- 1Section of Paediatric Infectious Disease, Department of Infectious Disease, Imperial College London, London, United Kingdom
- 2SSPC Pharma Research Centre, Department of Biology, Maynooth University, Maynooth, Ireland
- 3Institute of Microbiology and Infection, School of Biosciences, University of Birmingham, Birmingham, United Kingdom
- 4MRC Centre for Molecular Bacteriology and Infection, Department of Infectious Disease, Imperial College London, London, United Kingdom
The larvae of the insect Galleria mellonella, have recently been established as a non-mammalian infection model for the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex (MTBC). To gain further insight into the potential of this model, we applied proteomic (label-free quantification) and transcriptomic (gene expression) approaches to characterise the innate immune response of G. mellonella to infection with Mycobacterium bovis BCG lux over a 168 h time course. Proteomic analysis of the haemolymph from infected larvae revealed distinct changes in the proteome at all time points (4, 48, 168 h). Reverse transcriptase quantitative PCR confirmed induction of five genes (gloverin, cecropin, IMPI, hemolin, and Hdd11), which encoded proteins found to be differentially abundant from the proteomic analysis. However, the trend between gene expression and protein abundance were largely inconsistent (20%). Overall, the data are in agreement with previous phenotypic observations such as haemocyte internalization of mycobacterial bacilli (hemolin/β-actin), formation of granuloma-like structures (Hdd11), and melanization (phenoloxidase activating enzyme 3 and serpins). Furthermore, similarities in immune expression in G. mellonella, mouse, zebrafish and in vitro cell-line models of tuberculosis infection were also identified for the mechanism of phagocytosis (β-actin). Cecropins (antimicrobial peptides), which share the same α-helical motif as a highly potent peptide expressed in humans (h-CAP-18), were induced in G. mellonella in response to infection, giving insight into a potential starting point for novel antimycobacterial agents. We believe that these novel insights into the innate immune response further contribute to the validation of this cost-effective and ethically acceptable insect model to study members of the MTBC.
Introduction
Tuberculosis (TB) is the leading cause of global infectious disease mortality, with a quarter of the world’s population believed to be infected with the causative agent, Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB) (World Health Organization [WHO], 2020). A large majority of this population will live with a non-contagious and asymptomatic infection known as latent TB infection. Amongst these individuals, 5%–10% will develop active TB disease over their lifetime, serving as a reservoir for future transmission and infection (WHO, 2020). WHO is currently working to end the global TB epidemic by 2035. The first milestone goal is set for 2020, which will be missed by substantial margins (Reid et al., 2019). In order to meet the next milestone goal in 2035, significant advancement and increase in TB research output is needed to further understand the disease, and to identify novel mechanisms, drug targets and biomarkers, and the subsequent development of much needed tools to end the TB epidemic.
Animal infection models (e.g., mice, guinea pigs, macaques) have played an essential role in our current understanding of TB disease (Williams and Orme, 2016; Zhan et al., 2017). There are a wide variety of animal models used for TB research, but each comes with their limitations (Zhan et al., 2017). For example, in the most widely used mouse (C57Bl/6 and BALB/c) models, necrotic granulomas, a hallmark of TB, do not form (Orme, 2003). However, the ability to comprehensively study the immune response to infection, makes them useful despite their limitations. Furthermore, the use of animals is resource intensive, time consuming, requires the use of specialized animal facilities and is associated with ethical constraints, leading to a bottleneck in the research pipeline (Williams and Orme, 2016; Zhan et al., 2017). Over the past decade, the larvae of the insect, Galleria mellonella (Greater wax moth) have become increasingly popular as an infection model to study bacterial [e.g., Klebsiella pneumoniae (Insua et al., 2013), Escherichia coli (Alghoribi et al., 2014), Staphylococcus aureus (Sheehan et al., 2019)] and fungal [e.g., Candida albicans (Kelly and Kavanagh, 2011), Aspergillus fumigatus (Sheehan et al., 2018a) and Madurella mycetomatis (Sheehan et al., 2020b)] pathogens. Additionally the use of non-mammalian models, such as G. mellonella, in research is driven by the movement to reduce, replace and refine (3Rs) the use of vertebrate animals in scientific experimentation (Graham and Prescott, 2015). This insect model offers a number of advantages over conventional mammalian models: 1) low acquisition and maintenance costs, 2) accessibility, requiring minimal training and without the need for specialized equipment and facilities, 3) can tolerate incubation at 37°C, 4) no ethical constraints, 5) study of innate immunity in isolation from adaptive immunity, and 6) rapid infection cycle which allows for mid to high throughput data generation (Asai et al., 2019a). Furthermore pre-existing, non-mammalian infection models such as Drosophila melanogaster (fruit flies) and Danio rerio (zebrafish), are often incompatible with human pathogens, and require specialized facilities and equipment for infection and maintenance (Avdesh et al., 2012; Siva-Jothy et al., 2018).
Although the invertebrate G. mellonella lacks adaptive immunity, its innate immune system is complex and shares functional and anatomical similarities to those found in mammals (Wojda, 2017). The innate immune response of G. mellonella is broadly differentiated into two categories, cellular and humoral responses (Hillyer, 2016). The cellular response is driven by innate immune cells known as haemocytes (analogous to blood cells) (Pereira et al., 2018). At least six types of haemocytes have been identified in G. mellonella, with plasmatocytes and granulocytes being the most common types and the primary drivers of cellular functions such as phagocytosis, nodulation and encapsulation (Pereira et al., 2018). The humoral response is activated upon the detection of invading pathogens, through recognition of pathogen/damage associated molecular patterns (PAMPs/DAMPs) using pattern recognition receptors (PRRs), e.g., Toll-like receptors, β-1,3-glucan and IL-1R, and inducing signalling cascades, e.g., IMD, JNK, JAK-STAT pathways (Sheehan et al., 2018b). This leads to the expression and production of antimicrobial peptides (AMPs), mainly within the fat body (liver-like tissue), NADPH oxidase complex dependent production of reactive oxygen/nitrogen species (ROS/RNS) and hydrogen peroxide, which are secreted into the haemolymph found in the haemocoel (analogous to blood/blood vessel) (Sheehan et al., 2018b). The phenoloxidase (PO) cascade is responsible for modulation of melanization, which is a key process to localize and control infection through melanin deposition and production of phenolic compounds (Hillyer, 2016). The PO cascade system shares similarities with the mammalian complement cascade, e.g., both are initiated in response to pathogen recognition and are tightly regulated by proteases and protease inhibitors. However, they do differ in their final stages, i.e., melanization in insects and induction of cell lysis in mammals (Sheehan et al., 2018b).
Studies have demonstrated that G. mellonella is a viable host for mycobacterial species including both members of the MTB complex (MTBC), including MTB (Li et al., 2018; Asai et al., 2019a; Asai et al., 2019b; Asai et al., 2020), and non-tuberculous mycobacteria (NTM) (Entwistle and Coote, 2018; Meir et al., 2018; Kirubakar et al., 2020). Previously we established a G. mellonella – Mycobacterium bovis BCG lux model, characterised by establishment of intracellular and non-replicative but persistent infection, development of granuloma-like structures within the infected larvae, and a shift to a non-replicative lipid-rich BCG phenotype (Li et al., 2018). In addition, we demonstrated its capability as a rapid drug screen for antimycobacterial compounds, giving results within 96 h following infection (Asai et al., 2019b). We have employed BCG as a surrogate for MTB, due to its compliance with containment level (CL)/biosafety level (BSL) two facilities, thereby enabling researchers lacking specialized facilities (CL3/BSL3) to undertake TB research. While other surrogate mycobacteria exist, such as Mycobacterium smegmatis, BCG is considered to be superior due to its genetic similarity (>99.9% vs 70%) with MTB (Altaf et al., 2010). Furthermore, BCG has widely been used for in vitro/ex vivo mycobacterial growth inhibition assays (MGIAs) to study the immune mechanisms of mycobacterial control, proving to be a valuable organism in mycobacterial research (Roy et al., 2019; Tanner et al., 2019; Painter et al., 2020). Methodologies such as histopathology, transmission electron microscopy, bioluminescence, ex vivo haemocyte assays, and larval survival studies have typically been used to study the innate immune response to mycobacterial infection in G. mellonella (Li et al., 2018; Asai et al., 2019a; Asai et al., 2019b; Sheehan et al., 2019). However, greater knowledge of the larval innate immune system in response to mycobacterial infection is needed to further characterise and expand its potential as a model organism. In this study, and for the first time to our knowledge, we present a proteomic and reverse transcriptase quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) analysis of the innate immune response of G. mellonella to infection with a member of the MTBC over a time course of 168 h.
Methods
Mycobacteria Culture Conditions
M. bovis BCG lux, is a genetically modified bioluminescent Montréal vaccine strain which has been transformed with the shuttle plasmid vector pSMT1 expressing the luxAB genes of Vibrio harveyi (Snewin et al., 1999; Newton et al., 2011). BCG lux was cultured in Middlebrook 7H9 media (BD Difco, UK) supplemented with 0.2% glycerol (Sigma-Aldrich, UK), 0.05% polysorbate-80 (Sigma-Aldrich, UK) and 10% albumin dextrose catalase (BD Difco, UK), 50 µg/ml of hygromycin (Roche, UK), and incubated at 37°C in an orbital shaker. For enumeration of colony forming units (CFU), 10-fold serial dilutions of BCG lux were plated onto Middlebrook 7H11 agar (BD Difco, UK) supplemented with 0.5% glycerol, 10% oleic acid albumin dextrose catalase (BD Difco, UK), 50 µg/ml of hygromycin, and statically incubated at 37°C. The bioluminescence, relative light unit (RLU)/ml of BCG lux, was measured using a luminometer (Berthold Technologies, DE) and 1% decanal (Sigma-Aldrich) as the substrate. RLU was used as a relative and rapid estimation of CFU at a ratio of 3:1/4:1 in vitro and in vivo, respectively, as previously determined (Li et al., 2018).
G. mellonella Maintenance
Last instar G. mellonella larvae were purchased from Livefoods Direct, UK. Upon arrival, larvae were examined, and melanized or dead larvae were removed prior to storage in the dark at 18°C. Larvae were used within a week of arrival and were not fed during this period or throughout the experiment. Healthy larvae of approximately equal size (2–3 cm), weight (250 mg), motility and colour were picked for experimentation and acclimatised to room temperature before experimentation.
G. mellonella Infection With BCG lux
Mid-log phase BCG lux was prepared and injection of healthy G. mellonella larvae were carried out as previously described (Asai et al., 2019a). G. mellonella larvae were injected with 10 µl of BCG lux inoculum (1 x 105, 1 x 107 or 2 x 107 CFU) via the last left proleg of the larva. Injection is the preferred method over feeding, as dosing of BCG lux can be more accurately controlled. Infected larvae were transferred to a Petri dish lined with filter paper and incubated in a vented box at 37°C in the dark. N = 30 larvae were infected for each experimental group, unless otherwise stated, and each experiment consisted of three biological replicates (N = 90). The negative infection controls were naïve larvae, mock infected with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), with tween (0.05%, PBS-T). Survival of the infected larvae were recorded for up to 1-week post infection (pi). Larvae were considered dead when they failed to respond to touch. Where appropriate, a t-test was carried out to determine statistical significance.
Determination of BCG lux Load in G. mellonella
The survival of BCG lux in vivo, over a one week-time course was determined at 0, 24, 48, 72, 96, and 168 h pi. Five larvae were individually homogenized and the RLU of the homogenate was measured using a luminometer as previously described (Asai et al., 2019a). Background bioluminescence of the homogenate was previously reported as approximately 5,000 RLU/ml.
Preparation of Larval Haemolymph for Proteomic Analysis
Collection of haemolymph for proteomic analysis was carried out using our previously established protocol (Sheehan and Kavanagh, 2018; Sheehan et al., 2018a; Sheehan et al., 2019; Sheehan et al., 2020b). Briefly, larval haemolymph was collected at 4, 48, and 168 h pi for proteomic analysis. Larvae were punctured between the head and the thorax using a sterile 30-gauge needle. Haemolymph from 10 larvae was pooled (three drops [approximately 60 μl]/larva) into a sterile 1.5 ml reaction tube containing a few pellets of N-phenylthiourea on ice to prevent melanization. The haemolymph was centrifuged at 10,000 x g for 10 min to pellet the cells, and 30 µl of the cell free haemolymph was transferred into a fresh 1.5 ml reaction tube containing 270 µl of PBS. Three independent samples were collected. Haemolymph from uninfected naive larvae was collected as a reference control.
Label-Free Quantification (LFQ) Proteomics of Larval Haemolymph
Cell free haemolymph proteins (75 µg) were processed for proteomics using previously described and established protocols (Sheehan and Kavanagh, 2018; Sheehan et al., 2018a; Sheehan et al., 2019; Sheehan et al., 2020b). Protein identification from MS/MS data was performed using the Andromeda search engine in MaxQuant (v 1.2.2.5; http://maxquant.org/), correlating the data against the six-frame translation of the expressed sequence tags (EST) contigs for G. mellonella, with the addition of the proteomes of insect species Hyalophora cecropia, Manduca sexta, Bombyx mori (Vogel et al., 2011), and a proteomic database of M. bovis BCG (Brosch et al., 2007). The MS proteomic data and MaxQuant search output files were deposited to the ProteomeXchange Consortium via PRIDE partner repository with the dataset identifier PXD015250.
Data processing, statistical analysis, and graph generation were conducted using Persus (v 1.5.5.3). LFQ intensities were log2 transformed and one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and t-tests were carried out between the naïve reference and 4, 48, and 168 h BCG lux pi larval haemolymph samples. Significance was determined using p-value of 0.05 as a cut-off and Benjamini-Hochberg correction (Benjamini and Hochberg, 1995) was applied for false discovery rate. Proteins with non-existent values (absence or low abundance) were expressed as the imputation of the zero-value using a number close to the lowest value of the range of proteins plus or minus the standard deviation. Once imputed, these proteins were included in the analysis of total differentially expressed groups.
Reverse Transcriptase Quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR)
To quantify gene expression in G. mellonella larvae infected with BCG lux, five larvae were individually homogenized using a Ribolyser in a 2 ml lysing tube containing 900 µl of TRIzol (Thermo Fisher Scientific, UK) and six 1/8-inch metal beads (MP Biomedical, USA) at 4, 48 and 168 h pi. The lysate was processed to extract RNA using an RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, UK) following the manufacturer’s instructions. RNA of five larvae were pooled and cDNA was synthesised using the QuantiTect Reverse Transcription kit (Qiagen, UK), using 1 µg gDNA treated RNA as recommended by the manufacturer’s protocol. Real-time quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) was carried out using the QuantiFast SYBR® Green RT-PCR kit (Qiagen, UK) on a StepOne Plus real-time PCR system (Thermo Fisher Scientific, UK) targeting genes using primers in Table 1. The primer sequences for gloverin, cecropin, hemolin, insect metalloproteinase inhibitor (IMPI) and ubiquitin genes were acquired from prior publications (Dubovskiy et al., 2016; Lange et al., 2018b). The primer sequences for Hdd11 were designed using NCBI primer-BLAST and their specificity were checked against the G. mellonella genome. Specificity of all PCR amplicons were confirmed by agarose gel electrophoresis and staining. All PCR amplicons were sequenced and blasted against the G. mellonella nucleotide database (NCBI), which returned expected matches [NCBI ascension number: XM_026892927 (ubiquitin), XM_026898304 (cecropin), XM_026893524 (hemolin), XM_031907851 (Hdd11), XM_026909162 (gloverin), XM_031913565 (IMPI)]. Fold changes for each gene, relative to the naïve control at t = 0 h, are shown using the comparative CT (ΔΔCt) method using ubiquitin as the house keeping gene. Gene expression was determined using three independent experiments, and each sample was run in triplicate. The Mann-Whitney U test was used for statistical analyses.
Results
Larval Survival Following Infection With BCG lux
As previous work focused on larval and BCG lux survival over a time course of 96 h (Li et al., 2018; Asai et al., 2019a; Asai et al., 2019b), larval survival was determined over a longer 168 h time course for this proteomic and transcriptomic analysis (Figure 1). Larvae were considered dead when they failed to respond to touch. Larval survival decreased with increasing BCG lux inoculum density, where 2 x 107, 1 x 107, and 1 x 105 CFU resulted in 0, ~50 and 100% survival at 96 h pi, respectively. By 168 h pi, larvae infected with 1 x 107 and 1 x 105 CFU had ~15% and 100% survival, respectively. The PBS-T group displayed no fatalities, suggesting that neither injection procedure nor PBS-T induced adverse effects on survival outcome of the larvae. However, by 168 h pi some larvae in the 1 x 105 CFU and PBS-T groups began to pupate, entering their next stage of life cycle. These larvae were removed from the group and were omitted from the study. Over the course of infection larvae began to melanize at 48 h pi, which progressed steadily to extensive melanization at 96 h - 168 h pi. Larvae immunized with 1 x 105 CFU BCG lux, 48 h prior to infection with 2 x 107 CFU BCG lux, displayed a significant improvement in survival outcome at 96 h pi (t-test, p < 0.01) compared to those non-immunized (30% vs 3% respectively, Figure 2).
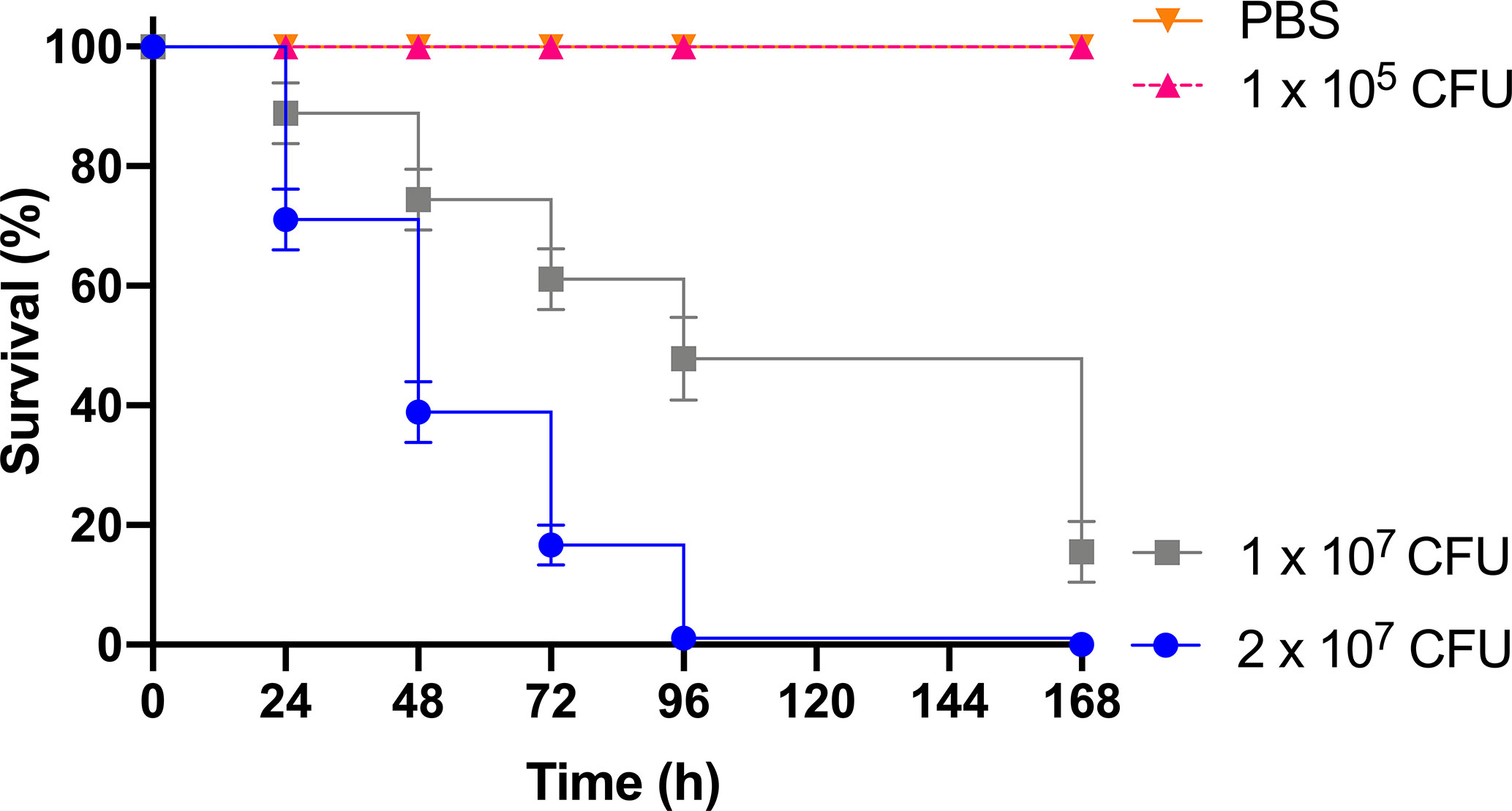
Figure 1 Survival curve of G. mellonella over a 168 h time course following infection with varying BCG lux inocula. Data represent three independent experiments, n=30 for each experimental group. Plotted are the mean and the standard deviation of the mean.
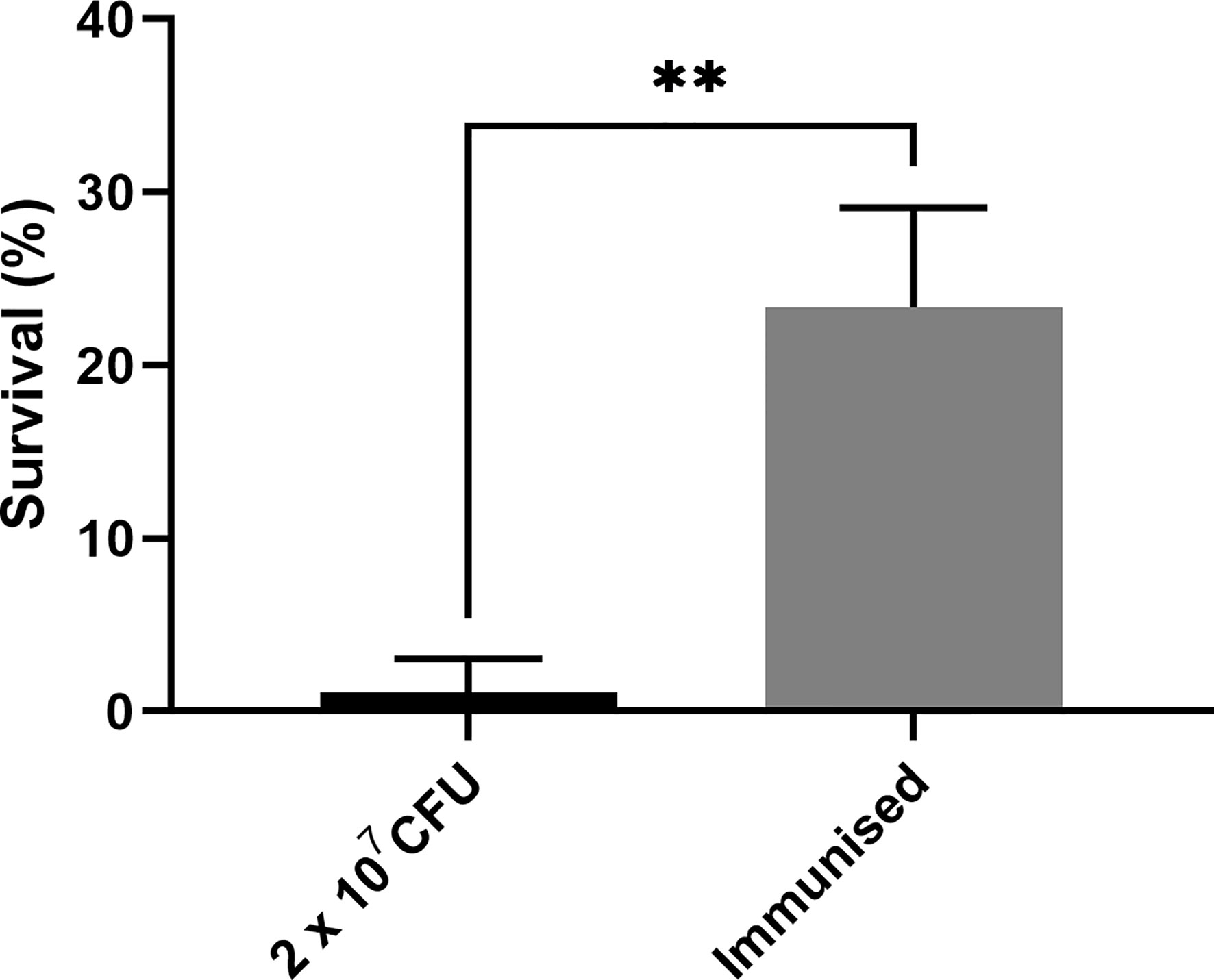
Figure 2 Survival of G. mellonella 96 h post infection immunized with a non-lethal dose of BCG lux 48 h pre infection. Data represent three independent experiments n = 30, n = 10 for each experimental repeat. Plotted are the mean and the standard deviation of the mean. ** = p < 0.01.
Survival of BCG lux Within G. mellonella
The survival of BCG lux (1 x 107 CFU) within G. mellonella was monitored over a 168 h time course, where bioluminescence of the larval homogenate was used as a rapid and validated method of quantifying changes in mycobacterial load in vivo (Figure 3). While previous data are available (Li et al., 2018), survival was repeated to ensure consistency with the survival curve for these experiments. The bioluminescence of BCG lux steadily decreased over the first 72 h of infection as the bacteria likely succumbed to the initial larval innate immune response. However, between 72 and 168 h pi, the reduction in bioluminescence became more gradual and plateaued by 168 h pi. These observations, consistent with our previous data (Li et al., 2018), indicate that by 72 to 96 h pi, BCG lux had evaded the larval innate immune response and established a persistent infection. Survival of BCG lux (1 x 105 CFU) was monitored similarly; at this lower dose RLU continued to decline until 96 h, where a slight increase in RLU was observed at 168 h pi (Supplementary Figure 1).
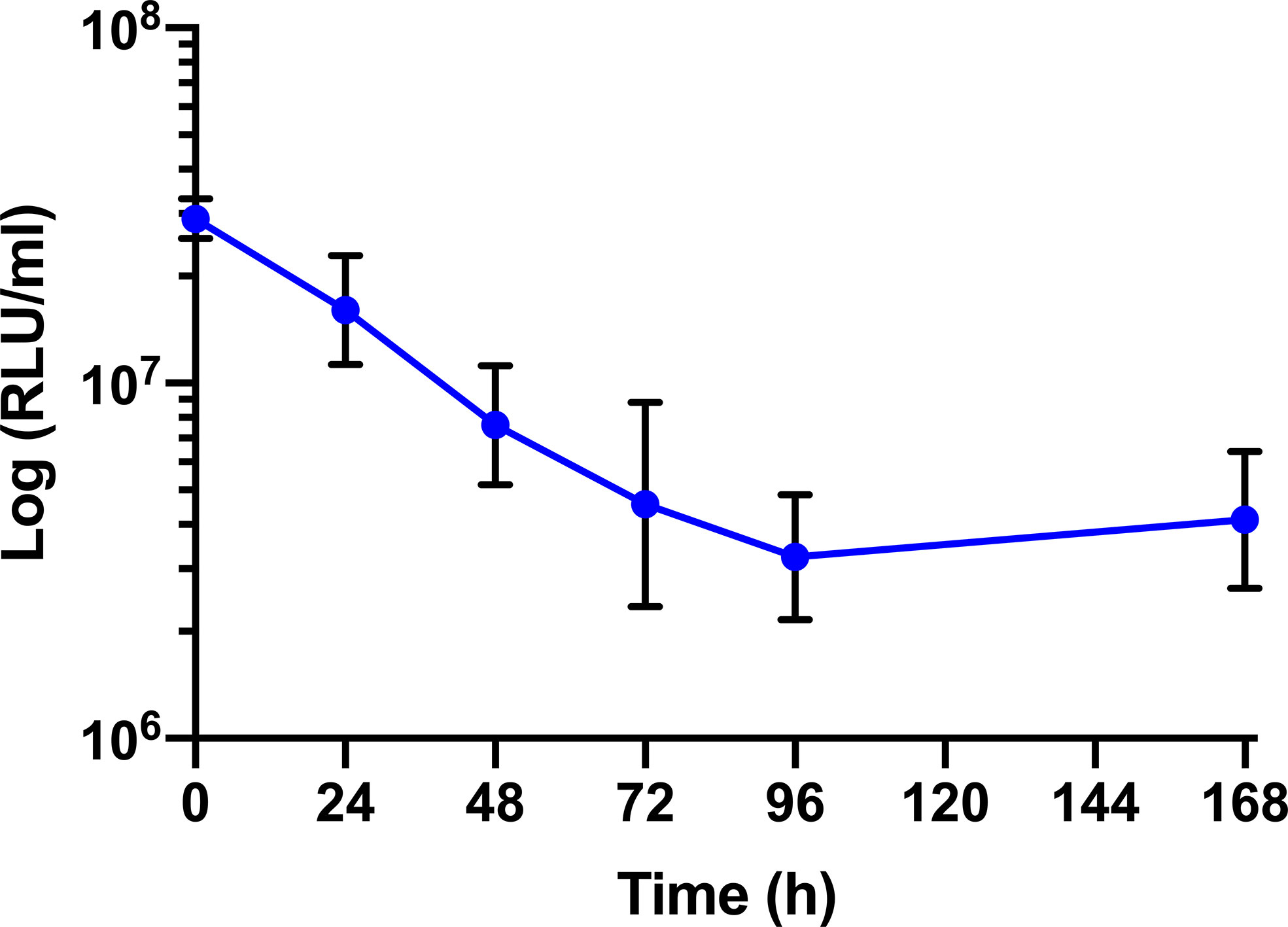
Figure 3 In vivo survival of BCG lux in G. mellonella. Changes in BCG lux bioluminescence (relative light units, RLU) within G. mellonella following infection (1 x 107 CFU) over a 168 h time course. Data represent three independent experiments each with five technical replicates. Plotted are the mean and the standard deviation of the mean. RLU : CFU is approximately 4:1 as previously described by Li et al., 2018.
Analysis of G. mellonella Proteome Following Infection With BCG lux
LFQ proteomic analysis was carried out on larval cell free haemolymph extracted from BCG lux (1 x 107 CFU) infected larvae at 4, 48, and 168 h pi, and the proteomic profiles were compared to that of 0 h control (naïve larvae). A total of 2013 peptides were identified representing 185 proteins with two or more peptide matches, of which 104 proteins were found at all time points. A number of differentially abundant proteins (ANOVA, p < 0.05), with a fold change of > ± 1.5 were found, i.e., 6 at 4 h pi, 54 at 48 h pi, and 86 at 168 h pi, and a total 11 proteins were deemed exclusive (LFQ signal found in all replicates of a given time point). These exclusive proteins were used in statistical analysis following imputation of the zero value as described in the methodology. Principal component analysis (PCA) of filtered proteins clearly distinguished the proteome of each time point, and clustered independent replicates of each time point together (Figure 4). The full list of differentially abundant proteins is available in Supplementary Tables 1–6.
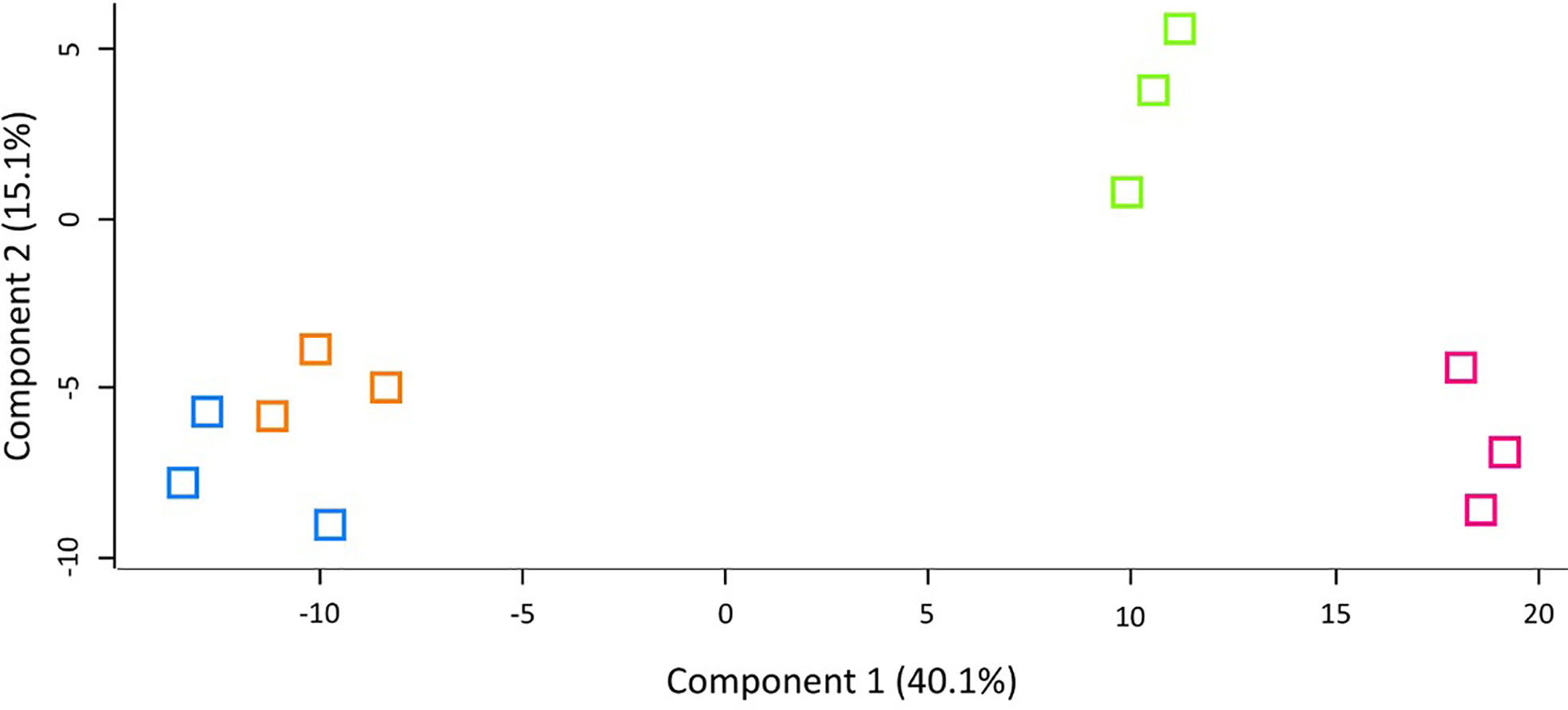
Figure 4 Principal component analysis (PCA) of G. mellonella haemolymph proteomic profiles following infection with BCG lux inoculum (1 x 107 CFU) after 0 h (blue), 4 h (orange), 48 h (green), and 168 h (pink). Number of larvae/time point/replicate n=10. PCA of three replicates included in label free quantification analysis with a clear distinction between each time point.
At 4 h pi with BCG lux, β-actin (+3.5 fold), hemolin (+2.2 fold) and arginine kinase (+1.6 fold) were found differentially more abundant in larval haemolymph compared to 0 h. Tubulin alpha chain (-2.4 fold), and heat shock protein 25.4 (-1.7 fold) were differentially less abundant in the larval haemolymph compared to 0 h (Figure 5A).
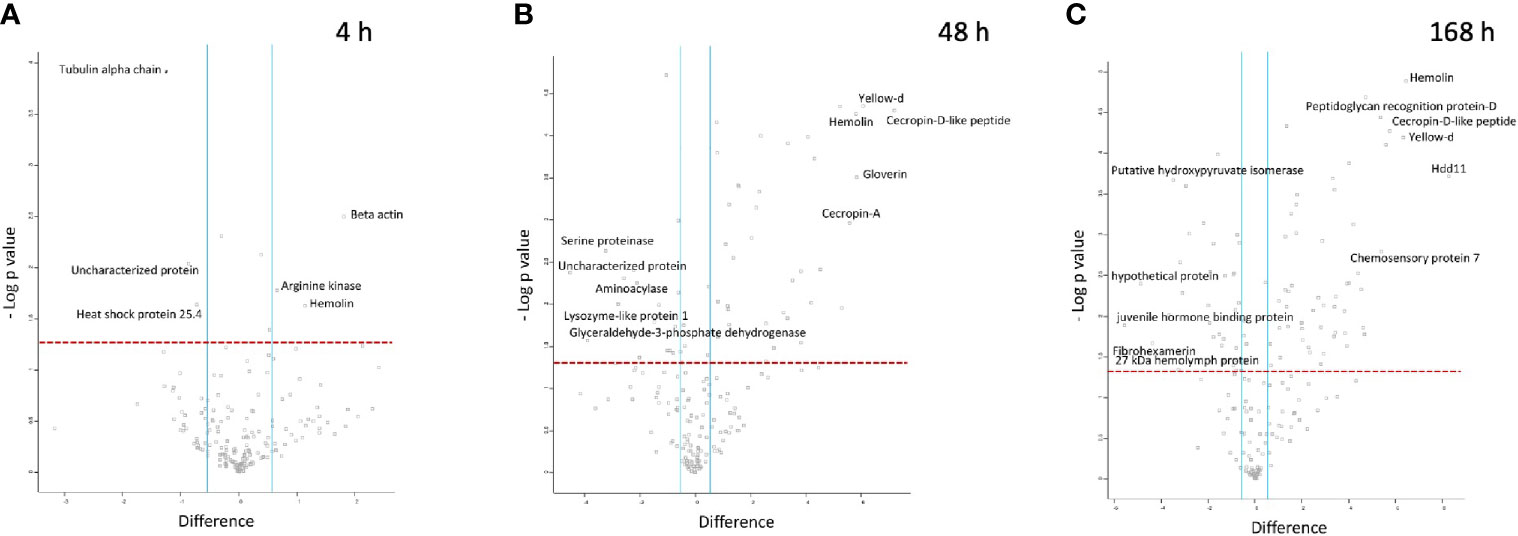
Figure 5 Proteomic responses of G. mellonella larvae following infection by BCG lux (1 x 107 CFU) after 4 h (A), 48 h (B), and 168 h (C). Volcano plots represent protein intensity difference (- log2 mean intensity difference) and significance in differences (- log P-value) based on a two-sided t-test. Proteins above the red dashed line are considered statistically significant (p value < 0.05) and those to the right and left of the vertical blue lines indicate relative fold changes > ± 1.5. These plots are based upon post imputed data. Each independent experiment consists of pooled haemolymph collected from 10 larvae. Data represent 3 independent experiments.
Larval proteins, which increased in relative abundance 48 h pi when compared to 0 h were cecropin-D-like peptide (+145.2 fold), gloverin (+56.3 fold), hemolin (+55.7 fold), cecropin-A (+47.5 fold), putative defence protein Hdd11 (+18.3 fold), serpin-4B (+14 fold), prophenoloxidase activating enzyme 3 (+14 fold), insect metalloproteinase inhibitor (+11.5 fold), serpin-11 (+5.9 fold), transgelin (+4.6 fold), Hdd-1 like protein (+2.9 fold), serpin-3a (+2.3 fold). Proteins which decreased in relative abundance 48 h pi were GAPDH (-14.7 fold), serine proteinase (-9.4 fold), lysozyme-like protein 1 (-4.74 fold), scolexin (-2.1 fold), and 27 kDa haemolymph protein (-1.9 fold) (Figure 5B).
Larval proteins which were increased in relative abundance at 168 h pi when compared to 0 h were putative defence protein Hdd11 (+310.1 fold), hemolin (+87.8 fold), cecropin-D-like peptide (+54.42 fold), chemosensory protein 7 (+42.2 fold), transgelin (+26.6 fold), prophenoloxidase activating enzyme 3 (+24.6 fold), serpin-4B (+20.9 fold), cecropin-A (+16.3 fold), serpin-11 (+15.1 fold), hdd1 (+10.8 fold), serpin-2 (+10.3 fold), gloverin (+7.61 fold), serpin-3a (+2.6 fold). Proteins which decreased in relative abundance 169 h pi were 27 kDa haemolymph protein (-9.6 fold), serine proteinase (-9.1 fold), GAPDH (-7.7 fold), scolexin (-1.9 fold), and apolipophorin (-1.7 fold) (Figure 5C).
BCG lux Proteins Detected in G. mellonella Haemolymph
LFQ proteomics analysis additionally identified 15 BCG lux proteins within the haemolymph of the infected larvae during the 168 h time course. At 4 h pi, ribonuclease VapC, 2,3 bisphosphoglycerate-dependent phosphoglycerate mutase, diacylglycerol O-acyltransferase, and adenosylhomocysteinase were detected. At 48 h pi, molybdoperin, acyl-CoA dehydrogenase (FadE23), and an uncharacterised protein containing an undecaprenyl diphosphate synthase domain were detected. However, no proteins with a known function associated with virulence, intracellular metabolism or survival, were detected at 168 h pi. A list of detected BCG lux proteins is available in Supplementary Table 7. The relative abundance of these proteins could not be determined, and these data are qualitative observations.
G. mellonella Gene Expression Following BCG lux Infection
G. mellonella larvae were challenged with high (1 x 107 CFU) and low (1x105 CFU) doses of BCG lux. Over a 168 h time course, the expression of five genes of the G. mellonella innate immune system were measured at 4, 48, and 168 h pi, via RT-qPCR using the ΔΔCt method, ubiquitin as the housekeeping gene, and naïve non-infected larvae as the reference. Expression of the house keeping gene ubiquitin and four others encoding proteins that were differentially expressed in the proteomic analysis, i.e., hemolin, IMPI, gloverin, and cecropin, were measured. Hemolin, and its encoded protein, was found to be differentially abundant at all time points, IMPI, and its encoded protein, was found in relatively consistent abundance at 48 and 168 h pi, as was Hdd11 and its encoded protein, which is of interest as it is involved in the formation of granuloma-like structures, which are a hallmark of TB infection (Sheehan et al., 2020b). For all five genes tested, the high dose BCG lux infection induced greater gene expression/suppression at all time points when compared to the low dose (Supplementary Figure 2). While none were statistically significant, all genes displayed a trend of reduction of gene expression over time. Gloverin and cecropin encode AMPs induced in G. mellonella in response to a number of bacterial and fungal pathogens (Tsai et al., 2016). The gene expression for the AMPs, gloverin, and cecropin, in response to high dose infection, significantly decreased between 4 h and 48 h pi (p < 0.0001). However, the level of gene expression was lower but of similar levels between 48 and 168 h pi for both genes (Figures 6A, B). For low dose expression gloverin, expression continued to decrease significantly between 4, 48, and 168 h pi (p < 0.0001), while cecropin mirrored high dose infection but at significantly lower levels of gene expression (Figures 6A, B, Supplementary Figures 2A, B). For the hemolin gene, high dose infection induced statistically significant reduction in gene expression between 48 and 168 h pi (Figure 6C) (p < 0.01). No significant reduction in gene expression was observed in low dose infection. High dose infection resulted in statistically significant higher levels of gene expression at all time points when compared to low dose infection (Supplementary Figure 2C) (P < 0.001 for 4 and 48 h pi and P < 0.05 for 168 h pi). For Hdd11, high dose infection induced greater levels of gene expression with a trend of reduction for all time points (Figure 6D and Supplementary Figure 2D). Finally, for the IMPI gene, induction of gene expression followed high dose infection and thereafter steadily decreased over time (Figure 6E), with apparent suppression between 48 and 168 h pi (p < 0.0001). Low dose infection led to a sustained level of gene induction between 4 and 48 h pi, and a reduced substantial gene suppression between 48 and 168 h pi (p < 0.01).
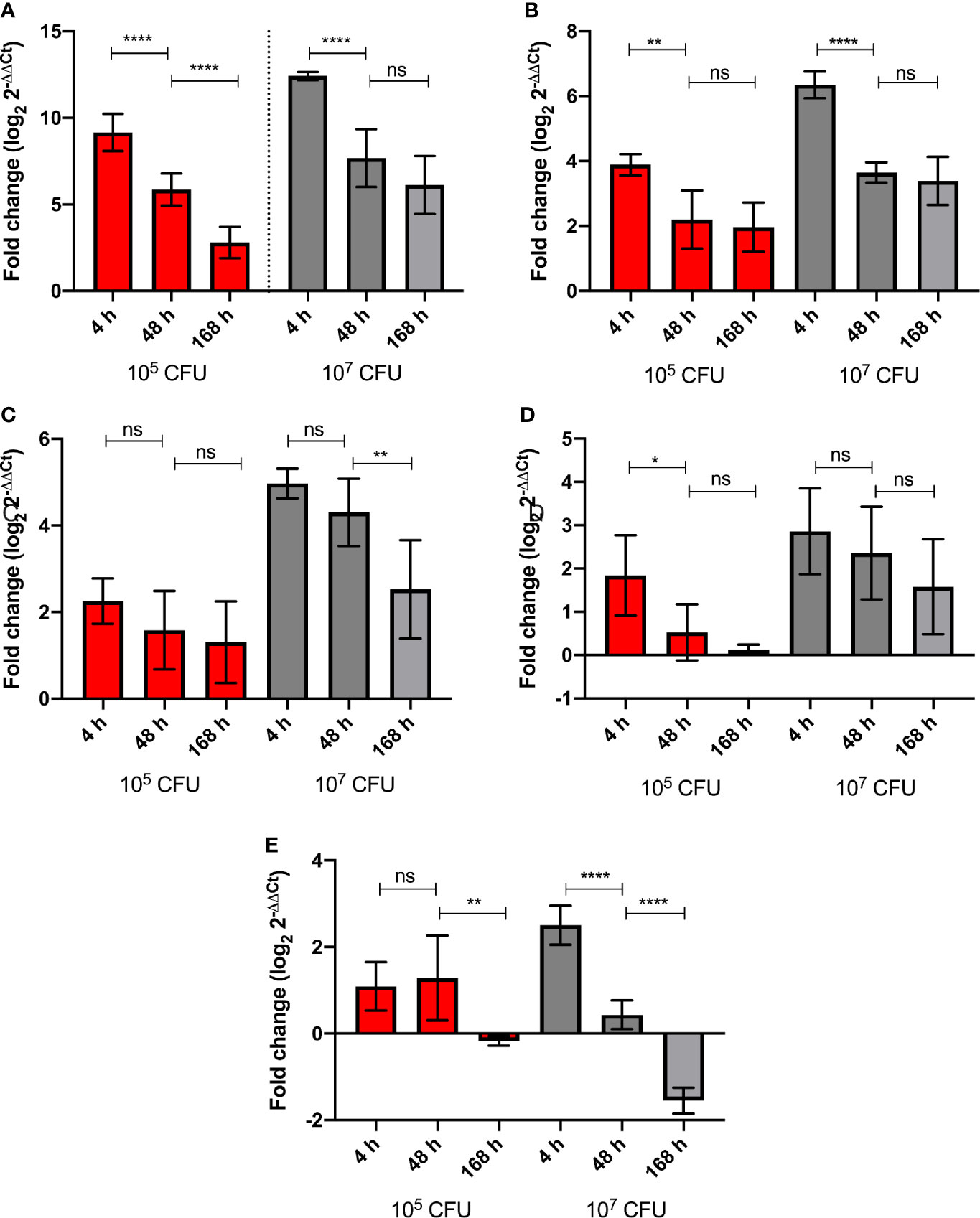
Figure 6 Level of G. mellonella gene expression was measured by RT-qPCR from RNA of larvae challenged with either low dose (105 CFU, red) or high dose (107 CFU, grey) BCG lux at 4, 48, and 168 h pi. The comparative ΔΔCt method was used for relative quantification of (A) gloverin, (B) cecropin, (C) hemolin, (D) Hdd11, and (E) IMPI using ubiquitin as a housekeeping gene. Data represent three independent experiments, each with RNA extracted from five larvae, which was pooled. Each independent experiment consisted of three technical repeats. Bar charts represent changes in gene expression expressed as fold change. Comparison of gene expression with each infectious dose over time was carried out using the Mann-Whitney U test; where *,**,****, and ns signifies p < 0.05, 0.01, 0.0001 and non-significant, respectively.
Discussion
Previously we described, using survival curves, bacterial counts, and electron microscopy, a BCG lux - G. mellonella infection model for the MTBC complex (Li et al., 2018; Asai et al., 2019a; Asai et al., 2019b). The aim of this study was to increase our understanding of the host-bacterial interactive biology, focusing on innate immunity, through proteomic and gene expression analyses. To accommodate the increased incubation period in this study, larval survival and changes in BCG lux load in vivo over the 168 h time course were examined, which was consistent with expected observations extrapolated from our prior studies (Li et al., 2018; Asai et al., 2019a; Asai et al., 2019b). Using this established model of BCG persistence, we characterised the larval innate immune response to BCG lux (1 x 107 CFU) at 4 h, 48 h, and 168 h pi using LFQ proteomics. Distinct changes in larval proteome in response to infection at all three time points were found, with the least changes in differentially abundant proteins being at 4 h pi.
Hemolin, a member of the immunoglobulin super family (Eleftherianos et al., 2007), was found to be more abundant in the infected larvae at all time points with increasing abundance over time, 4 h (+2.2 fold) 48 h (+55.7 fold) and 168 h (+87.8 fold) pi. Hemolin aids haemocyte aggregation and phagocytosis of foreign cells through recognition of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and lipoteichoic acid (LTA) of Gram-negative and -positive bacteria, as well as fungal β-1,3-glucan (Eleftherianos et al., 2007; Jung et al., 2019). Hemolin opsonizes microbial pathogens and binds to haemocytes, enhancing phagocytic uptake and eliminating invading pathogens (Aathmanathan et al., 2018). The interaction of hemolin with the structurally unique mycobacterial cell wall has not been described. However, as hemolin is able to recognize microbial molecular signatures, we speculate that G. mellonella hemolin may detect lipoglycans (noncanonical type V LTA) found in abundance on the mycobacterial cell wall (Mishra et al., 2011); this will be investigated in a future study.
As an intracellular pathogen, exploiting innate immune mechanisms to increase phagocytic uptake would be beneficial to mycobacteria. The increased abundance of β-actin at 4 h pi (+3.5 fold), may reflect the cytoskeletal redistribution and remodelling which takes place during phagocytosis (Rougerie et al., 2013). In line with this observation, infection of primary murine epithelial and lung cells with BCG has been shown to up-regulate actin redistribution (Alaridah et al., 2017). Studies of early granuloma structures in larval zebrafish found extensive reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton in granulomatous macrophages (Cronan et al., 2016). Therefore, the abundance of β-actin at 48 h and 168 h pi (+5.0 and +18.6 fold) may reflect haemocyte actin reorganization within developing granuloma-like structures. The presence and increasing abundance of β-actin in the cell-free haemolymph over time, likely reflects the equilibrium between live and dead host-cells in the granuloma-like structure (Cronan et al., 2018), with necrotic and/or lytic haemocytes likely releasing β-actin into the haemolymph.
AMPs were induced following infection with BCG lux. Cecropin A, cecropin-D-like protein, and gloverin were differentially more abundant than at 0 h at both 48 h and 168 h pi, but not at 4 h pi. Cecropins are amphipathic α-helical AMPs, reported to be effective against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria by permeating the bacterial cell wall (Zdybicka-Barabas et al., 2019). Gloverin is a glycine rich AMP efficacious against filamentous fungi and Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria (Wojda, 2017). As a relative comparison, gloverin (+121.7 fold), cecropin-D-like peptide (+73.7 fold), and cecropin-A (+10.56 fold) were also more abundant in larvae infected with 2 x 106 CFU of S. aureus 24 h pi (Sheehan et al., 2019). BCG lux infection led to increased expression of cecropin-D-like peptide (+145.2 fold), gloverin (+56.3 fold), and cecropin-A (+47.5 fold) at 48 h pi. Although variance in the infectious dose and time point complicates comparisons, the higher abundance of gloverin in response to a lower infectious dose of S. aureus may indicate that gloverin is preferentially expressed in the presence of Gram-positive bacteria, or alternatively the higher abundance of cecropin-D-like peptide may indicate BCG lux is a more potent inducer. In mammals, cathelicidins, cationic α-helical AMPs, are released by leukocytes in response to infection (Arranz-Trullén et al., 2017). The human cationic antimicrobial peptide 18 (h-CAP-18) is the leading AMP in TB therapeutics, with both bactericidal and immunomodulating activity (Arranz-Trullén et al., 2017). Immunomodulation of macrophages and neutrophils by LL-37, a proteolyzed component of h-CAP-18, has been reported during infection, such as the promotion of autophagy in human monocytes (Arranz-Trullén et al., 2017). A previous report indicates that Cecropin-A induces immunomodulating activity in macrophages, regulating inflammatory responses (Lee et al., 2015a). If similar activities occur in phagocytic haemocytes, then increased abundance of hemolin and cytoskeletal actin could result from upregulation of autophagy-related activities. The production of synthetic cecropin-D-like peptides has been reported (Correa et al., 2014b; Correa et al., 2014a). Cytotoxicity of cecropin-D-like peptides, has previously been determined against erythrocytes with haemolysis of 2.3% at 115 µM (Oñate-Garzón et al., 2017). Cecropin-D-like peptides have shown antimicrobial activity against Gram-positive (S. aureus) and negative (Pseudomonas aeruginosa and E. coli) bacteria through permeabilization and disruption of the cell membrane (Cytryńska et al., 2007; Oñate-Garzón et al., 2017). Therefore, in vitro drug screening against mycobacteria using synthetic G. mellonella AMPs, may reveal promising antimycobacterial properties.
Hdd11 (homologous to Noduler) is associated with the formation of nodules or granuloma-like structures; facilitated by crosslinking pathogens and haemocytes by Hdd11 (Gandhe et al., 2007; Sheehan et al., 2020b). In line with published histopathology data from BCG lux infected G. mellonella larvae (Li et al., 2018), where numbers of granuloma-like structures increased over time, the abundance of Hdd11 within the haemolymph increased +18.3 and +310 fold compared to 0 h, as infection progressed at 48 h and 169 h pi, respectively. The fungal granulomatous disease, mycetoma, caused by M. mycetomatis has been modelled using G. mellonella larvae. In larvae infected with M. mycetomatis, Hdd11 was +533 fold more abundant within the haemolymph at 168 h pi when compared to 0 h (Sheehan et al., 2020b). Although Hdd11 levels are higher in M. mycetomatis infection, this indicates that BCG lux induces a similar granulomatous response. Formation of early granuloma in humans is tightly regulated by the interaction between matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and tissue inhibitors of MMPs (TIMPs) (Parasa et al., 2017). IMPI, found differentially abundant at 48 h and 168 h pi, is an insect metalloproteinase inhibitor, but has no structural similarities to vertebrate or invertebrate TIMPs (Vilcinskas and Wedde, 2002). IMPI does not inhibit host MMP activity, its primary function is to inhibit microbial metalloproteinases. However, IMPI can additionally regulate endogenous metalloproteinases involved in metamorphosis and thereby, depending on the life stage of the larvae, potentially impact on the larval tissue response to infection (Wedde et al., 2007). MMPs and TIMPs have been identified in fruit flies, and it is likely similar systems exist in G. mellonella (Vilcinskas and Wedde, 2002). The challenge remains in identifying these systems, as the publicly available genome of G. mellonella is yet to be fully annotated (Lange et al., 2018a).
Another key invertebrate innate immune response is melanization, modulated through the PO cascade (Dubovskiy et al., 2013). Proteins associated with the PO cascade were more abundant at 48 h pi (phenoloxidase activating enzyme 3, serpin-3a, serpin-4b, and serpin-11) and 168 h pi (phenoloxidase activating enzyme 3, serpin-2, serpin-3a, serpin-4b, and serpin-11), but not at 4 h pi. In contrast, larvae challenged with a lower infectious dose of S. aureus (2 x 106 CFU) induced more abundant levels of phenoloxidase activating enzyme 3 and serpin-4b by 6 h pi compared to the 0 h control (Sheehan et al., 2019). This may reflect the more virulent or rapid growth of S. aureus, as the rate of mortality was 90% by 72 h pi (Sheehan et al., 2019). Previous studies using the G. mellonella – BCG lux infection model, found slow gradual melanization over 96 h, with little to no melanization within the first 24 h (Asai et al., 2019a). Serpins, a class of protease inhibitor which negatively regulates the PO cascade (Lu et al., 2014), were detected in response to BCG lux infection. We speculate that the lack of abundant PO cascade proteins at 4 h pi and the rate of larval melanization, reflects the slow growth and persistence of BCG lux infection leading to host modulation of the PO cascade to prevent uncontrollable melanization.
While distinct changes in proteomic signatures over the time course were detected, changes specific to mycobacteria infection were not identified. Despite the lack of a BCG specific response, G. mellonella larvae immunized with a non-lethal dose of BCG lux (1x105 CFU), 48 h prior to infection with a lethal dose of BCG lux (2x107 CFU), resulted in improved survival outcome when compared to the non-immunized control. This observation, commonly referred to as immune priming, has widely been reported in invertebrate infection models (Bergin et al., 2006; Sadd and Schmid-Hempel, 2006; Pham et al., 2007; Sheehan et al., 2020a). The precise mechanism, of how a non-lethal exposure to a pathogen leads to protection/immunity, remains unclear with a number of mechanisms being suggested (Sheehan et al., 2020a). However, it is known that non-lethal exposure typically leads to an increase in the number of circulating haemocytes and the production of AMPs (Bergin et al., 2006). Moreover, it is unclear as to whether these responses are pathogen type/class specific or are more generalized. Therefore, future studies will focus on whether immunization with non-lethal BCG dose leads to primed protection against other mycobacterial species, Gram-positive/negative bacteria and fungi.
LFQ proteomics analysis identified BCG lux proteins within the larval haemolymph giving qualitative insight into the response of the larval innate immune system. Most proteins detected were associated with intracellular adaptations and survival. At 4 h pi, proteins were associated with metabolic changes. These included: ribonuclease VapC and 2,3 bisphosphoglycerate-dependent phosphoglycerate mutase, both of which have been associated with regulation of metabolism in response to intracellular conditions and glucogenesis (Hillion et al., 2017; Sharrock et al., 2018). Adenosylhomocysteinase catalyses the reversible processing of S-adenosylmethionine dependent methyltransferase reaction and is essential for in vitro growth, and was upregulated in lung tissues of MTB infected mice (Singhal et al., 2012). Diacylglycerol O-acyltransferase is involved in the accumulation of triacylglycerol in MTB under stress (Sirakova et al., 2006). The presence of diacylglycerol O-acyltransferase is in agreement with the accumulation of lipid droplet structures in BCG lux in vivo in G. mellonella which have been observed using transmission electron microscopy (Li et al., 2018). At 48 h pi, proteins associated with intracellular survival were detected. Molybdoperin is induced in response to hypoxia and nitric oxide stress (Wang et al., 2013). Acyl-CoA dehydrogenase induced in response to cell envelope damage following oxidative and nitrosative stress, may have a role in recycling of fatty acids (Voskuil, 2013). An uncharacterised protein with an undecaprenyl diphosphate synthase domain, typically associated with cell wall synthesis was detected (Kaur et al., 2004). Abundance of this protein may be associated with thickening of the mycobacterial cell wall as a stress response to intracellular conditions (Ghazaei, 2018). Similar to 4 h pi, diacylglycerol O-acyltransferase was also detected at 48 h pi. These proteins in the haemolymph may be associated with MTB extracellular vesicles, as both diacylglycerol O-acyltransferase and acyl-CoA dehydrogenase have been detected in such structures. (Lee et al., 2015b). The presence of BCG lux proteins involved in intracellular adaptation and survival at 4 and 48 h pi indicate that the haemocytic environment is a mycobacterial stress-inducer.
The G. mellonella innate immune response to BCG lux was also investigated using RT-qPCR. The results show that infection with BCG lux at high (1 x 107 CFU) and low (1x105 CFU) doses, led to differential gene expression of innate immune genes, with higher dose infection inducing more substantial changes. Changes in gene expression were detected in gloverin, cecropin, IMPI, hemolin, and Hdd11 regardless of infectious dose when compared to the 0 h control. Induction of expression was highest at 4 h pi, and thereafter decreased over the time course despite the presence of a persistent infection. Similar observations were made in an RT-qPCR study of G. mellonella innate immune responses to infection with Riemerella anatipestifer, a Gram-negative bacterium, where genes involved in innate immunity (e.g., encoding AMPs and opsonin), were highest at 4 h pi, and declined over time (Liu et al., 2019). In this study, the trend between the presence of protein and the corresponding mRNA improved over the course of infection, but the abundance of protein was largely inconsistent with gene expression signals, with only 20% in agreement between 48-168 h pi. Proteins induced by genes expression at 4 h pi were mostly undetected in the proteomic analysis with the exception to hemolin. The discrepancy between the two datasets may be attributed to the preparation of the samples. The proteomic study was carried out on cell free haemolymph, whereas the gene expression study was carried out on mRNA prepared from the whole larva. Gene expression studies in both humans (Sonawane et al., 2017) and insects, Manduca sexta (Cao and Jiang, 2017) and Ceracris nigricornis Walker (Yuan et al., 2019), have highlighted the importance of acknowledging tissue specific expression of genes. It is unknown whether the genes examined in this study are expressed globally or are tissue specific. Nevertheless, the comparison of proteomics and transcriptomics has been an ongoing subject of discussion. A study that compared the correlation of proteome and transcriptome across developmental stages of fruit flies (Becker et al., 2018) and Epicauta chinensis (blister beetle) (Li et al., 2014) reported a low correlation (20%–34%) between mRNA levels and protein expression. Becker et al. 2018 adjusted for the translational delay of mRNA into protein (~ 4-6 h) for a small subset of genes in fruit flies, which showed modest improvements (+2.4%). This supports the idea that there are lags between the initiation of gene expression and protein biosynthesis, possibly due to the basal mRNA state (steady, long/short-term), downstream gene regulation, post-transcriptional modification to mRNA, and/or availability of biosynthetic material (Liu et al., 2016). Studies have determined that the correlation between these two Omics approaches, are modest at best (40%) (Gygi et al., 1999; Kumar et al., 2016), with correlation decreasing with increasing biological complexity, i.e., single cellular to multi-cellular organisms (Gygi et al., 1999; De Sousa Abreu et al., 2009; Schwanhüusser et al., 2011; Kumar et al., 2016; Meir et al., 2018). Furthermore, a comparative proteomic and transcriptomic study of 29 human tissue types revealed that a number of protein molecules synthesised per highly abundant transcript were near quadratic (Wang et al., 2019). It is generally speculated that abundance of protein/gene is regulated at the translational level through enhanced translational efficiency and protein stability (Vogel et al., 2010). The presentation of both the gene expression and proteomic data in this paper is the first of its kind for G. mellonella. We acknowledge that the number of genes tested are limited and a more comprehensive analysis to determine a broader correlation between transcriptome and proteome of G. mellonella is warranted in the future. As proteomics investigates the presence/absence and relative abundance of a protein, it is a more reliable indicator of the state of the innate immune response of G. mellonella at a given time point.
In conclusion, to our knowledge, this is the first report of the innate immune response of G. mellonella to mycobacterial infection using molecular transcriptomic and proteomic approaches. The proteomic profiles were unique over the course of infection. Responses were similar to those in G. mellonella infected with fungal granulomatous infectious disease. BCG lux proteins were detected, associated with intracellular survival and metabolism in vertebrate hosts, indicating that G. mellonella induces similar stress responses. RT-qPCR confirmed the proteomic analysis. However, gene expression and protein abundance was not always in agreement, and careful comparison of data should be made in future studies. Several targets for further studies, such hemolin as an opsonising agent and cecropin as an antimycobacterial agent, were identified and will be further investigated. While this study focused on the host response to infection, future studies will evaluate the mycobacterial response to humoral innate immunity of G. mellonella. The data presented here provide a vital insight into the G. mellonella – mycobacterial infection model and highlights its value for accelerating in TB research.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found in the article/Supplementary Material.
Author Contributions
MA, GS, YL, BR, KK, PL, and SN conceptualized the study. MA drafted the manuscript. MA, GS, and YL carried out the experimental procedures. MA and GS carried out experimental analysis. MA, GS, YL, BR, KK, PR, and SN reviewed, edited, and approved the manuscript for submission. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Centre (BBSRC) [BB/P001262/1] to PL and YL, and the National Centre for the Replacement, Refinement and Reduction of Animals in Research (NC3Rs) [NC/R001596/1] to PL, SN, BR, and YL. GS is the recipient of a Maynooth University doctoral studentship. The Q-exactive mass spectrometer was funded under the Science Foundation Ireland (SFI) Research Infrastructure Call 2012, [12/RI/2346] (3). This publication emanated from research supported in part by a research grant from the SFI and is co-funded under the European Regional Development Fund [12/RC/2275_P2].
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcimb.2021.619981/full#supplementary-material
Abbreviations
AMP, Antimicrobial peptides; BCG, Bacillus Calmette-Guérin; IMPI, Insect metalloproteinase inhibitor; LFQ, Label free quantification; MTB, Mycobacterium tuberculosis; MTBC, Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex; NTM, Non-tuberculous mycobacterium; PAMP/DAMP, Pathogen/damage associated molecular patterns; PPR, Pattern recognition receptors; PO, Phenoloxidase; ROS, Reactive oxygen species; RT-qPCR, Reverse transcriptase quantitative PCR; TB, Tuberculosis.
References
Aathmanathan V. S., Jothi N., Prajapati V. K., Krishnan M. (2018). Investigation of immunogenic properties of Hemolin from silkworm, Bombyx mori as carrier protein: An immunoinformatic approach. Sci. Rep. 8, 6957. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-25374-z
Alaridah N., Lutay N., Tenland E., Rönnholm A., Hallgren O., Puthia M., et al. (2017). Mycobacteria manipulate G-Protein-coupled receptors to increase mucosal Rac1 expression in the lungs. J. Innate Immun. 9, 318–329. doi: 10.1159/000453454
Alghoribi M. F., Gibreel T. M., Dodgson A. R., Beatson S. A., Upton M. (2014). Galleria mellonella infection model demonstrates high lethality of ST69 and ST127 uropathogenic Escherichia coli. PLoS One 9, e101547. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0101547
Altaf M., Miller C. H., Bellows D. S., O’Toole R. (2010). Evaluation of the Mycobacterium smegmatis and BCG models for the discovery of Mycobacterium tuberculosis inhibitors. Tuberculosis 90, 333–337. doi: 10.1016/j.tube.2010.09.002
Arranz-Trullén J., Lu L., Pulido D., Bhakta S., Boix E. (2017). Host antimicrobial peptides: The promise of new treatment strategies against tuberculosis. Front. Immunol. 8, 1499. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01499
Asai M., Li Y., Singh Khara J., Gladstone C. A., Robertson B. D., Langford P. R., et al. (2019a). Use of the invertebrate Galleria mellonella as an infection model to study the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex. J. Vis. Exp. 148, e59703. doi: 10.3791/59703
Asai M., Li Y., Singh Khara J., Robertson B. D., Langford P. R., Newton S. M. (2019b). Galleria mellonella: an infection model for screening compounds against the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex. Front. Microbiol. 10, 2630. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02630
Asai M., Li Y., Spiropoulos J., Cooley W., Everest D., Robertson B. D., et al. (2020). A novel biosafety level 2 compliant tuberculosis infection model using a ΔleuDΔpanCD double auxotroph of Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv and Galleria mellonella. Virulence 11, 811–824. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2020.1781486
Avdesh A., Chen M., Martin-Iverson M. T., Mondal A., Ong D., Rainey-Smith S., et al. (2012). Regular care and maintenance of a Zebrafish (Danio rerio) laboratory: An introduction. J. Vis. Exp. 69, e4196. doi: 10.3791/4196
Becker K., Bluhm A., Casas-Vila N., Dinges N., Dejung M., Sayols S., et al. (2018). Quantifying post-transcriptional regulation in the development of Drosophila melanogaster. Nat. Commun. 9, 4970. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-07455-9
Benjamini Y., Hochberg Y. (1995). Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. R. Stat. Soc Ser. B 57, 289–300. doi: 10.1111/j.2517-6161.1995.tb02031.x
Bergin D., Murphy L., Keenan J., Clynes M., Kavanagh K. (2006). Pre-exposure to yeast protects larvae of Galleria mellonella from a subsequent lethal infection by Candida albicans and is mediated by the increased expression of antimicrobial peptides. Microbes Infect. 8, 2105–2112. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2006.03.005
Brosch R., Gordon S. V., Garnier T., Eiglmeier K., Frigui W., Valenti P., et al. (2007). Genome plasticity of BCG and impact on vaccine efficacy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 104, 5596–5601. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0700869104
Cao X., Jiang H. (2017). An analysis of 67 RNA-seq datasets from various tissues at different stages of a model insect, Manduca sexta. BMC Genomics 18, 796. doi: 10.1186/s12864-017-4147-y
Correa W., Manrique-Moreno M., Behrends J., Patiño E., Marella C., Peláez-Jaramillo C., et al. (2014a). Galleria mellonella native and analogue peptides Gm1 and ΔGm1. II) Anti-bacterial and anti-endotoxic effects. Biochim. Biophys. Acta - Biomembr. 1838, 2739–2744. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2014.07.005
Correa W., Manrique-Moreno M., Patiño E., Peláez-Jaramillo C., Kaconis Y., Gutsmann T., et al. (2014b). Galleria mellonella native and analogue peptides Gm1 and ΔGm1. I) Biophysical characterization of the interaction mechanisms with bacterial model membranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta - Biomembr. 1838, 2728–2738. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2014.07.006
Cronan M. R., Beerman R. W., Rosenberg A. F., Saelens J. W., Johnson M. G., Oehlers S. H., et al. (2016). Macrophage epithelial reprogramming underlies mycobacterial granuloma formation and promotes infection. Immunity 45, 861–876. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2016.09.014
Cronan M. R., Matty M. A., Rosenberg A. F., Blanc L., Pyle C. J., Espenschied S. T., et al. (2018). An explant technique for high-resolution imaging and manipulation of mycobacterial granulomas. Nat. Methods 15, 1098–1107. doi: 10.1038/s41592-018-0215-8
Cytryńska M., Mak P., Zdybicka-Barabas A., Suder P., Jakubowicz T. (2007). Purification and characterization of eight peptides from Galleria mellonella immune hemolymph. Peptides 28, 533–546. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2006.11.010
De Sousa Abreu R., Penalva L. O., Marcotte E. M., Vogel C. (2009). Global signatures of protein and mRNA expression levels. Mol. Biosyst. 5, 1512–1526. doi: 10.1039/b908315d
Dubovskiy I. M., Whitten M. M. A., Kryukov V. Y., Yaroslavtseva O. N., Grizanova E. V., Greig C., et al. (2013). More than a colour change: Insect melanism, disease resistance and fecundity. Proc. R. Soc B Biol. Sci. 280, 20130584. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2013.0584
Dubovskiy I. M., Grizanova E. V., Whitten M. M. A., Mukherjee K., Greig C., Alikina T., et al. (2016). Immuno-physiological adaptations confer wax moth Galleria mellonella resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis. Virulence 7, 860–870. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2016.1164367
Eleftherianos I., Gökçen F., Felföldi G., Millichap P. J., Trenczek T. E., Ffrench-constant R. H., et al. (2007). The immunoglobulin family protein Hemolin mediates cellular immune responses to bacteria in the insect Manduca sexta. Cell. Microbiol. 9, 1137–1147. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2006.00855.x
Entwistle F. M., Coote P. J. (2018). Evaluation of greater wax moth larvae, Galleria mellonella, as a novel in vivo model for non-tuberculosis mycobacteria infections and antibiotic treatments. J. Med. Microbiol. 67, 585–597. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.000696
Gandhe A. S., John S. H., Nagaraju J. (2007). Noduler, a novel immune up-regulated protein mediates nodulation response in insects. J. Immunol. 179, 6943–6951. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.179.10.6943
Ghazaei C. (2018). Mycobacterium tuberculosis and lipids: Insights into molecular mechanisms from persistence to virulence. J. Res. Med. Sci. 23, 63. doi: 10.4103/jrms.JRMS_904_17
Graham M. L., Prescott M. J. (2015). The multifactorial role of the 3Rs in shifting the harm-benefit analysis in animal models of disease. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 795, 19–29. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2015.03.040
Gygi S. P., Rochon Y., Franza B. R., Aebersold R. (1999). Correlation between protein and mRNA abundance in yeast. Mol. Cell. Biol. 19, 1720–1730. doi: 10.1128/MCB.19.3.1720
Hillion M., Bernhardt J., Busche T., Rossius M., Maaß S., Becher D., et al. (2017). Monitoring global protein thiol-oxidation and protein S-mycothiolation in Mycobacterium smegmatis under hypochlorite stress. Sci. Rep. 7, 1195. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-01179-4
Hillyer J. F. (2016). Insect immunology and hematopoiesis. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 58, 102–118. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2015.12.006
Insua J. L., Llobet E., Moranta D., Pérez-Gutiérrez C., Tomás A., Garmendia J., et al. (2013). Modeling Klebsiella pneumoniae pathogenesis by infection of the wax moth Galleria mellonella. Infect. Immun. 81, 3552–3565. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00391-13
Jung J., Sajjadian S. M., Kim Y. (2019). Hemolin, an immunoglobulin-like peptide, opsonizes nonself targets for phagocytosis and encapsulation in Spodoptera exigua, a lepidopteran insect. J. Asia Pac. Entomol. 22, 947–956. doi: 10.1016/j.aspen.2019.08.002
Kaur D., Brennan P. J., Crick D. C. (2004). Decaprenyl diphosphate synthesis in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Bacteriol. 186, 7564–7570. doi: 10.1128/JB.186.22.7564-7570.2004
Kelly J., Kavanagh K. (2011). Caspofungin primes the immune response of the larvae of Galleria mellonella and induces a non-specific antimicrobial response. J. Med. Microbiol. 60, 189–196. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.025494-0
Kirubakar G., Schäfer H., Rickerts V., Schwarz C., Lewin A. (2020). Mutation on lysX from Mycobacterium avium hominissuis impacts the host-pathogen interaction and virulence phenotype. Virulence 11, 132–144. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2020.1713690
Kumar D., Bansal G., Narang A., Basak T., Abbas T., Dash D. (2016). Integrating transcriptome and proteome profiling: Strategies and applications. Proteomics 16, 2533–2544. doi: 10.1002/pmic.201600140
Lange A., Beier S., Huson D. H., Parusel R., Iglauer F., Frick J. S. (2018a). Genome sequence of Galleria mellonella (greater wax moth). Genome Announc. 6, e01220–e01217. doi: 10.1128/genomeA.01220-17
Lange A., Schäfer A., Bender A., Steimle A., Beier S., Parusel R., et al. (2018b). Galleria mellonella: A novel invertebrate model to distinguish intestinal symbionts from pathobionts. Front. Immunol. 9, 2114. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02114
Lee E., Shin A., Kim Y. (2015a). Anti-inflammatory activities of cecropin A and its mechanism of action. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 88, 31–44. doi: 10.1002/arch.21193
Lee J., Kim S. H., Choi D. S., Lee J. S., Kim D. K., Go G., et al. (2015b). Proteomic analysis of extracellular vesicles derived from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Proteomics 15, 3331–3337. doi: 10.1002/pmic.201500037
Li Q., Wang D., Lv S., Zhang Y. (2014). Comparative proteomics and expression analysis of five genes in Epicauta chinensis larvae from the first to fifth instar. PLoS One 9, e89607. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0089607
Li Y., Spiropoulos J., Cooley W., Singh Khara J., Gladstone C. A., Asai M., et al. (2018). Galleria mellonella - a novel infection model for the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex. Virulence 9, 1126–1137. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2018.1491255
Liu Y., Beyer A., Aebersold R. (2016). On the dependency of cellular protein levels on mRNA abundance. Cell 165, 535–550. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.03.014
Liu M., Huang M., Huang L., Biville F., Zhu D., Wang M., et al. (2019). New perspectives on Galleria mellonella larvae as a host model using Riemerella anatipestifer as a proof of concept. Infect. Immun. 87, e0079–e0019. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00072-19
Lu A., Zhang Q., Zhang J., Yang B., Wu K., Xie W., et al. (2014). Insect prophenoloxidase: The view beyond immunity. Front. Physiol. 5, 252. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2014.00252
Meir M., Grosfeld T., Barkan D. (2018). Establishment and validation of Galleria mellonella as a novel model organism to study Mycobacterium abscessus infection, pathogenesis, and treatment. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 62, e02539–e02517. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02539-17
Mishra A. K., Driessen N. N., Appelmelk B. J., Besra G. S. (2011). Lipoarabinomannan and related glycoconjugates: Structure, biogenesis and role in Mycobacterium tuberculosis physiology and host-pathogen interaction. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 35, 1126–1157. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2011.00276.x
Newton S., Martineau A., Kampmann B. (2011). A functional whole blood assay to measure viability of mycobacteria, using reporter-gene tagged BCG or M.Tb (BCG lux/M.Tb lux). J. Vis. Exp. 55, e3332. doi: 10.3791/3332
Oñate-Garzón J., Manrique-Moreno M., Trier S., Leidy C., Torres R., Patiño E. (2017). Antimicrobial activity and interactions of cationic peptides derived from Galleria mellonella cecropin D-like peptide with model membranes. J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 70, 238–245. doi: 10.1038/ja.2016.134
Orme I. M. (2003). The mouse as a useful model of tuberculosis. Tuberculosis 83, 112–115. doi: 10.1016/S1472-9792(02)00069-0
Painter H., Prabowo S. A., Cia F., Stockdale L., Tanner R., Willcocks S., et al. (2020). Adaption of the ex vivo mycobacterial growth inhibition assay for use with murine lung cells. Sci. Rep. 10, 3311. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-60223-y
Parasa V. R., Muvva J. R., Rose J. F., Braian C., Brighenti S., Lerm M. (2017). Inhibition of tissue matrix metalloproteinases interferes with Mycobacterium tuberculosis-induced granuloma formation and reduces bacterial load in a human lung tissue model. Front. Microbiol. 8, 2370. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.02370
Pereira T. C., de Barros P. P., de Oliveira Fugisaki L. R., Rossoni R. D., de Ribeiro F. C., de Menezes R. T., et al. (2018). Recent advances in the use of Galleria mellonella model to study immune responses against human pathogens. J. Fungi 4, E128. doi: 10.3390/jof4040128
Pham L. N., Dionne M. S., Shirasu-Hiza M., Schneider D. S. (2007). A specific primed immune response in Drosophila is dependent on phagocytes. PLoS Pathog. 3, e26. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.0030026
Reid M. J. A., Arinaminpathy N., Bloom A., Bloom B. R., Boehme C., Chaisson R., et al. (2019). Building a tuberculosis-free world: The Lancet Commission on tuberculosis. Lancet 393, 1331–1384. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)30024-8
Rougerie P., Miskolci V., Cox D. (2013). Generation of membrane structures during phagocytosis and chemotaxis of macrophages: Role and regulation of the actin cytoskeleton. Immunol. Rev. 256, 222–239. doi: 10.1111/imr.12118
Roy R. B., Sambou B., Uhía I., Roetynck S., Robertson B. D., Kampmann B. (2019). An auto-luminescent fluorescent BCG whole blood assay to enable evaluation of paediatric mycobacterial responses using minimal blood volumes. Front. Pediatr. 7, 151. doi: 10.3389/fped.2019.00151
Sadd B. M., Schmid-Hempel P. (2006). Insect immunity shows specificity in protection upon secondary pathogen exposure. Curr. Biol. 16, 1206–1210. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2006.04.047
Schwanhüusser B., Busse D., Li N., Dittmar G., Schuchhardt J., Wolf J., et al. (2011). Global quantification of mammalian gene expression control. Nature 473, 337–342. doi: 10.1038/nature10098
Sharrock A., Ruthe A., Andrews E. S. V., Arcus V. A., Hicks J. L. (2018). VapC proteins from Mycobacterium tuberculosis share ribonuclease sequence specificity but differ in regulation and toxicity. PLoS One 13, e0203412. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0203412
Sheehan G., Clarke G., Kavanagh K. (2018a). Characterisation of the cellular and proteomic response of Galleria mellonella larvae to the development of invasive aspergillosis. BMC Microbiol. 18, 63. doi: 10.1186/s12866-018-1208-6
Sheehan G., Garvey A., Croke M., Kavanagh K. (2018b). Innate humoral immune defences in mammals and insects: The same, with differences? Virulence 9, 1625–1639. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2018.1526531
Sheehan G., Dixon A., Kavanagh K. (2019). Utilization of Galleria mellonella larvae to characterize the development of Staphylococcus aureus infection. Microbiology 165, 863–875. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.000813
Sheehan G., Farrell G., Kavanagh K. (2020a). Immune priming: the secret weapon of the insect world. Virulence 11, 238–246. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2020.1731137
Sheehan G., Konings M., Lim W., Fahal A., Kavanagh K., Van de Sande W. J. (2020b). Proteomic analysis of the processes leading to Madurella mycetomatis grain formation in Galleria mellonella larvae. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 14, e0008190. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0008190
Sheehan G., Kavanagh K. (2018). Analysis of the early cellular and humoral responses of Galleria mellonella larvae to infection by Candida albicans. Virulence 9, 163–172. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2017.1370174
Singhal N., Sharma P., Kumar M., Joshi B., Bisht D. (2012). Analysis of intracellular expressed proteins of Mycobacterium tuberculosis clinical isolates. Proteome Sci. 10, 14. doi: 10.1186/1477-5956-10-14
Sirakova T. D., Dubey V. S., Deb C., Daniel J., Korotkova T. A., Abomoelak B., et al. (2006). Identification of a diacylglycerol acyltransferase gene involved in accumulation of triacylglycerol in Mycobacterium tuberculosis under stress. Microbiology 152, 2717–2725. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.28993-0
Siva-Jothy J. A., Prakash A., Vasanthakrishnan R. B., Monteith K. M., Vale P. F. (2018). Oral bacterial infection and shedding in Drosophila melanogaster. J. Vis. Exp. 135, e57676. doi: 10.3791/57676
Snewin V. A., Gares M., Ógaora P., Hasan Z., Brown I. N., Young D. B. (1999). Assessment of immunity to mycobacterial infection with luciferase reporter constructs. Infect. Immun. 67, 4586–4593. doi: 10.1128/IAI.67.9.4586-4593.1999
Sonawane A. R., Platig J., Fagny M., Chen C. Y., Paulson J. N., Lopes-Ramos C. M., et al. (2017). Understanding tissue-specific gene regulation. Cell Rep. 21, 1077–1088. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.10.001
Tanner R., Smith S. G., van Meijgaarden K. E., Giannoni F., Wilkie M., Gabriele L., et al. (2019). Optimisation, harmonisation and standardisation of the direct mycobacterial growth inhibition assay using cryopreserved human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. J. Immunol. Methods 469, 1–10. doi: 10.1016/j.jim.2019.01.006
Tsai C. J.-Y., Loh J. M. S., Proft T. (2016). Galleria mellonella infection models for the study of bacterial diseases and for antimicrobial drug testing. Virulence 7, 214–229. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2015.1135289
Vilcinskas A., Wedde M. (2002). Insect inhibitors of metalloproteinases. IUBMB Life 54, 339–343. doi: 10.1080/15216540216040
Vogel C., De Sousa Abreu R., Ko D., Le S. Y., Shapiro B. A., Burns S. C., et al. (2010). Sequence signatures and mRNA concentration can explain two-thirds of protein abundance variation in a human cell line. Mol. Syst. Biol. 6, 400. doi: 10.1038/msb.2010.59
Vogel H., Altincicek B., Glöckner G., Vilcinskas A. (2011). A comprehensive transcriptome and immune-gene repertoire of the lepidopteran model host Galleria mellonella. BMC Genomics 12, 308. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-12-308
Voskuil M. II (2013). Mycobacterium tuberculosis cholesterol catabolism requires a new class of acyl coenzyme a dehydrogenase. J. Bacteriol. 195, 4319–4321. doi: 10.1128/JB.00867-13
Wang F., Sambandan D., Halder R., Wang J., Batt S. M., Weinrick B., et al. (2013). Identification of a small molecule with activity against drug-resistant and persistent tuberculosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 110, E2510–E2517. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1309171110
Wang D., Eraslan B., Wieland T., Hallström B., Hopf T., Zolg D. P., et al. (2019). A deep proteome and transcriptome abundance atlas of 29 healthy human tissues. Mol. Syst. Biol. 15, e8503. doi: 10.15252/msb.20188503
Wedde M., Weise C., Nuck R., Altincicek B., Vilcinskas A. (2007). The insect metalloproteinase inhibitor gene of the lepidopteran Galleria mellonella encodes two distinct inhibitors. Biol. Chem. 8, 119–127. doi: 10.1515/BC.2007.013
Williams A., Orme I. M. (2016). Animal models of tuberculosis: an overview. Microbiol. Spectr. 4, TBTB2-004–2015. doi: 10.1128/microbiolspec.TBTB2-0004-2015
Wojda I. (2017). Immunity of the greater wax moth Galleria mellonella. Insect Sci. 24, 342–357. doi: 10.1111/1744-7917.12325
Yuan H., Chang H., Zhao L., Yang C., Huang Y. (2019). Sex- And tissue-specific transcriptome analyses and expression profiling of olfactory-related genes in Ceracris nigricornis Walker (Orthoptera: Acrididae). BMC Genomics 20, 808. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-6208-x
Zdybicka-Barabas A., Stączek S., Pawlikowska-Pawlęga B., Mak P., Luchowski R., Skrzypiec K., et al. (2019). Studies on the interactions of neutral Galleria mellonella cecropin D with living bacterial cells. Amino Acids 51, 175–191. doi: 10.1007/s00726-018-2641-4
Keywords: Galleria mellonella, Mycobacterium bovis BCG, tuberculosis, innate immunity, in vivo model, proteomics, gene expression
Citation: Asai M, Sheehan G, Li Y, Robertson BD, Kavanagh K, Langford PR and Newton SM (2021) Innate Immune Responses of Galleria mellonella to Mycobacterium bovis BCG Challenge Identified Using Proteomic and Molecular Approaches. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 11:619981. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.619981
Received: 22 October 2020; Accepted: 04 January 2021;
Published: 09 February 2021.
Edited by:
Christopher Lupfer, Missouri State University, United StatesReviewed by:
Ivan Dubovskiy, Novosibirsk State Agrarian University, RussiaAndreas Vilcinskas, University of Giessen, Germany
Krishnendu Mukherjee, University Hospital Münster, Germany
Copyright © 2021 Asai, Sheehan, Li, Robertson, Kavanagh, Langford and Newton. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Sandra M. Newton, cy5uZXd0b25AaW1wZXJpYWwuYWMudWs=; Paul R. Langford, cC5sYW5nZm9yZEBpbXBlcmlhbC5hYy51aw==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Masanori Asai
Masanori Asai Gerard Sheehan2,3†
Gerard Sheehan2,3† Sandra M. Newton
Sandra M. Newton