- 1School of Medicine, Tulane University, New Orleans, LA, United States
- 2Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, CA, United States
- 3University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, Canada
- 4SUNY Health Science Center, Brooklyn, NY, United States
- 5School of Medicine, Louisiana State University, New Orleans, LA, United States
- 6Sadeghi Center for Plastic Surgery, New Orleans, LA, United States
- 7School of Medicine, Boston University, Boston, MA, United States
- 8School of Medicine, Brown University, Providence, RI, United States
- 9Department of Surgery, Tulane University, New Orleans, LA, United States
We present a novel approach for localizing a large, non-palpable area of ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) for surgical resection using multiple SCOUT reflectors in a 45-year-old woman with DCIS of the left breast. Lesional resection using SCOUT MD™'s four unique reflectors was completed with real-time feedback from the SCOUT probe, providing information on distance, depth, and orientation around the perimeter of the calcifications. Successful DCIS resection was confirmed by post-resection tomosynthesis imaging of the partial mastectomy specimen, and negative margins were achieved. The patient synchronously chose contralateral breast reduction to achieve symmetry with the ipsilateral oncoplastic reduction mastoplasty. Advancements in SCOUT MD™ technology provide for improved intraoperative precision in the dissection with the use of four unique reflectors, while maintaining optimal cosmetic results by minimizing the removal of normal tissue. We believe these technological advancements in breast tumor localization will reduce rates of re-excision and the need for additional surgical management.
Introduction
The original SCOUT™ technology, which employs radar detection of a single reflector, revolutionized the localization and excision of non-palpable breast lesions (1–7). With the use of SCOUT™, surgeons can perform resections with more efficiency compared with the traditional, cumbersome, and time-consuming method of wire localization (6–9). However, with just one reflector, lesion visualization is limited to the orientation and positioning of that reflector (10, 11). Furthermore, bracketing a lesion with multiple reflectors of identical structure often causes confusion as to which reflector signal and site is being detected. Advancements with SCOUT MD™ now provide four unique reflectors, which can be deployed around the lesion, allowing for more precise isolation and resection with real-time radar feedback from multiple locations at once (1, 2). The use of unique reflectors allows for differentiation between signals, orienting the surgeon to the precise depth and distance of the dissection.
In this report, we describe the use of novel SCOUT MD™ technology to localize a large area of non-palpable ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) for surgical resection using multiple, unique SCOUT MD™ reflectors. This technique provided improved accuracy in dissection and optimal cosmetic outcomes.
This case report describes a pre-menopausal G3P1 45-year-old woman with a medical history significant only for hypertension and negative for any personal history of malignancy. Her family history was significant for breast cancer in her maternal great grandmother, who was diagnosed at age 40, and in two of her maternal second cousins. Prior familial genetic testing had not been performed; however, her personal Myriad genetic testing was negative for any significant mutations, and management guidelines recommended routine screening. She gave birth at the age of 29, after which she did not breastfeed. She had a history of using estrogen-based birth control for 25 years.
The patient presented in 2024, after a routine mammogram screening identified indeterminate calcifications in the upper outer quadrant of the left breast, classified as Breast Imaging-Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) 0. She denied any nipple discharge, breast discomfort, or other abnormalities on self-breast exams. Three days later, a subsequent diagnostic mammogram identified a BI-RADS 4C lesion with a 3.4 cm area of calcifications in a linear and segmental distribution, 7.9–11.3 cm from the nipple (Figure 1).
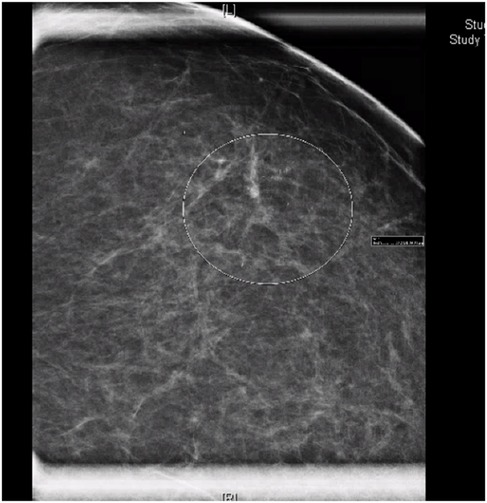
Figure 1. Mammogram of left breast demonstrating linear and segmental punctate calcifications over a 3.4 cm area, mid-depth. BI-RADS 4C.
Stereotactic core needle biopsy completed 2 weeks later, confirmed high-grade DCIS with solid pattern, focal minimal comedonecrosis, and focal microcalcifications in the left breast. No lymphovascular invasion was identified. MRI correlated the non-palpable area of abnormality with a 5.2 cm area of non-mass enhancement. MRI also noted a prominent level 1 left axillary lymph node with no internal mammary lymphadenopathy (Figure 2).
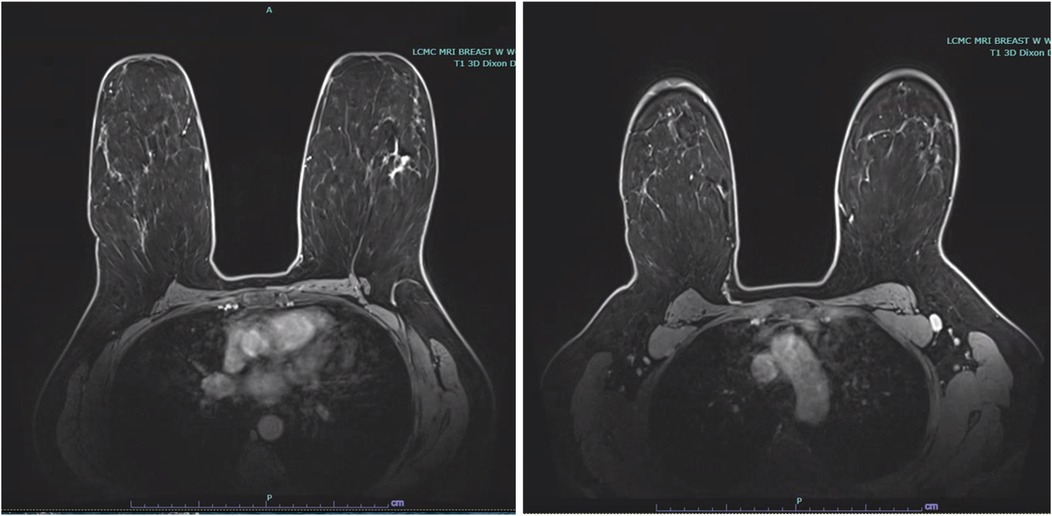
Figure 2. Bilateral breast MRI depicting malignancy in the upper outer quadrant of the left breast with non-mass enhancement measuring 5.2 cm, in addition to a prominent level 1 left axillary lymph node.
The patient was counseled on mastectomy with or without reconstruction vs. breast conservation and radiation therapy. With G-sized breasts and the extent of the calcifications, the patient was a suitable candidate for bilateral breast reduction and mastopexy with left upper outer quadrant oncoplastic partial mastectomy (12–14).
Oncoplastic reduction techniques vary based on the location of the tumor to simultaneously preserve and shape the breast to enhance and achieve symmetry. This technique allows for larger resection volumes, ensuring that clear margins are achieved, and the remaining unresected breast tissue can be rearranged based on anatomic vascular breast flaps to obtain an esthetic improvement. This technique remains a plausible option in patients with large breast volumes seeking reconstruction with breast conservation therapy. To maximize obtaining optimal margins, a plan for SCOUT MD™ bracketing with four reflectors for localization and guided resection was made. A sentinel lymph node biopsy was also encouraged, given the extensive area of calcifications, the location of high-grade DCIS in the upper outer quadrant, and the anticipation for oncoplastic adjacent tissue transfer and rearrangement. With the 20% risk of upstaging in high grade DCIS, this would avoid the challenge of a difficult biopsy in the future. The patient was amenable to this technique, as her treatment goals focused on complete resection and cosmetic optimization.
Methods
The patient described has provided consent for the publication of her case.
Two days before the partial mastectomy, four unique SCOUT reflectors were each placed around the 4 cm area of calcifications. Specifically, a double L SCOUT was advanced into the proximal aspect of the group of calcifications. Similarly, two double J SCOUT reflectors were deployed in the lateral aspect and within the medical aspect of the calcifications. The breast was compressed in the lateral to medial positioning, and the J/L combination reflector was deployed in the distal aspect of the calcifications, posteriorly. Knowing we would take a full-thickness segment from the anterior skin edge to the posterior chest wall, these margins were not marked. Ultrasound confirmed the successful SCOUT reflector placements within the left breast (Figure 3).
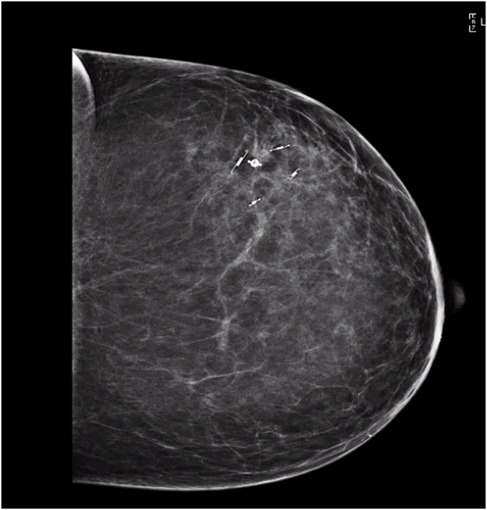
Figure 3. Ultrasound confirmation of SCOUT reflector locations around the calcified lesion. Calcifications surrounded by a double L shape proximally, double J shape laterally, double J shape medially, and JL shape distally.
On the day of surgery, lesional resection was completed with real-time feedback from the SCOUT probe, providing information on distance, depth, and orientation around the perimeter of the calcifications. The upper outer quadrant was dissected within the anterior subcutaneous plane, leaving a 1 cm thick skin flap in the upper outer quadrant. The two double J reflectors were identified medially and laterally using the SCOUT probe, and these were marked with a silk suture and single clips. Similarly, the anterior double L reflector was marked with two clips, and the posterior reflector (J/L) was marked with three clips. We dissected 2 cm grossly around all four SCOUT reflector signals. The dissection was advanced down to the pectoralis musculature of the chest wall. The anterior signal was dissected 5 cm from the nipple-areolar complex, and the distal location was dissected 15 cm from the nipple. Gross margins of >1 cm outside each reflector were provided using an intraoperative 3D specimen radiograph.
Given the extensive area of calcifications and high-grade DCIS in the upper outer quadrant as well as the complexity of the surgery, the sentinel lymph node biopsy was completed next. Through the superior lateral border of the pectoralis muscle, the clavipectoral fascia was opened to identify a deep level 1 left axillary sentinel lymph node, which was hot, blue, and palpable. The lymph node was dissected out and removed in its entirety.
Following resection, the plastic surgery team completed the bilateral breast reduction and lift, using anatomic vascular breast flaps to obtain esthetic improvement (Figure 4).
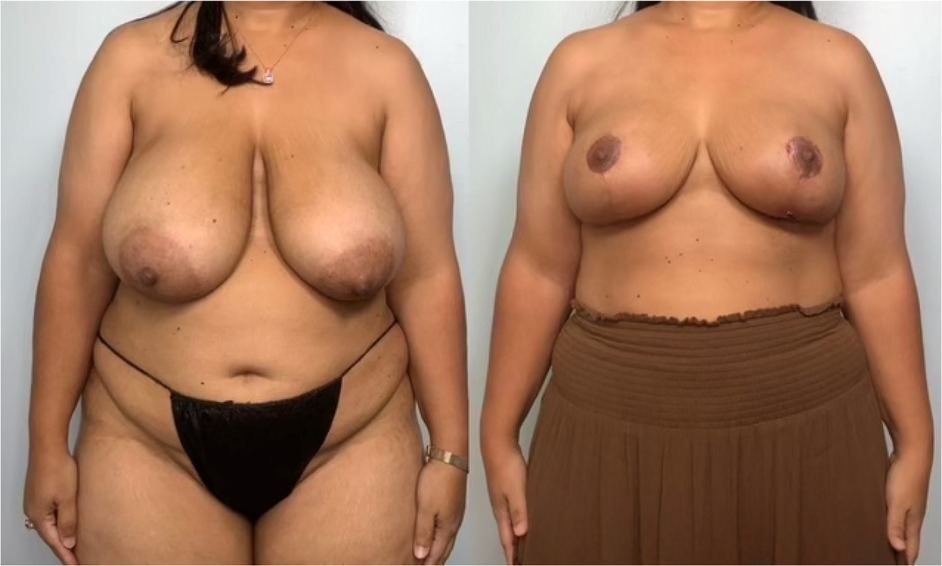
Figure 4. Patient before and after bilateral reduction mastoplasty. Initially, with G-sized breasts, she was reduced to C-sized breasts following the mastoplasty and lumpectomy.
Results
Successful DCIS resection with negative margins on pathology was achieved using SCOUT MD™ localization. With guided feedback from the four unique SCOUT signals, the borders of the non-palpable lesion were clearly identified, and an 18.5 cm × 15.7 cm × 8.5 cm specimen, weighing 430.5 g, was resected from the left breast. A single left axillary sentinel lymph node, identified by radioactive tracer, was removed, ultimately testing negative for any evidence of carcinoma on frozen section. The contralateral right breast reduction and lift was completed by the plastic surgery team, with 900 g of tissue from the benign reduction. Intraoperative tomosynthesis specimen radiograph and imaging confirmed all margins were grossly clear by at least 2 cm around the calcifications. Post-resection imaging of the left breast specimen confirmed the target SCOUT markers at the expected locations proximally, laterally, medially, and distally around the punctate calcifications (Figure 5).
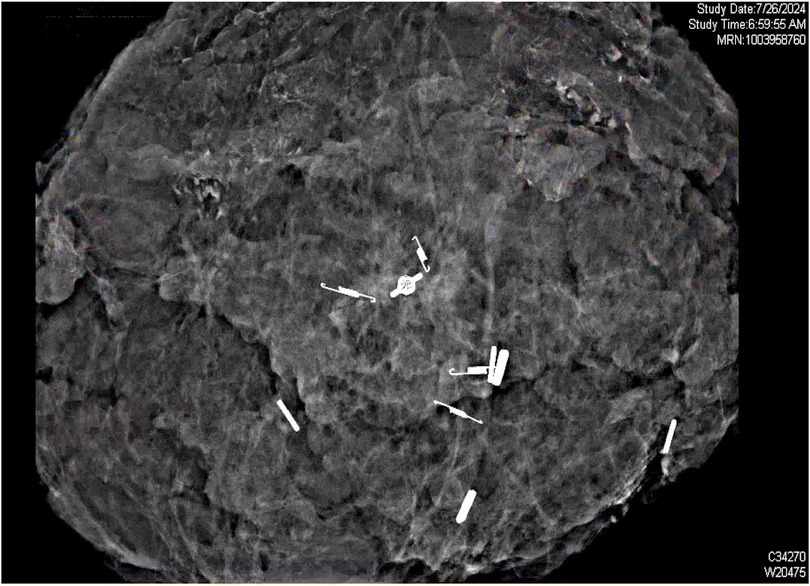
Figure 5. Post-resection ultrasound scan of the mass, identifying the four unique SCOUT reflectors surrounding the punctate calcifications in excised tissue.
Final histopathology of the non-palpable lesion confirmed at least 2 mm of high-grade DCIS, solid and cribriform type with comedonecrosis. Negative margins were confirmed with the closest margin being the anterior margin at 5.5 mm. Immunohistochemical staining was positive for ADH4, P63, CK5/14, and CK7/19+.
The patient's Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center risk of local recurrence was 11% and 18% at 5 and 10 years, respectively, which significantly reduced to 4% and 7% with the addition of radiation therapy (15). Given this information, she chose to receive adjuvant radiotherapy to the volume-reduced left breast for 6.5 weeks. She recovered from surgery well and tolerated radiotherapy with no difficulties. Today, she remains disease-free and satisfied with her symmetric oncoplastic partial mastectomy and breast reduction. She follows up every 6 months in the clinic for continued clinical surveillance and high-risk screening.
Discussion
The original SCOUT technology offers ease and precision to breast lesion isolation by utilizing radar detection of a small reflector placed in the tissue. However, challenges to the original SCOUT technology include a limited multidimensional perspective of the lesion, given the use of only one reflector signal. Strategies to bracket an impalpable lesion with multiple identical reflectors provides for more detailed orientation of the lesion; however, the reflector signals are easily confused, given poor differentiation between signal feedback.
Advancements with SCOUT MD™ now provide four unique reflectors, which can be deployed around the lesion, allowing for more precise isolation and resection. With real-time radar feedback from the unique reflectors surrounding the lesion, surgeons can differentiate between the signals and are more precisely oriented to the depth and distance of the dissection, optimizing margins of resection.
The use of SCOUT MD™ in tumor localization offers further precision of tumor resection, while maintaining patient and facility flexibility for scheduling (2–5). These advancements in SCOUT MD™ technology, employing four unique reflectors, provide precise information on orientation and depth of lesional borders throughout the resection. Utilizing four reflectors provides a full, three-dimensional orientation of the impalpable lesion during the dissection, a marked improvement from the two-dimensional orientation provided by only two reflectors. Furthermore, SCOUT MD™ facilitates optimal cosmetic results by minimizing the removal of normal tissue.
When compared with different wire-free techniques for preoperative localization of non-palpable breast lesions, SCOUT MD™ has certain advantages that promote patient satisfaction and surgical precision. Compared to Radioactive Seed Localization (RSL), SCOUT MD™ is non-radioactive, eliminating concerns for radiation safety and the need for nuclear medicine-approved facilities (10). While our case warranted a sentinel lymph node biopsy, this advantage still provided ease during reflector placement and DCIS resection. Furthermore, when compared to Magseed technology, SCOUT MD™ offers four unique signals to promote clarity of orientation during the dissection, and the localization is not limited by reflector depth (16).
We believe these technological advancements in breast tumor localization will reduce rates of re-excision and the need for additional surgical management.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material; further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
Ethical approval was not required for the studies involving humans because of the nature of this single, retrospective case report. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author contributions
AL: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. SC: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. AS: Methodology, Supervision, Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing. RC: Supervision, Writing – review & editing, Investigation, Methodology, Conceptualization.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. The authors declare that this study received funding from Merit Medical. The funder had no role in the study design, data collection and analysis, preparation of the manuscript, or the decision to submit for publication.
Acknowledgments
Thank you to the surgical teams at Tulane University School of Medicine, specifically the surgical oncology department and operating staff who assisted with this case. Thank you to Dr. Sadeghi and his plastic surgery team for their collaboration and correspondence.
Conflict of interest
RC has a consultant agreement with Merit Medical but owns no stock in the company.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence, and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Jadeja PH, Mango V, Patel S, Friedlander L, Desperito E, Ayala-Bustamante E, et al. Utilization of multiple SAVI SCOUT surgical guidance system reflectors in the same breast: a single-institution feasibility study. Breast J. (2018) 24(4):531–4. doi: 10.1111/tbj.12979
2. Falcon S, Weinfurtner RJ, Mooney B, Niell BL. SAVI SCOUT® localization of breast lesions as a practical alternative to wires: outcomes and suggestions for trouble-shooting. Clin Imaging. (2018) 52:280–6. doi: 10.1016/j.clinimag.2018.07.008
3. Farha MJ, Simons J, Kfouri J, Townsend-Day M. SAVI SCOUT® system for excision of non-palpable breast lesions. Am Surg. (2023) 89(6):2434–8. doi: 10.1177/00031348221096576
4. Vijayaraghavan GR, Ge C, Lee A, Roubil JG, Kandil DH, Dinh KH, et al. SAVI-SCOUT radar localization: transitioning from the traditional wire localization to wireless technology for surgical guidance at lumpectomies. Semin Ultrasound CT MR. (2023) 44(1):12–7. doi: 10.1053/j.sult.2022.10.004
5. Kasem I, Mokbel K. SAVI SCOUT® radar localisation of non-palpable breast lesions: systematic review and pooled analysis of 842 cases. Anticancer Res. (2020) 40(7):3633–43. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.14352
6. Baker JL, Haji F, Kusske AM, Fischer CP, Hoyt AC, Thompson CK, et al. SAVI SCOUT® localization of metastatic axillary lymph node prior to neoadjuvant chemotherapy for targeted axillary dissection: a pilot study. Breast Cancer Res Treat. (2022) 191(1):107–14. doi: 10.1007/s10549-021-06416-z
7. Tingen JS, McKinley BP, Rinkliff JM, Cornett WR, Lucas C. SAVI SCOUT radar localization versus wire localization for breast biopsy regarding positive margin, complication, and reoperation rates. Am Surg. (2020) 86(8):1029–31. doi: 10.1177/0003134820939903
8. Cox CE, Garcia-Henriquez N, Glancy MJ, Whitworth P, Cox JM, Themar-Geck M, et al. Pilot study of a new nonradioactive surgical guidance technology for locating nonpalpable breast lesions. Ann Surg Oncol. (2016) 23(6):1824–30. doi: 10.1245/s10434-015-5079-x
9. Mango VL, Wynn RT, Feldman S, Friedlander L, Desperito E, Patel SN, et al. Beyond wires and seeds: reflector-guided breast lesion localization and excision. Radiology. (2017) 284(2):365–71. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2017161661
10. Jeffries DO, Dossett LA, Jorns JM. Localization for breast surgery: the next generation. Arch Pathol Lab Med. (2017) 141(10):1324–9. doi: 10.5858/arpa.2017-0214-RA
11. Cornella KN, Palafox BA, Razavi MK, Loh CT, Markle KM, Openshaw LE. SAVI SCOUT as a novel localization and surgical navigation system for more accurate localization and resection of pulmonary nodules. Surg Innov. (2019) 26(4):469–72. doi: 10.1177/1553350619843757
12. Kijima Y, Yoshinaka H, Funasako Y, Natsugoe S, Aikou T. Oncoplastic surgery after mammary reduction and mastopexy for bilateral breast cancer lesions: report of a case. Surg Today. (2008) 38(4):335–9. doi: 10.1007/s00595-007-3628-z
13. Munhoz AM, Aldrighi CM, Montag E, Arruda E, Brasil JA, Filassi JR, et al. Outcome analysis of immediate and delayed conservative breast surgery reconstruction with mastopexy and reduction mammaplasty techniques. Ann Plast Surg. (2011) 67(3):220–5. doi: 10.1097/SAP.0b013e3181f77bba
14. Rodby KA, Robinson E, Danielson KK, Quinn KP, Antony AK. Age-dependent characteristics in women with breast cancer: mastectomy and reconstructive trends at an urban academic institution. Am Surg. (2016) 82(3):227–35. doi: 10.1177/000313481608200316
15. Manning AT, Sacchini VS. Conservative mastectomies for breast cancer and risk-reducing surgery: the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center experience. Gland Surg. (2016) 5(1):55–62. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2227-684X.2015.10.02
Keywords: breast cancer, SCOUT, lesion resection, DCIS, reflector
Citation: LaRussa A, Caputo S, Sadeghi A and Corsetti R (2025) Case Report: SCOUT MD™ four reflector technology—enhancing accuracy in breast lesion isolation. Front. Surg. 12:1683321. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2025.1683321
Received: 10 August 2025; Accepted: 18 September 2025;
Published: 8 October 2025.
Edited by:
Lorenzo Scardina, Fondazione Policlinico Universitario A. Gemelli—IRCCS, ItalyReviewed by:
Quratulain Sabih, University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, United StatesKaren Roa Tort, Instituto Politecnico Nacional, Mexico
Copyright: © 2025 LaRussa, Caputo, Sadeghi and Corsetti. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Anna LaRussa, YWxhcnVzc2FAdHVsYW5lLmVkdQ==
 Anna LaRussa
Anna LaRussa Sydney Caputo1,2
Sydney Caputo1,2