- 1Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing, China
- 2Department of General Surgery, The Thirteenth People’s Hospital of Chongqing (Chongqing Geriatrics Hospital), Chongqing, China
Background: The implantation of 125I seed is expected to improve the prognosis of patients undergoing stent placement for advanced extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (eCCA), but its efficacy and safety remain unclear.
Methods: Forty advanced eCCA patients who received percutaneous transhepatic biliary stenting (PTBS) (control group) and 40 PTBS combined with 125I seed implantation (125I group) were retrospectively analyzed. Changes in serum biochemical indicators and tumor markers as well as the occurrence of complications were observed in the two groups, and the durations of stent patency and survival were compared.
Results: The general information and preoperative baseline data did not significantly differ between the two groups (P < 0.05). Regardless of whether PTBS was combined with 125I seed implantation, the ALT/AST levels of patients after operation were significantly lower, jaundice was relieved. And the improvements in postoperative liver function and jaundice in patients in 125I group were better than those in control group. In addition, tumor markers in the two groups decreased significantly, and the decrease was more significant in patients in 125I group. There was no significant difference in the total complication rate between the two groups. The stent patency time and overall survival of the patients in the 125I group were longer than those in control group.
Conclusion: Biliary stenting combined with 125I seed implantation is a safe and effective treatment for patients with advanced eCCA, and it is superior to biliary stenting alone in improving liver function and prolonging the duration of stent patency and survival time.
1 Introduction
Cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) is a malignant tumor that occurs in the epithelial cells of the bile duct, with the second-degree bile duct used as an anatomical marker (1). Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma is located at the proximal segment of the secondary bile duct, while extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (eCCA) is found from the primary bile duct to the bile-pancreatic ampulla. eCCA encompasses perihilar cholangiocarcinoma (pCCA) and distal cholangiocarcinoma (dCCA). pCCA arises from the principle bile duct to the confluence of the hepatic duct and cystic duct, whereas dCCA extends from the cystic duct to the bile-pancreatic ampulla (2).
eCCA mainly manifests with bile duct obstruction, for which radical surgical resection is still the only curative means (3, 4). The 5-year survival rates of pCCA and dCCA patients after radical surgical resection are 20%–30% and 18%–43%, respectively (5–8). For eCCA patients who are inoperative, unwilling to undergo surgery, or who are in poor systemic condition and cannot tolerate surgery, the palliative treatment is mainly biliary drainage, which includes external biliary drainage and internal biliary drainage. The internal biliary drainage are in line with physiology to avoid body fluid loss (9).
The implantation of self-expandable metallic stent (SEMS) is the main means of bile-enteral drainage. However, the stent itself cannot stop tumor growth, and more than 50% of SEMSs are reblocked after 6 months due to tumor overgrowth, leading to rehospitalization and re-intervention and greatly reducing patients' quality of life (10–12). How to inhibit tumor growth, prolong the patency time of patients with biliary stents and overall survival (OS) and improve the quality of life of patients are major clinical problems at present.
125I particles are a low-energy radiation source, with the persistent emission of low-energy gamma rays capable of inducing damage to the DNA double strands of tumor cells (13, 14). This process effectively eradicates tumor cells across various stages of cell division, inhibits tumor proliferation, and facilitates apoptosis. The effective radiation radius of 125I particles is 1.7 cm, which delivers a high dose to tumor tissues and causes low damage to surrounding tissues (15); therefore, they have been widely used to treat malignant tumors. Especially, 125I particles are widely used in solid tumors, such as liver cancer, prostate cancer, lung cancer, and pancreatic cancer, and have achieved good efficacy (16–19). In recent years, researchers have applied radioactive stents combined with 125I seeds in the treatment of eCCA. However, studies of 125I seed implantation combined with biliary stenting in patients with extrahepatic BDT are relatively rare and heterogeneous (20, 21).
Therefore, in this study, we aimed to conduct a retrospective analysis to evaluate the potential enhancement in efficacy of biliary stenting when used in conjunction with 125I particles.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Study population
Patients with advanced eCCA who received PTBS (control group) or PTBS combined with 125I seed implantation (125I group) at our center between January 2018 and January 2022 were retrospectively analyzed. The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Second Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University and was in compliance with the Declaration of Helsinki. All patients signed informed consent before treatment.
The inclusion criteria were as follows: (1) Patients diagnosed clinically with eCCA; (2) Patients whose tumor were not resectable or who were unwilling to undergo surgical resection; (3) PS score: 0–1. The exclusion criteria included the following: (1) Patients with distant organ metastasis; (2) The full course of follow-up could not be performed; (3) Patients were complicated with severe portal hypertension and had a previous history of upper gastrointestinal bleeding or severe hypersplenism; (4) Significant abnormalities in coagulation function or liver and kidney failure were detected.
2.2 Technical methods
1. Percutaneous transhepatic biliary drainage (PTBD): The target bile duct for puncture and drainage is selected in combination with enhanced CT or enhanced MRI, and percutaneous transhepatic external bile duct drainage was performed under the guidance of ultrasound combined with x-ray (diameter less than or equal to 6 mm).
2. Biliary stenting: The selection of 8 mm or 10 mm stents was guided by the diameter of target bile ducts, site-specific obstruction characteristics, and physician's clinical judgment per standard clinical protocols. The guidewire was implanted in the intrahepatic bile duct through the PTBD channel, the sheath was implanted along the guidewire, the guidewire cooperated with the catheter through the bile duct tumor site and entered the distal bile duct, and the biliary metal was implanted along the guidewire. The stent covered the bile duct obstruction 2 cm beyond the proximal end and the distal end of the stenosis.
3. Biliary stenting combined with 125I seed implantation: a stent suitable for the diameter of the bile duct and the length of the obstructed segment and the long 6F sheath were placed side by side over the bile duct tumor; the stent was released first, and then the homemade 125I particles (PTBD tube plastic carrying 125I particles) were placed in parallel. The catheter with a soft inner core was trimmed to a suitable length for the bile duct tumor (the particle segment was 1 cm longer than the upper and lower ends of the bile duct tumor) and was delivered to the location of the bile duct tumor through the long sheath. Procedural and follow-up imaging of 125I stent-seed assembly was shown in Figure 1.
2.3 Data collection
A patient information database was established, which included patient age, sex, tumor location, and preoperative serological test results, including total bilirubin (TBIL), direct bilirubin (DBIL), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT), albumin (ALB), C-reactive protein (CRP), white blood cell (WBC), neutrophil count (NC), lymphocyte count (LC), platelet count (PLT), prothrombin time international normalized ratio (PT-INR), carbohydrate antigen 19-9 (CA19-9), and carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) levels.
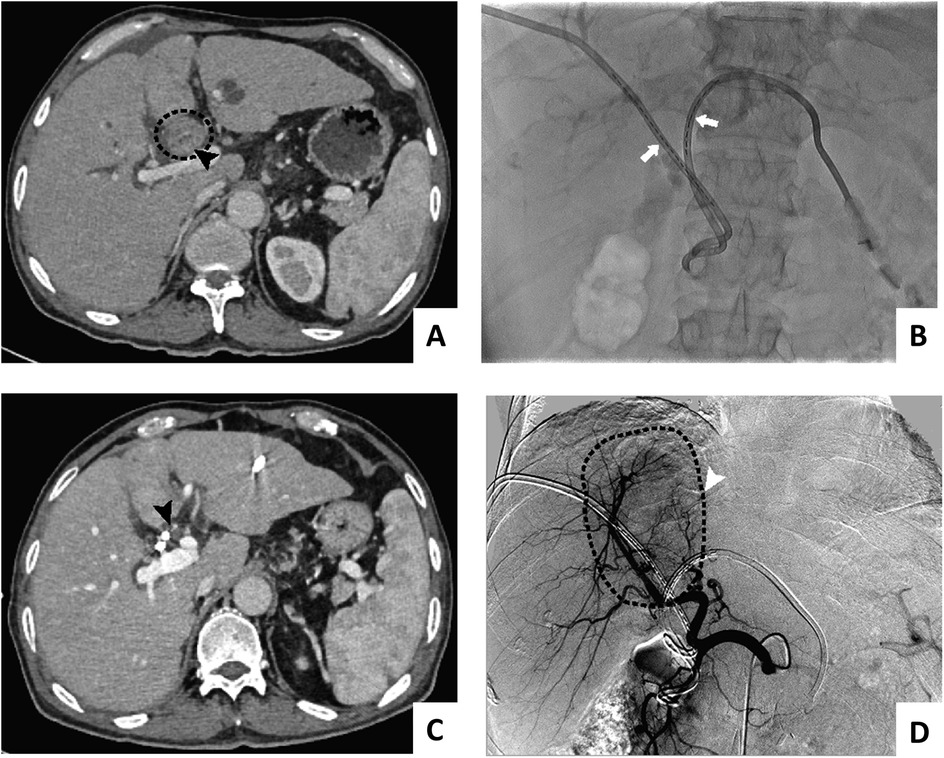
Figure 1. Procedural and follow-up imaging of 125I stent-seed assembly: pre-implantation (A), successful stent-seed implantation (B), 1-month follow-up imaging (projection 1) (C), 1-month follow-up imaging (projection 2) (D)
All patients were followed up until July 2024, or the patient died. The follow-up data included TBIL, DBIL, ALT, AST, ALP, ALB, CA19-9, and CEA levels.
2.4 Statistical analysis
SPSS software version 27 was used for the statistical analysis. Count data are expressed as percentages and frequencies and were compared via the Pearson chi-square test or the Pearson chi-square test with continuity correction. Continuous variables are expressed as the means ± standard deviations or medians with ranges, and comparisons were performed via t tests or Wilcoxon tests. OS and cumulative primary stent patency time were evaluated via Kaplan‒Meier analysis and compared via the log-rank test. A p value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3 Results
3.1 Baseline information
Forty advanced eCCA patients who received percutaneous transhepatic biliary stenting (PTBS) alone (control group) or 40 patients who received PTBS combined with 125I seed implantation (125I group) were included (Figure 2). The baseline clinical characteristics of these 80 patients are summarized in Table 1. In the control group, there were 17 males (42.5%) and 23 females (57.5%), and the mean age was 69.20 ± 6.90 years. Among them, 19 patients were were diagnosed with pCCA, and 21 patients were were diagnosed with dCCA. In the 125I group, there were 21 males (52.5%) and 19 females (47.5%), and the mean age was 69.33 ± 7.13 years. Among them, 13 patients were were were diagnosed with pCCA, and 27 patients were were diagnosed with dCCA. There were no significant differences in preoperative liver function, jaundice, or tumor markers between the two groups of patients (P > 0.05). A biliary stent or biliary stent combined with 125I particles was successfully implanted in both groups of patients, the biliary tract was unobstructed after operation, and the surgical success rate was 100%.
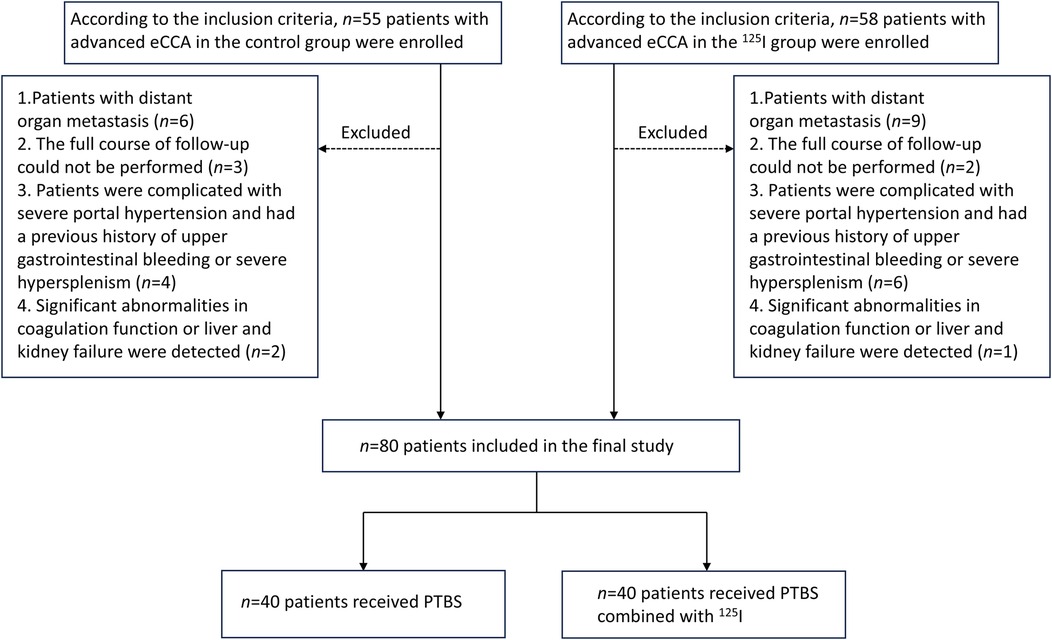
Figure 2. Patient enrollment flowchart. Schematic illustrating participant selection for the comparative study of 125I stent efficacy in eCCA patients undergoing PTBS. eCCA: extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma; PTBS: percutaneous transhepatic biliary stenting.
3.2 Postoperative liver function and jaundice
Compared with the preoperative level, liver function in both groups was significantly improved after operation. This improvement is evidenced by significant reductions in ALT, AST, and ALP levels at 1, 3, and 6 months following the operation (Figures 3A–C), alongside a significant increase in ALB levels (Figure 3D). There was no significant difference between the 125I group and the control group in the ALT, AST, and ALP levels at 1 month, but there was a significant difference between 3 and 6 months. The ALB levels at 1, 3, and 6 months in the 125I group were greater than those in the control group. The symptoms of jaundice in the two groups were significantly relieved in both groups, which was reflected in the significant decreases in TBIL and DBIL (Figures 3E,F). In addition, the TBIL and DBIL levels in the 125I group were significantly lower than those in the control group at 3 and 6 months. These results suggest that both biliary stenting alone and biliary biliary stenting combined with 125I seed implantation can improve postoperative liver function and reduce obstructive jaundice and that biliary stenting combined with 125I seed implantation are superior to biliary stenting alone.
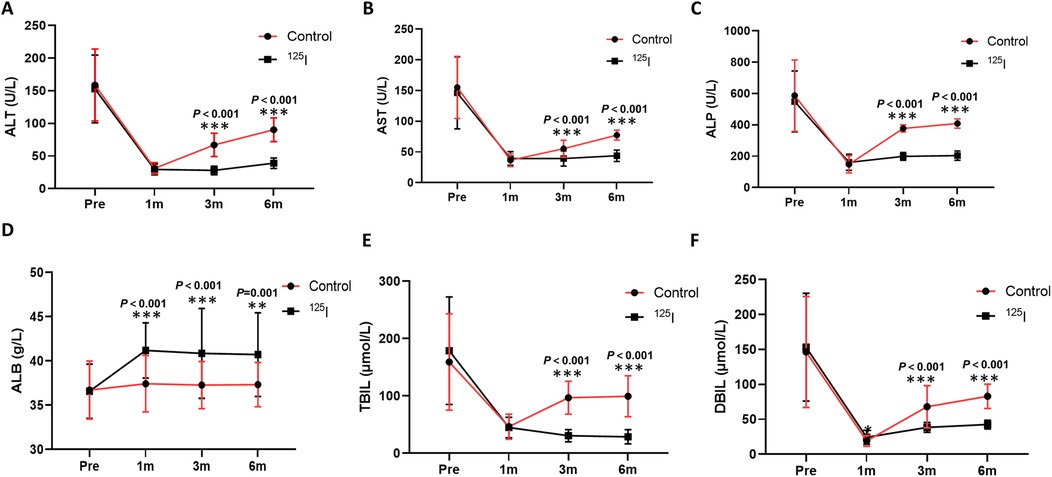
Figure 3. Comparison of ALT (A), AST (B), ALP (C), ALB (D), TBIL (E), and DBIL (F) levels between the two groups after operation. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. ALB, albumin; ALP, alkaline phosphatase; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; DBIL, direct bilirubin; TBIL, total bilirubin.
3.3 Postoperative tumor marker levels
CA19-9 and CEA levels after operation are shown in Table 2. Compared with the preoperative CEA and CA19-9 levals, the follow-up values of the patients with increased CEA and CA19-9 values after 1 month of treatment all decreased to different degrees (Figures 4A,B). In addition, the CEA and CA19-9 levels of the 125I group at 1 and 3 months after operation were lower than those of the control group.
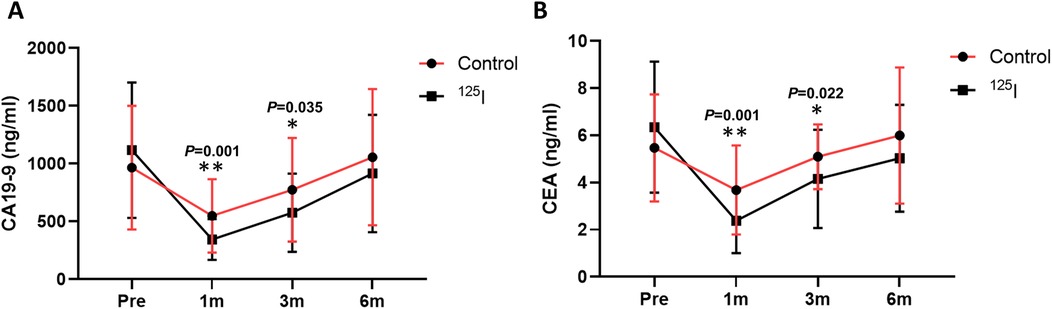
Figure 4. Comparison of CA19-9 (A) and CEA (B) levels between the two groups after operation. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. CA19-9, carbohydrate antigen 19-9; CEA, carcinoembryonic antigen.
3.4 Postoperative complications
As shown in Table 3, the overall incidence of early complications was 17.5% (14 patients), with 12.5% (5 patients) and 22.5% (9 patients) in the control group and the 125I group, respectively. There was no significant difference in the total incidence between the two groups. Specifically, 4 patients in the control group and the 125I group both developed cholangitis, and no patients in the two groups developed bile duct bleeding. Gastrointestinal complications (nausea and vomiting) occurred in 1 patient in the control group and 6 patients in the 125I group, respectively, but there was no significant difference between the two groups. The symptoms of nausea and vomiting were mild and were gradually relieved.
3.5 Bile duct patency and overall survival
The patency conditions of the stents in the two groups are shown in Figure 5A. The cumulative patency rates of the control group at 3, 6, and 12 months were 92.5%, 67.5% and 35%, respectively, and the median patency time was 8 months. The cumulative patency rates of the 125I group at 3, 6, and 12 months were 97.5%, 90% and 65%, respectively, and the median patency time was 14 months. The hazard ratio (HR) for the 125I group compared to the control group was 0.446 (95% CI: 0.271, 0.732), indicating a statistically significant difference and significantly longer patency time in the 125I group. The postoperative survival data are shown in Figure 5B. The cumulative survival rates of the control group at 3, 6, and 12 months were 97.5%, 75% and 37.5%, respectively, and the median survival time was 9 months. The cumulative survival rates of the 125I group at 3, 6, and 12 months were 97.5%, 92.5% and 67.5%, respectively, and the median survival time was 15 months. The HR for the 125I group compared to the control group was 0.452 (95% CI: 0.275, 0.742), demonstrating a statistically significant difference and significantly longer survival time in the 125I group.
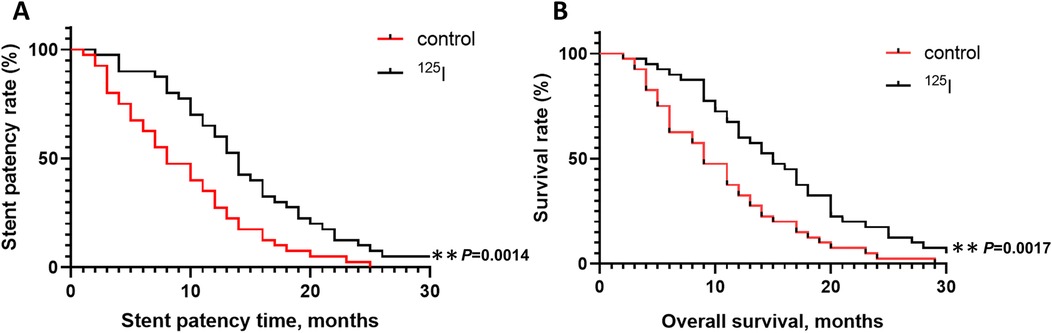
Figure 5. Stent patency rates of the 125I and control groups (A) overall survival rates of the 125I and control groups (B) *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.
4 Discussion
Self-expandable metal stent is a common choice for enteral drainage in eCCA patients, but its effectiveness is not satisfactory. In this study, we included 40 patients in the control group who underwent biliary stent implantation and 40 patients in the 125I group who underwent biliary stent implantation combined with 125I particles implantation. The results confirmed that, compared with the control group, the 125I group had significantly improved postoperative liver function, relieved symptoms of obstructive jaundice, reduced tumor marker levels, and prolonged stent patency time and OS without serious complications.
The most common symptom of eCCA is obstructive jaundice, and biliary drainage is an indispensable treatment technique for unresectable eCCA patients with obstructive jaundice. Endoscopic biliary stent placement was introduced in the 1980s; owing to its minimal invasiveness and practicability, it is now the preferred procedure for the palliative treatment of most eCCA patients. Although there are various types of stents, metal stents are recommended for unresectable cases because they have longer patency time than plastic stents do. In recent years, chemotherapy, immunotherapy and other methods prolong the survival of patients (22). However, a new difficulty arises: the bile duct will still be blocked again, and the patient will experience a recurrence of jaundice in a short period of time, which seriously affects the survival and quality of life of the patient (23).
Stent re-occlusion fundamentally arises from a cascade effect of tumor activity, foreign body reaction, and bile flow dysregulation. Neoplastic cells progressively invade the lumen through longitudinal overgrowth at stent margins or transverse ingrowth through stent interstices. Concurrently, the stent itself induces chronic inflammation and fibroblast activation, driving granulomatous hyperplasia and collagen-deposition stenosis. These processes collectively cause bile stagnation, promoting supersaturation and precipitation of bilirubin/cholesterol into sludge matrices that entrap calcium salts and bacterial biofilms, ultimately forming obstructive calcium bilirubinate stones. This self-reinforcing cycle, wherein obstruction exacerbates sludge formation, sludge accumulation accelerates infection and hyperplasia, and hyperplastic tissue further constricts the lumen, demands integrated therapeutic strategies targeting all pathological axes simultaneously. It is precisely this multidimensional challenge that makes biliary stenting combined with radioactive seed implantation a rational solution: the stent restores immediate drainage patency while the radionuclide's localized irradiation concurrently suppresses tumor proliferation, mitigates inflammatory hyperplasia, and delays sludge formation through continuous biological modulation (24, 25).
At present, 125I particles have been confirmed to be effective and safe in the treatment of portal vein tumor thrombi (26, 27). Because eCCA is discovered in the advanced stage and clinical cases are rare, the application of 125I seed implantation combined with biliary stenting in advanced eCCA is rare at home and abroad, the research directions are new, and there is currently no unified treatment guidelines. On the basis of the above studies combined with our previous clinical observations, we speculated that biliary stent with brachytherapy of 125I seed implantation may result in better treatment outcomes for patients with eCCA and provide a standardized treatment option for patients with advanced eCCA.
In this study, we collected the clinical data of 80 patients with advanced eCCA combined with obstructive jaundice. The results showed both groups effectively reduced obstructive jaundice, improved liver function, and reduced postoperative tumor marker levels in the short term. However, over time, in the stent alone group, tumor growth again caused lumen stenosis or blockage; the stent patency rates at 3 and 6 months after operation were 92.5% and 67.5%, respectively. Additionally, there was a rapid increase in ALT, AST, and bilirubin. In contrast, in the biliary stent combined with 125I seed implantation group, because 125I can perform long-term and low-dose radiation on tumor tissues, stent patency can be maintained for a longer time. The stent patency rates at 3 and 6 months, respectively, were 97.5%, 90%. Moreover, the ALT, AST, and bilirubin levels at 3 and 6 months were significantly lower than those in the biliary stent alone group, showing a gradual upward trend. The same situation was also observed for postoperative tumor marker levels. These advantages led to longer survival in the biliary stent combined with 125I seed implantation group, with a median survival of 15 months, which was significantly greater than that of the biliary stent alone group (9 months). With respect to the long-term efficacy of treatment for advanced eCCA, the implantation of a biliary stent combined with 125I seeds was superior to internal biliary stent implantation alone. Although more postoperative complications were observed in the biliary stent with 125I seed implantation group, the main complications were gastrointestinal symptoms (nausea, vomiting, etc.), which were relieved within a short time after operation and did not have a significant impact on patient's life.
This study has several limitations. Especially, our study was limited to a single-center, retrospective study, but the baseline levels of the included two groups of patients were not different, which makes up for this limitation to a certain extent.
5 Conclusion
In summary, the therapeutic efficacy of biliary stenting combined with 125I particles implantation for the treatment of advanced eCCA is superior to that of stenting alone. This combined approach effectively relieves biliary obstruction, facilitates the restoration of liver function, and extends both biliary tract patency and patient survival duration. Therefore, the integration of biliary stenting with 125I particle implantation represents a highly promising strategy for patients with advanced eCCA.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Ethics Committee of the Second Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation was not required from the participants or the participants' legal guardians/next of kin in accordance with the national legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
CC: Conceptualization, Data curation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. BW: Conceptualization, Data curation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. CM: Data curation, Investigation, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. SL: Data curation, Investigation, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by Chongqing medical scientific research project (joint project of Chongqing Health Commission and Science and Technology Bureau (Grant No.2024MSXM143).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Brindley PJ, Bachini M, Ilyas SI, Khan SA, Loukas A, Sirica AE, et al. Cholangiocarcinoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers. (2021) 7(1):65. doi: 10.1038/s41572-021-00300-2
2. Ilyas SI, Gores GJ. Pathogenesis, diagnosis, and management of cholangiocarcinoma. Gastroenterology. (2013) 145(6):1215–29. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2013.10.013
3. Patel T. Cholangiocarcinoma–controversies and challenges. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2011) 8(4):189–200. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2011.20
4. Razumilava N, Gores GJ. Cholangiocarcinoma. Lancet. (2014) 383(9935):2168–79. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)61903-0
5. Lee RM, Maithel SK. Approaches and outcomes to distal cholangiocarcinoma. Surg Oncol Clin N Am. (2019) 28(4):631–43. doi: 10.1016/j.soc.2019.06.014
6. Chua TC, Mittal A, Arena J, Sheen A, Gill AJ, Samra JS. Resection margin influences survival after pancreatoduodenectomy for distal cholangiocarcinoma. Am J Surg. (2017) 213(6):1072–6. doi: 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2016.09.049
7. Esnaola NF, Meyer JE, Karachristos A, Maranki JL, Camp ER, Denlinger CS. Evaluation and management of intrahepatic and extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Cancer. (2016) 122(9):1349–69. doi: 10.1002/cncr.29692
8. DeOliveira ML, Cunningham SC, Cameron JL, Kamangar F, Winter JM, Lillemoe KD, et al. Cholangiocarcinoma: thirty-one-year experience with 564 patients at a single institution. Ann Surg. (2007) 245(5):755–62. doi: 10.1097/01.sla.0000251366.62632.d3
9. Yang Y, Zhang X. An overview of extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: from here to where? Front Oncol. (2023) 13:1171098. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1171098
10. Chen W, Fang XM, Wang X, Sudarshan SKP, Hu XY, Chen HW. Preliminary clinical application of integrated 125I seeds stents in the therapy of malignant lower biliary tract obstruction. J Xray Sci Technol. (2018) 26(5):865–75. doi: 10.3233/XST-180403
11. Rustagi T, Jamidar PA. Intraductal radiofrequency ablation for management of malignant biliary obstruction. Dig Dis Sci. (2014) 59(11):2635–41. doi: 10.1007/s10620-014-3237-9
12. Steel AW, Postgate AJ, Khorsandi S, Nicholls J, Jiao L, Vlavianos P, et al. Endoscopically applied radiofrequency ablation appears to be safe in the treatment of malignant biliary obstruction. Gastrointest Endosc. (2011) 73(1):149–53. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2010.09.031
13. Ren F, Li B, Wang C, Wang Y, Cui B. Iodine-125 seed represses the growth and facilitates the apoptosis of colorectal cancer cells by suppressing the methylation of miR-615 promoter. BMC Cancer. (2022) 22(1):49. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-09141-4
14. Cheng J, Ma S, Yang G, Wang L, Hou W. The mechanism of computed tomography-guided 125I particle in treating lung cancer. Med Sci Monit. (2017) 23:292–9. doi: 10.12659/MSM.898526
15. Han H, Meng Y, Wang J. Effect of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt combined with (125)I particle implantation on portal vein tumor thrombus in hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J Transl Res. (2022) 14(3):1838–48.35422930
16. Katayama N, Yorozu A, Kikuchi T, Higashide S, Masui K, Kojima S, et al. Biochemical outcomes and toxicities in young men with prostate cancer after permanent iodine-125 seed implantation: prospective cohort study in 6662 patients. Brachytherapy. (2023) 22(3):293–303. doi: 10.1016/j.brachy.2022.12.001
17. Chen X, Zhu F, Wang B, Zhou Y, Xiong H, Fan T, et al. Clinical effect of iodine-125 seed implantation in patients with primary liver cancer and its effect on Th1/Th2 cells in peripheral blood. J Oncol. (2021) 2021:6199732. doi: 10.1155/2021/6199732
18. Zhou L, Yang H, Xie L, Sun J, Qian J, Zhu L. Comparison of image-guided iodine-125 seed interstitial brachytherapy and local chemotherapy perfusion in treatment of advanced pancreatic cancer. J Invest Surg. (2022) 35(1):1–6. doi: 10.1080/08941939.2020.1805057
19. Chen C, Wang W, Yu Z, Tian S, Li Y, Wang Y. Combination of computed tomography-guided iodine-125 brachytherapy and bronchial arterial chemoembolization for locally advanced stage III non-small cell lung cancer after failure of concurrent chemoradiotherapy. Lung Cancer. (2020) 146:290–6. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2020.06.010
20. Wu JZ, Li CL, Shi HB, Liu S, Yang W, Zhou WZ. Hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy following simultaneous metallic stent placement and iodine-125 seed strands for advanced cholangiocarcinoma causing malignant obstructive jaundice: a propensity score matching study. Jpn J Radiol. (2022) 40(4):396–403. doi: 10.1007/s11604-021-01212-7
21. Hu X, Pang Q, Liu H, Qian Z, Jin H, Zhou L, et al. Inflammation-based prognostic scores in patients with extrahepatic bile duct lesions treated by percutaneous transhepatic biliary stenting combined with (125)I seeds intracavitary irradiation. Clin Transl Oncol. (2019) 21(5):665–73. doi: 10.1007/s12094-018-1969-2
22. Valle J, Wasan H, Palmer DH, Cunningham D, Anthoney A, Maraveyas A, et al. Cisplatin plus gemcitabine versus gemcitabine for biliary tract cancer. N Engl J Med. (2010) 362(14):1273–81. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0908721
23. Xia MX, Cai XB, Pan YL, Wu J, Gao DJ, Ye X, et al. Optimal stent placement strategy for malignant hilar biliary obstruction: a large multicenter parallel study. Gastrointest Endosc. (2020) 91(5):1117–28. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2019.12.023
24. Ma ZH, Yang Y, Zou L, Luo KY. 125I Seed irradiation induces up-regulation of the genes associated with apoptosis and cell cycle arrest and inhibits growth of gastric cancer xenografts. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. (2012) 31(1):61. doi: 10.1186/1756-9966-31-61
25. Ma JX, Jin ZD, Si PR, Liu Y, Lu Z, Wu HY, et al. Continuous and low-energy 125I seed irradiation changes DNA methyltransferases expression patterns and inhibits pancreatic cancer tumor growth. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. (2011) 30(1):35. doi: 10.1186/1756-9966-30-35
26. Qiu Z, Yu C, Qiu X, Li Q, Li J, Chen Z, et al. Safety and efficacy of CT-guided iodine-125 brachytherapy for portal vein tumor thrombus in hepatocellular carcinoma. Acad Radiol. (2023) 30(Suppl 1):S53–60. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2023.02.006
Keywords: extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma, 125I seed implantation, biliary stenting, stent patency time, postoperative survival
Citation: Cheng C, Wang B, Miao C and Li S (2025) Efficacy and safety of biliary stenting combined with 125I seed implantation for the treatment of advanced extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Front. Surg. 12:1608312. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2025.1608312
Received: 8 April 2025; Accepted: 8 September 2025;
Published: 22 September 2025.
Edited by:
Bin-Yan Zhong, Soochow University, ChinaReviewed by:
Ikhwan Rinaldi, RSUPN Dr. Cipto Mangunkusumo, IndonesiaChang Hoon Oh, Samsung medical center, Republic of Korea
Copyright: © 2025 Cheng, Wang, Miao and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Shengwei Li, bGlzaGVuZ3dlaUBob3NwaXRhbC5jcW11LmVkdS5jbg==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Cai Cheng1,2,†
Cai Cheng1,2,† Shengwei Li
Shengwei Li