- Wenzhou TCM Hospital Affiliated to Zhejiang Chinese Medical University, Wenzhou, China
Introduction: This study aimed to evaluate the efficacy of acupuncture therapy in the postoperative rehabilitation of patients following arthroscopic rotator cuff repair.
Methods: Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) published up to October 31, 2024, were identified through systematic searches of EMBASE, Web of Science, China National Knowledge Infrastructure, China Science and Technology Journal Database, China Biomedical Literature Database, and Wanfang Database. Meta-analysis was conducted using RevMan 5.3 and Stata 18. A total of 18 studies involving 376 patients were included.
Results: The meta-analysis demonstrated that, compared to the control group, the acupuncture group showed significantly higher effective rates [OR = 5.02, 95% CI (2.32, 10.85), P < 0.001], improved Constant-Murley scores [MD = 7.27, 95% CI (3.96, 10.59), P < 0.001], greater range of motion in forward flexion [MD = 14.95, 95% CI (6.13, 23.77), P < 0.001], backward extension [MD = 6.58, 95% CI (3.56, 9.61), P < 0.001], abduction [MD = 16.24, 95% CI (6.79, 25.70), P < 0.001], external rotation [MD = 9.56, 95% CI (4.66, 14.47), P < 0.001], and significantly reduced pain according to Visual Analog Scale scores [MD = −1.45, 95% CI (−2.04, −0.86), P < 0.001].
Discussion: Acupuncture therapy, when compared to conventional treatments, may be beneficial for postoperative rehabilitation in patients after arthroscopic rotator cuff repair by reducing pain and improving shoulder joint mobility.
1 Introduction
Arthroscopic rotator cuff repair (ARCR) is the gold standard for treating rotator cuff injuries, with the advantages of less trauma, faster recovery and fewer complications (1). However, there are complications such as postoperative swelling and pain, shoulder stiffness, decreased muscle strength and muscle atrophy after ARCR (2, 3). Therefore, the availability of appropriate postoperative rehabilitation and the timing of rehabilitation are important factors in determining the degree of recovery of shoulder function in patients (4). At present, the main interventions are postoperative immobilization and functional exercises (5), but the lack of standardization of issues such as immobilization time and exercise modalities leads to poor rehabilitation outcomes (6, 7). Acupuncture is a therapeutic intervention within Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) that involves the insertion of fine metallic needles into specific anatomical points (acupoints) to regulate physiological functions or treat pathological conditions. According to the stimulation method, it is mainly categorized into hand acupuncture (e.g., millimeter acupuncture, wrist-ankle acupuncture, facial acupuncture, etc.), warm acupuncture and electroacupuncture. Relevant studies have showed its positive impact on interventions for shoulder pain symptoms (8–10). However, at present, a limited number of meta-analysis focus on acupuncture therapy for postoperative rehabilitation of ARCR. This paper systematically retrieved, organized, and screened randomized controlled trials (RCTs) focusing on the effects of acupuncture on postoperative rehabilitation of ARCR to prepare for a meta-analysis. The aim was to explore the potential benefits of acupuncture therapy in mitigating postoperative adverse effects associated with ARCR. By doing so, it sought to provide evidence-based support for the clinical application of acupuncture-assisted interventions in the postoperative rehabilitation of ARCR.
2 Data and methodology
2.1 Agreement and registration
This study was conducted in accordance with the PRISMA statement and AMSTAR guidelines (11, 12). The proposal reviewed is registered with PROSPERO (CRD42024604553).
2.2 Inclusion and exclusion criteria
2.2.1 Inclusion criteria
(1) The type of study is a randomized controlled trial including the effect of hand acupuncture, warm acupuncture, electroacupuncture, and other acupuncture therapies on the rehabilitation of postoperative patients with ARCR, with unlimited languages; (2) Measures for the control group were blank, sham acupuncture, or conventional treatment, and measures for the intervention group were acupuncture or combined acupuncture therapy based on the control group; (3) At least one of the following outcome indicators was reported effective rate, visual analogue scores (VAS) (13), Constant-Murley scores (CMS) (14), and postoperative shoulder mobility (forward flexion, backward extension, shoulder abduction, and external rotation).
2.2.2 Exclusion criteria
(1) Studies of patients who did not receive ARCR or other interventions included in the study; (2) Studies that the original text could not be obtained or the outcome indicators were not met; (3) Exclude non-RCT, duplicate publications, case reports, systematic reviews and meta-analysis, mechanism studies, dissertations, or animal experiments.
2.3 Document retrieval strategy
The computer search was conducted using EMBASE, Web of Science, China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), China Science and Technology Journal Database (CQVIP), China Biomedical Literature Database (SinoMed), and Wanfang Databases. This search was conducted to collect relevant clinical studies on the effects of acupuncture treatment on postoperative rehabilitation after ARCR from inception to October 31, 2024. The search method uses a combination of free words and subject terms, and is adapted to the different characteristics of each database. Table 1 provides the search strategy in detail.
2.4 Document screening and data extraction
The literature was managed using EndNote 21.4 software to summarize, de-duplicate, screen and extract research data. Initial screening was carried out by 2 independent researchers (Jia-Hao Chen and Wu Kai) using titles and abstracts, followed by re-screening using full text. In case of disagreement, it shall be resolved through discussion or consultation with the corresponding author (Qing-Lai Wang). The content of data extraction mainly includes author names, year of publication, sample size, interventions, and outcome indicators, etc.
2.5 Include research quality assessment
The Cochrane Collaboration Tool was used to assess the risk of bias of the included literature that met the inclusion criteria. The risk of bias was assessed as “low risk”, “high risk”, “unclear”. Disagreements were decided by discussion or by requesting the correspondent author.
2.6 Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was conducted using RevMan 5.4 and Stata 18 statistical software. The odds ratio (OR) and its 95% confidence interval (CI) were used for dichotomous variables, and the mean difference (MD) and its 95% CI were used for continuous variables. The I² test was used to assess heterogeneity between research results. When the statistical heterogeneity was low (P > 0.1, I2 < 50%), the fixed-effects model was used for analysis. When statistical heterogeneity was significant (P < 0.1, I2 > 50%), a random-effects model was used, and one-way sensitivity analysis was performed to assess the effect of included studies on the combined results for outcomes with significant heterogeneity. In cases where a unified effect value is not available for outcome indicators, a weighted mean () and combined standard deviation (S) is calculated using the formula below:
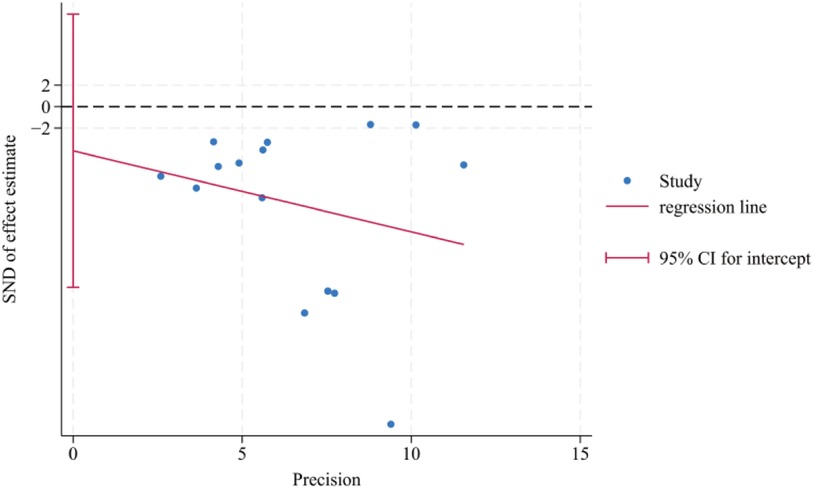
here denotes mean, denotes standard deviation, denotes sample size. For indicators with ≥10 included studies, meta-regression analysis was performed using Stata 18.0 software to explore sources of heterogeneity, and funnel plots, Egg tests, and Begg tests were constructed to assess publication bias (15). P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant publication bias. Evidence was graded using the GRADEpro software.
3 Result
3.1 Literature search results and bias risk assessment included in the study
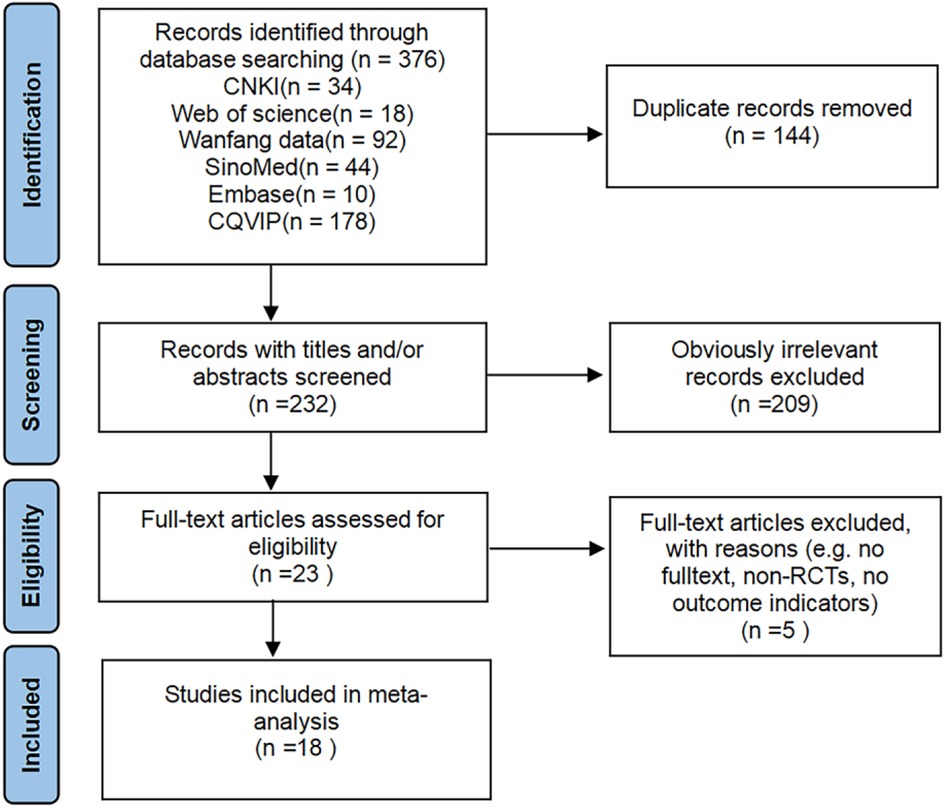
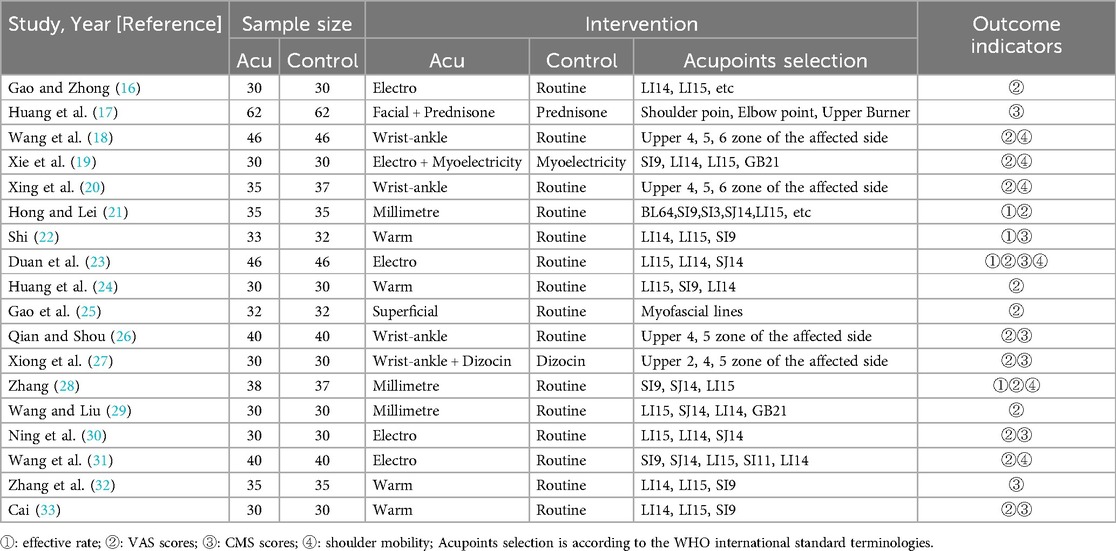
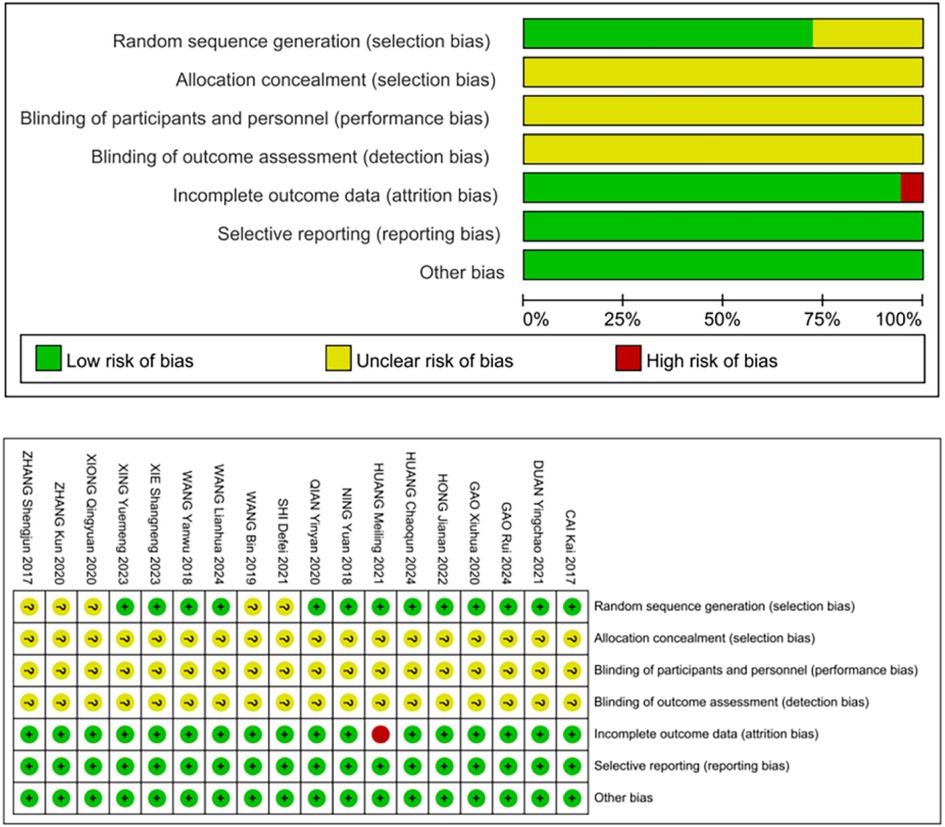
A total of 376 related literatures were initially retrieved, of which 144 were omitted due to repetition. Finally, 18 studies (16–33) of RCTs were included after excluding 214 studies based on title, abstract and full text. The publication years ranged from 2017 to 2024, with a total of 1304 patients, of which 652 were in the control group and 652 were in the acupuncture group. The literature screening process is shown in Figure 1. The basic characteristics of the included studies are shown in Table 2. All references refer to randomization, of which 13 studies (16–21, 23–26, 30, 31, 33) use the random number table method and 5 studies (22, 27–29, 32) refer to randomization without describing the method of random sequence generation. The quality assessment of the included studies is shown in Figure 2, and the result shows that the overall quality was good.
3.2 Meta analysis results
3.2.1 Effective rate
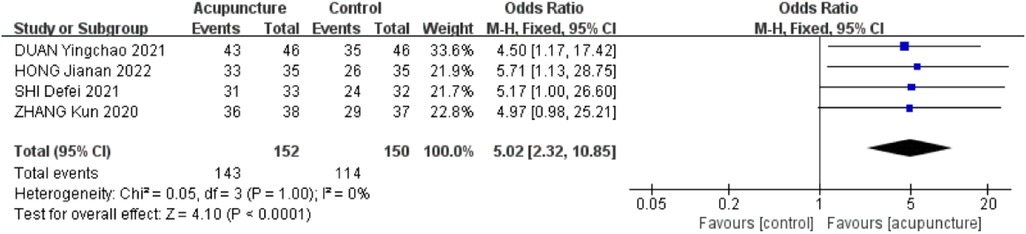
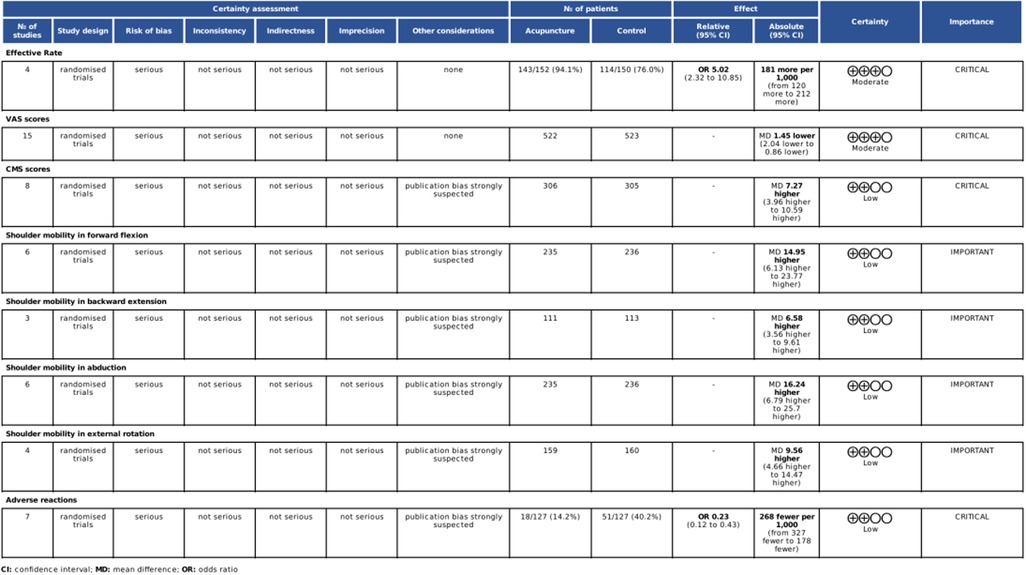
A total of 4 RCTs (21–23, 28) were included. The heterogeneity between the included research results was low (I2 = 0%, P = 1.00), so a fixed-effects model was used for meta-analysis. The results showed that the effective rate in the acupuncture group was significantly higher than that in the control group, and the difference was statistically significant [OR = 5.02,95% CI (2.32,10.85), P < 0.001, Figure 3].
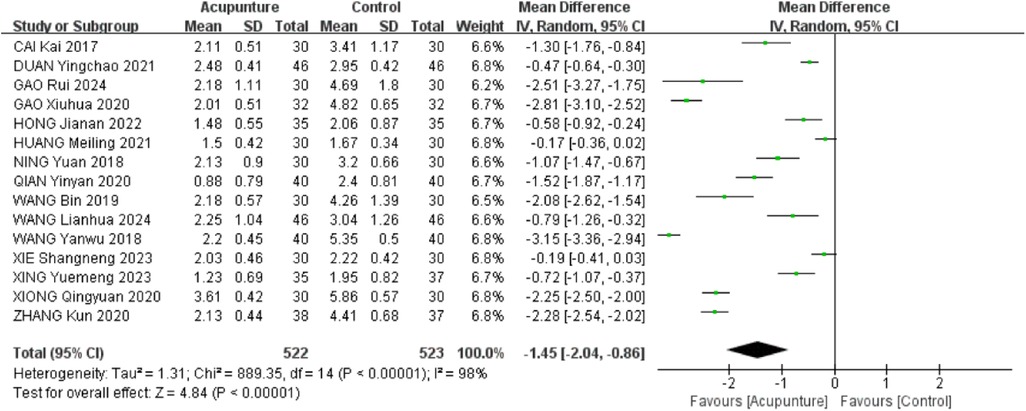
3.2.2 VAS scores
A total of 15 RCTs (16, 18–21, 23–31, 33) were included. The heterogeneity of the included research results was high (I2 = 98%, P < 0.001), so a random effects model was used for meta-analysis. The results showed that the VAS scores in the acupuncture group were significantly lower than that in the control group, and the difference was statistically significant [MD = −1.45, 95% CI (−2.04, −0.86), P < 0.001, Figure 4]. A meta-regression analysis was conducted using acupuncture type, treatment duration, and concurrent rehabilitation training as covariates. The findings indicated that acupuncture type (β = −.23, P = .256), treatment duration (β = −.20, P = .279), and concurrent rehabilitation training (β = .43, P = .589) did not exhibit statistical significance on the outcome, with small effect sizes. The adjusted R2 of 5.01% suggests that these variables offer limited explanation for inter-study heterogeneity, indicating other potential confounders such as stimulation intensity and acupoint selection.
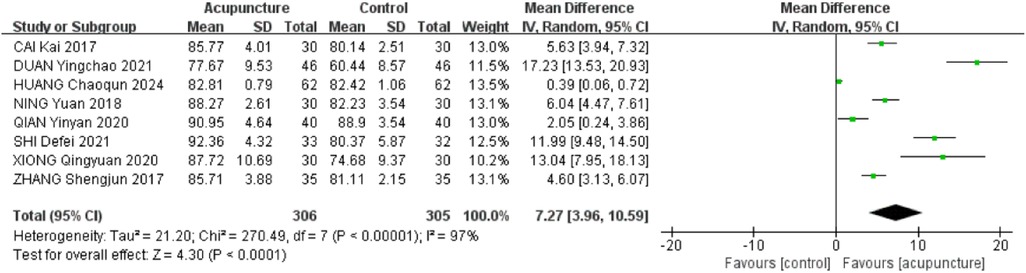
3.2.3 CMS scores
A total of 8 RCTs (17, 22, 23, 26, 27, 30, 32, 33) were included. The heterogeneity of the included research results was high (I2 = 97%, P < 0.001), so a random-effects model was used for meta-analysis. The results showed that the CMS scores in the acupuncture group was significantly higher than that in the control group, and the difference was statistically significant [MD = 7.27, 95% CI (3.96,10.59), P < 0.001, Figure 5].
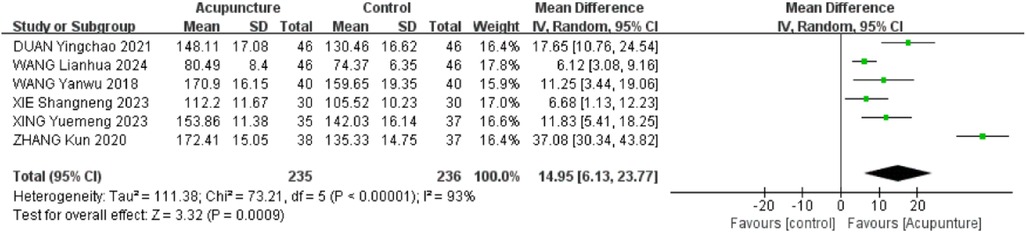
3.2.4 Shoulder mobility in forward flexion
Six RCTs (18–20, 23, 28, 31) were included. The heterogeneity of the included research results was high (I2 = 93%, P < 0.001), so a random effects model was used for meta-analysis. The results showed that the acupuncture group had a significant increase in forward flexion compared with the control group, and the difference was statistically significant [MD = 14.95, 95% CI (6.13,23.77), P < 0.001, Figure 6].
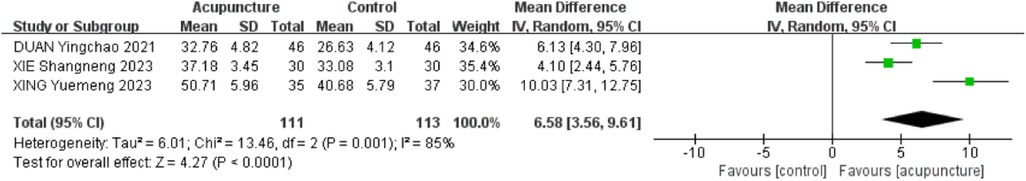
3.2.5 Shoulder mobility in backward extension
Three RCTs (19, 20, 23) were included. The heterogeneity of the included research results was high (I2 = 85%, P = 0.001), so a random effects model was used for meta-analysis. The results showed that the acupuncture group had a significant increase in backward extension compared to the control group, and the difference was statistically significant [MD = 6.58, 95% CI (3.56,9.61), P < 0.001, Figure 7].
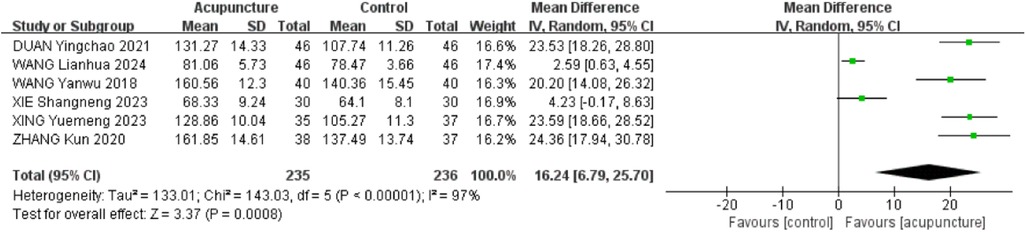
3.2.6 Shoulder mobility in abduction
Six RCTs (18–20, 23, 28, 31) were included. The heterogeneity of the included research results was high (I2 = 97%, P < 0.001), so a random effects model was used for meta-analysis. The results showed that the acupuncture group had a significant increase in abduction compared to the control group, and the difference was statistically significant [MD = 16.24, 95% CI (6.79,25.70), P < 0.001, Figure 8].
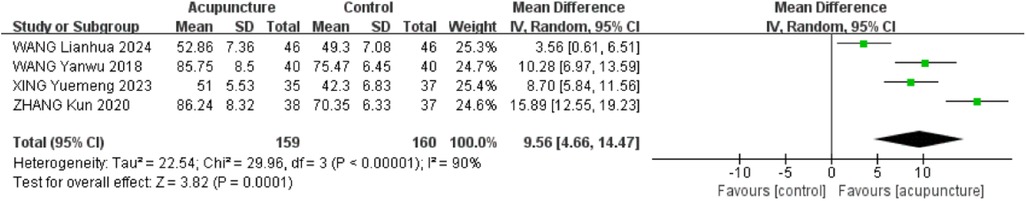
3.2.7 Shoulder mobility in external rotation
Four RCTs (18, 20, 28, 31) were included. The heterogeneity of the included research results was high (I2 = 90%, P < 0.001), so a random effects model was used for meta-analysis. The results showed that the acupuncture group had a significant increase in external rotation compared to the control group, and the difference was statistically significant [MD = 9.56, 95% CI (4.66,14.47), P < 0.001, Figure 9].
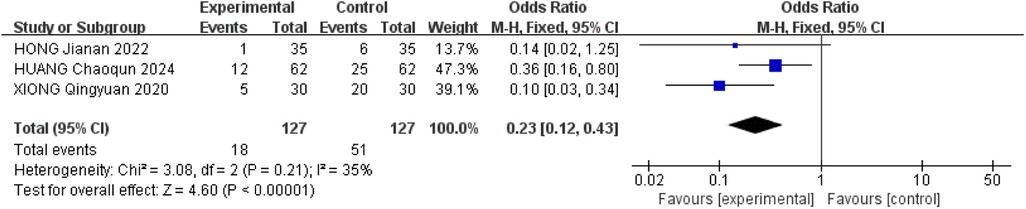
3.2.8 Adverse reactions
Adverse reactions were assessed in eighteen studies included in the analysis. Among these, eleven studies (16, 19, 22, 25, 26, 28–30, 32, 33) did not provide safety information, while seven studies (17, 18, 20, 21, 24, 27, 31) reported on adverse reactions. Specifically, four studies (18, 20, 24, 31) explicitly stated the absence of adverse reactions, while three studies (17, 21, 27) detailed a total of 66 adverse reactions. Moderate heterogeneity (P = 0.23, I2 = 35%) was observed among the study populations, leading to the utilization of a fixed-effects model. The analysis revealed a significant reduction in the risk of adverse reactions in the treatment group (OR = 0.23, 95% CI: 0.21–0.43, P < 0.001), indicating a statistically significant difference. The predominant adverse events reported were dizziness, pain, and mild gastrointestinal symptoms, supporting the favorable safety profile of acupuncture therapy for ARCR. These findings are represented in Figure 10.
3.3 Sensitivity analysis
The heterogeneity among the VAS scores, CMS scores, and shoulder mobility was substantial. Therefore, sensitivity analysis was performed to determine the source of heterogeneity for these outcomes. The sensitivity analysis was shown in Figure 11. The results remained consistent, suggesting that the stability of this study is good and the results are reliable.
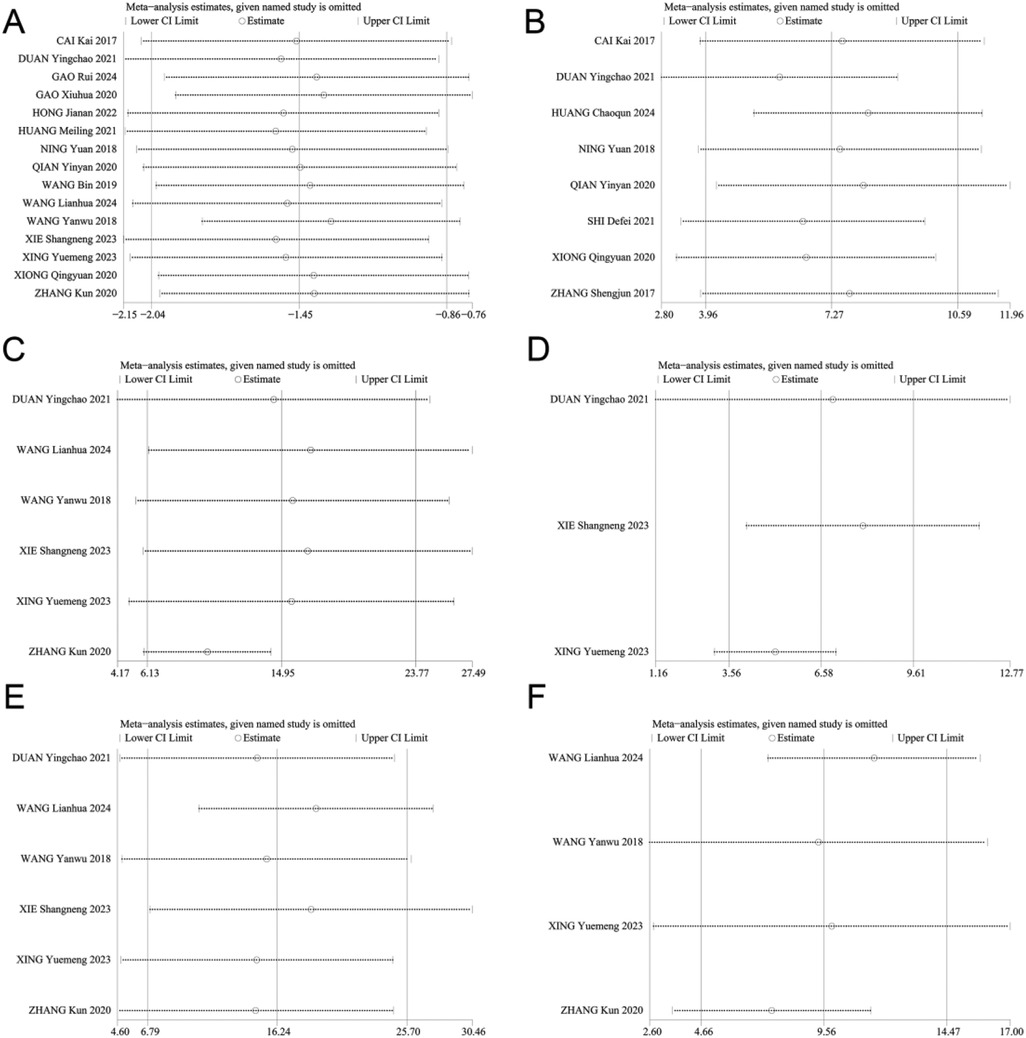
Figure 11. Sensitivity analysis of (A) VAS scores, (B) CMS scores, (C) forward flexion, (D) backward extension, (E) shoulder abduction, (F) external rotation.
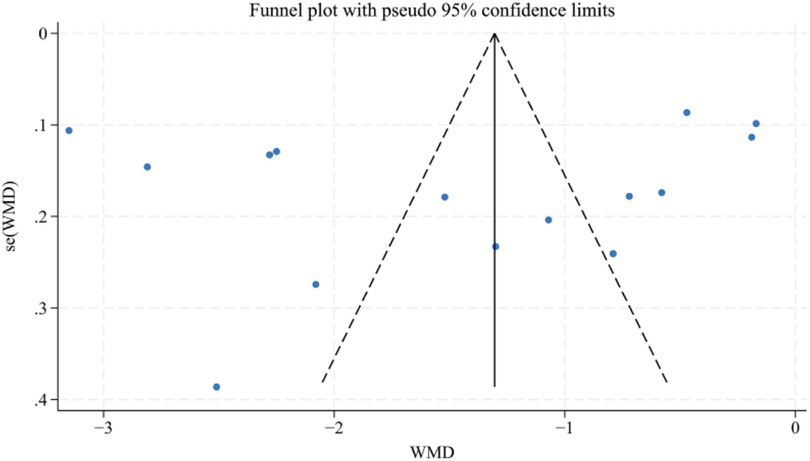
3.4 Analysis of publication bias
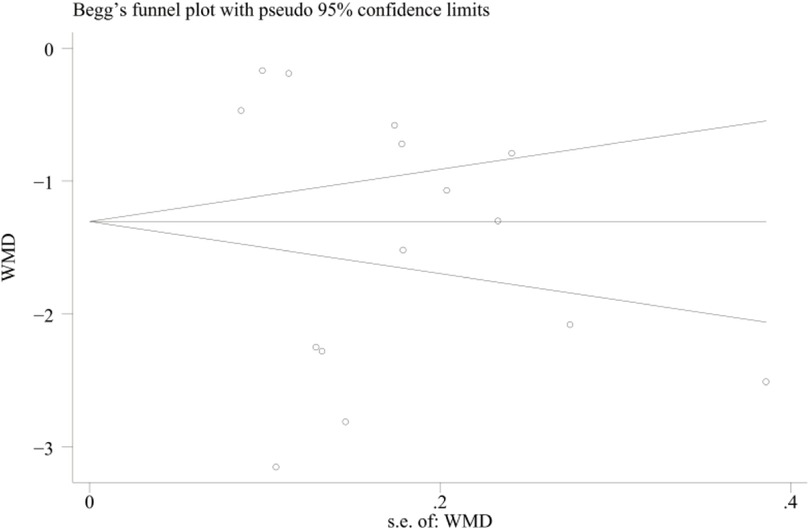
The VAS scores (n > 10) were analyzed using the Egger's test and the Begg's test for publication bias, and the results showed that there was no publication bias (Egger's test, t = −0.70, P = 0.497 > 0.05), (Begg's test, P = 0.322 > 0.05). In addition, the funnel plot showed that the distribution of each study point was basically symmetrical, indicating that there was no publication bias (Figures 12–14). Although there was a small amount of bias, the overall results were acceptable.
3.5 GRADE assessment of evidence quality
The GRADE assessment of evidence quality revealed that the effective rate and VAS scores were supported by moderate-quality evidence, while the CMS scores, shoulder mobility and adverse reactions were supported by low-quality evidence. Evidence degradation was primarily attributed to factors such as inadequate distribution concealment, absence of blinding, publication bias, and significant heterogeneity among studies, all of which undermine the reliability of the research findings. The results are shown in Figure 15.
4 Discussion
This meta-analysis aimed to quantify the impact of acupuncture therapy on postoperative rehabilitation for ARCR by summarizing the current RCTs results. It was found that acupuncture therapy showed a significant improvement in effective rate (OR = 5.02), VAS scores (MD = −1.45), CMS scores (MD = 7.27) and shoulder mobility in forward flexion (MD = 14.95), backward extension (MD = 6.58), shoulder abduction (MD = 16.24), external rotation (MD = 9.56). At present, few meta-analysis focus on acupuncture therapy intervention in postoperative rehabilitation for ARCR. This study aims to contribute to this under-explored area. Our conclusions provide some evidence-based support for adjunctive intervention of acupuncture therapy in postoperative rehabilitation of ARCR and confirm its potential therapeutic benefits. Despite heterogeneity among the studies included in the paper, publication bias detection and sensitivity analysis were performed separately, which indicated stable and reliable results.
The selected acupoints (LI14, LI15, SJ14) were chosen based on the Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) principle of “Local Points Selection” (34). From the TCM perspective, stimulating these specific points along the Hand Yangming Large Intestine meridian can promote meridian flow and regulate qi, which is considered beneficial for treating shoulder disorders (35). From a biomedical perspective, modern research has showed that acupuncture at these points can stimulate peripheral nerves and activate specific brain regions. For instance, LI14 and LI15 correspond to areas innervated by branches of the brachial plexus, particularly the axillary nerve and radial nerve. Acupuncture stimulation in these regions may help modulate pain transmission through the gate-control mechanism and activate endogenous pain-modulatory systems (36). Besides, functional MRI studies have shown that acupuncture at specific points can activate brain regions involved in pain processing and motor control, including the primary somatosensory cortex and motor cortex (37). Furthermore, these acupoints also show significant overlap with trigger points identified in myofascial pain syndrome, suggesting their potential role in releasing muscle tension and improving local circulation (38). Thus, The combination of LI14, LI15, and SI9, known as the “three shoulder points” in TCM, corresponds with Western medicine's understanding of comprehensive neuromuscular modulation in treating soft tissue shoulder disorders.
The effect of acupuncture on postoperative ARCR may be related to the following mechanisms: First, according to TCM theory, acupuncture is believed to facilitate the movement of qi and blood, and regulate the body's yin and yang balance. This corresponds to pain relief and the alleviation of soft tissue spasms in modern medicine (39, 40). Second, electroacupuncture can broaden the scope of acupoint stimulation by incorporating neuromuscular electrical stimulation, which helps to inhibit hyperreflexia and nociceptive hypersensitivity in the damaged area. Furthermore, it promotes the regeneration and repair of peripheral neuron axons, facilitating reinnervation. This process subsequently improves the function of innervated organs and prevents muscle atrophy (41–43). Finally, the heat conduction of warm acupuncture is transmitted to the acupoints through the handle of the needles along the needle. This process has been shown to enhance the induction of thermal stimulation at acupoints, promote the absorption of local inflammatory factors, thereby alleviating the pain caused by inflammatory factors in the shoulder joint. Additionally, it facilitates the expansion of blood vessels and lymphatic vessels in shoulder lesions, improving blood circulation, which in turn reduces inflammatory exudation and mitigates the adhesion of shoulder soft tissues (44–46).
Our research may have some limitations. Firstly, this paper included studies involving different types of acupuncture, acupoints and stimulus intensity, which may cause different outcome measures and generate heterogeneity. Secondly, all studies failed to mention blinding. and some of the literature had missed visits, which may cause selection bias and affect the reliability of the study results. Moreover, ARCR includes both small incision rotator cuff repair and total arthroscopic rotator cuff repair. However, this study did not restrict the type of surgery, which may have overlooked the impact of the surgery type on postoperative pain and joint mobility.
5 Conclusion
This study shows that acupuncture therapy may be beneficial for postoperative rehabilitation in patients after ARCR, as evidenced by improvements in the effective rate, CMS scores, and shoulder motion function, along with a notable reduction in VAS scores. The results must be viewed with caution due to the preliminary and heterogeneous nature of the included evidence. In the future, more well-designed, large sample size, high quality studies are needed to further validate the scientific validity of the conclusions.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
J-HC: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. KW: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Software, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. Q-lW: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
This research was funded by Wang Qinglai Famous and Elderly TCM Specialist Inheritance Workshop Construction Programme Project (grant number GZS2021034).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Chan K, MacDermid JC, Hoppe DJ, Ayeni OR, Bhandari M, Foote CJ, et al. Delayed versus early motion after arthroscopic rotator cuff repair: a meta-analysis. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. (2014) 23(11):1631–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jse.2014.05.021
2. Huberty DP, Schoolfield JD, Brady PC, Vadala AP, Arrigoni P, Burkhart SS. Incidence and treatment of postoperative stiffness following arthroscopic rotator cuff repair. Arthroscopy. (2009) 25(8):880–90. doi: 10.1016/j.arthro.2009.01.018
3. Chillemi C, Damo M, Proietti R, Polizzotti G, Ferrari S, Idone F, et al. Shoulder pain management strategies and early functional outcome after arthroscopic rotator cuff tear repair. A randomized controlled study. J Bodyw Mov Ther. (2024) 37:156–63. doi: 10.1016/j.jbmt.2023.11.003
4. Chen Y, Meng H, Li Y, Zong H, Yu H, Liu H, et al. The effect of rehabilitation time on functional recovery after arthroscopic rotator cuff repair: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PeerJ. (2024) 12:e17395. doi: 10.7717/peerj.17395
5. Thigpen CA, Shaffer MA, Gaunt BW, Leggin BG, Williams GR, Wilcox RB. The American society of shoulder and elbow Therapists’ consensus statement on rehabilitation following arthroscopic rotator cuff repair. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. (2016) 25(4):521–35. doi: 10.1016/j.jse.2015.12.018
6. Lee BG, Cho NS, Rhee YG. Effect of two rehabilitation protocols on range of motion and healing rates after arthroscopic rotator cuff repair: aggressive versus limited early passive exercises. Arthroscopy. (2012) 28(1):34–42. doi: 10.1016/j.arthro.2011.07.012
7. Kim YS, Chung SW, Kim JY, Ok JH, Park I, Oh JH. Is early passive motion exercise necessary after arthroscopic rotator cuff repair? Am J Sports Med. (2012) 40(4):815–21. doi: 10.1177/0363546511434287
8. Green S, Buchbinder R, Hetrick S. Acupuncture for shoulder pain. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. (2005) 2005(2):CD005319. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005319
9. Karamanlioglu DS, Kaysin MY, Begoglu FA, Akpinar P, Ozkan FU, Aktas I. Effects of acupuncture on pain and function in patients with subacromial impingement syndrome: a randomized sham-controlled trial. Integr Med Res. (2024) 13(2):101049. doi: 10.1016/j.imr.2024.101049
10. Zhang HN, Chen JG, Wang XY, Fan S, Bao A, Li HN, et al. Efficacy comparison between acupuncture and other modalities in the treatment of rotator cuff diseases: meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am J Transl Res. (2024) 16(2):599–616. doi: 10.62347/NCRJ1270
11. Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. J Clin Epidemiol. (2021) 134:178–89. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2021.03.001
12. Shea BJ, Reeves BC, Wells G, Thuku M, Hamel C, Moran J, et al. AMSTAR 2: a critical appraisal tool for systematic reviews that include randomized or non-randomized studies of healthcare interventions, or both. Br Med J. (2017) 358:j4008. doi: 10.1136/bmj.j4008
13. Goudman L, Pilitsis JG, Billet B, De Vos R, Hanssens K, Billot M, et al. The level of agreement between the numerical rating scale and visual analogue scale for assessing pain intensity in adults with chronic pain. Anaesthesia. (2024) 79(2):128–38. doi: 10.1111/anae.16151
14. Vrotsou K, Ávila M, Machón M, Mateo-Abad M, Pardo Y, Garin O, et al. Constant-Murley scores: systematic review and standardized evaluation in different shoulder pathologies. Qual Life Res. (2018) 27(9):2217–26. doi: 10.1007/s11136-018-1875-7
15. Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M, Minder C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. Br Med J. (1997) 315(7109):629–34. doi: 10.1136/bmj.315.7109.629
16. Gao R, Zhong P. A clinical study on promoting motor function rehabilitation of patients after rotator cuff repair surgery by electroacupuncture. Clin J Chin Med. (2024) 16(3):69–71. (In Chinese, English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7860.2024.03.017
17. Huang C, Zhang Y, Lin J, Tu Y, Zhuang J, Zhang X, et al. The effect of buccal acupuncture therapy on postoperative analgesia and rehabilitation in patients undergoing rotator cuff repair. J Wenzhou Med Univ. (2024) 54(3):205–10+16. (In Chinese, English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-9400.2024.03.005
18. Wang L, Wan F, Le M. Effects of wrist-ankle acupuncture combined with staged exercise rehabilitation training on postoperative patients with rotator cuff injury. Med J Chin People’s Health. (2024) 36(8):90–2. (In Chinese, English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0369.2024.08.027
19. Xie S, Lai J, Li Z, Ye Z, Huang Z. Effects of electroacupuncture combined with neuromuscular electrical stimulation on pain and function in elderly rotator cuff repair patients. Chin J Gerontol. (2023) 43(18):4403–6. (In Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2023.18.017
20. Xing Y, Wang Y, Duan Y, Wang Z, Cai B, Deng B. Effect of wrist-ankle acupuncture on functional recovery of the shoulder joint after arthroscopic rotator cuff repair. J Guangzhou Univ TCM. (2023) 40(07):1723–28. (In Chinese, English abstract). doi: 10.13359/j.cnki.gzxbtcm.2023.07.022
21. Hong J, Lei L. Analysis of the effect of combined acupuncture after arthroscopic rotator cuff repair in the treatment of rotator cuff tears. Med Diet Health. (2020) 20(03):70–2+76. (In Chinese).
22. Shi D. Therapeutic effect of “shoulder three needles” in treating residual symptoms of cold condensation and blood stasis in patients after rotator cuff repair surgery. Zhejiang J TCM. (2021) 56(08):607. (In Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0411-8421.2021.08.035
23. Duan Y, Xu L, Li L. Effect of conventional rehabilitation training combined with electroacupuncture on pain and joint function of patients after arthroscopic rotator cuff injury. China Modern Med. (2021) 28(24):105–8. (In Chinese, English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-4721.2021.24.030
24. Huang M, Xie W, Wang A, Lu J, Ye X, Wu B, et al. Therapeutic observation on moxibustion with warming needle promoting function recovery after rotator cuff repair. J Guangzhou Univ TCM. (2021) 38(01):74–8. (In Chinese, English abstract). doi: 10.13359/j.cnki.gzxbtcm.2021.01.015
25. Gao X, Jia M, Guo H, Wu Z, Sun J, Luo D, et al. The effect of the reperfusion approach of Fu’s needling with joint mobilization on postoperative rehabilitation of rotator cuff injury based on the theory of anatomy train. Clin J Chin Med. (2020) 12(26):102–5. (In Chinese, English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7860.2020.26.038
26. Qian Y, Shou L. Application of wrist—ankle acupuncture therapy to postoperative functional rehabilitation in patients with rotator cuff injuries. J Trad Chin Orthop Trauma. (2020) 32(05):11–4. (In Chinese, English abstract).
27. Xiong Q, Ding H, Wu J. Clinical effect of wrist and ankle acupuncture in the treatment of moderate and severe pain after shoulder arthroscopy. Contemp Med. (2020) 26(03):14–6. (In Chinese, English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-4393.2020.03.006
28. Zhang K. Study on the efficacy of acupuncture combined with joint release on postoperative rehabilitation of rotator cuff injury. Prac Clin J Integr Trad Chin Western Med. (2020) 20(17):30–1+61. (In Chinese). doi: 10.13638/j.issn.1671-4040.2020.17.014
29. Wang B, Liu Q. Snap-needle combined with rehabilitation training for the treatment of postoperative dysfunction of rotator cuff injury effectiveness observation. Med J Commun. (2019) 33(06):579–80+83. (In Chinese). doi: 10.19767/j.cnki.32-1412.2019.06.012
30. Ning Y, Sun F, Tong P. Application of electroacupuncture and rehabilitation exercises to postoperative rehabilitation of rotator cuff injuries. J Trad Chin Orthop Trauma. (2018) 30(01):29–31. (In Chinese, English abstract).
31. Wang Y, Wang C, Chen D, Ye X. Shoulder joint pain of rotator cuff injury treated with electroacupuncture and Mulligan’s mobilization: a randomized controlled trial. Chin Acupunct Moxibustion. (2018) 38(01):17–21. (In Chinese, English abstract). doi: 10.13703/j.0255-2930.2018.01.004
32. Zhang S, Sun F, Xu F. Observations on the efficacy of shoulder-three-points warm needling moxibustion plus conventional rehabilitation in recovery from rotator cuff repair. Shanghai J Acu-mox. (2017) 36(06):735–8. (In Chinese, English abstract). doi: 10.13460/j.issn.1005-0957.2017.06.0735
33. Cai K. Clinical observation on patients with rotator cuff repair treated with warm acupuncture and shoulder three needles. CJGMCM. (2017) 32(23):3443–4. (In Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8914.2017.23.042
34. Zhang Y, Chen S, Chen B, Wang K, Chen J, Chen Z, et al. ‘Local points selection’ from perspective of acupuncture contraindication. J Clin Acupunct Moxibustion. (2022) 38(04):90–3. doi: 10.19917/j.cnki.1005-0779.022082
35. Maciocia G. The Foundations of Chinese Medicine: A Comprehensive Text for Acupuncturists and Herbalists. 3rd ed. Nanjing: Elsevier (2015).
36. Jing W, You W. Acupuncture mechanisms: anesthesia, analgesia and protection on organ functions. World J Chin Med. (2015) 1(1):59–66. doi: 10.15806/j.issn.2311-8571.2014.0012
37. Huang Y. Utilizing functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) to explore the central mechanisms of acupuncture in treating cervical spondylosis (master's thesis). Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou, China (2012).
38. Luo D, Huang J, Zhao N. Clinical study on dry needling therapy based on myofascial TriggerPoints for neck-shoulder myofascial pain syndrome. New Chin Med. (2022) 54(05):205–10. doi: 10.13457/j.cnki.jncm.2022.05.048
39. Zhang R, Lao L, Ren K, Berman BM. Mechanisms of acupuncture-electroacupuncture on persistent pain. Anesthesiology. (2014) 120(2):482–503. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000000101
40. Vas J, Ortega C, Olmo V, Perez-Fernandez F, Hernandez L, Medina I, et al. Single-point acupuncture and physiotherapy for the treatment of painful shoulder: a multicentre randomized controlled trial. Rheumatology. (2008) 47(6):887–93. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/ken040
41. Lewis J, Sim J, Barlas P. Acupuncture and electro-acupuncture for people diagnosed with subacromial pain syndrome: a multicentre randomized trial. Eur J Pain. (2017) 21(6):1007–19. doi: 10.1002/ejp.1001
42. Heo J-W, Jo J-H, Lee J-J, Kang H, Choi T-Y, Lee MS, et al. Electroacupuncture for the treatment of frozen shoulder: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Med (Lausanne). (2022) 9:928823. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.928823
43. Chen ZY, Wang MH, Ye Z. Effect of electroacupuncture combined with rehabilitation techniques on shoulder function in patients with rotator cuff injuries. World J Clin Cases. (2024) 12(21):4582–9. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i21.4582
44. Wang H, Fan D, Lan Q, Gong H. Clinical efficacy of adhesion release under brachial Plexus block plus silver needle warm acupuncture on frozen shoulder and recovery of limb function. Altern Ther Health Med. (2025) 31(1):251–7.38639609
45. Xu C, Li X, Li J. Comparative study on curative effect and recurrence rate of chronic scapulohumeral periarthritis treated with different acupuncture techniques. Acupunct Res. (2024) 49(02):164–70. (In Chinese, English abstract). doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.20221004
Keywords: acupuncture therapy, arthroscopic rotator cuff repair, meta-analysis, postoperative rehabilitation, shoulder mobility
Citation: Chen J-H, Wu K and Wang Q-l (2025) Acupuncture therapy in postoperative rehabilitation for arthroscopic rotator cuff repair: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Surg. 12:1631880. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2025.1631880
Received: 20 May 2025; Accepted: 8 August 2025;
Published: 9 September 2025.
Edited by:
Angelo Alito, Univerisity of Messina, ItalyReviewed by:
Domiziano Tarantino, University of Naples Federico II, ItalyXun Luo, Kerry Rehabilitation Medicine Research Institute, China
Copyright: © 2025 Chen, Wu and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Qing-lai Wang, MTkzMjIwNjQ1M0BxcS5jb20=
 Jia-Hao Chen
Jia-Hao Chen Kai Wu
Kai Wu