- 1Department of Psychology of Developmental and Socialization Processes, Sapienza University of Rome, Rome, Italy
- 2Department of Psychology, University of studies G. d’Annunzio, Chieti Pescara, Italy
Natural environments have been widely recognized for their calming effects on individuals. However, access to such restorative environments can be limited by various circumstances. In these cases, Virtual Reality can be beneficial, as recent studies have shown that immersion in virtual natural environments has effects comparable to those of real nature. Various characteristics of natural environments can potentially influence the benefits they provide to humans. Additionally, the design of VR interventions can impact the experience and emotional response. This review aims to survey the current state of knowledge on the impact of virtual natural environments on emotion elicitation, addressing the types of interventions used in past studies, the variety of natural environments employed, and their differential impacts on emotional valence and arousal. This analysis shows how longer sessions, especially those involving interactive elements such as hand gestures, proved to be the most effective in enhancing emotional and physiological benefits. Among the various types of natural environments used, green spaces, particularly virtual forests, were the most frequently studied and showed consistent effectiveness in both reducing arousal and eliciting positive emotions. These findings can inform the development of new VR interventions designed to foster restoration and enhance positive emotional responses.
1 Introduction
1.1 The potential of nature on affective processes
Exposure to natural environments has been widely recognized for its potential to affect emotional and affective processes positively. However, in the research literature, the concept of a natural environment is multifaceted and not uniformly defined. An environment can be considered natural if it includes certain natural elements (Korpela, 2003; Kuo and Sullivan, 2001). Various types of natural environments exist, primarily distinguished as blue spaces and green spaces. Green spaces refer to natural areas such as parks, gardens, and forests in both urban and wilderness settings (van Dillen et al., 2012; Lee and Maheswaran, 2011; Maas et al., 2006). Blue spaces encompass aquatic environments, including oceans, lakes, rivers, and smaller water features like fountains and streams (Grellier et al., 2017; White et al., 2010).
However, this binary categorization of nature—into green and blue spaces—fails to capture the diversity of natural landscapes that might offer therapeutic benefits. The health advantages of many natural environments remain underexplored in the burgeoning literature on nature exposure. For example, “white space”, such as snow-covered landscapes, has been identified as potentially beneficial (Brooke and Williams, 2021; Finlay, 2018; Korpela et al., 2014; Olwig, 2005; Yli-Panula et al., 2022). Similarly, “brown space”, referring to deserts, and “red nature”, which includes volcanoes, are emerging concepts in the scholarly discussion of nature’s therapeutic effects (Nazif-Munoz et al., 2020; Olvera-Alvarez et al., 2021; Yin et al., 2022; Kotera et al., 2021).
Furthermore, various characteristics of natural environments can potentially influence the benefits they provide to humans, including dimensions, composition, location, and configuration of natural landscapes (Wheeler et al., 2015), tree canopy density (Jiang et al., 2016), and biodiversity (Cameron et al., 2020). Specific features of natural spaces might enhance the effects of certain interactions and offer diverse opportunities for physical activities, relaxation, and engagement (van Dillen et al., 2012). In this context, the concept of affordance is particularly relevant. Gibson (1979) highlighted that environments have properties that suggest their possible uses and action opportunities for people. The notion of affordance extends beyond physical actions to include opportunities for a variety of human behaviours, encompassing social, cognitive, and emotional dimensions (Brymer and Davids, 2014). In this regard, emotional affordance refers to the likelihood that a situation facilitates certain emotions (Schutte et al., 2008) along the dimensions of pleasure/displeasure and activation/relaxation (Roe and Aspinall, 2017).
Research also indicates that the effects of nature exposure vary depending on the type of human-nature interaction (Kahn Jr et al., 2018) and the characteristics of the exposure, such as the duration and frequency of visits to natural environments (Shanahan et al., 2015). Therefore, an important issue is the conceptualization of nature experience, that encompasses individuals’ perceptions and interactions with natural stimuli through various sensory modalities (Hartig et al., 2011).
Nature is widely acknowledged as a restorative environment, providing numerous benefits for human health, performance, and wellbeing. Interacting with nature offers a range of advantages: physiological, physical, affective, cognitive, and social. Physiologically, it helps stabilise heart rate and blood pressure, reduces muscle tension, and lowers cortisol levels (Hartig et al., 2014; Ulrich, 1983). Additionally, it is linked to reduced mortality from natural causes, respiratory diseases, cardiovascular diseases, and type 2 diabetes (Rojas-Rueda et al., 2019; Twohig-Bennett and Jones, 2018; Astell-Burt et al., 2014). Cognitive benefits include improved attention, executive function, and memory (Berman et al., 2008; Berto, 2014). Socially, nature reduces isolation and loneliness, and enhances perceptions of social support (Maas et al., 2009; Astell-Burt and Feng, 2021). Affectively, nature generally reduces stress, depression, anxiety, rumination, and negative emotions, while promoting positive emotions (Bratman et al., 2015; Ohly et al., 2016) and wellbeing (McMahan and Estes, 2015; Roberts et al., 2020), with long-term effects as well (e.g., Li D. et al., 2021; Vitale et al., 2022). Furthermore, research has shown how exposure to nature also has an effect on nature connectedness itself and on nature engagement (Leung et al., 2022), which in turn can have an effect on pro-environmental behaviour (Anderson and Krettenauer, 2021), and thus on social wellbeing.
Experimental studies have shown that exposure to natural environments can directly impact emotional processes by reducing negative emotions and enhancing positive ones (Berman et al., 2008; Hartig et al., 2003; 2011; van den Berg et al., 2003). Nature also benefits emotional processes indirectly by restoring attentional resources, thereby improving executive functioning and self-regulation (Berman et al., 2008; Kaplan and Berman, 2010; Berto, 2005). Hence, exposure to natural stimuli effectively influences both affective states (McMahan and Estes, 2015; Takayama et al., 2022) and emotion regulation processes (Vitale and Bonaiuto, 2024; Ríos-Rodríguez et al., 2024; Bratman et al., 2021).
Several theories explain nature’s restorative effects. From a philosophical and evolutionary standpoint, Fromm (1964) was the first to introduce the concept of Biophilia, which he described as a fundamental human inclination to seek connection with nature. This intrinsic tendency reflects an innate preference for natural or nature-associated environments over artificial or constructed settings. Fromm’s insight laid the groundwork for later theoretical developments, such as those of Wilson (1984), who extended the concept to evolutionary biology—suggesting that this affinity is not merely psychological, but rooted in adaptive survival mechanisms that favored individuals attuned to natural cues.
These initial theories have been expanded and experimentally tested and explained over the years by various authors. Ulrich (1983) proposed the Stress Reduction Theory (SRT) suggesting that humans are evolutionarily inclined to prefer natural environments, which helps reduce stress by lowering physiological arousal and negative emotions. Moreover, according to the Attention Restoration Theory (ART), by Kaplan and Kaplan (1989) nature enhances mental health by improving attention through effortless engagement with natural stimuli, offering a break from daily demands and providing captivating, non-demanding elements (Kaplan and Berman, 2010).
1.2 Virtual nature: opportunities and challenges
Although spending time in real natural environments may provide greater benefits for wellbeing compared to indirect experiences (Browning et al., 2020), a significant portion of evidence supporting nature’s therapeutic potential comes from studies using digital surrogates (McMahan and Estes, 2015). For instance, nature-based videos have shown potential in aiding recovery from physiological and psychological stress markers over the past 30 years (e.g., Meuwese et al., 2021; Ulrich et al., 1991). Even viewing static images of natural scenes can significantly increase positive emotions (Hartig et al., 1996), improve mood (van den Berg et al., 2003), restore attentional capacity (Berto, 2005), enhance executive attention (Berman et al., 2008), and reduce impulsivity (Berry et al., 2015).
The regenerative potential of digital nature representations through images, videos, and projections on various screen sizes has been extensively studied (Browning et al., 2020). However, these simulated forms of nature often fall short of fully replicating the qualities of real natural environments, potentially limiting their effectiveness (White et al., 2018). They may lack the extent and scale of natural settings, the ability to transport individuals away from their physical surroundings, offer personalised experiences, or engage multiple sensory modalities (Hedblom et al., 2019; Kjellgren and Buhrkall, 2010).
Advancements in Virtual Reality (VR) technology offer a way to overcome some of these limitations by allowing people to immerse themselves more completely in simulated natural environments. VR can be described as a computer-generated, three-dimensional simulation that allows navigation, interaction, and immersion in another environment (Briggs, 1996). This immersion is achieved by either sitting in a room with nature images projected on all visible surfaces (e.g., Annerstedt et al., 2013) or by using head-mounted displays (HMDs) that block out or reduce external sensory stimuli, enabling complete immersion in a panoramic view of an alternative environment (Furman et al., 2009; Mosso et al., 2009).
The benefits of nature contact appear to extend to these immersive digital environments provided through VR technology (Nukarinen et al., 2022; White et al., 2018). VR nature experiences have been linked to improvements in negative emotions, restorativeness, self-reported stress, anxiety, happiness, and creativity (e.g., Palanica et al., 2019; Schutte et al., 2017; Schebella et al., 2020; Yu et al., 2018; Grossi and Marocco, 2025; Marocco et al., 2025b). However, evidence is still mixed (e.g., Li H. et al., 2021), and further research is needed to evaluate the potential of using VR nature scenarios and their impact on emotional states and other relevant psychological variables.
However, it is crucial to recognize that, within the field of technological innovation, there are also constraints that impact users’ willingness to adopt new technologies (Marocco et al., 2024c). These limitations primarily arise from dimensions of User Experience that are closely linked to emotional perception, such as technical usability, user acceptance and domain suitability (Stickdorn and Schneider, 2011; Marocco et al., 2024a; b, c; d). Therefore, designing technology with a human-centered perspective (Talamo et al., 2021; Marocco and Talamo, 2022; Talamo et al., 2011) is essential for ensuring the effectiveness of this kind of VR interventions. Nevertheless, due to space constraints, this review will not primarily focus on the design perspective of VR technology or the impact of user acceptability on the emotional response. In the field of User Experience, indeed, emotions play a crucial role. The experience itself can be considered an intuitive and immediate perception of a feeling or an emotion, often preceding rational evaluation. Therefore, investigating how virtual nature elicits emotional responses is a foundational step toward understanding the overall experience of interaction with these technologies.
1.3 Aim of the present work
Hence, given the growing interest in the therapeutic potential of virtual natural environments, we decided to focus our narrative review on the role of virtual natural environments in emotion elicitation. Most of the existing literature has focused on the general emotional effects of VR, while relatively few studies and reviews have systematically examined the specific impact of virtual nature. A deeper analysis of the main reviews in the field (Somarathna et al., 2023, Liang et al., 2024; Bolouki, 2024; Spano et al., 2023; Li et al., 2023; Abdullah et al., 2021) reveals that many tend to overlook key dimensions that are essential to fully understanding the emotional impact of virtual nature. In particular, three recurring limitations can be identified: a lack of differentiation between types of natural environments (e.g., green or blue spaces); insufficient integration of explicit and implicit emotional measures; a lack of comparative analysis of different exposure modalities. In contrast to the studies discussed above and addressing these limitations, the present review provides a more differentiated perspective on the effects of virtual nature, which has been largely missing from prior reviews. Hence, this review will consolidate the current knowledge, identify gaps, and provide direction for future research, addressing the types of interventions used in past studies, the variety of natural environments utilised, and their differential impacts on emotional responses, measured both by explicit and implicit measures.
2 Methods
A state-of-the-art review was conducted to investigate the role of natural virtual environments in emotion elicitation through VR, adhering to established guidelines and criteria (e.g., Green et al., 2006; Sukhera, 2022). Narrative reviews are a form of qualitative research synthesis that describe the results of quantitative studies using diverse methodologies or theoretical frameworks, without focusing on the statistical significance of the findings (Baumeister and Leary, 1997; Siddaway, Wood and Hedges, 2019). This type of review is particularly suitable when a comprehensive understanding of the literature is desired in relation to a collection of quantitative studies that have employed various methodologies, or that have examined different theoretical conceptualizations, constructs, and relationships (Baumeister, 2013).
A narrative review method was chosen for this study due to the heterogeneous nature of the existing research on natural virtual environments and emotion elicitation. The studies in this field used a wide range of methodologies, theoretical perspectives, and constructs, making a narrative review the most appropriate approach to synthesise the findings. This type of review allows for a detailed and holistic examination of the literature, providing an integrated overview of the current state of knowledge. Additionally, narrative reviews are effective in identifying and discussing problems, weaknesses, contradictions, or controversies within a particular area of investigation (Baumeister and Leary, 1997).
In this review, we aim to survey the state of knowledge on the impact of natural virtual environments in emotion elicitation. This includes providing useful overviews and integrations of the existing literature, highlighting areas of consensus as well as points of contention. In doing so, we aim to provide valuable insights that can inform and guide future research and practice in this emerging field.
2.1 Research questions
This review aims to address several key research questions to better understand the impact of natural virtual environments on emotion elicitation, focusing specifically on two crucial components of emotions: valence and arousal. Indeed, emotions can be mapped within a two-dimensional framework encompassing emotional valence and arousal. Valence refers to the positivity or negativity of an emotion, while arousal indicates its intensity (Russell and Barrett, 1999; Lang et al., 1998; Russell, 2003).
The following questions were formulated to guide the analysis:
1. What types of interventions have been adopted by previous studies and which have been the most effective? This question seeks to identify the various methods used in past research to expose participants to natural virtual environments, including the length of exposure and the specific techniques employed, and evaluate their relative effectiveness in eliciting emotional responses.
2. What types of natural environments have been used? This inquiry aims to categorise and describe the different natural environments that have been featured in previous studies, providing a comprehensive overview of the settings used. Also, it refers to the differential effects of various types of natural environments, such as green (e.g., forests, parks), blue (e.g., oceans, rivers), white (e.g., snowy landscapes), and brown (e.g., deserts), on emotion elicitation within virtual reality contexts.
3. Which type of natural environment is most effective in eliciting emotions with positive valence? This question examines which natural environment is most successful in evoking positive emotional responses, such as happiness, contentment, or awe.
4. Which type of natural environment is most effective in reducing arousal? This query focuses on determining which specific natural environment has the greatest impact on lowering physiological arousal levels, contributing to a sense of calm and relaxation.
By addressing these research questions, the review aims to synthesize current knowledge and identify gaps in the literature, ultimately providing a foundation for future studies and practical applications in the field of virtual reality and emotion elicitation.
2.2 Searching and screening
With these questions in mind, a literature search was conducted in June 2024 to find empirical studies on the topic of interest. To ensure the inclusion of good-quality studies that have undergone peer review, the analysis focused exclusively on articles published in scientific journals, prioritising those that have been evaluated by experts in the field. The following databases were used to identify potentially relevant articles: Scopus, Google Scholar, and ScienceDirect.
For all databases, the same set of search keywords was used. About the VR-related literature, the keywords “virtual reality” and “VR” were used as search terms. For natural spaces, the keywords included “nature”, “natural environments”, and “natural scenarios”. Regarding the emotion-related literature, the adopted keywords were “emotion”, “mood”, “emotional states”, “affect”, and “affective states”. These search terms were used in combination to conduct the research across all databases, focusing on titles and abstracts, as follows: (“virtual reality” OR “VR”) AND (“nature” OR “natural environments” OR “natural scenarios”) AND (“emotion” OR “emotional states” OR “affect” OR “affective states”).
The search was limited to peer-reviewed journal articles published in English. Given the rapid evolution of VR technology over the past decade, we decided to focus only on research published in the last 10 years to exclude studies using outdated technology (LaValle, 2023). Characteristics such as sample type (e.g., clinical vs nonclinical), age, gender, and research design were not considered exclusion criteria for this review. The full list of inclusion and exclusion criteria is reported in Table 1.
2.3 Data extraction and synthesis of the evidence
After the selection of the articles, the data extraction was carried out for all the included studies, using a pre-established form. The main components of the data extraction form were: the year of publication and country of study; study design and methods; study sample; characteristics of the virtual nature environments and the intervention (duration and modality); assessment of emotions; and results.
Furthermore, a synthesis of the evidence is provided. First, a preliminary descriptive summary of the included studies is presented, detailing their characteristics in terms of year of publication, location, sample demographics, study design and methods, features of the virtual natural environments, interventions used, and methods for assessing emotions.
Then, a narrative synthesis was adopted to further synthesise the results. Based on the guidelines for discussing narrative reviews (Baumeister and Leary, 1997), which recommend section critiques rather than critiquing each individual study, the findings have been organised around the two key components of emotion elicitation: valence and arousal. Each section includes a summary of the methods and results of relevant studies, along with a brief outline of the major flaws and limitations in the evidence. This approach allows for a more cohesive and comprehensive discussion of the overall trends and insights within the literature on the potential of virtual nature in emotion elicitation.
3 Results
3.1 Study characteristics
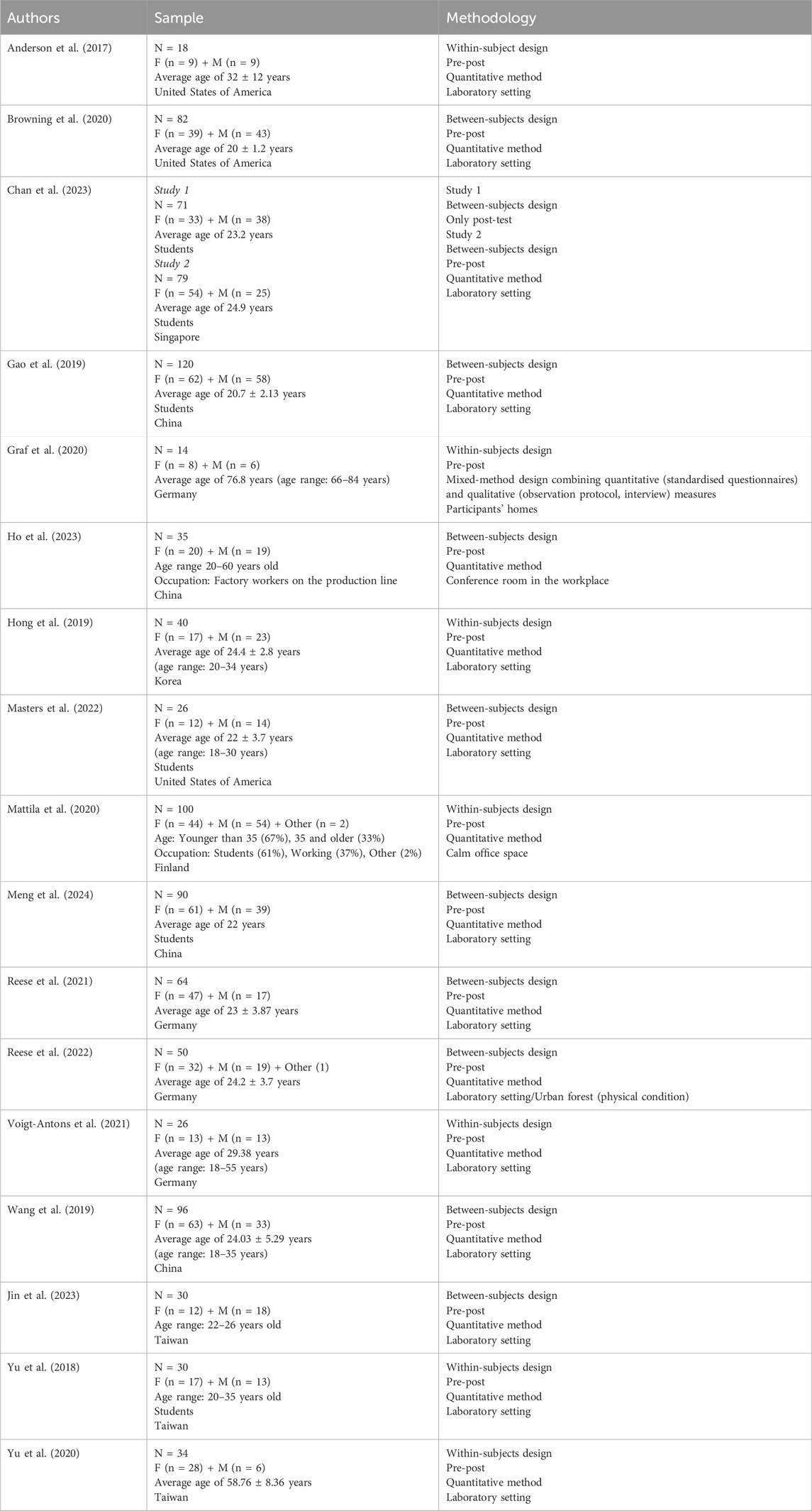
The studies obtained from the search were characterised in terms of participant description (including sample size and age range), country, and research design (refer to Table 2 for an overview).
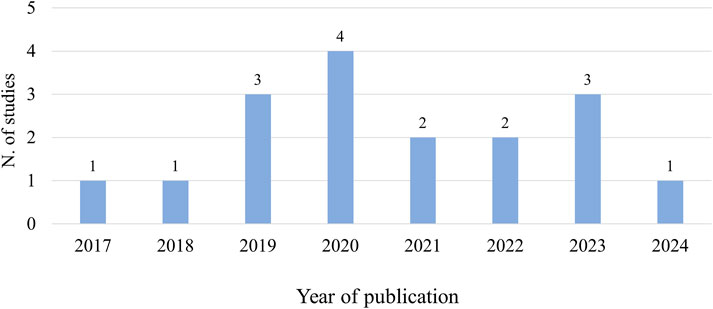
Furthermore, an overview of publication years of the reviewed studies is shown in Figure 1.
3.1.1 Location
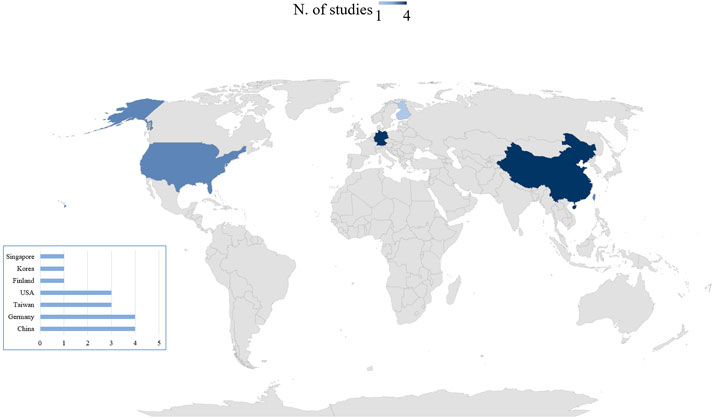
The included studies in the review were conducted in a diverse range of countries. Figure 2 displays a map illustrating the distribution of the reviewed studies across the different countries.
Specifically, there were four studies from Chinese Mainland (Gao et al., 2019; Ho et al., 2023; Meng et al., 2024; Wang et al., 2019), three from Taiwan (Jin et al., 2023; Yu et al., 2018; Yu et al., 2020), one from Singapore (Chan et al., 2023), and one from Korea (Hong et al., 2019). Additionally, four studies were conducted in Germany (Graf et al., 2020; Reese et al., 2021; Reese et al., 2022; Voigt-Antons et al., 2021), one in Finland (Mattila et al., 2020), three in the USA (Anderson et al., 2017; Browning et al., 2020; Masters et al., 2022).
This section may be divided by subheadings. It should provide a concise and precise description of the experimental results, their interpretation, as well as the experimental conclusions that can be drawn.
3.1.2 Sample characteristics
The reviewed studies included a diverse range of participant demographics. Sample sizes across the studies ranged from 14 to 120 participants. Age ranges were fairly consistent, covering mostly young and middle-aged adults, although Graf et al. (2020) specifically included older adults aged 66–84 years, with a mean age of 76.8 years.
All studies included both male and female participants, with some variations in gender distribution. Most studies utilised non-clinical samples, primarily composed of healthy participants, often university students, and excluded participants with psychiatric or chronic medical conditions that could interfere with the use of VR.
This diversity underscores the need for careful consideration of sample characteristics when interpreting the findings and implications of research on virtual natural environments and emotion elicitation.
3.1.3 Methodologies
Methodologically, the majority of the studies employed quantitative methods. Only one study, Graf et al. (2020), used a mixed-method design that combined quantitative (standardised questionnaires) and qualitative (observation protocol, interview) measures.
Regarding research design, the studies included both between-subjects (Browning et al., 2020; Chan et al., 2023; Gao et al., 2019; Ho et al., 2023; Masters et al., 2022; Meng et al., 2024; Reese et al., 2021; Reese et al., 2022; Wang et al., 2019; Jin et al., 2023) and within-subjects designs (Anderson et al., 2017; Graf et al., 2020; Hong et al., 2019; Mattila et al., 2020; Voigt-Antons et al., 2021; Yu et al., 2018; Yu et al., 2020).
Most studies used a pre-post test design to measure the impact of virtual natural environments on emotion elicitation. Only Chan et al. (2023) included a study (Study 1) with an only post-test design.
In terms of the setting, the majority of the studies were conducted in laboratory settings, with exceptions such as Ho et al. (2023), who used a conference room at participants’ workplaces, and Graf et al. (2020), who conducted their study in participants’ homes.
3.2 Virtual natural environments
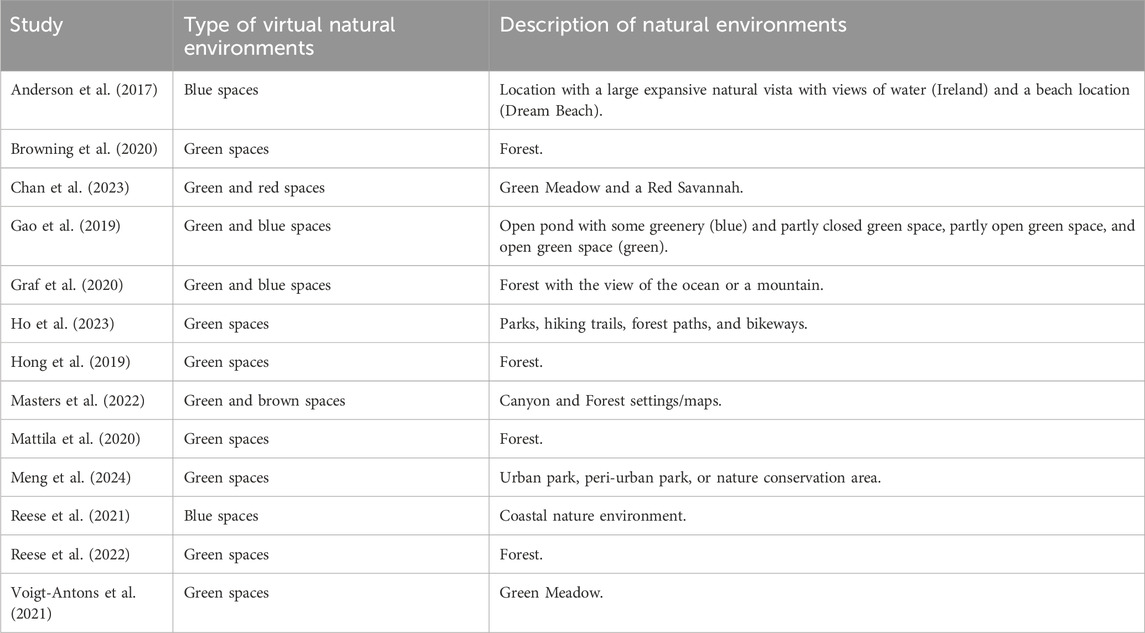
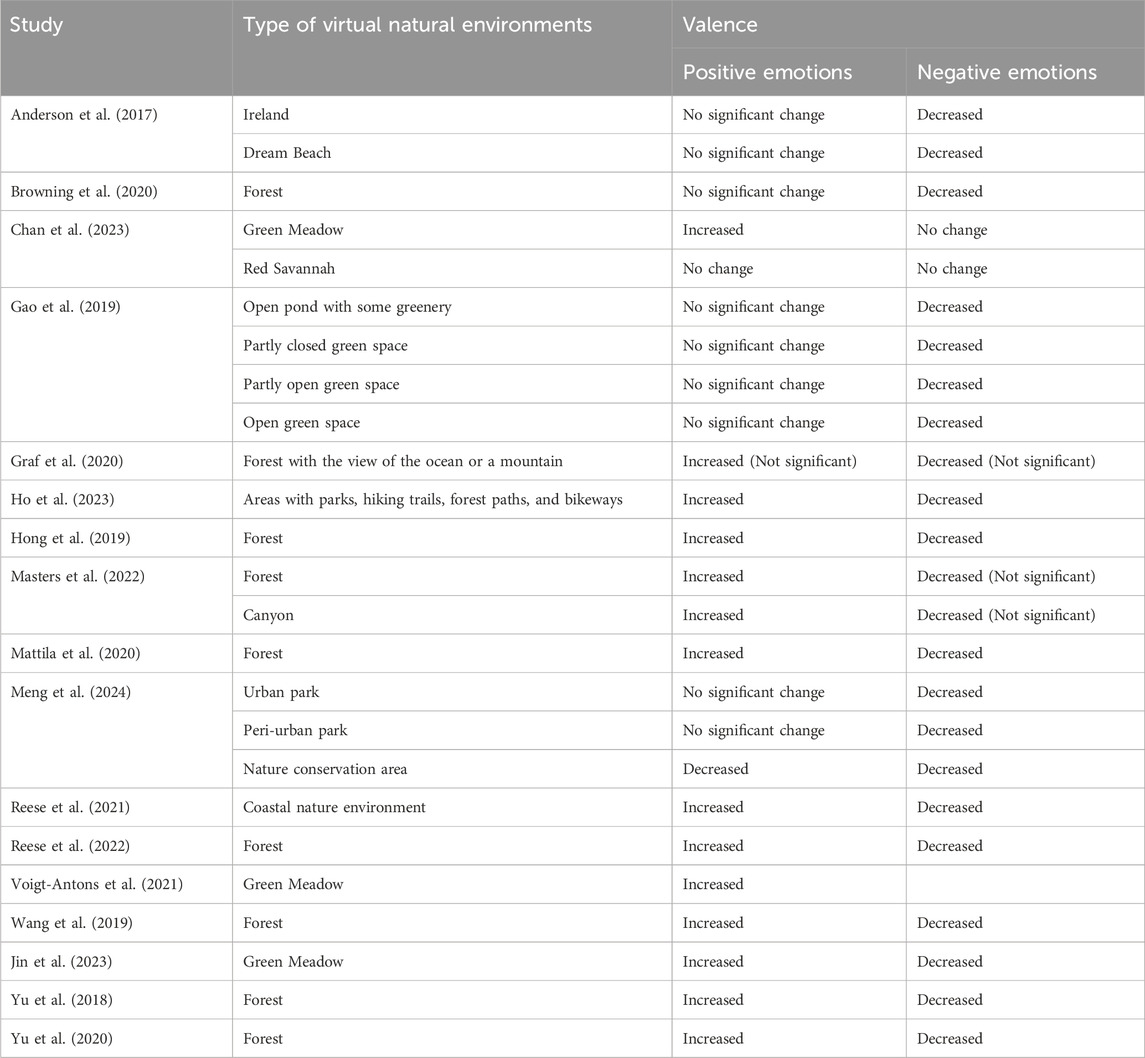
From the analysis of the literature, it emerged that most studies exploring the effect of virtual natural scenarios on emotions used green spaces (i.e., forests, meadows, parks), compared to other types of environments such as blue spaces (i.e., beaches, sea, waterfalls) or brown (i.e., deserts) and red environments (i.e., savannahs and canyons).
More specifically, a significant number of studies used forest environments (i.e., nine). Browning et al. (2020) used an outdoor forest setting, while Hong et al. (2019) recorded video at Minjuji Mountain using a 360-degree camera. Mattila et al. (2020) and Reese et al. (2022) focused on a general forest environment. Wang et al. (2019) examined seven different types of forest resting environments. Yu et al. (2018) used the natural forest of The Aowanda National Forest Recreation Area, and Yu et al. (2020) showed the Neidong National Forest Recreation Area in Taiwan. Some other studies focused on different kinds of environments or mixed environments. Specifically, Gao et al. (2019) examined both blue spaces, such as an open pond with some greenery, and green spaces with various levels of canopy cover, and Yu et al. (2018) used a waterfall environment in The Aowanda National Forest Recreation Area.
Meadow environments were used in three studies (Chan et al., 2023; Voigt-Antons et al., 2021; Jin et al., 2023), providing open, grassy landscapes with natural elements. Parks, particularly urban and peri-urban parks, were featured in two studies. Ho et al. (2023) used nature-based VR videos showing different areas such as parks, hiking trails, forest paths, and bikeways. Meng et al. (2024) focused on urban parks, peri-urban parks, and nature conservation areas.
Among the blue spaces, coastal environments were featured in two studies. Anderson et al. (2017) used locations over Ireland with large expansive natural vistas with views of water and beach locations on the Australian coast, while Reese et al. (2021) investigated a general coastal nature environment. Table 3 provides a description of all the included studies, categorized by the different types of virtual natural environments used in the research.
3.3 Interventions
The virtual environment interventions explored were designed with varying exposure durations and modalities.
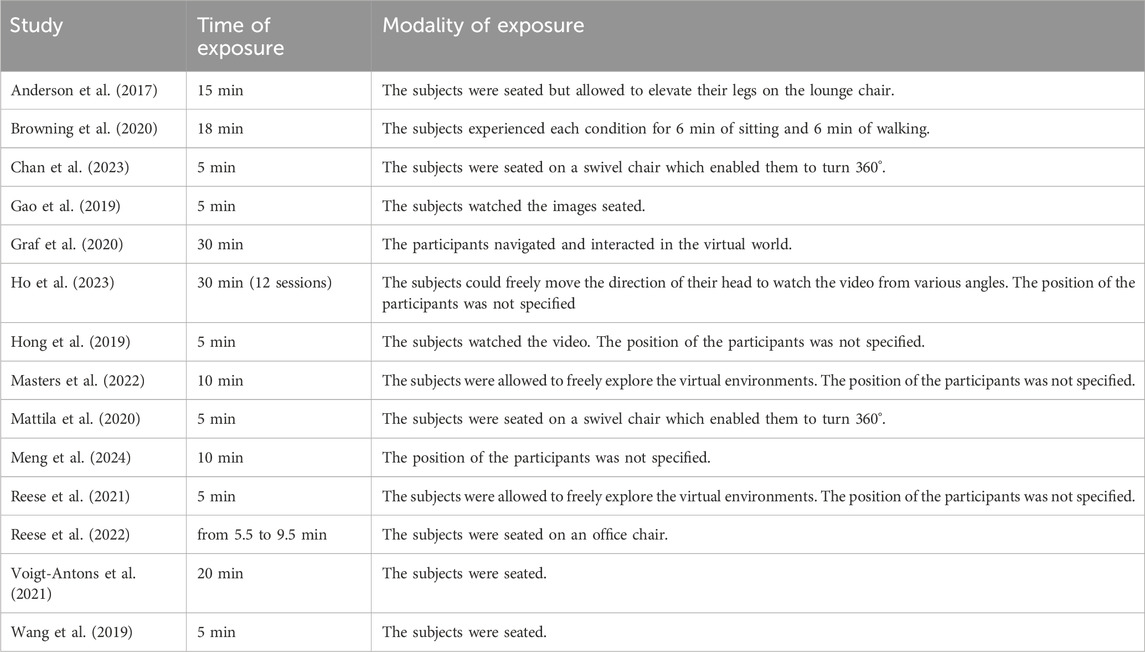
The durations can be broadly categorised into short (5–10 min), moderate (15–20 min), and long exposures (30 min). This categorization aims to synthesize and standardize the comparison of studies that employed heterogeneous exposure times. Although these intervals are not universally standardized, they were defined based on the most frequently recurring exposure durations found across the included studies.
The modalities of exposure in virtual natural environments included seated viewing, walking activities, or free exploration, with various levels of interaction.
For short exposure sessions, typically lasting between 5 and 10 min, participants were usually seated. In the studies by Gao et al. (2019), Hong et al. (2019), Wang et al. (2019), and Reese et al. (2021) participants were seated while they watched images/videos or navigated through the virtual scenery for 5 min. Chan et al. (2023) and Mattila et al. (2020) used a swivel chair, allowing participants to turn 360° while remaining seated for 5 min. In the study by Jin et al. (2023), participants interacted within the natural virtual scene for 5 min under varying conditions (no interaction, interaction with a handle, interaction with gestures). Reese et al. (2022) conducted a study where participants were asked to remain seated on an office chair for a duration ranging from 5.5 to 9.5 min. During this time, they had the freedom to move their body, arms, and head at their discretion. Meng et al. (2024) provided a 10-min VR immersion while seated. In the studies by Yu et al. (2018), (2020), participants watched videos in any comfortable seated position for 10 min. Masters et al. (2022) allowed participants to roam within the VR scenes or explore the virtual environment for 10 min each, respectively.
Moderate exposure studies, ranging from 15 to 20 min, often involved seated participants. Anderson et al. (2017) had participants seated for 15 min, with some in a supine position on a lounge chair for specific scenes. Voigt-Antons et al. (2021) involved participants in playing games while seated for 20 min. Browning et al. (2020) combined seated and walking experiences, alternating between 6 min of sitting and 6 min of walking, totalling 18 min, instructing participants to relax and enjoy the setting during the sitting component.
Long exposure sessions lasted around 30 min. Graf et al. (2020) enabled participants to explore the “VR Forest Walk” for 30 min, guiding them on how to navigate and interact in the virtual world. Ho et al. (2023) allowed participants to watch VR videos in a 360-degree format for 30 min (once a week for 12 weeks), encouraging them to move their heads freely to view from various angles.
An overview of the interventions’ characteristics, focusing on the duration and the modality of exposure to VR, is shown in Table 4.
3.4 Type of assessment
For the evaluation of the emotional experience, explicit or implicit measures are used. Explicit measures rely on the conscious and intentional assessment of participants. In this type of measurement, subjects are presented with direct questions or asked for subjective evaluations regarding a specific topic. On the other hand, implicit measures aim to assess individuals’ automatic and unconscious reactions. This type of measurement relies on indirect indicators of responses, such as reaction times or physiological measurements. In the included studies, it emerges that both implicit and explicit measurements were used, sometimes in combination. Specifically, implicit measures were used to assess arousal, while self-reports questionnaires were mostly adopted to obtain information about the valence of the emotional states.
3.4.1 Explicit measurements
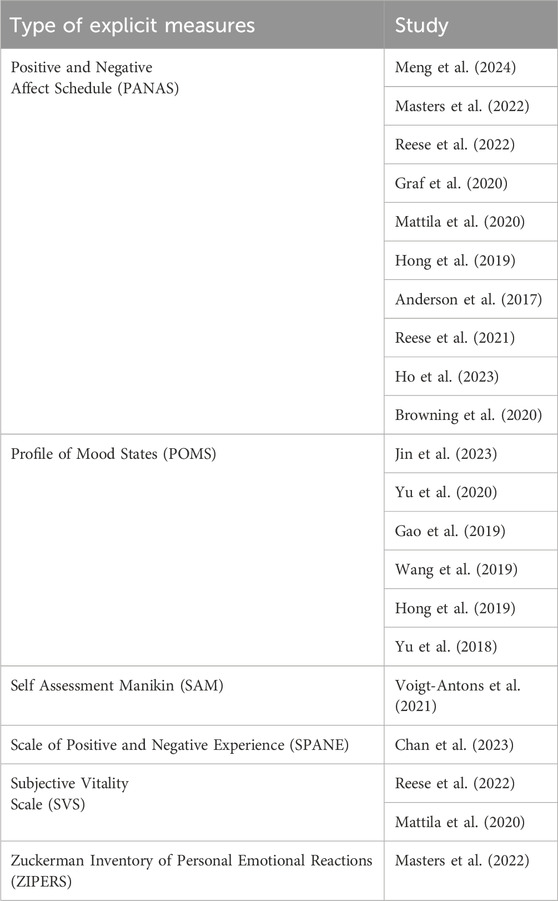
Among the explicit measures, the Positive and Negative Affect Schedule (PANAS; Watson, et al., 1988) is the most commonly used in the explored literature. The PANAS, in its original version, consists of 20 items, divided equally into two dimensions: positive affect (e.g., enthusiastic, interested, inspired, active) and negative affect (e.g., upset, scared, nervous, irritable). Seven studies, including those by Meng et al. (2024), Masters et al. (2022), Reese et al. (2022), Graf et al. (2020), Mattila et al. (2020), Hong et al. (2019), and Anderson et al. (2017), employed the PANAS in its original version to effectively assess positive and negative emotional states.
Four studies including Yu et al. (2020), Gao et al. (2019), Wang et al. (2019), and Yu et al. (2018) used another self-report tool to assess multiple mood dimensions, which is the Profile of Mood States (POMS; McNair et al., 1971). Jin et al. (2023) and Yu et al. (2020) employed the POMS Scale to assess six distinct mood dimensions, namely, Tension or Anxiety, Anger or Hostility, Vigor or Activity, Fatigue or Inertia, Depression or Dejection, and Confusion or Bewilderment. This tool not only captured the emotional experiences categorising them in two dimensions (positive and negative mood) but also allowed for the calculation of Total Mood Disturbance (TMD). In their analysis, TMD was derived by subtracting the Vigor scores from the cumulative scores of the negative mood dimensions, providing a measure of overall mood disturbance. Gao et al. (2019) and Yu et al. (2018) assessed seven mood states, including Esteem, as well as the traditional POMS dimensions. Gao et al. (2019) used the 40-item POMS Short Form (POMS-SF), while Yu et al. (2018) a Mandarin-translated questionnaire. Lastly, Wang et al. (2019) used the Brief POMS (BPOMS), a shorter version of the original POMS with 30 items. This version simplifies the assessment by focusing on five core dimensions: Tension, Anxiety, Fatigue, Vigor, and Confusion–Depression.
The study of Voigt-Antons et al. (2021) used the Self-Assessment Manikin (SAM; Bradley and Lang, 1994), a non-verbal, pictorial measurement scale, to assess the emotional states, specifically focusing on two dimensions: valence and arousal. They used SAM with a nine-point scale to measure valence and arousal, providing a quantitative assessment of the emotional responses.
Chan et al. (2023), used the Scale of Positive and Negative Experience (SPANE, Diener et al., 2010), which includes twelve items divided into two dimensions: positive affect and negative affect. Participants rated the extent to which they experienced each emotion on a scale from 1 (not much or not at all) to 5 (very much), providing a measure of their overall emotional state.
Mattila et al. (2020) and Reese et al. (2022) used the Subjective Vitality Scale (SVS; Ryan and Frederick, 1997), which refers to the state of feeling alive and alert–to having energy available to the self. Ultimately, Masters et al. (2022) used the Zuckerman Inventory of Personal Emotional Reactions (ZIPERS; Zuckerman, 1977) to investigate feelings evoked in specific environments. An overview of all the explicit measurements is presented in Table 5.
3.4.2 Implicit measurements
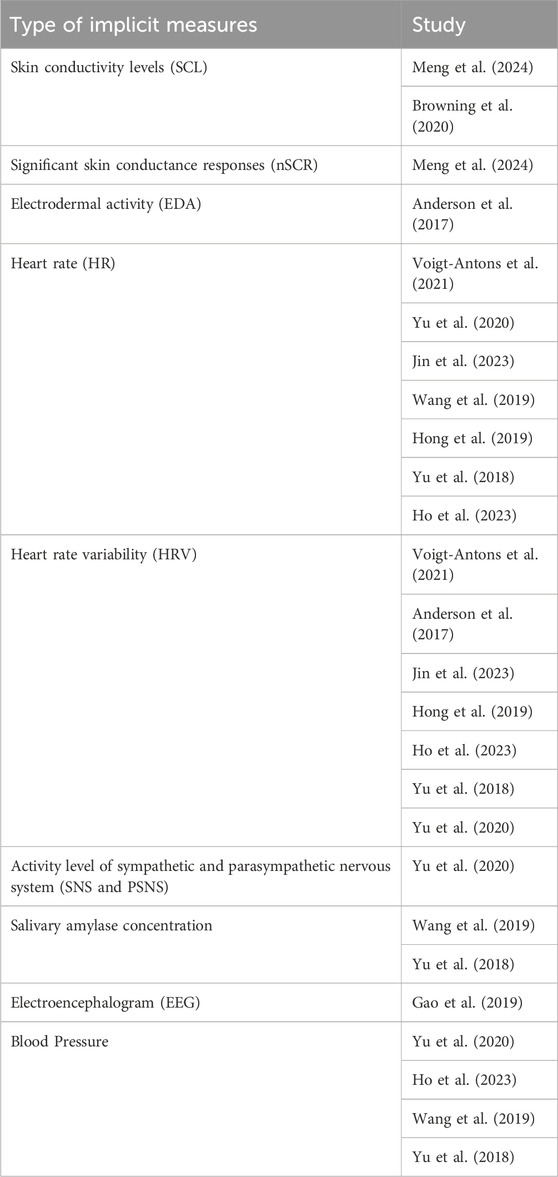
On the other hand, some of the included studies used a range of physiological measures, as implicit measures, to assess participants’ emotional and physiological responses to virtual natural environments. One common measure is the Skin Conductivity Levels (SCL), which was used by Meng et al. (2024) and Browning et al. (2020). This measure evaluates the skin’s electrical conductance, which varies with moisture levels and provides an indication of emotional arousal. Additionally, Non-Specific Skin Conductance Responses (nSCR), which measure distinct changes in skin conductance associated with emotional reactions, were used by Meng et al. (2024).
Electrodermal activity (EDA), another related measure, was employed by Anderson et al. (2017) to assess overall changes in the skin’s electrical conductance, reflecting sweating and emotional arousal. Contrary, Heart rate (HR) monitoring was a widely used measure across several reviewed studies, including those by Voigt-Antons et al. (2021), Yu et al. (2020), Jin et al. (2023), Wang et al. (2019), Hong et al. (2019), Yu et al. (2018), and Ho et al. (2023). This measure provides data on the number of heartbeats per minute, which can indicate levels of stress and relaxation.
Closely related is Heart Rate Variability (HRV), which measures the variation in time intervals between heartbeats. HRV provides a unique and non-invasive assessment of autonomic nervous system control over cardiovascular dynamics, which change during different affective states, thereby offering valuable insights into physiological arousal. This measure was used by Voigt-Antons et al. (2021), Anderson et al. (2017), Jin et al. (2023), Hong et al. (2019), and both studies by Yu et al. (2018), (2020).
Yu et al. (2020) also investigated the activity levels of the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems (SNS and PNS) to further understand stress and relaxation responses. Activation of the SNS redirects the body’s resources from processes like digestion and resting to organs involved in physical activity, such as the heart and pupils. In contrast, the PNS is activated during restful states, such as after eating or while relaxing.
Salivary amylase concentration, an indicator of stress response, was measured by Wang et al. (2019) and Yu et al. (2018). This measure evaluates the level of the amylase enzyme in saliva, which indicates stress-reactive bodily changes. Instead, the electroencephalogram (EEG) was used by Gao et al. (2019) to record electrical activity in the brain. Indeed, EEG can be used to detect many activities in the brain, such as stress.
Lastly, blood pressure was another measure used to detect stress. Studies by Yu et al. (2020), Ho et al. (2023), Wang et al. (2019), and Yu et al. (2018) incorporated this measure, which evaluates stress levels by monitoring hypertension. In fact, stress can elevate blood pressure and stimulate the nervous system to produce large amounts of vasoconstricting hormones, leading to increased blood pressure.
These indicators are commonly used in psychophysiological research to infer levels of emotional arousal. Although such measures are often associated with stress responses, it is important to clarify their interpretation in the context of this review. Specifically, while stress is typically connoted as a negative emotional state, physiological arousal refers more broadly to the intensity of an emotional reaction, regardless of its valence (i.e., whether positive or negative). In this review, we include these physiological measures not as direct indicators of stress, but as widely recognized tools for capturing the strength of emotional responses. To fully understand the psychological meaning of these responses, however, it is essential to interpret physiological data in conjunction with explicit self-report measures, which can provide insight into the valence and subjective evaluation of the emotional experience (Marocco et al., 2025a).
An overview of all the explicit measurements is presented in Table 6.
3.5 Summary of the evidence
This section summarizes the key findings from the reviewed studies regarding the impact of virtual nature interventions on emotional experiences, highlighting the major trends and insights. We will first examine the evidence related to the valence component of emotion elicitation, followed by an analysis of the arousal component.
3.5.1 Valence
Almost all the studies reviewed in this paper examined the effects of virtual natural environments on emotional valence. Specifically, Anderson et al. (2017) found that exposure to natural blue environments, including locations with large expansive vistas with water and beach locations, effectively reduced negative affect but did not significantly alter positive affect. This suggests that the soothing visual elements of water and beach scenes, combined with the comfortable setting, were able to reduce negative mood. Similarly, Browning et al. (2020) observed that while outdoor natural environments significantly increased positive affect, the VR nature condition (forest) did not show a statistically significant improvement in positive affect. However, all conditions, including the indoor control and VR nature, effectively reduced negative affect. The study involved participants sitting and walking in a VR forest setting, with instructions to relax and enjoy the environment. Gao et al. (2019) found that various blue and green natural environments significantly reduced negative mood without affecting positive mood, with partly open green space being the most effective. Also, Meng et al. (2024) noted no significant changes in positive affect after VR immersions in urban and peri-urban park scenarios, though unexpectedly the nature conservation area scenario resulted in a significant decrease in positive affect. However, all scenarios effectively reduced negative emotions.
Chan et al. (2023) reported that virtual green meadows significantly increased positive affect, whereas red savannah and museum conditions did not significantly change either positive or negative affect. This indicates that the green natural environment had a greater impact on positive emotions compared to the red one. Additionally, Graf et al. (2020) noted an increase in positive mood and a slight decrease in negative mood, though neither change was statistically significant. The study had participants interact in a virtual forest with an ocean or mountain view for 30 min.
Ho et al. (2023) showed that exposure to virtual natural environments, such as green areas of parks, hiking trails, forest paths, and bikeways, significantly increased positive affect and decreased negative emotions. In the study of Hong et al. (2019), the exposure to a virtual forest reported significant improvements in various dimensions of mood, including increased vigor and decreased tension-anxiety, depression-dejection, and anger-hostility. Similarly, Mattila et al. (2020) demonstrated significant improvements in positive emotional states after exposure to a forest in VR, where participants could rotate freely while seated. Additionally, Yu et al. (2018) and Yu et al. (2020) reported that virtual forest environments significantly reduced negative emotional states such as confusion, fatigue, anger-hostility, tension, and depression while increasing positive feelings and vigor. The first study involved younger adults, while the second focused on middle-aged and older adults, thus generalizing the effect across both age groups. Reese et al. (2021) and Reese et al. (2022) both found significant increases in positive affect and decreases in negative affect following VR immersions in coastal nature and forest environments, respectively. Voigt-Antons et al. (2021) reported that a VR nature experience significantly improved the valence of the emotions after a VR horror game. Wang et al. (2019) found that virtual forest environments effectively reduced mood disturbances, including anxiety and confusion, while increasing vigor. Finally, Masters et al. (2022) found no significant changes in either positive or negative affect, though there were trends in the data indicating a decrease in negative emotions and an increase in positive affect.
Table 7 provides an overview of the evidence regarding emotional responses in terms of valence.
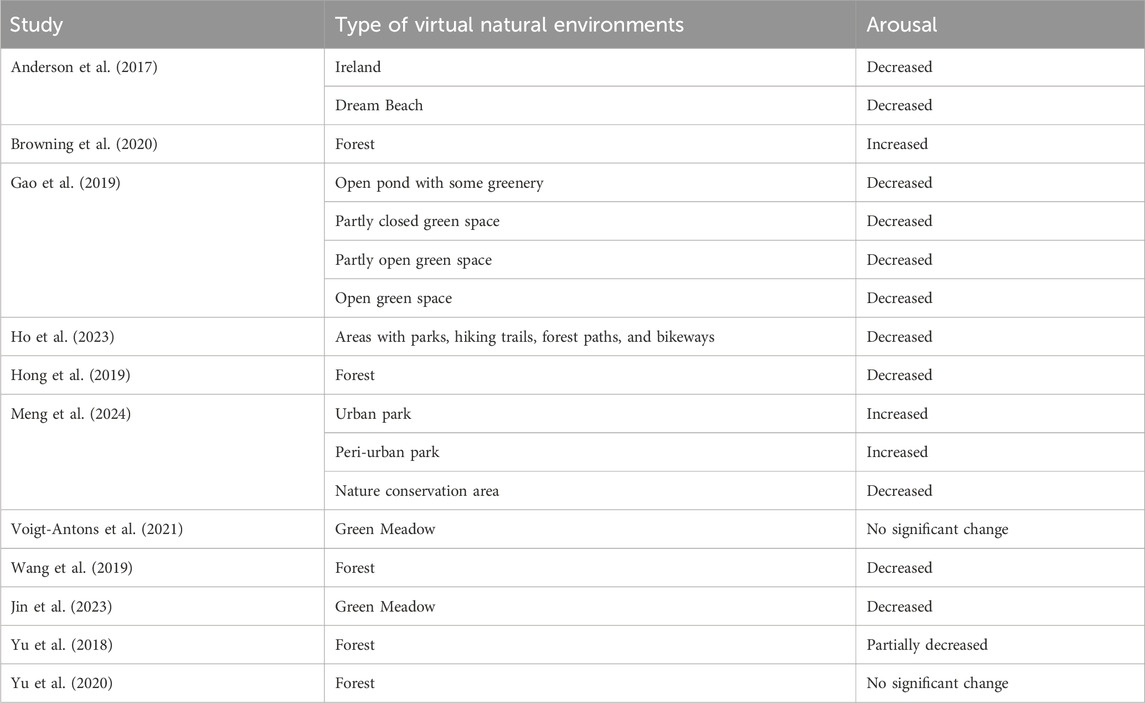
3.5.2 Arousal
The impact of virtual natural environments on arousal was also examined across a significant number of studies, where high arousal is also referred to as physiological stress and low arousal is also defined as relaxation or restoration. Anderson et al. (2017) found that exposure to blue natural scenarios resulted in a marked decrease in EDA compared to an indoor control scene, indicating a deeper and more sustained relaxation effect. Gao et al. (2019) found that various natural environments, including an open pond with greenery, partly closed green space, partly open green space, and open green space, all significantly decreased arousal as measured by EEG readings, indicating a calming effect across different natural blue and green settings. Ho et al. (2023) reported improvements in indicators of HRV compared to the control group (with no intervention), including standard deviations of all normal-to-normal intervals, low-frequency power, and high-frequency power, suggesting the power of VR nature in reducing physiological stress. Hong et al. (2019) found that a VR forest video significantly lowered the stress index and increased HRV, suggesting enhanced physiological resilience and reduced stress. Wang et al. (2019) found that virtual forest environments were more effective in reducing physiological stress indicators, such as blood pressure and salivary amylase levels, compared to forest environments with a higher level of artificiality. Jin et al. (2023) found that interaction with hand gestures in VR significantly reduced tension and anxiety compared to no interaction or interaction with handles, suggesting that a higher immersion produces the best effect on stress relief.
The study by Meng et al. (2024) revealed that immersion in the peri-urban park and nature conservation area was associated with a significantly faster and more consistent decrease in SCL compared to the urban park. Moreover, nSCR in the nature conservation area remained significantly lower than in the urban park. This result demonstrates how higher biodiversity levels are linked to faster and more substantial stress recovery.
Yu et al. (2018) found that participants’ systolic blood pressure and HR decreased over time, regardless of the type of environment (forest and urban). This suggests that the decrease in blood pressure and heart rate was not specifically influenced by the type of environment. In the same way, Yu et al. (2020), reproposing a similar study with older adults, observed no significant physiological differences between virtual natural and urban environments. The short duration of VR immersion (10 min) was considered a potential factor for the lack of significant physiological responses.
On the other hand, Browning et al. (2020) observed that both the nature conditions, whether outdoors or via VR, were associated with increased SCL, indicating higher physiological arousal. However, it should be noted that this increase in physiological arousal was accompanied by enhanced positive affect. This suggests that the heightened arousal was more associated with a state of excitement rather than relaxation, yet still having a positive impact on the emotional states.
Lastly, Voigt-Antons et al. (2021) reported no significant change in HRV after exposure to a virtual green meadow, arguing that the five-minute time span, participants spent in each condition, was too short for showing clearer results concerning arousal values and HR measures.
Table 8 provides an overview of the evidence regarding emotional responses in terms of arousal.
4 Discussion
Our narrative review examined 17 international studies conducted over the past 10 years to explore the impact of natural virtual environments on emotion elicitation. The main findings are outlined below, addressing our specific research questions.
4.1 What types of interventions have been adopted by previous studies and which have been the most effective?
The studies reviewed employed various methods to expose participants to virtual natural environments, with differences in the length of exposure and specific techniques used. The duration of exposure ranged from short sessions of 5 minutes (Chan et al., 2023; Gao et al., 2019; Hong et al., 2019; Mattila et al., 2020) to longer sessions of 30 min (Graf et al., 2020; Ho et al., 2023). The modalities included seated viewing with or without the possibility to move freely (Ho et al., 2023; Yu et al., 2018; Yu et al., 2020), walking in place (Browning et al., 2020), and interacting with the environment in different ways (Jin et al., 2023). The most effective interventions were those that combined longer durations with higher levels of interaction, allowing participants, through hand gestures, to immerse themselves deeply in the virtual natural environments. This comprehensive engagement appears crucial for maximizing the emotional and physiological benefits of VR nature experiences.
4.2 What types of natural environments have been used?
The studies included in the present review employed a broad spectrum of virtual natural environments, categorized into green, blue, red, and brown environments. Green spaces were the most frequently utilized, with a strong focus on virtual forests (Browning et al., 2020; Hong et al., 2019; Mattila et al., 2020; Reese et al., 2022; Yu et al., 2018; Yu et al., 2020). Parks, hiking trails, forest paths, and bikeways were examined by Ho et al. (2023), green meadows were investigated by Chan et al. (2023) and Jin et al. (2023), and urban parks, peri-urban parks, and nature conservation areas were included by Meng et al. (2024).
Blue spaces were represented in two studies: expansive vistas of water and beach locations were featured by Anderson et al. (2017), while coastal nature environments were explored by Reese et al. (2021). Moreover, some studies included different kinds of environments or mixed environments: open ponds and greenery, combining elements of blue and green spaces, were included by Gao et al. (2019), while mixed environments featuring forests with views of oceans or mountains were utilized by Graf et al. (2020).
Red and brown environments were less common, with two studies focusing on these settings: a red savannah was examined by Chan et al. (2023), and canyons along with forest environments were studied by Masters et al. (2022). No studies considering white environments were included in the review due to our specified inclusion criteria.
4.3 Which type of natural environment is most effective in eliciting emotions with positive valence?
This review reveals that virtual green meadows and forest environments are the most effective in eliciting positive emotions. Specifically, green meadows consistently demonstrated an ability to enhance positive affect across multiple studies (Chan et al., 2023; Voigt-Antons et al., 2021; Jin et al., 2023). This trend indicates that green meadows are particularly effective in generating positive emotional responses in virtual environments.
Similarly, virtual forests also showed a strong capacity to elicit positive emotions. Indeed, studies by Browning et al. (2020), Hong et al. (2019), Mattila et al. (2020), Masters et al. (2022), Reese et al. (2022), Wang et al. (2019), Yu et al. (2018), and Yu et al. (2020) found that forest environments increased positive emotions, although in some cases, these increases were not statistically significant. Despite the variability in significance, the consistent trend across multiple studies underscores the effectiveness of virtual forests in enhancing positive emotional experiences.
In contrast, other types of environments such as blue spaces (e.g., beaches, coastal environments) and red or brown environments (e.g., red savannahs, canyons) showed less consistent effects on positive emotions. For example, Anderson et al. (2017) and Reese et al. (2021) reported no significant change in positive affect from blue spaces, while Chan et al. (2023) and Masters et al. (2022) found mixed results for red and brown environments. Further exploration is needed to identify potential factors contributing to the variability in their effects.
4.4 Which type of natural environment is most effective in reducing arousal?
The analysis of the included studies reveals that virtual forests as green spaces are most effective in reducing arousal. Specifically, studies by Hong et al. (2019), Wang et al. (2019), and Yu et al. (2018) reported decreases in arousal associated with forest environments, indicating their effectiveness in promoting relaxation. Additionally, various types of green spaces, including open green space and partly closed green space, were discovered to be effective in decreasing arousal levels (Ho et al., 2023; Gao et al., 2019).
In contrast, green meadows demonstrated mixed results. While Jin et al. (2023) found a decrease in arousal associated with green meadows, Voigt-Antons et al. (2021) reported no significant change in arousal after exposure to a green meadow. This variability requires further exploration, given the limited number of studies conducted and analysed on these specific environments.
Blue spaces also showed a notable reduction in arousal, as evidenced by Anderson et al. (2017) and Gao et al. (2019), where expansive blue vistas and open ponds with greenery contributed to decreased arousal, validating the calming effect of water elements. However, it is important to note that the effect of blue spaces was less frequently studied compared to green environments.
In general, although the included studies revealed a positive impact of virtual natural environments on emotion elicitation, it is noteworthy that some evidence is still mixed and need for further exploration. Particularly, even if most of the studies reported a decrease in negative emotions, suggesting a positive impact of VR experience on emotional states, not all the research revealed significant effects in enhancing positive affect after the VR experience. For example, Gao et al. (2019), assessed no significant changes in emotions with positive valence but reported a reduction in negative valence emotions. Similarly, Meng et al. (2024) and Anderson et al. (2017) found positive emotions unaltered but negative ones decreased. Moreover, regarding reduction in emotional arousal, most of the studies reported a decreased arousal. However, some studies reported an increased arousal (Browning et al., 2020) or a not significant change (Voigt-Antons et al., 2021; Yu et al., 2020). These unexpected results may be attributed to methodological factors. In Browning et al.’s (2020) study, participants alternated between sitting and walking, a condition that may have physiologically stimulated them. Similarly, Voigt-Antons et al. (2021) involved participants in gameplay during the VR experience, potentially engaging mechanisms that heightened arousal rather than reducing it. Differently, in Yu et al. (2020), participants were seated in a comfortable position but the VR experience only lasted 10 min, a very short time to detect differences in physiological states. Further exploration of these dimensions is needed in future research.
5 Limitations and future directions
This state-of-the-art narrative review provides a comprehensive overview of current research about emotion elicitation through VR; however, it is important to acknowledge its limitations and suggest directions for future works.
Firstly, the selection of databases used for this review was limited to only three major sources. Although these databases are extensive and widely recognized, the exclusion of additional databases may have resulted in the omission of relevant studies. This limitation could have introduced a selection bias, potentially impacting the scope and comprehensiveness of the review. Therefore, future reviews should incorporate a broader range of databases to ensure a more exhaustive collection of relevant literature.
Secondly, this review did not include grey literature, that often contains valuable insights and can provide a more comprehensive perspective on the topic under investigation. The exclusion of these sources may have limited the understanding of the full spectrum of research findings and practical applications, being subject to potential publication bias. Incorporating grey literature in future reviews of VR’s potential in emotion elicitation would enhance the comprehensiveness and depth of the analysis.
Third, although the keyword strategy was designed to conceptually capture immersive virtual reality experiences in natural environments, it may have unintentionally excluded studies that used more specific or alternative terms—such as names of specific natural settings (e.g., “forest”, “park”, “lake”) or different terminology referring to VR (e.g., “simulated nature”). While many of these environments were in fact represented in the included studies, future reviews would benefit from adopting a more granular and inclusive keyword strategy that accounts for the evolving and interdisciplinary nature of this research field.
Another limitation is the lack of a formal quality assessment of the included studies. Quality assessment is crucial to ensure that conclusions are drawn from robust and reliable evidence. The absence of such an assessment means that this review may include studies of varying methodological quality, potentially affecting the reliability and validity of the conclusions. Future reviews about the topic should implement systematic quality assessments to evaluate the methodological rigour, risk of bias, and relevance of each study, thereby ensuring that findings are based on high-quality evidence.
Additionally, future reviews should consider analysing the impact of various dimensions of User Experience on the sense of presence and the emotions elicited. Understanding how factors such as usability, engagement, and satisfaction influence emotional responses and the sense of presence can provide deeper insights and inform the design of more effective and emotionally resonant user experiences. Additionally, future research should investigate the role of cybersickness and its impact on user experience and emotional responses within VR scenarios, particularly given its documented association with VR-induced stress (Martirosov et al., 2022). Moreover, given that our review encompassed studies employing diverse methodologies and sample populations, future reviews could explore the impact of virtual natural environments on emotion elicitation within specific populations, such as clinical groups. This would allow for a nuanced understanding of individual emotional responses to natural scenarios and support the development of therapies tailored to distinct emotional profiles.
Finally, further investigation into the moderating effects contributing to the divergent outcomes identified in this review may prove valuable for future research. Such exploration could help pinpoint and clarify the factors influencing emotional experiences elicited during exposure to natural VR scenarios.
By addressing these areas, future reviews can enhance the comprehensiveness and reliability of the findings, ultimately contributing to a more nuanced understanding of the factors that influence emotional experiences and the sense of presence.
6 Conclusion
The review of studies on virtual natural environments reveals several key insights into their effectiveness and variations in terms of emotion elicitation. Different interventions, including the duration of exposure and interaction methods, played a significant role in the effectiveness of virtual nature experiences. Longer sessions, especially those involving interactive elements such as hand gestures, proved to be the most effective in enhancing emotional and physiological benefits.
Among the various types of natural environments used, green spaces, particularly virtual forests, were the most frequently studied and showed consistent effectiveness in both reducing arousal and eliciting positive emotions. Green meadows also emerged as highly effective in evoking positive emotions, although their impact on reducing arousal showed some variability. Blue spaces, while less frequently studied, also contributed to reduced arousal, particularly in environments featuring expansive water vistas. In contrast, red and brown environments, such as red savannahs and canyons, were less common and showed less consistent effects on emotional outcomes.
Overall, the findings underscore the strong impact of green environments, particularly forests and meadows, in promoting relaxation and positive emotional states, with variations observed in less commonly studied environments like blue spaces.
Author contributions
SM: Writing – original draft, Methodology, Conceptualization, Writing – review and editing. VV: Writing – review and editing, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Conceptualization. EG: Writing – review and editing. VG: Writing – review and editing. MS: Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abdullah, S. S., Awang Rambli, D. R., Sulaiman, S., Alyan, E., Merienne, F., and Mohd Muhaiyuddin, N. D. (2021). The impact of virtual nature therapy on stress responses: a systematic qualitative review. Forests 12 (12), 1776. doi:10.3390/f12121776
Anderson, D. J., and Krettenauer, T. (2021). Connectedness to nature and pro-environmental behaviour from early adolescence to adulthood: a comparison of urban and rural Canada. Sustainability 13 (7), 3655. doi:10.3390/su1307365
Anderson, A. P., Mayer, M. D., Fellows, A. M., Cowan, D. R., Hegel, M. T., and Buckey, J. C. (2017). Relaxation with immersive natural scenes presented using virtual reality. Aerosp. Med. Hum. Perform. 88 (6), 520–526. doi:10.3357/amhp.4747.2017
Annerstedt, M., Jönsson, P., Wallergård, M., Johansson, G., Karlson, B., Grahn, P., et al. (2013). Inducing physiological stress recovery with sounds of nature in a virtual reality forest--results from a pilot study. Physiology Behav. 118, 240–250. doi:10.1016/j.physbeh.2013.05.023
Astell-Burt, T., and Feng, X. (2021). Time for ‘green’during COVID-19? Inequities in green and blue space access, visitation and felt benefits. Int. J. Environ. Res. public health 18 (5), 2757. doi:10.3390/ijerph18052757
Astell-Burt, T., Mitchell, R., and Hartig, T. (2014). The association between green space and mental health varies across the lifecourse. A longitudinal study. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 68 (6), 578–583. doi:10.1136/jech-2013-203767
Baumeister, R. F. (2013). “Writing a literature review,” in The portable mentor: expert guide to a successful career in psychology (New York, NY: Springer Science + Business Media), 119–132.
Baumeister, R. F., and Leary, M. R. (1997). Writing narrative literature reviews. Rev. General Psychol. 1 (3), 311–320. doi:10.1037//1089-2680.1.3.311
Berman, M. G., Jonides, J., and Kaplan, S. (2008). The cognitive benefits of interacting with nature. Psychol. Sci. 19 (12), 1207–1212. doi:10.1111/j.1467-9280.2008.02225.x
Berry, M. S., Repke, M. A., Nickerson, N. P., Conway III, L. G., Odum, A. L., and Jordan, K. E. (2015). Making time for nature: visual exposure to natural environments lengthens subjective time perception and reduces impulsivity. PloS One 10 (11), e0141030. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0141030
Berto, R. (2005). Exposure to restorative environments helps restore attentional capacity. J. Environ. Psychol. 25 (3), 249–259. doi:10.1016/j.jenvp.2005.07.001
Berto, R. (2014). The role of nature in coping with psycho-physiological stress: a literature review on restorativeness. Behav. Sci. 4 (4), 394–409. doi:10.3390/bs4040394
Bolouki, A. (2024). The impact of virtual reality natural and built environments on affective responses: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 34 (1), 73–89. doi:10.1080/09603123.2022.2130881
Bradley, M. M., and Lang, P. J. (1994). Measuring emotion: the self-assessment manikin and the semantic differential. J. Behav. Ther. Exp. Psychiatry 25, 49–59. doi:10.1016/0005-7916(94)90063-9
Bratman, G. N., Daily, G. C., Levy, B. J., and Gross, J. J. (2015). The benefits of nature experience: improved affect and cognition. Landsc. Urban Plan. 138, 41–50. doi:10.1016/j.landurbplan.2015.02.005
Bratman, G. N., Olvera-Alvarez, H. A., and Gross, J. J. (2021). The affective benefits of nature exposure. Soc. Personality Psychol. Compass 15, e12630. doi:10.1111/spc3.12630
Brooke, K., and Williams, A. (2021). Iceland as a therapeutic landscape: white wilderness spaces for well-being. GeoJournal 86 (3), 1275–1285. doi:10.1007/s10708-019-10128-9
Browning, M. H., Mimnaugh, K. J., Van Riper, C. J., Laurent, H. K., and LaValle, S. M. (2020). Can simulated nature support mental health? Comparing short, single-doses of 360-degree nature videos in virtual reality with the outdoors. Front. Psychol. 10, 2667. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2019.02667
Brymer, E., and Davids, K. (2014). Experiential learning as a constraint-led process: an ecological dynamics perspective. J. Adventure Educ. Outdoor Learn. 14 (2), 103–117. doi:10.1080/14729679.2013.789353
Cameron, R. W. F., Brindley, P., Mears, M., McEwan, K., Ferguson, F., Sheffield, D., et al. (2020). Where the wild things are! do urban green spaces with greater avian biodiversity promote more positive emotions in humans? Urban Ecosyst. 23 (2), 301–317. doi:10.1007/s11252-020-00929-z
Chan, S. H. M., Qiu, L., Esposito, G., Mai, K. P., Tam, K. P., and Cui, J. (2023). Nature in virtual reality improves mood and reduces stress: evidence from young adults and senior citizens. Virtual Real. 27 (4), 3285–3300. doi:10.1007/s10055-021-00604-4
Diener, E., Wirtz, D., Tov, W., Kim-Prieto, C., Choi, D.-w., Oishi, S., et al. (2010). New well-being measures: short scales to assess flourishing and positive and negative feelings. Soc. Indic. Res. 97 (2), 143–156. doi:10.1007/s11205-009-9493-y
Finlay, J. M. (2018). ‘Walk like a penguin’ older Minnesotans experiences of (non) therapeutic white space. Soc. Sci. Med. 198, 77–84. doi:10.1016/j.socscimed.2017.12.024
Fromm, E. (1964). The heart of man: its genius for good and evil. New York, NY: Harper & Row Publishers.
Furman, E., Jasinevicius, T. R., Bissada, N. F., Victoroff, K. Z., Skillicorn, R., and Buchner, M. (2009). Virtual reality distraction for pain control during periodontal scaling and root planing procedures. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 140 (12), 1508–1516. doi:10.14219/jada.archive.2009.0102
Gao, T., Zhang, T., Zhu, L., Gao, Y., and Qiu, L. (2019). Exploring psychophysiological restoration and individual preference in the different environments based on virtual reality. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 16 (17), 3102. doi:10.3390/ijerph16173102
Graf, L., Liszio, S., and Masuch, M. (2020). “Playing in virtual nature: improving mood of elderly people using VR technology,” in In Proceedings of Mensch und Computer 2020 (Magdeburg, Germany: Association for Computing Machinery), 155–164.
Green, B. N., Johnson, C. D., and Adams, A. (2006). Writing narrative literature reviews for peer-reviewed journals: secrets of the trade. J. Chiropr. Med. 5 (3), 101–117. doi:10.1016/s0899-3467(07)60142-6
Grellier, J., White, M. P., Albin, M., Bell, S., Elliott, L. R., Gascón, M., et al. (2017). BlueHealth: a study programme protocol for mapping and quantifying the potential benefits to public health and well-being from Europe’s blue spaces. BMJ Open 7 (6), e016188. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2017-016188
Grossi, E., and Marocco, S. (2025). The impact of natural virtual environments on perceived environmental restorativeness and individual restoration. PsyHub. 42, 92–110.
Hartig, T., Korpela, K. M., Evans, G. W., and Garling, T. (1996). “Validation of a measure of perceived environmental restorativeness” in Göteborg Psychological Reports, 26 (Göteborg, Sweden: Göteborg University, Department of Psychology), 1–64.
Hartig, T., Evans, G. W., Jamner, L. D., Davis, D. S., and Gärling, T. (2003). Tracking restoration in natural and urban field settings. J. Environ. Psychol. 23 (2), 109–123. doi:10.1016/s0272-4944(02)00109-3
Hartig, T., Van Den Berg, A. E., Hagerhall, C. M., Tomalak, M., Bauer, N., Hansmann, R., et al. (2011). “Health benefits of nature experience: psychological, social and cultural processes,” in In forests, trees and human health (Dordrecht: Springer), 127–168.
Hartig, T., Mitchell, R., De Vries, S., and Frumkin, H. (2014). Nature and health. Annu. Rev. Public Health 35, 207–228. doi:10.1146/annurev-publhealth-032013-182443
Hedblom, M., Gunnarsson, B., Iravani, B., Knez, I., Schaefer, M., Thorsson, P., et al. (2019). Reduction of physiological stress by urban green space in a multisensory virtual experiment. Sci. Rep. 9 (1), 10113. doi:10.1038/s41598-019-46099-7
Ho, M. H., Wu, M. S., and Yen, H. Y. (2023). Effects of virtual reality natural experiences on factory workers’ psychological and physiological stress. Front. Psychol. 14, 993143. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2023.993143
Hong, S., Joung, D., Lee, J., Kim, D. Y., Kim, S., and Park, B. J. (2019). The effects of watching a virtual reality (VR) forest video on stress reduction in adults. J. People, Plants, Environ. 22 (3), 309–319. doi:10.11628/ksppe.2019.22.3.309
Jiang, B., Li, D., Larsen, L., and Sullivan, W. C. (2016). A dose-response curve describing the relationship between urban tree cover density and self-reported stress recovery. Environ. Behav. 48 (4), 607–629. doi:10.1177/0013916514552321
Jin, Y. L., Chen, E. C., and Li, T. Y. (2023). “Study of different interaction methods on the healing effect of natural environment in virtual reality,” in 2023 9th international Conference on virtual reality (ICVR) (Xianyang, China: IEEE), 185–192.
Kahn Jr, P. H., Weiss, T., and Harrington, K. (2018). Modeling child–nature interaction in a nature preschool: a proof of concept. Front. Psychol. 835. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2018.00835
Kaplan, S., and Berman, M. G. (2010). Directed attention as a common resource for executive functioning and self-regulation. Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 5 (1), 43–57. doi:10.1177/1745691609356784
Kaplan, R., and Kaplan, S. (1989). The experience of nature: a psychological perspective. Cambridge, United Kingdom: Cambridge University Press.
Kjellgren, A., and Buhrkall, H. (2010). A comparison of the restorative effect of a natural environment with that of a simulated natural environment. J. Environ. Psychol. 30 (4), 464–472. doi:10.1016/j.jenvp.2010.01.011
Korpela, K. M. (2003). Negative mood and adult place preference. Environ. Behav. 35 (3), 331–346. doi:10.1177/0013916503035003002
Korpela, K., Borodulin, K., Neuvonen, M., Paronen, O., and Tyrväinen, L. (2014). Analyzing the mediators between nature-based outdoor recreation and emotional well-being. J. Environ. Psychol. 37, 1–7. doi:10.1016/j.jenvp.2013.11.003
Kotera, Y., Lyons, M., Vione, K. C., and Norton, B. (2021). Effect of nature walks on depression and anxiety: a systematic review. Sustainability 13 (7), 4015. doi:10.3390/su13074015
Kuo, F. E., and Sullivan, W. C. (2001). Aggression and violence in the inner city: effects of environment via mental fatigue. Environ. Behav. 33 (4), 543–571. doi:10.1177/00139160121973124
Lang, P. J., Bradley, M. M., and Cuthbert, B. N. (1998). Emotion and motivation: measuring affective perception. J. Clin. Neurophysiology 15 (5), 397–408. doi:10.1097/00004691-199809000-00004
Lee, A. C., and Maheswaran, R. (2011). The health benefits of urban green spaces: a review of the evidence. J. Public Health 33 (2), 212–222. doi:10.1093/pubmed/fdq068
Leung, G. Y., Hazan, H., and Chan, C. S. (2022). Exposure to nature in immersive virtual reality increases connectedness to nature among people with low nature affinity. J. Environ. Psychol. 83, 101863. doi:10.1016/j.jenvp.2022.101863
Li, D., Menotti, T., Ding, Y., and Wells, N. M. (2021). Life course nature exposure and mental health outcomes: a systematic review and future directions. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 18 (10), 5146. doi:10.3390/ijerph18105146
Li, H., Zhang, X., Wang, H., Yang, Z., Liu, H., Cao, Y., et al. (2021). Access to nature via virtual reality: a mini-review. Front. Psychol. 12, 725288. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2021.725288
Li, H., Ding, Y., Zhao, B., Xu, Y., and Wei, W. (2023). Effects of immersion in a simulated natural environment on stress reduction and emotional arousal: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Psychol. 13, 1058177. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2022.1058177
Liang, L., Gobeawan, L., Lau, S.-K., Lin, E. S., and Ang, K. K. (2024). Urban green spaces and mental well-being: a systematic review of studies comparing virtual reality versus real nature. Future Internet 16 (6), 182. doi:10.3390/fi16060182
Maas, J., Verheij, R. A., Groenewegen, P. P., De Vries, S., and Spreeuwenberg, P. (2006). Green space, urbanity, and health: how strong is the relation? J. Epidemiol. Community Health 60 (7), 587–592. doi:10.1136/jech.2005.043125
Maas, J., Van Dillen, S. M., Verheij, R. A., and Groenewegen, P. P. (2009). Social contacts as a possible mechanism behind the relation between green space and health. Health Place 15 (2), 586–595. doi:10.1016/j.healthplace.2008.09.006
Marocco, S., and Talamo, A. (2022). The contribution of activity theory to modeling multi-actor decision-making: a focus on human capital investments. Front. Psychol. 13, 997062. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2022.997062
Marocco, S., Barbieri, B., and Talamo, A. (2024a). Exploring facilitators and barriers to managers’ adoption of AI-based systems in decision making: a systematic review. A Syst. Rev. AI 5, 2538–2567. doi:10.3390/ai5040123
Marocco, S., Marini, M., and Talamo, A. (2024b). Enhancing organizational processes for service innovation: strategic organizational counseling and organizational network analysis. Front. Res. Metrics Anal. 9, 1270501. doi:10.3389/frma.2024.1270501
Marocco, S., Talamo, A., and Quintiliani, F. (2024c). Applying design thinking to develop AI-based multi-actor decision-support systems: a case study on human capital investments. Appl. Sci. 14, 5613. doi:10.3390/app14135613
Marocco, S., Talamo, A., and Quintiliani, F. (2024d). From service design thinking to the third generation of activity theory: a new model for designing AI-based decision-support systems. Front. Artif. Intell. 7, 1303691. doi:10.3389/frai.2024.1303691
Marocco, S., Vitale, V., Grossi, E., Presaghi, F., Bonaiuto, M., and Talamo, A. (2025a). Exploring the restorative effects of natural environments in virtual reality. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 22 (4), 535. doi:10.3390/ijerph22040535
Marocco, S., Vitale, V., Grossi, E., Presaghi, F., and Talamo, A. (2025b). The potential of virtual natural environments: a critical analysis of a VR-based mindfulness approach. Front. Psychol. 16, 1637669. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1637669
Martirosov, S., Bureš, M., and Zítka, T. (2022). Cyber sickness in low-immersive, semi-immersive, and fully immersive virtual reality. Virtual Real. 26 (1), 15–32. doi:10.1007/s10055-021-00507-4
Masters, R., Interrante, V., Watts, M., and Ortega, F. (2022). “Virtual nature: investigating the effect of biomass on immersive virtual reality forest bathing applications for stress reduction,” in In ACM symposium on applied perception 2022 (New Yor, NY: Association for Computing Machinery), 1–10.
Mattila, O., Korhonen, A., Pöyry, E., Hauru, K., Holopainen, J., and Parvinen, P. (2020). Restoration in a virtual reality forest environment. Comput. Hum. Behav. 107, 106295. doi:10.1016/j.chb.2020.106295
McMahan, E. A., and Estes, D. (2015). The effect of contact with natural environments on positive and negative affect: a meta-analysis. J. Posit. Psychol. 10 (6), 507–519. doi:10.1080/17439760.2014.994224
Meng, L., Li, S., and Zhang, X. (2024). Assessing biodiversity’s impact on stress and affect from urban to conservation areas: a virtual reality study. Ecol. Indic. 158, 111532. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2023.111532
Meuwese, D., Dijkstra, K., Maas, J., and Koole, S. L. (2021). Beating the blues by viewing Green: Depressive symptoms predict greater restoration from stress and negative affect after viewing a nature video. J. Environ. Psychol. 75, 101594. doi:10.1016/j.jenvp.2021.101594
Mosso, J. L., Gorini, A., De La Cerda, G., Obrador, T., Almazan, A., Mosso, D., et al. (2009). Virtual reality on mobile phones to reduce anxiety in outpatient surgery. Med. Meets Virtual Real. 17, 195–200. doi:10.3233/978-1-58603-964-6-195
Nazif-Munoz, J. I., Cedeno Laurent, J. G., Browning, M., Spengler, J., and Olvera Álvarez, H. A. (2020). Green, brown, and gray: associations between different measurements of land patterns and depression among nursing students in El Paso, Texas. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 17 (21), 8146. doi:10.3390/ijerph17218146
Nukarinen, T., Rantala, J., Korpela, K., Browning, M. H., Istance, H. O., Surakka, V., et al. (2022). Measures and modalities in restorative virtual natural environments: an integrative narrative review. Comput. Hum. Behav. 126, 107008. doi:10.1016/j.chb.2021.107008
Ohly, H., White, M. P., Wheeler, B. W., Bethel, A., Ukoumunne, O. C., Nikolaou, V., et al. (2016). Attention Restoration Theory: a systematic review of the attention restoration potential of exposure to natural environments. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health, Part B 19 (7), 305–343. doi:10.1080/10937404.2016.1196155
Olvera-Alvarez, H. A., Browning, M. H., Neophytou, A. M., and Bratman, G. N. (2021). Associations of residential brownness and greenness with fasting glucose in young healthy adults living in the desert. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 18 (2), 520. doi:10.3390/ijerph18020520
Olwig, K. R. (2005). Liminality, seasonality and landscape. Landsc. Res. 30 (2), 259–271. doi:10.1080/01426390500044473
Palanica, A., Lyons, A., Cooper, M., Lee, A., and Fossat, Y. (2019). A comparison of nature and urban environments on creative thinking across different levels of reality. J. Environ. Psychol. 63, 44–51. doi:10.1016/j.jenvp.2019.04.006
Reese, G., Kohler, E., and Menzel, C. (2021). Restore or get restored: The effect of control on stress reduction and restoration in virtual nature settings Sustainability 13 (4), 1995–1255. doi:10.3390/su13041995
Reese, G., Stahlberg, J., and Menzel, C. (2022). Digital shinrin-yoku: do nature experiences in virtual reality reduce stress and increase well-being as strongly as similar experiences in a physical forest? Virtual Real. 26 (3), 1245–1255. doi:10.1007/s10055-022-00631-9
Ríos-Rodríguez, M. L., Rosales, C., Hernández, B., and Lorenzo, M. (2024). Benefits for emotional regulation of contact with nature: a systematic review. Front. Psychol. 15, 1402885. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1402885
Roberts, A., Hinds, J., and Camic, P. M. (2020). Nature activities and wellbeing in children and young people: a systematic literature review. J. Adventure Educ. Outdoor Learn. 20 (4), 298–318. doi:10.1080/14729679.2019.1660195
Roe, J., Aspinall, P. A., and Ward Thompson, C. (2017). Coping with stress in deprived urban neighborhoods: what is the role of green space according to life stage? Front. Psychol. 8, 1760. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2017.01760
Rojas-Rueda, D., Nieuwenhuijsen, M. J., Gascon, M., Perez-Leon, D., and Mudu, P. (2019). Green spaces and mortality: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. Lancet Planet. Health 3 (11), e469–e477. doi:10.1016/s2542-5196(19)30215-3
Russell, J. A. (2003). Core affect and the psychological construction of emotion. Psychol. Rev. 110 (1), 145–172. doi:10.1037/0033-295x.110.1.145
Russell, J. A., and Barrett, L. F. (1999). Core affect, prototypical emotional episodes, and other things called emotion: dissecting the elephant. J. Personality Soc. Psychol. 76 (5), 805–819. doi:10.1037//0022-3514.76.5.805
Ryan, R. M., and Frederick, C. (1997). On energy, personality, and health: subjective vitality as a dynamic reflection of well-being. J. Personality 65 (3), 529–565. doi:10.1111/j.1467-6494.1997.tb00326.x
Schebella, M. F., Weber, D., Schultz, L., and Weinstein, P. (2020). The nature of reality: human stress recovery during exposure to biodiverse, multisensory virtual environments. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 17 (1), 56. doi:10.3390/ijerph17010056
Schutte, N. S., Malouff, J. M., Price, I., Walter, S., Burke, G., and Wilkinson, C. (2008). Person–situation interaction in adaptive emotional functioning. Curr. Psychol. 27, 102–111. doi:10.1007/s12144-008-9027-9
Schutte, N. S., Bhullar, N., Stilinović, E. J., and Richardson, K. (2017). The impact of virtual environments on restorativeness and affect. Ecopsychology 9 (1), 1–7. doi:10.1089/eco.2016.0042
Shanahan, D. F., Fuller, R. A., Bush, R., Lin, B. B., and Gaston, K. J. (2015). The health benefits of urban nature: how much do we need? BioScience 65 (5), 476–485. doi:10.1093/biosci/biv032
Siddaway, A. P., Wood, A. M., and Hedges, L. V. (2019). How to do a systematic review: a best practice guide for conducting and reporting narrative reviews, meta-analyses, and meta-syntheses. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 70 (1), 747–770. doi:10.1146/annurev-psych-010418-102803
Somarathna, R., Bednarz, T., and Mohammadi, G. (2023). Virtual reality for emotion elicitation – A review. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 14 (4), 2626–2645. doi:10.1109/TAFFC.2022.3181053
Spano, G., Theodorou, A., Reese, G., Carrus, G., Sanesi, G., and Panno, A. (2023). Virtual nature, psychological and psychophysiological outcomes: a systematic review. J. Environ. Psychol. 89, 102044. doi:10.1016/j.jenvp.2023.102044
Stickdorn, M., and Schneider, J. (2011). This is service design thinking: basics, tools, cases. English Edition. Vancouver, Canada: Bis Publisher.
Sukhera, J. (2022). Narrative reviews: flexible, rigorous, and practical. J. Graduate Med. Mducation 14 (4), 414–417. doi:10.4300/jgme-d-22-00480.1
Takayama, N., Morikawa, T., Koga, K., Miyazaki, Y., Harada, K., Fukumoto, K., et al. (2022). Exploring the physiological and psychological effects of digital shinrin-yoku and its characteristics as a restorative environment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 19 (3), 1202. doi:10.3390/ijerph19031202
Talamo, A., Giorgi, S., and Mellini, B. (2011). “Designing technologies for ageing: is simplicity always a leading criterion?,” in Proceedings of the 9th ACM SIGCHI Italian chapter international conference on computer-human interaction: facing complexity (New York, NY: ACM), 33–36.
Talamo, A., Marocco, S., and Tricol, C. (2021). “The flow in the funnel”: modeling organizational and individual decision-making for designing financial AI-based systems. Front. Psychol. 12, 697101. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2021.697101
Twohig-Bennett, C., and Jones, A. (2018). The health benefits of the great outdoors: a systematic review and meta-analysis of greenspace exposure and health outcomes. Environ. Res. 166, 628–637. doi:10.1016/j.envres.2018.06.030
Ulrich, R. S. (1983). “Aesthetic and affective response to natural environment,” in In behavior and the natural environment (Boston, MA: Springer US), 85–125.
Ulrich, R. S., Simons, R. F., Losito, B. D., Fiorito, E., Miles, M. A., and Zelson, M. (1991). Stress recovery during exposure to natural and urban environments. J. Environ. Psychol. 11 (3), 201–230. doi:10.1016/s0272-4944(05)80184-7
Van den Berg, A. E., Koole, S. L., and van der Wulp, N. Y. (2003). Environmental preference and restoration:(How) are they related? J. Environ. Psychol. 23 (2), 135–146. doi:10.1016/s0272-4944(02)00111-1
Van Dillen, S. M., de Vries, S., Groenewegen, P. P., and Spreeuwenberg, P. (2012). Greenspace in urban neighbourhoods and residents’ health: adding quality to quantity. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 66 (6), e8. doi:10.1136/jech.2009.104695
Vitale, V., and Bonaiuto, M. (2024). The role of nature in emotion regulation processes: an evidence-based rapid review. J. Environ. Psychol. 96, 102325. doi:10.1016/j.jenvp.2024.102325
Vitale, V., Martin, L., White, M. P., Elliott, L. R., Wyles, K. J., Browning, M. H. E. M., et al. (2022). Mechanisms underlying childhood exposure to blue spaces and adult subjective well-being: an 18-country analysis. J. Environ. Psychol. 84, 101876. doi:10.1016/j.jenvp.2022.101876
Voigt-Antons, J. N., Spang, R., Kojić, T., Meier, L., Vergari, M., and Möller, S. (2021). “Don’t worry be happy-using virtual environments to induce emotional states measured by subjective scales and heart rate parameters,” in 2021 IEEE virtual reality and 3D user interfaces (VR) (Lisboa, Portugal: IEEE), 679–686.
Wang, X., Shi, Y., Zhang, B., and Chiang, Y. (2019). The influence of forest resting environments on stress using virtual reality. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 16 (18), 3263. doi:10.3390/ijerph16183263
Watson, D., Clark, L. A., and Tellegen, A. (1988). Development and validation of brief measures of positive and negative affect: the PANAS scales. J. Personality Soc. Psychol. 54 (6), 1063–1070. doi:10.1037//0022-3514.54.6.1063
Wheeler, B. W., Lovell, R., Higgins, S. L., White, M. P., Alcock, I., Osborne, N. J., et al. (2015). Beyond greenspace: an ecological study of population general health and indicators of natural environment type and quality. Int. J. Health Geogr. 14 (1), 17. doi:10.1186/s12942-015-0009-5
White, M., Smith, A., Humphryes, K., Pahl, S., Snelling, D., and Depledge, M. (2010). Blue space: the importance of water for preference, affect, and restorativeness ratings of natural and built scenes. J. Environ. Psychol. 30 (4), 482–493. doi:10.1016/j.jenvp.2010.04.004
White, M. P., Yeo, N. L., Vassiljev, P., Lundstedt, R., Wallergård, M., Albin, M., et al. (2018). A prescription for “nature”–the potential of using virtual nature in therapeutics. Neuropsychiatric Dis. Treat., 3001–3013. doi:10.2147/NDT.S179038
Yin, J., Bratman, G. N., Browning, M. H., Spengler, J. D., and Olvera-Alvarez, H. A. (2022). Stress recovery from virtual exposure to a brown (desert) environment versus a green environment. J. Environ. Psychol. 81, 101775. doi:10.1016/j.jenvp.2022.101775
Yli-Panula, E., Jeronen, E., Matikainen, E., and Persson, C. (2022). Conserve my village—Finnish, Norwegian and Swedish students’ valued landscapes and well-being. Sustainability 14 (2), 671. doi:10.3390/su14020671
Yu, C. P., Lee, H. Y., and Luo, X. Y. (2018). The effect of virtual reality forest and urban environments on physiological and psychological responses. Urban For. Urban Green. 35, 106–114. doi:10.1016/j.ufug.2018.08.013
Yu, C. P., Lee, H. Y., Lu, W. H., Huang, Y. C., and Browning, M. H. (2020). Restorative effects of virtual natural settings on middle-aged and elderly adults. Urban For. Urban Green. 56, 126863. doi:10.1016/j.ufug.2020.126863
Keywords: nature, virtual reality, emotion elicitation, valence, arousal
Citation: Marocco S, Vitale V, Grossi E, Giffi V and Santoriello M (2025) The impact of natural virtual environments on emotion elicitation: a state-of-the-art review. Front. Virtual Real. 6:1638419. doi: 10.3389/frvir.2025.1638419
Received: 30 May 2025; Accepted: 31 July 2025;
Published: 22 August 2025.
Edited by:
Athina Papadopoulou, New York Institute of Technology, United StatesReviewed by:
James Lewis, Nottingham Trent University, United KingdomXingxing Jia, Nanjing Forestry University, China
Copyright © 2025 Marocco, Vitale, Grossi, Giffi and Santoriello. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Morena Santoriello, bW9yZW5hLnNhbnRvcmllbGxvQHBoZC51bmljaC5pdA==
 Silvia Marocco
Silvia Marocco Valeria Vitale
Valeria Vitale Elena Grossi
Elena Grossi Veronica Giffi2
Veronica Giffi2 Morena Santoriello
Morena Santoriello