- 1Department of Neurosurgery, The Third Hospital of Shijiazhuang, Shijiazhuang, China
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, The Second Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang, China
Objectives: To identify predictive prognostic factors through logistic regression analysis in patients with cervical degenerative disc disease (CDDD) undergoing anterior cervical discectomy and fusion (ACDF) combined with the Bagby and Kuslich (BAK/C) interbody fusion technique.
Methods: This retrospective study included 80 patients treated with ACDF and BAK/C between January and December 2020, with a 3-year follow-up. Patients were stratified into a control group (favorable recovery, n = 52) and an observation group (poor recovery, n = 28) based on pain relief and neurological improvement. Radiological fusion rates and Japanese Orthopaedic Association (JOA) scores were evaluated. Multivariate logistic regression was performed to assess independent predictors of outcomes.
Results: The control group exhibited significant JOA score improvement at the final follow-up (14.49 ± 0.25 vs. preoperative 10.74 ± 1.16, P < 0.001), while the observation group showed limited recovery (12.19 ± 0.32 vs. preoperative 11.15 ± 1.45, P < 0.001). The overall fusion rate was significantly higher in the control group (92.3% vs. 64.3%, P = 0.002). Multivariate analysis identified age ≥55 years (observation group: 62.35 ± 5.41 vs. control: 51.47 ± 6.37, P < 0.001), reduced bone mineral density (T-score: −2.1 ± 0.8 vs. −1.3 ± 0.6, P < 0.001), postoperative complications (46.4% vs. 13.5%, P = 0.003), and baseline disease severity as independent risk factors for poor outcomes (P < 0.05). The observation group demonstrated significantly higher pseudoarthrosis rates (35.7% vs. 9.6%, P = 0.003).
Conclusion: Advanced age, low bone density, and postoperative complications critically compromise outcomes of ACDF with BAK/C fusion. Preoperative bone density optimization, judicious use of augmented multi-level fixation, and precision patient selection are pivotal for improving prognosis. These findings provide evidence-based insights for individualized clinical decision-making.
Introduction
Degenerative diseases of the cervical intervertebral disc involve pathophysiological processes such as the reduction of intervertebral disc height and spinal cord compression due to disc degeneration, commonly referred to as cervical spondylosis (1). With an aging population and changing lifestyles, the prevalence of cervical degenerative disc disease (CDDD) is steadily increasing (2, 3). This condition significantly affects patients' quality of life, often leading to symptoms such as neck and shoulder pain, upper limb radiation pain, and sensory and motor dysfunction. These symptoms can severely impair patients' ability to work and engage in normal daily activities.
Anterior cervical discectomy and fusion (ACDF) is a widely used and effective surgical approach for treating CDDD. ACDF involves removing the intervertebral disc and bone tissue compressing the nerve structures through an anterior cervical incision, thereby alleviating nerve compression symptoms (4). Bone grafts and interbody devices are typically implanted to maintain intervertebral space stability and promote bone fusion (5). The main advantage of ACDF is the direct removal of the compressed structures, such as intervertebral discs and osteophytes, which relieves pressure on the nerves. Additionally, modern ACDF techniques are associated with high success rates, minimal trauma, and relatively quick postoperative recovery, with success rates exceeding 90% reported in contemporary practices (6). ACDF is effective for both single and multiple levels of degenerative disc disease, particularly in patients with prominent nerve root compression symptoms (7).
The Brantigan, Allograft, and Kuslich/Cadaveric (BAK/C) interbody fusion technique, a classic threaded cage design, is commonly used in conjunction with ACDF surgery to enhance the fusion success rate and stability (8). Despite increasing adoption of newer cage designs made from materials like polyetheretherketone (PEEK) or porous titanium, the BAK/C technique remains clinically relevant, particularly in resource-limited settings, due to its cost-effectiveness and proven mid-term outcomes (9). During BAK/C fusion, bone grafts—often sourced from the patient's own body or synthetic materials—are placed in the intervertebral space to promote vertebral fusion, thereby increasing the stability of the intervertebral space (10). This technique helps reduce postoperative intervertebral motion and alleviates cervical pain in patients. The BAK/C fusion method is particularly beneficial for patients with severe degenerative disc disease, unstable intervertebral spaces, or extensive disc resections.
However, despite the widespread clinical use of ACDF and BAK/C techniques, patient responses to treatment can vary significantly. While some patients experience substantial improvements in neurological function and pain relief, others may show minimal improvements or even worsening symptoms (11, 12). We hypothesize that patient-specific factors (age, bone quality, and postoperative care) rather than technical variables primarily determine clinical outcomes in BAK/C-assisted ACDF. Consequently, it is essential to explore the factors influencing the effectiveness of ACDF combined with BAK/C interbody fusion for treating CDDD. Previous studies have focused predominantly on implant-related factors (13), with limited analysis of modifiable patient characteristics. Understanding these predictors can help clinicians optimize treatment plans and improve surgical outcomes for patients (14).
This study retrospectively analyzed 80 patients with CDDD treated at our hospital between January and December 2020. The primary focus was to explore the factors influencing the curative effect of ACDF combined with BAK/C interbody fusion, through logistic regression analysis. This comprehensive factor analysis addresses a critical gap in existing literature by evaluating both surgical and patient-related variables over a 3-year follow-up period.
Methods and materials
Ethical considerations
This study received approval from The Third Hospital of Shijiazhuang Ethics Committee. The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. All participants provided written informed consent for retrospective data analysis through opt-out methodology, with personal identifiers removed during data processing.
Patient enrollment process
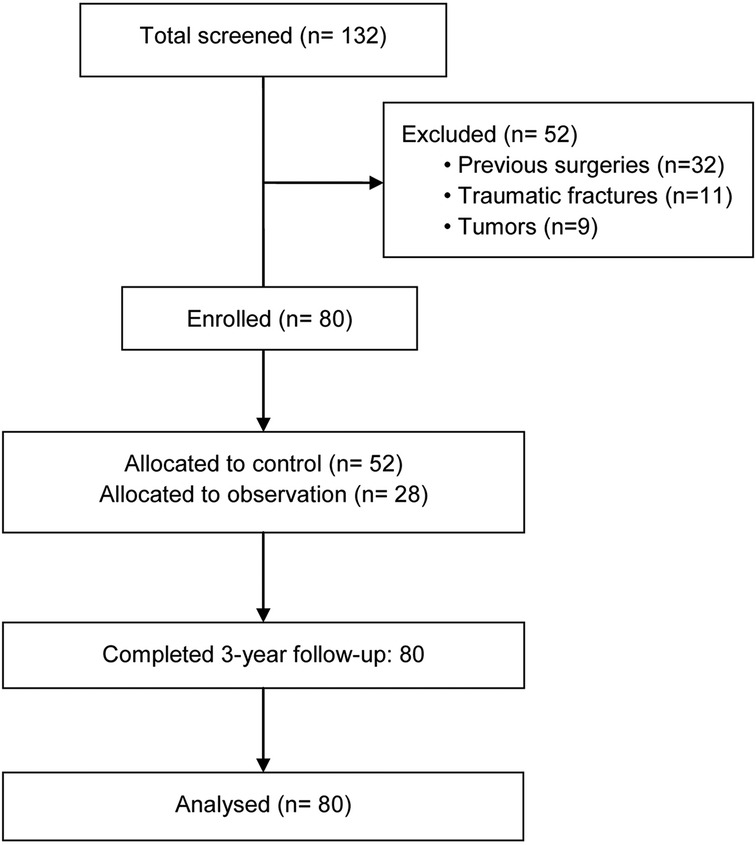
Between January-December 2020, 132 consecutive patients with CDDD were screened for eligibility at our institution. After excluding 52 patients (32 with previous cervical surgeries, 11 with traumatic fractures, and 9 with tumors), 80 patients met the inclusion criteria. These patients were subsequently divided into a control group (n = 52) and an observation group (n = 28) based on their 3-year follow-up outcomes (Figure 1).
General information
A retrospective analysis was conducted on 80 hospitalized patients with degenerative cervical intervertebral disc disease at our hospital from January to December 2020. All patients underwent ACDF surgery using the BAK/C technique. The age of the patients ranged from 36–75 years (mean 55.36 ± 7.28). Of the patients, 57 were male and 23 were female. All patients had a complete 3-year follow-up. Based on clinical outcomes reported at follow-up, the patients were divided into two groups: the control group (good neurological recovery, n = 52) and the observation group (minimal or worsened neurological recovery, n = 28). Good recovery was defined as having a postoperative Visual Analog Scale (VAS) score for neck/arm pain of ≤2 (representing minimal to no residual pain) combined with a Japanese Orthopaedic Association (JOA) score improvement of ≥4 points, which is considered a significant neurological recovery (15). Poor recovery was defined as a VAS score >2 with a JOA improvement of <2 points or any neurological deterioration (15). These thresholds were based on clinically meaningful changes, where a VAS score ≤2 correlates with excellent pain control (16), and a JOA improvement ≥4 points reflects substantial functional restoration (15). The combination of these was used to stringently define a favorable outcome. While other methods like ROC curve analysis could derive statistical cutoffs, our approach used established clinical benchmarks to ensure the relevance of the outcome groups.
Inclusion criteria
• Patients aged ≥ 18 years, regardless of gender.
• Diagnosed with degenerative cervical intervertebral disc disease based on clinical and imaging findings.
• Significant pain and/or neurological symptoms impacting quality of life, requiring surgery.
• Underwent anterior decompression and BAK/C interbody fusion.
• Availability of complete data for a minimum 3-year follow-up.
Exclusion criteria
• Serious cervical conditions (e.g., fracture, infection, tumor).
• Previous cervical surgery.
• Pregnant or lactating women.
Surgical technique
Under general anesthesia, patients were positioned supine with slight neck extension. A right anterior approach was used to expose the cervical spine. The anterior longitudinal ligament was opened, and the intervertebral space was distracted using a Casper distractor. After discectomy, a reamer was used to enlarge the disc space, and osteophytes were removed using a micro curette or Kerrison rongeur. All surgical procedures were performed by a team of two senior neurosurgeons (L.H. with >10 years experience, and another with >15 years experience) to minimize variability in technique. A standardized threaded cylindrical titanium alloy BAK/C cage (Zimmer Biomet, Warsaw, IN, USA) was consistently used in all patients. Anterior cervical plates were selectively used in multi-level procedures (n = 14/22 multi-level cases) based on intraoperative stability assessment using the White-Panjabi criteria (17). BAK/C fusion and autogenous bone fragments, harvested locally from the vertebral bodies, were used to repair spinal defects. Eight patients received additional bone grafting from the iliac crest due to poor local bone stock. Postoperatively, all patients wore a Philadelphia hard neck brace for 2 months.
Radiological evaluation
X-rays were obtained before surgery, 1 week post-op, at 6 months, and at the final follow-up. Bone mineral density was assessed preoperatively using dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) at the lumbar spine (GE Lunar Prodigy). Bone density was reported using the T-score, which compares a patient's BMD to that of a healthy, young adult reference population. The D-value, defined as the sagittal diameter of the spinal canal at the most compressed level, was measured on preoperative T2-weighted sagittal MRI scans to quantify the degree of baseline stenosis. Anteroposterior, lateral, and dynamic flexion-extension x-rays were evaluated independently by two spinal surgeons and one radiologist blinded to clinical outcomes. Firm fusion was indicated when both of the following criteria were met: (1) segmental motion on extension-flexion radiographs <2 degrees, and (2) bridging trabecular bone across ≥50% of the graft-host interface on CT scans (18). While CT scans were not routinely obtained for all patients at final follow-up, they were mandated for all cases where non-union was suspected on dynamic flexion-extension radiographs. This protocol ensured CT confirmation for all 15 cases of pseudoarthrosis reported in this study. Figure 2 shows primary fusion with BAK/C. The intervertebral height (anterior and posterior edges) was measured, and changes were calculated between post-op and final follow-up.
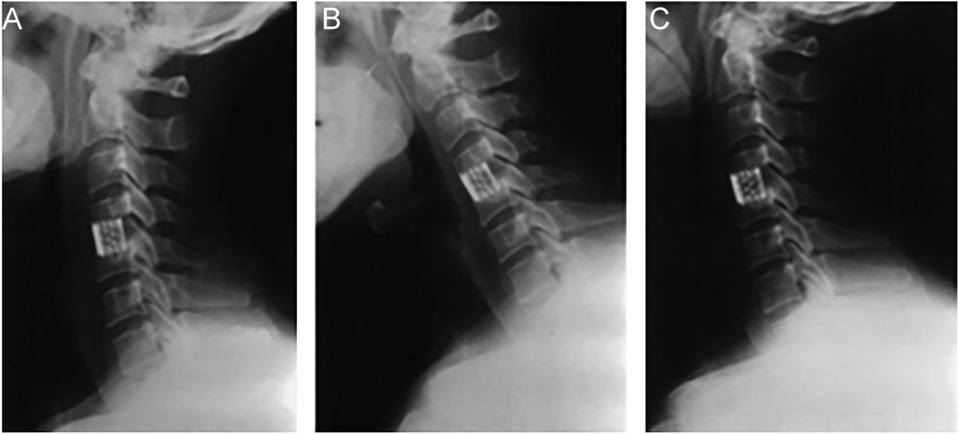
Figure 2. Representative radiographs of a patient undergoing single-level ACDF with a BAK/C cage at C5–6. (A) Preoperative lateral x-ray showing disc space narrowing and osteophyte formation. (B) Lateral x-ray at 1 week post-op showing cage placement and restored intervertebral height. (C) Lateral x-ray at the final 3-year follow-up demonstrating solid bony fusion and maintained alignment.
JOA score
The JOA scoring system (19) was used to assess neurological impairment in cervical spondylosis patients, evaluating sensory, motor, and activity functions. The total JOA score ranged from 0–17, with lower scores indicating more severe impairment. Neurological recovery rate was calculated as: (Postoperative score—Preoperative score)/(17—Preoperative score) × 100%. Scores of 15–17 were considered mild, 11–14 moderate, and 0–10 severe. The JOA score helped assess the neurological function and severity of the disease.
Statistical analysis
A post-hoc sensitivity analysis was performed using G*Power software (version 3.1) to determine the minimum effect size our study could reliably detect (20). With our sample sizes (n = 52 in the control group, n = 28 in the observation group), an alpha of 0.05, and a power of 80%, the analysis indicated that our study was sufficiently powered to detect an odds ratio of 2.75 or greater for the primary binary predictors in the logistic regression model. This confirms the adequacy of our sample size for identifying clinically meaningful risk factors. Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation for continuous variables and as frequencies (percentages) for categorical variables. The Student's t-test or Mann–Whitney U test was used for continuous data, and the chi-square test or Fisher's exact test was used for categorical data to compare groups. Complications were classified using the Spinal Adverse Events Severity system (21), categorized as intraoperative, early postoperative (<30 days), or late postoperative (>30 days). A P-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Statistical analysis was conducted using SPSS version 26.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA).
Results
General data analysis
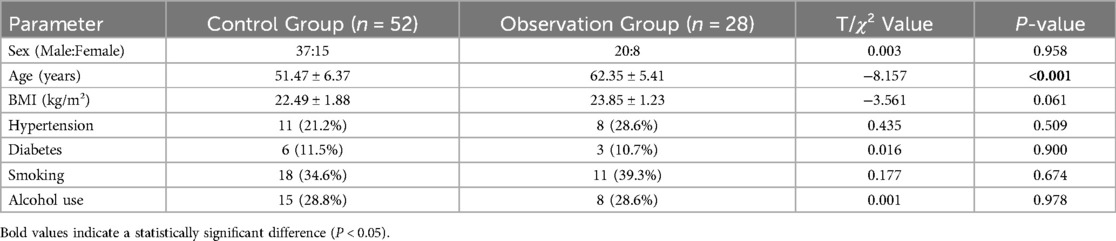
The baseline characteristics of the two groups are presented in Table 1. The male-to-female ratio in the control group was 37:15, with an average age of 51.47 ± 6.37 years and a BMI of 22.49 ± 1.88 kg/m². In the observation group, the male-to-female ratio was 20:8, with an average age of 62.35 ± 5.41 years and a BMI of 23.85 ± 1.23 kg/m². The average age of the observation group was significantly higher than that of the control group (P = 0.015). No significant differences were found in sex, BMI, hypertension, diabetes, smoking, or alcohol use between the two groups (P > 0.05).
Fusion segment distribution
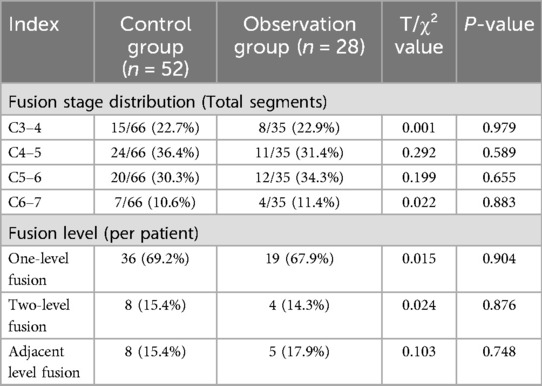
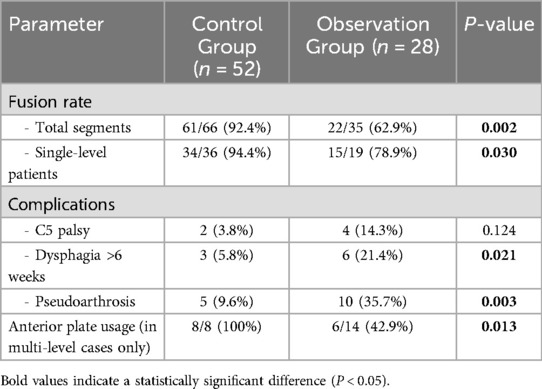
The distribution and fusion levels of the segments are detailed in Table 2. In the control group, ACDF with BAK/C involved 66 segments, with C4–5 being the most common level. Definitive fusion was achieved in 61/66 segments (92.4%). In the observation group, the procedure involved 35 segments, with C5–6 being the most common level. Definitive fusion was achieved in only 22/35 segments (62.9%). There were no significant differences in the distribution of operated levels or the number of levels fused (one, two, or adjacent) between the two groups (P > 0.05).
JOA scores of patients treated with ACDF and BAK/C
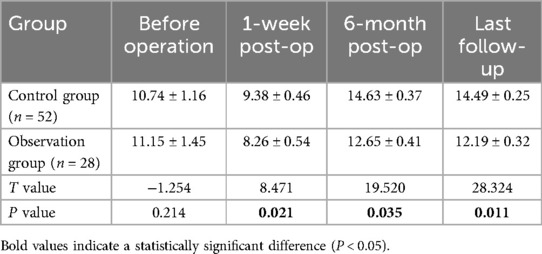
The JOA scores were used to evaluate cervical nerve function over time (Figure 3, Table 3). Preoperative JOA scores were comparable between groups (control: 10.74 ± 1.16 vs. observation: 11.15 ± 1.45, P = 0.475). At one week post-surgery, both groups showed transient JOA score reductions (control: 9.38 ± 0.46 vs. observation: 8.26 ± 0.54), though the difference was not statistically significant (P = 0.021). By the 6-month follow-up, the control group demonstrated superior recovery (14.63 ± 0.37 vs. 12.65 ± 0.41, P = 0.035), with sustained significant differences at the final follow-up (14.49 ± 0.25 vs. 12.19 ± 0.32, P = 0.011).
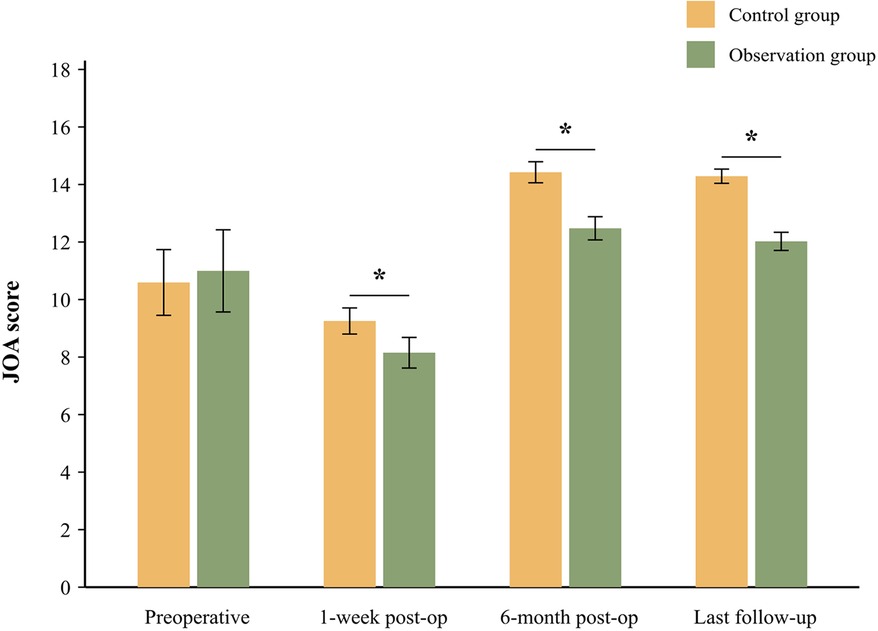
Figure 3. JOA scores of patients before and after the operation. Error bars represent standard deviation. *P < 0.05 indicates a significant difference between the control and observation groups at the specified time point.
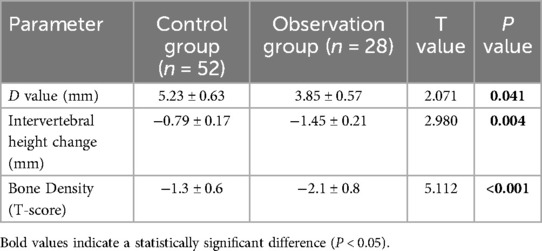
Radiological analysis of patients treated with ACDF and BAK/C
Radiological analysis revealed significant differences in key parameters (Table 4). The preoperative D-value (spinal canal diameter) was significantly lower in the observation group compared to the control group (3.85 ± 0.57 mm vs. 5.23 ± 0.63 mm, P = 0.041), indicating more severe baseline stenosis. Lumbar spine bone mineral density was also significantly lower in the observation group (T-score: −2.1 ± 0.8 vs. −1.3 ± 0.6, P < 0.001). The loss of intervertebral height at final follow-up was significantly greater in the observation group (−1.45 ± 0.21 mm vs. −0.79 ± 0.17 mm, P < 0.001). These findings indicate that the structural maintenance of the cervical vertebrae in the observation group was less effective compared to the control group.
Analysis of factors affecting treatment outcome
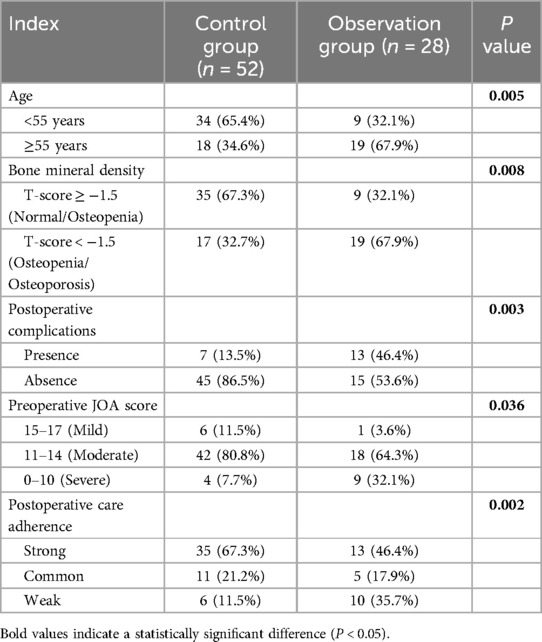
A univariate analysis was performed to examine factors influencing the treatment outcomes of ACDF combined with BAK/C fusion (Table 5). According to the preoperative JOA scores, the initial condition of patients in the observation group was more severe than in the control group. Significant differences were found between the two groups in terms of age, bone mineral density, rate of postoperative complications, initial condition, and patients' self-reported postoperative care adherence (P < 0.05).
Logistic regression analysis of factors influencing therapeutic effect
Multivariate logistic regression analysis revealed that age ≥55 years, low bone mineral density (T-score < −1.5), severe initial condition (preoperative JOA score ≤ 10), the presence of postoperative complications, and weak postoperative care adherence were all significant independent risk factors influencing the efficacy of ACDF combined with BAK/C interbody fusion in treating CDDD (P < 0.05) (Table 6).
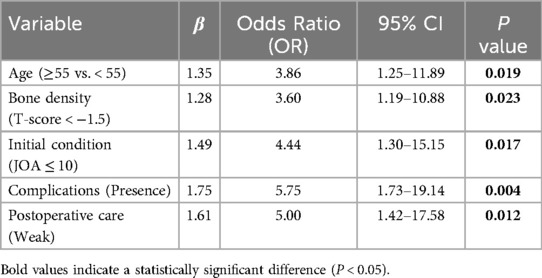
Table 6. Logistic regression analysis of influencing factors of therapeutic effect of ACDF and BAK/C.
Surgical outcomes
A dedicated analysis of surgical parameters (Table 7) revealed critical differences between groups. The control group demonstrated a significantly higher fusion rate in single-level procedures (94.4% vs. 78.9%, P = 0.03). Postoperative complications were significantly more frequent in the observation group, including persistent dysphagia (>6 weeks) and most notably, pseudoarthrosis (35.7% vs. 9.6%, P = 0.003). In multi-level cases, the use of anterior plating was significantly higher in the control group (100% vs. 42.9%, P = 0.001), correlating with better fusion outcomes in that cohort.
Discussion
Degenerative disease of the cervical intervertebral disc is a common condition, with its prevalence increasing due to the aging population. Anterior cervical discectomy and fusion (ACDF) remains a gold standard for surgical treatment, but the effectiveness may vary among patients (22). Therefore, investigating the factors influencing the treatment outcomes of these surgeries is crucial to making precise, evidence-based clinical decisions, ultimately improving therapeutic outcomes and patients' quality of life.
In this study, we retrospectively analyzed 80 patients who underwent ACDF and BAK/C interbody fusion for the treatment of CDDD. The aim was to explore the influencing factors affecting treatment efficacy. Multivariate logistic regression analysis revealed that advanced age, low bone mineral density, severe initial condition, postoperative complications, and poor postoperative care adherence were the primary factors influencing the treatment outcomes.
We identified age as a crucial factor significantly affecting treatment outcomes. As patients age, the severity of cervical degeneration tends to increase, leading to further degeneration of the intervertebral discs and structural imbalances in the cervical spine (23, 24). This aligns with studies showing that patients >60 years exhibit slower postoperative neurological recovery, with JOA score improvements lagging behind younger cohorts by approximately 8.3% (elderly recovery rate: 42.8% ± 28.5% vs. younger: 51.1% ± 32.2%, p < 0.05) (25). The reduced recovery in elderly patients correlates with lower preoperative JOA scores and age-related physiological limitations, though surgical intervention remains beneficial across all age groups (25, 26). These changes can exacerbate nerve root compression, and elderly patients often have weakened bone metabolism and repair functions, which can impede postoperative rehabilitation (27).
Bone mineral density was also found to be a key factor. The poor bone mineral density observed in the observation group is often associated with osteoporosis. Our findings corroborate recent evidence that low BMD, particularly T-scores < −2.0, significantly increases the risk of pseudoarthrosis and other mechanical complications after fusion surgery, as reduced BMD directly compromises implant stability and fusion success (28, 29). Specifically, osteoporotic patients (T-score ≤ −2.5) exhibit higher rates of pseudarthrosis and unplanned revisions due to weakened bone microstructure impairing graft integration, while low BMD also elevates risks of cage subsidence, screw loosening, and vertebral collapse (28, 29). Low bone density weakens the stability of the fusion segment, affecting the stability of the implant and hindering the fusion process. This significantly impacts the success of the surgery and its therapeutic efficacy.
Based on our findings, the severity of the patient's initial condition was another critical factor. The lower preoperative JOA scores and smaller D-values in the observation group suggested that their baseline condition was more severe. The 35% poor outcome rate (28/80) in our cohort aligns with historical controls reporting 30%–40% suboptimal results in patients with advanced degeneration (30). Severe initial conditions may result in significant neurological impairment. Although surgery can alleviate compression, the recovery of neurological function may take longer, emphasizing the importance of postoperative rehabilitation (31–33).
Postoperative complications were also found to play a significant role. Almost half of the patients in the observation group experienced postoperative complications. Notably, our pseudoarthrosis rate of 35.7% in the observation group exceeds rates reported with modern stand-alone or zero-profile implants (10%–20%) (34), potentially reflecting the older design of the BAK/C cage and the higher-risk profile of this patient subgroup. These considerations are critical as alternative motion-preserving strategies, such as cervical disc replacement (CDR), present different risk-benefit profiles, including lower pseudoarthrosis risk but potential for heterotopic ossification (35). In multi-level disease, the debate between fusion, arthroplasty, and hybrid surgery further underscores that surgical choices must be highly individualized to the patient's anatomy, bone quality, and functional goals (36).
It is also important to acknowledge the potential for selection bias inherent in this study's retrospective design. The allocation of patients into “favorable” and “poor” outcome groups was determined post-hoc, based on their 3-year results. Consequently, the observed significant differences in baseline characteristics, such as age and preoperative JOA scores, are expected findings that may reflect the natural history of the disease in these subgroups. While our multivariate logistic regression was employed to statistically adjust for these baseline differences and identify independent predictors, this observational design cannot establish causality. Future prospective studies are warranted to corroborate these risk factors in a more controlled setting.
Study limitations
Our findings should be interpreted in light of several limitations. First, the retrospective design introduces potential selection bias and unmeasured confounders. While we standardized the surgical team and primary implant, variations in operative time, blood loss, and the selective use of anterior plating in multi-level cases were not included in the main regression model and could have influenced outcomes. Second, the sample size (n = 80), while providing adequate power for the primary analysis, was insufficient for internal validation by splitting the data into training and testing sets. The absence of an external validation cohort means our findings require confirmation in other patient populations. Third, the 3-year follow-up precludes assessment of very late complications like adjacent segment degeneration. Finally, pseudoarthrosis was diagnosed radiographically with mandatory CT confirmation for suspected cases, but the absence of routine CT for all patients may underestimate its true prevalence (37).
Clinical implications
The identified risk factors (age, bone density) highlight actionable targets for preoperative optimization. For elderly patients, preoperative bone density screening and anti-osteoporotic therapy could enhance fusion success (38). In severe degenerative cases, hybrid techniques combining ACDF with dynamic stabilization may mitigate adjacent-level risks (39). Emerging technologies like 3D-printed titanium cages show promise in improving fusion rates in osteoporotic patients (40), warranting further comparative studies.
Conclusion
This study demonstrates that age ≥55 years and reduced bone mineral density (T-score < −1.5) are critical determinants of suboptimal outcomes following ACDF with BAK/C interbody fusion. The high pseudoarthrosis rate (35.7%) in at-risk patients underscores the necessity for preoperative bone density optimization and adoption of enhanced fusion technologies. These findings emphasize a precision medicine approach to surgical candidate selection and perioperative management in cervical degenerative disease.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Ethics Committee of The Third Hospital of Shijiazhuang. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
LH: Conceptualization, Project administration, Writing – review & editing, Methodology. AZ: Formal analysis, Writing – original draft, Investigation, Data curation. FZ: Writing – original draft, Formal analysis, Supervision. HL: Validation, Writing – original draft, Data curation. XS: Supervision, Investigation, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviations
ACDF, anterior cervical discectomy and fusion; BAK/C, Brantigan, Allograft, and Kuslich/Cadaveric; BMD, bone mineral density; CDDD, cervical degenerative disc disease; JOA: Japanese orthopaedic association; VAS, visual analog scale
References
1. Li G, Yang L, Wu G, Qian Z, Li H. An update of interbody cages for spine fusion surgeries: from shape design to materials. Expert Rev Med Devices. (2022) 19(12):977–89. doi: 10.1080/17434440.2022.2165912
2. Godlewski B, Dominiak M. Advantages and disadvantages of the use of various types of interbody implants in cervical spine surgery. Critical review of the literature. Ortop Traumatol Rehabil. (2020) 22(4):213–20. doi: 10.5604/01.3001.0014.3457
3. Alomar SA, Maghrabi Y, Baeesa SS. Outcome of anterior and posterior endoscopic procedures for cervical radiculopathy due to degenerative disk disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Global Spine J. (2022) 12(7):1546–60. doi: 10.1177/21925682211037270
4. Schuermans VNE, Smeets A, van de Kar LGC, Hermans SMM, Curfs I, Boselie TFM, et al. A systematic review on neurological outcomes for cervical degenerative myelopathy after anterior decompression surgery: motion preservation vs. fusion. Int J Spine Surg. (2022) 16(6):969–76. doi: 10.14444/8320
5. Disantostefano J. International classification of diseases 10th revision (ICD-10). J Nurse Pract. (2009) 5(1):56–7. doi: 10.1016/j.nurpra.2008.09.020
6. Robertson SC, Ashley MR. Complications of anterior cervical discectomy and fusion. Acta Neurochir Suppl. (2023) 130:169–78. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-12887-6_20
7. Hirvonen T, Marjamaa J, Siironen J, Koskinen S, Niemelä M, Koski-Palkén A. Young adults undergoing ACDF surgery exhibit decreased health-related quality of life in the long term in comparison to the general population. Spine J. (2021) 21(6):924–36. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2021.01.021
8. Mehren C, Heider F, Siepe CJ, Zillner B, Kothe R, Korge A, et al. Clinical and radiological outcome at 10 years of follow-up after total cervical disc replacement. Eur Spine J. (2017) 26(9):2441–9. doi: 10.1007/s00586-017-5204-6
9. Yan C, Zhang S. Clinical application of BAK intercervical fusion apparatus for anterior cervical decompression. Chin J Orthop Surg. (2003) 11(15):1020–2.
10. Choi BW, Choi MS. Radiological assessment of the effects of anterior cervical discectomy and fusion on distraction of the posterior ligamentum flavum in patients with degenerative cervical spines. Clin Orthop Surg. (2021) 13(4):499–504. doi: 10.4055/cios20262
11. Prakash SK, Mukerji N, Nath FP. Is tutobone an efficient alternative to other implants used in anterior cervical discectomy and fusion surgeries? Br J Neurosurg. (2017) 31(3):340–4. doi: 10.1080/02688697.2017.1297362
12. Iunes EA, Barletta EA, Barba Belsuzarri TA, Onishi FJ, Cavalheiro S, Joaquim AF. Correlation between different interbody grafts and pseudarthrosis after anterior cervical discectomy and fusion compared with control group: systematic review. World Neurosurg. (2020) 134:272–9. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2019.10.100
13. Wang L, Song YM, Liu LM, Liu H, Li T. Clinical and radiographic outcomes of dynamic cervical implant replacement for treatment of single-level degenerative cervical disc disease: a 24-month follow-up. Eur Spine J. (2014) 23(8):1680–7. doi: 10.1007/s00586-014-3180-7
14. Scerrati A, Germano A, Montano N, Visani J, Cacciola F, Raffa G, et al. Factors affecting functional outcome after anterior cervical discectomy and fusion: a multicenter study. J Craniovertebr Junction Spine. (2021) 12(2):144–8. doi: 10.4103/jcvjs.jcvjs_1_21
15. Stark PA, Myles PS, Burke JA. Development and psychometric evaluation of a postoperative quality of recovery score: the QoR-15. Anesthesiology. (2013) 118(6):1332–40. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0b013e318289b84b
16. Liu X, Tan B, Xiao B, Zou X, Liu S. Modified K-line for making decisions regarding the surgical approach in patients with K-line (-) OPLL. Orthop Surg. (2021) 13(4):1351–8. doi: 10.1111/os.12931
17. Isomi T, Panjabi MM, Wang JL, Vaccaro AR, Garfin SR, Patel T. Stabilizing potential of anterior cervical plates in multilevel corpectomies. Spine. (1999) 24(21):2219–23. doi: 10.1097/00007632-199911010-00008
18. Chen H, Zhou X, Fujita H, Onozuka M, Kubo KY. Age-related changes in trabecular and cortical bone microstructure. Int J Endocrinol. (2013) 2013:213234. doi: 10.1155/2013/213234
19. Oshima Y, Takeshita K, Kato S, Doi T, Matsubayashi Y. Comparison between the Japanese orthopaedic association (JOA) score and patient-reported JOA (PRO-JOA) score to evaluate surgical outcomes of degenerative cervical myelopathy. Global Spine J. (2022) 12(5):795–800. doi: 10.1177/2192568220964167
20. Kang H. Sample size determination and power analysis using the G*Power software. J Educ Eval Health Prof. (2021) 18:17. doi: 10.3352/jeehp.2021.18.17
21. Castle-Kirszbaum MD, Danks A, Xenos C, Lai L, Timms C, Drnda A, et al. Interobserver reliability of spinal adverse events severity system—neuro (SAVES-N): a prospective adverse event reporting system for neurosurgical cases. World Neurosurg. (2018) 116:e882–8. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2018.05.121
22. Farrokhi MR, Nikoo Z, Gholami M, Hosseini K. Comparison between acrylic cage and polyetheretherketone (PEEK) cage in single-level anterior cervical discectomy and fusion: a randomized clinical trial. Clin Spine Surg. (2017) 30(1):38–46. doi: 10.1097/BSD.0000000000000251
23. Hirvonen T, Siironen J, Marjamaa J, Niemelä M. Koski-Palkén A: anterior cervical discectomy and fusion in young adults leads to favorable outcome in long-term follow-up. Spine J. (2020) 20(7):1073–84. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2020.03.016
24. Li Z, Zhao Y, Tang J, Ren D, Guo J, Wang H, et al. A comparison of a new zero-profile, stand-alone Fidji cervical cage and anterior cervical plate for single and multilevel ACDF: a minimum 2-year follow-up study. Eur Spine J. (2017) 26(4):1129–39. doi: 10.1007/s00586-016-4739-2
25. Luo CA, Lim AS, Lu ML, Chiu PY, Lai PL, Niu CC. The surgical outcome of multilevel anterior cervical discectomy and fusion in myelopathic elderly and younger patients. Sci Rep. (2022) 12(1):4495. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-08243-8
26. Nakashima H, Tetreault LA, Nagoshi N, Nouri A, Kopjar B, Arnold PM, et al. Does age affect surgical outcomes in patients with degenerative cervical myelopathy? Results from the prospective multicenter AOSpine international study on 479 patients. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatr. (2016) 87(7):734–40. doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2015-311074
27. Muthu S, Jeyaraman M, Jeyaraman N. Evolution of evidence in spinal surgery—past, present and future scientometric analysis of randomized controlled trials in spinal surgery. World J Orthop. (2022) 13(9):853–69. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v13.i9.853
28. Pu M, Zhong W, Heng H, Yu J, Wu H, Jin Y, et al. Vertebral bone quality score provides preoperative bone density assessment for patients undergoing lumbar spine surgery: a retrospective study. J Neurosurg Spine. (2023) 38(6):705–1. doi: 10.3171/2023.1.SPINE221187
29. Patel A, Dada A, Saggi S, Yamada H, Ambati VS, Goldstein E, et al. Personalized approaches to spine surgery. Int J Spine Surg. (2024) 18(6):676–93. doi: 10.14444/8644
30. Qi M, Xu C, Liu Y, Cao P, Wang X, Chen H, et al. Comparison of clinical outcomes between cervical disc arthroplasty and anterior cervical discectomy and fusion for the treatment of single-level cervical spondylosis: a 10-year follow-up study. Spine J. (2023) 23(3):361–8. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2022.11.013
31. Wang XF, Meng Y, Liu H, Hong Y, Wang BY. Surgical strategy used in multilevel cervical disc replacement and cervical hybrid surgery: four case reports. World J Clin Cases. (2020) 8(17):3890–902. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i17.3890
32. Gornet MF, Burkus JK, Dryer RF, Peloza JH, Schranck FW, Copay AG. Lumbar disc arthroplasty versus anterior lumbar interbody fusion: 5-year outcomes for patients in the Maverick disc investigational device exemption study. J Neurosurg Spine. (2019) 31(3):347–56. doi: 10.3171/2019.2.SPINE181037
33. Hermansen A, Peolsson A, Hedlund R, Kammerlind AS. Balance problems and dizziness after neck surgery—associations with pain and health-related quality of life. Physiother Theory Pract. (2020) 36(10):1145–52. doi: 10.1080/09593985.2019.1571137
34. Basu S, Rathinavelu S. A prospective study of clinical and radiological outcomes of zero-profile cage screw implants for single-level anterior cervical discectomy and fusion: is segmental lordosis maintained at 2 years? Asian Spine J. (2017) 11(2):264–71. doi: 10.4184/asj.2017.11.2.264
35. Tabanli A, Akcay E, Yilmaz H, Ak C, Bologur O, Kayikci E. Comparison of the outcomes of anterior cervical discectomy and fusion and cervical disc replacement for cervical disc disease. J Coll Phys Surg Pak. (2024) 34(5):551–5. doi: 10.29271/jcpsp.2024.05.551
36. Tabanli A, Eren TK. Comparison of fusion, arthroplasty and hybrid surgery outcomes in patients with two-level cervical disc disease. Joint Dis Relat Surg. (2024) 35(3):596–602. doi: 10.52312/jdrs.2024.1663
37. Gajski D, Dennis AR, Arnautovic KI. Surgical anatomy of microsurgical 3-level anterior cervical discectomy and fusion C4-C7. Bosn J Basic Med Sci. (2021) 21(3):258–60. doi: 10.17305/bjbms.2020.4895
38. Mugge L, DeBacker Dang D, Caras A, Dang JV, Diekemper N, Green BA, et al. Osteoporosis as a risk factor for intraoperative complications and long-term instrumentation failure in patients with scoliotic spinal deformity. Spine. (2022) 47(20):1435–42. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0000000000004418
39. Mastronardi L, Roperto R, Cacciotti G, Calvosa F. Anterior cervical fusion with stand-alone trabecular metal cages to treat cervical myelopathy caused by degenerative disk disease. Observations in 88 cases with minimum 12-month follow-up. J Neurol Surg Part A. (2018) 79(6):496–501. doi: 10.1055/s-0038-1642008
Keywords: anterior cervical discectomy and fusion, BAK/C interbody fusion, cervical disc degenerative disease, pseudoarthrosis, bone mineral density, logistic regression analysis
Citation: Hao L, Zhang A, Zhao F, Liu H and Sun X (2025) Impact of factors on treatment outcomes in cervical degenerative disc disease: a logistic regression analysis of anterior decompression and interbody fusion with BAK/C technique. Front. Surg. 12:1637376. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2025.1637376
Received: 29 May 2025; Accepted: 12 August 2025;
Published: 24 September 2025.
Edited by:
Chen Xu, Shanghai Changzheng Hospital, ChinaReviewed by:
Yang Liu, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, United StatesJinhai Xu, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, China
Alper Tabanli, Tınaztepe University, Türkiye
Copyright: © 2025 Hao, Zhang, Zhao, Liu and Sun. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Liang Hao, Y2FycmV5aGFvQDE2My5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Liang Hao
Liang Hao Aobo Zhang2,†
Aobo Zhang2,†