains (e.g., chess, sports, music), indicated by the relevance of the above-described organizational routines. Deliberate practice is a complex intervention composed of rehearsal, experimentation, and reflection with advice and feedback from others. Hence, it is self-regulated and, similar to coaching, shares many characteristics with formal training settings: pursuing learning goals, being guided, following a curriculum, and practicing apart from the productive work activity. However, Goller (2017) as well as (Köhler and Rausch 2022) have argued that deliberate practice does not usually apply well to the ill-structured domains of most workplaces. In ill-structured domains, “adaptive expertise” (Hatano and Inagaki, 1984) or “horizontal expertise” (Gegenfurtner et al., 2024) for flexible problem solving and recurring adaptation to dynamic demands seem to be more important than “routine expertise.” Table 1 provides an overview of key characteristics of implicit, reactive and deliberative learning according to Eraut (2004, 2011) and references to related concepts by other authors.
Implicit, reactive, and deliberative learning form a taxonomy, since “most learning from experience has some implicit aspects, and […] awareness of explicit learning does not mean that implicit learning is not also taking place.” (Eraut, 2004, p. 250). Hence, deliberative learning is likely to also include processes of implicit and reactive learning; reactive learning is likely to also include processes of implicit learning. This taxonomy corresponds to the levels of mental regulation of activities as conceived by the long-standing line of research on “action regulation theory” within German work psychology (Frese and Zapf, 1994; Hacker, 2003, 2005). This view is that automated routine action can be part of knowledge-/rule-based action that, in turn, can be part of problem solving with the development of plans based on an intellectual analysis of the situation. Deliberative, reactive, and implicit learning describe levels of mental processing but not the actual activities that trigger, accompany, or follow these processes.
2.2 A review of informal workplace learning activities
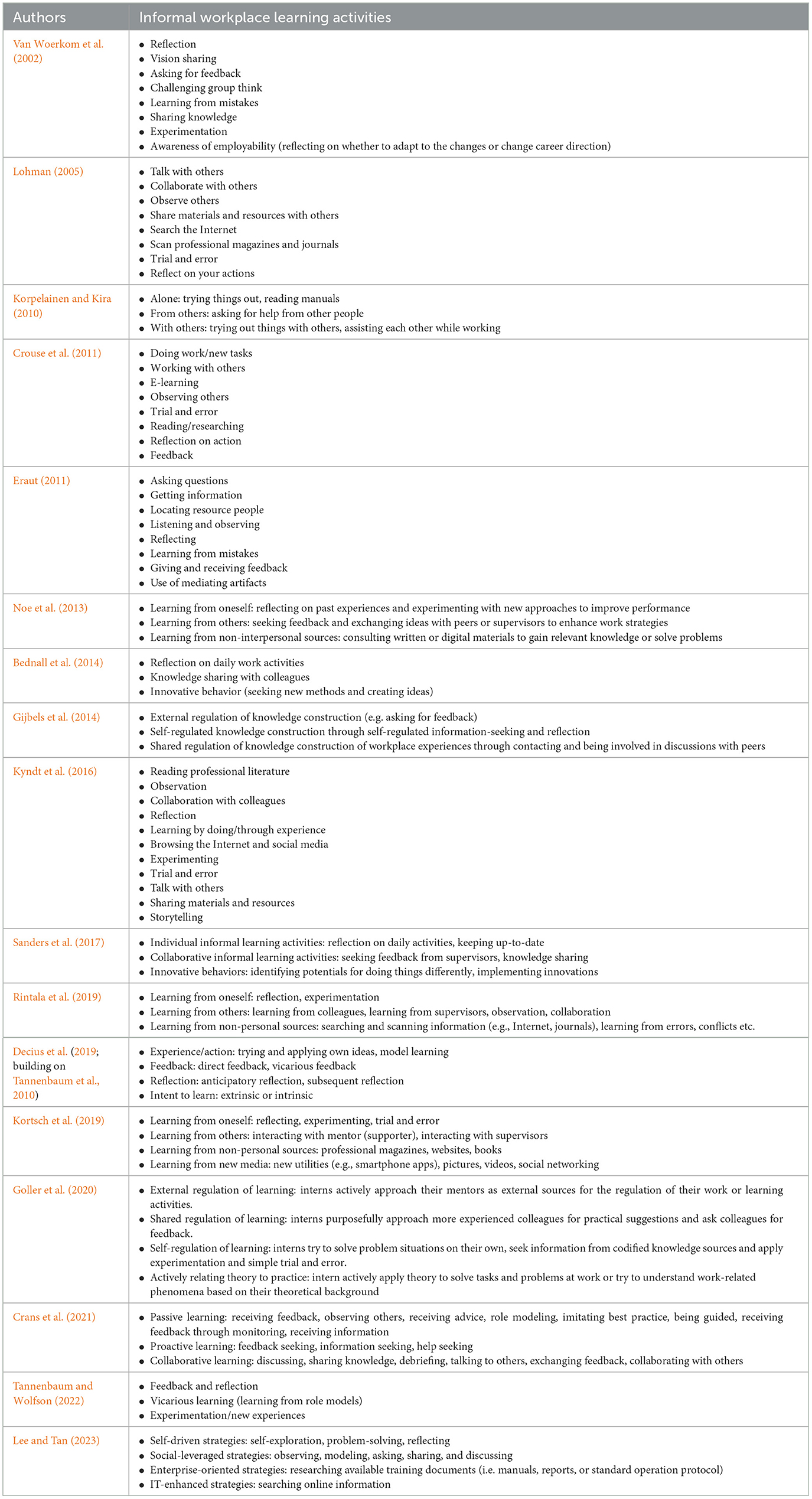
Based on the above definitions, workplace learning activities refer to all kinds of intentional behaviors that result in reactive or deliberative learning processes (that may also include implicit learning processes). Definitions of workplace learning activities must be based on reactive and deliberative learning, since implicit learning can take place in any work activity and, hence, is not triggered exclusively by workplace learning activities. Nevertheless, following the above line of argument, implicit learning may also be part of reactive and deliberative learning. These informal workplace learning activities are voluntary and self-paced (Bednall et al., 2014). Stressing the awareness of the learning processes, Van Woerkom et al. (2002, p. 376) considered reflection to be the umbrella term and referred to these activities as “critical reflective behaviors at work.” In the case of deliberative learning (i.e., intentional learning), these activities are also referred to as workplace learning strategies (Crouse et al., 2011; Lee and Tan, 2023).
Lists of informal workplace learning activities and strategies have been provided by many authors, based on a variety of theoretical foundations (or sometimes not based on theory). However, to the best of this author's knowledge, there is no comprehensive compilation and analysis of these lists, apart from a shorter and less focused compilation by Moore and Klein (2020) and a compilation of operationalizations by Decius et al. (2023). The compilation in Table 2 focuses on informal workplace learning activities to illustrate similarities and differences between the various approaches. Less focused lists of learning activities are not included. For instance, Beier et al. (2017, p. 184), in their “examples of autonomous learning activities,” also included hobbies, training programs, career development services, and other activities that are rather detached from concrete workplace activities. Goller et al. (2020) list “avoidance of learning” (e.g., denying errors), which is left out of Table 2 because it is not a learning activity. In the original table, Eraut (2011) also lists “work processes with learning as a by-product” that may trigger implicit learning, and “learning processes at or near the workplace” that comprise more formal approaches, such as being coached or attending crash courses. Maintaining the focus on informal workplace learning activities, only the middle column on “learning activities located within work or learning processes” has been included in Table 2. Crouse et al. (2011) also listed “taking courses and programmes” and Lee and Tan (2023) listed “enrolling in formal studies,” “participating in on-site training,” and “participating in e-learning courses,” which were left out here because they refer to formal learning. Decius et al.'s (2019) octagon model of informal workplace learning (an extension of Tannenbaum et al.'s, 2010 model) included extrinsic and intrinsic intents to learn, which are not activities in the narrow sense but are still listed in Table 2 for the completeness of the model. Most of the lists were derived from theoretical reasoning or narrative literature reviews; meanwhile, Kyndt et al. (2016) did conduct a systematic review, which was limited in focus to teachers' informal learning activities, however.
The informal workplace learning activities listed in Table 2 share a common focus on experiential and self-directed learning. Many of the lists cited here involve social interactions, such as talking to others, collaborating, and sharing knowledge or feedback, emphasizing the role of relationships in workplace learning. Activities like reflection and learning from errors or experimentation highlight processes of personal insight. Furthermore, some activities are more passive, such as observing or receiving feedback, while others involve more active engagement, like seeking feedback or experimenting. Some lists are unstructured, while others provide categorizations of activities. Some categorizations differentiate learning by regulatory processes, while other categorizations differentiate learning by social context. In the following section, informal workplace learning activities are categorized by a framework of problem-solving approaches.
2.3 A model of informal workplace learning as problem solving
Any trigger for an informal workplace learning activity in the above sense can be considered a problem situation, where “problem” signifies that an individual “… wants to transform a problem situation from the given state to the goal state but lacks an obvious method for accomplishing the transformation.” (Mayer and Wittrock, 2006, p. 288). Every work task that cannot be completed on a routine basis therefore represents a minor or major problem and, hence, requires reasoning (Duncker, 1945). In their book Innovative Performance Support: Strategies and Practices for Learning in the Workflow, which is very popular in the consulting industry, Gottfredson and Mosher (2011) identify five moments of need: Workers need support when they (1) learn something completely new, (2) learn more to expand in breadth and depth, (3) face difficulties when applying their knowledge to work situations, (4) solve problems because things do not work as intended, and (5) when they face change and have to change deeply ingrained work practices (i.e., routines). In their framework, the first two moments of need should be addressed by formal training, while the latter three moments of need correspond well to what is meant by problem situations in this paper.
Solving a problem means overcoming the knowledge gap by achieving an understanding of the situation, finding alternative solutions, deciding on and executing a solution, and evaluating goal achievement, which, hence, results in acquiring knowledge on how (not) to handle the given work task (Hung et al., 2008). This task-related learning can typically foster the acquisition of new competences or an adaptation of previously acquired competences (Wielenga-Meijer et al., 2010). Following the concept of progressive problem solving by Bereiter and Scardamalia (1993), learning in the workplace results from solving and reflecting on increasingly complex work tasks (Bereiter, 2002). However, to be able to learn from problem solving, Rausch et al. (2015) stressed that, to ensure learning opportunities, it is important for the problem solver to not delegate the problem but instead remain the “process owner.” This is the case, for instance, if the problem solver receives assistance in planning, but still implements the plan by himself/herself; if the problem solver receives assistance in implementing the plan, but still follows and reconstructs the implementation; or if the problem solver implements the plan unaided and is only provided feedback. These kinds of cooperative and collaborative problem solving are considered to support informal workplace learning, whereas delegating and free riding does not (Rausch et al., 2015). Similarly, Holmes and Littlejohn (2024) discuss the detrimental effects of AI-based intelligent tutoring system (ITS) on learner agency.
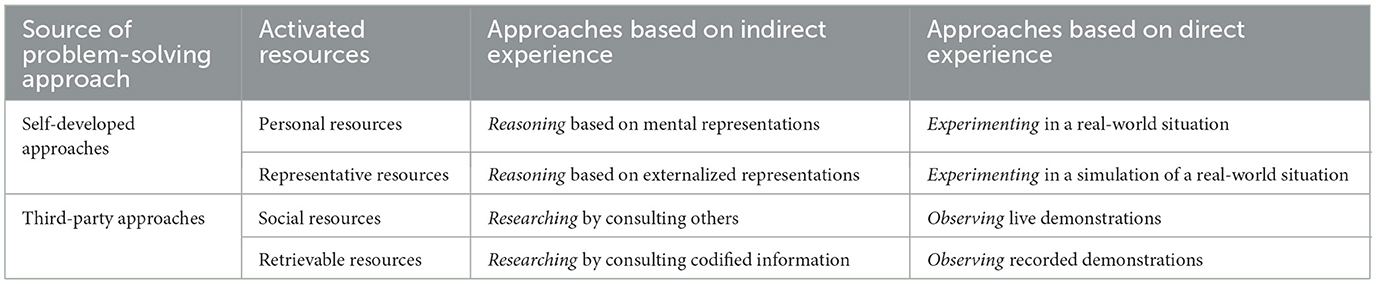
According to the German tradition of action regulation theory (Hacker, 2003, 2005; Hacker and Skell, 1993), every action starts with the perception of a discrepancy between a desired target and an undesired actual situation and includes the development and evaluation of different action plans based on prior knowledge and experience (“action-guiding mental models”). Problem solving is considered a special type of situation in which these mental models are not sufficient to develop an effective action plan. Problem solving corresponds to expanding these mental models to fill the gaps in an action plan (Dörner, 1997, 2001). To fill these gaps, (Dörner 2001) lists reasoning (i.e. combining available parts of action plans), exploring (i.e. testing hypotheses), observing others, and communicating with others, and researching codified action plans (e.g., manuals). Regarding similar problem-solving approaches, Hacker and Skell (1993) differentiate between learning based on one's own actions and learning from the mentally reconstructed actions of others. In several revisions, Rausch (2011), Rausch et al. (2015), and (Leiß et al. 2022) have classified approaches to problem solving in the workplace by whether the approach is based on an indirect experience (i.e., mental models of the world) or a direct real-world experience, and by whether the approach is self-developed (i.e., based on personal or representative resources) or whether it is a third-party approach that can be adapted (i.e., based on social or retrievable resources). The framework presented in Table 3 builds on these contributions and further develops them.
The classification of problem-solving approaches in the matrix in Table 3 is considered exhaustive: every problem-solving approach can be categorized according to these two dimensions, though, in practice, problem-solving processes will often involve several approaches and combinations of them. Revisiting the manifold workplace learning activities in Table 2, exhaustiveness means that all these activities can be assigned to one or more cells in the matrix of Table 3 and all of them relate to one or more of the resources listed there. Here is a brief explanation of the four problem-solving approaches, their variations, and resources:
• Reasoning refers to all kinds of operations on one's own mental model of the problem situation (i.e. personal resources). It includes awareness, reflection, mental simulation, interpolation, abstraction, reduction, analogies, and so forth. It is usually also the starting point of every problem-solving episode and has a central position for planning, monitoring, and evaluating the utilization of further resources and drawing conclusions. Reasoning can be supported by externalized representations (i.e., representative resources such as notepads, etc.) to model complex situations and reduce cognitive load.
• Experimenting refers to all kinds of hypothesis testing (i.e., testing well-considered solution attempts) and trial-and-error behavior (i.e., trying out several, rather arbitrary solutions quickly). Hypothesis testing is based on prior reasoning, while trial-and-error behavior is more spontaneous and therefore only advisable in safe, error-friendly, maybe simulated environments. Experimenting can result in the successful implementation of the ultimate solution. However, experimenting can also take place in simulations of the corresponding real-world problem (i.e., representative resources). For instance, transferring the quantitative information of a financial problem situation into a spreadsheet results in an externalized representation (see above) that can be used to simulate various future scenarios (e.g., based on varying interest rates).
• Researching refers to consulting others (i.e., social resources providing assistance, guidance, instruction, etc.) and consulting codified information (i.e., retrievable resources such as guidelines, manuals, checklists, etc.). In both cases, it refers to indirect, mediated experience and provides solution approaches from others that can be adopted by the problem solver.
• Observing, like experimenting, provides problem-solving approaches based on direct experience; however, unlike experimenting, these approaches are not self-developed but can be adopted. As with researching, the observation can relate directly to other individuals who are demonstrating their problem-solving approach (i.e., social resources) or be technologically mediated as with video tutorials (i.e., retrievable resources). The adoption of the observed problem-solving approaches, in turn, requires at least a minimum of reasoning.
In the following section, these problem-solving approaches are used to structure the discussion on technological trends that support informal workplace learning.
3 The role of AI tools in informal workplace learning
3.1 Generative and analytical AI tools
At the time of writing this paper, the most obvious opportunities for workplace learning in organizations have arisen from technological advancements in the fields of artificial intelligence (AI), immersive simulation environments, including extended reality, and digital communication and collaboration platforms, in general. First and foremost, in the public mind, AI is particularly associated with the fast development and increasing availability of tools providing generative artificial intelligence (genAI) based on large language models (LLM), initially boosted by OpenAI's ChatGPT (Alhusban et al., 2024; Budhwar et al., 2023). Referring to the role of genAI in human learning in general, Yan et al. (2024, p. 1) argued for advantages in “… scaling personalised support, diversifying learning materials, enabling timely feedback, and innovating assessment methods.” Regarding workplace learning, GenAI is particularly relevant in office work (Krishnasamy and Lee, 2024), provides a valuable resource for “… seeking immediate answers, guidance, or support in … work-related tasks,” (Fahad et al., 2024, p. 267) and thus enhances employees' performance and satisfaction (Brynjolfsson et al., 2025; Jo and Park, 2024). Xu et al. (2023) found that, in turn, informal workplace learning mediated the relation between AI opportunity perception and workplace wellbeing. GenAI applications are powerful problem-solving tools. Applied as an externalized representation, these tools process comprehensive and complex information and, thus, enhance reasoning by providing summaries, abstractions, analogies, analyses, and syntheses based on given information. Even more obvious, in researching further information, AI tools are very helpful, especially if they are fine-tuned and customized based on corporate knowledge corpi. However, not only is genAI developing rapidly, but analytical AI is also enabling ever better analyses of large amounts of multimodal data in real time (Bankins et al., 2023; Jagatheesaperumal et al., 2022). This enables advanced electronic performance monitoring (Kalischko and Riedl, 2021) which is a basis for feedback and thus, an important source of learning within work environments (Sitzmann and Ely, 2011; Wang et al., 2025). Meaningful and timely performance feedback also enables the acquisition of routine expertise by means of deliberate practice.
In the following sections, I discuss possible implementations of selected technologies to support informal learning in the workplace, concerning the categorization of problem-solving approaches and resources presented above. Some of the scenarios are already more or less widespread in practice; others are more forward-looking. In any case, the selection is to be considered subjective.
3.2 AI implementations in collaboration and simulation platforms
An already widespread, but important technological trend lies in the use of digital communication and collaboration platforms. These platforms are particularly important in the context of international teams and increasing remote work and can also facilitate informal workplace learning (Karhapää et al., 2023). These platforms are subject to the latest AI developments like no other technology in companies, as the extensive content is analyzed using analytical AI, and genAI contributes its own content in the form of AI agents (e.g., Microsoft's CoPilot; depending on the definition of an AI agent). Communication plays an important role in workplace learning activities when, for instance, seeking help, receiving feedback, observing others, sharing knowledge, and so forth (Crans et al., 2021; Hilkenmeier et al., 2021; Rausch et al., 2015). Collaboration platforms such as Microsoft Teams combine many basic features, such as collaborative office software for document editing, several channels for synchronous and asynchronous communication, and shared file management as well as numerous third-party plug-ins. Altogether, these platforms realize what Littlejohn et al. (2012, p. 229) outlined as “charting environments” for self-regulated informal workplace learning by allowing “… experts and novices to create and share knowledge by connecting with each other and the broader collective.” Increasingly enriched with AI functionalities, these platforms can actively recommend retrievable resources (i.e., codified information or recorded performance). If linked to an organization's skills management system, they can also recommend social resources for consulting more experienced others based on the context.
Further developed into so-called metaverses, future collaboration platforms promise an immersive experience based on the simulation of a work environment. Simulation-based learning environments have a long tradition in various domains (Hallinger and Wang, 2020), but new technological advancements offer even more immersive environments, comprising augmented reality (AR), virtual realities (VR), and virtual worlds within so-called metaverses (Damaševičius and Sidekerskiene, 2024). Metaverses are virtual shared spaces with the synergistic combination of the real world with the virtual world (Damaševičius and Sidekerskiene, 2024; Umbelino et al., 2024). They allow for experimenting in a simulation of the real-world situation to find problem solutions. In metaverses, users “… can engage with complex ecological systems […] in a risk-free setting, allowing for experimentation and exploration that would be impractical or impossible in the real world.” (Damaševičius and Sidekerskiene, 2024). Metaverses are not yet widely used in companies, but from a laboratory study, Hendriks et al. (2024) reported “… higher levels of immersion, social presence, and collaboration among team members in the metaverse,” (p. 686) as compared to groups collaborating via video conference. Digitally mediated presence rather restricts learning (Karhapää et al., 2024), while reduced social distance, in turn, facilitates advice-seeking (Korpelainen and Kira, 2010). Besides its use in immersive formal training, these simulations of work environments offer a virtual space for creating, sharing, and managing knowledge. Based on the Japanese concept of “ba” (= place), introduced in Nonaka and Takeuchi's (2019) circular knowledge management model SECI (socialization, externalization, combination, internalization), Umbelino et al. (2024) referred to simulated work environments as a “virtual ba.” Developing, maintaining, and updating such simulation environments is still very time-consuming. However, there are already AI applications that enable the creation of a simulation environment via text prompts (e.g., “Xara—XR Dialog Trainer” by afca AG).
3.3 The “AI ghost learner effect”
AI applications offer manifold resources for informal learning in the workplace but it may also result in what I call the “AI ghost learner effect”. To learn by the help of AI tools, it is important that employees remain “process owners” (see Section 2.3) and do not just delegate tasks to AI tools without reflecting on the results. This would resemble the “AI ghostwriter effect” found when using AI in text production (Draxler et al., 2024). Based on studies on academic writing, the authors defined the “AI ghostwriter effect” when students “… do not consider themselves the owners and authors of AI-generated text but refrain from publicly declaring AI authorship” (p. 1). Translated to the context of workplace learning, an “AI ghost learner effect” could occur when employees use AI-generated solutions or problem-solving strategies without engaging in deeper cognitive processing and reflection, thereby neglecting opportunities to learn. In such cases, employees may actually learn that “AI can handle that” but this learning remains superficial, as employees adopt AI outputs passively rather than actively integrating the resulting information into their own mental model. Similarly to the phenomenon reported by Draxler et al. (2024), employees may not perceive the implemented solution as their own, yet remain responsible for it. This, too, may create tensions similar to those described in academic contexts, as employees may “refrain from publicly declaring AI authorship.” At the same time, they may misinterpret their increased performance as an indicator of increased competence or even as evidence that further learning is no longer necessary. I label these phenomena as the “AI ghost learner effect.” One way to counteract this detachment is nudging, where AI can also play a supportive role.
3.4 AI-based nudging of informal workplace learning
Nudging refers to subtle interventions that guide individuals' behaviors in ways that are beneficial to themselves without restricting choices or significantly altering incentives (Thaler and Sunstein, 2008). Lim and Lee (2022) and Bell (2017) report findings on nudging learning in academic settings and Watkins and Marsick (2023) report a success story at IBM implementing nudging in more formal workplace learning. While there are studies on the effects of nudging engagement and performance in the workplace (Weintraub et al., 2021), there are hardly any empirical studies on nudging interventions to support informal workplace learning. Bell (2017) provides an overview of several “prompting strategies” that aim to trigger specific self-regulatory mechanisms (e.g., monitoring, metacognition) derived from research in formal learning environments. (Arya and Hindolia 2024, p. 2) raise the prospect that “organizations can cultivate a culture of ongoing learning and adaptation by skillfully incorporating nudging tactics.”
Nudging learning when using AI tools: “AI-assisted systems ideally would support learner agency to actively plan, perform, self-regulate, and reflect on their learning.” (Holmes and Littlejohn, 2024, p. 203). To foster informal workplace learning, the AI tool could be designed to trigger reflection by posing follow-up questions to encourage metacognition (e.g., “How does this solution compare to your initial task understanding?”), to promote self-assessment (e.g., “Do you think, your solution is adequate, accurate, and complete?”), to suggest further learning resources (e.g., “If you would like to find out more about these topics, take a look at this content: …”), and to support the transfer of learning (e.g., “Similar approaches could also help with the following workflows:…”). These triggers are initiated by the concrete use of an AI tool; hence, occasion and context are provided already by the user, which makes these triggers quite simple to implement in the context of collaboration platforms.
Nudging learning when using business software: even smarter implementations of nudging can be based on employees' behavior within productive business software like enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems. These ad-hoc help systems are referred to as electronic performance support systems (EPSS). An EPSS is defined as “… an electronic infrastructure that captures, stores, and distributes individual and corporate knowledge assets throughout an organization to enable individuals to achieve required levels of performance in the fastest possible time and with a minimum of support from other people.” (Noe and Ellingson, 2017, p. 368). An EPSS presents granular task-specific information to solve a problem at hand (Mao and Brown, 2007). To date, most implementation of EPSS has been rule-based, which means a limited number of predefined help texts are linked to predefined user behaviors based on hard-coded rules. With AI, however, the ad-hoc assistance could be tailored “… based on specific employee preferences, needs, or historical interactions.” (Alavi et al., 2024, p. 10). Current EPSS platforms often recommend videos that have been created by colleagues or developers beforehand for observing recorded performances based on anticipated problems of the users. Future videos could be created ad-hoc by generative AI and, hence, provide an even greater adaptability. In a survey study, Leiß et al. (2022) found that ERP users highly valued the features of existing EPSS and intensively used the more developed EPSS. The authors concluded that EPSS will play an important role in future workplace learning. The assistance provided by an EPSS, in turn, can be supplemented by the more general nudges suggested above and, for instance, by encouraging users to take notes after difficult tasks and even by making suggestions for these notes.
A general advantage of AI-based assistance is its adaptability based on user interactions. Moreover, Weinmann et al. (2016) emphasized the role of user interface design in digital nudging, because user-interface design elements guide people's behavior in digital choice environments such as business software. Hence, it is not just the functionality that makes digital nudging work but also the “look and feel” as perceived by the users.
3.5 AI tools as problem-solving resources
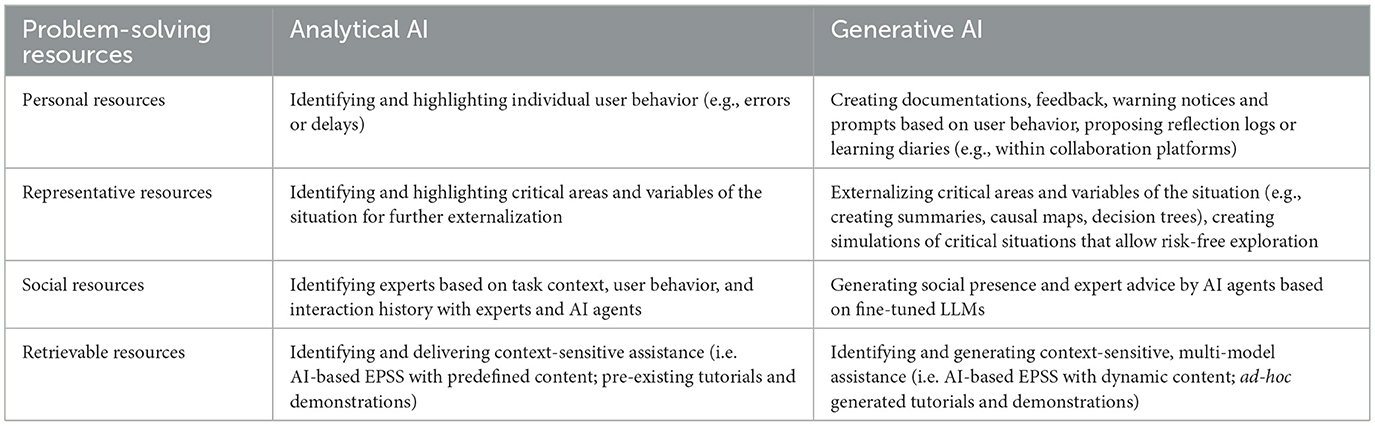
AI applications—based on analytical AI, generative AI or both—offer a multitude of affordances for informal workplace learning. However, to make sense of this diversity, it is helpful to analyze how these technologies can serve as a problem-solving resource, and in doing so, support distinct learning activities. Table 4 provides an overview of analytical and generative AI categorized by problem-solving resources as introduced above.
This perspective underscores that the learning potential of a technology does not lie in the technology itself, but results from its contextual use in the workplace. A single tool may support reasoning, experimenting, researching, observing or combinations of these—depending on how it is implemented. Therefore, workplace learning researchers and professionals should focus not only on the availability of particular technologies and tools but on the ways that these represent problem-solving resources, activate and support workplace learning activities and still ensure a human ownership of the problem-solving process.
4 Discussion
It is argued that informal workplace learning, due to ongoing technological advancements and changes in the organization of work, will become even more important in the future. This informal workplace learning ranges from unconscious, small-scale, everyday adaptation processes to intentional self-regulated learning activities. There are numerous lists focusing on informal workplace learning activities, but these lists often lack a systematic approach. Through the lens of problem solving, any work situation in which a routine solution is not immediately available is a problem situation that offers learning opportunities. Approaches to problem solving in the workplace can be classified by whether the approach is based on an indirect experience (i.e., mental models of the world) or a direct experience and by whether the approach is self-developed (i.e., based on personal or representative resources) or a third-party approach that can be adapted (i.e., based on social or retrievable resources). This scheme has resulted in four key informal workplace learning activities: reasoning, experimenting, researching (as consulting others or consulting codified information), and observing. These informal workplace activities are based on personal, representative, social, and retrievable resources. The conceptual benefit of this “lens of problem solving” lies in the fact that the matrix adapted from the problem-solving literature (1) is exhaustive, i.e. allows a categorization of all informal workplace learning activities (see Table 2), (2) thus allows a classification into self-developed vs. third-party approach based on indirect vs. direct experience and (3) names relevant resources in each case, which in turn facilitates the allocation and characterization of recent technological tools. By using the four resource types (personal, representative, social, retrievable) as analytical categories, the manifold opportunities that modern technologies afford for informal workplace learning support can be disentangled. At the same time as the conceptualization of informal learning presented here was being finalized, the article by Decius et al. (2024) was published, which models workplace learning from the perspective of theories of (meta-)cognition and memory and offers many interesting points of reference. Bringing these specific perspectives together offers great potential for enhancing our understanding and analysis of informal learning.
Contemporary technological trends offer manifold opportunities to support informal workplace learning. AI undoubtedly has a huge impact on problem solving in the workplace. However, limitations of AI-based tools include the generation of incorrect content due to “hallucinations” or already biased training data as well as risks such as overreliance and reduced transparency that may undermine critical thinking and hinder competence development. The extent and manner of the use of new technologies for workplace learning activities also depend on the extent to which corresponding work and learning practices are cultivated in the relevant communities (Karhapää et al., 2023). A paradox arises from the assumption of an “all-knowing” AI. If a workflow can completely be monitored and evaluated by AI, it is likely that this workflow can be completely automated—and then there may indeed be no need to learn this workflow, or a greatly reduced need to do so. More generally, in the face of digitalized work, Harteis (2022) has distinguished an “automation scenario” and a “tooling scenario,” similarly to “AI automation vs. AI augmentation” (Nguyen and Elbanna, 2025). The present paper has addressed cases of “tooling,” while, of course, many future workflows will be completely automated, too. Harteis (2022) describes the “tooling scenario” as one in which digital technologies support employees by extending their capabilities rather than replacing them. However, the remaining work tasks will be complex and ever-changing. Informal workplace learning will be more relevant than ever, and the technological developments, above all AI, will offer plenty opportunities to support this learning. The framework developed here can also be used to systematize other future technological workplace learning support interventions. Within the “tooling scenario,” the importance of “process ownership” must be emphasized in order to take advantage of the learning opportunities offered by using these tools. (Watkins and Marsick 2023, p. 44) described informal workplace learning as “… a way of putting control for learning in the hands of intrinsically motivated, purpose-driven employees who continuously learn.” Therefore, we need to prevent an “AI ghost-learner effect” (similar to the “AI ghostwriter effect”; Draxler et al., 2024), which leads to only superficial learning and occurs when employees adopt AI outputs passively without reflection.
Nudging—subtle interventions that guide individuals' behaviors (Thaler and Sunstein, 2008) also referred to as prompting (Bell, 2017)—is considered a promising approach to ensure process ownership and learning opportunities during AI-supported problem solving. So far, nudging has remained detached from concrete workflows and implemented at predefined intervals (Bell, 2017), like experience sampling (Seifried and Rausch, 2022). However, AI enables contextualized and timely nudges (prompts). Different types of nudging can be implemented during AI use, within EPSS, and in smart collaboration platforms. However, since there is hardly any empirical research, it will be important for future research to focus on the effects of nudging (prompting) strategies in the context of informal workplace learning (Bell, 2017). A possible downside of nudging might be that, to some degree, it formalizes informal learning, a general paradox addressed by Rintala et al. (2019) and also discussed in the context of cultivating communities of practice (Wenger et al., 2002).
The practical implications derived from this conceptual paper suggest that organizations should address all types of informal learning—ranging from implicit to deliberative learning—and should therefore intentionally design workflows and digital environments that support not just performance but also ensure informal opportunities to learn embedded in work processes. Different technologies can support different problem-solving resources. Practitioners should not ask “Which tool is best?” but “Which resource do we want to provide for which kind of work processes?” This more analytical perspective helps avoid technology-driven decisions and enables learning-driven designs of workflows and workflow support. Generative AI should be used to trigger and support learning, not to replace it. To avoid the “AI ghost-learner effect” (i.e., performing via AI without developing competence), organizations could implement nudging mechanisms that foster reflection. Simulated work environments (e.g., via metaverses) can function as representative resources, enabling experimentation with complex problems in situations where real-world trial and error would be too risky or costly. Collaboration platforms are already widely in use, but they are usually not intentionally designed to support informal workplace learning activities. Organizations can scaffold reflecting on, researching for, and the documentation of learning in these collaboration platforms. Creating social presence in collaboration platforms, encouraging a general learning orientation when collaborating in virtual teams or with AI agents, and using AI to connect these platform activities to skill profiles, skills ontologies, and context-sensitive learning materials will help further fostering reflection, researching, advice-seeking and knowledge sharing. In a similar vein, the integration of AI and real-time analytics within other software applications (e.g., enterprise resource planning systems; ERP) enables adaptive responses based on user behavior in the moment of need (e.g., tailored nudges, links to learning materials or experts). These developments, however, must be accompanied by clear ethical guidelines and compliance with data protection regulations, especially when user behavior is monitored or learning-related data is processed. Altogether, HRD should, of course, try to improve employees' AI adoption (Khandelwal et al., 2024) but, at the same time, by providing an adequate digital infrastructure can also foster “digitally minded and agile organizational cultures, structures, and workforce practices.” (Thite, 2022, p. 10).
The research implications derived from this conceptual paper suggests a closer look at problem-solving and learning processes in the workplace. With regard to workplace learning activities and resources, it is worthwhile to examine the conditions under which specific activities and resources are favored. Field experiments (e.g., waitlist control group designs) could be conducted to evaluate the implementation of the technological tools discussed above. The introduced concept of the “AI ghost-learner effect” calls for research on how employees maintain or loose a sense of ownership when they use AI tools to solve work-related problems and how nudging helps to counteract this. In doing so, some of the above questions could be addressed via interviews. However, to gain closer insights into everyday informal workplace learning, it seems advisable to use more fine-grained, in situ methods for data collection such as experience sampling or diaries (Rausch et al., 2022; Seifried and Rausch, 2022). Furthermore, many of the workplace learning activities discussed here generate digital traces, making the analysis of resulting log data a promising avenue for research. However, such analyses must be conducted with careful attention to ethical standards and data protection regulations, particularly when dealing with sensitive behavioral or performance-related information. In addition to these situational factors (within-person perspective), individual differences should also be taken into account (between-person perspective). A broad range of possible influencing factors at the personal level includes work experience, domain-specific competences, motivation, and technology acceptance including perceived usefulness and ease of use of digital tools. Finally, differences in organizational contexts such as the organization of work, the digital tool environment, team climate, psychological safety and so forth should also be considered as influencing factors (see 3-P model by Tynjälä, 2013). Multilevel analysis (i.e. hierarchical linear models, mixed models) enables researchers to disentangle within-person dynamics from between-person differences in intensive longitudinal designs.
5 Conclusion
In response to ongoing technological transformations and shifting work practices, this paper has emphasized the increasing importance of informal workplace learning as a key mechanism for adapting to changing demands. Building on a problem-solving perspective, a framework that categorizes informal learning activities is proposed that distinguishes reasoning, experimenting, researching, and observing and links these activities to various resources. This lens enables a systematic understanding of how emerging applications—based on analytical and generative AI—can support informal learning processes embedded in everyday work. These tools can foster learning through contextualized support and reflection prompts within specific business software or collaboration platforms. At the same time, if problem solving is overly delegated to AI, employees may lose learning opportunities—a risk that is termed the “AI ghost-learner effect.” To ensure that technology supports rather than replaces learning, intentional design of workflows and digital environments is needed. The framework developed here serves as a conceptual foundation for future empirical research on informal workplace learning in digitalized work contexts. It encourages analytical differentiation of learning activities and resources and invites investigations into the impact of specific technologies and corresponding implementation strategies.
Author contributions
AR: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. Open access publication fee was partly funded by the Open Access Publishing Fund at the University of Mannheim, Germany.
Acknowledgments
Special thanks go to Michael Goller who provided valuable feedback on an earlier version of the manuscript and to Timo Kortsch who provided valuable feedback in his role as guest editor of this research topic.
Conflict of interest
The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript. GenAI was used to research literature for a few selected passages and to revise the language of selected passages.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Alavi, M., Leidner, D. E., and Mousavi, R. (2024). Knowledge management perspective of generative artificial intelligence. JAIS 25, 1–12. doi: 10.17705/1jais.00859
Alhusban, M. I., Alshurafat, H., and Khatatbeh, I. N. (2024). Exploring professional perspectives on integrating generative artificial intelligence into corporate learning and development: an organizational change perspective. Dev. Learn. Organ. 39, 21–24. doi: 10.1108/DLO-05-2024-0131
Allvin, M., and Movitz, F. (2017). “Whose side istechnology on, really? On the interdependence of work and technology,” in An Introduction to Work and Organizational Psychology: An International Perspective, eds. F. Fraccaroli, and M. Sverke (Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley and Sons), 121–136. doi: 10.1002/9781119168058.ch7
Arya, J., and Hindolia, A. (2024). Nudging towards excellence: harnessing behavioral insights for organizational learning. Dev. Lear. in Organ. 39, 25–27. doi: 10.1108/DLO-01-2024-0019
Bankins, S., Ocampo, A. C., Marrone, M., Restubog, S. L. D., and Woo, S. E. (2023). A multilevel review of artificial intelligence in organizations: implications for organizational behavior research and practice. J. Organ. Behav. 45, 159–182. doi: 10.1002/job.2735
Bednall, T. C., Sanders, K., and Runhaar, P. (2014). Stimulating informal learning activities through perceptions of performance appraisal quality and human resource management system strength: a two-wave study. Acad. Manag. Learn. Educ. 13, 45–61. doi: 10.5465/amle.2012.0162
Beier, M. E., Torres, W. J., and Gilberto, J. M. (2017). “Continuous development throughout a career: a lifespan perspective on autonomous learning,” in Autonomous Learning in the Workplace, eds. J. E. Ellingson and R. A. Noe (New York, NY: Routledge), 179–200. doi: 10.4324/9781315674131-10
Bell, B. S. (2017). “Strategies for supporting self-regulation during self-directed learning in the workplace,” in Autonomous Learning in the Workplace, 1st Edn, eds. J. E. Ellingson and R. A. Noe (New York, NY: Routledge), 117–134. doi: 10.4324/9781315674131-7
Bereiter, C., and Scardamalia, M. (1993). Surpassing Ourselves – An Inquiry into the Nature and Implications of Expertise. Chicago, IL: Open Court.
Bergmann, F. (2019). New Work New Culture: Work We Want and a Culture That Strengthens Us. Alresford, Hampshire: John Hunt Publishing.
Billett, S. (2002). Toward a workplace pedagogy: guidance, participation, and engagement. Adult Educ. Q. 53, 27–43. doi: 10.1177/074171302237202
Billett, S. (2021). Mediating worklife learning and the digitalisation of work. Br. J. Educ. Technol. 52, 1580–1593. doi: 10.1111/bjet.13115
Brynjolfsson, E., Li, D., and Raymond, L. (2025). Generative AI at work. Q. J. Econ. 140, 889–942. doi: 10.1093/qje/qjae044
Budhwar, P., Chowdhury, S., Wood, G., Aguinis, H., Bamber, G. J., Beltran, J. R., et al. (2023). Human resource management in the age of generative artificial intelligence: perspectives and research directions on ChatGPT. Hum. Resour. Manag. J. 33, 606–659. doi: 10.1111/1748-8583.12524
Bughin, J., Hazan, E., Lund, S., Dahlström, P., Wiesinger, A., Subramaniam, A., et al. (2018). Skill Shift - Automation and the Future of the Workforce. Discussion Paper. McKinsey Global Institute. Available online at: https://www.mckinsey.com/featured-insights/future-of-work/skill-shift-automation-and-the-future-of-the-workforce# (Accessed August 15, 2025).
Cantrell, S., Griffiths, M., Jones, R., and Hiipakka, J. (2022). The Skills-Based Organization: A New Operating Model for Work and the Workforce. Deloitte Insights. New York, NY: Deloitte.
Cerasoli, C. P., Alliger, G. M., Donsbach, J. S., Mathieu, J. E., Tannenbaum, S. I., Orvis, K. A., et al. (2018). Antecedents and outcomes of informal learning behaviors: a meta-analysis. J. Bus. Psychol. 33, 203–230. doi: 10.1007/s10869-017-9492-y
Crans, S., Bude, V., Beausaert, S., and Segers, M. (2021). Social informal learning and the role of learning climate: toward a better understanding of the social side of learning among consultants. Hum. Resour. Dev. Q. 32, 507–355. doi: 10.1002/hrdq.21429
Crouse, P., Doyle, W., and Young, J. D. (2011). Workplace learning strategies, barriers, facilitators and outcomes: a qualitative study among human resource management practitioners. Hum. Resour. Dev. Int. 14, 39–55. doi: 10.1080/13678868.2011.542897
Cuyvers, K., van den Bossche, P., and Donche, V. (2020). Self-regulation of professional learning in the workplace: a state of the art and future perspectives. Vocat. Learn. 13, 281–312. doi: 10.1007/s12186-019-09236-x
Damaševičius, R., and Sidekerskiene, T. (2024). Virtual worlds for learning in metaverse: a narrative review. Sustainability 16:2032. doi: 10.3390/su16052032
Decius, J., Decius, L., and Beausaert, S. (2024). Integrating multiple theoretical perspectives on informal field-based learning: the self-regulated informal learning Cycle (SILC). Hum. Resour. Dev. Rev. 24, 247–278. doi: 10.1177/15344843241310631
Decius, J., Knappstein, M., Schaper, N., and Seifert, A. (2023). Investigating the multidimensionality of informal learning: validation of a short measure for white-collar workers. Hum. Resour. Dev. Q. 34, 45–74. doi: 10.1002/hrdq.21461
Decius, J., Kortsch, T., Paulsen, H., and Schmitz, A. (2022). Learning What You Really, Really Want: Towards a Conceptual Framework of New Learning in the Digital Work Environment. Honolulu, HI. Available online at: https://scholarspace.manoa.hawaii.edu/server/api/core/bitstreams/9f9a80b9-bf99-4e5e-bc39-b6329a531b35/content (Accessed August 15, 2025).
Decius, J., Schaper, N., and Seifert, A. (2019). Informal workplace learning: development and validation of a measure. Hum. Resour. Dev. Q. 30, 495–535. doi: 10.1002/hrdq.21368
Doornbos, A. J., Bolhuis, S., and Simons, P. R.-J. (2004). Modeling work-related learning on the basis of intentionality and developmental relatedness: a noneducational perspective. Hum. Resour. Dev. Rev. 3, 250–274. doi: 10.1177/1534484304268107
Dörner, D. (1997). The Logic of Failure: Recognizing and Avoiding Error in Complex Situations. Cambridge, MA: Perseus Books.
Draxler, F., Werner, A., Lehmann, F., Hoppe, M., Schmidt, A., Buschek, D., et al. (2024). The AI ghostwriter effect: when users do not perceive ownership of AI-Generated text but self-declare as authors. ACM Trans. Comput. Hum. Interact. 31, 1–40. doi: 10.1145/3637875
Endedijk, M. D., and Cuyvers, K. (2022). “Self-regulation of professional learning: towards a new era of research,” in Research Approaches on Workplace Learning, Vol. 31. Professional and Practice-Based Learning, eds. C. Harteis, D. Gijbels, and E. Kyndt (Cham: Springer International Publishing), 219–237. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-89582-2_10
Eraut, M. (2004). Informal learning in the workplace. Stud. Contin. Educ. 26, 247–273. doi: 10.1080/158037042000225245
Eraut, M. (2011). Informal learning in the workplace: evidence on the real value of work-based learning (WBL). Dev. Learn. Organ. 25, 8–12. doi: 10.1108/14777281111159375
Ericsson, K. A., Krampe, R. T., and Tesch-Römer, C. (1993). The role of deliberate practice in the acquisition of expert performance. Psychol. Rev. 100, 363–406. doi: 10.1037/0033-295X.100.3.363
Fahad, S. A., Salloum, S. A., and Shaalan, K. (2024). “The role of ChatGPT in knowledge sharing and collaboration within digital workplaces: a systematic review,” in Artificial Intelligence in Education: The Power and Dangers of ChatGPT in the Classroom, Vol. 144. Studies in Big Data, eds. A. Al-Marzouqi, S. A. Salloum, M. Al-Saidat, A. Aburayya, and B. Gupta (Cham: Springer Nature Switzerland), 259–282. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-52280-2_17
Frese, M., and Zapf, D. (1994). “Action as the core of work psychology: a German approach,” in Handbook of Industrial and Organizational Psychology, eds. H. C. Triandis, M. D. Dunnette, and L. M. Hough (Palo Alto, CA: Consulting Psychologists Press), 271–340.
Frey, C. B., and Osborne, M. A. (2017). The future of employment: how susceptible are jobs to computerisation? Technol. Forecast. Soc. 114, 254–280. doi: 10.1016/j.techfore.2016.08.019
Gegenfurtner, A., Gruber, H., Lehtinen, E., and Säljö, R. (2024). Horizontal transition of expertise. Frontline Learn. Res. 12, 20–44. doi: 10.14786/flr.v12i3.543
Gijbels, D., Donche, V., Van den Bossche, P., Ilsbroux, I., and Sammels, E. (2014). “Understanding work-related learning: the role of job characteristics and the use of different sources of learning,” in Promoting, Assessing, Recognizing and Certifying Lifelong Learning, eds. T. Halttunen, M. Koivisto, and S. Billett (Dordrecht: Springer Netherlands), 97–107. doi: 10.1007/978-94-017-8694-2_6
Goller, M. (2017). Human Agency at Work: An Active Approach towards Expertise Development. Wiesbaden: Springer VS.
Goller, M., Harteis, C., Gijbels, D., and Donche, V. (2020). Engineering students' learning during internships: exploring the explanatory power of the job demands-control-support model. J. Eng. Educ. 109, 307–324. doi: 10.1002/jee.20308
Gottfredson, C., and Mosher, B. (2011). Innovative Performance Support: Strategies and Practices for Learning in the Workflow. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill.
Gruber, H., and Harteis, C. (2018). Individual and Social Influences on Professional Learning: Supporting the Acquisition and Maintenance of Expertise, Vol. 24. Professional and Practice-Based Learning. Cham: Springer International Publishing. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-97041-7
Hacker, W. (2003). Action regulation theory: a practical tool for the design of modern work processes? Eur. J. Work Organ. Psychol. 12, 105–130. doi: 10.1080/13594320344000075
Hacker, W. (2005). Allgemeine Arbeitspsychologie: Psychische Regulation von Wissens-, Denk-Und Körperlicher Arbeit. Göttingen: Huber.
Hacker, W., and Skell, W. (1993). Lernen in der Arbeit. Berlin: Bundesinstitut für Berufsbildung Berlin.
Hallinger, P., and Wang, R. (2020). The evolution of simulation-based learning across the disciplines, 1965–2018: a science map of the literature. Simul. Gaming 51, 9–32. doi: 10.1177/1046878119888246
Harteis, C. (2002). Kompetenzfördernde Arbeitsbedingungen: Zur Konvergenz ökonomischer und pädagogischer Prinzipien betrieblicher Personal-und Organisationsentwicklung [Competence-Enhancing Working Conditions: On the Convergence of Economic and Pedagogical Principles in Corporate Personnel and Organizational Development]. Springer.
Harteis, C. (2022). “Research on workplace learning in times of digitalisation,” in Research Approaches on Workplace Learning, eds. C. Harteis, D. Gijbels, and E. Kyndt (Cham: Springer International Publishing), 415–428. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-89582-2_19
Harteis, C., Goller, M., and Gerholz, K.-H. (2022). “Digitalization of work: challenges for workplace learning,” in The SAGE Handbook of Learning and Work, eds. M. Malloch, L. Cairns, K. Evans, and B. O'Connor (London: SAGE Publications Ltd), 329–342. doi: 10.4135/9781529757217.n21
Hatano, G., and Inagaki, K. (1984). Two Courses of Expertise. 6. Annual Report. Research and Clinical Center for Child Development. Available online at: http://hdl.handle.net/2115/5206
Hendriks, P., Olt, C. M., Sturm, T., and Moos, C. C. (2024). Exploring team collaboration in the metaverse from a human capital perspective. J. Intellect. Cap. 25, 686–710. doi: 10.1108/JIC-02-2024-0055
Hilkenmeier, F., Goller, M., and Schaper, N. (2021). The differential influence of learner factors and learning context on different professional learning activities. Vocat. Learn. 14, 411–438. doi: 10.1007/s12186-021-09266-4
Hodkinson, P., and Hodkinson, H. (2004). “The complexities of workplace learning – problems and dangers in trying to measure attainment,” in Workplace Learning in Context, eds. H. Rainbird, A. Fuller, and A. Munro (London: Routledge), 259–275.
Holm, J. R., and Lorenz, E. (2022). The impact of artificial intelligence on skills at work in Denmark. N. Technol. Work Employ. 37, 79–101. doi: 10.1111/ntwe.12215
Holmes, W., and Littlejohn, A. (2024). “Artificial intelligence for professional learning,” in Handbook of Artificial Intelligence at Work, eds. M. Garcia-Murillo, I. MacInnes, and A. Renda (Northampton, MA: Edward Elgar Publishing), 191–211. doi: 10.4337/9781800889972.00018
Hung, W., Jonassen, D. H., and Liu, R. (2008). “Problem-based learning,” in Handbook of Research on Educational Communications and Technology, eds. J. M. Spector, J. G. van Merrienboer, M. D. Merrill, and M. Driscoll (Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum), 485–506. doi: 10.4324/9780203880869
Jacobs, R. L., and Park, Y. (2009). A proposed conceptual framework of workplace learning: implications for theory development and research in human resource development. Hum. Resour. Dev. Rev. 8, 133–150. doi: 10.1177/1534484309334269
Jagatheesaperumal, S. K., Rahouti, M., Ahmad, K., Al-Fuqaha, A., and Guizani, M. (2022). The duo of artificial intelligence and big data for industry 4.0: applications, techniques, challenges, and future research directions. IEEE Internet Things J. 9, 12861–12885. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2021.3139827
Jo, H., and Park, D.-H. (2024). Effects of ChatGPT's AI capabilities and human-like traits on spreading information in work environments. Sci. Rep. 14:7806. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-57977-0
Johnson, M., and Majewska, D. (2022). Formal, Non-Formal, and Informal Learning: What Are They, and How Can We Research Them? Research Report. Cambridge, MA: Cambridge University Press and Assessment.
Junker, T. L., Bakker, A. B., Derks, D., and Molenaar, D. (2023). Agile work practices: measurement and mechanisms. Eur. J. Work Organ. Psychol. 32, 1–22. doi: 10.1080/1359432X.2022.2096439
Kalischko, T., and Riedl, R. (2021). Electronic performance monitoring in the digital workplace: conceptualization, review of effects and moderators, and future research opportunities. Front. Psychol. 12:633031. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.633031
Kanfer, R., and Ackerman, P. L. (2005). “Work competence – a person-oriented perspective,” in Handbook of Competence and Motivation, eds. A. J. Elliot, and C. S. Dweck (New York, NY: Guilford Press), 336–353.
Karhapää, A., Hämäläinen, R., and Pöysä-Tarhonen, J. (2023). Digital work practices that promote informal workplace learning: digital ethnography in a knowledge work context. Stud. Contin. Educ. 47, 1–18. doi: 10.1080/0158037X.2023.2274596
Karhapää, A., Rikala, P., Pöysä-Tarhonen, J., and Hämäläinen, R. (2024). Digital environments as sites for informal workplace learning in knowledge work. J. Workplace Learn. 36, 19–36. doi: 10.1108/JWL-11-2023-0184
Khandelwal, K., Upadhyay, A. K., and Rukadikar, A. (2024). The synergy of human resource development (HRD) and artificial intelligence (AI) in today's workplace. Hum. Resour. Dev. Int. 27, 622–639. doi: 10.1080/13678868.2024.2375935
Kim, M., Beehr, T. A., and Prewett, M. S. (2018). Employee responses to empowering leadership: a meta-analysis. J. Lead. Organ. Stud. 25, 257–276. doi: 10.1177/1548051817750538
Kim, Y. (2021). “The changing concepts of expertise and expertise development,” in Expertise at Work, eds. M.-L. Germain, and R. S. Grenier (Cham: Springer International Publishing), 17–38. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-64371-3_2
Kittel, A., Kasselmann, S., Scheck, V., and Seufert, T. (2021). “LidA – lernen in der digitalisierten arbeitswelt, in Kompetenzen für die Digitale Transformation 2020, eds. L. Lehmann, D. Engelhardt, and W. Wilke (Berlin: Springer Berlin Heidelberg), 157–177. doi: 10.1007/978-3-662-62866-9_11
Köhler, D. P., and Rausch, A. (2022). Expertise development in the workplace through deliberate practice and progressive problem solving: insights from business-to-business sales departments. Vocat. Learn. 15, 569–597. doi: 10.1007/s12186-022-09301-y
Kolb, D. A. (2015). Experiential Learning: Experience as the Source of Learning and Development, 2nd Edn. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Education, Inc.
Korpelainen, E., and Kira, M. (2010). Employees' choices in learning how to use information and communication technology systems at work: strategies and approaches. Int. J. Train. Dev. 14, 32–53. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-2419.2009.00339.x
Kortsch, T., Schulte, E.-M., and Kauffeld, S. (2019). Learning work: informal learning strategies of German craft workers. EJTD 43, 418–434. doi: 10.1108/EJTD-06-2018-0052
Korunka, C., and Vartiainen, M. (2017). “Digital technologies at work are great, aren't they? The development of information and communication technologies (ICT) and Their relevance in the world of work,” in An Introduction to Work and Organizational Psychology: An International Perspective, eds. N. Chmiel, F. Fraccaroli, and M. Sverke (Hoboken, NJ: Wiley), 102–120. doi: 10.1002/9781119168058.ch6
Krishnasamy, S. K. L., and Lee, C.-S. (2024). “AI chatbots in the office: unveiling the social impacts on future workplace harmony,” in 2024 International Conference on ICT for Smart Society (ICISS) (New York, NY), 1–6. doi: 10.1109/ICISS62896.2024.10751425
Kubicek, B., Paškvan, M., and Korunka, C. (2015). Development and validation of an instrument for assessing job demands arising from accelerated change: the intensification of job demands scale (IDS). Eur. J. Work Organ. Psychol. 24, 898–913. doi: 10.1080/1359432X.2014.979160
Kyndt, E., and Beausaert, S. (2017). “How do conditions known to foster learning in the workplace differ across occupations?” in Autonomous Learning in the Workplace, eds. J. E. Ellingson, and R. A. Noe (New York, NY: Routledge), 201–218. doi: 10.4324/9781315674131-11
Kyndt, E., Gijbels, D., Grosemans, I., and Donche, V. (2016). Teachers' everyday professional development: mapping informal learning activities, antecedents, and learning outcomes. Rev. Educ. Res. 86, 1111–1150. doi: 10.3102/0034654315627864
Lane, M., and Williams, M. (2023). Defining and Classifying AI in the Workplace. OECD Social, Employment and Migration Working Papers. OECD. Available online at: http://file:///Users/andreasrausch/Downloads/59e89d7f-en.pdf (Accessed August 15, 2025).
Lee, W. C., and Tan, B. C. Y. (2023). Workplace learning strategies, enablers, and challenges in the context of digital innovation. JWL 35, 192–209. doi: 10.1108/JWL-04-2022-0045
Leiß, T. V., Rausch, A., and Seifried, J. (2022). Problem-solving and tool use in office work: the potential of electronic performance support systems to promote employee performance and learning. Front. Psychol. 13:869428. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.869428
Lemmetty, S., and Collin, K. (2020). Self-directed learning as a practice of workplace learning: interpretative repertoires of self-directed learning in ICT work. Vocat. Learn. 13, 47–70. doi: 10.1007/s12186-019-09228-x
Lim, K. K., and Lee, C. S. (2022). Nudging learning behaviour: a systematic review. Proc. Assoc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 59, 744–746. doi: 10.1002/pra2.712
Littlejohn, A., and Margaryan, A. (2014). “Technology-enhanced professional learning,” in International Handbook of Research in Professional and Practice-Based Learning. Springer International Handbooks of Education, eds. S. Billett, C. Harteis, and H. Gruber (Dordrecht: Springer Netherlands), 1187–1212. doi: 10.1007/978-94-017-8902-8_43
Littlejohn, A., Milligan, C., and Margaryan, A. (2012). Charting collective knowledge: supporting self-regulated learning in the workplace. J. Workplace Learn. 24, 226–238. doi: 10.1108/13665621211209285
Littlejohn, A., and Pammer-Schindler, V. (2022). “Technologies for professional learning,” in Research Approaches on Workplace Learning, Vol. 31. Professional and Practice-Based Learning, eds. C. Harteis, D. Gijbels, and E. Kyndt (Cham: Springer International Publishing), 321–346. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-89582-2_15
Lohman, M. C. (2005). A survey of factors influencing the engagement of two professional groups in informal workplace learning activities. Hum. Resourc. Dev. Q. 16, 501–527. doi: 10.1002/hrdq.1153
Lund, S., Madgavkar, A., Manyika, J., Smit, S., Ellingrud, K., Meaney, M., et al. (2021). The Future of Work after COVID-1919. Washington, DC: McKinsey Global Institute.
Malcolm, J., Hodkinson, P., and Colley, H. (2003). The interrelationships between informal and formal learning. J. Workplace Learn. 15, 313–318. doi: 10.1108/13665620310504783
Manz, C. C., and Sims, H. P. Jr. (1981). Vicarious learning: the influence of modeling on organizational behavior. Acad. Manag. Rev. 6, 105–113. doi: 10.2307/257144
Mao, J.-Y., and Brown, B. R. (2007). “The effectiveness of online task support vs. instructor-led training,” in Advances in End User Computing, ed. M. A. Mahmood (London: IGI Global), 77–100. doi: 10.4018/978-1-59140-926-7.ch004
Margaryan, A., Littlejohn, A., and Milligan, C. (2013). Self-regulated learning in the workplace: strategies and factors in the attainment of learning goals: self-regulated learning in the workplace. Int. J. Train. Dev. 17, 245–259. doi: 10.1111/ijtd.12013
Marsick, V. J., and Watkins, K. (1990). Informal and Incidental Learning in the Workplace. London: Routledge.
Mayer, R. E., and Wittrock, M. C. (2006). “Problem solving,” in Handbook of Educational Psychology, ed. P. A. Alexander, and P. H. Winne (Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Publishers), 287–303.
Meier, C., and Seufert, S. (2022). “AI-supported systems for integrated skills-management and skills-development,” in Artificial Intelligence Education in the Context of Work. Advances in Analytics for Learning and Teaching, eds. D. Ifenthaler and S. Seufert (Cham: Springer International Publishing), 3–25. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-14489-9_1
Moore, A. L., and Klein, J. D. (2020). Facilitating informal learning at work. TechTrends 64, 219–228. doi: 10.1007/s11528-019-00458-3
Nguyen, T., and Elbanna, A. (2025). Understanding human-ai augmentation in the workplace: a review and a future research agenda. Inf. Syst. Front. 1–21. doi: 10.1007/s10796-025-10591-5
Nieuwenhuis, L. F. M., and Van Woerkom, M. (2007). Goal rationalities as a framework for evaluating the learning potential of the workplace. Hum. Resour. Dev. Rev. 6, 64–83. doi: 10.1177/1534484306296432
Noe, R. A., and Ellingson, J. E. (2017). “Autonomous learning in the workplace: an introduction,” in Autonomous Learning in the Workplace, eds. J. E. Ellingson, and R. A. Noe (New York, NY: Routledge), 1–11. doi: 10.4324/9781315674131-1
Noe, R. A., Tews, M. J., and Marand, A. D. (2013). Individual differences and informal learning in the workplace. J. Vocat. Behav. 83, 327–335. doi: 10.1016/j.jvb.2013.06.009
Nonaka, I., and Takeuchi, H. (2019). The Wise Company: How Companies Create Continuous Innovation. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
OECD (2005). Definition and Selection of Key Competencies. Paris: OECD. Available online at: http://www.oecd.org/dataoecd/47/61/35070367.pdf
Parker, S. K., and Grote, G. (2022). Automation, algorithms, and beyond: why work design matters more than ever in a digital world. Appl. Psychol. 71, 1171–1204. doi: 10.1111/apps.12241
Parmigiani, A., and Howard-Grenville, J. (2011). Routines revisited: exploring the capabilities and practice perspectives. Acad. Manag. Ann. 5, 413–453. doi: 10.5465/19416520.2011.589143
Rausch, A. (2011). Erleben und Lernen am Arbeitsplatz in der betrieblichen Ausbildung. [Emotional Experience and Learning in the Workplace Within In-firm Vocational Education and Training]. Wiesbaden: VS Research.
Rausch, A., Goller, M., and Steffen, B. (2022). “Uncovering informal workplace learning by using diaries,” in Methods for Researching Professional Learning and Development, eds. M. Goller, E. Kyndt, S. Paloniemi, and C. Damşa (Cham: Springer), 43–70. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-08518-5_3
Rausch, A., Schley, T., and Warwas, J. (2015). Problem solving in everyday office work—a diary study on differences between experts and novices. Int. J. Lifelong Educ. 34, 448–467. doi: 10.1080/02601370.2015.1060023
Rausch, A., Seifried, J., and Harteis, C. (2017). Emotions, coping and learning in error situations in the workplace. J. Workplace Learn. 29, 374–393. doi: 10.1108/JWL-01-2017-0004
Rintala, H., Nokelainen, P., and Pylväs, L. (2019). “Informal workplace learning: turning the workplace into a learning site,” in Handbook of Vocational Education and Training, eds. S. McGrath, M. Mulder, J. Papier, and R. Suart (Cham: Springer International Publishing), 1–14. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-49789-1_97-1
Sanders, K., Yang, H., Shipton, H., and Bednall, T. (2017). “Effects of human resource management on informal learning,” in Autonomous Learning in the Workplace, eds. J. E. Ellingson and R. A. Noe (Routledge), 162–178.
Seifried, J., and Rausch, A. (2022). “Applying the experience sampling method to research on workplace learning,” in Methods for Researching Professional Learning and Development, Vol. 33. Professional and Practice-Based Learning, eds. M. Goller, E. Kyndt, S. Paloniemi, and C. Damşa (Cham: Springer International Publishing), 19–41. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-08518-5_2
Sitzmann, T., and Ely, K. (2011). A meta-analysis of self-regulated learning in work-related training and educational attainment: what we know and where we need to go. Psychol. Bull. 137, 421–442. doi: 10.1037/a0022777
Tannenbaum, S. I., Beard, R. L., McNall, L. A., and Salas, E. (2010). “Informal learning and development in organizations,” in n Learning, Training, and Development in Organization. The Organizational Frontiers Seriess, eds. S. W. J. Kozlowski and E. Salas (New York, NY: Routledge), 303–331.
Tannenbaum, S. I., and Wolfson, M. A. (2022). Informal (field-based) learning. Annu. Rev. Organ. Psychol. Organ. Behav. 9, 391–414. doi: 10.1146/annurev-orgpsych-012420-083050
Thaler, R. H., and Sunstein, C. R. (2008). Nudge: Improving Decisions about Health, Wealth, and Happiness. New Haven, CT: Yale University Press.
Thite, M. (2022). Digital human resource development: where are we? Where should we go and how do we go there? Hum. Resour. Dev. Int. 25, 87–103. doi: 10.1080/13678868.2020.1842982
Tynjälä, P. (2008). Perspectives into learning at the workplace. Educ. Res. Rev. 3, 130–154. doi: 10.1016/j.edurev.2007.12.001
Tynjälä, P. (2013). Toward a 3-P model of workplace learning: a literature review. Vocat. Learn. 6, 11–36. doi: 10.1007/s12186-012-9091-z
Umbelino, T. R., Da Costa, A. E., and Prado, G. M. (2024). “Potentials of the metaverse to facilitate organizational learning,” in Immersing in the Metaverse: Theoretical and Practical Reflections, 1st edn., eds. R. Pereira, N. Dos Santos, F. Gauthier, I. Reis, D. Ropelato, and E. Slomp (Editora Arquetipos), 227–256. doi: 10.54715/arque.978-65-84549-40-1.011
Van Woerkom, M., Nijhof, W. J., and Nieuwenhuis, L. F. M. (2002). Critical reflective working behaviour: a survey research. J. Eur. Ind. Train. 26, 375–383. doi: 10.1108/03090590210444955
Vuorikari, R., Kluzer, S., and Punie, Y. (2022). DigComp 2.2, The Digital Competence framework for Citizens: With new Examples of Knowledge, Skills and Attitudes. European Commission. Joint Research Centre. Available online at: https://data.europa.eu/doi/10.2760/115376 (Accessed August 15, 2025).
Wang, J., Zheng, W., Zhang, L., and Wu, Y. J. (2025). How Organizational electronic performance monitoring affects employee proactive behaviors: the psychological reactance perspective. Int. J. Hum.–Comput. Interact. 41, 1902–1916. doi: 10.1080/10447318.2024.2371690
Watkins, K. E., and Marsick, V. J. (1992). Towards a theory of informal and incidental learning in organizations. Int. J. Lifelong Educ. 11, 287–300. doi: 10.1080/0260137920110403
Watkins, K. E., and Marsick, V. J. (2023). Rethinking Workplace Learning and Development. Camberley: Edward Elgar Publishing. doi: 10.4337/9781802203776
Weinmann, M., Schneider, C., and Vom Brocke, J. (2016). Digital nudging. Bus. Inf. Syst. Eng. 58, 433–436. doi: 10.1007/s12599-016-0453-1
Weintraub, J., Cassell, D., and DePatie, T. P. (2021). Nudging flow through “SMART” goal setting to decrease stress, increase engagement, and increase performance at work. J. Occup. Organ. Psychol. 94, 230–258. doi: 10.1111/joop.12347
Wenger, E., McDermott, R. A., and Snyder, W. (2002). Cultivating Communities of Practice: A Guide to Managing Knowledge. Boston, MA: Harvard Business School Press.
Wielenga-Meijer, E. G. A., Taris, T. W., Kompier, M. A. J., and Wigboldus, D. H. J. (2010). From task characteristics to learning: a systematic review. Scand. J. Psychol. 51, 363–375. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-9450.2009.00768.x
Wolfson, M. A., Mathieu, J. E., Tannenbaum, S. I., and Maynard, M. T. (2019). Informal field-based learning and work design. J. Appl. Psychol. 104, 1283–1295. doi: 10.1037/apl0000408
Wolfson, M. A., Tannenbaum, S. I., Mathieu, J. E., and Maynard, M. T. (2018). A cross-level investigation of informal field-based learning and performance improvements. J. Appl. Psychol. 103, 14–36. doi: 10.1037/apl0000267
Xu, G., Xue, M., and Zhao, J. (2023). The relationship of artificial intelligence opportunity perception and employee workplace well-being: a moderated mediation model. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 20, 1–16. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20031974
Yan, L., Greiff, S., Teuber, Z., and Gašević, D. (2024). Promises and challenges of generative artificial intelligence for human learning. Nat. Hum. Behav. 8, 1839–1850. doi: 10.1038/s41562-024-02004-5
Keywords: informal learning, workplace learning, learning activities, problem solving, artificial intelligence (AI), electronic performance support systems (EPSS), nudging
Citation: Rausch A (2025) Artificial intelligence for informal workplace learning: a problem-solving perspective. Front. Organ. Psychol. 3:1555429. doi: 10.3389/forgp.2025.1555429
Received: 04 January 2025; Accepted: 12 September 2025;
Published: 16 October 2025.
Edited by:
Timo Kortsch, IU Internationale Hochschule, GermanyReviewed by:
Hilko Paulsen, Technical University of Braunschweig, GermanyMulugeta Gugssa, Bahir Dar University, Ethiopia
Copyright © 2025 Rausch. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Andreas Rausch, cmF1c2NoQHVuaS1tYW5uaGVpbS5kZQ==
 Andreas Rausch
Andreas Rausch