- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Peking University China-Japan Friendship School of Clinical Medicine, Beijing, China
- 2Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Suqian First People's Hospital, Suqian, Jiangsu, China
- 3Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Center for Osteonecrosis and Joint Preserving & Reconstruction, China-Japan Friendship Hospital, Beijing, China
Background: Chronic ankle instability (CAI) is a prevalent condition often treated with the Broström procedure, sometimes modified by Gould. This study aims to compare the clinical outcomes of patients undergoing the Broström procedure with and without the Gould modification, focusing on the implications for CAI management.
Methods: A comprehensive search was conducted across PubMed, EMBASE, Wiley Library, Science Direct, Europe PMC, and Scopus for studies comparing the Broström procedure with and without the Gould modification. The search spanned from the inception of these databases to October 12, 2024, using specific terms related to ankle instability and ligament repair.
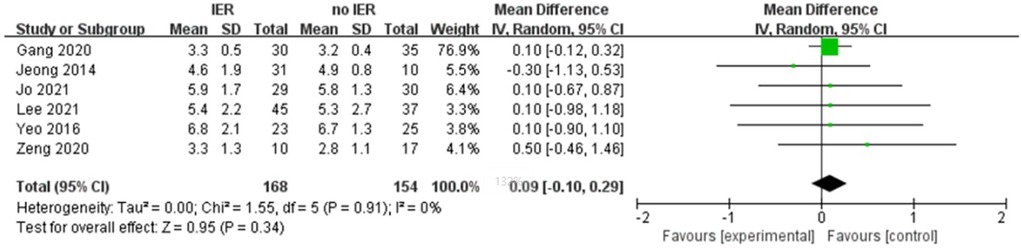
Results: Our meta-analysis revealed that there was no significant difference in AOFAS scores, indicating a weak correlation between AOFAS scores and reinforcement of the Inferior Extensor Retinaculum (IER) [mean difference −1.14 (−2.16, −0.11), p = 0.03 I2:0%, p = 1.000]. Similarly, the reinforcement of IER showed a low correlation with Karlsson scores [mean difference −0.15 (−2.25, 1.96), p = 0.89; I2: 48%, p = 0.07]. The results for talar tilt [mean difference −0.11° (−0.37, 0.15), p = 0.42; I2:0%, p = 0.87] and anterior talar translation [mean difference 0.09 mm (−0.10, 0.29), p = 0.34; I2:0%, p = 0.91] were similar between the two groups at follow-up. The funnel plots for AOFAS scores, talar tilt, and complications were symmetrical, indicating no publication bias or other biases in the studies.
Conclusions: The findings suggest that for patients with CAI, the Broström procedure with or without the Gould modification yields comparable postoperative functional outcomes. This has significant implications for the surgical management of CAI, potentially simplifying treatment protocols.
Level of evidence: Level II, systematic review of Level II studies.
Introduction
Ankle sprains are one of the most common recurrent injuries in the lower limbs. Additionally, approximately 20% of acute sprain patients develop chronic ankle instability (CAI) (1). When conservative rehabilitation for CAI fails, surgical treatment is required to reconstruct ankle joint mechanical stability. The original direct anatomical repair of the lateral ankle ligaments described by Broström in 1966 remains the most popular surgical procedure (2). Furthermore, in 1980, Gould proposed the idea of further tightening the inferior extensor retinaculum (IER) on the basis of the Broström procedure, and has achieved good clinical results (3–6). Subsequently, with the use and improvement of arthroscopic techniques, arthroscopic treatment of chronic ankle instability (CAI) has gradually become the mainstream surgery, with recent reports of anatomical repair of the lateral ankle ligaments with or without Gould modification (IER reinforcement) showing good results in the majority of cases (7–9). However, studies comparing the Broström procedure with vs. without the Gould modification—whether performed via open surgery or arthroscopically—have consistently reported no significant differences in clinical outcomes for chronic ankle instability (CAI) (10–18).
Another issue that has been observed in Behrens study is that approximately 64% of the inferior extensor retinaculum (IER) has an X-shaped structure, with only the anterior talofibular ligament (ATFL) located near it (19). However, the anterior talofibular ligament is a weak tissue band, and when used to reinforce ATFL repair, it may have minimal impact on improving ankle joint stability. Furthermore, in all cases, the superficial peroneal nerve essentially passes through the IER anatomically, which may lead to an increased risk of complications following the Broström procedure with Gould modification (12).
As there are conflicting conclusions in current literature and a lack of consensus among physicians regarding the performance of the Broström procedure with or without the Gould modification, the purpose of this review is to conduct a meta-analysis of the current literature and compare patient-reported outcome measures (PROM) in patients undergoing ankle ligament repair (with or without ankle bony reconstruction). We hypothesize that there is no significant clinical difference between patients undergoing the Broström procedure with the Gould modification and those without it.
Methods
This study follows the recommendation by the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses. PROSPERO Registration Number: CRD420251024846.
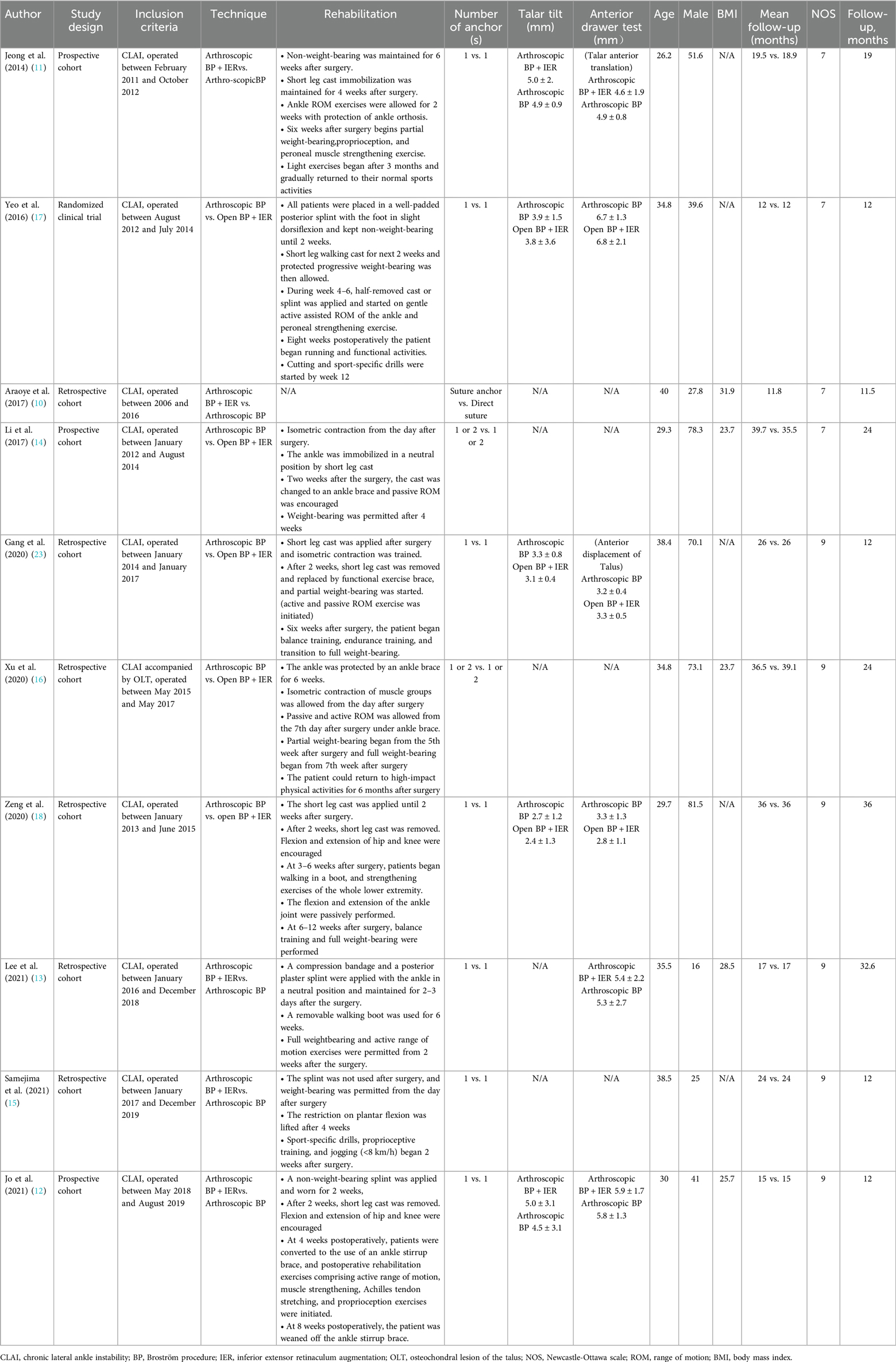
We conducted a search in PubMed, EMBASE, Wiley Library, Science Direct, Europe PMC, and Scopus, to retrieve all publications comparing the outcomes of patients undergoing the Broström procedure with or without the Gould modification. The search terms included: “(Brostrom OR Gould OR Inferior Extensor Retinaculum Augmentation OR Anterior Talofibular Ligament Repair OR inferior extensor retinaculum) AND (lateral ankle OR ankle instability)”, covering the period from the establishment of the databases to October 12, 2024. Two independent reviewers excluded review articles, case reports, case series, cadaveric studies, basic science research, animal studies, studies with incomplete reporting methods, and studies that did not directly compare the Broström procedure with the Gould modification to the Broström procedure without the Gould modification. At each stage of the selection process, any discrepancies in study selection were discussed and resolved by the two independent reviewers. The characteristics of the included studies were synthesized and described in the methods section. In cases where there were discrepancies in the assessment of risk of bias, the two reviewers discussed and resolved the differences. Table 1 describes the various rehabilitation regimens included in the selected studies. Ankle function scores (AOFAS and Karlsson scores), measurements of talar tilt, anterior talar translation were used to estimate the mean difference in outcomes, and odds ratios (OR) for complications.
The AOFAS score can be used to grade the level of ankle function (20). A score of 100 points is given if the patient is free of pain, has a wide range of sagittal and hindfoot motion, with no instability in the ankle or hindfoot, good alignment, able to walk more than six blocks, walk on any surface, no significant limping, and no restriction in daily or recreational activities, without the need for walking aids. Fifty points are assigned to function, 40 points to pain, and 10 points to alignment. The Karlsson-Peterson score, on the other hand, assesses functional outcomes based on joint instability, pain, swelling, and stiffness, with a maximum score of 100 (21). We conducted a meta-analysis using Review Manager 5.3. A restricted maximum likelihood (REML) random-effects model was applied to calculate the mean differences (MDs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for AOFAS score, Karlsson score, talar tilt, and anterior drawer test between the intervention and control groups. Additionally, a DerSimonian-Laird random-effects model was used to estimate the odds ratio (OR) and 95% CIs for complications. To assess interstudy heterogeneity, we performed I2 statistics and Cochran's Q-test, with I2 > 50% and p < 0.10 indicating substantial heterogeneity. Furthermore, we conducted a meta-regression analysis with age, male proportion, and BMI as covariates. Sensitivity analysis was performed by excluding studies with potential selection bias to evaluate the robustness of the results.
Results
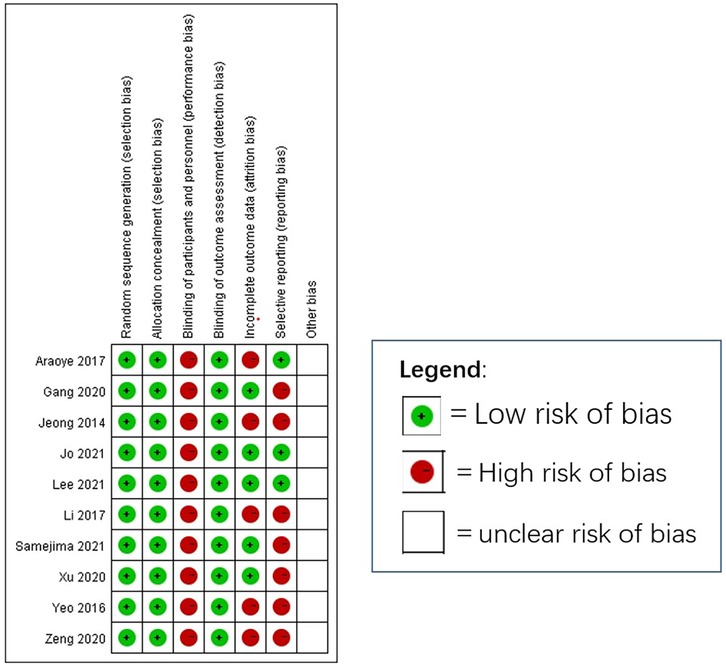
We initially identified 1,518 studies from the databases. After removing duplicates, 1,090 studies remained. Based on inclusion/exclusion criteria (e.g., randomized controlled trials, observational studies) and excluding non-comparative research (e.g., reviews, case reports, animal studies), we screened 28 studies for eligibility. Studies were excluded if they did not directly compare the Broström procedure with the Gould modification to the Broström procedure without the Gould modification. Ultimately, 10 studies (n = 635 patients) were included. The mean follow-up period was 19.5months (11.5–36 months) across all included studies. We summarized the selection process for each study in Figure 1 and presented the 10 studies in Table 1. Figure 2 (Cochrane risk of bias tool for randomized studies) provided a summary of the risk of bias assessment, with a κ score of 0.7, indicating substantial agreement. We analyzed four outcomes: ankle function scores (AOFAS and Karlsson scores), talar tilt, and anterior talar translation for the included studies.
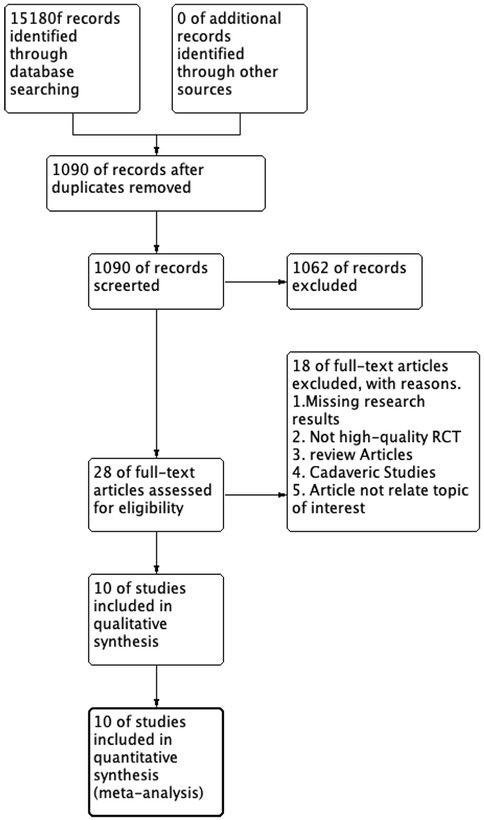
Figure 1. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses diagram on article selection for systematic review.
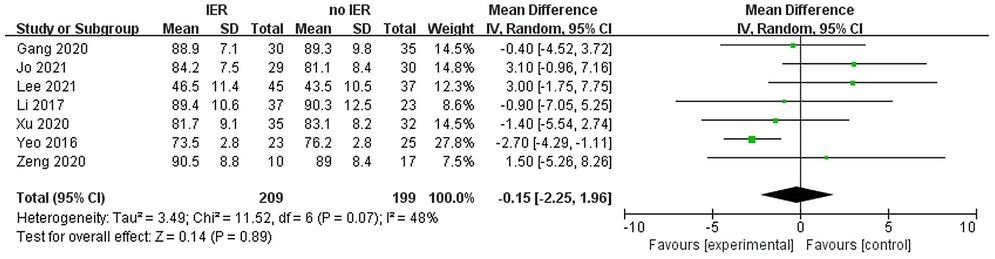
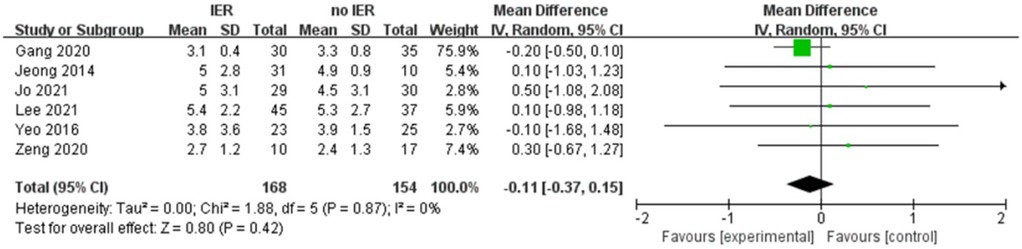
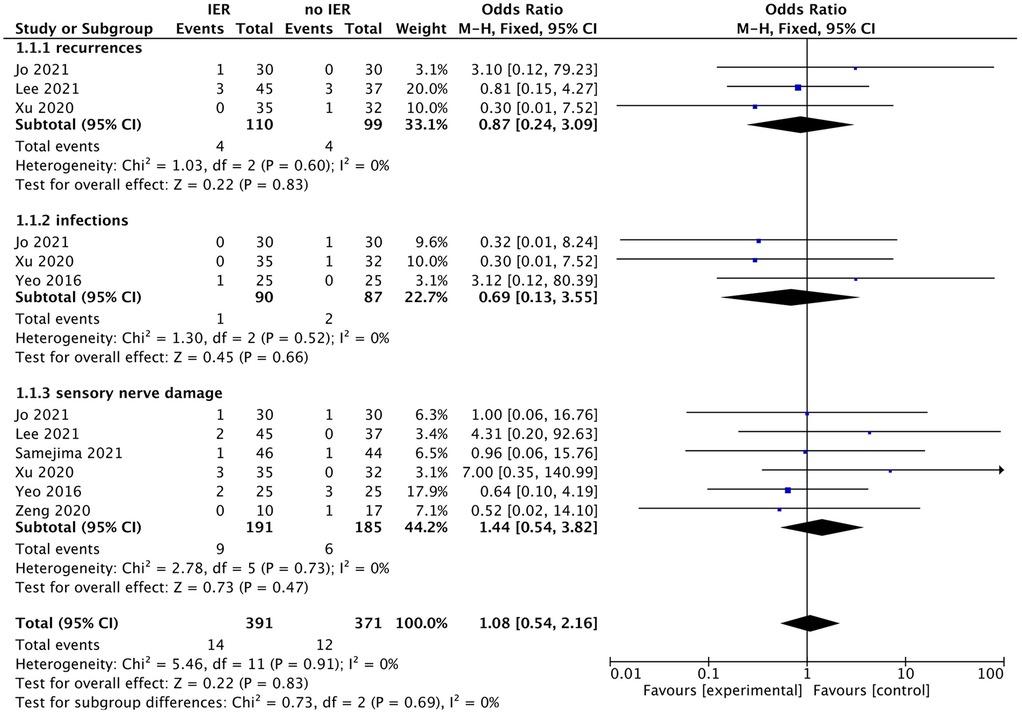
Our meta-analysis revealed that there was no significant difference in AOFAS scores, indicating a weak correlation between AOFAS scores and reinforcement of the Inferior Extensor Retinaculum (IER) [mean difference −1.14 (−2.16, −0.11), p = 0.03 I2:0%, p = 1.000] (Figure 3). Similarly, the reinforcement of IER showed a low correlation with Karlsson scores [mean difference −0.15 (−2.25, 1.96), p = 0.89; I2: 48%, p = 0.07] (Figure 4). The results for talar tilt [mean difference −0.11° (−0.37, 0.15), p = 0.42; I2:0%, p = 0.87] (Figure 5) and anterior talar translation [mean difference 0.09 mm (−0.10, 0.29), p = 0.34; I2:0%, p = 0.91] were similar between the two groups at follow-up (Figure 6). No statistically significant differences were observed between arthroscopic non-IER augmentation and open IER augmentation in postoperative AOFAS scores [mean difference −1.11, 95% CI (−1.80, −0.01), p = 0.66; I2 = 0%, p = 1.000] or Karlsson scores [mean difference −2.00, 95% CI (−2.23, −0.45), p = 0.56; I2 = 2.63%, p < 0.001]. While minor heterogeneity was detected in Karlsson scores for the open IER group (I2 = 2.62%), its clinical impact was negligible. Subgroup analyses revealed no statistically significant differences in specific complications between the Broström procedure with and without IER reinforcement. The pooled odds ratios (ORs) were as follows: Recurrence: OR = 0.87 [95% CI (0.24, 3.09), p = 0.83; I2 = 0%]. Infections: OR = 0.69 [95% CI (0.13, 3.55), p = 0.66; I2 = 0%]. Sensory nerve damage: OR = 1.44 [95% CI (0.54, 3.82), p = 0.47; I2 = 0%]. The homogeneity (I2 < 15%) across all subgroups suggests minimal variability in complication reporting between studies (Figure 7). The funnel plots for AOFAS scores (Figure 8), talar tilt, and complications were symmetrical, indicating no publication bias or other biases in the studies.
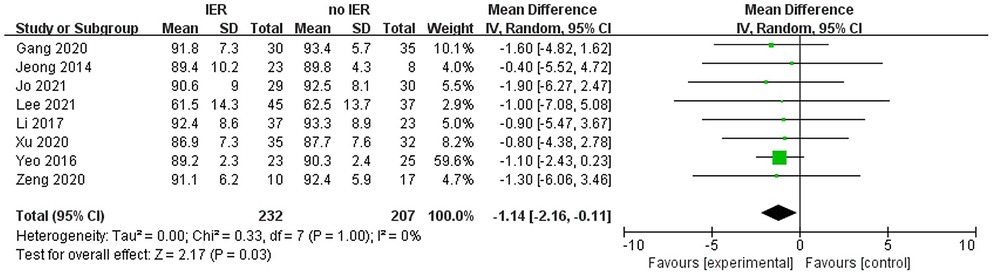
Figure 3. Forest plot comparing postoperative AOFAS, American orthopaedic foot & ankle society and between IER and noIER groups.
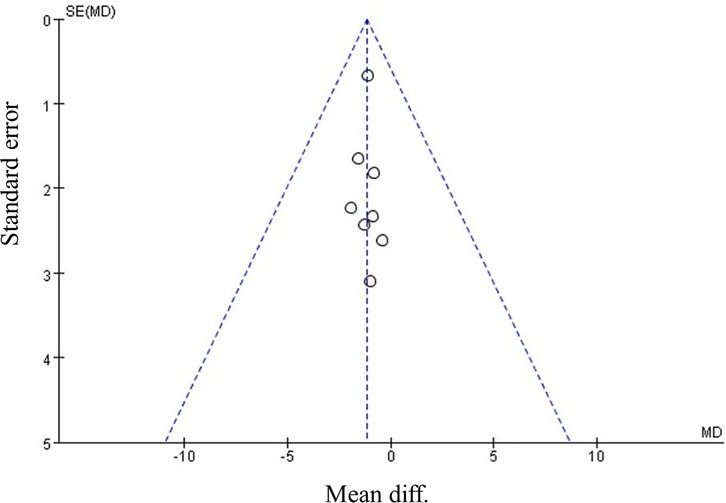
Figure 8. Funnel plot comparing postoperative AOFAS, American orthopaedic foot & ankle society between IER and noIER groups.
Discussion
The results of this meta-analysis indicate that there were no significant differences in postoperative AOFAS and Karlsson scores, as well as talar tilt angle and anterior translation, when comparing patients who underwent the Broström procedure with the Gould modification and those who did not undergo the Gould modification. These findings are also supported by the assessment of other outcome scores in our systematic review, such as the JSSF scale and SAFE-Q (15). Most ankle assessment systems consist of multiple components, including functional parameters reported by the patient (such as the ability to participate in daily and athletic activities), patient-reported parameters related to quality of life (such as pain), other forms of psychological or psychosocial measures, and clinical assessments such as range of motion and strength measurements. Although differences exist in the arthroscopic surgery, open surgery, and rehabilitation protocols among the included studies, the low heterogeneity in the summary results and the similar conclusions drawn indicate consistency. Araoye et al. observed no subjective instability in postoperative patients in both groups (with or without Gould modification) and reported high satisfaction levels (10). Additionally, in clinical trials where random allocation was not always feasible, the trial results were not affected. Jeong et al. also included an analysis of 10 patients with complications during follow-up, such as concomitant bone and cartilage injuries, ankle joint fractures, and subtalar instability (11). The clinical measurements and patient satisfaction did not show significant differences among the groups, as evidenced by the low heterogeneity (I2 = 0). While our analysis confirmed comparable rates of sensory nerve damage, infections, and recurrence between groups, the impact of these complications on patient-reported outcomes (PROs) such as quality of life, pain perception, or functional recovery remains unexplored. This limitation stems from inconsistent reporting of PROs in the included studies, which predominantly focused on clinician-assessed metrics (e.g., AOFAS scores). Moreover, the included studies had relatively shorter follow-up durations (with a mean of 11.5–36 months), which may be insufficient to capture long-term recurrence events. Future studies should prioritize integrating validated PRO measures (e.g., SF-36, FAAM) alongside traditional clinical outcomes to holistically evaluate the patient experience. Some studies indicate that the Gould modification may not provide anatomical repair, can increase surgical time and complexity, and may lead to complications such as superficial peroneal nerve or sural nerve neuritis with a reported complication rate of approximately 14% (8, 22). However, when the lateral ligament injury of the ankle is severe and complete anatomical reduction is not achievable, reinforcement of the Inferior Extensor Retinaculum (IER) might be used to enhance ankle stability. It is suggested in the research to add a grading system for the severity of ATFL (Anterior Talofibular Ligament) injuries: Grade 0, ligament is normal and continuous, no tear, normal thickness, and taut between the lateral malleolus and the talus neck; Grade 1, ligament is stretched, no tear, normal thickness, but reduced tension on palpation; Grade 2, partial avulsion of the fibula or talus involving the ATFL (including fibrous tissue) with normal thickness, but reduced tension on palpation; Grade 3, thinning of the ATFL, lack of mechanical resistance on palpation, with or without scar tissue; Grade 4, scar tissue replacing the ATFL. This grading system can help minimize selection bias and provide more precise understanding of the outcomes associated with different degrees of ATFL injuries in different surgical procedures.
Limitations
While the sample size (10 studies) may limit generalizability, pooled outcomes showed low heterogeneity, supporting result consistency. Most studies were retrospective, but sensitivity analyses confirmed robustness. Variability in surgical techniques and unreported preoperative status were noted; however, subgroup analyses (e.g., open vs. arthroscopic) revealed no significant differences. Future RCTs with standardized ATFL grading and surgical protocols could refine these findings.
Conclusions
The findings suggest that for patients with CAI, the Broström procedure with or without the Gould modification yields comparable postoperative functional outcomes. This has significant implications for the surgical management of CAI, potentially simplifying treatment protocols.
Author contributions
HaL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. HoL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Project administration, Writing – review & editing. MS: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Software, Writing – original draft. YZ: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Writing – review & editing. BW: Formal analysis, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing. JM: Formal analysis, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. Grants from Education and teaching reform research project of Capital Medical University (2023JYY388), Elite Medical Professionals project of China-Japan Friendship Hospital (No. ZRJY2021-TD01).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Mugno AT, Constant D. Recurrent ankle sprain. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing (2024). p. 1–4.
2. Broström L. Sprained ankles. V. Treatment and prognosis in recent ligament ruptures. Acta Chir Scand. (1966) 132(5):537–50.
3. Baumhauer JF, O'Brien T. Surgical considerations in the treatment of ankle instability. J Athl Train. (2002) 37(4):458–62.12937567
4. Karlsson J, Eriksson BI, Bergsten T, Rudholm O, Swärd L. Comparison of two anatomic reconstructions for chronic lateral instability of the ankle joint. Am J Sports Med. (1997) 25(1):48–53. doi: 10.1177/036354659702500109
5. Knupp M, Lang TH, Zwicky L, Lötscher P, Hintermann B. Chronic ankle instability (medial and lateral). Clin Sports Med. (2015) 34(4):679–88. doi: 10.1016/j.csm.2015.06.004
6. Li X, Killie H, Guerrero P, Busconi BD. Anatomical reconstruction for chronic lateral ankle instability in the high-demand athlete: functional outcomes after the modified Broström repair using suture anchors. Am J Sports Med. (2009) 37(3):488–94. doi: 10.1177/0363546508327541
7. Acevedo JI, Ortiz C, Golano P, Nery C. Arthrobroström lateral ankle stabilization technique: an anatomic study. Am J Sports Med. (2015) 43(10):2564–71. doi: 10.1177/0363546515597464
8. Corte-Real NM, Moreira RM. Arthroscopic repair of chronic lateral ankle instability. Foot Ankle Int. (2009) 30(3):213–7. doi: 10.3113/FAI.2009.0213
9. Cottom JM, Rigby RB. The “all inside” arthroscopic Broström procedure: a prospective study of 40 consecutive patients. J Foot Ankle Surg. (2013) 52(5):568–74. doi: 10.1053/j.jfas.2013.02.022
10. Araoye I, De Cesar Netto C, Cone B, Hudson P, Sahranavard B, Shah A. Results of lateral ankle ligament repair surgery in one hundred and nineteen patients: do surgical method and arthroscopy timing matter? Int Orthop. (2017) 41(11):2289–95. doi: 10.1007/s00264-017-3617-9
11. Jeong BO, Kim MS, Song WJ, SooHoo NF. Feasibility and outcome of inferior extensor retinaculum reinforcement in modified Broström procedures. Foot Ankle Int. (2014) 35(11):1137–42. doi: 10.1177/1071100714543645
12. Jo J, Lee JW, Kim HJ, Suh DH, Kim WS, Choi GW. Arthroscopic all-inside anterior talofibular ligament repair with and without Inferior extensor retinacular reinforcement: a prospective randomized study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. (2021) 103(17):1578–87. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.20.01696
13. Lee SH, Cho HG, Yang JH. Additional Inferior extensor retinaculum augmentation after all-inside arthroscopic anterior talofibular ligament repair for chronic ankle instability is not necessary. Am J Sports Med. (2021) 49(7):1721–31. doi: 10.1177/03635465211008097
14. Li H, Hua Y, Li H, Ma K, Li S, Chen S. Activity level and function 2 years after anterior talofibular ligament repair: a comparison between arthroscopic repair and open repair procedures. Am J Sports Med. (2017) 45(9):2044–51. doi: 10.1177/0363546517698675
15. Samejima Y, Inokuchi R, Iwashita K, Ikegami H, Musha Y, Jujo Y, et al. Arthroscopic ankle lateral ligament repair alone versus arthroscopic ankle lateral ligament repair with reinforcement by inferior extensor retinaculum. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. (2021) 141(6):987–95. doi: 10.1007/s00402-021-03771-w
16. Xu DL, Gan KF, Li HJ, Zhou SY, Lou ZQ, Wang Y, et al. Modified Broström repair with and without augmentation using suture tape for chronic lateral ankle instability. Orthop Surg. (2019) 11(4):671–8. doi: 10.1111/os.12516
17. Yeo ED, Lee KT, Sung IH, Lee SG, Lee YK. Comparison of all-inside arthroscopic and open techniques for the modified Broström procedure for ankle instability. Foot Ankle Int. (2016) 37(10):1037–45. doi: 10.1177/1071100716666508
18. Zeng G, Hu X, Liu W, Qiu X, Yang T, Li C, et al. Open Broström-Gould repair vs arthroscopic anatomical repair of the anterior talofibular ligament for chronic lateral ankle instability. Foot Ankle Int. (2020) 41(1):44–9. doi: 10.1177/1071100719875964
19. Behrens SB, Drakos M, Lee BJ, Paller D, Hoffman E, Koruprolu S, et al. Biomechanical analysis of Brostrom versus Brostrom-Gould lateral ankle instability repairs. Foot Ankle Int. (2013) 34(4):587–92. doi: 10.1177/1071100713477622
20. Kitaoka HB, Alexander IJ, Adelaar RS, Nunley JA, Myerson MS, Sanders M. Clinical rating systems for the ankle-hindfoot, midfoot, hallux, and lesser toes. Foot Ankle Int. (1994) 15(7):349–53. doi: 10.1177/107110079401500701
21. Karlsson J, Lundin O, Lossing IW, Peterson L. Partial rupture of the patellar ligament. Results after operative treatment. Am J Sports Med. (1991) 19(4):403–8. doi: 10.1177/036354659101900415
22. Kim ES, Lee KT, Park JS, Lee YK. Arthroscopic anterior talofibular ligament repair for chronic ankle instability with a suture anchor technique. Orthopedics. (2011) 34(4):420–767. doi: 10.3928/01477447-20110228-03
Keywords: anterior talofibular ligament (ATFL), meta-analysis, inferior extensor retinaculum, chronic ankle instability, ankle sprains
Citation: Liu H, Li H, Shen M, Zhou Y, Wang B and Ma J (2025) Chronic ankle instability: a meta-analysis and systematic review comparing clinical outcomes of anterior talofibular ligament repair with or without reinforcement of the lower extensor retinaculum. Front. Surg. 12:1572345. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2025.1572345
Received: 7 February 2025; Accepted: 1 May 2025;
Published: 19 May 2025.
Edited by:
Roberto Tedeschi, University of Bologna, ItalyReviewed by:
Cristian Indino, Humanitas San Pio X Hospital, ItalyShuming Huang, Fifth Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University, China
Copyright: © 2025 Liu, Li, Shen, Zhou, Wang and Ma. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Bailiang Wang, d2FuZ19vcnRob3BhZWRpY0AxMjYuY29t; Jinhui Ma, MTQwMjMxNzM0MEBxcS5jb20=
 Haoyang Liu
Haoyang Liu Hongxu Li1
Hongxu Li1 Mengran Shen
Mengran Shen Yu Zhou
Yu Zhou