- 1Department of Periodontology, Academic Centre for Dentistry Amsterdam, University of Amsterdam and Vrije Universiteit, Amsterdam, Netherlands
- 2Department of Vascular Medicine, Amsterdam UMC, Amsterdam, Netherlands
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Spaarne Gasthuis, Hoofddorp, Netherlands
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is associated with several microvascular and macrovascular complications, such as retinopathy, nephropathy, neuropathy, and cardiovascular diseases. The pathogenesis of these complications is complex, and involves metabolic and hemodynamic disturbances, including hyperglycemia, insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, hypertension, and immune dysfunction. These disturbances initiate several damaging processes, such as increased reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, inflammation, and ischemia. These processes mainly exert their damaging effect on endothelial and nerve cells, hence the susceptibility of densely vascularized and innervated sites, such as the eyes, kidneys, and nerves. Since the oral cavity is also highly vascularized and innervated, oral complications can be expected as well. The relationship between DM and oral diseases has received considerable attention in the past few decades. However, most studies only focus on periodontitis, and still approach DM from the limited perspective of elevated blood glucose levels only. In this review, we will assess other potential oral complications as well, including: dental caries, dry mouth, oral mucosal lesions, oral cancer, taste disturbances, temporomandibular disorders, burning mouth syndrome, apical periodontitis, and peri-implant diseases. Each oral complication will be briefly introduced, followed by an assessment of the literature studying epidemiological associations with DM. We will also elaborate on pathogenic mechanisms that might explain associations between DM and oral complications. To do so, we aim to expand our perspective of DM by not only considering elevated blood glucose levels, but also including literature about the other important pathogenic mechanisms, such as insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, hypertension, and immune dysfunction.
Introduction
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is defined as a group of metabolic diseases characterized by hyperglycemia resulting from defects in insulin secretion, insulin action, or both (1). In 2014, the global prevalence of DM was estimated to be 9% (2), and almost 1.6 million deaths worldwide were caused directly by DM in 2015 (3). DM is also associated with high morbidity due to a broad range of complications, such as retinopathy, nephropathy, neuropathy, and cardiovascular disease (4, 5). Prevention and management of these complications have become major aspects of modern diabetes care. Besides these well-known complications, oral complications of DM can be expected as well (6–8). As a result, the International Diabetes Federation (IDF) published the “guideline on oral health for people with diabetes” in 2009, which encourages implementation of oral care in diabetes care (9). Knowing which oral complications can be expected, how often these occur in patients with DM, and understanding of the underlying pathogenesis is essential for a successful implementation of the guideline. The large majority of studies into oral complications still approach patients with DM from the limited perspective of elevated blood glucose levels. However, we know that there are many other pathogenic mechanisms that contribute to the development of other diabetic complications, including hyperglycemia, insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, hypertension, and immune dysfunction. In this report, we will review the literature about oral complications of DM from this broader perspective. To understand the biological mechanisms that might be involved, the pathogenic mechanisms of the classic diabetic complications are discussed first.
Pathogenic Mechanisms of Diabetic Complications
Complications of DM can be divided into acute and chronic complications (1). Associations between acute effects of DM and oral complications have not yet been reported in the literature. Since oral complications are most likely the result of long-term effects of diabetes, the focus of this review will be on chronic complications. These complications are typically characterized by damage to the vasculature, usually grouped into microvascular and macrovascular diseases (5). Microvascular diseases include retinopathy, nephropathy and neuropathy. Macrovascular complications concern cardiovascular disease (CVD), such as coronary artery disease, cerebrovascular disease, and peripheral artery disease (10).
Hyperglycemia is the clinical characteristic that is used to define a patient with DM. However, several other—often intertwined—pathogenic mechanisms that characterize DM are also recognized: insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, hypertension, and immune dysfunction. In this section, we will describe how these pathogenic mechanisms are involved in the development and progression of chronic diabetic complications (Figure 1) (11). In the following sections, we will discuss possible associations between DM and oral complications by using the very same perspective each time.
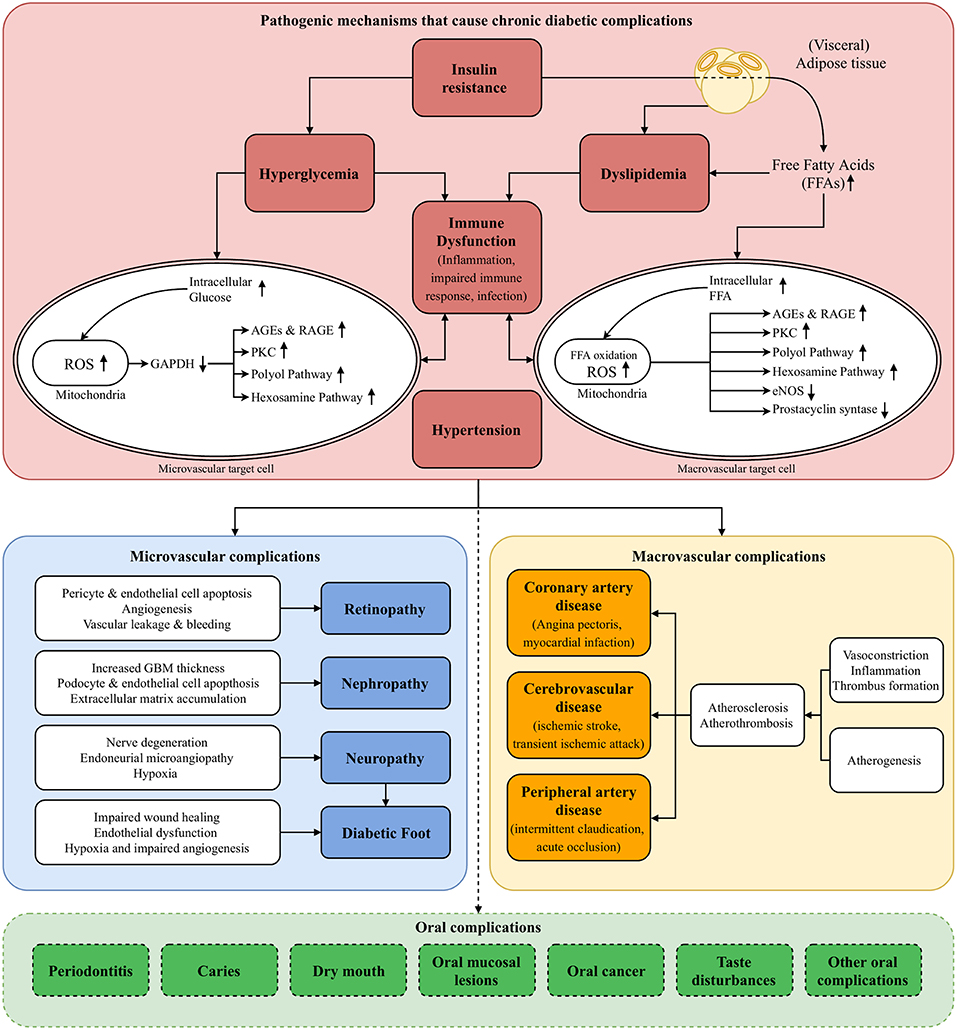
Figure 1. Pathogenesis of diabetic complications. The figure presents the pathogenic mechanisms of diabetes mellitus (DM; red block, section Pathogenic Mechanisms of Diabetic Complications of main text) that cause microvascular complications (blue block) and macrovascular complications (yellow block). Destruction of pancreatic B cells in T1DM and insulin resistance in T2DM result in hyperglycemia. The resulting increase of intracellular glucose in microvascular target cells, such as capillary endothelial cells, causes ROS production in the mitochondria, activating four pathogenic downstream pathways: polyol pathway, AGEs & RAGE pathway, PKC pathway, hexosamine pathway (section Hyperglycemia of main text). Especially in T2DM, insulin resistance and the abundance of (visceral) adipose tissue result in an excess flux of free fatty acids (FFAs), which are oxidized in the mitochondria of macrovascular endothelial cells. This causes activation of the same pathogenic pathways, and downregulation of protective enzymes such as eNOS and prostacyclin synthase. Pathway-selective insulin resistance also contributes to microvascular complications (section Insulin Resistance of main text). Moreover, insulin resistance and circulating FFAs result in dyslipidemia, contributing to both micro- and macrovascular complications (section Dyslipidemia of main text). Hypertension contributes to the harmful processes by activating endothelial cells, inducing a cellular inflammatory response and reducing the availability of nitric oxide, causing vasoconstriction (section Hypertension of main text). All these processes mainly exert their harmful effects by upregulation of a pro-inflammatory state at vulnerable sites. Together with an impaired immune response and consequently higher susceptibility for infections, this immune dysfunction plays a pivotal role in the development of diabetic complications (section Immune Dysfunction of main text). Possible oral complications that are discussed in this review are listed in the green block at the bottom of the figure (section Potential Oral Complications of Diabetes Mellitus of main text). eNOS, endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase; FFAs, Free Fatty Acids; GAPDH, Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate Dehydrogenase; GBM, Glomerular Basement Membrane; PKC, Protein Kinase C; (R)AGEs, (Receptor for) Advanced Glycation End products; ROS, Reactive Oxygen Species.
Hyperglycemia
Hyperglycemia is a key determinant for the development of complications in patients with T1DM or T2DM (12). This was demonstrated through several large trials, where intensive blood glucose control in patients with T2DM significantly reduced the risk for microvascular complications (13–18). In persons with T1DM, intensive blood glucose control also reduced the long-term risk for macrovascular complications (19), even years after the study was finished (20).
Despite the fact that each cell in the body is exposed to hyperglycemia, the damaging consequences mainly concern the endothelial cells and peripheral nerve cells (21). These target cells are not capable of maintaining a constant intracellular glucose level when blood glucose levels rise (22). The increased intracellular glucose levels trigger reactive oxygen species (ROS) production in the mitochondria. This is the upstream mechanism that causes inhibition of the enzyme glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH). Consequently, four downstream mechanisms that are involved in tissue damage are activated: (1) increased polyol pathway flux; (2) increased non-enzymatic formation of advanced glycation end-products (AGEs) and increased expression of receptors for AGEs (RAGEs); (3) activation of protein kinase C (PKC); and (4) increased hexosamine pathway activity (21).
1) Normally, the polyol pathway ensures that toxic components (aldehydes) are converted into harmless inactive alcohol by an enzyme called aldose reductase. However, in case of hyperglycemia, aldose reductase also converts the excess intracellular glucose into sorbitol. To do so, it consumes NADPH, which is crucial for the maintenance of the intracellular antioxidant reduced glutathione (GSH). Decreased amounts of GSH cause or worsen oxidative stress, leading to cell damage or death (21, 23).
2) The non-enzymatic formation of advanced glycation endproducts (AGEs) results from a complex interaction between glucose and lipids, proteins or nucleic acids (24). If hyperglycemia is persistent, AGEs can accumulate in both tissue and serum, causing tissue damage through several mechanisms. They can alter intracellular proteins and thereby change cellular function (25). Also, AGEs can diffuse out of the cell and cause disruption of the signaling between the cell and its membrane, causing cell dysfunction (25). Finally, after diffusing out of the cell, they can modify circulating plasma proteins, which in turn bind to AGE receptors (e.g., RAGE) on different types of cells, such as macrophages and endothelial cells. This then induces a pro-inflammatory state, reflected by elevated levels of inflammatory cytokines in plasma, such as interleukin 6 and 1 alpha (IL-6, IL-1α) and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) (21, 26). These processes further elicit ROS production and cause the vascular damage typical for diabetic complications (21, 23, 24, 26). AGES can also form cross-links within collagen fibers, which changes their structure and functionality. In combination with the abovementioned effects, this can result in damage to connective tissue in the joints, and eventually cause a condition called limited joint mobility (27).
3) Intracellular hyperglycemia also causes activation of protein kinase C (PKC), which has several effects on gene expression within the cells (21). PKC can activate nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB), which plays a pivotal role in the upregulation of inflammatory responses. For example, NF-κB regulates gene expression of IL-6, IL-1α, and TNF-α (28). Also, endothelin-1 (ET-1) is upregulated while endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) is downregulated, causing vasoconstriction and thereby abnormal blood flow (29, 30). Transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) are also upregulated, causing capillary and vascular occlusion (31, 32). An increased expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) causes increased vascular permeability and angiogenesis (33). All these processes are harmful for the vasculature (21).
4) In the healthy situation, intracellular glucose is mainly metabolized through glycolysis. However, in a state of hyperglycemia, part of that glucose is diverted into another pathway known as the hexosamine pathway. This pathway comprises a complex cascade of reactions, leading to increased productions of cytokines (such as PAI-1, TGF-α, and TGF-β1) which in fact are harmful for the blood vessels (25).
Throughout this report, we will refer to these processes as upstream (ROS production) and downstream (polyol, AGEs and RAGE, PKC and hexosamine) pathways of hyperglycemia. Since endothelial cells are the major target cells of hyperglycemia, it is not surprising that highly vascularized organs are particularly susceptible to tissue damage. For example, damage to endothelial cells in the retina and kidney cause retinopathy (34, 35) and nephropathy (36, 37), respectively. Also, injury to the vulnerable vascular supply of the peripheral nervous system is likely to cause hypoxia in the endoneurium (38). On top of that, neuronal cells themselves are also susceptible for damage caused by hyperglycemia. This results in damage to the nerve, particularly in the most-distal fibers, eventually causing peripheral neuropathy (38, 39).
Insulin Resistance
The second mechanism that is involved in chronic diabetic complications is insulin resistance. As its name already implies, insulin resistance is characterized by a reduced sensitivity of body cells to the actions of insulin. Since insulin resistance is closely related to obesity, it is more common in patients with T2DM, where it is an important cause for hyperglycemia. Besides its effect on blood glucose levels, insulin resistance also causes an excess flux of free fatty acids (FFAs) from adipose tissue into the bloodstream. This in turn increases the production and release of very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) in the liver, resulting in a dyslipidemia (40). The role of dyslipidemia is discussed in the next section. However, the circulating FFAs caused by insulin resistance also play a direct role in the development of macrovascular complications (i.e., CVD). Increased flux of FFAs into arterial endothelial cells causes increased FFA oxidation in their mitochondria, eliciting ROS production and subsequently activating the same four pathways that we discussed in the previous section (polyol, AGEs, PKC, and hexosamine) (21, 41). Furthermore, protective enzymes such as eNOS and prostacyclin synthase are downregulated due to insulin resistance (42), and adhesion of leukocytes to endothelial cells is increased (43). Together, these processes result in enhanced vasoconstriction, inflammation, and procoagulant alterations. In the arterial endothelial cells, this favors the development of atherosclerotic lesions, which are the main cause of CVD (23, 44–46). A large prospective trial indeed showed that having insulin resistance almost doubled the risk for CVD (47).
In contrast to the macrovascular endothelial cells, FFA oxidation is not increased in microvascular endothelial cells in case of insulin resistance (21). However, insulin resistance might be involved in microvascular damage through other mechanisms. DM and obesity are both associated with selective impairment of some insulin signaling pathways (e.g., the PI3K pathway) that reduce nitric oxide availability and cause a compensatory hyperinsulinemia (48). The abundant insulin would then act through other signaling pathways that are less affected by DM or obesity (e.g., the Ras/MAPK pathway). The upregulation of these specific pathways, and the reduced availability of nitric oxide have unfavorable effects on the microvasculature, such as impaired angiogenesis and vasoreactivity (48).
Dyslipidemia
Already announced in the insulin resistance section, dyslipidemia is the third pathogenic mechanism that plays a role in the development of diabetic complications. Dyslipidemia is more common in T2DM than in T1DM, and is typically characterized by high levels of triglycerides and small dense low density lipoprotein (sdLDL) cholesterol particles, in combination with low levels of high density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol (i.e., the “lipid triad”) (49). Typical characteristics of patients with T2DM, such as visceral adiposity, insulin resistance, and excess FFAs in the bloodstream play a major role in the development of this specific lipid profile. Because of its atherogenic properties, diabetic dyslipidemia is particularly important in the development of macrovascular complications (50). Several trials showed that lipid lowering therapy—especially with statins—indeed decreased the risk of CVD in patients with T2DM (51, 52). Dyslipidemia is also involved in microvascular complications, as shown in several intervention studies. Treatment with fibrates—hypolipidemic agents that lower triglyceride levels and increase HDL levels—prevented the progression of retinopathy (53), reduced albuminuria and prevented loss of glomerular filtration rate (GFR) (54). High levels of plasma triglycerides are also associated with progression of diabetic neuropathy (55). How dyslipidemia biologically contributes to the development of microvascular complications remains mostly unknown (56). However, it is suggested that oxidation of LDL cholesterol (oxLDL) causes increased ROS production in for example neuronal cells (57).
Hypertension
Hypertension, the fourth mechanism contributing to diabetic complications, is more common in patients with DM compared to the general population (58). In fact, hypertension and T2DM in particular share many etiologic factors, such as obesity, insulin resistance, and inflammation (59). As we discussed before, patients with T2DM have a higher risk for CVD, mainly due to hyperglycemia, insulin resistance, and dyslipidemia. Having high blood pressure increases that risk even more (58). A large randomized controlled trial showed that tight blood pressure control in patients with T2DM significantly reduced the risk for CVD (60). Besides macrovascular complications, hypertension is also considered as an important risk factor for microvascular complications such as retinopathy (61) and nephropathy (36). In the previously mentioned study, tight blood pressure control also resulted in a significant reduction in the risk and progression of microvascular complications (60). The biologic contribution of hypertension to diabetic complications remains to be further elucidated. However, it was demonstrated that hypertension in patients with T2DM resulted in endothelial activation, reflected by increased levels of soluble adhesion molecules such as E-selectin and vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM-1) (62). These adhesion molecules play in important role in the initiation of inflammation. Also, availability of nitric oxide might be decreased in the case of hypertension, resulting in vasoconstriction (63). Both processes are harmful for the vasculature and might eventually contribute to microvascular damage.
Immune Dysfunction: Impaired Immune Response and Proinflammatory State
As we have shown in Figure 1, immune dysfunction plays a pivotal role in the pathogenesis of diabetic complications. DM can have a negative effect on several aspects of the immune system. For example, the innate (polymorphonuclear neutrophils [PMNs], macrophages, and monocytes) and adaptive (T-lymphocytes) immune responses are often impaired (64). More specifically, PMNs show impaired chemotactic, phagocytic, and microbicidal properties in patients with DM (65, 66). Also, adherence of microorganisms to several cell types, such as epithelial and endothelial cells, is increased (64). The impaired immune response is the major reason why patients with DM are more prone to opportunistic infections. Lower respiratory tract infections, urinary tract infections, bacterial and mycotic skin and mucous membrane infections are all found to be increased in patients with DM (67). However, the most impeding infection is probably the diabetic foot (68). Trauma, deformity, and peripheral neuropathy are the most common underlying causes of foot ulcerations in individuals with DM (69). In these patients, healing of ulcerations is impaired, with a crucial role for the so-called pathogenic triad: neuropathy, ischemia (due to vascular damage and endothelial dysfunction), and trauma (70). This healing abnormality, in combination with the impaired immune response, causes ulcers to become a porte d'entrée for opportunistic micro-organisms. As a result, the tissue can get infected, which has major implications for further development of the diabetic foot (71). Eventually, if the infection does not resolve, amputation is the only remaining solution to prevent sepsis (72, 73).
The immune dysfunction characterizing DM also manifests itself as a chronic pro-inflammatory state (11). As a response to the metabolic and hemodynamic disturbances discussed before, endothelial cells in the target tissues are activated. This is characterized by increased expression of adhesion molecules (e.g., intracellular adhesion molecule 1 [ICAM-1] and VCAM-1) and release of chemotactic factors (e.g., CCL5 and CCL5), which initiates immune cell recruitment and infiltration into the tissue. These immune cells, and other cells at sites of complications (e.g., adipocytes), release a wide variety of cytokines (e.g., IL-1β, IL-6, and TGF-α) that amplify the inflammatory response even further. If the inflammation remains unresolved and becomes chronic, it contributes to the development and progression of neuropathy (38), nephropathy (74), and retinopathy (75).
Finally, immune dysfunction itself can be one of the causes of DM as well, since we know that T1DM is a form of diabetes that is caused by autoimmune destruction of pancreatic β cell. These patients are also susceptible to develop other autoimmune diseases: Graves' disease, Hashimoto's thyroiditis, Addison's disease, vitiligo, celiac sprue, autoimmune hepatitis, myasthenia gravis, and pernicious anemia (1).
Potential Oral Complications of Diabetes Mellitus
The previous section explained that chronic complications of DM are the result of persistent metabolic and hemodynamic disturbances that mainly target endothelial cells, typically affecting specific regions in the body. It has been proposed in literature that the oral cavity of patients with DM might be one of those regions, with an increased susceptibility for oral complications as a result (6, 76). This section aims to provide an up-to-date overview of the oral complications that are possibly associated with DM. Figure 2 presents clinical pictures and radiographs of the oral complications discussed in this review. Each oral complication is briefly introduced, after which we discuss the association with DM from an epidemiologic point of view. Next, we will use the five mechanisms we discussed before (hyperglycemia, insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, hypertension, and immune dysfunction) to assess possible pathogenic associations.
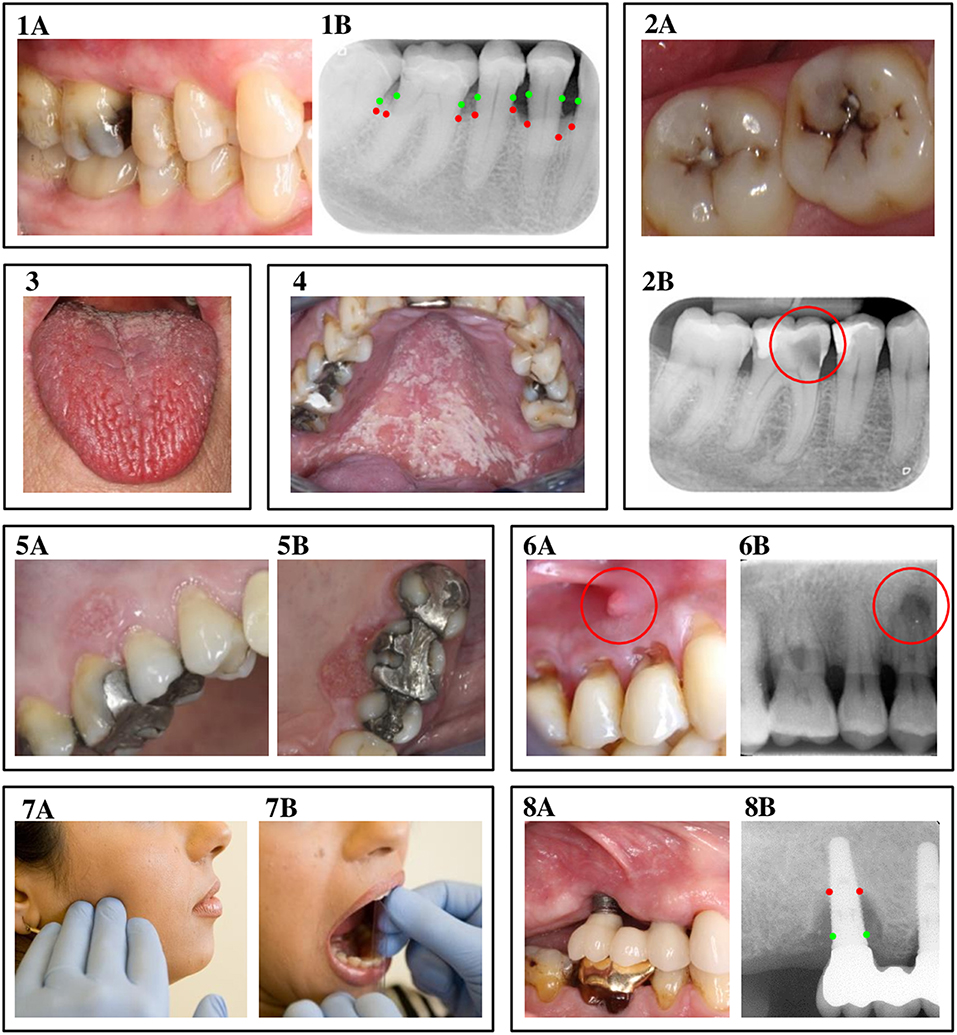
Figure 2. Oral complications of diabetes mellitus. 1A & 1B: Periodontitis. A clinical view of periodontitis is shown in figure 1A, with the corresponding radiograph displayed in image 1B. The green dots in image 1B indicate where the bone level originally was, while the red dots show the actual bone level as a result of inflammation. 2A & 2B: Dental caries. Image 2A displays a clinical view of dental caries, observed from the occlusal view. Picture 2B is a radiograph of an example of a deep carious lesion, marked by the red circle. 3. Hyposalivation. The photo in image 3 shows a clinical view of fissured tongue, caused by severe hyposalivation. 4. Oral candidiasis. Image 4 displays a clinical view of oral candidiasis, located at the palate. 5A & 5B: Oral cancer. At image 5, a clinical representation of leukoplakia and oral cancer is shown at the buccal (5A) and palatal (5B) site. 6A & 6B: Apical periodontitis. Figure 6A shows a fistula, caused by apical periodontitis, with image 6B as the corresponding radiograph, where the lesion at the apex of the tooth is marked by the red circle. 7A & 7B: Temporomandibular disorders. Image 7A indicates the location of pain often seen in patients with temporomandibular disorders, while 7B shows a measurement of limited jaw opening, another symptom of temporomandibular disorders. 8A & 8B: Peri-implantitis. At figure 8A, a clinical view of peri-implantitis is presented, with 8B as the corresponding radiograph. Again, the red dots indicate where ideally, the bone level should be, while the red dots show the actual reduced bone level as a result of the inflammatory process. The authors thank the following colleagues for providing clinical pictures and/or radiographs: Dr. AJP van Strijp (dental caries), Prof. Dr. M Laine (hyposalivation), Dr. P Wetselaar (temporomandibular disorders and apical periodontitis), all from ACTA, the Netherlands; Dr. RJJ van Es (oral cancer), UMC Utrecht, The Netherlands; Prof. Em. Dr. I van der Waal (oral candidiasis).
Periodontal Diseases
Background
Periodontal disease can be subdivided into gingivitis, which is a reversible inflammation of the gum (gingiva) around the teeth without loss of support, and periodontitis, which has the clinical appearance of gingivitis but also shows irreversible destruction of the supporting structures around the teeth (root cementum, periodontal ligament, and alveolar bone). Approximately 30–50% suffer from any form of periodontitis, including the mild and moderate variant, while the prevalence of severe periodontitis in adults is estimated to be approximately 9–11% (77, 78). Severe periodontitis was ranked as the sixth most prevalent disease worldwide in 2010 (79–81). Several types of periodontitis have been described: aggressive or chronic periodontitis, necrotizing gingivitis and periodontitis and finally periodontal abscesses (82, 83). Recently, a new classification and case definition has been introduced. The proposed case definition extends beyond description based on severity to include characterization of biological features of the disease and represents a first step towards adoption of precision medicine concepts to the management of periodontitis (84). Periapical periodontitis—a specific type of periodontitis affecting the periodontium around the apex of the tooth—and peri-implantitis—a chronic inflammation affecting the tissues around dental implants—will be discussed in separate sections.
Periodontal disease is the result of an aberrant inflammatory host response to the biofilm that resides around the teeth. In some susceptible subjects, an initial gingivitis can progress into chronic periodontitis (82). Several risk factors that might influence the susceptibility for periodontitis have been established in literature, clustered in five categories: environment (the subgingival microbiome), genetics, systemic diseases (e.g., DM and HIV/AIDS), lifestyle (e.g., oral hygiene, smoking, diet), and tooth related factors (e.g., iatrogenic causes or occlusal problems) (85, 86). In chronic periodontitis, irreversible loss of supporting tissue surrounding the teeth (due to destruction of gingival connective tissue fibers, root cementum, periodontal ligament, and alveolar bone) results in deep periodontal pockets and attachment loss, which are commonly used to define a patient with periodontitis (87). This impairing process eventually causes loosening of the teeth and ultimately, when no periodontal treatment has been initiated, in tooth loss (88).
Relationship With Diabetes Mellitus: Epidemiology
Periodontal disease has been linked with DM for a long time. Since Loë suggested to consider periodontal disease as the sixth complication of DM in 1993 (89), periodontitis became the most researched oral complication of DM. As summarized in several narrative reviews (7, 8, 90–95), meta-analysis (96, 97), and a major consensus report (98), DM is considered as a risk factor for the development, progression, and severity of periodontitis.
Many cross-sectional studies show an increased prevalence of periodontitis in patients with DM. However, longitudinal studies are relatively scarce, even though these studies are necessary for establishing causal relationships. An important source of evidence is the research conducted with the Pima Indians in the 1990s, a population with one of the highest T2DM prevalence in the world. Indeed, diabetic subjects within this population displayed an increased prevalence of periodontal disease (99, 100). More importantly however, analysis of longitudinal data from this population also showed that the incidence of periodontitis in patients with (poorly controlled) diabetes was more than twice as high, compared to subjects with well-controlled or no DM (101). The risk for alveolar bone loss was higher in the poorly controlled diabetes group, as well as the severity of disease progression (102). Other prospective cohort studies confirmed the increased incidence of periodontitis in patients with (pre)diabetes (103, 104). Glycemic control appeared to be of particular importance, as patients with well-controlled diabetes showed a similar risk for periodontitis as matching individuals without DM (102, 105). This was confirmed in a large trial, where glycemic control rather than the etiology of DM was associated with deterioration of pocket depth and periodontal attachment loss (106). Improving glycemic control in patients with DM and periodontitis reduced inflammation, expressed as gingival bleeding (107). Solid evidence on the association between periodontal abscesses and DM is lacking. However, based on clinical experiences, it is speculated that—while a single periodontal abscess usually is the result of local factors—multiple recurring abscesses might indicate an underlying systemic cause, such as uncontrolled DM (83).
The majority of studies used the former classification of chronic periodontitis or at least did not specify the presentation of the disease. Since a new classification and case definition for periodontitis has recently been proposed, we decided not to distinguish different types of periodontitis in relation to DM in this review (84).
Relationship With Diabetes Mellitus: Pathogenesis
From an epidemiologic point of view, DM has an adverse effect on periodontal health. A limited number of longitudinal studies even indicate a possible causal relationship. However, the biologic mechanisms behind this relationship are still not completely understood. Several studies do show pathologic changes in the gingival vasculature of patients and animals with diabetes, compared to control subjects without DM. Examples are basement membrane thickening, angiogenesis, and an increase in osmotic tissue pressure (108–112). This strengthens the hypothesis that DM might affect periodontal tissue in a way similar to how it affects retinal, neural, and renal tissue, namely through vascular damage. We hope to elucidate this by separately discussing the same five pathological mechanisms (hyperglycemia, insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, hypertension, and immune dysfunction) that cause the well-known systemic complications of DM (Figure 1):
Hyperglycemia
As we discussed earlier, poor glycemic control increases the risk for periodontitis in patients with DM, and improvement in HbA1c levels reduces periodontal inflammation (107). Apparently, just as in the well-known diabetic complications, hyperglycemia is a key pathological determinant for periodontitis. While the damaging processes through which hyperglycemia contributes to the development and progression of the well-known complications are well-established (21), this is not the case for DM-associated periodontal disease. However, there is evidence that the underlying upstream mechanism—oxidative stress—affects periodontal health as well (113). Low antioxidant levels are often interpreted as indicator for oxidative stress, and several studies indeed found decreased levels of antioxidants in serum, periodontal tissue, and saliva of patients with DM and periodontitis, compared to subjects without DM (114–117). One study found that the presence of T2DM in a rodent periodontitis model accelerated the decrease in gingival endothelial function (measured by Laser Doppler Flowmetry or LDF), mediated by oxidative stress (118).
Of the downstream effects of hyperglycemia (polyol pathway, AGE/RAGE, PKC, and hexosamine pathway) that might play a role in the pathogenesis of periodontal diseases, AGEs, and RAGE have been studied the most. We already mentioned that patients with DM are susceptible for joint related diseases, due to damage to the connective tissues in these joints, caused by AGEs accumulation. Periodontitis is also characterized by destruction of connective tissue, both in the gingiva and periodontal ligament, suggesting similar pathogenic pathways via AGE accumulation. AGEs and RAGE are both increased in gingival tissue (119) and saliva (120) of patients with T1DM and T2DM. The mechanisms by which AGEs are involved in periodontal tissue destruction are probably the same as in the well-known complications of DM: enhanced inflammation, impaired wound repair, and increased oxidative stress. In the specific case of periodontitis, this results in increased gingival connective tissue and periodontal ligament destruction and alveolar bone resorption (119–123). Increased levels of AGEs in serum of patients with DM were also significantly associated with deterioration of periodontitis (124). We know that AGEs are particularly important in the progression of periodontitis in persons with DM, because research showed that blocking RAGE reduced periodontal tissue breakdown (125).
There is limited evidence that the polyol pathway plays a role in periodontitis. Reduced glutathione (GSH) was one of the antioxidants that was found to be decreased in saliva (115, 117) and periodontal tissue (116) of patients with DM and periodontitis, compared to patients without DM. Another study also showed increased levels of oxidized glutathione (GSSH) in saliva (114). As mentioned before in this review, decreased levels of GSH and increased levels of GSSH are typical for increased polyol pathway flux caused by hyperglycemia. In another study, therapy with aldose reductase inhibitors—possibly obstructing flux of excess glucose into the polyol pathway—prevented alveolar bone loss in rats with DM. This could indicate that the polyol pathway is involved in the progression of periodontitis in patients with DM (126). However, a similar study showed similar results for non-diabetic rats, indicating that aldose reductase inhibitors might prevent alveolar bone loss through mechanisms other than obstructing the polyol pathway flux (127).
Protein kinase C (PKC) activity is also increased in patients with DM and periodontal disease (128), but whether it actually contributes to alveolar bone loss in these patients remains unclear. The possible role of the hexosamine pathway in hyperglycemia-associated periodontitis has not been studied yet.
Insulin resistance
Analysis of periodontal pocket depth in a large population without DM showed an independent association with our second pathogenic mechanism; insulin resistance. However, the association was interpreted as periodontal inflammation being a risk factor for insulin resistance, rather than the other way around (129). A comparable Korean cross-sectional study did not show such a relationship, but they did find impaired pancreatic β cell functioning in patients with periodontitis (130). In another large adult Korean population, insulin resistance was associated with periodontitis, but only in post-menopausal women (131). Furthermore, a large cohort from the United States suggested that the link between obesity and severe periodontitis was mediated through insulin resistance (132). However, the direction of the discovered relationships between insulin resistance and periodontitis could not be established in these cross-sectional studies. A study in Finland did not find an independent association between insulin resistance and periodontitis at baseline (133). However, in the same cohort, after 4 years of follow up, high levels of insulin resistance at baseline weakly but independently predicted the deepening of periodontal pockets (134). Also, in a non-diabetic rat model, obesity-induced insulin resistance resulted in endothelial dysfunction and inflammation of the gingiva, characterized by decreased eNOS expression and increased activity of PKC, NF-κB, and oxidative stress markers (135). Although this might indicate that insulin resistance negatively influences periodontal health, longitudinal studies with human subjects are necessary to confirm this hypothesis.
Dyslipidemia
The independent effect of lipid dysregulation on periodontal health has been studied in several populations without DM (136). Strikingly, the lipid profile typical for patients with DM (low levels of HDL; high levels of triglycerides and slightly increased LDL) was associated with worsened periodontal health, characterized by increased periodontal attachment loss, pocket depth, and bleeding gums (137). Comparable results were found in other cross-sectional studies, although it should be noted that different definitions of periodontitis and varying markers for dyslipidemia were used (138–140). The mechanism by which dyslipidemia contributes to periodontitis is not fully understood, and longitudinal studies to establish a causal relationship are missing. However, it is hypothesized that—similar to hyperglycemia—dyslipidemia stimulates a pro-inflammatory state, and thereby increases the susceptibility for periodontitis (141). Furthermore, it is thought that, besides glucose, lipids can also act as a source for ROS production in the gingiva through lipid peroxidation (LPO). Patients with DM and dyslipidemia have shown increased levels of markers for LPO (116, 142). These increased values were significantly correlated with parameters for periodontitis (% sites with bleeding, periodontal pockets ≥6 mm and pocket suppuration) and several inflammatory markers (IL-6, IL-10, TNF-α) (142). A relatively new insight is the beneficial effect of statin therapy on periodontal treatment outcome in patients without DM, as described in several recent systematic reviews (143–145). However, it should be noted that this is not necessarily caused by statins' lipid lowering effect; it could be the result of pleiotropic features of statins, such as antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects (143).
Hypertension
It is hypothesized that hypertension is associated with periodontal disease, although the majority of studies interpret this relationship as periodontitis being a risk factor for hypertension through inflammation (146). This hypothesis is mainly based on findings that periodontal therapy is beneficial for systolic and diastolic blood pressure (147). However, longitudinal research in the opposite direction is lacking; hypertension might very well be a risk factor for developing periodontitis as it is for other diabetic complications (148, 149). A recent systematic review and meta-analysis found an OR of 1.50 (95% CI: 1.27–1.78) for the association between the presence of hypertension and periodontitis, but again, the direction could not be established (150). It should also be stated that there is a major overlap in risk factors for both conditions. However, a few animal studies show that hypertension might negatively affect alveolar bone quality (151) and gingival vasculature (152), and that it can exacerbate experimental periodontitis (153). Treatment with an anti-hypertensive drug in an animal model with periodontitis resulted in decreased levels of inflammatory cytokines (IL-1β and TNF-α), reduced expression of markers for alveolar bone breakdown (MMP-2, MMP-9, RANKL/RANK), increased expression of a bone growth promoting marker (osteoprotegerin or OPG) and finally reduced alveolar bone loss (154).
Immune dysfunction: impaired immune response and proinflammatory state
As we stated in the background section, periodontitis is a chronic disease characterized by an aberrant inflammatory host response to the biofilm. However, in patients with DM, this pro-inflammatory state seems to be even more exaggerated. PMNs, but also monocytes and macrophages, produce more inflammatory mediators and ROS, which could contribute to tissue destruction in periodontal disease (128, 155–158). Prolonged retention of the PMN infiltrate ensures that the potentially damaging inflammatory response is maintained longer in patients with DM (159–161). Also, patients with DM show increased levels of inflammatory cytokines in gingival crevicular fluid and gingival tissue, such as IL-1β and IL-6, compared to healthy subjects (157, 162–166). TNF-α also contributes to periodontal tissue destruction by enhancing the inflammatory response and activating osteoclasts responsible for bone resorption (167). Another interesting cytokine is receptor activator of NF-κB ligand (RANKL), since it is also involved in the inflammatory processes seen in other diabetic vascular complications (44). In the case of periodontal disease, RANKL and the ratio with OPG determine whether bone is generated (low ratio) or resorbed (high ratio). Especially in patients with poorly controlled diabetes, this ratio is increased in the periodontal tissue (168–170) and gingival crevicular fluid (171, 172), with alveolar bone resorption as a consequence. Treatment with OPG, and thereby decreasing the RANKL/OPG ratio, even reversed alveolar bone loss in diabetic mice. This suggests that this ratio is important for the development or prevention of periodontitis in the presence of DM (169).
We discussed before that patients with DM are susceptible for opportunistic infections because of an impaired innate and adaptive immune response. In the case of periodontitis, especially the PMN response seems to be impaired, characterized by reduced chemotaxis (173, 174). This might cause opportunistic pathogens in the biofilm to persist over time, thereby causing the aberrant inflammation to retain, which enhances the progression of periodontitis (173–175). In that perspective, (severe) periodontitis in patients with DM can best be compared to the diabetic foot. Just as in this condition, the exaggerated inflammatory response to the unresolved infection with opportunistic micro-organisms is retained, which—in combination with poor wound healing—sometimes even results in tooth loss (176, 177).
Concluding Comments
Table 1 summarizes the studies on which the section above was based. Both prevalence and incidence of periodontitis are increased in patients with DM. There are many similarities to the pathogenesis of the well-known complications of DM. Glycemic control seems to be particularly important in the development and severity of periodontitis. However, there are indications that other metabolic disturbances also play a role, such as dyslipidemia, insulin resistance, and especially immune dysfunction.
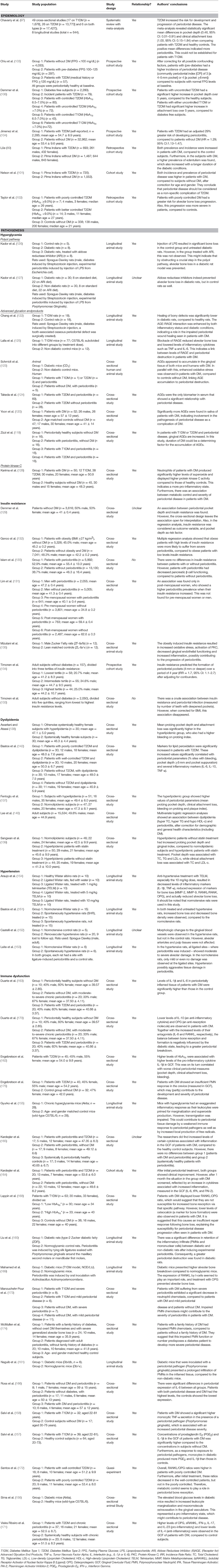
Table 1. Overview of studies investigating the association between diabetes mellitus and periodontal disease.
Dental Caries
Background
A definition often used to describe dental caries (i.e., tooth decay or cavities) is: “the localized destruction of susceptible dental hard tissues (enamel, dentine, root cementum) by acidic by-products from bacterial fermentation of dietary carbohydrates” (178). It can be subdivided into coronal caries (affecting the crown portion of the tooth) and root caries (affecting the root of the tooth). People are susceptible to caries throughout their entire life. The increasingly older western population shows an increase in retention of their natural dentition and therefore, these individuals remain susceptible for caries development, also at old age. Hence, an increase in prevalence of dental caries is observed in this age category (179). Despite this, a clear drop in the total prevalence of caries has been observed in developed countries over the last few decades (178, 180, 181). Nevertheless, the earlier mentioned “Global burden of disease 2010 study” estimates a global prevalence of 35% for dental caries, ranking this oral disease first on the list of the most common diseases of mankind (79, 80).
As can be deduced from the earlier mentioned definition, on the one hand, dental caries is the result of a complex interaction between acid producing bacteria and fermentable carbohydrates (such as: sucrose, fructose, and glucose). On the other hand, the ecology of the mouth, in this case determined to a great extent by the pH of saliva and competing non-cariogenic bacteria, is also important. In the healthy situation, there is a balance between the bacterial biofilm and the tooth minerals. If this balance is disturbed (often referred to as the ecological shift), bacteria in the dental biofilm (including Streptococcus mutans, other closely related Streptococci and some Lactobacilli) produce a sticky polysaccharide matrix and acids, causing demineralization of the hard dental tissues. Ultimately, this leads to cavitation. As human teeth are composed of non-shedding tissue, the aciduric bacteria can prolong this activity as long as they remain on the surface and have sufficient nutrition, in particular sucrose. Thus, poor oral hygiene and very regular intake of sucrose-rich or other fermentable carbohydrates-containing food, snacks, and soft-drinks—that also may be acidic—are cariogenic lifestyle habits. The process of demineralization can be stopped or even reversed, as there is a balance between demineralization and remineralization. This balance is influenced by the supply of calcium, phosphate, and fluoride, the composition and quantity of saliva (which serves as a buffer), diet and of course the presence of cariogenic bacteria in the dental plaque. In this way, physical, biological, environmental, and behavioral risk factors are involved in caries development (178).
Relationship With Diabetes Mellitus: Epidemiology
Several literature reviews that discuss the association between diabetes and dental caries, point to the lack of solid evidence for a clear correlation (6, 93, 182–184). The majority of studies have a cross-sectional design, investigating patients with T1DM. In many studies, these patients showed an increased prevalence of dental caries, compared to patients without DM (185–194). However, a considerable number of studies could not replicate these findings (195–201).
There is limited research available on the epidemiology of caries and T2DM. Some papers found an increased prevalence of dental caries (202–206), which was supported by investigations using diabetic animal models (207–209). On the contrary, several studies did not find a significant association between T2DM and caries (197, 210–212).
Longitudinal research with children and adults into the effect of DM on the development of dental caries is very rare. A prospective cohort study reported that poor glycemic control was associated with increased caries incidence within T1DM children (192). No longitudinal studies are available on patients with T2DM.
In general, the cross-sectional design of most studies, varying definitions of dental caries that limit generalizability, and possible differences between the mostly young T1DM and the generally older T2DM population, make it difficult to establish a clear epidemiologic association between DM and dental caries. It is worth noting that some studies even report a decreased prevalence of dental caries in patients with DM (213, 214). It can be speculated that this remarkable finding could be ascribed to proper diabetes care management. As we know, lifestyle adjustment and losing weight are important in diabetes care, especially for T2DM. Nutritional management (i.e., restrictions of carbohydrate intake) is a crucial part of the strategy to lose weight. For T1DM, restrictions in carbohydrate intake could be a strategy to achieve reduction in insulin doses. The relatively low, and/or more infrequent, intake of fermentable carbohydrates might reduce the risk for developing dental caries (93).
Relationship With Diabetes Mellitus: Pathogenesis
In contrast to periodontal disease, less is known about biologic explanations for the possible association between DM and dental caries. Nevertheless, we will review the same five pathologic mechanisms we discussed before. However, it is important to note several complicating factors. First, adult and elderly individuals with DM often suffer from periodontitis as discussed before. This is associated with gingival recession (i.e., receding gums), which exposes dental root surfaces that then become susceptible to root caries (183). As we will discuss in section Dry Mouth below, patients with DM also often suffer from decreased salivary flow rates and altered saliva composition. Since saliva acts as a buffer against the acidic by-products from the bacterial fermentation of carbohydrates, a change in mere quantity (i.e., hyposalivation) or composition of saliva could therefore influence that protective function against dental caries (203). For example, low salivary calcium and phosphate levels are associated with higher caries experience (215). Two studies indeed found lower calcium and phosphate levels in patients with DM, which was associated with higher caries prevalence (203, 204).
Hyperglycemia
Only a limited number of studies investigated the direct effect of hyperglycemia on dental caries. One animal study with diabetic rats showed that prevention of hyperglycemia by insulin treatment prevented the progression of dental caries (216). Studies with human subjects with either T1DM or T2DM found that an increased number of decayed teeth was associated with higher HbA1c levels (217, 218). A large Asian adult cohort investigated the relationship between dental caries and metabolic syndrome (219). Metabolic syndrome is defined by having three of the following five components: hyperglycemia, elevated triglycerides, lowered HDL levels, hypertension, and central obesity. Multivariate analysis on these individual components revealed a significant association between dental caries and hyperglycemia (219). Another study also found a significant association between dental caries and metabolic syndrome, but no relationships with the individual components were observed (220). Reports about the downstream pathways of hyperglycemia (polyol, AGEs, PKC, hexosamine) and upstream effects (ROS production) in relation to caries are lacking.
Interestingly, hyperglycemia results in increased levels of glucose in saliva of patients with DM (221). This could be important, as glucose might serve as a source of nutrition for the cariogenic bacteria in the dental biofilm. Indeed, some studies found an association between these increased salivary glucose levels and dental caries in patients with DM (192, 222), however, others did not (193, 196). Therefore, at this point, there is inconclusive evidence that salivary hyperglycemia is associated with increased dental caries.
Insulin resistance
One study compared the decayed, missing, and filled teeth (DMFT) index—a marker for experienced and current caries—between obese, insulin-resistant (OB-IR) patients and healthy controls. The DMFT index, as well as one of its components (decayed teeth), were increased in patients with insulin resistance (223).
Dyslipidemia
Research into the involvement of dyslipidemia in dental caries is limited to those studies we mentioned above, which investigated dyslipidemia as a component of metabolic syndrome. None of those found a relationship, as only hyperglycemia was significantly associated with decayed teeth (219, 220).
Hypertension
A recent study with indigenous Brazilian adolescents revealed that hypertension was significantly associated with dental caries (OR = 1.95, 95% CI: 1.03–3.66) (224). Another study found a significant association between and dental caries—measured as DMFT and DMFS (Decayed, Missing due to caries, Filled teeth/Surface)—and self-reported hypertension (225).
Immune dysfunction: impaired immune response and proinflammatory state
There is no evidence that inflammation plays a role in dental caries, as is the case for periodontitis or the chronic systemic complications of DM. However, the impaired immune defense against opportunistic pathogens might influence the number of cariogenic bacteria in saliva and dental biofilm. Increased counts of streptococci and lactobacilli were observed in the supragingival plaque (the biofilm on teeth along and above the gum margins) of patients with DM, which was associated with increased caries incidence (213, 226). Another study showed that, especially in persons with poorly controlled DM, the presence of caries was associated with high levels of lactobacilli and Streptococcus mutans, compared to patients with well-controlled DM (199). One study proposed that elevated levels of salivary glucose—presumably caused by obesity or DM—favors a relative abundance of aciduric bacteria that increases the risk for developing dental caries (227). Others did not find any differences in cariogenic bacteria in saliva between patients with and without DM (210).
Concluding Comments
Summarizing the findings of the studied literature in Table 2, it becomes clear that several studies observe an increased prevalence of dental caries in patients with DM. Although it is conceivable that caries and DM are associated, the lack of longitudinal research prevents us from making causal assumptions. Moreover, it is not clear whether the increased prevalence is a direct result of DM, or that other factors contribute to the association. For example, certain lifestyle aspects, such as an unhealthy diet with high carbohydrates intake, increases the risk for DM as well as for dental caries.
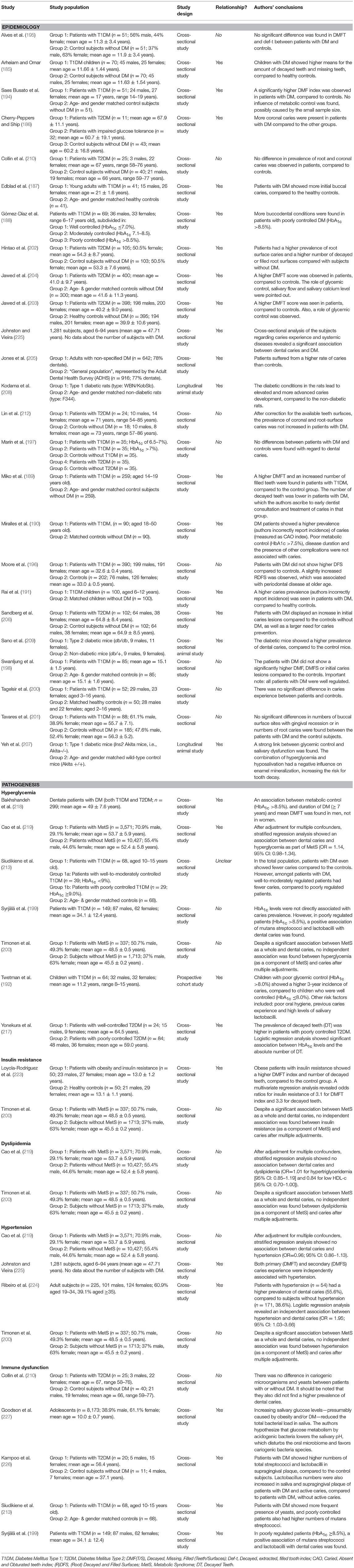
Table 2. Overview of studies investigating the association between diabetes mellitus and dental caries.
Dry Mouth
Background
The term “dry mouth” can be interpreted in several ways. Usually, two distinctive phenomena are referred to in literature when speaking of dry mouth. The first is the objective measurement of reduced salivary flow rate, called hyposalivation or salivary gland hypofunction. This is usually defined as “an unstimulated whole saliva flow rate of < 0.1 mL/min, collected for 5 to 15 min, or chewing-stimulated whole saliva flow rate of < 0.7 mL/min, collected for 5 min” (228). The second condition often referred to as “dry mouth” is xerostomia, which addresses the subjective experience of a dry mouth by the patient (229). Even though these conditions are closely related, patients with hyposalivation do not necessarily suffer from xerostomia. And vice versa, although many patients with xerostomia do actually have underlying hyposalivation, this is not always the case. This suggests that other mechanisms could partly explain the dry mouth sensation in some patients, such as a change in saliva composition, a sensory dysfunction or a cognitive problem (230–232).
When defining hyposalivation as an unstimulated whole saliva flow rate of < 0.1 mL/min, research showed that approximately 20% of individuals across all ages were affected, while the prevalence was ~3% when using the stimulated whole saliva flow rate definition (< 0.7 mL/min) (233). The prevalence of xerostomia is subject of discussion, as estimations in literature range from 1 to 65% (234). This wide range is mainly the result of high variation in defining xerostomia and methods of diagnosis, and implies that there is need for large population-based research. However, it is clear that the prevalence of both conditions increases with age (234). Furthermore, medication use is one of the major causes of both xerostomia and hyposalivation (235), as well as Sjögren syndrome and radiation therapy of the head and neck region (229). Xerostomia is also associated with several autoimmune diseases, graft-vs.-host disease after undergoing bone marrow transplantation, HIV infection, and renal failure (236).
Relationship With Diabetes Mellitus: Epidemiology
The experience of a dry mouth is one of the most frequently mentioned oral complaints by patients with DM. In a way, this is not surprising, considering the fact that the population with T2DM generally consists of relatively older individuals, and we now know that the prevalence of xerostomia and hyposalivation increases with age. Also, many patients with DM suffer from one or more complications and/or comorbidities, for which they possibly receive medication that increases the risk for oral dryness (e.g., anti-cholinergic and anti-hypertensive medication).
Varying definitions and methods of diagnosing hyposalivation and xerostomia make it difficult to establish a direct association with DM. Nevertheless, many cross-sectional studies reported a diminished salivary flow rate in patients with DM, compared to control subjects without DM. This finding applies for patients with T1DM (237–243), as well as for individuals with T2DM (204, 206, 239, 241, 244–252). However, it should be noted that in several of these studies, the measured decrease in salivary flow rate did not necessarily fulfill the earlier mentioned criteria to be classified as hyposalivation. This could be one of the reasons why some studies did not find an increased prevalence of xerostomia in patients with T1DM (237, 253) or T2DM (243, 244, 253). This is supported by the suggestion that in general, a salivary flow rate above the threshold of 0.1–0.3 mL/min is sufficient to prevent xerostomia in most individuals (254). Still, there is sufficient literature that reports an increased prevalence of xerostomia in patients with T1DM (240, 241, 243, 255–257) and T2DM (206, 247, 248, 257, 258).
Relationship With Diabetes Mellitus: Pathogenesis
Although many cross-sectional studies report an increased prevalence of xerostomia and a decreased salivary flow rate in patients with DM, the mechanisms underlying these observations remain unclear. Secretion of saliva by the parotid gland—the largest salivary glands—is regulated by the autonomic nervous system, which led to the hypothesis that diabetic neuropathy might somehow be involved in the development of dry mouth experience. However, studies investigating this theory present contradictory results. Decreased (240, 259), comparable (241, 260), or even increased (261) salivary flow rates are observed in patients with DM, having peripheral or autonomic neuropathy, compared to subjects without DM and/or patients with DM without neuropathy. It should be noted that tricyclic anti-depressants, sometimes prescribed to relieve neuropathic pain, are associated with the development of dry mouth and therefore is another xerogenic drug (235).
There are a few studies that actually observed structural changes in the salivary glands of patients with DM, in particular in the parotid glands. Vacuolization of acini (the saliva secretory cells) in the parotid gland was observed, which indicated an early form of degeneration (262). Another study also showed atrophy of the acini, lipid droplets in epithelial cells of the acini and ducts, and adipose infiltration in the stromae (263). On the contrary, a study into the submandibular gland of patients with T2DM observed enlargement of the acini, independent of impaired glandular function or metabolic control. This might indicate a compensatory mechanism to counteract hyposalivation (264). Asymptomatic enlargement of the parotid gland is also frequently observed in patients with DM, which could indicate similar compensatory mechanisms against hyposalivation or xerostomia (265). The pathological mechanisms of how DM contributes to these structural changes are still matter of discussion, and solid research is scarce. Below, we summarize possible mechanisms of action how DM might induce xerostomia or hyposalivation, again via the established pathological mechanisms of diabetic complications.
Hyperglycemia
In general, patients with poor glycemic control present significantly lower salivary flow rate and higher prevalence of xerostomia, compared to subjects with well-controlled DM (240, 241, 244, 245). This suggests that, again, hyperglycemia is a driving force in the pathogenic association between DM and dry mouth. However, the downstream pathways of hyperglycemia (polyol, AGEs, PKC, and hexosamine) are completely unexplored in human study subjects, as well as the common upstream effect of increased oxidative stress. One animal study suggests that the expression of AGEs and RAGE in the lacrimal glands (which secrete the aqueous layer of the tear film) might cause eye dryness (266). Theoretically, that could also account for the salivary glands, causing oral dryness. Indeed, submandibular salivary glands of diabetic rats also showed increased expression of RAGE, which resulted in an inflammatory upregulation through NF-κB activation (267). However, this hypothesis has not been studied in humans so far and demands further research.
Hyperglycemia in patients with DM can cause polyuria and osmotic diuresis, possibly leading to dehydration, which is associated with hyposalivation (268, 269). Also, a fairly novel class of antidiabetic drugs (SGLT-2 inhibitor) prevents reabsorption of glucose in the kidneys, and thereby increases urinary glucose excretion (i.e., glycosuria). This could lead to dehydration and increased thirst, both associated with oral dryness (270). Other xerogenic medications that patients with DM often need (e.g., anti-hypertensives) might also partly explain the association between DM, hyperglycemia and reduced salivary flow or xerostomia (241).
Insulin resistance
Research into the role of insulin resistance in the pathogenesis of hyposalivation and xerostomia is limited to a few animal studies. Increased ROS production, an upregulated inflammatory response (271) and an altered lipid profile (272) were observed in the submandibular and parotid salivary gland of insulin resistant rats. The pro-inflammatory state observed in salivary glands did not alter their structural morphology (273).
Dyslipidemia
As we mentioned earlier, some studies observed an accumulation of lipid droplets in epithelial cells of the salivary glands (263, 264). This might be the consequence of the excess flux of free fatty acids (FFAs), resulting from insulin resistance (see section Insulin Resistance). In several tissue types, accumulation of lipids induces lipotoxicity, which can lead to cell apoptosis (274). It is hypothesized that these processes could also affect the salivary glands and thereby cause hyposalivation, but this theory has not been investigated yet (264). As a matter of fact, to the best of our knowledge, the independent role of dyslipidemia in the association between xerostomia/hyposalivation and DM has not been investigated in humans. One animal study showed that saturated fatty acids (SFAs) induced an inflammatory response, reflected by increased production of IL-6 through NF-κB activation in the salivary glands epithelial cells (275).
Hypertension
One study showed that patients with hypertension and without DM had reduced submandibular and sublingual salivary flow rates, compared to healthy controls. The salivary flow rates of the hypertensive patients were comparable with those of patients with DM, while stimulated parotid and unstimulated whole salivary flow did not differ across the groups. However, it was not clear whether these differences were a consequence of the hypertension itself, possible anti-hypertensive medication use, or both (276).
Immune dysfunction: impaired immune response and proinflammatory state
As described above, DM and its metabolic disturbances could be associated with dry mouth, sometimes mediated by inflammatory processes. However, this remains rather speculative, since most of those studies investigated diabetic animal models. Moreover, the inflammatory state observed in some studies did not necessarily affect salivary flow rate, xerostomia or salivary gland morphology.
Some studies suggest that Sjögren syndrome—an autoimmune disease affecting the salivary glands—could be the underlying cause of dry mouth in patients with DM (277, 278). However, there is no convincing evidence for this hypothesis.
Concluding Comments
Dry mouth is a very often heard complaint by patients with DM, and the majority of epidemiological studies indeed report an increased prevalence of xerostomia and a decreased salivary flow rate. Especially poor glycemic control negatively impacts both the prevalence and severity of dry mouth. Older age, dehydration and medication use also seem to be important determinants in this association. However, there is hardly any research into other pathogenic pathways that could explain the association between DM and dry mouth, and longitudinal studies are also lacking. Table 3 summarizes the literature on which this section was based.
Oral Mucosal Lesions
Background
The name oral mucosal lesion is used as an umbrella term for any abnormal change to the mucosal surface in the oral cavity. This concerns numerous different types of lesions, and it is beyond the scope of this review to discuss them all individually. Often, oral mucosal lesions are classified based on the pathology, morphology, or location of the lesion. Shulman et al. classify: “candida-related lesions, tobacco-related lesions, acute conditions, tongue conditions, red/white conditions, raised conditions, and other conditions.” Possible locations where mucosal lesions can be observed are: the hard palate, gingiva, lip, tongue, buccal mucosa, vestibule, labial mucosa, commissure, floor of the mouth, and the soft palate (279).
Despite the heterogeneity of oral mucosal lesions, several studies tried to estimate their prevalence. A large epidemiologic study from the U.S. (17,235 individuals >17 years old) concluded that 27.9% of the population had at least one lesion (279). In a German population, 33.8% of adults aged 35–44 years and 33.9% of adults aged 65–74 years were without any oral mucosal lesion (280). Somewhat similar figures were reported in a Slovenian population aged 25–75 years, where 38.4% had no oral mucosal lesions (281). A Chilean study showed a prevalence of 53% for one or more oral mucosal lesions, although in this study, only individuals older than 65 years were included (282). From the majority of studies, it can be concluded that tobacco use seems to be the most important risk factor for having any type of oral mucosal lesions, followed by (ill-fitting) removable dentures. The prevalence of oral mucosal lesions increases with age and is higher in males (279). Ethnicity might also play a role. For example, non-Hispanic whites in the US had increased odds of having a lesion, compared to non-Hispanic blacks and Mexican-Americans (279).
The large majority of studies investigating the association between DM and oral mucosal lesions focus on Candida-related lesions. For this reason, we will also focus especially on these forms of mucosal lesions, while we will only briefly discuss non-candidal oral mucosal lesions at the end of this section.
Relationship With Diabetes Mellitus: Epidemiology (Candida-Related Oral Lesions)
Candida is a genus of yeasts, with Candida albicans as the most common species, and it can be found on the skin and on all mucosal surfaces. It exists in healthy individuals as a commensal organism, but causes opportunistic infections in susceptible patients, such as patients with HIV/AIDS, persons using immunosuppressive medication and individuals with poorly controlled DM (283). Oral candidal infection (candidiasis) has several clinical manifestations, including median rhomboid glossitis (redness and loss of papillae on the dorsal side of the tongue), angular cheilitis (inflammation of the corners of the mouth) and denture stomatitis (inflammation and redness underneath a denture). Assessment of the association between DM and Candida-related lesions is hampered by the complexity of the lesions, variations in study populations and interaction with other local risk factors (284). Moreover, there are no longitudinal studies investigating a possible causal relationship between DM and Candida-related lesions. However, cross-sectional studies investigating the previously mentioned candidal manifestations showed a higher prevalence of median rhomboid glossitis (285), denture stomatitis (286, 287), and angular cheilitis (288) in patients with T1DM or T2DM, compared to healthy controls. In one study, the overall prevalence of Candida-related lesions was 15% in patients with DM, compared to 3% in healthy controls (285). One study found an increased overall prevalence of fungal infections—including candidiasis—in patients with DM (289), while another study in complete denture wearers did not find an increased prevalence (290). Furthermore, one study found increased counts of Candida pseudohyphae in patients with T1DM, compared to healthy controls (285). This might partly explain the increased prevalence of candidal infections the latter authors observed. However, other studies show conflicting results, as they did not find an increased colonization of Candida in individuals with T1DM and T2DM (291, 292).
Relationship With Diabetes Mellitus: Pathogenesis (Candida-Related Oral Lesions)
This section will discuss the pathogenesis of candidal lesions in relation to DM, again by means of the previously utilized pathologic phenomena related to DM: hyperglycemia, insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, hypertension, and immune dysfunction.
Hyperglycemia
Several studies found that the increased prevalence of Candida-related oral lesions was associated with poor metabolic control, indicating that hyperglycemia is important for this association (285, 293, 294). However, besides these observational studies, very little is known about its exact pathogenic role. There are no studies investigating the downstream effects of hyperglycemia that are involved in the well-known complications of DM (polyol, AGE/RAGE, PKC, and hexosamine pathways). Interestingly, one study showed that inhibition of AGE formation in diabetic rats improved the microbicidal activity of PMNs against C. albicans (295). However, it should be noted that this study concerned peritoneal PMNs and Candida infection, but AGEs might be involved in oral candidal lesions as well. This has not been confirmed or investigated yet.
As we have discussed before, salivary glucose levels are often increased in patients with DM due to hyperglycemia. Similar to the suggestions for cariogenic oral streptococci, glucose can also act as a source of nutrition for yeast species such as Candida. Indeed, several studies found an association between increased glucose levels in saliva and the growth of Candida in the oral cavity of patients with DM (292, 296).
Dyslipidemia
Two animal studies observed an increased systemic infection with C. albicans after inducing hyperlipidemia, with increased LDL or VLDL levels in particular (297, 298). It should be further elucidated whether this is the case for humans as well, and if this is also applicable specifically for the oral cavity.
Insulin resistance and hypertension
Currently, there are no studies that investigated the effect of insulin resistance or hypertension on Candida colonization or Candida-related oral lesions.
Immune dysfunction: impaired immune response and proinflammatory state
As we discussed before, patients with DM are susceptible for hyposalivation. Saliva has several innate immune defensive mechanisms to protect the oral mucosa against microorganisms such as Candida. Examples are mechanical washing, its buffering capacity and the presence of antifungal components such as histatins and mucins (299). If patients with DM develop hyposalivation, these mechanisms are impaired, and as such, hyposalivation is an important risk factor for oral candidiasis (300). This was confirmed in a study, where patients with both DM and hyposalivation had higher counts of Candida species in their saliva (247). One study showed that both hyposalivation and the presence of DM were independent predictors of oral candidiasis (299).
We discussed before that the impaired innate immune response makes patients with DM susceptible to infections. The decreased phagocytosis and killing capabilities of the PMNs might cause overgrowth of Candida, eventually causing candidal infection (301). Furthermore, we mentioned that patients with DM have increased adhesion of microorganisms to several cell types. Adhesion to epithelial cells of the oral cavity is a prerequisite for Candida colonization; interestingly, buccal and palatal epithelial cells from patients with DM showed increased adhesion capacities for Candida in ex vivo experiments (287, 302).
Relationship With Diabetes Mellitus (Non-candida Related Lesions)
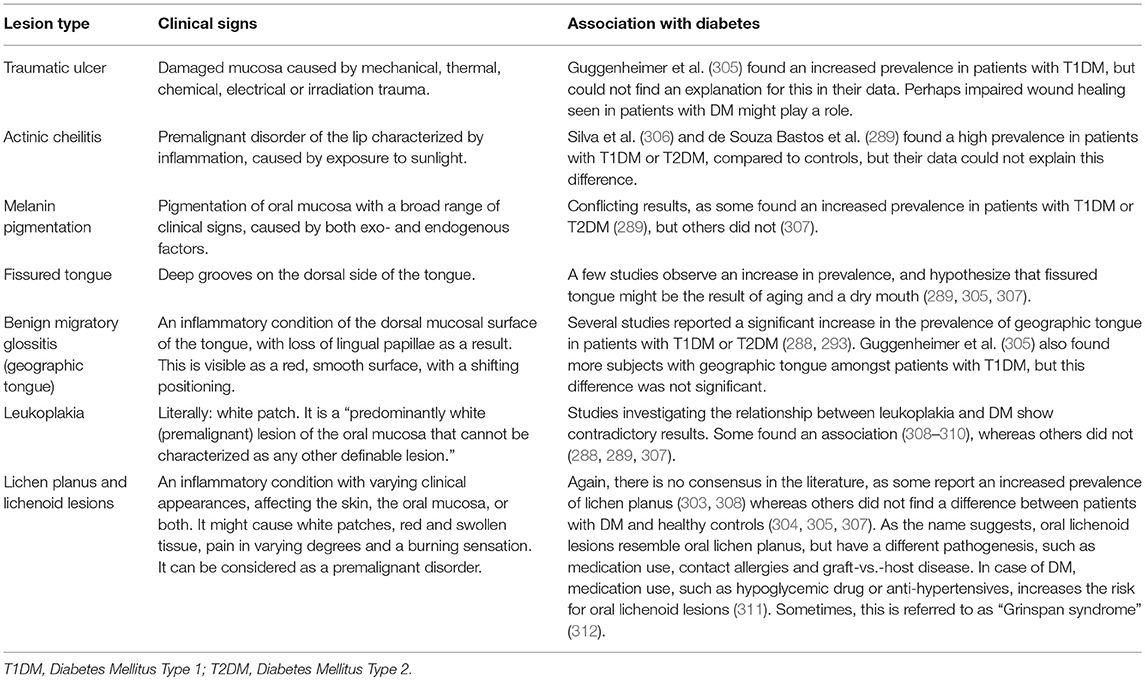
Several studies investigated only one non-candida related mucosal lesions (303, 304), while others studied several types of mucosal lesions (289, 305–309), but none of those studies investigated possible underlying biologic mechanisms. For this reason, all individual lesion types that might be associated with DM are presented separately in Table 4, together with their clinical signs. This concerns: traumatic ulcer, actinic cheilitis, melanin pigmentation, fissured tongue, benign migratory glossitis (geographic tongue), leukoplakia, lichen planus, and other lichenoid lesions. The (pre)malignant mucosal lesions will be discussed in more detail in section Oral Cancer.
Concluding Comments
From an epidemiologic point of view, the prevalence of candida-related oral mucosal lesions is increased in patients with DM. However, longitudinal studies are lacking, and not much is known about the pathogenesis behind the increased prevalence. It is highly likely that the impaired immune response enables Candida species to act as opportunistic organisms. Table 5 provides an overview of the literature that discusses the association between Candida-related lesions. As for non-candida related mucosal lesions, the evidence is too limited to establish a relationship with DM.
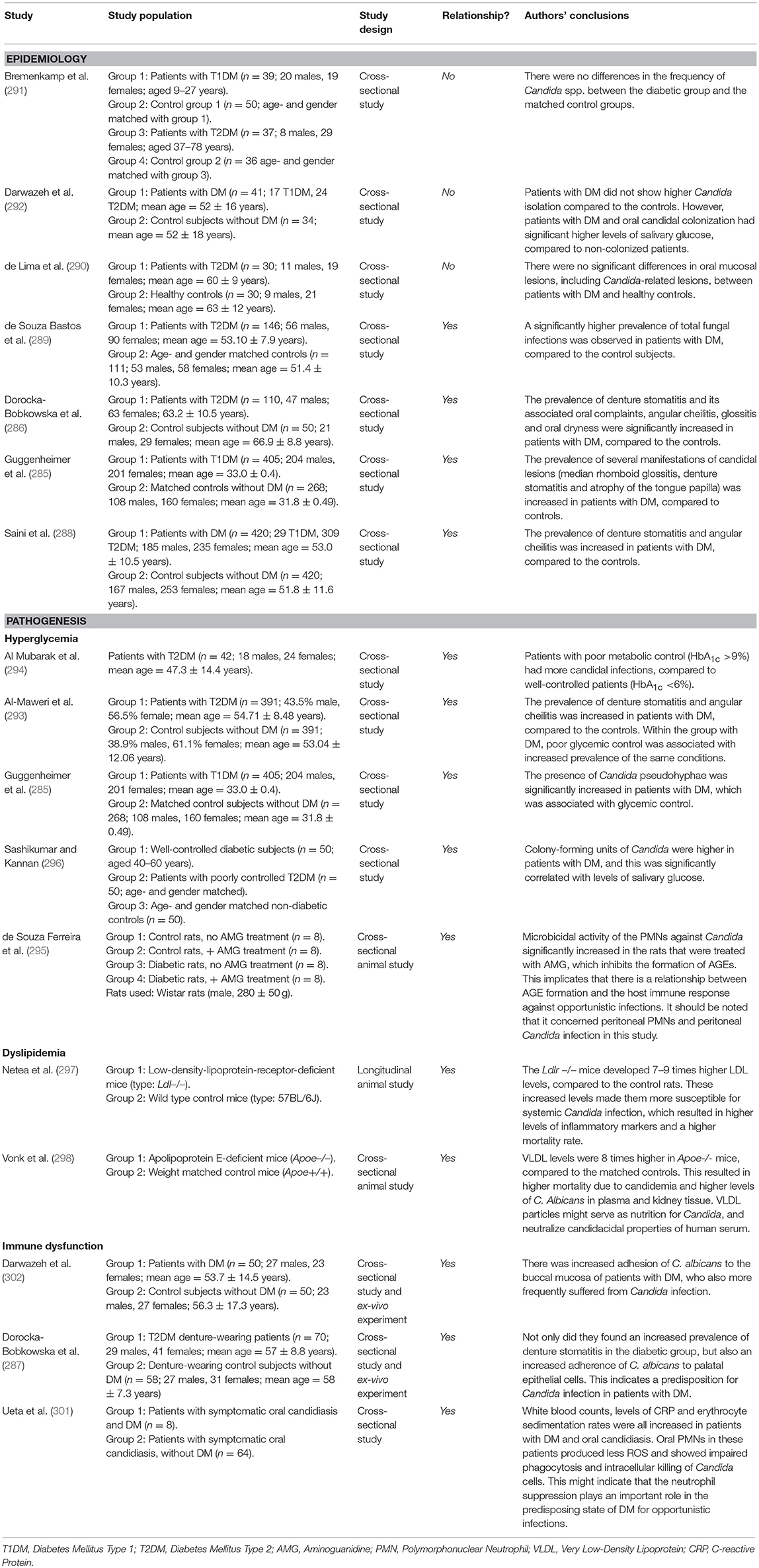
Table 5. Overview of studies investigating the association between diabetes mellitus and oral candidal lesions.
Oral Cancer
Background
This section focuses on cancers of the lip, tongue, oral cavity, and oropharynx. Oral and oropharyngeal cancers together are ranked as the sixth most common type of cancer, but prevalence and incidence vary greatly between countries and regions (313). The global incidence was estimated to be 263,900 in 2008, causing 128,000 deaths worldwide (314). Many possible risk factors have been identified, including: smoking, tobacco and betel nut chewing, alcohol abuse, snuff dipping, sunlight, radiation, viruses, and immune dysfunction (313). Many risk factors are culture dependent, hence the varying epidemiologic figures across regions. For example, 75% of all cases in the US could be attributed to alcohol and tobacco use (315), while in Taiwan and neighboring countries, betel nut chewing was the main risk factor (314). Survival rates also vary between countries, age groups, and types of cancer, but in general, the 5-year survival is estimated to be ~50% for cancers of the tongue, oral cavity, and oropharynx, and 90% for cancers of the lip (313). As we mentioned in section Dry Mouth, radiation therapy of cancer in the head and neck region can cause dry mouth (229).
Relationship With Diabetes Mellitus: Epidemiology
Patients with DM have an increased risk for developing cancer in several organs and tissues, as well as an increase in cancer mortality, compared to subjects without DM (316). A recent meta-analysis showed that this is also the case for oral cancer (317). One cross-sectional Hungarian study showed an increased prevalence of oral cancer in patients with T2DM or T1DM compared to controls, as well as an over-representation of T2DM in individuals with oral cancer (310). A Brazilian cross-sectional study, which we also discussed in the previous section, revealed an increased prevalence of potentially malignant mucosal lesions (actinic cheilitis, lichen planus, leukoplakia, and nicotinic stomatitis) in patients with T2DM (289). A similar study from Malaysia showed contradicting results, as no association between DM and precancerous lesions was found (288). However, a large cross-sectional study from the US also observed that DM was an independent predictor for oral leukoplakia, which is considered as a pre-malignant lesion (318). The same was found in a cross-sectional study from India, but only for women (309). Two case-control studies from Italy presented contradicting results, as one did find an increased risk for cancer of the oral cavity in patients with DM (319), while the other did not (320).
There are also several longitudinal studies investigating the incidence of—and risk for—oral cancer in diabetic cohorts. One Danish population-based cohort study compared the incidence of several types of cancer in a large diabetic population (n = 109,581) with expected incidences based on a national cancer registry record. They found that the incidence of “cancer of the mouth” was increased 2-fold in the diabetic population younger than 50 years (321). Two large Taiwanese cohort studies from the same group also investigated the risk for head and neck cancer in patients with T2DM, with oral cancer specifically. The first did not find an increased risk, possibly due to a relatively short follow-up period (2 years), and no matching of study subjects (322). However, after matching the patients and prolonging the follow-up period in their second study, they showed an increased risk for oral cancer and oropharyngeal cancer in patients with T2DM (323).
Besides its effect on cancer incidence, DM also negatively affects the prognosis of patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC). In another Taiwanese study, overall survival, recurrence-free survival, and cancer-specific survival were all decreased in patients with OSCC and DM, compared to patients with OSCC without DM (324). This was also observed in a large prospective cohort study from the US, where DM was associated with an increased risk for mortality from cancer of the oral cavity or pharynx (325).
Relationship With Diabetes Mellitus: Pathogenesis
The pathogenesis behind the epidemiologic association between DM an oral cancer is complex and remains to be fully elucidated. In an attempt to explain the increased risk for oral cancer by means of the pathological mechanisms that we have been using throughout this review, it appears that only hyperglycemia and dyslipidemia have been studied, albeit very limited. There is no data available on the role of hypertension, insulin resistance and immune dysfunction.
Hyperglycemia
Although it is likely that hyperglycemia is important for the increased risk of oral cancer in patients with DM, there is only limited evidence for that hypothesis. In one study, elevated levels of HbA1c were associated with an increased risk for oral leukoplakia, a pre-malignant oral mucosal lesion (326). The downstream pathways of hyperglycemia (polyol, AGE/RAGE, PKC, hexosamine) are largely unexplored. Interestingly, inhibition of the polyol pathway in a diabetic animal model significantly lowered the number of premalignant lesions in the colon (327). It would be interesting to investigate whether this is the case for animal and human oral mucosal tissues as well.
One in vitro study observed increased cell migration when oral cancer cell lines were treated with AGEs. This was probably the result of increased expression of RAGE, MMP-2, and MMP-9 (328) Increased migration of cancer cells is one of the important characteristics of cancer malignancy. In another in vitro study, oral cancer cells were again treated with AGEs, which resulted in a decreased p53 expression. P53 is an important tumor suppressor, regulating cell survival and cell death; decreased expression usually promotes cell survival and inhibits cell death. Therefore, AGEs are probably involved in the survival rate of oral cancer cells through p53 suppression, and might worsen the prognosis of oral cancer in patients with DM (329). This poor prognosis was confirmed in patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma, where increased RAGE expression in tumors decreased disease-free survival (330). One study found that one specific RAGE gene polymorphism significantly increased the risk for oral cancer in patients with DM (331). RAGE also seems to be important for the invasiveness of oral mucosal tumor cells, since metastatic tumor cells showed a higher expression of RAGE. Suppression of RAGE in oral squamous carcinoma cell lines decreased the invasive activity (332).
Dyslipidemia
One study had a closer look at the individual components of the metabolic syndrome (hyperglycemia, elevated triglycerides, lowered HDL levels, hypertension, and central obesity), which revealed that subjects with hypertriglyceridemia had a higher risk for developing oral pre-malignancies (333).
Concluding Comments
Table 6 presents an overview of the literature that discusses the association between DM and oral cancer. As is the case for other types of cancer, epidemiologic research seems to indicate that the prevalence and even incidence of oral premalignant lesions and oral cancer is increased in patients with DM. Considering the potentially devastating and even fatal effects of oral cancer, these findings are worrying. There is a lack of research into possible pathogenic pathways that explain the association between DM and oral cancer. As long as it remains unknown why patients with DM are at higher risk for oral cancer, targeted prevention and treatment programs are unlikely to succeed.
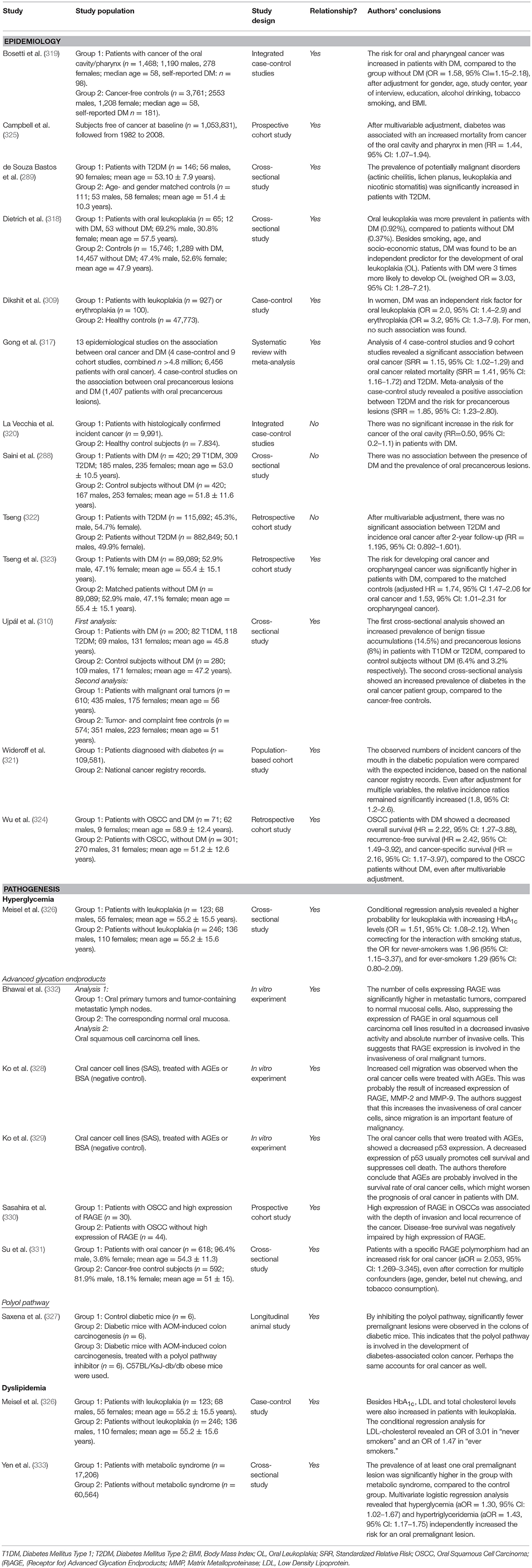
Table 6. Overview of studies investigating the association between diabetes mellitus and oral cancer.
Taste Disturbance
Background
Gustatory dysfunction (i.e., taste disturbance) is generally classified into three major types: dysgeusia, a distortion or alteration in taste sensation; hypogeusia, a partial loss of taste and ageusia, a complete loss of taste (334). Compared to for example olfactory dysfunction, gustatory dysfunction is relatively rare. Estimations of the prevalence of any disturbance of taste in the adult population range from 0.93% in the US (335) to 2.5% in Sweden (336). The prevalence of severe hypogeusia or ageusia is lower, with 0.83% of a study population that attended a chemosensory clinic. In the general population, this will probably be even lower (337). As is the case for other sensory functions, such as hearing or smell, the risk for gustatory dysfunction increases with age (338). The prevalence is doubled in individuals aged 45–65, and even tripled in those aged 66 and older, compared to subjects aged 18–44 (335). Especially women aged 50 years or older seem to be susceptible for taste disturbances (336). Besides older age, many other risk factors have been proposed in literature, including physiological changes, oral and systemic diseases, iatrogenic causes, nutritional deficiencies, and lifestyle behavior (338).
Relationship With Diabetes Mellitus: Epidemiology
Epidemiologic research into the association between DM and taste disturbances is limited to a few cross-sectional studies. Nevertheless, both hypogeusia and ageusia were observed more frequently in patients with T1DM (339, 340) and T2DM (340, 341), compared to healthy controls. Another way of defining taste disturbances is by measuring detection thresholds for certain tastes (e.g., sweet or salty), after exposure to certain taste stimuli (e.g., chemical or electrical), with higher thresholds indicating reduced taste sensation. In both patients with T1DM (339, 340, 342) and patients with T2DM (340, 343–345), these thresholds were generally elevated, compared to healthy controls. One study did not find an association (346). Taste disturbances can have important consequences, especially for patients with DM. Research has shown that diminished taste perception resulted in a tendency toward consumption of beverages with a higher sucrose concentration with a higher sweet taste intensity. This might indicate a preference for sweeter foods or beverages that probably are higher in carbohydrates and calories (347). Besides a possible increase in glucose supplies, this could also increase the risk to develop obesity, a major risk factor for T2DM and its complications.
Relationship With Diabetes Mellitus: Pathogenesis
Unfortunately, there is no literature available that investigated the same pathogenic pathways we have been using throughout this report. However, a few explanations why patients with DM more frequently suffer from taste impairment have been proposed. For example, the increased susceptibility for dry mouth we discussed in section Dry Mouth, might increase the risk for taste disturbances. One study found that, of all patients with a subjective complaint of taste disturbance, 63% also had a sensation of oral dryness, often regardless of the actual salivary flow (336). Another study showed that hyposalivation was indeed associated with hypogeusia in a general elderly population (348). Furthermore, since gustation is a sensory function with neural involvement, it is conceivable that the typical neuropathy associated with DM is one of the causative factors for impaired gustatory function in patients with DM. Three studies from the same research group showed that taste impairment in individuals with T1DM was significantly associated with peripheral neuropathy (339, 349, 350). One animal study observed decreased innervation of taste buds in diabetic rats, compared to non-diabetic control rats (351). Another study with diabetic rats showed increased cell apoptosis in their taste buds (352). Humans with T1DM also had decreased vascularization of the tip of the tongue (353). The above findings indicate that the tongue, with the taste buds in particular, is susceptible for vascular and neuronal damage.
Concluding Comments
Studies investigating the association between taste impairments and DM can be found in Table 7. Although it remains a relatively rare condition, patients with DM seem to be susceptible for certain forms and gradations of taste impairment. However, there is a lack of solid longitudinal research, and many common risk factors can obscure a possible association. Besides a few careful suggestions that neural and vascular degeneration might play a role, the pathogenesis remains largely unexplored.
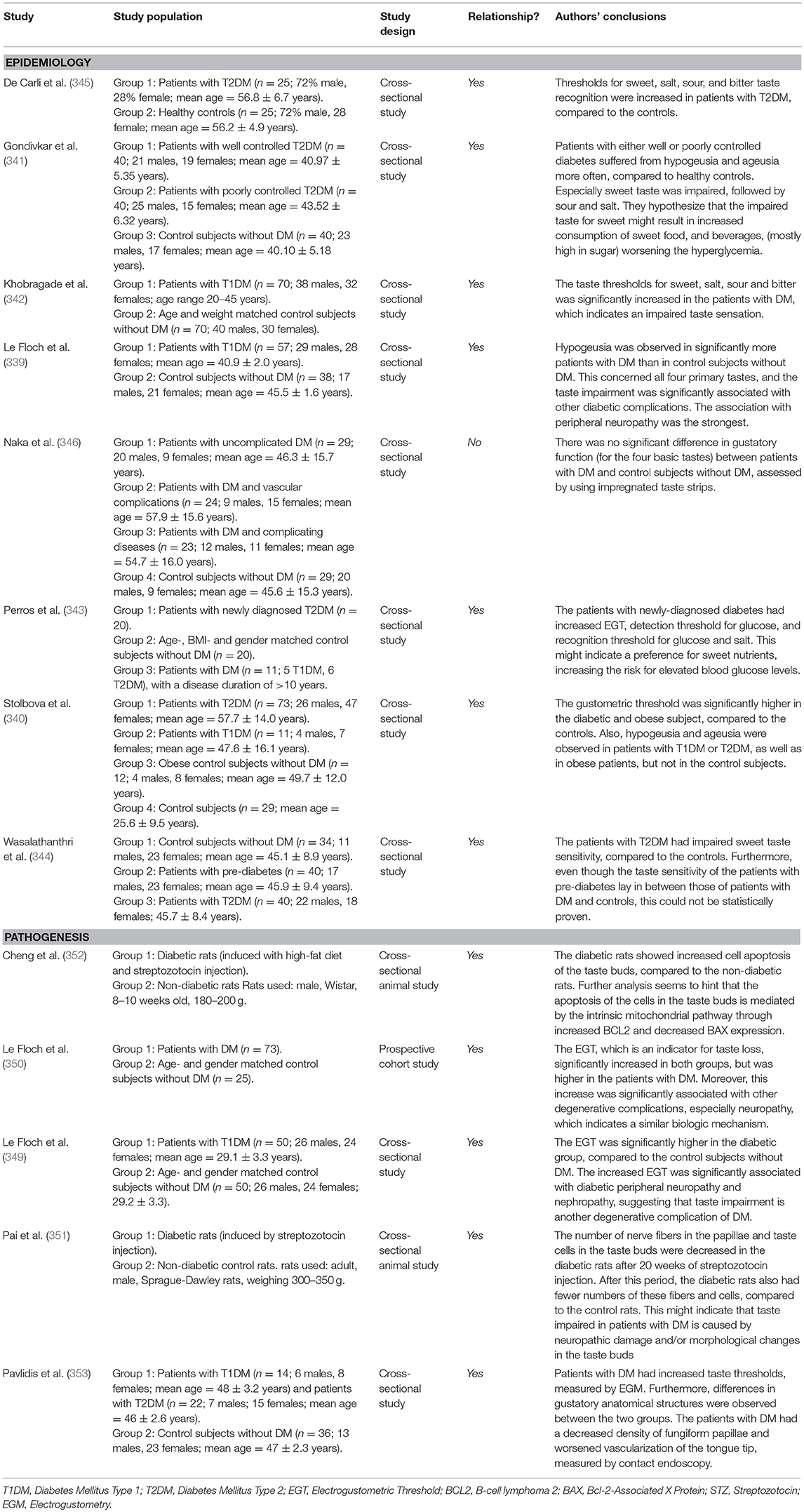
Table 7. Overview of studies investigating the association between diabetes mellitus and taste impairment.
Other Oral Complications
The following conditions affecting the oral cavity have been mentioned in the literature as possible complications of DM, but evidence for an epidemiologic or pathologic association is too scarce to dedicate a separate section. Table 8 provides an overview of the literature that discusses the associations between each of these oral conditions and DM.
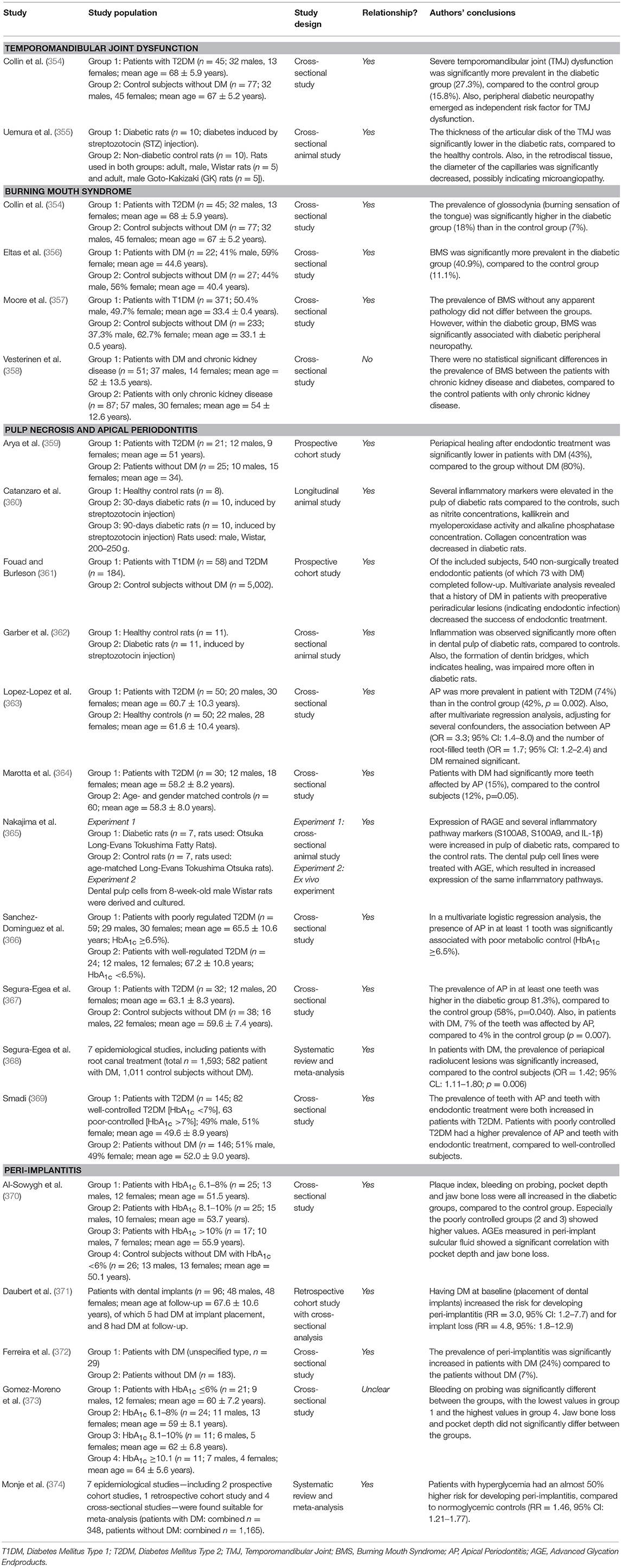
Table 8. Overview of studies investigating the association between diabetes mellitus and other oral complications.
Temporomandibular Disorders (TMD)
Temporomandibular disorder (TMD) is an umbrella term that comprises several conditions affecting the temporomandibular region. The principal clinical feature of TMD is pain during mastication, often accompanied by joint sounds and/or limited opening of the jaw. It is estimated that ~10% of the adult population suffers from TMD (375). Earlier in this report, we mentioned that patients with DM are susceptible for joint disorders, primarily through the damaging effects of AGEs on connective tissue. From that perspective, the temporomandibular joint could be affected as well. One study found that the prevalence of temporomandibular joint (TMJ) dysfunction was increased in patients with DM (354). More interestingly, the latter investigators also found that within the diabetic group, peripheral diabetic neuropathy was an independent risk factor for TMJ dysfunction. In a recent animal study, morphologic changes in the TMJ and the capillaries of the retrodiscal tissue were compared between diabetic rats and normal rats. In the diabetic rats, the articular disc of the TMJ was significantly thinner at several sites, compared to the control rats. Also, the capillaries of the retrodiscal tissue were significantly decreased in diameter (355). These findings suggest that TMD might be associated with DM, possibly with involvement of microvascular damage. Research into the pathogenic pathways (hyperglycemia, insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, hypertension, and immune dysfunction) should confirm this hypothesis.
Burning Mouth Syndrome
Burning mouth syndrome (BMS) is a chronic pain syndrome. Usually, two types are distinguished: primary (i.e., idiopathic) BMS if there are no underlying diseases that can explain the complaints, and secondary BMS, when there is an oral or systemic disorder that could explain the condition. In the literature, many synonyms for BMS are used (e.g., glossodynia, sore tongue, or stomatodynia), which complicates estimations regarding epidemiology. BMS rarely affects individuals younger than 30, and estimations of the total prevalence range from 0.7 to 4.6% (376). A prospective cohort study from the US found an incidence rate of 11.4 per 100,000 person-years, and showed a strong association with female gender and age (377). Despite the major impact BMS has on quality of life, the pathogenesis is unknown to a large extent. The general complaint of patients with BMS is pain, more specifically a burning, scalding, tingling, or numb feeling at one or more sites in the mouth, such as the tongue, lip, and hard palate (376). Although pain is the principle complaint, patients with BMS also often experience xerostomia, dysgeusia, and other sensory disorders in the oral region. Also, candidiasis is more prevalent in individuals with BMS, and often causes a burning sensation of the oral mucosa (376). Apparently, there is significant overlap with other oral conditions and complaints that are associated with DM as well. This overlap, together with a lack of a uniform definition of BMS, complicates epidemiologic research into the association with DM. Increased prevalence of BMS in patients with DM compared to healthy subjects has been reported (354, 356), while others did not find any differences in prevalence of BMS (358). In one study, within the people suffering from both DM and BMS, a significant association of BMS with peripheral neuropathy was observed (357). This could indicate that BMS is another symptom of neuropathy in patients with DM, although this theory remains to be confirmed.
Pulp Necrosis and Apical Periodontitis
Dental pulp necrosis is the death of cells and tissue inside the root canals and pulp chamber, which can be either symptomatic or asymptomatic. The effect of DM on the dental pulp has mainly been investigated in animal studies. Both acute and chronic effects of hyperglycemia on dental pulp were observed in diabetic rats, characterized by increased inflammation and damage to structural components of the dental pulp (360). This was confirmed in another study, where hyperglycemia in rats resulted in increased inflammation in the dental pulp, which impaired healing after pulp capping (362). Expression of RAGE was also increased in diabetic rats, while treatment of cultured dental pulp cells of diabetic rats with AGEs also resulted in increased inflammatory pathways (365). This generally observed inflammatory response increases the risk for pulp necrosis (378). However, the clinical relevance of these findings are questionable, since well-designed studies with human subjects are lacking.
Closely related to pulp necrosis is periapical or apical periodontitis (AP), a condition in which the periodontal ligament and surrounding alveolar bone around the apex of the tooth is affected. AP is the result of an inflammatory response to an infection of the pulp canals, often caused by caries, trauma, or attrition (379). It is estimated that more than 60% of individuals older than 60 years suffer from at least one AP lesion, but it is often asymptomatic (380). Similar to the marginal form of periodontitis as discussed before (section Periodontal Diseases), the driving force of AP is the inflammatory response to microbial pathogens, which—in the case of AP—find their way beyond the tooth apex. Considering the pathologic similarity between AP and periodontitis, it is highly conceivable that AP is also associated with DM. Several narrative reviews conclude that DM is a risk factor for developing AP, and negatively influences endodontic treatment success (378–382). Multiple cross-sectional studies also show an increased prevalence of AP and an increased number of teeth affected by AP in patients with DM, compared to healthy controls (363, 364, 366–369). Interestingly, two prospective treatment studies showed that treatment of AP is less successful in patients with T2DM, compared to healthy controls (359, 361). Considering the high prevalence of AP, and its similarities to periodontitis, it is rather surprising that so little is known about a possible relationship with DM. Longitudinal studies investigating this relationship should confirm whether DM is a risk factor for the development and severity of AP.
Peri-implant Disease
Peri-implant diseases are inflammatory lesions in the tissues around dental implants. As in periodontal diseases, two entities of the condition are recognized: peri-implant mucositis and peri-implantitis (383). Peri-implant mucositis can be compared with gingivitis, affecting the soft tissues surrounding the implant, while peri-implantitis corresponds with periodontitis, also affecting the supporting jaw bone (384). Among individuals with dental implants, the prevalence of peri-implantitis over a 5–15 year period is estimated to range from 15 to 28% (383, 385–388). There is limited epidemiological evidence for an association between DM and peri-implant diseases. Several recent review articles assessed the influence of systemic conditions, among which DM, on the development of peri-implant diseases (389–392). Despite limited evidence of often low quality, it is suggested that poorly controlled DM increases the risk for peri-implantitis, while well-controlled DM is not associated. A systematic review confirmed this, as the meta-analysis of seven studies revealed that patients with hyperglycemia had an almost 50% higher risk for peri-implantitis, compared to normoglycemic subjects (RR = 1.46, 95% CI: 1.21–1.77) (374). On the contrary, one study did not find any differences in jaw bone loss and pocket depth around dental implants between patients with well-controlled and poorly controlled DM. However, it should be noted that the bleeding tendency of the mucosa around implants was associated with higher HbA1c levels (373). A cross-sectional analysis showed a higher prevalence of peri-implantitis in patients with DM, compared to subjects without DM (372). This finding was confirmed in another study, where the researchers found an increased risk for peri-implantitis in patients that suffered from DM at the time of implant placement, compared to patients without DM (RR = 3.0, 95% CI: 1.2–7.7) (371). Interestingly, one study observed a significant correlation between AGEs concentration—measured in peri-implant sulcular fluid and increased in the groups with DM—and pocket depth and jaw bone loss around implants (370).
Concluding Comments
Prevention and management of well-known complications of DM, such as retinopathy, nephropathy, and neuropathy, are crucial aspects of modern diabetes care. In order to achieve the same for oral complications, this review has provided diabetes care professionals with extensive background knowledge about potential oral complications that can occur in patients with DM. A considerable body of evidence suggests that several oral complications are more prevalent in patients with DM, including periodontitis, dry mouth, dental caries, oral candida infections, oral cancer, and taste disorders. In the case of periodontitis and oral cancer, there are even longitudinal studies that show a temporal association. Some studies suggest that the pathogenic pathways that cause microvascular complications of DM also seem to be involved in oral complications. Even though this is not so evident for all oral complications we discussed, their generally increased prevalence cannot be ignored. Often, there is a lack of decent research that prevents us from establishing or rejecting clear associations between DM and oral diseases and conditions. Therefore, thorough, well-designed research is necessary.
Considering the major impact of oral complications on quality of life, prevention and early management of oral pathologies in diabetes care practice will be crucial. Although this review has provided some insight, recognizing signs and symptoms of oral complications will remain a major challenge for diabetes care professionals. Therefore, as is already the case for the well-known diabetic complications, we strongly encourage an interdisciplinary approach of DM care professionals together with the dental field professionals, to manage potential oral complications.
Author Contributions
MV, BL, VG, and WT contributed to the conception and drafting of the review. MV and WT reviewed the literature.
Funding
This work is part of the Ph.D. track of MV, which is funded by Sunstar Suisse SA.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
1. American Diabetes Association. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care (2014) 37(Suppl. 1):S81–90. doi: 10.2337/dc14-S081
2. World Health Organization. Global Status Report on Noncommunicable Diseases 2014: Attaining the Nine Global Noncommunicable Diseases Targets; A Shared Responsability. (2014).
3. Global Health Estimates 2015: Deaths by Cause Age Sex by Country and by Region 2000-2015. [Internet]. (2016). Available online at: http://www.who.int/entity/healthinfo/global_burden_disease/GHE2015_Deaths_Global_2000_2015.xls.
4. Global Report on Diabetes [Internet]. World Health Organization (2016). Available online at: http://www.who.int/diabetes/global-report/en/.
5. Fowler MJ. Microvascular and macrovascular complications of diabetes. Clin Diabetes (2008) 26:77–82. doi: 10.2337/diaclin.26.2.77
6. Ship JA. Diabetes and oral health: an overview. J Am Dent Assoc. (2003) 134 Spec No:4–10s. doi: 10.14219/jada.archive.2003.0367
7. Lamster IB, Lalla E, Borgnakke WS, Taylor GW. The relationship between oral health and diabetes mellitus. J Am Dent Assoc (2008) 139:19-24S. doi: 10.14219/jada.archive.2008.0363
8. D'Aiuto F, Gable D, Syed Z, Allen Y, Wanyonyi KL, White S, et al. Evidence summary: the relationship between oral diseases and diabetes. Br Dent J. (2017) 222:944–8. doi: 10.1038/sj.bdj.2017.544
9. IDF Clinical Guidelines Task Force. IDF Guideline on Oral Health for People With Diabetes. Brussels: International Diabetes Federation (2009).
10. Alberti KG, Zimmet PZ. Definition, diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus and its complications. Part 1: diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus provisional report of a WHO consultation. Diabet Med. (1998) 15:539–53.
11. Forbes JM, Cooper ME. Mechanisms of diabetic complications. Physiol Rev. (2013) 93:137–88. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00045.2011
12. American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes-−2014. Diabetes Care (2014) 37(Suppl. 1):S14–80. doi: 10.2337/dc14-S014
13. UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Effect of intensive blood-glucose control with metformin on complications in overweight patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 34). Lancet (1998) 352:854–65.
14. UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33). Lancet (1998) 352:837–53.
15. Holman RR, Paul SK, Bethel MA, Matthews DR, Neil HA. 10-year follow-up of intensive glucose control in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. (2008) 359:1577–89. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0806470
16. Duckworth W, Abraira C, Moritz T, Reda D, Emanuele N, Reaven PD, et al. Glucose control and vascular complications in veterans with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. (2009) 360:129–39. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0808431
17. Patel A, MacMahon S, Chalmers J, Neal B, Billot L, Woodward M, et al. Intensive blood glucose control and vascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. (2008) 358:2560–72. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0802987
18. Ismail-Beigi F, Craven T, Banerji MA, Basile J, Calles J, Cohen RM, et al. Effect of intensive treatment of hyperglycaemia on microvascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes: an analysis of the ACCORD randomised trial. Lancet (2010) 376:419–30. doi: 10.1016/s01406736(10)60576-4
19. Nathan DM, Cleary PA, Backlund JY, Genuth SM, Lachin JM, Orchard TJ, et al. Intensive diabetes treatment and cardiovascular disease in patients with type 1 diabetes. N Engl J Med. (2005) 353:2643–53. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa052187
20. Nathan DM, Zinman B, Cleary PA, Backlund JY, Genuth S, Miller R, et al. Modern-day clinical course of type 1 diabetes mellitus after 30 years' duration: the diabetes control and complications trial/epidemiology of diabetes interventions and complications and Pittsburgh epidemiology of diabetes complications experience (1983-2005). Arch Intern Med. (2009) 169:1307–16. doi: 10.1001/archinternmed.2009.193
21. Brownlee M. The pathobiology of diabetic complications: a unifying mechanism. Diabetes (2005) 54:1615–25. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.54.6.1615
22. Kaiser N, Sasson S, Feener EP, Boukobza-Vardi N, Higashi S, Moller DE, et al. Differential regulation of glucose transport and transporters by glucose in vascular endothelial and smooth muscle cells. Diabetes (1993) 42:80–9.
23. Giacco F, Brownlee M. Oxidative stress and diabetic complications. Circ Res. (2010) 107:1058–70. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.110.223545
24. Singh R, Barden A, Mori T, Beilin L. Advanced glycation end-products: a review. Diabetologia (2001) 44:129–46. doi: 10.1007/s001250051591
25. Brownlee M. Biochemistry and molecular cell biology of diabetic complications. Nature (2001) 414:813–20. doi: 10.1038/414813a
26. Ahmed N. Advanced glycation endproducts—role in pathology of diabetic complications. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. (2005) 67:3–21. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2004.09.004
27. Abate M, Schiavone C, Salini V, Andia I. Management of limited joint mobility in diabetic patients. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. (2013) 6:197–207. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S33943
28. Yerneni KK, Bai W, Khan BV, Medford RM, Natarajan R. Hyperglycemia-induced activation of nuclear transcription factor kappaB in vascular smooth muscle cells. Diabetes (1999) 48:855–64.
29. Kuboki K, Jiang ZY, Takahara N, Ha SW, Igarashi M, Yamauchi T, et al. Regulation of endothelial constitutive nitric oxide synthase gene expression in endothelial cells and in vivo: a specific vascular action of insulin. Circulation (2000) 101:676–81. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.101.6.676
30. Park JY, Takahara N, Gabriele A, Chou E, Naruse K, Suzuma K, et al. Induction of endothelin-1 expression by glucose: an effect of protein kinase C activation. Diabetes (2000) 49:1239–48. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.49.7.1239
31. Suzuki M, Akimoto K, Hattori Y. Glucose upregulates plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 gene expression in vascular smooth muscle cells. Life Sci. (2002) 72:59–66. doi: 10.1016/s0024-3205(02)02182-3
32. Koya D, Jirousek MR, Lin YW, Ishii H, Kuboki K, King GL. Characterization of protein kinase C beta isoform activation on the gene expression of transforming growth factor-beta, extracellular matrix components, and prostanoids in the glomeruli of diabetic rats. J Clin Invest. (1997) 100:115–26.
33. Rask-Madsen C, King GL. Differential regulation of VEGF signaling by PKC-alpha and PKC-epsilon in endothelial cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2008) 28:919–24. doi: 10.1161/atvbaha.108.162842
34. Yau JW, Rogers SL, Kawasaki R, Lamoureux EL, Kowalski JW, Bek T, et al. Global prevalence and major risk factors of diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes Care (2012) 35:556–64. doi: 10.2337/dc11-1909
35. Fong DS, Aiello L, Gardner TW, King GL, Blankenship G, Cavallerano JD, et al. Retinopathy in diabetes. Diabetes Care (2004) 27(Suppl. 1):s84–7. doi: 10.2337/diacare.27.2007.S84
36. Gross JL, De Azevedo MJ, Silveiro SP, Canani LH, Caramori ML, Zelmanovitz T. Diabetic nephropathy: diagnosis, prevention, and treatment. Diabetes Care (2005) 28:164–76. doi: 10.2337/diacare.28.1.164
37. Adler AI, Stevens RJ, Manley SE, Bilous RW, Cull CA, Holman RR. Development and progression of nephropathy in type 2 diabetes: the United Kingdom Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS 64). Kidney Int. (2003) 63:225–32. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1755.2003.00712.x
38. Yagihashi S, Mizukami H, Sugimoto K. Mechanism of diabetic neuropathy: Where are we now and where to go? J Diabetes Invest. (2011) 2:18–32. doi: 10.1111/j.2040-1124.2010.00070.x
39. Boulton AJ. Management of diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Clin Diabetes (2005) 23:9–15. doi: 10.2337/diaclin.23.1.9
40. Ginsberg HN. Insulin resistance and cardiovascular disease. J Clin Invest. (2000) 106:453–8. doi: 10.1172/jci10762
41. Evans JL, Goldfine ID, Maddux BA, Grodsky GM. Are oxidative stress– activated signaling pathways mediators of insulin resistance and β-cell dysfunction? Diabetes (2003) 52:1–8. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.52.1.1
42. Du X, Edelstein D, Obici S, Higham N, Zou MH, Brownlee M. Insulin resistance reduces arterial prostacyclin synthase and eNOS activities by increasing endothelial fatty acid oxidation. J Clin Invest. (2006) 116:1071–80. doi: 10.1172/jci23354
43. Rask-Madsen C, Li Q, Freund B, Feather D, Abramov R, Wu IH, et al. Loss of insulin signaling in vascular endothelial cells accelerates atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E null mice. Cell Metab. (2010) 11:379–89. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2010.03.013
44. Beckman JA, Creager MA, Libby P. Diabetes and atherosclerosis: epidemiology, pathophysiology, and management. JAMA (2002) 287:2570–81. doi: 10.1001/jama.287.19.2570
45. Rask-Madsen C, King GL. Vascular complications of diabetes: mechanisms of injury and protective factors. Cell Metab. (2013) 17:20–33. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2012.11.012
46. Boyle PJ. Diabetes mellitus and macrovascular disease: mechanisms and mediators. Am J Med. (2007) 120(9 Suppl. 2):S12–7. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2007.07.003
47. Hanley AJ, Williams K, Stern MP, Haffner SM. Homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance in relation to the incidence of cardiovascular disease: the San Antonio Heart Study. Diabetes Care (2002) 25:1177–84. doi: 10.2337/diacare.25.7.1177
48. Groop PH, Forsblom C, Thomas MC. Mechanisms of disease: pathway-selective insulin resistance and microvascular complications of diabetes. Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab. (2005) 1:100–10. doi: 10.1038/ncpendmet0046
49. Bardini G, Rotella CM, Giannini S. Dyslipidemia and diabetes: reciprocal impact of impaired lipid metabolism and beta-cell dysfunction on micro- and macrovascular complications. Rev Diabet Stud. (2012) 9:82–93. doi: 10.1900/rds.2012.9.82
50. Wu L, Parhofer KG. Diabetic dyslipidemia. Metabolism (2014) 63:1469–79. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2014.08.010
51. Ginsberg HN, Elam MB, Lovato LC, Crouse JR III, Leiter LA, Linz P, et al. Effects of combination lipid therapy in type 2 diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. (2010) 362:1563–74. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1001282
52. Keech A, Simes RJ, Barter P, Best J, Scott R, Taskinen MR, et al. Effects of long-term fenofibrate therapy on cardiovascular events in 9795 people with type 2 diabetes mellitus (the FIELD study): randomised controlled trial. Lancet (2005) 366:1849–61. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(05)67667-2
53. Chew EY, Ambrosius WT, Davis MD, Danis RP, Gangaputra S, Greven CM, et al. Effects of medical therapies on retinopathy progression in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. (2010) 363:233–44. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1001288
54. Davis TM, Ting R, Best JD, Donoghoe MW, Drury PL, Sullivan DR, et al. Effects of fenofibrate on renal function in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: the Fenofibrate Intervention and Event Lowering in Diabetes (FIELD) Study. Diabetologia (2011) 54:280–90. doi: 10.1007/s00125-010-1951-1
55. Wiggin TD, Sullivan KA, Pop-Busui R, Amato A, Sima AA, Feldman EL. Elevated triglycerides correlate with progression of diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes (2009) 58:1634–40. doi: 10.2337/db08-1771
56. Leiter LA. The prevention of diabetic microvascular complications of diabetes: Is there a role for lipid lowering? Diabetes Res Clin Pract. (2005) 68:S3–14. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2005.03.015
57. Vincent AM, Callaghan BC, Smith AL, Feldman EL. Diabetic neuropathy: cellular mechanisms as therapeutic targets. Nat Rev Neurol. (2011) 7:573–83. doi: 10.1038/nrneurol.2011.137
58. Adler AI, Stratton IM, Neil HA, Yudkin JS, Matthews DR, Cull CA, et al. Association of systolic blood pressure with macrovascular and microvascular complications of type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 36): prospective observational study. BMJ (2000) 321:412–9. doi: 10.1136/bmj.321.7258.412
59. Cheung BMY, Li C. Diabetes and Hypertension: Is There a Common Metabolic Pathway? Curr Atheroscler Rep. (2012) 14:160–6. doi: 10.1007/s11883-012-0227-2
60. UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Tight blood pressure control and risk of macrovascular and microvascular complications in type 2 diabetes: UKPDS 38. BMJ (1998) 317:703–13.
61. Kostev K, Rathmann W. Diabetic retinopathy at diagnosis of type 2 diabetes in the UK: a database analysis. Diabetologia (2013) 56:109–11. doi: 10.1007/s00125-012-2742-7
62. Boulbou MS, Koukoulis GN, Makri ED, Petinaki EA, Gourgoulianis KI, Germenis AE. Circulating adhesion molecules levels in type 2 diabetes mellitus and hypertension. Int J Cardiol. (2005) 98:39–44. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2003.07.037
63. Schalkwijk CG, Stehouwer CD. Vascular complications in diabetes mellitus: the role of endothelial dysfunction. Clin Sci. (2005) 109:143–59. doi: 10.1042/cs20050025
64. Geerlings SE, Hoepelman AI. Immune dysfunction in patients with diabetes mellitus (DM). FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. (1999) 26:259–65.
65. Alba-Loureiro TC, Munhoz CD, Martins JO, Cerchiaro GA, Scavone C, Curi R, et al. Neutrophil function and metabolism in individuals with diabetes mellitus. Braz J Med Biol Res. (2007) 40:1037–44. doi: 10.1590/s0100-879x2006005000143
66. Mowat A, Baum J. Chemotaxis of polymorphonuclear leukocytes from patients with diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. (1971) 284:621–7.
67. Muller LM, Gorter KJ, Hak E, Goudzwaard WL, Schellevis FG, Hoepelman AI, et al. Increased risk of common infections in patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Clin Infect Dis. (2005) 41:281–8. doi: 10.1086/431587
68. Casqueiro J, Casqueiro J, Alves C. Infections in patients with diabetes mellitus: A review of pathogenesis. Indian J Endocrinol Metab (2012) 16(Suppl. 1):S27–36. doi: 10.4103/2230-8210.94253
69. Reiber GE, Vileikyte L, Boyko EJ, del Aguila M, Smith DG, Lavery LA, et al. Causal pathways for incident lower-extremity ulcers in patients with diabetes from two settings. Diabetes Care (1999) 22:157–62.
70. Falanga V. Wound healing and its impairment in the diabetic foot. Lancet (2005) 366:1736–43. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(05)67700-8
71. Brem H, Tomic-Canic M. Cellular and molecular basis of wound healing in diabetes. J Clin Invest. (2007) 117:1219–22. doi: 10.1172/jci32169
72. Moxey PW, Gogalniceanu P, Hinchliffe RJ, Loftus IM, Jones KJ, Thompson MM, et al. Lower extremity amputations–a review of global variability in incidence. Diabet Med. (2011) 28:1144–53. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-5491.2011.03279.x
73. Margolis DJ, Malay DS, Hoffstad OJ, Leonard CE, MaCurdy T, de Nava KL, et al. Incidence of Diabetic Foot Ulcer and Lower Extremity Amputation Among Medicare Beneficiaries, 2006 to 2008: Data Points #2. Data Points Publication Series. Rockville, MD: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US) (2011).
74. Mora C, Navarro JF. Inflammation and diabetic nephropathy. Curr Diab Rep. (2006) 6:463–8. doi: 10.1007/s11892-006-0080-1
75. Tang J, Kern TS. Inflammation in diabetic retinopathy. Prog Retin Eye Res. (2011) 30:343–58. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2011.05.002
76. Mealey BL, Rose LF. Diabetes mellitus and inflammatory periodontal diseases. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. (2008) 15:135–41. doi: 10.1097/MED.0b013e3282f824b7
77. Eke PI, Dye BA, Wei L, Slade GD, Thornton-Evans GO, Borgnakke WS, et al. Update on prevalence of periodontitis in adults in the United States: NHANES 2009 to 2012. J Periodontol. (2015) 86:611–22. doi: 10.1902/jop.2015.140520
78. Wahlin Å, Papias A, Jansson H, Norderyd O. Secular trends over 40 years of periodontal health and disease in individuals aged 20–80 years in Jönköping, Sweden: Repeated cross-sectional studies. J Clin Periodontol. (2018) 45:1016–24. doi: 10.1111/jcpe.12978
79. Marcenes W, Kassebaum NJ, Bernabe E, Flaxman A, Naghavi M, Lopez A, et al. Global burden of oral conditions in 1990-2010: a systematic analysis. J Dent Res. (2013) 92:592–7. doi: 10.1177/0022034513490168
80. Murray CJ, Vos T, Lozano R, Naghavi M, Flaxman AD, Michaud C, et al. Disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) for 291 diseases and injuries in 21 regions, 1990–2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet (2013) 380:2197–223. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61689-4
81. Petersen PE, Ogawa H. The global burden of periodontal disease: towards integration with chronic disease prevention and control. Periodontol 2000 (2012) 60:15–39. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0757.2011.00425.x
82. Armitage GC. Development of a classification system for periodontal diseases and conditions. Ann Periodontol. (1999) 4:1–6.
83. Herrera D, Alonso B, Arriba L, Santa Cruz I, Serrano C, Sanz M. Acute periodontal lesions. Periodontol 2000 (2014) 65:14–77. doi: 10.1111/prd.12022
84. Tonetti MS, Greenwell H, Kornman KS. Staging and grading of periodontitis: framework and proposal of a new classification and case definition. J Clin Periodontol. (2018) 45(Suppl. 20):S149–61. doi: 10.1111/jcpe.12945
85. Genco RJ, Borgnakke WS. Risk factors for periodontal disease. Periodontol 2000 (2013) 62:59–94. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0757.2012.00457.x
86. Loos BG, Papantonopoulos G, Jepsen S, Laine ML. What is the contribution of genetics to periodontal risk? Dent Clin North Am. (2015) 59:761–80. doi: 10.1016/j.cden.2015.06.005
87. Page RC, Eke PI. Case definitions for use in population-based surveillance of periodontitis. J Periodontol (2007) 78:1387–99. doi: 10.1902/jop.2007.060264
88. Pihlstrom BL, Michalowicz BS, Johnson NW. Periodontal diseases. Lancet (2005) 366:1809–20. doi: 10.1016/S0140-673667728-8
89. Löe H. Periodontal disease: the sixth complication of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care (1993) 16:329–34. doi: 10.2337/diacare.16.1.329
90. Taylor GW, Graves DT, Lamster IB. Periodontal disease as a complication of diabetes mellitus. In: Lamster IB, editor. Diabetes Mellitus and Oral Health: An Interprofessional Approach. 1st ed: Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons (2014). p. 121–41. doi: 10.1002/9781118887837.ch6
91. Preshaw PM, Bissett SM. Periodontitis: oral complication of diabetes. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. (2013) 42:849–67. doi: 10.1016/j.ecl.2013.05.012
92. Mealey BL, Ocampo GL. Diabetes mellitus and periodontal disease. Periodontol 2000 (2007) 44:127–53. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0757.2006.00193.x
93. Taylor GW, Manz MC, Borgnakke WS. Diabetes, periodontal diseases, dental caries, and tooth loss: a review of the literature. Compend Contin Educ Dent. (2004) 25:179–84, 86–8, 90; quiz 92.
94. Taylor GW, Borgnakke W. Periodontal disease: associations with diabetes, glycemic control and complications. Oral Dis. (2008) 14:191–203. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-0825.2008.01442.x
95. Preshaw PM, Alba AL, Herrera D, Jepsen S, Konstantinidis A, Makrilakis K, et al. Periodontitis and diabetes: a two-way relationship. Diabetologia (2012) 55:21–31. doi: 10.1007/s00125-011-2342-y
96. Khader YS, Dauod AS, El-Qaderi SS, Alkafajei A, Batayha WQ. Periodontal status of diabetics compared with nondiabetics: a meta-analysis. J Diabetes Complications (2006) 20:59–68. doi: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2005.05.006
97. Chavarry NG, Vettore MV, Sansone C, Sheiham A. The relationship between diabetes mellitus and destructive periodontal disease: a meta-analysis. Oral Health Prev Dent. (2009) 7:107–27.
98. Chapple IL, Genco R, working group 2 of the joint EFPAAPw. Diabetes and periodontal diseases: consensus report of the Joint EFP/AAP Workshop on Periodontitis and Systemic Diseases. J Periodontol (2013) 84(4 Suppl.):S106–12. doi: 10.1902/jop.2013.1340011
99. Emrich LJ, Shlossman M, Genco RJ. Periodontal disease in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Periodontol. (1991) 62:123–31.
100. Shlossman M, Knowler WC, Pettitt DJ, Genco RJ. Type 2 diabetes mellitus and periodontal disease. J Am Dent Assoc. (1990) 121:532–6. doi: 10.14219/jada.archive.1990.0211
101. Nelson RG, Shlossman M, Budding LM, Pettitt DJ, Saad MF, Genco RJ, et al. Periodontal disease and NIDDM in Pima Indians. Diabetes Care (1990) 13:836–40. doi: 10.2337/diacare.13.8.836
102. Taylor GW, Burt BA, Becker MP, Genco RJ, Shlossman M. Glycemic control and alveolar bone loss progression in type 2 diabetes. Ann Periodontol. (1998) 3:30–9. doi: 10.1902/annals.1998.3.1.30
103. Chiu SY, Lai H, Yen AM, Fann JC, Chen LS, Chen HH. Temporal sequence of the bidirectional relationship between hyperglycemia and periodontal disease: a community-based study of 5,885 Taiwanese aged 35-44 years (KCIS No. 32). Acta Diabetol. (2015) 52:123–31. doi: 10.1007/s00592-014-0612-0
104. Jimenez M, Hu FB, Marino M, Li Y, Joshipura KJ. Type 2 diabetes mellitus and 20 year incidence of periodontitis and tooth loss. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. (2012) 98:494–500. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2012.09.039
105. Tsai C, Hayes C, Taylor GW. Glycemic control of type 2 diabetes and severe periodontal disease in the US adult population. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol. (2002) 30:182–92. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0528.2002.300304.x
106. Demmer RT, Holtfreter B, Desvarieux M, Jacobs DR, Kerner W, Nauck M, et al. The Influence of Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes on Periodontal Disease Progression: Prospective results from the Study of Health in Pomerania (SHIP). Diabetes Care (2012) 35:2036–42. doi: 10.2337/dc11-2453
107. Katagiri S, Nitta H, Nagasawa T, Izumi Y, Kanazawa M, Matsuo A, et al. Effect of glycemic control on periodontitis in type 2 diabetic patients with periodontal disease. J Diabetes Invest. (2013) 4:320–5. doi: 10.1111/jdi.12026
108. Listgarten MA, Ricker FH Jr, Laster L, Shapiro J, Cohen DW. Vascular basement lamina thickness in the normal and inflamed gingiva of diabetics and non-diabetics. J Periodontol. (1974) 45:676–84. doi: 10.1902/jop.1974.45.9.676
109. Sakallioglu EE, Ayas B, Sakallioglu U, Yavuz U, Acikgoz G, Firatli E. Osmotic pressure and vasculature of gingiva in experimental diabetes mellitus. J Periodontol. (2007) 78:757–63. doi: 10.1902/jop.2007.060332
110. Frantzis TG, Reeve CM, Brown AL Jr. The ultrastructure of capillary basement membranes in the attached gingiva of diabetic and nondiabetic patients with periodontal disease. J Periodontol. (1971) 42:406–11.
111. Tesseromatis C, Kotsiou A, Parara H, Vairaktaris E, Tsamouri M. Morphological changes of gingiva in streptozotocin diabetic rats. Int J Dent. (2009) 2009:725628. doi: 10.1155/2009/725628
112. Lin JH, Duffy JL, Roginsky MS. Microcirculation in diabetes mellitus. Hum Pathol. (1975) 6:77–96. doi: 10.1016/S0046-8177(75)80110-9
113. Bullon P, Newman HN, Battino M. Obesity, diabetes mellitus, atherosclerosis and chronic periodontitis: a shared pathology via oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction? Periodontol 2000 (2014) 64:139–53. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0757.2012.00455.x
114. Barnes VM, Kennedy AD, Panagakos F, Devizio W, Trivedi HM, Jonsson T, et al. Global metabolomic analysis of human saliva and plasma from healthy and diabetic subjects, with and without periodontal disease. PLoS ONE (2014) 9:e105181. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0105181
115. Gumus P, Buduneli N, Cetinkalp S, Hawkins SI, Renaud D, Kinane DF, et al. Salivary antioxidants in patients with type 1 or 2 diabetes and inflammatory periodontal disease: a case-control study. J Periodontol. (2009) 80:1440–6. doi: 10.1902/jop.2009.090159
116. Monea A, Mezei T, Popsor S, Monea M. Oxidative stress: a link between diabetes mellitus and periodontal disease. Int J Endocrinol. (2014) 2014:917631. doi: 10.1155/2014/917631
117. Arana C, Moreno-Fernández AM, Gómez-Moreno G, Morales-Portillo C, Serrano-Olmedo I, de la Cuesta Mayor MC, et al. Increased salivary oxidative stress parameters in patients with type 2 diabetes: relation with periodontal disease. Endocrinol Diabetes Nutr. (2017) 64:258–64. doi: 10.1016/j.endien.2017.03.010
118. Sugiyama S, Takahashi SS, Tokutomi FA, Yoshida A, Kobayashi K, Yoshino F, et al. Gingival vascular functions are altered in type 2 diabetes mellitus model and/or periodontitis model. J Clin Biochem Nutr. (2012) 51:108–13. doi: 10.3164/jcbn.11-103
119. Zizzi A, Tirabassi G, Aspriello S, Piemontese M, Rubini C, Lucarini G. Gingival advanced glycation end-products in diabetes mellitus-associated chronic periodontitis: an immunohistochemical study. J Periodontal Res. (2013) 48:293–301. doi: 10.1111/jre.12007
120. Yoon M-S, Jankowski V, Montag S, Zidek W, Henning L, Schlüter H, et al. Characterisation of advanced glycation endproducts in saliva from patients with diabetes mellitus. Biochem. Biophys Res. Commun. (2004) 323:377–81. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.08.118
121. Lalla E, Lamster IB, Schmidt AM. Enhanced interaction of advanced glycation end products with their cellular receptor RAGE: implications for the pathogenesis of accelerated periodontal disease in diabetes. Ann Periodontol. (1998) 3:13–9. doi: 10.1902/annals.1998.3.1.13
122. Chang P-C, Chung M-C, Wang Y-P, Chien L-Y, Lim JC, Liang K, et al. Patterns of diabetic periodontal wound repair: a study using micro-computed tomography and immunohistochemistry. J. Periodontol. (2012) 83:644–52. doi: 10.1902/jop.2011.110325
123. Schmidt AM, Weidman E, Lalla E, Yan S, Hori O, Cao R, et al. Advanced glycation endproducts (AGEs) induce oxidant stress in the gingiva: a potential mechanism underlying accelerated periodontal disease associated with diabetes. J Periodontal Res. (1996) 31:508–15. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1996.tb01417.x
124. Takeda M, Ojima M, Yoshioka H, Inaba H, Kogo M, Shizukuishi S, et al. Relationship of serum advanced glycation end products with deterioration of periodontitis in type 2 diabetes patients. J Periodontol. (2006) 77:15–20. doi: 10.1902/jop.2006.77.1.15
125. Lalla E, Lamster IB, Feit M, Huang L, Spessot A, Qu W, et al. Blockade of RAGE suppresses periodontitis-associated bone loss in diabetic mice. J Clin Invest. (2000) 105:1117–24. doi: 10.1172/JCI8942
126. Kador PF, Hamada T, Reinhardt RA, Blessing K. Effect of an aldose reductase inhibitor on alveolar bone loss associated with periodontitis in diabetic rats. Postgrad Med. (2010) 122:138–44. doi: 10.3810/pgm.2010.05.2151
127. Kador PF, O'Meara JD, Blessing K, Marx DB, Reinhardt RA. Efficacy of structurally diverse aldose reductase inhibitors on experimental periodontitis in rats. J Periodontol. (2011) 82:926–33. doi: 10.1902/jop.2010.100442
128. Karima M, Kantarci A, Ohira T, Hasturk H, Jones V, Nam B, et al. Enhanced superoxide release and elevated protein kinase C activity in neutrophils from diabetic patients: association with periodontitis. J Leukoc Biol. (2005) 78:862–70. doi: 10.1189/jlb.1004583
129. Demmer RT, Squillaro A, Papapanou PN, Rosenbaum M, Friedewald WT, Jacobs DR Jr., et al. Periodontal infection, systemic inflammation, and insulin resistance: results from the continuous National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 1999-2004. Diabetes Care (2012) 35:2235–42. doi: 10.2337/dc12-0072
130. Islam SK, Seo M, Lee YS, Moon SS. Association of periodontitis with insulin resistance, beta-cell function, and impaired fasting glucose before onset of diabetes. Endocr J. (2015) 62:981–9. doi: 10.1507/endocrj.EJ15-0350
131. Lim SG, Han K, Kim HA, Pyo SW, Cho YS, Kim KS, et al. Association between insulin resistance and periodontitis in Korean adults. J Clin Periodontol. (2014) 41:121–30. doi: 10.1111/jcpe.12196
132. Genco RJ, Grossi SG, Ho A, Nishimura F, Murayama Y. A Proposed model linking inflammation to obesity, diabetes, and periodontal infections. J Periodontol. (2005) 76:2075–84. doi: 10.1902/jop.2005.76.11-S.2075
133. Timonen P, Suominen-Taipale L, Jula A, Niskanen M, Knuuttila M, Ylostalo P. Insulin sensitivity and periodontal infection in a non-diabetic, non-smoking adult population. J Clin Periodontol. (2011) 38:17–24. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051X.2010.01642.x
134. Timonen P, Saxlin T, Knuuttila M, Suominen AL, Jula A, Tervonen T, et al. Role of insulin sensitivity and beta cell function in the development of periodontal disease in adults without diabetes. J Clin Periodontol. (2013) 40:1079–86. doi: 10.1111/jcpe.12162
135. Mizutani K, Park K, Mima A, Katagiri S, King GL. Obesity-associated Gingival Vascular Inflammation and Insulin Resistance. J Dent Res. (2014) 93:596–601. doi: 10.1177/0022034514532102
136. Zhou X, Zhang W, Liu X, Zhang W, Li Y. Interrelationship between diabetes and periodontitis: role of hyperlipidemia. Arch Oral Biol. (2015) 60:667–74. doi: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2014.11.008
137. Fentoglu O, Oz G, Tasdelen P, Uskun E, Aykac Y, Bozkurt FY. Periodontal status in subjects with hyperlipidemia. J Periodontol. (2009) 80:267–73. doi: 10.1902/jop.2009.080104
138. Awartani F, Atassi F. Evaluation of periodontal status in subjects with hyperlipidemia. J Contemp Dent Pract. (2010) 11:33–40.
139. Sangwan A, Tewari S, Singh H, Sharma RK, Narula SC. Periodontal status and hyperlipidemia: statin users versus non-users. J Periodontol. (2013) 84:3–12. doi: 10.1902/jop.2012.110756
140. Lee JB, Yi HY, Bae KH. The association between periodontitis and dyslipidemia based on the Fourth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. J Clin Periodontol. (2013) 40:437–42. doi: 10.1111/jcpe.12095
141. Fentoglu O, Bozkurt FY. The bi-directional relationship between periodontal disease and hyperlipidemia. Eur J Dent. (2008) 2:142–6.
142. Bastos AS, Graves DT, Loureiro APdM, Rossa Júnior C, Abdalla DSP, Faulin TdES, et al. Lipid peroxidation is associated with the severity of periodontal disease and local inflammatory markers in patients with type 2 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2012) 97:E1353–62. doi: 10.1210/jc.2011-3397
143. Muniz F, Taminski K, Cavagni J, Celeste RK, Weidlich P, Rosing CK. The effect of statins on periodontal treatment-a systematic review with meta-analyses and meta-regression. Clin Oral Investig. (2018) 22:671–87. doi: 10.1007/s00784-018-2354-9
144. Bertl K, Parllaku A, Pandis N, Buhlin K, Klinge B, Stavropoulos A. The effect of local and systemic statin use as an adjunct to non-surgical and surgical periodontal therapy-A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Dent. (2017) 67:18–28. doi: 10.1016/j.jdent.2017.08.011
145. Bertl K, Steiner I, Pandis N, Buhlin K, Klinge B, Stavropoulos A. Statins in nonsurgical and surgical periodontal therapy. A systematic review and meta-analysis of preclinical in vivo trials. J Periodontal Res. (2018) 53:267–87. doi: 10.1111/jre.12514
146. Tsioufis C, Kasiakogias A, Thomopoulos C, Stefanadis C. Periodontitis and blood pressure: the concept of dental hypertension. Atherosclerosis (2011) 219:1–9. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2011.04.030
147. D'Aiuto F, Orlandi M, Gunsolley JC. Evidence that periodontal treatment improves biomarkers and CVD outcomes. J Clin Periodontol. (2013) 40(Suppl. 14):S85–105. doi: 10.1111/jcpe.12061
148. Macedo Paizan ML, Vilela-Martin JF. Is there an association between periodontitis and hypertension? Curr Cardiol Rev. (2014) 10:355–61. doi: 10.2174/1573403x10666140416094901
149. Tsakos G, Sabbah W, Hingorani AD, Netuveli G, Donos N, Watt RG, et al. Is periodontal inflammation associated with raised blood pressure? Evidence from a National US survey. J Hypertens. (2010) 28:2386–93. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0b013e32833e0fe1
150. Martin-Cabezas R, Seelam N, Petit C, Agossa K, Gaertner S, Tenenbaum H, et al. Association between periodontitis and arterial hypertension: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am Heart J. (2016) 180:98–112. doi: 10.1016/j.ahj.2016.07.018
151. Bastos MF, Brilhante FV, Goncalves TE, Pires AG, Napimoga MH, Marques MR, et al. Hypertension may affect tooth-supporting alveolar bone quality: a study in rats. J Periodontol. (2010) 81:1075–83. doi: 10.1902/jop.2010.090705
152. Castelli WA, Diaz-Perez R, Nasjleti CE, Caffesse RG. Effect of renovascular hypertension of the morphology of oral blood vessels. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. (1978) 46:576–82.
153. Leite CL, Redins CA, Vasquez EC, Meyrelles SS. Experimental-induced periodontitis is exacerbated in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Clin Exp Hypertens. (2005) 27:523–31. doi: 10.1081/ceh-200067688
154. Araujo AA, Souza TO, Moura LM, Brito GA, Aragao KS, Araujo LS, et al. Effect of telmisartan on levels of IL-1, TNF-alpha, down-regulated COX-2, MMP-2, MMP-9 and RANKL/RANK in an experimental periodontitis model. J Clin Periodontol. (2013) 40:1104–11. doi: 10.1111/jcpe.12160
155. Gyurko R, Siqueira CC, Caldon N, Gao L, Kantarci A, Van Dyke TE. Chronic hyperglycemia predisposes to exaggerated inflammatory response and leukocyte dysfunction in Akita mice. J Immunol. (2006) 177:7250–6. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.177.10.7250
156. Sima C, Rhourida K, Van Dyke T, Gyurko R. Type 1 diabetes predisposes to enhanced gingival leukocyte margination and macromolecule extravasation in vivo. J Periodontal Res. (2010) 45:748–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.2010.01295.x
157. Salvi GE, Yalda B, Collins JG, Jones BH, Smith FW, Arnold RR, et al. Inflammatory mediator response as a potential risk marker for periodontal diseases in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus patients. J Periodontol. (1997) 68:127–35. doi: 10.1902/jop.1997.68.2.127
158. Salvi GE, Collins JG, Yalda B, Arnold RR, Lang NP, Offenbacher S. Monocytic TNF alpha secretion patterns in IDDM patients with periodontal diseases. J Clin Periodontol. (1997) 24:8–16.
159. Graves D, Liu R, Alikhani M, Al-Mashat H, Trackman P. Diabetes-enhanced inflammation and apoptosis—impact on periodontal pathology. J Dent Res. (2006) 85:15–21. doi: 10.1177/154405910608500103
160. Liu R, Bal HS, Desta T, Krothapalli N, Alyassi M, Luan Q, et al. Diabetes enhances periodontal bone loss through enhanced resorption and diminished bone formation. J Dent Res. (2006) 85:510–4. doi: 10.1177/154405910608500606
161. Naguib G, Al-Mashat H, Desta T, Graves DT. Diabetes prolongs the inflammatory response to a bacterial stimulus through cytokine dysregulation. J Invest Dermatol. (2004) 123:87–92. doi: 10.1111/j.0022-202X.2004.22711.x
162. Engebretson SP, Hey-Hadavi J, Ehrhardt FJ, Hsu D, Celenti RS, Grbic JT, et al. Gingival crevicular fluid levels of interleukin-1β and glycemic control in patients with chronic periodontitis and type 2 diabetes. J Periodontol. (2004) 75:1203–8. doi: 10.1902/jop.2004.75.9.1203
163. Duarte P, De Oliveira M, Tambeli C, Parada C, Casati M, Nociti F. Overexpression of interleukin-1β and interleukin-6 may play an important role in periodontal breakdown in type 2 diabetic patients. J Periodontal Res. (2007) 42:377–81. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.2006.00961.x
164. Kardeşler L, Buduneli N, Çetinkalp Ş, Lappin D, Kinane DF. Gingival crevicular fluid IL-6, tPA, PAI-2, albumin levels following initial periodontal treatment in chronic periodontitis patients with or without type 2 diabetes. Inflamm Res. (2011) 60:143–51. doi: 10.1007/s00011-010-0248-7
165. Kardeşler L, Buduneli N, Bıyıkoğlu B, Çetinkalp Ş, Kütükçüler N. Gingival crevicular fluid PGE 2, IL-1ß, t-PA, PAI-2 levels in type 2 diabetes and relationship with periodontal disease. Clin Biochem. (2008) 41:863–8. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2008.04.013
166. Ross JH, Hardy DC, Schuyler CA, Slate EH, Mize T, Huang Y. Expression of periodontal interleukin-6 protein is increased across patients with neither periodontal disease nor diabetes, patients with periodontal disease alone and patients with both diseases. J Periodontal Res. (2010) 45:688–94. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.2010.01286.x
167. Nishimura F, Iwamoto Y, Mineshiba J, Shimizu A, Soga Y, Murayama Y. Periodontal disease and diabetes mellitus: the role of tumor necrosis factor-α in a 2-way relationship. J Periodontol. (2003) 74:97–102. doi: 10.1902/jop.2003.74.1.97
168. Lappin DF, Eapen B, Robertson D, Young J, Hodge PJ. Markers of bone destruction and formation and periodontitis in type 1 diabetes mellitus. J Clin Periodontol. (2009) 36:634–41. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051X.2009.01440.x
169. Mahamed DA, Marleau A, Alnaeeli M, Singh B, Zhang X, Penninger JM, et al. G (–) Anaerobes–reactive CD4+ T-cells trigger RANKL-mediated enhanced alveolar bone loss in diabetic NOD Mice. Diabetes (2005) 54:1477–86. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.54.5.1477
170. Duarte P, Neto J, Casati M, Sallum E, Nociti F. Diabetes modulates gene expression in the gingival tissues of patients with chronic periodontitis. Oral Dis. (2007) 13:594–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-0825.2006.01348.x
171. Vieira Ribeiro F, de Mendonça AC, Santos VR, Bastos MF, Figueiredo LC, Duarte PM. Cytokines and bone-related factors in systemically healthy patients with chronic periodontitis and patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic periodontitis. J Periodontol. (2011) 82:1187–96. doi: 10.1902/jop.2011.100643
172. Santos VR, Lima JA, Gonçalves TED, Bastos MF, Figueiredo LC, Shibli JA, et al. Receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappa B ligand/osteoprotegerin ratio in sites of chronic periodontitis of subjects with poorly and well-controlled type 2 diabetes. J Periodontol. (2010) 81:1455–65. doi: 10.1902/jop.2010.100125
173. Manouchehr-Pour M, Spagnuolo PJ, Rodman HM, Bissada NF. Comparison of neutrophil chemotactic response in diabetic patients with mild and severe periodontal disease. J Periodontol. (1981) 52:410–5.
174. McMullen JA, Van Dyke TE, Horoszewicz HU, Genco RJ. Neutrophil chemotaxis in individuals with advanced periodontal disease and a genetic predisposition to diabetes mellitus. J Periodontol. (1981) 52:167–73.
175. Engebretson SP, Vossughi F, Hey-Hadavi J, Emingil G, Grbic JT. The influence of diabetes on gingival crevicular fluid β-glucuronidase and interleukin-8. J Clin Periodontol. (2006) 33:784–90. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051x.2006.00984.x
176. Graves DT, Kayal RA. Diabetic complications and dysregulated innate immunity. Front Biosci. (2008) 13:1227. doi: 10.2741/2757
177. Taylor JJ, Preshaw PM, Lalla E. A review of the evidence for pathogenic mechanisms that may link periodontitis and diabetes. J Clin Periodontol. (2013) 40:S113–34. doi: 10.1111/jcpe.12059
178. Selwitz RH, Ismail AI, Pitts NB. Dental caries. Lancet (2007) 369:51–9. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(07)60031-2
179. Anderson M. Risk assessment and epidemiology of dental caries: review of the literature. Pediatr Dent. (2001) 24:377–85.
180. Marthaler T. Changes in dental caries 1953–2003. Caries Res. (2004) 38:173–81. doi: 10.1159/000077752
181. Petersen PE. The World Oral Health Report 2003: continuous improvement of oral health in the 21st century–the approach of the WHO Global Oral Health Programme. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol. (2003) 31:3–24. doi: 10.1046/j.2003.com122.x
182. Lamster IB. Non-periodontal oral complications of diabetes mellitus. In: Lamster IB, editor. Diabetes Mellitus and Oral Health: An Interprofessional Approach. 1st ed: Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons (2014). p. 157–90. doi: 10.1002/9781118887837.ch8
183. Garton B, Ford P. Root caries and diabetes: risk assessing to improve oral and systemic health outcomes. Aust Dent J. (2012) 57:114–22. doi: 10.1111/j.1834-7819.2012.01690.x
184. Leite RS, Marlow NM, Fernandes JK. Oral health and type 2 diabetes. Am J Med Sci. (2013) 345:271–3. doi: 10.1097/MAJ.0b013e31828bdedf
185. Arheiam A, Omar S. Dental caries experience and periodontal treatment needs of 10-to 15-year old children with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Int Dent J. (2014) 64:150–4. doi: 10.1111/idj.12091
186. Cherry-Peppers G, Ship JA. Oral health in patients with type II diabetes and impaired glucose tolerance. Diabetes Care (1993) 16:638–41. doi: 10.2337/diacare.16.4.638
187. Edblad E, Lundin S-Å, Sjödin B, Åman J. Caries and salivary status in young adults vvith type 1 diabetes. Swed Dent J. (2001) 25:53.
188. Gómez-Díaz RA, Ramírez-Soriano E, Tanus Hajj J, Bautista Cruz E, Jiménez Galicia C, Villasis-Keever MA, et al. Association between carotid intima-media thickness, buccodental status, and glycemic control in pediatric type 1 diabetes. Pediatr Diabetes (2012) 13:552–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-5448.2012.00868.x
189. Miko S, Ambrus S, Sahafian S, Dinya E, Tamas G, Albrecht M. Dental caries and adolescents with type 1 diabetes. Br Dent J. (2010) 208:E12. doi: 10.1038/sj.bdj.2010.290
190. Miralles L, Silvestre FJ, Hernández-Mijares A, Bautista D, Llambes F, Grau D. Dental caries in type 1 diabetics: influence of systemic factors of the disease upon the development of dental caries. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. (2006) 11:162.
191. Rai K, Hegde A, Kamath A, Shetty S. Dental caries and salivary alterations in type i diabetes. J Clin Pediatr Dent. (2011) 36:181–4. doi: 10.17796/jcpd.36.2.x436ln878221g364
192. Twetman S, Johansson I, Birkhed D, Nederfors T. Caries incidence in young type 1 diabetes mellitus patients in relation to metabolic control and caries-associated risk factors. Caries Res. (2002) 36:31–5. doi: 10.1159/000057587
193. Twetman S, Nederfors T, Stahl B, Aronson S. Two-year longitudinal observations of salivary status and dental caries in children with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Pediatr Dent. (1992) 14:184–8.
194. Saes Busato IM, Bittencourt MS, Machado MA, Gregio AM, Azevedo-Alanis LR. Association between metabolic control and oral health in adolescents with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. (2010) 109:e51–6. doi: 10.1016/j.tripleo.2009.10.037
195. Alves C, Menezes R, Brandão M. Salivary flow and dental caries in Brazilian youth with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Indian J Dent Res. (2012) 23:758. doi: 10.4103/0970-9290.111254
196. Moore PA, Weyant RJ, Etzel KR, Guggenheimer J, Mongelluzzo MB, Myers DE, et al. Type 1 diabetes mellitus and oral health: assessment of coronal and root caries. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol. (2001) 29:183–94. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0528.2001.290304.x
197. Marín NP, Rodríguez JPL, Solis CEM, Loyola APP, Macías JFR, Rosado JCO, et al. Caries, periodontal disease and tooth loss in patients with diabetes mellitus types 1 and 2. Acta Odontol Latinoam. (2008) 21:127–33.
198. Swanljung O, Meurman JH, Torkko H, Sandholm L, Kaprio E, Mäenpää J. Caries and saliva in 12–18-year-old diabetics and controls. Eur J Oral Sci. (1992) 100:310–3. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0722.1992.tb01077.x
199. Syrjälä A-MH, Niskanen MC, Ylöstalo P, Knuuttila ML. Metabolic control as a modifier of the association between salivary factors and dental caries among diabetic patients. Caries Res. (2003) 37:142–7. doi: 10.1159/000069020
200. Tagelsir A, Cauwels R, van Aken S, Vanobbergen J, Martens LC. Dental caries and dental care level (restorative index) in children with diabetes mellitus type 1. Int J Paediatr Dent. (2011) 21:13–22. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-263X.2010.01094.x
201. Tavares M, Depaola P, Soparkar P, Joshipura K. The prevalence of root caries in a diabetic population. J Dent Res. (1991) 70:979–83. doi: 10.1177/00220345910700061401
202. Hintao J, Teanpaisan R, Chongsuvivatwong V, Dahlén G, Rattarasarn C. Root surface and coronal caries in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol. (2007) 35:302–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0528.2007.00325.x
203. Jawed M, Shahid SM, Qader SA, Azhar A. Dental caries in diabetes mellitus: role of salivary flow rate and minerals. J Diabetes Compl. (2011) 25:183–6. doi: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2010.07.001
204. Jawed M, Khan RN, Shahid SM, Azhar A. Protective effects of salivary factors in dental caries in diabetic patients of Pakistan. Exp Diabetes Res. (2012) 2012:947304. doi: 10.1155/2012/947304
205. Jones RB, McCallum RM, Kay EJ, Kirkin V, McDonald P. Oral health and oral health behaviour in a population of diabetic outpatient clinic attenders. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol. (1992) 20:204–7.
206. Sandberg GE, Sundberg HE, Fjellstrom CA, Wikblad KF. Type 2 diabetes and oral health: a comparison between diabetic and non-diabetic subjects. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. (2000) 50:27–34. doi: 10.1016/S0168-8227(00)00159-5
207. Yeh C-K, Harris SE, Mohan S, Horn D, Fajardo R, Chun Y-HP, et al. Hyperglycemia and xerostomia are key determinants of tooth decay in type 1 diabetic mice. Lab Invest. (2012) 92:868–82. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2012.60
208. Kodama Y, Matsuura M, Sano T, Nakahara Y, Ozaki K, Narama I, et al. Diabetes enhances dental caries and apical periodontitis in caries-susceptible WBN/KobSlc rats. Comp Med. (2011) 61:53–9.
209. Sano T, Matsuura T, Ozaki K, Narama I. Dental caries and caries-related periodontitis in type 2 diabetic mice. Vet Pathol. (2011) 48:506–12. doi: 10.1177/0300985810380394
210. Collin H-L, Uusitupa M, Niskanen L, Koivisto A-M, Markkanen H, Meurman JH. Caries in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. (1998) 85:680–5. doi: 10.1016/S1079-2104(98)90035-X
211. Marlow NM, Slate EH, Bandyopadhyay D, Fernandes JK, Salinas CF. An evaluation of serum albumin, root caries, and other covariates in Gullah African Americans with type-2 diabetes. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol. (2011) 39:186–92. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0528.2010.00586.x
212. Lin BPJ, Taylor GW, Allen DJ, Ship JA. Dental caries in older adults with diabetes mellitus. Spec Care Dent. (1999) 19:8–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1754-4505.1999.tb01361.x
213. Siudikiene J, Machiulskiene V, Nyvad B, Tenovuo J, Nedzelskiene I. Dental caries and salivary status in children with type 1 diabetes mellitus, related to the metabolic control of the disease. Eur J Oral Sci. (2006) 114:8–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0722.2006.00277.x
214. Matsson L, Koch G. Caries frequency in children with controlled diabetes. Scand J Dent Res. (1975) 83:327–32.
215. Leone CW, Oppenheim FG. Physical and chemical aspects of saliva as indicators of risk for dental caries in humans. J Dent Educ. (2001) 65:1054–62.
216. Nakahara Y, Sano T, Kodama Y, Ozaki K, Matsuura T. Glycemic control with insulin prevents progression of dental caries and caries-related periodontitis in diabetic WBN/KobSlc rats. Toxicol Pathol. (2013) 41:761–9. doi: 10.1177/0192623312464307
217. Yonekura S, Usui M, Murano S. Association between numbers of decayed teeth and HbA1c in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Ups J Med Sci. (2017) 122:108–13. doi: 10.1080/03009734.2017.1285838
218. Bakhshandeh S, Murtomaa H, Vehkalahti M, Mofid R, Suomalainen K. Dental findings in diabetic adults. Caries Res. (2008) 42:14–8. doi: 10.1159/000111745
219. Cao X, Wang D, Zhou J, Yuan H, Chen Z. Relationship between dental caries and metabolic syndrome among 13 998 middle-aged urban Chinese. J Diabetes (2017) 9:378–85. doi: 10.1111/1753-0407.12424
220. Timonen P, Niskanen M, Suominen-Taipale L, Jula A, Knuuttila M, Ylostalo P. Metabolic syndrome, periodontal infection, and dental caries. J Dent Res. (2010) 89:1068–73. doi: 10.1177/0022034510376542
221. Mascarenhas P, Fatela B, Barahona I. Effect of diabetes mellitus type 2 on salivary glucose–a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. PLoS ONE (2014) 9:e101706. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0101706
222. Siudikiene J, Machiulskiene V, Nyvad B, Tenovuo J, Nedzelskiene I. Dental caries increments and related factors in children with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Caries Res. (2008) 42:354–62. doi: 10.1159/000151582
223. Loyola-Rodriguez JP, Villa-Chavez C, Patinio-Marin N, Aradillas-Garcia C, Gonzalez C, de la Cruz-Mendoza E. Association between caries, obesity and insulin resistance in Mexican adolescents. J Clin Pediatr Dent. (2011) 36:49–53. doi: 10.17796/jcpd.36.1.e25411r576362262
224. Ribeiro LS, Santos JN, Vieira CL, Caramelli B, Ramalho LM, Cury PR. Association of dental infections with systemic diseases in Brazilian Native Indigenous: a cross-sectional study. J Am Soc Hypertens. (2016) 10:413–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jash.2016.02.012
225. Johnston L, Vieira AR. Caries experience and overall health status. Oral Health Prev Dent. (2014) 12:163–70. doi: 10.3290/j.ohpd.a31670
226. Kampoo K, Teanpaisan R, Ledder RG, McBain AJ. Oral bacterial communities in individuals with type 2 diabetes who live in southern Thailand. Appl Environ Microbiol. (2014) 80:662–71. doi: 10.1128/aem.02821-13
227. Goodson JM, Hartman ML, Shi P, Hasturk H, Yaskell T, Vargas J, et al. The salivary microbiome is altered in the presence of a high salivary glucose concentration. PLoS ONE (2017) 12:e0170437. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0170437
228. von Bültzingslöwen I, Sollecito TP, Fox PC, Daniels T, Jonsson R, Lockhart PB, et al. Salivary dysfunction associated with systemic diseases: systematic review and clinical management recommendations. Oral Surg Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endodontol. (2007) 103:S57. e1–15. doi: 10.1016/j.tripleo.2006.11.010
229. Guggenheimer J, Moore PA. Xerostomia: Etiology, recognition and treatment. J Am Dent Assoc. (2003) 134:61–9. doi: 10.14219/jada.archive.2003.0018
230. Ship JA, Fox PC, Baum BJ. How much saliva is enough? J Am Dent Assoc. (1991) 122:63–9. doi: 10.14219/jada.archive.1991.0098
231. Navazesh M, Christensen C, Brightman V. Clinical criteria for the diagnosis of salivary gland hypofunction. J Dent Res. (1992) 71:1363–9. doi: 10.1177/00220345920710070301
232. Hopcraft M, Tan C. Xerostomia: an update for clinicians. Austral Dent J. (2010) 55:238–44. doi: 10.1111/j.1834-7819.2010.01229.x
233. Flink H, Bergdahl M, Tegelberg A, Rosenblad A, Lagerlof F. Prevalence of hyposalivation in relation to general health, body mass index and remaining teeth in different age groups of adults. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol. (2008) 36:523–31. doi: 10.1111/j.16000528.2008.00432.x
234. Orellana M, Lagravère M, Boychuk D, Major P, Flores-Mir C, Ortho C. Prevalence of xerostomia in population-based samples: a systematic review. J Public Health Dent. (2006) 66:152–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1752-7325.2006.tb02572.x
235. Scully C. Drug effects on salivary glands: dry mouth. Oral Dis (2003) 9:165–76. doi: 10.1034/j.1601-0825.2003.03967.x
236. Mortazavi H, Baharvand M, Movahhedian A, Mohammadi M, Khodadoustan A. Xerostomia due to systemic disease: a review of 20 conditions and mechanisms. Ann Med Health Sci Res. (2014) 4:503–10. doi: 10.4103/2141-9248.139284
237. Ben-Aryeh H, Cohen M, Kanter Y, Szargel R, Laufer D. Salivary composition in diabetic patients. J Diabetic Compl. (1988) 2:96–9.
238. López ME, Colloca ME, Páez RG, Schallmach JN, Koss MA, Chervonagura A. Salivary characteristics of diabetic children. Braz Dent J. (2003) 14:26–31. doi: 10.1590/S0103-64402003000100005
239. Mata AD, Marques D, Rocha S, Francisco H, Santos C, Mesquita MF, et al. Effects of diabetes mellitus on salivary secretion and its composition in the human. Mol Cell Biochem. (2004) 261:137–42. doi: 10.1023/B:MCBI.0000028748.40917.6f
240. Moore PA, Guggenheimer J, Etzel KR, Weyant RJ, Orchard T. Type 1 diabetes mellitus, xerostomia, and salivary flow rates. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. (2001) 92:281–91. doi: 10.1067/moe.2001.117815
241. Sreebny LM, Yu A, Green A, Valdini A. Xerostomia in diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care (1992) 15:900–4. doi: 10.2337/diacare.15.7.900
242. Karjalainen K, Knuuttila M, Käär M. Salivary factors in children and adolescents with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Pediatr Dent. (1995) 18:306–11.
243. Malicka B, Kaczmarek U, Skoskiewicz-Malinowska K. Prevalence of xerostomia and the salivary flow rate in diabetic patients. Adv Clin Exp Med. (2014) 23:225–33. doi: 10.17219/acem/37067
244. Chávez EM, Borrell LN, Taylor GW, Ship JA. A longitudinal analysis of salivary flow in control subjects and older adults with type 2 diabetes. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. (2001) 91:166–73. doi: 10.1067/moe.2001.112054
245. Chavez EM, Taylor GW, Borrell LN, Ship JA. Salivary function and glycemic control in older persons with diabetes. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. (2000) 89:305–11. doi: 10.1016/S1079-2104(00)70093-X
246. Kao C-H, Tsai S-C, Sun S-S. Scintigraphic evidence of poor salivary function in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care (2001) 24:952–3. doi: 10.2337/diacare.24.5.952-a
247. Khovidhunkit SO, Suwantuntula T, Thaweboon S, Mitrirattanakul S, Chomkhakhai U, Khovidhunkit W. Xerostomia, hyposalivation, and oral microbiota in type 2 diabetic patients: a preliminary study. J Med Assoc Thai (2009) 92:1220–8.
248. Lin C-C, Sun S-S, Kao A, Lee C-C. Impaired salivary function in patients with noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus with xerostomia. J Diabetes Compl. (2002) 16:176–9. doi: 10.1016/s1056-8727(01)00174-x
249. Quirino M, Birman EG, Paula CR. Oral manifestations of diabetes mellitus in controlled and uncontrolled patients. Braz Dent J. (1995) 6:131–6.
250. Vasconcelos ACU, Soares MSM, Almeida PC, Soares TC. Comparative study of the concentration of salivary and blood glucose in type 2 diabetic patients. J Oral Sci. (2010) 52:293–8. doi: 10.2334/josnusd.52.293
251. Montaldo L, Montaldo P, Papa A, Caramico N, Toro G. Effects of saliva substitutes on oral status in patients with Type 2 diabetes. Diabet Med. (2010) 27:1280–3. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-5491.2010.03063.x
252. Lasisi TJ, Fasanmade AA. Salivary flow and composition in diabetic and non-diabetic subjects. Niger J Physiol Sci. (2012) 27:79–82.
253. Ben-Aryeh H, Serouya R, Kanter Y, Szargel R, Laufer D. Oral health and salivary composition in diabetic patients. J Diabetes Compl. (1993) 7:57–62.
254. Dawes C. How much saliva is enough for avoidance of xerostomia? Caries Res. (2004) 38:236–40. doi: 10.1159/000077760
255. Busato IMS, Ignácio SA, Brancher JA, Moysés ST, Azevedo-Alanis LR. Impact of clinical status and salivary conditions on xerostomia and oral health-related quality of life of adolescents with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol. (2012) 40:62–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0528.2011.00635.x
256. Ivanovski K, Naumovski V, Kostadinova M, Pesevska S, Drijanska K, Filipce V. Xerostomia and salivary levels of glucose and urea in patients with diabetes. Prilozi (2012) 33:219–29.
257. Silveira Lessa L, Duarte Simões Pires P, Ceretta RA, Reynaud Toreti Becker I, Bisognin Ceretta L, Tuon L, et al. Meta-analysis of prevalence of xerostomia in diabetes mellitus. Int Arch Med. (2015) 8, 1–13. doi: 10.3823/1823
258. Carda C, Mosquera-Lloreda N, Salom L, Gomez de Ferraris ME, Peydro A. Structural and functional salivary disorders in type 2 diabetic patients. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. (2006) 11:E309–14.
259. Newrick P, Bowman C, Green D, O'Brien I, Porter S, Scully C, et al. Parotid salivary secretion in diabetic autonomic neuropathy. J Diabetes Compl. (1991) 5:35–7.
260. Sandberg GE, Wikblad KF. Oral dryness and peripheral neuropathy in subjects with type 2 diabetes. J Diabetes Compl. (2003) 17:192–8. doi: 10.1016/S1056-8727(02)00220-9
261. Lamey PJ, Fisher BM, Frier BM. The effects of diabetes and autonomic neuropathy on parotid salivary flow in man. Diabet Med. (1986) 3:537–40.
262. Monteiro MM, D'Epiro TTS, Bernardi L, Fossati ACM, dos Santos MF, Lamers ML. Long-and short-term diabetes mellitus type 1 modify young and elder rat salivary glands morphology. Arch Oral Biol. (2017) 73:40–7. doi: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2016.08.028
263. Carda C, Carranza M, Arriaga A, Díaz A, Peydró A, Gomez dFM. Structural differences between alcoholic and diabetic parotid sialosis. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. (2004) 10:309–14.
264. Lilliu MA, Solinas P, Cossu M, Puxeddu R, Loy F, Isola R, et al. Diabetes causes morphological changes in human submandibular gland: a morphometric study. J Oral Pathol Med. (2015) 44:291–5. doi: 10.1111/jop.12238
265. Russotto SB. Asymptomatic parotid gland enlargement in diabetes mellitus. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. (1981) 52:594–8. doi: 10.1016/0030-4220(81)90075-X
266. Alves M, Calegari VC, Cunha DA, Saad MJ, Velloso LA, Rocha EM. Increased expression of advanced glycation end-products and their receptor, and activation of nuclear factor kappa-B in lacrimal glands of diabetic rats. Diabetologia (2005) 48:2675–81. doi: 10.1007/s00125-005-0010-9
267. Fukuoka CY, Simoes A, Uchiyama T, Arana-Chavez VE, Abiko Y, Kuboyama N, et al. The effects of low-power laser irradiation on inflammation and apoptosis in submandibular glands of diabetes-induced rats. PLoS ONE (2017) 12:e0169443. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0169443
268. Ship JA, Fischer DJ. The relationship between dehydration and parotid salivary gland function in young and older healthy adults. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. (1997) 52:M310–9.
269. Sreebny LM, Schwartz SS. A reference guide to drugs and dry mouth−2nd edition. Gerodontology (1997) 14:33–47.
270. Chao EC, Henry RR. SGLT2 inhibition — a novel strategy for diabetes treatment. Nat Rev Drug Discov. (2010) 9:551–9. doi: 10.1038/nrd3180
271. Ittichaicharoen J, Apaijai N, Tanajak P, Sa-Nguanmoo P, Chattipakorn N, Chattipakorn SC. Impaired mitochondria and intracellular calcium transients in the salivary glands of obese rats. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. (2017) 42:420–9. doi: 10.1139/apnm-2016-0545
272. Matczuk J, Zalewska A, Lukaszuk B, Knas M, Maciejczyk M, Garbowska M, et al. Insulin resistance and obesity affect lipid profile in the salivary glands. J Diabetes Res. (2016) 2016:8163474. doi: 10.1155/2016/8163474
273. Mozaffari MS, Abdelsayed R, Zakhary I, El-Salanty M, Liu JY, Wimborne H, et al. Submandibular gland and caries susceptibility in the obese Zucker rat. J Oral Pathol Med. (2011) 40:194–200. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0714.2010.00965.x
274. Kusminski CM, Shetty S, Orci L, Unger RH, Scherer PE. Diabetes and apoptosis: lipotoxicity. Apoptosis (2009) 14:1484–95. doi: 10.1007/s10495-009-0352-8
275. Shikama Y, Ishimaru N, Kudo Y, Bando Y, Aki N, Hayashi Y, et al. Effects of free fatty acids on human salivary gland epithelial cells. J Dent Res. (2013) 92:540–6. doi: 10.1177/0022034513487378
276. Dodds MWJ, Yeh CK, Johnson DA. Salivary alterations in type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus and hypertension. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol. (2000) 28:373–81. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0528.2000.028005373.x
277. Binder A, Maddison PJ, Skinner P, Kurtz A, Isenberg DA. Sjogren's syndrome: association with type-1 diabetes mellitus. Br J Rheumatol. (1989) 28:518–20.
278. Ramos-Casals M, Brito-Zeron P, Siso A, Vargas A, Ros E, Bove A, et al. High prevalence of serum metabolic alterations in primary Sjogren's syndrome: influence on clinical and immunological expression. J Rheumatol. (2007) 34:754–61.
279. Shulman JD, Beach MM, Rivera-Hidalgo F. The prevalence of oral mucosal lesions in US adults: data from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1988–1994. J Am Dent Assoc. (2004) 135:1279–86. doi: 10.14219/jada.archive.2004.0403
280. Reichart PA. Oral mucosal lesions in a representative cross-sectional study of aging Germans. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol. (2000) 28:390–8. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0528.2000.028005390.x
281. Kovač-Kavčič M, Skalerič U. The prevalence of oral mucosal lesions in a population in Ljubljana, Slovenia. J Oral Pathol Med. (2000) 29:331–5. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0714.2000.290707.x
282. Espinoza I, Rojas R, Aranda W, Gamonal J. Prevalence of oral mucosal lesions in elderly people in Santiago, Chile. J Oral Pathol Med. (2003) 32:571–5. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0714.2003.00031.x
283. Akpan A, Morgan R. Oral candidiasis. Postgrad Med J. (2002) 78:455–9. doi: 10.1136/pmj.78.922.455
284. Soysa N, Samaranayake L, Ellepola A. Diabetes mellitus as a contributory factor in oral candidosis. Diabet Med. (2006) 23:455–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-5491.2005.01701.x
285. Guggenheimer J, Moore PA, Rossie K, Myers D, Mongelluzzo MB, Block HM, et al. Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus and oral soft tissue pathologies. II. Prevalence and characteristics of Candida and candidal lesions. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. (2000) 89:570–6. doi: 10.1067/moe.2000.104477
286. Dorocka-Bobkowska B, Zozulinska-Ziolkiewicz D, Wierusz-Wysocka B, Hedzelek W, Szumala-Kakol A, Budtz-Jorgensen E. Candida-associated denture stomatitis in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. (2010) 90:81–6. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2010.06.015
287. Dorocka-Bobkowska B, Budtz-Jörgensen E, WłSoch S. Non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus as a risk factor for denture stomatitis. J Oral Pathol Med. (1996) 25:411–5.
288. Saini R, Al-Maweri SA, Saini D, Ismail NM, Ismail AR. Oral mucosal lesions in non oral habit diabetic patients and association of diabetes mellitus with oral precancerous lesions. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. (2010) 89:320–6. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2010.04.016
289. de Souza Bastos A, Leite ARP, Spin-Neto R, Nassar PO, Massucato EMS, Orrico SRP. Diabetes mellitus and oral mucosa alterations: prevalence and risk factors. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. (2011) 92:100–5. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2011.01.011
290. de Lima DC, Nakata GC, Balducci I, Almeida JD. Oral manifestations of diabetes mellitus in complete denture wearers. J Prosthet Dent. (2008) 99:60–5. doi: 10.1016/S0022-3913(08)60010-4
291. Bremenkamp RM, Caris AR, Jorge AO, Back-Brito GN, Mota AJ, Balducci I, et al. Prevalence and antifungal resistance profile of Candida spp. oral isolates from patients with type 1 and 2 diabetes mellitus. Arch Oral Biol. (2011) 56:549–55. doi: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2010.11.018
292. Darwazeh A, MacFarlane T, McCuish A, Lamey PJ. Mixed salivary glucose levels and candidal carriage in patients with diabetes mellitus. J Oral Pathol Med. (1991) 20:280–3.
293. Al-Maweri SA, Ismail NM, Ismail AR, Al-Ghashm A. Prevalence of oral mucosal lesions in patients with type 2 diabetes attending hospital universiti sains malaysia. Malays J Med Sci. (2013) 20:39–46.
294. Al Mubarak S, Robert AA, Baskaradoss JK, Al-Zoman K, Al Sohail A, Alsuwyed A, et al. The prevalence of oral Candida infections in periodontitis patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Infect Public Health (2013) 6:296–301. doi: 10.1016/j.jiph.2012.12.007
295. de Souza Ferreira C, Pennacchi PC, Araujo TH, Taniwaki NN, de Araujo Paula FB, da Silveira Duarte SM, et al. Aminoguanidine treatment increased NOX2 response in diabetic rats: Improved phagocytosis and killing of Candida albicans by neutrophils. Eur J Pharmacol. (2016) 772:83–91. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2015.12.044
296. Sashikumar R, Kannan R. Salivary glucose levels and oral candidal carriage in type II diabetics. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. (2010) 109:706–11. doi: 10.1016/j.tripleo.2009.12.042
297. Netea MG, Demacker PN, de Bont N, Boerman OC, Stalenhoef AF, van der Meer JW, et al. Hyperlipoproteinemia enhances susceptibility to acute disseminated Candida albicans infection in low-density-lipoprotein-receptor-deficient mice. Infect Immun. (1997) 65:2663–7.
298. Vonk AG, De Bont N, Netea MG, Demacker PN, van der Meer JW, Stalenhoef AF, et al. Apolipoprotein-E-deficient mice exhibit an increased susceptibility to disseminated candidiasis. Med Mycol. (2004) 42:341–8. doi: 10.1080/13693780410001657135
299. Billings M, Dye BA, Iafolla T, Grisius M, Alevizos I. Elucidating the role of hyposalivation and autoimmunity in oral candidiasis. Oral Dis. (2017) 23:387–94. doi: 10.1111/odi.12626
300. Kadir T, Pisiriciler R, Akyuz S, Yarat A, Emekli N, Ipbuker A. Mycological and cytological examination of oral candidal carriage in diabetic patients and non-diabetic control subjects: thorough analysis of local aetiologic and systemic factors. J Oral Rehabil. (2002) 29:452–7. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2842.2002.00837.x
301. Ueta E, Osaki T, Yoneda K, Yamamoto T. Prevalence of diabetes mellitus in odontogenic infections and oral candidiasis: an analysis of neutrophil suppression. J Oral Pathol Med. (1993) 22:168–74.
302. Darwazeh AM, Lamey PJ, Samaranayake LP, MacFarlane TW, Fisher BM, Macrury SM, et al. The relationship between colonisation, secretor status and in-vitro adhesion of Candida albicans to buccal epithelial cells from diabetics. J Med Microbiol. (1990) 33:43–9.
303. Petrou-Amerikanou C, Markopoulos AK, Belazi M, Karamitsos D, Papanayotou P. Prevalence of oral lichen planus in diabetes mellitus according to the type of diabetes. Oral Dis. (1998) 4:37–40.
304. Van Dis ML, Parks ET. Prevalence of oral lichen planus in patients with diabetes mellitus. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. (1995) 79:696–700.
305. Guggenheimer J, Moore PA, Rossie K, Myers D, Mongelluzzo MB, Block HM, et al. Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus and oral soft tissue pathologies: I. Prevalence and characteristics of non-candidal lesions. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. (2000) 89:563–9. doi: 10.1067/moe.2000.104476
306. Silva MFA, Barbosa KGN, Pereira JV, Bento PM, Godoy GP, Gomes DQdC. Prevalence of oral mucosal lesions among patients with diabetes mellitus types 1 and 2. An Bras Dermatol. (2015) 90:49–53. doi: 10.1590/abd1806-4841.20153089
307. Mohsin SF, Ahmed SA, Fawwad A, Basit A. Prevalence of oral mucosal alterations in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients attending a diabetic center. Pak J Med Sci. (2014) 30:716–9.
308. Albrecht M, Banoczy J, Dinya E, Tamas G Jr. Occurrence of oral leukoplakia and lichen planus in diabetes mellitus. J Oral Pathol Med. (1992) 21:364–6.
309. Dikshit RP, Ramadas K, Hashibe M, Thomas G, Somanathan T, Sankaranarayanan R. Association between diabetes mellitus and pre-malignant oral diseases: a cross sectional study in Kerala, India. Int J Cancer (2006) 118:453–7. doi: 10.1002/ijc.21345
310. Ujpál M, Matos O, Bíbok G, Somogyi A, Szabó G, Suba Z. Diabetes and oral tumors in hungary epidemiological correlations. Diabetes Care (2004) 27:770–4.
311. Al-Hashimi I, Schifter M, Lockhart PB, Wray D, Brennan M, Migliorati CA, et al. Oral lichen planus and oral lichenoid lesions: diagnostic and therapeutic considerations. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endodontol. (2007) 103:S25.e1–12. doi: 10.1016/j.tripleo.2006.11.001
312. Lamey PJ, Gibson J, Barclay SC, Miller S. Grinspan's syndrome: a drug-induced phenomenon? Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. (1990) 70:184–5. doi: 10.1016/0030-4220(90)90116-A
313. Warnakulasuriya S. Global epidemiology of oral and oropharyngeal cancer. Oral Oncol. (2009) 45:309–16. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2008.06.002
314. Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. (2011) 61:69–90. doi: 10.3322/caac.20107
315. Blot WJ, McLaughlin JK, Winn DM, Austin DF, Greenberg RS, Preston-Martin S, et al. Smoking and drinking in relation to oral and pharyngeal cancer. Cancer Res. (1988) 48:3282–7.
316. Vigneri P, Frasca F, Sciacca L, Pandini G, Vigneri R. Diabetes and cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer (2009) 16:1103–23. doi: 10.1677/erc-09-0087
317. Gong Y, Wei B, Yu L, Pan W. Type 2 diabetes mellitus and risk of oral cancer and precancerous lesions: a meta-analysis of observational studies. Oral Oncol. (2015) 51:332–40. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2015.01.003
318. Dietrich T, Reichart PA, Scheifele C. Clinical risk factors of oral leukoplakia in a representative sample of the US population. Oral Oncol. (2004) 40:158–63. doi: 10.1016/s1368-8375(03)00145-3
319. Bosetti C, Rosato V, Polesel J, Levi F, Talamini R, Montella M, et al. Diabetes mellitus and cancer risk in a network of case-control studies. Nutr Cancer (2012) 64:643–51. doi: 10.1080/01635581.2012.676141
320. La Vecchia C, Negri E, Franceschi S, D'Avanzo B, Boyle P. A case-control study of diabetes mellitus and cancer risk. Br J Cancer (1994) 70:950–3.
321. Wideroff L, Gridley G, Mellemkjaer L, Chow WH, Linet M, Keehn S, et al. Cancer incidence in a population-based cohort of patients hospitalized with diabetes mellitus in Denmark. J Natl Cancer Inst. (1997) 89:1360–5.
322. Tseng CH. Oral cancer in Taiwan: is diabetes a risk factor? Clin Oral Investig. (2013) 17:1357–64. doi: 10.1007/s00784-012-0820-3
323. Tseng KS, Lin C, Lin YS, Weng SF. Risk of head and neck cancer in patients with diabetes mellitus: a retrospective cohort study in Taiwan. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. (2014) 140:746–53. doi: 10.1001/jamaoto.2014.1258
324. Wu CH, Wu TY, Li CC, Lui MT, Chang KW, Kao SY. Impact of diabetes mellitus on the prognosis of patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma: a retrospective cohort study. Ann Surg Oncol. (2010) 17:2175–83. doi: 10.1245/s10434-010-0996-1
325. Campbell PT, Newton CC, Patel AV, Jacobs EJ, Gapstur SM. Diabetes and cause-specific mortality in a prospective cohort of one million U.S. adults. Diabetes Care (2012) 35:1835–44. doi: 10.2337/dc12-0002
326. Meisel P, Dau M, Sumnig W, Holtfreter B, Houshmand M, Nauck M, et al. Association between glycemia, serum lipoproteins, and the risk of oral leukoplakia: the population-based Study of Health in Pomerania (SHIP). Diabetes Care (2010) 33:1230–2. doi: 10.2337/dc09-1262
327. Saxena A, Shoeb M, Tammali R, Ramana KV, Srivastava SK. Aldose reductase inhibition suppresses azoxymethane-induced colonic premalignant lesions in C57BL/KsJ-db/db mice. Cancer Lett. (2014) 355:141–7. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2014.09.006
328. Ko SY, Ko HA, Shieh TM, Chang WC, Chen HI, Chang SS, et al. Cell migration is regulated by AGE-RAGE interaction in human oral cancer cells in vitro. PLoS ONE (2014) 9:e110542. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0110542
329. Ko SY, Ko HA, Shieh TM, Chi TC, Chen HI, Chen YT, et al. Advanced glycation end products influence oral cancer cell survival via Bcl-xl and Nrf-2 regulation in vitro. Oncol Lett. (2017) 13:3328–34. doi: 10.3892/ol.2017.5809
330. Sasahira T, Kirita T, Bhawal UK, Yamamoto K, Ohmori H, Fujii K, et al. Receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) is important in the prediction of recurrence in human oral squamous cell carcinoma. Histopathology (2007) 51:166–72. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.2007.02739.x
331. Su S, Chien M, Lin C, Chen M, Yang S. RAGE gene polymorphism and environmental factor in the risk of oral cancer. J Dent Res. (2015) 94:403–11. doi: 10.1177/0022034514566215
332. Bhawal UK, Ozaki Y, Nishimura M, Sugiyama M, Sasahira T, Nomura Y, et al. Association of expression of receptor for advanced glycation end products and invasive activity of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oncology (2005) 69:246–55. doi: 10.1159/000087910
333. Yen AM, Chen SL, Chiu SY, Chen HH. Association between metabolic syndrome and oral pre-malignancy: a community- and population-based study (KCIS No. 28). Oral Oncol. (2011) 47:625–30. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2011.04.011
334. Schiffman SS. Effects of aging on the human taste system. Ann N Y Acad Sci. (2009) 1170:725–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.03924.x
335. Hoffman HJ, Cruickshanks KJ, Davis B. Perspectives on population-based epidemiological studies of olfactory and taste impairment. Ann N Y Acad Sci. (2009) 1170:514–30. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.04597.x
336. Bergdahl M, Bergdahl J. Perceived taste disturbance in adults: prevalence and association with oral and psychological factors and medication. Clin Oral Investig. (2002) 6:145–9. doi: 10.1007/s00784-002-0169-0
337. Pribitkin E, Rosenthal MD, Cowart BJ. Prevalence and causes of severe taste loss in a chemosensory clinic population. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. (2003) 112:971–8. doi: 10.1177/000348940311201110
338. Imoscopi A, Inelmen EM, Sergi G, Miotto F, Manzato E. Taste loss in the elderly: epidemiology, causes and consequences. Aging Clin Exp Res. (2012) 24:570–9. doi: 10.3275/8520
339. Le Floch J-P, Le Lievre G, Sadoun J, Perlemuter L, Peynegre R, Hazard J. Taste impairment and related factors in type I diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care (1989) 12:173–8.
340. Stolbova K, Hahn A, Benes B, Andel M, Treslova L. Gustometry of diabetes mellitus patients and obese patients. Int Tinnitus J. (1999) 5:135–40.
341. Gondivkar SM, Indurkar A, Degwekar S, Bhowate R. Evaluation of gustatory function in patients with diabetes mellitus type 2. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. (2009) 108:876–80. doi: 10.1016/j.tripleo.2009.08.015
342. Khobragade RS, Wakode SL, Kale AH. Physiological taste threshold in type 1 diabetes mellitus. Indian J Physiol Pharmacol. (2012) 56:42–7.
343. Perros P, MacFarlane TW, Counsell C, Frier BM. Altered taste sensation in newly-diagnosed NIDDM. Diabetes Care (1996) 19:768–70.
344. Wasalathanthri S, Hettiarachchi P, Prathapan S. Sweet taste sensitivity in pre-diabetics, diabetics and normoglycemic controls: a comparative cross sectional study. BMC Endocr Disord. (2014) 14:1. doi: 10.1186/1472-6823-14-67
345. De Carli L, Gambino R, Lubrano C, Rosato R, Bongiovanni D, Lanfranco F, et al. Impaired taste sensation in type 2 diabetic patients without chronic complications: a case-control study. J Endocrinol Invest. (2018) 41:765–72. doi: 10.1007/s40618-017-0798-4
346. Naka A, Riedl M, Luger A, Hummel T, Mueller CA. Clinical significance of smell and taste disorders in patients with diabetes mellitus. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. (2010) 267:547–50. doi: 10.1007/s00405-009-1123-4
347. Noel CA, Sugrue M, Dando R. Participants with pharmacologically impaired taste function seek out more intense, higher calorie stimuli. Appetite (2017) 117(Suppl. C):74–81. doi: 10.1016/j.appet.2017.06.006
348. Satoh-Kuriwada S, Shoji N, Kawai M, Uneyama H, Kaneta N, Sasano T. Hyposalivation strongly influences hypogeusia in the elderly. J Health Sci. (2009) 55:689–98. doi: 10.1248/jhs.55.689
349. Le Floch J, Lièvre GL, Verroust J, Philippon C, Peynegre R, Perlemuter L. Factors related to the electric taste threshold in type 1 diabetic patients. Diabet Med. (1990) 7:526–31. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-5491.1990.tb01436.x
350. Le Floch JP, Le Lievre G, Labroue M, Peynegre R, Perlemuter L. Early detection of diabetic patients at risk of developing degenerative complications using electric gustometry: a five-year follow-up study. Eur J Med. (1992) 1:208–14.
351. Pai MH, Ko TL, Chou HC. Effects of streptozotocin-induced diabetes on taste buds in rat vallate papillae. Acta Histochem. (2007) 109:200–7. doi: 10.1016/j.acthis.2006.10.006
352. Cheng B, Pan S, Liu X, Zhang S, Sun X. Cell apoptosis of taste buds in circumvallate papillae in diabetic rats. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes (2011) 119:480–3. doi: 10.1055/s-0031-1279714
353. Pavlidis P, Gouveris H, Kekes G, Maurer J. Electrogustometry thresholds, tongue tip vascularization, and density and morphology of the fungiform papillae in diabetes. B ENT (2014) 10:271–8.
354. Collin HL, Niskanen L, Uusitupa M, Toyry J, Collin P, Koivisto AM, et al. Oral symptoms and signs in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. A focus on diabetic neuropathy. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. (2000) 90:299–305. doi: 10.1067/moe.2000.107536
355. Uemura M, Toda I, Kawashima W, Yoshimoto G, Fang YR, Xu YJ, et al. Morphological study of the articular disc and capillary of the retrodiscal tissue in a type 2 spontaneous diabetes mellitus rat model. Okajimas Folia Anat Jpn. (2016) 92:53–9. doi: 10.2535/ofaj.92.53
356. Eltas A, Tozoglu U, Keles M, Canakci V. Assessment of oral health in peritoneal dialysis patients with and without diabetes mellitus. Perit Dial Int. (2012) 32:81–5. doi: 10.3747/pdi.2010.00113
357. Moore PA, Guggenheimer J, Orchard T. Burning mouth syndrome and peripheral neuropathy in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes Compl. (2007) 21:397–402. doi: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2006.08.001
358. Vesterinen M, Ruokonen H, Furuholm J, Honkanen E, Meurman JH. Clinical questionnaire study of oral health care and symptoms in diabetic vs. non-diabetic predialysis chronic kidney disease patients. Clin Oral Investig. (2012) 16:559–63. doi: 10.1007/s00784-011-0543-x
359. Arya S, Duhan J, Tewari S, Sangwan P, Ghalaut V, Aggarwal S. Healing of apical periodontitis after nonsurgical treatment in patients with Type 2 diabetes. J Endod. (2017) 43:1623–7. doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2017.05.013
360. Catanzaro O, Dziubecki D, Lauria LC, Ceron CM, Rodriguez RR. Diabetes and its effects on dental pulp. J Oral Sci. (2006) 48:195–9. doi: 10.2334/josnusd.48.195
361. Fouad AF, Burleson J. The effect of diabetes mellitus on endodontic treatment outcome: data from an electronic patient record. J Am Dent Assoc. (2003) 134:43–51; quiz 117–8. doi: 10.14219/jada.archive.2003.0016
362. Garber SE, Shabahang S, Escher AP, Torabinejad M. The effect of hyperglycemia on pulpal healing in rats. J Endod. (2009) 35:60–2. doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2008.09.010
363. Lopez-Lopez J, Jane-Salas E, Estrugo-Devesa A, Velasco-Ortega E, Martin-Gonzalez J, Segura-Egea JJ. Periapical and endodontic status of type 2 diabetic patients in Catalonia, Spain: a cross-sectional study. J Endod. (2011) 37:598–601. doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2011.01.002
364. Marotta PS, Fontes TV, Armada L, Lima KC, Rocas IN, Siqueira JF Jr. Type 2 diabetes mellitus and the prevalence of apical periodontitis and endodontic treatment in an adult Brazilian population. J Endod. (2012) 38:297–300. doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2011.11.001
365. Nakajima Y, Inagaki Y, Kido J, Nagata T. Advanced glycation end products increase expression of S100A8 and A9 via RAGE-MAPK in rat dental pulp cells. Oral Dis. (2015) 21:328–34. doi: 10.1111/odi.12280
366. Sanchez-Dominguez B, Lopez-Lopez J, Jane-Salas E, Castellanos-Cosano L, Velasco-Ortega E, Segura-Egea JJ. Glycated hemoglobin levels and prevalence of apical periodontitis in type 2 diabetic patients. J Endod. (2015) 41:601–6. doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2014.12.024
367. Segura-Egea JJ, Jimenez-Pinzon A, Rios-Santos JV, Velasco-Ortega E, Cisneros-Cabello R, Poyato-Ferrera M. High prevalence of apical periodontitis amongst type 2 diabetic patients. Int Endod J. (2005) 38:564–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2591.2005.00996.x
368. Segura-Egea JJ, Martin-Gonzalez J, Cabanillas-Balsera D, Fouad AF, Velasco-Ortega E, Lopez-Lopez J. Association between diabetes and the prevalence of radiolucent periapical lesions in root-filled teeth: systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Oral Investig. (2016) 20:1133–41. doi: 10.1007/s00784-016-1805-4
369. Smadi L. Apical periodontitis and endodontic treatment in patients with type II diabetes mellitus: comparative cross-sectional survey. J Contemp Dent Pract. (2017) 18:358–62. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-2046
370. Al-Sowygh ZH, Ghani SMA, Sergis K, Vohra F, Akram Z. Peri-implant conditions and levels of advanced glycation end products among patients with different glycemic control. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. (2018) 20:345–51. doi: 10.1111/cid.12584
371. Daubert DM, Weinstein BF, Bordin S, Leroux BG, Flemming TF. Prevalence and predictive factors for peri-implant disease and implant failure: a cross-sectional analysis. J Periodontol. (2015) 86:337–47. doi: 10.1902/jop.2014.140438
372. Ferreira SD, Silva GL, Cortelli JR, Costa JE, Costa FO. Prevalence and risk variables for peri-implant disease in Brazilian subjects. J Clin Periodontol. (2006) 33:929–35. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051X.2006.01001.x
373. Gomez-Moreno G, Aguilar-Salvatierra A, Rubio Roldan J, Guardia J, Gargallo J, Calvo-Guirado JL. Peri-implant evaluation in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients: a 3-year study. Clin Oral Implants Res. (2015) 26:1031–5. doi: 10.1111/clr.12391
374. Monje A, Catena A, Borgnakke WS. Association between diabetes mellitus/hyperglycaemia and peri-implant diseases: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Periodontol. (2017) 44:636–48. doi: 10.1111/jcpe.12724
375. LeResche L. Epidemiology of temporomandibular disorders: implications for the investigation of etiologic factors. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. (1997) 8:291–305.
376. Scala A, Checchi L, Montevecchi M, Marini I, Giamberardino MA. Update on burning mouth syndrome: overview and patient management. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. (2003) 14:275–91. doi: 10.1177/154411130301400405
377. Kohorst JJ, Bruce AJ, Torgerson RR, Schenck LA, Davis MD. A population-based study of the incidence of burning mouth syndrome. Mayo Clin Proc. (2014) 89:1545–52. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2014.05.018
378. Lima SM, Grisi DC, Kogawa EM, Franco OL, Peixoto VC, Goncalves-Junior JF, et al. Diabetes mellitus and inflammatory pulpal and periapical disease: a review. Int Endod J. (2013) 46:700–9. doi: 10.1111/iej.12072
379. Segura-Egea JJ, Martin-Gonzalez J, Castellanos-Cosano L. Endodontic medicine: connections between apical periodontitis and systemic diseases. Int Endod J. (2015) 48:933–51. doi: 10.1111/iej.12507
380. Figdor D. Apical periodontitis: a very prevalent problem. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. (2002) 94:651–2. doi: 10.1067/moe.2002.130322
381. Sasaki H, Hirai K, Martins CM, Furusho H, Battaglino R, Hashimoto K. Interrelationship between periapical lesion and systemic metabolic disorders. Curr Pharm Des. (2016) 22:2204–15. doi: 10.2174/1381612822666160216145107
382. Bender IB, Bender AB. Diabetes mellitus and the dental pulp. J Endod. (2003) 29:383–9. doi: 10.1097/00004770-200306000-00001
383. Zitzmann NU, Berglundh T. Definition and prevalence of peri-implant diseases. J Clin Periodontol (2008) 35(8 Suppl.):286–91. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051X.2008.01274.x
384. Lindhe J, Meyle J. Peri-implant diseases: Consensus Report of the Sixth European Workshop on Periodontology. J Clin Periodontol. (2008) 35(8 Suppl.):282–5. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051X.2008.01283.x
385. Klinge B, Meyle J. Peri-implant tissue destruction. The Third EAO Consensus Conference 2012. Clin Oral Implants Res. (2012) 23(Suppl. 6):108–10. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0501.2012.02555.x
386. Roos-Jansaker AM, Lindahl C, Renvert H, Renvert S. Nine- to fourteen-year follow-up of implant treatment. Part II: presence of peri-implant lesions. J Clin Periodontol. (2006) 33:290–5. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051X.2006.00906.x
387. Fransson C, Lekholm U, Jemt T, Berglundh T. Prevalence of subjects with progressive bone loss at implants. Clin Oral Implants Res. (2005) 16:440–6. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0501.2005.01137.x
388. Derks J, Schaller D, Hakansson J, Wennstrom JL, Tomasi C, Berglundh T. Effectiveness of implant therapy analyzed in a Swedish population: prevalence of peri-implantitis. J Dent Res. (2016) 95:43–9. doi: 10.1177/0022034515608832
389. Turri A, Rossetti PH, Canullo L, Grusovin MG, Dahlin C. Prevalence of peri-implantitis in medically compromised patients and smokers: a systematic review. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants (2016) 31:111–8. doi: 10.11607/jomi.4149
390. Naujokat H, Kunzendorf B, Wiltfang J. Dental implants and diabetes mellitus-a systematic review. Int J Implant Dent. (2016) 2:5. doi: 10.1186/s40729-016-0038-2
391. Renvert S, Quirynen M. Risk indicators for peri-implantitis. A narrative review. Clin Oral Implants Res. (2015) 26(Suppl. 11):15–44. doi: 10.1111/clr.12636
Keywords: diabetes mellitus, oral complications, hyperglycemia, insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, hypertension, immune dysfunction
Citation: Verhulst MJL, Loos BG, Gerdes VEA and Teeuw WJ (2019) Evaluating All Potential Oral Complications of Diabetes Mellitus. Front. Endocrinol. 10:56. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2019.00056
Received: 21 August 2018; Accepted: 22 January 2019;
Published: 18 February 2019.
Edited by:
Ioan Andrei Veresiu, Iuliu Haţieganu University of Medicine and Pharmacy, RomaniaReviewed by:
Federico Biscetti, Catholic University of Sacred Heart, ItalyMohd Ashraf Ganie, Sher-I-Kashmir Institute of Medical Sciences, India
Copyright © 2019 Verhulst, Loos, Gerdes and Teeuw. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Martijn J. L. Verhulst, bS52ZXJodWxzdEBhY3RhLm5s
 Martijn J. L. Verhulst
Martijn J. L. Verhulst Bruno G. Loos1
Bruno G. Loos1 Victor E. A. Gerdes
Victor E. A. Gerdes