- 1Department of Clinical Laboratory, The First Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou, China
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou, China
- 3Department of Infectious Diseases, Sir Run Run Shaw Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou, China
- 4School of Laboratory Medicine and Life Science, Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou, China
- 5Biomedicine Discovery Institute, Department of Microbiology, Faculty of Medicine, Nursing and Health Sciences, Monash University, Clayton, VIC, Australia
Tigecycline is a last-resort antibiotic for infections caused by carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae (CRKP). This study aimed to broaden our understanding of the acquisition of collateral hypersensitivity by CRKP, as an evolutionary trade-off of developing resistance to tigecycline. Experimental induction of tigecycline resistance was conducted with tigecycline-sensitive CRKP clinical isolates. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing, microbial fitness assessment, genotypic analysis and full-genome sequencing were carried out for these clinical isolates and their resistance-induced descendants. We found that tigecycline resistance was successfully induced after exposing CRKP clinical isolates to tigecycline at gradually increased concentrations, at a minor fitness cost of bacterial cells. Quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) found higher expression of the efflux pump gene acrB (5.3–64.5-fold) and its regulatory gene ramA (7.4–65.8-fold) in resistance-induced strains compared to that in the tigecycline-sensitive clinical isolates. Stable hypersensitivities to aminoglycosides and other antibiotics were noticed in resistance-induced strains, showing significantly lowered MICs (X 4 – >500 times). Full genome sequencing and plasmid analysis suggested the induced collateral hypersensitivity might be multifaceted, with the loss of an antimicrobial resistance (AMR) plasmid being a possible major player. This study rationalized the sequential combination of tigecycline with aminoglycosides for the treatment of CRKP infections.
Introduction
Carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae (CRKP) has emerged as one of the deadliest causes of hospital-acquired infections and poses a serious therapeutic concern (Petrosillo et al., 2013). Overproduction of various carbapenemases in CRKP, such as Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemase (KPC) and metallo-β-lactamases (MBLs), renders the bacteria resistant to nearly all β-lactam antibiotics including carbapenems (Petrosillo et al., 2013).
Tigecycline and colistin are the very few options in the antibiotic arsenal for infections caused by carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae (Stein and Babinchak, 2013; Sun et al., 2013). Resistance to tigecycline of Klebsiella or other Enterobacteriaceae has emerged after its wide use in clinical settings, either as a monotherapy or in combination with other antibiotics (Woodford et al., 2007; Poulakou et al., 2009; Hirsch and Tam, 2010; Sekowska and Gospodarek, 2010; Stein and Babinchak, 2013; Sun et al., 2013; Gonzalez-Padilla et al., 2015). Underlying molecular mechanisms of tigecycline resistance are complex, with the upregulation of resistance-nodulation-division (RND) efflux pumps being a major contributor. Efflux pump systems related to tigecycline resistance include AcrAB-TolC and its positive regulators, ramA, SoxS, MarA or its negative regulator ramR (Hentschke et al., 2010; Roy et al., 2013; Villa et al., 2014; He et al., 2015; Juan et al., 2016; Xu et al., 2016), OqxAB and its positive regulator rarA and negative regulator oqxR (Zhong et al., 2014; Juan et al., 2016), and KpgABC (Nielsen et al., 2014; Juan et al., 2016). Structural alteration of the 30S ribosomal subunit protein S10 is another important resistance mechanism, mediated by mutations in the rpsJ gene and consequential target site modifications (Villa et al., 2014). A unique enzymatic inactivation mechanism mediated by Tet(X3) and Tet(X4), has also been associated with tigecycline resistance of numerous carbapenems-resistant Enterobacteriaceae (He et al., 2019; Sun et al., 2019).
Development of collateral sensitivity is a widespread evolutionary trade-off that occurs in many Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria (Barbosa et al., 2017; Lozano-Huntelman et al., 2020). Only a limited number of studies have examined collateral sensitivity in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Du et al. (2018) found that K. pneumoniae synchronously regained susceptibility to imipenem and meropenem when the patient developed resistance to tigecycline after long-term antibiotic treatment (Du et al., 2018). Villa et al. (2013) reported a reversion to susceptibility to carbapenems of a CRKP clinical isolate under the pressure of tigecycline (Villa et al., 2013). Proposed mechanisms mediating collateral sensitivity include plasticity of mobile elements in the host bacterium (Stohr et al., 2020), change of global gene expression associated with mutations in resistance genes (Maltas and Wood, 2019), amino acid deletions/substitutions that might result in reduced antibiotic hydrolase activity (Frohlich et al., 2019), and resistance mutations in regulatory genes for efflux pumps (Villa et al., 2013; Barbosa et al., 2017). Membrane-potential-altering mutations may also contribute to reversion of bacterial susceptibility to several unrelated classes of antibiotics, by changing the proton-motive force (PMF) and diminishing the activity of PMF-dependent major efflux pumps (Pal et al., 2015; Furusawa et al., 2018).
Recent emergence of CRKP clinical isolates that are resistant to both tigecycline and colistin, and discovery of a plasmid-mediated colistin resistance gene mcr-1 highlight the pressing need of developing more effective antimicrobial strategies for CRKP infections (Zhang et al., 2018). This study aimed to establish a comprehensive understanding of collateral sensitivity that accompany the development of tigecycline resistance in CRKP, and to rationalize the combination antibiotic therapy using tigecycline and aminoglycosides for CRKP infections.
Materials and Methods
Bacterial Isolates
Fifty CRKP isolates were from patients visiting the First Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University and clinically diagnosed with CRKP infections between December 2013 and 2014. These clinical isolates were identified to a species level using the following tests: the Vitek II Identification System (bioMérieux Vitec Inc., Hazelwood, MO, United States) and MALDI Biotyper Identification System (MALDI-TOF MS, BioMérieux, Craponne, France).
Pulsed-Field Gel Electrophoresis Analysis
Genomic DNA of K. pneumoniae clinical isolates was digested with restriction endonuclease XbaI (Takara Bio, Dalian, China). DNA fragments were separated in a Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) CHEF-Mapper XA system (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, United States) in 0.5 × Tris-borate-EDTA buffer at 14°C and 120 V for 19 h, with pulse times ranging from 5 s to 35 s. PFGE results were analyzed using Quantity One 1-D Analysis 4.6.9 (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, United States) Software.
Antimicrobial Susceptibility Test
Antimicrobial susceptibility of 50 CRKP isolates to 15 first-line antibiotics were initially tested with the Vitek II Identification System (bioMérieux Vitec Inc., Hazelwood, MO, United States) and then confirmed by the CLSI recommended broth microdilution or agar dilution methods. The MICs of tigecycline for K. pneumoniae clinical isolates and resistance-induced strains were interpreted using breakpoints recommended by the European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST) criteria (susceptible, ≤1.0 μg/ml; medium, 1.0–2.0 μg/ml; resistant, >2.0 μg/ml) (European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing Steering, 2006). Susceptibility of other antimicrobial agents for K. pneumoniae was determined by the agar dilution method according to the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (M100-S24, 2014). Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 was used as a quality control.
In vitro Induction of Tigecycline Resistance
Four clinical isolates susceptible to tigecycline (K467, K43, K521, and K428) and one tigecycline-resistant clinical isolate (K537) were used to study tigecycline resistance induction and collateral sensitivity of CRKP. These five clinical isolates were assigned to sequence types by Multilocus sequence typing (MLST), according to the K. pneumoniae MLST website.1 Tigecycline resistance was induced for the tigecycline-susceptible clinical isolates, by gradually exposing them to tigecycline at serially increasing concentrations at a 24 h interval (1/4 MIC to a higher concentration at which there was no bacterial growth) (Liu et al., 2011).
Examining General Antimicrobial-Resistance Determinants for Tigecycline Resistance
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and sequencing were carried out to examine the presence of common antimicrobial-resistant genes in these 5 CRKP clinical isolates and four resistance-induced strains, including ESBLs genes (blaCTX–M–1blaCTX–M–9, blaTEM, blaSHV, blaVEB and blaPER), AmpC genes (blaCMY, blaFOX, blaMOX, blaDHA), carbapenemase genes (blaKPC, blaSPM, blaIMP, blaVIM, blaGES, blaNDM, blaOXA–23, blaOXA–48), PMQR genes (qnrA, qnrB, qnrC, qnrD, qnrS, qepA, aac(6′)-Ib-cr, oqxA, oqxB), and 16S-RMTase genes (armA, rmtA, rmtB, rmtC, rmtD, rmtE). The mutation of chromosomal genes gyrA and parC was also examined. Primer sequences for PCR assays were adapted from other published studies (Doi and Arakawa, 2007; Dallenne et al., 2010; Park et al., 2012) and are available on request. Nucleotide sequences were compared by BLAST to align drug-resistance gene nucleotide sequences2.
Outer Membrane Proteins Analysis
A crude outer membrane fraction of CRKP clinical isolates and resistance-induced strains was obtained by growing the bacteria to a mid-log phase, followed by sonication. Outer membrane proteins (OMPs) were separated by sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE). K. pneumoniae ATCC 13883 was used as a control for OMP profiling (Shi et al., 2013). The outer membrane protein encoding genes were further amplified using multiple primer pairs among the 4 paired strains (Zhang et al., 2014).
Inhibition of Efflux Pumps With CCCP
Efflux pump inhibitor carbonyl cyanide m-chlorophenylhydrazone (CCCP, 10 mg/l) was used to examine the impact of efflux pumps on tigecycline resistance (Zhong et al., 2014). Minimum inhibitory concentrations of tigecycline for CRKP clinical isolates and resistance-induced strains were determined by the broth microdilution method in the presence or absence of CCCP. Four times or greater reduction of tigecycline MICs in the presence of CCCP was adopted as a significant inhibition effect for efflux pumps (He et al., 2015).
Analysis of acrR, ramR and oqxR Mutations
Efflux pump regulator encoding genes including acrR, ramR and oqxR were amplified by PCR with specific primers (Bialek-Davenet et al., 2011; Lin et al., 2016). The nucleotide sequences of acrR, ramR and oqxR were analyzed using a basic local alignment search tool (BLAST)3 with K. pneumoniae subsp. pneumoniae MGH 78578 as the reference strain (GenBank accession no. CP000647) (Hentschke et al., 2010).
Quantitative Real-Time PCR
The relative expression levels of genes encoding efflux pumps AcrB and OqxB and their regulators ramA and rarA were evaluated using a 7500 Real-Time PCR (RT-PCR) system and rpoB as the housekeeping gene (Stein and Babinchak, 2013; He et al., 2015). All experiments were performed in triplicate. The relative expression of the target genes was analyzed using the comparative Ct method (2–Δ Δ Ct) with the Agilent MxPro software.
Genome Sequencing and Annotation
Whole-genome shotgun sequencing was carried out for 5 CRKP clinical isolates and 4 resistance-induced strains, using a standard run of Illumina HiSeq2000 sequencing using a generating 2 × 100 paired-end libraries (500-bp insert size) sequencing strategy according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Clean reads were assembled into scaffolds using Velvet version 1.2.07. Post-Assembly Genome Improvement Toolkit (PAGIT) was then used to extend the initial contiguous sequences (contigs) and correct sequencing errors. Open reading frames (ORFs) were identified using Glimmer version 3.0. Protein-coding sequences were further BLAST-searched against the Antimicrobial Resistance Database (ARDB).
Plasmid Analysis
Plasmids of 5 CRKP clinical isolates and 4 resistance-induced strains were analyzed by S1-nuclease pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (S1-PFGE). Plasmid DNA was extracted using a QIAGEN Plasmid Midi Kit (Qiagen, shanghai, China) according to the manufacturer’s instructions, and was separated by electrophoresis in 0.8% agarose at 120 V for 1 h. The plasmids of E. coli V517 served as a size marker.
Data Analysis and Statistical Methods
One-way ANOVA or a non-parametric test (Mann-Whitney U test) was carried out to compare two means, depending on the data distribution. Statistical significance was assumed at p value of less than 0.05. Data analysis was performed using Minitab 16 software (Minitab, State College, PA, United States).
Results
Microbiological Characteristics of CRKP Clinical Isolates
Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis analysis of 50 CRKP clinical isolates showed five clusters, suggesting clonally distinct nature of these isolates (Figure 1A). Antimicrobial susceptibility tests showed that all CRKP isolates were resistant to first-line antibiotics except tigecycline and colistin; one isolate was found to be resistant to tigecycline (K537, MIC 8 mg/L, see Table 1). One representative strain from each cluster (designated as K537, K521, K467, K428, and K43) was chosen for further studies. MLST found that the tigecycline-resistant clinical isolate K537 and tigecycline-sensitive isolates K521, K467, K428, and K43 belonged to sequence types ST39, ST11, ST11, ST37, and ST3623, respectively.
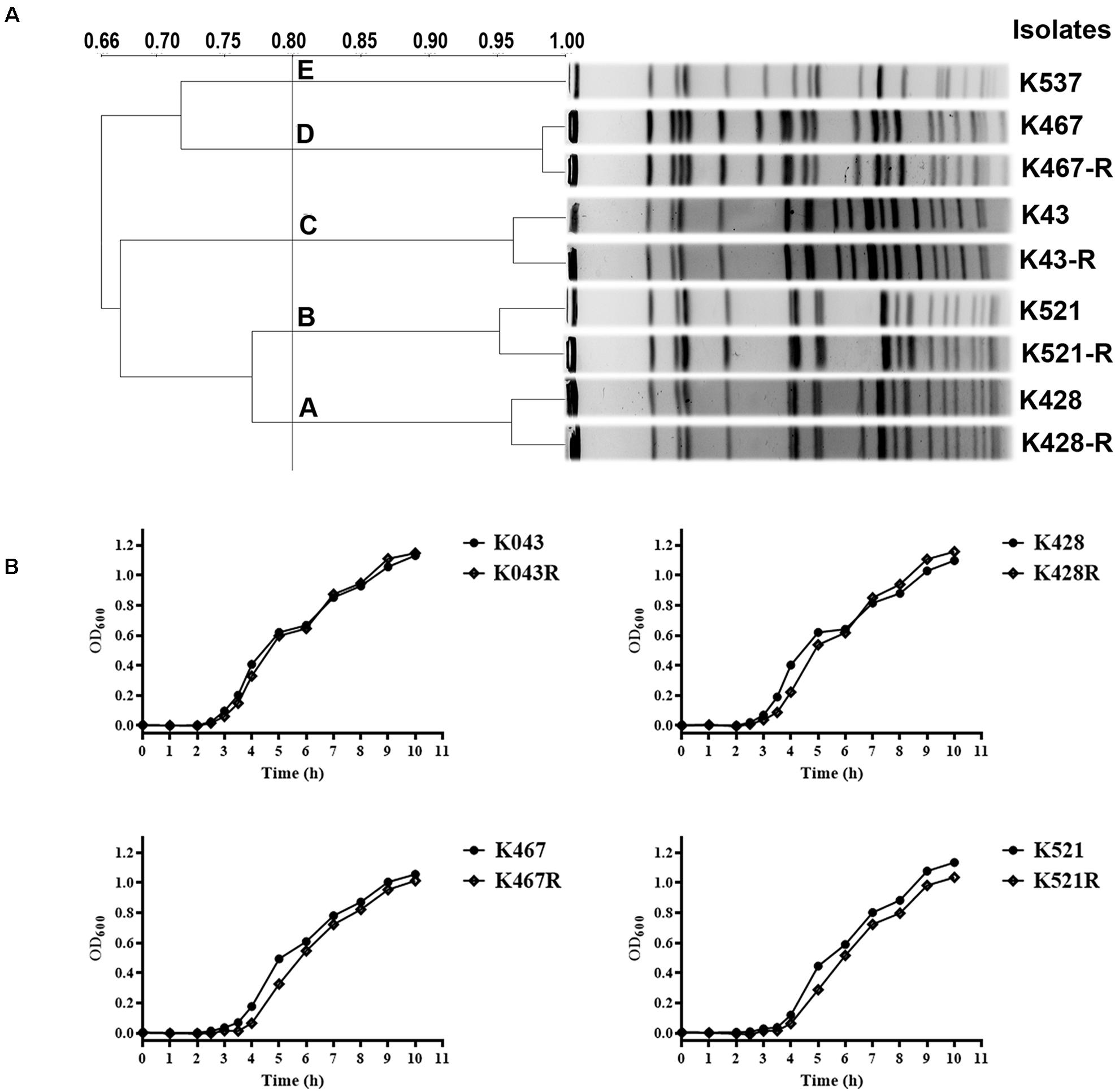
Figure 1. (A) Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) analysis of five representative carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae (CRKP) clinical isolates and their resistance-induced descendants; (B) Growth dynamics of four resistance-induced strains and their parental clinical isolates.
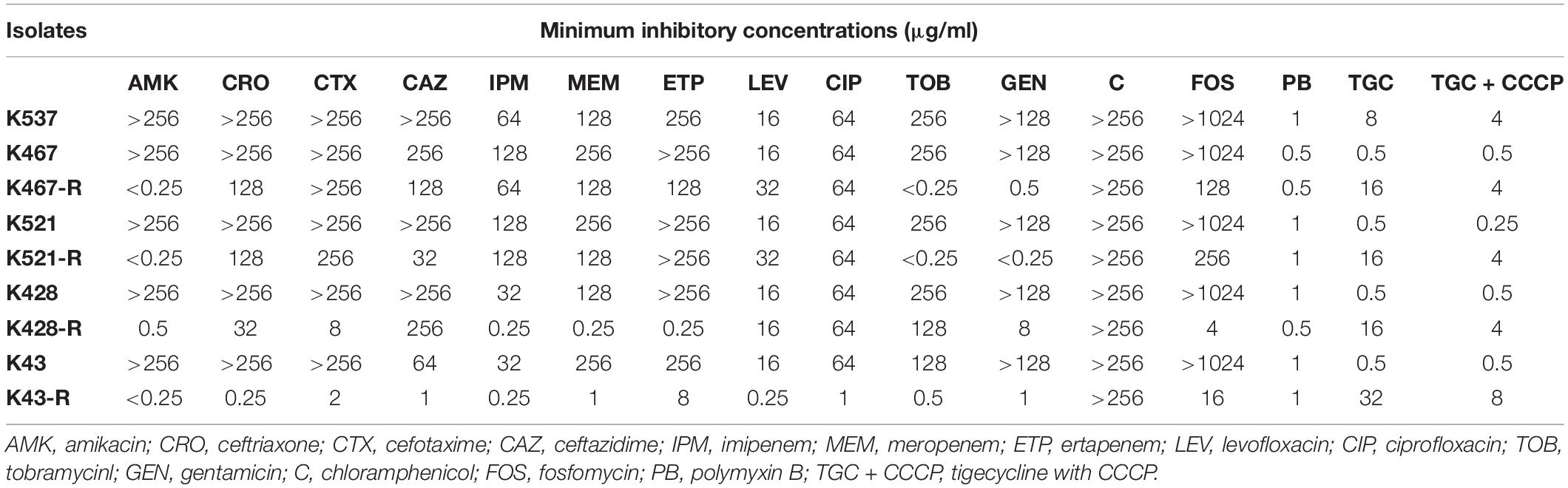
Table 1. Antimicrobial susceptibility of five CRKP clinical isolates and four resistance-induced descendant strains.
Experimental Induction of Tigecycline Resistance in CRKP
Four tigecycline-sensitive clinical isolates (K467, K521, K428, and K43) were treated with tigecycline at gradually increased concentrations to induce tigecycline resistance. Significant increases in the MICs of tigecycline (32- – 64- fold) were achieved for the descendant strains in comparison with their parental clinical isolates (Table 1). PFGE analysis further confirmed the origin of the resistance-induced CRKP strains (Figure 1A). The induced tigecycline-resistance remained stable after sixteen passages of CRKP in an antibiotic-free growth medium. Comparing the growth dynamics of tigecycline-sensitive clinical isolates and their resistance-induced descendant strains showed a minor but universal fitness loss (Figure 1B).
Molecular Mechanisms Underpinning Experimental Induction of Tigecycline Resistance
We examined the role of adenosine triphosphate (ATP)-driven efflux pumps in the resistance of CRKP to many antibiotics including tigecycline. Using the efflux pump inhibitor CCCP partially restored the susceptibility of all five tigecycline-resistant strains (Table 1). Gene expression of pump- and regulator- encoding genes including acrB, ramA, oqxB, and rarA was evaluated (Figure 2). All tigecycline-resistant strains showed higher expression of acrB (6. 9-, 19. 3-, 15. 6-, 5. 3-, 64.5-fold for K537, K467-R, K521-R, K428-R, and K43-R, respectively) and its regulator gene ramA (7. 4-, 12. 2-, 13. 5-, 34. 5-, 65.8-fold, respectively). Over-expression of oqxB and rarA was seen in K43-R (12.5-fold and 2.5-fold) and K521-R (2.7-fold and 5.9-fold).
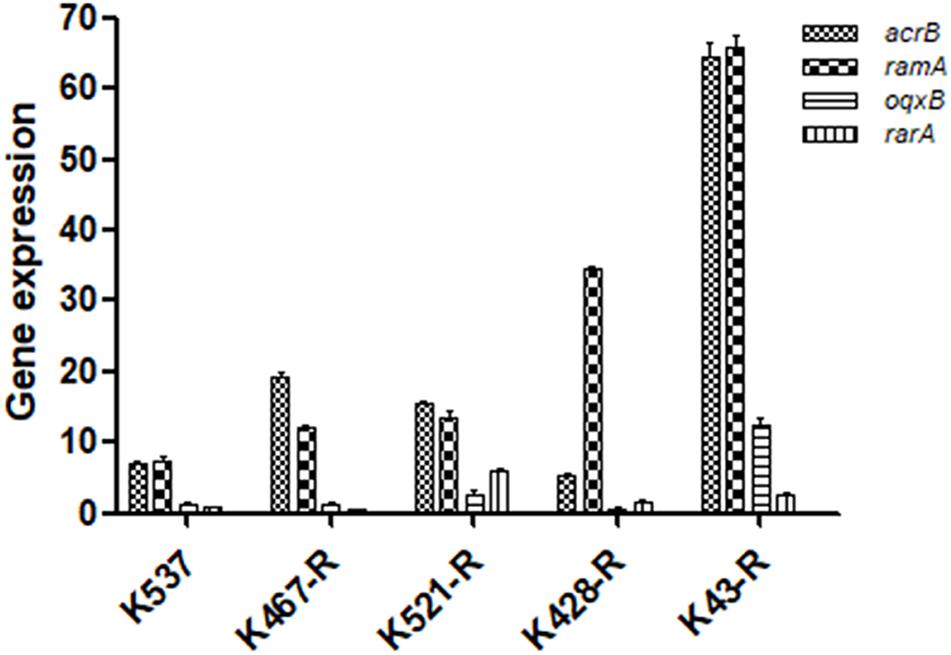
Figure 2. Expression of pump and regulator encoding genes including acrB, ramA, oqxB, and rarA in five tigecycline-resistant CRKP strains. The values were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD).
We also sequenced genes encoding other important regulators of efflux pumps, including acrR, ramR, and oqxR. No mutation was identified in acrR and ramR. Mutations in oqxR were found; no difference between tigecycline-sensitive clinical isolates and their resistance-induced counterparts indicated no direct link between oqxR mutation and experimentally induced tigecycline resistance (Table 2). SDS-PAGE was carried out to study the role of three major OMPs (ompK34, ompK35, and ompK36) on tigecycline resistance, that may affect the diffusion of tigecycline to its target sites. Using the porin profile of K. pneumoniae ATCC 13883 as a control, OmpK36 was missing on SDS-PAGE and amplification of its encoding gene with PCR was unsuccessful (Figure 3), suggesting that a deletion and/or rearrangement of its encoding gene might have occurred in strains with clinical background. Same SDS-PAGE results for tigecycline-sensitive clinical isolates and resistance-induced descendant strains, again suggested no direct association between these OMPs and induced tigecycline resistance.
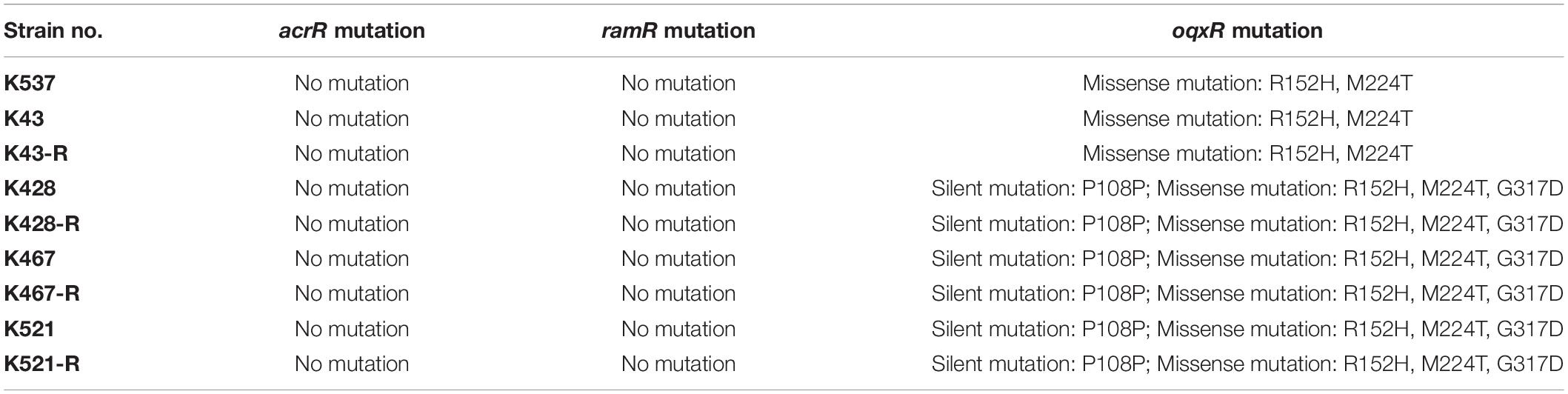
Table 2. Mutations of acrR, ramR and oqxR in five clinical isolates and four resistance-induced descendant strains.
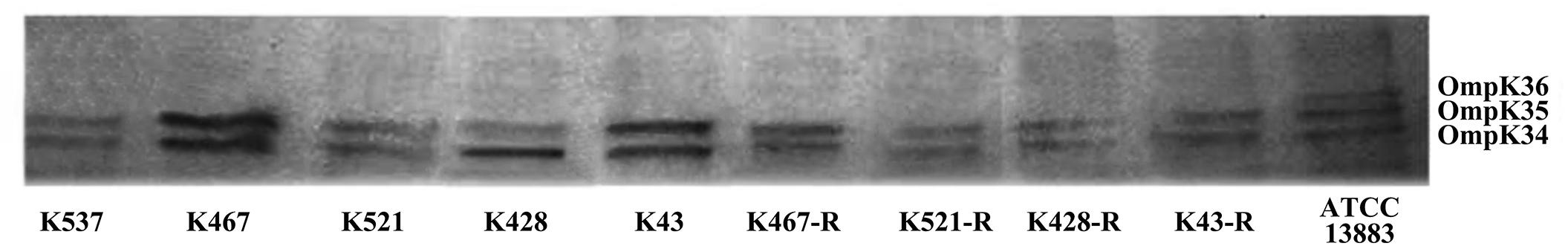
Figure 3. Sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) of outer membrane proteins (OMPs) in five CRKP clinical isolates and four resistance-induced descendants.
Emergence of Collateral Sensitivity in Tigecycline-Resistant CRPK
Interestingly, prolonged exposure of CRKP to tigecycline reversed their resistance to all tested antibiotics except chloramphenicol and tigecycline; significantly lowered MICs of different antibiotics were found for all resistance-induced descendant strains (Table 1). The level of acquired hypersensitivity seemed to be antibiotic and strain dependent. Up to 2048-fold decreases in the MIC of cephalosporins and carbapenems were observed when tigecycline-sensitive clinical isolates were converted into tigecycline-resistant descendant strains; up to 64-fold and 512-fold decreases in the MIC were found when fluoroquinolones and fosfomycin were tested, respectively. At least 2 out of 4 tigecycline-sensitive and tigecycline-resistant pairs showed relatively small changes in the MIC of these non-aminoglycoside antibiotics (≤4-fold for cephalosporins and carbapenems, ≤2-fold for fluoroquinolones, and ≤16-fold for fosfomycin). More significant decreases in the MIC were noticed for aminoglycosides when compared with other antibiotics (Table 1). Most resistance-induced strains had MICs of amikacin, tobramycin and gentamicin 250-fold lower than that of their parental clinical isolates. The induced hypersensitivity of CRKP to aminoglycosides and other antibiotics remained stable after regrowth in an antibiotic-free medium for 16 passages.
Evaluating Common Antibiotic Resistance Determinants for Collateral Hypersensitivity of CRKP
Some common antibiotic resistance determinants were examined for 5 CRKP clinical isolates and 4 resistance-induced descendent strains. All isolates harbored the KPC-2 carbapenemase-encoding gene (blaKPC–2) and genes encoding other β-lactamases including SHV (sulf-hydryl variable) and TEM (Temoniera in). Genes encoding CTX-M-type ESBLs were only found in the K467 pairs and K521 pairs. Some other common AMR genes conferring antibiotic resistance in CRKP were sequenced, including gyrA encoding the DNA gyrase and parC encoding DNA topoisomerase that are responsible for fluoroquinolone resistance. An amino acid substitution of S83I was detected in gyrA in all 9 strains and S80I was detected in parC in the K428, K467, and K521 pairs. gyrA mutation D87G was found in the K467 and K521 pairs. The plasmid-carrying quinolone resistance gene qnrS was also detected in K537 and K467 pairs. Interestingly, the 16S-rRNA methylase encoding gene rmtB, a gene that confers resistance to most clinically relevant aminoglycosides, was found in K467 and K521 but missing in their resistance-induced counterparts.
Whole Genome Sequencing Broadened Our Understanding of Collateral Sensitivity in CRKP
Common genetic determinants seemed to be inadequate to explain the induced hypersensitivity to aminoglycosides of CRKP. We thus performed a next-generation full genome sequencing for all nine strains selected for this study, intending to identify molecular determinants that differ between the tigecycline-sensitive and tigecycline-resistant groups. Despite the significant difference in the bacterial resistance to multiple antibiotics including aminoglycosides, no obvious chromosome-related genetic difference was found (Supplementary Figure 1 and Supplementary Table 1, for reviewers’ information only). Full genome sequencing of CRKP revealed several antibiotic-resistance related mutations that were not unique to the tigecycline-sensitive parental strains or their tigecycline-resistant descendants, including: 1) a 4bp mutation in non-coding region between ybhN and ybhL in the K428 pairs, 2) a 11bp insertion in the non-coding region between garK-1 and tRNA_anti-like, a 10bp insertion in the non-coding region between kp467_02292 and kp467_02293 and a 4bp mutation in the gene encoding DNA polymerase IV (dinB_4) in the K467 pairs, 3) and a 12bp insertion in the non-coding region between kp521_05022 and kp521_05023 in the K521 pairs (Table 3). Several key AMR mobile elements were found in the parental clinical isolates but not the descendants, including rmtB (K467 and K521 pairs), blaTEM–1E (K521 pair), fosA3 (K467 and K521 pairs) (Supplementary Figure 1). As rmtB and fosA3 are often co-carried on a large AMR plasmid, we hypothesized that loss of an AMR plasmid might have occurred to compensate the fitness cost. S1-PFGE revealed that all clinical isolates contained multiple plasmids ranging from 2.1 kb to 54.2 kb in size (Figure 4). One plasmid of 54.2–5.6 kb was absent in K43-R but present in K43, and one plasmid of approximately 2.1 kb was missing in K467-R but not the parental clinical isolate.
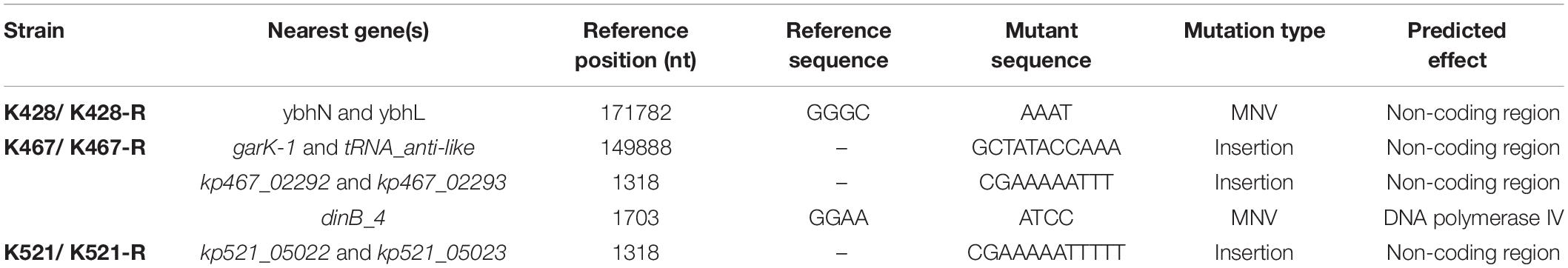
Table 3. Mutations observed in the four clinical isolates and their resistance-induced descendant strains.
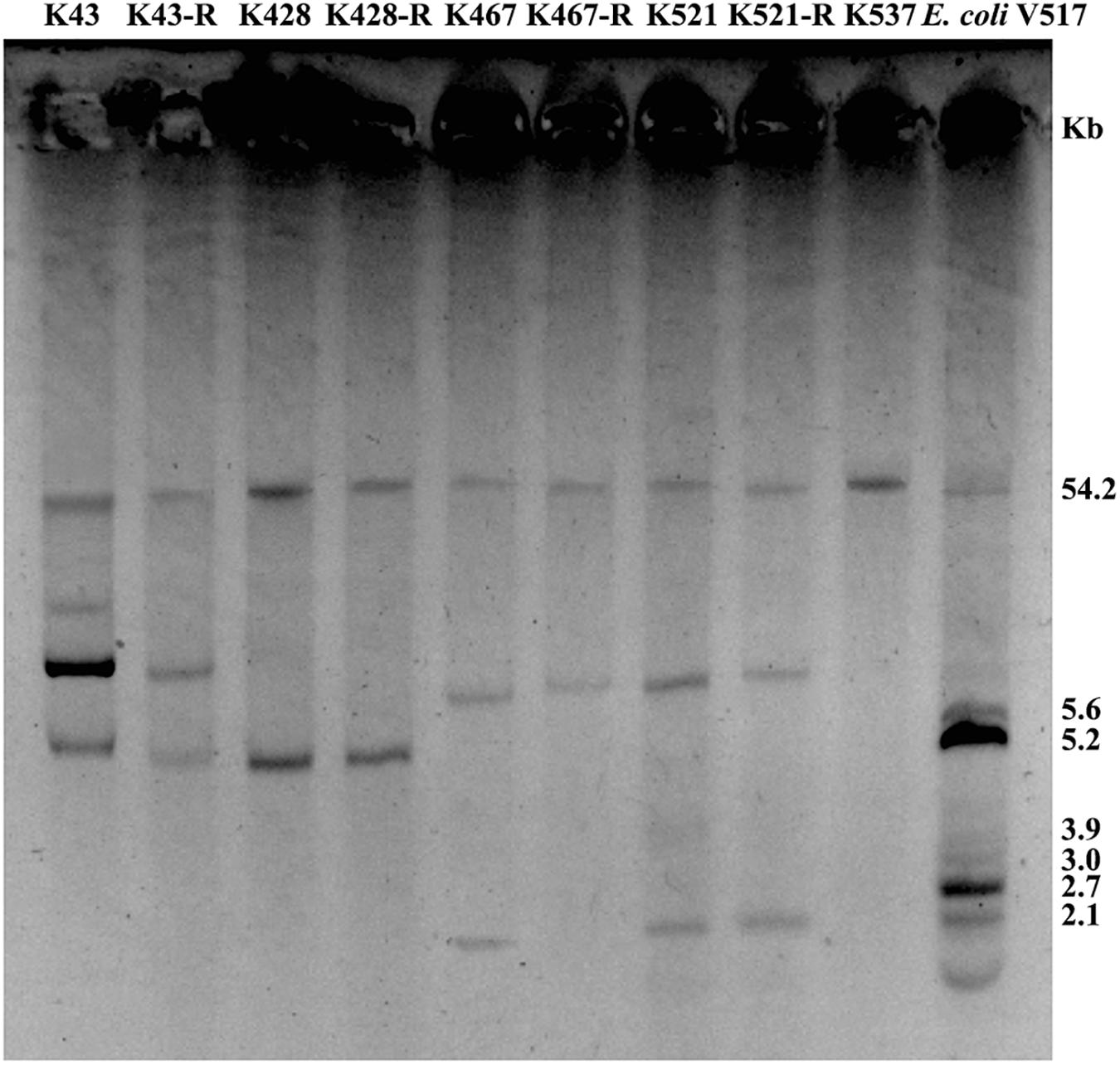
Figure 4. Plasmid analysis of five CRKP clinical isolates and four resistance-induced strains. Escherichia coli V517 was used as a control.
Discussion
Extended spectrum beta lactamase-producing CRKP are now among the most critical pathogens advised by the recent WHO global priority list of antibiotic-resistant bacteria (WHO, 2020). The overuse of tigecycline and colistin in clinical settings has promoted CRKP to develop resistance to both last-resort antibiotics (Zhang et al., 2018), highlighting a pressing clinical need for alternative strategies such as antibiotic combination therapy. This study intended to increase our understanding of collateral sensitivity in CRKP that tolerates tigecycline treatment, and such knowledge might serve as the foundation of a promising combination therapy for otherwise “untreatable” CRKP infections.
Carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates used in this study have distinct PFGE patterns and belong to different sequence types, supporting the non-dominant clonal nature of CRKP encountered in a hospital environment (Chiu et al., 2017). Development of resistance or non-susceptibility to tigecycline has been linked to prolonged use of tigecycline or other antibiotics (Lin et al., 2016). Our mechanistic study of tigecycline resistance only found an association between the reduced tigecycline susceptibility and the overexpression of acrB/ramA in CRKP. No significant difference in the expression of oqxB and rarA, or missense/silent mutations in oqxR, acrR or ramR was found when comparing tigecycline-sensitive clinical isolates and their resistance-induced descendants.
Enterobacteriaceae is known to be able to regain collateral sensitivity to many first-line antibiotics when developing resistance to tigecycline, in particular aminoglycosides (Fang et al., 2016; Barbosa et al., 2017). The underlying mechanisms of collateral sensitivity have been proposed but not been fully disclosed (Barbosa et al., 2017). Barbosa et al. (2017) reported that resistance mutation in the regulatory genes of efflux pumps such as nalC or mexZ might resensitize β-lactam-adapted bacterial populations to aminoglycosides (Barbosa et al., 2017). Previously reported collateral sensitivity in K. pneumoniae was supported by mild decreases in MICs of several first-line antibiotics, by 2–10 times (Fang et al., 2016). We, however, found dramatic changes in MICs of aminoglycosides (>100 times) for all 4 experimentally induced tigecycline-resistant strains. Current mechanisms of aminoglycoside resistance do not seem to sufficiently explain the much greater level of collateral sensitivity of CRKP found in this study (Wachino et al., 2020). We hypothesized that accumulative mechanisms drove the development of collateral hypersensitivity of tigecycline-resistant CRKP. We assessed such trade-offs through whole-genome sequencing of clinical isolates and experimentally induced resistant strains. Genomes of our clinical isolates and resistance-induced descendent strains have high similarity to CRKP clinical isolates of different ST (ST15, ST512, ST11 and ST17) sequenced by others (Hua et al., 2014; Villa et al., 2014; Xu et al., 2017; Du et al., 2018); no major chromosome-related genetic difference were found (Fang et al., 2016). We did find loss of a major AMR plasmid in at least two laboratory evolved strains (K43-R and K467-R). It has been proposed that the co-carriage of various important AMR determinants such as blaKPC–2, blaTEM–1, blaCTX–M–14, and rmtB on one plasmid could provide evolutionary benefits to bacteria in an antibiotic-rich environment (Sheng et al., 2012). K. pneumoniae is an opportunistic pathogen that is well-known for its diversity of antibiotic resistance genes, with significantly more varied DNA composition, and higher plasmid burden than other Gram-negative pathogens (Wyres and Holt, 2018). The high burden of plasmid carriage in K. pneumoniae, however, may result in a comparatively lower fitness of the bacterium (Wyres and Holt, 2018). The complex bacterium-plasmid interaction results in not only the adaption of the host to plasmid, but also specific adaption of plasmid to the host. We thus reasoned the voluntary loss of an AMR plasmid under the long-term pressure of tigecycline might also offer survival advantages to the bacterium (Sheng et al., 2012).
Limitations of this study include that only a small number of isolates were used and the structure of the AMR plasmids involved in collateral sensitivity was not further investigated, due to the limited time frame of this study. Another evident limitation is that tigecycline-resistant clinical isolate failed to show any sensitivity to aminoglycoside or other antibiotics and did not provide direct support to the proposed theory. However, theory raised from this experimental study was supported by findings of several recent clinical studies. Stohr et al. (2020) reported loss of the KPC-gene carrying plasmid and plasmid recombination in KPC-producing K. pneumoniae clinical isolates from two patients in a hospital outbreak (Stohr et al., 2020). Fang et al. (2016) also isolated tigecycline non-susceptible clinical isolates that had a 2–4-fold decreases in the MICs to aminoglycosides relative to its tigecycline-sensitive ancestral isolates (Fang et al., 2016).
Conclusion
Carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae may develop collateral hypersensitivity to aminoglycosides and other antibiotics, accompanying the development of bacterial resistance to tigecycline. This experimental study provides a proof of concept to support the sequentially combinational use of tigecycline and aminoglycosides for the treatment of CRKP infections. Antimicrobial susceptibility tests of CRKP should be frequently repeated to provide more specific and accurate guidance for its treatment (Stohr et al., 2020).
Data Availability Statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found below: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/, PRJNA706839.
Author Contributions
YQ and T-LZ: conceptualization and supervision. H-LC, YJ, and M-ML: methodology and validation. H-LC, YJ, and YQ: software. H-LC and M-ML: formal analysis, investigation, and writing—original draft preparation. H-LC, J-MC, and CZ: resources. H-LC and YJ: data curation. CZ, X-XZ, and YQ: writing—review and editing. YS, T-LZ, and YQ: funding acquisition. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 81802069), the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number LY14H190005), the Planned Science and Technology Project of Wenzhou (grant number Y20150312), and Zhejiang Province Program for the Cultivation of High-level Innovative Health Talents.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the reviewers who helped to improve this paper.
Supplementary Materials
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmicb.2021.674502/full#supplementary-material
Supplementary Figure 1 | Schematic diagram of comparison of chromosome-harboring or plasmid- harboring resistance genes between tigecycline-sensitive and -resistant pairs (K467 and K521 only). The white arrows illustrate the resistance genes among which the red framed arrows indicate the loss of genes in tigecycline-resistant strains.
Footnotes
- ^ https://bigsdb.pasteur.fr/klebsiella/klebsiella.html
- ^ http://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi
- ^ http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/BLAST
References
Barbosa, C., Trebosc, V., Kemmer, C., Rosenstiel, P., Beardmore, R., Schulenburg, H., et al. (2017). Alternative evolutionary paths to bacterial antibiotic resistance cause distinct collateral effects. Mol. Biol. Evol. 34, 2229–2244. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msx158
Bialek-Davenet, S., Marcon, E., Leflon-Guibout, V., Lavigne, J. P., Bert, F., Moreau, R., et al. (2011). In vitro selection of ramR and soxR mutants overexpressing efflux systems by fluoroquinolones as well as cefoxitin in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 55, 2795–2802. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00156-11
Chiu, S. K., Chan, M. C., Huang, L. Y., Lin, Y. T., Lin, J. C., Lu, P. L., et al. (2017). Tigecycline resistance among carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella Pneumoniae: clinical characteristics and expression levels of efflux pump genes. PLoS One 12:e0175140. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0175140
Dallenne, C., Da Costa, A., Decre, D., Favier, C., and Arlet, G. (2010). Development of a set of multiplex PCR assays for the detection of genes encoding important beta-lactamases in Enterobacteriaceae. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 65, 490–495. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkp498
Doi, Y., and Arakawa, Y. (2007). 16S ribosomal RNA methylation: emerging resistance mechanism against aminoglycosides. Clin. Infect. Dis. 45, 88–94. doi: 10.1086/518605
Du, X., He, F., Shi, Q., Zhao, F., Xu, J., Fu, Y., et al. (2018). The rapid emergence of tigecycline resistance in blaKPC-2 harboring Klebsiella pneumoniae, as mediated in vivo by mutation in tetA during tigecycline treatment. Front. Microbiol. 9:648. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.00648
European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing Steering (2006). EUCAST technical note on tigecycline. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 12, 1147–1149. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2006.01578.x
Fang, L., Chen, Q., Shi, K., Li, X., Shi, Q., He, F., et al. (2016). Step-wise increase in tigecycline resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae associated with mutations in ramR, lon and rpsJ. PLoS One 11:e0165019. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0165019
Frohlich, C., Sorum, V., Thomassen, A. M., Johnsen, P. J., Leiros, H. S., and Samuelsen, O. (2019). OXA-48-mediated ceftazidime-avibactam resistance is associated with evolutionary trade-offs. mSphere 4:e00024-19. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00024-19
Furusawa, C., Horinouchi, T., and Maeda, T. (2018). Toward prediction and control of antibiotic-resistance evolution. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 54, 45–49. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2018.01.026
Gonzalez-Padilla, M., Torre-Cisneros, J., Rivera-Espinar, F., Pontes-Moreno, A., Lopez-Cerero, L., Pascual, A., et al. (2015). Gentamicin therapy for sepsis due to carbapenem-resistant and colistin-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 70, 905–913. doi: 10.1093/jac/dku432
He, F., Fu, Y., Chen, Q., Ruan, Z., Hua, X., Zhou, H., et al. (2015). Tigecycline susceptibility and the role of efflux pumps in tigecycline resistance in KPC-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae. PLoS One 10:e0119064. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0119064
He, T., Wang, R., Liu, D., Walsh, T. R., Zhang, R., Lv, Y., et al. (2019). Emergence of plasmid-mediated high-level tigecycline resistance genes in animals and humans. Nat. Microbiol. 4, 1450–1456. doi: 10.1038/s41564-019-0445-2
Hentschke, M., Wolters, M., Sobottka, I., Rohde, H., and Aepfelbacher, M. (2010). ramR mutations in clinical isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae with reduced susceptibility to tigecycline. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 54, 2720–2723. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00085-10
Hirsch, E. B., and Tam, V. H. (2010). Detection and treatment options for Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemases (KPCs): an emerging cause of multidrug-resistant infection. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 65, 1119–1125. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkq108
Hua, X., Chen, Q., Li, X., Feng, Y., Ruan, Z., and Yu, Y. (2014). Complete genome sequence of Klebsiella pneumoniae sequence type 17, a multidrug-resistant strain isolated during tigecycline treatment. Genome Announc. 2:e01337-14. doi: 10.1128/genomeA.01337-14
Juan, C. H., Huang, Y. W., Lin, Y. T., Yang, T. C., and Wang, F. D. (2016). Risk factors, outcomes, and mechanisms of tigecycline-nonsusceptible Klebsiella pneumoniae bacteremia. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 60, 7357–7363. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01503-16
Lin, Y. T., Huang, Y. W., Huang, H. H., Yang, T. C., Wang, F. D., and Fung, C. P. (2016). In vivo evolution of tigecycline-non-susceptible Klebsiella pneumoniae strains in patients: relationship between virulence and resistance. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 48, 485–491. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2016.07.008
Liu, Y., Li, J., Du, J., Hu, M., Bai, H., Qi, J., et al. (2011). Accurate assessment of antibiotic susceptibility and screening resistant strains of a bacterial population by linear gradient plate. Sci. China Life Sci. 54, 953–960. doi: 10.1007/s11427-011-4230-6
Lozano-Huntelman, N. A., Singh, N., Valencia, A., Mira, P., Sakayan, M., Boucher, I., et al. (2020). Evolution of antibiotic cross-resistance and collateral sensitivity in Staphylococcus epidermidis using the mutant prevention concentration and the mutant selection window. Evol. Appl. 13, 808–823. doi: 10.1111/eva.12903
Maltas, J., and Wood, K. B. (2019). Pervasive and diverse collateral sensitivity profiles inform optimal strategies to limit antibiotic resistance. PLoS Biol. 17:e3000515. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3000515
Nielsen, L. E., Snesrud, E. C., Onmus-Leone, F., Kwak, Y. I., Aviles, R., Steele, E. D., et al. (2014). IS5 element integration, a novel mechanism for rapid in vivo emergence of tigecycline nonsusceptibility in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 58, 6151–6156. doi: 10.1128/AAC.03053-14
Pal, C., Papp, B., and Lazar, V. (2015). Collateral sensitivity of antibiotic-resistant microbes. Trends Microbiol. 23, 401–407. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2015.02.009
Park, K. S., Kim, M. H., Park, T. S., Nam, Y. S., Lee, H. J., and Suh, J. T. (2012). Prevalence of the plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance genes, aac(6’)-Ib-cr, qepA, and oqxAB in clinical isolates of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL)-producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae in Korea. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 42, 191–197.
Petrosillo, N., Giannella, M., Lewis, R., and Viale, P. (2013). Treatment of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae: the state of the art. Expert Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 11, 159–177. doi: 10.1586/eri.12.162
Poulakou, G., Kontopidou, F. V., Paramythiotou, E., Kompoti, M., Katsiari, M., Mainas, E., et al. (2009). Tigecycline in the treatment of infections from multi-drug resistant gram-negative pathogens. J. Infect. 58, 273–284. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2009.02.009
Roy, S., Datta, S., Viswanathan, R., Singh, A. K., and Basu, S. (2013). Tigecycline susceptibility in Klebsiella pneumoniae and Escherichia coli causing neonatal septicaemia (2007-10) and role of an efflux pump in tigecycline non-susceptibility. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 68, 1036–1042. doi: 10.1093/jac/dks535
Sekowska, A., and Gospodarek, E. (2010). Susceptibility of Klebsiella spp. to tigecycline and other selected antibiotics. Med. Sci. Monit. 16, BR193–BR196.
Sheng, J. F., Li, J. J., Tu, S., Sheng, Z. K., Bi, S., Zhu, M. H., et al. (2012). blaKPC and rmtB on a single plasmid in Enterobacter amnigenus and Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates from the same patient. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 31, 1585–1591. doi: 10.1007/s10096-011-1481-x
Shi, W., Li, K., Ji, Y., Jiang, Q., Wang, Y., Shi, M., et al. (2013). Carbapenem and cefoxitin resistance of Klebsiella pneumoniae strains associated with porin OmpK36 loss and DHA-1 beta-lactamase production. Braz. J. Microbiol. 44, 435–442. doi: 10.1590/S1517-83822013000200015
Stein, G. E., and Babinchak, T. (2013). Tigecycline: an update. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 75, 331–336. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2012.12.004
Stohr, J., Verweij, J. J., Buiting, A. G. M., Rossen, J. W. A., and Kluytmans, J. (2020). Within-patient plasmid dynamics in Klebsiella pneumoniae during an outbreak of a carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae. PLoS One 15:e0233313. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0233313
Sun, J., Chen, C., Cui, C. Y., Zhang, Y., Liu, X., Cui, Z. H., et al. (2019). Plasmid-encoded tet(X) genes that confer high-level tigecycline resistance in Escherichia coli. Nat. Microbiol. 4, 1457–1464. doi: 10.1038/s41564-019-0496-4
Sun, Y., Cai, Y., Liu, X., Bai, N., Liang, B., and Wang, R. (2013). The emergence of clinical resistance to tigecycline. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 41, 110–116. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2012.09.005
Villa, L., Capone, A., Fortini, D., Dolejska, M., Rodriguez, I., Taglietti, F., et al. (2013). Reversion to susceptibility of a carbapenem-resistant clinical isolate of Klebsiella pneumoniae producing KPC-3. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 68, 2482–2486. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkt235
Villa, L., Feudi, C., Fortini, D., Garcia-Fernandez, A., and Carattoli, A. (2014). Genomics of KPC-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae sequence type 512 clone highlights the role of RamR and ribosomal S10 protein mutations in conferring tigecycline resistance. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 58, 1707–1712. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01803-13
Wachino, J. I., Doi, Y., and Arakawa, Y. (2020). Aminoglycoside resistance: updates with a focus on acquired 16S Ribosomal RNA methyltransferases. Infect. Dis. Clin. North Am. 34, 887–902. doi: 10.1016/j.idc.2020.06.002
WHO (2020). Essential Medicines and Health Products. Available online at: http://www.who.int/medicines/publications/global-priority-list-antibiotic-resistant-bacteria (accessed February 15, 2021).
Woodford, N., Hill, R. L., and Livermore, D. M. (2007). In vitro activity of tigecycline against carbapenem-susceptible and -resistant isolates of Klebsiella spp. and Enterobacter spp. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 59, 582–583. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkl514
Wyres, K. L., and Holt, K. E. (2018). Klebsiella pneumoniae as a key trafficker of drug resistance genes from environmental to clinically important bacteria. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 45, 131–139. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2018.04.004
Xu, H., Zhou, Y., Zhai, X., Du, Z., Wu, H., Han, Y., et al. (2016). Emergence and characterization of tigecycline resistance in multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates from blood samples of patients in intensive care units in northern China. J. Med. Microbiol. 65, 751–759. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.000299
Xu, J., Gao, M., Hong, Y., and He, F. (2017). Draft genome sequence of a tigecycline-resistant KPC-2-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae ST15 clinical isolate from China. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 11, 156–158. doi: 10.1016/j.jgar.2017.10.017
Zhang, R., Dong, N., Huang, Y., Zhou, H., Xie, M., Chan, E. W., et al. (2018). Evolution of tigecycline- and colistin-resistant CRKP (carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae) in vivo and its persistence in the GI tract. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 7:127. doi: 10.1038/s41426-018-0129-7
Zhang, Y., Jiang, X., Wang, Y., Li, G., Tian, Y., Liu, H., et al. (2014). Contribution of beta-lactamases and porin proteins OmpK35 and OmpK36 to carbapenem resistance in clinical isolates of KPC-2-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 58, 1214–1217. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02045-12
Keywords: collateral sensitivity, CRKP, aminoglycosides, tigecycline, antimicrobial resistance
Citation: Chen H-l, Jiang Y, Li M-m, Sun Y, Cao J-m, Zhou C, Zhang X-x, Qu Y and Zhou T-l (2021) Acquisition of Tigecycline Resistance by Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Confers Collateral Hypersensitivity to Aminoglycosides. Front. Microbiol. 12:674502. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.674502
Received: 01 March 2021; Accepted: 10 June 2021;
Published: 02 July 2021.
Edited by:
Shaolin Wang, China Agricultural University, ChinaCopyright © 2021 Chen, Jiang, Li, Sun, Cao, Zhou, Zhang, Qu and Zhou. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Tie-li Zhou, d3l6dGxpQDE2My5jb20=; Yue Qu, eXVlLnF1QG1vbmFzaC5lZHU=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Hua-le Chen
Hua-le Chen Yan Jiang
Yan Jiang Mei-mei Li3
Mei-mei Li3 Jian-ming Cao
Jian-ming Cao Cui Zhou
Cui Zhou Yue Qu
Yue Qu Tie-li Zhou
Tie-li Zhou