- 1Center for Experimental Medicine, The Third Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha, China
- 2Department of Neurology, The Third Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha, China
- 3Center for Clinical Research on Neurological Diseases, The First Affiliated Hospital, Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China
Parkinson's disease (PD), is the second most common neurodegenerative disorder worldwide. Genetic, environmental factors, and aging are its primary development contributors. Recently the nuclear undecaprenyl pyrophosphate synthase 1 homolog (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) gene (NUS1) was reported as a candidate gene for PD, which raised our interest in the relationship between NUS1 and PD. This study was aimed to further explore the role of NUS1 variants in PD development. Genetic analysis for 308 Han-Chinese PD patients and 308 ethnically matched controls using whole exome sequencing was conducted. Additionally, a total of 60 articles involving in whole exome/whole genome sequencing or direct sequencing of the NUS1 gene from PubMed database between July 1, 2011 and August 26, 2020 were reviewed to evaluate PD-associated NUS1 variants. No potentially pathogenic NUS1 variant was found in 308 PD cases, and no frequency biases between 308 PD cases and 308 controls were observed for the only non-synonymous variant p.Asp179Glu (genotype: χ2 = 0.093, P = 0.761; allele: χ2 = 0.092, P = 0.762). No pathogenic or disease-associated NUS1 variant was reported in the 5,636 PD cases of the 60 articles. In summary, current findings indicate that NUS1 variant is not a common genetic factor contributing to PD.
Introduction
Parkinson's disease (PD), initially named “paralysis agitans” by James Parkinson in 1817, is the second most prevalent neurodegenerative disorder with an incidence of 10–18 per 100,000 individuals worldwide yearly (1, 2). This common disorder affects 1% of total people over 60 and ~4–5% of total people at 85 or older (3, 4). The typical PD pathological characteristics are loss of dopaminergic neurons within the substantia nigra, α-synuclein accumulation in the Lewy bodies, and neuroinflammation (2). It is a complex multifactorial neurodegenerative disorder, in which environmental, genetic factors and increasing age contribute to its development (5), and has a heterogeneous disease progression characterized by a set of clinical features, including bradykinesia, rest tremor, rigidity, postural instability, and a good response to dopaminergic treatment, as well as other non-motor manifestations (2, 6–9). Age has been reported as the single greatest risk factor for sporadic PD (3, 4), while conservative heritability estimates due to common PD genetic risk are about 30% (10).
Revolutionary technologies, especially second-generation sequencing, have expedited the discovery of various PD-associated genes (11). Causative mutations and susceptibility variants are involved in PD pathogenesis by resulting in multiple cellular processes dysfunction, including synaptic function, protein aggregates, intracellular trafficking, ubiquitin-proteasome system, mitochondrial function, autophagy lysosomal pathway, neurite structure, and prion-like transmission (2, 12). In addition to mutations causing monogenic PD which accounts for <5–10% of all cases, the list of susceptibility variants contributing to the development of PD in sporadic cases is steadily increasing (12–15).
The nuclear undecaprenyl pyrophosphate synthase 1 homolog (S. cerevisiae) gene (NUS1) was recently proposed as a candidate disease-causing gene for PD (16), which raised our interest in potential association between the NUS1 gene variants and PD. Genetic analysis was conducted in Han-Chinese PD patients and controls from mainland China to further explore the role of NUS1 gene variants in PD.
Methods
Subjects and Clinical Assessments
Sequencing data for NUS1 coding regions and exon-intron boundaries were extracted from an in-house PD-control exome database. The database contained exome sequencing data for 308 Han-Chinese patients clinically diagnosed with PD [male/female: 154/154, 216 unrelated sporadic cases and 92 probands with familial PD (at least 1 PD-affected family member in 3 generations)] and 308 ethnically matched controls (male/female: 154/154, mean age 58.07 ± 13.59 years) with no signs or family history of PD or similar disorders. All patients enrolled in the study were clinically assessed and diagnosed with PD based on the International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society (MDS) clinical diagnostic criteria by two independent neurologists from the Third Xiangya Hospital, Central South University (9). The mean age of PD patients was 58.55 ± 11.81 years and the mean age at disease onset was 54.71 ± 12.65 years [33 early onset PD (EOPD, onset age ≤ 40 years old)] (17). The study received the approval from the Institutional Review Board of the Third Xiangya Hospital of Central South University, China, and informed consents about using peripheral blood samples and clinical information for research and publication were signed by all participants.
Genetic Analysis
The standard phenol-chloroform extraction procedure was used to extract genomic DNA (gDNA) from peripheral blood leukocytes (18, 19). The genetic analysis was performed using whole exome sequencing. Whole exome sequencing was conducted using the extracted gDNA to construct an in-house PD-control exome database. All variants, including single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and insertions-deletions (InDels), were further annotated with population databases including the 1,000 Genomes Project, the Exome Aggregation Consortium (ExAC), and the Genome Aggregation Database (gnomAD) (20). Variant's potential impact on protein structure or function was predicted by bioinformatic tools including MutationTaster, Sorting Intolerant from Tolerant (SIFT), Protein Variation Effect Analyzer (PROVEAN), and Protein Analysis Through Evolutionary Relationships (PANTHER), and Polymorphism Phenotyping version 2 (PolyPhen-2) (21). Sanger sequencing was applied to further NUS1 variant confirmation using the following primers: 5′-GCAAGAACTTCTGGGCCT-3′ and 5′-AGAGTAACAGAGCAACGTGAA-3′.
Statistical Analysis and PubMed Database Screening
Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium was applied to estimate the normal deviation of genotypes in 308 controls. Genotypic and allelic frequencies were calculated, and Pearson's χ2 tests were completed for testing significances of genotypic and allelic frequency differences between the 308 PD patients and 308 controls, in which a two-tailed P <0.05 was considered statistically significant (22, 23). All statistical analysis was performed using Predictive Analytics Software Statistics 18.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL). Whole exome/whole genome sequencing studies aimed to identify the disease-causing and/or susceptibility variants for PD were screened through PubMed database using the following search terms: “exome sequencing” or “whole genome sequencing” and “Parkinson's disease”. In addition, a PubMed search using search terms “NUS1” and “Parkinson's disease” was also performed to screen genetic study of the NUS1 gene in PD patients. These studies were included for searching PD-associated NUS1 variants.
Results
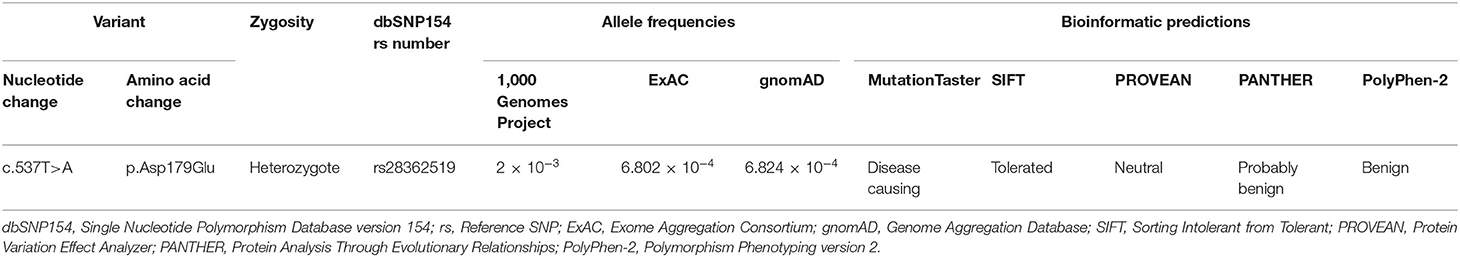
No potentially pathogenic NUS1 variant was found in 308 PD cases. Only a known single-nucleotide NUS1 non-synonymous variant (c.537T>A, p.Asp179Glu, rs28362519) was detected in 5 PD patients and 6 controls, and confirmed by Sanger sequencing. It was recorded in 1,000 Genomes Project, ExAC, and gnomAD with relative high allele frequencies. This variant was predicted to be disease causing by MutationTaster, while SIFT, PROVEAN, PANTHER, and PolyPhen-2 predicted it had no impact on protein structure or function (Table 1). Genotypic distributions of the rs28362519 variant complied with Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium in the control group (P > 0.05). No frequency biases between 308 PD cases and 308 controls were observed for this variant (genotype: χ2 = 0.093, P = 0.761; allele: χ2 = 0.092, P = 0.762; Table 2). No pathogenic or disease-associated NUS1 variants in the 5,142 PD cases containing at least 116 EOPD was reported in the 59 articles retrieved in PubMed database between July 1, 2011 and August 26, 2020 (Supplementary Table 1). Additionally, a genetic study also showed a negative result in 494 sporadic PD cases by direct sequencing of full coding regions and exon-intron boundaries of the NUS1 gene (24).
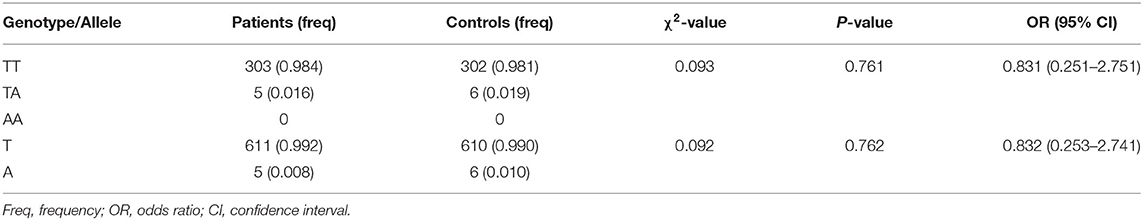
Table 2. Genotypic and allelic distributions of rs28362519 in Han-Chinese patients with Parkinson's disease and ethnically matched controls.
Discussion
PD is a neurological disorder arising from a complex interplay among genetic, environmental cues, and aging (16, 25). The synuclein alpha gene (SNCA) was discovered as the first causative gene for PD in 1997 (3, 26), and since then, dramatic progress has been made in identification of disease-causing gene for Mendelian PD (27, 28). As of this writing, at least 23 disease-causing loci and 19 genes have been identified to be responsible for monogenic PD form which explained <10% of all cases (12, 13). Susceptibility variants in certain genes, such as the glucosylceramidase beta (GBA), microtubule associated protein tau (MAPT), SNCA, and leucine rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) genes, have also been reported to increase PD risk (8, 12).
Intriguingly, variants in the NUS1 gene were reported to be responsible for PD in Chinese patients (16). The NUS1 gene, mapped to chromosome 6q22.1, encodes a membrane protein-Nogo-B receptor (NgBR), which is required for the biosynthesis of dolichol and protein glycosylation (29, 30). Homozygous NUS1 mutations in this gene were previously described to cause congenital disorder of glycosylation type Iaa (CDG1AA, OMIM 617082) (30), while rare heterozygous mutations were reported in two cases with autosomal dominant mental retardation-55 with seizures (MRD55, OMIM 617831) (31).
In this study, exome sequencing data involving coding regions and exon-intron boundaries of NUS1, were meticulously evaluated in 308 Han-Chinese patients containing 33 EOPD and 308 ethnically matched controls. Despite great interest, no association was found between the NUS1 variant p.Asp179Glu and PD phenotype, indicating that variants in the NUS1 gene may not be a primary genetic contributor to PD. The power analysis involving 5,944 PD cases (308 in this study and 5,636 from 60 articles) and 308 controls revealed that NUS1 mutations accountable for monogenic PD should affect <0.5% in general PD cases (power = 0.909) as the non-essential genetic contributor.
The findings lure us to hold curiosity about the real impacts of NUS1 in PD. Moreover, Guo et al.'s study lacked evidence of co-segregation of NUS1 variants in families (16), which raises concerns whether the NUS1 gene is indeed a disease-causing gene for monogenic PD. Our suspicion is supported by the following observations: (i) The de novo heterozygous NUS1 c.691+3dupA variant may be related to PD in an individual with PD phenotype (16), but other gene variants causing autosomal recessive parkinsonism should be excluded. In one report 44 to 82 de novo single-nucleotide variants occur in an individual genome, and some de novo variants, located in regulatory regions, may result in a disease phenotype (32). (ii) If the de novo NUS1 gene variant indeed caused autosomal dominant PD, it is of interest to discard the priority of screening variants in familial PD cases. Enough familial PD cases could be acquired for verifying the pathogenicity of heterozygous NUS1 variants, due to 5,089 sporadic PD cases enrolled in Guo et al.'s study and ~10–15% of PD cases having family history (16, 33). (iii) Since NUS1 variants were found in sporadic PD cases, it is of interest to abandon screening the variants in relatives. All the 26 NUS1 variant carriers having unavailable relatives and lack of detailed data involving exclusion of all known or unknown PD-causing gene mutations further query the core role of NUS1 variants in PD. (iv) Mouse models with genetic deficiencies in transcription factor genes, such as the engrailed homeobox 1/2 gene (En1/2) and the paired like homeodomain 3 gene (Pitx3), exhibited features of PD, especially dopaminergic neuronal loss in the substantia nigra, but no definite pathogenic gene mutations were found in PD patients (34). Moreover, Drosophila with mutant spinocerebellar ataxia 3 (SCA3) selectively expressed in dopaminergic neurons, a non-PD causative gene deficiency, also presents PD-like phenotype (35). These challenge the persuasiveness of functional studies in Drosophila models (16).
In summary, current findings indicate that NUS1 variant is not a common genetic contributor to PD. However, some limitations to this study should be acknowledged: (i) The possibility that a few of whole exome/whole genome sequencing studies might miss certain NUS1 variant(s) during sequence capture cannot be excluded. (ii) Some whole exome/whole genome sequencing studies focusing on investigating the disease-causing and/or susceptibility variants for PD in other databases such as the Cochrane and Embase databases may be missed. Further studies involving NUS1 variants in familial PD, particularly in EOPD, using high-coverage next-generation sequencing, and throughout functional studies in main pathobiological pathways underpinning PD (3), including autophagy, endocytosis, mitochondrial biology, immune response, and lysosomal function, are warranted to expose the real role of the NUS1 gene in PD development.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics Statement
The study involving human participants was reviewed and approved by the Institutional Review Board of the Third Xiangya Hospital of Central South University in Changsha, Hunan, China (approval number: 2018-S400). The patients/participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author Contributions
HD and LY conceived and designed this study. ZS and WZ collected the patient samples and clinical data. XC and XL performed the experiments. WL and HD analyzed the data. XC and LY wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFC1306604), National Natural Science Foundation of China (81670216, 81800219, and 81873686), the Lotus Scholars Program of Hunan Province (to HD), Scientific Research Project of Health and Family Planning Commission of Hunan Province (B20180729), and Hunan Provincial Innovation Foundation for Postgraduate (CX20190252).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
The authors appreciate all the participants and investigators participated in the study for their contributions.
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fneur.2020.583182/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Pires AO, Teixeira FG, Mendes-Pinheiro B, Serra SC, Sousa N, Salgado AJ. Old and new challenges in Parkinson's disease therapeutics. Prog Neurobiol. (2017) 156:69–89. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2017.04.006
2. Kalia LV, Lang AE. Parkinson's disease. Lancet. (2015) 386:896–912. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61393-3
3. Billingsley KJ, Bandres-Ciga S, Saez-Atienzar S, Singleton AB. Genetic risk factors in Parkinson's disease. Cell Tissue Res. (2018) 373:9–20. doi: 10.1007/s00441-018-2817-y
4. Ryan BJ, Hoek S, Fon EA, Wade-Martins R. Mitochondrial dysfunction and mitophagy in Parkinson's: from familial to sporadic disease. Trends Biochem Sci. (2015) 40:200–10. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2015.02.003
5. Ascherio A, Schwarzschild MA. The epidemiology of Parkinson's disease: risk factors and prevention. Lancet Neurol. (2016) 15:1257–72. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(16)30230-7
6. Merola A, Romagnolo A, Dwivedi AK, Padovani A, Berg D, Garcia-Ruiz PJ, et al. Benign versus malignant Parkinson disease: the unexpected silver lining of motor complications. J Neurol. (2020) 267:2949–60. doi: 10.1007/s00415-020-09954-6
7. Espay AJ, Schwarzschild MA, Tanner CM, Fernandez HH, Simon DK, Leverenz JB, et al. Biomarker-driven phenotyping in Parkinson's disease: a translational missing link in disease-modifying clinical trials. Mov Disord. (2017) 32:319–24. doi: 10.1002/mds.26913
8. Quadri M, Mandemakers W, Grochowska MM, Masius R, Geut H, Fabrizio E, et al. International Parkinsonism Genetics Network. LRP10 genetic variants in familial Parkinson's disease and dementia with Lewy bodies: a genome-wide linkage and sequencing study. Lancet Neurol. (2018) 17:597–608. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(18)30179-0
9. Postuma RB, Berg D, Stern M, Poewe W, Olanow CW, Oertel W, et al. MDS clinical diagnostic criteria for Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord. (2015) 30:1591–601. doi: 10.1002/mds.26424
10. Noyce AJ, Nalls MA. Mendelian randomization - the key to understanding aspects of Parkinson's disease causation? Mov Disord. (2016) 31:478–83. doi: 10.1002/mds.26492
11. Singleton AB, Farrer MJ, Bonifati V. The genetics of Parkinson's disease: progress and therapeutic implications. Mov Disord. (2013) 28:14–23. doi: 10.1002/mds.25249
12. Deng H, Wang P, Jankovic J. The genetics of Parkinson disease. Ageing Res Rev. (2018) 42:72–85. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2017.12.007
13. Jankovic J, Sherer T. The future of research in Parkinson disease. JAMA Neurol. (2014) 71:1351–2. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2014.1717
14. Klein C, Westenberger A. Genetics of Parkinson's disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. (2012) 2:a008888. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a008888
15. Boot E, Butcher NJ, Udow S, Marras C, Mok KY, Kaneko S, et al. Typical features of Parkinson disease and diagnostic challenges with microdeletion 22q11.2. Neurology. (2018) 90:e2059–67. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000005660
16. Guo JF, Zhang L, Li K, Mei JP, Xue J, Chen J, et al. Coding mutations in NUS1 contribute to Parkinson's disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. (2018) 115:11567–72. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1809969115
17. Trinh J, Lohmann K, Baumann H, Balck A, Borsche M, Brüggemann N, et al. International Parkinson's Disease Genomics Consortium (IPDGC). Utility and implications of exome sequencing in early-onset Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord. (2019) 34:133–7. doi: 10.1002/mds.27559
18. Chen X, Deng S, Xu H, Hou D, Hu P, Yang Y, et al. Novel and recurring NOTCH3 mutations in two Chinese patients with CADASIL. Neurodegener Dis. (2019) 19:35–42. doi: 10.1159/000500166
19. Fan K, Zhu H, Xu H, Mao P, Yuan L, Deng H. The identification of a transthyretin variant p.D38G in a Chinese family with early-onset leptomeningeal amyloidosis. J Neurol. (2019) 266:232–41. doi: 10.1007/s00415-018-9125-z
20. Xiang Q, Yuan L, Cao Y, Xu H, Li Y, Deng H. Identification of a heterozygous mutation in the TGFBI gene in a Hui-Chinese family with corneal dystrophy. J Ophthalmol. (2019) 2019:2824179. doi: 10.1155/2019/2824179
21. Chen Q, Yuan L, Deng X, Yang Z, Zhang S, Deng S, et al. A missense variant p.Ala117Ser in the transthyretin gene of a Han Chinese family with familial amyloid polyneuropathy. Mol Neurobiol. (2018) 55:4911–7. doi: 10.1007/s12035-017-0694-0
22. Yuan L, Deng X, Song Z, Deng S, Zheng W, Mao P, et al. Systematic analysis of genetic variants in patients with essential tremor. Brain Behav. (2018) 8:e01100. doi: 10.1002/brb3.1100
23. Yuan L, Song Z, Deng X, Yang Z, Yang Y, Guo Y, et al. Genetic analysis of FBXO2, FBXO6, FBXO12, and FBXO41 variants in Han Chinese patients with sporadic Parkinson's disease. Neurosci Bull. (2017) 33:510–4. doi: 10.1007/s12264-017-0122-5
24. Chen X, Xiao Y, Zhou M, Lin Y, Guo W, Huang S, et al. Genetic analysis of NUS1 in Chinese patients with Parkinson's disease. Neurobiol Aging. (2019) 86:202.e5–6. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2019.09.002
25. Marras C, Canning CG, Goldman SM. Environment, lifestyle, and Parkinson's disease: implications for prevention in the next decade. Mov Disord. (2019) 34:801–11. doi: 10.1002/mds.27720
26. Nussbaum RL. The identification of alpha-synuclein as the first Parkinson disease gene. J Parkinsons Dis. (2017) 7:S43–9. doi: 10.3233/JPD-179003
27. Douglas MR, Lewthwaite AJ, Nicholl DJ. Genetics of Parkinson's disease and parkinsonism. Expert Rev Neurother. (2007) 7:657–66. doi: 10.1586/14737175.7.6.657
28. Puschmann A. New genes causing hereditary Parkinson's disease or parkinsonism. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. (2017) 17:66. doi: 10.1007/s11910-017-0780-8
29. Harrison KD, Park EJ, Gao N, Kuo A, Rush JS, Waechter CJ, et al. Nogo-B receptor is necessary for cellular dolichol biosynthesis and protein N-glycosylation. EMBO J. (2011) 30:2490–500. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2011.147
30. Park EJ, Grabińska KA, Guan Z, Stránecký V, Hartmannová H, Hodaňová K, et al. Mutation of Nogo-B receptor, a subunit of cis-prenyltransferase, causes a congenital disorder of glycosylation. Cell Metab. (2014) 20:448–57. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2014.06.016
31. Hamdan FF, Myers CT, Cossette P, Lemay P, Spiegelman D, Laporte AD, et al. High rate of recurrent de novo mutations in developmental and epileptic encephalopathies. Am J Hum Genet. (2017) 101:664–85. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2017.09.008
32. Acuna-Hidalgo R, Veltman JA, Hoischen A. New insights into the generation and role of de novo mutations in health and disease. Genome Biol. (2016) 17:241. doi: 10.1186/s13059-016-1110-1
33. Verstraeten A, Theuns J, Van Broeckhoven C. Progress in unraveling the genetic etiology of Parkinson disease in a genomic era. Trends Genet. (2015) 31:140–9. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2015.01.004
34. Wang R, Yang S, Nie T, Zhu G, Feng D, Yang Q. Transcription factors: potential cell death markers in Parkinson's disease. Neurosci Bull. (2017) 33:552–60. doi: 10.1007/s12264-017-0168-4
Keywords: NUS1, Parkinson's disease, genetic analysis, whole exome sequencing, whole genome sequencing
Citation: Yuan L, Chen X, Song Z, Le W, Zheng W, Liu X and Deng H (2020) Extended Study of NUS1 Gene Variants in Parkinson's Disease. Front. Neurol. 11:583182. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.583182
Received: 19 July 2020; Accepted: 15 September 2020;
Published: 27 October 2020.
Edited by:
Mathias Toft, University of Oslo, NorwayReviewed by:
Joanne Trinh, University of Lübeck, GermanyLuca Marsili, University of Cincinnati, United States
Copyright © 2020 Yuan, Chen, Song, Le, Zheng, Liu and Deng. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hao Deng, aGRlbmcwMDhAeWFob28uY29t
 Lamei Yuan
Lamei Yuan Xiangyu Chen
Xiangyu Chen Zhi Song
Zhi Song Weidong Le
Weidong Le Wen Zheng
Wen Zheng Xin Liu
Xin Liu Hao Deng
Hao Deng