- 1Department of Genetics, Cell Biology and Anatomy, University of Nebraska Medical Center, Nebraska, NE, United States
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, Translational and Vascular Research Group, Penn State Milton S. Hershey Medical Center, Hershey, PA, United States
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are emerging as a powerful tool in regenerative medicine due to their ability to differentiate into mesenchymal lineages, such as bone, cartilage, and fat, along with their low immunogenicity and strong immunomodulatory properties. Unlike traditional cell therapies that rely on engraftment, MSCs primarily function through paracrine signaling—secreting bioactive molecules like vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β), and exosomes. These factors contribute to tissue repair, promote angiogenesis, and modulate immune responses in damaged or inflamed tissues. Recent studies have identified mitochondrial transfer as a novel therapeutic mechanism, where MSCs donate mitochondria to injured cells, restoring their bioenergetic function. This has expanded the therapeutic potential of MSCs to include conditions such as acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and myocardial ischemia. Clinically, MSCs have shown efficacy in diseases like graft-versus-host disease (GVHD), Crohn’s disease, and COVID-19. Trials such as REMODEL and REMEDY have demonstrated improved clinical outcomes, further validating MSC-based interventions. However, several challenges remain, including variability in cell potency, poor engraftment, and inconsistent results across clinical trials. Advances in genetic engineering such as CRISPR-modified MSCs and biomaterial scaffolds are being developed to enhance therapeutic efficacy and cell survival. Additionally, AI-driven platforms are being utilized to personalize MSC therapy and optimize cell selection. Innovative approaches like 3D bioprinting and scalable manufacturing are paving the way for more consistent and precise therapies. Moving forward, the integration of mechanistic insights with robust quality control and regulatory frameworks essential to translating MSC therapies from bench to bedside and ensuring their reliable application in clinical practice.
1 Introduction: mesenchymal stem cells and their therapeutic potential
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) were first identified in the 1970s by Friedenstein and colleagues, who isolated them from bone marrow aspirates (Fridenshtein et al., 1969). These cells stood out due to their ability to adhere to plastic surfaces and form fibroblast-like colonies, distinguishing them from other bone marrow-derived cells (Friedenstein et al., 1970). Since their discovery, MSCs have been found in a wide variety of postnatal tissues, including adipose tissue, umbilical cord (Gronthos et al., 2001), dental pulp (Kadar et al., 2009), synovial fluid (Morito et al., 2008), menstrual blood (Chen et al., 2019), and hair follicles (Wang et al., 2020). Among these sources, adipose-derived MSCs (AD-MSCs) (Gronthos et al., 2001) and umbilical cord-derived MSCs (UC-MSCs), have garnered particular interest due to their abundance and ease of isolation. Hair follicle-derived MSCs (HF-MSCs), obtained from the dermal papilla or sheath, also represent an accessible and promising source due to their multipotent differentiation capacity and regenerative potential (Las Heras et al., 2022). Figure 1.
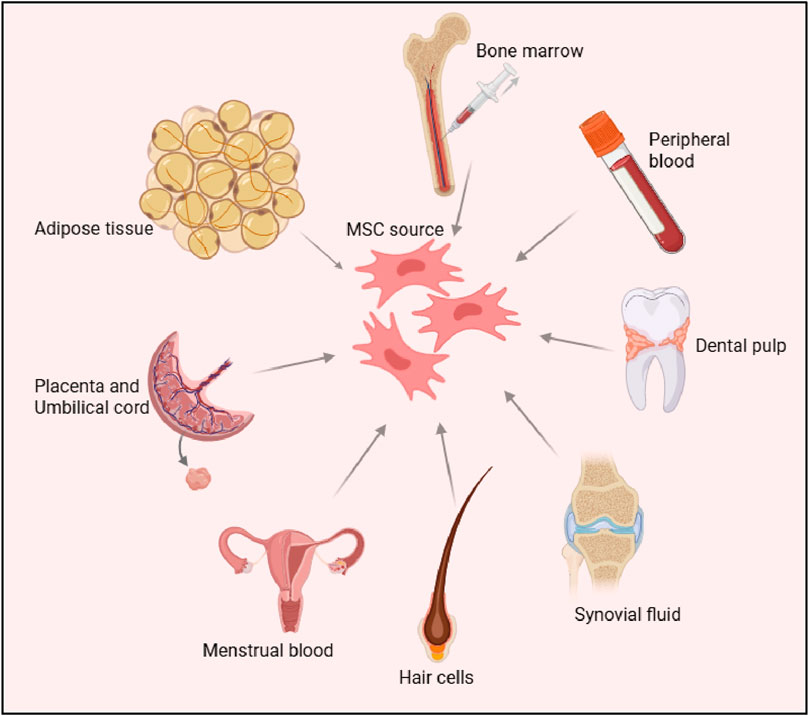
Figure 1. Sources of Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) The figure illustrates various tissue sources for deriving MSCs, including bone marrow, peripheral blood, adipose tissue, dental pulp, placenta, umbilical cord, synovial fluid, menstrual blood and hair follicle cells. These sources highlight the diverse origins of MSCs, which are widely studied for their regenerative and therapeutic potential.
Unlike pluripotent stem cells such as embryonic stem cells (ESCs) and induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), MSCs are classified as multipotent (Sensebe et al., 2010). This means they can differentiate into several mesenchymal lineages including osteoblasts, chondrocytes, and adipocytes but they do not share the broader differentiation potential of pluripotent cells.
To promote standardization across research studies, the International Society for Cellular Therapy (ISCT) established minimal criteria to define MSCs. These include: (a) adherence to plastic when cultured under standard conditions; (b) expression of specific surface markers CD73, CD90, and CD105 alongside the absence of hematopoietic markers such as CD34, CD45, and CD14; and (c) the ability to differentiate into osteogenic, chondrogenic, and adipogenic lineages in vitro (Dominici et al., 2006). One of the defining immunological features of MSCs is their lack of major histocompatibility complex class II (MHC-II) expression, which reduces their immunogenicity (Machado Cde et al., 2013). This low immunogenic profile supports their use in allogeneic settings, allowing for “off-the-shelf” therapeutic applications without the need for strict HLA matching. As a result, MSCs have become highly attractive for regenerative medicine and cell-based therapies (Kot et al., 2019).
1.1 Mechanisms Underlying MSC therapeutic effects
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) exert their therapeutic effects primarily through two mechanisms: direct differentiation into tissue-specific cell types and paracrine signaling via the secretion of bioactive molecules (Bagno et al., 2022; Han et al., 2022). Although early research focused heavily on their ability to differentiate, more recent findings emphasize that the predominant therapeutic impact of MSCs arises from their paracrine activity (Baglio et al., 2015). This includes the release of extracellular vesicles (EVs), cytokines, and growth factors that influence surrounding cells and tissues (Chen et al., 2008).
In terms of immunomodulation, MSCs interact with both innate and adaptive immune systems to help restore immune balance. They inhibit T-cell proliferation through the secretion of immunosuppressive agents such as prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO), and programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1), thereby tempering overactive immune responses (Glennie et al., 2005; Selmani et al., 2008). Moreover, MSCs guide macrophage polarization by converting pro-inflammatory M1 macrophages into anti-inflammatory M2 phenotypes through signaling molecules like interleukin-10 (IL-10) and transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) (Murray et al., 2014). This shift plays a critical role in autoimmune conditions such as multiple sclerosis, where MSCs also promote the expansion of regulatory T cells (Tregs) to enhance immune tolerance (Hu et al., 2024).
In addition to their immunomodulatory effects, MSCs secrete a wide array of trophic factors that support tissue repair. Their secretome contains growth factors, chemokines, and EVs that collectively foster regeneration. For example, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) promote new blood vessel formation, improving perfusion to injured areas (Han et al., 2022; Patel et al., 2021). Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) contributes to antifibrotic effects by limiting collagen accumulation in organs like the liver and lungs (Dohi et al., 2000; Kwiecinski et al., 2011). Meanwhile, insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) and stromal-derived factor-1 (SDF-1) play protective roles by inhibiting cell death and preserving tissue structure (Al-Samerria and Radovick, 2021; Heo et al., 2019). These diverse and complementary mechanisms highlight the broad therapeutic potential of MSCs across a range of diseases and injury models.
1.2 Mitochondrial transfer: a novel mechanism
Recent research has uncovered an innovative mechanism by which mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) facilitate tissue repair: the transfer of mitochondria (Li et al., 2019). Through the development of tunneling nanotubes slender, dynamic membrane structures MSCs can deliver healthy mitochondria directly to damaged cells, thereby restoring cellular energy production in compromised tissues (Delage et al., 2016; Luchetti et al., 2022). This mechanism has shown significant potential in conditions characterized by mitochondrial dysfunction, such as acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and myocardial ischemia (Lee et al., 2024; Lesnefsky et al., 2017).
In ARDS, MSCs have been observed to transfer mitochondria to alveolar epithelial cells, resulting in increased ATP generation, decreased oxidative stress, and improved survival outcomes in preclinical models (Wang et al., 2025). Similarly, in the context of myocardial ischemia, mitochondrial transfer to cardiomyocytes helps counteract ischemia-reperfusion injury by stabilizing mitochondrial membrane potential and reducing cell death (Xu et al., 2025). This novel mechanism underscores the adaptive capabilities of MSCs and broadens their therapeutic scope beyond traditional paracrine signaling, offering a promising new avenue for treating diseases marked by impaired cellular energetics.
1.3 Therapeutic applications of MSCs
The broad therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) is reflected in their effectiveness across a wide range of clinical conditions. In autoimmune and inflammatory diseases, MSCs have shown significant clinical benefit (Zaripova et al., 2023). For example, in a phase III trial of Remestemcel-L, an MSC product derived from bone marrow, infusions markedly alleviated symptoms in pediatric patients with steroid-refractory acute GVHD, with an overall response rate of 70.4% at day 28 and durable benefit (Kurtzberg et al., 2020). In cases of treatment-resistant rheumatoid arthritis (RA), intra-articular injections of MSCs have been found to reduce synovial inflammation and promote cartilage regeneration (Lopez-Santalla et al., 2020). Similarly, preclinical studies on inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) highlight the ability of MSCs to modulate immune responses (Saadh et al., 2024); MSC treatment reduces colitis severity by inducing macrophage polarization toward an anti-inflammatory state through the secretion of interleukin-10 (IL-10) (Hosseini-Asl et al., 2020; Shi et al., 2019).
In neurological disorders, MSCs offer unique therapeutic advantages due to their capacity to cross the blood-brain barrier and release neuroprotective factors. For instance, MSC-derived exosomes have been shown to slow motor neuron degeneration in animal models of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) (Gschwendtberger et al., 2023), and ongoing clinical trials such as MASTERS-2 are investigating intravenous MSC therapy to promote neurogenesis and angiogenesis in stroke patients (Li et al., 2021). In the realm of cardiovascular medicine, MSCs also play a pivotal role (Bagno et al., 2018). Studies like the PARACCT trial report that allogeneic MSCs help reduce scar formation and enhance ejection fraction in patients recovering from myocardial infarction (MI) (Jackson et al., 2012). Furthermore, MSC-secreted factors contribute to the attenuation of adverse ventricular remodeling in heart failure, helping to maintain cardiac function (Guan et al., 2025; Ranganath et al., 2012).
The COVID-19 pandemic underscored the therapeutic relevance of MSCs in acute respiratory conditions. Clinical trials such as REMEDY demonstrated that umbilical cord-derived MSCs (UC-MSCs) could lower mortality rates and improve oxygenation in patients with severe COVID-19 by suppressing cytokine storms and supporting lung tissue repair (Can and Coskun, 2020; Li et al., 2025). These examples collectively emphasize the wide-ranging clinical applications of MSCs, driven by their immunomodulatory, regenerative, and protective capabilities.
1.4 Advantages over other stem cell types
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) offer several key advantages over embryonic stem cells (ESCs) and induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), making them particularly well-suited for clinical use. From an ethical standpoint, MSCs avoid the controversies linked to ESCs, as their isolation does not involve the destruction of embryos (Lo and Parham, 2009). In terms of safety, MSCs present a significantly lower risk of tumor formation, especially when compared to the teratoma-forming potential of pluripotent stem cells (Lee and Hong, 2017). Moreover, the establishment of allogeneic MSC banks allows for readily available, “off-the-shelf” therapeutic products, enabling rapid intervention in urgent clinical scenarios such as acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) or myocardial infarction (Garcia-Bernal et al., 2021). These practical advantages coupled with MSCs’ robust immunomodulatory and regenerative functions make them a compelling and scalable option for widespread therapeutic applications (Patel et al., 2013).
1.5 Challenges and controversies
Despite their therapeutic potential MSC therapies face several critical challenges that hinder clinical translation. One major obstacle is the variability in MSC potency, influenced by factors such as donor age, tissue origin (e.g., bone marrow vs adipose tissue), and in vitro culture conditions (Zhou et al., 2021). This heterogeneity complicates standardization and leads to inconsistent therapeutic outcomes. Another limitation is the poor engraftment efficiency of MSCs; studies indicate that less than 5% of intravenously administered cells successfully home to and persist in target tissues (Burdick et al., 2016). As a result, there is a growing need for strategies that enhance MSC trafficking and retention at injury sites (Ullah et al., 2019).
Clinical trial results have also been mixed. While MSC-based treatments have shown encouraging outcomes in conditions like graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) (Kadri et al., 2023) and severe COVID-19, trials for other diseases such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) have failed to achieve primary endpoints (Broekman et al., 2018). These inconsistencies highlight the importance of developing biomarker-guided approaches to better identify patients who are most likely to benefit and refining delivery methods to improve efficacy. Bridging the gap between preclinical promise and clinical success will require deeper mechanistic insights and innovative bioengineering solutions to fully realize the therapeutic capabilities of MSCs.
2 Mechanistic insights: how MSCs exert their effects in vivo
MSCs exhibit remarkable therapeutic potential through a diverse array of biological mechanisms that allow them to repair injured tissues, modulate immune responses, and restore homeostasis across various disease conditions (Jimenez-Puerta et al., 2020). While early research emphasized their capacity for direct differentiation into tissue-specific cell types, contemporary studies reveal that MSCs primarily act through paracrine signaling, immunomodulation, and novel cell-to-cell interactions such as mitochondrial transfer (Velarde et al., 2022). These mechanisms operate synergistically, allowing MSCs to adapt dynamically to injury microenvironments, even in the absence of long-term engraftment. Below, we delve into the molecular and cellular pathways underpinning MSC functionality, integrating preclinical discoveries with clinical evidence to illustrate their translational relevance.
2.1 Paracrine signaling: the secretome as a driver of regeneration
The paracrine activity of MSCs mediated by their secretome, a rich cocktail of EVs, growth factors, cytokines, and chemokines, it is now recognized as the cornerstone of their therapeutic effects (Gonzalez-Gonzalez et al., 2020; Ulpiano et al., 2023; Malhotra et al., 2022) Figure 2. Unlike terminally differentiated cells, MSCs secrete bioactive molecules that act on neighboring cells to promote angiogenesis, suppress apoptosis, and mitigate fibrosis, creating a regenerative niche conducive to healing (Gong et al., 2017; Nazarie Ignat et al., 2021; Zou et al., 2023). For instance, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) secreted by MSCs stimulate endothelial cell proliferation and blood vessel formation, a process critical for revascularization ischemic tissues in conditions such as myocardial infarction (MI) and diabetic ulcers (Patel et al., 2023; Patel et al., 2021; Potapova et al., 2007). In the landmark PARACCT trial, allogeneic MSC administration in MI patients reduced infarct scar size by 33% and improved left ventricular ejection fraction, outcomes attributed in part to VEGF-driven angiogenesis (Natsumeda et al., 2017; Williams et al., 2013).
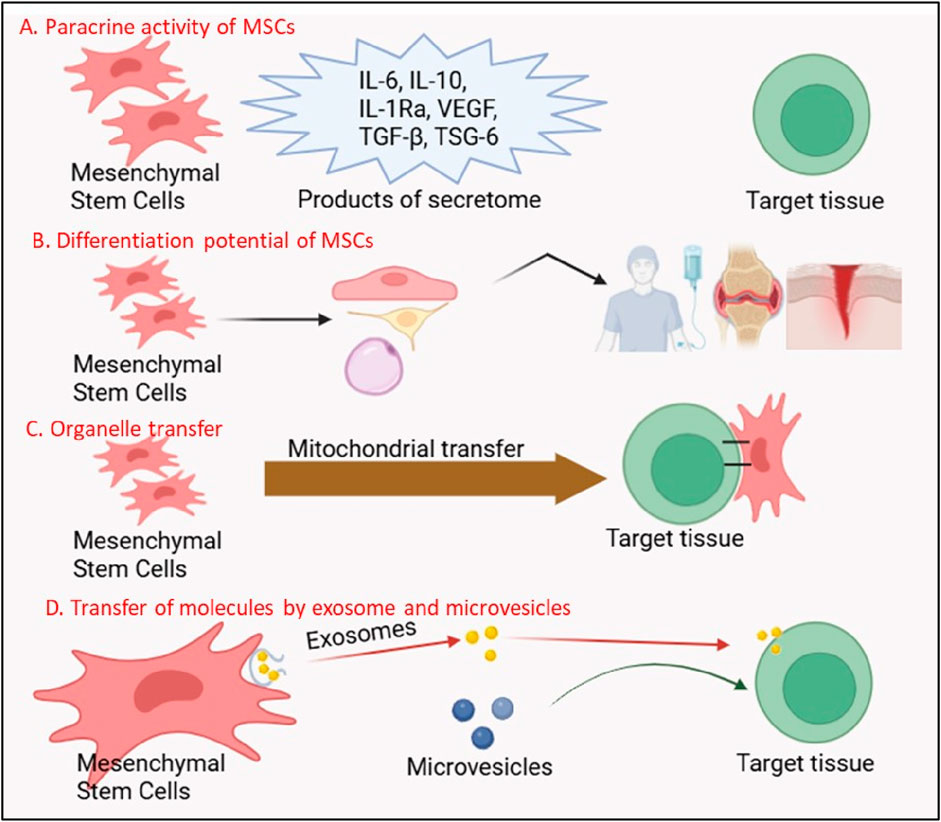
Figure 2. Multifunctional Mechanisms of Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) in Regenerative Therapy. The figure illustrates four key mechanisms through which MSCs exert their therapeutic effects: (A) Paracrine Activity of MSCs: MSCs secrete a variety of bioactive molecules, including anti-inflammatory cytokines (IL-6, IL-10, IL-1Ra), growth factors (VEGF, TGF-β), and tissue-protective factors (TSG-6), which modulate immune responses and promote tissue repair. (B) Differentiation Potential of MSCs: MSCs possess the ability to differentiate into multiple cell lineages (e.g., osteocytes, chondrocytes, adipocytes), contributing directly to tissue regeneration. The secretome of MSCs further supports this process by creating a regenerative microenvironment. (C) Organelle Transfer: MSCs can transfer functional organelles, such as mitochondria, to damaged cells, restoring cellular metabolism and enhancing survival in target tissues. (D) Transfer of Molecules by Exosomes and Microvesicles: MSCs release exosomes and microvesicles containing proteins, nucleic acids, and signaling molecules, which are taken up by recipient cells to mediate therapeutic effects, including immune modulation and tissue repair.
Extracellular vesicles, particularly exosomes, are pivotal mediators of MSC paracrine effects Figure 2. These nanosized lipid bilayer vesicles carry proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids (e.g., microRNAs, mRNAs) that reprogram recipient cells. In neurological disorders like amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), MSC-derived exosomes deliver neuroprotective miRNAs (e.g., miR-21-5p) to motor neurons, inhibiting pro-apoptotic pathways and delaying disease progression in rodent models (Chen et al., 2021; Malhotra et al., 2022). Similarly, in acute kidney injury, MSC exosomes enriched with miR-30c-5p suppress mitochondrial fission and oxidative stress, preserving renal function (Tsuji et al., 2023). The MASTERS-2 clinical trial, which investigates intravenous MSC therapy for ischemic stroke, has identified exosomal miR-124 as a key mediator of neurogenesis and angiogenesis, bridging preclinical findings to human applications (Yang et al., 2017).
The anti-fibrotic and anti-apoptotic properties of the MSC secretome further underscore its therapeutic versatility (Alfarano et al., 2012; Giacomini et al., 2023). Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) secreted by MSCs inhibits TGF-β1-driven collagen deposition in fibrotic liver and lung tissues (Wei et al., 2021), while insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) and stromal-derived factor-1 (SDF-1) activate survival pathways in cardiomyocytes and neurons, respectively (Baglio et al., 2012; Park et al., 2016). In idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), MSC-conditioned media reduces myofibroblast activation and collagen synthesis in preclinical models, prompting ongoing Phase II trials (e.g., AETHER-1) exploring aerosolized MSC secretions as a non-cell-based therapy (Filidou et al., 2022).
2.2 Immunomodulation: orchestrating immune homeostasis
MSCs possess a unique ability to dynamically modulate immune responses, balancing pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory signals to restore homeostasis (Faria et al., 2023). This immunomodulatory capacity is context-dependent: MSCs suppress hyperactive immune reactions in autoimmune diseases while enhancing pathogen clearance in infections (Chen et al., 2024). A key mechanism is their interaction with T cells. By secreting prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) and indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO), MSCs inhibit T-cell proliferation and shift the Th1/Th17-Th2/Treg balance toward tolerance (Terraza-Aguirre et al., 2020). In graft-versus-host disease (GVHD), a life-threatening complication of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, MSC infusions reduce pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g., IFN-γ, IL-17) and expand regulatory T cells (Tregs), as demonstrated in the Phase III REMODEL trial, where 60% of steroid-refractory GVHD patients achieved complete remission (Kebriaei et al., 2020).
Macrophage polarization represents another critical axis of MSC-mediated immunomodulation. MSCs reprogram pro-inflammatory M1 macrophages into anti-inflammatory M2 phenotypes via interleukin-10 (IL-10) and transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) (Cao et al., 2010; Lu et al., 2023). In inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), this shift reduces colonic inflammation (Saadh et al., 2023) and promotes mucosal healing, as evidenced by decreased TNF-α and increased IL-10 levels in murine colitis models (Jung et al., 2015). Clinical trials in Crohn’s disease patients (e.g., Cx601 trial) have shown that locally administered MSCs induce fistula closure through macrophage reprogramming, highlighting translational success (Molendijk et al., 2015).
MSCs also interact with dendritic cells (DCs) and natural killer (NK) cells to fine-tune immunity. By inhibiting DC maturation and antigen presentation via cell-cell contact and soluble factors (e.g., galectin-3), MSCs prevent excessive T-cell activation (Duffy et al., 2011; Simovic Markovic et al., 2016; Sioud et al., 2010; Spaggiari et al., 2009). Simultaneously, they suppress NK cell cytotoxicity by downregulating activating receptors (e.g., NKG2D), reducing tissue damage in conditions like rheumatoid arthritis (RA) (Dehnavi et al., 2023). Intra-articular MSC injections in RA patients have reduced synovial inflammation and cartilage degradation, correlating with diminished NK cell activity and IL-6 levels in synovial fluid (Augello et al., 2007; Papadopoulou et al., 2012).
2.3 Mitochondrial transfer and beyond: direct cellular rejuvenation
Emerging research has unveiled a groundbreaking mechanism by which MSCs directly rejuvenate injured cells: mitochondrial transfer Figure 2. Through tunneling nanotubes dynamic membrane channels connecting cells MSCs donate functional mitochondria to energy-depleted cells, restoring ATP production and mitigating oxidative stress (Luchetti et al., 2022). In acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), MSC-derived mitochondria integrate into alveolar epithelial cells, rescuing them from apoptosis and improving gas exchange in preclinical models (Su et al., 2021). A randomized controlled trial conducted in Indonesia evaluated umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stromal cells (UC-MSCs) as an adjuvant therapy for critically ill COVID-19 patients and demonstrated a 2.5-fold increase in survival, likely due to immunomodulatory effects such as reduced interleukin-6 levels (Dilogo et al., 2021).
Mitochondrial transfer also plays a pivotal role in cardiovascular repair. In myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury, MSCs donate mitochondria to cardiomyocytes, preserving mitochondrial membrane potential and reducing infarct size by 40% in rodent studies (Huang et al., 2021). This process is enhanced under hypoxic conditions, which upregulate MSC TNT formation. Beyond mitochondria, MSCs transfer lysosomes to cells with defective autophagy, as seen in neurodegenerative diseases like Parkinson’s, where lysosomal delivery clears α-synuclein aggregates and restores neuronal health (Shin and Lee, 2020).
Complementing these direct interactions, MSC-derived extracellular vesicles carry mitochondrial components (e.g., mitochondrial DNA, proteins) that independently boost cellular bioenergetics. In stroke models, MSC-EVs enriched with mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase enhance neuronal survival (Hermann et al., 2025), while in aging-related osteoporosis, mitochondrial tRNA transfers from MSCs rejuvenate osteoblast function (Jia et al., 2020). These findings underscore the adaptability of MSCs, which employ both secretory and direct contact-dependent strategies to address diverse pathologies.
2.4 Integration of mechanisms and clinical translation
The therapeutic efficacy of MSCs in vivo arises from the synergistic integration of paracrine, immunomodulatory, and direct cellular mechanisms (Fontaine et al., 2016). For example, in COVID-19-associated ARDS, MSCs concurrently mitigate cytokine storms (via PGE2 and IDO) (Zhang et al., 2022), promote lung vascular repair (via VEGF), and rejuvenate alveolar cells (via mitochondrial transfer) (Tunstead et al., 2024), as evidenced by improved oxygenation and reduced mortality in clinical trials. Similarly, in heart failure, MSC secretome factors (e.g., SDF-1) recruit endogenous stem cells, while mitochondrial transfer enhances cardiomyocyte survival, collectively improving cardiac output (Chung et al., 2015).
However, challenges persist in optimizing MSC homing, survival, and engraftment. Less than 5% of systemically administered MSCs reach target tissues due to pulmonary sequestration and anoikis (Gorshkova et al., 1996; Masterson et al., 2021). Innovations such as magnetic nanoparticle labeling, hypoxia preconditioning, and 3D bio printed scaffolds enhance MSC retention and potency (De Palma et al., 2025). For instance, MSCs preconditioned with TNF-α exhibit upregulated CXCR4 expression, improving homing to ischemic myocardium (Ziaei et al., 2014).
The mechanistic diversity of MSCs spanning paracrine signaling, immune regulation, and direct cellular rejuvenation positions them as versatile therapeutic agents. By leveraging these pathways through bioengineering and targeted delivery, researchers can unlock their full potential, bridging the gap between preclinical promise and clinical reality.
3 Preclinical evidence: animal models, efficacy, and safety profiling
The preclinical evaluation of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) in animal models has been instrumental in validating their therapeutic potential, elucidating mechanisms of action, and establishing safety profiles prior to human trials (Lee et al., 2014). These studies span a wide array of diseases, leveraging rodents, rabbits, pigs, and non-human primates to mimic human pathologies (Feng et al., 2014; Liu et al., 2016; Pelizzo et al., 2015; Xun et al., 2022). While preclinical data have consistently highlighted the efficacy of MSCs in mitigating tissue damage, modulating immune responses, and promoting regeneration (Cao et al., 2015; Dimarino et al., 2013; Schafer et al., 2016), they also expose critical limitations and translational gaps that complicate the extrapolation of results to clinical settings (Caplan et al., 2019; Levy et al., 2020). This section synthesizes disease-specific preclinical applications of MSCs, underscores their successes, and interrogates the challenges inherent in animal models that hinder seamless translation to human therapies.
3.1 Disease-specific applications in preclinical studies
Preclinical research has demonstrated the versatility of MSCs across diverse disease domains, including cardiovascular, neurological, autoimmune, and degenerative disorders. In cardiovascular diseases, rodent models of myocardial infarction (MI) have been pivotal in establishing MSC efficacy (Zhou et al., 2021). For instance, intramyocardial injection of bone marrow-derived MSCs (BM-MSCs) in rats reduced infarct size by 30%–40%, improved left ventricular ejection fraction, and enhanced angiogenesis through secretion of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and stromal-derived factor-1 (SDF-1) (Poomani et al., 2022). Similarly, porcine models of ischemia-reperfusion injury revealed that MSC therapy attenuated ventricular remodeling and fibrosis, with adipose-derived MSCs (AD-MSCs) outperforming BM-MSCs in promoting cardiomyocyte survival due to their higher angiogenic cytokine output (Gubert et al., 2021; Hegde et al., 2024).
In neurological disorders, MSC efficacy has been explored in rodent models of stroke, traumatic brain injury (TBI), and neurodegenerative diseases (van Velthoven et al., 2017). Intravenously administered MSCs in middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) mice migrated to ischemic brain regions, secreted brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), and reduced infarct volume by 50%, correlating with improved motor function (Jeong et al., 2014). In Alzheimer’s disease (AD) transgenic mice, MSC-derived exosomes carrying miR-29c-3p suppressed β-amyloid aggregation and neuroinflammation, delaying cognitive decline (Sha et al., 2021). Studies using Parkinson’s disease models have shown that intranasally administered MSCs can cross the blood-brain barrier, reduce dopaminergic neuron loss, and improve motor coordination through mechanisms involving mitochondrial transfer and modulation of glial cell activity.
Autoimmune and inflammatory diseases have also been a focus, with murine models of multiple sclerosis (experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis, EAE) and rheumatoid arthritis (collagen-induced arthritis, CIA) showcasing MSC immunomodulatory prowess (Constantinescu et al., 2011; Lopez-Santalla et al., 2021). In EAE mice, systemic MSC administration reduced demyelination and Th17-mediated inflammation by expanding regulatory T cells (Tregs) and suppressing dendritic cell activation. CIA models demonstrated that intra-articular MSC injections lowered synovial IL-6 and TNF-α levels, while promoting cartilage repair through chondrocyte differentiation (Lu et al., 2016). Notably, MSC therapy in a lupus-prone (MRL/lpr) mouse model extended survival by curtailing autoantibody production and renal inflammation, findings that informed subsequent Phase I/II trials in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients (Guo et al., 2023).
Pulmonary diseases, including idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), have benefited from preclinical MSC studies (Yuan et al., 2024). Bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice revealed that MSC-derived hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) suppressed TGF-β1-driven collagen deposition and myofibroblast activation, improving lung compliance (Shukla et al., 2009). In LPS-induced ARDS models, MSCs attenuated alveolar edema and neutrophil infiltration via prostaglandin E2 (PGE2)-mediated macrophage polarization to the M2 phenotype (Hezam et al., 2023). These outcomes were replicated in porcine models of ventilator-induced lung injury, where MSC therapy reduced systemic cytokine storms and improved oxygenation, laying the groundwork for COVID-19 clinical trials.
Orthopedic applications of MSCs, particularly in bone and cartilage repair, have been validated in large animal models. Ovine osteochondral defect studies demonstrated that MSC-loaded scaffolds enhanced hyaline cartilage regeneration and subchondral bone integration, outperforming microfracture techniques (Araki et al., 2015; Wang et al., 2024). Similarly, canine models of spinal cord injury showed that MSC-seeded hydrogels promoted axonal regrowth and functional recovery, with MRI evidence of reduced lesion volume (Cai et al., 2023; Straley et al., 2010).
3.2 Limitations and translational gaps in animal models
Despite promising preclinical outcomes, the translation of MSC therapies to the clinic remains hampered by several key limitations. One major challenge is the discrepancy in disease pathophysiology between animal models and human conditions. For instance, bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis in mice does not replicate the chronic, multifactorial progression of IPF in humans, which involves complex genetic and environmental interactions (Lawson et al., 2013). Similarly, rodent stroke models often lack relevant comorbidities such as hypertension or diabetes, leading to overly optimistic assessments of therapeutic efficacy (Macrae, 2011). The use of young, genetically uniform animals further limits clinical relevance, as human patients are typically older and biologically diverse, with diminished regenerative potential (Osier et al., 2016)
Species-specific immune responses also hinder translation. Murine macrophages display distinct cytokine profiles and polarization behaviors compared to human cells, often exaggerating MSCs anti-inflammatory effects (Chen et al., 2023). While humanized mouse models improve immunological relevance, they are expensive and still do not fully replicate human immune complexity (Chuprin et al., 2023). Additionally, although MSCs are considered immune-privileged in rodents, clinical studies show they may be recognized and cleared in immunocompetent humans, reducing their long-term effectiveness (Ankrum et al., 2014).
Technical inconsistencies further complicate translation. Variability in MSC sourcing, donor age, culture protocols, and delivery methods affects cell behavior and therapeutic outcomes (Heyman et al., 2025; Kolliopoulos et al., 2023). For example, intravenous MSCs often become sequestered in the lungs, while local injections improve tissue retention but are less applicable for systemic diseases (Sanchez-Diaz et al., 2021). Most preclinical studies also lack long-term follow-up, missing delayed adverse effects such as tumorigenicity. Rare cases of MSC-induced osteosarcoma in immunodeficient mice raise safety concerns, especially in immunosuppressed patients (Christodoulou et al., 2018). Finally, dose scaling from small animals to humans remains imprecise, with large-animal studies underutilized due to high costs. To bridge these gaps, researchers are adopting humanized models, organ-on-chip platforms, and machine learning to better simulate human physiology and refine preclinical study designs (Ching et al., 2021; Ingber, 2022).
4 Clinical translation: progress and pitfalls in human trials
The development of MSC therapies has been characterized by both promising breakthroughs and significant hurdles. Over the past 2 decades, numerous clinical trials have explored the application of MSCs across a broad spectrum of diseases including autoimmune, degenerative, inflammatory, and ischemic conditions providing valuable insights into their safety, therapeutic potential, and translational limitations (Hussen et al., 2024; Patel et al., 2013). Early-phase studies (Phase I/II) have largely confirmed the safety and feasibility of MSC administration, with preliminary evidence supporting their clinical benefit in select cases (Harris et al., 2018). However, as trials have advanced to Phase III, challenges related to standardization, scalability, and reproducibility have become increasingly evident, particularly under heightened regulatory oversight (Taylor et al., 2022). These issues highlight the inherent complexities of translating MSC-based therapies into routine clinical use. This section reviews the progress made in human trials, distills lessons learned from early and late-stage studies, and examines the key barriers that must be overcome to fully realize the clinical potential of MSC therapies (Hetta et al., 2025; da Silva et al., 2025).
4.1 Phase I/II trials: safety and early efficacy
Phase I and II trials represent critical early stages in the clinical translation of MSC therapies, focusing primarily on safety while offering initial insights into efficacy. Globally, over 1,200 MSC-related trials have been registered, the majority in these early phases (Galderisi et al., 2022; Guan et al., 2025). Across diverse delivery routes intravenous, intra-articular, intramyocardial, and intrathecal MSC therapies have shown consistent short-term safety, with minimal adverse effects (Bagno et al., 2022). For instance, intravenous infusion of BM-MSCs in GVHD patients at doses up to 10 million cells/kg produced no acute toxicity or ectopic tissue formation. Likewise, intra-articular injections of AD-MSCs in osteoarthritis were well-tolerated, with only transient swelling (Song et al., 2020).
These trials also provide compelling early evidence of efficacy. A pivotal Phase II study (NCT00366145) in steroid-refractory GVHD reported a 70% response rate following BM-MSC infusion, prompting further validation in the Phase III REMODEL trial (Kebriaei et al., 2020). In Crohn’s disease-related fistulas, the Cx601 trial showed a 50% closure rate with local AD-MSC administration, leading to EMA approval of Alofisel in 2018 (Panes et al., 2018). The POSEIDON trial for ischemic cardiomyopathy found that allogeneic MSCs improved ejection fraction and reduced scar size. In neurology, MASTERS-2 demonstrated improved stroke outcomes and MRI evidence of white matter repair, while MSCs slowed disease progression in ALS and reduced mortality in severe COVID-19 cases (Hare et al., 2017).
However, key challenges persist. Product variability due to donor age, tissue source, and culture conditions continues to affect consistency. Optimal dosing and delivery remain unresolved, as intravenous MSCs are largely sequestered in the lungs. Moreover, patient selection is often suboptimal, with few trials stratifying based on biomarkers of response. These limitations underscore the need for more precise trial design to enhance reproducibility and therapeutic impact.
4.2 Phase III trials and regulatory challenges
Phase III trials serve as the definitive evaluation of MSC therapies, demanding robust evidence of efficacy, safety, and clinical benefit compared to standard care. While several MSC products have progressed to this stage, results have been inconsistent, reflecting the complexities of large-scale translation (Parekkadan and Milwid, 2010; Cesnik and Svajger, 2024).
In acute GVHD, the Phase III REMODEL trial (NCT02336230) achieved a 60% complete response rate with BM-MSCs, leading to the approval of Temcell in Japan in 2015 the first globally sanctioned allogeneic MSC product (Kurtzberg et al., 2020; Galipeau, 2020). In contrast, the Phase III STAR trial for chronic GVHD failed to meet its primary endpoint, underscoring disease-specific differences in MSC responsiveness (Kadri et al., 2023). Similarly, the ADMIRE-CD trial demonstrated a 53% fistula closure rate in Crohn’s disease patients, securing EMA approval for Alofisel, though the FDA withheld approval due to concerns over long-term durability (Garcia-Olmo et al., 2022).
Cardiovascular trials have proven more challenging. The CHART-1 trial in chronic heart failure showed neutral results despite promising earlier data, likely due to variability in cell potency and delivery (Rheault-Henry et al., 2021; Tompkins et al., 2017). The CHART-1 trial utilized cardiopoietic MSCs that underwent lineage-specific induction, representing a differentiated MSC therapy rather than native MSC administration (Dilogo et al., 2021). The TRIDENT trial also failed to demonstrate significant improvement in myocardial infarction (Piccini et al., 2011). Neurological studies faced similar setbacks; the NeuroNEXT ALS trial showed no survival benefit, and MASTERS-2 revealed reduced effect sizes in Phase III, reflecting challenges in scaling early success to broader populations (Cudkowicz et al., 2022; Shefner and Cudkowicz, 2024).
These discrepancies underscore systemic issues in late-stage MSC development:
a. Product Standardization: Unlike pharmaceuticals, MSCs are live products sensitive to manufacturing variables. The absence of universal potency assays metrics quantifying MSC function (e.g., immunosuppressive capacity, VEGF secretion) has led to batch-to-batch variability. For example, Prochymal, an MSC product for GVHD, faced criticism for inconsistent IDO enzyme activity across batches, potentially undermining efficacy (Chinnadurai et al., 2018).
b. Placebo Effects and Trial Design: Many MSC trials lack adequate blinding, particularly in open-label surgical deliveries (e.g., intramyocardial injections), inflating placebo effects. The ACT34-CMI trial for critical limb ischemia was confounded by high placebo responses, obscuring MSC benefits (Losordo et al., 2011; Losordo et al., 2012).
c. Regulatory Fragmentation: Global regulatory agencies impose conflicting requirements. The EMA emphasizes long-term safety and immunogenicity data, while the FDA prioritizes mechanistic biomarkers and potency assays (Kang et al., 2023). Japan’s PMDA, meanwhile, fast-tracks MSC approvals based on Phase II data for unmet needs, creating uneven commercial landscapes.
To overcome manufacturing and regulatory challenges, MSC innovators are embracing advanced technologies such as closed-system bioreactors and xenogen-free culture media to enhance consistency, while improved cryopreservation extends shelf life without compromising cell viability (Rogers et al., 2021). Trials like MSC-NTF in ALS have demonstrated the benefits of potency standardization through neurotrophic factor enrichment. Regulatory agencies are also evolving; the FDA’s 2022 draft guidance recommends potency assays aligned with mechanism of action, such as IDO activity for immunomodulatory products, promoting better translational alignment (Hoang et al., 2025).
MSC therapies have reached a pivotal stage in clinical translation. While early-phase trials affirm safety and signal therapeutic promise in conditions from GVHD to COVID-19 ARDS, Phase III failures have underscored the need for improved standardization, mechanistic clarity, and precision in trial design (Horie et al., 2020; Ragel et al., 2023). Successes like Alofisel and Temcell show that with robust manufacturing and targeted applications, regulatory approval is attainable (Lu and Allickson, 2024). Future progress hinges on biomarker-guided patient selection, validated potency assays, and adaptive clinical strategies to fully realize the potential of MSCs in regenerative medicine.
5 Biosafety and immunogenicity: addressing concerns in MSC therapies
MSC therapies represent a promising frontier in regenerative medicine and immunomodulation, offering therapeutic potential for a wide range of diseases, including osteoarthritis, myocardial infarction, GVHD, and autoimmune disorders (Guo et al., 2020; Mancuso et al., 2019). Their clinical appeal lies in their capacity to differentiate into multiple lineages, secrete trophic factors that promote tissue repair, and modulate immune responses (Ayala-Cuellar et al., 2019). However, as these therapies advance in clinical use, two critical concerns biosafety and immunogenicity must be thoroughly addressed to ensure therapeutic efficacy and patient safety.
Biosafety challenges include risks such as tumorigenicity, unintended differentiation, microbial contamination, genetic instability from extended culture, and issues related to manufacturing consistency (Neri, 2019). Although MSCs are generally considered non-tumorigenic, prolonged in vitro expansion may introduce chromosomal abnormalities or oncogenic mutations, increasing the risk of malignant transformation (Momin et al., 2010; Tarte et al., 2010). Rare cases of ectopic tissue formation have been observed in animal studies, though they are infrequent in clinical trials (Fujiwara et al., 2023). To mitigate these risks, regulatory agencies mandate rigorous preclinical testing, including karyotyping, tumorigenicity assays, and genetic stability evaluations via comparative genomic hybridization or next-generation sequencing (Sato et al., 2019). The route of MSC administration also influences safety; while systemic infusion may cause pulmonary entrapment or embolism, localized delivery can limit systemic exposure and off-target effects. Long-term follow-up in clinical trials remains essential for monitoring delayed adverse events.
Immunogenicity, though less severe in MSCs compared to other cell types, presents nuanced challenges, especially in allogeneic applications (Li et al., 2024b). MSCs were once considered immune-privileged due to low MHC class II and co-stimulatory molecule expression (Kapranov et al., 2016). However, repeated dosing or inflammatory environments can prompt immune recognition, especially through HLA mismatches, leading to T-cell or antibody-mediated responses (Ravindranath et al., 2021). MSCs display context-dependent behavior acting as immunosuppressive under certain conditions (e.g., via PGE2 and TGF-β secretion), yet potentially immunogenic when primed by interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) or Toll-like receptor (TLR) activation (Haddad and Saldanha-Araujo, 2014). Strategies to reduce immunogenicity include HLA matching, genetic editing to knock out MHC expression using CRISPR-Cas9, IFN-γ priming to enhance IDO activity, and encapsulation within biomaterials to evade immune surveillance (Hoerster et al., 2020).
MSC source and culture conditions significantly affect both safety and immune compatibility. UC-MSCs often show higher proliferative rates and lower immunogenicity compared to BM-MSCs (Hori et al., 2024). Serum-free media and xenogen-free protocols reduce variability and contamination risks, while 3D and hypoxic cultures help preserve MSC functionality (Gottipamula et al., 2013). Standardized potency assays measuring factors like IDO or PGE2 support batch consistency, while emerging tools such as single-cell RNA sequencing enable deeper characterization of MSC subpopulations with favorable safety profiles (Xie et al., 2022).
Finally, evolving regulatory frameworks are critical to balancing innovation with patient protection. Phase I trials focus on acute toxicity and biosafety, while later stages include immunogenicity monitoring via anti-MSC antibody detection and T-cell assays. Predictive biomarkers, such as soluble HLA-G or extracellular vesicle signatures, are being explored (Shan et al., 2024). As gene-edited or cytokine-engineered MSCs enter trials, regulatory oversight must adapt to assess new risks like insertional mutagenesis or transgene immunogenicity (Jadlowsky et al., 2024). In safeguarding MSC therapy requires an integrated, multidisciplinary approach encompassing advanced manufacturing, precise immunological assessment, and dynamic regulatory adaptation (Fernandez-Santos et al., 2022). Only through such comprehensive strategies can MSCs realize their full clinical potential while maintaining the highest standards of safety and efficacy.
6 Scalability and manufacturing: barriers to commercialization
The commercialization of MSC therapies faces major hurdles, including biological variability, regulatory complexity, and challenges in scalable, cost-effective manufacturing (Beheshtizadeh et al., 2022; Zhou et al., 2021). Ensuring product consistency, viability during storage, and compliance with quality standards remains difficult. Overcoming these bottlenecks requires innovations in bioprocessing, automation, and logistics, alongside harmonized regulatory frameworks to streamline development and ensure broad clinical accessibility.
6.1 Standardization challenges: donor variability and product heterogeneity
Achieving product consistency is a major barrier to MSC commercialization. Unlike small-molecule drugs, MSCs are living cells whose therapeutic function varies with donor characteristics (e.g., age, sex, health), tissue source (bone marrow, adipose, umbilical cord), and culture conditions (media, oxygen levels) (Mastrolia et al., 2019; Maged et al., 2024). For example, MSCs from older donors exhibit reduced proliferation and diminished secretion of regenerative factors. AD-MSCs produce more VEGF, favoring ischemic indications, while BM-MSCs are often more immunomodulatory (Maged et al., 2024). This biological variability complicates dose standardization and contributes to inconsistent clinical outcomes, as seen in Prochymal’s Phase III failure for GVHD, partly due to variable IDO activity (Kadri et al., 2023). The lack of standardized potency assays further exacerbates the issue. Current ISCT criteria (CD73/CD90/CD105 expression and trilineage differentiation) fail to predict clinical efficacy (Cesnik and Svajger, 2024; Robb et al., 2019). Regulators now recommend mechanism-specific potency tests, e.g., IDO for immunosuppression or VEGF for angiogenesis but integrating these assays into large-scale production remains technically and economically challenging.
6.2 Bioprocessing hurdles: from laboratory to industrial scale
Scaling MSC production from lab-scale flasks to industrial-scale bioreactors poses significant technical and economic hurdles (Haskell et al., 2024). Traditional 2D culture systems like T-flasks are labor-intensive, space-consuming, and yield limited cell numbers (∼108 cells per batch), insufficient for clinical demand (Haskell et al., 2024). Microcarrier-based 3D bioreactors offer a 100-fold increase in output but require precise control of variables like shear stress and oxygenation. Systems like Lonza’s Cocoon® automate expansion in closed environments, yet challenges remain in maintaining consistent cell potency aggregates often develop hypoxia-induced senescence (Tang et al., 2025). Cost of goods (COGs) also constrain scalability. GMP-grade, xenogeneic-free media (e.g., human platelet lysate) costs $500–$1,000 per liter, and large-scale doses (100–200 million cells) for indications like myocardial infarction may require $20,000–$50,000 in media alone. Cryopreservation adds further expense, with cold-chain logistics increasing COGs by ∼30% due to the need for ultra-low temperatures (−150°C) and specialized storage systems. Together, these issues complicate the path to commercial viability.
6.3 Regulatory and quality control complexities
Navigating regulatory pathways for MSC therapies is complex and inconsistent across regions. Agencies like the FDA and EMA classify MSCs as advanced therapy medicinal products (ATMPs), requiring cGMP compliance, thorough safety evaluations, and detailed manufacturing documentation (Detela and Lodge, 2019). However, divergent guidelines complicate approval, for example, the EMA mandates 24-month tumorigenicity studies in immunodeficient mice, whereas the FDA emphasizes in vitro genomic stability assays (Calvisi et al., 2023). Such differences delay global market access, as seen with Alofisel (darvadstrocel), approved in Europe but still under FDA review pending more long-term data.
QC remains a critical challenge. Standard release criteria focus on viability (>70%), sterility, and surface marker identity, but functional assays like immunosuppressive mixed lymphocyte reactions or angiogenesis tests are rarely performed at scale due to cost and timing. This gap risks releasing subpotent products, exemplified by a Phase II COPD trial where MSCs with low hepatocyte growth factor secretion failed to improve outcomes.
6.4 Innovations driving scalable manufacturing
Despite significant challenges, advances in bioprocessing and automation are enabling scalable MSC production. Closed-system bioreactors like the Xpansion® platform facilitate high-density 3D culture, reducing media use by 60% and doubling yields (Song et al., 2024). Synthetic peptide substrates replace traditional coatings, improving reproducibility and reducing batch variability. Emerging lyophilization methods promise to eliminate cold-chain dependence, with early data showing 80% viability post-reconstitution.
Machine learning (ML) is revolutionizing quality control, using AI-driven analysis of omics and secretome data for real-time potency prediction and release testing (Wei et al., 2023). For example, Cellino Biotech’s ML platform cuts production costs by 70%. Concurrently, CRISPR-engineered MSCs with enhanced homing (CXCR4) or anti-inflammatory (IL-10) traits are advancing in trials, potentially lowering dose requirements and costs (Zhou et al., 2021; Hazrati et al., 2022). Overcoming scalability and manufacturing barriers demands collaboration across academia, industry, and regulators to standardize processes, adopt disruptive technologies, and align reimbursement with therapeutic value. Addressing these will enable MSC therapies to transition from niche innovations to accessible mainstream treatments in regenerative medicine.
7 Emerging strategies: engineering and enhancing MSC functionality
MSCs hold great therapeutic promise but face hurdles like poor engraftment, limited survival, and functional variability. To overcome these, researchers are developing advanced strategies including CRISPR gene editing, biomaterial scaffolds, and synthetic biology tools to boost MSC regenerative, immunomodulatory, and homing abilities (Abubakar et al., 2023; Christidi et al., 2018). Innovations such as bioengineered exosomes and tailored genetic modifications are enhancing efficacy and specificity, paving the way for more effective, disease-targeted MSC therapies (Cao et al., 2024).
7.1 Genetic engineering: precision-enhanced MSCs
Genetic engineering is pivotal in enhancing the therapeutic potential of MSCs. Techniques like CRISPR-Cas9 and lentiviral vectors enable precise gene edits to boost survival, targeting, and secretion of therapeutic molecules (Damasceno et al., 2020). For example, MSCs overexpressing CXCR4 demonstrate improved homing to ischemic tissues, with a Phase I trial in critical limb ischemia showing a 40% perfusion increase (Ullah et al., 2019). IL-10-engineered MSCs have reduced synovial inflammation by 70% in rheumatoid arthritis models (Choi et al., 2008; Li et al., 2024a). Advanced approaches using synthetic biology allow programmable behaviors, such as hypoxia-inducible VEGF expression for myocardial repair. Safety mechanisms like suicide genes (e.g., HSV-TK) allow conditional elimination of MSCs, enhancing clinical control (Kim et al., 2011; Shen et al., 2008). These strategies improve efficacy while addressing safety concerns in MSC-based therapies.
7.2 Preconditioning: priming MSCs for enhanced performance
Preconditioning MSCs with biochemical or physical stimuli enhances their therapeutic potential without genetic modification. Hypoxic preconditioning (1%–5% O2) simulates ischemic tissue conditions, increasing survival gene expression (e.g., Bcl-2) and angiogenic factors like VEGF and SDF-1 (Schepici et al., 2022; Zhuo et al., 2024). In a porcine myocardial infarction model, hypoxia-treated MSCs improved cardiac function by 50% over normoxic controls (Chen et al., 2018). Cytokine priming with IFN-γ or TNF-α enhances immunomodulatory effects by upregulating IDO and PD-L1, beneficial in GVHD. 3D spheroid culture restores in vivo-like MSC phenotypes, increasing paracrine activity and ECM production (Sarsenova et al., 2022; Elmi et al., 2025). In stroke models, spheroid-derived MSCs tripled BDNF and GDNF secretion, improving neuronal survival by 60%. Mechanical preconditioning further boosts MSC secretomes, supporting tissue repair in tendon and vascular injuries (Cunningham et al., 2018).
7.3 Biomaterial scaffolds: guiding MSC integration and retention
Biomaterial scaffolds are transforming MSC therapy by enhancing cell retention, survival, and differentiation through structural and biochemical cues (Zhao et al., 2021). Hydrogels made from hyaluronic acid, collagen, or decellularized ECM provide protective niches and controlled release of therapeutic factors (Saldin et al., 2017). In equine osteoarthritis, MSC-loaded thermoresponsive chitosan hydrogels achieved 80% cartilage defect filling in 12 weeks (Spiller et al., 2011; Atwal et al., 2023). Electrospun nanofibers functionalized with RGD peptides or laminin promote MSC adhesion and alignment, aiding nerve and muscle repair (Amores de Sousa et al., 2020). Advanced 3D-printed scaffolds, such as β-TCP, enable anatomically tailored implantation and showed superior calvarial bone healing in rabbits (Guerrero et al., 2024; Turnbull et al., 2018). Smart scaffolds with embedded sensors or drug reservoirs allow real-time monitoring and condition-responsive factor release, improving outcomes in diabetic wound models through glucose-triggered VEGF secretion (Mirani et al., 2023).
7.4 Exosome engineering: harnessing MSC-Derived nanovesicles
MSC-derived exosomes are emerging as promising cell-free therapies, offering regenerative benefits without the risks of cell transplantation (Roszkowski, 2024). However, their natural lack of targeting specificity limits efficacy. To enhance precision, exosomes are engineered with surface ligands like CD47 or RGD and loaded with therapeutic cargo such as siRNA or miRNAs (Kim et al., 2024; Zeng et al., 2023). In glioblastoma, RVG-tagged exosomes delivered miR-124 across the blood-brain barrier, reducing tumor volume by 65% (Galardi et al., 2023) (Aili et al., 2021). Techniques like electroporation improve cargo loading, and clinical trials by companies like Codiak Biosciences are underway.
7.5 Combination therapies: synergizing MSCs with drugs or cells
Combining MSCs with pharmacological agents or complementary cell types enhances therapeutic efficacy (Abu-El-Rub et al., 2022). MSCs with anti-inflammatory drugs like tocilizumab or JAK inhibitors show synergistic effects, reducing autoantibodies by 90% in refractory lupus trials (Scott, 2017). In cancer therapy, MSCs engineered to express TRAIL improve chemotherapy by targeting resistant cancer stem cells (Fakiruddin et al., 2018; Minev et al., 2024). Co-transplantation strategies, such as MSCs with endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) or CAR-T cells, enhance outcomes doubling capillary density in limb ischemia and halving cytokine release syndrome severity in leukemia models (Rossi et al., 2017).
7.6 AI and machine learning: optimizing MSC manufacturing
Artificial intelligence is revolutionizing MSC bioprocessing by optimizing culture conditions, donor matching, and therapeutic predictions (Cerbo et al., 2024). Deep learning models identify biomarkers like miR-335-5p for chondrogenic potential and refine bioreactor settings to boost efficiency. AI platforms, such as DeepCell, enhance quality control with 95% accuracy in detecting senescent cells (Nosrati and Nosrati, 2023). Together with genetic engineering and biomaterial advances, AI is driving the development of precision-engineered MSC therapies (Mahima Choudhury et al., 2025). As these innovations converge, scalable and effective MSC products become increasingly feasible, though robust safety and regulatory frameworks remain essential for clinical translation.
8 Future directions: personalized medicine and advanced delivery systems
The next frontier in MSC therapy lies in integrating personalized medicine with cutting-edge delivery technologies. As the field moves beyond the conventional “one-size-fits-all” paradigm, advances in genomics, biomaterials, and bioengineering are converging to create tailored MSC treatments that align with individual patient profiles and disease-specific microenvironments. These innovations are poised to overcome long-standing challenges, such as poor engraftment, off-target effects, and inconsistent therapeutic outcomes, paving the way for precision regenerative medicine.
Personalized MSC therapies are being revolutionized through biomarker discovery and multi-omics profiling. By leveraging genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, and metabolomics, researchers can map MSC heterogeneity with unprecedented granularity. For example, single-cell RNA sequencing has identified MSC subsets with distinct therapeutic potentials, such as PD-L1+ cells for immunosuppression or CXCR4+ cells for tissue homing. This stratification allows clinicians to match MSC profiles with patient biomarkers. A 2023 study found that rheumatoid arthritis patients with high IL-6 levels responded better to IFN-γ-primed MSCs, offering a biomarker-driven approach to preconditioning. Autologous customization, using tools like CRISPR-Cas9, further allows correction of genetic mutations or enhancement of therapeutic genes. Clinical trials using gene-edited MSCs to express dystrophin in Duchenne muscular dystrophy have shown promise. Similarly, iPSC-derived MSCs provide a scalable and patient-specific source, currently under evaluation for disorders like age-related macular degeneration. Rieger et al. demonstrated that the genetic profile of patients with non-ischemic dilated cardiomyopathy significantly influenced responsiveness to MSC therapy, with variant-negative individuals deriving the most benefit. These findings underscore the value of precision medicine in MSC-based interventions (Rieger et al., 2019). Machine learning tools are being employed to predict patient responses and optimize MSC product selection. DeepCell Therapeutics, for instance, developed an AI model that successfully stratified stroke patients based on imaging and molecular profiles, reducing trial failure rates.
Advanced delivery systems are enhancing MSC retention, targeting, and therapeutic duration. Biomaterial-assisted platforms like hydrogels, decellularized ECM, and adhesion molecule-infused scaffolds are improving engraftment and guiding MSC differentiation. 3D and 4D bioprinting technologies enable the construction of precise, vascularized tissues with functional gradients. In goat models, bio printed cartilage patches restored joint function, while shape-memory scaffolds adapted to body contours in pediatric microtia patients. Furthermore, stimuli-responsive carriers offer targeted and controlled release. Magnetic nanoparticle-labeled MSCs have achieved over 90% targeting accuracy, and optogenetically engineered MSCs can secrete VEGF in response to light, improving diabetic ulcer treatment.
Digital health integration and closed-loop systems represent the next step in adaptive MSC therapy. Smart implants with biosensors can monitor MSC viability and tissue regeneration, transmitting data in real time. In spinal cord injury models, graphene-based neural interfaces tracked recovery and activated stimulatory cues to enhance repair. Closed-loop systems, such as glucose-responsive devices, have been adapted to release cytokine-secreting MSCs in inflammatory environments, maintaining disease remission. Genetic circuits responsive to tumor DNA allow MSCs to deliver anti-cancer agents like TRAIL specifically within tumor sites, minimizing systemic exposure.
While MSC therapies have demonstrated immense preclinical promise, clinical success requires overcoming biological, technical, and regulatory hurdles. The fusion of personalized omics data, sophisticated delivery systems, and real-time monitoring is transforming MSC therapy into a precise, patient-tailored modality. As these innovations mature, the vision of safe, scalable, and effective MSC-based treatments is becoming an attainable reality.
9 Final synthesis
The gap between preclinical promise and clinical reality for MSC therapies is neither unbridgeable nor inevitable. By embracing standardization, personalization, and innovation, the field can transform MSCs from a promising tool into a mainstay of regenerative medicine. The path forward demands humility to learn from past failures and audacity to pioneer technologies that redefine healing. As these cells navigate the complex journey from bench to bedside, their ultimate success will hinge not just on scientific ingenuity, but on our collective commitment to translating hope into tangible, equitable health outcomes.
Author contributions
JP: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Methodology, Software. MeS: Writing – original draft, Data curation, Visualization. MaS: Writing – review and editing, Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abubakar, M., Masood, M. F., Javed, I., Adil, H., Faraz, M. A., Bhat, R. R., et al. (2023). Unlocking the mysteries, bridging the gap, and unveiling the multifaceted potential of stem cell therapy for cardiac tissue regeneration: a narrative review of current literature, ethical challenges, and future perspectives. Cureus 15, e41533. doi:10.7759/cureus.41533
Abu-El-Rub, E., Khasawneh, R. R., and Almahasneh, F. (2022). Prodigious therapeutic effects of combining mesenchymal stem cells with magnetic nanoparticles. World J. Stem Cells 14, 513–526. doi:10.4252/wjsc.v14.i7.513
Aili, Y., Maimaitiming, N., Mahemuti, Y., Qin, H., Wang, Y., and Wang, Z. (2021). The role of exosomal miRNAs in glioma: biological function and clinical application. Front. Oncol. 11, 686369. doi:10.3389/fonc.2021.686369
Alfarano, C., Roubeix, C., Chaaya, R., Ceccaldi, C., Calise, D., Mias, C., et al. (2012). Intraparenchymal injection of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells reduces kidney fibrosis after ischemia-reperfusion in cyclosporine-immunosuppressed rats. Cell. Transpl. 21, 2009–2019. doi:10.3727/096368912x640448
Al-Samerria, S., and Radovick, S. (2021). The role of Insulin-like growth Factor-1 (IGF-1) in the control of neuroendocrine regulation of growth. Cells 10, 2664. doi:10.3390/cells10102664
Amores De Sousa, M. C., Rodrigues, C. A. V., Ferreira, I. A. F., Diogo, M. M., Linhardt, R. J., Cabral, J. M. S., et al. (2020). Functionalization of electrospun nanofibers and fiber alignment enhance neural stem cell proliferation and neuronal differentiation. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 8, 580135. doi:10.3389/fbioe.2020.580135
Ankrum, J. A., Ong, J. F., and Karp, J. M. (2014). Mesenchymal stem cells: immune evasive, not immune privileged. Nat. Biotechnol. 32, 252–260. doi:10.1038/nbt.2816
Araki, S., Imai, S., Ishigaki, H., Mimura, T., Nishizawa, K., Ueba, H., et al. (2015). Improved quality of cartilage repair by bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells for treatment of an osteochondral defect in a cynomolgus macaque model. Acta Orthop. 86, 119–126. doi:10.3109/17453674.2014.958807
Atwal, A., Dale, T. P., Snow, M., Forsyth, N. R., and Davoodi, P. (2023). Injectable hydrogels: an emerging therapeutic strategy for cartilage regeneration. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 321, 103030. doi:10.1016/j.cis.2023.103030
Augello, A., Tasso, R., Negrini, S. M., Cancedda, R., and Pennesi, G. (2007). Cell therapy using allogeneic bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells prevents tissue damage in collagen-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 56, 1175–1186. doi:10.1002/art.22511
Ayala-Cuellar, A. P., Kang, J. H., Jeung, E. B., and Choi, K. C. (2019). Roles of mesenchymal stem cells in tissue regeneration and immunomodulation. Biomol. Ther. Seoul. 27, 25–33. doi:10.4062/biomolther.2017.260
Baglio, S. R., Pegtel, D. M., and Baldini, N. (2012). Mesenchymal stem cell secreted vesicles provide novel opportunities in (stem) cell-free therapy. Front. Physiol. 3, 359. doi:10.3389/fphys.2012.00359
Baglio, S. R., Rooijers, K., Koppers-Lalic, D., Verweij, F. J., Perez Lanzon, M., Zini, N., et al. (2015). Human bone marrow- and adipose-mesenchymal stem cells secrete exosomes enriched in distinctive miRNA and tRNA species. Stem Cell. Res. Ther. 6, 127. doi:10.1186/s13287-015-0116-z
Bagno, L. L., Salerno, A. G., Balkan, W., and Hare, J. M. (2022). Mechanism of action of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs): impact of delivery method. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 22, 449–463. doi:10.1080/14712598.2022.2016695
Bagno, L., Hatzistergos, K. E., Balkan, W., and Hare, J. M. (2018). Mesenchymal stem cell-based therapy for cardiovascular disease: progress and challenges. Mol. Ther. 26, 1610–1623. doi:10.1016/j.ymthe.2018.05.009
Beheshtizadeh, N., Gharibshahian, M., Pazhouhnia, Z., Rostami, M., Zangi, A. R., Maleki, R., et al. (2022). Commercialization and regulation of regenerative medicine products: promises, advances and challenges. Biomed. Pharmacother. 153, 113431. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113431
Broekman, W., Khedoe, P., Schepers, K., Roelofs, H., Stolk, J., and Hiemstra, P. S. (2018). Mesenchymal stromal cells: a novel therapy for the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease? Thorax 73, 565–574. doi:10.1136/thoraxjnl-2017-210672
Burdick, J. A., Mauck, R. L., and Gerecht, S. (2016). To serve and protect: hydrogels to improve stem cell-based therapies. Cell. Stem Cell. 18, 13–15. doi:10.1016/j.stem.2015.12.004
Cai, M., Chen, L., Wang, T., Liang, Y., Zhao, J., Zhang, X., et al. (2023). Hydrogel scaffolds in the treatment of spinal cord injury: a review. Front. Neurosci. 17, 1211066. doi:10.3389/fnins.2023.1211066
Calvisi, D. F., Boulter, L., Vaquero, J., Saborowski, A., Fabris, L., Rodrigues, P. M., et al. (2023). Criteria for preclinical models of cholangiocarcinoma: scientific and medical relevance. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 20, 462–480. doi:10.1038/s41575-022-00739-y
Can, A., and Coskun, H. (2020). The rationale of using mesenchymal stem cells in patients with COVID-19-related acute respiratory distress syndrome: what to expect. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 9, 1287–1302. doi:10.1002/sctm.20-0164
Cao, J., Lv, G., and Wei, F. (2024). Engineering exosomes to reshape the immune microenvironment in breast cancer: molecular insights and therapeutic opportunities. Clin. Transl. Med. 14, e1645. doi:10.1002/ctm2.1645
Cao, Q., Wang, Y., Zheng, D., Sun, Y., Wang, Y., Lee, V. W., et al. (2010). IL-10/TGF-beta-modified macrophages induce regulatory T cells and protect against adriamycin nephrosis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 21, 933–942. doi:10.1681/asn.2009060592
Cao, W., Cao, K., Cao, J., Wang, Y., and Shi, Y. (2015). Mesenchymal stem cells and adaptive immune responses. Immunol. Lett. 168, 147–153. doi:10.1016/j.imlet.2015.06.003
Caplan, H., Olson, S. D., Kumar, A., George, M., Prabhakara, K. S., Wenzel, P., et al. (2019). Mesenchymal stromal cell therapeutic delivery: translational challenges to clinical application. Front. Immunol. 10, 1645. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2019.01645
Cerbo, V. D., Song, H. W., Herbst, L., Hart, S. J., Ladi, R., Jiang, S., et al. (2024). Artificial intelligence, machine learning, and digitalization systems in the cell and gene therapy sector: a guidance document from the ISCT industry committees. Cytotherapy. doi:10.1016/j.jcyt.2025.05.003
Cesnik, A. B., and Svajger, U. (2024). The issue of heterogeneity of MSC-Based advanced therapy medicinal products-a review. Front. Cell. Dev. Biol. 12, 1400347. doi:10.3389/fcell.2024.1400347
Chen, Q. Y., Wen, T., Wu, P., Jia, R., Zhang, R., and Dang, J. (2021). Exosomal proteins and miRNAs as mediators of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Front. Cell. Dev. Biol. 9, 718803. doi:10.3389/fcell.2021.718803
Chen, B., Chen, Z., He, M., Zhang, L., Yang, L., and Wei, L. (2024). Recent advances in the role of mesenchymal stem cells as modulators in autoinflammatory diseases. Front. Immunol. 15, 1525380. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2024.1525380
Chen, L., Qu, J., and Xiang, C. (2019). The multi-functional roles of menstrual blood-derived stem cells in regenerative medicine. Stem Cell. Res. Ther. 10, 1. doi:10.1186/s13287-018-1105-9
Chen, L., Tredget, E. E., Wu, P. Y., and Wu, Y. (2008). Paracrine factors of mesenchymal stem cells recruit macrophages and endothelial lineage cells and enhance wound healing. PLoS One 3, e1886. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0001886
Chen, S., Saeed, A., Liu, Q., Jiang, Q., Xu, H., Xiao, G. G., et al. (2023). Macrophages in immunoregulation and therapeutics. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 8, 207. doi:10.1038/s41392-023-01452-1
Chen, Z., Chen, L., Zeng, C., and Wang, W. E. (2018). Functionally improved mesenchymal stem cells to better treat myocardial infarction. Stem Cells Int. 2018, 1–14. doi:10.1155/2018/7045245
Ching, T., Toh, Y. C., Hashimoto, M., and Zhang, Y. S. (2021). Bridging the academia-to-industry gap: Organ-On-A-Chip platforms for safety and toxicology assessment. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 42, 715–728. doi:10.1016/j.tips.2021.05.007
Chinnadurai, R., Rajan, D., Qayed, M., Arafat, D., Garcia, M., Liu, Y., et al. (2018). Potency analysis of mesenchymal stromal cells using a combinatorial assay matrix approach. Cell. Rep. 22, 2504–2517. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2018.02.013
Choi, J. J., Yoo, S. A., Park, S. J., Kang, Y. J., Kim, W. U., Oh, I. H., et al. (2008). Mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing interleukin-10 attenuate collagen-induced arthritis in mice. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 153, 269–276. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2249.2008.03683.x
Christidi, E., Huang, H. M., and Brunham, L. R. (2018). CRISPR/Cas9-mediated genome editing in human stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes: applications for cardiovascular disease modelling and cardiotoxicity screening. Drug Discov. Today Technol. 28, 13–21. doi:10.1016/j.ddtec.2018.06.002
Christodoulou, I., Goulielmaki, M., Devetzi, M., Panagiotidis, M., Koliakos, G., and Zoumpourlis, V. (2018). Mesenchymal stem cells in preclinical cancer cytotherapy: a systematic review. Stem Cell. Res. Ther. 9, 336. doi:10.1186/s13287-018-1078-8
Chung, E. S., Miller, L., Patel, A. N., Anderson, R. D., Mendelsohn, F. O., Traverse, J., et al. (2015). Changes in ventricular remodelling and clinical status during the year following a single administration of stromal cell-derived factor-1 non-viral gene therapy in chronic ischaemic heart failure patients: the STOP-HF randomized phase II trial. Eur. Heart J. 36, 2228–2238. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehv254
Chuprin, J., Buettner, H., Seedhom, M. O., Greiner, D. L., Keck, J. G., Ishikawa, F., et al. (2023). Humanized mouse models for immuno-oncology research. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 20, 192–206. doi:10.1038/s41571-022-00721-2
Constantinescu, C. S., Farooqi, N., O'Brien, K., and Gran, B. (2011). Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) as a model for multiple sclerosis (MS). Br. J. Pharmacol. 164, 1079–1106. doi:10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01302.x
Cudkowicz, M. E., Lindborg, S. R., Goyal, N. A., Miller, R. G., Burford, M. J., Berry, J. D., et al. (2022). A randomized placebo-controlled phase 3 study of mesenchymal stem cells induced to secrete high levels of neurotrophic factors in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Muscle Nerve 65, 291–302. doi:10.1002/mus.27472
Cunningham, C. J., Redondo-Castro, E., and Allan, S. M. (2018). The therapeutic potential of the mesenchymal stem cell secretome in ischaemic stroke. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 38, 1276–1292. doi:10.1177/0271678x18776802
Damasceno, P. K. F., De Santana, T. A., Santos, G. C., Orge, I. D., Silva, D. N., Albuquerque, J. F., et al. (2020). Genetic engineering as a strategy to improve the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem/stromal cells in regenerative medicine. Front. Cell. Dev. Biol. 8, 737. doi:10.3389/fcell.2020.00737
Da Silva, M. M. A., Rocco, P. R. M., and Cruz, F. F. (2025). Challenges and limitations of mesenchymal stem cell therapy for lung diseases in clinical trials. Expert Opin. Emerg. Drugs 30, 83–86. doi:10.1080/14728214.2025.2489700
Dehnavi, S., Sadeghi, M., Tavakol Afshari, J., and Mohammadi, M. (2023). Interactions of mesenchymal stromal/stem cells and immune cells following MSC-Based therapeutic approaches in rheumatoid arthritis. Cell. Immunol. 393-394, 104771. doi:10.1016/j.cellimm.2023.104771
Delage, E., Cervantes, D. C., Penard, E., Schmitt, C., Syan, S., Disanza, A., et al. (2016). Differential identity of filopodia and tunneling nanotubes revealed by the opposite functions of actin regulatory complexes. Sci. Rep. 6, 39632. doi:10.1038/srep39632
De Palma, S. T., Hermans, E. C., Shamorkina, T. M., Trayford, C., Van Rijt, S., Heck, A. J. R., et al. (2025). Hypoxic preconditioning enhances the potential of mesenchymal stem cells to treat neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury. Stroke 56, 1872–1882. doi:10.1161/strokeaha.124.048964
Detela, G., and Lodge, A. (2019). EU regulatory pathways for ATMPs: Standard, accelerated and adaptive pathways to marketing authorisation. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 13, 205–232. doi:10.1016/j.omtm.2019.01.010
Dilogo, I. H., Aditianingsih, D., Sugiarto, A., Burhan, E., Damayanti, T., Sitompul, P. A., et al. (2021). Umbilical cord mesenchymal stromal cells as critical COVID-19 adjuvant therapy: a randomized controlled trial. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 10, 1279–1287. doi:10.1002/sctm.21-0046
Dimarino, A. M., Caplan, A. I., and Bonfield, T. L. (2013). Mesenchymal stem cells in tissue repair. Front. Immunol. 4, 201. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2013.00201
Dohi, M., Hasegawa, T., Yamamoto, K., and Marshall, B. C. (2000). Hepatocyte growth factor attenuates collagen accumulation in a murine model of pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 162, 2302–2307. doi:10.1164/ajrccm.162.6.9908097
Dominici, M., Le Blanc, K., Mueller, I., Slaper-Cortenbach, I., Marini, F., Krause, D., et al. (2006). Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The international society for cellular therapy position statement. Cytotherapy 8, 315–317. doi:10.1080/14653240600855905
Duffy, M. M., Ritter, T., Ceredig, R., and Griffin, M. D. (2011). Mesenchymal stem cell effects on T-cell effector pathways. Stem Cell. Res. Ther. 2, 34. doi:10.1186/scrt75
Elmi, F., Soltanmohammadi, F., Fayeghi, T., Farajnia, S., and Alizadeh, E. (2025). Preventing MSC aging and enhancing immunomodulation: novel strategies for cell-based therapies. Regen. Ther. 29, 517–539. doi:10.1016/j.reth.2025.04.014
Fakiruddin, K. S., Ghazalli, N., Lim, M. N., Zakaria, Z., and Abdullah, S. (2018). Mesenchymal stem cell expressing TRAIL as targeted therapy against sensitised tumour. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 19, 2188. doi:10.3390/ijms19082188
Faria, J., Calcat, I. C. S., Skovronova, R., Broeksma, B. C., Berends, A. J., Zaal, E. A., et al. (2023). Mesenchymal stromal cells secretome restores bioenergetic and redox homeostasis in human proximal tubule cells after ischemic injury. Stem Cell. Res. Ther. 14, 353. doi:10.1186/s13287-023-03563-6
Feng, M., Li, Y., Han, Q., Bao, X., Yang, M., Zhu, H., et al. (2014). Preclinical safety evaluation of human mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in cerebrum of nonhuman Primates. Int. J. Toxicol. 33, 403–411. doi:10.1177/1091581814545244
Fernandez-Santos, M. E., Garcia-Arranz, M., Andreu, E. J., Garcia-Hernandez, A. M., Lopez-Parra, M., Villaron, E., et al. (2022). Optimization of mesenchymal stromal cell (MSC) manufacturing processes for a better therapeutic outcome. Front. Immunol. 13, 918565. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2022.918565
Filidou, E., Kandilogiannakis, L., Tarapatzi, G., Spathakis, M., Steiropoulos, P., Mikroulis, D., et al. (2022). Anti-inflammatory and anti-fibrotic effect of immortalized mesenchymal-stem-cell-derived conditioned medium on human lung myofibroblasts and epithelial cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 4570. doi:10.3390/ijms23094570
Fontaine, M. J., Shih, H., Schafer, R., and Pittenger, M. F. (2016). Unraveling the mesenchymal stromal cells' paracrine immunomodulatory effects. Transfus. Med. Rev. 30, 37–43. doi:10.1016/j.tmrv.2015.11.004
Fridenshtein, A., Piatetskii, S., and Petrakova, K. V. (1969). Osteogenesis in transplants of bone marrow cells. Arkh Anat. Gistol. Embriol 56, 3–11. doi:10.1242/dev.16.3.381
Friedenstein, A. J., Chailakhjan, R. K., and Lalykina, K. S. (1970). The development of fibroblast colonies in monolayer cultures of guinea-pig bone marrow and spleen cells. Cell. Tissue Kinet. 3, 393–403. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2184.1970.tb00347.x
Fujiwara, C., Miyazaki, S., Katoh, Y., Ito, T., Koyama, A., Takahashi, N., et al. (2023). Ectopic pancreatic acinar cell carcinoma in the thoracic cavity of F344 rat. J. Toxicol. Pathol. 36, 139–143. doi:10.1293/tox.2022-0114
Galderisi, U., Peluso, G., and Di Bernardo, G. (2022). Clinical trials based on mesenchymal stromal cells are exponentially increasing: where are we in recent years? Stem Cell. Rev. Rep. 18, 23–36. doi:10.1007/s12015-021-10231-w
Galipeau, J. (2020). Mesenchymal stromal cells for graft-versus-host disease: a trilogy. Biol. Blood Marrow Transpl. 26, e89–e91. doi:10.1016/j.bbmt.2020.02.023
Garcia-Bernal, D., Garcia-Arranz, M., Yanez, R. M., Hervas-Salcedo, R., Cortes, A., Fernandez-Garcia, M., et al. (2021). The current status of mesenchymal stromal cells: controversies, unresolved issues and some promising solutions to improve their therapeutic efficacy. Front. Cell. Dev. Biol. 9, 650664. doi:10.3389/fcell.2021.650664
Garcia-Olmo, D., Gilaberte, I., Binek, M., Ajl, D. H., Lindner, D., Selvaggi, F., et al. (2022). Follow-up study to evaluate the long-term safety and efficacy of darvadstrocel (mesenchymal stem cell treatment) in patients with perianal fistulizing crohn's disease: ADMIRE-CD phase 3 randomized controlled trial. Dis. Colon Rectum 65, 713–720. doi:10.1097/dcr.0000000000002325
Giacomini, C., Graneli, C., Hicks, R., and Dazzi, F. (2023). The critical role of apoptosis in mesenchymal stromal cell therapeutics and implications in homeostasis and normal tissue repair. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 20, 570–582. doi:10.1038/s41423-023-01018-9
Glennie, S., Soeiro, I., Dyson, P. J., Lam, E. W., and Dazzi, F. (2005). Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells induce division arrest anergy of activated T cells. Blood 105, 2821–2827. doi:10.1182/blood-2004-09-3696
Gong, M., Yu, B., Wang, J., Wang, Y., Liu, M., Paul, C., et al. (2017). Mesenchymal stem cells release exosomes that transfer miRNAs to endothelial cells and promote angiogenesis. Oncotarget 8, 45200–45212. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.16778
Gonzalez-Gonzalez, A., Garcia-Sanchez, D., Dotta, M., Rodriguez-Rey, J. C., and Perez-Campo, F. M. (2020). Mesenchymal stem cells secretome: the cornerstone of cell-free regenerative medicine. World J. Stem Cells 12, 1529–1552. doi:10.4252/wjsc.v12.i12.1529
Gorshkova, I. N., Kiseleva, N. G., Akhmedzhanov, N. M., and Perova, N. V. (1996). Effect of enduracin on the activity of a cholesterol ester transfer protein in blood plasma of people with hypercholesteremia. Biull Eksp. Biol. Med. 121, 185–187. doi:10.1007/bf02446628
Gottipamula, S., Muttigi, M. S., Kolkundkar, U., and Seetharam, R. N. (2013). Serum-free media for the production of human mesenchymal stromal cells: a review. Cell. Prolif. 46, 608–627. doi:10.1111/cpr.12063
Gronthos, S., Franklin, D. M., Leddy, H. A., Robey, P. G., Storms, R. W., and Gimble, J. M. (2001). Surface protein characterization of human adipose tissue-derived stromal cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 189, 54–63. doi:10.1002/jcp.1138
Gschwendtberger, T., Thau-Habermann, N., Von Der Ohe, J., Luo, T., Hass, R., and Petri, S. (2023). Protective effects of EVs/exosomes derived from permanently growing human MSC on primary murine ALS motor neurons. Neurosci. Lett. 816, 137493. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2023.137493
Guan, A., Alibrandi, L., Verma, E., Sareen, N., Guan, Q., Lionetti, V., et al. (2025). Clinical translation of mesenchymal stem cells in ischemic heart failure: challenges and future perspectives. Vasc. Pharmacol. 159, 107491. doi:10.1016/j.vph.2025.107491
Gubert, F., Da Silva, J. S., Vasques, J. F., De Jesus Goncalves, R. G., Martins, R. S., De Sa, M. P. L., et al. (2021). Mesenchymal stem cells therapies on fibrotic heart diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22, 7447. doi:10.3390/ijms22147447
Guerrero, J., Maevskaia, E., Ghayor, C., Bhattacharya, I., and Weber, F. E. (2024). Optimizing filament-based TCP scaffold design for osteoconduction and bone augmentation: insights from in vivo rabbit models. J. Funct. Biomater. 15, 174. doi:10.3390/jfb15070174
Guo, F., Pan, Q., Chen, T., Liao, S., Li, S., Li, A., et al. (2023). hUC-MSC transplantation therapy effects on lupus-prone MRL/Lpr mice at early disease stages. Stem Cell. Res. Ther. 14, 211. doi:10.1186/s13287-023-03432-2
Guo, Y., Yu, Y., Hu, S., Chen, Y., and Shen, Z. (2020). The therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cells for cardiovascular diseases. Cell. Death Dis. 11, 349. doi:10.1038/s41419-020-2542-9
Haddad, R., and Saldanha-Araujo, F. (2014). Mechanisms of T-cell immunosuppression by mesenchymal stromal cells: what do we know so far? Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 1–14. doi:10.1155/2014/216806
Han, Y., Yang, J., Fang, J., Zhou, Y., Candi, E., Wang, J., et al. (2022). The secretion profile of mesenchymal stem cells and potential applications in treating human diseases. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 7, 92. doi:10.1038/s41392-022-00932-0
Hare, J. M., Difede, D. L., Rieger, A. C., Florea, V., Landin, A. M., El-Khorazaty, J., et al. (2017). Randomized comparison of allogeneic versus autologous mesenchymal stem cells for nonischemic dilated cardiomyopathy: POSEIDON-DCM trial. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 69, 526–537. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2016.11.009
Harris, V. K., Stark, J., Vyshkina, T., Blackshear, L., Joo, G., Stefanova, V., et al. (2018). Phase I trial of intrathecal mesenchymal stem cell-derived neural progenitors in progressive multiple sclerosis. EBioMedicine 29, 23–30. doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.02.002
Haskell, A., White, B. P., Rogers, R. E., Goebel, E., Lopez, M. G., Syvyk, A. E., et al. (2024). Scalable manufacture of therapeutic mesenchymal stromal cell products on customizable microcarriers in vertical wheel bioreactors that improve direct visualization, product harvest, and cost. Cytotherapy 26, 372–382. doi:10.1016/j.jcyt.2024.01.009
Hazrati, A., Malekpour, K., Soudi, S., and Hashemi, S. M. (2022). CRISPR/Cas9-engineered mesenchymal stromal/stem cells and their extracellular vesicles: a new approach to overcoming cell therapy limitations. Biomed. Pharmacother. 156, 113943. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113943
Hegde, M., Singh, A. K., Kannan, S., Kolkundkar, U., and Seetharam, R. N. (2024). Therapeutic applications of engineered mesenchymal stromal cells for enhanced angiogenesis in cardiac and cerebral ischemia. Stem Cell. Rev. Rep. 20, 2138–2154. doi:10.1007/s12015-024-10787-3
Heo, J. I., Kim, K. I., Woo, S. K., Kim, J. S., Choi, K. J., Lee, H. J., et al. (2019). Stromal cell-derived factor 1 protects brain vascular endothelial cells from radiation-induced brain damage. Cells 8, 1230. doi:10.3390/cells8101230
Hermann, D. M., Wang, C., Mohamud Yusuf, A., Herz, J., Doeppner, T. R., and Giebel, B. (2025). Extracellular vesicles lay the ground for neuronal plasticity by restoring mitochondrial function, cell metabolism and immune balance. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 271678X251325039, 271678X251325039. doi:10.1177/0271678x251325039
Hetta, H. F., Elsaghir, A., Sijercic, V. C., Ahmed, A. K., Gad, S. A., Zeleke, M. S., et al. (2025). Clinical progress in mesenchymal stem cell therapy: a focus on rheumatic diseases. Immun. Inflamm. Dis. 13, e70189. doi:10.1002/iid3.70189
Heyman, E., Olenic, M., De Vlieghere, E., De Smet, S., Devriendt, B., Thorrez, L., et al. (2025). Donor age and breed determine mesenchymal stromal cell characteristics. Stem Cell. Res. Ther. 16, 99. doi:10.1186/s13287-025-04236-2
Hezam, K., Wang, C., Fu, E., Zhou, M., Liu, Y., Wang, H., et al. (2023). Superior protective effects of PGE2 priming mesenchymal stem cells against LPS-Induced acute lung injury (ALI) through macrophage immunomodulation. Stem Cell. Res. Ther. 14, 48. doi:10.1186/s13287-023-03277-9
Hoang, V. T., Nguyen, Q. T., Phan, T. T. K., Pham, T. H., Dinh, N. T. H., Anh, L. P. H., et al. (2025). Tissue engineering and regenerative medicine: perspectives and challenges. MedComm 6, e70192. doi:10.1002/mco2.70192
Hoerster, K., Uhrberg, M., Wiek, C., Horn, P. A., Hanenberg, H., and Heinrichs, S. (2020). HLA class I knockout converts allogeneic primary NK cells into suitable effectors for Off-the-Shelf immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 11, 586168. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2020.586168
Hori, A., Takahashi, A., Miharu, Y., Yamaguchi, S., Sugita, M., Mukai, T., et al. (2024). Superior migration ability of umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) toward activated lymphocytes in comparison with those of bone marrow and adipose-derived MSCs. Front. Cell. Dev. Biol. 12, 1329218. doi:10.3389/fcell.2024.1329218
Horie, S., Mcnicholas, B., Rezoagli, E., Pham, T., Curley, G., Mcauley, D., et al. (2020). Emerging pharmacological therapies for ARDS: COVID-19 and beyond. Intensive Care Med. 46, 2265–2283. doi:10.1007/s00134-020-06141-z
Hosseini-Asl, S. K., Mehrabani, D., and Karimi-Busheri, F. (2020). Therapeutic effect of mesenchymal stem cells in ulcerative colitis: a review on achievements and challenges. J. Clin. Med. 9, 3922. doi:10.3390/jcm9123922
Huang, J., Li, R., and Wang, C. (2021). The role of mitochondrial quality control in cardiac ischemia/reperfusion injury. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 5543452. doi:10.1155/2021/5543452
Hu, H., Li, H., Li, R., Liu, P., and Liu, H. (2024). Re-establishing immune tolerance in multiple sclerosis: focusing on novel mechanisms of mesenchymal stem cell regulation of Th17/Treg balance. J. Transl. Med. 22, 663. doi:10.1186/s12967-024-05450-x
Hussen, B. M., Taheri, M., Yashooa, R. K., Abdullah, G. H., Abdullah, S. R., Kheder, R. K., et al. (2024). Revolutionizing medicine: recent developments and future prospects in stem-cell therapy. Int. J. Surg. 110, 8002–8024. doi:10.1097/js9.0000000000002109
Ingber, D. E. (2022). Human organs-on-chips for disease modelling, drug development and personalized medicine. Nat. Rev. Genet. 23, 467–491. doi:10.1038/s41576-022-00466-9
Jackson, W. M., Nesti, L. J., and Tuan, R. S. (2012). Mesenchymal stem cell therapy for attenuation of scar formation during wound healing. Stem Cell. Res. Ther. 3, 20. doi:10.1186/scrt111
Jadlowsky, J. K., Chang, J. F., Spencer, D. H., Warrington, J. M., Levine, B. L., June, C. H., et al. (2024). Regulatory considerations for genome-edited T-cell therapies. Cancer Immunol. Res. 12, 1132–1135. doi:10.1158/2326-6066.cir-24-0482
Jeong, C. H., Kim, S. M., Lim, J. Y., Ryu, C. H., Jun, J. A., and Jeun, S. S. (2014). Mesenchymal stem cells expressing brain-derived neurotrophic factor enhance endogenous neurogenesis in an ischemic stroke model. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 1–10. doi:10.1155/2014/129145
Jia, Y., Qiu, S., Xu, J., Kang, Q., and Chai, Y. (2020). Exosomes secreted by young mesenchymal stem cells promote new bone formation during distraction osteogenesis in older rats. Calcif. Tissue Int. 106, 509–517. doi:10.1007/s00223-019-00656-4
Jimenez-Puerta, G. J., Marchal, J. A., Lopez-Ruiz, E., and Galvez-Martin, P. (2020). Role of mesenchymal stromal cells as therapeutic agents: potential mechanisms of action and implications in their clinical use. J. Clin. Med. 9, 445. doi:10.3390/jcm9020445
Jung, W. Y., Kang, J. H., Kim, K. G., Kim, H. S., Jang, B. I., Park, Y. H., et al. (2015). Human adipose-derived stem cells attenuate inflammatory bowel disease in IL-10 knockout mice. Tissue Cell. 47, 86–93. doi:10.1016/j.tice.2014.12.001
Kadar, K., Kiraly, M., Porcsalmy, B., Molnar, B., Racz, G. Z., Blazsek, J., et al. (2009). Differentiation potential of stem cells from human dental origin - promise for tissue engineering. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 60 (Suppl. 7), 167–175.
Kadri, N., Amu, S., Iacobaeus, E., Boberg, E., and Le Blanc, K. (2023). Current perspectives on mesenchymal stromal cell therapy for graft versus host disease. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 20, 613–625. doi:10.1038/s41423-023-01022-z
Kang, S. L., Woo, J. H., Kim, N. H., Kwon, J. Y., and Kim, S. M. (2023). Necessity of strengthening the current clinical regulatory for companion diagnostics: an institutional comparison of the FDA, EMA, and MFDS. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 30, 447–458. doi:10.1016/j.omtm.2023.08.008
Kapranov, N. M., Davydova, Y. O., Petinati, N., Bakshinskayte, M. V., Galtseva, I. V., Drize, N. I., et al. (2016). Immune privileged features of multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells are lost after Co-Cultivation with allogeneic lymphocytes in vitro. Blood 128, 5722. doi:10.1182/blood.v128.22.5722.5722
Kebriaei, P., Hayes, J., Daly, A., Uberti, J., Marks, D. I., Soiffer, R., et al. (2020). A phase 3 randomized study of Remestemcel-L versus placebo added to second-line therapy in patients with steroid-refractory acute graft-versus-host disease. Biol. Blood Marrow Transpl. 26, 835–844. doi:10.1016/j.bbmt.2019.08.029
Kim, H. I., Park, J., Zhu, Y., Wang, X., Han, Y., and Zhang, D. (2024). Recent advances in extracellular vesicles for therapeutic cargo delivery. Exp. Mol. Med. 56, 836–849. doi:10.1038/s12276-024-01201-6
Kim, S. H., Moon, H. H., Kim, H. A., Hwang, K. C., Lee, M., and Choi, D. (2011). Hypoxia-inducible vascular endothelial growth factor-engineered mesenchymal stem cells prevent myocardial ischemic injury. Mol. Ther. 19, 741–750. doi:10.1038/mt.2010.301
Kolliopoulos, V., Tiffany, A., Polanek, M., and Harley, B. A. C. (2023). Donor variability in human mesenchymal stem cell osteogenic response as a function of passage conditions and donor sex. Cold Spring Harbor, NY: bioRxiv. doi:10.1101/2023.11.12.566781
Kot, M., Baj-Krzyworzeka, M., Szatanek, R., Musial-Wysocka, A., Suda-Szczurek, M., and Majka, M. (2019). The importance of HLA assessment in Off-the-Shelf allogeneic mesenchymal stem cells based-therapies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20, 5680. doi:10.3390/ijms20225680
Kurtzberg, J., Abdel-Azim, H., Carpenter, P., Chaudhury, S., Horn, B., Mahadeo, K., et al. (2020). A phase 3, single-arm, prospective study of Remestemcel-L, Ex Vivo culture-expanded adult human mesenchymal stromal cells for the treatment of pediatric patients who failed to respond to steroid treatment for acute graft-versus-host disease. Biol. Blood Marrow Transpl. 26, 845–854. doi:10.1016/j.bbmt.2020.01.018
Kwiecinski, M., Noetel, A., Elfimova, N., Trebicka, J., Schievenbusch, S., Strack, I., et al. (2011). Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) inhibits collagen I and IV synthesis in hepatic stellate cells by miRNA-29 induction. PLoS One 6, e24568. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0024568
Las Heras, K., Royo, F., Garcia-Vallicrosa, C., Igartua, M., Santos-Vizcaino, E., Falcon-Perez, J. M., et al. (2022). Extracellular vesicles from hair follicle-derived mesenchymal stromal cells: isolation, characterization and therapeutic potential for chronic wound healing. Stem Cell. Res. Ther. 13, 147. doi:10.1186/s13287-022-02824-0
Lawson, W. E., Oury, T. D., Sisson, T. H., Raghavendran, K., and Hogaboam, C. M. (2013). Animal models of fibrotic lung disease. Am. J. Respir. Cell. Mol. Biol. 49, 167–179. doi:10.1165/rcmb.2013-0094tr
Lee, H. K., Lim, S. H., Chung, I. S., Park, Y., Park, M. J., Kim, J. Y., et al. (2014). Preclinical efficacy and mechanisms of mesenchymal stem cells in animal models of autoimmune diseases. Immune Netw. 14, 81–88. doi:10.4110/in.2014.14.2.81
Lee, H. Y., and Hong, I. S. (2017). Double-edged sword of mesenchymal stem cells: cancer-Promoting versus therapeutic potential. Cancer Sci. 108, 1939–1946. doi:10.1111/cas.13334
Lee, S. E., Kim, I. H., Kang, Y. C., Kim, Y., Yu, S. H., Yeo, J. S., et al. (2024). Mitochondrial transplantation attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome. BMC Pulm. Med. 24, 477. doi:10.1186/s12890-024-03304-2
Lesnefsky, E. J., Chen, Q., Tandler, B., and Hoppel, C. L. (2017). Mitochondrial dysfunction and myocardial ischemia-reperfusion: implications for novel therapies. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 57, 535–565. doi:10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-010715-103335
Levy, O., Kuai, R., Siren, E. M. J., Bhere, D., Milton, Y., Nissar, N., et al. (2020). Shattering barriers toward clinically meaningful MSC therapies. Sci. Adv. 6, eaba6884. doi:10.1126/sciadv.aba6884
Li, Y. L., Chen, E. G., and Ren, B. B. (2025). Umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stromal cells: promising therapy for heart failure. World J. Cardiol. 17, 101153. doi:10.4330/wjc.v17.i1.101153
Li, C., Cheung, M. K. H., Han, S., Zhang, Z., Chen, L., Chen, J., et al. (2019). Mesenchymal stem cells and their mitochondrial transfer: a double-edged sword. Biosci. Rep. 39. doi:10.1042/bsr20182417
Li, C., Sun, Y., Xu, W., Chang, F., Wang, Y., and Ding, J. (2024a). Mesenchymal stem cells-involved strategies for rheumatoid arthritis therapy. Adv. Sci. (Weinh) 11, e2305116. doi:10.1002/advs.202305116
Liu, X., Fang, Q., and Kim, H. (2016). Preclinical studies of mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) administration in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD): a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One 11, e0157099. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0157099
Li, W., Shi, L., Hu, B., Hong, Y., Zhang, H., Li, X., et al. (2021). Mesenchymal stem cell-based therapy for stroke: current understanding and challenges. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 15, 628940. doi:10.3389/fncel.2021.628940
Li, Y., Jin, M., Guo, D., Shen, S., Lu, K., Pan, R., et al. (2024b). Unveiling the immunogenicity of allogeneic mesenchymal stromal cells: challenges and strategies for enhanced therapeutic efficacy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 180, 117537. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2024.117537
Lo, B., and Parham, L. (2009). Ethical issues in stem cell research. Endocr. Rev. 30, 204–213. doi:10.1210/er.2008-0031
Lopez-Santalla, M., Bueren, J. A., and Garin, M. I. (2021). Mesenchymal stem/stromal cell-based therapy for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: an update on preclinical studies. EBioMedicine 69, 103427. doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2021.103427
Lopez-Santalla, M., Fernandez-Perez, R., and Garin, M. I. (2020). Mesenchymal stem/stromal cells for rheumatoid arthritis treatment: an update on clinical applications. Cells 9, 1852. doi:10.3390/cells9081852
Losordo, D. W., Henry, T. D., Davidson, C., Sup Lee, J., Costa, M. A., Bass, T., et al. (2011). Intramyocardial, autologous CD34+ cell therapy for refractory angina. Circ. Res. 109, 428–436. doi:10.1161/circresaha.111.245993
Losordo, D. W., Kibbe, M. R., Mendelsohn, F., Marston, W., Driver, V. R., Sharafuddin, M., et al. (2012). A randomized, controlled pilot study of autologous CD34+ cell therapy for critical limb ischemia. Circ. Cardiovasc Interv. 5, 821–830. doi:10.1161/circinterventions.112.968321
Luchetti, F., Carloni, S., Nasoni, M. G., Reiter, R. J., and Balduini, W. (2022). Tunneling nanotubes and mesenchymal stem cells: new insights into the role of melatonin in neuronal recovery. J. Pineal Res. 73, e12800. doi:10.1111/jpi.12800
Lu, D., Jiao, X., Jiang, W., Yang, L., Gong, Q., Wang, X., et al. (2023). Mesenchymal stem cells influence monocyte/macrophage phenotype: regulatory mode and potential clinical applications. Biomed. Pharmacother. 165, 115042. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115042
Lu, P., Cao, Y., Wang, M., Zheng, P., Hou, J., Zhu, C., et al. (2016). Mature dendritic cells cause Th17/Treg imbalance by secreting TGF-beta1 and IL-6 in the pathogenesis of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Cent. Eur. J. Immunol. 41, 143–152. doi:10.5114/ceji.2016.60987
Lu, W., and Allickson, J. (2024). Mesenchymal stromal cell therapy: progress to date and future outlook. Mol. Ther. 33, 2679–2688. doi:10.1016/j.ymthe.2025.02.003
Machado Cde, V., Telles, P. D., and Nascimento, I. L. (2013). Immunological characteristics of mesenchymal stem cells. Rev. Bras. Hematol. Hemoter. 35, 62–67. doi:10.5581/1516-8484.20130017
Macrae, I. M. (2011). Preclinical stroke research--advantages and disadvantages of the Most common rodent models of focal ischaemia. Br. J. Pharmacol. 164, 1062–1078. doi:10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01398.x
Maged, G., Abdelsamed, M. A., Wang, H., and Lotfy, A. (2024). The potency of mesenchymal stem/stromal cells: does donor sex matter? Stem Cell. Res. Ther. 15, 112. doi:10.1186/s13287-024-03722-3
Mahima Choudhury, A. J. D., Candland, DANIEL R., Deans, TARA L., and Deans, T. L. (2025). Advancing cell therapies with artificial intelligence and synthetic biology. Curr. Opin. Biomed. Eng. 34, 100580. doi:10.1016/j.cobme.2025.100580
Malhotra, P., Shukla, M., Meena, P., Kakkar, A., Khatri, N., Nagar, R. K., et al. (2022). Mesenchymal stem cells are prospective novel off-the-shelf wound management tools. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 12, 79–104. doi:10.1007/s13346-021-00925-6
Mancuso, P., Raman, S., Glynn, A., Barry, F., and Murphy, J. M. (2019). Mesenchymal stem cell therapy for osteoarthritis: the critical role of the cell secretome. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 7, 9. doi:10.3389/fbioe.2019.00009
Masterson, C. H., Tabuchi, A., Hogan, G., Fitzpatrick, G., Kerrigan, S. W., Jerkic, M., et al. (2021). Intra-vital imaging of mesenchymal stromal cell kinetics in the pulmonary vasculature during infection. Sci. Rep. 11, 5265. doi:10.1038/s41598-021-83894-7
Mastrolia, I., Foppiani, E. M., Murgia, A., Candini, O., Samarelli, A. V., Grisendi, G., et al. (2019). Challenges in clinical development of mesenchymal stromal/stem cells: concise review. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 8, 1135–1148. doi:10.1002/sctm.19-0044
Minev, T., Balbuena, S., Gill, J. M., Marincola, F. M., Kesari, S., and Lin, F. (2024). Mesenchymal stem cells - the secret agents of cancer immunotherapy: promises, challenges, and surprising twists. Oncotarget 15, 793–805. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.28672
Mirani, B., Hadisi, Z., Pagan, E., Dabiri, S. M. H., Van Rijt, A., Almutairi, L., et al. (2023). Smart dual-sensor wound dressing for monitoring cutaneous wounds. Adv. Healthc. Mater 12, e2203233. doi:10.1002/adhm.202203233
Molendijk, I., Bonsing, B. A., Roelofs, H., Peeters, K. C., Wasser, M. N., Dijkstra, G., et al. (2015). Allogeneic bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells promote healing of refractory perianal fistulas in patients with crohn's disease. Gastroenterology 149, 918–927.e6. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2015.06.014
Momin, E. N., Vela, G., Zaidi, H. A., and Quinones-Hinojosa, A. (2010). The oncogenic potential of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of cancer: directions for future research. Curr. Immunol. Rev. 6, 137–148. doi:10.2174/157339510791111718
Morito, T., Muneta, T., Hara, K., Ju, Y. J., Mochizuki, T., Makino, H., et al. (2008). Synovial fluid-derived mesenchymal stem cells increase after intra-articular ligament injury in humans. Rheumatol. Oxf. 47, 1137–1143. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/ken114
Murray, P. J., Allen, J. E., Biswas, S. K., Fisher, E. A., Gilroy, D. W., Goerdt, S., et al. (2014). Macrophage activation and polarization: nomenclature and experimental guidelines. Immunity 41, 14–20. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2014.06.008
Natsumeda, M., Florea, V., Rieger, A. C., Tompkins, B. A., Banerjee, M. N., Golpanian, S., et al. (2017). A combination of allogeneic stem cells promotes cardiac regeneration. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 70, 2504–2515. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2017.09.036
Nazarie Ignat, S. R., Gharbia, S., Hermenean, A., Dinescu, S., and Costache, M. (2021). Regenerative potential of mesenchymal stem cells' (MSCs) secretome for liver fibrosis therapies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22, 13292. doi:10.3390/ijms222413292
Neri, S. (2019). Genetic stability of mesenchymal stromal cells for regenerative medicine applications: a fundamental biosafety aspect. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20, 2406. doi:10.3390/ijms20102406
Nosrati, H., and Nosrati, M. (2023). Artificial intelligence in regenerative medicine: applications and implications. Biomimetics (Basel) 8, 442. doi:10.3390/biomimetics8050442
Osier, N. D., Pham, L., Savarese, A., Sayles, K., and Alexander, S. A. (2016). Animal models in genomic research: techniques, applications, and roles for nurses. Appl. Nurs. Res. 32, 247–256. doi:10.1016/j.apnr.2016.07.016
Panes, J., Garcia-Olmo, D., Van Assche, G., Colombel, J. F., Reinisch, W., Baumgart, D. C., et al. (2018). Long-term efficacy and safety of stem cell therapy (Cx601) for complex perianal fistulas in patients with crohn's disease. Gastroenterology 154, 1334–1342 e4. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2017.12.020
Papadopoulou, A., Yiangou, M., Athanasiou, E., Zogas, N., Kaloyannidis, P., Batsis, I., et al. (2012). Mesenchymal stem cells are conditionally therapeutic in preclinical models of rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 71, 1733–1740. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2011-200985
Parekkadan, B., and Milwid, J. M. (2010). Mesenchymal stem cells as therapeutics. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 12, 87–117. doi:10.1146/annurev-bioeng-070909-105309
Park, C. Y., Choi, S. C., Kim, J. H., Choi, J. H., Joo, H. J., Hong, S. J., et al. (2016). Cardiac stem cell secretome protects cardiomyocytes from hypoxic injury partly via monocyte chemotactic Protein-1-Dependent mechanism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 17, 800. doi:10.3390/ijms17060800
Patel, D. M., Shah, J., and Srivastava, A. S. (2013). Therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cells in regenerative medicine. Stem Cells Int. 2013, 1–15. doi:10.1155/2013/496218
Patel, J. C., Gupta, A., Kumar, P., Waidha, K. M., Deep, A., Kumar, A., et al. (2023). Cardiovascular diseases display etiological and seasonal trend in human population: evidence from seasonal cardiovascular comorbid diseases (SCCD) index. Am. J. Hum. Biol. 35, e23867. doi:10.1002/ajhb.23867
Patel, J. C., Singh, A., Tulswani, R., Sharma, Y. K., Khurana, P., and Ragumani, S. (2021). Identification of VEGFA-Centric temporal hypoxia-responsive dynamic cardiopulmonary network biomarkers. Life Sci. 281, 119718. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119718
Pelizzo, G., Avanzini, M. A., Icaro Cornaglia, A., Osti, M., Romano, P., Avolio, L., et al. (2015). Mesenchymal stromal cells for cutaneous wound healing in a rabbit model: pre-clinical study applicable in the pediatric surgical setting. J. Transl. Med. 13, 219. doi:10.1186/s12967-015-0580-3
Piccini, J. P., Al-Khatib, S. M., Hellkamp, A. S., Anstrom, K. J., Poole, J. E., Mark, D. B., et al. (2011). Mortality benefits from implantable cardioverter-defibrillator therapy are not restricted to patients with remote myocardial infarction: an analysis from the sudden cardiac death in heart failure trial (SCD-HeFT). Heart rhythm. 8, 393–400. doi:10.1016/j.hrthm.2010.11.033
Poomani, M. S., Mariappan, I., Perumal, R., Regurajan, R., Muthan, K., and Subramanian, V. (2022). Mesenchymal stem cell (MSCs) therapy for ischemic heart disease: a promising frontier. Glob. Heart 17, 19. doi:10.5334/gh.1098
Potapova, I. A., Gaudette, G. R., Brink, P. R., Robinson, R. B., Rosen, M. R., Cohen, I. S., et al. (2007). Mesenchymal stem cells support migration, extracellular matrix invasion, proliferation, and survival of endothelial cells in vitro. Stem Cells 25, 1761–1768. doi:10.1634/stemcells.2007-0022
Ragel, E. J., Harris, L. K., and Campbell, R. A. (2023). Acute respiratory distress syndrome: potential of therapeutic interventions effective in treating progression from COVID-19 to treat progression from other illnesses-a systematic review. BMJ Open Respir. Res. 10, e001525. doi:10.1136/bmjresp-2022-001525
Ranganath, S. H., Levy, O., Inamdar, M. S., and Karp, J. M. (2012). Harnessing the mesenchymal stem cell secretome for the treatment of cardiovascular disease. Cell. Stem Cell. 10, 244–258. doi:10.1016/j.stem.2012.02.005
Ravindranath, M. H., El Hilali, F., and Filippone, E. J. (2021). The impact of inflammation on the immune responses to transplantation: tolerance or rejection? Front. Immunol. 12, 667834. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.667834
Rheault-Henry, M., White, I., Grover, D., and Atoui, R. (2021). Stem cell therapy for heart failure: medical breakthrough, or dead end? World J. Stem Cells 13, 236–259. doi:10.4252/wjsc.v13.i4.236
Rieger, A. C., Myerburg, R. J., Florea, V., Tompkins, B. A., Natsumeda, M., Premer, C., et al. (2019). Genetic determinants of responsiveness to mesenchymal stem cell injections in non-ischemic dilated cardiomyopathy. EBioMedicine 48, 377–385. doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.09.043
Robb, K. P., Fitzgerald, J. C., Barry, F., and Viswanathan, S. (2019). Mesenchymal stromal cell therapy: progress in manufacturing and assessments of potency. Cytotherapy 21, 289–306. doi:10.1016/j.jcyt.2018.10.014
Rogers, R. E., Haskell, A., White, B. P., Dalal, S., Lopez, M., Tahan, D., et al. (2021). A scalable system for generation of mesenchymal stem cells derived from induced pluripotent cells employing bioreactors and degradable microcarriers. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 10, 1650–1665. doi:10.1002/sctm.21-0151
Rossi, E., Smadja, D., Goyard, C., Cras, A., Dizier, B., Bacha, N., et al. (2017). Co-injection of mesenchymal stem cells with endothelial progenitor cells accelerates muscle recovery in hind limb ischemia through an endoglin-dependent mechanism. Thromb. Haemost. 117, 1908–1918. doi:10.1160/th17-01-0007
Roszkowski, S. (2024). Therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes for regenerative medicine applications. Clin. Exp. Med. 24, 46. doi:10.1007/s10238-023-01282-z
Saadh, M. J., Mikhailova, M. V., Rasoolzadegan, S., Falaki, M., Akhavanfar, R., Gonzales, J. L. A., et al. (2023). Therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem/stromal cells (MSCs)-based cell therapy for inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) therapy. Eur. J. Med. Res. 28, 47. doi:10.1186/s40001-023-01008-7
Saadh, M. J., Mikhailova, M. V., Rasoolzadegan, S., Falaki, M., Akhavanfar, R., Gonzales, J. L. A., et al. (2024). Editorial expression of concern: therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem/stromal cells (MSCs)-based cell therapy for inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) therapy. Eur. J. Med. Res. 29, 549. doi:10.1186/s40001-024-02140-8
Saldin, L. T., Cramer, M. C., Velankar, S. S., White, L. J., and Badylak, S. F. (2017). Extracellular matrix hydrogels from decellularized tissues: structure and function. Acta Biomater. 49, 1–15. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2016.11.068
Sanchez-Diaz, M., Quinones-Vico, M. I., Sanabria De La Torre, R., Montero-Vilchez, T., Sierra-Sanchez, A., Molina-Leyva, A., et al. (2021). Biodistribution of mesenchymal stromal cells after administration in animal models and humans: a systematic review. J. Clin. Med. 10, 2925. doi:10.3390/jcm10132925
Sarsenova, M., Kim, Y., Raziyeva, K., Kazybay, B., Ogay, V., and Saparov, A. (2022). Recent advances to enhance the immunomodulatory potential of mesenchymal stem cells. Front. Immunol. 13, 1010399. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2022.1010399
Sato, Y., Bando, H., Di Piazza, M., Gowing, G., Herberts, C., Jackman, S., et al. (2019). Tumorigenicity assessment of cell therapy products: the need for global consensus and points to consider. Cytotherapy 21, 1095–1111. doi:10.1016/j.jcyt.2019.10.001
Schafer, R., Spohn, G., and Baer, P. C. (2016). Mesenchymal stem/stromal cells in regenerative medicine: can preconditioning strategies improve therapeutic efficacy? Transfus. Med. Hemother 43, 256–267. doi:10.1159/000447458
Schepici, G., Gugliandolo, A., and Mazzon, E. (2022). Mesenchymal stromal cells preconditioning: a new strategy to improve neuroprotective properties. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 2088. doi:10.3390/ijms23042088
Scott, L. J. (2017). Tocilizumab: a review in rheumatoid arthritis. Drugs 77, 1865–1879. doi:10.1007/s40265-017-0829-7
Selmani, Z., Naji, A., Zidi, I., Favier, B., Gaiffe, E., Obert, L., et al. (2008). Human leukocyte antigen-G5 secretion by human mesenchymal stem cells is required to suppress T lymphocyte and natural killer function and to induce CD4+CD25highFOXP3+ regulatory T cells. Stem Cells 26, 212–222. doi:10.1634/stemcells.2007-0554
Sensebe, L., Krampera, M., Schrezenmeier, H., Bourin, P., and Giordano, R. (2010). Mesenchymal stem cells for clinical application. Vox Sang. 98, 93–107. doi:10.1111/j.1423-0410.2009.01227.x
Shan, Y., Zhang, M., Tao, E., Wang, J., Wei, N., Lu, Y., et al. (2024). Pharmacokinetic characteristics of mesenchymal stem cells in translational challenges. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 9, 242. doi:10.1038/s41392-024-01936-8
Sha, S., Shen, X., Cao, Y., and Qu, L. (2021). Mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles ameliorate alzheimer's disease in rat models via the microRNA-29c-3p/BACE1 axis and the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Aging (Albany NY) 13, 15285–15306. doi:10.18632/aging.203088
Shefner, J. M., and Cudkowicz, M. E. (2024). Failures to replicate: what recent negative phase 3 trials have taught us about amyotrophic lateral sclerosis clinical research. Ann. Neurol. 96, 211–215. doi:10.1002/ana.26999
Shen, F., Fan, Y., Su, H., Zhu, Y., Chen, Y., Liu, W., et al. (2008). Adeno-associated viral vector-mediated hypoxia-regulated VEGF gene transfer promotes angiogenesis following focal cerebral ischemia in mice. Gene Ther. 15, 30–39. doi:10.1038/sj.gt.3303048
Shin, J. Y., and Lee, P. H. (2020). Mesenchymal stem cells modulate misfolded alpha-synuclein in parkinsonian disorders: a multitarget disease-modifying strategy. Stem Cell. Res. 47, 101908. doi:10.1016/j.scr.2020.101908
Shi, X., Chen, Q., and Wang, F. (2019). Mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of ulcerative colitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of experimental and clinical studies. Stem Cell. Res. Ther. 10, 266. doi:10.1186/s13287-019-1336-4
Shukla, M. N., Rose, J. L., Ray, R., Lathrop, K. L., Ray, A., and Ray, P. (2009). Hepatocyte growth factor inhibits epithelial to myofibroblast transition in lung cells via Smad7. Am. J. Respir. Cell. Mol. Biol. 40, 643–653. doi:10.1165/rcmb.2008-0217oc
Simovic Markovic, B., Nikolic, A., Gazdic, M., Nurkovic, J., Djordjevic, I., Arsenijevic, N., et al. (2016). Pharmacological inhibition of Gal-3 in mesenchymal stem cells enhances their capacity to promote alternative activation of macrophages in dextran sulphate sodium-induced colitis. Stem Cells Int. 2016, 2640746. doi:10.1155/2016/2640746
Sioud, M., Mobergslien, A., Boudabous, A., and Floisand, Y. (2010). Evidence for the involvement of galectin-3 in mesenchymal stem cell suppression of allogeneic T-cell proliferation. Scand. J. Immunol. 71, 267–274. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3083.2010.02378.x
Song, H. W., Prochazkova, M., Shao, L., Traynor, R., Underwood, S., Black, M., et al. (2024). CAR-T cell expansion platforms yield distinct T cell differentiation states. Cytotherapy 26, 757–768. doi:10.1016/j.jcyt.2024.03.003
Song, N., Scholtemeijer, M., and Shah, K. (2020). Mesenchymal stem cell immunomodulation: mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 41, 653–664. doi:10.1016/j.tips.2020.06.009
Spaggiari, G. M., Abdelrazik, H., Becchetti, F., and Moretta, L. (2009). MSCs inhibit monocyte-derived DC maturation and function by selectively interfering with the generation of immature DCs: central role of MSC-Derived prostaglandin E2. Blood 113, 6576–6583. doi:10.1182/blood-2009-02-203943
Spiller, K. L., Maher, S. A., and Lowman, A. M. (2011). Hydrogels for the repair of articular cartilage defects. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 17, 281–299. doi:10.1089/ten.teb.2011.0077
Straley, K. S., Foo, C. W., and Heilshorn, S. C. (2010). Biomaterial design strategies for the treatment of spinal cord injuries. J. Neurotrauma 27, 1–19. doi:10.1089/neu.2009.0948
Su, Y., Guo, H., and Liu, Q. (2021). Effects of mesenchymal stromal cell-derived extracellular vesicles in acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS): current understanding and future perspectives. J. Leukoc. Biol. 110, 27–38. doi:10.1002/jlb.3mr0321-545rr
Tang, B., Chen, Y., Zhuang, Z., Zhang, Y., and Yan, X. (2025). 3D recombinant collagen microcarriers for large-scale msc manufacturing in single-use systems. Cytotherapy 27, S77–S78. doi:10.1016/j.jcyt.2025.03.146
Tarte, K., Gaillard, J., Lataillade, J. J., Fouillard, L., Becker, M., Mossafa, H., et al. (2010). Clinical-grade production of human mesenchymal stromal cells: occurrence of aneuploidy without transformation. Blood 115, 1549–1553. doi:10.1182/blood-2009-05-219907
Taylor, B. P., Rebok, G. W., and Marsiske, M. (2022). Good clinical practice improves rigor and transparency: lessons from the ACTIVE trial. Psychol. Aging 37, 43–50. doi:10.1037/pag0000653
Terraza-Aguirre, C., Campos-Mora, M., Elizondo-Vega, R., Contreras-Lopez, R. A., Luz-Crawford, P., Jorgensen, C., et al. (2020). Mechanisms behind the immunoregulatory dialogue between mesenchymal stem cells and Th17 cells. Cells 9, 1660. doi:10.3390/cells9071660
Tompkins, B. A., Rieger, A. C., Florea, V., Banerjee, M. N., and Hare, J. M. (2017). New insights into cell-based therapy for heart failure from the CHART-1 study. Eur. J. Heart Fail 19, 1530–1533. doi:10.1002/ejhf.955
Tsuji, K., Nakanoh, H., Fukushima, K., Kitamura, S., and Wada, J. (2023). MicroRNAs as biomarkers and therapeutic targets for acute kidney injury. Diagn. (Basel) 13, 2893. doi:10.3390/diagnostics13182893
Tunstead, C., Volkova, E., Dunbar, H., Hawthorne, I. J., Bell, A., Crowe, L., et al. (2024). The ARDS microenvironment enhances MSC-Induced repair via VEGF in experimental acute lung inflammation. Mol. Ther. 32, 3422–3432. doi:10.1016/j.ymthe.2024.08.003
Turnbull, G., Clarke, J., Picard, F., Riches, P., Jia, L., Han, F., et al. (2018). 3D bioactive composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Bioact. Mater 3, 278–314. doi:10.1016/j.bioactmat.2017.10.001
Ullah, M., Liu, D. D., and Thakor, A. S. (2019). Mesenchymal stromal cell homing: mechanisms and strategies for improvement. iScience 15, 421–438. doi:10.1016/j.isci.2019.05.004
Ulpiano, C., Da Silva, C. L., and Monteiro, G. A. (2023). Bioengineered mesenchymal-stromal-cell-derived extracellular vesicles as an improved drug delivery system: methods and applications. Biomedicines 11, 1231. doi:10.3390/biomedicines11041231
Van Velthoven, C. T., Dzietko, M., Wendland, M. F., Derugin, N., Faustino, J., Heijnen, C. J., et al. (2017). Mesenchymal stem cells attenuate MRI-Identifiable injury, protect white matter, and improve long-term functional outcomes after neonatal focal stroke in rats. J. Neurosci. Res. 95, 1225–1236. doi:10.1002/jnr.23954
Velarde, F., Ezquerra, S., Delbruyere, X., Caicedo, A., Hidalgo, Y., and Khoury, M. (2022). Mesenchymal stem cell-mediated transfer of mitochondria: mechanisms and functional impact. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 79, 177. doi:10.1007/s00018-022-04207-3
Wang, B., Liu, X. M., Liu, Z. N., Wang, Y., Han, X., Lian, A. B., et al. (2020). Human hair follicle-derived mesenchymal stem cells: isolation, expansion, and differentiation. World J. Stem Cells 12, 462–470. doi:10.4252/wjsc.v12.i6.462
Wang, J., Meng, S., Chen, Y., Wang, H., Hu, W., Liu, S., et al. (2025). MSC-Mediated mitochondrial transfer promotes metabolic reprograming in endothelial cells and vascular regeneration in ARDS. Redox Rep. 30, 2474897. doi:10.1080/13510002.2025.2474897
Wang, M., Wu, Y., Li, G., Lin, Q., Zhang, W., Liu, H., et al. (2024). Articular cartilage repair biomaterials: strategies and applications. Mater Today Bio 24, 100948. doi:10.1016/j.mtbio.2024.100948
Wei, J. J., Tang, L., Chen, L. L., Xie, Z. H., Ren, Y., Qi, H. G., et al. (2021). Mesenchymal stem cells attenuates TGF-β1-Induced EMT by increasing HGF expression in HK-2 cells. Iran. J. Public Health 50, 908–918. doi:10.18502/ijph.v50i5.6108
Wei, L., Niraula, D., Gates, E. D. H., Fu, J., Luo, Y., Nyflot, M. J., et al. (2023). Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) in precision oncology: a review on enhancing discoverability through multiomics integration. Br. J. Radiol. 96, 20230211. doi:10.1259/bjr.20230211
Williams, A. R., Suncion, V. Y., Mccall, F., Guerra, D., Mather, J., Zambrano, J. P., et al. (2013). Durable scar size reduction due to allogeneic mesenchymal stem cell therapy regulates whole-chamber remodeling. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2, e000140. doi:10.1161/jaha.113.000140
Xie, Z., Yu, W., Ye, G., Li, J., Zheng, G., Liu, W., et al. (2022). Single-cell RNA sequencing analysis of human bone-marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells and functional subpopulation identification. Exp. Mol. Med. 54, 483–492. doi:10.1038/s12276-022-00749-5
Xu, H., Chen, X., Luo, S., Jiang, J., Pan, X., He, Y., et al. (2025). Cardiomyocyte-specific Piezo1 deficiency mitigates ischemia-reperfusion injury by preserving mitochondrial homeostasis. Redox Biol. 79, 103471. doi:10.1016/j.redox.2024.103471
Xun, C., Deng, H., Zhao, J., Ge, L., and Hu, Z. (2022). Mesenchymal stromal cell extracellular vesicles for multiple sclerosis in preclinical rodent models: a meta-analysis. Front. Immunol. 13, 972247. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2022.972247
Yang, J., Zhang, X., Chen, X., Wang, L., and Yang, G. (2017). Exosome mediated delivery of miR-124 promotes neurogenesis after ischemia. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 7, 278–287. doi:10.1016/j.omtn.2017.04.010
Yuan, D., Bao, Y., and El-Hashash, A. (2024). Mesenchymal stromal cell-based therapy in lung diseases; from research to clinic. Am. J. Stem Cells 13, 37–58. doi:10.62347/jawm2040
Zaripova, L. N., Midgley, A., Christmas, S. E., Beresford, M. W., Pain, C., Baildam, E. M., et al. (2023). Mesenchymal stem cells in the pathogenesis and therapy of autoimmune and autoinflammatory diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24, 16040. doi:10.3390/ijms242216040
Zeng, H., Guo, S., Ren, X., Wu, Z., Liu, S., and Yao, X. (2023). Current strategies for exosome cargo loading and targeting delivery. Cells 12, 1416. doi:10.3390/cells12101416
Zhang, X., Wei, X., Deng, Y., Yuan, X., Shi, J., Huang, W., et al. (2022). Mesenchymal stromal cells alleviate acute respiratory distress syndrome through the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 7, 307. doi:10.1038/s41392-022-01124-6
Zhao, X., Li, Q., Guo, Z., and Li, Z. (2021). Constructing a cell microenvironment with biomaterial scaffolds for stem cell therapy. Stem Cell. Res. Ther. 12, 583. doi:10.1186/s13287-021-02650-w
Zhou, T., Yuan, Z., Weng, J., Pei, D., Du, X., He, C., et al. (2021). Challenges and advances in clinical applications of mesenchymal stromal cells. J. Hematol. Oncol. 14, 24. doi:10.1186/s13045-021-01037-x
Zhuo, H., Chen, Y., and Zhao, G. (2024). Advances in application of hypoxia-preconditioned mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes. Front. Cell. Dev. Biol. 12, 1446050. doi:10.3389/fcell.2024.1446050
Ziaei, R., Ayatollahi, M., Yaghobi, R., Sahraeian, Z., and Zarghami, N. (2014). Involvement of TNF-Alpha in differential gene expression pattern of CXCR4 on human marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Mol. Biol. Rep. 41, 1059–1066. doi:10.1007/s11033-013-2951-2
Keywords: mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), paracrine signaling, immunomodulation, regulatory, clinical evidence, regenerative medicine
Citation: Patel JC, Shukla M and Shukla M (2025) From bench to bedside: translating mesenchymal stem cell therapies through preclinical and clinical evidence. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 13:1639439. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2025.1639439
Received: 02 June 2025; Accepted: 23 July 2025;
Published: 30 July 2025.
Edited by:
Andreina Schoeberlein, University of Bern, SwitzerlandReviewed by:
Francesco Alviano, University of Bologna, ItalyJoshua Hare, University of Miami, United States
Copyright © 2025 Patel, Shukla and Shukla. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Manish Shukla, bXNodWtsYTFAcGVubnN0YXRlaGVhbHRoLnBzdS5lZHU=, bWFuaXNodWtsYWRyZG9AZ21haWwuY29t
 Jai Chand Patel
Jai Chand Patel Meenakshi Shukla
Meenakshi Shukla Manish Shukla
Manish Shukla