- 1New Drug Incubator Department, Italfarmaco Group, Milan, Italy
- 2Preclinical Drug Development Department, Italfarmaco Group, Milan, Italy
- 3Department of Experimental Oncology, IEO European Institute of Oncology IRCCS, Milan, Italy
- 4Department of Oncology and Hematology-Oncology (DIPO), University of Milan, Milan, Italy
By Spadotto V, Ripamonti C, Ghiroldi A, Galbiati E, Pozzi P, Noberini R, Bonaldi T, Steinkühler C and Fossati G (2025). Front. Immunol. 16:1546939. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1546939
In the published article, there was an error in Figure 6 as published. There was a mistake in the axes of Figure 6C and Figure 6D as published, and as a result, the list of the genes were not correct. The corrected Figure 6 and its caption “ITF3756 downregulates monocytes activation and differentiation markers activated by TNF-α and promotes a less immunosuppressive phenotype in TNF-α stimulated monocytes. Purified human monocytes were treated for 2h with ITF3756 (1μM) and then stimulated with TNF-α (100ng/ml) for 4h. RNAseq data obtained as described before were used for this analysis. (A) Analysis of the modulation of specific markers of monocytes-derived cell population by TNF-α (left panel) and by the combination of TNF-α and ITF3756 (right panel). Fold changes (FC) are calculated versus the unstimulated control cells or versus the TNF-α stimulated cells, respectively. (B–D) Analysis of the modulation by TNF-α and by the combination of TNF-α and ITF3756 of a list of inhibitory immune checkpoints (31). Fold changes (FC) are calculated versus the unstimulated control cells in (B), versus the TNF-α stimulated cells in (C) and between ITF3756 and unstimulated control cells in (D). Significant differentially expressed genes are represented as circles, while non-significant genes are shown as triangles” appear below.
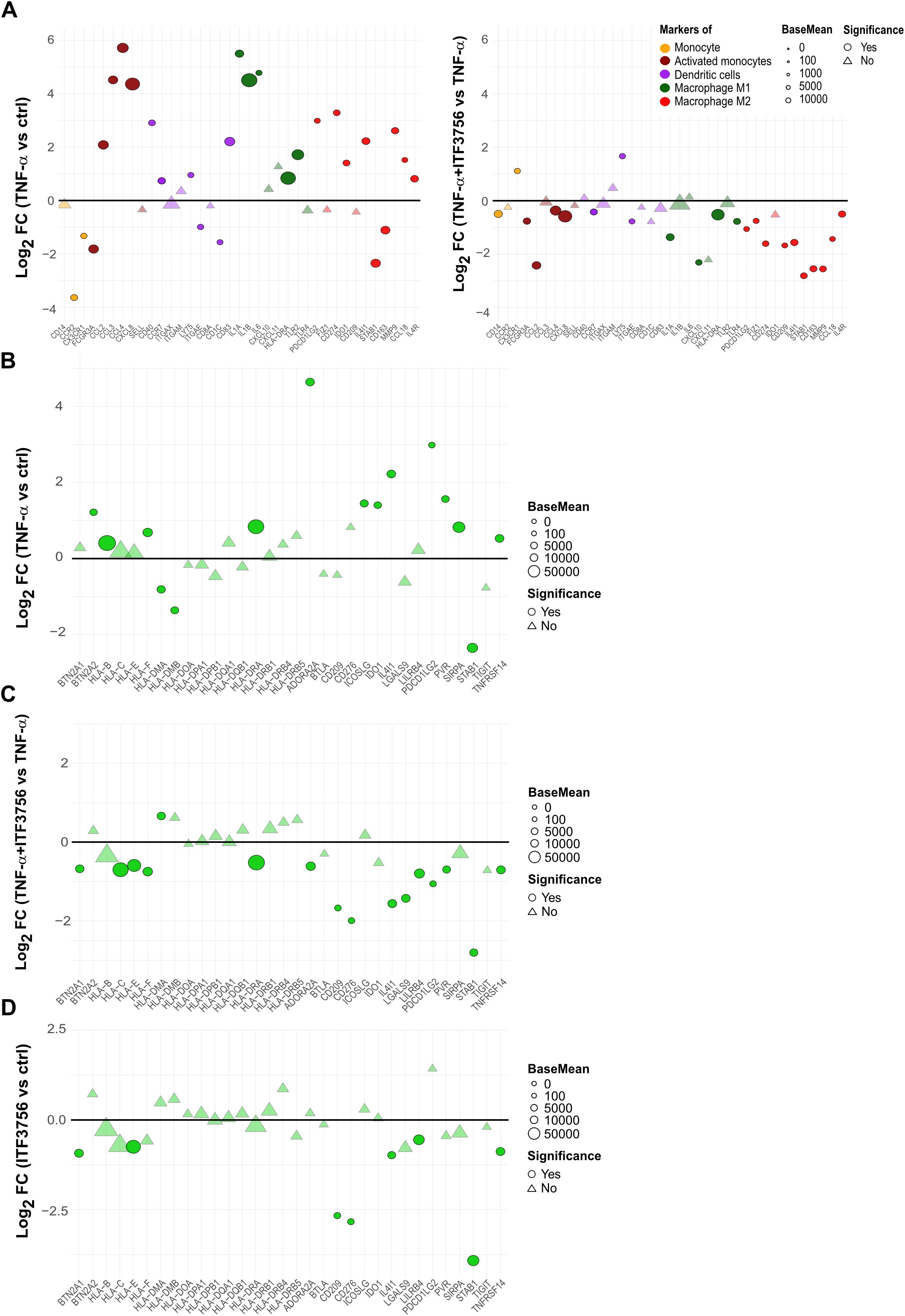
Figure 6. ITF3756 downregulates monocytes activation and differentiation markers activated by TNF-α and promotes a less immunosuppressive phenotype in TNF-α stimulated monocytes. Purified human monocytes were treated for 2h with ITF3756 (1μM) and then stimulated with TNF-α (100ng/ml) for 4h. RNAseq data obtained as described before were used for this analysis. (A) Analysis of the modulation of specific markers of monocytes-derived cell population by TNF-α (left panel) and by the combination of TNF-α and ITF3756 (right panel). Fold changes (FC) are calculated versus the unstimulated control cells or versus the TNF-α stimulated cells, respectively. (B–D) Analysis of the modulation by TNF-α and by the combination of TNF-α and ITF3756 of a list of inhibitory immune checkpoints (31). Fold changes (FC) are calculated versus the unstimulated control cells in (B), versus the TNF-α stimulated cells in (C) and between ITF3756 and unstimulated control cells in (D). Significant differentially expressed genes are represented as circles, while non-significant genes are shown as triangles.
The original article has been updated.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: HDAC6, monocytes, immuno-checkpoints, TNF-α, dendritic cells
Citation: Spadotto V, Ripamonti C, Ghiroldi A, Galbiati E, Pozzi P, Noberini R, Bonaldi T, Steinkühler C and Fossati G (2025) Correction: HDAC6 inhibition by ITF3756 modulates PD-L1 expression and monocyte phenotype: insights for a promising immune checkpoint blockade co-treatment therapy. Front. Immunol. 16:1645773. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1645773
Received: 12 June 2025; Accepted: 21 July 2025;
Published: 05 August 2025.
Edited and Reviewed by:
S. Paul Gao, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, United StatesCopyright © 2025 Spadotto, Ripamonti, Ghiroldi, Galbiati, Pozzi, Noberini, Bonaldi, Steinkühler and Fossati. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Gianluca Fossati, Zy5mb3NzYXRpQGl0YWxmYXJtYWNvZ3JvdXAuY29t
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Valeria Spadotto1†
Valeria Spadotto1† Chiara Ripamonti
Chiara Ripamonti Andrea Ghiroldi
Andrea Ghiroldi Gianluca Fossati
Gianluca Fossati