- Division of Hematology, Oncology, Stem Cell Transplantation and Regenerative Medicine, Department of Pediatrics, Stanford University, School of Medicine, Stanford, CA, United States
Comprising only 1-10% of the circulating T cell population, γδT cells play a pivotal role in cancer immunotherapy due to their unique amalgamation of innate and adaptive immune features. These cells can secrete cytokines, including interferon-γ (IFN-γ) and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), and can directly eliminate tumor cells through mechanisms like Fas/FasL and antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC). Unlike conventional αβT cells, γδT cells can target a wide variety of cancer cells independently of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) presentation and function as antigen-presenting cells (APCs). Their ability of recognizing antigens in a non-MHC restricted manner makes them an ideal candidate for allogeneic immunotherapy. Additionally, γδT cells exhibit specific tissue tropism, and rapid responsiveness upon reaching cellular targets, indicating a high level of cellular precision and adaptability. Despite these capabilities, the therapeutic potential of γδT cells has been hindered by some limitations, including their restricted abundance, unsatisfactory expansion, limited persistence, and complex biology and plasticity. To address these issues, gene-engineering strategies like the use of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T therapy, T cell receptor (TCR) gene transfer, and the combination with γδT cell engagers are being explored. This review will outline the progress in various engineering strategies, discuss their implications and challenges that lie ahead, and the future directions for engineered γδT cells in both monotherapy and combination immunotherapy.
1 Introduction
Immunotherapy has revolutionized cancer treatment, effectively integrating with established medical practices such as surgery and chemotherapy (1, 2). This approach boosts the immune system’s capability to target and eliminate malignant cells, thereby increasing antitumor efficacy and minimizing off-target effects (3). Within the realm of immunotherapy, various strategies have been developed, including the use of immune cells, checkpoint inhibitors, and cytokines. Notably, T cell-based therapies, particularly Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) T cell therapy, have demonstrated significant success against blood cancers (4). In parallel, therapies utilizing NK cells, macrophages, and B cells are emerging as novel treatments for solid tumors and other malignancies (5–7).
Immune cells play crucial roles in the body’s defense mechanisms, including T cells, which are central to cell-mediated immune responses; B cells, which produce antibodies and mediate humoral immunity; and NK cells, which can induce apoptosis in infected or malignant cells as part of the innate immune response (3). Among these immune cells, γδT cells stand out for their unique role in bridging innate and adaptive immunity (8–10). They target and kill cancer cells without the restriction of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules, thus having a broader recognition on cancer cells, including those deficient in MHC class I. γδT cells are adept at secreting cytokines like interferon-γ (IFN-γ) and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), and they can directly eliminate tumor cells through mechanisms such as Fas/FasL and antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) (11). Their ability to migrate to peripheral tissues and respond rapidly to target cells (12), coupled with their lack of involvement in graft-versus-host disease (GvHD) (13, 14), makes them ideal candidates for off-the-shelf cell therapy solutions.
Furthermore, γδT cells are crucial in orchestrating anti-tumor immune responses. They can act as professional antigen-presenting cells (APCs) or influence other APCs like dendritic cells, thereby enhancing the activation of αβT cells and the overall immune response against tumors (15, 16). Theproduction of cytokines, including IL-17 and IL-22, by γδT cells plays a vital role in shaping the tumor microenvironment (TME), thereby influencing tumor growth in various contexts (16–23). This dual role highlights the complexity and importance of γδT cells in tumor immunology and fuels ongoing research into leveraging their therapeutic potential in novel cancer immunotherapies, such as adoptive cell therapy (ACT) (9, 24–27).
Despite their significant therapeutic promise, the clinical application of γδT cells faces challenges. As a minor subset of T cells, they often struggle with in vivo survival and proliferation (28), limited persistence, and potential functional suppression upon infiltrating the complex TME (29, 30). To overcome these obstacles, recent advancements in gene-engineering technologies are paving the way for optimizing the therapeutic potential of γδT cells in cancer treatment (8, 9, 15, 28, 31, 32). By genetically modifying these cells to express CARs or enhancing their native T cell receptors (TCRs), their specificity and cytotoxicity against tumor cells can be significantly bolstered. The use of genetic editing tools like CRISPR/Cas9 to knock out inhibitory receptors or to insert cytokine genes further enhances their proliferative and cytotoxic capacities. Concurrently, combination therapies are being explored to enhance the anti-tumor activity of γδT cells, including the use of bispecific antibodies, checkpoint blockade, and cytokine co-administration.
This review aims to deliver a comprehensive overview of cutting-edge approaches to augment γδT cell immunotherapy. It delves into the biological underpinnings and inherent advantages of γδT cells pertinent to their role in immunotherapeutic applications, as well as scrutinizes the forefront of gene-engineering methods being crafted to surmount existing barriers within γδT cell treatment modalities. Additionally, the synergy of gene-modified γδT cells with other treatment modalities is explored, informed by recent clinical research findings. These studies will shed light on the prospective trajectory of γδT cell immunotherapy, underscoring its potential to significantly enhance treatment outcomes for cancer patients.
2 Properties and functions of γδT cells
2.1 γδT cells ontogeny and γδTCRs diversity
γδT cells are the first T cell lineage to develop in the thymus and can be observed in humans as early as 12.5 weeks of gestational age. However, once generated, these cells will expand and mature extrathymically, and their gene repertoire changes in response to age (33). γδT cells derive their name from their TCRs, which are made up of gamma and delta chains. Like αβT cells, γδT cells undergo somatic V(D)J rearrangement, a process that generates diverse TCRs to respond to a wide range of antigens (34). However, in contrast to αβTCRs, γδTCRs allow cross-reactivity with multiple ligands and each combination is associated with different functional avidities (35). Despite the fact that V(D)J rearrangement of γδT cells generates less diversity than αβT cells, TCR δ chains have a higher potential of diversity at the complementarity-determining region 3 (CDR3) junction and can provide information on a person’s unique history of infection (33, 36, 37).
2.2 Tumor targeting mechanisms
γδT cells target real and perceived immunological insults through the production and release of soluble factors. One example of this is when γδT cells recognize pathogen specific antibodies and stress-induced antigens. In response, γδT cells will produce Th1 cytokines including IFN-γ and TNF-α. Subsequently, γδT cells also release cytotoxic granules containing perforin and granzyme, further promoting pathogen degradation (38). Additionally, there is evidence in literature suggesting that Vγ9Vδ2 cells–a subset of γδT cells (discussed in the next section) can act as sensors of a dysregulated isoprenoid metabolism that target specifically cancer cells (39). Moreover, several recent studies have indicated that different subsets of γδT cells may have remarkably different functions in targeting tumor cells (40–43). Therefore, it is important to understand the structure and subsets of γδT cells, which we describe in the next section.
2.3 γδT cell subsets
This section will focus on two main subsets of γδT cells: Vδ1 and Vγ9Vδ2.
2.3.1 Vδ1 γδT cells
Vδ1 T cells are primarily localized in various human tissues, particularly abundant in the intestine, skin, spleen, and liver (44) (Figure 1). Their properties, particularly their inherent tissue-specific adaptations, have attracted growing interest in the context of cancer immunosurveillance and immunotherapy applications. Phenotypically, these tissue-resident Vδ1 T cells express homing chemokine receptors (e.g., CXCR3, CXCR6) as well as tissue-retention markers (e.g., CD69, CD103, and CD49a) (45–47). Intratumoral Vδ1 T cells have been detected in several solid tumors, exhibiting features of tissue-resident memory T cells (TRM) (46, 47). There are also peripheral Vδ1 cells that preferentially express CCR5, CCR6, and CXCR3 (48).
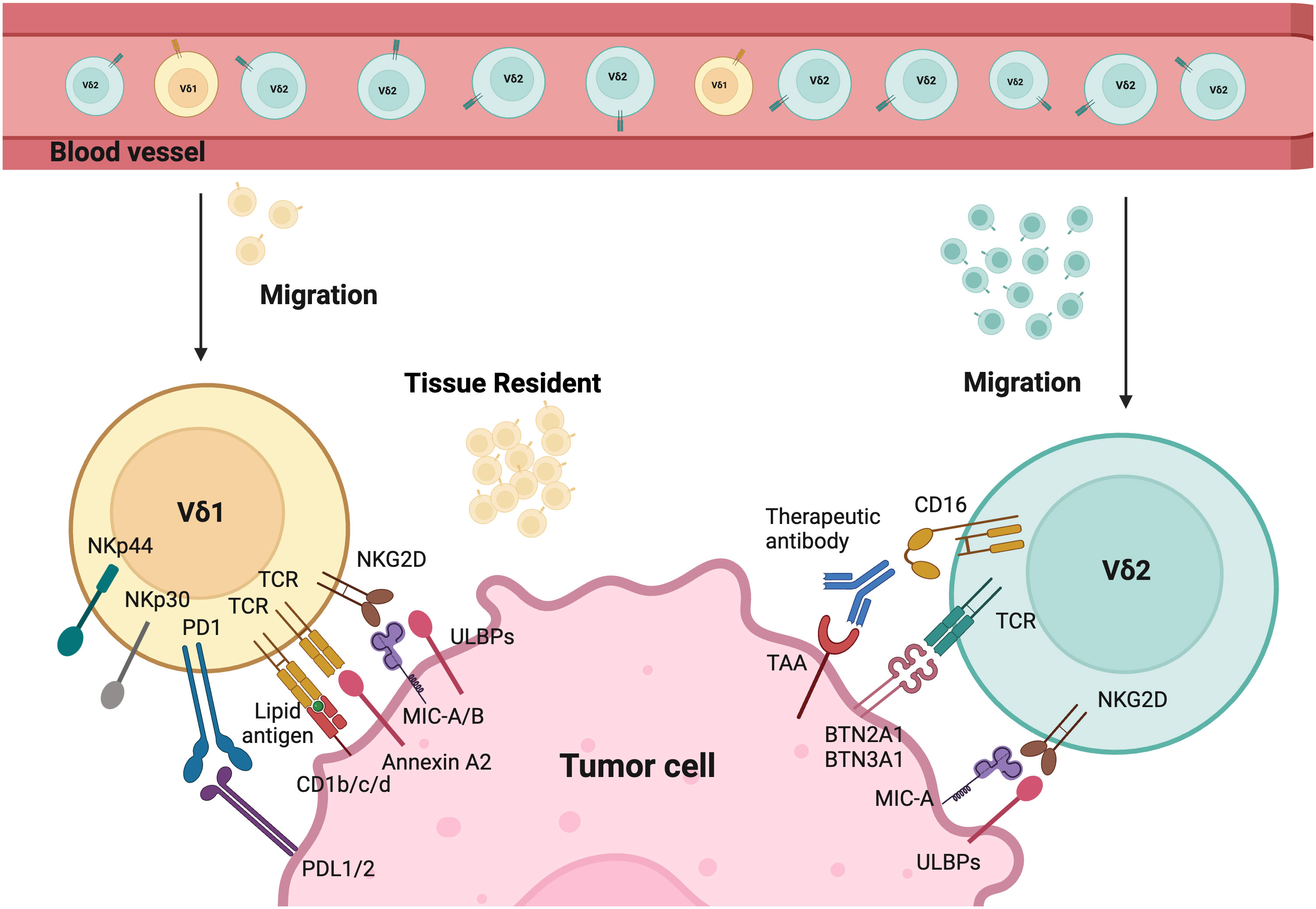
Figure 1 Tumor targeting mechanisms of Vδ1 and Vδ2. Different γδT cells activation modes by tumor cells. The tissue resident Vδ1 T cells recognize cancer cells via their specific Vδ1 T cell receptors (TCRs), which bind Annexin A2 and lipid antigens presented by CD1. Besides, Vδ1 T cells also use NKG2D and natural cytotoxicity receptors (NCRs) such as NKp30, NKp44, and NKp46 for tumor cell recognition. Vδ2 T cells are predominant in the peripheral blood and can migrate into tumor tissues. Their specific Vδ2 TCRs recognize BTN3A1 and BTN2A1 after the isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP) accumulation. CD16 expressed by Vδ2 T cells can bind therapeutic antibodies to trigger Vδ2-mediated antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC). In addition, both Vδ1 and Vδ2 T cells express natural killer receptors (NKRs), which recognize tumor cells by binding to MHC class I chain-related protein A and B (MICA/B), and UL16-binding proteins (ULBPs). Created with BioRender.com.
Additionally, Vδ1 T cells have private TCR repertoires and significant TCR diversity that mainly originate from TRD repertoires (49). They also manifest features of adaptive immunity, including long-lasting functional memory in γδT cells and adaptive clonal expansion, particularly in response to viral infections (49–51). Studies demonstrate that Vδ1 T cells recognize tumor antigens or cell stress signals through γδTCR and various activating receptors shared with NK cells. These include NK group 2 member D (NKG2D), natural cytotoxicity receptors (NCR, such as NKp30, NKp44, NKp46), and coactivating/adhesion DNAX-activating molecule (DNAM-1) (52–56). Their ligands are frequently expressed on stressed neoplastic cells, for instance, MHC class I chain-related protein A and B (MICA/B), UL16-binding proteins (ULBP) 1-4 are common ligands for NKG2D. Vδ1+ T cells can be directly activated through NKG2D upon the expression of its ligand (e.g., MICA) on tumors, without the need for overt TCR stimulation as seen in αβT cells (55, 57). Moreover, the expression of NCRs on Vδ1 T cells is correlated with increased granzyme B and enhanced cytotoxicity against lymphoid leukemia cells (55). Evidence in the literature suggests that Vδ1 T cells can recognize stress-induced antigens including non-classical MHC class I-like molecules, such as CD1 family (including CD1c, CD1d), MICA/B, ULBP molecules (including ULBP3), and annexin A2 (52–54, 58–62). Interestingly, Vδ1+ T cells are less susceptible to activation-induced cell death (AICD) compared to Vδ2+ T cells. Despite variations in their antigen recognition, both Vδ2 and Vδ1 T cells share similar cytotoxic mechanisms via the perforin/granzyme-B mediated secretory pathway and death receptor pathways such as TRAIL/TRAIL-R, Fas/FasL (38).
Recognition of CD1d is dependent on the presence of lipid and glycolipid on foreign antigens, suggesting that Vδ1 T cells could recognize these antigens in a lipid-dependent manner (63). Bai et al.’s study directly demonstrates this principle of antigen presentation of MHC and lipid recognition by Vδ1 T cells (64). However, the exact mechanism of CD1d recognition in Vδ1 T cells is still unclear and remains an area of continued investigation.
Furthermore, MICA, a stress-induced antigen, triggers activation and expansion of Vδ1 subset via NKG2D when it is expressed on the surface of tumor cells (52–54). These cells have also been shown to recognize ULBP3, a “kill me” signal, expressed on leukemic B cells, suggesting an additional mechanism through which these cells can participate in anti-tumor immune regulation (60).
With advances in innovative isolation techniques and deepening comprehension of Vδ1 T cells, these cells hold high promise as a potential candidate for cancer immunotherapy, particularly as tissue-associated or tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes. Their manipulation using well-designed cell engagers or immune checkpoint inhibitors in situ represents an accessible and cost-effective approach. In the future, the use of single cell sequencing/proteomics techniques will be essential to dissect the heterogeneity and functional plasticity of Vδ1 T cells shaped by the TME, thereby aiding their clinical implementation.
2.3.2 Vγ9Vδ2 γδT cells
Vγ9Vδ2 (Vδ2) T cells are among the most studied subsets of γδT cells, partially because these cells represent the most abundant subset in peripheral blood (Figure 1). Vγ9Vδ2 cells are generally considered as the first line of defense, forming an essential part of the innate immunity. All Vγ9Vδ2 T cells consist of a public Vγ9 chain and private Vδ2 chain. However, Vδ2 T cells can be further divided into two subclasses (Vγ9+Vδ2+ and Vγ9-Vδ2+) that exhibit distinct properties. Vγ9+Vδ2+ T cells exhibit innate characteristics, while Vγ9-Vδ2+ T cells show adaptive features and undergo pathogen-driven differentiation similar to conventional CD8+ T cells (44, 65, 66).
Similarly, the recognition of Vδ2 cells is mediated by γδTCR or NK cell-activating receptors such as NKG2D and DNAM1. These cells are unique due to their semi-invariant property that allows recognition of specific antigens. Vδ2+ TCRs are capable to recognize phosphoantigens (P-Ag), non-peptide antigens that accumulated in tumor cells due to their dysregulated mevalonate pathway (67). The activation of γδ T cells is intricately linked to the recognition of P-Ag. This process heavily involves the proteins butyrophilin 2A1 (BTN2A1) and butyrophilin 3A1 (BTN3A1). BTN2A1 binds to Vγ9+ γδTCRs. BTN3A1 acts as a critical mediator by presenting P-Ag to γδ T cells through its intracellular B30.2 domain (68). This interaction is pivotal for initiating the downstream signaling pathways that lead to γδ T cell activation and immune responses. Furthermore, Vγ9Vδ2 T cells have distinct patterns of development in fetus and adults. Fetal Vγ9Vδ2T cells are generated in the fetal thymus, while adult Vγ9Vδ2 T cells are developed after birth in response to environmental stimuli and expanded polyclonally by microbial P-Ag exposure (37, 69). The CD16+ Vδ2 T cells can also mediate ADCC upon binding to tumor-specific antibodies, which is absent in Vδ1 T cells (70). Additionally, these cells can function like professional APCs by phagocytosing and processing target antigens, then presenting them with MHC molecules. This process, in turn, induces CD4+ and CD8+ responses in αβT cells (16, 71–73).
Recent studies suggest both subclasses of Vγ9Vδ2 T cells play key roles in the immune defense against pathogens and tumor cells. The number of Vγ9Vδ2 T cells increases dramatically during some infections and these cells display potent cytotoxic activity. During stimulation with non-peptidic antigens, Vγ9Vδ2 T cells can be activated via a dual mechanism involving the recognition of FcγRIIIa (CD16a) following the TCR-CD3 complex, which are cell surface antigens for T lymphocytes and NK cells (74). This activation schema belies a keystone role for Vγ9Vδ2 T cells in the defense of pathological infection as well as tumorigenesis.
3 Sources of γδT cells and their expansion strategies
3.1 Sources of γδT cells
The successful clinical application of γδT cell-based immunotherapy must address several challenges, starting with the selection of appropriate sources (Figure 2). Inconsistent effects of autologous γδT cells have prompted investigators to design standardized cell products. Because HLA-matching is not required, fully allogeneic mismatched or haplo-identical γδT cells sourced from healthy donors have emerged as an appealing approach with a commendable safety profile (75, 76). A thorough investigation into the donor’s infection history can also benefit patient outcomes when used as a screening criterion. For instance, the reactivation of cytomegalovirus (CMV) in patients receiving HSCT can potentially induce the expansion of Vδ2neg γδT cell clones, which exhibit dual reactivity to CMV and acute myeloid leukemia (AML) (77–79). Another challenge lies in determining which γδT cell subset will be more effective for a specific tumor considering their differing characteristics, particularly their chemotaxis ability and tumor cytotoxicity. Up to now, the main sources of γδT cells include cord blood, peripheral blood, skin, and inducible pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs).
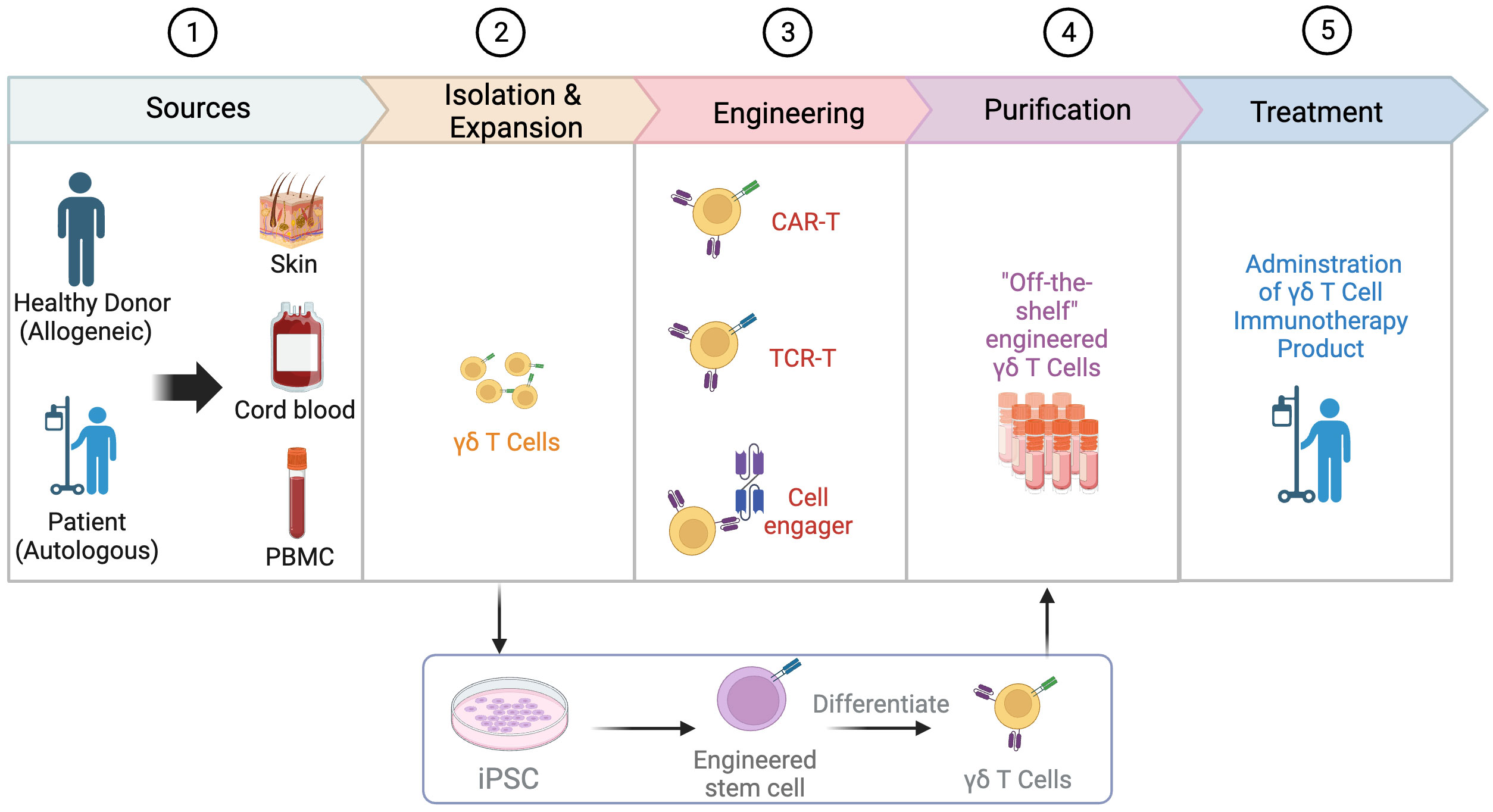
Figure 2 Process of engineering γδT cells. The process of engineering γδT cells involves several key steps. Common sources of γδT cells include the skin, cord blood, and peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs), with the allogeneic pathway involving isolation from a healthy donor and the autologous pathway involving isolation from the patient’s own cells. After isolation, γδT cells are expanded and engineered through various strategies such as the use of chimeric antigen receptors (CARs), T cell receptor (TCR) transfer, and cell engager. Engineered γδT cells can also be derived from induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs). In the next step, γδT cells go through purification to develop “off-the-shelf” engineered γδT cells. Finally, the engineered γδT cell product is administered to patients as a form of immunotherapy. Created with BioRender.com.
The developmental trajectory of γδT cells reveals that Vδ1+ cells constitute the predominant population (approximately 50%) of γδT cells in cord blood at birth, while Vδ2+ cells typically represent 25% (80). Over time, Vγ9Vδ2 T cells emerge as the predominant subset (over 75%) of the γδT cell population in peripheral blood by adulthood, with less than 10% being Vδ1+ (80). Therefore, cord blood has been explored for its predominant expansion of Vδ1+ cells, or occasional viable expansion of Vδ2+ cells (81–83). However, there are several challenges associated with the in vitro expansion of γδT cells from cord blood, including a low number of γδT cells (less than 1% of cord blood lymphocytes), phenotypically and functionally immature γδT cells, and a poor response to IL-2 and phosphoantigen stimulation (80). In contrast, γδT cells isolated from peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) are predominantly Vγ9Vδ2 (84). Due to their relative convenience and availability, PBMCs provide easy and stable access for expanding Vγ9Vδ2 T cells and viable Vδ1+ cells such as Delta One T (DOT) cells. Additionally, owing to natural tissue tropism of Vδ1+ cells, human tissues such as skin also provide an alternative source of Vδ1+ cells through enzymatic digestion or other methods (85, 86). Despite the roles of skin γδT cells in the cutaneous malignances such as melanoma, complex skin γδT cell subsets necessitate a thorough investigation for therapeutic strategies (87).
In addition to γδT cells derived from donors, these cells can also be generated from iPSCs (88, 89). Two companies, Century Therapeutics and CytoMed Therapeutics, have developed platforms that enrich γδT cells from healthy donor leukapheresis and then reprogram them into T cell-derived iPSCs (TiPSCs). TiPSCs are engineered with CAR expression, followed by directed differentiation into γδ CAR-T cells (Figure 2) (90). During this process, the genome characterization of a single CAR-TiPSC clone enables the production of a highly uniform clonal γδ CAR-T cell bank (> 95% CAR expression) and minimal DNA mutation caused by engineering (90, 91). This off-the-shelf platform provides an appealing source of γδT cells with several benefits: overcoming quantitative limitations of γδT, reducing the wait time for ex vivo expansion of γδT cells, and not relying on the ex vivo expansion efficiency of PBMC-derived γδT cells (92). Importantly, TiPSC-derived γδT cells retain cytotoxicity to solid and blood tumor through both γδTCR and NKG2D (92). However, this complex manufacturing process is time-consuming and needs more evaluation on potential risks.
Overall, most of the research is adopting PBMC and cord blood as the primary source of γδT cells. In contrast, investigations into skin-derived and iPSC-derived γδT cells are still in the preclinical stages. Our current understanding of the migration and colonization of γδT cells in peripheral tissues primarily relies on research conducted in mice. Further studies involving humans will significantly advance our comprehension of tissue-specific γδT cells, potentially expanding the applications of Vδ1+ cells in immunotherapy.
3.2 Strategies to expand γδT cells: prerequisite for therapeutic infusion
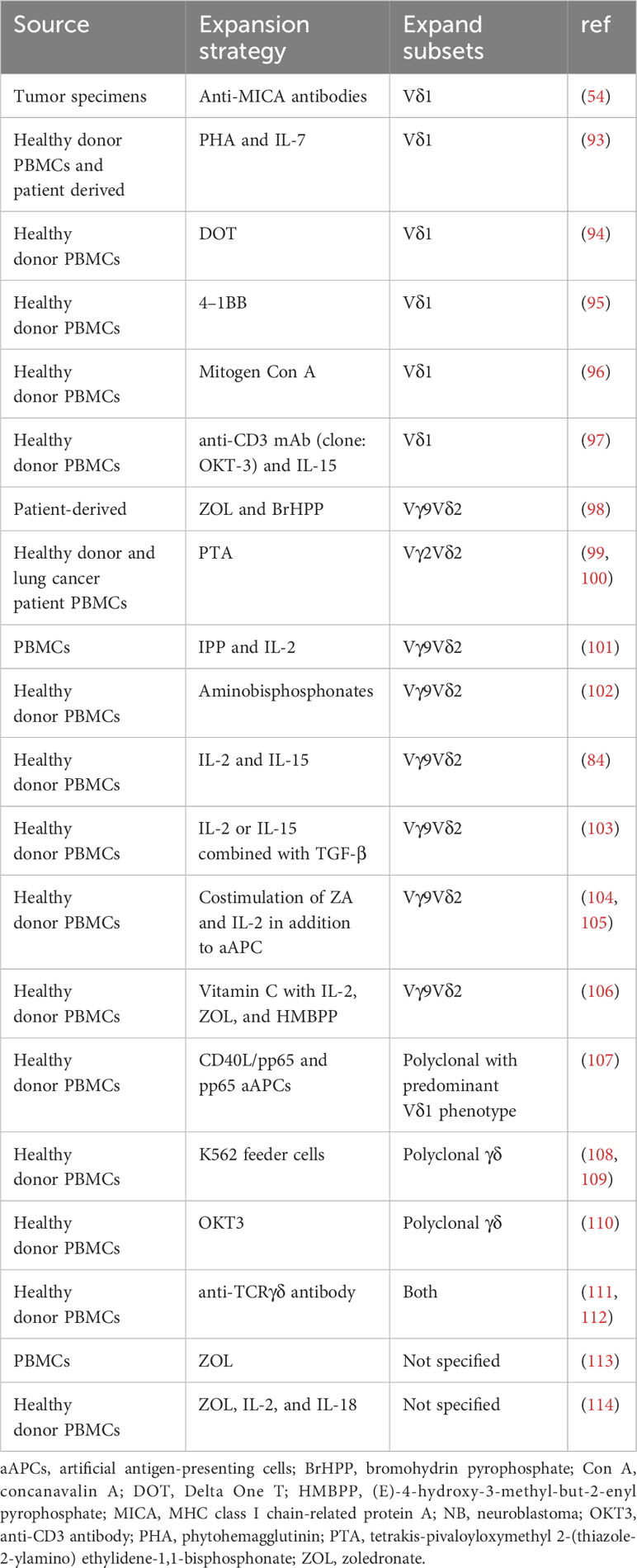
The clinical-scale manufacturing of γδT cells requires robust and highly reproducible expansion methods that meet good manufacturing practice (GMP) standards. Current approaches mainly include cytokine only, synthetic p-Ag and bisphosphonate (BP) stimulation, antibody-based expansion, and feeder cell-based strategies as summarized in Table 1. Undoubtably, cytokine combinations strategies simplify the manufacturing process but often produce insufficient expansion.
p-Ag or BPs have been recognized as the most established approaches to selectively expand Vδ2+ γδT cells (9). Zoledronic acid (ZOL), a BP, has been widely used to numerically expand Vγ9Vδ2 T cells in vivo and ex vivo. ZOL can be used alone or in combination with IL-2 to achieve these effects (115). ZOL (5 uM) and IL-2 (1000IU/ml) administration over 14 days has been reported to initiate an over 4000-fold proliferation and expansion of γδT cells (mainly Vγ9Vδ2) from PBMCs of both healthy donors and patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (116). However, the expansion folds and purities of γδT cells vary in different published results.
Current protocols for expanding Vδ1+ T cells in vitro primarily rely on mitogenic plant lectins such as phytohemagglutinin (PHA) or concanavalin-A (ConA), which induce AICD in Vγ9Vδ2 T cells (93, 117). To transition from the laboratory to the clinic, more efforts have been made to avoid potentially hazardous components. Almeida et al. first developed a clinical-grade two-step method through combination of cytokines (IL-1β, IL-4, IL-21, and IFN-γ) and anti-CD3 mAb (clone: OKT-3) to achieve the expansion of Vδ1+ T cells (94). This method enables large-scale expansion (up to 2,000-fold) of Vδ1+ T cells known as DOT cells (94). GDX012, based on DOT cells, has been granted orphan drug designation by FDA for AML treatment and is currently undergoing evaluation in a phase I trial (NCT05001451). Recently, Ferry et al. also apply only anti-CD3 mAb and IL-15 to stimulate αβTCR- and CD56-depleted PBMC, resulting in robust Vδ1 cell expansion (97).
The feeder cell-based method utilizing artificial antigen-presenting cells (aAPCs) has been explored to provide γδT cells with a sustained activation and costimulation signal. K562, a human chronic erythroleukemic cell line lacking MHC expression, is primarily used as aAPCs. These cells are engineered with costimulatory molecules (like CD80, CD86, CD137) and antigens (e.g., CMV antigen-pp65), allowing for the targeted expansion of specific γδT cell subsets (108, 118). Deniger et al. first activated and propagated polyclonal γδT cells utilizing K562-based aAPCs as irradiated feeders (108, 118). This method requires the additional labor-intensive manufacturing process of culturing feeder cells, yet it mitigates the AICD effects in γδT cells associated with prolonged antigen exposure. Additionally, methods of removing all residual feeder cells before infusion remains a hurdle to clinical implementation of this approach. To address this, several solutions have been proposed, such as gamma-irradiation of aAPCs and the transduction of aAPCs with an inducible suicide gene (107). The ex vivo aAPC expanded donor-derived γδT cells are under evaluation of safety and cell dose in a phase I/II trial (NCT05015426) in patients with high-risk acute leukemia (104).
In the future, efforts should focus more on eliminating the use of xenogeneic serum and feeder cells and integrating GMP/pharmaceutical-grade reagents into the expansion process. An example of such a method is the protocol proposed by Bold et al. in a recently published article, which has shown better outcomes in terms of expansion and purity (119). Further efforts can be directed towards enhancing the rate of γδT cell expansion, optimizing the procedure, and lowering manufacturing costs. Besides assessing quantity, evaluating the quality of expanded γδT cells–such as memory and exhaustion phenotypes, is crucial for maximizing therapeutic efficacy and requires further investigations.
4 Engineering strategies: the advances and advantages of γδT cell-based immunotherapy
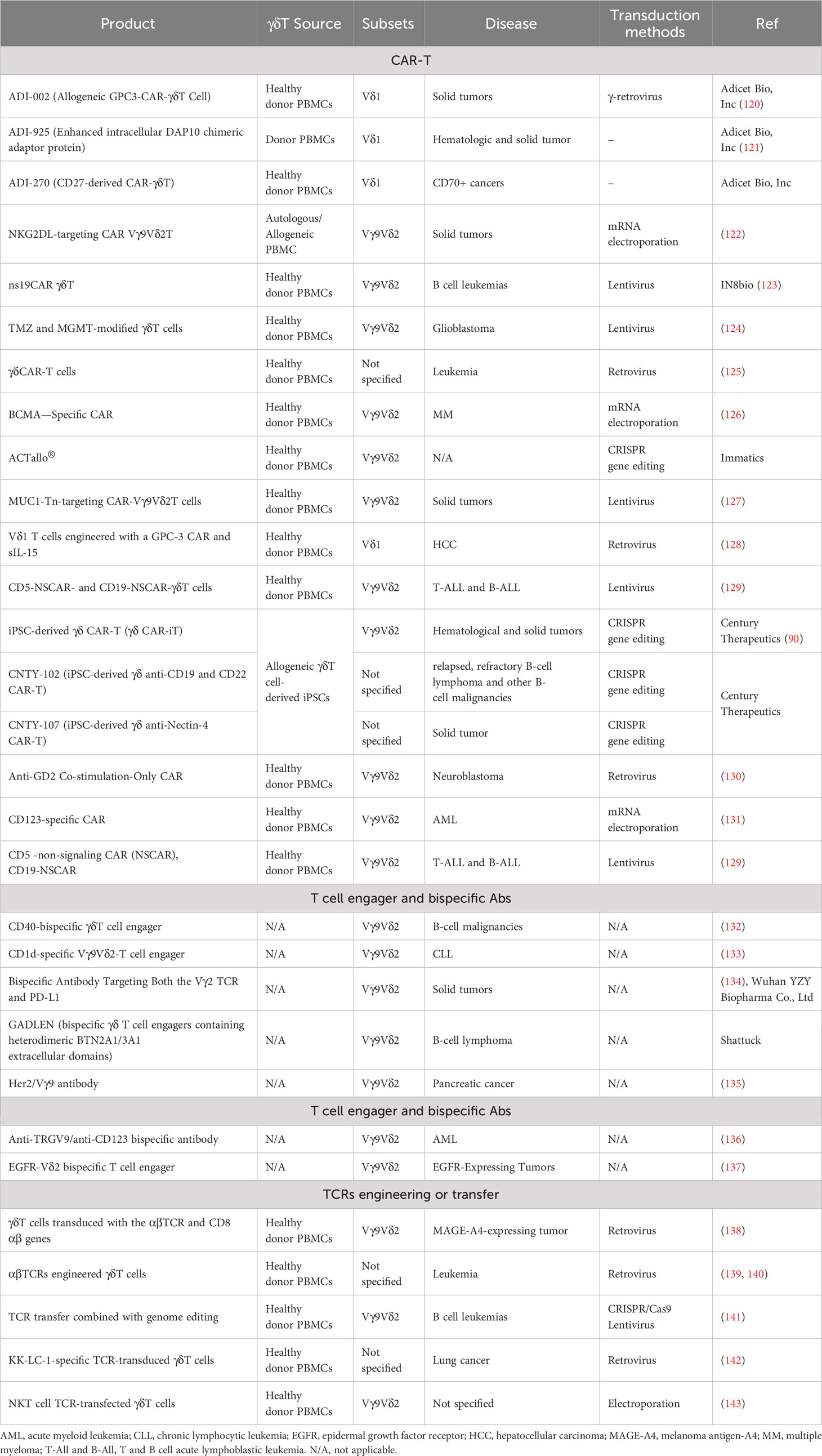
To date, the pharmaceutical industry has explored three primary categories of strategies for γδT cell engineering, which encompass: (1) CAR-T therapy; (2) antibody-based approaches, such as cell engagers or bispecific antibodies; and (3) engineering or transfer of TCRs. CAR-T therapy remains the predominant approach, while antibody-based strategies are gaining prominence due to several advantages. Research is ongoing to investigate combination of therapies aimed at maximizing the unique capabilities of γδT cells. Lists of engineering strategies and ongoing clinical trials are presented in Tables 2, 3, respectively.
4.1 γδ CAR-T cell therapy: extend from but exceed the conventional αβ CAR-T therapy
CAR-T therapy, with its potential for HLA-independent tumor antigen recognition, has found its place as a key player in cancer immunotherapy. Traditionally, αβT cells have been the main candidates for CAR development (150). However, despite their effectiveness, these cells present several limitations. They are susceptible to GvHD, can cause severe and potentially lethal toxicities, contribute to the development of cytokine release syndrome (CRS), and pose issues related to antigen escape (150). These challenges have spurred an interest in alternative solutions, with γδT cells showing potential to offset these limitations.
Given the wealth of limitations associated with αβT cells, γδT cells are garnering interest as an alternative for CAR-T therapy. These cells do not instigate GvHD, curb antigen escape resulting in decreased relapse rates, and retain beneficial traits such as a less differentiated phenotype with enhanced antigen presentation capacity (125, 151). With these advantages, γδ CAR-T cells may have the potential to overcome the obstacles that have historically troubled conventional αβ CAR-T therapy.
The primary goal of CAR design is producing extracellular domains capable of targeting unique tumor cell antigens while sparing healthy tissues (150, 152). Owing to the deficit of tumor-specific antigens, lineage-specific antigens have been a key focus in CAR T cell development. Under investigation are promising candidates like CD19 (153, 154), GD2 (130, 155), GPC-3 (128), CD123 (131, 156), CD5, CEA, CD20 (10), B7H3 B7H3 (157), and PSCA (151) (Table 2). While CD19-targeting CAR-T products have earned FDA approval for treating B-cell lymphoma and leukemia, they carry risks, like CRS, neurotoxicity, and B-cell aplasia, primarily due to on-target off-tumor toxicities (152, 153). Interestingly, γδ anti-CD19 CAR-T cells have been reported to produce fewer inflammatory cytokines compared to their αβ counterparts, suggesting a potential decrease in cytokine-mediated side effects (90).
However, the optimization of CAR for highly specific antigen recognition remains vital. Recent studies have investigated the incorporation of ligands like NKG2DL and inhibitory receptor programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1) into CAR constructs to improve safety or efficacy (158). Some attempts have even added T cell antigen coupling (TAC) components to γδT cells, thereby redirecting them to target tumors with reduced off-tumor toxicity compared to conventional CAR-T cells (159, 160) (Figure 3D). Adicet Bio is working on CAR designs that target tumor intracellular antigens using their TCR-Like monoclonal antibodies (TCRLs) technology (91).
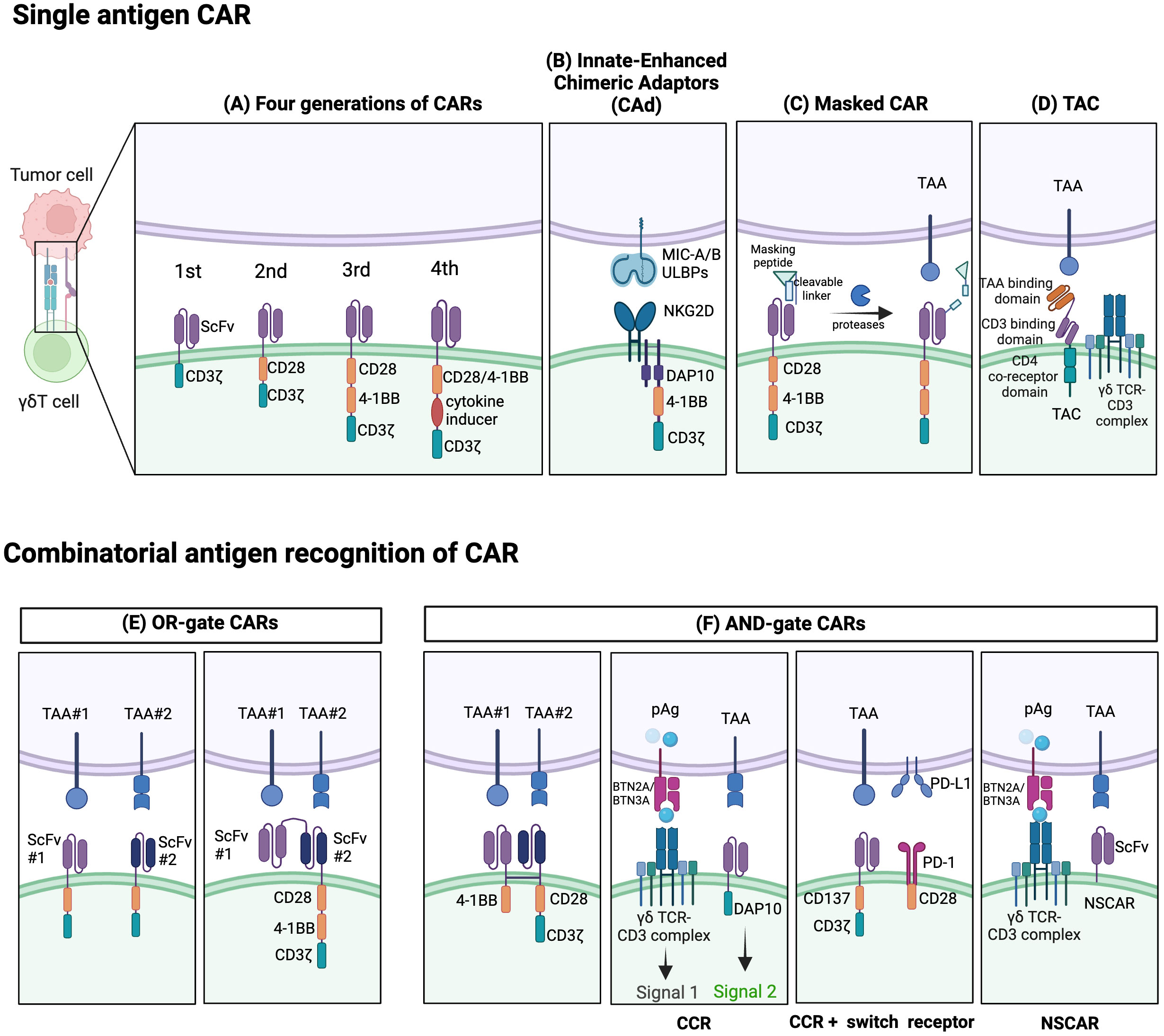
Figure 3 Established strategies for CAR- γδT cells. Single-antigen CAR recognition: (A) Conventional CARs are classified as first-, second-, third-, or fourth generation depending on their number of costimulatory domains. (B) Innate enhanced DAP10 chimeric adaptor (CAd), combined with 4–1BB and modified CD3ζ co-stimulation, enhances tumor targeting through endogenous NKG2D receptors. (C) The masked CAR (mCAR) incorporates a masking peptide. When proteases are present in the tumor microenvironment (TME), the linker is cleaved, releasing the masking peptide, and activating the CAR. This mechanism helps reduce on-target off-tumor toxicity. (D) A T cell antigen coupler (TAC) is also designed to reduce toxicity and promote more efficient anti-tumor response. It is comprised of a tumor-associated antigen (TAA) binding domain, CD3 binding domain, and CD4 co-receptor domain. Combinatorial antigen CAR recognition: (E) OR-gate CARs enable dual-targeting of antigens with separate single-chain variable fragment (scFv) domains. To prevent antigen escape, they can be designed to have two consecutive scFv domains connected to the standard CAR chassis. (F) AND-gate CARs are only activated when both antigens are present simultaneously, employing two separate receptors comprising the CD3ζ and costimulatory domains. A chimeric costimulatory receptors (CCR)-based AND-gate has its CD3ζ signaling domain from a γδTCR and can target multiple antigens which can enhance cytotoxicity and prevent tonic CD3ζ signaling. CCR can also be paired with a switch receptor which can be an inhibitor receptor such as programmed death-1 (PD-1) along with a costimulatory domain like CD28. Non-signaling CARs (NSCARs) do not possess signaling domains and utilize an antigen-specific tumor targeting mechanism. Created with BioRender.com.
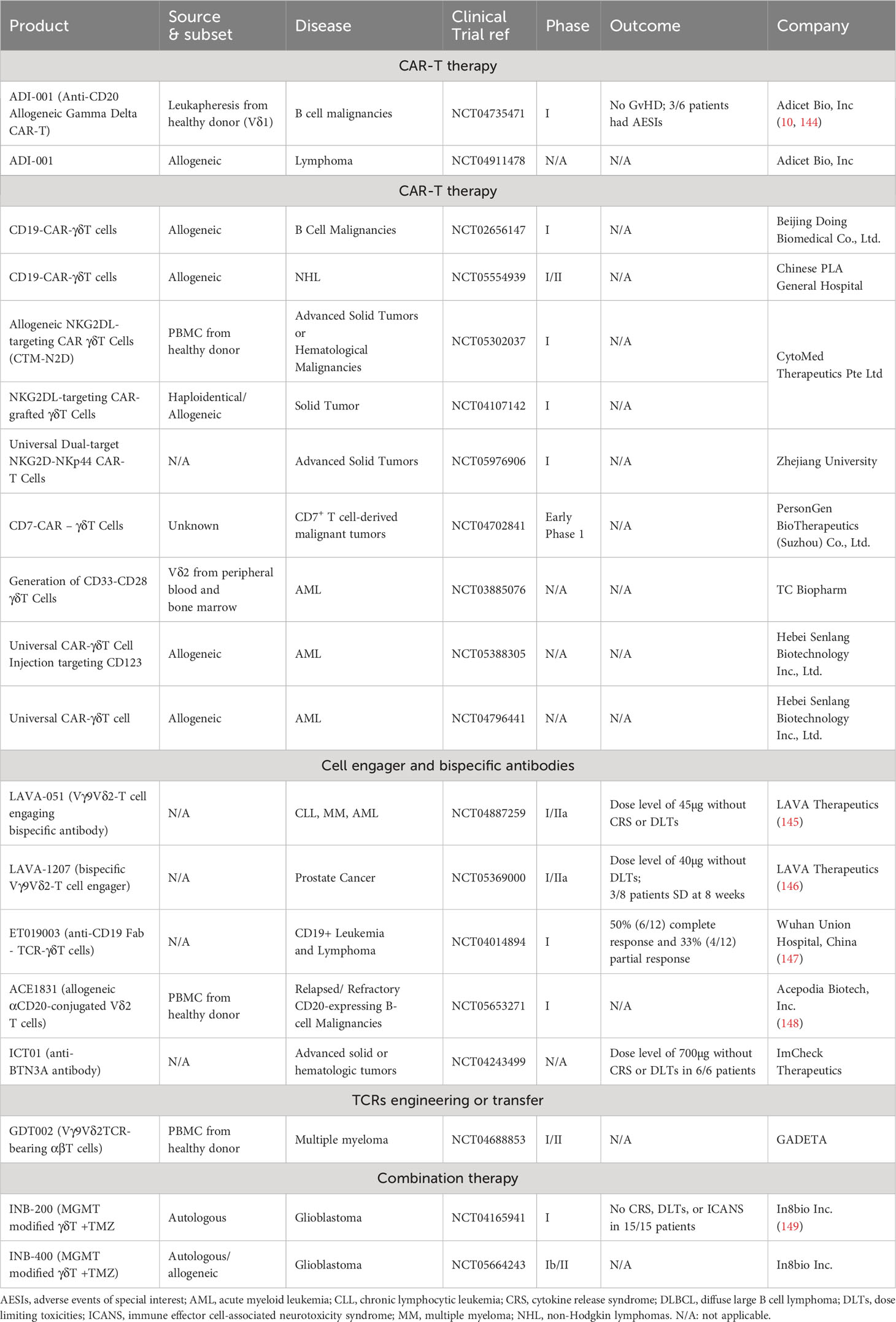
Clinical trials are in progress for CAR-γδT cells targeting various antigens such as CD19 (NCT02656147, NCT05554939), CD20, NKG2DL, CD7, CD33, CD28, and CD123 (Table 3). While many of these trials have yet to disclose their results, some promising preliminary findings have been reported. For instance, Adicet Bio, Inc. is testing an allogeneic CD20 CAR+ Vδ1 γδT cell called ADI-001, designed for patients with refractory B cell malignancies (NCT04735471). Their early report shows a 71% overall response rate and 63% complete response rate among patients with aggressive B-Cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma, all without the presentation of GvHD (91).
One challenge with CAR-T therapy is its potential ineffectiveness in tumors exhibiting heterogeneity or low antigen expression. Dual-specific CARs, which target two antigens concurrently, are proposed as a potential solution, although this requires further investigation (161). Other research focuses on fine-tuning other CAR components, including the intracellular signaling and transmembrane domain, with construction of Boolean logic gates for combinatorial antigen sensing. Balancing the DNA length of dual-CAR plasmids and transduction efficiency necessitates further study.
Recent innovative extracellular designs aimed at enhancing safety also include the development of ON/OFF switches like the masked CAR. Here, the antigen-binding site of CAR is coupled with a masking peptide through a protease-sensitive linker. Activation of masked CAR-T cells occurs when tumor microenvironment proteases cleave this linker, causing the masking peptide to detach, and revealing the antigen-binding site (162) (Figure 3C). In essence, this provides a level of control, reducing risks associated with unregulated CAR-T activation (162).
To sum up, while there are promising advancements in the development of γδT cell-based CAR-T therapies, it is critical to continue fine-tuning these interventions for increasing specificity and safety. A combination of innovative design strategies and rigorous clinical trials may bring forth the next generation of cancer immunotherapies. The hope is for these novel treatments to cure more patients, more reliably, with fewer side effects, revolutionizing the approach to cancer treatment.
4.1.1 Co-stimulatory domain design and combinatorial strategies: emphasize the unique characteristics of γδT cells
Over the years, CARs have progressed through several generations, differentiated by the quantity and nature of their co-stimulatory domains, like CD28 and 4-1BB, which play a pivotal role in γδT cell activation and cytotoxic function (163) (Figure 3A). Initial designs of CAR γδT cells were largely based on pre-existing CAR-αβT designs, failing to capitalize on the unique benefits of γδT cells due to a dearth of knowledge on the fundamental CAR signaling mechanisms in γδT cells. CAR-αβT cells recognize tumor cells through the CAR pathway while completely bypassing the αβTCR. Meanwhile, in CAR-γδT cells, the inherent γδTCR signal can synergize with logic-gated CARs, providing MHC-independent cytotoxicity and downstream CD3ζ signals. Besides, CAR-γδT cells retain multiple activating NK receptors alongside CAR and TCRγδ, potentially enhancing recognition and activation. In the tumor immunoescape setting, CAR-γδT cells have been proved the ability to recognize antigen-negative tumor cells in CAR-independent manner (125). CARs designed for γδT cells can also incorporate γδT cell-specific signaling domains, such as NKG2D-DAP10, as an intracellular costimulatory domain for activation. Despite this development, contemporary research on CAR γδT cells predominantly employs second or third-generation designs. It has been observed, though, that single antigen recognition in these CARs leads to poor discrimination between tumor and healthy cells, contributing to on-target off-tumor toxicity. Furthermore, CAR-T cells exhibit strong limitations in treating T cell malignancies due to difficulties like lethal T cell aplasia and CAR-T cell fratricide stemming from shared target antigens (129). Even extending CAR T cell therapies to T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) has proven challenging, despite shared molecular commonalities with B cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL).
Moreover, CARs providing both CD3ζ stimulus and CD28 co-stimulation are prone to tonic signaling, leading to functional exhaustion and impaired CAR-T cell function. A unique construct called ADI-925 has been developed by Adicet Bio to help tackle this. It incorporates an enhanced intracellular DAP10 chimeric adaptor (CAd), 4–1BB, and a modified CD3ζ co-stimulation, designed to enhance tumor targeting through endogenous NKG2D receptors (121, 164) (Figure 3B).
Novel strategies are also emerging, employing Boolean logic gates (like AND, OR, AND NOT) enabling CAR-T cells to detect multiple antigens, reducing off-tumor toxicity and minimizing potential antigen escape (Figures 3E, F). Dual-targeting CAR γδT cells, like those targeting GD2 and PTK7 in preclinical studies for neuroblastoma, were developed to help avoid antigen escape through an OR-gate strategy) (165). Though promising, tandem bispecific OR-gate CAR-T cells may induce excessive CD3ζ signaling during co-stimulation, necessitating alternative strategies (165).
Bi-specific CARs with split co-stimulatory signals and a shared CD3ζ domain have emerged as another strategy, allowing for optimal CAR-T cell activation only when both antigens are simultaneously present (161, 166). Furthermore, ideas like chimeric costimulatory receptors (CCRs), also known as recognition-based logic-gated CAR, and non-signaling CARs (NSCARs) have been proposed to mitigate on-target off-tumor toxicity (123, 129). CCRs, traditional CARs without CD3ζ signaling domain, provide co-stimulation whilst avoiding tonic CD3ζ signaling of γδT cells. Thus, these reduce on-target off-tumor toxicity by separating co-stimulatory input from the primary TCR signal (129). Moreover, CCRs have the potential to target malignant cells while sparing healthy tissues in scenarios where the target antigen is broadly expressed (123, 129). Fisher et al. developed a co-stimulation-only CAR, wherein the CAR is fit only to provide co-stimulation, thereby restricting tonic signaling but still facilitating rapid downstream response upon activation (164). Concurrently, CAR-γδT cytotoxicity can be selectively triggered by both the CAR signal and the inherent γδTCR signal when encountering cancer cells (130). CCR can also function as a switch chimeric receptor combined with a second-generation CAR (Figure 3B). The switch receptor typically includes an inhibitory receptor (e.g. PD-1 or TIGIT) and an intracellular costimulatory signal (167). For instance, the PD-1-CD28 construct as anti-PD-L1 CCR can potentially convert the inhibitory signal into an activating one (167). Such a design can accelerate activation of CAR-T cells and improve their survival in the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment (167, 168). On the other hand, NSCARs capitalize on γδT cells’ MHC-independent cytotoxic capacity while eliminating all CAR signaling domains (129). This results in antigen-specific tumor cell-targeting capability without influencing T cell activation, as demonstrated by Fleischer et al. with CD5-NSCAR- and CD19-NSCAR-engineered γδT cells, designed specifically for T-ALL and B-ALL relief (129).
Despite the promise of these technologies, factors like NSCAR shedding on γδT cells and antigen downregulation in target cells have somewhat limited their translational application in clinical therapies. Additionally, the necessity of intracellular signaling domains in CAR design is being reconsidered when applied to γδT cells. Deletion of these domains can potentially allow for the transduction of multiple NSCARs, due to a decrease in overall CAR size.
In conclusion, recent years have seen significant expansion in the approaches to T cell engineering, including innovations such as synNotch receptors, iCAR, and several others (158, 169). However, the design and development of CARs for γδT cells haven’t kept pace. A deeper understanding of γδT cell cytotoxicity mechanisms and further research into these novel CAR structures will be critical in achieving maximum safety and efficacy, thereby unlocking the full potential of CAR γδT cell therapies.
4.1.2 CAR transduction methods
The primary methodologies for CAR-T therapy involve permanent DNA-based transfection methods that include viral transduction (using lentiviruses or retroviruses) and non-viral transfection, typically utilizing transposon systems like Sleeping Beauty and Piggy Bac (170) (Table 2). While lentiviruses and retroviruses are commonly used, concerns about their safety, predominantly due to their immunogenic properties, and their complex and costly manufacturing processes may limit their utility. Despite these concerns, retrovirally-modified CAR-T cells have proven tolerable safety profiles in extensive clinical trials (171). However, the transduction of γδT cells has been challenged due to their relatively limited proliferation and susceptibility to AICD compared to that of αβT cells (172). Gammaretroviruses necessitate active cell proliferation for the penetration of viral nucleic acids into the nucleus. This poses a challenge for the transduction of γδT cells compared to αβT cells, demanding necessary specific proliferative stimuli for effective γδT cell transduction (172).
Simultaneously, advancements are being made in non-viral technologies to address some drawbacks associated with viral transductions, such as potential oncogenesis, immunogenicity, and high cost (170). Non-viral transposon vectors possess simpler manufacturing processes, cost efficiency, enhanced safety, stable integration of large sequence (>10 kb), but often face efficiency challenges (173). These non-viral integrative vectors rely on temporary cell pore formation or endocytosis, accomplished via various chemical or physical techniques, including electroporation and liposomes (174).
More recently, non-permanent gene transfer methods that utilize non-integrating gene delivery like mRNA-based CAR expression have started to gain traction (154). The utilization of mRNA in CAR-T cells allows for a “biodegradable” approach, in which the cell’s potency is short-term. The use of mRNA electroporation was first applied in early stages of αβ CAR-T development, but initial clinical trials indicated a lack of efficacy, potentially due to the poor quality and quantity of patient-derived autologous αβT cells (NCT02623582). This led researchers to explore the use of allogeneic Vγ9Vδ2 T cells from healthy donors. Investigations revealed that after mRNA electroporation, CAR expression persisted for up to 120 hours, with peak expression at the 24-hour mark (175). Enhanced anti-AML activity of mRNA-based anti-CD123 γδ CAR-T was observed both in vivo and in vitro (131). Despite these promising results, the transient nature of receptor expression means that further applications may need to employ strategies such as repeated or intratumoral injections to ensure therapeutic efficacy. Future advancements in CAR γδT cell therapy may favor non-viral integrating and lipid nanoparticles technological platforms (170).
In the domain of hematological malignancies, CAR γδT cell therapy holds formidable promise. However, the development of universal CAR γδT cells capable of effectively treating solid tumors remains a pressing need, necessitating ongoing research to overcome the physical and immunological challenges associated with solid tumor immunity. Given the unique stimulatory signals and recognition mechanisms of γδT cells, it is evident that the design of CARs for these cells needs to undergo revisions and refinements as our understanding of their biological mechanisms deepens. In essence, while there has been substantial progress in the field of CAR γδT cell therapy, future work that ensures the safety, efficacy, and broad applicability of this promising therapy modality, especially in the context of solid tumors, remains a critical need in the field.
4.2 Cell engagers or bispecific antibodies: easier ways to enhance γδT cells recognition
Cell engagers and bispecific antibodies have become an increasingly attractive immunotherapeutic method for enhancing the anti-cancer activity of γδT cells. Bispecific T cell engagers (bsTCEs) are specially designed antibodies, each having two separate binding areas aimed at individual components like tumor-associated antigens (TAAs) and the TCR complex (Vδ2 or Vγ9) (176). The flexibility of bsTCEs allows for varied applications, such as MHC-independent targeting of TAAs by γδT cells, immune checkpoint modulation, and controlling inflammatory and other signaling pathways (176). These functionalities provide several unique advantages, including their small molecular size and high versatility, eliminating the need for additional co-stimulatory signals for T cell activation, low picomolar range for the half-maximal effective concentration (EC50), effectiveness against both blood-borne and solid tumors, excellent safety profile, and efficient and cost-effective production (177). Most frequently, cell engagers incorporate a fragment-based design or lgG/lgG-like formats (136, 137). Fragment-based designs principally modify constructs such as scFv (178), Fab (135), or single-domain antibodies (sdAbs, also known as VHH) (176) into their binding regions (Figures 4A-C). sdAbs, originating from the variable domain of heavy-chain-only antibodies, have attracted attention because of their unique features, including small size, target specificity, and minor immunogenicity (179). Currently, cell engagers can be applied both as stand-alone therapies and in partnership with allogeneic γδT cells to generate readily available products.
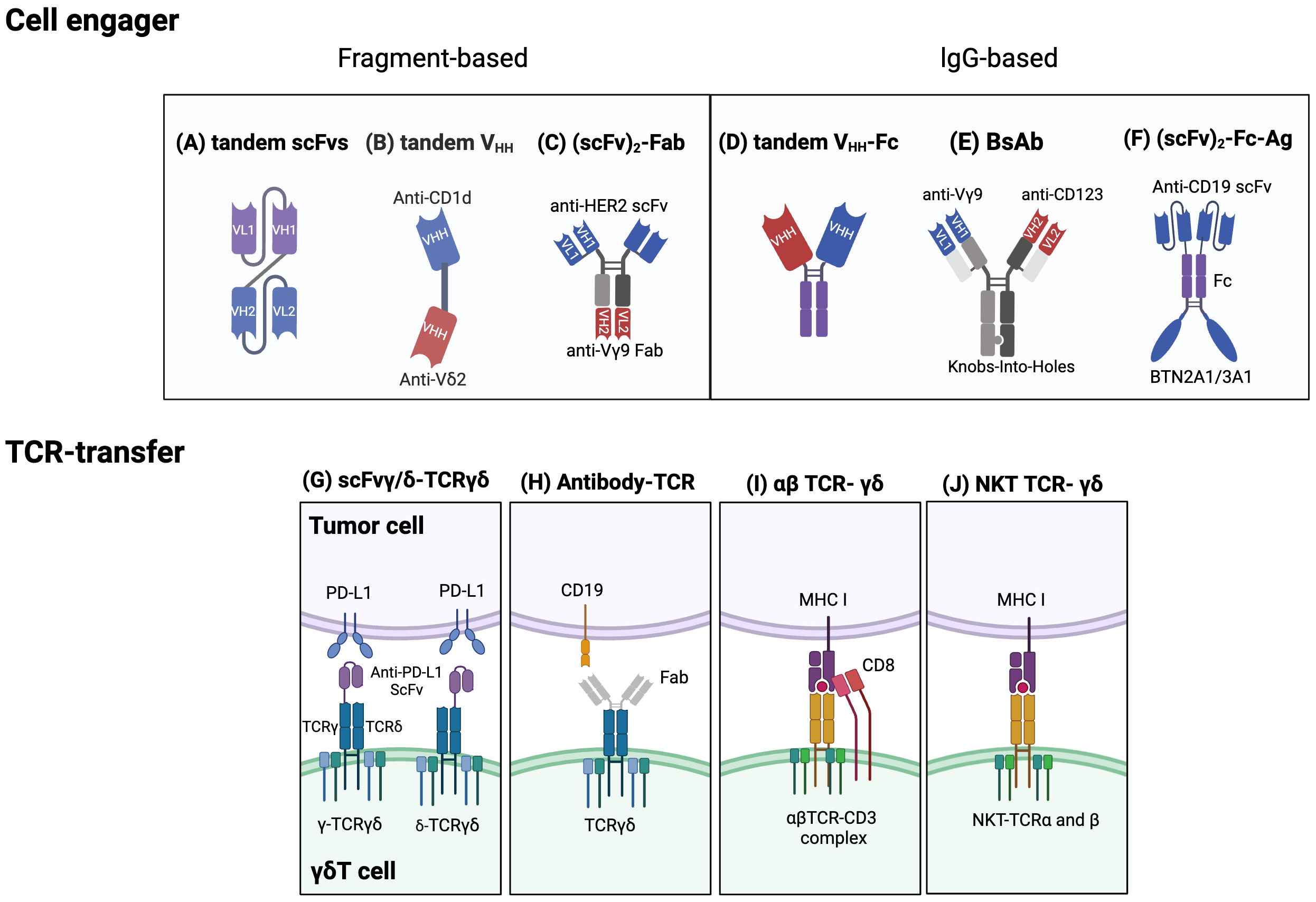
Figure 4 Established strategies for engineering γδT cells. Cell engager designs: Fragment based cell engagers include tandem single-chain variable fragment (scFv), tandem variable heavy chain (VHH), and (scFv)2-Fab. (A) A tandem scFv antibody comprises two different scFvs joined by a linker. (B) Tandem VHH is depicted as a bispecific T cell engager (bsTCE) with an anti-CD1d VHH linked to an anti-Vδ2 VHH. (C) An example of (scFv)2-Fab antibody, Her2/Vγ9, is composed of an anti-Vγ9 Fab domain and two anti-Her2 scFvs. This design selectively recruits γδ T cells and enhances cytotoxicity. IgG based cell engagers encompass tandem VHH-Fc, bispecific antibodies (BsAb), and (scFv)2-Fc-Ag. (D) Tandem VHH-Fc antibodies involve two VHHs linked to a Fc domain. (E) One type of BsAb connects an anti-Vγ9 domain and an anti-CD123 domain via Knobs-into-holes heterodimerization technology. (F) (scFv)2-Fc-Ag is shown as an anti-CD19 scFv connected to a BTN2A1/3A1 domain via an Fc linker. Engineering γδTCRs and transferring specific αβT-TCR or NKT-TCRs into γδT cells: (G) One approach to engineering γδTCRs is to fuse an anti- programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1) scFv to either the γ or δ chain of γδTCR to limit T cell exhaustion. (H) Another approach is an antibody-TCR, such as an anti-CD19 Fab domain linked to a γδTCR. (I) αβTCRs and CD8 αβ genes can be transferred to γδT cells to enable targeting specific tumor cells and avoid TCR mispairing. (J) Natural killer T (NKT) cell-derived αβTCRs can also be transferred into γδT cells to enhance proliferation, IFN-γ production, and antitumor effects. Created with BioRender.com.
The first CD3-targeting bsTCEs, exemplified by blinatumomab and Tebentafusp, yielded significant positive outcomes in B-cell malignancy and melanoma patients during clinical trials (NCT03070392) (180). However, adverse effects like CRS and immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome (ICANS) constrained their clinical usage (177). Further, CD3-targeting bsTCEs may unintentionally activate other CD3+ T cell subsets, which could depress tumor-specific immune responses (137). As a category of innate T cells, γδT cells present a logical choice for engagement to reduce CRS and off-tumor toxicity.
The successful usage of bsTCEs in LAVA Therapeutics’ Gammabody platform, employing tandem single-domain antibodies (VHHs) (Figure 4D), exemplifies their potential. These include EGFR-Vδ2, CD1d-Vδ2, CD40-Vδ2, and PSMA-Vδ2 bsTCEs (Table 3). EGFR-Vδ2 bsTCEs have displayed compelling activation of Vγ9Vδ2 T cells which induce cytotoxicity against EGFR+ tumor cells (137, 154). The CD1d-Vδ2 bsTCE, or LAVA-051, has shown anti-tumor potential against hematological malignancies expressing CD1d in preclinical models (176). Its specificity for NKT and Vγ9Vδ2-T cells, alongside low-nanomolar range EC50 values in vitro, further demonstrates its potential (176).
Bispecific antibodies (bsAbs) comprise a class of engineered antibodies with two distinct binding sites, setting them apart from traditional antibodies (181) (Figures 4D-F). These antibodies, as exemplified by anti-Vγ9/CD123 bsAbs, selectively rally Vγ9+ γδT cells, promoting cell conjugate formation between γδT cells and AML cells (136). As such, these cell engagers can enhance Vγ9Vδ2+ T cell cytotoxicity against B-cell lymphoma, particularly when accompanied by a co-stimulatory signal pair (178). ImCheck Therapeutics’ humanized anti-BTN3A antibody, ICT01, serves as another example. It operates by recognizing three distinct BTN3A forms and prompting their activated conformation, thereby selectively activating Vγ9Vδ2 T cells in an antigen-independent manner (182).
In a phase I/II clinical trial, ICT01 showed tolerable safety profile and increased infiltration of Vγ9Vδ2 T cells into tumor tissue in patients with advanced solid tumors (NCT04243499). (Table 3) Besides, LAVA-1207 (PSMA-Vδ2 bsTCEs) has shown a favorable safety profile and clinical symptom improvement (decreased PSA level) in a Phase 1/2a clinical trial involving metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) patients (N=20, NCT05369000) (137).
Notably, as cell engagers depend on the activation and migration of the patient’s inherent γδT cell pool, initial Vγ9δ2T cell counts could be a useful predictor for clinical outcomes. Take, for instance, a melanoma patient with a high baseline count of circulating Vγ9Vδ2 T cells who showed considerable tumor infiltration of Vγ9+ T cells post ICT01 administration (182). Cell engagers can also be combined with γδT cell-based therapies to develop easily available TAA-targeting γδT cell products (148).
Acepodia’s technology, for instance, conjugates antibodies to cells to create products like ACE1831, which is the CD20-targeting γδT cells (148). This product is currently under phase I trial for patients with relapsed/refractory B-cell lymphomas (NCT05653271). Other products, ACE2016 (EGFR-targeting γδT) and ACE1708 (PD-L1-targeting γδT), are in the preclinical exploratory stage (183).
In conclusion, while cell engagers and bispecific antibodies present significant potential compared to CAR-T therapy, their definitive superiority is yet to be determined. Like CAR-T therapy, cell engagers also encounter hurdles such as immune escape owing to loss of target antigen expression and an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment. Further research is needed to modify cell engagers specifically for γδT cells, paving the way for effective treatments in the future.
4.3 TCRs engineering or transfer: a highly specific and reproducible manner
Harnessing natural receptors through the engineering or transfer of T cell receptors (TCRs) serves as an alternative approach to the use of synthetic ones. The transduction of cancer-specific TCRs is an appealing strategy for generating large volumes of readily available, antigen-specific T cells. Transferring cancer-specific αβTCR engenders T cell specificity, simplifying procedures compared to isolating specific T cell subsets. However, the transgenic transfer of αβTCRs to other αβT cells runs the risk of triggering TCR competition and mispairing. Recognizing these limitations, γδT cells are appreciated as safe and ideal carriers for antigen-specific effector cells because TCR-α and -β chains can’t pair with TCR-γ and -δ chains (138, 184). To produce cytotoxic γδT cells capable of attacking tumor cells and secreting cytokines via αβ and γδTCR-dependent activity, one can isolate tumor antigen-specific αβ CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes and clone their TCR αβ genes (138) (Figure 4I). However, a notable reduction in γδTCR expression post αβTCR transduction was observed, likely due to competition for limited CD3 molecules (138).
Van der Veken et al. demonstrated that αβTCR -transduced γδT cells display sustained in vivo endurance and can elicit a recall response (139, 184). More so, infusing αβTCRs from invariant natural killer T (iNKT) cells into γδT cells can create bi-potential T cells with NKT cell functionality (143) (Figure 4J). Other research endeavors are concentrated on transferring γδTCR to αβT cells to leverage the superior understanding of their effects and memory function mechanisms (185). One product, GDT002, which contains Vγ9Vδ2TCR-expressing αβT cells, allows αβT cells to detect augmented phosphoantigens in stressed or malignant cells (185). An ongoing phase 1/2 study is investigating GDT002’s safety and tolerability in patients with multiple myeloma. Furthermore, strategies for engineering TCRγδ involve fusing with single-chain variable fragments (scFv) or Fab fragments from antibodies. For example, one study used CRISPR/Cas9 to fuse an anti-PD-L1 scFv to the TCRγ or δ chain in activated γδT cells, creating scFv-γ/δ-TCRγδ cells that showcased anti-tumor capacity akin to traditional CAR-T cells (186) (Figure 4G). Alternatively, the Fab domain of an antibody can be connected to the C-terminal signaling domain of the γ and δ chains of the TCR, creating an antibody-TCR construct (187) (Figure 4H). The use of the TCR alongside endogenous costimulatory molecules can lower co-stimulation input compared to CAR constructs, thus diminishing cytokine release and mitigating the exhaustion phenotype (187). Anti-CD19 Fab – TCR-γδT cells or ET019003, for instance, have displayed similar anti-tumor actions against B-cell lymphoma as CAR-T cells in vivo (187).
Promisingly, a phase I clinical trial (NCT04014894) indicates that, aside from showing agreeable safety profiles, ET019003 has achieved an impressive clinical response rate (87.5%) among patients with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (188). However, TCR gene transduction or engineering research has somewhat stagnated in recent years, possibly due to complex manufacturing processes involved. In summary, the exploration of novel therapeutic approaches incorporating γδT cells continues to expand, with significant potential for future cancer treatment innovations.
4.4 Combination therapy
CAR-T cell therapy has proven extremely promising for treating hematologic malignancies. However, distinct issues related to the immunosuppressive microenvironment of solid tumors require further refinement and personalization of this approach. A potential solution could be combination therapies that adequately address the complexity of solid malignancies.
The concurrent usage of CAR-T/bsTCE therapies and immune checkpoint inhibitors is recognized as a potentially effective strategy to overcome immune system suppression. Exhaustion status, marked by the upregulation of inhibitory receptors, can potentially compromise the therapeutic efficacy of CAR-T cells (189). In a murine model of bone metastatic prostate cancer, γδ CAR-T cells persisted in the tumor-bearing tibia for approximately 21 days post-infusion. However, these cells exhibited an upregulation of PD-1 expression while simultaneously losing expression of activation markers (151). Consequently, the combination of therapies such as ICT01 and pembrolizumab, an anti-PD1 antibody, exhibited favorable safety profiles in a phase I clinical trial (NCT04243499). This suggests that the co-administration of CAR-T/bsTCE therapy with anti-PD-1/PD-L1 antibodies could potentially boost treatment benefits (151).
Chemotherapy and radiotherapy, owing to their immune-sensitizing attributes, are plausible options for combination therapy with immunotherapy (190). Temozolomide (TMZ), a chemotherapy mainstay for glioblastoma (GBM), transiently heightens the expression of stress-associated antigens such as NKG2DL on tumor cells. Engineering γδT cells to express the methylguanine DNA methyltransferase (MGMT) can thus potentially confer TMZ resistance, enabling the engineered cells to operate efficiently despite the presence of therapeutic concentrations of chemotherapy. The amalgamation of TMZ and MGMT-modified autologous γδT cells, or drug resistant immunotherapy (DRI), showed improved survival outcomes in a model of high-grade gliomas compared to monotherapy (124).
In a phase I clinical trial, INB-200 (an example of DRI) displayed a favorable safety profile, extended progression-free survival (PFS), and presented no dose-limiting toxicities, CRS, or neurotoxicity in glioblastoma multiforme patients (NCT04165941). As a result, autologous DRI- γδT cells (INB-400) have proceeded to a phase II clinical trial, and MGMT-modified allogeneic γδT cells (INB-410) are currently undergoing a phase Ib clinical trial (NCT05664243). The product INB-400/410, developed by IN8bio, has been granted FDA Orphan Drug Designation for the Treatment of Newly Diagnosed Glioblastoma.
As it stands, most approved combination immunotherapies largely rely on a combination of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) and have emerged as first-line treatments for several major cancer types (191). The future of combination immunotherapies with γδT cells likely extends beyond ICI-based approaches, aiming for control and eradication of established tumors. Further research in this area will be instrumental in harnessing the full therapeutic potential of γδT cells.
5 Challenges and limitations
Tapping into the potential of genetically engineered γδT cells holds the promises of breakthroughs in cancer immunotherapy, albeit with scientific and technical hurdles. The multifaceted nature of γδT cell biology coupled with the complexities of genetic manipulation throws inevitable challenges in the way of optimizing therapeutic potential.
The extensive heterogeneity of γδT cells, which includes various subsets with distinct antigen recognition patterns, homing properties, and effector functionalities, presents a significant challenge in standardizing genetic engineering strategies (192). Additionally, our understanding of the γδTCR repertoire lags behind that of αβTCRs (141). Although cell engagers and bispecific antibodies have shown potential to robustly activate γδT cells, effective signal optimization is still underway (178). Certain constraints of gene-engineering, such as the need for CD8 or other co-stimulators which γδT cells lack, and the intricate manufacturing processes involved, serve as significant obstacles (138). Although gene-transduction techniques, such as mRNA electroporation and lentiviral transduction, have seen noticeable advancements over the past years, the efficiency of integrating genes into γδT cells using either viral or non-viral vectors is yet to reach optimal levels. mRNA electroporation allows for rapid expression and poses fewer risks of insertional mutations, while also being associated with lower cellular toxicity. However, this method only provides transient expression of CARs, requiring multiple infusions of CAR T-cells and an extension of their cytotoxic lifespans from a therapeutic perspective (154). On the other hand, lentiviral transduction, often considered time-consuming, also carries the risk of damaging essential genes or regulatory sequences during the period required for expression (193–195)..
In comparison to αβ CAR-T cells, γδ CAR-T cells often present less complete clearance of tumor cells in vivo. This characteristic could be attributed to reduced persistence of γδ CAR-T in the immunosuppressive microenvironment (125, 196), necessitating multiple infusions and a large supply of γδ CAR-T cells. Furthermore, CAR-T cells could potentially contribute to antigen loss in target cells, resulting in diminished antigen density (197).
While the introduction of bispecific T cell engagers has propelled cancer immunotherapy, especially against hematological malignancies by offering an easy and cost-effective treatment option, their efficacy remains undermined by co-triggering of immunosuppressive T cell populations, such as regulatory T cells (Tregs) (137). Even though the combination of CAR and bispecific γδT cell engagers has shown promising results towards improving anti-tumor efficacy and reducing cytotoxicity, the tumor cells’ ability to evade the immune system strengthened by γδT cells is still under investigation (198).
Interestingly, γδT cells, under certain conditions, may also promote tumor growth (199, 200). This trait might be influenced by the TME or interactions with other immune cells. γδT cells have been known to promote tumor growth by producing IL-17, a process influenced by factors such as TME-related metabolism, microbial products, and inflammatory cells (201, 202). Considering the association of γδT cells with autoimmune diseases, a thorough investigation of their long-term clinical outcomes is essential when their activation or suppression is incorporated into treatments (203).
Implementing engineered γδT cell immunotherapy in a clinical setting presents its own set of challenges. Identifying suitable patients and healthy donors and creating standardized monitoring guidelines are crucial. Determining the correct dosage—whether based on body weight or the number of cells per infusion—and understanding its relation to treatment success is a significant hurdle. There is also a pressing need to address the risk of disease recurrence post-treatment, bolster the therapy’s durability, and decide whether to opt for monotherapy (with a single or several doses) or a combination approach (204). In addition, as production is resource-intensive and coupled with strict regulatory, ethical, and safety considerations, and high costs. Thus, widespread access to this form of therapy is limited. To fully employ the potential of γδT cell therapies, extensive research and collaboration are necessary.
6 Conclusions and future perspectives
γδT cell-based immunotherapies represent a promising frontier in cancer treatment, introducing innovative approaches to overcome the limitations of traditional therapies. The development of gene-engineering strategies, such as CAR T therapy, bispecific antibodies and cell engagers, and TCR gene transfer, has significantly advanced the efficacy of γδT cells, addressing their challenges in abundance, expansion, and targeting efficiency. Despite these strides, hurdles such as the nuanced understanding of γδT cell behaviors, targeting solid tumors effectively, and preventing post-treatment relapse persist.
The remarkable potential of γδT cell therapies lies in their ability to offer a paradigm shift in cancer treatment, utilizing their unique properties for more precise, potent, and personalized interventions. Their versatility in recognizing cancer cells without MHC restriction provides a substantial advantage in reducing the risk of immune escape and addressing tumor heterogeneity.
Looking ahead, research must focus on understanding γδT cells’ metabolic needs and cytokine profiles within the tumor microenvironment to enhance their antitumor activity. Additionally, it is critical to develop strategies that improve the persistence of CAR γδT cells and maintain target antigen visibility, ensuring long-term therapeutic success. The exploration of Vδ1 subsets and the creation of iPSC-derived γδT cells hold promise for developing universally applicable CAR γδT cell therapies. Furthermore, optimizing the engineering of γδT cells for safer and more efficient delivery, coupled with the strategic combination of these therapies with other treatments, will enhance efficacy and durability.
Emphasis should also be placed on designing therapies that reduce the risk of relapse and increase sustainability. Regulatory, manufacturing, and logistical challenges will need to be addressed to facilitate the clinical translation of these therapies. The ultimate goal is to harness the full therapeutic potential of γδT cells, offering new hope to patients with various types of cancer.
The future of γδT cell immunotherapy lies in the convergence of molecular biology, genetic engineering, and clinical research. As our understanding evolves, so will the potential of γδT cells as a powerful tool in the arsenal against cancer, paving the way for more effective, tailored, and sustainable cancer treatments.
Author contributions
MY: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. WW: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. IH: Writing – review & editing. JH: Writing – review & editing. ZY: Writing – review & editing. AB: Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by Lorry Lokey Faculty Scholar.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Mizukoshi E, Kaneko S. Immune cell therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hematol Oncol. (2019) 12:52. doi: 10.1186/s13045-019-0742-5
2. Riley RS, June CH, Langer R, Mitchell MJ. Delivery technologies for cancer immunotherapy. Nat Rev Drug Discovery. (2019) 18:175–96. doi: 10.1038/s41573-018-0006-z
3. Zhang Y, Zhang Z. The history and advances in cancer immunotherapy: understanding the characteristics of tumor-infiltrating immune cells and their therapeutic implications. Cell Mol Immunol. (2020) 17:807–21. doi: 10.1038/s41423-020-0488-6
4. Labanieh L, Mackall CL. Car immune cells: design principles, resistance and the next generation. Nature. (2023) 614:635–48. doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-05707-3
5. Myers JA, Miller JS. Exploring the nk cell platform for cancer immunotherapy. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. (2021) 18:85–100. doi: 10.1038/s41571-020-0426-7
6. Burger JA, Wiestner A. Targeting B cell receptor signalling in cancer: preclinical and clinical advances. Nat Rev Cancer. (2018) 18:148–67. doi: 10.1038/nrc.2017.121
7. Mantovani A, Allavena P, Marchesi F, Garlanda C. Macrophages as tools and targets in cancer therapy. Nat Rev Drug Discovery. (2022) 21:799–820. doi: 10.1038/s41573-022-00520-5
8. Mensurado S, Blanco-Domínguez R, Silva-Santos B. The emerging roles of Γδ T cells in cancer immunotherapy. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. (2023) 20:178–91. doi: 10.1038/s41571-022-00722-1
9. Yazdanifar M, Barbarito G, Bertaina A, Airoldi I. Γδ T cells: the ideal tool for cancer immunotherapy. Cells. (2020) 9:1305. doi: 10.3390/cells9051305
10. Nishimoto KP, Barca T, Azameera A, Makkouk A, Romero JM, Bai L, et al. Allogeneic cd20-targeted Γδ T cells exhibit innate and adaptive antitumor activities in preclinical B-cell lymphoma models. Clin Trans Immunol. (2022) 11:e1373. doi: 10.1002/cti2.1373
11. Lopes N, Silva-Santos B. Functional and metabolic dichotomy of murine Γδ T cell subsets in cancer immunity. Eur J Immunol. (2021) 51:17–26. doi: 10.1002/eji.201948402
12. Khairallah C, Chu TH, Sheridan BS. Tissue adaptations of memory and tissue-resident gamma delta T cells. Front Immunol. (2018) 9:2636. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02636
13. Wiebking V, Lee CM, Mostrel N, Lahiri P, Bak R, Bao G, et al. Genome editing of donor-derived T-cells to generate allogenic chimeric antigen receptor-modified T cells: optimizing αβ T cell-depleted haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Haematologica. (2021) 106:847–58. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2019.233882
14. Ye W, Kong X, Zhang W, Weng Z, Wu X. The roles of Γδ T cells in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Cell Transplant. (2020) 29:963689720966980. doi: 10.1177/0963689720966980
15. Lee D, Rosenthal CJ, Penn NE, Dunn ZS, Zhou Y, Yang L. Human Γδ T cell subsets and their clinical applications for cancer immunotherapy. Cancers (Basel). (2022) 14:3005. doi: 10.3390/cancers14123005
16. Brandes M, Willimann K, Moser B. Professional antigen-presentation function by human Γδ T cells. Science. (2005) 309:264–8. doi: 10.1126/science.1110267
17. Imbert C, Olive D. Γδ T cells in tumor microenvironment. Adv Exp Med Biol. (2020) 1273:91–104. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-49270-0_5
18. Agerholm R, Bekiaris V. Evolved to protect, designed to destroy: il-17-producing Γδ T cells in infection, inflammation, and cancer. Eur J Immunol. (2021) 51:2164–77. doi: 10.1002/eji.202049119
19. Zhang H, Chai W, Yang W, Han W, Mou W, Xi Y, et al. The increased il-17-producing Γδt cells promote tumor cell proliferation and migration in neuroblastoma. Clin Immunol. (2020) 211:108343. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2020.108343
20. Mensurado S, Rei M, Lança T, Ioannou M, Gonçalves-Sousa N, Kubo H, et al. Tumor-associated neutrophils suppress pro-tumoral il-17+ Γδ T cells through induction of oxidative stress. PloS Biol. (2018) 16:e2004990. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.2004990
21. Chen X, Morrissey S, Chen F, Yan J. Novel insight into the molecular and metabolic mechanisms orchestrating il-17 production in Γδ T cells. Front Immunol. (2019) 10:2828. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02828
22. Ma Y, Aymeric L, Locher C, Mattarollo SR, Delahaye NF, Pereira P, et al. Contribution of il-17-producing gamma delta T cells to the efficacy of anticancer chemotherapy. J Exp Med. (2011) 208:491–503. doi: 10.1084/jem.20100269
23. Wakita D, Sumida K, Iwakura Y, Nishikawa H, Ohkuri T, Chamoto K, et al. Tumor-infiltrating il-17-producing gammadelta T cells support the progression of tumor by promoting angiogenesis. Eur J Immunol. (2010) 40:1927–37. doi: 10.1002/eji.200940157
24. Jhita N, Raikar SS. Allogeneic gamma delta T cells as adoptive cellular therapy for hematologic Malignancies. Explor Immunol. (2022) 2:334–50. doi: 10.37349/ei.2022.00054
25. Bertaina A, Roncarolo MG. Graft engineering and adoptive immunotherapy: new approaches to promote immune tolerance after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Front Immunol. (2019) 10:1342. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01342
26. Xu Y, Xiang Z, Alnaggar M, Kouakanou L, Li J, He J, et al. Allogeneic Vγ9vδ2 T-cell immunotherapy exhibits promising clinical safety and prolongs the survival of patients with late-stage lung or liver cancer. Cell Mol Immunol. (2021) 18:427–39. doi: 10.1038/s41423-020-0515-7
27. Vydra J, Cosimo E, Lesný P, Wanless RS, Anderson J, Clark AG, et al. A phase I trial of allogeneic Γδ T lymphocytes from haploidentical donors in patients with refractory or relapsed acute myeloid leukemia. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. (2023) 23:e232–e9. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2023.02.003
28. Saura-Esteller J, de Jong M, King LA, Ensing E, Winograd B, de Gruijl TD, et al. Gamma delta T-cell based cancer immunotherapy: past-present-future. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:915837. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.915837
29. Godfrey DI, Le Nours J, Andrews DM, Uldrich AP, Rossjohn J. Unconventional T cell targets for cancer immunotherapy. Immunity. (2018) 48:453–73. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2018.03.009
30. Chen D, Guo Y, Jiang J, Wu P, Zhang T, Wei Q, et al. Gammadelta T cell exhaustion: opportunities for intervention. J Leukoc Biol. (2022) 112:1669–76. doi: 10.1002/JLB.5MR0722-777R
31. Deng J, Yin H. Gamma delta (Γδ) T cells in cancer immunotherapy; where it comes from, where it will go? Eur J Pharmacol. (2022) 919:174803. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2022.174803
32. Hu Y, Hu Q, Li Y, Lu L, Xiang Z, Yin Z, et al. Γδ T cells: origin and fate, subsets, diseases and immunotherapy. Signal Transduction Targeted Ther. (2023) 8:434. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01653-8
33. Parker CM, Groh V, Band H, Porcelli SA, Morita C, Fabbi M, et al. Evidence for extrathymic changes in the T cell receptor gamma/delta repertoire. J Exp Med. (1990) 171:1597–612. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.5.1597
34. Saito H, Kranz DM, Takagaki Y, Hayday AC, Eisen HN, Tonegawa S. Complete primary structure of a heterodimeric T-cell receptor deduced from cdna sequences. Nature. (1984) 309:757–62. doi: 10.1038/309757a0
35. Gründer C, van Dorp S, Hol S, Drent E, Straetemans T, Heijhuurs S, et al. Γ9 and Δ2cdr3 domains regulate functional avidity of T cells harboring Γ9δ2tcrs. Blood. (2012) 120:5153–62. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-05-432427
36. Chien Y-h, Konigshofer Y. Antigen recognition by Γδ T cells. Immunol Rev. (2007) 215:46–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2006.00470.x
37. Ravens S, Fichtner AS, Willers M, Torkornoo D, Pirr S, Schöning J, et al. Microbial exposure drives polyclonal expansion of innate Γδ T cells immediately after birth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2020) 117:18649–60. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1922588117
38. Ramstead AG, Jutila MA. Complex role of Γδ T-cell-derived cytokines and growth factors in cancer. J Interferon Cytokine Res. (2012) 32:563–9. doi: 10.1089/jir.2012.0073
39. Li J, Herold MJ, Kimmel B, Müller I, Rincon-Orozco B, Kunzmann V, et al. Reduced expression of the mevalonate pathway enzyme farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase unveils recognition of tumor cells by Vγ9vδ2 T cells1. J Immunol. (2009) 182:8118–24. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0900101
40. Christopoulos P, Bukatz D, Kock S, Malkovsky M, Finke J, Fisch P. Improved analysis of tcrγδ Variable region expression in humans. J Immunol Methods. (2016) 434:66–72. doi: 10.1016/j.jim.2016.04.009
41. Chabab G, Boissière-Michot F, Mollevi C, Ramos J, Lopez-Crapez E, Colombo P-E, et al. Diversity of tumor-infiltrating, Γδ T-cell abundance in solid cancers. Cells. (2020) 9:1537.
42. Nguyen S, Chevalier MF, Benmerzoug S, Cesson V, Schneider AK, Rodrigues-Dias SC, et al. Vδ2 T cells are associated with favorable clinical outcomes in patients with bladder cancer and their tumor reactivity can be boosted by bcg and zoledronate treatments. J Immunother Cancer. (2022) 10:e004880. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2022-004880
43. Bruni E, Cimino MM, Donadon M, Carriero R, Terzoli S, Piazza R, et al. Intrahepatic cd69(+)Vδ1 T cells re-circulate in the blood of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer and limit tumor progression. J Immunother Cancer. (2022) 10:e004579. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2022-004579
44. Bukowski JF, Morita CT, Band H, Brenner MB. Crucial role of tcrγ Chain junctional region in prenyl pyrophosphate antigen recognition by Γδ T cells1. J Immunol. (1998) 161:286–93. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.161.1.286
45. Hunter S, Willcox CR, Davey MS, Kasatskaya SA, Jeffery HC, Chudakov DM, et al. Human liver infiltrating Γδ T cells are composed of clonally expanded circulating and tissue-resident populations. J Hepatol. (2018) 69:654–65. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.05.007
46. Wu Y, Biswas D, Usaite I, Angelova M, Boeing S, Karasaki T, et al. A local human Vδ1 T cell population is associated with survival in nonsmall-cell lung cancer. Nat Cancer. (2022) 3:696–709. doi: 10.1038/s43018-022-00376-z
47. Zakeri N, Hall A, Swadling L, Pallett LJ, Schmidt NM, Diniz MO, et al. Characterisation and induction of tissue-resident gamma delta T-cells to target hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Commun. (2022) 13:1372. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-29012-1
48. Glatzel A, Wesch D, Schiemann F, Brandt E, Janssen O, Kabelitz D. Patterns of chemokine receptor expression on peripheral blood Γδ T lymphocytes: strong expression of ccr5 is a selective feature of Vδ2/Vγ9 Γδ T cells1. J Immunol. (2002) 168:4920–9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.168.10.4920
49. Davey MS, Willcox CR, Joyce SP, Ladell K, Kasatskaya SA, McLaren JE, et al. Clonal selection in the human Vδ1 T cell repertoire indicates Γδ Tcr-dependent adaptive immune surveillance. Nat Commun. (2017) 8:14760. doi: 10.1038/ncomms14760
50. Di Lorenzo B, Ravens S, Silva-Santos B. High-throughput analysis of the human thymic Vδ1+ T cell receptor repertoire. Sci Data. (2019) 6:115. doi: 10.1038/s41597-019-0118-2
51. Ravens S, Schultze-Florey C, Raha S, Sandrock I, Drenker M, Oberdörfer L, et al. Human Γδ T cells are quickly reconstituted after stem-cell transplantation and show adaptive clonal expansion in response to viral infection. Nat Immunol. (2017) 18:393–401. doi: 10.1038/ni.3686
52. Bauer S, Groh V, Wu J, Steinle A, Phillips JH, Lanier LL, et al. Activation of nk cells and T cells by nkg2d, a receptor for stress-inducible mica. Science. (1999) 285:727–9. doi: 10.1126/science.285.5428.727
53. Groh V, Rhinehart R, Secrist H, Bauer S, Grabstein KH, Spies T. Broad tumor-associated expression and recognition by tumor-derived gamma delta T cells of mica and micb. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (1999) 96:6879–84. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.12.6879
54. Qi J, Zhang J, Zhang S, Cui L, He W. Immobilized mica could expand human Vδ1 Γδ T cells in vitro that displayed major histocompatibility complex class I chain-related a-dependent cytotoxicity to human epithelial carcinomas. Scandinavian J Immunol. (2003) 58:211–20. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-3083.2003.01288.x
55. Correia DV, Fogli M, Hudspeth K, da Silva MG, Mavilio D, Silva-Santos B. Differentiation of human peripheral blood Vδ1+ T cells expressing the natural cytotoxicity receptor nkp30 for recognition of lymphoid leukemia cells. Blood. (2011) 118:992–1001. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-02-339135
56. Mikulak J, Oriolo F, Bruni E, Roberto A, Colombo FS, Villa A, et al. Nkp46-expressing human gut-resident intraepithelial Vδ1 T cell subpopulation exhibits high antitumor activity against colorectal cancer. JCI Insight. (2019) 4:e125884. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.125884
57. Wu Y, Kyle-Cezar F, Woolf RT, Naceur-Lombardelli C, Owen J, Biswas D, et al. An innate-like Vδ1(+) Γδ T cell compartment in the human breast is associated with remission in triple-negative breast cancer. Sci Transl Med. (2019) 11:eaax9364. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aax9364
58. Luoma Adrienne M, Castro Caitlin D, Mayassi T, Bembinster Leslie A, Bai L, Picard D, et al. Crystal structure of Vδ1 t cell receptor in complex with cd1d-sulfatide shows mhc-like recognition of a self-lipid by human Γδ T cells. Immunity. (2013) 39:1032–42. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2013.11.001
59. Uldrich AP, Le Nours J, Pellicci DG, Gherardin NA, McPherson KG, Lim RT, et al. Cd1d-lipid antigen recognition by the Γδ Tcr. Nat Immunol. (2013) 14:1137–45. doi: 10.1038/ni.2713
60. Poggi A, Venturino C, Catellani S, Clavio M, Miglino M, Gobbi M, et al. Vdelta1 T lymphocytes from B-cll patients recognize ulbp3 expressed on leukemic B cells and up-regulated by trans-retinoic acid. Cancer Res. (2004) 64:9172–9. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.Can-04-2417
61. Marlin R, Pappalardo A, Kaminski H, Willcox CR, Pitard V, Netzer S, et al. Sensing of cell stress by human Γδ Tcr-dependent recognition of annexin A2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2017) 114:3163–8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1621052114
62. Groh V, Steinle A, Bauer S, Spies T. Recognition of stress-induced mhc molecules by intestinal epithelial gammadelta T cells. Science. (1998) 279:1737–40. doi: 10.1126/science.279.5357.1737
63. Spada FM, Grant EP, Peters PJ, Sugita M, Melián A, Leslie DS, et al. Self-recognition of cd1 by Γ/Δ T cells: implications for innate immunity. J Exp Med. (2000) 191:937–48. doi: 10.1084/jem.191.6.937
64. Bai L, Picard D, Anderson B, Chaudhary V, Luoma A, Jabri B, et al. The majority of cd1d-sulfatide-specific T cells in human blood use a semiinvariant Vδ1 tcr. Eur J Immunol. (2012) 42:2505–10. doi: 10.1002/eji.201242531
65. Davey MS, Willcox CR, Hunter S, Kasatskaya SA, Remmerswaal EBM, Salim M, et al. The human Vδ2+ T-cell compartment comprises distinct innate-like Vγ9+ and adaptive Vγ9- subsets. Nat Commun. (2018) 9:1760. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-04076-0
66. McMurray JL, von Borstel A, Taher TE, Syrimi E, Taylor GS, Sharif M, et al. Transcriptional profiling of human Vδ1 T cells reveals a pathogen-driven adaptive differentiation program. Cell Rep. (2022) 39:110858. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.110858
67. Benzaïd I, Mönkkönen H, Stresing V, Bonnelye E, Green J, Mönkkönen J, et al. High phosphoantigen levels in bisphosphonate-treated human breast tumors promote vgamma9vdelta2 T-cell chemotaxis and cytotoxicity in vivo. Cancer Res. (2011) 71:4562–72. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.Can-10-3862
68. Rigau M, Ostrouska S, Fulford TS, Johnson DN, Woods K, Ruan Z, et al. Butyrophilin 2a1 is essential for phosphoantigen reactivity by Γδ T cells. Science. (2020) 367:eaay5516. doi: 10.1126/science.aay5516
69. Papadopoulou M, Tieppo P, McGovern N, Gosselin F, Chan JKY, Goetgeluk G, et al. Tcr sequencing reveals the distinct development of fetal and adult human Vγ9vδ2 T cells. J Immunol. (2019) 203:1468–79. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1900592
70. Fisher JP, Yan M, Heuijerjans J, Carter L, Abolhassani A, Frosch J, et al. Neuroblastoma killing properties of Vδ2 and Vδ2-negative Γδt cells following expansion by artificial antigen-presenting cells. Clin Cancer Res. (2014) 20:5720–32. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-13-3464
71. Brandes M, Willimann K, Bioley G, Lévy N, Eberl M, Luo M, et al. Cross-presenting human gammadelta T cells induce robust cd8+ Alphabeta T cell responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2009) 106:2307–12. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0810059106
72. Himoudi N, Morgenstern DA, Yan M, Vernay B, Saraiva L, Wu Y, et al. Human Γδ T lymphocytes are licensed for professional antigen presentation by interaction with opsonized target cells. J Immunol. (2012) 188:1708–16. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1102654
73. Mao C, Mou X, Zhou Y, Yuan G, Xu C, Liu H, et al. Tumor-activated tcrγδ T cells from gastric cancer patients induce the antitumor immune response of tcrαβ T cells via their antigen-presenting cell-like effects. J Immunol Res. (2014) 2014:593562. doi: 10.1155/2014/593562
74. Lafont V, Liautard J, Liautard JP, Favero J. Production of tnf-α by human Vγ9vδ2 T cells via engagement of fcγriiia, the low affinity type 3 receptor for the fc portion of igg, expressed upon tcr activation by nonpeptidic antigen1. J Immunol. (2001) 166:7190–9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.166.12.7190
75. Alnaggar M, Xu Y, Li J, He J, Chen J, Li M, et al. Allogenic Vγ9vδ2 T cell as new potential immunotherapy drug for solid tumor: A case study for cholangiocarcinoma. J Immunother Cancer. (2019) 7:36. doi: 10.1186/s40425-019-0501-8
76. Kierkels GJJ, Scheper W, Meringa AD, Johanna I, Beringer DX, Janssen A, et al. Identification of a tumor-specific allo-hla-restricted Γδtcr. Blood Adv. (2019) 3:2870–82. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2019032409
77. Scheper W, van Dorp S, Kersting S, Pietersma F, Lindemans C, Hol S, et al. Γδt cells elicited by cmv reactivation after allo-sct cross-recognize cmv and leukemia. Leukemia. (2013) 27:1328–38. doi: 10.1038/leu.2012.374
78. Willcox CR, Pitard V, Netzer S, Couzi L, Salim M, Silberzahn T, et al. Cytomegalovirus and tumor stress surveillance by binding of a human Γδ T cell antigen receptor to endothelial protein C receptor. Nat Immunol. (2012) 13:872–9. doi: 10.1038/ni.2394
79. Gaballa A, Alagrafi F, Uhlin M, Stikvoort A. Revisiting the role of Γδ T cells in anti-cmv immune response after transplantation. Viruses. (2021) 13:1031. doi: 10.3390/v13061031
80. Kalyan S, Kabelitz D. Defining the nature of human Γδ T cells: A biographical sketch of the highly empathetic. Cell Mol Immunol. (2013) 10:21–9. doi: 10.1038/cmi.2012.44
81. Berglund S, Gaballa A, Sawaisorn P, Sundberg B, Uhlin M. Expansion of gammadelta T cells from cord blood: A therapeutical possibility. Stem Cells Int. (2018) 2018:8529104. doi: 10.1155/2018/8529104
82. Benveniste PM, Roy S, Nakatsugawa M, Chen ELY, Nguyen L, Millar DG, et al. Generation and molecular recognition of melanoma-associated antigen-specific human Γδ T cells. Sci Immunol. (2018) 3:eaav4036. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.aav4036
83. Hur G, Choi H, Lee Y, Sohn H-J, Kim S-Y, Kim T-G. In vitro expansion of VΔ1+ T cells from cord blood by using artificial antigen-presenting cells and anti-cd3 antibody. Vaccines. (2023) 11:406.
84. Khan MWA, Otaibi AA, Sherwani S, Alshammari EM, Al-Zahrani SA, Khan WA, et al. Optimization of methods for peripheral blood mononuclear cells isolation and expansion of human gamma delta T cells. Bioinformation. (2021) 17:460–9. doi: 10.6026/97320630017460
85. Cruz MS, Diamond A, Russell A, Jameson JM. Human αβ and Γδ T cells in skin immunity and disease. Front Immunol. (2018) 9:1304. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01304
86. Cai Y, Shen X, Ding C, Qi C, Li K, Li X, et al. Pivotal role of dermal il-17-producing Γδ T cells in skin inflammation. Immunity. (2011) 35:649. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2011.10.006
87. Castillo-González R, Cibrian D, Sánchez-Madrid F. Dissecting the complexity of Γδ T-cell subsets in skin homeostasis, inflammation, and Malignancy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2021) 147:2030–42. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2020.11.023
88. Guo R, Li W, Li Y, Li Y, Jiang Z, Song Y. Generation and clinical potential of functional T lymphocytes from gene-edited pluripotent stem cells. Exp Hematol Oncol. (2022) 11:27. doi: 10.1186/s40164-022-00285-y
89. Themeli M, Kloss CC, Ciriello G, Fedorov VD, Perna F, Gonen M, et al. Generation of tumor-targeted human T lymphocytes from induced pluripotent stem cells for cancer therapy. Nat Biotechnol. (2013) 31:928–33. doi: 10.1038/nbt.2678
90. Wallet MA, Nishimura T, Del Casale C, Lebid A, Salantes B, Santostefano K, et al. Induced pluripotent stem cell-derived gamma delta car-T cells for cancer immunotherapy. Blood. (2021) 138:2771. doi: 10.1182/blood-2021-149095
91. Available online at: https://investor.adicetbio.com/news-releases/news-release-details/adicet-bio-reports-positive-data-ongoing-adi-001-phase-1-trial-0.
92. Murai N, Koyanagi-Aoi M, Terashi H, Aoi T. Re-generation of cytotoxic Γδt cells with distinctive signatures from human Γδt-derived ipscs. Stem Cell Rep. (2023) 18:853–68. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2023.02.010
93. Wu D, Wu P, Wu X, Ye J, Wang Z, Zhao S, et al. Ex vivo expanded human circulating Vδ1 Γδt cells exhibit favorable therapeutic potential for colon cancer. Oncoimmunology. (2015) 4:e992749. doi: 10.4161/2162402x.2014.992749
94. Almeida AR, Correia DV, Fernandes-Platzgummer A, da Silva CL, da Silva MG, Anjos DR, et al. Delta one T cells for immunotherapy of chronic lymphocytic leukemia: clinical-grade expansion/differentiation and preclinical proof of concept. Clin Cancer Res. (2016) 22:5795–804. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-16-0597
95. Lee SJ, Kim YH, Hwang SH, Kim YI, Han IS, Vinay DS, et al. 4–1bb signal stimulates the activation, expansion, and effector functions of Γδ T cells in mice and humans. Eur J Immunol. (2013) 43:1839–48. doi: 10.1002/eji.201242842
96. Siegers GM, Dhamko H, Wang X-H, Mathieson AM, Kosaka Y, Felizardo TC, et al. Human Vδ1 Γδ T cells expanded from peripheral blood exhibit specific cytotoxicity against B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia-derived cells. Cytotherapy. (2011) 13:753–64. doi: 10.3109/14653249.2011.553595
97. Ferry GM, Agbuduwe C, Forrester M, Dunlop S, Chester K, Fisher J, et al. A simple and robust single-step method for car-Vδ1 Γδt cell expansion and transduction for cancer immunotherapy. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:863155. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.863155
98. Chargui J, Combaret V, Scaglione V, Iacono I, Péri V, Valteau-Couanet D, et al. Bromohydrin pyrophosphate-stimulated Vγ9δ2 T cells expanded ex vivo from patients with poor-prognosis neuroblastoma lyse autologous primary tumor cells. J Immunother. (2010) 33:591–8. doi: 10.1097.CJI.0b013e3181dda207
99. Okuno D, Sugiura Y, Sakamoto N, Tagod MSO, Iwasaki M, Noda S, et al. Comparison of a novel bisphosphonate prodrug and zoledronic acid in the induction of cytotoxicity in human Vγ2vδ2 T cells. Front Immunol. (2020) 11:1405. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01405
100. Wang Y, Wang L, Seo N, Okumura S, Hayashi T, Akahori Y, et al. Car-modified VΓ9vΔ2 T cells propagated using a novel bisphosphonate prodrug for allogeneic adoptive immunotherapy. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:10873.
101. Rincon-Orozco B, Kunzmann V, Wrobel P, Kabelitz D, Steinle A, Herrmann T. Activation of Vγ9vδ2 T cells by nkg2d1. J Immunol. (2005) 175:2144–51. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.175.4.2144
102. Wang H, Sarikonda G, Puan K-J, Tanaka Y, Feng J, Giner J-L, et al. Indirect stimulation of human Vγ2vδ2 T cells through alterations in isoprenoid metabolism. J Immunol. (2011) 187:5099–113. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1002697
103. Peters C, Meyer A, Kouakanou L, Feder J, Schricker T, Lettau M, et al. Tgf-β Enhances the cytotoxic activity of Vδ2 T cells. OncoImmunology. (2019) 8:e1522471. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2018.1522471
104. Boucher JC, Yu B, Li G, Shrestha B, Sallman D, Landin AM, et al. Large scale ex vivo expansion of Γδ T cells using artificial antigen-presenting cells. J Immunother. (2023) 46:5–13. doi: 10.1097/cji.0000000000000445
105. Choi H, Lee Y, Hur G, Lee S-E, Cho H-I, Sohn H-J, et al. Γδ T cells cultured with artificial antigen-presenting cells and il-2 show long-term proliferation and enhanced effector functions compared with Γδ T cells cultured with only il-2 after stimulation with zoledronic acid. Cytotherapy. (2021) 23:908–17. doi: 10.1016/j.jcyt.2021.06.002
106. Kouakanou L, Xu Y, Peters C, He J, Wu Y, Yin Z, et al. Vitamin C promotes the proliferation and effector functions of human Γδ T cells. Cell Mol Immunol. (2020) 17:462–73. doi: 10.1038/s41423-019-0247-8
107. Polito VA, Cristantielli R, Weber G, Del Bufalo F, Belardinilli T, Arnone CM, et al. Universal ready-to-use immunotherapeutic approach for the treatment of cancer: expanded and activated polyclonal Γδ Memory T cells. Front Immunol. (2019) 10:2717. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02717
108. Deniger DC, Maiti SN, Mi T, Switzer KC, Ramachandran V, Hurton LV, et al. Activating and propagating polyclonal gamma delta T cells with broad specificity for Malignancies. Clin Cancer Res. (2014) 20:5708–19. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-13-3451
109. Landin AM, Cox C, Yu B, Bejanyan N, Davila M, Kelley L. Expansion and enrichment of gamma-delta (Γδ) T cells from apheresed human product. J Vis Exp. (2021) 175:e62622. doi: 10.3791/62622
110. Dokouhaki P, Han M, Joe B, Li M, Johnston MR, Tsao M-S, et al. Adoptive immunotherapy of cancer using ex vivo expanded human Γδ T cells: A new approach. Cancer Lett. (2010) 297:126–36. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2010.05.005
111. Kang N, Zhou J, Zhang T, Wang L, Lu F, Cui Y, et al. Adoptive immunotherapy of lung cancer with immobilized anti-tcrγδ Antibody-expanded human Γδ T cells in peripheral blood. Cancer Biol Ther. (2009) 8:1540–9. doi: 10.4161/cbt.8.16.8950
112. Zhou J, Kang N, Cui L, Ba D, He W. Anti-Γδ Tcr antibody-expanded Γδ T cells: A better choice for the adoptive immunotherapy of lymphoid Malignancies. Cell Mol Immunol. (2012) 9:34–44. doi: 10.1038/cmi.2011.16
113. Kondo M, Izumi T, Fujieda N, Kondo A, Morishita T, Matsushita H, et al. Expansion of human peripheral blood Γδ T cells using zoledronate. J Vis Exp. (2011) 55:e3182. doi: 10.3791/3182
114. Li W, Kubo S, Okuda A, Yamamoto H, Ueda H, Tanaka T, et al. Effect of il-18 on expansion of Γδ T cells stimulated by zoledronate and il-2. J Immunother. (2010) 33:287–96. doi: 10.1097/CJI.0b013e3181c80ffa
115. Holmen Olofsson G, Idorn M, Carnaz Simões AM, Aehnlich P, Skadborg SK, Noessner E, et al. Vγ9vδ2 T cells concurrently kill cancer cells and cross-present tumor antigens. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:645131. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.645131
116. Kondo M, Sakuta K, Noguchi A, Ariyoshi N, Sato K, Sato S, et al. Zoledronate facilitates large-scale ex vivo expansion of functional gammadelta T cells from cancer patients for use in adoptive immunotherapy. Cytotherapy. (2008) 10:842–56. doi: 10.1080/14653240802419328
117. Siegers GM, Ribot EJ, Keating A, Foster PJ. Extensive expansion of primary human gamma delta T cells generates cytotoxic effector memory cells that can be labeled with feraheme for cellular mri. Cancer Immunol Immunother. (2013) 62:571–83. doi: 10.1007/s00262-012-1353-y
118. Tan W-K, Tay JC, Zeng J, Zheng M, Wang S, Therapeutics T, et al. Expansion of Gamma Delta T Cells - a Short Review on Bisphosphonate and K562-Based Methods. J Immunol Sci. (2018) 2:6–12. doi: 10.29245/2578-3009/2018/3.1133
119. Bold A, Gross H, Holzmann E, Knop S, Hoeres T, Wilhelm M. An optimized cultivation method for future in vivo application of Γδ T cells. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1185564. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1185564
120. Makkouk A, Yang X, Barca T, Lucas A, Turkoz M, Wong J, et al. 119 adi-002: an il-15 armored allogeneic ‘Off-the-shelf’ Vδ1 gamma delta car T cell therapy for solid tumors targeting glypican-3 (Gpc3). J ImmunoTher Cancer. (2021) 9:A128–A. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2021-SITC2021.119
121. Herrman M, Barca T, Yang X, Tabrizizad M, Smith-Boeck M, Kiru L, et al. 198 innate-enhanced chimeric adaptors (Cad): A newly-described approach for augmenting potency of Γδ T cell immunotherapy. J ImmunoTher Cancer. (2022) 10:A211–A. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2022-SITC2022.0198
122. Ang WX, Ng YY, Xiao L, Chen C, Li Z, Chi Z, et al. Electroporation of Nkg2d Rna Car Improves Vγ9vδ2 t Cell Responses against Human Solid Tumor Xenografts. Mol Ther Oncolytics. (2020) 17:421–30. doi: 10.1016/j.omto.2020.04.013
123. Ding L, Li Y, Haak MT, Lamb L. Abstract 1777: A non-signaling car for gamma-delta (Γδ) T cells to preserve healthy tissues. Cancer Res. (2023) 83:1777–. doi: 10.1158/1538-7445.Am2023-1777
124. Lamb LS, Pereboeva L, Youngblood S, Gillespie GY, Nabors LB, Markert JM, et al. A combined treatment regimen of mgmt-modified Γδ T cells and temozolomide chemotherapy is effective against primary high grade gliomas. Sci Rep. (2021) 11:21133. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-00536-8
125. Rozenbaum M, Meir A, Aharony Y, Itzhaki O, Schachter J, Bank I, et al. Gamma-delta car-T cells show car-directed and independent activity against leukemia. Front Immunol. (2020) 11:1347. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01347
126. Zhang X, Ng YY, Du Z, Li Z, Chen C, Xiao L, et al. Vγ9vδ2 T cells expressing a bcma—Specific chimeric antigen receptor inhibit multiple myeloma xenograft growth. PloS One. (2022) 17:e0267475. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0267475
127. Zhai X, You F, Xiang S, Jiang L, Chen D, Li Y, et al. Muc1-tn-targeting chimeric antigen receptor-modified Vγ9vδ2 T cells with enhanced antigen-specific anti-tumor activity. Am J Cancer Res. (2021) 11:79–91.
128. Makkouk A, Yang XC, Barca T, Lucas A, Turkoz M, Wong JTS, et al. Off-the-shelf Vδ1 gamma delta T cells engineered with glypican-3 (Gpc-3)-specific chimeric antigen receptor (Car) and soluble il-15 display robust antitumor efficacy against hepatocellular carcinoma. J Immunother Cancer. (2021) 9:e003441. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2021-003441
129. Fleischer LC, Becker SA, Ryan RE, Fedanov A, Doering CB, Spencer HT. Non-signaling chimeric antigen receptors enhance antigen-directed killing by Γδ T cells in contrast to αβ T cells. Mol Ther Oncolytics. (2020) 18:149–60. doi: 10.1016/j.omto.2020.06.003
130. Fisher J, Abramowski P, Wisidagamage Don ND, Flutter B, Capsomidis A, Cheung GW-K, et al. Avoidance of on-target off-tumor activation using a co-stimulation-only chimeric antigen receptor. Mol Ther. (2017) 25:1234–47. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2017.03.002
131. Zhang X, Ang WX, Du Z, Ng YY, Zha S, Chen C, et al. A cd123-specific chimeric antigen receptor augments anti-acute myeloid leukemia activity of Vγ9vδ2 T cells. Immunotherapy. (2022) 14:321–36. doi: 10.2217/imt-2021-0143
132. de Weerdt I, Lameris R, Scheffer GL, Vree J, de Boer R, Stam AG, et al. A bispecific antibody antagonizes prosurvival cd40 signaling and promotes Vγ9vδ2 T cell–mediated antitumor responses in human B-cell Malignancies. Cancer Immunol Res. (2021) 9:50–61. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.Cir-20-0138
133. de Weerdt I, Lameris R, Ruben JM, de Boer R, Kloosterman J, King LA, et al. A bispecific single-domain antibody boosts autologous Vγ9vδ2-T cell responses toward cd1d in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Clin Cancer Res. (2021) 27:1744–55. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-20-4576
134. Yang R, He Q, Zhou H, Gong C, Wang X, Song X, et al. Vγ2 X pd-L1, a bispecific antibody targeting both the Vγ2 tcr and pd-L1, improves the anti-tumor response of Vγ2vδ2 T cell. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:923969. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.923969
135. Oberg H-H, Peipp M, Kellner C, Sebens S, Krause S, Petrick D, et al. Novel bispecific antibodies increase Γδ T-cell cytotoxicity against pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Res. (2014) 74:1349–60. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.Can-13-0675
136. Ganesan R, Chennupati V, Ramachandran B, Hansen MR, Singh S, Grewal IS. Selective recruitment of Γδ T cells by a bispecific antibody for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia. (2021) 35:2274–84. doi: 10.1038/s41375-021-01122-7
137. King LA, Toffoli EC, Veth M, Iglesias-Guimarais V, Slot MC, Amsen D, et al. A bispecific Γδ T-cell engager targeting egfr activates a potent Vγ9vδ2 T cell-mediated immune response against egfr-expressing tumors. Cancer Immunol Res. (2023) 11(9):1237–52. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.Cir-23-0189
138. Hiasa A, Nishikawa H, Hirayama M, Kitano S, Okamoto S, Chono H, et al. Rapid αβ Tcr-mediated responses in Γδ T cells transduced with cancer-specific tcr genes. Gene Ther. (2009) 16:620–8. doi: 10.1038/gt.2009.6
139. van der Veken LT, Hagedoorn RS, van Loenen MM, Willemze R, Falkenburg JHF, Heemskerk MHM. αβ T-cell receptor engineered Γδ T cells mediate effective antileukemic reactivity. Cancer Res. (2006) 66:3331–7. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.Can-05-4190
140. Ishihara M, Miwa H, Fujiwara H, Akahori Y, Kato T, Tanaka Y, et al. αβ-T cell receptor transduction gives superior mitochondrial function to Γδ-T cells with promising persistence. iScience. (2023) 26:107802. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.107802
141. Legut M, Dolton G, Mian AA, Ottmann OG, Sewell AK. Crispr-mediated tcr replacement generates superior anticancer transgenic T cells. Blood. (2018) 131:311–22. doi: 10.1182/blood-2017-05-787598
142. Ichiki Y, Shigematsu Y, Baba T, Shiota H, Fukuyama T, Nagata Y, et al. Development of adoptive immunotherapy with kk-lc-1-specific tcr-transduced Γδt cells against lung cancer cells. Cancer Sci. (2020) 111:4021–30. doi: 10.1111/cas.14612
143. Shimizu K, Shinga J, Yamasaki S, Kawamura M, Dörrie J, Schaft N, et al. Transfer of mrna encoding invariant nkt cell receptors imparts glycolipid specific responses to T cells and Γδt cells. PloS One. (2015) 10:e0131477. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0131477
144. Neelapu SS, Hamadani M, Miklos DB, Holmes H, Hinkle J, Kennedy-Wilde J, et al. A phase 1 study of adi-001: anti-cd20 car-engineered allogeneic gamma delta (Γδ) T cells in adults with B-cell Malignancies. J Clin Oncol. (2022) 40:7509–. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2022.40.16_suppl.7509
145. Broijl A, Donk N, Bosch F, Mateos M-V, Rodríguez-Otero P, Tucci A, et al. Phase I dose escalation of lava-051, a novel bispecific gamma-delta T-cell engager (Gammabody), in relapsed/refractory hematological Malignancies. J Clin Oncol. (2022) 40:2577–. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2022.40.16_suppl.2577
146. Mehra N, Robbrecht D, Voortman J, Parren PWHI, Macia S, Veeneman J, et al. Early dose escalation of lava-1207, a novel bispecific gamma-delta T-cell engager (Gammabody), in patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (Mcrpc). J Clin Oncol. (2023) 41:153–. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2023.41.6_suppl.153
147. He P, Liu H, Zimdahl B, Wang J, Luo M, Chang Q, et al. A novel antibody-tcr (Abtcr) T-cell therapy is safe and effective against cd19-positive relapsed/refractory B-cell lymphoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. (2023) 149:2757–69. doi: 10.1007/s00432-022-04132-9
148. Li H-K, Wu T-S, Kuo Y-C, Hsiao C-W, Yang H-P, Lee C-Y, et al. 251 application of antibody-cell conjugation technology in a novel off-the-shelf cd20-targeting gamma delta T cell therapy ace1831. J ImmunoTher Cancer. (2022) 10:A266–A. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2022-SITC2022.0251
149. Nabors LB, Lamb LS, Beelen MJ, Pillay T, Haak MT, Youngblood S, et al. Phase 1 trial of drug resistant immunotherapy: A first-in-class combination of mgmt-modified Γδ T cells and temozolomide chemotherapy in newly diagnosed glioblastoma. J Clin Oncol. (2021) 39:2057–. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2021.39.15_suppl.2057
150. Sterner RC, Sterner RM. Car-T cell therapy: current limitations and potential strategies. Blood Cancer J. (2021) 11:69. doi: 10.1038/s41408-021-00459-7
151. Frieling JS, Tordesillas L, Bustos XE, Ramello MC, Bishop RT, Cianne JE, et al. Γδ-enriched car-T cell therapy for bone metastatic castrate-resistant prostate cancer. Sci Adv. (2023) 9:eadf0108. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adf0108
152. June CH, Sadelain M. Chimeric antigen receptor therapy. New Engl J Med. (2018) 379:64–73. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1706169
153. Shah NN, Lee DW, Yates B, Yuan CM, Shalabi H, Martin S, et al. Long-term follow-up of cd19-car T-cell therapy in children and young adults with B-all. J Clin Oncol. (2021) 39:1650–9. doi: 10.1200/jco.20.02262
154. Becker SA, Petrich BG, Yu B, Knight KA, Brown HC, Raikar SS, et al. Enhancing the Effectiveness of Γδ T cells by Mrna Transfection of Chimeric Antigen Receptors or Bispecific T cell Engagers. Mol Ther Oncolytics. (2023) 29:145–57. doi: 10.1016/j.omto.2023.05.007
155. Rischer M, Pscherer S, Duwe S, Vormoor J, Jürgens H, Rossig C. Human Γδ T cells as mediators of chimaeric-receptor redirected anti-tumour immunity. Br J Haematol. (2004) 126:583–92. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.2004.05077.x
156. Cummins KD, Frey N, Nelson AM, Schmidt A, Luger S, Isaacs RE, et al. Treating relapsed/refractory (Rr) aml with biodegradable anti-cd123 car modified T cells. Blood. (2017) 130:1359–. doi: 10.1182/blood.V130.Suppl_1.1359.1359
157. Wang Y, Ji N, Zhang Y, Chu J, Pan C, Zhang P, et al. B7h3-targeting chimeric antigen receptor modification enhances antitumor effect of Vγ9vδ2 T cells in glioblastoma. J Trans Med. (2023) 21:672. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04514-8
158. Fedorov VD, Themeli M, Sadelain M. Pd-1- and ctla-4-based inhibitory chimeric antigen receptors (Icars) divert off-target immunotherapy responses. Sci Transl Med. (2013) 5:215ra172. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3006597
159. Helsen CW, Hammill JA, Lau VWC, Mwawasi KA, Afsahi A, Bezverbnaya K, et al. The chimeric tac receptor co-opts the T cell receptor yielding robust anti-tumor activity without toxicity. Nat Commun. (2018) 9:3049. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-05395-y
160. Asbury S, Yoo SM, Bramson J. 101 engineering gamma/delta T cells with the T-cell antigen coupler receptor effectively induces antigen-specific tumor cytotoxicity in vitro and in vivo. J ImmunoTher Cancer. (2020) 8:A63–A4. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2020-SITC2020.0101
161. Hirabayashi K, Du H, Xu Y, Shou P, Zhou X, Fucá G, et al. Dual-targeting car-T cells with optimal co-stimulation and metabolic fitness enhance antitumor activity and prevent escape in solid tumors. Nat Cancer. (2021) 2:904–18. doi: 10.1038/s43018-021-00244-2
162. Han X, Bryson PD, Zhao Y, Cinay GE, Li S, Guo Y, et al. Masked chimeric antigen receptor for tumor-specific activation. Mol Ther. (2017) 25:274–84. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2016.10.011
163. Zhang C, Liu J, Zhong JF, Zhang X. Engineering car-T cells. biomark Res. (2017) 5:22. doi: 10.1186/s40364-017-0102-y
164. Fisher J, Sharma R, Don DW, Barisa M, Hurtado MO, Abramowski P, et al. Engineering Γδt cells limits tonic signaling associated with chimeric antigen receptors. Sci Signaling. (2019) 12:eaax1872. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aax1872
165. Jonus HC, Lee JY, Silva JA, Spencer HT, Goldsmith KC. Abstract 4093: dual targeted car immunotherapy for neuroblastoma using Γδ T cells. Cancer Res. (2023) 83:4093–. doi: 10.1158/1538-7445.Am2023-4093
166. Zah E, Lin MY, Silva-Benedict A, Jensen MC, Chen YY. T cells expressing cd19/cd20 bispecific chimeric antigen receptors prevent antigen escape by Malignant B cells. Cancer Immunol Res. (2016) 4:498–508. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.Cir-15-0231
167. Supimon K, Sangsuwannukul T, Sujjitjoon J, Chieochansin T, Junking M, Yenchitsomanus P-t. Cytotoxic activity of anti-mucin 1 chimeric antigen receptor T cells expressing pd-1-cd28 switch receptor against cholangiocarcinoma cells. Cytotherapy. (2023) 25:148–61. doi: 10.1016/j.jcyt.2022.10.006
168. Liao Q, Mao Y, He H, Ding X, Zhang X, Xu J. Pd-L1 chimeric costimulatory receptor improves the efficacy of car-T cells for pd-L1-positive solid tumors and reduces toxicity in vivo. biomark Res. (2020) 8:57. doi: 10.1186/s40364-020-00237-w
169. Roybal Kole T, Rupp Levi J, Morsut L, Walker Whitney J, McNally Krista A, Park Jason S, et al. Precision tumor recognition by T cells with combinatorial antigen-sensing circuits. Cell. (2016) 164:770–9. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.01.011
170. Moretti A, Ponzo M, Nicolette CA, Tcherepanova IY, Biondi A, Magnani CF. The past, present, and future of non-viral car T cells. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:867013. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.867013
171. Scholler J, Brady TL, Binder-Scholl G, Hwang W-T, Plesa G, Hege KM, et al. Decade-long safety and function of retroviral-modified chimeric antigen receptor T cells. Sci Trans Med. (2012) 4:132ra53–ra53. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3003761
172. Fisher J, Anderson J. Engineering approaches in human gamma delta T cells for cancer immunotherapy. Front Immunol. (2018) 9:1409. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01409
173. Anderson J, Barisa M. Enhancing the Effectiveness of Γδ T cells by Mrna Transfection of Chimeric Antigen Receptors or Bispecific T cell Engagers. Mol Ther Oncolytics. (2023) 30:151–2. doi: 10.1016/j.omto.2023.08.003
174. Deniger DC, Switzer K, Mi T, Maiti S, Hurton L, Singh H, et al. Bispecific T-cells expressing polyclonal repertoire of endogenous Γδ T-cell receptors and introduced cd19-specific chimeric antigen receptor. Mol Ther. (2013) 21:638–47. doi: 10.1038/mt.2012.267
175. Harrer DC, Simon B, Fujii S-i, Shimizu K, Uslu U, Schuler G, et al. Rna-transfection of Γ/Δ T cells with a chimeric antigen receptor or an α/β T-cell receptor: A safer alternative to genetically engineered α/β T cells for the immunotherapy of melanoma. BMC Cancer. (2017) 17:551. doi: 10.1186/s12885-017-3539-3
176. Lameris R, Ruben JM, Iglesias-Guimarais V, de Jong M, Veth M, van de Bovenkamp FS, et al. A bispecific T cell engager recruits both type 1 nkt and Vγ9vδ2-T cells for the treatment of cd1d-expressing hematological Malignancies. Cell Rep Med. (2023) 4:100961. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2023.100961
177. Goebeler M-E, Bargou RC. T cell-engaging therapies — Bites and beyond. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. (2020) 17:418–34. doi: 10.1038/s41571-020-0347-5
178. Lai AY, Patel A, Brewer F, Evans K, Johannes K, González LE, et al. Cutting edge: bispecific Γδ T cell engager containing heterodimeric btn2a1 and btn3a1 promotes targeted activation of Vγ9vδ2(+) T cells in the presence of costimulation by cd28 or nkg2d. J Immunol. (2022) 209:1475–80. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2200185
179. Arbabi-Ghahroudi M. Camelid single-domain antibodies: historical perspective and future outlook. Front Immunol. (2017) 8:1589. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01589
180. Nathan P, Hassel JC, Rutkowski P, Baurain JF, Butler MO, Schlaak M, et al. Overall survival benefit with tebentafusp in metastatic uveal melanoma. N Engl J Med. (2021) 385:1196–206. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2103485
181. Ma J, Mo Y, Tang M, Shen J, Qi Y, Zhao W, et al. Bispecific antibodies: from research to clinical application. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:626616. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.626616
182. De Gassart A, Le K-S, Brune P, Agaugué S, Sims J, Goubard A, et al. Development of ict01, a first-in-class, anti-btn3a antibody for activating Vγ9vδ2 T cell–mediated antitumor immune response. Sci Trans Med. (2021) 13:eabj0835. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.abj0835
183. Li H-K, Wu T-S, Leng P-R, Kuo Y-C, Cheng Z-F, Lee C-Y, et al. Abstract lb089: ace2016: an off-the-shelf egfr-targeting Γδ2 T cell therapy against egfr-expressing solid tumors. Cancer Res. (2023) 83:LB089–LB. doi: 10.1158/1538-7445.Am2023-lb089
184. van der Veken LT, Coccoris M, Swart E, Falkenburg JHF, Schumacher TN, Heemskerk MHM. αβ T cell receptor transfer to Γδ T cells generates functional effector cells without mixed tcr dimers in vivo1. J Immunol. (2009) 182:164–70. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.182.1.164
185. Drent E, Bisso A, Baardman S, Verweij D, Salcedo E, Coomans C, et al. Abstract 2818: targeting solid tumors with gdt002, a first-in-class Γδtcr-based T cell therapy. Cancer Res. (2022) 82:2818–. doi: 10.1158/1538-7445.Am2022-2818
186. Chen Z, Lin C, Pei H, Yuan X, Xu J, Zou M, et al. Antibody-based binding domain fused to tcrγ Chain facilitates T cell cytotoxicity for potent anti-tumor response. Oncogenesis. (2023) 12:33. doi: 10.1038/s41389-023-00480-4
187. Xu Y, Yang Z, Horan LH, Zhang P, Liu L, Zimdahl B, et al. A novel antibody-tcr (Abtcr) platform combines fab-based antigen recognition with gamma/delta-tcr signaling to facilitate T-cell cytotoxicity with low cytokine release. Cell Discovery. (2018) 4:62. doi: 10.1038/s41421-018-0066-6
188. Li C, Zhou F, Wang J, Chang Q, Du M, Luo W, et al. Novel cd19-specific Γ/Δ Tcr-T cells in relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. J Hematol Oncol. (2023) 16:5. doi: 10.1186/s13045-023-01402-y
189. Moon EK, Wang LC, Dolfi DV, Wilson CB, Ranganathan R, Sun J, et al. Multifactorial T-cell hypofunction that is reversible can limit the efficacy of chimeric antigen receptor-transduced human T cells in solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res. (2014) 20:4262–73. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-13-2627
190. Menon H, Chen D, Ramapriyan R, Verma V, Barsoumian HB, Cushman TR, et al. Influence of low-dose radiation on abscopal responses in patients receiving high-dose radiation and immunotherapy. J Immunother Cancer. (2019) 7:237. doi: 10.1186/s40425-019-0718-6
191. Lu L, Zhan M, Li XY, Zhang H, Dauphars DJ, Jiang J, et al. Clinically approved combination immunotherapy: current status, limitations, and future perspective. Curr Res Immunol. (2022) 3:118–27. doi: 10.1016/j.crimmu.2022.05.003
192. Park JH, Lee HK. Function of gammadelta T cells in tumor immunology and their application to cancer therapy. Exp Mol Med. (2021) 53:318–27. doi: 10.1038/s12276-021-00576-0
193. Lino CA, Harper JC, Carney JP, Timlin JA. Delivering crispr: A review of the challenges and approaches. Drug Delivery. (2018) 25:1234–57. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2018.1474964
194. Zhang P, Zhang G, Wan X. Challenges and new technologies in adoptive cell therapy. J Hematol Oncol. (2023) 16:97. doi: 10.1186/s13045-023-01492-8
195. Wang RN, Wen Q, He WT, Yang JH, Zhou CY, Xiong WJ, et al. Optimized protocols for Γδ T cell expansion and lentiviral transduction. Mol Med Rep. (2019) 19:1471–80. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2019.9831
196. Gustafsson K, Herrmann T, Dieli F. Editorial: understanding gamma delta T cell multifunctionality - towards immunotherapeutic applications. Front Immunol. (2020) 11:921. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00921
197. Hamieh M, Dobrin A, Cabriolu A, van der Stegen SJC, Giavridis T, Mansilla-Soto J, et al. Car T cell trogocytosis and cooperative killing regulate tumour antigen escape. Nature. (2019) 568:112–6. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1054-1
198. Huang SW, Pan CM, Lin YC, Chen MC, Chen Y, Jan CI, et al. Bite-secreting car-gammadeltat as a dual targeting strategy for the treatment of solid tumors. Adv Sci (Weinh). (2023) 10:e2206856. doi: 10.1002/advs.202206856
199. Jin C, Lagoudas GK, Zhao C, Bullman S, Bhutkar A, Hu B, et al. Commensal microbiota promote lung cancer development via gammadelta T cells. Cell. (2019) 176:998–1013 e16. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.12.040
200. Coffelt SB, Kersten K, Doornebal CW, Weiden J, Vrijland K, Hau CS, et al. Il-17-producing gammadelta T cells and neutrophils conspire to promote breast cancer metastasis. Nature. (2015) 522:345–8. doi: 10.1038/nature14282
201. Lopes N, McIntyre C, Martin S, Raverdeau M, Sumaria N, Kohlgruber AC, et al. Distinct metabolic programs established in the thymus control effector functions of gammadelta T cell subsets in tumor microenvironments. Nat Immunol. (2021) 22:179–92. doi: 10.1038/s41590-020-00848-3
202. Wu P, Wu D, Ni C, Ye J, Chen W, Hu G, et al. Gammadeltat17 cells promote the accumulation and expansion of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in human colorectal cancer. Immunity. (2014) 40:785–800. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2014.03.013
203. Ganapathy T, Radhakrishnan R, Sakshi S, Martin S. Car gammadelta T cells for cancer immunotherapy. Is the field more yellow than green? Cancer Immunol Immunother. (2023) 72:277–86. doi: 10.1007/s00262-022-03260-y
Keywords: γδT cells, immunotherapy, engineering, cellular therapy, cancer, CAR-T
Citation: Yuan M, Wang W, Hawes I, Han J, Yao Z and Bertaina A (2024) Advancements in γδT cell engineering: paving the way for enhanced cancer immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 15:1360237. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1360237
Received: 22 December 2023; Accepted: 07 March 2024;
Published: 21 March 2024.
Edited by:
Jonathan Fisher, University College London, United KingdomReviewed by:
Prashant Sharma, University of Arizona, United StatesBrian Petrich, Expression Therapeutics, United States
Martin Wilhelm, Nürnberg Hospital, Germany
Copyright © 2024 Yuan, Wang, Hawes, Han, Yao and Bertaina. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Wenjun Wang, d2VuanVuMjdAc3RhbmZvcmQuZWR1; Alice Bertaina, YWxpY2ViMUBzdGFuZm9yZC5lZHU=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Megan Yuan
Megan Yuan Wenjun Wang
Wenjun Wang Isobel Hawes
Isobel Hawes Junwen Han
Junwen Han Zhenyu Yao
Zhenyu Yao Alice Bertaina
Alice Bertaina