- 1Business School, Nantong University, Nantong, Jiangsu, China
- 2Institute for Translational Neuroscience, Second Affiliated Hospital of Nantong University, Nantong, Jiangsu, China
- 3Ginling College, Nanjing Normal University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, China
- 4College of Economics and Management, Hunan University of Arts and Science, Changde, Hunan, China
Background: Creative deviance is key to producing breakthrough innovations and maintaining core competencies for a team. In contrast, intra-team co-opetition, an important influence on the allocation of team resources, may affect employees' creative deviance.
Methods: This study analyzed the impact mechanism of intra-team co-opetition on employee creative deviance based on the conservation of resources theory. We collected data from 205 employees in scenario experiment and 354 employees in the questionnaire.
Results: The findings of polynomial regression and response surface analysis indicate that consistency in competition and cooperation within teams can lead to lesser knowledge power loss. When competition and cooperation levels within teams are inconsistent, they may not be able to attain their intended results. Furthermore, we found that when competition and cooperation levels within teams are inconsistent, knowledge power loss in the “low competition-high cooperation” combination was lower than the “high competition-low cooperation” combination. Thus, knowledge power loss can mediate between intra-team co-opetition and employee creative deviance.
Conclusion: This study reveals the micro-mechanism of different combinations of co-opetition within the team, enriches the research results in the field of co-opetition and creative deviance, and provides reference for promoting team innovation performance and emerging more breakthrough innovation achievements.
Introduction
Today's rapidly evolving digital landscape characterized by disruptive technologies and shifting market dynamics, enterprises face unprecedented pressure. In order to enhance their core competitiveness and maintain their market position, enterprises must adopt a strategy of innovation. This entails actively promoting and encouraging employees to propose and implement innovative ideas (Anderson et al., 2014). Nevertheless, a persistent managerial dilemma arises: While formal innovation channels are essential, they often prove insufficient (Yang et al., 2024). When employees passionately believe in the value of an idea that falls outside these sanctioned pathways or faces bureaucratic inertia, they may find themselves at a crossroads. Faced with this innovation impasse, some employees feel compelled to transcend the conventional boundaries of their role and organizational norms in order to pursue their novel ideas-a phenomenon known as creative deviance (Criscuolo et al., 2014). Although creative deviance may waste valuable employee work time and resources, and even cause project delays, it can be highly beneficial for the emergence of breakthrough achievements (Globocnik and Salomo, 2015; Shukla and Kark, 2020). It has been demonstrated that creative deviance by employees is a prevalent phenomenon. It is therefore of great theoretical and practical significance to undertake a detailed examination of the mechanisms that drive employee creative deviance.
Creative deviance is defined as individual behaviors that are characterized by spontaneity. To date, academics have extensively addressed the organizational, leadership, and individual levels in dissecting the antecedents of employee creative deviance. However, research at the team level has been slightly underdeveloped (Augsdörfer, 2004; Chen and Hou, 2016; Kumar et al., 2024). Given their close interaction, teams are more likely to stimulate or constrain creative deviance among employees than other forms of workplace organization (Zhu et al., 2018; Zhang and Pan, 2022). Currently, research has only explored the impact of work control and other factors on creative deviance at the team level, starting from the perspective of rebellion of creative deviance (e.g., Du and Chen, 2019; Wang et al., 2019; Globocnik et al., 2022). However, a resource-based perspective on the antecedents of creative deviance remains underexplored. Given that creative deviance is characterized by defiance, secrecy, and high risk, sufficient resource backing is a prerequisite for such behavior. Employees' perceptions of resource gain or loss significantly influence their motivation to engage in deviant innovation. Empirical evidence suggests that the co-opetitive relationships within teams are a critical determinant of team innovation performance. The intra-team co-opetition shapes members' resource perceptions, which can serve as an effective strategy to encourage creative deviance (Avital and Singh, 2011; Ramírez-López et al., 2021).
Intra-team co-opetitive relationship can be defined as a relationship in which members of a team engage in both cooperative and competitive behaviors with one another in pursuit of shared task goals and limited resources within the team. On the one hand, a balance between competition and cooperation increases the success rate of employees in accomplishing creative deviance and producing successful outputs (Park et al., 2014). On the other hand, collaborating with competitors carries the risk of having ideas or results appropriated by the other party, making reports to superiors, and making it difficult to sustain the completion of creative deviance (Gnyawali and Park, 2011). However, the above conclusions are inevitably biased. The reason for this is that the above studies do not take into account the diversity in the intensity of competition and cooperation within teams. The intensity of competition and cooperation within a team varies from high to low and combines with each other to form four types of “co-opetition” relationships. At the same time, different “co-opetition” relationships can have significantly different effects on team members' behavioral patterns (Ramírez-López et al., 2021), including creative deviance. Therefore, it remains to be further explored how intra-team co-opetition affects creative deviance.
Employee knowledge represents a significant work resource, employee creative deviance cannot be separated from the acquisition, expansion, processing and application of knowledge. The examination of the relationship between co-opetition and creative deviance from a resource-based perspective not only transcends the limitations of conventional macro-level approaches focused on value re-creation, but also enables a more nuanced, micro-level investigation (George et al., 2014). The theory of resource conservation posits that employees perceive the risk of resource loss to be greater than the risk of resource gain (Hobfoll, 2001). In a context where competition and cooperation coexist within a team, employees inevitably share knowledge with their colleagues to achieve common task goals. However, the knowledge sharing process diminishes employees' control over their knowledge. Such knowledge power loss may itself be accompanied by concerns about resource depletion, thus reducing their willingness to engage in potentially high-risk behaviors (such as creative deviance). This study specifically focuses on the knowledge power loss as a key mechanism. Knowledge power loss is the fear of losing the unique value of one's knowledge, the exclusivity of knowledge, and the organizational power on which one's knowledge is based to gain the respect of others, as a result of sharing knowledge with one's colleagues. It weakens the individual's negotiating position, decision-making authority, or access to future opportunities (Li and Liu, 2014). Based on the aforementioned theoretical perspective and analysis, this study aims to explore how competitive and cooperative relationships within teams influence employees' creative deviance, with the role of knowledge power loss serving as a key entry point for understanding this process.
In light of the aforementioned analysis, this paper seeks to examine the role of intra-team co-opetition in influencing employees' creative deviance, with a particular focus on the mediating effect of loss of knowledge power as a function of resource conservation theory. We expanded our research on the antecedents of creative deviance from the team level. Our objective is to contribute to the research on creative deviance and to facilitate the emergence of more breakthrough achievements and promote innovative management practices within organizations. Besides, we employ polynomial regression and response surface analysis to obtain a comprehensive understanding of the interaction processes and micro-mechanisms between intra-team co-opetition. This enriches Intra-team co-opetition A more in-depth explanation of how to improve individual behavior at the micro level, and helps to accurately describe the mechanism and boundary conditions of the impact of Intra-team co-opetition on creative deviance, making an important contribution to unlocking the black box.
Theoretical basis and research hypothesis
Intra-team co-opetition and knowledge power loss
According to the conservation of resources theory, resources are beneficial abilities or tools used to achieve goals; knowledge is considered one of these resources. Critically, within organizational contexts, knowledge often translates into power-the ability to influence others, secure valuable tasks, or access further opportunities, making it a particularly significant resource. Knowledge power derives from its scarcity, value, and the individual's control over it. When under stress, people will do everything possible to conserve their resources. Surplus and deficit resources impact individuals in different ways. People who feel under-resourced are more vulnerable to resource loss. This initial loss can lead to future losses, creating a “loss spiral”. Knowledge power loss thus becomes a key mechanism through which the initial resource loss triggers the “loss spiral.” In contrast, sufficient resources can enhance an employee's perception of resource access, leading to future gains and a “gain spiral” (Hobfoll, 1989, 2001).
In scenarios with consistent intra-team co-opetition, two combinations of “high-high” and “low-low” intra-team co-opetition may occur. In “high-high” team, intense competition makes members vulnerable to resource threats. Collaborative networks are the most effective means of acquiring, maintaining, and multiplying resources, thereby effectively countering such threats. While knowledge sharing may result in the loss of uniqueness, collaborative networks serve as a powerful buffer against individual resource losses. Members leverage resource integration and mutual benefit mechanisms to effectively transform the fear of individual losses triggered by competition into confidence in collective resource gains. ultimately leading to a reduction in members' sense of knowledge power loss (Hobfoll, 2001; Hakanen et al., 2008).
In contrast, in a low-competition, low-cooperation environment, low competitiveness eliminates resource-draining sources such as intense substitution threats and performance comparisons. Team members do not need to expend psychological resources (such as energy and focus) to defend against competitive threats or utilize unique knowledge to maintain their status or competitive advantage. Low cooperation implies low task interdependence among members, reducing the value of individual knowledge resources to others. Members tend to assess their existing knowledge resources as “sufficient” and “secure.” Therefore, employees are less likely to feel a loss of knowledge power. Thus, in a “low competition, low cooperation” environment, members perceive their knowledge resources as relatively abundant and less susceptible to challenge, leading to a decrease in the sense of knowledge power loss (Hobfoll, 1989; Pereira and Mohiya, 2021).
With the vast growth of individual considerations regarding territorial boundaries, the positive aspects of co-opetition among team members can become imbalanced (Huang et al., 2015). Competition and cooperation are contradictory yet coexisting relationships. Under the pressure of such relationships, when the intra-team co-opetition level is inconsistent, individuals may abandon cooperation and turn to competition to protect their interests and power or retain cooperation to maximize mutual goals. This inconsistent co-opetition relationship can cause varying individual perceptions regarding the limited resources and power within the team. When team competition is stronger, individuals are likelier to preserve constructive resources that aid their development. Their worries and fears over losing knowledge power will be greater. When team cooperation is stronger, individuals are likelier to share their knowledge with others to generate more resources and a “gain spiral.” However, their sense of knowledge power loss will still be at a high level. Therefore, when there is more consistency and intra-team co-opetition, competition, and cooperation are more balanced, employees feel less like they are losing knowledge power. As such, the present study offers the following hypothesis:
H1a. The more consistent the intra-team co-opetition, the lower the knowledge power loss.
High cooperation fosters dense collaborative networks, which act as collective resource reservoirs (Hobfoll, 2001; Hakanen et al., 2008). When individuals face competitive pressures, they can leverage these networks. Sharing knowledge, rather than being perceived solely as a loss of individual uniqueness, becomes an investment into the “shared pool”. This pool enriched by contributions from others, offers access to a broader, more diverse set of resources such as complementary knowledge, skills, social support and opportunities, than any individual possesses alone (Das and Teng, 2000; Ritala and Hurmelinna-Laukkanen, 2013). Based on the “gain spiral” of the conservation of resource theory (Hobfoll, 2001) is activated: individuals invest their unique knowledge expecting and receiving reciprocal or collective gains that exceed the perceived cost of sharing. This transforms the fear of individual loss triggered by competition into confidence in collective gain. The perceived value and security of their overall resource portfolio increase, significantly mitigating the sense of net knowledge power loss.
In contrast, the “low-low” co-opetition configuration, while characterized by lower immediate threat perception due to the absence of intense competition (Hobfoll, 1989; Yu, 2019), also features low cooperation and thus minimal resource exchange or integration. The perceived “sufficiency” and “security” of individual knowledge resources stem largely from stasis and lack of challenge or demand. There is little impetus or mechanism for resource investment or significant gain. Resources remain largely isolated and dormant. While this avoids the acute threat-induced “loss spiral” associated with high competition without cooperation, it also fails to generate the dynamic resource gains and collective security inherent in the “high-high” synergy. The sense of knowledge power loss is low primarily because the knowledge resource is neither highly valued by others nor under active threat. It represents a state of resource equilibrium, but one with lower potential for growth and resilience compared to the gain spirals enabled by high co-opetition (Renzl, 2008; Ghobad and D'Ambra, 2013). Based on the above analysis, this paper puts forward the following hypothesis:
H1b. “High-high” combinations negatively impact knowledge power loss more than “low-low” combinations based on consistent intra-team co-opetition.
Excluding cases where intra-team co-opetition relationships are consistent, we next explore contexts where intra-team co-opetition relationships are inconsistent. Employees' knowledge power loss can be triggered by a lack of precise understanding regarding the value of shared knowledge by others or organizations in addition to a lack of trust among colleagues (Renzl, 2008; Li and Liu, 2014). The conservation of resource theory implies that employees in a low-competition and high-cooperation environment can build a positive, mutually beneficial organizational culture. This can mitigate resource loss and reduce the threat of losing future resources while effectively alleviating the “loss spiral.” By considering trust among colleagues as a valued resource, employees can establish more benefits for themselves, retain their knowledge, foster knowledge-sharing, and enhance communication within the team. This, in turn, can decrease the degree of knowledge power loss (Lazarus, 1991). On the other hand, according to the conservation of research theory, employees in a high-competition, low-cooperation environment will try to retain or obtain resources to meet their goals and achieve results. As these employees may be anxious, others may be seen as competitors in the race for resources. Employees might use team resources for their own benefit, where colleague trust is no longer a priority. Employees might make negative judgments about their colleagues' behavior (Sun et al., 2021), decreasing their willingness to share knowledge. Their fear of knowledge power loss will be greater as a result. Thus, the present study developed the following hypothesis:
H1c. When intra-team competition and intra-team cooperation levels are inconsistent, knowledge power loss will be lower in the low competition-high cooperation environment than the high competition-low cooperation environment.
The mediating role of knowledge power loss
Creative deviance can be initiated by individual employees who discretely engage in bottom-up, non-procedural innovative work for the company's benefit without formal authorization from management (Criscuolo et al., 2014). Based on the conservation of resource theory, individuals within an organization actively obtain, conserve, protect, and develop self-interested resources. They also react psychologically and behaviorally to resource additions and losses (Hobfoll, 1989). However, even though knowledge is a valued resource, employees do not necessarily rely on or maintain it to the same degree. The unequal dependence and maintenance can lead to power imbalances within an organization. Thus, there will be differences in the type and amount of knowledge resources of employees within the team, leading to potential knowledge differences and a power imbalance (Shi et al., 2021).
Studies suggest that a sense of power affects an individual's creative deviance (Wulani and Junaedi, 2021; Wang and Yu, 2022). Knowledge power loss erodes employees' belief in the unique value of their insights, undermining the core justification for defying norms (Mainemelis, 2010). Without confidence in their knowledge's competitive edge, they anticipate higher rejection of unauthorized ideas, deterring deviance. At the same time, Employees perceiving knowledge power loss view creative deviance-requiring significant cognitive/social resources-as a catastrophic risk. Potential failure could accelerate resource depletion (e.g., reputational damage), forcing strict adherence to sanctioned procedures. Besides, knowledge is tied to professional identity (Galinsky et al., 2003; Olckers and Van Zyl, 2019), its loss triggers identity threat. Employees redirect energy from proactive innovation to protecting remaining resources, depleting motivation for high-risk creative deviance. Thus, the level of knowledge power loss is high, and they will not continue secretly engaging in creative deviance due to potential risk.
Based on hypotheses 1b and 1c, consistent intra-team co-opetition with “high competition-high cooperation” and inconsistent intra-team co-opetition with “low competition-high cooperation” can cause lower knowledge power loss. The negative impact on knowledge power loss is more significant in the “high-competition-low cooperation” environment. Higher levels of knowledge power loss led to decreased creative deviance. The present study proposes that knowledge power loss mediates the relationship between intra-team co-opetition and employee creative deviance. In summary, the specific theoretical model diagram is shown in Figure 1.
H2. Knowledge power loss mediates the relationship between intra-team co-opetition and employee creative deviance.
Research methodology and data analysis
Study 1: scenario experiment
Experimental context development
This study used a two (intra-team competition: high vs. low) and two (intra-team cooperation: high vs. low) between-subjects design. We combined variable definitions, measurement scales, and descriptions of circumstances used in existing experimental studies to manipulate distinct levels of intra-team competition and intra-team cooperation. First, we introduced subjects to the work scenario based on the following description: “You have worked at Kanben for 3 years in a clothing sales company, specifically in the market research department. Your main responsibility is to draft market research reports with your colleagues. In the past 2 months, your department head, Manager Wang, assigned you to complete a survey on the user experience of a new shirt in location A”.
Next, subjects successively read descriptions involving intra-team competition and intra-team cooperation. The intra-team rivalry and cooperation script was based on the scale developed by Baruch and Lin (2012). Since it is challenging to manipulate high and low competitiveness in the same context, the present study developed manipulation scripts of varying intensities for intra-team competitiveness. The experimental materials are in the Appendix A.
Response scale
The first part of the response scale measured whether subjects correctly assessed the intra-team competition and intra-team cooperation stimuli, with three items measuring intra-team competition (e.g., “Our team members have a “win-lose” relationship”) and three items measuring intra-team cooperation (e.g., “Our team members seek compatible attitude in terms of teamwork”). We utilized three items to measure intra-team cooperation (e.g., “Our team members seek compatible attitude in terms of teamwork”). This study measured intra-team competition and intra-team cooperation using a 5-point Likert scale (1 = “completely disagree” and 5 = “completely agree”). Cronbach's alpha for the intra-team competition Scale was 0.943, and the intra-team cooperation scale was 0.898.
The second part of the response scale measured knowledge power loss. This study used the scale developed by Kankanhalli et al. (2005) with four items (e.g., “Sharing my knowledge through EKRs (lectronic knowledge repositories) makes me lose my unique value in the organization”) and a Cronbach's alpha for the knowledge power loss was 0.934.
The third part of the response scale measured creative deviance. This study developed the following scenario based on Criscuolo et al.'s (2014) scale: “Through a user experience survey in location A, you learned that most purchasers in location A thought that the shirt collar in your new product was too large and hoped that it could be improved. You report this finding to Manager Wang. He responds that a professional designer developed the shirt; the user's dissatisfaction may be due to regional cultural influences, so not to worry about it. You later learned about the shirt collar design and concluded that the collar was indeed incorrectly designed.” Following the scenario, we asked the subjects to answer three questions: (1) “I have the flexibility to work my way around my official work plan, digging into new potentially valuable business opportunities.” The Cronbach's alpha for this scale was 0.809.
Finally, this study asked subjects to provide demographic information regarding gender, age, education, and years of employment.
Attention test
To determine whether subjects responded carefully, this study used two attention test items for screening. Specifically, we asked subjects to select either “yes” or “no.” The two items were “Your supervisor is Manager Zhang” and “Your department is the marketing department.”
Main flow and experiment structure
This contextual experiment prompted the subjects to read the instruction materials carefully and thoughtfully. After reading the materials, we asked the respondents to imagine that they were the protagonists in the scenario and to answer the experimental questions based on their true feelings. We randomly distributed the contextual experiment's four scenarios. The four scenarios corresponded to “high-high,” “high-low,” “low-high” and “low-low” attributes of the team's competitive relationship. The number of subjects in the four scenarios was as follows: (1) “high-high,”: 38 participants; (2) “high-low,”: 62 participants; (3) “low-high”: 53 participants; (4) “low-low”: 52 participants.
Experimental results
Experimental manipulation check
The present study first determined whether the manipulations of intra-team competition and intra-team cooperation were valid. Regarding intra-team competition manipulation, subjects' perceptions of the intra-team competition were significantly higher in the high intra-team competition group than in the low intra-team competition group (M HighIntra − teamCompetition = 4.443, SD = 0.457, M LowIntra − teamCompetition = 2.092, SD = 325, t (178) = 42.257, p < 0.001). Regarding intra-team cooperation manipulation, subjects' perceptions of the organized competitive environment were significantly higher within the high intra-team cooperation group. Further, the subjects' perceptions of an organizationally competitive environment were significantly higher than within the low intra-team cooperation group [M highintra − teamcooperation= 4.054, SD = 0.549, M lowintra − teamcooperation= 2.216, SD=0.603, t(203) = 22.552, p < 0.001]. Therefore, the study findings were valid regarding the manipulation of intra-team competition and intra-team cooperation.
Confirmatory factor analyses
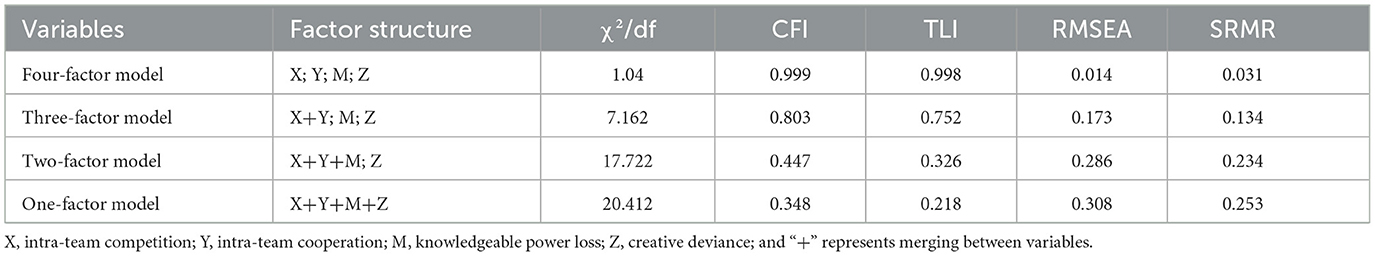
We further conducted a validated factor analysis to test the discriminant validity of the collected data using Mplus software. Each model's specific fit indices are presented in the Table 1 below. This table shows that the best fit was the four models (χ2/df = 1.04, CFI = 0.999, TLI = 0.998, SRMR = 0.014, RMSEA = 0.031). Where χ2/df was < 3, CFI and TLI were more significant than 0.9, SRMR was < 0.05, and RMSEA was < 0.08, which meets the study criteria.
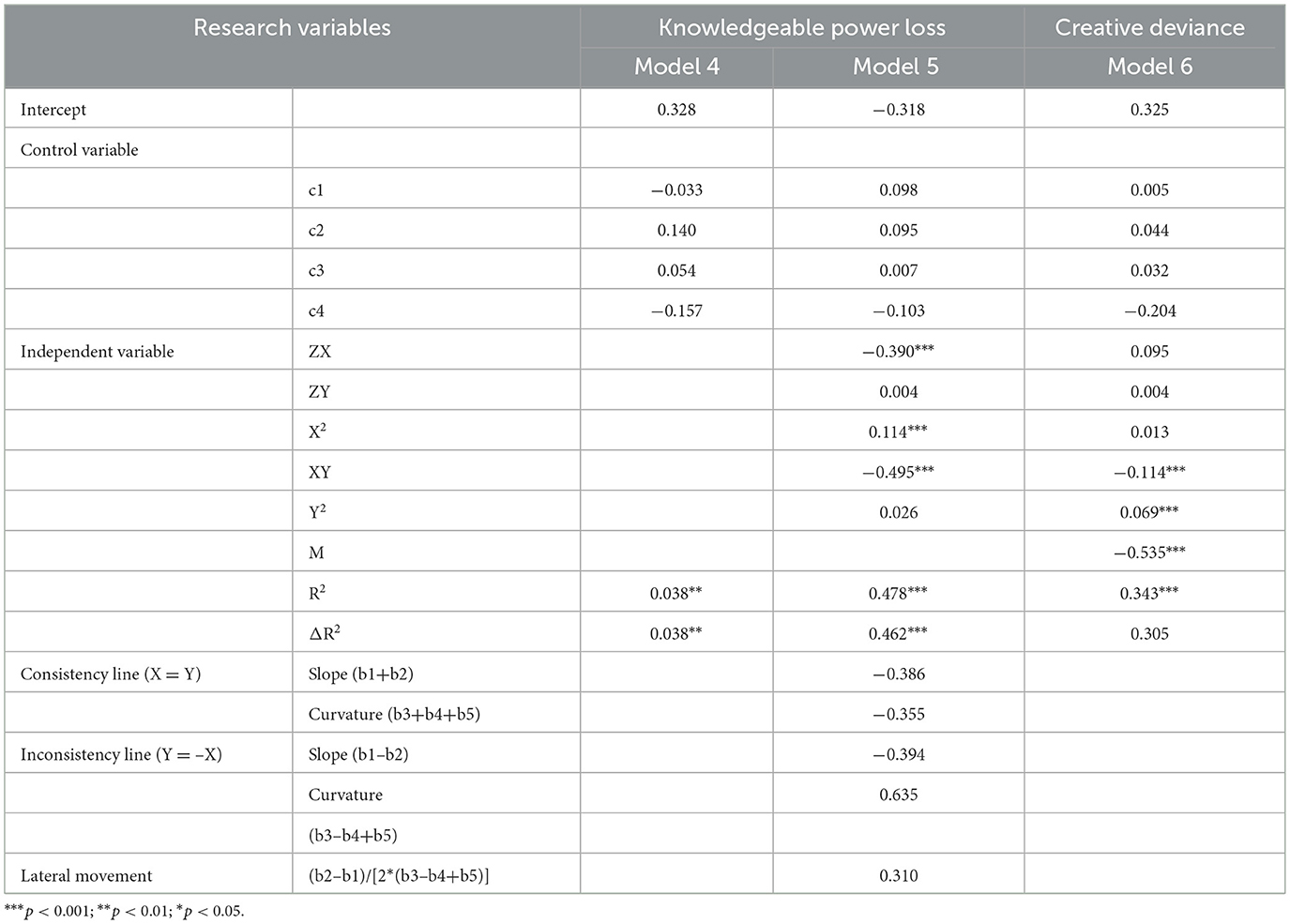
Descriptive statistics and correlation analysis
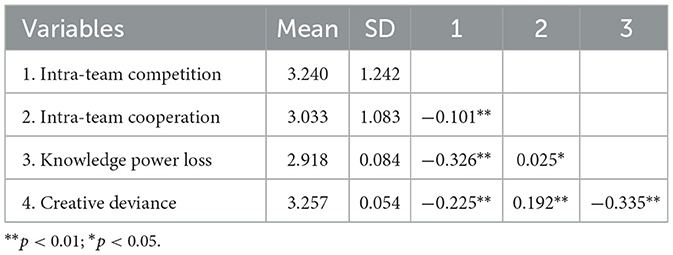
This experiment analyzed each variable's descriptive statistics and correlation coefficients using SPSS 26.0. The results are presented in the table below. The descriptive statistics and correlation analysis results of the research variables in Study 1 are shown in Table 2. Table 2 indicates that intra-team cooperation and knowledge power loss were positively correlated (γ = 0.025, p < 0.05), intra-team competition and knowledge power loss were significantly negatively correlated (γ = −0.326, p < 0.01), and knowledge power loss and creative deviance were significantly negatively correlated (γ = −0.335, p < 0.01).
Hypothesis testing
The hypothesis testing session of this study followed the recommendations of Edwards and Parry (1993) and used polynomial regression analysis and response surface analysis to test the hypotheses. The formula for polynomial regression is as follows:
Where M represents the mediating variable (knowledge power loss), X is intra-team competition, Y represents intra-team cooperation, X2 is the squared term of intra-team competition, X × Y is the cross-multiplier of intra-team competition and intra-team cooperation, Y2 denotes the squared term of intra-team cooperation, b1–b5 represent the regression coefficients, and e represents the regression equation residuals.
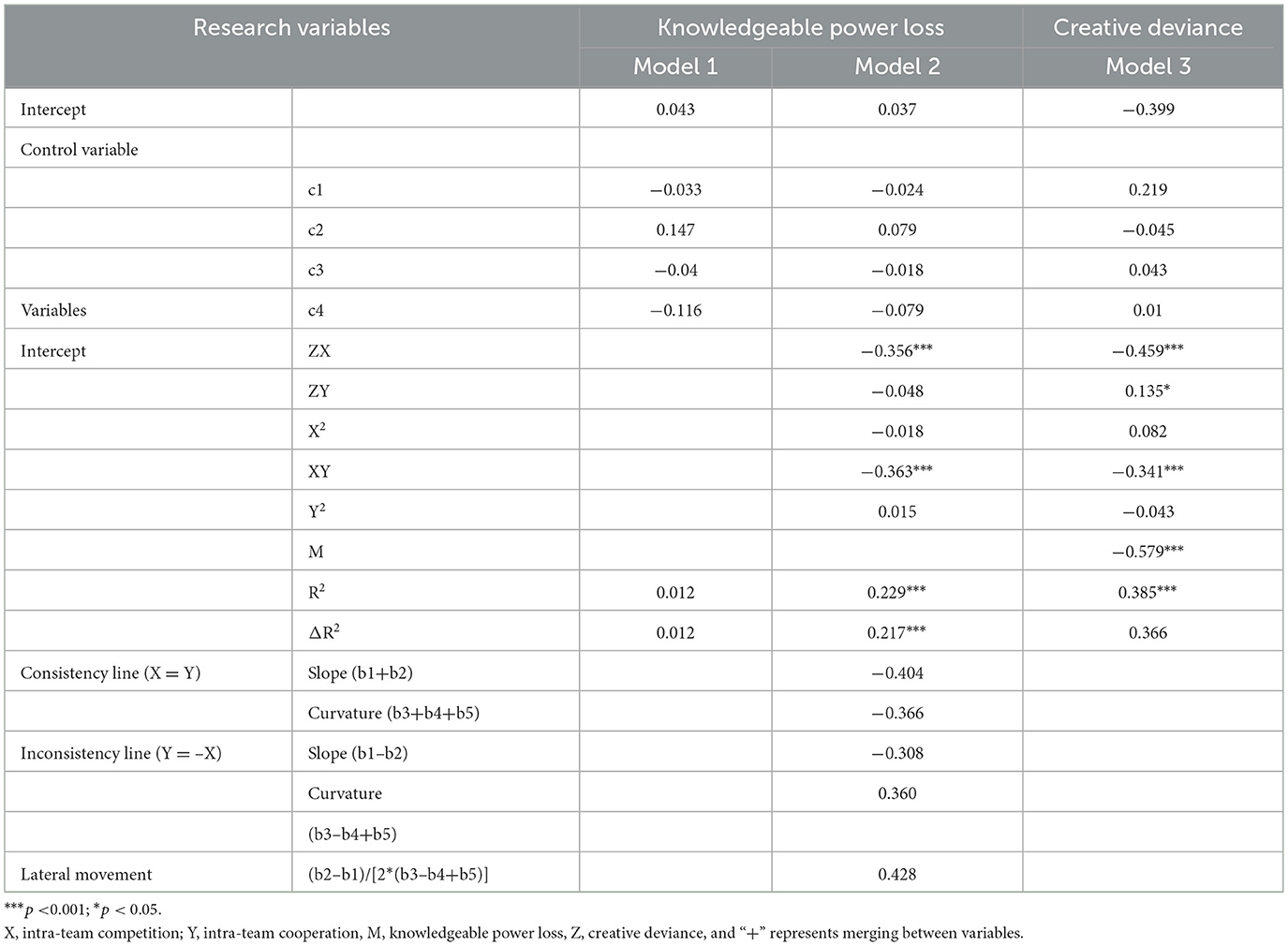
The results of the polynomial regression in Study 1 are presented in Table 3. We performed response surface analyses on the models that included the mediating variables, as shown in Figure 2.
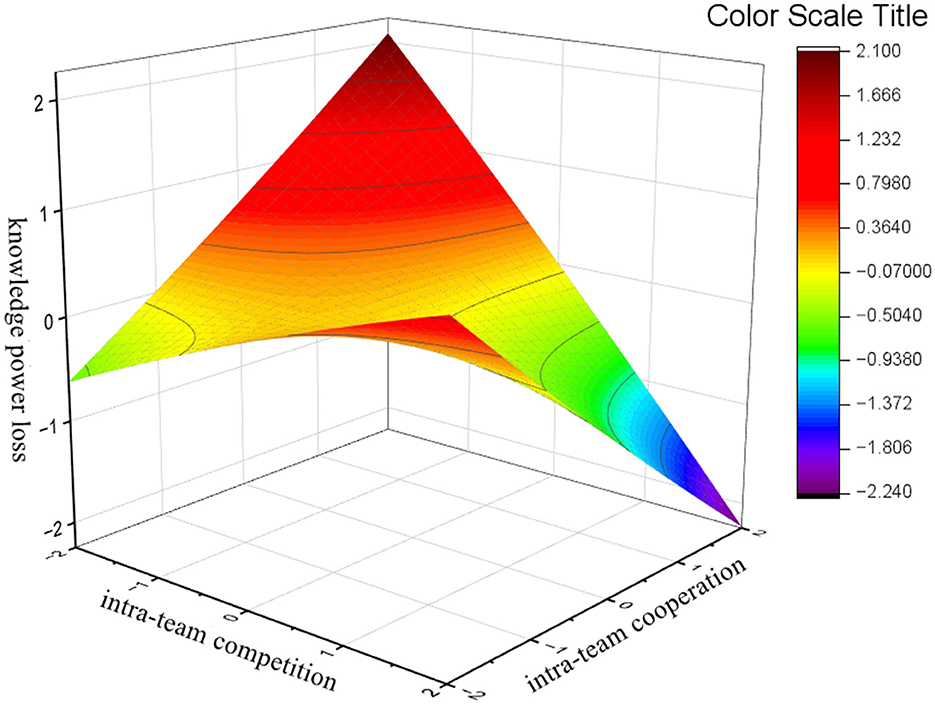
Figure 2. Three-dimensional representation of the combined effect of the intra-team co-opetition toward knowledge power loss: response surface analysis graphs.
The consistency line results indicate a significant combined effect of the three secondary terms regarding knowledge power loss (F = 11.011, p < 0.001). The response surface curvature along the inconsistency line (b3–b4+b5) was significantly positive. This indicates a linear relationship with knowledge power loss when both intra-team competition and cooperation levels were consistent. Thus, H1a is supported.
H1b proposed that the “high-high” combination would have a greater negative impact on the knowledge power loss than the “low-low” combination in the occurrence of intra-team co-opetition. Combined with the response surfaces in Table 3 and Figure 2, the response surface had a significantly negative slope along the consistency line (b1+ b2 = −0.404, p < 0.01). This suggests that knowledge power loss diminished along the consistency line. Therefore, H1b is supported.
H1c predicted that when intra-team competition is inconsistent with intra-team cooperation, knowledge power loss would be lower in low-competition, high-cooperation combinations than in high-competition, low-cooperation combinations. Combining the response surfaces in Table 3 and Figure 2 indicates that the response surface slope along the inconsistency curve is significantly negative (b1–b2 = −0.308, p < 0.01). The offset is 0.428 < 0.5, combined with the response surface. Therefore, Figure 2 indicates that H1c is supported.
We used the block variable approach to test the mediating effect of knowledge power loss between intra-team competitive relationships and employee creative deviance. Specifically, we calculated the direct effect of the block variable of the intra-team competitive relationship to the mediating variable and running process to obtain the indirect effect of −0.580, where the 95% CI was [−0.763, −0.412], which did not contain 0. This indicates that the mediating effect was significant, and H2 is verified.
The scenario-based experiment conducted in Study 1 is advantageous because it can assess causality. However, limitations to this method need to be addressed. For example, differences between the subjects' real-life work situations and the experimental material's simulated situations may have existed. Additionally, the method typically has high internal validity but low external validity. Study 1 also had shortcomings. As such, we conducted Study 2 to further test the research hypothesis through a questionnaire to improve external validity to address this issue.
Study 2: questionnaire
Sample selection and data collection
This study's sample data was collected from leaders and subordinates in several enterprise types in the eastern region of China. We distributed the questionnaire at multiple time points. We primarily used the “leader-subordinate” matching method. Subordinates (employees) were asked to respond to intra-team co-opetition and knowledge power loss measures while team leaders evaluated their subordinates' creative deviance.
We matched the coded correspondence of the employee and leader questionnaires and distributed 400 questionnaires to employees. We received 360 completed questionnaires. After excluding invalid questionnaires, 354 valid employee samples were obtained with an effective response rate of 90%. We also distributed 400 leader questionnaires and received 370 completed questionnaires. After excluding invalid questionnaires, we obtained 354 valid leader samples with an effective response rate of 88.5%.
Of the employee survey participants, 48.90% were female, and 51.10% were male. Regarding age, 11.3%, 29.4%, 25.1%, 20.6%, and 13.6% were under 20, 21–30, 31–40, 41–50, and over 50 years old, respectively. Regarding educational level, 20.1%, 26.8%, 34.9%, and 18.9% of the participants held high school/junior college and below, vocational high school/junior college, bachelor's/master's degree and above, respectively. Regarding years of work experience, 24.6%, 31.1%, 27.4%, and 16.9% of the participants had worked for 0–3 years, 4–6 years, 7–9 years, and 10 years and above, respectively.
Scale selection and variable measurement
This study conducted empirical survey research. To verify the model and hypotheses, we used questionnaires based on established scales from international studies commonly used in current applications and have been empirically tested. We scored each question on a 5-point Likert scale, where 1 represents “strongly disagree,” and 5 represents “strongly agree.”
For intra-team co-opetition, the present study primarily used the scale developed by Baruch and Lin (2012), including 10 items such as “Our team members “swim or sink” together.” There were five items for intra-team competition with a Cronbach's alpha coefficient of 0.822. There were five items for intra-team cooperation with a Cronbach's alpha coefficient of 0.869.
Regarding knowledge power loss, we primarily used the scale developed by Kankanhalli et al. (2005), including four items. For example, “Sharing my knowledge through EKRs (lectronic knowledge repositories) makes me lose my unique value in the organization,” with a Cronbach's alpha coefficient of 0.880.
We used Criscuolo et al.'s (2014) scale for creative deviance, including “I have the flexibility to work my way around my official work plan, digging into new potentially valuable business opportunities” This scale contains five items with a Cronbach's alpha coefficient of 0.953.
To ensure accurate study results, we controlled for demographic characteristics, including the employees' gender, age, education, and years of work experience as the control variables.
Questionnaire results
Confirmatory factor analyses
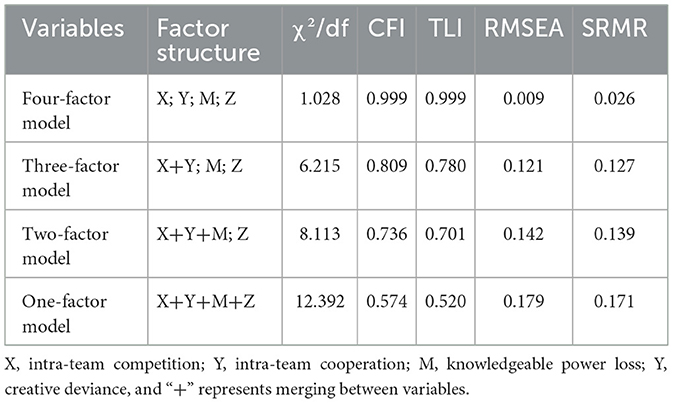
This study conducted a validated factor analysis to test the discriminant validity of the collected data using Mplus software. Each model's specific fit indices are presented in Table 4. Table 4 shows that the best fit was the four models (χ2/df = 1.028, CFI = 0.999, TLI = 0.999, SRMR = 0.009, RMSEA = 0.026). The χ2/df was < 3, CFI and TLI were more significant than 0.9, SRMR was < 0.05, and RMSEA was < 0.08, consistent with the study criteria.
Descriptive statistics and correlation analysis
This experiment analyzed each variable's descriptive statistics and correlation coefficients using SPSS 26.0. The results are presented in Table 5. Specifically, intra-team cooperation and knowledge power loss were positively correlated (γ = 0.002, p < 0.01). Intra-team competition and knowledge power loss were significantly negatively correlated (γ = −0.493, p < 0.01). Furthermore, knowledge power loss and creative deviance were significantly negatively correlated (γ = −0.536, p < 0.01).
Hypothesis testing
The hypothesis testing session of this study used polynomial regression and response surface analysis to test the study hypotheses. The formula for polynomial regression is as follows:
Where M represents the dependent variable, X is intra-team competition, Y represents intra-team cooperation, X2 is the squared term of intra-team competition, X × Y is the cross-multiplier of intra-team competition and intra-team cooperation, and Y2 represents the squared term of intra-team cooperation. b1–b5 represent the regression coefficients, and e represents the regression equation residuals.
Study 2′s polynomial regression results are presented in Table 6. We performed response surface analysis on the model, as shown in Figure 3.
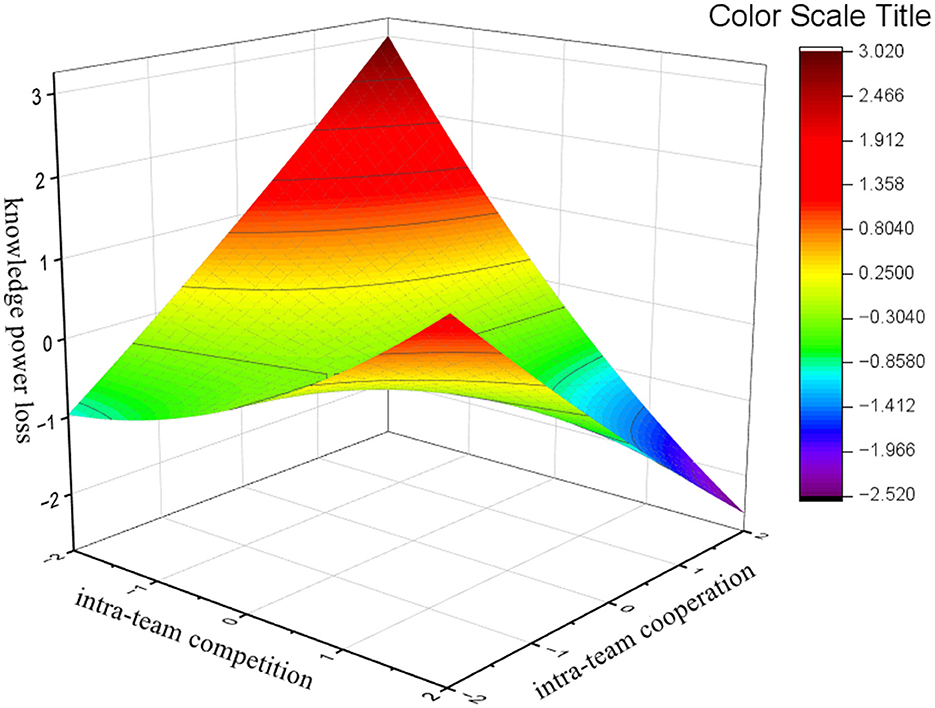
Figure 3. Three-dimensional representation of the combined effect of the intra-team co-opetition toward knowledge power loss: response surface analysis graphs.
The consistency line results indicate a significant combined effect of the three secondary terms overall on knowledge power loss (F = 61.000, p < 0.01). The response surface curvature along the inconsistency line (b3–b4+b5) was significantly positive. This indicates a linear relationship with loss of knowledge power when the intra-team competition and cooperation levels are consistent. Thus, H1a is supported. H1b proposed that the “high-high” combination would have a greater negative effect on the knowledge power loss than the “low-low” combination when intra-team competition and cooperation are aligned. Combining the modes in Table 6 with the response surfaces in Figure 3 shows a significantly negative slope along the congruence line (b1+b2 = −0.386, p < 0.01). Thus, H1b is supported. H1c predicted that when intra-team competition and intra-team cooperation are inconsistent, knowledge power loss would be lower in low-competition, high-cooperation combinations than within high-competition, low-cooperation combinations. Combining the model in Table 6 and the response surface in Figure 3 indicates that the response surface slope along the inconsistency curve (b1–b2) was significantly negative. It had an offset of 0.310 < 0.5, which, combined with the response surface in Figure 3, indicates that H1c is supported.
To test the mediating effect of the knowledge power loss between intra-team competitiveness and employee creative deviance, we used the block variable method. Specifically, we calculated the direct effect of the block variable of the intra-team competition relationship to the mediating variable: this was the matching effect of intra-team competition and intra-team cooperation on the knowledge power loss and running process to obtain the indirect effect of −0.536, with a 95% CI of [−0.659, −0.414], which did not contain 0. This indicates that the mediating effect was significant, and H2 is verified.
Discussion and conclusion
Based on the theory of resource conservation, this study constructed the research framework of “intra-team co-opetition-knowledge power loss-employee creative deviance.” We explored the intra-team co-opetition influence mechanism on employee creative deviance. As such, we present the following conclusions based on the theoretical analysis and empirical research. The more consistent the intra-team co-opetition relationship is, the lower the knowledge power loss is. Regarding the consistent intra-team co-opetition relationships, the negative impact of a “high-high” combination on knowledge power loss was greater than in the “low-low” combinations. When the level of intra-team competition and intra-team cooperation was inconsistent, knowledge power loss was lower in the low competition-high cooperation combination than the high competition-low cooperation combination. And knowledge power loss mediates the relationship between intra-team competition and employee creative deviance.
Theoretical implications
This study's theoretical contributions include the following. First, while most research has focused on inter-organizational and intra-organizational levels, this dissertation shifts the focus to the intra-team level. Existing empirical studies at this level primarily address knowledge sharing, team performance, and perceived work efficiency, but they often overlook the micro-level dynamics of intra-team co-opetition and its effects on organizational, team, and individual behaviors (Tsai, 2002; Wang et al., 2023; Yang and Dong, 2023). Our study bridges this gap by examining how intra-team co-opetition shape creative deviance. Unlike prior studies that conceptualize co-opetition as an aggregate or linear construct (Bendig et al., 2018; Nguyen et al., 2018; Gernsheimer et al., 2021), we theorize intra-team co-opetition as a multidimensional configuration and empirically examine how its structural alignment influences creative deviance. We use polynomial regression as the research method, first categorizing the coopetition relationships within teams into two conditions based on the degree of matching: consistent and inconsistent. These two conditions are then further divided into four different dimension “‘high-high', ‘low-low', ‘high-low', and ‘low-high”' for detailed analysis. A theoretical model is constructed to examine how coopetition relationships within teams influence employees' deviant innovation. This approach helps to finely depict the mechanisms and boundary conditions through which team coopetition affects deviant innovation, making an important contribution to opening the black box in this area. This dissertation offers a novel perspective and expands the research landscape for future studies on intra-team co-opetition and creative deviance, providing a foundational theoretical framework for subsequent analyses.
Second, prior research has predominantly examined factors influencing creative deviance at the organizational, leadership, and individual levels, neglecting intra-team dynamics (Augsdorfer, 2005; Schiavone and Simoni, 2011; Zhao, 2022). We deconstruct the nuanced effects of co-opetition combinations, revealing that the consistency (vs. inconsistency) of competition and cooperation levels significantly impacts knowledge power loss. Using polynomial regression, we show that “high-high” and “low-low” co-opetition combinations lead to lower loss than imbalanced “high-low” or “low-high” scenarios, challenging the traditional view of competition and cooperation as independent constructs. the response surface analysis visually demonstrates the nonlinear dynamics of co-opetition, highlighting that knowledge power loss declines more steeply along the consistency line (X = Y) than the inconsistency line (Y = –X). This methodological innovation enriches our understanding of how team co-opetition micro-mechanisms drive individual behavior, beyond the linear analyses commonly used in prior research. Also, the findings of this study contribute to expanding the antecedent variables associated with creative deviance.
Finally, existing literature on knowledge power loss has mainly explored its relationship with knowledge sharing and hiding (Li and Liu, 2014; Moghavvemi et al., 2017). By introducing knowledge power loss as a mediator, we bridge the gap between team co-opetition and creative deviance from a resource conservation perspective. Unlike prior studies that focus on macro-level value creation (George et al., 2014) or individual motivation (Wulani and Junaedi, 2021), we demonstrate that co-opetition influences employees' willingness to engage in creative deviance by shaping their perceptions of knowledge resource loss (Hobfoll, 2001). By introducing knowledge power loss as a mediating variable, this research enriches the discourse on its implications, thereby elucidating the impact of intra-team co-opetition on employee creative deviance.
Practical implications
This study provides important insights for managers seeking to balance cooperation and competition within teams to foster innovation while minimizing potential risks, such as knowledge power loss. Understanding the dynamics of intra-team co-opetition is crucial for developing targeted strategies that enhance creative deviance without jeopardizing knowledge resources.
First, in high-competition low-cooperation scenarios, team members are more likely to protect their knowledge to maintain a competitive edge, thus increasing the potential for knowledge power loss. Managers should implement strategies that promote psychological safety and trust within the team, reducing fears of knowledge appropriation. For instance, creating structured mechanisms for knowledge sharing-such as regular team meetings and collaborative platforms-can help ensure that knowledge is distributed without significant perceived risks. Additionally, leaders can encourage team members to view shared knowledge as a collective asset, fostering a sense of mutual benefit rather than individual territoriality. Moreover, leaders should set clear expectations about the value of collaboration, emphasizing how sharing knowledge can lead to mutual innovation gains, even in competitive contexts. Managers might consider instituting formal recognition systems that reward both individual achievements and collaborative efforts, reinforcing the value of cooperation even when competition is present.
Second, in collectivist cultures, where group harmony and cooperation are emphasized, the balance between competition and cooperation within teams might differ. The collectivist orientation can enhance the expression of creative deviance, as team members are more inclined to engage in behaviors that serve the group's collective goals, even if they are non-conformist. Managers in such contexts should leverage the cultural tendency toward mutual benefit and group cohesion to reduce the sense of knowledge power loss. Encouraging an environment where knowledge sharing is framed as contributing to the success of the team can significantly enhance creativity and innovation. Leaders should also be mindful of the potential for cultural norms to influence co-opetition dynamics. In collectivist settings, competition may be less about individual advancement and more about improving the team's collective output. As such, fostering a cooperative atmosphere that minimizes threats to individual knowledge power while encouraging collective innovation can be more effective than solely focusing on reducing competition.
Finally, to optimize team performance, managers should focus on creating a balance between competition and cooperation that aligns with the team's specific task goals and cultural context. When intra-team co-opetition is aligned, the negative impact on knowledge power loss is minimized, and team members feel more secure in their roles. Managers should monitor the intensity of both competition and cooperation, adjusting them as needed to ensure that the team remains motivated yet collaborative. In practice, this means that managers should continuously assess the team's dynamics and adjust leadership styles accordingly. For example, in teams experiencing high levels of both competition and cooperation, a transformational leadership style may help motivate members to leverage both their competitive spirit and collaborative efforts toward innovative outcomes. On the other hand, in teams with low levels of cooperation, a more directive leadership style may be necessary to ensure that team members understand the importance of collaboration in reducing knowledge power loss.
To enhance the practical value of this study, we reorganize the managerial implications based on the four specific intra-team co-opetition configurations: (1) high competition-high cooperation, (2) low competition-low cooperation, (3) high competition-low cooperation, and (4) low competition-high cooperation. Each configuration presents unique challenges and opportunities for fostering creative deviance while managing knowledge power loss.
(1) High competition-high cooperation (consistent)
This configuration provides both motivational drive and resource exchange. Managers should formalize cross-functional collaborative mechanisms such as team-based innovation projects or knowledge-sharing contests, where competition is encouraged but outcomes are co-owned. Recognizing both individual contributions and collective results can help reduce fears of knowledge appropriation while leveraging the synergy between competition and collaboration.
(2) Low competition-low cooperation (consistent)
In this setting, innovation risks are low, but so is the stimulus for proactive behavior. Managers should introduce challenge-based tasks or periodic rotations to increase task interdependence and break silos. Creating a safe space for experimentation—such as innovation labs or trial initiatives—can spark moderate creative deviance without high social risk.
(3) High competition-low cooperation (inconsistent)
This configuration risks the highest knowledge power loss due to fierce rivalry and limited trust. Managers must reduce fear of knowledge theft by implementing transparent evaluation systems, intellectual contribution tracking, and digital documentation of innovation efforts. Trust-building interventions, such as peer-review mechanisms or coaching circles, can soften the cut-throat dynamics.
(4) Low competition-high cooperation (inconsistent)
While high cooperation facilitates sharing, low competition may lower urgency or initiative. To activate creative deviance, managers should amplify goal clarity and encourage self-initiated innovation through recognition systems that reward exploratory behavior. Promoting shared ownership of innovation success can increase psychological safety and reduce knowledge protectionism.
By aligning team management strategies with each co-opetition pattern, organizations can optimize innovation outcomes while effectively mitigating the risk of knowledge power loss.
Research limitations and perspectives
This study explored the influence mechanism of intra-team co-opetition on employee creative deviance from an innovative research perspective. At the same time, this study also has certain limitations. Firstly, this study tested the mediating effect of knowledge power loss. However, other factors, such as emotional exhaustion and psychological ownership, may impact the relationship between intra-team co-opetition relationships and creative deviance in the path of influence. Thus, future research should explore more variables to deepen the research regarding creative deviance. Secondly, this study mainly collected survey questionnaires through online forms. Due to practical constraints, the sample could only cover parts of eastern China and did not cover a wider area. In the future, the sample data collection area can be expanded to cover central and western China, making the sample more representative. Finally, the study sample mainly comes from companies in the eastern region of China, where the collectivist culture's “guanxi” (relationship networks) and high power distance characteristics may amplify the uniqueness of the research findings. The “high competition-low cooperation” combination in Chinese teams may intensify knowledge hiding behaviors due to the “face culture,” whereas Western teams may be more inclined to view competition as a demonstration of individual ability. Future research could verify the cultural universality of the co-opetition mechanism through cross-cultural comparative studies.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Ethics statement
Ethical approval was not required for the study involving humans in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent to participate in this study was not required from the participants in accordance with the national legislation and the institutional requirements.
Author contributions
MZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. JZ: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. QL: Data curation, Investigation, Project administration, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. LW: Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. XZ: Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Resources, Writing – review & editing. SH: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing. ZN: Formal analysis, Visualization, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. The authors gratefully acknowledge the grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Project Nos. 72202109 and 72272078).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/forgp.2025.1576922/full#supplementary-material
References
Anderson, N., Potočnik, K., and Zhou, J. (2014). Innovation and creativity in organizations: a state-of-the-science review, prospective commentary, and guiding framework. J. Manage. 40, 1297–1333. doi: 10.1177/0149206314527128
Augsdorfer, P. (2005). Bootlegging and path dependency. Res. Policy. 34, 1–11. doi: 10.1016/j.respol.2004.09.010
Avital, M., and Singh, B. (2011). Collaboration trumps competition in high-tech project teams. Int. J. Organisation. Design Eng. 1, 292–314. doi: 10.1504/IJODE.2011.043808
Baruch, Y., and Lin, C. P. (2012). All for one, one for all: coopetition and virtual team performance. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change. 79, 1155–1168. doi: 10.1016/j.techfore.2012.01.008
Bendig, D., Enke, S., Thieme, N., and Brettel, M. (2018). Performance implications of cross-functional coopetition in new product development: the mediating role of organizational learning. Indust. Market. Managem. 73, 137–153. doi: 10.1016/j.indmarman.2018.02.007
Chen, A. S. Y., and Hou, Y. H. (2016). The effects of ethical leadership, voice behavior and climates for innovation on creativity: a moderated mediation examination. Lead Q. 27, 1–13. doi: 10.1016/j.leaqua.2015.10.007
Criscuolo, P., Salter, A., and Ter Wal, A. L. (2014). Going underground: bootlegging and individual innovative performance. Organizat. Sci. 25, 1287–1305. doi: 10.1287/orsc.2013.0856
Das, T. K., and Teng, B. S. (2000). A resource-based theory of strategic alliances. J. Manage. 26, 31–61. doi: 10.1177/014920630002600105
Du, Y., and Chen, L. (2019). “To violate instructions or not to? Effect of job control on creative deviance,” in Academy of Management Annual Meeting Proceedings 2019, 1.
Edwards, J. R., and Parry, M. E. (1993). On the use of polynomial regression equations as an alternative to difference scores in organizational research. Acad. Manag. J. 36, 1577–1613. doi: 10.5465/256822
Galinsky, A. D., Gruenfeld, D. H., and Magee, J. C. (2003). From power to action. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 85, 453–466. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.85.3.453
George, E., Depeige, A., and Sindakis, S. (2014). Dynamics of ultra-organizational co-opetition and circuits of knowledge: a knowledge-based view of value ecology. J. Knowl. Managem. 18, 1020–1035. doi: 10.1108/JKM-06-2014-0249
Gernsheimer, O., Kanbach, D. K., and Gast, J. (2021). Coopetition research-A systematic literature review on recent accomplishments and trajectories. Indust. Market. Managem. 96, 113–134. doi: 10.1016/j.indmarman.2021.05.001
Ghobad, I. S., and D'Ambra, J. (2013). Modeling high-quality knowledge sharing in cross-functional software development teams. Inf. Process. Manag. 49, 138–157. doi: 10.1016/j.ipm.2012.07.001
Globocnik, D., Birgit, P. H., and Søren, S. (2022). Organizational antecedents to bootlegging and consequences for the newness of the innovation portfolio. J. Prod. Innovat. Managem. 39, 717–745. doi: 10.1111/jpim.12626
Globocnik, D., and Salomo, S. (2015). Do formal management practices impact the emergence of bootlegging behavior? J. Prod. Innovat. Managem. 32, 505–521. doi: 10.1111/jpim.12215
Gnyawali, D. R., and Park, B. J. R. (2011). Co-opetition between giants: collaboration with competitors for technological innovation. Res. Policy. 40, 650–663. doi: 10.1016/j.respol.2011.01.009
Hakanen, J. J., Perhoniemi, R., and Toppinen-Tanner, S. (2008). Positive gain spirals at work: from job resources to work engagement, personal initiative and work-unit innovativeness. J. Vocat. Behav. 73, 78–91. doi: 10.1016/j.jvb.2008.01.003
Hobfoll, S. E. (1989). Conservation of resources: a new attempt at conceptualizing stress. Am. Psychol. 44, 513. doi: 10.1037/0003-066X.44.3.513
Hobfoll, S. E. (2001). The influence of culture, community, and the nested-self in the stress process: advancing conservation of resources theory. Appl. Psychol. 50, 337–421. doi: 10.1111/1464-0597.00062
Huang, C. F., Zhang, Z. T., and Ding, M. Z. (2015). A research review of the co-opetition relationship in intra-teams. Commerc. Res. 1, 124–131.
Kankanhalli, A., Tan, B. C., and Wei, K. K. (2005). Contributing knowledge to electronic knowledge repositories: an empirical investigation. MIS Quart. 29, 113–143. doi: 10.2307/25148670
Kumar, N., Jin, Y., and Liu, Z. (2024). The nexus between servant leadership and employee's creative deviance for creativity inside learning and performance goal-oriented organizations. Managem. Deci. 62, 1117–1137. doi: 10.1108/MD-09-2022-1294
Lazarus, R. S. (1991). Progress on a cognitive-motivational-relational theory of emotion. Am. Psychol. 46, 819. doi: 10.1037/0003-066X.46.8.819
Li, W. D., and Liu, H. (2014). An empirical study on relationship of mutual trust and R&D professionals' knowledge sharing intentions: the mediating effects of knowledge power loss and reciprocity. Manage. Rev. 26, 128–138.
Mainemelis, C. (2010). Stealing fire: creative deviance in the evolution of new ideas. Acad. Managem. Rev. 35, 558–578. doi: 10.5465/AMR.2010.53502801
Moghavvemi, S., Sharabati, M., Paramanathan, T., and Rahin, N. M. (2017). The impact of perceived enjoyment, perceived reciprocal benefits and knowledge power on students' knowledge sharing through Facebook. Int. J. Managem. Educ. 15, 1–12. doi: 10.1016/j.ijme.2016.11.002
Nguyen, N. P., Ngo, L. V., Bucic, T., and Phong, N. D. (2018). Cross-functional knowledge sharing, coordination and firm performance: the role of cross-functional competition. Indust. Market. Managem. 71, 123–134. doi: 10.1016/j.indmarman.2017.12.014
Olckers, C., and Van Zyl, L. E. (2019). Psychometric properties of the psychological ownership questionnaire. Aust. J. Psychol. 71, 127–136. doi: 10.1111/ajpy.12232
Park, B. J. R., Srivastava, M. K., and Gnyawali, D. R. (2014). Walking the tight rope of coopetition: impact of competition and cooperation intensities and balance on firm innovation performance. Indust. Market. Managem. 43, 210–221. doi: 10.1016/j.indmarman.2013.11.003
Pereira, V., and Mohiya, M. (2021). Share or hide? Investigating positive and negative employee intentions and organizational support in the context of knowledge sharing and hiding. J. Bus. Res. 129, 368–381. doi: 10.1016/j.jbusres.2021.03.011
Ramírez-López, C., Till, K., Boyd, A., Bennet, M., Piscione, J., Bradley, S., et al. (2021). Co-opetition: cooperation among competitors to enhance applied research and drive innovation in elite sport. Br. J. Sports Med. 55, 522–523. doi: 10.1136/bjsports-2020-102901
Renzl, B. (2008). Trust in management and knowledge sharing: the mediating effects of fear and knowledge documentation. Omega 36, 206–220. doi: 10.1016/j.omega.2006.06.005
Ritala, P., and Hurmelinna-Laukkanen, P. (2013). Incremental and radical innovation in coopetition-the role of absorptive capacity and appropriability. J. Prod. Innovat. Managem. 30, 154–169. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-5885.2012.00956.x
Schiavone, F., and Simoni, M. (2011). An experience-based view of co-opetition in R&D networks. Eur. J. Innovat. Managem. 14, 136–154. doi: 10.1108/14601061111124867
Shi, C., Zhang, F., Zhu, P., and Shi, Q. (2021). How is knowledge perceived as power? A multilevel model of knowledge power in innovation networks. Front. Psychol. 12:630762. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.630762
Shukla, J., and Kark, R. (2020). Now you do it, now you don't: The mixed blessing of creative deviance as a prosocial behavior. Front. Psychol. 11:313. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2020.00313
Sun, B., Yu, X., Yuan, X., Sun, C., and Li, W. (2021). The effect of social perspective-taking on interpersonal trust under the cooperative and competitive contexts: the mediating role of benevolence. Psychol. Res. Behav. Manag. 14, 817–826. doi: 10.2147/PRBM.S310557
Tsai, W. (2002). Social structure of “coopetition” within a multiunit organization: coordination, competition, and intraorganizational knowledge sharing. Organizat. Sci. 13, 179–190. doi: 10.1287/orsc.13.2.179.536
Wang, H. Y., Cui, Z., Zou, C., Jiali, Y., and Zhao, D. (2019). Loyal or rebel? Employee bootleg innovation in Chinese context. Adv. Psychol. Sci. 27, 975–989. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1042.2019.00975
Wang, H. Y., and Yu, J. L. (2022). The influence mechanism of sense of power on creative deviance: an explanation based on Chinese native culture. Modern Finance Econ. J. Tianjin Univers. Finance Econ. 42, 3–19.
Wang, Y. W., Liu, Y. Z., Wang, J. H., and Yang, K. R. (2023). Research on the influence mechanism of leader-subordinate employee creativity evaluation matching on bootleg innovation. Chin. J. Managem. 20, 1169–1179.
Wulani, F., and Junaedi, M. (2021). Passive leadership and deviant behaviors: the moderating effect of power distance and collectivism. J. Managem. Dev. 40, 324–338. doi: 10.1108/JMD-07-2020-0216
Yang, N., Chen, H., and Wang, X. H. (2024). Paradoxical leadership behavior and employee creative deviance: the role of paradox mindset and leader-member exchange. J. Bus. Psychol. 39, 697–713. doi: 10.1007/s10869-023-09902-x
Yang, S. H., and Dong, X. H. (2023). Empirical test on the transformation mechanism of employees' bootlegging innovation to enterprise innovation performance from the perspective of innovation process. Contemp. Econ. Managem. 45, 66–75. doi: 10.13253/j.cnki.ddjjgl.2023.11.008
Yu, P. L. (2019). Interfirm coopetition, trust, and opportunism: a mediated moderation model. Rev. Manager. Sci. 13, 1069–1092. doi: 10.1007/s11846-018-0279-y
Zhang, Y., and Pan, C. (2022). A study on the influence of ambidextrous leadership on the deviant innovation behavior of knowledge workers. Age 4:19. doi: 10.53469/jgebf.2022.04(09).19
Zhao, B. B. (2022). The influence of transformational leadership on employees' bootleg innovative behavior-based on the effect of moderated series mediation. J. Xi'an Univers. Architect. Technol. 41, 59–66. doi: 10.15986/j.1008-7192.2022.05.008
Keywords: intra-team co-opetition, creative deviance, knowledge power loss, polynomial regression, scenario experiment, the COR theory
Citation: Zhang M, Zhang J, Lin Q, Wang L, Zhang X, He S and Nie Z (2025) Examining the impact mechanism of intra-team co-opetition on employee creative deviance. Front. Organ. Psychol. 3:1576922. doi: 10.3389/forgp.2025.1576922
Received: 21 February 2025; Accepted: 14 August 2025;
Published: 02 September 2025.
Edited by:
Abdul Haeba Ramli, Universitas Esa Unggul, IndonesiaReviewed by:
Paula Andrea Pavez, San Sebastián University, ChileShaham Saleem, Beijing Institute of Technology, China
Chen Ding, Nanjing University, China
Copyright © 2025 Zhang, Zhang, Lin, Wang, Zhang, He and Nie. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Siyu He, c2l5dWhlMTExQDE2My5jb20=; Zitong Nie, bmlleml0MDQwMkBnbWFpbC5jb20=
 Min Zhang
Min Zhang Jinyu Zhang
Jinyu Zhang Qingxuan Lin
Qingxuan Lin Lei Wang
Lei Wang Xufan Zhang
Xufan Zhang Siyu He
Siyu He Zitong Nie4*
Zitong Nie4*