- 1Department of Biochemistry, McGill University, Montreal, QC, Canada
- 2Goodman Cancer Research Centre, McGill University, Montreal, QC, Canada
- 3Department of Biochemistry, Microbiology and Immunology, and Ottawa Institute of Systems Biology, University of Ottawa, Ottawa, ON, Canada
Metformin is one of the most commonly prescribed medications for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Numerous reports have suggested potential anti-cancerous and cancer preventive properties of metformin, although these findings vary depending on the intrinsic properties of the tumor, as well as the systemic physiology of patients. These intriguing studies have led to a renewed interest in metformin use in the oncology setting, and fueled research to unveil its elusive mode of action. It is now appreciated that metformin inhibits complex I of the electron transport chain in mitochondria, causing bioenergetic stress in cancer cells, and rendering them dependent on glycolysis for ATP production. Understanding the mode of action of metformin and the consequences of its use on cancer cell bioenergetics permits the identification of cancer types most susceptible to metformin action. Such knowledge may also shed light on the varying results to metformin usage that have been observed in clinical trials. In this review, we discuss metabolic profiles of cancer cells that are associated with metformin sensitivity, and rationalize combinatorial treatment options. We use the concept of bioenergetic flexibility, which has recently emerged in the field of cancer cell metabolism, to further understand metabolic rearrangements that occur upon metformin treatment. Finally, we advance the notion that metabolic fitness of cancer cells increases during progression to metastatic disease and the emergence of therapeutic resistance. As a result, sophisticated combinatorial approaches that prevent metabolic compensatory mechanisms will be required to effectively manage metastatic disease.
Metformin
A Drug With A Long History
Metformin was first discovered in the 1920s by a French physician from a plant called Goat's Rue (1). It was found that animals grazing on this plant had low blood glucose levels [reviewed in Witters (2)]. Subsequently, it was determined that the active compound responsible for lowering blood glucose was a guanidine moiety. Early synthetic homologues of guanidine were created for the treatment of diabetes, although they proved to be hepatotoxic and were rapidly discontinued. Renewed interest in guanidine in the 1960s led to the creation of a family of biguanide compounds [reviewed in White (3)]. Phenformin was the first biguanide family member prescribed to diabetic patients (4); however, its use was associated with the development of lactic acidosis (5). The biguanide metformin was better tolerated relative to phenformin by diabetic patients and was approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the 1990s for the treatment of type 2 diabetes (6). Metformin is an extremely safe medication; rarely associated with the development of lactic acidosis (7). Additionally, metformin has global appeal as it is a low cost medication with generic versions also available.
It has been reported that patients with diabetes are more likely to develop cancer in their lifetime compared to non-diabetic individuals (8). A retrospective report published in 2005 suggested that metformin users have lower incidences of cancer relative to patients prescribed other type 2 diabetic medications (9). Moreover, users of diabetic medications other than metformin displayed increased cancer-related mortality (10). The study by Evans et al. (9) sparked great interest in the academic community, and metformin has been, or currently is being investigated in 310 individual clinical trials for its role in the prevention or treatment of various types of cancer. However, there is currently no consensus regarding which cancers are most likely to benefit from metformin treatment. Completed clinical trials have varied in outcome depending on trial design, cancer type, stage of cancer, timing of metformin treatment, and combinatorial therapies or treatments given in addition to metformin. Individual clinical studies have shown that metformin is associated with increased survival of diabetic patients with lung (11), colorectal (12), and prostate (13, 14) cancers. Moreover, metformin is associated with reduced risk of developing pancreatic (15), breast (16), colorectal (17) or liver (18) cancers. Recently, studies have been developed to investigate potential anti-cancer roles of metformin in non-diabetic patients given the increasing literature supporting its action in cancers, as well as the fact that metformin is associated with less hypoglycemic episodes than other diabetic medications (19). One randomized control trial on metformin monotherapy in advanced melanoma showed no benefit; however, the authors propose a more effective strategy would involve combining metformin with BRAF inhibitors and screening for patients with p53 polymorphisms (20). Such a trial in advanced melanoma has been completed (NCT02143050)1, and another combining metformin with cancer immunotherapy is ongoing (NCT03311308)2. One randomized trial of metformin combinatorial treatment with standard of care chemotherapy showed no benefit in advanced pancreatic cancer (21), despite large meta-analysis showing significant survival in metformin treated pancreatic patients (22). These studies highlight a need for more rigorous planning of clinical trials that focus more on potential predictive biomarkers (23). Additionally, a randomized trial with metformin monotherapy in early stage breast cancer is ongoing (NCT01101438)3, as well as a trial combining metformin with neo-adjuvant chemotherapy in HER2+ breast cancer (NCT03238495)4. These studies will reveal whether metformin's mode of action in cancer extends beyond its ability to reduce blood glucose levels, as glucose levels in healthy patients will not be affected by metformin treatment. Overall, the current available data support continued efforts toward examining the potential therapeutic role of metformin in various cancers, both in diabetic and non-diabetic patients.
Molecular Targets of Metformin
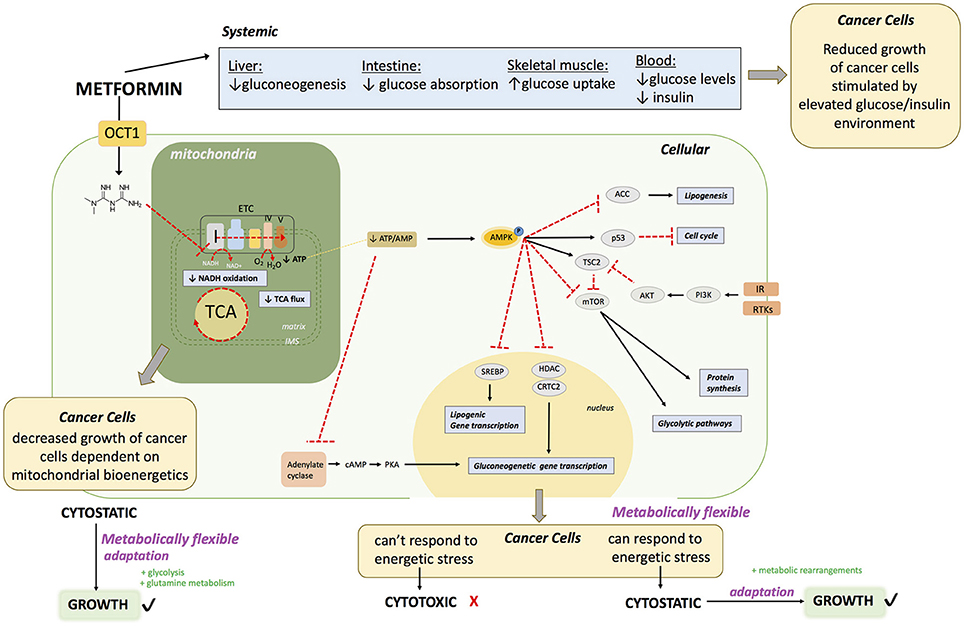
Metformin is known to act on the liver, gut and skeletal muscle to globally lower blood glucose levels in diabetic patients with hyperglycemia (24) (Figure 1). The first report of a direct molecular target of metformin was in 2000 (25) showing that metformin acts on complex I of the electron transport chain (ETC) of mitochondria. However, the experiments in this study were performed under harsh experimental conditions that included incubation of mitochondria at low temperature (8°C) for extended periods of time (400 min) in the presence of high dose (10 mM) of metformin. The conclusions were rapidly challenged when a study showed that metformin had no direct effect on mitochondrial complex I (26). As a result, this controversy remained, and for over a decade following these initial observations the molecular mechanism of metformin was characterized as unknown or incompletely described. Various targets have been proposed by several groups, including complex II and IV of the ETC (27), LKB1/AMPK (28–30), adenylate cyclase (31), AMP deaminase (32), NADPH oxidase (33) and mitochondrial glycerophosphate dehydrogenase (34). Elucidation of a key molecular target of metformin came in 2014 when three groups, using differential approaches and experimental conditions published novel and conclusive evidence on the inhibitory properties of metformin on complex I (35–37). This included work on permeabilized cells and cancer cells that do not express complex I (37), isolated mitochondria (35, 36) and purified complex I (36). It is now generally accepted that a direct molecular target of metformin is complex I (24, 38, 39). Many of the other proposed effects and targets of metformin may be explained by a shift in NAD/NADH caused by complex I inhibition, leading to decreased activity of enzymes that depend on the fine balance of cellular NAD/NADH. Inhibition of mitochondrial glycerophosphate dehydrogenase could also perturb NAD/NADH (40). The controversies surrounding the action of metformin on cells may be partly explained by the varying concentrations used in experimental systems (28).
Bioenergetic Stress: Metabolic Disruption
Complex I is the entry point for reduced NADH in the ETC. Direct inhibition of complex I by metformin in cells decreases the proton gradient and mitochondrial oxygen consumption rate (35), diminishes tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA) activity and metabolites (35, 41–45) and leads to decreased cellular ATP levels (25, 26, 43) (Figure 1). The inhibition of mitochondrial respiration and ATP production by metformin results in a compensatory increase in glycolysis (35, 43) as well as increased activity of glycolytic enzymes. These metabolic adaptations are engaged in an attempt to restore cellular ATP levels. However, if the compensatory activation of glycolysis cannot meet the cellular ATP requirements, AMPK becomes activated in order to potentiate catabolic metabolism, and inhibit anabolic reactions (30, 43, 47, 46). Phosphorylation and activation of AMPK leads to phosphorylation and inactivation of ACC, one of the most characterized targets of AMPK, causing a reduction in lipogenesis (48, 49). Metformin increases the levels of AMP causing inhibition of adenylate cyclase (31). Metformin also inhibits mTORC1 signaling (50, 51). Overall, metformin treatment causes at least a transient decrease in cellular energy status, leading to a global decrease in ATP consuming processes. In proliferating cells, this can elicit a cytostatic state that is associated with reduced proliferation, explaining some clinical observations of decreased progression of cancer cell growth. Cancer cells that cannot eventually compensate for this reduced energy status may undergo apoptosis (52, 53).
Metformin enters the cell via an OCT transporter; commonly OCT1 expressed on the surface of hepatocytes. Metformin acts directly on mitochondria to inhibit complex I of the ETC. This causes 1) diminished NADH oxidation at complex I, resulting in a buildup of NADH, 2) diminished TCA cycle activity due to allosteric inhibition of enzymes in the TCA cycle from increased NADH/NAD, 3) diminished flow of electrons throughout the ETC, and ultimately diminished oxygen consumption and ATP production at complex V (ATP synthase). This can lead to decreased growth of a subset of cancers that heavily rely on mitochondrial bioenergetics. Failure to rearrange metabolic programs leads to decreased ATP levels. Diminished ATP levels in the cell leads to AMPK activation. In hepatocytes, this drop in ATP leads to a decrease in gluconeogenesis due to allosteric inhibition of several leads to a decreased absorption of glucose. In the muscles, this leads to increased glucose uptake and eventually a decrease in hyperglycemia in the blood; with reduced glucose and insulin levels. The reduction in blood glucose and insulin levels may impair the growth of a subset of cancers that proliferate in an environment dictated by type 2 diabetes. At a cellular level, activation of AMPK leads (1) to inactivation of ACC, leading to a decrease in lipogenesis, (2) activation of p53 leading to a decrease in cell cycle progression, (3) inactivation of mTOR leading to decreased protein synthesis and glycolytic pathways. Inactivation of mTOR may be useful in a subset of cancers that have RTKs or IR activation. AMPK activation also leads to (4) decreased transcription of gluconeogenic genes by inhibition of HDAC and CRTC2, which is also achieved by (5) adenylate cyclase inhibition. Furthermore, AMPK activation causes (6) a decrease of lipogenic gene expression by inhibition of SREBP. The end result of metformin exposure is cellular energetic stress. If the cancer cells are metabolically flexible, allowing them to successfully respond to this stress by rearranging metabolic programs, metformin has a cytostatic effect, however if cells fail to cope, metformin has a cytotoxic effect.
OCT1: organic transporter 1, TCA: tricarboxylic acid cycle, AMPK: 5′ adenosine monophosphate- activated protein kinase, IR: insulin receptor ACC acetyl-CoA carboxylase: mTOR: mammalian target of rapamycin, RTKs: receptor tyrosine kinases. cAMP: Cyclic adenosine monophosphate, AKT: protein kinase B, SREBP: Sterol regulatory element binding protein, HDAC: histone deacetylase, CRTC2: CREB-regulated transcription coactivator 2.
Metformin: Bioenergetic Medicine
Bioenergetic Medicine
Metformin is now classified as a bioenergetic disruptor and such drugs represent an exciting strategy to treat metabolic disorders, including cancer. Bioenergetic drugs affect ATP generating pathways, namely glycolysis, and oxidative phosphorylation. Bioenergetics is undeniably coupled to the proliferative potential of cancer cells. The focus of bioenergetic medicine (54) is not solely to impact ATP production, but also to disrupt biosynthetic pathways that rely on precursor metabolites found in ATP generating pathways for cancer cell proliferation. For example, glucose metabolism has been targeted using glycolysis inhibitors, such as 2-deoxyglucose (2-DG), a non-metabolizable glucose analog, which has been employed in clinical trials for various cancer types. Although many in vitro or murine studies demonstrate profound effects of 2-DG treatment on the growth of various cancer cell models (55–57), many clinical trials with 2-DG have been terminated early due to lack of early clinical efficacy as well as side effects, notably extreme exhaustion and cardiac arrhythmias in patients (NCT00633087)5. A completed study investigating an optimal dosage of 2-DG for solid tumors in combination with docetaxel treatment noted only moderate effects on stabilizing disease (58). However, significant side effects, including fatigue and nausea, were noted in many of patients (58).
In addition to glucose, many cancers are dependent on glutamine for their growth and are said to suffer from glutamine “addiction” (59). The expression of glutaminase is also up regulated in various cancer types (60–62). Murine tumor xenografts show promising anti-growth responses to inhibition of glutamine (glutaminase) metabolism (63, 64), and clinical trials are currently ongoing to test the efficacy of inhibiting glutaminase using a small molecule inhibitor (CB-839, Calithera Biosciences) in multiple types and stages of cancer (NCT020718626; NCT020718887; NCT03163667)8. It has also been suggested that metastatic progression is accompanied by increased glutamine utilization, and thus more aggressive prostate cancer cells were more sensitive to the glutaminase inhibitor CB-839 (65). However, to date, there are no glutaminase inhibitors approved for usage in cancer treatment.
Sensitivity to Metformin: A Metabolic Profile
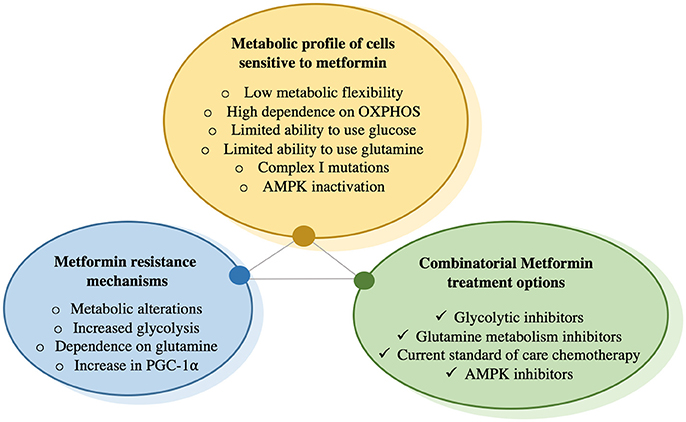
Performing clinical trials in patients to determine which cancer type will benefit most from metformin treatment is undeniably important to understand the potential of this drug in oncology. With recent advancements, especially the identification of a molecular target of metformin, an alternative strategy to elucidate metformin's potential in oncology is to establish a “metformin sensitivity” profile at the cellular level to identify those cancer cell types most sensitive to its effects (Figure 2). This entails (1) understanding the metabolic changes that occur upon metformin treatment, (2) determining the cancer cell types most susceptible to these changes, (3) identifying those patients that would best benefit from metformin treatment and lastly, 4) defining combinatorial therapies that work best with metformin treatment in order to prevent compensatory mechanisms. This approach represents a rational and streamlined method to identify patients who would be most responsive to metformin treatment. However, it is difficult to predict whether the effects observed at the cellular level will translate in vivo. Therefore, the comparisons of the results obtained in vitro, in vivo and in clinical trials are necessary to reveal the full potential of metformin in the oncology setting.
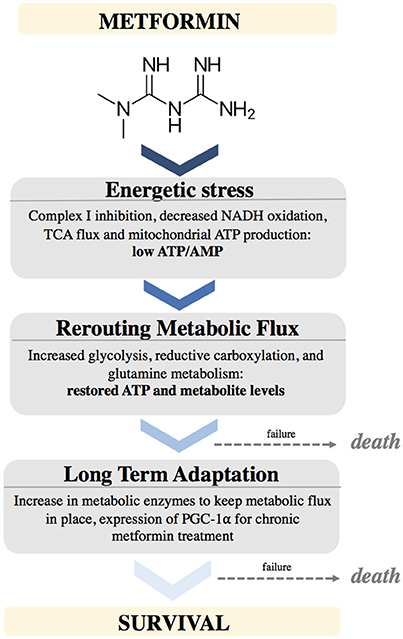
Figure 2. Schematic depicting the effects of Metformin on cellular metabolism and adaptations needed to support cancer cell survival.
To identify cancer cells most susceptible to metformin, we first need to recognize its mechanism of action and identify the internal cellular changes that occur upon treatment. Metformin inhibits complex I of the ETC in mitochondria, leading to perturbation in NAD/NADH and decreased oxygen consumption. This leads to diminished TCA activity and metabolite levels, as well as potential energetic stress leading to AMPK activation. Cells compensate for these metformin-mediated effects by increasing glucose uptake and glycolysis, and switching to glutamine utilization, as a way of refueling the TCA and providing biosynthetic intermediates for lipid production required to synthesize membranes (35, 42, 43, 66, 67). Hence, cancer cells exposed to metformin need to rearrange and reroute metabolic flux. It is increasingly evident that metformin alters substrate utilization in the mitochondria (45). As a result, cancer cells that would be most susceptible to metformin's action would have a high reliance on OXPHOS as a source of ATP and lack metabolic flexibility to efficiently engage glycolysis. For example, cancer cells with defective mitochondria may not be able to successfully switch mitochondrial substrate utilization due to mutations or defects in these metabolic pathways. As a result, cells with defective mitochondria could be more sensitive to metformin treatment due to their inability to alter mitochondrial substrate utilization. In support of this point, complex I mutations have been shown to predict sensitivity to phenformin (68). It is possible that cancer cells with oxidative phosphorylation deficits may thus be more sensitive to biguanides than normal tissues.
It is becoming more apparent that numerous metabolic programs and adaptations in cancer cells are mediated by the metabolic regulator PGC-1α (69). We predict that cancer cells expressing low PGC-1α levels, or that fail to upregulate PGC-1α in the presence of metformin, would be more sensitive as they may not efficiently engage adaptive programs to promote survival. Additionally, cancer cells with inactive or impaired AMPK signaling may be more sensitive to metformin treatment, as AMPK is the main energy sensor in the cell, and AMPK activation upon exposure to metformin contributes significantly to the upregulation of PGC-1α and its adaptive programs (70). Although previously controversial, AMPK is not required for metformin action; however, AMPK signaling is advantageous as an adaptive response to cope with energetic stress (71).
Metformin causes energetic stress in cells by inhibiting complex I of the electron transport chain in mitochondria. This causes a decrease in NADH oxidation, decreased TCA flux, leading to low levels of TCA metabolites. This causes a temporarily low ATP/AMP ratio. Cells react by rewiring metabolic flux. This includes up regulating pathways to support increased glycolysis, increased glutamine utilization to provide alternative sources of ATP as well as metabolites. Cells that fail to metabolically adapt to this stress will undergo cell death. After longer exposure to metformin, cells will adapt by stably increasing enzymes needed to maintain these metabolic pathways, partially by upregulating PGC-1α expression (Figure 2).
Metabolic Flexibility: Targeting Metformin Resistance
It has recently been shown that chronic exposure to metformin in cancer cells ultimately leads to drug resistance and that this is linked to increased PGC-1α levels (41). Metformin resistant cells are metabolically flexible and able to switch fuel sources from oxidative metabolism to glycolysis and glutamine metabolism in the context of metformin-mediated inhibition of oxidative phosphorylation. Although at first it may seem counterintuitive to increase the level of PGC-1α, a key regulator of OXPHOS and mitochondrial biogenesis, upon inhibition of OXPHOS by metformin, it is now appreciated that PGC-1α clearly has functions outside of its classic role in mitochondrial metabolism. We argue that PGC-1α supports metabolic flexibility upon bioenergetic stresses. Elevated PGC-1α levels in the presence of metformin reprograms cellular metabolism and creates a new metabolic state that promotes an alternate source of ATP production through stimulation of glycolysis as well as facilitating anabolic metabolism by diverting mitochondrial metabolites that would normally be used for ATP production for use in anabolic reactions. In support of this point, PGC-1α controls numerous metabolic programs in cancer, notably glucose (41, 72), glutamine (73), fat (74), and one carbon metabolism (70). This ability of PGC-1α to support numerous metabolic programs in breast cancer cells allows for an enhanced fuel flexibility to cope with bioenergetic stressors such as metformin (41).
After developing a greater understanding of the metabolic rearrangements that occur upon metformin treatment (Figure 2), rational combinatorial treatments can be devised to combat adaptive mechanisms (Figure 3). The most immediate strategy would be to combine metformin with glycolysis inhibitors to prevent the adaptive glycolytic activity seen with metformin treatment alone. Blocking oxidative phosphorylation and glycolysis would stop the two main sources of ATP production, ultimately leading to cell death. Indeed, when breast cancer cells treated with metformin are deprived of glucose, this results in almost 100% cell death in just 72 h, even in the presence of glutamine (35). Additionally, it has been shown that cells with mutations leading to either impaired glucose utilization or mitochondrial DNA mutations are more sensitive to the effects of biguanides (68). Other reports have shown similar results by combining metformin with inhibitors of glycolysis and thus preventing ATP production (75, 76). One concern is that all cells are capable of engaging glycolysis and OXPHOS for ATP production, although their degree of dependence on either pathway can vary. Rapidly proliferating cells require much more ATP than differentiated cells, thus targeting ATP producing pathways could prove beneficial, as this rationale has been the basis of chemotherapy for decades. Another potential metabolic combination therapy could be the targeting of regulators of metabolic flexibility, notably PGC-1α. A small molecule compound was recently found to reduce PGC-1α-dependent gluconeogenic activity in the liver by increasing PGC-1α acetylation, leading to an amelioration of glucose homeostasis in a murine model of diabetes (77). However, the role of PGC-1α in gluconeogenesis is far more developed than in cancer, and cancer specific post-translational modifications on PGC-1α are far less understood.
In addition, metformin is currently used in clinical trials as a combinational therapy with already established treatment options, such as chemotherapy. It has been suggested that combinatorial treatment of metformin with chemotherapy may sensitize cancer cells to chemotherapy treatment, leading to improved treatment efficacy and lower doses of administered chemotherapy (78–82). In murine models, combinatorial metformin treatment with the chemotherapeutic agent doxorubicin led to reduced mammary tumor mass and relapse compared to either drug alone when performing xenograft experiments (83, 84). There is also data showing that metformin has synergistic effects with various chemotherapy agents, including Pemetrexed in cell lines of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), (85) EGFR-TKI in patients with NSCLC (86), Trichostatin in osteosarcoma cell lines (87), Simvastatin in animal models of metastatic prostate cancer (88) and Nelfinavir in cervical cancer xenografts (89). It has also been suggested that metformin may lead to a re-sensitization of cancer cells that have become resistance to chemotherapy, the predominant cause of treatment failure in patients undergoing treatment (45, 84, 90, 91). One study showed that metformin reduces the differences in metabolism between chemotherapy resistant and sensitive cells (92). Furthermore, metformin was shown to target metabolic programs that chemoresistant cancer cells become reliant on, including OXPHOS and glutamine metabolism (92).
Overall, metabolic flexibility is required to adapt to bioenergetic stress, such as metformin exposure. Additionally, cancer cells treated with chemotherapeutic agents display vast metabolic arrangements enabling them to become resistant. Targeting this flexibility by inhibiting compensatory metabolic shifts, such as using inhibitors of glycolysis or glutamine metabolism, may prove useful. It is becoming clear that attacking only one aspect of cellular growth or one metabolic pathway will ultimately lead to metabolic rearrangements and the emergence of resistance. Targeting both cellular proliferation and metabolism could prove to be a more efficacious strategy. Another approach could be to overload the compensatory metabolic pathways by drastically increasing ATP demand through the use of chemotherapeutic agents.
The features of cancer cells that would make them most sensitive to metformin treatment are described. Cells become resistant to chronic exposure to metformin by increasing glucose uptake as well as glycolysis, increasing glutamine utilization as a vital metabolite precursor for biosynthetic needs, as well as increase in PGC-1α expression, which has been shown to increase metabolic flexibility that is needed to overcome metformin-mediated bioenergetic stress. To prevent compensatory mechanisms by cells exposed to metformin, this drug can be combined with glycolysis inhibitors that prevent metabolism of glucose to lactate, or glutamine metabolism inhibitors, which prevent glutamine utilization. There is also data suggesting that metformin has synergetic effects with certain chemotherapies and may re-sensitize cancer cells that have become resistant to chemotherapy.
Future of Metformin in Oncology
Development of Novel Complex I Inhibitors in Oncology
In addition to metformin, various mitochondrial drugs are being developed for potential uses in oncology, and have been shown to alter mitochondrial metabolism. These include: (1) small molecule BAY 87-2242 that was developed as a complex I inhibitor, leading to a reduction of melanoma tumor growth in murine models (93), (2) Xanthohumol that leads to the overproduction of ROS and eventual apoptosis in cancer cells (94), (3) Canagliflozin, a proposed inhibitor of complex I and mitochondrial glutamate dehydrogenase (95), which reduces the proliferation of prostate and lung cancer cells (96), 4] Fenofibrate, another proposed complex I inhibitor, that depletes cellular ATP and induces cytotoxicity in glioblastoma (97) and 5) small molecule inhibitor JC1-20679 developed to inhibit complex I, slowing the growth of a panel of cancer cell lines (98). These results highlight the importance of mitochondrial metabolism in cancer and support the notion of targeting mitochondria for cancer therapeutic purposes. At this stage, it is unknown whether some of these molecules will be approved for usage in clinical trials, as toxicity in humans has not yet been demonstrated for all these drugs. However, Canaglifozin is already used for the treatment of type 2 diabetes; but the FDA has recently added additional Warning and Precautions stating that this drug causes increased ketoacidosis, decreased bone density, and increased risk of leg and foot amputations (99, 100). Developing an effective drug for oncology is clearly not as simple as just synthesizing potent mitochondrial inhibitors. It is important to appreciate that complex I inhibitors, like rotenone or MPTP, can induce neurodegeneration in murine models (101, 102). However, metformin intake has been associated with better cognitive function in patients with Huntington's Disease (103). Indeed, it has been shown that metformin confers protection against mutant Huntingtin by modulating mitochondrial dynamics and activating AMPK (104).
In addition to metformin, phenformin is being revisited for usage in cancer therapy. Phenformin, like metformin, is a complex I inhibitor (36); however, it is transported with a greater affinity and kinetics into cells (105). For this reason, phenformin rapidly accumulates in cancer cells. Additionally, phenformin uptake will not depend on the genetic variation of transporters (OCT family), which have been shown to influence metformin uptake and efficacy due to individual polymorphisms (106). Phenformin is currently in a few clinical trials including a phase I clinical trial to determine optimal dosage for combined treatment with small molecule targeted therapies (Dabrafenib and Trametinib) for patients with BRAF mutated melanoma (NCT03026517)9. It is being examined whether phenformin can reduce melanoma resistance to traditional targeted therapies. It is possible that phenformin will become more rapidly used in future clinical trials; however, accurate dosage, which is effective yet minimizes side effects, has always been an issue, and is a key reason for its rapid discontinued use in diabetes (107). Therefore, there is still a need to determine optimal doses of phenformin for oncology application, while minimizing side effects such as lactic acidosis and gastrointestinal distress. With optimal dosage of phenformin, it may even be possible to decrease the dosage of chemotherapeutic agents.
Lastly, an emerging field in cancer metabolism is the development of organelle targeted therapeutics (108), which could be utilized to specifically localize and compartmentalize therapies to potentially minimize adverse effects. This notion could be used to reduce administered doses of therapy, while maximizing dose in the compartmentalized region, although this research area needs to be developed further.
Author Contributions
SA wrote most of the text for this manuscript. SA, PS and JS-P contributed to the concepts, writing and editing of the manuscript.
Funding
Research conducted in the authors' laboratories were supported from grants from the Terry Fox Research Institute (TFF-PPG-242122) and the CIHR (PJT-148650).
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Footnotes
1. ^ NCT02143050 Study of Dabrafenib, Trametinib and Metformin for Melanoma Patients., (https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02143050).
2. ^ NCT03311308 A Trial of Pembrolizumab and Metformin Versus Pembrolizumab Alone in Advanced Melanoma., (https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT03311308).
3. ^ NCT01101438 A Phase III Randomized Trial of Metformin vs Placebo in Early Stage Breast Cancer., (https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01101438).
4. ^ NCT03238495 Randomized Trial of Neo-adjuvant Chemotherapy With or Without Metformin for HER2 Positive Operable Breast Cancer., (https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT03238495).
5. ^ NCT00633087 A Phase I/II Trial of 2-Deoxyglucose (2DG) for the Treatment of Advanced Cancer and Hormone Refractory Prostate Cancer. (https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00633087).
6. ^ NCT02071862 Study of the Glutaminase Inhibitor CB-839 in Solid Tumors.
7. ^ NCT02071888 Study of the Glutaminase Inhibitor CB-839 in Hematological Tumors.
8. ^ NCT03163667 CB-839 With Everolimus vs. Placebo With Everolimus in Patients With RCC.
9. ^ NCT03026517 Clinical Trial of Phenformin in Combination With Dabrafenib and Trametinib for Patients With BRAF-mutated Melanoma.
References
1. Bailey CJ, Day C. Traditional plant medicines as treatments for diabetes. Diabetes Care (1989) 12:553–64. doi: 10.2337/diacare.12.8.553
2. Witters LA. The blooming of the French lilac, J Clin Invest. (2001) 108:1105–7. doi: 10.1172/JCI14178
3. White JR Jr. a brief history of the development of diabetes medications. Diabetes Spectr. (2014) 27:82–6. doi: 10.2337/diaspect.27.2.82
5. McGuinness ME, Talbert RL. Phenformin-induced lactic acidosis: a forgotten adverse drug reaction. Ann Pharmacother (1993) 27:1183–7. doi: 10.1177/106002809302701004
6. Bailey CJ, Turner RC. Metformin. N Engl J Med. (1996) 334:574–9. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199602293340906
7. Lalau JD, Race JM. Lactic acidosis in metformin therapy: searching for a link with metformin in reports of “metformin-associated lactic acidosis”. Diabetes Obes Metab. (2001) 3:195–201. doi: 10.1046/j.1463-1326.2001.00128.x
8. Giovannucci E, Harlan DM, Archer MC, Bergenstal RM, Gapstur SM, Habel LA, et al. Diabetes and cancer: a consensus report. Diabetes Care (2010) 33:1674–85. doi: 10.2337/dc10-0666
9. Evans JM, Donnelly LA, Emslie-Smith AM, Alessi DR, Morris AD. Metformin and reduced risk of cancer in diabetic patients. BMJ (2005) 330:1304–5. doi: 10.1136/bmj.38415.708634.F7
10. Bowker SL, Majumdar SR, Veugelers P, Johnson JA. Increased cancer-related mortality for patients with type 2 diabetes who use sulfonylureas or insulin. Diabetes Care (2006) 29:254–8. doi: 10.2337/diacare.29.02.06.dc05-1558
11. Tian RH, Zhang YG, Wu Z, Liu X, Yang JW, Ji HL. Effects of metformin on survival outcomes of lung cancer patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis. Clin Transl Oncol. (2016) 18:641–9. doi: 10.1007/s12094-015-1412-x
12. Meng F, Song L, Wang W. Metformin improves overall survival of colorectal cancer patients with diabetes: a meta-analysis. J Diabetes Res. (2017) 2017:5063239. doi: 10.1155/2017/5063239
13. He XX, Tu SM, Lee MH, Yeung SC. Thiazolidinediones and metformin associated with improved survival of diabetic prostate cancer patients. Ann Oncol. (2011) 22:2640–5. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdr020
14. Spratt DE, Zhang C, Zumsteg ZS, Pei X, Zhang Z, Zelefsky MJ. Metformin and prostate cancer: reduced development of castration-resistant disease and prostate cancer mortality. Eur Urol. (2013) 63:709–16. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2012.12.004
15. Wang Z, Lai ST, Xie L, Zhao JD, Ma NY, Zhu J, et al. Metformin is associated with reduced risk of pancreatic cancer in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. (2014) 106:19–26. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2014.04.007
16. Col NF, Ochs L, Springmann V, Aragaki AK, Chlebowski RT. Metformin and breast cancer risk: a meta-analysis and critical literature review. Breast Cancer Res Treat. (2012) 135:639–46. doi: 10.1007/s10549-012-2170-x
17. Nie Z, Zhu H, Gu M. Reduced colorectal cancer incidence in type 2 diabetic patients treated with metformin: a meta-analysis. Pharm Biol. (2016) 54:2636–42. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2016.1176057
18. Zhang H, Gao C, Fang L, Zhao HC, Yao SK. Metformin and reduced risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in diabetic patients: a meta-analysis. Scand J Gastroenterol. (2013) 48:78–87. doi: 10.3109/00365521.2012.719926
19. Bodmer M, Meier C, Krahenbuhl S, Jick SS, Meier CR. Metformin, sulfonylureas, or other antidiabetes drugs and the risk of lactic acidosis or hypoglycemia: a nested case-control analysis. Diabetes Care (2008) 31:2086–91. doi: 10.2337/dc08-1171
20. Montaudie H, Cerezo M, Bahadoran P, Roger C, Passeron T, Machet L, Arnault JP, Verneuil L, Maubec E, Aubin F, et al. Metformin monotherapy in melanoma: a pilot, open-label, prospective, and multicentric study indicates no benefit. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. (2017) 30:378–80. doi: 10.1111/pcmr.12576
21. Kordes S, Pollak MN, Zwinderman AH, Mathot RA, Weterman MJ, Beeker A, et al. Metformin in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer: a double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. (2015) 16:839–47. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(15)00027-3
22. Li X, Li T, Liu Z, Gou S, Wang C. The effect of metformin on survival of patients with pancreatic cancer: a meta-analysis. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:5825. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-06207-x
23. Bhaw-Luximon A, Jhurry D. Metformin in pancreatic cancer treatment: from clinical trials through basic research to biomarker quantification. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. (2016) 142:2159–2171. doi: 10.1007/s00432-016-2178-4
24. Foretz M, Guigas B, Bertrand L, Pollak M, Viollet B. Metformin: from mechanisms of action to therapies. Cell Metab. (2014) 20:953–66. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2014.09.018
25. Owen MR, Doran E, Halestrap AP. Evidence that metformin exerts its anti-diabetic effects through inhibition of complex 1 of the mitochondrial respiratory chain. Biochem J. (2000) 348(Pt 3):607–14. doi: 10.1042/bj3480607
26. El-Mir MY, Nogueira V, Fontaine E, Averet N, Rigoulet M, Leverve X. Dimethylbiguanide inhibits cell respiration via an indirect effect targeted on the respiratory chain complex I. J Biol Chem. (2000) 275:223–8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.275.1.223
27. Drahota Z, Palenickova E, Endlicher R, Milerova M, Brejchova J, Vosahlikova M, et al. Biguanides inhibit complex I, II and IV of rat liver mitochondria and modify their functional properties. Physiol Res. (2014) 63:1–11. Available online at: http://www.biomed.cas.cz/physiolres/pdf/63/63_1.pdf
28. He L, Wondisford FE. Metformin action: concentrations matter. Cell Metab. (2015) 21:159–62. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2015.01.003
29. Shaw RJ, Lamia KA, Vasquez D, Koo SH, Bardeesy N, Depinho RA, et al. The kinase LKB1 mediates glucose homeostasis in liver and therapeutic effects of metformin. Science (2005) 310:1642–6. doi: 10.1126/science.1120781
30. Zhou G, Myers R, Li Y, Chen Y, Shen X, Fenyk-Melody J, et al. Role of AMP-activated protein kinase in mechanism of metformin action. J Clin Invest. (2001) 108:1167–74. doi: 10.1172/JCI13505
31. Miller RA, Chu Q, Xie J, Foretz M, Viollet B, Birnbaum MJ. Biguanides suppress hepatic glucagon signalling by decreasing production of cyclic AMP. Nature (2013) 494:256–60. doi: 10.1038/nature11808
32. Ouyang J, Parakhia RA, Ochs RS. Metformin activates AMP kinase through inhibition of AMP deaminase. J Biol Chem. (2011) 286:1–11. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.121806
33. Piwkowska A, Rogacka D, Jankowski M, Dominiczak MH, Stepinski JK, Angielski S. Metformin induces suppression of NAD(P)H oxidase activity in podocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2010) 393:268–73. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.01.119
34. Madiraju AK, Erion DM, Rahimi Y, Zhang XM, Braddock DT, Albright RA, Prigaro BJ, Wood JL, Bhanot S, MacDonald MJ, et al. Metformin suppresses gluconeogenesis by inhibiting mitochondrial glycerophosphate dehydrogenase. Nature (2014) 510:542–6. doi: 10.1038/nature13270
35. Andrzejewski S, Gravel SP, Pollak M, St-Pierre J. Metformin directly acts on mitochondria to alter cellular bioenergetics. Cancer Metab. (2014) 2:12. doi: 10.1186/2049-3002-2-12
36. Bridges HR, Jones AJ, Pollak MN, Hirst J. Effects of metformin and other biguanides on oxidative phosphorylation in mitochondria. Biochem J. (2014) 462:475–87. doi: 10.1042/BJ20140620
37. Wheaton WW, Weinberg SE, Hamanaka RB, Soberanes S, Sullivan LB, Anso E, Glasauer A, Dufour E, Mutlu GM, Budigner GS, et al. Metformin inhibits mitochondrial complex I of cancer cells to reduce tumorigenesis. Elife (2014) 3:e02242. doi: 10.7554/eLife.02242
38. Luengo A, Sullivan LB, Heiden MG. Understanding the complex-I-ty of metformin action: limiting mitochondrial respiration to improve cancer therapy. BMC Biol. (2014) 12:82. doi: 10.1186/s12915-014-0082-4
39. Pernicova I, Korbonits M. Metformin–mode of action and clinical implications for diabetes and cancer. Nat Rev Endocrinol. (2014) 10:143–56. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2013.256
40. Baur JA, Birnbaum MJ. Control of gluconeogenesis by metformin: does redox trump energy charge? Cell Metab. (2014) 20:197–99. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2014.07.013
41. Andrzejewski S, Klimcakova E, Johnson RM, Tabaries S, Annis MG, McGuirk S, et al. PGC-1α promotes breast cancer metastasis and confers bioenergetic flexibility against metabolic drugs. Cell Metab. (2017) 26:778–87.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2017.09.006
42. Fendt SM, Bell EL, Keibler MA, Davidson SM, Wirth GJ, Fiske B, et al. (2013). Metformin decreases glucose oxidation and increases the dependency of prostate cancer cells on reductive glutamine metabolism. Cancer Res. (2017) 73:4429–38. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-0080
43. Griss T, Vincent EE, Egnatchik R, Chen J, Ma EH, Faubert B, et al. Metformin antagonizes cancer cell proliferation by suppressing mitochondrial-dependent biosynthesis. PLoS Biol. (2015) 13:e1002309. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1002309
44. Janzer A, German NJ, Gonzalez-Herrera KN, Asara JM, Haigis MC, Struhl K. Metformin and phenformin deplete tricarboxylic acid cycle and glycolytic intermediates during cell transformation and NTPs in cancer stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. (2014) 111:105749. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1409844111
45. Liu X, Romero IL, Litchfield LM, Lengyel E, Locasale JW. Metformin targets central carbon metabolism and reveals mitochondrial requirements in human cancers. Cell Metab. (2016) 24:728–39. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2016.09.005
46. Bogachus LD, Turcotte LP. Genetic downregulation of AMPK-alpha isoforms uncovers the mechanism by which metformin decreases FA uptake and oxidation in skeletal muscle cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. (2010) 299:C1549–61. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00279.2010
47. Rena G, Hardie DG, Pearson ER. The mechanisms of action of metformin. Diabetologia (2017) 60:1577–85. doi: 10.1007/s00125-017-4342-z
48. Hardie DG, Ross FA, Hawley SA. (2012). AMPK: a nutrient and energy sensor that maintains energy homeostasis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. (2017) 13:251–62. doi: 10.1038/nrm3311
49. Loubiere C, Goiran T, Laurent K, Djabari Z, Tanti JF, Bost F. Metformin-induced energy deficiency leads to the inhibition of lipogenesis in prostate cancer cells. Oncotarget (2015) 6:15652–61. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3404
50. Dowling RJ, Zakikhani M, Fantus IG, Pollak M, Sonenberg N. Metformin inhibits mammalian target of rapamycin-dependent translation initiation in breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. (2007) 67:10804–12. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-2310
51. Liu X, Chhipa RR, Pooya S, Wortman M, Yachyshin S, Chow LM, Kumar A, Zhou X, Sun Y, Quinn B, et al. Discrete mechanisms of mTOR and cell cycle regulation by AMPK agonists independent of AMPK. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. (2014) 111:E435–44. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1311121111
52. Bhat M, Yanagiya A, Graber T, Razumilava N, Bronk S, Zammit D, Zhao Y, Zakaria C, Metrakos P, Pollak M, et al. Metformin requires 4E-BPs to induce apoptosis and repress translation of Mcl-1 in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Oncotarget (2017) 8:50542–56. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.10671
53. Takahashi A, Kimura F, Yamanaka A, Takebayashi A, Kita N, Takahashi K, et al. Metformin impairs growth of endometrial cancer cells via cell cycle arrest and concomitant autophagy and apoptosis. Cancer Cell Int. (2014) 14:53. doi: 10.1186/1475-2867-14-53
55. Ben Sahra I, Laurent K, Giuliano S, Larbret F, Ponzio G, Gounon P, Le Marchand-Brustel Y, Giorgetti-Peraldi S, Cormont M, Bertolotto C, et al. Targeting cancer cell metabolism: the combination of metformin and 2-deoxyglucose induces p53-dependent apoptosis in prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res. (2010) 70:2465–75. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-2782
56. Huang CC, Wang SY, Lin LL, Wang PW, Chen TY, Hsu WM, et al. Glycolytic inhibitor 2-deoxyglucose simultaneously targets cancer and endothelial cells to suppress neuroblastoma growth in mice. Dis Model Mech. (2015) 8:1247–54. doi: 10.1242/dmm.021667
57. Kurtoglu M, Gao N, Shang J, Maher JC, Lehrman MA, Wangpaichitr M, et al. Under normoxia, 2-deoxy-D-glucose elicits cell death in select tumor types not by inhibition of glycolysis but by interfering with N-linked glycosylation. Mol Cancer Ther. (2007) 6:3049–58. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-07-0310
58. Raez LE, Papadopoulos K, Ricart AD, Chiorean EG, Dipaola RS, Stein MN, Rocha Lima CM, Schlesselman JJ, Tolba K, Langmuir VK, et al. A phase I dose-escalation trial of 2-deoxy-D-glucose alone or combined with docetaxel in patients with advanced solid tumors. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. (2013) 71:523–30. doi: 10.1007/s00280-012-2045-1
59. Wise DR, Thompson CB. Glutamine addiction: a new therapeutic target in cancer. Trends Biochem Sci. (2010) 35:427–33. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2010.05.003
60. Craze ML, Cheung H, Jewa N, Coimbra NDM, Soria D, El-Ansari R, Aleskandarany MA, Wai Cheng K, Diez-Rodriguez M, Nolan CC, et al. MYC regulation of glutamine-proline regulatory axis is key in luminal B breast cancer. Br J Cancer (2018) 118:258–65. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2017.387
61. Huang F, Zhang Q, Ma H, Lv Q, Zhang T. Expression of glutaminase is upregulated in colorectal cancer and of clinical significance. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. (2014) 7:1093–100. Available online at: http://www.ijcep.com/files/ijcep1401009.pdf
62. Pan T, Gao L, Wu G, Shen G, Xie S, Wen H, et al. Elevated expression of glutaminase confers glucose utilization via glutaminolysis in prostate cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2015) 456:452–8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.11.105
63. Wang JB, Erickson JW, Fuji R, Ramachandran S, Gao P, Dinavahi R, Wilson KF, Ambrosio AL, Dias SM, Dang CV, et al. Targeting mitochondrial glutaminase activity inhibits oncogenic transformation. Cancer Cell (2010) 18:207–19. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2010.08.009
64. Xiang Y, Stine ZE, Xia J, Lu Y, O'Connor RS, Altman BJ, Hsieh AL, Gouw AM, Thomas AG, Gao P, et al. Targeted inhibition of tumor-specific glutaminase diminishes cell-autonomous tumorigenesis. J Clin Invest. (2015) 125:2293–306. doi: 10.1172/JCI75836
65. Zacharias NM, McCullough C, Shanmugavelandy S, Lee J, Lee Y, Dutta P, McHenry J, Nguyen L, Norton W, Jones LW, et al. Metabolic differences in glutamine utilization lead to metabolic vulnerabilities in prostate cancer. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:16159. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-16327-z
66. Javeshghani S, Zakikhani M, Austin S, Bazile M, Blouin MJ, Topisirovic I, et al. Carbon source and myc expression influence the antiproliferative actions of metformin. Cancer Res. (2012) 72:6257–67. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-2907
67. Viollet B, Guigas B, Sanz Garcia N, Leclerc J, Foretz M, Andreelli F. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of metformin: an overview. Clin Sci. (2012) 122:253–70. doi: 10.1042/CS20110386
68. Birsoy K, Possemato R, Lorbeer FK, Bayraktar EC, Thiru P, Yucel B, et al. Metabolic determinants of cancer cell sensitivity to glucose limitation and biguanides. Nature (2014) 508:108–12. doi: 10.1038/nature13110
69. Deblois G, St-Pierre J, Giguere V. The PGC-1/ERR signaling axis in cancer. Oncogene (2013) 32:3483–90. doi: 10.1038/onc.2012.529
70. Audet-Walsh E, Papadopoli DJ, Gravel SP, Yee T, Bridon G, Caron M, et al. The PGC-1alpha/ERRalpha axis represses one-carbon metabolism and promotes sensitivity to anti-folate therapy in breast cancer. Cell Rep. (2016) 14:920–31. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2015.12.086
71. Chaube B, Malvi P, Singh SV, Mohammad N, Viollet B, Bhat MK. AMPK maintains energy homeostasis and survival in cancer cells via regulating p38/PGC-1alpha-mediated mitochondrial biogenesis. Cell Death Discov. (2015) 1:15063. doi: 10.1038/cddiscovery.2015.63
72. Klimcakova E, Chenard V, McGuirk S, Germain D, Avizonis D, Muller WJ, et al. PGC-1alpha promotes the growth of ErbB2/Neu-induced mammary tumors by regulating nutrient supply. Cancer Res. (2012) 72:1538–46. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-2967
73. McGuirk S, Gravel SP, Deblois G, Papadopoli DJ, Faubert B, Wegner A, Hiller K, Avizonis D, Akavia UD, Jones RG, et al. PGC-1alpha supports glutamine metabolism in breast cancer. Cancer Metab. (2013) 1:22. doi: 10.1186/2049-3002-1-22
74. Bhalla K, Hwang BJ, Dewi RE, Ou L, Twaddel W, Fang HB, Vafai SB, Vazquez F, Puigserver P, Boros L, et al. PGC1alpha promotes tumor growth by inducing gene expression programs supporting lipogenesis. Cancer Res. (2011) 71:6888–98. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-1011
76. Chaube B, Malvi P, Singh SV, Mohammad N, Meena AS, Bhat MK. Targeting metabolic flexibility by simultaneously inhibiting respiratory complex I and lactate generation retards melanoma progression. Oncotarget (2015) 6:37281–99. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6134
77. Sharabi K, Lin H, Tavares CDJ, Dominy JE, Camporez JP, Perry RJ, Schilling R, Rines AK, Lee J, Hickey M, et al. Selective chemical inhibition of PGC-1alpha gluconeogenic activity ameliorates type 2 diabetes. Cell (2017) 169:148–60 e115. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.03.001
78. Hanna RK, Zhou C, Malloy KM, Sun L, Zhong Y, Gehrig PA, et al. Metformin potentiates the effects of paclitaxel in endometrial cancer cells through inhibition of cell proliferation and modulation of the mTOR pathway. Gynecol Oncol. (2012) 125:458–69. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2012.01.009
79. Iliopoulos D, Hirsch HA, Struhl K. Metformin decreases the dose of chemotherapy for prolonging tumor remission in mouse xenografts involving multiple cancer cell types. Cancer Res. (2011) 71:3196–201. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-3471
80. Lin CC, Yeh HH, Huang WL, Yan JJ, Lai WW, Su WP, et al. Metformin enhances cisplatin cytotoxicity by suppressing signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 activity independently of the liver kinase B1-AMP-activated protein kinase pathway. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. (2013) 49:241–50. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2012-0244OC
81. Rocha GZ, Dias MM, Ropelle ER, Osorio-Costa F, Rossato FA, Vercesi AE, et al. Metformin amplifies chemotherapy-induced AMPK activation and antitumoral growth. Clin Cancer Res. (2011) 17:3993–4005. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-2243
82. Zhang HH, Guo XL. Combinational strategies of metformin and chemotherapy in cancers. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. (2016) 78:13–26. doi: 10.1007/s00280-016-3037-3
83. Hirsch HA, Iliopoulos D, Tsichlis PN, Struhl K. Metformin selectively targets cancer stem cells, and acts together with chemotherapy to block tumor growth and prolong remission. Cancer Res. (2009) 69:7507–11. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-2994
84. Shafiei-Irannejad V, Samadi N, Yousefi B, Salehi R, Velaei K, Zarghami N. Metformin enhances doxorubicin sensitivity via inhibition of doxorubicin efflux in P-gp-overexpressing MCF-7 cells. Chem Biol Drug Des. (2017) 91:269–76. doi: 10.1111/cbdd.13078
85. Zhang Y, Feng X, Li T, Yi E, Li Y. Metformin synergistic pemetrexed suppresses non-small-cell lung cancer cell proliferation and invasion in vitro. Cancer Med. (2017) 6:1965–75. doi: 10.1002/cam4.1133
86. Chen H, Yao W, Chu Q, Han R, Wang Y, Sun J, et al. Synergistic effects of metformin in combination with EGFR-TKI in the treatment of patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer and type 2 diabetes. Cancer Lett. (2015) 369:97–102. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2015.08.024
87. Duo J, Ma Y, Wang G, Han X, Zhang C. Metformin synergistically enhances antitumor activity of histone deacetylase inhibitor trichostatin a against osteosarcoma cell line. DNA Cell Biol. (2013) 32:156–64. doi: 10.1089/dna.2012.1926
88. Babcook MA, Shukla S, Fu P, Vazquez EJ, Puchowicz MA, Molter JP, Oak CZ, MacLennan GT, Flask CA, Lindner DJ, et al. Synergistic simvastatin and metformin combination chemotherapy for osseous metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. (2014) 13:2288–302. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-14-0451
89. Xia C, Chen R, Chen J, Qi Q, Pan Y, Du L, et al. Combining metformin and nelfinavir exhibits synergistic effects against the growth of human cervical cancer cells and xenograft in nude mice. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:43373. doi: 10.1038/srep43373
90. Qu C, Zhang W, Zheng G, Zhang Z, Yin J, He Z. Metformin reverses multidrug resistance and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) via activating AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) in human breast cancer cells. Mol Cell Biochem. (2014) 386:63–71. doi: 10.1007/s11010-013-1845-x
91. Yang SH, Li S, Lu G, Xue H, Kim DH, Zhu JJ, et al. Metformin treatment reduces temozolomide resistance of glioblastoma cells. Oncotarget (2016) 7:78787–803. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12859
92. Cioce M, Valerio M, Casadei L, Pulito C, Sacconi A, Mori F, Biagioni F, Manetti C, Muti P, Strano S, et al. Metformin-induced metabolic reprogramming of chemoresistant ALDHbright breast cancer cells. Oncotarget (2014) 5:4129–43. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.1864
93. Schockel L, Glasauer A, Basit F, Bitschar K, Truong H, Erdmann G, Algire C, Hagebarth A, Willems PH, Kopitz C, et al. Targeting mitochondrial complex I using BAY 87-2243 reduces melanoma tumor growth. Cancer Metab. (2015) 3:11. doi: 10.1186/s40170-015-0138-0
94. Zhang B, Chu W, Wei P, Liu Y, Wei T. Xanthohumol induces generation of reactive oxygen species and triggers apoptosis through inhibition of mitochondrial electron transfer chain complex I. Free Radic Biol Med. (2015) 89:486–97. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2015.09.021
95. Secker PF, Beneke S, Schlichenmaier N, Delp J, Gutbier S, Leist M, et al. Canagliflozin mediated dual inhibition of mitochondrial glutamate dehydrogenase and complex I: an off-target adverse effect. Cell Death Dis. (2018) 9:226. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-0273-y
96. Villani LA, Smith BK, Marcinko K, Ford RJ, Broadfield LA, Green AE, et al. The diabetes medication Canagliflozin reduces cancer cell proliferation by inhibiting mitochondrial complex-I supported respiration. Mol Metab. (2016) 5:1048–56. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2016.08.014
97. Wilk A, Wyczechowska D, Zapata A, Dean M, Mullinax J, Marrero L, Parsons C, Peruzzi F, Culicchia F, Ochoa A, et al. Molecular mechanisms of fenofibrate-induced metabolic catastrophe and glioblastoma cell death. Mol Cell Biol. (2015) 35:182–98. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00562-14
98. Akatsuka A, Kojima N, Okamura M, Dan S, Yamori T. A novel thiophene-3-carboxamide analog of annonaceous acetogenin exhibits antitumor activity via inhibition of mitochondrial complex I. Pharmacol Res Perspect. (2016) 4:e00246. doi: 10.1002/prp2.246
99. FDA (2015). FDA Drug Safety Communication: FDA Revises Label of Diabetes Drug Canagliflozin (Invokana, Invokamet) to Include Updates on Bone Fracture Risk and New Information on Decreased Bone Mineral Density. Drug Safety and Availability (FDA Drug Safety Communication).
100. FDA (2017). FDA Drug Safety Communication: Interim Clinical Trial Results Find Increased Risk of Leg and Foot Amputations, Mostly Affecting the Toes, with the Diabetes Medicine Canagliflozin. Drug Safety and Availability (FDA Drug Safety Communication).
101. Betarbet R, Sherer TB, MacKenzie G, Garcia-Osuna M, Panov AV, Greenamyre JT. Chronic systemic pesticide exposure reproduces features of Parkinson's disease. Nat Neurosci. (2000) 3:1301–6. doi: 10.1038/81834
102. Sherer TB, Kim JH, Betarbet R, Greenamyre JT. Subcutaneous rotenone exposure causes highly selective dopaminergic degeneration and alpha-synuclein aggregation. Exp Neurol. (2003) 179:9–16. doi: 10.1006/exnr.2002.8072
103. Hervas D, Fornes-Ferrer V, Gomez-Escribano AP, Sequedo MD, Peiro C, Millan JM, et al. Metformin intake associates with better cognitive function in patients with Huntington's disease. PLoS ONE (2017) 12:e0179283. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0179283
104. Jin J, Gu H, Anders NM, Ren T, Jiang M, Tao M, et al. Metformin protects cells from mutant huntingtin toxicity through activation of AMPK and modulation of mitochondrial dynamics. Neuromolecular Med. (2016) 18:581–92. doi: 10.1007/s12017-016-8412-z
105. Sogame Y, Kitamura A, Yabuki M, Komuro S. A comparison of uptake of metformin and phenformin mediated by hOCT1 in human hepatocytes. Biopharm Drug Dispos. (2009) 30:476–84. doi: 10.1002/bdd.684
106. Shu Y, Sheardown SA, Brown C, Owen RP, Zhang S, Castro RA, Ianculescu AG, Yue L, Lo JC, Burchard EG, et al. Effect of genetic variation in the organic cation transporter 1 (OCT1) on metformin action. J Clin Invest. (2007) 117:1422–31. doi: 10.1172/JCI30558
107. Assan R, Heuclin C, Girard JR, LeMaire F, Attali JR. Phenformin-induced lactic acidosis in diabetic patients. Diabetes (1975) 24:791–800. doi: 10.2337/diab.24.9.791
108. Kalyanaraman B, Cheng G, Hardy M, Ouari O, Lopez M, Joseph J, et al. A review of the basics of mitochondrial bioenergetics, metabolism, and related signaling pathways in cancer cells: Therapeutic targeting of tumor mitochondria with lipophilic cationic compounds. Redox Biol. (2018) 14:316–27. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2017.09.020
Keywords: metformin, phenformin, mitochondria, diabetes, cancer, breast cancer, metabolism, mitochondrial drugs
Citation: Andrzejewski S, Siegel PM and St-Pierre J (2018) Metabolic Profiles Associated With Metformin Efficacy in Cancer. Front. Endocrinol. 9:372. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2018.00372
Received: 04 May 2018; Accepted: 21 June 2018;
Published: 21 August 2018.
Edited by:
Frederic Bost, Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique (CNRS), FranceReviewed by:
Bin Zheng, Harvard Medical School, United StatesDaniel Rotroff, Cleveland Clinic, United States
Federica Barbieri, Università di Genova, Italy
Copyright © 2018 Andrzejewski, Siegel and St-Pierre. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Julie St-Pierre, anVsaWUuc3QtcGllcnJlQHVvdHRhd2EuY2E=
 Sylvia Andrzejewski
Sylvia Andrzejewski Peter M. Siegel
Peter M. Siegel Julie St-Pierre
Julie St-Pierre