- 1Department of Woman and Child Health and Public Health, Fondazione Policlinico Universitario A. Gemelli Istituto di Ricovero e Cura a Carattere Scientifico (IRCCS), Rome, Italy
- 2Centro di Salute Globale, Università Cattolica del Sacro Cuore, Roma, Italy
- 3Pediatric Clinic, Department of Medicine and Surgery, University of Parma, Parma, Italy
Background: Duration of humoral and cellular memory in children previously infected SARS-CoV-2 or vaccinated and subsequent risk of reinfection is still not fully elucidated.
Methods: Systematic review of studies retrieved from medical databases and article reference lists.
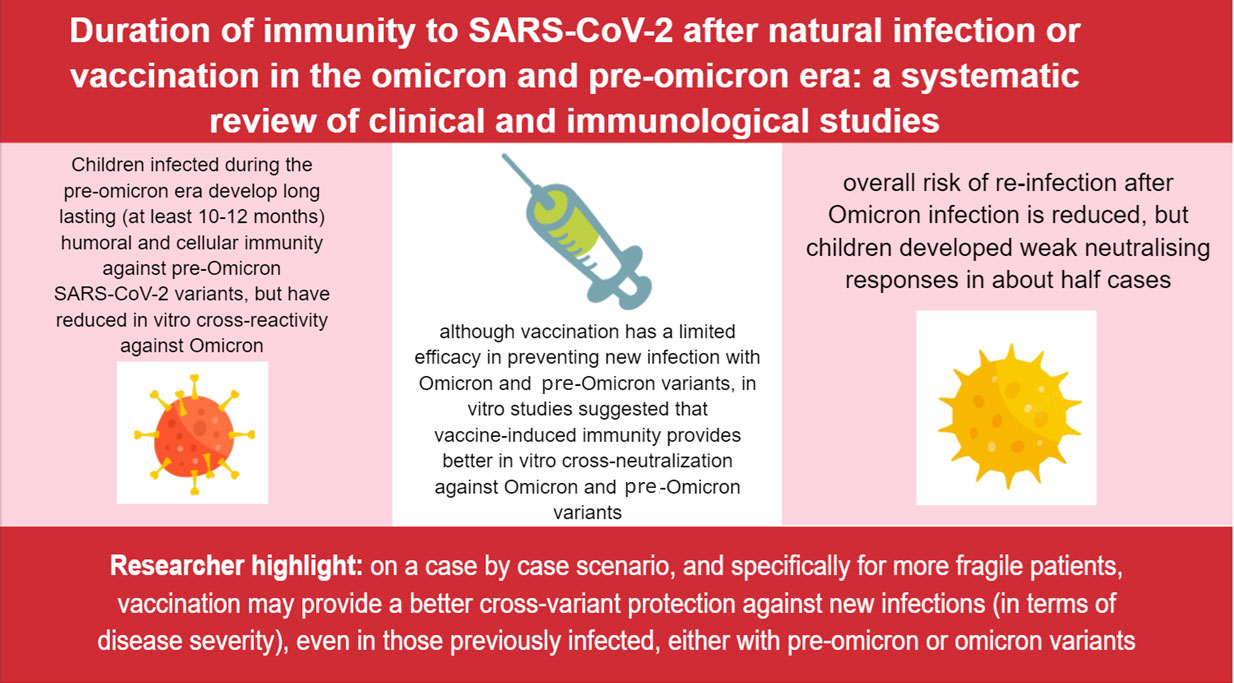
Results: From 2420 identified articles, 24 met the inclusion criteria. Children infected during the pre-omicron era developed long lasting (at least 10-12 months) humoral and cellular immunity against pre-Omicron SARS-CoV-2 variants, but have reduced in vitro cross-reactivity against Omicron. Conversely, although vaccination has a limited efficacy in preventing new infection with pre-Omicron and Omicron variants, in vitro studies suggested that vaccine-induced immunity provides better in vitro cross-neutralization against pre-Omicron and Omicron variants. Preprints published after the period of inclusion of our review suggested that overall risk of infection after Omicron infection is reduced, but children developed weak neutralizing responses in about half cases.
Conclusions: Available evidence, although limited, suggested a long-lasting but unperfect protection of previous infections or vaccination against pre-Omicron and Omicron variants. Based on our findings, it might be reasonable to offer families of children infected before Omicron a booster vaccination. A similar indication should be proposed also for those infected with Omicron, specifically for more fragile children at higher risk of COVID-19-related complications, based on better cross-variant neutralisation induced by vaccination.
Systematic review registration: PROSPERO, identifier ID 353189.
Introduction
Since the first description of SARS-CoV-2, the pandemic has significantly evolved through different phases in terms of epidemiologic, clinical and virologic perspectives. Initially, the clinical impact of Covid-19 on adults has been massive and healthcare systems worldwide have struggled in providing support to the massive number of patients requiring admission. Initially, children had been relatively spared from the pandemic and represented a minimal percentage of cases (1), particularly of the most severe ones (2),. Later, several different variants have emerged with improved transmissibility and different ability to cause severe disease (3), and the number of children diagnosed with Covid-19 or requiring hospitalisation increased significantly, although the number of critical diseases remained low. Importantly, while the number of MIS-C cases also dropped, it has become evident that also children could develop Long COVID after SARS-CoV-2 infection (4).
In the meantime, different vaccines have been produced, which are effective against severe disease, although efficacy in preventing transmission is low, particularly since the Omicron era. Although the same efficacy has been demonstrated in children in the short time follow-up of initial trials run by drug companies (5), a rare but real complication in young males - acute myocarditis - have been documented by several independent reports (6). This side effect, along with the observation that most children developed a mild or asymptomatic disease, led some authors or countries to question the need of vaccinating children, as a less clear benefit-risk ratio can be demonstrated in children compared with adults (7). To make the scenario even more complicated, a huge number of children have been infected during Omicron wave and authors have claimed that previous infection would confer enough immunity to protect against severe disease in case of reinfections, therefore further questioning the utility of COVID-19 vaccines in children.
Given these rapidly evolving scenarios and growing and fast amount of publications, in order to better understand the risks of COVID-19 after previous infections or vaccination, we performed a systematic review of available studies that assessed the duration of immunity after disease or vaccination in children, evaluating clinical information (clinically evident reinfection) and immunological findings (duration of humoral or cellular immunity). Such an approach can provide better evidence and information on how to organise vaccination campaigns in the current context of massive SARS-CoV-2 circulation, but also a general better understanding on the development of immunity after respiratory infections.
Methods
Our systematic review and meta-analysis was performed along with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews (PRISMA) extension for scoping reviews (Supplementary Table S1) (8). The protocol of this systematic review and meta-analysis was registered in the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (PROSPERO) database (ID 353189).
Search strategy
The literature search strategy (Supplementary Table S2) was aimed at identifying those clinical studies evaluating duration of cellular mediated or humoral immunity developed after SARS-CoV-2 natural infection or vaccination in the paediatric population.
The systematic search was conducted according to the following PICOS approach: Population: paediatric patients who have been vaccinated against SARS-CoV-2 or got infected by SARS-CoV-2; Intervention: evaluation of cellular mediated or humoral immunity; Comparison between immunity after natural infection and immunity after vaccination; Outcomes: duration of immunity after natural infection and after vaccination against SARS-CoV-2; Study design: observational cohort studies (either prospective or retrospective).
A systematic search of PubMed was performed from March 7th until April 6th, 2022. Additional relevant studies were also identified by hand-searching reviews on the topic and exploring the list of references of selected papers.
Since a number of relevant preprints have been published after the conclusion of our systematic review specifically addressing the immunological responses and risk of infection during and after the Omicron waves, we performed a search update on July 13th, 2022 and relevant papers have been subsequently included in an updated results section.
Eligibility criteria and identification of studies
The systematic review included only clinical studies aimed at determining the duration of cellular mediated or humoral immunity after natural infection or vaccination against SARS-CoV-2, or the cases of reinfections after previous infection or vaccination.
The analysis included observational cohort studies either prospective or retrospective, all including children aged <18 years. Studies that do not assess the duration of immunity after infection/vaccination and those without available paediatric data were excluded, as well as reviews, meta-analysis, editorials, and case series/reports. Papers written in a non-European language were excluded. All in vitro and animal experimental studies were also excluded.
Study selection
All studies published between February 1st, 2021, and July 13th, 2022 were considered (N= 2420). To enhance consistency, all reviewers (four residents and one senior) screened the same numbers of publications, discussed results, and amended the screening and data extraction before beginning screening for this review. The same five reviewers, working in pairs, assessed the titles, abstracts and full text of all publications identified by the search. Disagreements on study selection and data extraction were solved by consensus and discussion with other reviewers, if needed.
Outcome measures
The major outcome of interest was evaluating duration of immunity, developed by paediatric patients after SARS-CoV-2 natural infection or vaccination, with a distinction between:
(i) duration of cellular mediated immunity developed after SARS-CoV-2 natural infection or vaccination;
(ii) duration of humoral immunity developed after SARS-CoV-2 natural infection or vaccination;
The secondary outcome comprised:
(i) number of infections and disease severity after vaccination or after natural infection;
(ii) neutralizing activity of cellular mediated or humoral immunity against variants;
(iii) specific comments on T and B compartment of cellular immunity.
Data extraction
Four reviewers independently analyzed the studies included in the review, extracting data related to patients and methods characteristics, duration of cellular mediated or humoral immunity, clinical results and reported outcomes. Results were checked again, across the original manuscript, by a fifth researcher.
Data synthesis
Characteristics of the included (and excluded) studies were presented in tabulated form on an Excel sheet. The data were collected in columns: study citation; year; study country; number of children included; age of group; the sex of the group; study population (healthy, comorbidities, both); possible comorbidities of the study’s pediatric population; duration of immunity after vaccination or infection; methods of study; if vaccination, specify which vaccine; if infection, specify which variants (if known) or wave (report study period); length of follow-up; in clinical findings: number of infections and disease severity after vaccination or after natural infection; in humoral immunity: main findings, specific comments on neutralizing antibodies and on neutralizing activity against variants; in cellular immunity: main findings, specific comments on B cell or T cell compartment and on activities against variants; study limitation and other comments.
Quality assessment in individual studies
The quality of included studies with comments about study limitations, including whether children’s ages would be translated into specific age groups for analysis, were assessed by two reviewers (Supplementary Table S3).
None of the quality assessors were blinded.
Results
Study selection and description (synthesis of results)
Of the 2420 identified articles, 2371 were initially excluded following review of the titles and/or abstracts. Eight duplicates were removed after comparison of the different searches. At a second review, five more articles were excluded based on the abstract by a senior reviewer, and further 6 studies were excluded due to wrong interventions or outcomes, and six more studies for not including paediatric patients. Ultimately, 24 articles were included in the review (Figure 1).
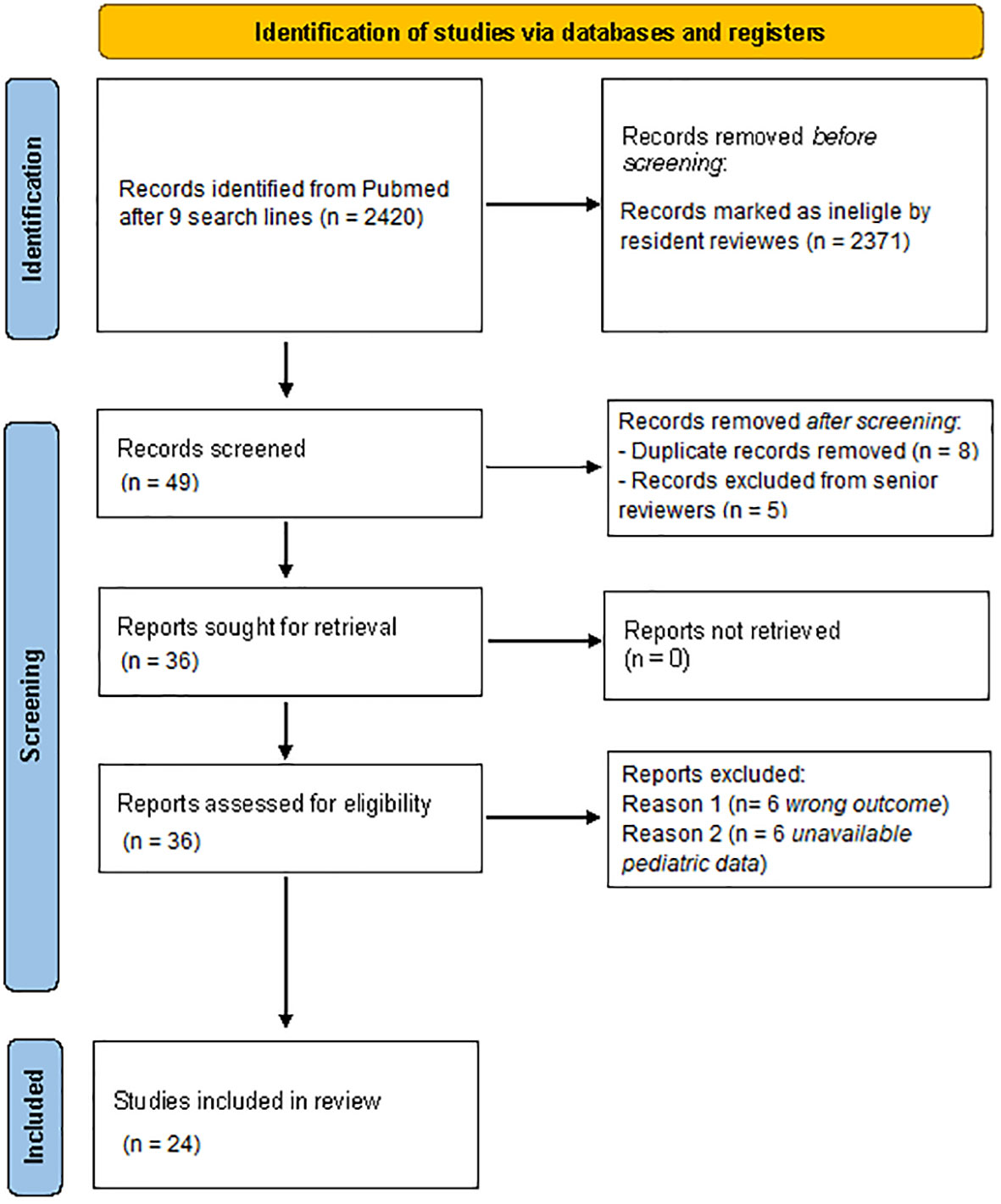
Figure 1 Flowchart of the study selection according to the PRISMA guidelines. Performed following “Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021;372:n71. Doi: 10.1136/bmj.n71”.
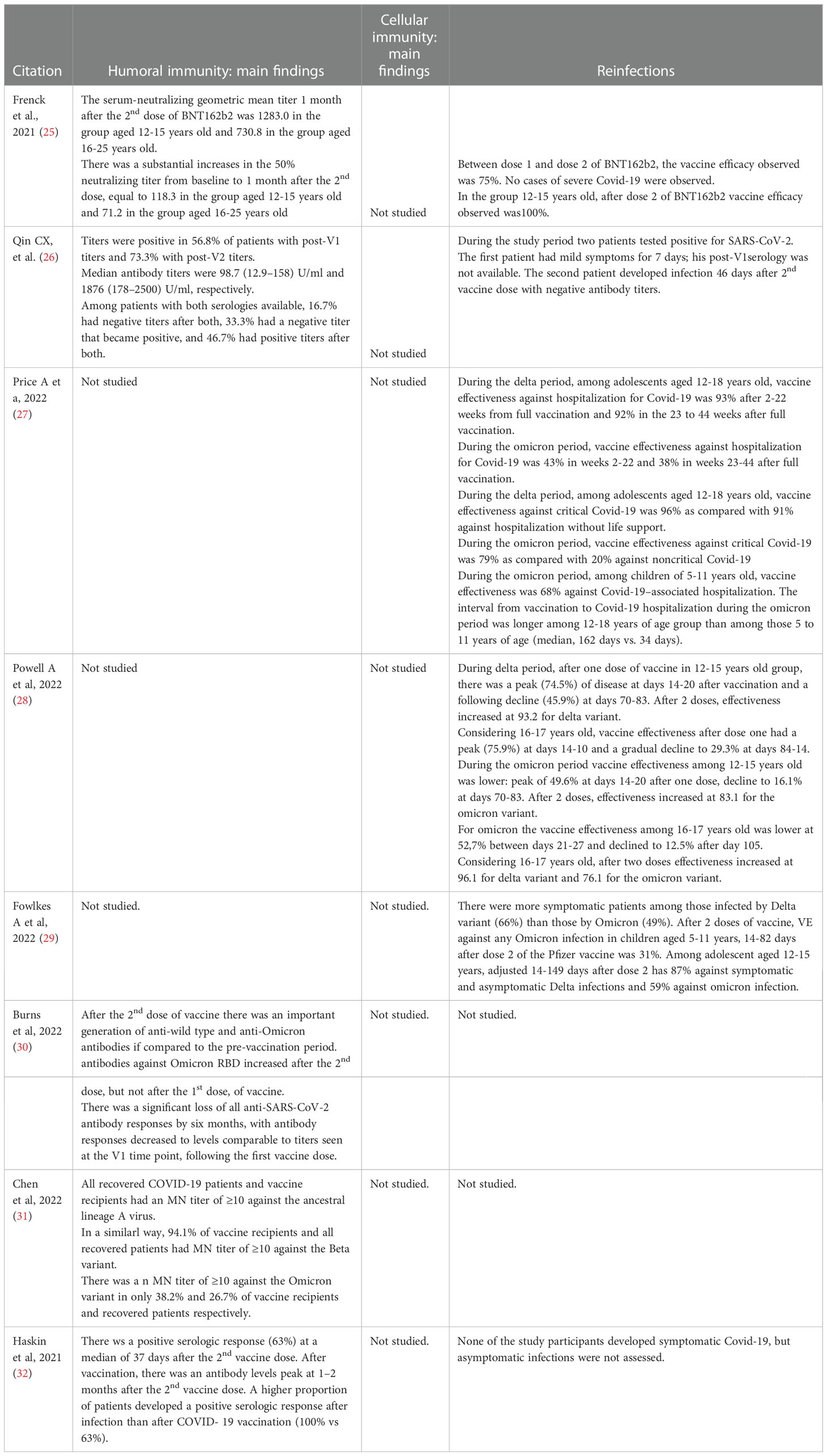
The main demographic and clinical characteristics of the enrolled cohorts, aims and outcomes for each study are presented in Table 1; the main findings of each study assessing the duration of humoral and cellular immune responses after infections are presented in Tables 2 and 3 respectively. Cases of microbiologically confirmed reinfections were only analyzed in vaccine efficacy studies, and are summarized in Table 4, along with immunological analyses.
Duration of Immune responses after infection
Fifteen studies (9–23) analyzed duration of humoral immunity after SARS-CoV-2 natural infection (Table 2 for further details). All these studies documented a seroconversion in the majority of children who have been infected with SARS-CoV-2. The duration of follow up after infection was different, ranging from a minimum of three months (18) to a maximum of twelve months (20). Two studies (11, 14) found different duration of immunity in children of different ages. In particular, Interiano et al. (11) reported longer persistence of IgG responses in children aged 12-19 rather than in those aged 0-11 years. Conversely, Breuer et al. (14) evidenced higher and more lasting antibody levels in children younger than 6 years. One study (15) underlined different duration of immunity related to a different severity of infection: IgG levels decrease more significantly in patients with mild/moderate infection rather than in severe/critical ones. Only one study (21) compared the duration of immunity in immunocompetent and immunocompromised patients, showing no significant differences. Seven studies (10, 12, 13, 16, 18, 20–22) made comments on neutralizing antibodies. Only one study (20) evaluated the humoral immunity developed against viral variants, showing similar activity against different variants.
Six (19–24) studies analyzed cellular immunity developed after SARS-CoV-2 infection. Only one study comments about B cell compartment and it found that SARS-CoV-2 specific B cells are positively associated with anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG and neutralization activity (22). On the other hand, the same studies (19–24) reported the development of a specific T cell response after infection in children. Three studies (19, 20, 23) also analyzed duration of specific T cell immunity, reporting detectable T cell response for six to twelve months after initial infection. Two studies (23, 24) reported differences in duration of T cell immunity between adults and children; in particular, T cell responses seemed to be significantly lower and faster in decline in children than in adults infected by SARS-CoV-2. Only one study (20) reported data about activity against viral variants, showing a significant cross-reactivity of T cell compartment between variants. Further details are available in Tables 1–3.
Duration of immune responses or cases of reinfections after vaccination
Eight studies discussed humoral and cellular memory and re-infections after SARS-CoV-2 vaccination. In six studies (25, 27, 29–32), paediatric population received BNT162b2 (Comirnaty, Pfizer-BioNTech), and in the remaining two studies (26, 28) received BNT162b2 (Comirnaty, Pfizer-BioNTech) or mRNA-1273 (Spikevax, Moderna). There are five clinical studies (25, 26, 30–32) which analyzed the duration of immune responses after SARS-CoV-2 vaccination. None of them examined the duration of cellular immunity in the paediatric population. One study highlighted that 12-to-15-year-old recipients have greater neutralizing antibodies titers after second dose of vaccination relative to 16-to-25-year-old participants (25). Robust humoral immunity after only two doses of vaccine was shown (26, 30). Prior immunity may matter, as shown in a separate study, after a third vaccination, 100% of those with prior positive responses increased or have preserved maximum antibodies titers, compared to 54.5% with prior negative response (26). This immunity may not last long, as loss of all anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibody responses was shown in one study 6 months after vaccination (30). Two studies compared serologic response after infection and after SARS-CoV-2 vaccination, showing that recovered COVID-19 patients had a higher serum neutralization antibody titer compared to vaccinated participants (31, 32). Moreover, antibody levels among COVID-19 positive patients continued to remain high, even 6–8 months following the infection (32).
Six studies analyzed efficacy of SARS-CoV-2 vaccines in preventing reinfections and infection caused by other variants, like Delta and Omicron variant (25–29, 32). Different studies showed that there were no cases of infection by SARS-CoV-2 with an onset at 7 or more days after the second dose of BNT162b2 recipients (25, 32). In this paediatric population only a few cases of mildly symptomatic infection that did not require hospitalisation have occurred (26). The efficacy of the vaccine differs according to variants of the virus, being higher for Delta variant rather than for Omicron variant in 12-15-years-old and 16-17-years-old children (28). Two doses of Pfizer- BioNTech vaccine were effective in preventing 87% infection by Delta variant and 59% by Omicron variant (29). Morover, BNT162b2 vaccination reduced the risk of Omicron-associated hospitalisation by two thirds among children 5-to-11-year-old and registered a lower protection against Omicron-associated rather than Delta-associated hospitalisation among adolescents 12-to-18-year-age (27). Further details are available in Tables 1 and 4.
New key publications released after the systematic review
Importantly, a number of relevant studies have been published after the end of study search of our systematic review to further understand current scenarios of protection of children after infection or vaccination, which might be useful to understand how to deal with current pre-Omicron and Omicron waves.
Di Chiara et al. assessed anti–SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain (S-RBD) IgG kinetics in 697 patients with mild/asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection, including 351 children or older siblings and 346 parents, up to one year after initial infection (33). Children had significantly higher S-RBD IgG titers than older patients across all follow-up time points, and longitudinal analysis of 56 study participants sampled at least twice during follow-up demonstrated the persistence of antibodies up to 10 months from infection in all age classes, despite a progressive decline over time.
Khaitan et al,. as part of the DISCOVER study (34), measured neutralizing Abs (nAbs) and IgG Abs to SARS-CoV-2 Ags and spike protein variants in symptomatic and asymptomatic children. They found that children developed nAbs that remained detectable longer than in adults but waned in titer over time and broad IgG Abs that also waned in level over time. Moreover, nAb levels were lower postinfection than those reported after immunization, suggesting that children might benefit from a booster as adults do (35).
Tang et al. in the USA analyzed virus-neutralizing capacity against SARS-CoV-2 Alpha, Beta, Gamma, Delta and Omicron variants in 177 paediatric patients hospitalised with severe acute COVID-19, MIS-C, and mild COVID-19 during 2020 and early 2021 (36). They found that children retained neutralizing antibodies in the convalescent post-acute phase, but it tended to decrease with time, and the neutralizing activity against Omicron was poor in all age groups. Conversely, vaccination induced a broader neutralizing antibody response against VOCs in naïve children compared with the natural immunity following SARS-CoV-2 infection (36).
Bartsch et al. investigated vaccine-induced humoral immune response in 6-to-11-years-old children and seems to confirm the importance of booster dose in previously infected paediatric population. Indeed vaccinated children elicited robust cross-VOC antibody responses and a 100 μg doses resulted in higher preserved Omicron-specific functional humoral immunity rather than those with diagnosed of COVID-19 or MIS-C (37). Importantly, a South Korean population cohort study of 3.2 million adolescents identified 29285 SARS-CoV-2 infection, 11 of which were classified as critical. None of these critical cases were vaccinated and overall estimate of vaccine effectiveness of two doses against preventing infection was 75.5% to 80.4% in the immediate post-vaccination month, but this waned to near 40% over two months post-vaccination (38). Lin and colleagues provided further data on the protection against hospitalization related to omicron variant in children 5 to 11 years of age who had receives vaccination and had had previous SARS-CoV-2 infection (39).
Discussion
SARS-CoV-2 infection frequently leads to mild or asymptomatic infections in children, although in rare cases they can develop critical acute disease (40), a severe post hyperinflammatory syndrome (MIS-C) (41) or even Long Covid (42). Although the causes are not yet fully established, current evidence suggested that more efficient innate (43) and local tissue responses, better thymic function, cross-reactive immunity (44), different expression of Treg cells (45), and better nasal immunity (46) can play a role in this observed age-dependent risk of severe disease. Although these mechanisms may explain differences in disease expression, duration of immunity against new SARS-CoV-2 infections in children previously infected or vaccinated remains poorly understood. In fact, while social events, interactions, relationships and being in close environments (such as schools) may theoretically provide a perfect setting for COVID-19 transmission, all these aspects are of critical importance for appropriate child development. Not by chance, prolonged lockdowns and school closures have had a catastrophic negative impact on child wellbeing worldwide (47). Therefore, a critical appraisal of current evidence in term of duration of SARS-CoV-2 immunity in children is mandatory and might offer physicians, policy makers and parents appropriate information to implement the most balanced decisions that, at the same time, protect children from consequences of COVID-19 but also allow them to live all the necessary experiences for their proper growth. In this regard, our systematic review on duration of immunity in children previously infected or vaccinated, the first one to our knowledge, provides important and practical information. Specifically, studies addressing duration of humoral and cellular immunity suggested that, in vitro, children retained appropriate memory and cross-reactive protection against pre-Omicron strain for about 10-12 months, although only a few studies focused on cellular memory and none included also information about clinical reinfections. Studies evaluating protection after vaccination suggested that children developed short protection against asymptomatic or mild infection but maintained good protection against severe/critical disease. Unfortunately, the number of available studies is limited and no data about long-term protection after both natural infection and vaccination in children are available.
It is important to highlight that the available studies addressing duration of immunity after SARS-CoV-2 infection mostly focused on immunological (either humoral or cellular) parameters, and only a few addressed the real-world impact of reinfections in children. The first study was published by Mensah et al. in the UK, where they prospectively evaluated risk of SARS-CoV-2 reinfection in children and compared this with the risk in adults during Delta and pre-Delta periods (48). Overall, they found that children had a lower risk of reinfections compared with adults (72.53 per 100 000 vs 21.53 per 100 000), and a similar rate of hospitalisations or pediatric intensive care unit (PICU) admissions in children during the first or second infection (2.7% and 2.4% hospitalisations during first and second episode, and seven and four PICU admissions, respectively). A similar preprint from Israel during Delta period showed that previously infected children remained protected against reinfection to a high degree for 18 months, although in this case severity of reinfections was not reported (49).
More recent studies, although supportive of comparatively longer period of immunity after natural infection, continue to support vaccinating children with prior immunity from pre-Omicron strains to maximize protection against Omicron and potential future strains (36–38, 50–52).
Less information is available about protection in children already infected with Omicron, although three recent preprints from Portugal (53), Qatar (54) and Denmark (55) that included both adults and children suggested that infection with Omicron provided substantial protection against reinfection (56). Importantly, these studies have been performed in countries that implemented impactful vaccination campaigns and, therefore, it is probable that such positive findings were due to an immune cross-stimulation by both vaccinations and Omicron infection, rather than Omicron alone. In addition, these studies did not include immunological parameters. Conversely, Dowell et al. from the UK recently released a preprint antibody and cellular immune response following Omicron infection in children aged 6-14 years and related this to prior SARS-CoV-2 infection and vaccination status (57). Interestingly, primary Omicron infection elicited a weak antibody response in 53% of children, while a secondary Omicron infection following prior infection induced better neutralizing antibodies. Importantly, vaccination elicited the highest levels of antibody response and was also strongly immunogenic following prior natural infection with Omicron. Although cellular responses against Omicron were strong in all children infected with Omicron, this study further reinforced the hypothesis that a vaccine booster after natural infection could be an appropriate precautionary strategy to discuss with families, awaiting further evidence and new scenarios particularly for children at highest risk of severe COVID-19, MIS-C or Long COVID.
Our study has limitations to address. First, studies on the topic are heterogeneous and mostly focused on only a part of the immunological or clinical data that can give a better overview of the real protection of children after a previous SARS-CoV-2 infection or vaccination. For example, most studies focused on duration of humoral immunity while a minority also included cellular immunity, non of them having long-term follow-up to address if those patients with evidence of humoral/cellular memory were protected from symptomatic infections. Secondly, duration of follow-up was variable, ranging from weeks to 12-18 months. Third, most studies were performed during the pre-Omicron era and a minority addressed cross-protection against pre-Omicron and Omicron variants. Therefore, the information provided does not allow to derive firm conclusions, but mostly a guidance awaiting more solid evidence. Fourth, neutralizing activities were specifically studied in a minority of studies and usually on a subgroup of the originally enrolled studies. Fifth, no conclusion con be drawn about protection of children with comorbidities after infection or vaccination because studies included patients with great variability of pathological condition, although our findings were encouraging. Importantly, one recent study coordinated by an Italian group showed that children with inflammatory bowel disease with distinct immune suppressive treatment had a good safety and immunogenicity profile following SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination (58). While perinatally infected HIV children or previously transplanted patients had a different immunological response which suggested their eligibility for booster doses (59, 60). However, the paucity of data and differences in study population do not allow to derive firm conclusions. Importantly, no studies so far have evaluated the role of immune memory from previous infection or vaccination in preventing long covid after re-infections, while a few studies have suggested that previous memory can be associated with a lower risk of developing MIS-C (61, 62).
In conclusion, the analyzed literature suggested that most children infected during the pre-Omicron era developed long lasting (at least 10-12 months) humoral and cellular immunity against pre-Omicron SARS-CoV-2 variants, but have reduced in vitro cross-reactivity against Omicron. These data seem in line with the two studies addressing re-infections after previous COVID-19, showing a low but possible risk of new infections in children infected before Omicron, with a risk of a similar or lower disease severity compared to previous infection. Conversely, although vaccination had a limited efficacy in preventing new infection with Omicron, in vitro studies suggested that vaccine-induced immunity provided better in vitro cross-neutralization against Omicron.
All together, these data suggested that, until better evidence is available and given difficulties in predicting future variations of SARS-CoV-2 and their impacts (63, 64), it might be reasonable to offer families of children infected before Omicron a booster vaccination, probably not earlier than six months since previous infection. For those with a known infection during Omicron, a more cautious approach could be suggested. Since adult and preliminary paediatric studies suggested that vaccination may induce a general better cross-variant neutralization also in those infected with Omicron, for more fragile children a booster vaccination should be considered, pending proper discussion with the family. However., it is important to highlight that the effect of booster in providing better neutralization protection against new post-Omicron variants is still unknown.
Importantly, in such a rapidly evolving scenario, new studies addressing the protection against new variants, even in children infected with Omicron, are urgently needed.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
DB and SE conceptualized the study. LC, CG, FC and FB performed data collection and data synthesis. DB, LC, CG, FC and FB wrote the first draft of the manuscript. DB and SE revised and wrote the final draft of the manuscript. SE supervised the manuscript. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Conflict of interest
DB participated at the ESPID2022 meeting discussing roles of Covid-19 in children, in a session sponsored by Pfizer.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2022.1024924/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Viner RM, Mytton OT, Bonell C, Melendez-Torres GJ, Ward J, Hudson L, et al. Susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 infection among children and adolescents compared with adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Pediatr (2021) 175(2):143–56. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2020.4573
2. Verdoni L, Mazza A, Gervasoni A, Martelli L, Ruggeri M, Ciuffreda M, et al. An outbreak of severe Kawasaki-like disease at the Italian epicentre of the SARS-CoV-2 epidemic: an observational cohort study. Lancet. (2020) 395(10239):1771–8. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31103-X
3. Available at: https://www.who.int/activities/tracking-SARS-CoV-2-variants (Accessed august 2022).
4. Pazukhina E, Andreeva M, Spiridonova E, Bobkova P, Shikhaleva A, El-Taravi Y, et al. Prevalence and risk factors of post-COVID-19 condition in adults and children at 6 and 12 months after hospital discharge: a prospective, cohort study in Moscow (StopCOVID). BMC Med (2022) 20(1):244. doi: 10.1186/s12916-022-02448-4
5. Available at: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/covid-19-vaccines (Accessed May 7th, 2022).
6. Wong HL, Hu M, Zhou CK, Lloyd PC, Amend KL, Beachler DC, et al. Risk of myocarditis and pericarditis after the COVID-19 mRNA vaccination in the USA: a cohort study in claims databases. Lancet. (2022) 399(10342):2191–9. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(22)00791-7
7. Zimmermann P, Pittet LF, Finn A, Pollard AJ, Curtis N. Should children be vaccinated against COVID-19? Arch Dis Child (2022) 107(3):e1. doi: 10.1136/archdischild-2021-323040
8. Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ (2021) 372:n71. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n71
9. Bloise S, Marcellino A, Testa A, Dilillo A, Mallardo S, Isoldi S, et al. Serum IgG levels in children 6 months after SARS-CoV-2 infection and comparison with adults. Eur J Pediatr (2021) 180(11):3335–42. doi: 10.1007/s00431-021-04124-w
10. Toh ZQ, Higgins RA, Do LAH, Rautenbacher K, Mordant FL, Subbarao K, et al. Persistence of SARS-CoV-2-Specific IgG in children 6 months after infection, Australia. Emerg Infect Dis (2021) 27(8):2233–5. doi: 10.3201/eid2708.210965
11. Interiano C, Muze S, Turner B, Gonzalez M, Rogers B, Jerris R, et al. Dataset for longitudinal evaluation of the Abbott ARCHITECT SARS-CoV-2 IgM and IgG assays in a pediatric population divided by age. Data Brief (2021) 36:107110. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2021.107110
12. Ireland G, Jeffery-Smith A, Zambon M, Hoschler K, Harris R, Poh J, et al. Antibody persistence and neutralising activity in primary school students and staff: Prospective active surveillance, June to December 2020, England. EClinicalMedicine. (2021) 41:101150. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.101150
13. Mayanskiy N, Luchkina P, Fedorova N, Lebedin Y, Ponomareva N. Seroconversion and dynamics of the anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibody response related to a hospital COVID-19 outbreak among pediatric oncology patients. Leukemia. (2021) 35(6):1820–2. doi: 10.1038/s41375-021-01288-0
14. Breuer A, Raphael A, Stern H, Odeh M, Fiszlinski J, Algur N, et al. SARS-CoV-2 antibodies started to decline just four months after COVID-19 infection in a paediatric population. Acta Paediatr (2021) 110(11):3054–62. doi: 10.1111/apa.16031
15. Oygar PD, Ozsurekci Y, Gurlevik SL, Aykac K, Kukul MG, Cura Yayla BC, et al. Longitudinal follow-up of antibody responses in pediatric patients with COVID-19 up to 9 months after infection. Pediatr Infect Dis J (2021) 40(8):e294–9. doi: 10.1097/INF.0000000000003199
16. Garrido C, Hurst JH, Lorang CG, Aquino JN, Rodriguez J, Pfeiffer TS, et al. Asymptomatic or mild symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection elicits durable neutralizing antibody responses in children and adolescents. JCI Insight (2021) 6(17):e150909. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.150909
17. Messiah SE, DeSantis SM, Leon-Novelo LG, Talebi Y, Brito FA, Kohl HW, et al. Durability of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies from natural infection in children and adolescents. Pediatrics. (2022) 149(6):e2021055505. doi: 10.1542/peds.2021-055505
18. Han MS, Um J, Lee EJ, Kim KM, Chang SH, Lee H, et al. Antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 in children with COVID-19. J Pediatr Infect Dis Soc (2022) 11(6):267–73. doi: 10.1093/jpids/piac012
19. Tsang HW, Chua GT, To KKW, Wong JSC, Tu W, Kwok JSY, et al. Assessment of SARS-CoV-2 immunity in convalescent children and adolescents. Front Immunol (2021) 12:797919. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.797919
20. Dowell AC, Butler MS, Jinks E, Tut G, Lancaster T, Sylla P, et al. Children develop robust and sustained cross-reactive spike-specific immune responses to SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nat Immunol (2022) 23(1):40–9. doi: 10.1038/s41590-021-01089-8
21. Kinoshita H, Durkee-Shock J, Jensen-Wachspress M, Kankate VV, Lang H, Lazarski CA, et al. Robust antibody and T cell responses to SARS-CoV-2 in patients with antibody deficiency. J Clin Immunol (2021) 41(6):1146–53. doi: 10.1007/s10875-021-01046-y
22. Cotugno N, Ruggiero A, Bonfante F, Petrara MR, Zicari S, Pascucci GR, et al. Virological and immunological features of SARS-CoV-2-infected children who develop neutralizing antibodies. Cell Rep (2021) 34(11):108852. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.108852
23. Kaaijk P, Pimentel VO, Emmelot ME, Poelen MCM, Cevirgel A, Schepp RM, et al. Children and adults with mild COVID-19: Dynamics of the memory T cell response up to 10 months. Front Immunol (2022) 13:817876. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.817876
24. Cohen CA, Li APY, Hachim A, Hui DSC, Kwan MYW, Tsang OTY, et al. SARS-CoV-2 specific T cell responses are lower in children and increase with age and time after infection. Nat Commun (2021) 12(1):4678. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-24938-4
25. Frenck RW Jr, Klein NP, Kitchin N, Gurtman A, Absalon J, Lockhart S, et al. Safety, immunogenicity, and efficacy of the BNT162b2 covid-19 vaccine in adolescents. N Engl J Med (2021) 385(3):239–50. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2107456
26. Qin CX, Auerbach SR, Charnaya O, Danziger-Isakov LA, Ebel NH, Feldman AG, et al. Antibody response to 2-dose SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination in pediatric solid organ transplant recipients. Am J Transplant (2022) 22(2):669–72. doi: 10.1111/ajt.16841
27. Price AM, Olson SM, Newhams MM, Halasa NB, Boom JA, Sahni LC, et al. BNT162b2 protection against the omicron variant in children and adolescents. N Engl J Med (2022) 386(20):1899–909. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2202826
28. Powell AA, Kirsebom F, Stowe J, McOwat K, Saliba V, Ramsay ME, et al. Effectiveness of BNT162b2 against COVID-19 in adolescents. Lancet Infect Dis (2022) 22(5):581–3. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00177-3
29. Fowlkes AL, Yoon SK, Lutrick K, Gwynn L, Burns J, Grant L, et al. Effectiveness of 2-dose BNT162b2 (Pfizer BioNTech) mRNA vaccine in preventing SARS-CoV-2 infection among children aged 5-11 years and adolescents aged 12-15 years - PROTECT cohort, July 2021-February 2022. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep (2022) 71(11):422–8. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm7111e1
30. Burns MD, Boribong BP, Bartsch YC, Loiselle M, St Denis KJ, Sheehan ML, et al. Durability and cross-reactivity of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine in adolescent children. Vaccines (Basel) (2022) 10(4):492. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10040492
31. Chen LL, Chua GT, Lu L, Chan BP, Wong JS, Chow CC, et al. Omicron variant susceptibility to neutralizing antibodies induced in children by natural SARS-CoV-2 infection or COVID-19 vaccine. Emerg Microbes Infect (2022) 11(1):543–7. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2022.2035195
32. Haskin O, Ashkenazi-Hoffnung L, Ziv N, Borovitz Y, Dagan A, Levi S, et al. Serological response to the BNT162b2 COVID-19 mRNA vaccine in adolescent and young adult kidney transplant recipients. Transplantation. (2021) 105(11):e226–33. doi: 10.1097/TP.0000000000003922
33. Di Chiara C, Cantarutti A, Costenaro P, Donà D, Bonfante F, Cosma C, et al. Long-term immune response to SARS-CoV-2 infection among children and adults after mild infection. JAMA Netw Open (2022) 5(7):e2221616. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.21616
34. Khaitan A, Datta D, Bond C, Goings M, Co K, Odhiambo EO, et al. Level and duration of IgG and neutralizing antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 in children with symptomatic or asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection. Immunohorizons. (2022) 6(6):408–15. doi: 10.4049/immunohorizons.2200029
35. Available at: https://medicine.iu.edu/news/2022/04/discover-study-results (Accessed May 1st, 2022).
36. Tang J, Novak T, Hecker J, Grubbs G, Zahra FT, Bellusci L, et al. Cross-reactive immunity against the SARS-CoV-2 omicron variant is low in pediatric patients with prior COVID-19 or MIS-c. Nat Commun (2022) 13(1):2979. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-30649-1
37. Bartsch YC, St Denis KJ, Kaplonek P, Kang J, Lam EC, Burns MD, et al. SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination elicits robust antibody responses in children. Sci Transl Med (2022), eabn9237. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.abn9237
38. Kim J, Choe YJ, Lee H, Choi EH, Jang EJ, Kim RK, et al. Long-term effectiveness associated with the BNT162b2 vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 infection among adolescents in south Korea. JAMA Netw Open (2022) 5(8):e2227205. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.27205
39. Lin DY, Gu Y, Xu Y, Zeng D, Wheeler B, Young H, et al. Effects of vaccination and previous infection on omicron infections in children. N Engl J Med (2022) 387(12):1141–3. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2209371
40. Gonzalez-Dambrauskas S, Vasquez-Hoyos P, Camporesi A, Cantillano EM, Dallefeld S, Dominguez-Rojas J, et al. Critical coronavirus and kids epidemiological (CAKE) study investigators. Paediatric Crit COVID-19 mortality multinational prospective cohort Lancet Reg Health Am (2022) 12:100272. doi: 10.1016/j.lana.2022.100272
41. Buonsenso D, Mariani F, Pierri L, Morello R, Yock-Corrales A, Del Aguila O, et al. Association between coagulation profile and clinical outcome in children with SARS-CoV-2 infection or MIS-c: A multicenter cross-sectional study. Children (Basel) (2022) 9(2):279. doi: 10.3390/children9020279
42. Buonsenso D, Munblit D, Pazukhina E, Ricchiuto A, Sinatti D, Zona M, et al. Post-COVID condition in adults and children living in the same household in Italy: A prospective cohort study using the ISARIC global follow-up protocol. Front Pediatr (2022) 10:834875. doi: 10.3389/fped.2022.834875
43. Valentini P, Sodero G, Buonsenso D. The relationship between COVID-19 and innate immunity in children: A review. Children (Basel) (2021) 8(4):266. doi: 10.3390/children8040266
44. Brodin P. SARS-CoV-2 infections in children: Understanding diverse outcomes. Immunity. (2022) 55(2):201–9. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2022.01.014
45. Di Sante G, Buonsenso D, De Rose C, Tredicine M, Palucci I, De Maio F, et al. Immunopathology of SARS-CoV-2 infection: A focus on T regulatory and b cell responses in children compared with adults. Children (Basel) (2022) 9(5):681. doi: 10.3390/children9050681
46. Pierce CA, Sy S, Galen B, Goldstein DY, Orner E, Keller MJ, et al. Natural mucosal barriers and COVID-19 in children. JCI Insight (2021) 6(9):e148694. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.148694
47. Buonsenso D, Roland D, De Rose C, Vásquez-Hoyos P, Ramly B, Chakakala-Chaziya JN, et al. Schools closures during the COVID-19 pandemic: A catastrophic global situation. Pediatr Infect Dis J (2021) 40(4):e146–50. doi: 10.1097/INF.0000000000003052
48. Mensah AA, Campbell H, Stowe J, Seghezzo G, Simmons R, Lacy J, et al. Risk of SARS-CoV-2 reinfections in children: a prospective national surveillance study between January, 2020, and July, 2021, in England. Lancet Child Adolesc Health (2022) 6(6):384–92. doi: 10.1016/S2352-4642(22)00059-1
49. Patalon T, Saciuk Y, Ohayon Hadad H, Perez G, Peretz A, Ben-Tov A, et al. Naturally-acquired immunity dynamics against SARS-CoV-2 in children and adolescents. medRxiv (2022), 22276650.
50. Walter EB, Talaat KR, Sabharwal C, Gurtman A, Lockhart S, Paulsen GC, et al. Evaluation of the BNT162b2 covid-19 vaccine in children 5 to 11 years of age. N Engl J Med (2022) 386(1):35–46. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2116298
51. Zambrano LD, Newhams MM, Olson SM, Halasa NB, Price AM, Boom JA, et al. Effectiveness of BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech) mRNA vaccination against multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children among persons aged 12-18 years - united states, July-December 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep (2022) 71(2):52–8. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm7102e1
52. Olson SM, Newhams MM, Halasa NB, Price AM, Boom JA, Sahni LC, et al. Effectiveness of pfizer-BioNTech mRNA vaccination against COVID-19 hospitalization among persons aged 12-18 years - united states, June-September 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep (2021) 70(42):1483–8. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm7042e1
53. Malato J, Ribeiro RM, Leite PP, Casaca P, Fernandes E, Antunes C, et al. BA.5 infection in individuals exposed to prior SARS-CoV-2 variants. medRxiv (2022), 22277602.
54. Altarawneh HN, Chemaitelly H, Ayoub HH, Hasan MR, Coyle P, Yassine HM, et al. Protection of SARS-CoV-2 natural infection against reinfection with the omicron BA.4 or BA.5 subvariants. medRxiv (2022), 22277448.
55. Hansen CH, Friis NU, Bager P, Stegger M, Fonager J, Fomsgaard A, et al. Risk of reinfection, vaccine protection, and severity of infection with the BA.5 omicron subvariant: A Danish nation-wide population-based study in Denmark. Lancet Infect Dis. (2022) S1473-3099(22)00595–3. doi: 10.2139/ssrn.4165630.
56. Malato J, Ribeiro RM, Leite PP, Casaco P, Fernandes E, Antunes C, et al. Risk of BA.5 infection among persons exposed to previous SARS-CoV-2 variants. N Engl J Med (2022) 387(10):953–4. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2209479
57. Dowell AC, Lancaster T, Bruton R, Ireland G, Bentley C, Sylla P. Primary omicron infection elicits weak antibody response but robust cellular immunity in children. bioRxiv (2022), 501570. doi: 10.1101/2022.07.26.501570
58. Cotugno N, Franzese E, Angelino G, Amodio D, Romeo EF, Rea F, et al. Evaluation of safety and immunogenicity of BNT162B2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine in IBD pediatric population with distinct immune suppressive regimens. Vaccines (Basel) (2022) 10(7):1109. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10071109
59. Morrocchi E, Pighi C, Pascucci GR, Cotugno N, Medri C, Amodio D, et al. Perinatally human immunodeficiency virus-infected adolescents and young adults demonstrate distinct BNT162b2 messenger RNA coronavirus disease 2019 vaccine immunogenicity. Clin Infect Dis (2022) 75(Supplement_1):S51–60. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciac408
60. Cotugno N, Pighi C, Morrocchi E, Ruggiero A, Amodio D, Medri C, et al. BNT162B2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine in heart and lung transplanted young adults: Is an alternative SARS-CoV-2 immune response surveillance needed? Transplantation (2022) 106(2):e158–60. doi: 10.1097/TP.0000000000003999
61. Zambrano LD, Newhams MM, Olson SM, Halasa NB, Price AM, Boom JA, et al. Overcoming COVID-19 investigators. effectiveness of BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech) mRNA vaccination against multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children among persons aged 12-18 years - united states, July-December 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep (2022) 71(2):52–8. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm7102e1
62. Levy M, Recher M, Hubert H, Javouhey E, Fléchelles O, Leteurtre S, et al. Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children by COVID-19 vaccination status of adolescents in France. JAMA. (2022) 327(3):281–3. doi: 10.1001/jama.2021.23262
63. Katz SE, Edwards K. Protecting children against omicron. JAMA. (2022) 327(22):2195–7. doi: 10.1001/jama.2022.7315
Keywords: COVID-19, SARS-CoV-2, vaccine, immunity, children
Citation: Buonsenso D, Cusenza F, Passadore L, Bonanno F, De Guido C and Esposito S (2023) Duration of immunity to SARS-CoV-2 in children after natural infection or vaccination in the omicron and pre-omicron era: A systematic review of clinical and immunological studies. Front. Immunol. 13:1024924. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1024924
Received: 22 August 2022; Accepted: 12 December 2022;
Published: 11 January 2023.
Edited by:
Thierry Defrance, Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale (INSERM), FranceReviewed by:
Mark Daniel Hicar, University at Buffalo, United StatesPaul Austin Moss, University of Birmingham, United Kingdom
Copyright © 2023 Buonsenso, Cusenza, Passadore, Bonanno, De Guido and Esposito. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Danilo Buonsenso, ZGFuaWxvYnVvbnNlbnNvQGdtYWlsLmNvbQ==
 Danilo Buonsenso
Danilo Buonsenso Francesca Cusenza3
Francesca Cusenza3