- Department of Computing, SeeVR Lab, Goldsmiths, University of London, London, United Kingdom
Digital twin technologies have become increasingly relevant in virtual reality, offering precise 1:1 mapping between physical environments and their virtual counterparts. While previous work has focused on object interaction through passive haptics, little attention has been given to how such environments can support social and embodied interactions that feel natural and expressive. In this work, we extend the digital twin paradigm by integrating full-body avatars, hand tracking, and voice-driven facial animation into a location-based VR environment. To explore the interactive potential of this dual-realm environment, we propose three categories of cross-realm embodied interaction: (1) Tangible interaction, exemplified by spatially aligned object manipulation; (2) Social gesture, supported through expressive hand and body movement; and (3) Social touch, including co-located tactile actions such as handshakes and hugs. We developed a prototype system showing all three embodied interactions, supported by passive haptics, precise spatial alignment, and real-time multiplayer synchronization. We also introduced a low-cost, Wi-Fi-based motion tracking prototype to enhance interaction with movable physical elements. We evaluate the system through expert interviews, identifying key themes related to spatial trust, tactile realism, and interpersonal presence. Our findings suggested that precise alignment and embodied social cues significantly enhance immersion and social connectedness. This work contributes towards a replicable framework for designing socially immersive digital twin experiences and opens new directions for location-based VR in collaborative and educational contexts.
1 Introduction
The concept of a digital twin, defined as a virtual counterpart of a real-world environment, has evolved beyond its original industrial applications and is now increasingly explored in immersive technologies such as virtual reality (VR) (Grieves and Vickers, 2017a; Tao et al., 2022). With the rapid growth of consumer-grade VR devices like the Meta Quest, Pico Neo3, and Apple Vision Pro, location-based VR has become increasingly accessible, enabling users to move freely within tracked physical environments. In recent years, several commercially operated VR experiences have emerged that exemplify this trend. For example, Horizon of Khufu offers a ticketed immersive tour through a digitally reconstructed Great Pyramid of Giza, combining redirected walking with educational storytelling in a large-scale physical venue (Emissive and Excurio, 2023). Similarly, iQIYI’s Luoyang VR experience invites the public to explore a narrative-rich virtual city rooted in Chinese historical settings (Kharpal, 2023). These examples use spatial redirection and narrative structures, rather than precise alignment between physical and virtual spaces. Nevertheless, they still represent meaningful integrations of VR and physical environments, and share conceptual relevance with the dual-realm settings explored in this paper.
While prior research has established foundational techniques for achieving one-to-one spatial alignment and implementing passive haptic feedback in VR (Hoffman, 1998; Simeone et al., 2015), these systems have largely focused on individual user interaction with physical objects. The social and embodied dimensions of interaction, including body language, proxemic awareness, and physical touch, have received far less attention in the context of digital twin environments. As a result, many current applications fail to fully leverage the capabilities of modern VR hardware to support co-located collaboration and social presence.
In this work, we address this gap by designing a dual-realm VR prototype that integrates spatially precise aligned physical environments with embodied full-body avatars, passive haptics, and real-time multi-user interaction. The system is situated in a physical laboratory that is digitally scanned and mapped to a virtual environment, enabling participants to move naturally and interact both with physical objects and with one another through their avatars. Our prototype supports three types of embodied cross-realm interaction that together enhance social presence and user immersion. The first is tangible interaction, which involves manipulating physical objects that are spatially aligned with their virtual counterparts. The second focuses on social gestures, allowing users to express themselves through body movement, such as pointing, miming, or other non-verbal cues. Finally, the system enables social touch, including familiar interpersonal physical contacts such as handshakes, high-fives, and hugs. These are made possible through body tracking and passive haptic feedback, allowing users to physically enact social behaviours that feel intuitive and grounded in real-world movement.
Beyond enhancing expressiveness and presence, the use of full-body avatars also serves a practical function in supporting spatial awareness and collision avoidance in shared physical spaces. By making users’ bodies visible to one another in VR, the system reduces the risk of unintended physical contact, contributing to a safer and more coordinated multi-user experience. Additionally, we explore a custom-built Wi-Fi-based motion tracking module to extend physical interaction to movable objects and improve full-body tracking without requiring external lighthouse systems. Together, these features contribute to a more immersive, intuitive, and socially engaging form of interaction within location-based digital twin environments.
In the following sections, we describe the implementation of the prototype, detail the interaction design framework, and present insights from expert interviews that assess how spatial alignment, haptics, and avatar embodiment impact presence, safety, and co-located social interaction.
2 Related work
Previous studies have examined concepts and technologies relevant to dual-realm concept, wherein virtual and physical environments are tightly coupled. Notable areas include synchronized visuals through digital twin approaches, passive haptic to enhance user interaction, and the integration of embodied avatars in VR. These strands of research collectively explore how aligning digital and physical spaces affects human–object and human–human interactions. In the following subsections, we review these foundational works and discuss how they inform our proposed design.
2.1 A digital twin concept approach
As a virtual representation of a physical object, product or environment (Enders and Hoßbach, 2019; Grieves and Vickers, 2017b), Digital twins is a concept introduced by Michael Grieves in 2003 (Grieves and Vickers, 2017a). Initially applied to the physical and digital worlds integration in military and aerospace industries, digital twins have since expanded to fields like manufacturing, energy, healthcare, and education (Tao et al., 2022; Zhang et al., 2022). Typically, digital twins are used to simulate, monitor, and optimize performance in real-time, with an emphasis on the connection between two parts—the virtual and the real (Liu et al., 2021; Enders and Hoßbach, 2019). This technology has become increasingly valuable in various industries and has expanded from military applications to manufacturing and beyond, focusing on training and educational functionalities (Fuller et al., 2020; Wilhelm et al., 2021; Enders and Hoßbach, 2019). For instance, digital twins help in training scenarios by creating immersive environments where workers can interact with a virtual model of the equipment before handling the real machinery. They also facilitate remote assistance, allowing experts to guide on-site workers through complex procedures by viewing the digital twin of the equipment and providing real-time instructions.
Additionally, digital twins have integrated with mixed reality technologies (e.g., HoloLens (Microsoft, 2025), Oculus passthrough function (Platforms, 2025b)) for manufacturing processes and workstations (Kritzinger et al., 2018). This integration provides real-time visualizations of machinery operations, enabling predictive maintenance by overlaying data directly onto physical equipment (Zhu et al., 2019). At this stage, researchers have started to notice that digital twins often lack realism. Building on this observation, the study by Havard et al. (2019) provides a case study discussing the design of a workstation involving collaboration between humans and robotic arms. The interactive capabilities of these devices have opened up new possibilities for experience design and brought digital twin applications into a new phase of human-centred design. (Wilhelm et al., 2021). conducted a review of the human-centred classification of digital twins from 2016 to 2020, noting a rapid increase in digital twin-based interaction since 2017. The scope of applications has broadened significantly, encompassing not only augmented reality but also the integration of virtual reality (Malik et al., 2020; Kuts et al., 2019), as well as research on human-robot interactions, particularly in human-robot collaboration (Horváth and Erdős, 2017; Bilberg and Malik, 2019; Segura et al., 2020).
In previous studies, such as Kritzinger et al. (2018), the focus has been on data flow, which emphasizes the data processes between the physical and virtual worlds. However, this research direction has gradually expanded to include visualization (Zhu et al., 2019) and interaction (Wilhelm et al., 2021). Despite these advancements, from an industry perspective, design, application, and user research remain relatively limited outside of the manufacturing domain (Enders and Hoßbach, 2019). As a result, As a result, research on user interaction within virtual environments and spatially mapped physical contexts remains underdeveloped, especially in relation to multiplayer human-to-human interactions in dual-realm settings. However, digital twins are increasingly driving innovation by creating new connections between humans and objects, making object-human and human-to-human important parts of digital twin interactions (Wilhelm et al., 2021).
2.2 Synchronized visuals and aligned physical sensation
Beyond the context of digital twins, the study most closely related to our use of digitally mapped physical objects in VR is the work by Hoffman (1998). Their experiment involved a virtual plate that was synchronized and aligned with a real plate, allowing both to be simultaneously controlled, rotated, and touched. Participants were divided into two conditions: a “see only, no touch” group and a “see and touch” group. In the “see only, no touch” condition, participants could visually perceive the virtual plate, but were unable to physically interact with it. While the “see and touch” condition allowed participants to not only see the virtual plate but also physically touch and manipulate the real plate, which was spatially aligned with the virtual representation. This setup provided an early demonstration of dual-realm interaction based on aligned physical–virtual objects.
This concept was not widely connected with the idea of digital twins in later research but instead was explored more extensively under the term ‘passive haptic’ or ‘tangible interaction’ within the field of virtual environments (Simeone et al., 2015; Rettinger and Rigoll, 2023). Both approaches share the core idea of using real-world physical objects to enhance virtual interaction through touch and spatial alignment. While tangible interaction does not always involve strict digital twin mappings of real-world objects, prior research in this area has shown strong benefits across a variety of domains. Tangible objects have been shown to improve user interaction (Wang et al., 2020; Hinckley et al., 1994). As Jones et al. (2020) points out, accuracy in the size, shape, and behaviour of these virtual objects is vital for ensuring realistic interactions. Whether a user picks up a virtual bottle or moves a virtual chair, aligning these with the physical object’s weight and texture enhances the sense of realism. The ability to interact with these movable virtual entities in real time is crucial for creating an immersive digital twin experience. Havard et al. (2019) also emphasizes the importance of maintaining accurate spatial alignment of physical entities and their digital counterparts, ensuring that users can interact naturally within both realms.
Studies also have explored spatial mapping at the level of larger environmental structures. Insko (2001) developed a digital twin version of a real training environment, aligning physical room structures boundaries. Their study examined how passive haptics, achieved through spatial alignment, influenced cognitive mapping and spatial knowledge transfer in training scenarios. As noted in Simeone et al. (2015), the term “object” is often used to describe physical elements used in substitutional or immersive systems. However, such objects may also refer to large-scale architectural features, including walls, floors, or tables, as long as they are meaningfully aligned with the virtual surroundings. This broader interpretation allows reality mapping to encompass both fine-grained object manipulation and environmental-scale alignment. Currently, the use of technical tools like LiDAR and 3D scanning (Zhang et al., 2022) facilitates this alignment, making it possible for a virtual wall to perfectly match its physical counterpart in size and position, thereby maintaining immersion. This accurate representation of the physical layout in VR allows users to interact with both static elements through passive haptics, reinforcing the sense of presence in the environment (Insko, 2001).
More recently, studies focused on the use of passive haptics to enhance interaction in mixed reality environments (Johnson-Glenberg et al., 2023). By connecting physical 3D-printed objects, such as a burette, to virtual actions in a chemistry titration experiment, participants physically manipulated the burette demonstrated better recall of the experimental procedure and made greater use of relevant gestures during post-test recalls. Johnson-Glenberg et al. (2023) find that interacting with these tangible objects not only increased user engagement but also significantly improved learning outcomes. Notably, Johnson-Glenberg et al. (2023) also proposes a model which builds upon an influential “Virtual Continuum” model, first introduced in 1994 (Milgram and Kishino, 1994). The “Virtual Continuum” model describes a spectrum from the real world to fully virtual environments. While Johnson-Glenberg et al. (2023) expanded this framework by introducing an eXtended Reality(XR) Spectrum that incorporates both visual and haptic dimensions, emphasizing the importance of tactile interaction. Their work aligns with earlier findings, such as Hoffman (1998)’s work, which highlighted the critical role of touch in improving the perception of realism in virtual environments.
Passive haptics emphasis on strict spatial alignment between virtual and physical objects, Simeone et al. (2015) introduced the concept of Substitutional Reality. Unlike passive haptics, Substitutional Reality allows for differences between what users see in the virtual environment and what they touch in the real world. This opens up more creative possibilities for designing dual-realm experiences. In their study, the authors created different virtual environments, such as a medieval courtyard and a spaceship, where real objects were reused but shown in different ways to match the setting. Instead of requiring a perfect match, they explored how physical objects could be represented with changes in shape, temperature, or weight. They found that exact replicas offer the best user immersion and interaction experience, while lighter substitutes are easier to handle and reduce fatigue. This shift not only relaxes spatial design constraints but also expands the passive haptics to include variations in physical sensations.
Further expanding on these concepts, Peck and Gonzalez-Franco (2021) explored how passive haptics contribute to perceiving touch from other avatars within a virtual environment. This social haptic feedback amplifies interpersonal connection, creating a more vivid and interactive virtual experience. Together, these studies underline the importance of passive haptic technologies in making virtual environments more tangible and immersive, particularly in tasks requiring both object manipulation and social interaction.
2.3 Embodied avatar and social cues
Since the 1990s, Mel Slater and colleagues have conducted extensive research on immersion and avatars in VR, introducing key concepts such as embodiment and place illusion to explain the sense of immersion in virtual environments, like the feeling of being transported to another place (Slater, 2009). Allowing users to embody an avatar enhances immersion by making them feel as though they are one with the avatar’s body (Kilteni et al., 2012).
2.3.1 Physical locomotion
In dual-realm environments, embodied avatar with natural walking becomes both possible and advantageous. Specifically, avatar embodiment in such settings offers two key benefits. First, in terms of comfort and presence, prior research has shown that intuitive physical locomotion leads to greater user comfort, increased safety, and reduced motion sickness compared to controller-based movement (Cherni et al., 2020). When users move through the environment with their own bodies, rather than relying on teleportation or continuous movement by controller, they are more likely to feel immersed. In hybrid virtual-physical scenarios, enabling movement through full-body avatars and bare-foot walking offers a more natural and engaging locomotion experience.
Second, in social and safety contexts, combining avatar embodiment with physical locomotion prevents accidental collisions. In traditional VR settings, mismatches between real and virtual elements can cause users to unintentionally bump into physical objects or other participants. A common solution is to display virtual guardian boundaries, which warn users as they approach the limits of the tracked area (de Schot et al., 2023). However, in digital twin environments where the virtual space is precisely mapped onto the physical world, such virtual boundaries become unnecessary for environmental awareness, as users are already surrounded by accurately aligned physical structures. Nevertheless, these systems often fall short in multiplayer contexts, where users may still collide with each other due to a lack of mutual visibility. Embodied avatars address this issue by making each user’s body visible in the virtual environment in real time. This visual presence supports spatial awareness among participants and prevents unintended collisions not only with physical objects but also with other users in dual-realm setting.
In addition, while prior studies on reality mapping and passive haptics have primarily focused on interactions between users and physical objects (Simeone et al., 2015; Jones et al., 2020; Havard et al., 2019; Insko, 2001), the role of self-avatars in supporting human-to-human interaction within dual-realm environments has received little attention. This highlights a gap in existing digital twin research, where spatial alignment has often prioritized static or object-based elements, with less emphasis on the embodied presence and movement of co-located users. Incorporating self-avatars into these environments not only strengthens individual embodiment, but also enables new forms of spatial awareness and social interaction between users sharing the same physical space.
2.3.2 Social interaction
By being able to see and interact with each other’s full-body avatars without taking off their VR headsets, users can engage in both non-verbal signals within the virtual environment and touchable social cues in dual-realm experience. Burgoon et al. (2016) underscore the importance of touch in building and maintaining social relationships, highlighting its role in reinforcing interpersonal bonds. In terms of tactile feedback in the digital twin set up, full-body avatars could provide a form of passive body feedback when interacting with others, addressing a gap in current research, which mainly focuses on virtual spaces where feedback is usually delivered through controller vibrations (Sziebig et al., 2009).
Social Gesture and Cues As hand tracking technology in VR has become an integral feature (Buckingham, 2021), interactions with virtual objects have become more diverse. Users can now perform interactions (Platforms, 2025a) like poking physics buttons, executing complex hand grabs, and gesture recognition through intuitive hand use in the real world. This also means that actions like handshakes can be fully synchronized with tactile feedback in a ‘dual-realm’ setup. For social cues, virtual hands can almost replicate all gestures that can be expressed in real life. In both virtual and real-world interactions, the recognition and appropriate response to these non-verbal cues are essential for enhancing communication and building stronger interpersonal relationships (Burgoon et al., 2016). Understanding the significance of such cues can be a valuable focus of ‘dual-realm’ design, as it could help improve social dynamics between the virtual and physical realms, making communication more effective and enriching in virtual environments through the use of embodied avatars and their body language.
Therefore, our project also incorporates research on non-verbal communication as a gestural interaction design reference for both hand and body languages. For example, thumbs up as universally recognised hand gesture, a simple yet powerful non-verbal cue signifying approval or agreement (Mehrabian, 1972). Similarly, the act of nodding as body language (Ekman and Friesen, 1969), signifies agreement or understanding, providing subtle yet effective feedback that fosters dialogue. Conversely, shaking the head communicates disagreement or refusal, serving as a clear, non-verbal indication of a negative response.
Social Touch In addition to gestures, physical touch interactions like hug can express warmth, affection, or solidarity, conveying emotions that may be difficult to articulate. The high five, often employed in celebratory contexts, exemplifies the use of physical touch to express camaraderie, excitement, or mutual achievement (Givens, 2005). Previous studies define such physical interactions occurring between individuals in shared physical space as interpersonal or social touch (Huisman, 2017). This is a broad category encompassing a wide range of meaningful physical contact, including tapping on the shoulder, handshakes, hugs, and stroking.
In social dual-realm settings using avatars, social touch becomes an expressive tool for co-located interaction. Van Erp and Toet (2015) categorized everyday social touch into three types, among which greeting-related touch—such as shaking hands, embracing, kissing, backslapping, and cheek-tweaking—is especially relevant to our collaborative scenario. Beyond greetings, other forms of social touch such as those found in intimate contexts (e.g., cuddling) or corrective/disciplinary contexts (e.g., a spank on the bottom) may also represent potential, though more complex, interaction styles within immersive environments.
3 Materials and methods
3.1 Apparatus
The dual-realm prototype was developed using the Unity game engine in early 2022 version, which supports various VR devices, including the Oculus Quest 1 and Quest 2, and was later tested on the Quest Pro in 2023. A LiDAR camera-based 3D scan software captured the physical laboratory environment, which was then optimized with Instant Meshes and further refined in Blender to ensure accurate scale and maintain robust frame rates. The processed virtual environment was imported into Unity, where avatars created in VRoid Studio were integrated using the UniVRM extension. Hand tracking and gesture recognition were provided by the Oculus Interaction SDK, while Normcore enabled real-time multiplayer functionality—synchronizing avatar movements, voice communication, and object ownership across multiple users. This modular VR tracker features a D1 Mini ESP32 board, a GY-BNO08X 9-axis IMU, a 1200mAh lithium battery with a charging module, utilizes SlimeVR’s open-source calibration software, and includes a magnetic module supporting up to 9-pin external data connections.
3.2 Implementation
3.2.1 Cross-realm interaction in dual-realm
Our digital twin environmental design functions as a dual-realm setup, where the visuals are virtual and the haptics are real, illustrate in Dual-Realm Spectrum in Figure 1. Further technical details on how this environmental reality mapping is implemented are provided in Section 3.2.2.
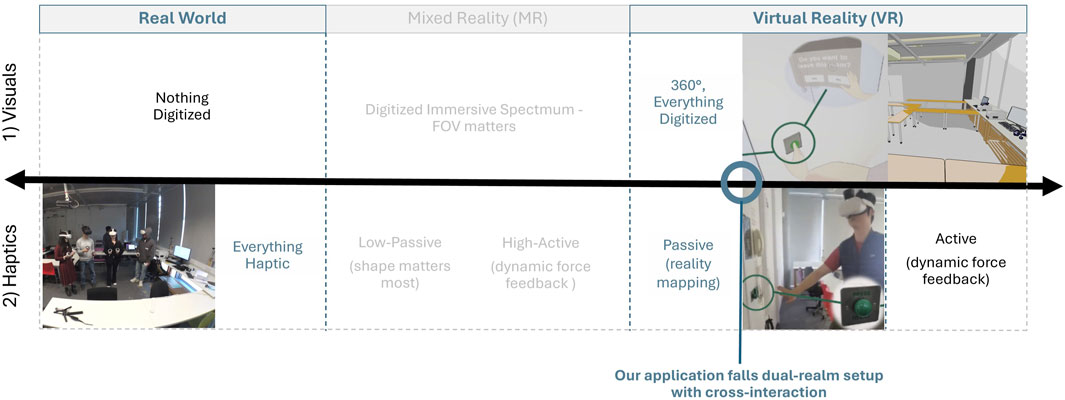
Figure 1. Dual-Realm Spectrum adapted from Johnson-Glenberg et al. (2023): The top row represents Visuals and the second row represents Haptics. From left, reality transitions to virtual. Regions of the spectrum not addressed in this study are grayed out. The blue circles highlight the position of our dual-realm environment within this spectrum. As an illustrative case of cross-realm interaction, we put a virtual push-button as example. It is visually rendered in VR, yet physically represented by a real-world switch, enabling users to perceive passive tactile feedback when pressing it.
1) Visuals: The environment is fully virtual. The user wears a VR headset that displays 360-degree virtual content, including the virtual environment and a virtual avatar, which is controlled by the user through hand and body tracking.
2) Haptics: The tactile experience is purely touchable and natural based on the mapped physical environment.
The dual-realm design supports a range of interaction possibilities. Figure 2 provides an overview of the embodied cross-realm interaction either currently implemented or planned for future iterations of the project. The diagram is structured along two dimensions: the x-axis represents the contact modality (ranging from purely virtual to dual-realm physical contact), while the y-axis captures the social dimension (ranging from individual to shared, multi-user interactions). We categorize interaction types based on whether they involve physical contact—with objects or bodies—and whether they incorporate social cues. To clarify the sensory conditions at the four corners of the interaction space, we annotate them based on the “see” and “touch” conditions defined by Hoffman (1998), indicating whether interactions involve visual perception only or both visual and tactile engagement.
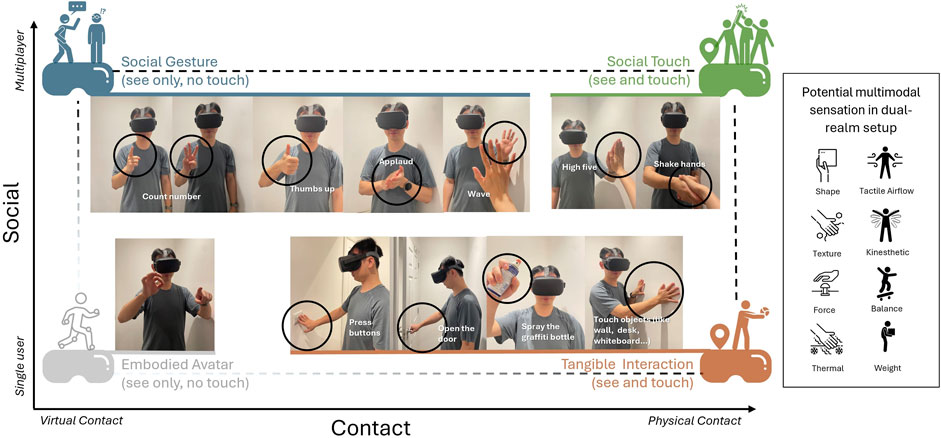
Figure 2. The Embodied cross-realm interaction Diagram. Interactions along two key dimensions: contact modality and social embodiment. Potential multimodal sensations lie beyond the current prototype and are shown as future design examples.
Based on these dimensions, our prototype implements three primary categories of embodied cross-realm interaction: tangible interaction, social gesture, and social touch. Each of these is supported through dual-realm integration, combining fully virtual visuals with physical, real-world feedback.
3.2.1.1 Tangible Interaction–Spraying the Graffiti Bottle
This interaction demonstrates direct physical engagement with a mapped real-world object. A virtual spray can is spatially aligned with a real hand sanitizer bottle placed in the environment. When users pick up and press the bottle, they receive passive tactile feedback that enhances the illusion of spraying within the virtual scene. This simple yet effective mapping reinforces the sense of physical presence and helps blur the boundary between the digital and physical realms. The spatial configuration and interaction flow are shown in Figure 2.
3.2.1.2 Social Gesture–Body Language in Drawing Game
This interaction illustrates a form of avatar-mediated, non-contact social expression. Through full-body inverse kinematics (IK) tracking, users are able to convey ideas and emotions entirely through gestures. In a collaborative drawing task, participants guess prompts using movements such as pointing, miming, or shifting posture—without speaking or touching. These embodied gestures foster intuitive communication and social engagement, as visualized in Figure 2.
3.2.1.3 Social Touch–Shaking Hands, High Fives, and Hugs
Social touch interactions extend the same tracking infrastructure by enabling simulated physical contact between users. Hand tracking allows users to perform familiar gestures like handshakes and high fives to greet one another or celebrate achievements. Full-body tracking further supports more emotionally expressive interactions, such as hugs, enhancing the sense of interpersonal presence. These socially embodied gestures are also illustrated in Figure 2, emphasizing the role of hand-based contact in enhancing social immersion.
Full-body IK tracking ensures that users can experience physical sensations associated with hugging within the virtual environment. In this application, a drawing game Figure 3 is designed, and users communicate with each other through non-verbal cues and body language to convey ideas and guess each other’s drawings. This social cross-realm interaction adds dimension to this body-tracking VR experience, where words are replaced by expressive gestures and movements.
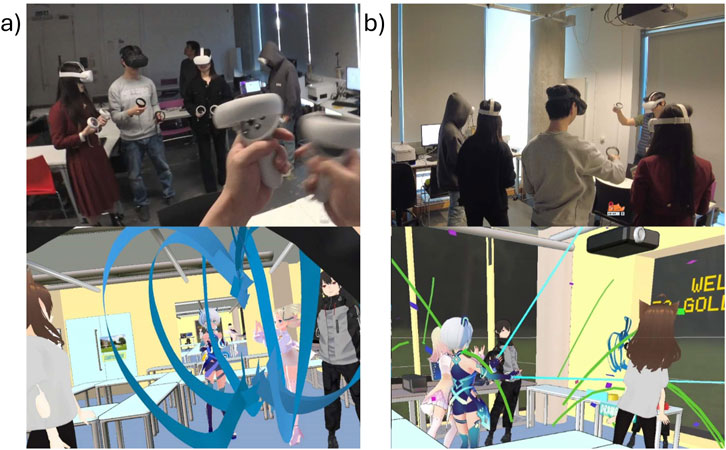
Figure 3. Multiplayer social interaction guess-and-draw game, where players use hand and body movements (such as pointing) to convey non-verbal cues. The figure illustrates cross-realm interaction through co-located multiplayer engagement, illustrated from (a) the host’s first-person view and (b) a third-person perspective. The top row shows participants in the physical environment and the bottom row shows the corresponding virtual environment.
3.2.2 Technique pipeline
As illustrated in Figure 4, the entire technical pipeline underpins this dual-realm experience, encompassing processes for environment capture and alignment, avatar generation, motion tracking, and multiplayer functionality. Specific implementation details for each stage of the pipeline are provided as followed.
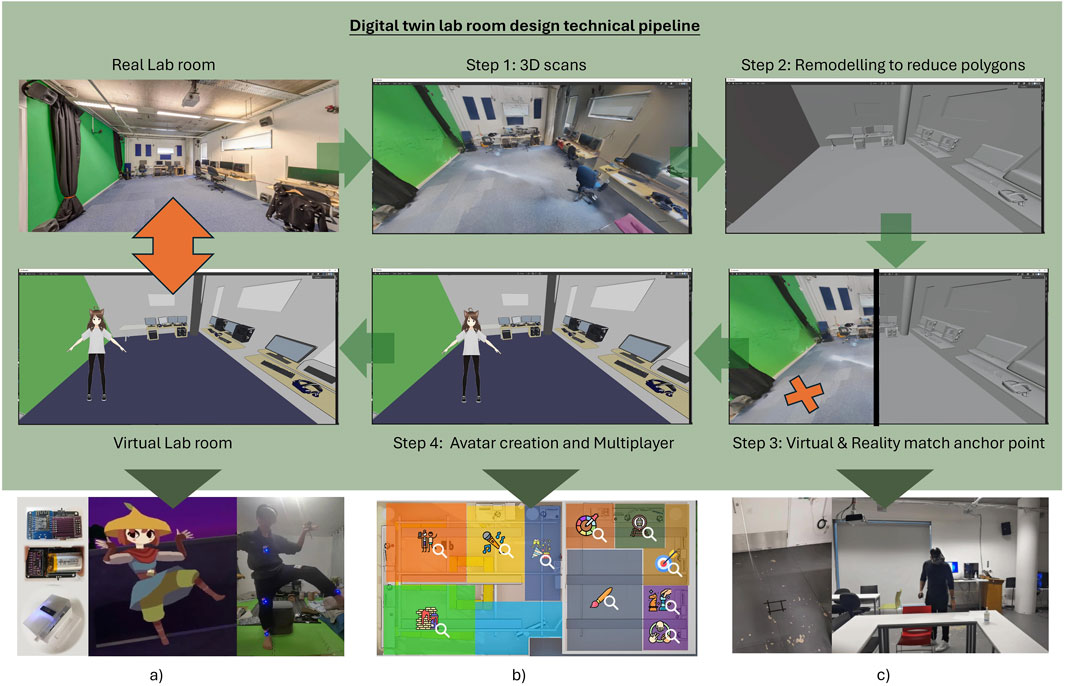
Figure 4. Technical pipeline and design overview, including reality mapping, avatar creation and advanced tracking integration. (a) Modular VR tracker full body tracking. (b) Spatial interactive design. (c) Taped anchor and alignment test.
3.2.2.1 [Step 1-3] Reality Mapping: Achieving Accurate Virtual-Physical Synchronization.
The alignment of the virtual and physical rooms is the key to this location-based VR experience. Thus, to make this function work, two main challenges need to be solved in this project: one is to ensure the physical room and objects match perfectly, and the other is to accurately move the headset’s relative location in both virtual and real spaces.
For the first challenge, three distinct LiDAR camera-based 3D scan software were tested to conduct 3D scans of the room for accuracy. To ensure the environment was compatible with VR, we faced a common issue: a large number of polygons can be problematic for VR performance, particularly since the demo uses standalone Oculus Quest 1 and 2. Therefore, we remodelled the entire environment using Blender. During the remodelling process, we used a relative scale and conducted multiple tests to ensure that the space within Blender was measured precisely. When the 3D model was imported into Unity, we carefully ensured that all the model’s scales exactly matched the real world, without modifying any scales during development. Finally, we tested it within the VR headset, taking care not to modify the dimensions or arrangement of any objects.
Once the alignment in the model space was confirmed, we also showcased in Figures 4b how we divided the physical area into virtual functional zones for the location-based experience. These zones were designed according to the physical space, determining what types of interactions were most suitable. Additionally, we defined the size of the areas and the forms of interaction based on the physical layout to ensure an optimal experience.
The second challenge was addressing the synchronization between the actual laboratory and the VR headset environment. Although the new Special Anchor function should now make this process easier, the temporary solution at that time was to maintain precise location alignment using the origin anchor point. This point, which represents the starting angle and position of the VR headset, was tested in advance by developers. We marked the point on the ground of the real-world scene with tape (see Figures 4c), ensuring that each time the experience began, we calibrated and re-centred all Quest devices on that marker. Additionally, we blocked the proximity sensor on the devices to prevent them from going into sleep mode. As a result, the VR device would enter the virtual scene at the same location and angle. This approach allowed the device to automatically calibrate the virtual world, ensuring a mapping that accurately matches reality.
3.2.2.2 [Step 4]Full-Body Self-Avatar Representation for Multiplayer Interactions.
The creation of avatars in this VR project is facilitated using VRoid Studio (pixiv Inc, 2025), a tool that allows for the customization of 3D cartoon-style humanoid avatars. Users can select face shapes, hairstyles, clothing, and more, and these avatars can be easily imported into game engines by using the UniVRM (an extension of glTF 2.0) (Consortium, 2025) to support 3D avatar file (.vrm) in Unity. Additionally, the integrated Shader Graphs MToon for URP VR (simplestargame, 2025) allows for toon shading effects when the avatars are imported into Unity. For the avatar animations, these 3D avatars are embedded with body rigging and blendshapes upon creation. The former supports body movement, while the latter enables facial animations. As shown in Figure 5, our VR application enables VR devices to track the user’s movements and apply them directly to the avatar’s body.
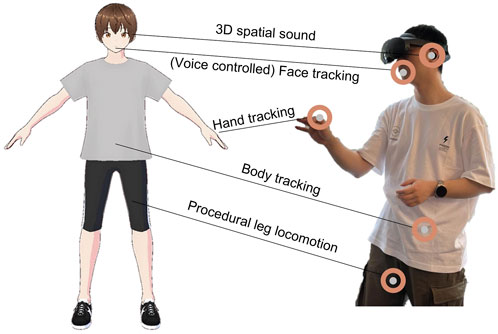
Figure 5. Human motion capture supported by the VR devices sensors, mapped to avatar models to drive model animations through tracking.
Body tracking: With the VR headset and controllers, capture the movements of the head, and hands. In terms of avatar leg movement, the project leverages Final IK, a Unity plugin that enables realistic body animation using Inverse Kinematics (IK). This allows the VR headset and controllers to track the user’s movements and apply them directly to the avatar’s body. For full-body tracking in Demo 1.0 and Demo 2.0, a 3-point tracking system is employed.
Lip movement by voice: The Oculus Lipsync SDK works with the VRM plugin, enabling lip movement through Viseme (Bear and Harvey, 2017), which is a common concept used for voice-driven lip movement. The VRM plugin also provides an eye blink function as an additional facial expression. Although the facial blendshapes for our current avatars are not fully comprehensive, there is potential for future use of more advanced avatars with facial blendshape standards, such as ARKit’s 52 facial blendshapes. In our later Quest Pro projects, we aim to implement full facial expression tracking using the VR headset to capture the entire range of facial movements.
Hand and finger tracking: We applied the latest Oculus Interaction SDK at the time, which supported hand tracking and gesture recognition for VR devices. However, during development, the SDK did not support full-body rigged avatars with hand tracking. Therefore, most projects used controllers, which tracked the hand positions, as implemented in our Demo 1.0 for hand and arm tracking using controllers.
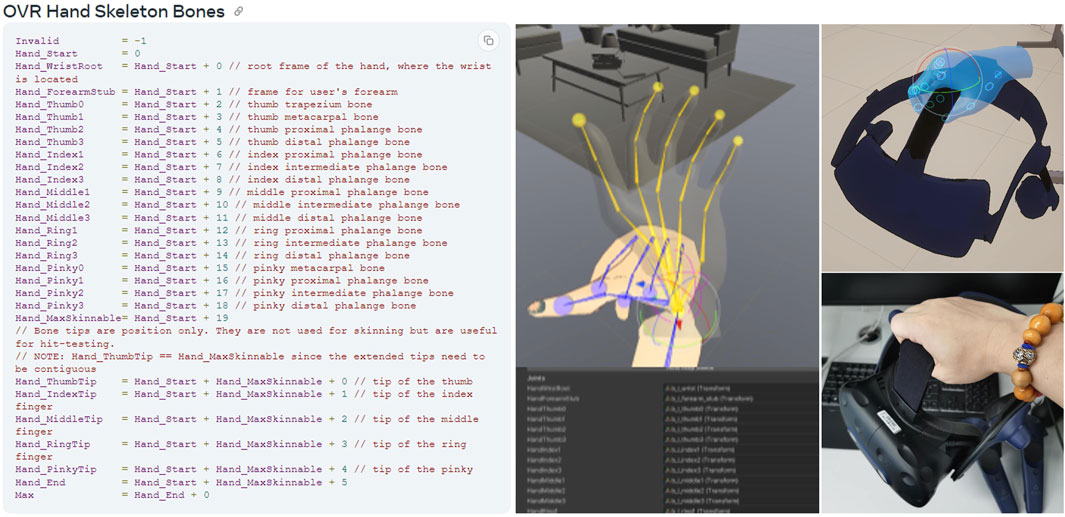
In Demo 2.0, we wrote a custom script to map the SDK’s “OVR hand skeleton,” which supports hand skeleton bones (Platforms, 2023), to the finger rigging of our created avatars. This allowed us to synchronize the full-body avatar’s finger movements. In Figure 6, where the left side shows the SDK’s skeleton bones name (such as thumb, index, ring, and pinky) in the code. The middle image demonstrates an example of the process of mapping the wrong avatar hand rigging rotations to the correct hand tracking positions. We also implemented the interaction of picking up virtual objects from different angles by recording specific poses for the interactable objects (On the right side of Figure 6). This feature also supports simultaneous interaction with virtual and physical objects, such as grabbing the spray bottle and pressing the spray button, as shown in Figure 1.
The system’s capabilities are further augmented by the incorporation of voice chat, achieved through the Normcore plugin (Normal, 2025), providing a seamless communication channel within the multiplayer environment.
After successfully implementing the single-user environment and avatar interactions, we enabled multiplayer functionality. Technically, we integrated Normcore, a powerful networking solution for developing real-time multiplayer experiences in Unity. It provides the necessary networking components to handle player synchronization, real-time communication, and data transfer between multiple users.
In our project, custom scripts built on Normcore synchronize several variables, including entering the multiplayer interaction room, object transformations such as position and scale changes, and avatar movements like lip movements and finger movements across multiple devices. Other synchronized features include virtual object ownership, ensuring that two players cannot simultaneously pick up the same object, voice chat, and controlling the visibility of virtual objects in the “guess and drawing” game.
9-Point Full-body Motion Capture and Movable Object Tracking: An issue identified in this project is that easily movable objects (e.g., chairs) can pose challenges to the sustained operation of this precisely aligned digital twin experience, as well as lead to some deficiencies (e.g., gates and cabinet doors) in cross-realm interaction. To address this problem, a Wi-Fi-based VR tracker prototype that operates independently of any lighthouse system is explored. These VR trackers can also improve the full-body avatar to 9-point tracking.
This bespoke device draws inspiration from the SlimeVR (SlimeVR Contributors, 2023) open-source initiative. A 9-axis motion sensor has been utilised to combine with Wi-Fi to transmit information. Thus, this offers a cost-effective alternative to optical tracking methods. In an extension of the foundational VR tracking capabilities, the unit has been enhanced to become a modular VR tracker with magnetic connectivity (Figures 4a). Moreover, a 9-pin magnet port has been integrated into the tracker. This port enables the possibility of incorporating additional functionalities such as supplementary batteries, triggers, buttons, rolling wheels, lights, and various sensors. There is also potential for further development, given the availability of a 9-pin magnet port, which includes two pins designated for power.
3.3 Pilot study
3.3.1 Participant
Six individuals (4 Male, 2 Female) with diverse expertise in immersive technologies participated in the interviews. The group included a professor and a lecturer specializing in virtual and augmented reality (P1, P5), three postgraduate students with backgrounds in user interface design, VR interaction, and 3D modeling (P2, P3, P4), and a PhD candidate who also works as a teaching assistant in interaction design (P6). Collectively, the participants bring experience across computing, interaction design, digital art, and virtual human research, with practical involvement in VR development and a strong familiarity with theoretical foundations in the field.
3.3.2 Expert interviews
This paper is based on an interview process that explores the usability and cross-realm interaction features in a location-based social VR environment. The interviews focused on understanding participants’ perceptions of digital twin synchronisation, passive haptic feedback, and social presence. The six participants had prior experience using the application being evaluated, which allowed them to provide informed feedback based on their previous interactions with the system.
Participants were first introduced to the VR system, which featured hand tracking, full-body avatars, and synchronised physical-virtual object interactions. After completing their interaction with the system, each participant took part in a semi-structured interview designed to capture their perceptions of several key aspects of the digital twin environment.
Given the small number of participants, thematic analysis was used to extract expert insights rather than to achieve theoretical saturation. This approach follows Braun and Clarke’s guidance that thematic analysis can be applied to small samples when the aim is to generate rich, qualitative understanding within a focused domain.
The interview questions covered the following topics.
1. Understanding of Digital Twin in VR: Participants were asked about their comprehension of the digital twin concept, specifically in the context of VR environments, referencing previous works by Jones et al. (2020) and Pires et al. (2019), as well as concepts from Enders and Hoßbach (2024).
2. Twinning Alignment: Participants evaluated the alignment between virtual and physical counterparts, with a focus on size, shape, and tactile accuracy during interactions (Hoffman, 1998; Enders and Hoßbach, 2024; Kolesnichenko et al., 2019).
3. Passive Haptic Feedback: Participants reflected on their tactile experiences when interacting with virtual objects and avatars, drawing on existing research on passive haptics (Hoffman, 1998; Jones et al., 2020).
4. Intuitiveness and Naturalness: Using the Haptic Fidelity Framework (Muender et al., 2022), participants were asked how intuitive and natural the interactions felt, especially with respect to physical-to-virtual transitions.
5. Haptics and Presence: Drawing from Witmer & Singer’s Presence Questionnaire (Witmer and Singer, 1998), participants described how well they could navigate the virtual environment using touch and how this impacted their sense of presence. This discussion extended to haptic interactions with avatars, building on findings from Gonzalez-Franco and Berger (2019).
6. Social Presence and Interaction Quality: Participants shared insights on social interactions within the VR environment, particularly how avatars conveyed non-verbal communication and affected social presence, referencing Bailenson et al. (2006) work on social presence (Bailenson et al., 2006).
7. User Experience: Based on the User Experience Questionnaire (Schrepp and Hinderks, 2017), participants evaluated the attractiveness, perspicuity, efficiency, and novelty of the passive haptics in the VR setup, commenting on how well the system captured their attention and how they perceived its overall usability.
8. Suggestions for Future Applications: Participants were also invited to share potential applications for location-based VR systems across different fields such as education, entertainment, and remote work.
3.3.3 Qualitative method
We analyzed participants responses using the thematic analysis method (Clarke and Braun, 2013), identifying key themes that reflect their experiences and perceptions of the design and functionality of our system, particularly focusing on synchronized alignment, passive haptic and presence, and social interaction. Although our sample consisted of six expert participants, prior literature suggests that in small-scale exploratory studies, thematic analysis remains appropriate, particularly when the aim is to extract expert insights rather than to reach thematic saturation or generalizability. For example, (Oyekoya et al., 2021), conducted two focus groups involving certified bullying prevention trainers—one group with eleven participants and a second with only four. Despite the smaller size of the second group, the themes and insights that emerged mirrored those of the first group, which the authors interpreted as evidence of thematic saturation. Their findings validate the use of small expert samples for collecting rich qualitative data in interactive system research, particularly in the context of early-stage VR design and evaluation.
We used NVivo 12 to assign quotes and generate initial codes from the interview transcripts. Coding was conducted inductively, then identified themes by grouping related codes into broader conceptual categories that captured shared meanings across participants’ responses. This process resulted in four themes: (1) Collision Safety and Spatial Awareness, (2) Haptic Engagement and Presence, (3) Organic Response Reflecting Believability, and (4) Social Interaction, Expression, and Interpersonal Distance. These themes are described in detail in the following section, each supported by direct quotes to illustrate participant perspectives.
3.3.4 Qualitative method
We analyzed participants’ responses using thematic analysis (Clarke and Braun, 2013), identifying key themes that reflect their experiences and perceptions of the system’s design and functionality—particularly in relation to synchronized alignment, passive haptics and presence, and social interaction.
Thematic analysis is widely used in qualitative research for identifying and interpreting patterns across data. It is also considered appropriate for small-scale exploratory studies, particularly when the goal is to extract expert insights rather than to achieve thematic saturation or broad generalizability. For example, (Oyekoya et al., 2021), conducted two focus groups involving certified bullying prevention trainers—one group with eleven participants and a second with only four. Despite the smaller size of the second group, the themes and insights that emerged mirrored those of the first group, which the authors interpreted as evidence of thematic saturation. Their findings validate the use of small expert samples for collecting rich qualitative data in interactive system research, particularly in the context of early-stage VR design and evaluation.
In our case, all six participants were researchers with expertise in immersive technologies and provided detailed, informed feedback. We used NVivo 12 to support the analysis: quotes from interview transcripts were coded inductively, focusing on participants’ reflections around spatial interaction, realism, haptic feedback, and social dynamics. Related codes were then grouped into broader conceptual categories, resulting in four themes: (1) Collision Safety and Spatial Awareness, (2) Haptic Engagement and Presence, (3) Organic Response Reflecting Believability, and (4) Social Interaction, Expression, and Interpersonal Distance. These are presented in the following section, supported by representative quotes.
4 Result
As the project was initially implemented as part of a VR module coursework, no formal research questions and user evaluation was originally planned. And with a series of software updates, it would not be possible to now set this up for a formal user study. However, our project has been showcased to visitors during lab tours and industry event days. To evaluate the user experience of the system, we conducted after-experience interviews with six participants who interacted with this VR environment in the physical lab. All of them are researchers in the area of immersive technology and was able to provide expert feedback on the system.
4.1 Theme 1 - Collision Safety and Spatial Awareness.
The codes related to “nervous walking,” “keep a safe distance,” “avoid injury or bumping into things,” and “moving confidently” are frequently mentioned during discussions about the initial adaptation phase of the VR experience. These codes reflect users’ concerns about the synchronization and precision of virtual and physical alignment in the VR environment. This theme, therefore, focuses on users’ perceptions of safety and spatial awareness and highlights users’ need to avoid potential risks and collisions in the virtual space, particularly in the context of digital twin VR environments.
We observed that most users with prior VR experience were initially cautious, especially regarding the play area boundaries setup, which typically relies on virtual rather than physical obstacles to signal spatial boundaries. This cautiousness stems from concerns about the potential mismatch between the virtual and physical spaces. One participant mentioned, “I think the expectation was low at that time just because there were not a lot of examples of that done well. So there was a bit of apprehension in using, you know in engaging with it and there was a period of time to actually trust the alignment of the system. So at first, movements are quite hesitant. And then over a period of time when you start to, you know, feel that mapping you know you recognise.” However, as users grew more familiar with the 1:1 alignment of the virtual and real environments, they noted, “It took a bit of time to trust the environment. At first, I didn’t fully believe that it was safe or 1:1 aligned. Once I confirmed that everything was where it was supposed to be, I felt more comfortable.” This growing confidence was encapsulated by another participant who shared, “Then you know your movements become a bit more confident.” Additionally, participants indicated that in the process of familiarizing themselves with the digital twin setting, trying more tactile feedback and confirming alignment also built greater trust while walking freely. As one participant noted, “I probably started by touching things with my hands, making sure it was safe.”
Overall, from a spatial perspective, users provided positive feedback regarding the safety of cross-realm interaction in this digital twin environment. For example, one participant mentioned, “So you always have to worry a little bit, but it felt much safer than other virtual environments.”
4.2 Theme 2 - Haptic Engagement and Presence.
Codes such as “haptics increase presence” and “passive haptics help immersive solidify where you were” indicate that tactile feedback is crucial for enhancing immersion and presence. This theme focuses on how this digital twin environment enhances user experience through realism and immersion by leveraging real haptics—specifically the cross-realm interactions we designed.
Participants directly linked haptics to increased immersion and presence. For instance, one participant noted, “It made the environment feel more immersive with real interactions,” while another shared, “What gives an amazing sense of presence is that you feel like you’re haptically touching the virtual objects.” Realism in the virtual environment extends beyond visual accuracy; it also encompasses tactile and spatial sensations. As one participant explained, “And in general, it helps with the immersion to, you know, to be able to have an object that you can feel, and it matches with what you’re seeing.” This realism is further enhanced by tactile experiences such as the “resistance of the wall and leaning against,” or the instinctive action of reaching out to touch the edge of a door before passing through it: “Just in case, like if you’re passing through a door, you would naturally reach out to the edge of the door to feel where that edge begins, and then use that to kind of guide you into this, the new space. So there’s a lot of kind of touch first, then engage, you know.” These tactile interactions contribute to a sense of co-presence, as one participant described: “That’s the funny thing. You are both in the room, but, like, both in the virtual, both in the virtual room.”
Furthermore, the twinning of real and virtual spaces also affected how participants perceived others in the environment. For example, one participant noted, “The twinning worked for, you know, even just positioning of how to interact with other people as well as myself. So in terms of proximity and how I control myself and how I move around people.” The passive haptic feedback during social interactions, such as body language, further enhanced the sense of others’ presence. One participant commented, “The high five one was like it reminds you of like, you know, the VR chat kind of and the, what’s that, rec room kind of social interactions. It kind of just makes you feel like the other person is really there.”
Overall, from a tactile realism perspective, the cross-realm interaction in the virtual environment significantly enhances the authenticity and engagement of interactions, while also increasing the sense of presence for both oneself and others.
4.3 Theme 3 - Organic Response Reflecting Believability
The codes indicate that users reflect on interactions and object handling in the virtual environment to align with their real-life experiences. Keywords like “affordance of expect in real life,” “intuitive pick up,” “reflect the way of life,” and “naturally explore environment” suggest that users prefer interactions that feel natural and are consistent with their everyday experiences. This aligns with the design intention behind cross-realm interaction, which emphasizes natural and intuitive interactions enhanced by passive haptics within the digital twin environment.
Users’ desire for intuitive interactions in the virtual environment reflects their need for a seamless and believable experience. As one participant mentioned, “I’d worked to make it feel more believable, more realistic, even though it was, you know, it’s an abstract thing of leaving experience, but the way it was kind of integrated into digestically in the space made it quite believable.” For instance, the code “intuitive pick up” suggests that users appreciate when virtual objects can be manipulated in a way that feels natural, similar to how they would handle objects in real life. One participant explained, “Perceived touch was quite organic because it was happening when you, when they reached out to touch you, you would actually feel a touch.” Another participant emphasized the responsiveness of interactions, adding, “I specifically really like those because they had sort of the style that would match real life, whereas if you press the button it would go down a little bit so you can see that it’s reacting to what you are doing, it’s not just a static object where you press and the shape, nothing changes but the button gets activated.”
On a more functional level, this naturalness also helps reduce the learning curve, as another participant noted: “Yeah, that part was very clear for me because the interaction that you were doing pretty much matched with how you would interact with that in real life. So it was not like something that you need to learn new from scratch. You just need to perform what you probably already know and do that in VR. So there wasn’t much of a training or a learning curve.”
Overall, from a natural interaction perspective, the cross-realm interaction alignment enhances the user experience by making the virtual environment more relatable and improving the responsiveness of objects.
4.4 Theme 4 - Social Interaction, Expression, and Interpersonal Distance
This theme addresses the experience of social interactions and expressions between people in virtual environments. Codes like “react to other’s behaviour” “strong social cue,” and “body movement help connecting with others” highlight how users perceive and establish social connections through cues and body language in the virtual setting.
One participant mentioned, “Even it didn’t affect mine, but it’s like I would notice other people rather.” This suggests that virtual social signals enhance users’ ability to notice and interact with others. Another participant elaborated, “…realizing that you had kind of like free movement and mapping with your fingers and your hands kind of brought extra bandwidth to explore different types of gestures that you can do….the cool gestures I can do. Look how I can express myself with other people, and then it’s kind of its own reward when people acknowledge that and respond to it.” Building on this awareness of others, participants often emphasized and exaggerated their expressions to engage in meaningful physical interactions, especially in the absence of passive haptics, such as when waving. One participant shared, “I think some of it was kind of play-acting. You like wave big waves and, you know, yeah, big movements.” Another participant added, referencing drawing and guessing, “Definitely, definitely. I mean, when you’re with other people and you can see how their expressions or their cues are, it even makes you more expressive…to respond to what they’re gesturing. So it definitely made you conscious of what they were trying to communicate or how they were feeling at the time, because obviously the facial expression wasn’t completely mapped, so you kind of…I am more expressive in body language.”
Interestingly, in situations involving tactile feedback, participants mentioned that closer interactions, such as shaking hands or giving high fives, created a sense of friendliness. For example, one participant observed, “I’m not sure about avoiding conflict or things like that; for me, it’s more about having a closer interaction with other people.” Reflecting on the nature of these interactions, another participant added, “I feel that the system because it allowed for more nonverbal communication, did make people unnecessarily friendlier. However, they seemed friendly because they would naturally and organically want to experiment with that, especially if it was your first time in that experience and everyone was testing things out, so everyone just appears more friendly, I suppose.”
From a social perspective, proximity was mentioned, as in “The twinning worked for, you know, even just the positioning of how to interact with other people as well as myself. So, in terms of proximity how I control myself and how I move around people.” However, cross-realm interaction had the potential to bring people closer together. For instance, one participant suggested, “I think it could be used to help people socialise, like in team-building activities for new employees.”
In conclusion, these themes, rooted in the alignment between virtual and real cross-realm interactions, passive haptics, and the social environment, offer a comprehensive and in-depth understanding of the design from the users’ perspectives, providing valuable insights and guidance for future design efforts.
5 Discussion
The user feedback presented above offers some insights into how participants experienced and interpreted embodied cross-realm interaction within a digital twin VR environment. These findings can be revisited through the lens of our design dimensions in the embodied cross-realm interaction diagram (Figure 2): tangible interaction, social gesture, and social touch.
5.1 Tangible Interaction
Theme 2 (Haptic Engagement and Presence) and Theme 3 (Organic Response Reflecting Believability) strongly support the role of tangible interaction in enhancing realism and reducing the learning curve. Participants responded positively to interactions where virtual objects offered intuitive affordances and tactile feedback. This validates the importance of aligning physical feedback with virtual affordances and suggests that tangible elements serve as effective anchors for immersion.
5.2 Social Gesture
Themes 3 and 4 revealed that gestures—particularly exaggerated or expressive ones—served as a substitute for missing facial expressions and verbal communication. These findings support the role of body gestures in social expression and interaction, especially in co-located, hybrid VR settings. The perceived “play-acting” and use of large body movements further highlight the expressive potential of avatars in such settings.
5.3 Social Touch
Theme 4 highlighted how proximity-based interactions like high fives or handshakes contributed to a sense of friendliness and co-presence. These forms of touch—although simple—played an important role in creating social bonds, even in the absence of complex haptic hardware. This underlines the emotional power of social touch in shared VR environments and supports its inclusion as a core category of cross-realm interaction.
In summary, across all themes, participants emphasized the importance of alignment between physical and virtual spaces—not only for individual confidence and safety (Theme 1), but also for social coordination. The system’s spatial fidelity appeared to reduce cognitive load and foster more natural interactions, suggesting that cross-realm alignment is not only a technical requirement but also a social enabler. These findings suggest several implications for future design. First, designers should consider embedding simple but meaningful tactile interactions to reinforce realism. Second, social gestures and touches should be supported in avatar systems to facilitate expression and connection. Finally, the alignment of virtual and physical space should be treated not only as an immersion mechanism but also as an enabler for safer and more expressive social interaction.
6 Contribution and future work
This study presents a dual-realm VR system that integrates spatially aligned digital twin environments with full-body avatars and passive haptic interaction, enabling users to engage in natural, embodied, and socially expressive multi-user interactions. By connecting virtual visuals with physical sensations, the system supports three types of cross-realm interaction: tangible object manipulation, non-verbal social gestures, and physical social touch. By enabling natural, intuitive interactions and employing natural locomotion, the system reduces motion sickness, allowing users to move comfortably and confidently within the virtual space. This seamless integration between virtual and physical elements significantly enhances user immersion and reduces the learning curve. Together, these features create a more responsive and engaging user experience in location-based VR.
Insights from expert interviews revealed that participants experienced a strong sense of spatial trust and interpersonal awareness. Full-body avatars not only improved social expressiveness but also contributed to real-world safety by helping users avoid unintended collisions. These findings highlight the importance of combining passive haptics with embodied social cues to support intuitive, co-located interaction in virtual environments.
The system also introduces lightweight, Wi-Fi-based VR trackers that provide a flexible and low-cost solution for full-body motion capture and real-world object tracking. Without requiring external lighthouse systems, these trackers enable new forms of spatial data collection, particularly for movable elements such as doors or handheld objects. This capability supports future research in interactive behaviour, environmental UX, and embodied computing.
In future development, we plan to extend the system’s tracking capabilities to include facial expressions and eye gaze, further enhancing avatar realism and expressiveness. The system offers promising applications in education, social VR, and remote collaboration, creating new opportunities for immersive experience design and human-centred research in virtual reality.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Goldsmiths, University of London. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author contributions
JZ: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Formal Analysis. FM: Formal Analysis, Writing – review & editing. YP: Software, Writing – review & editing. HD: Software, Writing – review & editing. XP: Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work received support from the Arts and Humanities Research Council (AH/T011416/1) to JZ, FM and XP. YP and XP are supported by the Economic and Social Research Council (ES/W003120/1). Views and opinions expressed are however those of the author(s) only and do not necessarily reflect those of the UKRI. UKRI cannot be held responsible for them.
Acknowledgments
We would like to extend our gratitude to Marco Gillies, MengMeng Guo, Nima Jamalian, Songkai Jia, Tara Collingwoode-Williams, and Zimu Cheng for their invaluable feedback and suggestions during the testing phase, as well as for their participation in the final in-depth interviews.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Bailenson, J. N., Yee, N., Merget, D., and Schroeder, R. (2006). The effect of behavioural realism and form realism of real-time avatar faces on verbal disclosure, nonverbal disclosure, emotion recognition, and copresence in dyadic interaction. Presence Teleoperators & Virtual Environ. 15 (4), 359–372. doi:10.1162/pres.15.4.359
Bear, H. L., and Harvey, R. (2017). Phoneme-to-viseme mappings: the good, the bad, and the ugly. Speech Commun. 95, 40–67. doi:10.1016/j.specom.2017.07.001
Bilberg, A., and Malik, A. A. (2019). Digital twin driven human–robot collaborative assembly. CIRP Ann. 68, 499–502. doi:10.1016/j.cirp.2019.04.011
Buckingham, G. (2021). Hand tracking for immersive virtual reality: opportunities and challenges. Front. Virtual Real. 2, 728461. doi:10.3389/frvir.2021.728461
Burgoon, J. K., Guerrero, L. K., and Floyd, K. (2016). Nonverbal communication. Commun. Res. 34, 678–709. doi:10.4324/9781315663425
Cherni, H., Métayer, N., and Souliman, N. (2020). Literature review of locomotion techniques in virtual reality. Int. J. Virtual Real. 20, 1–20. doi:10.20870/IJVR.2020.20.1.3183
Clarke, V., and Braun, V. (2013). Successful qualitative research: a practical guide for beginners. London: Sage.
Consortium, V. (2025). “UniVRM: VRM implementation for unity,” in Tech. rep. (GitHub). Available online at: https://github.com/vrm-c/UniVRM (Accessed April 5, 2025).
Contributors, S. V. R. (2023). “SlimeVR - full body tracking without cameras,” in Tech. rep. (GitHub). Available online at: https://github.com/SlimeVR (Accessed April 4, 2025).
de Schot, L., Nilsson, D., Lovreglio, R., Cunningham, T., and Till, S. (2023). Exploring single-line walking in immersive virtual reality. Fire Saf. J. 140, 103882. doi:10.1016/j.firesaf.2023.103882
Ekman, P., and Friesen, W. V. (1969). The repertoire of nonverbal behavior: categories, origins, usage, and coding. Semiotica 1, 49–98. doi:10.1515/semi.1969.1.1.49
Emissive and Excurio (2023). Horizon of Khufu - london. Tech. Rep., Available online at: https://horizonkheopsexperience.com/london/. (Accessed April 4, 2025).
Fuller, A., Fan, Z., Day, C., and Barlow, C. (2020). Digital twin: enabling technologies, challenges and open research. IEEE Access 8, 108952–108971. doi:10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2998358
Givens, D. B. (2005). The nonverbal dictionary of gestures, signs, and body language cues. J. Nonverbal Stud. 9, 120–137.
Gonzalez-Franco, M., and Berger, C. C. (2019). Avatar embodiment enhances haptic confidence on the out-of-body touch illusion. IEEE Trans. Haptics. 12 (3), 319–326. doi:10.1109/TOH.2019.2925038
Grieves, M., and Vickers, J. (2017a). “Digital twin: mitigating unpredictable, undesirable emergent behavior in complex systems,” in Transdisciplinary perspectives on complex systems: new findings and approaches, 85–113.
Grieves, M., and Vickers, J. (2017b). “Digital twin: mitigating unpredictable, undesirable emergent behavior in complex systems,” in Transdisciplinary perspectives on complex systems: new findings and approaches (Springer), 85–113. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-38756-7_4
Havard, V., Jeanne, B., Lacomblez, M., and Baudry, D. (2019). Digital twin and virtual reality: a co-simulation environment for design and assessment of industrial workstations. Prod. & Manuf. Res. 7, 472–489. doi:10.1080/21693277.2019.1660283
Hinckley, K., Pausch, R., Goble, J. C., and Kassell, N. F. (1994). Passive real-world interface props for neurosurgical visualization. Proc. SIGCHI Conf. Hum. factors Comput. Syst., 452–458. doi:10.1145/191666.191821
Hoffman, H. (1998). “Physically touching virtual objects using tactile augmentation enhances the realism of virtual environments,” in Proceedings. IEEE 1998 virtual reality annual international symposium (cat. No.98CB36180), 59–63. doi:10.1109/VRAIS.1998.658423
Horváth, G., and Erdős, G. (2017). Gesture control of cyber physical systems. Procedia Cirp 63, 184–188. doi:10.1016/j.procir.2017.03.312
Huisman, G. (2017). Social touch technology: a survey of haptic technology for social touch. IEEE Trans. haptics 10, 391–408. doi:10.1109/toh.2017.2650221
Insko, B. E. (2001). Passive haptics significantly enhances virtual environments. The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.
Johnson-Glenberg, M. C., Yu, C. S., Liu, F., Amador, C., Bao, Y., Yu, S., et al. (2023). Embodied mixed reality with passive haptics in stem education: randomized control study with chemistry titration. Front. Virtual Real. 4, 1047833. doi:10.3389/frvir.2023.1047833
Jones, D., Snider, C., Nassehi, A., Yon, J., and Hicks, B. (2020). Characterising the digital twin: a systematic literature review. CIRP J. Manuf. Sci. Technol. 29, 36–52. doi:10.1016/j.cirpj.2020.02.002
Kharpal, A. (2023). China’s Netflix iQIYI launches an immersive VR ride based on its own show. Tech. rep., CNBC. Available online at: https://www.cnbc.com/2023/02/20/chinas-netflix-iqiyi-launches-an-immersive-vr-ride-based-on-its-own-show.html. (Accessed April 4, 2025).
Kilteni, K., Groten, R., and Slater, M. (2012). The sense of embodiment in virtual reality. Presence Teleoperators & Virtual Environ. 21, 373–387. doi:10.1162/PRES_a_00124
Kolesnichenko, A., McVeigh-Schultz, J., and Isbister, K. (2019). “Understanding emerging design practices for avatar systems in the commercial social VR ecology,” in Proceedings of the 2019 Designing Interactive Systems Conference (pp. 241–252).
Kritzinger, W., Karner, M., Traar, G., Henjes, J., and Sihn, W. (2018). Digital twin in manufacturing: a categorical literature review and classification. Ifac-PapersOnline 51, 1016–1022. doi:10.1016/j.ifacol.2018.08.474
Kuts, V., Otto, T., Tähemaa, T., and Bondarenko, Y. (2019). Digital twin based synchronised control and simulation of the industrial robotic cell using virtual reality. J. Mach. Eng. 19, 128–145. Available online at: https://yadda.icm.edu.pl/baztech/element/bwmeta1.element.baztech-864b3bb2-f435-4a9e-af97-ab8b3470a8c8.
Liu, M., Fang, S., Dong, H., and Xu, C. (2021). Review of digital twin about concepts, technologies, and industrial applications. J. Manuf. Syst. 58, 346–361. doi:10.1016/j.jmsy.2020.06.017
Malik, A. A., Masood, T., and Bilberg, A. (2020). Virtual reality in manufacturing: immersive and collaborative artificial-reality in design of human-robot workspace. Int. J. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 33, 22–37. doi:10.1080/0951192x.2019.1690685
Mehrabian, A. (1972). Nonverbal communication. J. Nonverbal Behav. 27, 1–20. doi:10.4324/9781351308724
Microsoft (2025). Microsoft HoloLens. Tech. Rep. Available online at: https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/hololens (Accessed April 5, 2025).
Milgram, P., and Kishino, F. (1994). A taxonomy of mixed reality visual displays. IEICE Trans. Inf. Syst. 77, 1321–1329. Available online at: https://globals.ieice.org/en_transactions/information/10.1587/e77-d_12_1321/_p.
Muender, T., Bonfert, M., Reinschluessel, A. V., Malaka, R., and Döring, T. (2022). Haptic Fidelity Framework: Defining the Factors of Realistic Haptic Feedback for Virtual Reality”, in Proceedings of the 2022 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (Article No. 431, pp. 1–17). doi:10.1145/3491102.3501953
Normal (2025). “Normcore documentation,” in Tech. rep. (Normal). Available online at: https://normcore.io/documentation/ (Accessed April 5, 2025).
Oyekoya, O., Urbanski, J., Shynkar, Y., Baksh, A., and Etsaghara, M. (2021). Exploring first-person perspectives in designing a role-playing vr simulation for bullying prevention: a focus group study. Front. Virtual Real. 2, 672003. doi:10.3389/frvir.2021.672003
Peck, T. C., and Gonzalez-Franco, M. (2021). Avatar embodiment. a standardized questionnaire. Front. Virtual Real. 1. doi:10.3389/frvir.2020.575943
Pires, F., Cachada, A., Barbosa, J., Moreira, A. P., and Leitão, P. (2019). “Digital Twin in Industry 4.0: Technologies, Applications and Challenges”, in 2019 IEEE 17th International Conference on Industrial Informatics (INDIN) 721–726. doi:10.1109/INDIN41052.2019.8972134
pixiv Inc (2025). “VRoid Studio,” in Tech. rep. (pixiv Inc.). Available online at: https://vroid.com/en/studio (Accessed April 5, 2025).
Platforms, M. (2023). “Hand tracking interactions in unity — Meta developer documentation,” in Tech. rep. (Meta). Available online at: https://developers.meta.com/horizon/documentation/unity/unity-handtracking-interactions/ (Accessed April 5, 2025).
Platforms, M. (2025a). “Hand tracking design,” in Tech. rep. (Meta). Available online at: https://developers.meta.com/horizon/resources/hands-design-interactions (Accessed April 5, 2025).
Platforms, M. (2025b). “Use passthrough on Meta quest,” in Tech. rep. (Meta). Available online at: https://www.meta.com/en-gb/help/quest/articles/in-vr-experiences/oculus-features/passthrough/ (Accessed April 5, 2025).
Rettinger, M., and Rigoll, G. (2023). Touching the future of training: investigating tangible interaction in virtual reality. Front. virtual Real. 4, 1187883. doi:10.3389/frvir.2023.1187883
Schrepp, M., Hinderks, A., et al. (2017). Design and evaluation of a short version of the user experience questionnaire (ueq-s)
Segura, Á., Diez, H. V., Barandiaran, I., Arbelaiz, A., Álvarez, H., Simões, B., et al. (2020). Visual computing technologies to support the operator 4.0. Comput. & Industrial Eng. 139, 105550. doi:10.1016/j.cie.2018.11.060
Simeone, A. L., Velloso, E., and Gellersen, H. (2015). “Substitutional reality: using the physical environment to design virtual reality experiences,” in Proceedings of the 33rd annual ACM conference on human factors in computing systems, 3307–3316.
simplestargame (2025). “Shader Graphs MToon for URP VR,” in Tech. rep. (GitHub). Available online at: https://github.com/simplestargame/ShaderGraphsMToonForURPVR (Accessed April 5, 2025).
Slater, M. (2009). Place illusion and plausibility can lead to realistic behaviour in immersive virtual environments. Philosophical Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 364, 3549–3557. doi:10.1098/rstb.2009.0138
Sziebig, G., Solvang, B., Kiss, C., and Korondi, P. (2009). “Vibro-tactile feedback for vr systems,” in 2009 2nd Conference on human system interactions (IEEE), 406–410.
Tao, F., Xiao, B., Qi, Q., Cheng, J., and Ji, P. (2022). Digital twin modeling. J. Manuf. Syst. 64, 372–389. doi:10.1016/j.jmsy.2022.06.015
Van Erp, J. B., and Toet, A. (2015). Social touch in human–computer interaction. Front. digital Humanit. 2, 2. doi:10.3389/fdigh.2015.00002
Wang, P., Bai, X., Billinghurst, M., Zhang, S., Han, D., Sun, M., et al. (2020). Haptic feedback helps me? a vr-sar remote collaborative system with tangible interaction. Int. J. Human–Computer Interact. 36, 1242–1257. doi:10.1080/10447318.2020.1732140
Wilhelm, J., Petzoldt, C., Beinke, T., and Freitag, M. (2021). Review of digital twin-based interaction in smart manufacturing: enabling cyber-physical systems for human-machine interaction. Int. J. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 34, 1031–1048. doi:10.1080/0951192x.2021.1963482
Witmer, B. G., and Singer, M. J. (1998). Measuring presence in virtual environments: a presence questionnaire. Presence Teleoperators Virtual Environ. 7, 225–240. doi:10.1162/105474698565686
Zhang, Y., Pang, L., Wang, D., and Liu, S. (2022). Influences of digital twin technology on learning effect. J. Eng. Sci. & Technol. Rev. 15, 140–145. doi:10.25103/jestr.154.20
Keywords: digital twin, virtual reality, social interaction, passive haptic, hand tracking, embodiment, full-body avatar, social presence
Citation: Zhang J, Ma F, Pi Y, Du H and Pan X (2025) Digital twin embodied interactions design: Synchronized and aligned physical sensation in location-based social VR. Front. Virtual Real. 6:1499845. doi: 10.3389/frvir.2025.1499845
Received: 21 September 2024; Accepted: 29 April 2025;
Published: 21 May 2025.
Edited by:
Xiaogang Jin, Zhejiang University, ChinaReviewed by:
Oyewole Oyekoya, Hunter College (CUNY), United StatesFrancisco Silva-Díaz, Universidad Autónoma de Chile, Chile
Copyright © 2025 Zhang, Ma, Pi, Du and Pan. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ju Zhang, ai56aGFuZ0Bnb2xkLmFjLnVr
 Ju Zhang
Ju Zhang Fang Ma
Fang Ma Yuke Pi
Yuke Pi Haoyang Du
Haoyang Du Xueni Pan
Xueni Pan