- 1Department of Clinical Laboratory, Jieyang People’s Hospital, Jieyang, Guangdong, China
- 2Precision Medicine Centre, Puning People’s Hospital, Puning, Guangdong, China
A Correction on:
Elevated mean arterial pressure and risk of impaired fasting glucose: a multicenter cohort study revealing age and sex interactions
By Lin Y, Zou J, Hong M, Huang X and Wu J (2025). Front. Endocrinol. 16:1580036. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1580036
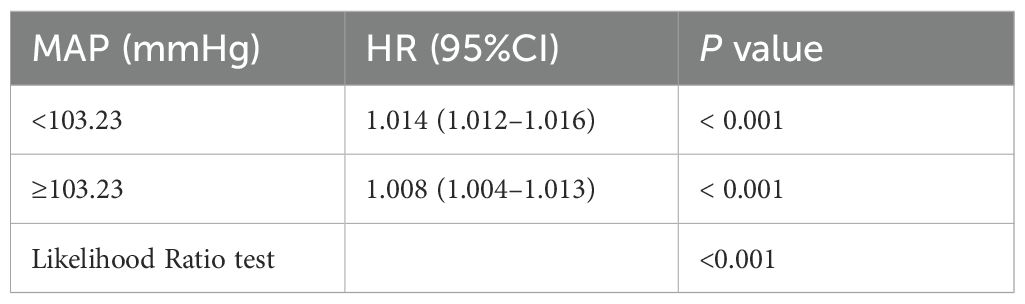
There was a mistake in Table 3 as published. The range “≥103.23–” should be revised to “≥103.23” for accuracy. The corrected Table 3 appears below.
During the final proofreading stage, we identified a non-citable reference in our manuscript. While we previously removed the relevant content from the background section, we recognize that the 2nd sentences in Paragraph 2 of the discussion section also requires deletion.
A correction has been made to the 2nd and 3rd sentences in Paragraph 2 of the Discussion section:
“For instance, a cohort study of a Chinese population undergoing physical examinations has confirmed the positive association between MAP and diabetes (14)”.
The original version of this article has been updated.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: mean arterial pressure, impaired fasting glucose, cohort study, age interaction, sex interaction
Citation: Lin Y, Zou J, Hong M, Huang X and Wu J (2025) Correction: Elevated mean arterial pressure and risk of impaired fasting glucose: a multicenter cohort study revealing age and sex interactions. Front. Endocrinol. 16:1649984. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1649984
Received: 19 June 2025; Accepted: 07 July 2025;
Published: 21 July 2025.
Edited and Reviewed by:
Åke Sjöholm, Gävle Hospital, SwedenCopyright © 2025 Lin, Zou, Hong, Huang and Wu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Juan Wu, anVhbnd1bHVja0AxNjMuY29t
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Yuye Lin
Yuye Lin Junzhong Zou
Junzhong Zou Miaoling Hong
Miaoling Hong Xudong Huang
Xudong Huang Juan Wu
Juan Wu