- 1Department of Ultrasound Medicine, Taihe Hospital, Hubei University of Medicine, Shiyan, China
- 2Department of Thoracic Surgery, Beilun District People’s Hospital of Ningbo, Ningbo, China
- 3Department of Thoracic Surgery, Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan, China
- 4Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery, Taikang Tongji (Wuhan) Hospital, Wuhan, China
- 5Department of Thoracic Surgery, The People's Hospital of Honghu, Jingzhou, China
- 6Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery, Taihe Hospital, Hubei University of Medicine, Shiyan, China
- 7Department of Oncology, Taihe Hospital, Hubei University of Medicine, Shiyan, China
As a pivotal component of the m6A methyltransferase complex, KIAA1429 plays a critical regulatory role in the pathogenesis of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), driving tumorigenesis, metastasis, and therapeutic resistance through epigenetic mechanisms. Clinically, KIAA1429 overexpression correlates with aggressive disease progression and poor patient prognosis to conventional therapies. This review comprehensively examines the dysregulated expression patterns and functions of KIAA1429 in NSCLC, elucidating its m6A-dependent modulation of key downstream effectors (Such as the HOXA1, DAPK3, and BTG2) that orchestrate malignant transformation. We highlight the emerging potential of KIAA1429 as a novel molecular target for precision therapy in NSCLC.
1 Introduction
As is widely recognized, non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) represents one of the most prevalent malignancies worldwide, with a persistently low 5-year survival rate among patients (1–3). Consequently, improving the prognosis of cancer patients remains a key focus in oncology research. In recent years, targeted therapy has emerged as a crucial treatment modality for NSCLC patients (4–6). Notably, Hishida et al., reported a study involving 14 patients who underwent pulmonary resection following systemic therapy. Among them, 8 patients received epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors (EGFR-TKIs), while 6 did not. With a median follow-up of 5 years, the EGFR-TKI group demonstrated a significantly higher 5-year overall survival (OS) rate of 83% compared to a mere 33% 5-year recurrence-free survival rate in the non-EGFR-TKI group (4). However, the development of EGFR-TKI resistance has become a major clinical challenge, serving as a primary cause of tumor recurrence or progression in NSCLC patients. Recent studies have revealed the critical involvement of N6-methyladenosine (m6A)-related genes in cancer proliferation and metastasis (7–17). For instance, Li et al., demonstrated that insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 2 (IGF2BP2) is upregulated in lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) cells. Their findings indicated that IGF2BP2 overexpression enhances solute carrier family 7 member 11 (SLC7A11) mRNA stability through m6A modification, thereby promoting cell viability and suppressing ferroptosis (14). Specifically, BRAF mutations can affect KIAA1429's localization within cells, leading to increased cytoplasmic expression and enhanced resistance to chemotherapy in colorectal cancer (17). KIAA1429, a core component of the m6A methyltransferase complex, has been shown to play a pivotal role in cell metastasis, proliferation, and drug resistance (18–31). For instance, Xu et al., demonstrated that KIAA1429 is significantly upregulated in LUAD tissues and cell lines. KIAA1429 promotes LINC01106 expression through m6A modification, ultimately enhancing tumor cell proliferation, invasion, migration, and xenograft tumor growth in nude mice (18, 21). In addition, Zhao et al., reported that elevated KIAA1429 expression correlates with clinically aggressive features in LUAD patients, including larger tumor diameter, lymph node metastasis, advanced disease stage, and poorer overall survival. Their work further elucidated that KIAA1429 knockdown suppresses MUC3A expression, thereby inhibiting LUAD cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and inducing cell cycle arrest (21). In light of these discoveries, this review systematically examines the expression patterns, functional significance, and clinical implications of KIAA1429 in NSCLC. It elucidates the molecular mechanisms by which KIAA1429 promotes malignant phenotypes through m6A-dependent regulation of target genes, while also evaluating its potential as a novel therapeutic target for NSCLC treatment.
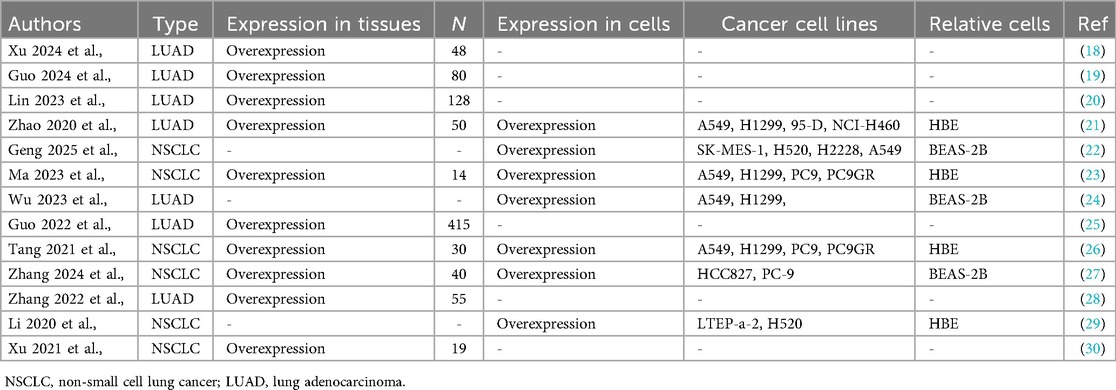
2 Expression profile of KIAA1429 and its association with prognosis in NSCLC patients
Aberrant expression of KIAA1429 has been linked to poor OS in various cancers (32–35), and KIAA1429 is significantly overexpressed in both NSCLC tissues and cell lines (Table 1). For example, Xu et al., demonstrated that KIAA1429 is highly expressed in NSCLC tissues, particularly in the LUAD subtype. Compared to normal bronchial epithelial cells (HBE), KIAA1429 levels were markedly elevated in multiple NSCLC cell lines, including the A549, H1299, 95-D, NCI-H460, PC9, PC9GR, LTEP-a-2, and H520 cells. Similarly, when compared to the normal lung epithelial cell line (BEAS-2B), KIAA1429 expression was significantly higher in NSCLC SK-MES-1, H520, H2228, A549, H1299, HCC827, and PC9 cells (Table 1). In addition, KIAA1429 overexpression correlates with shorter OS in both NSCLC and LUAD patients. Additionally, high KIAA1429 expression is associated with the advanced pathological stage in both NSCLC and LUAD patients, and associated with the smoking history, larger tumor size, lymph node metastasis, distant metastasis, higher T-stage, and tumor invasion depth in LUAD patients (Table 2). These findings suggest that KIAA1429 may serve as a potential prognostic biomarker and contribute to tumor aggressiveness in NSCLC.
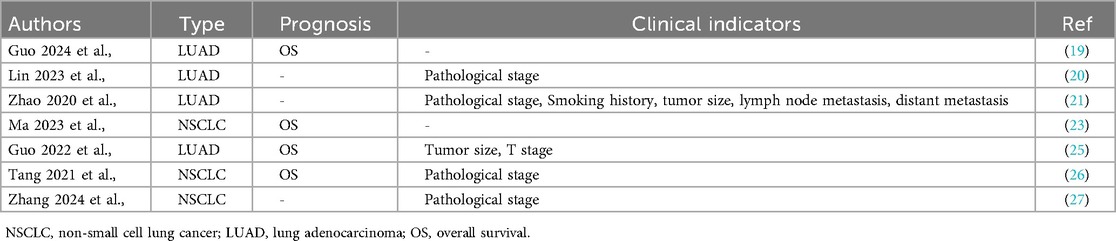
Table 2. The relationship between the clinicopathological characteristics of NSCLC and KIAA1429 overexpression.
3 Molecular functions and signaling mechanisms of KIAA1429
3.1 KIAA1429 as an oncogenic driver in NSCLC progression
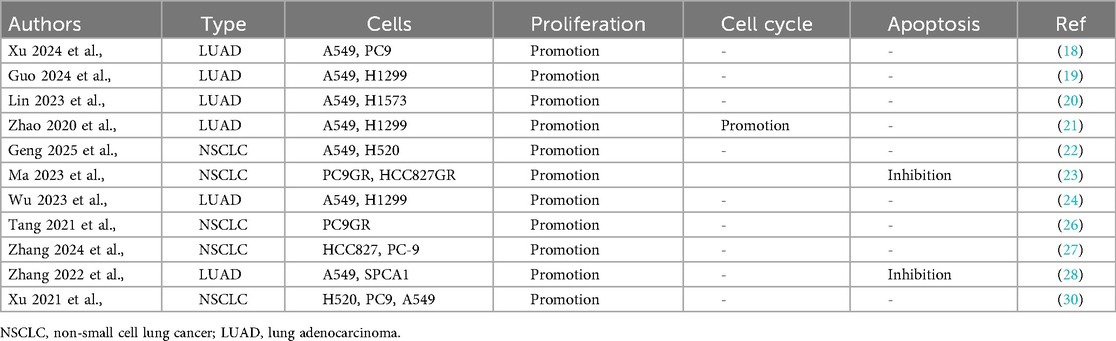
Accumulating evidence demonstrates that KIAA1429 functions as a critical oncogenic factor in NSCLC pathogenesis. Xu et al., demonstrated that KIAA1429 overexpression significantly enhances the proliferative capacity of multiple NSCLC cell lines, including the A549, PC9, H1299, H1573, H520, PC9GR, HCC827GR, HCC827, and SPCA1 (Table 3). KIAA1429 overexpression was found to accelerate cell cycle transition in LUAD A549 and H1299 cells (Table 3). Ma et al., reported that elevated KIAA1429 expression exerts anti-apoptotic effects in NSCLC PC9GR, HCC827GR, A549, and SPCA1 cells (Table 3). Additionally, Guo et al., revealed that KIAA1429 overexpression promotes the cell migration in NSCLC A549, PC9, H1299, H460, H1573, HCC827GR, PC9GR, HCC827, SPCA1, and H520 cells, and cell invasion in NSCLC A549, PC9, H1573, HCC827GR, H1299, HCC827, SPCA1, and H520 cells (Table 4).
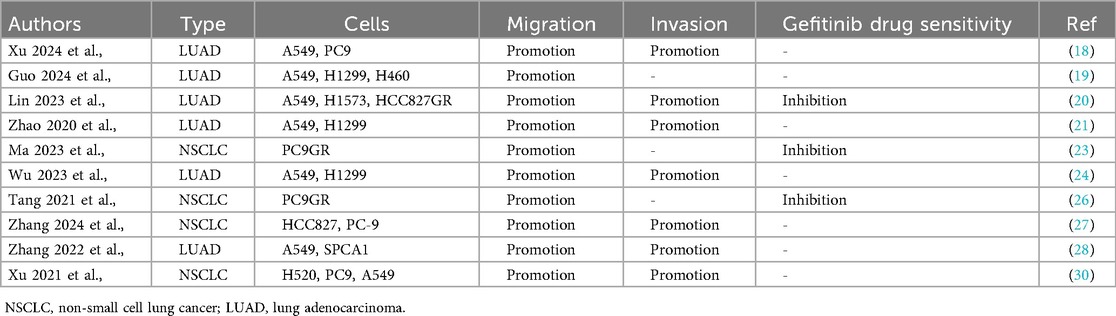
Table 4. In vitro functional characterization of KIAA1429 in cancer cell metastasis and drug sensitivity.
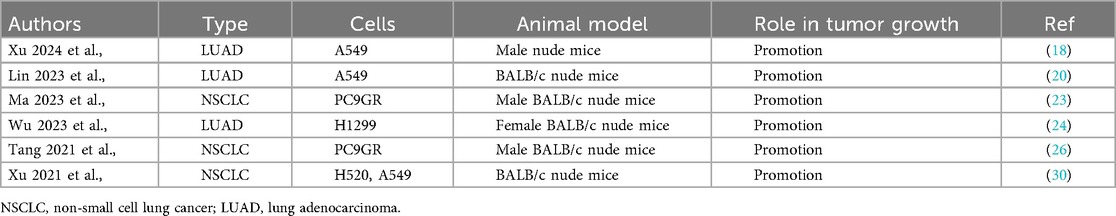
Xu et al., further validated these findings using xenograft mouse models, showing that KIAA1429 overexpression enhances tumor growth in NSCLC A549, PC9GR, H1299, and H520 cell-derived tumors (Table 5). These collective findings strongly support the oncogenic role of KIAA1429 in NSCLC, where it drives tumor growth, survival, and metastasis.
3.2 KIAA1429 as an oncogenic driver in gefitinib resistance of NSCLC
Gefitinib, a first-generation EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI), is a standard targeted therapy for NSCLC harboring EGFR mutations. However, acquired resistance to gefitinib remains a major clinical challenge. Emerging evidence suggests that aberrant expression of KIAA1429 contributes to gefitinib resistance in NSCLC (20, 23, 26). For example, Lin et al., demonstrated that KIAA1429 overexpression promotes gefitinib resistance in HCC827GR and PC9GR cell lines, two established models of acquired TKI resistance (Table 4). These findings highlight the potential therapeutic value of targeting KIAA1429 to restore gefitinib sensitivity in resistant tumors, improve treatment outcomes for NSCLC patients and delay disease progression.
3.3 Signaling mechanisms involving KIAA1429 in NSCLC
3.3.1 N6-methyladenosine (m6A)-dependent regulation
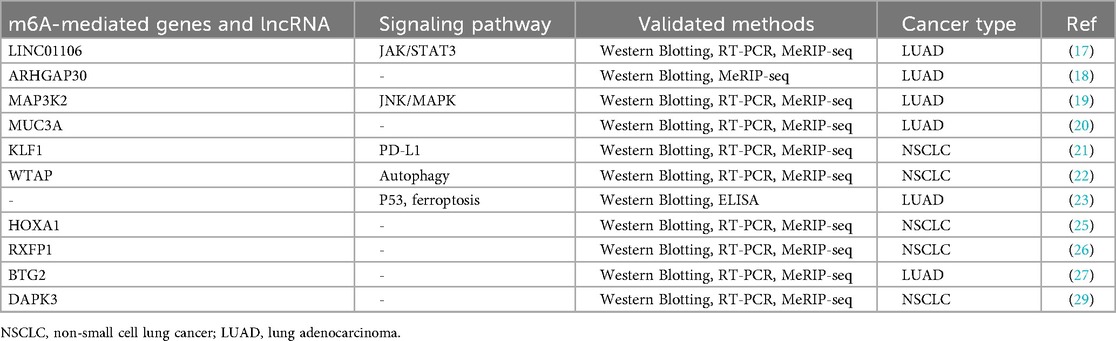
As a core component of the m6A methyltransferase complex, KIAA1429 plays a crucial role in maintaining complex stability and directing site-specific m6A modifications through recognition of specific RNA sequences or structural motifs. m6A modification dynamically regulates multiple aspects of RNA metabolism, including splicing, stability, translation, and degradation (36, 37). Current studies have identified that KIAA1429 mediates m6A-dependent regulation of multiple oncogenic targets. Emerging evidence has demonstrated that KIAA1429-mediated m6A modification modulates the expression of multiple downstream targets including LINC01106, ARHGAP30, MAP3K2, MUC3A, KLF1, WTAP, HOXA1, RXFP1, BTG2, and DAPK3, which collectively drive NSCLC progression, metastasis, and the development of gefitinib resistance (Table 6). For example, Zhao et al., demonstrated that KIAA1429 knockdown suppresses MUC3A expression through m6A modification, subsequently inhibiting LUAD cell Proliferation, Cell cycle progression, Migratory capacity and Invasive potential (21). These findings establish KIAA1429 as a master regulator of oncogenic m6A modifications in NSCLC pathogenesis.
3.3.2 Non-m6A dependent signaling pathways in NSCLC
Beyond m6A modification, KIAA1429 promotes tumor growth, metastasis, and gefitinib resistance in NSCLC through multiple signaling pathways including JAK2/STAT3, EMT, PI3K/AKT, PD-L1, autophagy, ferroptosis, p53 signaling pathways (Table 6). Xu et al., revealed that KIAA1429-mediated LINC01106 stabilization activates JAK2/STAT3 signaling by Increasing p-JAK2 and p-STAT3 levels promoting in vitro and in vivo tumor growth and metastasis (18). Guo et al., reported that KIAA1429 silencing suppresses EMT markers MMP2, ZEB1, β-catenin, and N-cadherin, and Restores E-cadherin expression to inhibit PI3K/AKT activation (19, 21). The multifaceted involvement of KIAA1429 in these pathways highlights its potential as a prognostic biomarker for treatment response.
4 Summary and future perspectives
KIAA1429 has emerged as a critical oncogenic regulator in NSCLC, exerting multifaceted roles in tumor progression, metastasis, and drug resistance. KIAA1429 is significantly upregulated in NSCLC tissues and cell lines, correlating with poor prognosis, advanced tumor stage, and metastasis. KIAA1429 promotes cell proliferation, migration, and invasion, and suppresses apoptosis and confers gefitinib resistance using m6A-dependent RNA methylation, influencing key oncogenes/tumor suppressors (such as the LINC01106, MUC3A, BTG2) and non-m6A pathways: Activates JAK2/STAT3, PI3K/AKT, PD-L1, and disrupts p53, autophagy, and ferroptosis. Despite these advances, several key questions remain. How does KIAA1429 selectively target specific RNAs for m6A modification? Are there tissue-specific or mutation-dependent regulatory networks? Can KIAA1429 inhibition synergize with existing therapies (such as the EGFR-TKIs)? KIAA1429 represents a promising therapeutic target and prognostic marker in NSCLC. Future studies should focus on elucidating its precise mechanisms, developing targeted inhibitors, and validating its clinical utility. Addressing these challenges may open new avenues for overcoming drug resistance and improving NSCLC treatment outcomes.
Author contributions
HL: Writing – original draft, Funding acquisition, Validation, Visualization. KS: Data curation, Investigation, Visualization, Resources, Writing – original draft. LL: Writing – original draft, Funding acquisition, Validation. B-HY: Data curation, Visualization, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. TL: Data curation, Validation, Writing – review & editing. X-FR: Writing – review & editing, Methodology, Formal analysis. QG: Data curation, Writing – review & editing, Funding acquisition, Investigation. DL: Data curation, Validation, Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing, Funding acquisition.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Guo Q, Wang SH, Ji YM, Tong S, Li D, Ding XC, et al. The roles and mechanisms of TRAT1 in the progression of non-small cell lung cancer. Curr Med Sci. (2022) 42(6):1186–200. doi: 10.1007/s11596-022-2625-1
2. Zhao Y, Wan Y, He T. Circ_SAR1A regulates the malignant behavior of lung cancer cells via the miR-21-5p/TXNIP axis. J Clin Lab Anal. (2022) 36(5):e24366. doi: 10.1002/jcla.24366
3. Cheng Y, Wang S, Mu X. Long non-coding RNA LINC00511 promotes proliferation, invasion, and migration of non-small cell lung cancer cells by targeting miR-625-5p/GSPT1. Transl Cancer Res. (2021) 10(12):5159–73. doi: 10.21037/tcr-21-1468
4. Hishida T, Oka N, Yano K, Omura S, Okubo Y, Masai K, et al. Initial single-institutional experience with salvage surgery for stage IV non-small-cell lung cancer. Interdiscip Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. (2025) 40(3):ivaf029. doi: 10.1093/icvts/ivaf029
5. Hotta K, Saeki S, Sakata S, Yamaguchi M, Harada D, Bessho A, et al. Five-year outcomes with gefitinib induction and chemoradiotherapy in EGFR-mutant stage III non-small-cell lung cancer: LOGIK0902/OLCSG0905 phase II study. Int J Clin Oncol. (2025) 30(3):497–503. doi: 10.1007/s10147-025-02696-3
6. Tripathi A, Kashyap A, Tripathi G, Yadav J, Bibban R, Aggarwal N, et al. Tumor reversion: a dream or a reality. Biomark Res. (2021) 9(1):31. doi: 10.1186/s40364-021-00280-1
7. Sun Y, Shen W, Hu S, Lyu Q, Wang Q, Wei T, et al. METTL3 promotes chemoresistance in small cell lung cancer by inducing mitophagy. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. (2023) 42(1):65. doi: 10.1186/s13046-023-02638-9
8. Ye M, Chen J, Lu F, Zhao M, Wu S, Hu C, et al. Down-regulated FTO and ALKBH5 co-operatively activates FOXO signaling through m6A methylation modification in HK2 mRNA mediated by IGF2BP2 to enhance glycolysis in colorectal cancer. Cell Biosci. (2023) 13(1):148. doi: 10.1186/s13578-023-01100-9
9. Ouyang P, Li K, Xu W, Chen C, Shi Y, Tian Y, et al. METTL3 recruiting M2-type immunosuppressed macrophages by targeting m6A-SNAIL-CXCL2 axis to promote colorectal cancer pulmonary metastasis. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. (2024) 43(1):111. doi: 10.1186/s13046-024-03035-6
10. Li L, Zeng J, He S, Yang Y, Wang C. METTL14 decreases FTH1 mRNA stability via m6A methylation to promote sorafenib-induced ferroptosis of cervical cancer. Cancer Biol Ther. (2024) 25(1):2349429. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2024.2349429
11. He P, Liu X, Yu G, Wang Y, Wang S, Liu J, et al. METTL3 facilitates prostate cancer progression via inducing HOXC6 m6A modification and stabilizing its expression through IGF2BP2-dependent mechanisms. Mol Cell Biochem. (2024 Jul) 479(7):1707–20. doi: 10.1007/s11010-024-05023-y
12. Li L, Wang F, Deng Z, Zhang G, Zhu L, Zhao Z, et al. DCLRE1B promotes tumor progression and predicts immunotherapy response through METTL3-mediated m6A modification in pancreatic cancer. BMC Cancer. (2023 Nov 7) 23(1):1073. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-11524-8
13. Yan Q, Wong W, Lei J, Liang D, Yang J, Gong L, et al. LNCAROD was stabilized through N6-methyladenosine methylation and exerted its anticancer effects in lung squamous cell carcinoma by inhibiting SIRT1 activity via CCAR2. Transl Lung Cancer Res. (2025) 14(4):1351–70. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-2025-267
14. Li B, Li SY, Yan YC. IGF2BP2-mediated M6a modifies SLC7A11 to regulate proliferation and ferroptosis in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Adv Clin Exp Med. (2025). doi: 10.17219/acem/200588
15. Zhang Y, Tian R, Feng X, Xiao B, Yue Q, Wei J, et al. Overexpression of METTL3 in lung cancer cells inhibits radiation-induced bystander effect. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2025) 761:151714. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2025.151714
16. Li Y, Niu J, Sun Z, Liu J. FTO-mediated m6A methylation of KCNAB2 inhibits tumor property of non-small cell lung cancer cells and M2 macrophage polarization by inactivating the PI3K/AKT pathway. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. (2025) 39(4):e70232. doi: 10.1002/jbt.70232
17. Wan T, He M, Liu Z, Zhou Y, Zhou Y, Xiao W, et al. Phosphorylation of KIAA1429 promotes oxaliplatin resistance through activating the FZD7-Wnt signaling in BRAFV600E-mutated colorectal cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. (2025) 44(1):187. doi: 10.1186/s13046-025-03449-w
18. Xu D, Wang Z, Li F. KIAA1429 induces m6A modification of LINC01106 to enhance the malignancy of lung adenocarcinoma cells via the JAK/STAT3 pathway. Crit Rev Immunol. (2024) 44(6):49–61. doi: 10.1615/CritRevImmunol.2024052728
19. Guo W, Wang T, Huai Q, Guo L, Wang X, He J. KIAA1429 regulates lung adenocarcinoma proliferation and metastasis through the PI3K/AKT pathway by modulating ARHGAP30 expression. Thorac Cancer. (2024) 15(18):1397–409. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.15327
20. Lin X, Ye R, Li Z, Zhang B, Huang Y, Du J, et al. KIAA1429 promotes tumorigenesis and gefitinib resistance in lung adenocarcinoma by activating the JNK/ MAPK pathway in an m6A-dependent manner. Drug Resist Updat. (2023) 66:100908. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2022.100908
21. Zhao W, Xie Y. KIAA1429 promotes the progression of lung adenocarcinoma by regulating the m6A level of MUC3A. Pathol Res Pract. (2021) 217:153284. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2020.153284
22. Geng R, Ren M, Ma Y, Su W. Mechanism of the KIAA1429/KLF1/PD-L1 axis in regulating immune escape in non-small cell lung cancer. Cell Biochem Biophys. (2025) 83(2):1835–45. doi: 10.1007/s12013-024-01592-3
23. Ma B, Xiu L, Ding L. The m6 RNA methylation regulator KIAA1429 is associated with autophagy-mediated drug resistance in lung cancer. FASEB Bioadv. (2024) 6(4):105–17. doi: 10.1096/fba.2023-00083
24. Wu Y, Li H, Huang Y, Chen Q. Silencing of m6A methyltransferase KIAA1429 suppresses the progression of non-small cell lung cancer by promoting the p53 signaling pathway and ferroptosis. Am J Cancer Res. (2023) 13(11):5320–33.38058803
25. Guo L, Huai Q, Zhou B, Ying J, Guo W. Comprehensive analysis of the prognostic impact and immune implication of KIAA1429 in lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Innov. (2022) 1(4):328–43. doi: 10.1002/cai2.40
26. Tang J, Han T, Tong W, Zhao J, Wang W. N6-methyladenosine (m6A) methyltransferase KIAA1429 accelerates the gefitinib resistance of non-small-cell lung cancer. Cell Death Discov. (2021) 7(1):108. doi: 10.1038/s41420-021-00488-y
27. Zhang Z, Guo J, Gong C, Wu S, Sun Y. KIAA1429-mediated RXFP1 attenuates non-small cell lung cancer tumorigenesis via N6-methyladenosine modification. Cancer Biomark. (2024):CBM230188. doi: 10.3233/CBM-230188
28. Zhang C, Sun Q, Zhang X, Qin N, Pu Z, Gu Y, et al. Gene amplification-driven RNA methyltransferase KIAA1429 promotes tumorigenesis by regulating BTG2 via m6A-YTHDF2-dependent in lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Commun (Lond). (2022) 42(7):609–26. doi: 10.1002/cac2.12325
29. Li N, Zhan X. Identification of pathology-specific regulators of m6A RNA modification to optimize lung cancer management in the context of predictive, preventive, and personalized medicine. EPMA J. (2020) 11(3):485–504. doi: 10.1007/s13167-020-00220-3
30. Xu Y, Chen Y, Yao Y, Xie H, Lu G, Du C, et al. VIRMA contributes to non-small cell lung cancer progression via N6-methyladenosine-dependent DAPK3 post-transcriptional modification. Cancer Lett. (2021) 522:142–54. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2021.08.027
31. Husain A, Khadka A, Ehrlicher A, Saint-Geniez M, Krishnan R. Substrate stiffening promotes VEGF-A functions via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2022) 586:27–33. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2021.11.030
32. Shan M, Liu D, Sun L, Yang M, He M, Zhang Y, et al. KIAA1429 facilitates metastasis via m6A-YTHDC1-dependent RND3 down-regulation in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett. (2024) 584:216598. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2023.216598
33. Cheng X, Li M, Rao X, Zhang W, Li X, Wang L, et al. KIAA1429 regulates the migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma by altering m6A modification of ID2 mRNA. Onco Targets Ther. (2019) 12:3421–8. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S180954
34. Lan T, Li H, Zhang D, Xu L, Liu H, Hao X, et al. KIAA1429 contributes to liver cancer progression through N6-methyladenosine-dependent post-transcriptional modification of GATA3. Mol Cancer. (2019) 18(1):186. doi: 10.1186/s12943-019-1106-z
35. Liu H, Yang M, Zhang C, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Chen Y. M6a transferase KIAA1429 mediates the upregulation of LncRNA LINC00968 promoting the progression of gastric cancer cells. Hereditas. (2025) 162(1):34. doi: 10.1186/s41065-025-00393-9
36. Huang J, Guo J, Jia R. N6-Methyladenosine methyltransferase component KIAA1429 is a potential target of cancer therapy. Biomolecules. (2024) 14(10):1319. doi: 10.3390/biom14101319
Keywords: KIAA1429, m6A modification, non-small cell lung cancer, molecular target, gefitinib resistance
Citation: Liu H, Shi K, Liu L, You B-H, Liu T, Ren X-F, Guo Q and Li D (2025) KIAA1429 in non-small cell lung cancer: bridging m6A epigenetics to therapeutic innovation. Front. Surg. 12:1643120. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2025.1643120
Received: 8 June 2025; Accepted: 18 August 2025;
Published: 20 October 2025.
Edited by:
Nestor Villamizar, University of Miami Health System, United StatesReviewed by:
Amjad Husain, Cancer Research Institute, IndiaCopyright: © 2025 Liu, Shi, Liu, You, Liu, Ren, Guo and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Dan Li, bHE5NDk2NjEyNTlAMTYzLmNvbQ==
†These authors share first authorship
 Hui Liu1,†
Hui Liu1,† Ke Shi
Ke Shi Qiang Guo
Qiang Guo Dan Li
Dan Li