- Yueyang Hospital of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai, China
Background: Pelvic fractures (PF) are complex injuries often requiring multidisciplinary management. Robot-assisted fracture Fixation (RAFF) systems have emerged as a promising innovation in PF treatment, offering improved precision, reduced radiation exposure, and minimally invasive techniques. This scoping review aims to synthesize the current evidence on the accuracy, safety, and efficiency of RAFF systems in managing PF, highlighting their benefits, limitations, and future potential.
Methods: A scoping review was conducted adhering to PRISMA-ScR guidelines. Databases including PubMed and Web of Science were searched to identify studies evaluating RAFF systems for PF. Eligible studies involved adult patients undergoing robot-assisted interventions for PF and reported outcomes on accuracy, operative time, blood loss, and complications. Data extraction focused on study design, robotic platform, outcomes, and methodological quality assessed via MINORS and RoB-2.
Results: Twelve studies were included, comprising case reports, case series, and one comparative study. RAFF systems demonstrated high accuracy in fracture reduction with reduced fluoroscopic exposure and minimal blood loss. Functional outcomes assessed by Matta criteria and Majeed scores were favorable. However, most studies were limited by small sample sizes and lack of long-term follow-up. No high-quality randomized controlled trials were identified.
Conclusions: RAFF systems show significant potential in improving surgical outcomes for PF, offering enhanced precision and reduced operative risks. Nevertheless, robust, high-quality studies are needed to establish the long-term efficacy and economic viability of these systems. Standardized protocols and multicenter trials are critical for advancing the application of robotics in orthopedic trauma surgery.
1 Introduction
Pelvic fractures (PF) are complex, high-energy injuries often associated with life-threatening hemorrhage (1, 2). Traditional open surgery poses challenges due to excessive bleeding, leading to the adoption of minimally invasive techniques like computer-navigated percutaneous screw placement (3). Management of PF requires a multidisciplinary approach, including pelvic stabilization, angiographic embolization, and damage control strategies (2, 4). Early identification and treatment of life-threatening injuries are crucial, with a focus on controlling hemorrhage from various sources (5).
Robot-assisted fracture Fixation (RAFF) systems has emerged as a promising approach to improve surgical outcomes in pelvic fracture treatment. These systems provide benefits like precise preoperative planning, real-time 3D navigation, and minimally invasive procedures (6, 7). Studies have shown that RAFF systems achieve high accuracy in fracture reduction, with mean errors ranging from 1.3 to 3.4 mm (8). Robot-assisted percutaneous screw fixation for pelvic and acetabular fractures is more accurate, has less radiation exposure, and is more efficient than traditional methods (7, 9). However, functional outcomes appear similar between robotic and traditional methods (10).Clinical applications have shown promising results, with high rates of excellent or good outcomes based on Matta criteria (6). Integration of multiple robotic systems, such as the combination of the Starr Frame with the Da Vinci robot, can further enhance treatment options for complex cases involving sacral nerve injuries (11). As surgeons gain experience with these systems, operation times significantly decrease while maintaining accuracy (12). RAFF systems differ from traditional navigation systems primarily in their robotic manipulation capabilities. While navigation systems solely offer real-time guidance and positional feedback to surgeons for manual intervention, robotic systems additionally include mechanical manipulators capable of executing surgical actions, thus enhancing precision and reducing human variability.
The TiRobot was one of the earliest systems used for pelvic fractures, with its application in this field dating back to 2018, Jilin University First Hospital's trauma department applied TiRobot from May 2018 to April 2021 for minimally invasive percutaneous screw fixation of pelvic fractures (13). The application of robotic technology in orthopedic trauma surgery is still in its early stages, with ongoing research focusing on expanding its clinical indications and addressing limitations (14). This scoping review aimed to evaluate the role and adoption of new robotic platforms in the management of pelvic fractures, specifically assessing their application in Robot-assisted fracture Fixation and percutaneous screw fixation techniques. The objective is to identify and map the current evidence on the accuracy, safety, and efficiency of these systems compared to traditional methods, as well as to provide insights on functional outcomes and highlight future research priorities for expanding the clinical use of robotic technology in orthopedic trauma surgery.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Search strategy and data sources
This scoping review was conducted with a systematic approach, adhering to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR) statement (15), to address the following question: “What is the current evidence supporting the performance of RAFF systems in the management of pelvic fractures?”
The initial search was conducted in PubMed to identify all emerging surgical robots currently available or undergoing testing in preclinical and clinical trials for pelvic fracture treatment. Systems identified include a real-time 3D navigation-based robot, and hybrid approaches combining mechanical tools such as the Starr Frame with robotic platforms like the Da Vinci robot and an autonomous reduction robot, while dual-robotic systems like the TiRobot and Artis Zeego also showed promise. Robotic platforms primarily focused on precise screw placement, improved accuracy in fracture reduction, and reduced surgical risks and radiation exposure, though existing multiport platforms such as the Intuitive Surgical Da Vinci robot series were excluded from the review.
In accordance with the PCC format, the following criteria were applied in selecting studies for this scoping review on RAFF systems in managing pelvic fractures:
Population (P): Adult patients (>18 years) diagnosed with pelvic fractures, requiring surgical intervention, regardless of the complexity of the fracture or underlying injury mechanism.
Concept (C): Application of Robot-assisted fracture Fixation (RAFF) systems, specifically focusing on emerging robotic technologies that enhance minimally invasive fracture reduction and percutaneous screw fixation. Systems considered include real-time 3D navigation-based robots, combinations of platforms like the Da Vinci robot, autonomous reduction robots, and dual-robotic systems such as TiRobot and Artis Zeego, while excluding traditional multiport platforms.
Context (C): Studies from clinical settings, including tertiary care and specialized trauma hospitals, where these innovative robotic systems have been implemented and evaluated for pelvic fracture treatment.
All reported outcomes across the included studies were analyzed, encompassing intraoperative, postoperative, short-term outcomes, functional results, and cost evaluations. A broad range of study designs was considered, including case reports, though review articles were excluded. Studies that contained single case reports or small series embedded within a larger series were omitted. In cases where redundancy could not be assessed due to missing registration protocol numbers or different inclusion periods, studies were flagged in the results and retained. Abstracts lacking complete case details and conference communications were excluded, with only studies published in English included in the analysis.
The literature search and selection process were conducted independently by two reviewers (B.W., J.Z.). In accordance with PRISMA guidelines, all records were compiled into a single database, duplicates were removed, and the remaining articles were screened for relevance based on titles and abstracts. Any discrepancies were resolved through discussion and consensus, and if consensus was not reached, a senior author (G.W.) was consulted to make a final determination on inclusion. Subsequently, the two reviewers conducted independent full-text reviews to confirm the eligibility of each article.
2.2 Data extraction and synthesis
Data extracted from the selected studies were recorded in an electronic spreadsheet. The following information was collected: first author's name, year of publication, study design, study period, type of robotic platform used, total number of patients/procedures, number of patients treated for pelvic fractures, patient demographics (including sex, age, and body mass index), fracture type and location, preoperative injury assessment, type of preoperative stabilization, surgical intervention details, number and type of robotic and assistant arms used, intraoperative outcomes, postoperative outcomes, accuracy of fracture reduction, short-term outcomes, long-term outcomes, functional recovery, learning curve of the robotic system, radiation exposure, and cost analysis.
2.3 Quality assessment
The quality and risk of bias in the included studies were evaluated using the MINORS (Methodological Index for Non-Randomized Studies) scoring system. In this system, each item is scored as follows: 0 if the item is not reported, 1 if the item is reported but inadequately addressed, and 2 if the item is both reported and adequately addressed. The highest possible score is 16 for non-comparative studies and 24 for comparative studies. Case reports were excluded from this quality assessment due to their inherently high risk of bias. For randomized controlled trials, the revised Cochrane risk-of-bias tool (RoB 2) was applied to ensure a comprehensive assessment (16).
3 Results
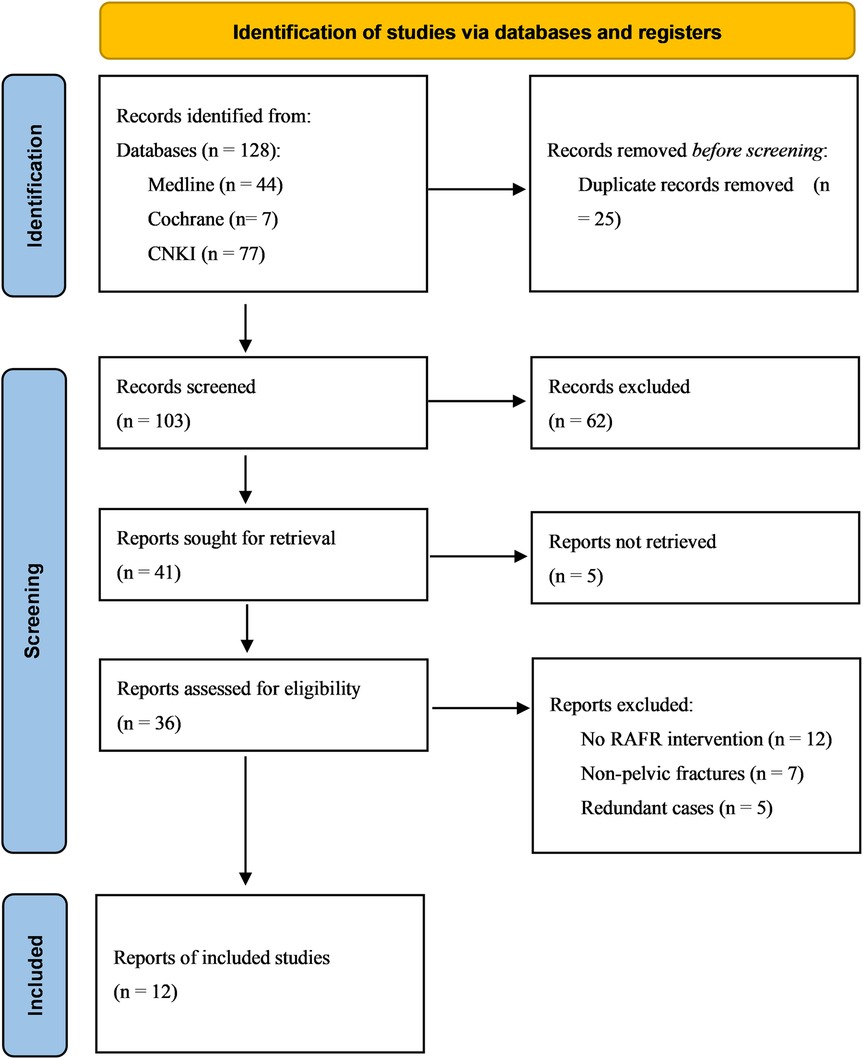
The initial database search identified a total of 128 studies, of which 25 were duplicates. After screening the titles and abstracts of the 103 remaining articles, 62 were excluded due to irrelevance. Five articles could not be retrieved despite efforts, leaving 36 articles for full-text review. Among these, 24 were excluded: 12 did not involve RAFF intervention, 7 were not focused on pelvic fractures, and 5 were redundant cases. Ultimately, 12 studies met the inclusion criteria and were selected for qualitative synthesis of the literature (Figure 1).
Among the included studies, 1 was case report, 10 were case series, and 1 was comparative study. Two studies were randomized controlled trials. No randomized controlled trials (RCTs) were identified.
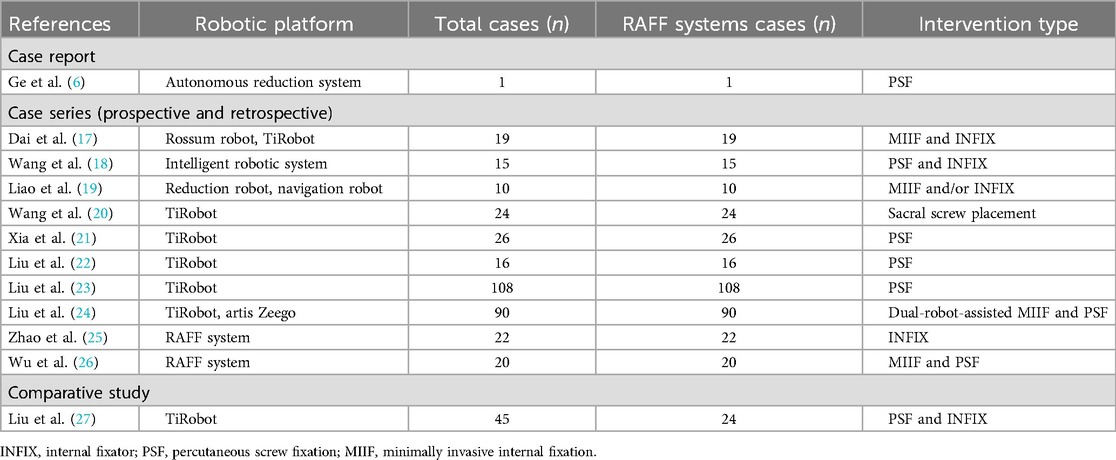
Overall, a total of 396 patients were included, of whom 375 underwent interventions using a RAFF system with a robotic platform. The most commonly reported intervention was percutaneous screw fixation (PSF, n = 191), followed by minimally invasive internal fixation (MIIF, n = 49), sacral screw placement (n = 24), and internal fixator (INFIX, n = 56). Additionally, 76 cases involved dual-robot-assisted or mixed interventions that were not distinctly categorized. These interventions demonstrated the versatility of robotic platforms in treating various pelvic fracture types.
The mean MINORS score for non-comparative studies ranged from 7 to 13, reflecting moderate methodological quality. The single comparative study reported a clear advantage in surgical precision and reduced fluoroscopy frequency using the TiRobot system compared to conventional methods. No studies presented a randomized design, limiting the ability to assess high-level evidence for RAFF systems.
3.1 Robotic platforms
The studies reviewed utilized three robotic platforms: the Rossum Robot (Beijing Jishuitan Hospital and Rossum Robot Co., Ltd., Beijing, China), TiRobot (TINAVI Medical Technologies Co., Ltd., Beijing, China), and a dual robotic system combining TiRobot with the Artis Zeego system (Siemens, Germany). The Rossum Robot featured a six-degree-of-freedom (6-DOF) manipulator, elastic traction, and mirrored path planning capabilities, enabling high precision in pelvic fracture reduction (17). TiRobot, the most commonly used system, provided sub-millimeter precision, advanced navigation, and automatic trajectory correction (21, 23, 27). The Artis Zeego system introduced real-time 3D imaging for superior surgical visualization and planning, enhancing the dual robotic system's functionality (24). The types of RAFF systems and their applications across included studies are summarized in Table 1.
3.2 Baseline characteristics
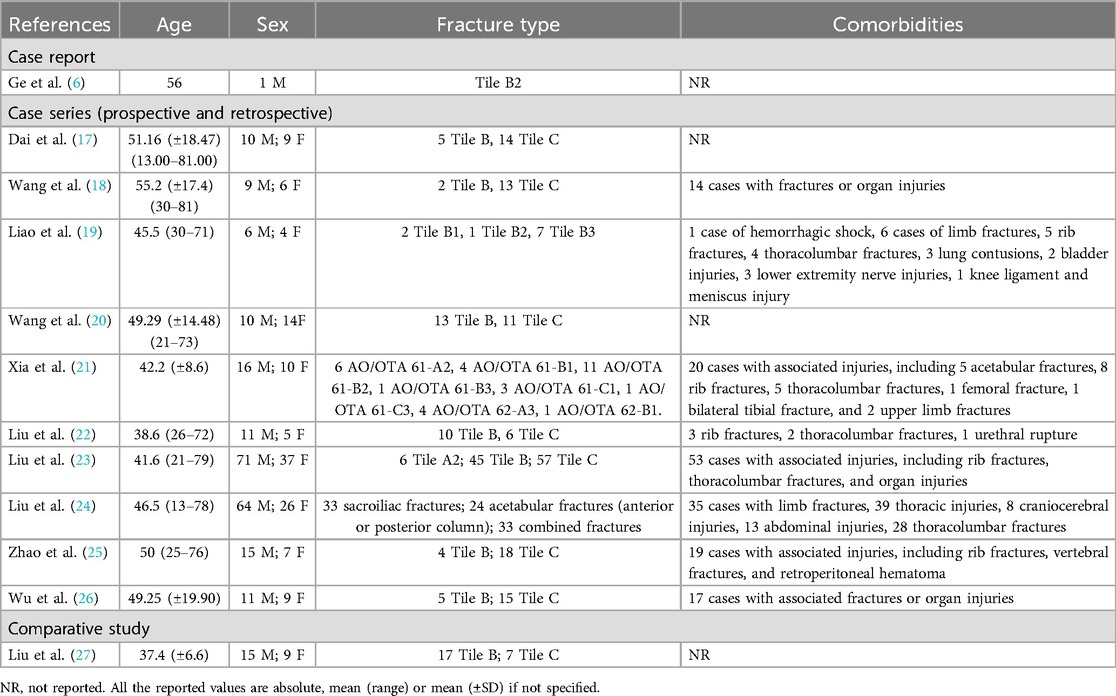
Across the studies, the patient population included individuals aged 13–81 years, with an average age ranging from 38.5 to 56 years. Male patients predominated (55%–62%). Most fractures were classified as Tile B (68.5%–72%), with Tile C fractures comprising the remainder. Preoperative preparation involved routine CT imaging, 3D reconstructions, and skeletal traction in cases of vertical instability (6, 17, 18, 23, 26). Table 2 presents the demographic characteristics, fracture types, and comorbidities of the study population.
3.3 Operative time and blood loss
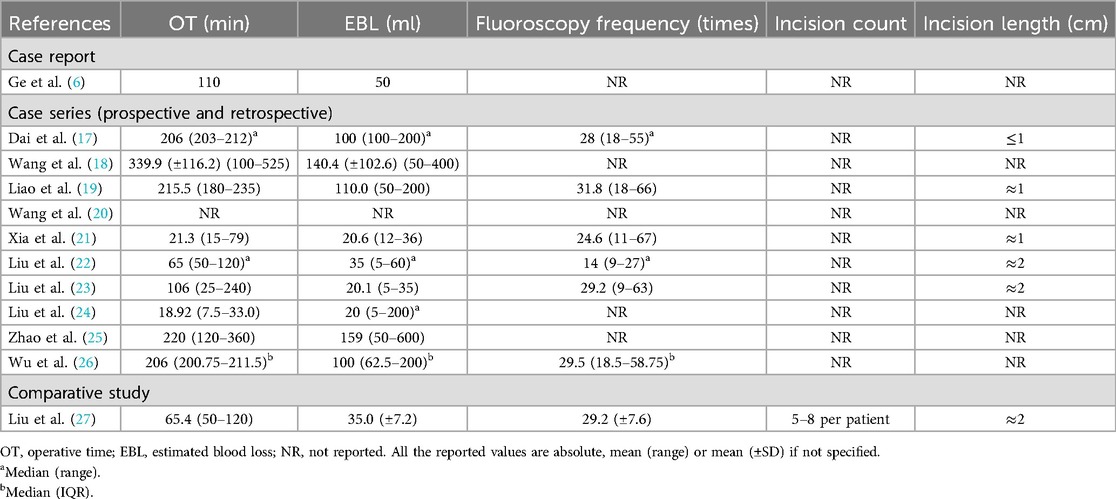
Operative times varied across studies, ranging from 65 to 339 minutes, with an average of 18.9 minutes required for screw implantation in TiRobot-assisted cases. Intraoperative blood loss was minimal, averaging between 20 and 140 ml, reflecting the minimally invasive nature of the procedures (6, 19, 20, 22). Operative time, estimated blood loss, and fluoroscopy frequency are detailed in Table 3.
3.4 Fluoroscopic exposure and incision details
The number of fluoroscopic exposures averaged 14–32 instances per procedure, significantly lower than traditional methods. Incisions were typically less than 2 cm in length, with a mean of 1.5 cm, underscoring the minimally invasive approach (18, 20, 24, 27).
3.5 Postoperative outcomes and follow-up
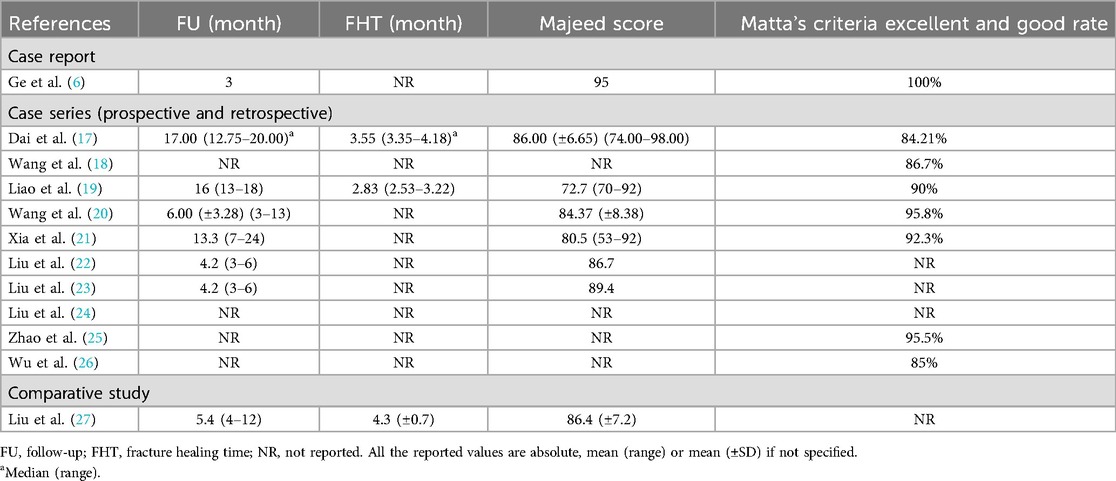
Follow-up durations ranged from 3 to 17 months (6, 17, 19, 21). Fracture healing times averaged 3.5 months (17, 19, 27), and postoperative functional outcomes were excellent, with Majeed scores ranging from 86.7 to 89.4 (17, 22, 23). Reduction quality, assessed using Matta criteria, achieved excellent-to-good rates of 84.21%–95.8% (17, 22, 23, 26), demonstrating the effectiveness of robotic assistance in achieving anatomical alignment (17, 19, 25). Follow-up duration, healing time, and functional scores are provided in Table 4.
3.6 Complications
Intraoperative complications were rare, with no reports of vascular or neural injuries. Postoperative issues, such as minor screw misalignments, were promptly corrected (22, 24). Only one case of cortical perforation resulted in a switch to hybrid surgery (22).
3.7 Quality assessment
The methodological quality of the included studies was assessed using the MINORS criteria and RoB-2 tool. For the non-comparative studies, MINORS scores ranged from 7 to 13 out of a possible 16, indicating moderate methodological quality. The only comparative study scored 17 out of 24.
Two studies were initially labeled as randomized controlled trials; however, upon review, both lacked sufficient information on randomization procedures and blinding. These were reclassified as non-randomized comparative studies. According to the RoB-2 tool, both studies were judged to have “some concerns” regarding risk of bias due to the absence of protocol registration and limited reporting of outcome blinding.
3.8 Economic and operational considerations
Economic analyses were limited but suggested potential cost savings due to shorter operative times and reduced radiation exposure (22, 24). Learning curve studies indicated that surgical teams required approximately 10 cases to achieve proficiency in robotic systems (23, 27).
4 Discussion
The integration of robotic platforms into pelvic fracture surgery has rapidly evolved, showcasing significant advancements in precision and safety over traditional approaches. Despite this, the evidence supporting the superiority of robotic systems over manual methods remains under development, primarily due to the limited availability of large-scale, high-quality studies (6, 17–27).
This review synthesizes data from studies employing robotic platforms such as the TiRobot, Rossum Robot, and dual robotic systems combining TiRobot with the Artis Zeego system. While these technologies have been instrumental in enhancing operative precision and reducing complications, their application in pelvic fractures is still relatively nascent, with most studies published between 2016 and 2024 (6, 17–27). A recurring limitation in the literature is the prevalence of small case series or single-institution experiences, which constrains the generalizability of findings. Moreover, overlapping study populations and duplicate reporting are common, as evidenced by the frequent reuse of patient data in sequential publications (6, 17–20, 24). Such overlaps not only introduce potential selection and reporting bias but also limit the overall novelty of available evidence, as multiple studies may derive from the same institutional database. This concern underscores the need for more diverse, independent, and multicenter research efforts.
Furthermore, the strength of the evidence is limited by the predominance of retrospective case series and non-comparative designs, which inherently carry a higher risk of bias. Patient characteristics and comorbidities are often underreported, with most studies focusing on basic demographics such as age and fracture classification. Although this provides a baseline understanding, it fails to account for critical factors like the Charlson Comorbidity Index or the American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) score, which are pivotal for evaluating postoperative risks and outcomes (19, 22). Preoperative preparations, including 3D imaging and skeletal traction, were standardized across studies, facilitating the adoption of advanced robotic systems (18, 20).
Intraoperative outcomes are promising, with robotic platforms demonstrating reduced operative times, minimal blood loss, and low fluoroscopic exposure compared to conventional techniques. Incision lengths and fluoroscopy frequency are consistently reported as minimal, reflecting the advantages of minimally invasive procedures (21, 23, 26). However, these benefits are partially offset by the steep learning curve associated with robotic systems, as surgical teams require approximately 10–15 cases to achieve proficiency (24, 25, 27).
Postoperative outcomes highlight the effectiveness of robotic platforms in achieving high-quality reductions and functional recovery. Matta criteria reveal excellent-to-good reduction rates exceeding 90% in most studies, and Majeed scores consistently indicate favorable functional outcomes (17, 21, 24, 26). Nonetheless, the studies often lack long-term follow-up, limiting the assessment of sustained functional and structural integrity.
A significant limitation is the sparse reporting of complications, with most studies emphasizing their rarity but failing to provide detailed accounts. While robotic systems reduce the risk of vascular or neural damage, minor complications such as screw misalignment are occasionally noted (6, 18, 21). Economic analyses remain scarce, though preliminary data suggest cost savings due to shorter operative times and reduced radiation exposure (25, 27). Moreover, very few studies pre-registered protocols or reported detailed bias mitigation strategies, which further limits confidence in their findings. Future studies should adhere to standardized reporting and methodological rigor to enhance transparency and comparability.
Future research must prioritize multicenter randomized controlled trials to validate the clinical and economic benefits of robotic platforms. Given the steep learning curve and institutional concentration of existing data, future trials should also address the generalizability of findings across diverse settings and surgical teams. Additionally, the transferability of robotic skills across platforms and the role of expertise in optimizing outcomes warrant further exploration. As robotic technologies continue to evolve, integrating standardized reporting frameworks and comprehensive data collection will be crucial for advancing the field (21, 24, 27).
In addition, mechanical reduction frames such as Matta's frame, widely used for pelvic fracture reduction, should be considered separately from robotic platforms due to their purely mechanical nature without robotic manipulation.
5 Conclusions
RAFF systems represent a transformative advancement in the surgical management of pelvic fractures, providing improved precision, reduced radiation exposure, and minimized invasiveness compared to traditional methods. Platforms such as the TiRobot, Rossum Robot, and dual systems combining TiRobot with Artis Zeego have demonstrated feasibility and safety in achieving high-quality fracture reductions, as evidenced by favorable Matta criteria and Majeed scores. Despite these advantages, the current literature is predominantly based on small-scale studies, case series, and single-center experiences, with no high-quality randomized controlled trials available.
Functional outcomes following robotic-assisted procedures appear comparable to traditional methods, but the overall benefits of robotics—reduced blood loss, shorter fluoroscopic exposure, and enhanced accuracy—highlight their potential in improving patient recovery and safety. However, the steep learning curve and limited economic evaluations remain significant challenges.
Future research should prioritize multicenter, randomized controlled trials and standardized reporting of outcomes to validate the clinical and economic efficacy of RAFF systems. Expanding the use of robotics in orthopedic trauma surgery will require addressing these knowledge gaps and integrating advanced technologies with surgical expertise. Robust evidence will ultimately determine the long-term role of robotic platforms in transforming the management of pelvic fractures.
Author contributions
BW: Writing – original draft. GW: Writing – original draft. JZ: Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the Hospital-level Research Project of Yueyang Hospital of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine (Project No. KY111.30.236).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to extend their special thanks to Dr. Heng Li (Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine Affiliated Pudong New Area TCM Hospital) for his substantial intellectual contribution, particularly in the areas of study design, literature synthesis, and methodological refinement. His critical input and sustained engagement were pivotal in shaping the direction and rigor of this review, to a degree comparable to that of the lead authorship. We also gratefully acknowledge Dr. Fei Lin for valuable assistance with literature retrieval, Dr. Jinyu Qian for contributions to figure preparation, and Dr. Xichen Tang for reference verification. Their support greatly enhanced the comprehensiveness and accuracy of the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Moreno C, Moore EE, Rosenberger A, Cleveland HC. Hemorrhage associated with major pelvic fracture: a multispecialty challenge. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. (1986) 26:987. doi: 10.1097/00005373-198611000-00005
2. Wong JM-L, Bucknill A. Fractures of the pelvic ring. Injury. (2017) 48:795–802. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2013.11.021
3. Yu T, Cheng X-L, Qu Y, Dong R-P, Kang M-Y, Zhao J-W. Computer navigation-assisted minimally invasive percutaneous screw placement for pelvic fractures. WJCC. (2020) 8:2464–72. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i12.2464
4. Biffl WL, Smith WR, Moore EE, Gonzalez RJ, Morgan SJ, Hennessey T, et al. Evolution of a multidisciplinary clinical pathway for the management of unstable patients with pelvic fractures. Ann Surg. (2001) 233:843. doi: 10.1097/00000658-200106000-00015
5. Matsushima K, Love B, Tadlock MD. Damage Control for Pelvic Fracture Bleeding. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press (2019). p. 335–42. doi: 10.1017/9781108698665.038
6. Ge Y, Zhao C, Wang Y, Wu X. Robot-assisted autonomous reduction of a displaced pelvic fracture: a case report and brief literature review. JCM. (2022) 11:1598. doi: 10.3390/jcm11061598
7. Wu X, Wang J, Sun X, Zhao C. Guidance for treatment of pelvic acetabular injuries with precise minimally invasive internal fixation based on the orthopaedic surgery robot positioning system. Orthop Surg. (2019) 11:341–7. doi: 10.1111/os.12452
8. Shi C, Zhao X, Wu X, Zhao C, Zhu G, Shi S, et al. Real-Time 3D navigation-based semi-automatic surgical robotic system for pelvic fracture reduction. 2021 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS) (2021). p. 9498–503. doi: 10.1109/IROS51168.2021.9636647
9. Zhao CP, Wang J, Su Y, Han W, Zhou L, Wang MY. Clinical research on robot-assisted percutaneous pelvic and acetabular screws surgery. J Peking Univ. Health Sci. (2017).
10. Schuijt HJ, Hundersmarck D, Smeeing DPJ, van der Velde D, Weaver MJ. Robot-assisted fracture fixation in orthopaedic trauma surgery: a systematic review. OTA International. (2021) 4:e153. doi: 10.1097/OI9.0000000000000153
11. Peng Y, Zhang W, Zhang G, Wang X, Zhang S, Ma X, et al. Using the starr frame and Da vinci surgery system for pelvic fracture and sacral nerve injury. J Orthop Surg Res. (2019) 14:29. doi: 10.1186/s13018-018-1040-6
12. Liu K, You M, Huang M, Chen C, Rui B, Gao H, et al. Preliminary application study of dual-robotic navigated minimally invasive treatment by TiRobot and artis zeego on pelvic fractures. Chin J Reparative Reconstr Surg. (2022).
13. Guang Y, Baochang Q, Tianhao Z. Efficacy of TiRobot-assisted minimally invasive percutaneous screw fixation for pelvic fractures. Chin J Orthop Trauma. (2022) 24:200–5. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115530-20211206-00561
14. Zhu Z, Zheng G, Zhang C. Development and clinical application of robot-assisted technology in traumatic orthopedics. Chin J Reparative Reconstr Surg. (2022).
15. Tricco AC, Lillie E, Zarin W, O’Brien KK, Colquhoun H, Levac D, et al. PRISMA extension for scoping reviews (PRISMA-ScR): checklist and explanation. Ann Intern Med. (2018) 169:467–73. doi: 10.7326/M18-0850
16. Sterne JAC, Savović J, Page MJ, Elbers RG, Blencowe NS, Boutron I, et al. Rob 2: a revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. Br Med J. (2019) 366:l4898. doi: 10.1136/bmj.l4898
17. Dai Y, Zeng Y, Wu Z, Zhao C, Wang J, Wu X. Clinical efficacy of intelligent pelvic fracture reduction robots combined with TiRobot for unstable pelvic fractures. J Capital Med Univ. (2024) 45:763–72.
18. Wang X, Wu Z, Zeng Y, Li C, Zhou J, Hong S, et al. Intelligent robot-assisted percutaneous fixation of pelvic fractures. Chin J Orthop Surg. (2024) 32:1507–10. doi: 10.20184/j.cnki.Issn1005-8478.100512
19. Liao J, Dai Y, Wu Z, Zeng Y, Li C, Wang X, et al. Analysis of the efficacy of reduction robots combined with navigation robots in minimally invasive treatment of tile B-type pelvic fractures. Chin J Reconstr Surg. (2024) 38:954–60.
20. Wang X, Wu Z, Zeng Y, Li C, Zhou J, Hong S. Accuracy and clinical efficacy of robot-assisted sacroiliac screw placement for posterior pelvic ring fractures. Chin J Orthop. (2024) 37:605–8.
21. Xia H., Liao Y., Kaesel , Wang S., Mao F., Zhang D., Zhao J. Application of orthopedic robots in internal fixation of pelvic and acetabular fractures. Chin J Bone Jt Inj 2022, 37, 1284–7.
22. Liu H, Duan S, Jia F, Liu S, Chen H, Wang Y, et al. TiRobot-assisted percutaneous hollow screw fixation for unstable pelvic fractures. J Shandong Univ. (2017) 55:103–9.
23. Liu H, Duan S, Zhao G, Zhang Z, Zhu L, Wang X, et al. Clinical analysis of 108 cases of orthopedic robotic-assisted minimally invasive treatment of pelvic ring injuries. J Shandong Univ. (2019) 57:52–9.
24. Liu K, You M, Huang M, Chen C, Rui B, Gao H, et al. Preliminary application of the TiRobot combined with the artis zeego system in minimally invasive treatment of pelvic fractures. Chin J Reconstr Surg. (2022) 36:929–33.
25. Zhao C, Cao Q, Sun X, Wu X, Zhu G, Wang Y. Intelligent robot-assisted minimally invasive reduction system for reduction of unstable pelvic fractures. Injury. (2023) 54:604–14. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2022.11.001
26. Wu Z, Dai Y, Zeng Y. Intelligent robot-assisted fracture reduction system for the treatment of unstable pelvic fractures. J Orthop Surg Res. (2024) 19:271. doi: 10.1186/s13018-024-04761-5
Keywords: pelvic fractures, robot-assisted fracture fixation, minimally invasive surgery, TiRobot, orthopedic trauma, surgical precision, Matta criteria
Citation: Wu B, Wang G and Zheng J (2025) Robot-assisted fracture fixation for pelvic fractures: a scoping review of emerging technologies. Front. Surg. 12:1559419. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2025.1559419
Received: 12 January 2025; Accepted: 7 July 2025;
Published: 14 October 2025.
Edited by:
Yu Wang, Beihang University, ChinaReviewed by:
Muhammad Usman Saeed, Central South University, ChinaFederico Bove, ASST GOM Niguarda, Italy
Copyright: © 2025 Wu, Wang and Zheng. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Gengqi Wang, d2FuZ2dlbmdxaUAxMjYuY29t; Jun Zheng, ZHVkdTgyMzhAMTYzLmNvbQ==
 Boyi Wu
Boyi Wu Gengqi Wang*
Gengqi Wang*