- 1Department of Traumatology & Orthopedics, Wuxi Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Wuxi, China
- 2School of Integrative Medicine, Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing, Jiangsu, China
- 3Laboratory of New Techniques of Restoration & Reconstruction, Institute of Traumatology & Orthopedics, Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing, China
- 4School of Nursing, Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing, Jiangsu, China
- 5Yancheng Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Yancheng Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Yancheng, China
- 6Jiangsu CM Clinical Innovation Center of Degenerative Bone & Joint Disease, Wuxi Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Wuxi, Jiangsu, China
- 7Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Nanjing Hospital of Chinese Medicine Affiliated to Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing, China
Objective: This study aimed to construct a nomogram to predict the likelihood of early recurrence in patients with lumbar disc herniation (LDH) following unilateral biportal endoscopic (UBE) surgery.
Methods: A retrospective analysis was conducted on LDH patients who underwent UBE surgery in our department between January 1, 2022, and December 31, 2023. The eligible cohort was randomly divided into training and validation sets in a 7:3 ratio. Key predictors for the nomogram were identified through a combination of least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) regression and multivariate logistic regression analysis. The model's performance was assessed using the C-index, the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC), calibration curves, and decision curve analysis. The validation set was used to further evaluate the model's robustness.
Results: A total of 289 patients were included in the study, among whom 50 experienced recurrent LDH (rLDH). Five risk factors were identified as significant predictors for rLDH: width of protrusion base (WPB), bone removal range (BRR), Modic changes, type of LDH, and middle vertebral space height (MVH). The C-index values for the training and validation sets were 0.834 and 0.804, respectively. The AUC values were 0.834 (95% CI: 0.750–0.918) in the training set and 0.804 (95% CI: 0.697–0.910) in the validation set. Calibration curves demonstrated excellent concordance between the predicted and observed outcomes. Decision curve analysis indicated that using the nomogram to predict rLDH risk provided a positive net benefit when the threshold probability was between 4% and 63%.
Conclusion: This study successfully developed and validated a nomogram to predict early recurrence in LDH patients following UBE surgery. The model provides a valuable tool for clinicians to assess individual rLDH risk, enabling timely interventions to improve postoperative outcomes.
1 Introduction
Lumbar disc herniation (LDH) is a prevalent clinical condition that often manifests as pain and numbness in the lower back and legs, significantly impairing patients' daily activities (1). Unilateral biportal endoscopic (UBE) surgery has become a widely adopted clinical approach due to its numerous advantages, including minimal trauma, a clear surgical field, reduced bleeding, low risk of nerve injury, low infection rates, and rapid recovery (2). However, some patients remain at risk of recurrent lumbar disc herniation (rLDH).
Recurrent LDH is defined as herniation at the same vertebral level causing symptomatic compression, irrespective of the time interval since the initial surgery (3). The recurrence of LDH may be attributed to factors such as nerve element compression by scar tissue during discectomy, residual disc fragments, or reactive tissues such as portions of the disc endplate, vertebrae, or fibrous rings (4). Reported recurrence rates range from 5%–18% among patients with LDH following their initial surgery (5). Recurrence exacerbates lower back and limb pain, with severe cases necessitating a second surgical intervention (6).
A second surgery often poses challenges due to fibrosis and scarring at the operative site caused by the primary procedure, making minimally invasive revision surgery more difficult. Additionally, recurrence imposes significant physical, psychological, and financial burdens on patients while straining medical resources. Hence, the prevention and early identification of rLDH are critical.
This study aims to establish and validate a predictive model to assess the early risk of developing rLDH after UBE surgery in LDH patients. By offering a user-friendly nomogram, we aim to enable clinicians to easily estimate individual recurrence risk, facilitating timely interventions and improving patient outcomes.
2 Design and methods
2.1 Research population
To ensure statistical robustness, a priori sample size calculation was performed using the formula for logistic regression:
where Zα/2 = 1.96 (95% confidence level), Zβ = 0.84(80% power), P = 0.15 expected recurrence rate from prior literature (5, 6), and δ = 0.05 (margin of error). This yielded a minimum sample size of 246. To account for potential data loss and enhance model generalizability, 289 patients were ultimately enrolled.
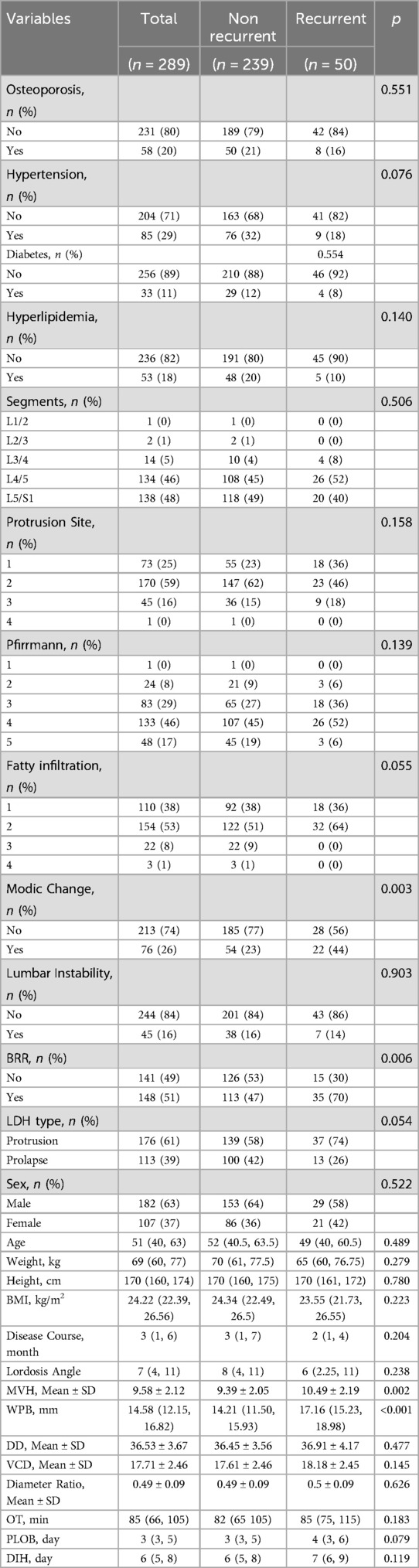
This retrospective study included data from 289 patients diagnosed with lumbar disc herniation (LDH) who underwent unilateral biportal endoscopic (UBE) surgery in the Spinal Department of Wuxi Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing University of Traditional Chinese Medicine between January 1, 2022, and December 31, 2023. Among these, 50 patients experienced recurrence of LDH (rLDH), while the remaining 239 did not. Recurrence was assessed through clinical and imaging follow-up at 12 months postoperatively. Patients with unresolved symptoms underwent additional MRI scans to confirm recurrence. The study was approved by the Ethics Review Committee of the Wuxi Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine.
2.2 Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Inclusion criteria:
1. Age between 17 and 87 years.
2. Underwent unilateral two-channel spinal endoscopy.
3. First-time surgery.
4. Availability of complete clinical data.
Exclusion criteria:
1. History of lumbar surgery or contraindications to surgery or anesthesia.
2. Presence of lumbar tumors.
3. Diagnosis of mental illness.
4. Severe heart, liver, or kidney dysfunction.
5. Lumbar spine fractures, malformations, or tuberculosis.
The study design and patient selection process are illustrated in Figure 1.
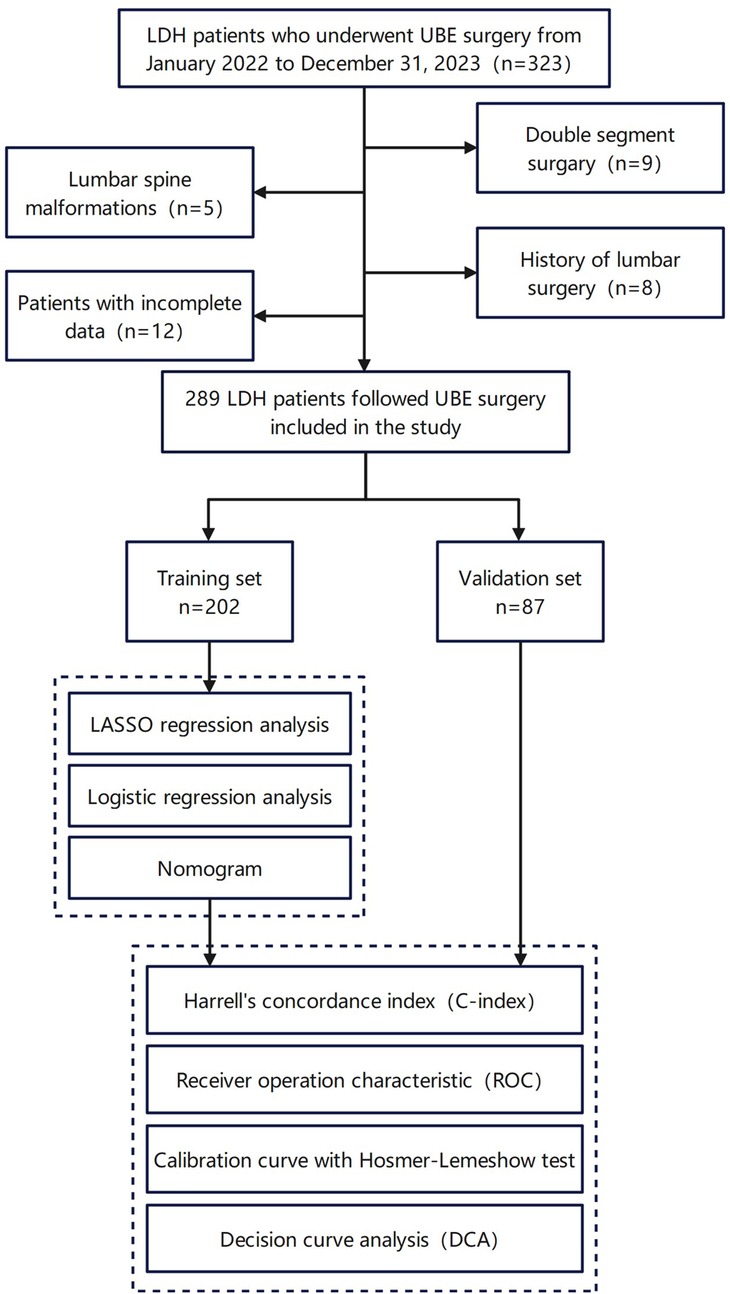
Figure 1. The design process of the research. This figure includes the inclusion and exclusion of patients, as well as the final number and grouping of study participants.
2.3 Data collection and potential predictors
The dataset comprised the following three categories of clinical parameters:
2.3.1 Patient baseline characteristics
Sex, age, height, weight, body mass index (BMI), osteoporosis, hypertension, diabetes, hyperlipidemia, disease duration, postoperative time to ambulation (PLOB), and length of hospital stay (DIH).
2.3.2 Operative data
Surgical segment, bone removal range (BRR), and operation time (OT). BRR was quantified as the percentage of the superior articular process resected during surgery (low resection: <50%) using pre- and postoperative CT scans.
2.3.3 Imaging parameters
LDH Type: Classified as protrusion (contained) or prolapse (non-contained) based on the Michigan State University (MSU) classification criteria.Width of Protrusion Base (WPB): Maximum transverse diameter of the herniated disc base on axial MRI.Middle Vertebral. Height (MVH): Distance between midpoints of adjacent vertebral endplates on sagittal MRI.
Disc diameter (DD), vertebral canal diameter (VCD), and diameter ratio (DD/VCD). Degeneration and Stability Assessments: Lumbar instability, Pfirrmann degeneration grade (PC), fat infiltration classification (FIC), and lumbar lordotic angle (LLA). Modic changes were classified as Type III based on MRI criteria (vertebral endplate sclerosis without bone marrow edema).
2.4 Logistic regression analysis and nomogram development
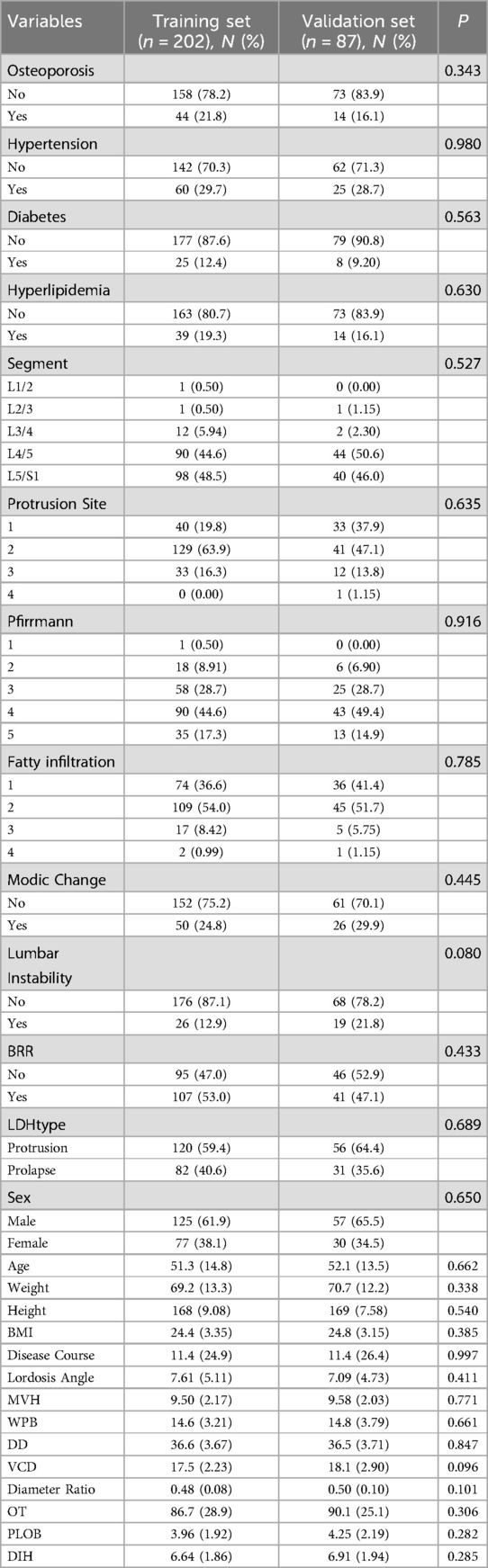
The 289 patients were randomly divided into training and validation sets in a 7:3 ratio (7, 8). No significant differences were observed in demographic or clinical characteristics between the two groups. LASSO regression analysis was performed on the training set to identify potential predictors, effectively eliminating variables with minimal correlation or multicollinearity to address high-dimensional data issues (9). Multivariate logistic regression analysis was then applied to identify five key predictive variables, which were used to construct a nomogram based on the training set. The model was subsequently validated using the validation set.
2.5 Model performance and validation
Model performance was assessed using discrimination and calibration metrics (10). Discrimination was quantified using Harrell's concordance index (C-index) and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis, with an AUC value above 0.80 considered indicative of good discrimination (11–13). Calibration was evaluated using calibration curves and the Hosmer-Lemeshow test, assessing the agreement between predicted and observed rLDH occurrence rates (14). Decision curve analysis (DCA) was conducted to evaluate the model's clinical utility and net benefit (15). All assessments were performed using bootstrap validation with 1,000 resamples.
2.6 Statistical analysis
Statistical analyses and data visualization were performed using R software version 4.4.1 (The R Project for Statistical Computing, https://www.r-project.org). Continuous variables with a normal distribution were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD), while those with a skewed distribution were presented as the median [M] and interquartile range [Q25–Q75]. Independent t-tests were used for group comparisons of continuous data with equal variance, while unequal variance t-tests were applied for datasets with unequal variances. Model fit was evaluated using the Hosmer-Lemeshow goodness-of-fit test. Model performance was assessed using discrimination metrics (C-statistic) and calibration curves. To mitigate overfitting and quantify optimism, the nomogram underwent internal validation with bootstrap resampling (1,000 iterations), and an optimism-corrected C-statistic was calculated. Clinical validity and net benefit of the nomogram were further assessed using DCA (15).
Logistic regression analysis and nomogram development were performed using R packages including rms, pROC, forestplot, corrplot, glmnet, caret, CBCgrps, nortest, ggpubr, compareGroups, regplot, ggplot2, and rmda. Bilateral p-values < 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
3 Results
3.1 Patient characteristics
As shown in Table 1, this study included 289 eligible patients, who were randomly assigned to the training set (n = 202) and validation set (n = 87). Among them, 50 patients developed recurrent lumbar disc herniation (rLDH) postoperatively, with 32 in the training set and 18 in the validation set. Statistical analysis revealed no significant differences between the training and validation sets in baseline characteristics (P > 0.05). Details of the baseline characteristics are presented in Table 2.
3.2 Identification of predictive factors
To identify the most relevant predictive factors, a two-step filtering process was employed. First, least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) regression was performed, which helped to minimize overfitting and enhance model robustness by selecting six potential predictors: Middle Vertebral Height (MVH), Modic Change, Width of Protrusion Base (WPB), Bone Removal Range (BRR), and LDH Type (Figures 2A,B).
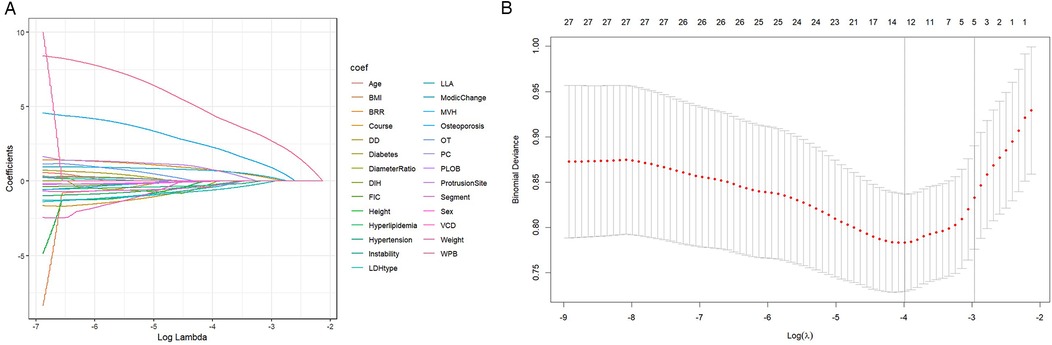
Figure 2. LASSO regression path diagram for variable selection. (A) Variable screening: The convergence point of the curve in the figure indicates the key variables selected, including WPB, BRR, etc. (B) Penalty coefficient: The X-axis shows the influence of the change of penalty coefficient on variable screening. The model prevents overfitting by controlling the penalty coefficient.
Subsequently, multivariate logistic regression analysis confirmed the independence of these predictors. Key findings included:
• MVH (OR = 0.30, 95% CI: 0.12–0.499, P = 0.001)
• Modic Change (OR = 1.16, 95% CI: 0.40–1.93, P = 0.003)
• WPB (OR = 0.30, 95% CI: 0.19–0.42, P < 0.001)
• BRR (OR = 1.22, 95% CI: 0.48–2.022, P = 0.002)
• LDH Type (OR = −1.04, 95% CI: −1.86 to −0.28, P = 0.009).
A nomogram was subsequently developed to predict the probability of rLDH using these five predictive variables (Figure 3).
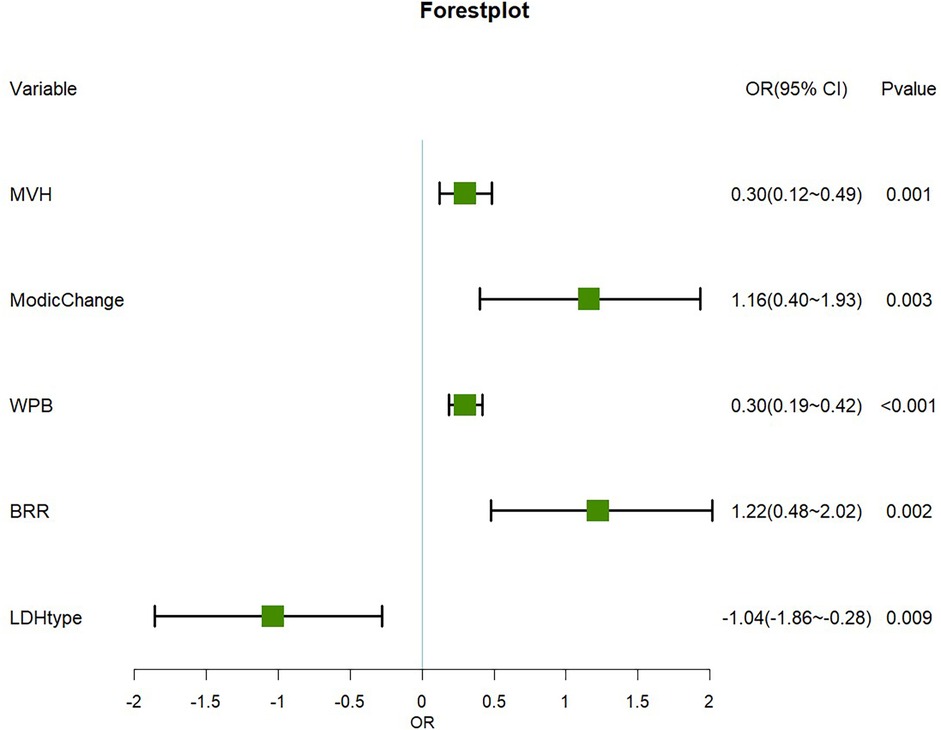
Figure 3. Forest plot of the main predictor variables. Important risk factors: WPB, BRR, Modic changes and MVH significantly increase the risk of recurrence (OR > 0). Protective factor: The LDH type was determined as the protective factor (OR < 0).
3.3 Development of an individualized prediction model
The nomogram integrated the identified predictors and revealed their relative contributions to the risk of rLDH. Among the predictors, WPB emerged as the strongest risk factor, followed by MVH, Modic Change, and BRR. On the other hand, disc prolapse were identified as protective factors. The nomogram provides a personalized assessment of recurrence risk, facilitating clinical decision-making (Figure 4).
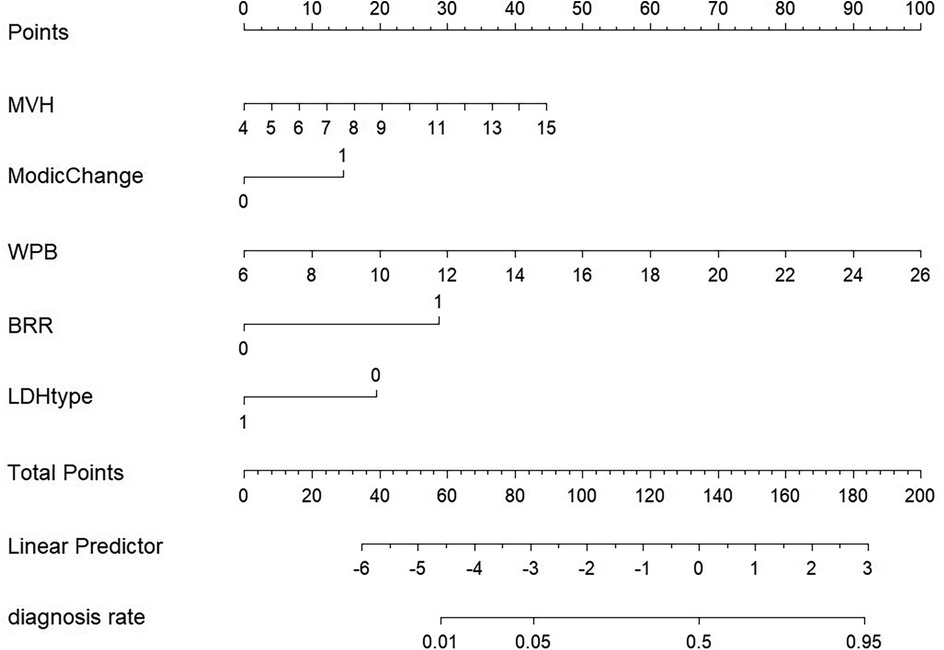
Figure 4. Column diagram model. A cumulative score helps doctors assess individual risk. Risk factors include widthprotruded base (WPB), extent of bone resection (BRR), Modic changes, type of lumbar disc herniation (LDH type), and middle vertebral height (MVH).
3.4 Predictive model validation
3.4.1 Discrimination
The model demonstrated strong discriminative ability, as indicated by C-index values of 0.834 for the training set and 0.804 for the validation set. Additionally, area under the curve (AUC) values were 0.834 (95% CI: 0.750–0.918) in the training set and 0.804 (95% CI: 0.697–0.910) in the validation set, further supporting the model's robust discrimination (Figures 5A,B).
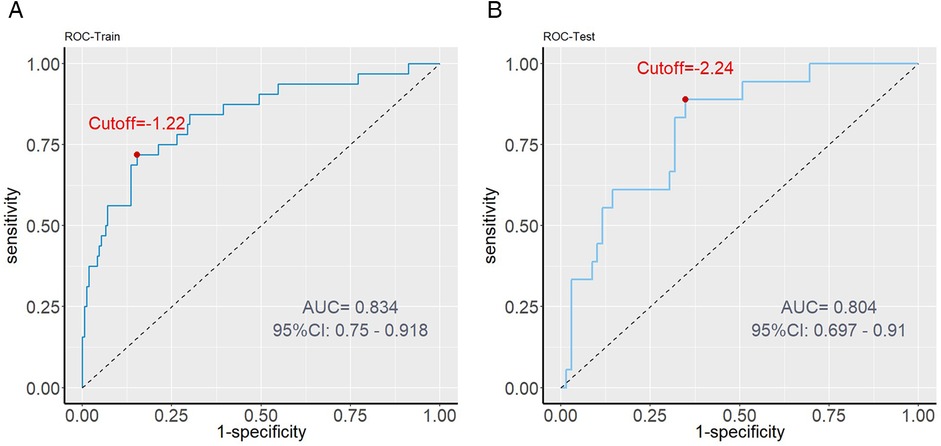
Figure 5. ROC curve analysis. (A) Training set performance: The AUC value is 0.834, indicating that the model has high predictive ability in internal data. (B) Validation set performance: AUC value of 0.804 proves the robustness of the model in external data.
3.4.2 Calibration
The calibration curves showed excellent agreement between predicted and actual probabilities of rLDH occurrence in both the training (χ² = 7.92, df = 8, P = 0.442) and validation sets (χ² = 7.90, df = 8, P = 0.444). These results indicate that the model is well-calibrated (Figure 6).
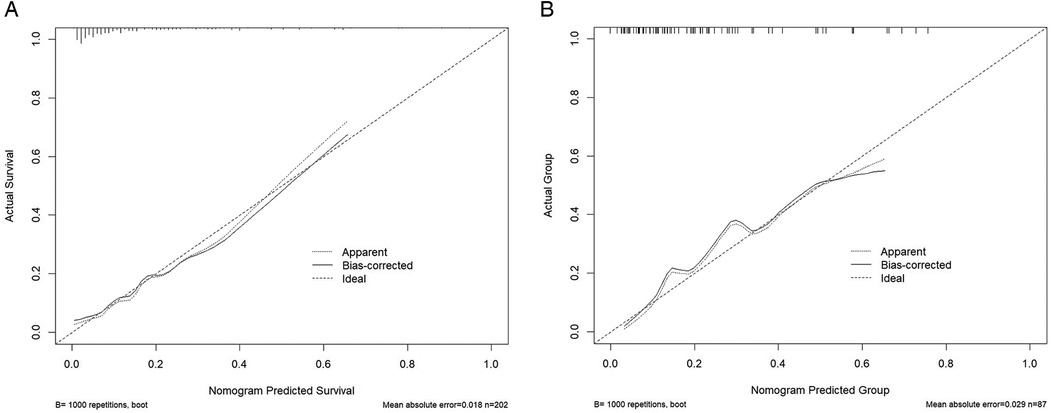
Figure 6. Calibration curve. (A) Training set calibration: The training set curve is close to the diagonal, indicating that the predicted value is highly consistent with the actual value. (B) Verification set calibration: The verification set curve further proves that the model has good calibration ability.
3.4.3 Clinical application
Decision curve analysis (DCA) demonstrated that the nomogram provides significant net benefits for predicting rLDH across a wide range of risk thresholds (4%–63%) in both the training and validation sets. This suggests the nomogram's practical utility in guiding clinical interventions (Figure 7).
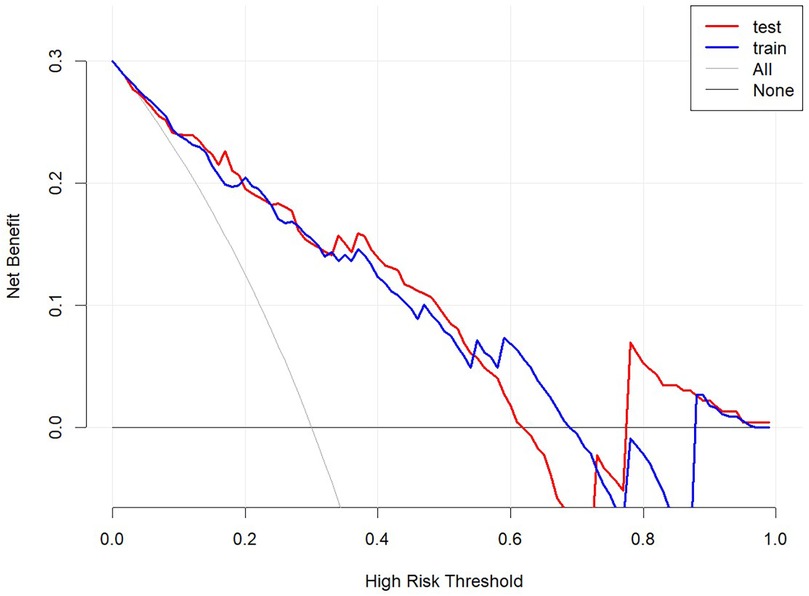
Figure 7. Decision curve analysis. Net benefit curve: Within the threshold probability range of 4%–63%, the model provides A higher net benefit than no intervention or full intervention strategies. Baseline comparison: The baseline comparison indicates that the model forecasts better and can effectively reduce unnecessary interventions.
4 Discussion
The causes of recurrent lumbar disc herniation (rLDH) following endoscopic surgery remain a topic of considerable debate (16, 17). While previous studies have examined a wide range of factors associated with rLDH, the conclusions often vary. For instance, Guray Bulut et al. found that variables such as gender, age, diabetes mellitus (DM), obesity, surgical level, disc degeneration, and disc type were not significantly associated with rLDH, though hypertension (HT) appeared more prevalent in recurrent cases (18). Mengxian Jia, using a directed mutation-guided SVM model, highlighted factors like herniated disc level, Modic changes, disc height, disc length, and disc width as critical predictors for rLDH (19). Furthermore, multivariate logistic regression analysis by other researchers showed that comorbid diabetes and smoking significantly increased the risk of recurrence (20). Despite these findings, many of these factors remain insufficiently validated, necessitating further investigation.
To address this gap, we developed and validated the first nomogram specifically designed to assess rLDH risk in lumbar disc herniation (LDH) patients undergoing unilateral biportal endoscopic (UBE) surgery. By incorporating key clinical features—WPB, BRR, Modic Change, LDH Type, and MVH—this model demonstrated excellent predictive performance and offers clinicians a valuable tool for early intervention and risk mitigation.
In this study, WPB emerged as the strongest risk factor. A larger protrusion base indicates more extensive annulus fibrosus damage, increasing the likelihood of residual nucleus pulposus fragments after surgery. This often necessitates more aggressive annulus removal to achieve decompression, which may, in turn, exacerbate annular tears and defects. These defects not only accelerate disc degeneration but also contribute to nerve root adhesion and aseptic inflammation, both of which are significant contributors to chronic postoperative low back pain (21).
Similarly, LDH Type was identified as a critical predictor. Shan et al. reported that free disc herniation independently increases recurrence risk after lumbar discectomy (22), while Yurac et al. highlighted the role of non-encapsulated disc herniation and annular rupture in predicting rLDH (23). Yao et al. found that central disc herniation was associated with recurrence, likely due to challenges in adequately removing contralateral nucleus pulposus tissue (24). Although variations exist in reported findings, there is consensus that annular rupture and central or free disc herniation are significant risk factors for recurrence.
Our findings indicate that patients with higher MVH and more extensive BRR are at greater risk of early rLDH. The intervertebral discs and facet joints are critical for maintaining the biomechanical stability of the lumbar spine. Studies suggest that removing more than 50% of the superior facet joint during surgery significantly destabilizes the lumbar spine (25, 26). Furthermore, finite element analyses have shown that removing the base of the upper articular process increases facet joint stress more than removing its tip, particularly during lateral flexion, extension, and rotation (27). These findings underscore the importance of minimizing structural damage to preserve stability and reduce the risk of rLDH.
Type III Modic changes, characterized by sclerotic endplate alterations, may exacerbate disc degeneration through impaired nutrient supply, aligning with our findings. Modic Change is another key predictor of rLDH. It results from cartilage endplate fractures and inflammatory responses that impair the nutrient supply to the intervertebral disc, hindering annulus fibrosus repair and promoting disc degeneration (28, 29). Studies have confirmed Modic Change as a risk factor for postoperative recurrence, consistent with our findings (24, 30).
The developed model provides an effective tool for estimating the likelihood of early recurrence following single-segment UBE surgery in LDH patients. This predictive ability supports personalized patient management in several ways:
1. Preoperative Assessment: A thorough patient evaluation, including detailed history-taking and clinical examination, can identify high-risk patients. For such individuals, clinicians may consider more aggressive surgical approaches or alternative treatments to mitigate recurrence risks.
2. Risk Communication: By using the nomogram, clinicians can engage in informed discussions with patients and their families about surgical risks, outcomes, and postoperative expectations, improving shared decision-making and patient satisfaction.
3. Postoperative Monitoring and Intervention: High-risk patients can benefit from closer monitoring and early intervention strategies, potentially preventing recurrence and improving outcomes.
5 Limitations
However, the study had various limitations: Our model is trained and validated using data from a single center, and its generalization to other centers and regions needs to be clarified. Nevertheless, we have done our best to include variables that are easy to collect and to simplify the model to prevent overfitting. Of course, teams from other centers are also welcome to join our research and contribute more multi-center data to the research. The sample size of our study is still small. The maximum follow-up duration of 12 months may underestimate long-term recurrence rates. Future studies with extended follow-up periods are warranted to validate our findings. Although model performance is evaluated by training and validation sets, sample size may limit the generalization of results. As recognized, external validation provides a more rigorous assessment of model robustness. In contrast, noise or bias in the external validation data set may mask the actual model performance found through internal validation (31, 32). The study was conducted on patients from a single healthcare facility, and it remains challenging to eliminate the selection bias and information bias associated with a single-center sample. For example, excluding recurrent LDH cases likely underestimates the role of scar adhesion in long-term recurrence. Exclusive focus on Type III Modic changes limits generalizability to other subtypes. Further studies should explore the differential impacts of Modic I and II changes on recurrence risk (33, 34). Therefore, conducting multi-center and prospective cohort studies is essential for more thorough exploration. While using nomograms improves models' interpretability, machine learning models' interpretability remains challenging.
For non-technical people, such as clinicians and patients, the model's decision-making process may need to be more transparent. In the future, we aim to integrate machine learning models into electronic medical record systems. This integration will allow us to predict individual cases by extracting patient information and metrics. Subsequently, we plan to present the predictions directly to doctors and patients to improve the usability of the model.
6 Conclusion
This study identified five independent predictors of recurrent lumbar disc herniation (rLDH) in patients undergoing unilateral biportal endoscopic (UBE) surgery, culminating in the development of an innovative nomogram model. The model exhibited excellent internal and external validation performance, offering clinicians a reliable tool for identifying high-risk patients and enabling personalized care and targeted management strategies. However, further extensive research and multi-center validation are necessary to enhance the model's generalizability and robustness.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by IRB of Wuxi Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation was not required from the participants or the participants' legal guardians/next of kin in accordance with the national legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
YR: Conceptualization, Methodology, Formal analysis, Writing – original draft. KW: Methodology, Investigation, Writing – original draft. YP: Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. TZha: Data curation, Methodology, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YM: Project administration, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. LW: Project administration, Writing – review & editing. YG: Writing – review & editing, Visualization. SC: Formal analysis, Data curation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YS: Investigation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. TZhu: Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. SW: Investigation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. ZH: Funding acquisition, Data curation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. JW: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. HY: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 82274546), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82205142), the Top Talent Support Program for young and middle-aged people of Wuxi Health Committee (HB 2023073) and the Postgraduate Research & Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province (KYCX22_2062).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Fei-Long W, Cheng-Pei Z, Kai-Long Z, Du MR, Liu Y, Heng W, et al. Comparison of different operative approaches for lumbar disc herniation: a network meta-analysis and systematic review. Pain Physician. (2021) 24(4):e381–92. doi: 10.36076/ppj.2021.24.e381
2. Kim KR, Park JY. The technical feasibility of unilateral bi portal endoscopic decompression for the unpredicted complication following minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: case report. Neurospine. (2020) 17(Suppl 1):S154–9. doi: 10.14245/ns.2040174.087
3. Swartz KR, Trost GR. Recurrent lumbar disc herniation. Neurosurg Focus. (2003) 15(3):E10. doi: 10.3171/foc.2003.15.3.10
4. Li Z, Tang J, Hou S, Ren D, Li L, Lu X, et al. Four-year follow-up results of transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion as revision surgery for recurrent lumbar disc herniation after conventional discectomy. J Clin Neurosci. (2015) 22(2):331–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2014.06.098
5. Wang HF, Song Y, Wang NG. Comparative analysis of unilateral biportal endoscopic discectomy, percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy, and fenestration discectomy in treatment of lumbar disc herniation. Chin J Reparative Reconstr Surg. (2022) 36(10):1200–6. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.202205129
6. Kang TW, Park SY, Oh H, Lee SH, Park JH, Suh SW. Risk of reoperation and infection after percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy and open lumbar discectomy: a nationwide population-based study. Bone Joint J. (2021) 103-B(8):1392–9. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.103B8.BJJ-2020-2541.R2
7. Groos D, Adde L, Aubert S, Boswell L, de Regnier R-A, Fjørtoft T, et al. Development and validation of a deep learning method to predict cerebral palsy from spontaneous movements in infants at high risk. JAMA Netw Open. (2022) 5:e2221325. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.21325
8. Chen Q, Pan T, Wang YN, Schoepf UJ, Bidwell SL, Qiao H, et al. A coronary CT angiography radionics model to identify vulnerable plaque and predict cardiovascular events. Radiology. (2023) 307:e221693. doi: 10.1148/radiol.221693
9. Hu J-Y, Wang Y, Tong X-M, Yang T. When to consider logistic LASSO regression in multivariate analysis? Eur J Surg Oncol. (2021) 47:2206. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2021.04.011
10. Mejia OAV, Borgomoni GB, Palma Dallan LR, Mioto BM, Duenhas Accorsi TA, Lima EG, et al. Quality improvement program in Latin America decreases mortality after cardiac surgery: a before-after intervention study. Int J Surg. (2022) 106:106931. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2022.106931
11. Yu A, Li Y, Zhang H, Hu G, Zhao Y, Guo J, et al. Development and validation of a preoperative nomogram for predicting the surgical difficulty of laparoscopic colectomy for right colon cancer: a retrospective analysis. Int J Surg. (2023) 109:870–8. doi: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000000352
12. Mandrekar JN. Receiver operating characteristic curve in diagnostic test assessment. J Thorac Oncol. (2010) 5:1315–6. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e3181ec173d
13. Révész D, van Kuijk SMJ, Mols F, van Duijnhoven FJB, Winkels RM, Kant I, et al. External validation and updating of prediction models for estimating the 1-year risk of low health-related quality of life in colorectal cancer survivors. J Clin Epidemiol. (2022) 152:127–39. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2022.09.019
14. Osinaike B, Ayandipo O, Onyeka T, Alagbe-Briggs O, Mohammed A, Oyedepo O, et al. Nigerian surgical outcomes—report of a 7-day prospective cohort study and external validation of the African surgical outcomes study surgical risk calculator. Int J Surg. (2019) 68:148–56. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2019.06.003
15. Van Calster B, Wynants L, Verbeek JFM, Verbakel JY, Christodoulou E, Vickers AJ, et al. Reporting and interpreting decision curve analysis: a guide for investigators. Eur Urol. (2018) 74:796–804. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2018.08.038
16. Quah C, Syme G, Swamy GN, Nanjayan S, Fowler A, Calthorpe D, et al. Obesity and recurrent intervertebral disc prolapse after lumbar microdiscectomy. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. (2014) 96(2):140–3. doi: 10.1308/003588414X13814021676873
17. Li Y, Wang B, Li H, Chang X, Wu Y, Hu Z, et al. Adjuvant surgical decision-making system for lumbar intervertebral disc herniation after percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy: a retrospective nonlinear multiple logistic regression prediction model based on a large sample. Spine J. (2021) 21(12):2035–48. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2021.07.012
18. Bulut G, Işık S, Etli MU, Yaltırık CK. The impact of demographic characteristics, obesity, surgical level, and intervertebral disc properties on recurrence of lumbar disc herniation. World Neurosurg. (2024) 190:e748–53. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2024.07.214
19. Jia M, Lai J, Li K, Chen J, Huang K, Ding C, et al. Optimizing prediction accuracy for early recurrent lumbar disc herniation with a directional mutation-guided SVM model. Comput Biol Med. (2024) 173:108297. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2024.108297
20. Dokponou YCH, Obame FLO, Mouhssani M, Sofia EA, Siba Z, Saad ME, et al. Cross-sectional study of recurrent disc herniation risk factors and predictors of outcomes after primary lumbar discectomy: a STROBE compliance. Interdiscip Neurosurg. (2023) 33:101777. doi: 10.1016/j.inat.2023.101777
21. DePalma MJ, Ketchum JM, Saullo TR, Laplante BL. Is the history of a surgical discectomy related to the source of chronic low back pain. Pain Physician. (2012) 15(1):E53–58. doi: 10.36076/ppj.2012/15/E53
22. Shan Z-M, Ren X-S, Shi H, Zheng S-J, Zhang C, Zhuang S-Y, et al. Machine learning prediction model and risk factor analysis of reoperation in recurrent lumbar disc herniation patients after percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy. Global Spine J. (2024) 14(8):2240–51. doi: 10.1177/21925682231173353
23. Yurac R, Zamorano JJ, Lira F, Valiente D, Ballesteros V, Urzúa A. Risk factors for the need of surgical treatment of a first recurrent lumbar disc herniation. Eur Spine J. (2016) 25(5):1403–8. doi: 10.1007/s00586-015-4272-8
24. Yao Y, Liu H, Zhang H, Wang H, Zhang C, Zhang Z, et al. Risk factors for recurrent herniation after percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy. World Neurosurg. (2017) 100:1–6. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2016.12.089
25. Gibson JNA, Cowie JG, Iprenburg M. Transforaminal endoscopic spinal surgery: the future gold standard for discectomy?–A review. Surgeon. (2012) 10(5):290–6. doi: 10.1016/j.surge.2012.05.001
26. Yu Y, Zhou Q, Xie Y, Wang X, Fan X, Gu D, et al. Effect of percutaneous endoscopic lumbar foraminoplasty of different facet joint portions on lumbar biomechanics: a finite element analysis. Orthop Surg. (2020) 12(4):1277–84. doi: 10.1111/os.12740
27. Wu Z, Sun H, Zhang Y, Xiao L, Zhao Q. Biomechanical finite element analysis of percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy via a transforaminal approach. World Neurosurg. (2024) 185:e291–8. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2023.10.108
28. Chen Y, Yang H, Wang Y, Zou J. Relationship of endplate changes and low back pain after discectomy. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. (2019) 184:105449. doi: 10.1016/j.clineuro.2019.105449
29. Urban JP, Smith S, Fairbank JC. Nutrition of the intervertebral disc. Spine. (2004) 29(23):2700–9. doi: 10.1097/01.brs.0000146499.97948.52
30. Ren G, Liu L, Zhang P, Xie Z, Wang P, Zhang W, et al. Machine learning predicts recurrent lumbar disc herniation following percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy. Global Spine J. (2024) 14(1):146–52. doi: 10.1177/21925682221097650
31. Lee JH, Choi KC, Lee JH. Could the splitting of the annulus during percutaneous endoscopic lumbar diskectomy (PELD) be a culprit for recurrent disk herniation? An analysis of the reherniation pattern after PELD. World Neurosurg. (2019) 132:e623–9. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2019.08.061
32. McGirt MJ, Eustacchio S, Varga P, Vilendecic M, Trummer M, Gorensek M, et al. A prospective cohort study of close interval computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging after primary lumbar discectomy: factors associated with recurrent disc herniation and disc height loss. Spine. (2009) 34(19):2044–51. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181b34a9a
33. Park CH, Park ES, Lee SH, Lee KK, Kwon YK, Kang MS, et al. Risk factors for early recurrence after transforaminal endoscopic lumbar disc decompression. Pain Physician. (2019) 2(22.2):E133–8. doi: 10.36076/ppj/2019.22.E133
Keywords: LDH, UBE, recurrence, nomogram, prediction model
Citation: Rong Y, Wang K, Pan Y, Zhang T, Ma Y, Wang L, Guo Y, Chen S, Shao Y, Zhu T, Wu S, Hua Z, Wang J and Yu H (2025) Nomogram for prediction of recurrence in patients with lumbar disc herniation after unilateral biportal endoscopy spinal surgery: a retrospective study. Front. Surg. 12:1564825. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2025.1564825
Received: 22 January 2025; Accepted: 30 April 2025;
Published: 16 June 2025.
Edited by:
Osvaldo Mazza, Bambino Gesù Children's Hospital (IRCCS), ItalyReviewed by:
Sherwan Hamawandi, Hawler Medical University, IraqYoukang Dong, Yunnan University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, China
Copyright: © 2025 Rong, Wang, Pan, Zhang, Ma, Wang, Guo, Chen, Shao, Zhu, Wu, Hua, Wang and Yu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jianwei Wang, d3h6eTAwNkBuanVjbS5lZHUuY24=; Hao Yu, eXVoYW80OTU0MjIxOTBAcXEuY29t
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Yi Rong1,†
Yi Rong1,† Tianchi Zhang
Tianchi Zhang Yong Ma
Yong Ma Lining Wang
Lining Wang Yang Guo
Yang Guo Jianwei Wang
Jianwei Wang