- 1Department of Medicine, University of California San Diego, La Jolla, CA, USA
- 2Department of Medicine, Metabolic Physiology and Ultrastructural Biology Laboratory, VA San Diego Healthcare System, San Diego, CA, USA
Chromogranin A (CgA) is a prohormone and granulogenic factor in endocrine and neuroendocrine tissues, as well as in neurons, and has a regulated secretory pathway. The intracellular functions of CgA include the initiation and regulation of dense-core granule biogenesis and sequestration of hormones in neuroendocrine cells. This protein is co-stored and co-released with secreted hormones. The extracellular functions of CgA include the generation of bioactive peptides, such as pancreastatin (PST), vasostatin, WE14, catestatin (CST), and serpinin. CgA knockout mice (Chga-KO) display: (i) hypertension with increased plasma catecholamines, (ii) obesity, (iii) improved hepatic insulin sensitivity, and (iv) muscle insulin resistance. These findings suggest that individual CgA-derived peptides may regulate different physiological functions. Indeed, additional studies have revealed that the pro-inflammatory PST influences insulin sensitivity and glucose tolerance, whereas CST alleviates adiposity and hypertension. This review will focus on the different metabolic roles of PST and CST peptides in insulin-sensitive and insulin-resistant models, and their potential use as therapeutic targets.
Introduction
The human chromogranin A (gene, CHGA; protein, CgA) gene encodes a 439-amino-acid mature protein of approximately 48–52 kDa with a coiled-coil structure (1–6). Initially detected in chromaffin granules of the adrenal medulla, this evolutionarily conserved protein is ubiquitously distributed in secretory vesicles of endocrine, neuroendocrine, and neuronal cells. CgA plays a pivotal role in the initiation and regulation of dense-core secretory granule biogenesis and hormone sequestration at the trans-Golgi network in neuroendocrine cells (4, 7–9). Increased levels of CgA have been identified in the blood of patients suffering from carcinoids or other neuroendocrine tumors (10–14), heart failure, renal failure, hypertension, rheumatoid arthritis, and inflammatory bowel disease (15–23), indicating an important role of CgA to influence human health and disease (24). Structurally, CgA has 8–10 dibasic sites and is proteolytically cleaved by prohormone convertases (25–27), cathepsin L (28), plasmin (29, 30), and kallikrein (31), generating biologically active peptides including the dysglycemic peptide pancreastatin (PST) (CgA250–301) (32, 33); WE14 (hCgA324–337) which acts as the antigen for highly diabetogenic CD4+ T cell clones (34–38); the vasodilating, antiadrenergic, and antiangiogenic peptide vasostatin 1 (CgA1–76) (39–43); the antiadrenergic, antihypertensive, antibacterial, proangiogenic, and antiobesigenic peptide catestatin (CST) (CgA352–372) (44–56); and the proadrenergic peptide serpinin (CgA402–439) (57, 58). Several of these CgA-derived peptides have opposing counter-regulatory effects. For example, cardiac contractility in rodents is controlled by vasostatin (hCgA1–76) and CST (hCgA352–372), which are antiadrenergic (51, 59) as well as serpinin (hCgA402–439), which is proadrenergic (58) (Figure 1A). Likewise, angiogenesis is controlled by vasostatin acting in an antiangiogenic manner (43, 56) and CST acting as in a proangiogenic manner (50, 56). These CgA-derived peptides, with diverse functions, emphasize the importance of the CgA proprotein in the regulation of physiological functions (Figure 1A). Accordingly, Chga whole-body knockout mice present a complex set of metabolic phenotypes and are obese, hyperadrenergic, and hypertensive (48, 60–63). Chga-KO mice have become an important model to study the roles of individual CgA-derived peptides through analysis of phenotypes after supplementation (48, 55, 60, 61, 64). Here, we will focus on how two of these peptides, PST and CST, act as important modulators of insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism.
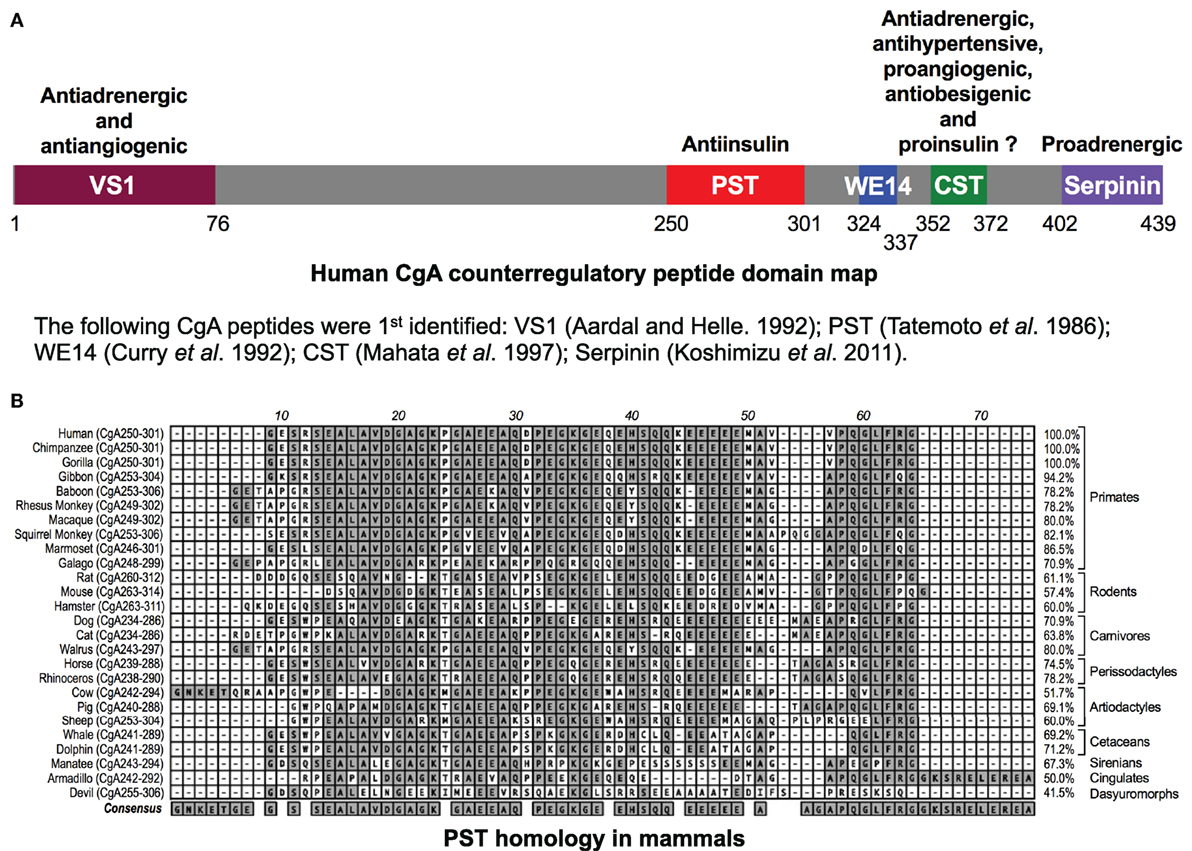
Figure 1. (A) Schematic depiction of the domains of the chromogranin A (CgA) protein. Relative locations of vasostatin (VS1), pancreastatin (PST), WE14, catestatin (CST), and serpinin domains in CgA have been illustrated along with the description of their basic functional properties. (B) PST homology in mammals. Clustal-W program of MacVector (version 9.0) was used for PST domain alignments across 26 mammalian species. PST amino acid domains were shown on the left and percentage homology as compared to human sequence (100%) was shown on the right. The following gene accession numbers were used for this analysis: human (J03483), chimpanzee (XM_510135), western lowland gorilla (XM_004055595), northern white-cheeked gibbon (XM_003260903), olive baboon (NC_018155.1), rhesus monkey (XM_001092629), crab-eating macaque (AB_169793), Bolivian squirrel monkey (XM_003939842), white-tufted-ear marmoset (XM_002754214), small-eared galago (XM_003786997), Norway rat (XM_346781), house mouse (NM_007693), Chinese hamster (NW_003614307), dog (XM_003639191), cat (XM_003987967), Pacific walrus (XM_004394490), horse (NM_001081814), southern white rhinoceros (XM_004434217), cow (NM_181005), pig (XM_001925714), sheep (XM_004017959), killer whale (XM_004262352), bottle-nosed dolphin (XM_004315772), Florida manatee (XM_004376681), nine-banded armadillo (XM_004475519), and Tasmanian devil (XM_003756143). -, gaps in the alignment.
PST Inhibits Glucose-Stimulated Insulin Secretion (GSIS)
PST, a C-terminally glycine-amidated 49-mer peptide, was identified in 1986 as a potent inhibitor of glucose-stimulated insulin secretion (GSIS) (32). Two molecular forms were detected in human plasma: a 52 amino acid form (CgA250–301) and a larger form with a molecular weight of 15–21 kDa (65). Although the PST sequence is well conserved in mammals, showing 41.5% homology between humans and the Tasmanian devil, no homology could be detected in submammalian vertebrates (Figure 1B) (66–68). PST inhibits GSIS in vivo in mice, rats, dogs, and pigs, as well as in vitro from isolated rat islets (69). In the perfused rat pancreas, PST inhibits unstimulated and stimulated insulin secretion (70–73). In PST-deficient Chga-KO mice, GSIS was ~1.7-fold higher at 7 and 15 min after administration of glucose, confirming the inhibitory role of PST in GSIS (60). In addition, PST inhibits glucagon secretion induced by low glucose (74) but had no effect on somatostatin secretion (75). In addition to inhibition of GSIS, PST inhibits insulin-stimulated glucose transport in primary rat and mouse adipocytes (60, 76, 77), differentiated 3T3-L1 adipocytes (68, 78), and primary hepatocytes (60). PST also increases nitric oxide (NO) levels in HTC rat hepatoma cells (79), L6 myotubes (68), and in livers of Chga-KO mice (60), showing that PST inhibits insulin action. Since NO inhibits GSIS (80) and PST increases NO production (60, 68, 79), we believe that PST likely inhibits GSIS through activation of the NO pathway (Figure 2A).
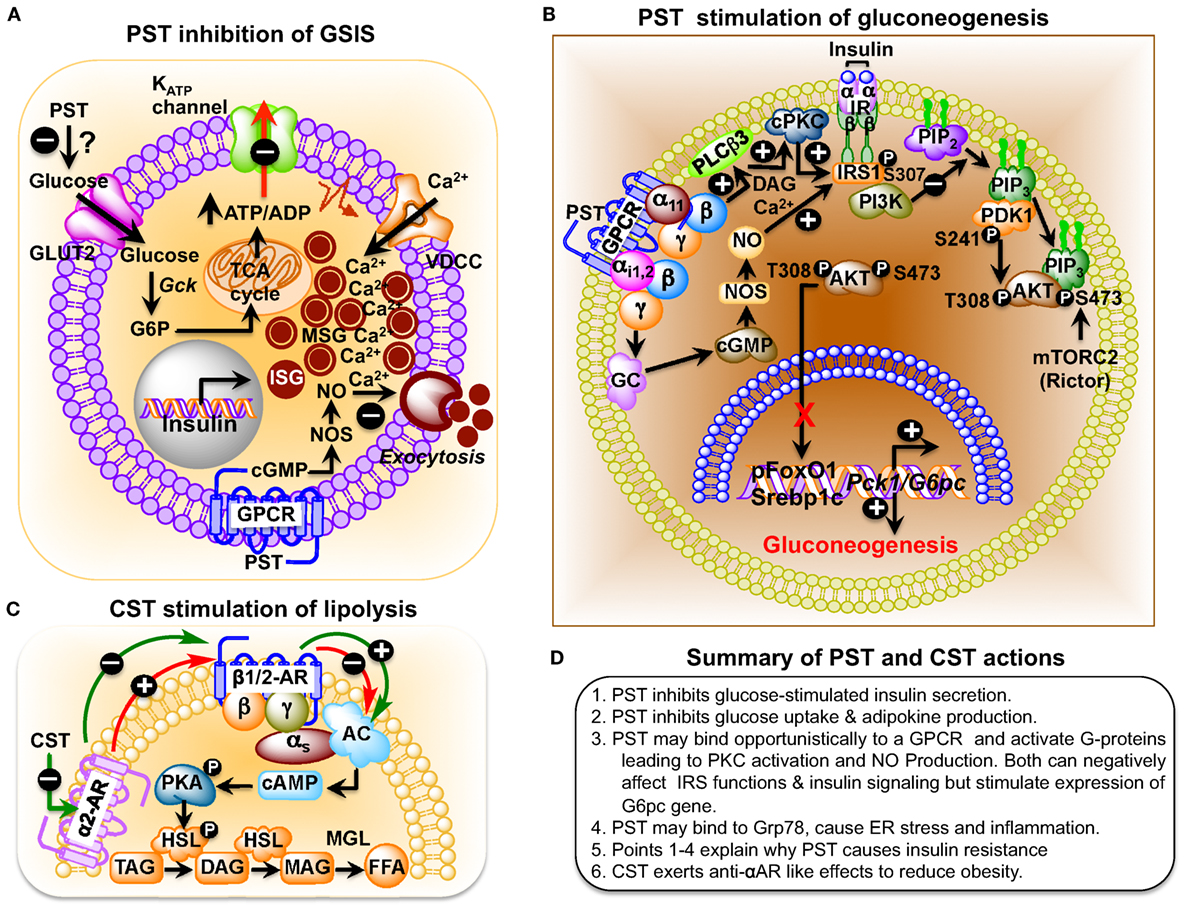
Figure 2. (A) Schematic representation of the role of pancreastatin (PST) in the regulation of insulin secretion from pancreatic beta cells. PST-induced nitric oxide (NO) production, following a guanylate cyclase–cGMP–NOS pathway, inhibits glucose-stimulated insulin secretion (GSIS). (B) Schematic diagram showing PST inhibition of gluconeogenesis in hepatocytes. PST initiates a GTP-binding protein linked signaling cascade leading to activation of diacylglycerol (DAG) and calcium-dependent conventional PKC (cPKC), which attenuates IRS–PI3K–PDK1–AKT signaling pathway. In addition, stimulation of the cGMP–NOS pathway also assaults this signaling pathway by nitrosylation of IRS. Thus, PST-mediated suppression of this pathway allows forkhead box protein O1 (FoxO1) and sterol regulatory element-binding transcription factor 1c (SREBP1c) to stimulate expression of gluconeogenic genes, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase 1 (Pck1) (also known as Pepck) and glucose-6-phosphatase (G6pc) (also known as G6Pase), and thus prevent insulin action. Under control conditions, insulin would have activated this signaling pathway, causing phosphorylation of FoxO1 (promoting its exclusion from the nucleus) and preventing processing of SREBP1 proprotein to SREBP1c with consequent inhibition of expression of gluconeogenic genes and gluconeogenesis. (C) Catestatin (CST) stimulation of lipolysis in adipocytes. Activation of α2-adrenergic receptor (α2-AR) inhibits β1/2-AR-induced lipolysis in a dominant way in obesity. CST enhances lipolysis by inhibiting α2-AR, which promotes β1/2-AR action and the consequent downstream signaling. Hormone-sensitive lipase (HSL) is an intracellular, neutral lipase that has broad substrate specificity, catalyzing the hydrolysis of triacylglycerol (TAG), diacylglycerol (DAG), monoacylglycerol (MAG), and cholesteryl esters. Its activity against DAG is about 10- and 5-fold higher than its activity against TAG and MAG, respectively, whereas its activity against cholesteryl esters is about twice its activity toward TAG. The hydrolytic activity of HSL against TAG and cholesteryl esters, but not against DAG, is stimulated by phosphorylation mediated primarily by PKA (84). AC, adenylyl cyclase; FFA, free fatty acids; MGL, monoacylglycerol lipase; PKA, protein kinase A. (D) Summary of PST and CST actions.
PST Regulates Hepatic Glucose Metabolism
PST treatment inhibits insulin-stimulated glycogen synthesis in primary hepatocytes (81) and activates glycogenolysis in the rat liver, implicating a direct anti-insulin effect on liver metabolism (82, 83). PST-deficient Chga-KO mice show greater suppression of hepatic glucose production (HGP) compared to wild-type (WT) mice during insulin clamp studies (60). Decreased glucose production in Chga-KO mice was also supported by decreased glucose production during pyruvate tolerance tests and decreased mRNA transcript levels of the gluconeogenic genes, such as the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase 1 and glucose-6-phosphatase (G6pc), compared to WT mice that were restored to WT levels after supplementation of PST to Chga-KO mice (60). PST activates gluconeogenesis by decreasing phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate 2 at tyrosine residues through activation of conventional PKC and increases production of NO with subsequent attenuated phosphorylation of protein kinase B (AKT), forkhead box protein O1, and reduced matured sterol regulatory element-binding transcription factor 1c (SREBP1c) (Figure 2B) (60). These findings are consistent with the anti-insulin action of PST.
PST Influences Lipid Metabolism
In addition to glucose metabolism, PST also modulates lipid metabolism. PST decreases insulin-stimulated synthesis of lipids in rat adipocytes (85), which is consistent with the PST-dependent increased expression of hepatic lipogenic genes in Chga-KO mice, including Srebp1c, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma, and glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase (Gpat) (60). PST also stimulates release of glycerol and free fatty acids from rat adipocytes, which is completely inhibited by insulin (85). In humans, PST augments free fatty acid efflux into the circulation, resulting in an overall spillover of ~4.5-fold, which is consistent with the reported lipolytic action of PST (85), confirming the anti-insulin effects of PST.
PST Promotes Inflammation and Insulin Resistance
Since PST inhibits the action of insulin on glucose and lipid metabolism, one would expect improved insulin sensitivity in PST-deficient mice. Indeed, Chga-KO mice show improved hepatic insulin sensitivity as assessed by insulin tolerance tests (ITTs) showing increased hypoglycemia, and insulin clamp studies showing increased suppression of HGP. Improved hepatic insulin sensitivity was abolished when Chga-KO mice were treated with PST, implicating a positive correlation between PST and the development of insulin resistance (60). Similarly, type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients show a substantial increase in plasma PST levels (~3.7-fold) (77). Gestational diabetic subjects and patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus also show increased plasma PST levels (86, 87).
Feeding mice a high fat diet (HFD) creates obesity, leading to hyperinsulinemia and inflammation (88–92). ITT studies revealed that HFD-fed Chga-KO mice displayed improved insulin sensitivity compared to WT mice, demonstrating the importance of PST in the development of IR (64). This was reinforced by hyperinsulinemic–euglycemic clamp studies, where Chga-KO-HFD mice displayed increased glucose infusion rates, higher insulin-stimulated glucose disposal rates (IS-GDRs), and suppressed HGP. Recent studies implicate dissociation between obesity and insulin resistance as long as the inflammation is suppressed (64). The presence of supraphysiological levels of PST can reconnect obesity with insulin resistance by introducing inflammation. In the absence of PST, animals are insulin sensitive despite obesity. This is reminiscent of rosiglitazone-treated WT-HFD mice, which are insulin sensitive but obese (93–95).
The hallmarks of insulin resistance in HFD mice are obesity, hyperinsulinemia, and increased inflammation (88–92). Suppression of inflammation in HFD mice can improve insulin sensitivity (93–95). Therefore, the resistance to diet-induced insulin resistance in Chga-KO mice may reflect less inflammation in Chga-KO mice even after HFD feeding. PST treatment caused increased expression of the pro-inflammatory genes interleukin 1-beta, tumor necrosis factor alpha (Tnfa), interleukin 6 (IL6), chemokine C–C motif ligand 2 (Ccl2), and nitric oxide synthase 2a. Whereas expression of anti-inflammatory genes such as arginase 1 (Arg1), interleukin 10 (IL10), and C-type lectin domain family member 10a (Clec10a) in adipose tissues was higher in Chga-KO-HFD mice than WT controls, PST treatment significantly reduced the expression of Arg1 and IL10. Consistent with gene expression data, the plasma levels of IL12p70, Ifng, and chemokine C–C motif ligand 3-like 1 (Ccl3l1), IL6, and chemokine C–X–C motif ligand 1 (Cxcl1) showed significantly decreased levels in Chga-KO-HFD versus WT-HFD plasma. PST treatment of Chga-KO-HFD mice raised plasma levels of IL12p70 and Ccl2, but had no effect on other proteins measured. PST also exerted direct effects on peritoneal macrophage cultures obtained from WT and Chga-KO mice. CgA-deficient peritoneal macrophages demonstrated attenuated response to LPS in the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines as well as decreased chemotaxis in response to cytokines (64). PST treatment increased the expression of Tnfa and Ccl2 in Chga-KO macrophages (64). Thus, it appears that PST acts as a pro-inflammatory peptide but its loss is likely only partially responsible for the improved inflammation seen in Chga-KO mice (Figure 2D).
Although clamp studies with Chga-KO mice fed normal chow diet (NCD) indicated decreased glucose disposal, meaning muscle insulin resistance (60), surprisingly, reduced muscle insulin sensitivity in lean Chga-KO mice was reversed by HFD feeding as demonstrated by improved IS-GDR in muscle of HFD-fed Chga-KO mice. Can feeding a high amount of lipids to CgA-deficient mice regenerate cells and repair muscle dysfunction? What kind of lipid could that be? These unorthodox results on the regulation of muscle insulin sensitivity by a CgA-derived protein need further investigation. In this regard, one provocative speculation may deserve some investigation. HFD-induced ceramide and sphingolipids were implicated in the mobilization and differentiation of bone marrow-derived stem/progenitor cells, which are involved in the repair of tissues in ischemic heart disease (96). More specifically, sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) acts as a trophic factor for skeletal muscle cell regeneration (97). Sphingolipids are important structural components of cell membranes and are derived from ceramide. Ceramide production is increased in obesity and after HFD feeding (98, 99). Ceramide can be deacylated to sphingosine, which is then phosphorylated by sphingosine kinases to yield S1P. Since this improvement in muscle insulin sensitivity by HFD happened in Chga-KO mice, not in WT-DIO mice, absence of CgA protein or peptides triggered this unusual phenomenon. Therefore, it will be very important to investigate the roles of these dietary lipids in muscle repair and the functional relationship of these lipids with the CgA protein and CgA-derived peptides. Alternatively, it is also possible that the absence of CgA protein and its derivatives stimulated release of some myokines in response to dietary lipids, which would otherwise remain suppressed in WT-DIO mice. This response to HFD in Chga-KO mice could be muscle specific because muscle expresses CgA (100), and liver and adipose tissue do not (3, 46). Effects of CgA deficiency on liver and adipose tissue may be more systemic in nature, a part of which is carried out by CgA-deficient macrophages (64).
PST Promotes Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Stress by Attenuating Expression of Grp78
The accumulation of unfolded and misfolded proteins in the ER lumen, termed ER stress, leads to activation of signaling pathways to counteract defects in protein folding (101–106). This unfolded protein response (UPR) increases repair activities, reduces global protein synthesis, and activates ER-associated protein degradation. However, if ER stress becomes chronic and UPR cannot cope with the repair demands, protein-folding homeostasis breaks down, leading to activation of apoptotic pathways (103, 107, 108). Thus, ER stress and the UPR play important roles in the pathogenesis of multiple human metabolic diseases including insulin resistance, diabetes, obesity, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, and atherosclerosis (109, 110). The immunoglobulin binding protein (BiP) [also called glucose-regulated protein 78 (Grp78)], is an ER chaperone that is required for protein folding. BiP/Grp78 is a peptide-stimulated ATPase of the Hsp70 family that prevents protein aggregation by stabilizing intermediates in the protein-folding process.
Using ligand affinity chromatography with biotinylated human PST (hCgA273–301-amide) as “bait” on a murine liver homogenate (as “prey”), we found that PST interacts in a pH-dependent fashion with Grp78 (78). Whereas NCD-fed Chga-KO livers show increased expression of Grp78, PST caused dose-dependent inhibition of Grp78 ATPase activity and inhibited increased expression of Grp78 during UPR activation (by tunicamycin) in hepatocytes (78). In hepatocytes, PST increased expression of G6pc. These results indicate that a major hepatic target of PST is the adaptive UPR chaperone Grp78 and that ATPase activity associated with Grp78 is involved in the suppression of glucose production by attenuating G6pc expression (78). Grp78s ATPase activity is required to suppress expression of G6pc; ER stress and suppression of glucose utilization appear to augment Grp78 expression (111). Although it is not clear how circulating PST might contact the ER luminal protein Grp78 to modulate ER and insulin action, it has been reported that Grp78 translocates to the cell surface under some pathological conditions (112, 113).
Modulation of Metabolism by Naturally Occurring Variants of PST
Single-nucleotide polymorphism analysis of PST, both in vivo and in vitro, showed greater inhibition of insulin-stimulated glucose uptake by Gly297Ser variants followed by the Glu287Arg variants compared to WT-PST (77). The in vitro studies also revealed increased expression of gluconeogenic genes by PST variants as compared to WT-PST, with comparable potencies by Glu287Arg and Gly297Ser variants (68). The Gly297Ser subjects displayed markedly elevated plasma glucose and cholesterol compared to the Gly297Gly individuals. Interestingly, whereas the variants of PST in the C-terminal half of the molecule at 287 (Glu287Arg) and at 297 (Gly297Ser) enhance anti-insulin effects and elevate plasma glucose by inhibition of glucose uptake and stimulation of gluconeogenic effects, experimental deletion of the three N-terminal amino acids Pro–Glu–Gly on human WT-PST demonstrated the opposite effects by reducing plasma glucose level and hepatic gluconeogenesis in a rodent model of obesity (64). Therefore, finding variants in the N-terminal end of PST among the human population may lead to discovery of an allele which would confer protection against insulin resistance and can be used as an insulin-sensitizing peptide such as a N-terminal variant of PST (lacking three amino acids from the N-terminal end) called PSTv1 (64).
Regulation of Insulin Sensitivity by the PST Antagonist PSTv1
The elevated levels of plasma PST observed in T2DM patients (77) implied that preventing PST action might serve a therapeutic purpose of controlling insulin resistance and diabetes. To demonstrate a direct in vivo role of PST in the regulation of insulin sensitivity, WT-HFD mice were injected with the PST variant, PSTv1, which is a competitive antagonist of native PST. PSTv1 lacks the first three N-terminal residues of native PST and blocks PST-mediated inhibition of glucose uptake and leptin secretion in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. As predicted, chronic PSTv1 treatment lowered fasting plasma glucose levels in WT-HFD mice and improved glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity (64). These results suggested that in WT-HFD mice, where the level of PST is high, PSTv1 administration competes with the native PST and phenocopies Chga-KO mice. This demonstrates the potential of PST as a therapeutic target for treatment of insulin resistance and diabetes.
CST Decreases Hypertension and Obesity
Hypertensive patients show elevated levels of plasma CgA but decreased plasma CST (114, 115). Low plasma CST predicts augmented pressor responses to environmental stimuli (114). In rats, CST reduces blood pressure responses to activation of sympathetic outflow by electrical stimulation (116). This vasodepressor effect of CST was mediated by massive release of histamine with subsequent vasodilation by histamine-induced production of NO. CST is a potent endogenous inhibitor of catecholamine secretion (44–47, 117–120) and catecholamine-mediated hypertension (48, 121). Chga-KO mice showed hyperadrenergic and hypertensive phenotypes that were normalized by intraperitoneal administration of CST (48). CSTs hypotensive effect was also documented in a polygenic model of high blood pressure mice (121). Other studies showed that CST also provides cardioprotection by inhibiting the opening of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore and stimulating the reperfusion injury salvage kinase pathway (122–127).
Catestatin-deficient Chga-KO mice are obese on an NCD (48). Chronic CST administration to Chga-KO mice reduced epididymal fat pad size to WT level (~25% reduction with respect to body weight of Chga-KO mice) (55). CST decreased plasma triglyceride levels in Chga-KO mice by increasing lipolysis (increased plasma glycerol and non-esterified fatty acids) through inhibition of α2-adrenergic receptor (α2-AR) (Figure 2C) (55). While inhibition of α2-AR by CST indirectly facilitates β-AR mediated lipolysis, CST can also have direct effect on ATGL (adipose triacylglycerol lipase) and HSL (hormone sensitive lipase) via activation of AMPK (128) as it has been demonstrated that activation of AMPK promote lipolysis in adipose tissue through ATGL and HSL. CST-treated Chga-KO mice show increased palmitate oxidation but decreased incorporation into lipids, which indicates that CST inhibits expansion of adipose tissue but promotes fatty acid uptake in the liver for oxidation. CST induced expression of several fatty acid oxidation genes including carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1a, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-a, acyl-CoA oxidase 1, and uncoupling protein 2, supporting increased fatty acid oxidation in the liver. In addition, CST increased expression of the fatty acid transporter gene Cd36 and the lipogenic gene glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase 4 (Gpat4), indicating that CST stimulates fatty acid incorporation into triglycerides but not de novo lipogenesis. Overall, CST promoted lipid flux from the adipose tissue toward the liver for beta-oxidation (55). These obesity-reducing effects of CST are mediated by inhibition of α2-AR signaling and enhancement of leptin receptor signaling. In contrast to the negative metabolic effects of PST, CST has beneficial effects that could be utilized in therapeutic treatment of hypertension and obesity.
Conclusion and Future Perspectives
Chromogranin A is one of the few protein molecules, which can be processed into both negative and positive regulators such as PST and CST for fine-tuning and maintaining metabolic homeostasis. With respect to the pathway of lipid disposal, studies on the direct effect of CST, through activation of AMPK, on lipolytic activities of ATGL and HSL may generate exciting information. Although the metabolic effects of PST and CST have been well investigated, how they transmit signals into cells remains to be determined. Are there specific receptors for these peptides? Alternatively, can they opportunistically bind to some non-specific BiPs on the cell surface and get endocytosed? In some cells such as neutrophils, CST has been shown to be permeable (53). With respect to PST, its binding to Grp78 may occur opportunistically on the cell surface when Grp78, usually a luminal protein, translocates to the cell surface, which occurs under some pathological conditions (112, 113). Whether such interaction happens or not should be a matter of future investigation. If that happens, Grp78 would be able to carry PST to the luminal compartment and initiate a reaction with a small G-protein binding molecule leading to a cascade described in Figure 2B. In addition, although PST has been established as an anti-insulin peptide, the mechanisms underlying PST-dependent regulation of insulin secretion are poorly understood. Other CgA-derived pro-insulin peptides may also exist and need to be further investigated. These efforts, as well as generation of PST antagonists, may lead to development of powerful therapeutic treatments for insulin resistance and diabetes. Beyond PST and CST, additional studies should shed light on the role of other CgA-derived peptides in metabolism, with implications for treatment of metabolic disease.
Author Contributions
SM conceived the idea. GB and SM contributed equally to researching the data and writing of the manuscript.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Sumana Mahata for editing the review article.
Funding
There is no financial support from funding organization. The research was supported by Mahata’s home equity loan.
References
1. Konecki DS, Benedum UM, Gerdes HH, Huttner WB. The primary structure of human chromogranin A and pancreastatin. J Biol Chem (1987) 262(35):17026–30.
2. Mouland AJ, Bevan S, White JH, Hendy GN. Human chromogranin A gene. Molecular cloning, structural analysis, and neuroendocrine cell-specific expression. J Biol Chem (1994) 269(9):6918–26.
3. Winkler H, Fischer-Colbrie R. The chromogranins A and B: the first 25 years and future perspectives. Neuroscience (1992) 49(3):497–528. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(92)90222-N
4. Iacangelo AL, Eiden LE. Chromogranin A: current status as a precursor for bioactive peptides and a granulogenic/sorting factor in the regulated secretory pathway. Regul Pept (1995) 58(3):65–88. doi:10.1016/0167-0115(95)00069-N
5. Taupenot L, Harper KL, O’Connor DT. Mechanisms of disease: the chromogranin-secretogranin family. N Engl J Med (2003) 348:1134–49. doi:10.1056/NEJMra021405
6. Mosley CA, Taupenot L, Biswas N, Taulane JP, Olson NH, Vaingankar SM, et al. Biogenesis of the secretory granule: chromogranin A coiled-coil structure results in unusual physical properties and suggests a mechanism for granule core condensation. Biochemistry (2007) 46(38):10999–1012. doi:10.1021/bi700704r
7. Kim T, Tao-Cheng J, Eiden LE, Loh YP. Chromogranin A, an “on/off” switch controlling dense-core secretory granule biogenesis. Cell (2001) 106(4):499–509. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(01)00459-7
8. Taupenot L, Harper KL, Mahapatra NR, Parmer RJ, Mahata SK, O’Connor DT. Identification of a novel sorting determinant for the regulated pathway in the secretory protein chromogranin A. J Cell Sci (2002) 115(Pt 24):4827–41. doi:10.1242/jcs.00140
9. Elias S, Delestre C, Ory S, Marais S, Courel M, Vazquez-Martinez R, et al. Chromogranin A induces the biogenesis of granules with calcium- and actin-dependent dynamics and exocytosis in constitutively secreting cells. Endocrinology (2012) 153(9):4444–56. doi:10.1210/en.2012-1436
10. O’Connor DT, Bernstein KN. Radioimmunoassay of chromogranin A in plasma as a measure of exocytotic sympathoadrenal activity in normal subjects and patients with pheochromocytoma. N Engl J Med (1984) 311(12):764–70. doi:10.1056/NEJM198409203111204
11. O’Connor DT, Deftos LJ. Secretion of chromogranin A by peptide-producing endocrine neoplasms. N Engl J Med (1986) 314(18):1145–51. doi:10.1056/NEJM198605013141803
12. Corti A, Gasparri A, Chen FX, Pelagi M, Brandazza A, Sidoli A, et al. Characterisation of circulating chromogranin A in human cancer patients. Br J Cancer (1996) 73(8):924–32. doi:10.1038/bjc.1996.183
13. Gregorc V, Spreafico A, Floriani I, Colombo B, Ludovini V, Pistola L, et al. Prognostic value of circulating chromogranin A and soluble tumor necrosis factor receptors in advanced nonsmall cell lung cancer. Cancer (2007) 110(4):845–53. doi:10.1002/cncr.22856
14. Corti A. Chromogranin A and the tumor microenvironment. Cell Mol Neurobiol (2010) 30(8):1163–70. doi:10.1007/s10571-010-9587-8
15. Ceconi C, Ferrari R, Bachetti T, Opasich C, Volterrani M, Colombo B, et al. Chromogranin A in heart failure; a novel neurohumoral factor and a predictor for mortality. Eur Heart J (2002) 23(12):967–74. doi:10.1053/euhj.2001.2977
16. Rosjo H, Masson S, Latini R, Flyvbjerg A, Milani V, La Rovere MT, et al. Prognostic value of chromogranin A in chronic heart failure: data from the GISSI-heart failure trial. Eur J Heart Fail (2010) 12(6):549–56. doi:10.1093/eurjhf/hfq055
17. Bernini GP, Moretti A, Ferdeghini M, Ricci S, Letizia C, D’Erasmo E, et al. A new human chromogranin ‘A’ immunoradiometric assay for the diagnosis of neuroendocrine tumours. Br J Cancer (2001) 84(5):636–42. doi:10.1054/bjoc.2000.1659
18. O’Connor DT, Pandlan MR, Carlton E, Cervenka JH, Hslao RJ. Rapid radioimmunoassay of circulating chromogranin A: in vitro stability, exploration of the neuroendocrine character of neoplasia, and assessment of the effects of organ failure. Clin Chem (1989) 35(8):1631–7.
19. O’Connor DT. Plasma chromogranin A. Initial studies in human hypertension. Hypertension (1985) 7(3 Pt 2):176–9. doi:10.1161/01.HYP.7.3_Pt_2.I76
20. Giampaolo B, Angelica M, Antonio S. Chromogranin ‘A’ in normal subjects, essential hypertensives and adrenalectomized patients. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) (2002) 57(1):41–50. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2265.2002.01557.x
21. Tombetti E, Colombo B, Di Chio MC, Sartorelli S, Papa M, Salerno A, et al. Chromogranin-A production and fragmentation in patients with Takayasu arteritis. Arthritis Res Ther (2016) 18:187. doi:10.1186/s13075-016-1082-2
22. Sciola V, Massironi S, Conte D, Caprioli F, Ferrero S, Ciafardini C, et al. Plasma chromogranin A in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis (2009) 15(6):867–71. doi:10.1002/ibd.20851
23. Zissimopoulos A, Vradelis S, Konialis M, Chadolias D, Bampali A, Constantinidis T, et al. Chromogranin A as a biomarker of disease activity and biologic therapy in inflammatory bowel disease: a prospective observational study. Scand J Gastroenterol (2014) 49(8):942–9. doi:10.3109/00365521.2014.920910
24. Loh YP, Cheng Y, Mahata SK, Corti A, Tota B. Chromogranin A and derived peptides in health and disease. J Mol Neurosci (2012) 48(2):347–56. doi:10.1007/s12031-012-9728-2
25. Metz-Boutigue MH, Garcia-Sablone P, Hogue-Angeletti R, Aunis D. Intracellular and extracellular processing of chromogranin A. Determination of cleavage sites. Eur J Biochem (1993) 217(1):247–57. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb18240.x
26. Taylor CV, Taupenot L, Mahata SK, Mahata M, Wu H, Yasothornsrikul S, et al. Formation of the catecholamine release-inhibitory peptide catestatin from chromogranin A. Determination of proteolytic cleavage sites in hormone storage granules. J Biol Chem (2000) 275(30):22905–15. doi:10.1074/jbc.M001232200
27. Lee JC, Taylor CV, Gaucher SP, Toneff T, Taupenot L, Yasothornsrikul S, et al. Primary sequence characterization of catestatin intermediates and peptides defines proteolytic cleavage sites utilized for converting chromogranin A into active catestatin secreted from neuroendocrine chromaffin cells. Biochemistry (2003) 42(23):6938–46. doi:10.1021/bi0300433
28. Biswas N, Rodriguez-Flores JL, Courel M, Gayen JR, Vaingankar SM, Mahata M, et al. Cathepsin L co-localizes with chromogranin A in chromaffin vesicles to generate active peptides. Endocrinology (2009) 150(8):3547–57. doi:10.1210/en.2008-1613
29. Jiang Q, Taupenot L, Mahata SK, Mahata M, O’Connor DT, Miles LA, et al. Proteolytic cleavage of chromogranin A (CgA) by plasmin: selective liberation of a specific bioactive CgA fragment that regulates catecholamine release. J Biol Chem (2001) 276:25022–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.M101545200
30. Biswas N, Vaingankar SM, Mahata M, Das M, Gayen JR, Taupenot L, et al. Proteolytic cleavage of human chromogranin A containing naturally occurring catestatin variants: differential processing at catestatin region by plasmin. Endocrinology (2008) 149(2):749–57. doi:10.1210/en.2007-0838
31. Benyamin B, Maihofer AX, Schork AJ, Hamilton BA, Rao F, Schmid-Schonbein GW, et al. Identification of novel loci affecting circulating chromogranins and related peptides. Hum Mol Genet (2016). doi:10.1093/hmg/ddw380
32. Tatemoto K, Efendic S, Mutt V, Makk G, Feistner GJ, Barchas JD. Pancreastatin, a novel pancreatic peptide that inhibits insulin secretion. Nature (1986) 324(6096):476–8. doi:10.1038/324476a0
33. Sanchez-Margalet V, Gonzalez-Yanes C, Najib S, Santos-Alvarez J. Metabolic effects and mechanism of action of the chromogranin A-derived peptide pancreastatin. Regul Pept (2010) 161(1–3):8–14. doi:10.1016/j.regpep.2010.02.005
34. Curry WJ, Shaw C, Johnston CF, Thim L, Buchanan KD. Isolation and primary structure of a novel chromogranin A-derived peptide, WE-14, from a human midgut carcinoid tumour. FEBS Lett (1992) 301(3):319–21. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(92)80266-J
35. Stadinski BD, Delong T, Reisdorph N, Reisdorph R, Powell R, Armstrong M, et al. Chromogranin A is an autoantigen in type 1 diabetes. Nat Immunol (2010) 11:225–31. doi:10.1038/ni.1844
36. Delong T, Baker RL, He J, Barbour G, Bradley B, Haskins K. Diabetogenic T-cell clones recognize an altered peptide of chromogranin A. Diabetes (2012) 61(12):3239–46. doi:10.2337/db12-0112
37. Gottlieb PA, Delong T, Baker RL, Fitzgerald-Miller L, Wagner R, Cook G, et al. Chromogranin A is a T cell antigen in human type 1 diabetes. J Autoimmun (2014) 50:38–41. doi:10.1016/j.jaut.2013.10.003
38. Jin N, Wang Y, Crawford F, White J, Marrack P, Dai S, et al. N-terminal additions to the WE14 peptide of chromogranin A create strong autoantigen agonists in type 1 diabetes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A (2015) 112(43):13318–23. doi:10.1073/pnas.1517862112
39. Aardal S, Helle KB. The vasoinhibitory activity of bovine chromogranin A fragment (vasostatin) and its independence of extracellular calcium in isolated segments of human blood vessels. Regul Pept (1992) 41(1):9–18. doi:10.1016/0167-0115(92)90509-S
40. Aardal S, Helle KB, Elsayed S, Reed RK, Serck-Hanssen G. Vasostatins, comprising the N-terminal domain of chromogranin A, suppress tension in isolated human blood vessel segments. J Neuroendocrinol (1993) 5(4):405–12. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2826.1993.tb00501.x
41. Tota B, Mazza R, Angelone T, Nullans G, Metz-Boutigue MH, Aunis D, et al. Peptides from the N-terminal domain of chromogranin A (vasostatins) exert negative inotropic effects in the isolated frog heart. Regul Pept (2003) 114(2–3):123–30. doi:10.1016/S0167-0115(03)00112-5
42. Corti A, Mannarino C, Mazza R, Angelone T, Longhi R, Tota B. Chromogranin A N-terminal fragments vasostatin-1 and the synthetic CGA 7-57 peptide act as cardiostatins on the isolated working frog heart. Gen Comp Endocrinol (2004) 136(2):217–24. doi:10.1016/j.ygcen.2003.12.012
43. Pike SE, Yao L, Jones KD, Cherney B, Appella E, Sakaguchi K, et al. Vasostatin, a calreticulin fragment, inhibits angiogenesis and suppresses tumor growth. J Exp Med (1998) 188(12):2349–56. doi:10.1084/jem.188.12.2349
44. Mahata SK, O’Connor DT, Mahata M, Yoo SH, Taupenot L, Wu H, et al. Novel autocrine feedback control of catecholamine release. A discrete chromogranin A fragment is a noncompetitive nicotinic cholinergic antagonist. J Clin Invest (1997) 100(6):1623–33. doi:10.1172/JCI119686
45. Mahata SK, Mahata M, Wakade AR, O’Connor DT. Primary structure and function of the catecholamine release inhibitory peptide catestatin (chromogranin A344-364): identification of amino acid residues crucial for activity. Mol Endocrinol (2000) 14(10):1525–35. doi:10.1210/me.14.10.1525
46. Mahata SK, Mahapatra NR, Mahata M, Wang TC, Kennedy BP, Ziegler MG, et al. Catecholamine secretory vesicle stimulus-transcription coupling in vivo. Demonstration by a novel transgenic promoter/photoprotein reporter and inhibition of secretion and transcription by the chromogranin A fragment catestatin. J Biol Chem (2003) 278:32058–67. doi:10.1074/jbc.M305545200
47. Wen G, Mahata SK, Cadman P, Mahata M, Ghosh S, Mahapatra NR, et al. Both rare and common polymorphisms contribute functional variation at CHGA, a regulator of catecholamine physiology. Am J Hum Genet (2004) 74(2):197–207. doi:10.1086/381399
48. Mahapatra NR, O’Connor DT, Vaingankar SM, Hikim AP, Mahata M, Ray S, et al. Hypertension from targeted ablation of chromogranin A can be rescued by the human ortholog. J Clin Invest (2005) 115(7):1942–52. doi:10.1172/JCI24354
49. Briolat J, Wu SD, Mahata SK, Gonthier B, Bagnard D, Chasserot-Golaz S, et al. New antimicrobial activity for the catecholamine release-inhibitory peptide from chromogranin A. Cell Mol Life Sci (2005) 62(3):377–85. doi:10.1007/s00018-004-4461-9
50. Theurl M, Schgoer W, Albrecht K, Jeschke J, Egger M, Beer AG, et al. The neuropeptide catestatin acts as a novel angiogenic cytokine via a basic fibroblast growth factor-dependent mechanism. Circ Res (2010) 107(11):1326–35. doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.110.219493
51. Angelone T, Quintieri AM, Brar BK, Limchaiyawat PT, Tota B, Mahata SK, et al. The antihypertensive chromogranin A peptide catestatin acts as a novel endocrine/paracrine modulator of cardiac inotropism and lusitropism. Endocrinology (2008) 149(10):4780–93. doi:10.1210/en.2008-0318
52. Radek KA, Lopez-Garcia B, Hupe M, Niesman IR, Elias PM, Taupenot L, et al. The neuroendocrine peptide catestatin is a cutaneous antimicrobial and induced in the skin after injury. J Invest Dermatol (2008) 128(6):1525–34. doi:10.1038/sj.jid.5701225
53. Zhang D, Shooshtarizadeh P, Laventie BJ, Colin DA, Chich JF, Vidic J, et al. Two chromogranin A-derived peptides induce calcium entry in human neutrophils by calmodulin-regulated calcium independent phospholipase A2. PLoS One (2009) 4(2):e4501. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0004501
54. Angelone T, Quintieri AM, Pasqua T, Gentile S, Tota B, Mahata SK, et al. Phosphodiesterase type-2 and NO-dependent S-nitrosylation mediate the cardioinhibition of the antihypertensive catestatin. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol (2012) 302(2):H431–42. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00491.2011
55. Bandyopadhyay GK, Vu CU, Gentile S, Lee H, Biswas N, Chi NW, et al. Catestatin (chromogranin A(352-372)) and novel effects on mobilization of fat from adipose tissue through regulation of adrenergic and leptin signaling. J Biol Chem (2012) 287(27):23141–51. doi:10.1074/jbc.M111.335877
56. Crippa L, Bianco M, Colombo B, Gasparri AM, Ferrero E, Loh YP, et al. A new chromogranin A-dependent angiogenic switch activated by thrombin. Blood (2013) 121(2):392–402. doi:10.1182/blood-2012-05-430314
57. Koshimizu H, Cawley NX, Kim T, Yergey AL, Loh YP. Serpinin: a novel chromogranin A-derived, secreted peptide up-regulates protease nexin-1 expression and granule biogenesis in endocrine cells. Mol Endocrinol (2011) 25:732–44. doi:10.1210/me.2010-0124
58. Tota B, Gentile S, Pasqua T, Bassino E, Koshimizu H, Cawley NX, et al. The novel chromogranin A-derived serpinin and pyroglutaminated serpinin peptides are positive cardiac beta-adrenergic-like inotropes. FASEB J (2012) 26(7):2888–98. doi:10.1096/fj.11-201111
59. Cerra MC, De Iuri L, Angelone T, Corti A, Tota B. Recombinant N-terminal fragments of chromogranin-A modulate cardiac function of the Langendorff-perfused rat heart. Basic Res Cardiol (2006) 101(1):43–52. doi:10.1007/s00395-005-0547-2
60. Gayen JR, Saberi M, Schenk S, Biswas N, Vaingankar SM, Cheung WW, et al. A novel pathway of insulin sensitivity in chromogranin A null mice: a crucial role for pancreastatin in glucose homeostasis. J Biol Chem (2009) 284:28498–509. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.020636
61. Gayen JR, Gu Y, O’Connor DT, Mahata SK. Global disturbances in autonomic function yield cardiovascular instability and hypertension in the chromogranin A null mouse. Endocrinology (2009) 150(11):5027–35. doi:10.1210/en.2009-0429
62. Gayen JR, Zhang K, Ramachandrarao SP, Mahata M, Chen Y, Kim H-S, et al. Role of reactive oxygen species in hyperadrenergic hypertension: biochemical, physiological, and pharmacological evidence from targeted ablation of the chromogranin A gene. Circ Cardiovasc Genet (2010) 3:414–25. doi:10.1161/CIRCGENETICS.109.924050
63. Dev NB, Gayen JR, O’Connor DT, Mahata SK. Chromogranin A and the autonomic system: decomposition of heart rate variability by time and frequency domains, along with non-linear characteristics during chromogranin A ablation, with “rescue” by its catestatin. Endocrinology (2010) 151:2760–8. doi:10.1210/en.2009-1110
64. Bandyopadhyay GK, Lu M, Avolio E, Siddiqui JA, Gayen JR, Wollam J, et al. Pancreastatin-dependent inflammatory signaling mediates obesity-induced insulin resistance. Diabetes (2015) 64(1):104–16. doi:10.2337/db13-1747
65. Kitayama N, Tateishi K, Funakoshi A, Miyasaka K, Shimazoe T, Kono A, et al. Pancreastatin molecular forms in normal human plasma. Life Sci (1994) 54(21):1571–8. doi:10.1016/0024-3205(94)90028-0
66. Bartolomucci A, Possenti R, Mahata SK, Fischer-Colbrie R, Loh YP, Salton SR. The extended granin family: structure, function, and biomedical implications. Endocr Rev (2011) 32(6):755–97. doi:10.1210/er.2010-0027
67. Valicherla GR, Hossain Z, Mahata SK, Gayen JR. Pancreastatin is an endogenous peptide that regulates glucose homeostasis. Physiol Genomics (2013) 45(22):1060–71. doi:10.1152/physiolgenomics.00131.2013
68. Allu PK, Chirasani VR, Ghosh D, Mani A, Bera AK, Maji SK, et al. Naturally occurring variants of the dysglycemic peptide pancreastatin: differential potencies for multiple cellular functions and structure-function correlation. J Biol Chem (2014) 289(7):4455–69. doi:10.1074/jbc.M113.520916
69. Ahren B, Bertrand G, Roye M, Ribes G. Pancreastatin modulates glucose-stimulated insulin secretion from the perfused rat pancreas. Acta Physiol Scand (1996) 158(1):63–70. doi:10.1046/j.1365-201X.1996.525291000.x
70. Efendic S, Tatemoto K, Mutt V, Quan C, Chang D, Ostenson CG. Pancreastatin and islet hormone release. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A (1987) 84(20):7257–60. doi:10.1073/pnas.84.20.7257
71. Peiro E, Miralles P, Silvestre RA, Villanueva ML, Marco J. Pancreastatin inhibits insulin secretion as induced by glucagon, vasoactive intestinal peptide, gastric inhibitory peptide, and 8-cholecystokinin in the perfused rat pancreas. Metabolism (1989) 38(7):679–82. doi:10.1016/0026-0495(89)90107-8
72. Peiro E, Degano P, Silvestre RA, Marco J. Inhibition of insulin release by amylin is not mediated by changes in somatostatin output. Life Sci (1991) 49(10):761–5. doi:10.1016/0024-3205(91)90109-O
73. Schmidt WE, Creutzfeldt W. Pancreastatin – a novel regulatory peptide? Acta Oncol (1991) 30(4):441–9. doi:10.3109/02841869109092399
74. von Schonfeld J, Kleimann J, Muller MK, Runzi M, Goebell H. Glucose-dependent effects of pancreastatin on insulin and glucagon release. Int J Pancreatol (1991) 10(2):143–9.
75. Peiro E, Degano P, Miralles P, Silvestre RA, Marco J. Homologous pancreastatin inhibits insulin secretion without affecting glucagon and somatostatin release in the perfused rat pancreas. Regul Pept (1991) 34(3):159–67. doi:10.1016/0167-0115(91)90175-G
76. González-Yanes C, Sánchez-Margalet V. Pancreastatin modulates insulin signaling in rat adipocytes: mechanisms of cross-talk. Diabetes (2000) 49(8):1288–94. doi:10.2337/diabetes.49.8.1288
77. O’Connor DT, Cadman PE, Smiley C, Salem RM, Rao F, Smith J, et al. Pancreastatin: multiple actions on human intermediary metabolism in vivo, variation in disease, and naturally occurring functional genetic polymorphism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab (2005) 90(9):5414–25. doi:10.1210/jc.2005-0408
78. Biswas N, Friese RS, Gayen JR, Bandyopadhyay G, Mahata SK, O’Connor DT. Discovery of a novel target for the dysglycemic chromogranin A fragment pancreastatin: interaction with the chaperone GRP78 to influence metabolism. PLoS One (2014) 9(1):e84132. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0084132
79. Sanchez-Margalet V, Gonzalez-Yanes C, Najib S. Pancreastatin, a chromogranin A-derived peptide, inhibits DNA and protein synthesis by producing nitric oxide in HTC rat hepatoma cells. J Hepatol (2001) 35(1):80–5. doi:10.1016/S0168-8278(01)00071-X
80. Mosen H, Salehi A, Henningsson R, Lundquist I. Nitric oxide inhibits, and carbon monoxide activates, islet acid alpha-glucoside hydrolase activities in parallel with glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. J Endocrinol (2006) 190(3):681–93. doi:10.1677/joe.1.06890
81. Sanchez V, Lucas M, Calvo JR, Goberna R. Glycogenolytic effect of pancreastatin in isolated rat hepatocytes is mediated by a cyclic-AMP-independent Ca(2+)-dependent mechanism. Biochem J (1992) 284(Pt 3):659–62. doi:10.1042/bj2840659
82. Sanchez V, Calvo JR, Goberna R. Glycogenolytic effect of pancreastatin in the rat. Biosci Rep (1990) 10(1):87–91. doi:10.1007/BF01116856
83. Sanchez-Margalet V, Calvo JR, Goberna R. Glucogenolytic and hyperglycemic effect of 33-49 C-terminal fragment of pancreastatin in the rat in vivo. Horm Metab Res (1992) 24(10):455–7. doi:10.1055/s-2007-1003361
84. Kraemer FB, Shen WJ. Hormone-sensitive lipase: control of intracellular tri-(di-)acylglycerol and cholesteryl ester hydrolysis. J Lipid Res (2002) 43(10):1585–94. doi:10.1194/jlr.R200009-JLR200
85. Sanchez-Margalet V, Gonzalez-Yanes C. Pancreastatin inhibits insulin action in rat adipocytes. Am J Physiol (1998) 275(6 Pt 1):E1055–60.
86. Funakoshi A, Tateishi K, Shinozaki H, Matsumoto M, Wakasugi H. Elevated plasma levels of pancreastatin (PST) in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM). Regul Pept (1990) 30(2):159–64. doi:10.1016/0167-0115(90)90056-3
87. Sanchez-Margalet V, Lobon JA, Gonzalez A, Fernandez-Soto ML, Escobar-Jimenez F, Goberna R. Increased plasma pancreastatin-like levels in gestational diabetes: correlation with catecholamine levels. Diabetes Care (1998) 21(11):1951–4. doi:10.2337/diacare.21.11.1951
88. Hotamisligil GS, Shargill NS, Spiegelman BM. Adipose expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha: direct role in obesity-linked insulin resistance. Science (1993) 259(5091):87–91. doi:10.1126/science.7678183
89. Yudkin JS, Stehouwer CD, Emeis JJ, Coppack SW. C-reactive protein in healthy subjects: associations with obesity, insulin resistance, and endothelial dysfunction: a potential role for cytokines originating from adipose tissue? Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol (1999) 19(4):972–8. doi:10.1161/01.ATV.19.4.972
90. Festa A, D’Agostino R Jr, Howard G, Mykkanen L, Tracy RP, Haffner SM. Chronic subclinical inflammation as part of the insulin resistance syndrome: the Insulin Resistance Atherosclerosis Study (IRAS). Circulation (2000) 102(1):42–7. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.102.1.42
91. Pradhan AD, Manson JE, Rifai N, Buring JE, Ridker PM. C-reactive protein, interleukin 6, and risk of developing type 2 diabetes mellitus. JAMA (2001) 286(3):327–34. doi:10.1001/jama.286.3.327
92. Glass CK, Olefsky JM. Inflammation and lipid signaling in the etiology of insulin resistance. Cell Metab (2012) 15(5):635–45. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2012.04.001
93. Pini M, Rhodes DH, Castellanos KJ, Cabay RJ, Grady EF, Fantuzzi G. Rosiglitazone improves survival and hastens recovery from pancreatic inflammation in obese mice. PLoS One (2012) 7(7):e40944. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0040944
94. Zhao D, McCully BH, Brooks VL. Rosiglitazone improves insulin sensitivity and baroreflex gain in rats with diet-induced obesity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther (2012) 343(1):206–13. doi:10.1124/jpet.112.194738
95. Foryst-Ludwig A, Hartge M, Clemenz M, Sprang C, Hess K, Marx N, et al. PPARgamma activation attenuates T-lymphocyte-dependent inflammation of adipose tissue and development of insulin resistance in obese mice. Cardiovasc Diabetol (2010) 9:64. doi:10.1186/1475-2840-9-64
96. Klyachkin YM, Karapetyan AV, Ratajczak MZ, Abdel-Latif A. The role of bioactive lipids in stem cell mobilization and homing: novel therapeutics for myocardial ischemia. Biomed Res Int (2014) 2014:653543. doi:10.1155/2014/653543
97. Danieli-Betto D, Peron S, Germinario E, Zanin M, Sorci G, Franzoso S, et al. Sphingosine 1-phosphate signaling is involved in skeletal muscle regeneration. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol (2010) 298(3):C550–8. doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00072.2009
98. Turpin SM, Nicholls HT, Willmes DM, Mourier A, Brodesser S, Wunderlich CM, et al. Obesity-induced CerS6-dependent C16:0 ceramide production promotes weight gain and glucose intolerance. Cell Metab (2014) 20(4):678–86. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2014.08.002
99. Ussher JR, Koves TR, Cadete VJ, Zhang L, Jaswal JS, Swyrd SJ, et al. Inhibition of de novo ceramide synthesis reverses diet-induced insulin resistance and enhances whole-body oxygen consumption. Diabetes (2010) 59(10):2453–64. doi:10.2337/db09-1293
100. Tang K, Pasqua T, Biswas A, Mahata S, Tang J, Tang A, et al. Muscle injury, impaired muscle function and insulin resistance in chromogranin A-knockout mice. J Endocrinol (2017) 232(2):137–53. doi:10.1530/JOE-16-0370
101. Ozcan U, Yilmaz E, Ozcan L, Furuhashi M, Vaillancourt E, Smith RO, et al. Chemical chaperones reduce ER stress and restore glucose homeostasis in a mouse model of type 2 diabetes. Science (2006) 313(5790):1137–40. doi:10.1126/science.1128294
102. Ozcan U, Cao Q, Yilmaz E, Lee AH, Iwakoshi NN, Ozdelen E, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress links obesity, insulin action, and type 2 diabetes. Science (2004) 306(5695):457–61. doi:10.1126/science.1103160
103. Hetz C. The unfolded protein response: controlling cell fate decisions under ER stress and beyond. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol (2012) 13(2):89–102. doi:10.1038/nrm3270
104. Fu S, Watkins SM, Hotamisligil GS. The role of endoplasmic reticulum in hepatic lipid homeostasis and stress signaling. Cell Metab (2012) 15(5):623–34. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2012.03.007
105. Ozcan L, Tabas I. Role of endoplasmic reticulum stress in metabolic disease and other disorders. Annu Rev Med (2012) 63:317–28. doi:10.1146/annurev-med-043010-144749
106. Oakes SA, Papa FR. The role of endoplasmic reticulum stress in human pathology. Annu Rev Pathol (2015) 10:173–94. doi:10.1146/annurev-pathol-012513-104649
107. Tabas I, Ron D. Integrating the mechanisms of apoptosis induced by endoplasmic reticulum stress. Nat Cell Biol (2011) 13(3):184–90. doi:10.1038/ncb0311-184
108. Cao SS, Kaufman RJ. Unfolded protein response. Curr Biol (2012) 22(16):R622–6. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2012.07.004
109. Back SH, Kaufman RJ. Endoplasmic reticulum stress and type 2 diabetes. Annu Rev Biochem (2012) 81:767–93. doi:10.1146/annurev-biochem-072909-095555
110. Wang S, Kaufman RJ. The impact of the unfolded protein response on human disease. J Cell Biol (2012) 197(7):857–67. doi:10.1083/jcb.201110131
111. Zhang LH, Zhang X. Roles of GRP78 in physiology and cancer. J Cell Biochem (2010) 110(6):1299–305. doi:10.1002/jcb.22679
112. Pfaffenbach KT, Lee AS. The critical role of GRP78 in physiologic and pathologic stress. Curr Opin Cell Biol (2011) 23(2):150–6. doi:10.1016/j.ceb.2010.09.007
113. Kammoun HL, Chabanon H, Hainault I, Luquet S, Magnan C, Koike T, et al. GRP78 expression inhibits insulin and ER stress-induced SREBP-1c activation and reduces hepatic steatosis in mice. J Clin Invest (2009) 119(5):1201–15. doi:10.1172/JCI37007
114. O’Connor DT, Kailasam MT, Kennedy BP, Ziegler MG, Yanaihara N, Parmer RJ. Early decline in the catecholamine release-inhibitory peptide catestatin in humans at genetic risk of hypertension. J Hypertens (2002) 20:1335–45. doi:10.1097/00004872-200207000-00020
115. O’Connor DT, Zhu G, Rao F, Taupenot L, Fung MM, Das M, et al. Heritability and genome-wide linkage in US and australian twins identify novel genomic regions controlling chromogranin A: implications for secretion and blood pressure. Circulation (2008) 118(3):247–57. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.709105
116. Kennedy BP, Mahata SK, O’Connor DT, Ziegler MG. Mechanism of cardiovascular actions of the chromogranin A fragment catestatin in vivo. Peptides (1998) 19(7):1241–8. doi:10.1016/S0196-9781(98)00086-2
117. Mahata SK, Mahata M, Parmer RJ, O’Connor DT. Desensitization of catecholamine release: the novel catecholamine release-inhibitory peptide catestatin (chromogranin A344-364) acts at the receptor to prevent nicotinic cholinergic tolerance. J Biol Chem (1999) 274(5):2920–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.5.2920
118. Herrero CJ, Ales E, Pintado AJ, Lopez MG, Garcia-Palomero E, Mahata SK, et al. Modulatory mechanism of the endogenous peptide catestatin on neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors and exocytosis. J Neurosci (2002) 22(2):377–88.
119. Mahata SK, Mahata M, Wen G, Wong WB, Mahapatra NR, Hamilton BA, et al. The catecholamine release-inhibitory “catestatin” fragment of chromogranin A: naturally occurring human variants with different potencies for multiple chromaffin cell nicotinic cholinergic responses. Mol Pharmacol (2004) 66(5):1180–91. doi:10.1124/mol.104.002139
120. Mahapatra NR, Mahata M, Mahata SK, O’Connor DT. The chromogranin A fragment catestatin: specificity, potency and mechanism to inhibit exocytotic secretion of multiple catecholamine storage vesicle co-transmitters. J Hypertens (2006) 24(5):895–904. doi:10.1097/01.hjh.0000222760.99852.e0
121. Biswas N, Gayen J, Mahata M, Su Y, Mahata SK, O’Connor DT. Novel peptide isomer strategy for stable inhibition of catecholamine release: application to hypertension. Hypertension (2012) 60(6):1552–9. doi:10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.112.202127
122. Penna C, Alloatti G, Gallo MP, Cerra MC, Levi R, Tullio F, et al. Catestatin improves post-ischemic left ventricular function and decreases ischemia/reperfusion injury in heart. Cell Mol Neurobiol (2010) 30(8):1171–9. doi:10.1007/s10571-010-9598-5
123. Bassino E, Fornero S, Gallo MP, Ramella R, Mahata SK, Tota B, et al. A novel catestatin-induced antiadrenergic mechanism triggered by the endothelial PI3K–eNOS pathway in the myocardium. Cardiovasc Res (2011) 91(4):617–24. doi:10.1093/cvr/cvr129
124. Perrelli MG, Tullio F, Angotti C, Cerra MC, Angelone T, Tota B, et al. Catestatin reduces myocardial ischaemia/reperfusion injury: involvement of PI3K/Akt, PKCs, mitochondrial K(ATP) channels and ROS signalling. Pflugers Arch (2013) 465:1031–40. doi:10.1007/s00424-013-1217-0
125. Penna C, Pasqua T, Amelio D, Perrelli MG, Angotti C, Tullio F, et al. Catestatin increases the expression of anti-apoptotic and pro-angiogenetic factors in the post-ischemic hypertrophied heart of SHR. PLoS One (2014) 9(8):e102536. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0102536
126. Bassino E, Fornero S, Gallo MP, Gallina C, Femmino S, Levi R, et al. Catestatin exerts direct protective effects on rat cardiomyocytes undergoing ischemia/reperfusion by stimulating PI3K–Akt–GSK3beta pathway and preserving mitochondrial membrane potential. PLoS One (2015) 10(3):e0119790. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0119790
127. Angelone T, Quintieri AM, Pasqua T, Filice E, Cantafio P, Scavello F, et al. The NO stimulator, catestatin, improves the Frank–Starling response in normotensive and hypertensive rat hearts. Nitric Oxide (2015) 50:10–9. doi:10.1016/j.niox.2015.07.004
Keywords: obesity, insulin resistance, inflammation, chromogranin A knockout, pancreastatin, catestatin
Citation: Bandyopadhyay GK and Mahata SK (2017) Chromogranin A Regulation of Obesity and Peripheral Insulin Sensitivity. Front. Endocrinol. 8:20. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2017.00020
Received: 13 December 2016; Accepted: 23 January 2017;
Published: 08 February 2017
Edited by:
Gaetano Santulli, Columbia University, USAReviewed by:
Anne-Francoise Burnol, Institut national de la santé et de la recherche médicale, FranceMarialuisa Appetecchia, Istituti Fisioterapici Ospitalieri (IRCCS), Italy
Hiroki Mizukami, Hirosaki University, Japan
Copyright: © 2017 Bandyopadhyay and Mahata. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) or licensor are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Sushil K. Mahata, c21haGF0YUB1Y3NkLmVkdQ==
 Gautam K. Bandyopadhyay1
Gautam K. Bandyopadhyay1 Sushil K. Mahata
Sushil K. Mahata