In the published article, there was an error in Figure 1 as published. The figure failed to include the details on the individual node references. The corrected Figure 1 and its caption appear below.
FIGURE 1
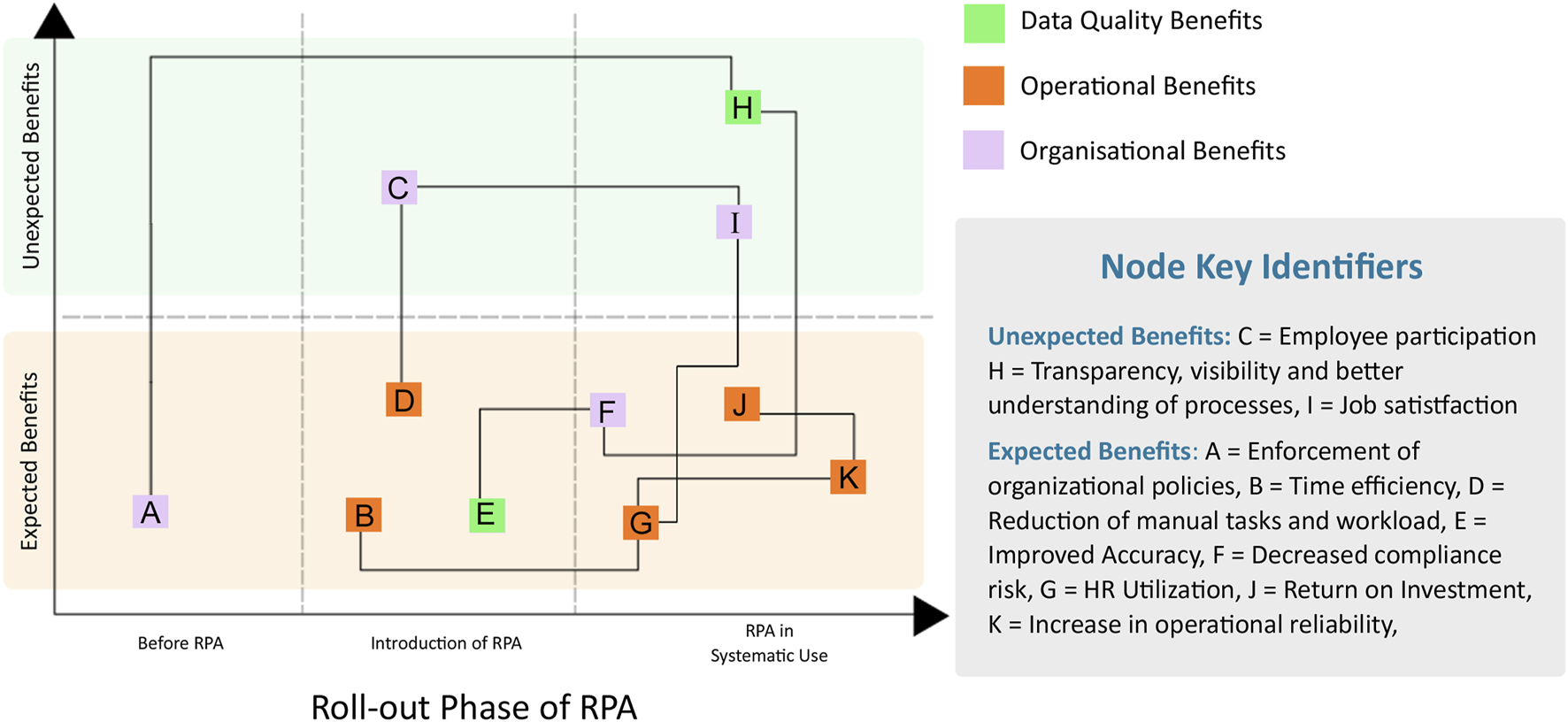
The benefits of robotic process automation (RPA). Additional details are found in Table 1.
In the published article, Table 1 was mistakenly not included in the publication. The missing material appears below.
TABLE 1
| Node | Phase | Benefit | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Expected Benefits | |||
| A | Before RPA | Enforcement of organizational policies | Automation defaults to observing organizational policies in a systematic way |
| B | Introduction of RPA | Improvement in time efficiency | Reduction in time for case processing and booking |
| D | Introduction of RPA | Reduction of manual tasks and workload | Reduction of repetitive, mundane, tedious manual tasks |
| E | Introduction of RPA | Improvement in data accuracy | Automate data processing in systematic way. Decrease potential errors and mistakes in safety case review and processing |
| F | RPA in Systematic Use | Decrease in compliance risk | Timelier fulfillment of compliance and audit requirements for regulatory bodies |
| G | RPA in Systematic Use | Improvement in human resource utilization | Better utilization of staff, focus on cases which require human intervention |
| J | RPA in Systematic Use | Return on investment | Increase capability for high volume case processing without increasing staff |
| K | RPA in Systematic Use | Increase in operational reliability | Allows the organization to operate reliably, even when faced with unexpected challenges |
| Unexpected Benefits | |||
| C | Introduction of RPA | Improved employee participation | Staff is relieved from repetitive tasks and able to focus on improving overall business processes and decision making |
| H | RPA in Systematic Use | Improvement in transparency, visibility and better understanding of processes | Business processes and business rules are judiciously executed, processes are documented and explainable to stakeholders |
| I | RPA in Systematic Use | Improvement in job satisfaction | Empower staff to focus on the most important tasks which lead to better job fulfillment |
Details on the benefits of robotic process automation (RPA).
In the published article, Table 1 should now be updated as Table 2 and any associated references to Table 1 should refer to Table 2, with no changes to its legend or content.
The authors apologize for this errors and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Statements
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Summary
Keywords
pharmacovigilance, machine learning-ML, drug safety, vaccines safety, artificial intelligence
Citation
Painter JL, Kassekert R and Bate A (2023) Corrigendum: An industry perspective on the use of machine learning in drug and vaccine safety. Front. Drug Saf. Regul. 3:1244115. doi: 10.3389/fdsfr.2023.1244115
Received
21 June 2023
Accepted
30 June 2023
Published
04 December 2023
Volume
3 - 2023
Edited by
Taxiarchis Botsis, Johns Hopkins University, United States
Reviewed by
Cristiano Matos, Escola Superior de Tecnologia da Saúde de Coimbra, ESTeSC-IPC, Portugal
Updates
Copyright
© 2023 Painter, Kassekert and Bate.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Andrew Bate, andrew.x.bate@gsk.com
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.