- Department of Neurosurgery, Pamela Youde Nethersole Eastern Hospital, Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China
Objectives: To enhance surgical safety with frequent intra-operative neuro-monitoring (IONM) of the blink reflex (BR) in posterior skull base neurosurgery.
Background: There are reports stating the potential of facial nerve function preservation using BR IONM but none stating that it helps to protect corneal sensation and vision.
Methods: A prospective cohort of 42 consecutive patients with lesions in proximity to the brainstem was operated between January 2021 and April 2024. BR, which is considered the electronic equivalent of the corneal reflex, is elicited by electrical stimulation of the supraorbital nerves. Recording electrodes for R1 responses are placed over orbicularis oculi muscle at the lower eyelid. BR signal loss or an amplitude drop by half or more in R1 from the baseline is regarded as a significant change in BR response. Pre-operative tumour volume and maximal midline shift (MLS) of the brainstem are measured, using readily identifiable anatomical landmarks, namely cerebral aqueduct, median sulcus of the fourth ventricle, and mid-point of interpeduncular fossa. Patients' intra-operative findings and post-operative clinical outcomes are correlated and reported.
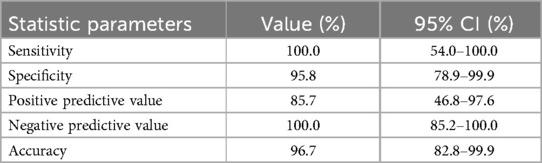
Results: BR IONM has a very high accuracy rate (96.7%) in predicting post-operative corneal complications, but can only be successfully done in 30 out of 42 patients (71.4%). There were 17 female and 13 male patients, with age ranging from 41 to 81 (mean 62.0). Ten underwent microvascular decompression and 20 had excision of tumours of size ranging from 1.1 to 81.6 cm3 (mean 21.6 cm3). For the tumour cases, Mann-Whitney U test for unpaired data showed statistically significant difference in tumour volume (p = 0.0016; 37.8 vs. 13.0 cm3) and maximal MLS of the brainstem (p = 0.0271; 8.1 vs. 4.8 mm) regarding the significant change in BR response. This suggests that BR change is a good sentinel indicator of how much brainstem neural tissue is mechanically stretched during excision of the tumour.
Conclusions: Frequent IONM of BR is feasible, safe, and useful in the preservation of corneal sensation, especially for patients with large posterior fossa tumours and a distorted brainstem. For patients with the significant change in BR response, prompt referral to the ophthalmologist is useful for the prevention of keratitis and corneal ulceration.
Introduction
To enhance the surgical safety of posterior skull base neurosurgery, besides the basic somatosensory evoked potential (SSEP), motor evoked potential (MEP), brainstem auditory evoked potential, and lower cranial nerves electromyography (EMG) monitoring, it is possible to perform direct brainstem stimulation for corticospinal tract motor response (1) and SSEP response (2) via scalp recordings. There are reports stating the potential of facial nerve function preservation (3) on frequent intra-operative neuro-monitoring (IONM) of the blink reflex (BR) but none stating that it helps to protect corneal sensation and vision.
Corneal reflex, corneal sensation, and the neural pathway
The corneal reflex is an involuntary blinking of the eyelids, normally within 0.1 s, in response to the stimulation of the cornea. In conscious healthy subjects, stimulation should elicit both a direct and consensual response (blinking of the opposite eye). BR, as a relatively novel entity of IONM, is considered the electronic equivalent of this reflex.
Eric Kugelberg first described this reflex in humans in 1952 (4). The reflex and its pathway were described in detail by Jun Kimura in 2001 in conscious subjects (5). Vedran Deletis first reported how to record BR intra-operatively under general anaesthesia using propofol in 2009 with a successful rate of 86.2% (6). When the cornea is touched, an afferent impulse from either free nerve endings or mechanoreceptors within the corneal epithelium is sent by way of nasociliary nerve and its long ciliary nerve branches of the ophthalmic division of the trigeminal nerve (CN V) to the principal sensory nucleus (aka chief sensory nucleus) of CN V that is located in the rostral pons. Axons then project bilaterally to facial motor nucleus, which initiating the efferent motor response via the temporal and zygomatic branches of the facial nerve (CN VII), leading to the contraction of orbicularis oculi muscles and coordinated eye closure (blink). The rate of blinking is modulated by the blinking centre at the globus pallidus of the basal ganglia (7).
There are two stages to this reflex (8). Large-diameter myelinated A-beta fibers activate the initial movement of the eyelid on the ipsilateral side and provide the early response. Other smaller fiber types activate the late-stage reflex, which stimulates facial nerves bilaterally so that both eyes blink. Inputs from the secondary motor system (e.g., interpositus nucleus of the cerebellum, red nucleus, and reticular activating system) can also modulate this late-stage reflex (9).
Reduced corneal reflex and blinking can occur in various physiological and pathological conditions like old age, pregnancy (10), glaucoma, diabetes, herpetic keratitis, progressive supranuclear palsy, and Parkinson's disease (11, 12). Loss of sensory innervation of the cornea can result in a vision-threatening clinical condition known as neurotrophic keratopathy, which is characterized by reduced corneal sensation, tear film abnormalities and, in the most severe cases, persistent corneal epithelial defects, ulceration, and perforation of the stroma (12).
Method
A prospective cohort of consecutive patients was operated for lesions in proximity to the brainstem under general anaesthesia between January 2021 and April 2024. Consent was obtained for IONM. Total intravenous anaesthesia (TIVA) was used. The body temperature and the haemodynamics of the patients as well as the infusion rate of anaesthetic agents, namely propofol at 10 mg/kg/h and remifentanil at 10 µg/kg/h, were kept stable throughout the period of IONM. The depth of anaesthesia was monitored with bispectral index (BIS), which was maintained at the range of 40–60. Muscle relaxants were not used, except for endotracheal intubation.
BR is elicited by direct electrical stimulation of the supraorbital nerves, which produces a compound motor action potential response of the facial nerve, with two components, R1 and R2. The early R1 response is relatively synchronous and constant in duration and shape. The second response R2 is a late bilateral response, which corresponds to the clinically observable blink. The latter response is asynchronous, and it rapidly habituates and disappears bilaterally. Compressive lesions of trigeminal nerve, such as tumours or aneurysms, involve the afferent limb of the reflex arc and prolong the latency of ipsilateral R1 and bilateral R2. Facial nerve lesions affect the efferent limb of the blink reflex arc and delay the latency of ipsilateral R1 and R2. As previously reported, R2 response is not elicitable under general anaesthesia (13). The setup and the pathway for BR are depicted in Figure 1.
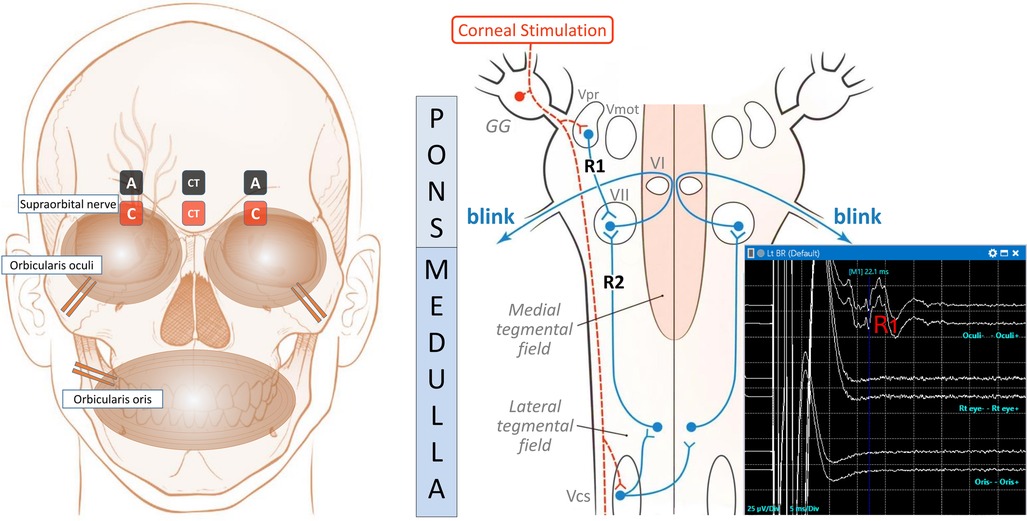
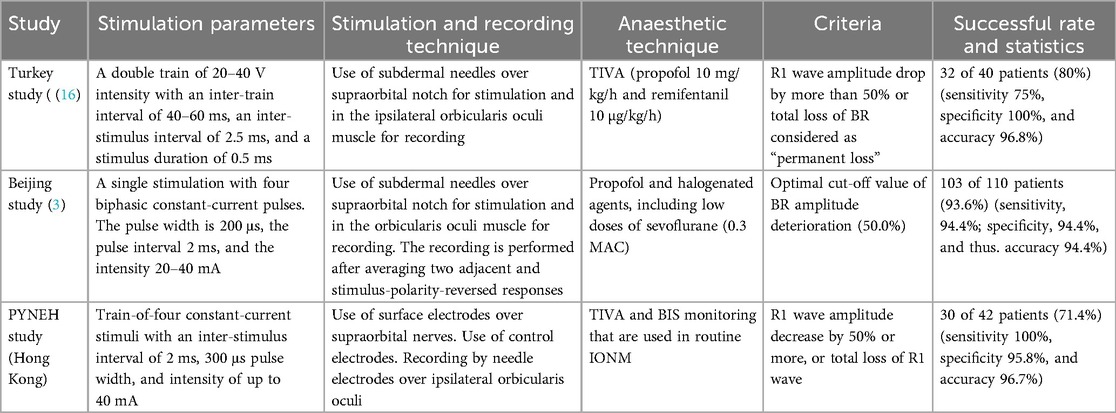
Figure 1. The setup, the pathway, and the typical BR IONM recordings. The left diagram shows the locations of the stimulating and recording electrodes for electrically induced blink reflexes in the ipsilateral orbicularis oculi muscle. A reference subdermal electrode is placed on the lateral aspect of the cheek. A pair of stimulating surface electrodes, spaced 2 cm apart, is used to stimulate the ipsilateral supraorbital nerve with the anode (A, black colour) positioned above the eyebrow, and the cathode (C, red colour) over the supraorbital notch. Recording needle electrodes are positioned at the ipsilateral orbicularis oculi muscle near the lower eyelid. In addition, a pair of recording control surface electrodes (CT) in the midline, along with needle electrodes at orbicularis oris muscles, act as the control to detect unintentional spread of stimulating electricity causing movement artefacts. The right schematic depicts the blink reflex pathways for R1 and R2 responses in conscious subjects. It is modified from Maciel et al. (14). The dotted orange line denotes the afferent pathway. The supraorbital nerve conveys the corneal stimulus to the Gasserian ganglion (GG) and then to the primary trigeminal nucleus (Vpr) and trigeminal motor nucleus (Vmot), where the ipsilateral R1 response is received via an oligosynaptic arc to the facial nucleus (VII). The supraorbital nerve also transports the afferent impulse to the caudal spinal trigeminal nucleus (Vcs) via the descending spinal tract of the trigeminal nerve in the lower brainstem. The efferent impulse (blue line) travels via the medullary pathway, which ascends bilaterally to connect to VII in the pons, looping around abducens nuclei (VI), and produces the R2 responses, which are clinically visible as bilateral blinking responses in conscious subjects. The right lower graph depicts the normal R1 response during left BR IONM under general anaesthesia, with a latency peak at 22.1 ms in the upper line. There should not be corresponding signals at that particular time in the middle and lower lines, which respectively, show the signals over the contralateral right eye via CT electrodes and orbicularis oris electrodes. They act as the control to detect movement artefacts. The scale is 25 µV/Div in the Y-axis for the amplitude, and 5 ms/Div on the X-axis for the time. R2 response is not elicitable under general anaesthesia.
Stimulation and recording parameters and diagnostic criteria
A stable R1 response is elicited using a train-of-four constant-current stimuli with an inter-stimulus interval of 2 ms, 300 μs pulse width and intensity of up to 40 mA at our hospital. Recording parameters are a time sweep of 50 ms and an amplification of 25–50 μV with a bandpass of 10–3 k Hz. The intensity required for optimal R1 response is found to be quite variable among individual patients due to inter-personal variability of response to anaesthesia as well as brain pathologies. In principle, the intensity of stimulation can be increased until there is a movement artefact in the EMG of contralateral orbicularis oculi or ipsilateral orbicularis oris. By convention, it is common to define an amplitude drop by half or more of a wave from the baseline as a significant change in IONM and thus we arbitrarily adopt it as our definition in the beginning. R1 signal loss or amplitude drop by half or more from the baseline is regarded as a significant change in BR response.
Frequency of stimulation
The BR can be monitored very frequently, as shown in the waterfall diagram in Figure 2. Stable BR tracings as the baseline are acquired before the opening of the skull bone. BR is recorded again as another reference after the opening of dura when there will be loss of cerebrospinal fluid and exposure of the brain to the cooler atmospheric air. It is well known that most IONM waveforms are temperature sensitive. At this point, the temperature of the operating field may gradually fall from normal core body temperature to room temperature unless warm normal saline irrigation is administered frequently. Then, during the micro-dissection, nonstop BR monitoring is performed, and it can be acquired as frequent as every minute. Finally, upon the closure of dura, the last BR will be recorded.
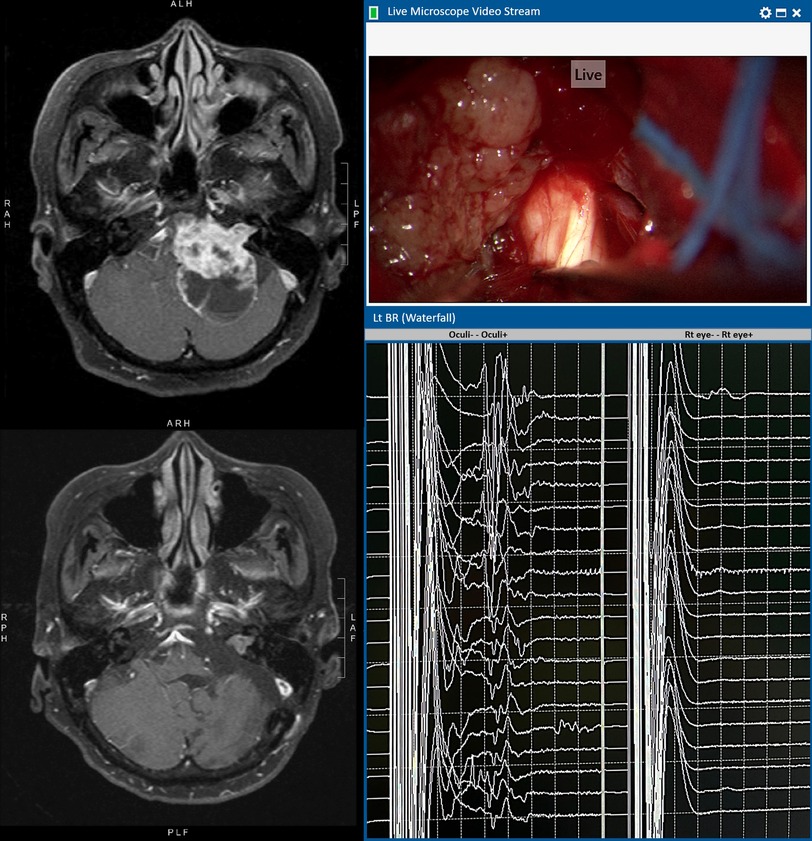
Figure 2. An illustrative case of left vestibular schwannoma with T1WI contrast MRI before (upper) and after (lower) operation. Intra-operative microscopic view shows that the cisternal portion of the trigeminal nerve is encased by the tumour. The left BR waterfall diagram shows preserved R1 waves throughout the operation. The tracing on the right shows no untoward movement artefacts detected by the control electrodes over the contralateral right eye. The facial nerve remained intact anatomically and physiologically (responsive to 0.1 mA stimulation) at the end of operation. Post-operatively, there is no facial nerve palsy and the corneal reflex is normal.
Clinical assessment and metrics
In this study, standardized clinical assessment of corneal reflex and sensation is performed. The patient is approached from the side, out of the line of vision to avoid eliciting a menace response. The cornea is lightly touched with a thin strand of clean cotton. Blinking and tearing in that eye (direct corneal reflex) are observed as well as blinking over the other eye (consensual corneal reflex). The patient is asked to compare the sensation of touch over the cornea bilaterally. It is classified as a decreased response if there is a delay in blink or decreased sensation of touch over the cornea.
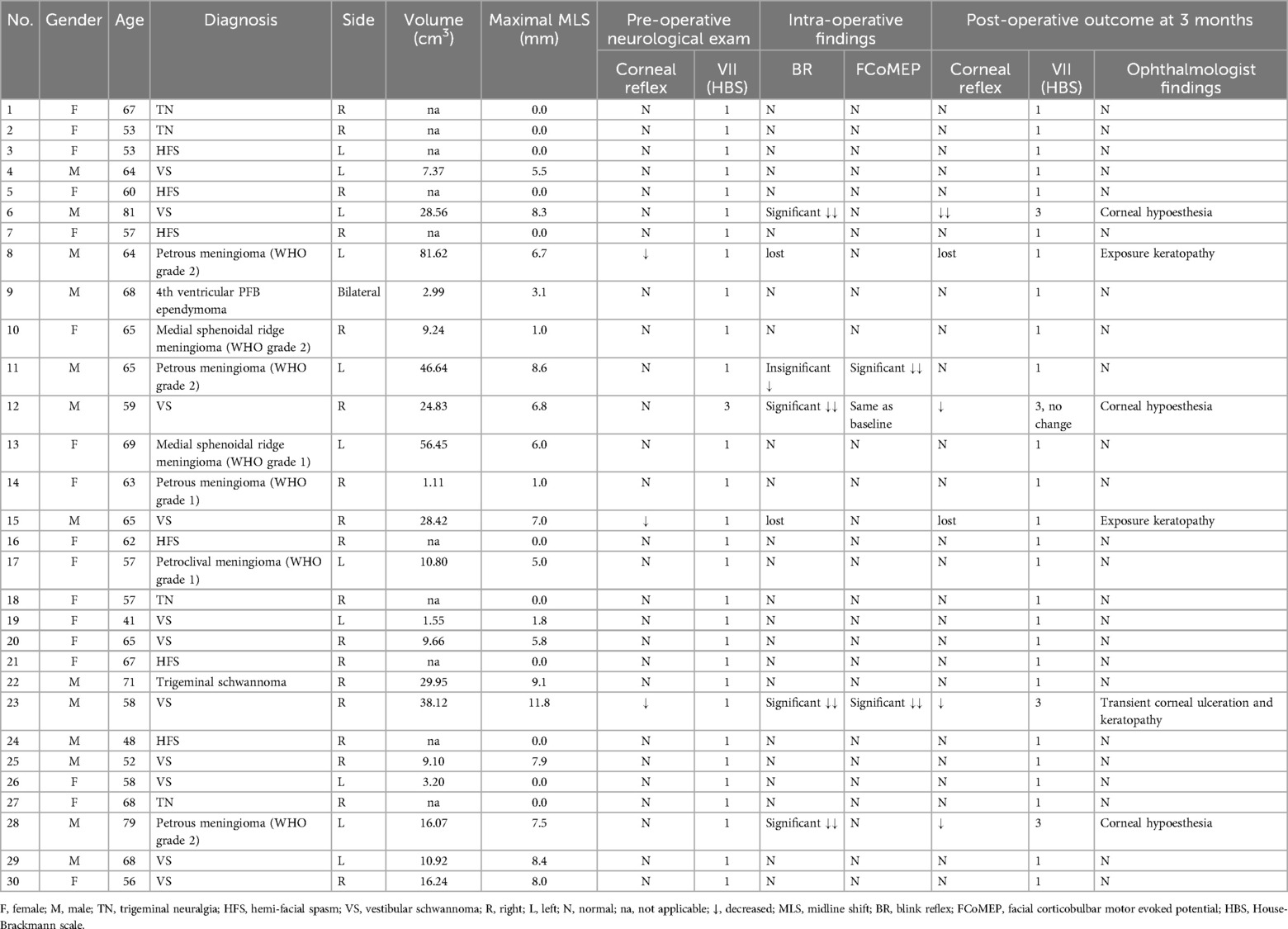
In addition, the facial nerve function is assessed according to the House-Brackmann grading system, pre-operatively, as well as on day one and at third month post-operatively. During the follow-up, the patients are assessed by clinicians who have access to the imaging and operation records. However, they do not know about the exact intra-operative BR findings that are archived by the IONM nurses during the operation. Pre-operative tumour volume is determined by volumetric measurement in a neuronavigation planning software with the tumour contouring done by the neurosurgeon. The maximal midline shift (MLS) of the brainstem is measured, using readily identifiable anatomical landmarks, namely cerebral aqueduct, mid-point of interpeduncular fossa, and median sulcus of the fourth ventricle in the T2-weighted images (T2WI) of the MRI (Figure 3). Patients' intra-operative findings and post-operative clinical outcomes are correlated and reported. Data are analysed using IBM SPSS Statistics version 29.0 using non-parametric tests with statistical significance set at p < 0.05.
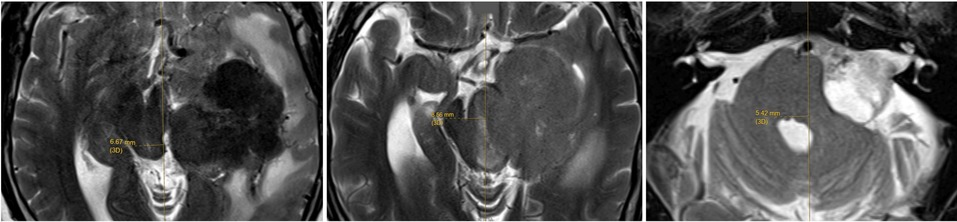
Figure 3. The maximal midline shift of brainstem is measured, using readily identifiable anatomical landmarks, namely cerebral aqueduct (left), mid-point of interpeduncular fossa, and median sulcus of the fourth ventricle in the T2WI MRI.
Results
There are 42 consecutive patients included in this study, and BR IONM is possible in 30 out of 42 patients (71.4%). There are 17 female and 13 male patients, with age ranging from 41 to 81 (mean 62.0). The average latency of R1 in 30 patients under general anaesthesia is 13.3 ms (range from 11.9–14.4 ms). The mean and median duration of follow-up are 95.3 and 89.9 weeks, respectively. Ten patients underwent microvascular decompression (trigeminal neuralgia in four and hemi-facial spasm in six) and 20 excision of tumours of size ranging from 1.1 to 81.6 cm3 (mean 21.6 cm3). For the tumour cases, Mann-Whitney U test for unpaired data show statistically significant difference in tumour volume (p = 0.0016; 37.8 vs. 13.0 cm3) and maximal MLS of the brainstem (p = 0.0271; 8.1 vs. 4.8 mm) regarding significant change in BR response. This suggests that BR change is a good sentinel indicator of how much brainstem neural tissue is mechanically stretched during the excision of the tumour.
Diagnostic accuracy of BR
In the 30 patients with successful BR IONM, their BR is decreased significantly (four patients; 13.3%) or lost (two patients; 6.7%) in a total of six patients (20%) at the end of operation. For all patients with transient drop in R1 during the surgery, there are no new deficits if the R1 recovered at the end of operation. There is one (patient 11) with diminished but not reaching 50% amplitude drop in R1 and the patient does not have post-operative corneal sensation problem or ulceration. For the four patients (13.3%) with significant decrease in BR response, all have decreased ipsilateral corneal sensation and one has transient ulceration and keratopathy post-operatively, while for the two patients (6.7%) with BR lost, all have corneal ulcerations and exposure keratitis documented and managed by ophthalmologists. Considering all significant changes in BR and all post-operative corneal complications as post-operative neurological deficits, the statistic parameters of using BR response in detection of deficits are listed in Table 1 as follows.
Discussion
In a study of 30 healthy conscious adult subjects, the average latency of R1 is at 10.7 ms and R2 at 33.3 ms (15). Our average latency of R1 in 30 patients under general anaesthesia is 13.3 ms (range from 11.9 to 14.4 ms). The latency can vary with the level and method of anaesthesia.
Merits and disadvantages of the various stimulation paradigms
For the stimulation parameters and recording techniques, there are slight variations in the literature, which are summarized in Table 2. Although TIVA is routinely used in IONM, there can be occasions that it is necessary to change the rate of infusion of anaesthetic agents. We use a train-of-four stimuli to overcome the inhibitory effect of the inadvertent fluctuation of anaesthetic drugs to ensure having a satisfactory R1 waveform in BR monitoring. The use of the train in stimulation is also reported by the Turkey (16) and Beijing (3) groups. We do not use halogenated agents, as in the Beijing (3) group, lest they can affect the other modalities of IONM.
We use surface electrodes over supraorbital nerves for more reliable stimulation, and this is similar to using surface electrodes for median nerve stimulation in SSEP. We find that subdermal needle electrodes can sometimes be far away from the nerve or inadvertently puncture and damage the nerve. The presence of control electrodes can detect and avoid inadvertent current spread that leads to false-positive signals that could be mistakenly recorded as genuine R1. This borrows the concept of detecting after-discharges in direct cortical stimulation in awake craniotomy that helps to determine the maximal safe and effective stimulation.
Criteria for the significant change in BR IONM
We use the criteria of R1 wave amplitude decrease by 50% or more, or total loss of R1 wave as the criteria for significant change in BR IONM. This supports the criteria that were used by the Turkey (16) and Beijing (3) groups and has comparable satisfactory overall accuracies.
In one patient (No.26), there is no MLS despite the volume of the tumour being 3.2 cm3. This can sometimes happen when the tumour is mainly over the cistern and/or cerebellar region and not causing any shift in the brainstem. For example, for Koos grade I to III vestibular schwannoma, there will not be a significant shift in the brainstem in the pre-operative MRI. If, during excision of the tumour, using appropriate dynamic retraction after CSF is duly released from the cistern, it is possible to remove the tumour without causing a significant shift in the brainstem. Therefore, it is important to consider the parameter of maximal MLS in addition to the tumour volume when using BR IONM.
Correlation of BR with facial MEP and facial palsy
Studies postulated that BR can predict post-operative facial palsy even better than facial corticobulbar MEP (FCoMEP) (13, 14). In our two patients (patients 8 and 15) with complete BR loss but intact FCoMEP, although they have corneal sensation disturbances and ulcerations, they do not have post-operative facial palsy. Both patients are managed early by ophthalmologists within post-operative two days and have a satisfactory outcome. We believe that BR may have a role that is more than another supplementary monitoring of facial nerve function as its neural pathway included both trigeminal and facial nerves pathways and R1 in BR is mainly related to the trigeminal pathway.
In addition, FCoMEP may cause extraneous movement interfering the microsurgery (3). This extraneous movement can also create false-positive recordings in intra-operative FCoMEP and BR monitoring, due to the vicinity of the facial muscles. In our study, we utilize the As Low As Reasonably Practicable principle in all our intra-operative stimulation, and in our experience, the pick-up rate of extraneous orbicularis oculi responses by FCoMEP is two out of 30 patients (6.7%). These are cases (case 11 and case 23 in Table 3) that increasing stimulation by no more than 20% from baseline was given for recording when the FCoMEPs show a reduction in amplitude. Furthermore, in our study, we stimulate the ipsilateral supraorbital nerve while using a pair of control electrodes placed in the midline to detect and avoid unwanted movement artefacts. As a result, there is no interference with microsurgery at all when utilizing BR.
With regard to the impact on management, for patients with significant change in BR, we suggest early involvement of ophthalmologists and meticulous preventive eye care measures such as temporary tarsorrhaphy to avoid undesirable complications like exposure keratitis, ulceration, blindness, and other visual disturbances.
Limitations of the current study
The current study presents a prospective cohort of 42 consecutive patients with posterior skull base neurosurgery using frequent BR IONM for monitoring of the corneal reflex and sensation under general anaesthesia. Given the variability in patient outcomes and the complexity of skull surgeries, this relatively small sample size may limit the study's statistical power to detect significant associations or draw definitive conclusions. Nevertheless, we reported statistically significant findings as well as the diagnostic accuracy of BR using our described method of electrode placement, stimulation and recording parameters, and diagnostic criteria. We hope that our report of the novel use of this technique may arouse the interest of the skull base neurosurgery community and possibly lead to further verification of our findings in a larger cohort.
Conclusion
Frequent BR IONM is feasible, safe, and useful in the preservation of corneal sensation, especially for patients with large posterior fossa tumours and a distorted brainstem. BR IONM has a very high accuracy rate (96.7%), but can only be successfully done in 71.4% of our patients. This can be related to absent or diminished BR due to various reasons. For patients with significant change in BR response, prompt referral to the ophthalmologist is useful for the prevention of keratitis and corneal ulceration.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
Ethical approval was not required for the studies involving humans because the study was conducted using existing electrodes for stimulation and recording and therefore no additional procedure was involved. Consent from all patients was obtained. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
ML: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. SC: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Yang Y, Neidert MC, Velz J, Kälin V, Sarnthein J, Regli L, et al. Mapping and monitoring of the corticospinal tract by direct brainstem stimulation. Neurosurgery. (2022) 91(3):496–504. doi: 10.1227/neu.0000000000002065
2. Le S, Nguyen V, Lee L, Cho SC, Malvestio C, Jones E, et al. Direct brainstem somatosensory evoked potentials for cavernous malformations. J Neurosurg. (2022) 137(1):156–62. doi: 10.3171/2021.7.JNS21317
3. Liu J, Fan X, Yang L, Tao X, Jin Y, Li K, et al. Predictive value of Blink reflex and facial corticobulbar motor evoked potential in cerebellopontine angle tumor surgery. Clin Neurophysiol. (2024) 162:165–73. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2024.03.033
5. Kimura J. The blink reflex. In: Kimura J, editor. Electrodiagnosis in Diseases of Nerve and Muscle: Principles and Practice. 3rd Edition. New York, NY: Oxford University Press (2001). p. 409–38. ISBN 0195129776, 9780195129779
6. Deletis V, Urriza J, Ulkatan S, Fernandez-Conejero I, Lesser J, Misita D. The feasibility of recording blink reflexes under general anesthesia. Muscle Nerve. (2009) 39(5):642–6. doi: 10.1002/mus.21257
7. Peterson DC, Hamel RN. Corneal reflex. In: StatPearls Editorial Board, editors. StatPearls. Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls Publishing (2024). Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK534247/ (Accessed July 25, 2023).
8. Manning KA, Evinger C. Different forms of blinks and their two-stage control. Exp Brain Res. (1986) 64(3):579–88. doi: 10.1007/BF00340495
9. Delgado-García JM, Gruart A. The role of interpositus nucleus in eyelid conditioned responses. Cerebellum. (2002) 1(4):289–308. doi: 10.1080/147342202320883597
10. Riss B, Riss P. Corneal sensitivity in pregnancy. Ophthalmologica. (1981) 183(2):57–62. doi: 10.1159/000309139
11. Reddy VC, Patel SV, Hodge DO, Leavitt JA. Corneal sensitivity, blink rate, and corneal nerve density in progressive supranuclear palsy and Parkinson disease. Cornea. (2013) 32(5):631–5. doi: 10.1097/ICO.0b013e3182574ade
12. Yang AY, Chow J, Liu J. Corneal innervation and sensation: the eye and beyond. Yale J Biol Med. (2018) 91(1):13–21. Available at: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5872636/29599653
13. Simioni V, Capone JG, Sette E, Granieri E, Farneti M, Cavallo MA, et al. Intraoperative monitoring of sensory part of the trigeminal nerve using blink reflex during microvascular decompression for trigeminal neuralgia. Acta Neurochir. (2018) 160(1):165–9. doi: 10.1007/s00701-017-3405-8
14. Maciel CB, Youn TS, Barden MM, Dhakar MB, Zhou SE, Pontes-Neto OM, et al. Corneal reflex testing in the evaluation of a comatose patient: an ode to precise semiology and examination skills. Neurocrit Care. (2020) 33(2):399–404. doi: 10.1007/s12028-019-00896-0
15. Nahantchi AA, Seck LB, Diagne SN, Soda M, Basse AM, Mourabit S, et al. Normative values of the blink reflex. Afr J Neurol Sci. (2022) 41(1):52–8. Available at: https://www.ajol.info/index.php/ajns/article/view/245047
Keywords: posterior skull base surgery, intra-operative neuro-monitoring, blink reflex, corneal reflex, predictive value
Citation: Lee MWY and Chau S-w (2025) Intra-operative blink reflex neurophysiological monitoring in posterior skull base neurosurgery. Front. Surg. 12:1485459. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2025.1485459
Received: 23 August 2024; Accepted: 4 June 2025;
Published: 25 June 2025.
Edited by:
Tak Lap Poon, Queen Elizabeth Hospital (QEH), Hong Kong SAR, ChinaReviewed by:
Abdullah M. Al-Qudah, University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, United StatesXianlun Zhu, Chinese University of Hong Kong, China
Copyright: © 2025 Lee and Chau. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Michael W. Y. Lee, bWljaGFlbHd5bGVlQHlhaG9vLmNvbQ==
 Michael W. Y. Lee
Michael W. Y. Lee Shu-wah Chau
Shu-wah Chau