- 1Department of Burn and Plastic Surgery, Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi, Guizhou, China
- 2Emergency Intensive Care Unit, Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi, Guizhou, China
- 3The 2011 Collaborative Innovation Center of Tissue Damage Repair and Regeneration Medicine, Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi, Guizhou, China
- 4Guizhou Provincial Collaborative Innovation Center for Tissue Injury Repair and Regenerative Medicine, Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, 2011, Zunyi, Guizhou, China
Surgical wound tension, a core biomechanical factor in tissue repair, is clinically important because high tension can cause microcirculatory disturbances, leading to inhibition of cell migration and collagen deposition, and increasing complications such as wound dehiscence and incisional hernia. Therefore, the concept of “active tension reduction” has been emphasized, including preoperative optimization of biomechanical distribution, intraoperative layered combined subcutaneous tension-reducing suturing, and postoperative dynamic management. However, the difficulty in standardizing wound tension quantification presents clinical challenges. In summary, this study integrates the biomechanical mechanisms of surgical wound tension with clinical practice to explore a systematic strategy from tension assessment to novel intervention techniques.
Introduction
The regulation of wound tension can be traced back to 3,000 BC (1). With the widespread use of aseptic operation and anesthesia, this subjective judgment began to shift to the study of the biomechanical mechanism of tension (2). The advent of buried vertical mattress suture 100 years ago promoted the development of subcutaneous suture by redistributing tension to promote wound healing (3). The emergence of tensiometers can quantify the tension of the wound (4). With the optimization of suturing technology (5), the development of reverse traction devices (6) and new materials (7, 8), the understanding of tension has shifted from subjective judgment to the study of biomechanical mechanisms, providing strong support for the safety and aesthetics of wound healing.
Surgical wound tension plays a key role in the process of wound healing and scar formation and is a key factor affecting the quality of healing. High tension can cause separation of wound edges, reduce local blood supply, stimulate excessive proliferation of fibroblasts and disrupt collagen metabolism. This can lead to chronic inflammation, fibrosis and scar widening. In severe cases, it can induce hypertrophic scars or scar contracture deformities, affecting the patient's appearance and function (9). Mechanical tension has differential effects in the inflammatory, proliferative, and tissue remodeling phases of wound healing. This differential effect can induce biological responses such as chronic inflammation, fibrosis, angiogenesis, and extracellular matrix remodeling through complex signal transduction and feedback mechanisms, affecting wound healing and scar formation (10).
During the inflammatory phase, high tension can activate the integrin-focal adhesion kinase pathway, promote the release of proinflammatory factors (TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6), and induce the activation of the proinflammatory signaling pathway (NF-κB), thereby prolonging the inflammatory phase and aggravating the local inflammatory microenvironment (11). In addition, the high-tension state of the wound can regulate the polarization of macrophages to M1, resulting in the inability to transition from the inflammatory phase to the proliferation phase, further aggravating the inflammatory response (12, 13). Excessive tension leads to tissue hypoxia, which in turn activates hypoxia-inducible factor, promotes the accumulation of reactive oxygen species(ROS), aggravates oxidative stress and cell damage, and further prolongs the inflammatory phase (14, 15).
During the proliferation phase, high tension inhibits fibroblast proliferation, causing cell morphology changes and differentiation into myofibroblasts, leading to excessive deposition and disordered arrangement of type I collagen in the extracellular matrix (ECM). This excessive presence and abnormal deposition of myofibroblasts increases scar formation (16). At the same time, high tension can cause disordered collagen fiber arrangement, and a large amount of disordered collagen deposition leads to scar hyperplasia, resulting in scar hyperplasia (hypertrophic scars, keloids, etc.) (7). Excessive wound tension leads to insufficient local tissue perfusion, affecting the formation of new blood vessels, the insufficient growth of granulation tissue, and loose wound closure, increasing the risk of wound dehiscence and infection (17).
During the tissue remodeling stage, tension has a particularly significant effect on scar formation. Continuous tension can induce the secretion of profibrotic factors such as TGF-β, leading to collagen arrangement and scar formation (18, 19). In addition, the imbalance of ECM remodeling caused by high tension can also lead to complications such as secondary injury or chronic ulcers (20).
Causes of surgical wound tension and its biomechanical mechanism for healing
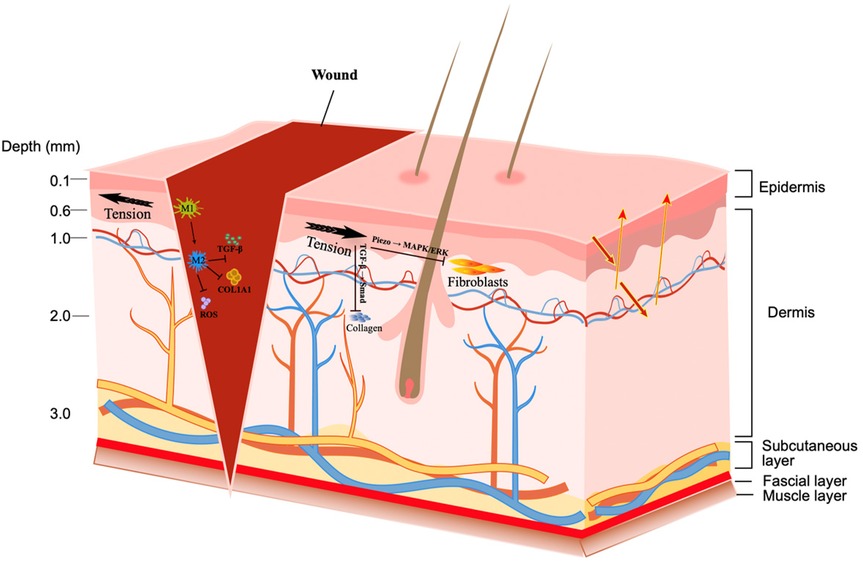
The tension on surgical wounds is the key to postoperative healing. Excessive tension can easily induce wound dehiscence, delayed healing, non-healing of wounds, abnormal proliferation of scar tissue, and infection (21). The formation of tension is caused by multiple factors such as the inherent properties of tissue structure, the specificity of anatomical regions, surgical operation methods, and postoperative care (22, 23) (Figure 1).
Analysis of the causes of surgical wound tension
Tissue characteristics (such as collagen fibers, tissue tension, etc.) and anatomical structures (such as muscle fascia, ECM, etc.) can be considered the basis for tension formation. When the incision deviates from the axis of natural skin relaxation, the increased tension may cause the collagen structure in the dermis to be torn, and the retraction drive to increase dramatically (24). Especially in the facial and joint areas, the skin is thin and elastic. Once it moves, it will stimulate dynamic traction, making it difficult for the wound to heal (25). Large-area skin tears or deep structure damage (such as fascia) require strong mechanical tension to be forcibly resisted during suturing. Due to the lack of soft tissue buffer, stress concentration is more likely to occur under the action of mechanical tension in bone protrusions such as the heel and sacrum, resulting in prolonged wound healing (26). Similarly, rough sutures and lack of layered fixation will cause tension to be concentrated on the epidermis while the fascia will not bear the force; sutures that are too thin are easy to tear, and those that are too thick will cause strong inflammation. Postoperative management is a “continuous challenge” that affects high wound tension. Early or intense postoperative activities will increase the local mechanical tension of the wound, leading to wound dehiscence or scar widening (27). The failure to use braces to fix joints after surgery, the failure to use negative pressure devices properly after high-tension wound sutures, and the continued swelling of tissues caused by systemic factors of the patient (28) are factors that continuously affect wound healing and cannot be ignored.
Effects of surgical wound tension on cells and tissues
The influence of tension mechanism on surgical wounds involves complex regulation at multiple levels, including the dynamic balance of cell behavior, molecular signaling pathways, and inflammatory response. When the tension is greater, the proliferation of fibroblasts can be inhibited. In addition, tension activates the Piezo1/2 channel (Piezo1/2, as mechanosensitive cation channels, are overexpressed in keloid myofibroblasts), which can inhibit the active migration of fibroblasts through the MAPK/ERK pathway (29, 30). The traction force of the wound surface is the power source for wound closure, but excessive tension induces abnormal matrix deposition and forms fibrosis (31, 32). Tension activates TGF-β1 through integrin β1, which in turn initiates the phosphorylation reaction of Smad2/3, increases the expression of collagens such as COL1A1 and COL3A1, and causes matrix accumulation (33–35). High tension also activates NOX2, increases ROS levels, and induces the release of NLRP3 and IL-1β, forming a vicious cycle of “tension-oxidation-inflammation” (36). In the early stage of inflammation, mechanical tension can induce macrophages to polarize toward the M1 type, and promote the release of a large number of inflammatory factors by activating the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB axis (37, 38). At the same time, tension also inhibits the JAK2/STAT3 and TRAF6/NF-κB pathways, hindering the process of inflammation relief (39). In addition, high tension induces the expression of chemokines such as CXCL8, driving neutrophils to gather in the injured area, resulting in increased tissue inflammatory response (40, 41).
The dynamic characteristics of tension distribution show diverse characteristics
Wound tension is in dynamic balance with the anatomical structure of the skin. The skin is composed of the epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous tissue. The arrangement direction of collagen fibers in the dermis (i.e., Langer's lines) determines the distribution of local tension (42). The thickness of the fat layer also affects stress distribution and can buffer deep tension under vertical load. The fascia layer and muscle activity also participate in tension regulation. The fascia connects different tissues and maintains mechanical balance (43). Stress concentration at the wound edge will put fibroblasts in a hypertonic state, delay healing and aggravate fibrosis, and even affect tissue structure and function (44). Stress concentration can change the local mechanical microenvironment, disrupt cell migration, and ECM reconstruction (45). Increasing the strength of suture density can increase the tensile strength of the wound, especially in short incisions such as 3 mm, where the enhancement effect is more obvious (46). However, too dense sutures can also increase local stiffness and may also lead to poor tissue blood supply, affecting the repair effect (47). Suture density should be finely adjusted based on wound location, biomechanical requirements, and tissue characteristics. Future research needs to further reveal the three-dimensional structural relationship between suture density and tension distribution, and explore its stability and adaptability in a dynamic healing environment (48).
The figure shows the epidermis, dermis, subcutaneous tissue, fascia, and muscle layers. Once a wound is formed, the black arrow indicates the direction of tension. Reducing wound hypertension can modulate macrophage polarization toward M2, inhibiting the expression of TGF-β1, COL1A1, and ROS. Tension activates Piezo1/2 pathways, inhibiting active fibroblast migration through the MAPK/ERK pathway. Tension activates TGF-β1 via integrin β1, in turn initiating Smad2/3 phosphorylation, leading to collagen matrix accumulation.
Method for quantitative assessment of surgical wound tension
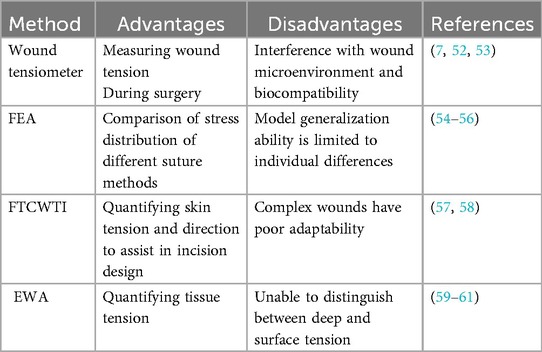
Traditional tension judgment relies on the doctor's personal subjective experience and lacks systematic and objective quantitative evaluation. Wound size was once mistakenly believed to be positively correlated with tension size (49, 50). Quantification of tension is expected to be more objective and reliable for tension measurement and management. Surgical tension assessment is shifting from traditional mechanical methods to intelligent detection, and more technologies are being introduced into the clinic. In the future, dynamic tension monitoring is expected to be achieved by combining intelligent sensing technology (51). Currently, methods for quantitative assessment of surgical wound tension include wound tensiometers, finite element analysis, Fourier transform combined with topological imaging, and elastic wave analysis (Table 1).
Wound tensiometers can directly measure wound tension and monitor it in real time during surgery. By analyzing the mechanical threshold of ischemic injury and the critical point of hypertrophic scar formation observed in clinical practice (7, 52), the threshold of wound closure can be objectively quantified (for example, a threshold between 5.4 and 6.0 N is considered “safe”). However, it relies on contact measurement, which may interfere with the wound microenvironment, and the biocompatibility of long-term implantation remains a difficult issue (53).
The personalized modeling feature of finite element analysis (FEA) can be used to compare the stress distribution of different suture methods. such as Ding screw tension band is better than the traditional Kirschner wire method (54). FEA can also quantify aortic aneurysm wall stress (55) and oral graft design tissue stress (56), providing a basis for optimizing surgical strategies. However, the generalization ability of the model is limited to individual differences and requires more clinical data support.
Fourier transform combined with topological images(FTCWTI)can quantify skin tension and direction, assisting in incision design (57). Its multimodal imaging can quantify wound morphology, but it is less adaptable to complex wounds (such as deep ulcers) (58). Elastic wave analysis (EWA) quantifies tissue tension by measuring surface wave velocity without destroying the wound structure (59). When predicting clinically relevant tension values, the accuracy rate can reach over 85% (60). However, due to the influence of skin moisture and thickness, it cannot distinguish between deep and surface tension, and other technologies need to be combined (61).
In addition, Confocal microscopy can be used to evaluate living skin, but its applicability to chronic wounds still needs to be verified (62, 63). The distance between cells is regulated by the mechanical properties of the cells and the geometry of the wound, which indirectly reflects the tension state (64, 65). Gold nano-DNA probes can image intercellular tension and help quantify microscale mechanics (66). Objective quantitative assessment of tension will help scientifically evaluate the difficulty of wound healing and achieve personalized treatment.
Clinical management strategies for surgical wounds
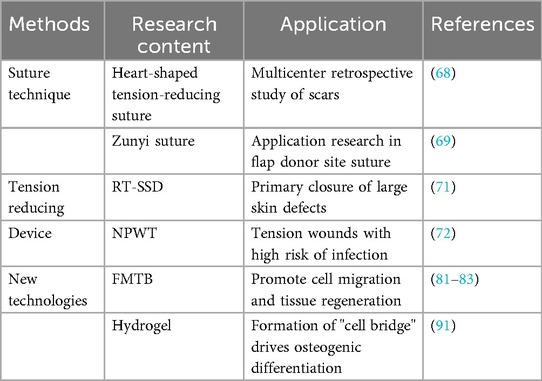
Clinical management of surgical wounds has shifted from traditional experience to precision medicine. The optimization and improvement of traditional technologies and the innovation of new intervention technologies have jointly opened up new wound healing goals (Table 2).
Optimization and improvement of traditional technologies. Traditional technologies are centered on disinfection, debridement, and suturing. The exploration of super-tension-reducing suture methods plays a key role in long-term tension maintenance, scar minimization and functional recovery (67). Traditional methods (such as continuous suture and interrupted suture) have limited effects on long-term tension maintenance and scar control. New suturing techniques (such as heart-shaped tension-reducing suture and Zunyi suture) disperse stress more evenly than traditional techniques and reduce stress concentration (68, 69). Improvements in suture materials and structures can shorten operation time and improve tension resistance (70).
Traditional tension-reducing devices can provide a variety of solutions for high-tension wound healing, but they need to be selected according to wound type, location, and individual differences of patients. The reverse-traction skin-stretching device (RT-SSD) applies reverse tension to both sides of the wound by rotating the traction device, stretching collagen fibers, breaking elastin, inhibiting fibrosis, and thus reducing skin tension, especially for primary closure of large skin defects (71). Negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT) reduces edema, reduces incision line tension, enhances granulation tissue formation, reduces the risk of wound dehiscence and infection, and is suitable for tension wounds with high infection risk (72). Tension-reducing patches reduce wound edge tension by adhesion and prevent scar hyperplasia. After the use of negative pressure or stretching devices, tension-reducing patches can further maintain a low tension state.
New intervention technologies continue to promote innovation in wound management, especially showing potential in chronic wounds. Compared with traditional technologies, these technologies can achieve dynamic balance in the mechanical microenvironment, promote scarless healing, precisely fill complex wounds, control infection, and provide real-time monitoring capabilities (73–76).
Mechanical shielding hydrogels reduce external force interference through physical barriers, reduce tension and inflammation, and reduce scar formation (77, 78). Force-Modulating Tissue Bridges (FMTB) can serve as a hub for mechanical-biological coupling, and their application can be applied from basic mechanisms to clinical prognosis (79, 80). By combining the bioactivity and mechanical stability of hydrogels, they can simulate the natural microenvironment and promote cell migration and tissue regeneration (81–83). Bioactive hydrogel dressings have anti-infection, immunomodulatory, and angiogenic functions (84–86). Combining topological structures with drugs (such as lovastatin) can synergistically inhibit mechanical transduction and reduce fibrosis (87). 3D printed hydrogels can customize their structures and accurately load drugs/cells to adapt to complex wounds (88). Smart hydrogels can sense pH or enzyme changes, dynamically release drugs, and regulate tension distribution (89). Elastin hydrogels have shown reduced neutrophil recruitment, increased M2 macrophages, and increased numbers of newly formed hair follicles in a deep second-degree burn model (90). Studies have found that curvature fibers in hydrogels can promote the formation of “cell bridges” by enhancing cytoskeletal tension, bridging myosin-II in cells to generate directional forces and drive osteogenic differentiation (91). This mechanism can be extended to wound repair, guiding cell migration and tissue regeneration through mechanics.
Challenges and future directions
At present, there is a lack of objective standards for assessing the tension of surgical wounds. The tension of different parts and ages varies greatly. Clinical practice relies more on subjective assessment or indirect indicators (such as fascial pressure, etc.) (92). Although FMTB and NPWT have certain potential, they are limited by high costs and a lack of long-term data. The suture anchoring method can induce scar models in mice (93), and the Retroflex model can simulate human pathological scars (94), which improves research efficiency. However, animal skin differs significantly from human skin in stiffness, thickness, and collagen content (95). Existing animal models cannot fully simulate the immune response and healing process of human skin (96). Although the diabetes model is used to study delayed healing, it is still difficult to fully simulate chronic ulcers (97).
Currently, clinical evidence is mostly retrospective or small-sample studies, and there is a lack of high-quality randomized controlled trials (RCTs) (98). Existing RCTs have a significant risk of publication bias, and comparative studies on wound closure effectiveness are mostly based on low-quality evidence (such as single-center quasi-RCTs) (99). Although new designs such as stepped-wedge RCTs (SW-RCTs), registry-based RCTs (RB-RCTs), and trials-within-cohorts (TwiCs) have been proposed and have certain advantages, they are still in the exploratory stage (100). The decision on which design is most suitable for each specific setting should be made on a case-by-case basis and expanded using the unified standard of reporting of trials.
Future development directions may be through multimodal evaluation, personalized treatment and interdisciplinary integration. The new tensiometer combines 3D and biomarker analysis to dynamically monitor the mechanical environment of the wound (101). Skin stiffness and viscoelasticity vary with individual differences. Increased stiffness or decreased viscoelasticity indicates scar formation or delayed healing (102). Further address the limitations of animal models by improving animal models, developing humanized technologies, and targeting mechanistic regulation strategies to promote clinical translation. Interdisciplinary integration is becoming a trend. In the future, we should focus on intelligent responsive materials, mechanical-biological coupling optimization, and the construction of a preclinical standardized evaluation system (103).
Conclusion
The precise management of surgical wound tension must be based on biomechanical mechanisms. Tension is a key factor affecting healing quality and scar formation. Further research is needed to elucidate the cellular signaling networks of different tissue types (such as skin, fascia, and tendon) under dynamic tension. Through the development of quantitative tools (such as wound tensiometers, Fourier transform, FEA) and new technologies (such as hydrogels, FMTB), as well as suture technology optimization and individualized solutions guided by biomechanical models, we can ultimately achieve a paradigm shift from “passive closure” to “active regulation”, improve healing quality and reduce the risk of complications. Suturing techniques should be optimized and guided by biomechanical models to establish a personalized “patient-wound-procedure” approach. The future of surgical wound tension management lies in achieving precision, intelligence, and personalization, requiring multidisciplinary collaboration to achieve better patient outcomes.
Author contributions
FG: Conceptualization, Methodology, Software, Validation, Investigation, Data curation, Writing – original draft. BW: Validation, Data curation, Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing. PQ: Validation, Data curation, Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing. ZW: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing, Supervision.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. Provincial-Ministry Collaborative Innovation Center Project (Ministry of Education, Science and Technology Letter [2020] No. 39); National Natural Science Foundation of China (82360445); Guizhou Maotai Hospital Research and Talent Development Fund (mtyk2022-13); Shanghai Wang Zhengguo Trauma Medicine Development Foundation [SZYZ-TR-05].
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Custer PL. Laudable pus, cocaine, and the evolution of wound management. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg. (2025). doi: 10.1097/IOP.0000000000002893
2. Parikh UM, Mentz J, Collier I, Davis MJ, Abu-Ghname A, Colchado D, et al. Strategies to minimize surgical scarring: translation of lessons learned from bedside to bench and back. Adv Wound Care. (2022) 11(6):311–29. doi: 10.1089/wound.2021.0010
3. Zhang W, Xie J, Zeng A. The origin and development of interrupted subcuticular suture: an important technique for achieving optimum wound closure. Dermatol Surg. (2022) 48(6):619–24. doi: 10.1097/DSS.0000000000003437
4. Lackmann F, Rohwedder T, Maron A, Stegen L, Brunnberg M, Brunnberg L, et al. Quantification of skin wound tension using a newly designed wound tensiometer. Tierarztl Prax Ausg K Kleintiere Heimtiere. (2023) 51(6):386–93. doi: 10.1055/a-2150-0587
5. Zhang W, Zhou X, Liu Z, Long X, Wang X, Zeng A, et al. Using a modified running intracutaneous butterfly suture technique for wound closure: achieving tension reduction, dead space elimination, and perfect apposition. Aesthetic Plast Surg. (2025). doi: 10.1007/s00266-025-04813-z
6. Cui Y, Yuan B, Zhang Y, Ren G, Dou M, Peng C, et al. Reverse-traction skin-stretching device for primary closure of large skin defects. Arch Dermatol Res. (2023) 315(4):751–60. doi: 10.1007/s00403-022-02408-1
7. Fu D, Huang J, Wu X, Li Y, Zhang Y, Chen L, et al. Shape-fixing hydrogel promotes scarless healing of wounds under tension. Acta Biomater. (2024) 183:173–90. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2024.05.036
8. Fernandes MG, da Silva LP, Cerqueira MT, Ibañez R, Murphy CM, Reis RL, et al. Mechanomodulatory biomaterials prospects in scar prevention and treatment. Acta Biomater. (2022) 150:22–33. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2022.07.042
9. Zhang WH, An Y, Zhao ZM. Research progress on the mechanism of mechanical tension affecting wound healing and scar formation at different stages. Zhong Hua Zheng Xing Wai Ke Za Zhi. (2024) 40(2):243–8. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn114453-20211021-00412
10. Sharma Y, Ghatak S, Sen CK, Mohanty S. Emerging technologies in regenerative medicine:the future of wound care and therapy. J Mol Med. (2024) 102(12):1425–50. doi: 10.1007/s00109-024-02493-x
11. Wen CC, Huang SM, Wang YW. Anatomical anal stenosis after PPH: insights from a retrospective study and rat model. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25(6):3543. doi: 10.3390/ijms25063543
12. Xie X-T, Gao C-H, Tan L-F, Chen L-X, Fan J-X, Xiong W, et al. Gene-engineered polypeptide hydrogels with on-demand oxygenation and ECM-cell interaction mimicry for diabetic wound healing. Biomaterials. (2025) 316:122984. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2024.122984
13. Yuan L, He Q, Zhang Y, Luo H, Xiang W, Deng C, et al. 6-Gingerol Microneedle promotes diabetic wound healing by regulating macrophage polarization. Int Immunopharmacol. (2025) 151:114288. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2025.114288
14. Zhang F, Zhang H, Wang S, Gao M, Du K, Chen X, et al. A dynamically phase-adaptive regulating hydrogel promotes ultrafast anti-fibrotic wound healing. Nat Commun. (2025) 16(1):3738. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-58987-w
15. Liu Y, Zhu M, Ou J, Li K, Ju X, Tian Y, et al. Multi-responsive sodium hyaluronate/tannic acid hydrogels with ROS scavenging ability promote the healing of diabetic wounds. Int J Biol Macromol. (2024) 278(Pt 3):134896. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.134896
16. Bretl M, Cheng L, Kendziorski C, Thibeault SL. RNA-sequencing demonstrates transcriptional differences between human vocal fold fibroblasts and myofibroblasts. BMC Genomics. (2025) 26(1):347. doi: 10.1186/s12864-025-11533-w
17. Wang T, Li Y, Hao L, Liu Y, Liu D, Zhang C, et al. Coriander-derived exosome-like nanovesicles laden hydrogel with antioxidant property accelerates wound healing. Macromol Biosci. (2025) 2:e2400640. doi: 10.1002/mabi.202400640
18. Zhang M, Dong Q, Yang K, Chen R, Zhang J, Xiao P, et al. Hyaluronic acid hydrogels with excellent self-healing capacity and photo-enhanced mechanical properties for wound healing. Int J Biol Macromol. (2024) 267(Pt 1):131235. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.131235
19. Berry CE, Downer M Jr, Morgan AG, Griffin M, Liang NE, Kameni L, et al. The effects of mechanical force on fibroblast behavior in cutaneous injury. Front Surg. (2023) 10:1167067. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2023.1167067
20. Zulkiflee I, Amirrah IN, Fadilah NIM, Wee MFMR, Yusop SM, Maarof M, et al. Characterization of dual-layer hybrid biomatrix for future use in cutaneous wound healing. Materials. (2023) 16(3):1162. doi: 10.3390/ma16031162
21. Kang M, Ko UH, Oh EJ, Kim HM, Chung HY, Shin JH. Tension-sensitive HOX gene expression in fibroblasts for differential scar formation. J Transl Med. (2025) 23(1):168. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06191-1
22. Hoppstädter M, Püllmann D, Seydewitz R, Kuhl E, Böl M. Correlating the microstructural architecture and macrostructural behaviour of the brain. Acta Biomater. (2022) 51:379–95. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2022.08.034
23. Hou Z, Wang T, Wang L, Wang J, Zhang Y, Zhou Q, et al. Skin-adhesive and self-healing diagnostic wound dressings for diabetic wound healing recording and electrophysiological signal monitoring. Mater Horiz. (2024) 11(8):1997–2009. doi: 10.1039/d3mh02064a
24. Zahouani H, Ayadh M, Abellan M-A, Bigouret A. Considering the effect of residual tension forces on the wavelength anisometry of skin imaging by 2D skin tension integrity model. Sci Rep. (2024) 14(1):31963. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-83490-5
25. Cho H, Dohi T, Wakai H, Quong WL, Linh NDT, Usami S, et al. In the face and neck, keloid scar distribution is related to skin thickness and stiffness changes associated with movement. Wound Repair Regen. (2024) 32(4):419–28. doi: 10.1111/wrr.13180
26. Geng Y, Liu J, Yin X, Zhao R, Zhu L. Reconstruction for extensive sacrococcygeal defects in complex tumor patients with personalized customized gluteus maximus myocutaneous flaps. J Tissue Viability. (2024) 33(4):883–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jtv.2024.08.008
27. Goldberg ZN, Jain A, Wu R, Cognetti DM, Goldman RA. Social determinants of health impact complications following free-flap reconstruction for head and neck cancer. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. (2025) 172(1):91–9. doi: 10.1002/ohn.953
28. Lopez-Lopez V, Hiciano-Guillermo A, Martinez-Alarcon L, Delegido A, Alconchel F, Pons JA, et al. Postoperative negative-pressure incision therapy after liver transplant (PONILITRANS study): a randomized controlled trial. Surgery. (2023) 173(4):1072–8. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2022.11.011
29. Liu X, Niu W, Zhao S, Zhang W, Zhao Y, Li J. Piezo1: the potential new therapeutic target for fibrotic diseases. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. (2023) 184:42–9. doi: 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2023.09.001
30. Vasileva VY, Sudarikova AV, Chubinskiy-Nadezhdin VI. Functional coupling of Piezo1 channels and Ca2+-activated ion channels in the plasma membrane: fine-tunable interplay with wide-range signaling effects. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. (2025) 328(4):C1338–45. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00094.2025
31. Movrin V, Krajnc M. Initiation of epithelial wound closure by an active instability at the purse string. Biophys J. (2025) 124(1):107–14. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2024.11.008
32. Short WD, Olutoye OO, Padon BW, Parikh UM, Colchado D, Vangapandu H, et al. Advances in non-invasive biosensing measures to monitor wound healing progression. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. (2022) 10:952198. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.952198
33. Katoh K. Integrin and its associated proteins as a mediator for mechano-signal transduction. Biomolecules. (2025) 15(2):166. doi: 10.3390/biom15020166
34. Li K, Zhang Y, Zhao W, Wang R, Li Y, Wei L, et al. DPP8/9 Inhibition attenuates the TGF-β1-induced excessive deposition of extracellular matrix (ECM) in human mesangial cells via Smad and Akt signaling pathways. Toxicol Lett. (2024) 395:1–10. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2024.03.001
35. Verma BK, Chatterjee A, Kondaiah P, Gundiah N. Substrate stiffness modulates TGF-β activation and ECM-associated gene expression in fibroblasts. Bioengineering. (2023) 10(9):998. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering10090998
36. Chang HI, Chen CN, Huang KY. Mechanical stretch-induced NLRP3 inflammasome expression on human annulus fibrosus cells modulated by endoplasmic Reticulum stress. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23(14):7951. doi: 10.3390/ijms23147951
37. Liu F, Yang Y, Dong H, Zhu Y, Feng W, Wu H. Essential oil from Cinnamomum cassia presl bark regulates macrophage polarization and ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury through TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway. Phytomedicine. (2024) 129:155651. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155651
38. Wang D, Tan Z, Yang J, Li L, Li H, Zhang H, et al. Perfluorooctane sulfonate promotes atherosclerosis by modulating M1 polarization of macrophages through the NF-κB pathway. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. (2023) 249:114384. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2022.114384
39. Kong L, Sun P, Pan X, Xiao C, Song B, Song Z. Glycerol monolaurate regulates apoptosis and inflammation by suppressing lipopolysaccharide-induced ROS production and NF-κB activation in avian macrophages. Poult Sci. (2024) 103(8):103870. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2024.103870
40. Zhang Y, Fu Q, Sun W, Yue Q, He P, Niu D, et al. Mechanical forces in the tumor microenvironment: roles, pathways, and therapeutic approaches. J Transl Med. (2025) 23(1):313. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06306-8
41. Sapudom J, Alatoom A, Tipay PS, Teo JC. Matrix stiffening from collagen fibril density and alignment modulates YAP-mediated T-cell immune suppression. Biomaterials. (2025) 315:122900. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2024.122900
42. Ayadh M, Guillermin A, Abellan M-A, Bigouret A, Zahouani H. The assessment of natural human skin tension orientation and its variation according to age for two body areas: forearm and thigh. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. (2023) 141:105798. doi: 10.1016/j.jmbbm.2023.105798
43. Stecco C, Pratt R, Nemetz LD, Schleip R, Stecco A, Theise ND. Towards a comprehensive definition of the human fascial system. J Anat. (2025) 246(6):1084–98. doi: 10.1111/joa.14212
44. Chen Q, Li S, Li K, Zhao W, Zhao C. A skin stress shielding platform based on body temperature-induced shrinking of hydrogel for promoting scar-less wound healing. Adv Sci. (2024) 11(41):e2306018. doi: 10.1002/advs.202306018
45. Xue C, Dou J, Zhang S, Yu H, Zhang S. Shikonin potentiates skin wound healing in Sprague-Dawley rats by stimulating fibroblast and endothelial cell proliferation and angiogenesis. J Gene Med. (2024) 26(1):e3633. doi: 10.1002/jgm.3633
46. Xue C, Yang M, Tian H, Wang Y. Biomechanical changes and effect on different corneal wound healing in rabbits: a comparative study. Clin Biomech. (2025) 125:106506. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiomech.2025.106506
47. Pereira X, De Oliveira P, Tagerman D, Romero-Velez G, Liu R, Malcher F. How I do it: using physics and progressive defect tensioning to close large hernia defects during MIS ventral hernia repair. Hernia. (2024) 29(1):55. doi: 10.1007/s10029-024-03230-6
48. Min P, Zhang S, Sinaki DG, Yao P, Hu F, Wang X, et al. Using Zhang’s supertension-relieving suture technique with slowly-absorbable barbed sutures in the management of pathological scars: a multicenter retrospective study. Burns Trauma. (2023) 11:tkad026. doi: 10.1093/burnst/tkad026
49. Khan A, Yang H, Habib DRS, Ali D, Wu JY. Development of a machine learning-based tension measurement method in robotic surgery. Surg Endosc. (2025) 39(5):3422–8. doi: 10.1007/s00464-025-11658-9
50. Li S, Zhao X, Deng Y, Zhao Y, Liu Y, Wang D, et al. Affecting factors for abdominal incisional tension in surgery of dogs and cats. Res Vet Sci. (2023) 156:88–94. doi: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2022.11.014
51. Wu YJ, Wu LP, Yu MF. The clinical value of intelligent wound measurement devices in patients with chronic wounds: a scoping review. Int Wound J. (2024) 21(3):e14843. doi: 10.1111/iwj.14843
52. Xu Y, Li T, Zhou H, Lu Y, Yuan Y, Zhao B, et al. A self-powered bioelectronic suture via hybrid laser treatment. Adv Healthc Mater. (2025) 14(18):e2501329. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202501329
53. Liu H, Laflamme S, Zellner EM, Aertsens A, Bentil SA, Rivero IV, et al. Soft elastomeric capacitor for strain and stress monitoring on sutured skin tissues. ACS Sens. (2021) 6(10):3706–14. doi: 10.1021/acssensors.1c01477
54. Liu Y, Zhang X, Yu S, Gao M, Han C, Xue B, et al. Finite element analysis of a novel patellar fracture fixation method. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. (2024) 25(1):1073. doi: 10.1186/s12891-024-08235-x
55. Mitsuishi A, Nakamura H, Miura Y, Miyata T, Orihashi K, Yoshida K, et al. Significant thrombus in saccular aneurysm in a patient with polycythemia: a case report. J Cardiothorac Surg. (2024) 19(1):134. doi: 10.1186/s13019-024-02645-7
56. Kyparissis K, Kladovasilakis N, Daraki M-S, Raptis A, Tsantrizos P, Moulakakis K, et al. Numerical evaluation of abdominal aortic aneurysms utilizing finite element method. Diagnostics. (2025) 15(6):697. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15060697
57. Nagle M, Price S, Trotta A, Destrade M, Fop M, Ní Annaidh A. Analysis of in vivo skin anisotropy using elastic wave measurements and Bayesian modelling. Ann Biomed Eng. (2023) 51(8):1781–94. doi: 10.1007/s10439-023-03185-2
58. Howell RS, Liu HH, Khan AA, Woods JS, Lin LJ, Saxena M, et al. Development of a method for clinical evaluation of artificial intelligence-based digital wound assessment tools. JAMA Netw Open. (2021) 4(5):e217234. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.7234
59. Feng X, Li G-Y, Jiang Y, Shortt-Nguyen O, Yun S-H. Optical coherence elastography measures mechanical tension in the Lens and capsule. Acta Biomater. (2025) 199:252–61. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2025.05.009
60. Nagle M, Conroy Broderick H, Vedel C, Destrade M, Fop M, Ní Annaidh A. A Gaussian process approach for rapid evaluation of skin tension. Acta Biomater. (2024) 182:54–66. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2024.05.025
61. Abbas DB, Lavin CV, Fahy EJ, Griffin M, Guardino N, King M, et al. Standardizing dimensionless cutometer parameters to determine in vivo elasticity of human skin. Adv Wound Care. (2022) 11(6):297–310. doi: 10.1089/wound.2021.0082
62. Antoszewska M, Spychalski P, Kekonen A, Viik J, Barańska-Rybak W. Bioimpedance sensor array for monitoring chronic wounds: validation of method feasibility. Int Wound J. (2024) 21(8):e14899. doi: 10.1111/iwj.14899
63. Han Y, Sun Y, Yang F, Liu Q, Fei W, Qiu W, et al. Non-invasive imaging of pathological scars using a portable handheld two-photon microscope. Chin Med J. (2024) 137(3):329–37. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000002715
64. Han IS, Hua J, White JS, O’Connor JT, Nassar LS, Tro KJ, et al. After wounding, a G-protein coupled receptor promotes the restoration of tension in epithelial cells. Mol Biol Cell. (2024) 35(5):ar66. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E23-05-0204
65. Babu NK, Sreepadmanabh M, Dutta S, Bhattacharjee T. Interplay of geometry and mechanics in epithelial wound healing. Phys Rev E. (2024) 110(5-1):054411. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.110.054411
66. Wang X-H, Wang M, Pan J-B, Zhu J-M, Cheng H, Dong H-Z, et al. Fluorescent probe for imaging intercellular tension: molecular force approach. RSC Adv. (2024) 14(32):22877–81. doi: 10.1039/D4RA02647K
67. Chen J, Mo Y, Chen Y, Ma Z, Shen S, Sang H, et al. Application and effect of tension-reducing suture in surgical treatment of hypertrophic scar. BMC Surg. (2024) 24(1):119. doi: 10.1186/s12893-024-02390-7
68. Li L, Shao Q, He W, Wang T, Wang F. Close orthopedic surgery skin incision with combination of barbed sutures and running subcuticular suturing technique for less dermal tension concentration: a finite element analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. (2023) 18(1):333. doi: 10.1186/s13018-023-03755-z
69. Chang SS, Mo XJ, Wei ZR, Li H, Zhou J, Shi CS, et al. Application of zunyi suture method in suturing the donor site of anterolateral thigh flap. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. (2021) 35(4):477–82. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.202008101
70. Förster CE, Calabretti I, Gubser L, Schötzau A, Fellmann-Fischer B, Heinzelmann-Schwarz V, et al. Comparison of different suture techniques for laparoscopic vaginal cuff closure. Sci Rep. (2024) 14(1):4860. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-55586-5
71. Jian J, Ji-Qiu C, Zheng-Li C, Shen-Jun S, Lei L, Jie Z, et al. Automatic wound closure system: closure of large wounds by stretching the skin around the wound. Updates Surg. (2024) 76(6):2429–39. doi: 10.1007/s13304-024-01850-2
72. Ainslie-Garcia M, Anderson LA, Bloch BV, Board TN, Chen AF, Craigie S, et al. International delphi study on wound closure and dressing management in joint arthroplasty: part 1: total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. (2024) 39(4):878–83. doi: 10.1016/j.arth.2023.12.032
73. Guo Z, Xiong Y, Zhang S, Yuan T, Xia J, Wei R, et al. Naturally derived highly resilient and adhesive hydrogels with application as surgical adhesive. Int J Biol Macromol. (2023) 253(Pt 5):127192. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.127192
74. Li S, Luo M, Li J, Huang Q, Lei B. Sprayable nanocomposites hydrogel for wound healing and skin regeneration. Adv Healthc Mater. (2024) 13(32):e2402549. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202402549
75. Liu C, Li M, Liu Z, Shi Z, Wang X, Huang F. Chitosan thermogelation and cascade mineralization via sequential CaCO incorporations for wound care. Int J Biol Macromol. (2024) 266(Pt 2):131076. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.131076
76. Yang Z, Wang C, Zhang Z, Yu F, Wang Y, Ding J, et al. A pH responsive tannic acid/quaternized carboxymethyl chitosan/oxidized sodium alginate hydrogels for accelerated diabetic wound healing and real-time monitoring. Int J Biol Macromol. (2024) 264(Pt 2):130741. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.130741
77. Chang L, Du H, Xu F, Xu C, Liu H. Hydrogel-enabled mechanically active wound dressings. Trends Biotechnol. (2024) 42(1):31–42. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2023.06.004
78. Cai C, Zhu H, Chen Y, Guo Y, Yang Z, Li H, et al. Mechanoactive nanocomposite hydrogel to accelerate wound repair in movable parts. ACS Nano. (2022) 16(12):20044–56. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.2c07483
79. Jilberto J, DePalma SJ, Lo J, Kobeissi H, Quach L, Lejeune E, et al. A data-driven computational model for engineered cardiac microtissues. Acta Biomater. (2023) 172:123–34. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2023.10.025
80. Pfyffer D, Smith AC, Weber KA 2nd, Grillhoesl A, Mach O, Draganich C, et al. Prognostic value of tissue bridges in cervical spinal cord injury: a longitudinal, multicentre, retrospective cohort study. Lancet Neurol. (2024) 23(8):816–25. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(24)00173-X
81. Hao R, Niu X, Jiang X, Liu K, Ma X, Chen C. Transglutaminase-triggered dual gradients of mechanical and biochemical cues self-assembling peptide hydrogel for guiding MC3T3-E1 cell behaviors. Int J Biol Macromol. (2025) 285:138281. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.138281
82. Sahan AZ, Baday M, Patel CB. Biomimetic hydrogels in the study of cancer mechanobiology: overview, biomedical applications, and future perspectives. Gels. (2022) 8(8):496. doi: 10.3390/gels8080496
83. Caprio ND, Davidson MD, Daly AC, Burdick JA. Injectable MSC spheroid and microgel granular composites for engineering tissue. Adv Mater. (2024) 36(14):e2312226. doi: 10.1002/adma.202312226
84. Wu H, Wang T, Liang Y, Chen L, Li Z. Self-assembled and dynamic bond crosslinked herb-polysaccharide hydrogel with anti-inflammation and pro-angiogenesis effects for burn wound healing. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. (2024) 233:113639. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2023.113639
85. Oprita EI, Iosageanu A, Craciunescu O. Natural polymeric hydrogels encapsulating small molecules for diabetic wound healing. Gels. (2023) 9(11):867. doi: 10.3390/gels9110867
86. Kaur H, Gogoi B, Sharma I, Das DK, Azad MA, Pramanik DD, et al. Hydrogels as a potential biomaterial for multimodal therapeutic applications. Mol Pharm. (2024) 21(10):4827–48. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.4c00595
87. Chen Z, Xiao L, Hu C, Shen Z, Zhou E, Zhang S, et al. Aligned lovastatin-loaded electrospun nanofibers regulate collagen organization and reduce scar formation. Acta Biomater. (2023) 164:240–52. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2023.04.015
88. Zhou X, Yu X, You T, Zhao B, Dong L, Huang C, et al. 3D Printing-based hydrogel dressings for wound healing. Adv Sci. (2024) 11(47):e2404580. doi: 10.1002/advs.202404580
89. Alberts A, Bratu AG, Niculescu A-G, Grumezescu AM. New perspectives of hydrogels in chronic wound management. Molecules. (2025) 30(3):686. doi: 10.3390/molecules30030686
90. Tian DM, Wan HH, Chen JR, Ye YB, He Y, Liu Y, et al. In situ formed elastin-based hydrogels enhance wound healing via promoting innate immune cells recruitment and angiogenesis. Mater Today Bio. (2022) 15:100300. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2022.100300
91. Sun Q, Pei F, Zhang M, Zhang B, Jin Y, Zhao Z, et al. Curved nanofiber network induces cellular bridge formation to promote stem cell mechanotransduction. Adv Sci. (2023) 10(3):e2204479. doi: 10.1002/advs.202204479
92. Miller BT, Ellis RC, Maskal SM, Petro CC, Krpata DM, Prabhu AS, et al. Abdominal wall tension and early outcomes after posterior component separation with transversus abdominis release: does a “tension-free” closure really matter?. J Am Coll Surg. (2024) 238(6):1115–20. doi: 10.1097/XCS.0000000000001049
93. Li Y, Liu A, Wang J, Yang C, Lv K, He W, et al. Suture-anchored cutaneous tension induces persistent hypertrophic scarring in a novel murine model. Burns Trauma. (2024) 12:tkae051. doi: 10.1093/burnst/tkae051
94. Li L, Wang Y, Meng J, Wang X, Wu X, Wo Y, et al. Sele-targeted siRNA liposome nanoparticles inhibit pathological scars formation via blocking the cross-talk between monocyte and endothelial cells: a preclinical study based on a novel mice scar model. J Nanobiotechnology. (2024) 22(1):733. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-03003-4
95. Martyts A, Sachs D, Hiebert P, Junker H, Robmann S, Hopf R, et al. Biomechanical and biochemical changes in murine skin during development and aging. Acta Biomater. (2024) 186:316–29. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2024.07.013
96. Cirka H, Nguyen TT. Comparative analysis of animal models in wound healing research and the utility for humanized mice models. Adv Wound Care. (2025) 14(9):479–512. doi: 10.1089/wound.2024.0082
97. Tan MLL, Chin JS, Madden L, Becker DL. Challenges faced in developing an ideal chronic wound model. Expert Opin Drug Discov. (2023) 18(1):99–114. doi: 10.1080/17460441.2023.2158809
98. Foley MP, Fahey C, Byrne A-M, Lowery A, Walsh SR. Systematic review and meta-analysis of prophylactic negative pressure wound therapy devices for major lower extremity amputations. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. (2025) 70(3):346–56. doi: 10.1016/j.ejvs.2025.04.026
99. Smet S, Probst S, Holloway S, Fourie A, Beele H, Beeckman D. The measurement properties of assessment tools for chronic wounds: a systematic review. Int J Nurs Stud. (2021) 121:103998. doi: 10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2021.103998
100. Augustinus S, van Goor IWJM, Berkhof J, Daamen LA, Groot Koerkamp B, Mackay TM, et al. Alternative randomized trial designs in surgery: a systematic review. Ann Surg. (2022) 276(5):753–60. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000005620
101. Mota FAR, Passos MLC, Santos JLM, Saraiva MLMFS. Comparative analysis of electrochemical and optical sensors for detection of chronic wounds biomarkers: a review. Biosens Bioelectron. (2024) 251:116095. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2024.116095
102. Medina-Lombardero S, Bain C, Charlton L, Pellicoro A, Rocliffe H, Cash J, et al. The biomechanics of wounds at physiologically relevant levels: understanding skin’s stress-shielding effect for the quantitative assessment of healing. Mater Today Bio. (2024) 25:100963. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2024.100963
Keywords: surgical wound tension, wound healing, biomechanics, quantitative evaluation, clinical management
Citation: Gong F, Wan B, Qi P and Wei Z (2025) Biomechanical mechanism and clinical management progress of surgical wound tension. Front. Surg. 12:1674382. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2025.1674382
Received: 28 July 2025; Accepted: 28 August 2025;
Published: 22 September 2025.
Edited by:
Shuo Chen, Northeastern University, ChinaReviewed by:
Septian Mixrova Sebayang, Harapan Bangsa University, IndonesiaPeiru Min, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, China
Archita Sharma, Texas A and M University, United States
Copyright: © 2025 Gong, Wan, Qi and Wei. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zairong Wei, emFpcm9uZ3dlaUAxNjMuY29t
 Feiyu Gong
Feiyu Gong Bingjie Wan2
Bingjie Wan2